Speech vs. presentation: What’s the difference?
- Written by: Joby Blume
- Categories: Visual communication , Industry insights
- Comments: 6

What’s the difference between a presentation and a speech? Many people use the words interchangeably, but there are two main areas of difference according to the dictionary definitions. Whether one accepts the dictionary definition is another matter – my four year-old daughter sometimes refuses – but that makes further discussion pretty difficult.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary (OED), a speech is defined as:
a formal address or discourse delivered to an audience
According to the Scrabble fan’s choice – the Collins English Dictionary – a speech is:
a talk or address delivered to an audience
Note that in the Collins definition, the part about being formal is missing.

Presentation
Both the Oxford English and Collins dictionaries define presentation as including some sort of visual element. The OED definition is:
a speech or talk in which a new product, idea, or piece of work is shown and explained to an audience
Note that this includes the word ‘shown’. The Collins definition is even clearer in explicitly mentioning the use of illustrative material:
a verbal report presented with illustrative material, such as slides, graphs, etc
The Collins Dictionary also notes how the word presentation is used more generally to talk about how things are shown – ‘ the manner of presenting, esp the organization of visual details to create an overall impression’.
Presentations and speeches
Does the distinction hold perfectly? No. Firstly, people use the terms interchangeably, so of course the real world is full of speeches that are called presentations and presentations that are called speeches. Which leads to a natural blurring of the boundaries. Second, some presentations are very formal indeed, and some set-piece speeches (e.g. The State of the Union Address ) can have visuals added to them but without the orator interacting with them.
The boundaries aren’t sharp. But, according to the definition, a speech is a talk or address, and a presentation is a talk with the use of some sort of visual aid.
Speech vs. presentation
Why does this matter? Because giving a speech – for a lot of people – seems harder than giving a presentation. Bad slides are actually worse than no slides . But the reason so many speakers want slides or props is because they find it too hard to deliver speeches, and because effective visual aids makes it easier for them to get their points across.
Effective visuals – that support a speaker – make delivering presentations easier than delivering speeches for most people. Not everyone feels they can hold an audience with simply the sound of their own voice.
Great speeches are, well… great. But they aren’t the same as presentations, and shouldn’t be held up as examples of what those giving presentations should emulate.
P.S. For more on words and definitions, see Meaning and Necessity by Saul Kripke.

Related articles
Presentation agency or marketing agency.
- Industry insights
In the agency world, it’s fair to say that PowerPoint design sits somewhere at the bottom of the pile. Working with a specialist presentation design company will generally deliver better results, with less effort, and typically at lower cost. So why do some companies still not use presentation agencies for slide design?

How to make the ULTIMATE sales presentation
- Sales presentations / Sales messaging / Visual communication
- Comments: 8
Sales presentations are the cornerstone of many companies’ sales efforts, yet so often they aren’t given the time and attention they deserve. Thrown together at the last-minute, often your sales reps stand up in front of a sales presentation that's nothing more than a glorified page of notes. Read this article for everything you need to make the ultimate sales presentation.

Choosing a presentation design agency
- PowerPoint design / Visual communication / Industry insights
- Comments: 2
Choosing a presentation design agency for your enterprise is a lot harder than buying a product. With presentation design services, you don’t know what you’re going to get until the project is nearly finished. What you get from the studio isn’t the exact same thing as what any other business ends up with. So how do you choose the right presentation design firm for your company?

This is very interesting. I do appreciate it.
well… i found this information very useful,,,, thanks
This has helped me with my assignment thanks a lot
It is useful information it helps me doing anassignment.thanks
Deference between speech and presentation
Speech Vs Presentation Vs Debate Compitation? Speech: Speech Eleborate In Your Ideas That You Have Crammed(Ratafication). Presetation:To Suggest Anything Infront Of All Student By Using Your Slides Its Own Way That You Have Worked For Project. Debate Compitation:To Disscuss Your Ideas With One Another..
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Join the BrightCarbon mailing list for monthly invites and resources
BrightCarbon staff are knowledgeable with excellent skills, and are unfailingly enthusiastic for each new presentation. Sarah Appleton Brown Practice Plus Group

- How to Order
Speech Writing
Presentation Speech
Writing A Presentation Speech In English: Tips And Examples
11 min read

People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
Understanding Speech Format - Simple Steps for Outlining
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
Understanding Special Occasion Speech: Types, Steps, Examples and Tips
Introduction Speech- Tips & Examples
How to Write A Good Acceptance Speech?
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech | Writing Tips & Examples
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide
A Graduation Speech Writing Guide with Examples
Presentations are a common part of our personal and professional lives. Whether you're a student, an employee, or an entrepreneur, learning the art of presentations is a valuable skill.
A well-crafted presentation speech can inspire, inform, and engage your audience, leaving a lasting impact.
So how can you craft an engaging presentation speech?
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of creating and delivering a compelling presentation, step by step. From writing your speech to mastering public speaking techniques, we've got you covered.
So, let's dive in!
- 1. What is a Presentation Speech?
- 2. How to Write a Presentation Speech?
- 3. Ways to Start a Presentation Speech
- 4. How to End a Presentation Speech?
- 5. Presentation Speech Examples
- 6. Tips for Making Your Presentations More Engaging
- 7. Presentation Speech Topics
What is a Presentation Speech?
A presentation speech is a type of public speaking where the speaker formally delivers information, ideas, or proposals to an audience. This type of speech is typically structured to introduce a topic, convey key points clearly, and engage listeners effectively.
The goal of a presentation speech is to inform, persuade, or entertain the audience. They often use visual aids, storytelling, and other techniques to improve understanding and retention.
Main Components of a Presentation Speech
The key elements that set a presentation speech apart are its intentionality and structure. Here's a breakdown of these crucial aspects:
- Purpose
Every presentation speech has a clear purpose, which could be:
- To persuade
- To entertain
- To inspire and motivate
Understanding your purpose is the foundation upon which you build your speech.
A presentation speech typically follows the basic speech format that includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction lays out the context, the body conveys the main content, and the conclusion reinforces the key points.
Effective presentation speeches are tailored to the needs and expectations of the audience. Knowing your audience helps you choose the right tone, style, and content.
- Visual Aids
Presentation speeches often make use of visual aids like slides, props, or multimedia elements to enhance the message and keep the audience engaged.
How to Write a Presentation Speech?
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you effectively write a presentation speech.
Step 1: Determine the Audience
The first step in crafting a presentation speech is to understand your audience. Consider their background, knowledge, interests, and expectations. Are they experts in the subject, or are they new to it? This information will shape the tone and depth of your speech.
Step 2: Choose a Topic
Select a topic that aligns with both your expertise and the interests of your audience. Your topic should be engaging and relevant. It could be a current issue, a problem-solving solution, or a subject of general interest. Make sure your passion for the topic shines through.
Step 3: Research and Gather Information
To build a strong speech, gather credible information from a variety of sources. Use books, articles, online resources, and expert interviews. Keep track of your sources and make note of key statistics, quotes, and examples that support your message.
Step 4: Make an Outline
Creating a structured outline for your presentation speech is essential for keeping your message organized and ensuring that your audience can follow your points easily.
Here's how to construct a well-organized presentation speech outline:
Start with an opening to grab your audience's attention. Briefly highlight your expertise related to the topic. Clearly articulate the objective of your speech and what the audience will gain. Present your first main point with supporting evidence, examples, and statistics. Transition to your second main point, providing real-world applications or relatable stories. Conclude with your third main point, connecting it with previous points. Introduce visual aids at appropriate points to enhance your message. Recap the main takeaways from your presentation. Conclude with a memorable statement, call to action, or thought-provoking question. Express gratitude for their time and attention. Mention the Q&A session and invite questions from the audience. |
Step 5: Review and Revise
After you've written your speech, review it for clarity, coherence, and conciseness. Here are the steps you should take for reviewing your speech:
- Make sure that each point supports your main message and is easy to understand.
- Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Practice your speech in front of a mirror or with a friend. Pay attention to your delivery, pacing, and timing. Make necessary revisions based on your practice sessions.
Remember that a well-written presentation speech not only conveys your knowledge but also connects with your audience on a personal level. Your goal is to inform, persuade, or inspire, and the steps outlined here will help you achieve just that.
Ways to Start a Presentation Speech
Now that you’ve written your presentation and its content, the time has come to deliver your speech. If you're thinking how to start a presentation speech that grabs your audience's attention right from the beginning we have that covered for you.
Here are some simple yet powerful ways to hook your readers from the beginning:
- Ask a Thought-Provoking Question: Start with a question that makes your audience think about the topic you're going to discuss.
For example, "Have you ever wondered how technology will shape our future?"
- Tell a Story or Anecdote: Share a brief story or personal anecdote related to your topic. Stories capture attention and make your speech more relatable.
For instance, "When I was a child, I once..."
- Use a Surprising Fact or Statistic: Begin with an interesting fact or statistic that will surprise your audience.
For example, "Did you know that over 90% of people use their smartphones within 10 minutes of wa king up?"
- Start with a Relevant Quote: Begin with a quote from a notable person that relates to your topic. Quotes can inspire and set the tone for your speech.
For instance, "Steve Jobs once said, 'Your work is going to fill a large part of your life, and the only way to be truly satisfied is to do what you believe is great work.'"
- Pose a Problem and Offer a Solution: Introduce a problem your audience can relate to, and then hint at the solution you'll discuss.
For example, "Many of us struggle with time management. Today, I'll share some effective strategies to help you maximize your productivity."
How to End a Presentation Speech?
Ending your presentation speech effectively is just as important as starting strong. Here’s how to wrap up with impact:
- Summarize Key Points: Recap the main ideas you've discussed. Remind your audience of the key takeaways to reinforce your message.
- End with a Memorable Statement: Leave a lasting impression by concluding with a powerful statement, a thought-provoking question, or a call to action related to your topic.
- Thank Your Audience: Express gratitude for their time and attention. A simple "Thank you for listening" goes a long way in showing appreciation.
- Invite Questions (if applicable): If there’s time for questions, invite the audience to ask any they may have. This encourages engagement and shows you value their input.
- Leave Them Thinking: End with something that makes your audience reflect on what they've learned or consider how they might apply your ideas in their own lives or work.
Presentation Speech Examples
Taking help from good and structured presentation speeches will allow you to write and deliver the address smoothly. Here are some presentation speech samples for students that can help you write a well-structured presentation.
Award Presentation Speech Example
Product Presentation Speech Example
Thesis Presentation Speech Example
Presentation Speech Script Sample
Presentation Speech Template
Famous Presentation Speeches
Here are five examples of famous presentation speeches that have made a significant impact:
- Al Gore - An Inconvenient Truth (2006) : Al Gore's presentation used slides and visuals to raise awareness about climate change, documented in the film "An Inconvenient Truth."
- Susan Cain - The Power of Introverts (2012) : Susan Cain's TED Talk celebrated introverted personalities and their strengths in a society that often values extroversion.
- Bill Gates - Innovating to Zero! (2010) : Bill Gates' TED Talk emphasized the urgency of reducing carbon emissions to zero to address climate change, proposing innovative solutions.
- Sheryl Sandberg - Why We Have Too Few Women Leaders (2010) : Sheryl Sandberg's TED Talk highlighted barriers women face in leadership roles and urged women to pursue their ambitions.
- Tony Robbins - Why We Do What We Do (TED Talk, 2006)? : Tony Robbins' TED Talk explored the psychology of motivation and behavior, offering insights into personal and professional development.
Tips for Making Your Presentations More Engaging
Here are some additional tips for giving better presentations:
- Use expressive body language: Gestures and movement can help highlight important points and keep your audience engaged. It shows your enthusiasm and makes your presentation more dynamic.
- Adjust your voice tone and pace: Varying your voice tone and speaking pace adds emphasis and maintains listener interest. It's like adding melody to your speech to keep things lively and engaging.
- Manage nervousness with relaxation techniques: Before your presentation, try deep breathing or visualization exercises to calm your nerves. Feeling relaxed helps you speak confidently and connect better with your audience.
- Add humor or anecdotes: A well-placed joke or personal story can lighten the mood and make your presentation memorable. It also helps to connect with your audience on a more personal level.
- Use visuals wisely: Visual aids like slides or charts should complement your speech, not replace them. Use them to illustrate key points visually and help reinforce understanding.
- Maintain eye contact: Look at your audience while speaking. It builds trust and keeps them engaged. It shows you're speaking directly to them, not just reading off slides.
- Speak naturally, avoid reading: Practice your presentation enough that you can speak comfortably without reading word-for-word from slides or notes. Natural speech is more engaging and shows your expertise.
- Stay focused and present: Practice mindfulness techniques to stay grounded and focused during your presentation. Being present helps you react to audience cues and adjust your delivery accordingly.
Presentation Speech Topics
Now that you know how to write and deliver an engaging presentation, you may be wondering about a topic to speak on. You need a strong and interesting topic to make your presentation speech impactful.
Here are some presentation speech ideas to help you out:
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Job Market
- Climate Change and Sustainable Practices
- The Power of Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
- The Art of Time Management
- The Future of Renewable Energy
- The Psychology of Decision-Making
- Mental Health Awareness and Reducing Stigma:
- Innovations in Space Exploration
- The Art of Negotiation
- The Role of Music in Society
Need more ideas for your presentation speech? Our informative speech topics blog lists 100+ topics that are sure to inspire your next presentation.
To Conclude, remember, creating a successful presentation speech comes down to careful planning, delivering with enthusiasm, and understanding your audience. Outline your main points clearly, use visuals that grab attention, and practice confident body language to keep everyone engaged.
Need further help in making your presentation speech? No worries!
MyPerfectWords.com is a professional speech writing service that provides versatile academic help. Whether you have a speech or a research paper to write, come to us. We have a team of experts to help you with all your writing needs.
Place a do my essay for me request now to get expert help.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to start a presentation speech in class.
To start a presentation speech in class, begin with a captivating opening like a question, story, or surprising fact related to your topic. This grabs your classmates' attention and sets the tone for your presentation.
How to introduce yourself in a presentation as a student?
Introduce yourself briefly by stating your name, grade, or class, and any relevant information about your background or interests related to the presentation topic. Keep it concise and focus on how your experience or perspective adds value to your presentation.
What are some effective presentation starting words?
Here are some good presentation starting words:
- "Have you ever wondered..."
- "Imagine a world where..."
- "Today, I'm going to talk about..."
- "Let's dive into..."
- "I'd like to begin by..."
How to speak during a presentation?
Speaking during a presentation involves several key techniques:
- Speak clearly and at a moderate pace to ensure your audience can follow.
- Use varied tones to emphasize important points and maintain interest.
- Practice pauses to allow your audience time to digest information.
- Maintain eye contact to build rapport and keep listeners engaged.
- Use gestures and body language to enhance your message and express enthusiasm.
What are some 'How to' speech presentation topics?
'How to' speech presentation topics can include practical skills or processes that are informative and engaging:
- How to effectively manage your time in college
- How to improve your study habits
- How to improve your public speaking skills as a student
- How to conduct meetings in the workplace
- How to develop strong leadership skills
- How to create an effective business plan
- How to create a budget and stick to it
- How to improve customer service skills in your role
- How to build a basic website
- How to negotiate a salary or contract effectively

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


- PRESENTATION SKILLS
What is a Presentation?
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The formal presentation of information is divided into two broad categories: Presentation Skills and Personal Presentation .
These two aspects are interwoven and can be described as the preparation, presentation and practice of verbal and non-verbal communication.
This article describes what a presentation is and defines some of the key terms associated with presentation skills.
Many people feel terrified when asked to make their first public talk. Some of these initial fears can be reduced by good preparation that also lays the groundwork for making an effective presentation.
A Presentation Is...
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team.
A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other ‘speaking engagements’ such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across in a video conference.
To be effective, step-by-step preparation and the method and means of presenting the information should be carefully considered.
A presentation requires you to get a message across to the listeners and will often contain a ' persuasive ' element. It may, for example, be a talk about the positive work of your organisation, what you could offer an employer, or why you should receive additional funding for a project.
The Key Elements of a Presentation
Making a presentation is a way of communicating your thoughts and ideas to an audience and many of our articles on communication are also relevant here, see: What is Communication? for more.
Consider the following key components of a presentation:
Ask yourself the following questions to develop a full understanding of the context of the presentation.
When and where will you deliver your presentation?
There is a world of difference between a small room with natural light and an informal setting, and a huge lecture room, lit with stage lights. The two require quite different presentations, and different techniques.
Will it be in a setting you are familiar with, or somewhere new?
If somewhere new, it would be worth trying to visit it in advance, or at least arriving early, to familiarise yourself with the room.
Will the presentation be within a formal or less formal setting?
A work setting will, more or less by definition, be more formal, but there are also various degrees of formality within that.
Will the presentation be to a small group or a large crowd?
Are you already familiar with the audience?
With a new audience, you will have to build rapport quickly and effectively, to get them on your side.
What equipment and technology will be available to you, and what will you be expected to use?
In particular, you will need to ask about microphones and whether you will be expected to stand in one place, or move around.
What is the audience expecting to learn from you and your presentation?
Check how you will be ‘billed’ to give you clues as to what information needs to be included in your presentation.
All these aspects will change the presentation. For more on this, see our page on Deciding the Presentation Method .
The role of the presenter is to communicate with the audience and control the presentation.
Remember, though, that this may also include handing over the control to your audience, especially if you want some kind of interaction.
You may wish to have a look at our page on Facilitation Skills for more.
The audience receives the presenter’s message(s).
However, this reception will be filtered through and affected by such things as the listener’s own experience, knowledge and personal sense of values.
See our page: Barriers to Effective Communication to learn why communication can fail.
The message or messages are delivered by the presenter to the audience.
The message is delivered not just by the spoken word ( verbal communication ) but can be augmented by techniques such as voice projection, body language, gestures, eye contact ( non-verbal communication ), and visual aids.
The message will also be affected by the audience’s expectations. For example, if you have been billed as speaking on one particular topic, and you choose to speak on another, the audience is unlikely to take your message on board even if you present very well . They will judge your presentation a failure, because you have not met their expectations.
The audience’s reaction and therefore the success of the presentation will largely depend upon whether you, as presenter, effectively communicated your message, and whether it met their expectations.
As a presenter, you don’t control the audience’s expectations. What you can do is find out what they have been told about you by the conference organisers, and what they are expecting to hear. Only if you know that can you be confident of delivering something that will meet expectations.
See our page: Effective Speaking for more information.
How will the presentation be delivered?
Presentations are usually delivered direct to an audience. However, there may be occasions where they are delivered from a distance over the Internet using video conferencing systems, such as Skype.
It is also important to remember that if your talk is recorded and posted on the internet, then people may be able to access it for several years. This will mean that your contemporaneous references should be kept to a minimum.
Impediments
Many factors can influence the effectiveness of how your message is communicated to the audience.
For example background noise or other distractions, an overly warm or cool room, or the time of day and state of audience alertness can all influence your audience’s level of concentration.
As presenter, you have to be prepared to cope with any such problems and try to keep your audience focussed on your message.
Our page: Barriers to Communication explains these factors in more depth.
Continue to read through our Presentation Skills articles for an overview of how to prepare and structure a presentation, and how to manage notes and/or illustrations at any speaking event.
Continue to: Preparing for a Presentation Deciding the Presentation Method
See also: Writing Your Presentation | Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves | Dealing with Questions Learn Better Presentation Skills with TED Talks

Presentation Speech
Presentation speech generator.

A speech template typically varies in context. This would depend on the purpose of the speech and how a speaker wishes to deliver it. It consists of key points that must be elaborated during the discussion. For any speaker, the goal is to covey a message in a clear and compelling manner.
However, public speaking is definitely not for everybody. There are several factors that must be considered when delivering a speech in word . With this in mind, it’s important for a speaker to present a speech that is sure to captivate an audience.
Retirement Presentation

Size: 164 KB
Award Presentation Speech

Size: 19 KB
Graduation Presentation

What Is a Presentation Speech?
A presentation speech typically consists of a presenter, an audience, and a message. It is a means of communication that is used to get a point across. This is usually given during group discussions, such as company meetings and the like.
How to Prepare a Speech Presentation
A speech presentation requires enough preparation for it to be effective. This would mean that the speaker must prepare an informative speech along with its supporting visual aids. But first, you must think about the purpose of the speech and the type of audience the speech will be delivered to.
With this, you will be able to gather enough materials that will be used for your speech presentation. This would include intensive research through journals, articles, interviews, and testimonies. By doing this, you may create a concise statement that states your purpose.
Constructing an outline will also create a good foundation for your speech outline . This will help you focus on key points that need to be emphasized in your speech.
Finally, you need to finalize it. Check for any mistakes in wording and transitions and make the necessary changes.
Sample Presentation Speech

Financial Results Presentation

Tips for Effective Presentations
- Connect with your audience. Interact with your listeners and make them feel as if they are a part of the conversation. A passionate speaker is sure to attract an audience.
- Concentrate on your central message. Focus on the message you want to relay to your audience by providing key points.
- Use visuals. Providing supporting visuals will allow your audience to further understand your message. You can use images, charts, graphs, and the like.
- Maintain eye contact. Eye contact is essential for face-to-face communication. This is sure to attract attentive listeners.
- Start out strongly. For any speech, such as a valedictorian speech , you’ll want to give a good first impression. A few minutes into your speech, you should be able to build a strong connection with your audience.
- Tell stories. Creating mental scenarios for your audience will help them pay attention. This speech in pdf will allow them to understand the point of your presentation and the morals that must be remembered.
- Move around. If possible, do not limit yourself to one position. Walk around and use hand gestures to emphasize your points. Allow your listeners to feel your passion for the subject.
- Come prepared. Have your materials ready and be sure to practice beforehand. You don’t want to be left stuttering during your presentation. This will only make your audience doubt your credibility.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a presentation speech for a new project proposal
Help me write a presentation speech for our annual report
The Differences Between Speech and Presentation You May Not Know

Have you ever thought about the difference between speech and presentation? It might seem like those things look the same, but you should understand the huge differences between them. And once you know it, you will excel at both of them.
Many people still seem to confuse those two things and use the words interchangeably without knowing they are different. So, for example, we checked the meaning of those words in the Merriam-Webster dictionary and discovered two different meanings.
While speech is described as “a formal talk that a person gives to an audience,” a presentation is “a meeting at which something, especially a new product or idea, or piece of work, is shown to a group of people.”
From the definition alone, you can see that one says ‘talk’ and the other says ‘shown.’ But what’s the meaning of those words? To make things clearer, here are the differences between speech and presentation.
Memorizing the material
The first difference between speech and presentation is the way you present the information. Even though they look the same, you indeed feel the differences between speech and presentation by your own experience.
Let’s start with the most subtle difference between speech and presentation: how we present the material based on what we memorize. We tend to make everything so clear to the audience during presentations, which requires a lot of memorization.
The same thing may apply during speeches, but because speeches are not made to tell every single detail of the thing that you want to explain, you might not need to memorize every detail in the fabric.
Fact is, you may even expand your topic during speeches, but not in presentation. So, for example, during your speech on the importance of trees, you may expand to include what’s happening to our environment.
However, if you talk about a specific topic during a presentation, you may want to put further details in it instead of expanding the topic. So, during a presentation, you may memorize more details.
While in speeches, you may memorize the related topics that can support your point. In this case, we may talk about the second difference between those things. In this case, we may speak of the second difference between those things.
Visual aids
There is a reason why both of them use visual aids, and we will show you the difference between each use. The first is about speech. During a lesson, as mentioned above, you need to master your topic to the rate that you can expand it further.
What’s the connection between that and visual aids? Speeches mainly use visual aids to help themselves remember the points they want to talk about. While in presentation, the use of visual aids is to help the audiences understand.
In this case, we can expand the difference between the two. While in speeches, the visual aid design is not that important, the design in presentation is highly regarded. Not all lessons use visual aids because of that reason.
However, it doesn’t mean that visual aids are not crucial in speeches. One of the examples is a video or picture to tell the audience about a story. It surely will help the audience understand what you are talking about.
But in presentation, frequently, your visual aids alone can help the audiences understand what you are talking about. This is why your visual aids, such as PowerPoint presentations, need to be as clear as possible and as attractive as possible.
How visual aids help us in both speeches and presentations is intended to make the following difference clearer. And the next difference is how you share your vision about the topic you are delivering to the audience.
Sharing your vision
Have you ever seen a debate competition? In that competition, you might not see someone presenting their arguments with a well-designed PowerPoint presentation slide. Instead, they speak in front of the adjudicators and the audience with a small paper as a note.
We are not talking about the visual aids here, but we may look at the speaker’s notes. There, they mostly write only about the points that they want to deliver. But what’s the difference between the notes and the presentation handouts that we bring?
In presentation handouts, we also write notes, but our messages are primarily about what the speaker wants to highlight. However, the notes in a debate are about things they want to convince the audience.
Yes, the difference comes from how we speak about the topic in front of the audience. A speaker in speeches wants to convince the audience about their view or stance. They want to spread their vision about things.
While a presenter might not care much about their vision, speakers usually include the advantages, disadvantages, resolutions, plans, or generally accepted things. For example, take a look at how salesmen or saleswomen in their sales.
The ones who do speeches would tell inspiring, motivating, or heartwarming things to sell their products. While the ones presenting their sales would focus more on the advantages, disadvantages, or their products’ unique features.
Preparation time between speech and presentation
This one difference is exciting and a little bit controversial. Why? Because what we want to tell you might shake your view about the differences between those two. What is it? It is about how you prepare for the upcoming speech/presentation.
Supported by Art of Presentation, it says that presenting is a well-prepared action. So it would help if you worked very well in preparing the things you want to deliver to the audience to make sure you can give as well as possible.
You might need to fact-check everything, create PowerPoint presentation slides , getting things correlated with one another. You might also at least practice how you will present to make sure you will nail the presentation.
But with speeches, you may not need to practice anything or prepare for the things you want to deliver. It is because speeches are more like art than just telling people about things. See how we differentiate an excellent orator from a bad one?
Good orators may talk about things as they will, and people will still get their point. However, some good people may not even prepare anything except their own story created spontaneously in the venue.
The difference in stories to deliver between speech and presentation
From the distinction above, you might be able to guess what’s the following difference. While speeches are more about the speaker’s creativity, preservations are more about how you process information and deliver almost the same thing in a descriptive way.
A good orator needs to have a million ways to deliver the information to the audience. On the other hand, a good presenter needs to find the best descriptive way to show the presentation without getting their stories out of context.
You can train yourself into a good orator by collecting exciting stories and experiences to tell your future audiences. This way, you can show a million stories based on things you have collected in your speeches and get the audience to understand your points.
On the other hand, you can train yourself into a good presenter by trial and error in presenting. Then, later on, you can choose the best descriptive way to make them get your points and always use that in your future presentations to get the same result.
That is because your presentation is helped a lot by the visual aids we mentioned above. In addition, you can always correlate your presentation with visual aids.
Detailed information versus convincing words
If you are presenting something, you will primarily use more accurate data. And when someday you are giving a speech to other people, you mostly will tell them stories you created or experienced.
Again, the way we speak in a presentation is different from how we say in a speech. We don’t need to make things too strict in a lesson, but we need to be as professional as possible during a presentation.
But looking deeper into the reasons, we have different ‘languages’ in delivering those things. For example, while presenting something, we tend to give detailed information without trying to make up words or explanations.
Things are different with speeches when we can be as creative in our stories as possible. In this case, our words do not need to be very detailed. The reason for that is because our primary mission is to convince the audiences no matter what.
Now, can you imagine a huge gap between presenting descriptively with detailed information about the thing you want to talk about and how to make a convincing story no matter what? Yes, that huge gap is going to tell you the difference between speech and presentation.
Those are the differences we can easily spot between speech and presentation. We hope it will help you understand what you want to do next before doing any of those things.
Author bio:
This article is written by Ulfah, an SEO & Content Manager, and is currently working for RRGraph Design. Say hello through her LinkedIn .

At SlideBazaar, we help you create engaging and memorable presentations. Choose from our collection of professional templates or opt for our custom design services for a personalized touch. Your presentations deserve to be elevated to new heights, and we’re here to help you achieve just that!
BROWSE BY CATEGORY
- PowerPoint Templates
- Keynote Presentations
- Infographic
- Free slides
QUICK LINKS
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- DMCA Policy
EMAIL NEWSLETTER
Get updates of our PowerPoint templates and slide designs before anyone else.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides 8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
Written by: Krystle Wong Aug 11, 2023

From persuasive pitches that influence opinions to instructional demonstrations that teach skills, the different types of presentations serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences.
Presentations that are tailored to its objectives and audiences are more engaging and memorable. They capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
Don’t worry if you’re no designer — Whether you need data-driven visuals, persuasive graphics or engaging design elements, Venngage can empower you to craft presentations that stand out and effectively convey your message.
Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface, extensive presentation template library and customizable design options make it a valuable tool for creating slides that align with your specific goals and target audience.
Click to jump ahead:
8 Different types of presentations every presenter must know
How do i choose the right type of presentation for my topic or audience, types of presentation faq, 5 steps to create a presentation with venngage .

When it comes to presentations, versatility is the name of the game. Having a variety of presentation styles up your sleeve can make a world of difference in keeping your audience engaged. Here are 8 essential presentation types that every presenter should be well-acquainted with:
1. Informative presentation
Ever sat through a presentation that left you feeling enlightened? That’s the power of an informative presentation.
This presentation style is all about sharing knowledge and shedding light on a particular topic. Whether you’re diving into the depths of quantum physics or explaining the intricacies of the latest social media trends, informative presentations aim to increase the audience’s understanding.
When delivering an informative presentation, simplify complex topics with clear visuals and relatable examples. Organize your content logically, starting with the basics and gradually delving deeper and always remember to keep jargon to a minimum and encourage questions for clarity.
Academic presentations and research presentations are great examples of informative presentations. An effective academic presentation involves having clear structure, credible evidence, engaging delivery and supporting visuals. Provide context to emphasize the topic’s significance, practice to perfect timing, and be ready to address anticipated questions.
2. Persuasive presentation
If you’ve ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you’ve experienced a persuasive presentation .
This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective. Expect to encounter solid evidence, logical reasoning and a dash of emotional appeal.
With persuasive presentations, it’s important to know your audience inside out and tailor your message to their interests and concerns. Craft a compelling narrative with a strong opening, a solid argument and a memorable closing. Additionally, use visuals strategically to enhance your points.
Examples of persuasive presentations include presentations for environmental conservations, policy change, social issues and more. Here are some engaging presentation templates you can use to get started with:

3. Demonstration or how-to presentation
A Demonstration or How-To Presentation is a type of presentation where the speaker showcases a process, technique, or procedure step by step, providing the audience with clear instructions on how to replicate the demonstrated action.
A demonstrative presentation is particularly useful when teaching practical skills or showing how something is done in a hands-on manner.
These presentations are commonly used in various settings, including educational workshops, training sessions, cooking classes, DIY tutorials, technology demonstrations and more. Designing creative slides for your how-to presentations can heighten engagement and foster better information retention.
Speakers can also consider breaking down the process into manageable steps, using visual aids, props and sometimes even live demonstrations to illustrate each step. The key is to provide clear and concise instructions, engage the audience with interactive elements and address any questions that may arise during the presentation.

4. Training or instructional presentation
Training presentations are geared towards imparting practical skills, procedures or concepts — think of this as the more focused cousin of the demonstration presentation.
Whether you’re teaching a group of new employees the ins and outs of a software or enlightening budding chefs on the art of soufflé-making, training presentations are all about turning novices into experts.
To maximize the impact of your training or instructional presentation, break down complex concepts into digestible segments. Consider using real-life examples to illustrate each point and create a connection.
You can also create an interactive presentation by incorporating elements like quizzes or group activities to reinforce understanding.
5. Sales presentation
Sales presentations are one of the many types of business presentations and the bread and butter of businesses looking to woo potential clients or customers. With a sprinkle of charm and a dash of persuasion, these presentations showcase products, services or ideas with one end goal in mind: sealing the deal.
A successful sales presentation often has key characteristics such as a clear value proposition, strong storytelling, confidence and a compelling call to action. Hence, when presenting to your clients or stakeholders, focus on benefits rather than just features.
Anticipate and address potential objections before they arise and use storytelling to showcase how your offering solves a specific problem for your audience. Utilizing visual aids is also a great way to make your points stand out and stay memorable.
A sales presentation can be used to promote service offerings, product launches or even consultancy proposals that outline the expertise and industry experience of a business. Here are some template examples you can use for your next sales presentation:

6. Pitch presentation
Pitch presentations are your ticket to garnering the interest and support of potential investors, partners or stakeholders. Think of your pitch deck as your chance to paint a vivid picture of your business idea or proposal and secure the resources you need to bring it to life.
Business presentations aside, individuals can also create a portfolio presentation to showcase their skills, experience and achievements to potential clients, employers or investors.
Craft a concise and compelling narrative. Clearly define the problem your idea solves and how it stands out in the market. Anticipate questions and practice your answers. Project confidence and passion for your idea.
7. Motivational or inspirational presentation
Feeling the need for a morale boost? That’s where motivational presentations step in. These talks are designed to uplift and inspire, often featuring personal anecdotes, heartwarming stories and a generous serving of encouragement.
Form a connection with your audience by sharing personal stories that resonate with your message. Use a storytelling style with relatable anecdotes and powerful metaphors to create an emotional connection. Keep the energy high and wrap up your inspirational presentations with a clear call to action.
Inspirational talks and leadership presentations aside, a motivational or inspirational presentation can also be a simple presentation aimed at boosting confidence, a motivational speech focused on embracing change and more.
8. Status or progress report presentation
Projects and businesses are like living organisms, constantly evolving and changing. Status or progress report presentations keep everyone in the loop by providing updates on achievements, challenges and future plans. It’s like a GPS for your team, ensuring everyone stays on track.
Be transparent about achievements, challenges and future plans. Utilize infographics, charts and diagrams to present your data visually and simplify information. By visually representing data, it becomes easier to identify trends, make predictions and strategize based on evidence.

Now that you’ve learned about the different types of presentation methods and how to use them, you’re on the right track to creating a good presentation that can boost your confidence and enhance your presentation skills .
Selecting the most suitable presentation style is akin to choosing the right outfit for an occasion – it greatly influences how your message is perceived. Here’s a more detailed guide to help you make that crucial decision:
1. Define your objectives
Begin by clarifying your presentation’s goals. Are you aiming to educate, persuade, motivate, train or perhaps sell a concept? Your objectives will guide you to the most suitable presentation type.
For instance, if you’re aiming to inform, an informative presentation would be a natural fit. On the other hand, a persuasive presentation suits the goal of swaying opinions.
2. Know your audience
Regardless if you’re giving an in-person or a virtual presentation — delve into the characteristics of your audience. Consider factors like their expertise level, familiarity with the topic, interests and expectations.
If your audience consists of professionals in your field, a more technical presentation might be suitable. However, if your audience is diverse and includes newcomers, an approachable and engaging style might work better.

3. Analyze your content
Reflect on the content you intend to present. Is it data-heavy, rich in personal stories or focused on practical skills? Different presentation styles serve different content types.
For data-driven content, an informative or instructional presentation might work best. For emotional stories, a motivational presentation could be a compelling choice.
4. Consider time constraints
Evaluate the time you have at your disposal. If your presentation needs to be concise due to time limitations, opt for a presentation style that allows you to convey your key points effectively within the available timeframe. A pitch presentation, for example, often requires delivering impactful information within a short span.
5. Leverage visuals
Visual aids are powerful tools in presentations. Consider whether your content would benefit from visual representation. If your PowerPoint presentations involve step-by-step instructions or demonstrations, a how-to presentation with clear visuals would be advantageous. Conversely, if your content is more conceptual, a motivational presentation could rely more on spoken words.

6. Align with the setting
Take the presentation environment into account. Are you presenting in a formal business setting, a casual workshop or a conference? Your setting can influence the level of formality and interactivity in your presentation. For instance, a demonstration presentation might be ideal for a hands-on workshop, while a persuasive presentation is great for conferences.
7. Gauge audience interaction
Determine the level of audience engagement you want. Interactive presentations work well for training sessions, workshops and small group settings, while informative or persuasive presentations might be more one-sided.
8. Flexibility
Stay open to adjusting your presentation style on the fly. Sometimes, unexpected factors might require a change of presentation style. Be prepared to adjust on the spot if audience engagement or reactions indicate that a different approach would be more effective.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach, and the best type of presentation may vary depending on the specific situation and your unique communication goals. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the most effective presentation type to successfully engage and communicate with your audience.
To save time, use a presentation software or check out these presentation design and presentation background guides to create a presentation that stands out.
What are some effective ways to begin and end a presentation?
Capture your audience’s attention from the start of your presentation by using a surprising statistic, a compelling story or a thought-provoking question related to your topic.
To conclude your presentation , summarize your main points, reinforce your key message and leave a lasting impression with a powerful call to action or a memorable quote that resonates with your presentation’s theme.
How can I make my presentation more engaging and interactive?
To create an engaging and interactive presentation for your audience, incorporate visual elements such as images, graphs and videos to illustrate your points visually. Share relatable anecdotes or real-life examples to create a connection with your audience.
You can also integrate interactive elements like live polls, open-ended questions or small group discussions to encourage participation and keep your audience actively engaged throughout your presentation.
Which types of presentations require special markings
Some presentation types require special markings such as how sales presentations require persuasive techniques like emphasizing benefits, addressing objections and using compelling visuals to showcase products or services.
Demonstrations and how-to presentations on the other hand require clear markings for each step, ensuring the audience can follow along seamlessly.
That aside, pitch presentations require highlighting unique selling points, market potential and the competitive edge of your idea, making it stand out to potential investors or partners.
Need some inspiration on how to make a presentation that will captivate an audience? Here are 120+ presentation ideas to help you get started.
Creating a stunning and impactful presentation with Venngage is a breeze. Whether you’re crafting a business pitch, a training presentation or any other type of presentation, follow these five steps to create a professional presentation that stands out:
- Sign up and log in to Venngage to access the editor.
- Choose a presentation template that matches your topic or style.
- Customize content, colors, fonts, and background to personalize your presentation.
- Add images, icons, and charts to enhancevisual style and clarity.
- Save, export, and share your presentation as PDF or PNG files, or use Venngage’s Presentation Mode for online showcasing.
In the realm of presentations, understanding the different types of presentation formats is like having a versatile set of tools that empower you to craft compelling narratives for every occasion.
Remember, the key to a successful presentation lies not only in the content you deliver but also in the way you connect with your audience. Whether you’re informing, persuading or entertaining, tailoring your approach to the specific type of presentation you’re delivering can make all the difference.
Presentations are a powerful tool, and with practice and dedication (and a little help from Venngage), you’ll find yourself becoming a presentation pro in no time. Now, let’s get started and customize your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

30 Examples: How to Conclude a Presentation (Effective Closing Techniques)
By Status.net Editorial Team on March 4, 2024 — 9 minutes to read
Ending a presentation on a high note is a skill that can set you apart from the rest. It’s the final chance to leave an impact on your audience, ensuring they walk away with the key messages embedded in their minds. This moment is about driving your points home and making sure they resonate. Crafting a memorable closing isn’t just about summarizing key points, though that’s part of it, but also about providing value that sticks with your listeners long after they’ve left the room.
Crafting Your Core Message
To leave a lasting impression, your presentation’s conclusion should clearly reflect your core message. This is your chance to reinforce the takeaways and leave the audience thinking about your presentation long after it ends.
Identifying Key Points
Start by recognizing what you want your audience to remember. Think about the main ideas that shaped your talk. Make a list like this:
- The problem your presentation addresses.
- The evidence that supports your argument.
- The solution you propose or the action you want the audience to take.
These key points become the pillars of your core message.
Contextualizing the Presentation
Provide context by briefly relating back to the content of the whole presentation. For example:
- Reference a statistic you shared in the opening, and how it ties into the conclusion.
- Mention a case study that underlines the importance of your message.
Connecting these elements gives your message cohesion and makes your conclusion resonate with the framework of your presentation.
30 Example Phrases: How to Conclude a Presentation
- 1. “In summary, let’s revisit the key takeaways from today’s presentation.”
- 2. “Thank you for your attention. Let’s move forward together.”
- 3. “That brings us to the end. I’m open to any questions you may have.”
- 4. “I’ll leave you with this final thought to ponder as we conclude.”
- 5. “Let’s recap the main points before we wrap up.”
- 6. “I appreciate your engagement. Now, let’s turn these ideas into action.”
- 7. “We’ve covered a lot today. To conclude, remember these crucial points.”
- 8. “As we reach the end, I’d like to emphasize our call to action.”
- 9. “Before we close, let’s quickly review what we’ve learned.”
- 10. “Thank you for joining me on this journey. I look forward to our next steps.”
- 11. “In closing, I’d like to thank everyone for their participation.”
- 12. “Let’s conclude with a reminder of the impact we can make together.”
- 13. “To wrap up our session, here’s a brief summary of our discussion.”
- 14. “I’m grateful for the opportunity to present to you. Any final thoughts?”
- 15. “And that’s a wrap. I welcome any final questions or comments.”
- 16. “As we conclude, let’s remember the objectives we’ve set today.”
- 17. “Thank you for your time. Let’s apply these insights to achieve success.”
- 18. “In conclusion, your feedback is valuable, and I’m here to listen.”
- 19. “Before we part, let’s take a moment to reflect on our key messages.”
- 20. “I’ll end with an invitation for all of us to take the next step.”
- 21. “As we close, let’s commit to the goals we’ve outlined today.”
- 22. “Thank you for your attention. Let’s keep the conversation going.”
- 23. “In conclusion, let’s make a difference, starting now.”
- 24. “I’ll leave you with these final words to consider as we end our time together.”
- 25. “Before we conclude, remember that change starts with our actions today.”
- 26. “Thank you for the lively discussion. Let’s continue to build on these ideas.”
- 27. “As we wrap up, I encourage you to reach out with any further questions.”
- 28. “In closing, I’d like to express my gratitude for your valuable input.”
- 29. “Let’s conclude on a high note and take these learnings forward.”
- 30. “Thank you for your time today. Let’s end with a commitment to progress.”
Summarizing the Main Points
When you reach the end of your presentation, summarizing the main points helps your audience retain the important information you’ve shared. Crafting a memorable summary enables your listeners to walk away with a clear understanding of your message.
Effective Methods of Summarization
To effectively summarize your presentation, you need to distill complex information into concise, digestible pieces. Start by revisiting the overarching theme of your talk and then narrow down to the core messages. Use plain language and imagery to make the enduring ideas stick. Here are some examples of how to do this:
- Use analogies that relate to common experiences to recap complex concepts.
- Incorporate visuals or gestures that reinforce your main arguments.
The Rule of Three
The Rule of Three is a classic writing and communication principle. It means presenting ideas in a trio, which is a pattern that’s easy for people to understand and remember. For instance, you might say, “Our plan will save time, cut costs, and improve quality.” This structure has a pleasing rhythm and makes the content more memorable. Some examples include:
- “This software is fast, user-friendly, and secure.”
- Pointing out a product’s “durability, affordability, and eco-friendliness.”
Reiterating the Main Points
Finally, you want to circle back to the key takeaways of your presentation. Rephrase your main points without introducing new information. This reinforcement supports your audience’s memory and understanding of the material. You might summarize key takeaways like this:
- Mention the problem you addressed, the solution you propose, and the benefits of this solution.
- Highlighting the outcomes of adopting your strategy: higher efficiency, greater satisfaction, and increased revenue.
Creating a Strong Conclusion
The final moments of your presentation are your chance to leave your audience with a powerful lasting impression. A strong conclusion is more than just summarizing—it’s your opportunity to invoke thought, inspire action, and make your message memorable.
Incorporating a Call to Action
A call to action is your parting request to your audience. You want to inspire them to take a specific action or think differently as a result of what they’ve heard. To do this effectively:
- Be clear about what you’re asking.
- Explain why their action is needed.
- Make it as simple as possible for them to take the next steps.
Example Phrases:
- “Start making a difference today by…”
- “Join us in this effort by…”
- “Take the leap and commit to…”
Leaving a Lasting Impression
End your presentation with something memorable. This can be a powerful quote, an inspirational statement, or a compelling story that underscores your main points. The goal here is to resonate with your audience on an emotional level so that your message sticks with them long after they leave.
- “In the words of [Influential Person], ‘…'”
- “Imagine a world where…”
- “This is more than just [Topic]; it’s about…”
Enhancing Audience Engagement
To hold your audience’s attention and ensure they leave with a lasting impression of your presentation, fostering interaction is key.
Q&A Sessions
It’s important to integrate a Q&A session because it allows for direct communication between you and your audience. This interactive segment helps clarify any uncertainties and encourages active participation. Plan for this by designating a time slot towards the end of your presentation and invite questions that promote discussion.
- “I’d love to hear your thoughts; what questions do you have?”
- “Let’s dive into any questions you might have. Who would like to start?”
- “Feel free to ask any questions, whether they’re clarifications or deeper inquiries about the topic.”
Encouraging Audience Participation
Getting your audience involved can transform a good presentation into a great one. Use open-ended questions that provoke thought and allow audience members to reflect on how your content relates to them. Additionally, inviting volunteers to participate in a demonstration or share their experiences keeps everyone engaged and adds a personal touch to your talk.
- “Could someone give me an example of how you’ve encountered this in your work?”
- “I’d appreciate a volunteer to help demonstrate this concept. Who’s interested?”
- “How do you see this information impacting your daily tasks? Let’s discuss!”
Delivering a Persuasive Ending
At the end of your presentation, you have the power to leave a lasting impact on your audience. A persuasive ending can drive home your key message and encourage action.
Sales and Persuasion Tactics
When you’re concluding a presentation with the goal of selling a product or idea, employ carefully chosen sales and persuasion tactics. One method is to summarize the key benefits of your offering, reminding your audience why it’s important to act. For example, if you’ve just presented a new software tool, recap how it will save time and increase productivity. Another tactic is the ‘call to action’, which should be clear and direct, such as “Start your free trial today to experience the benefits first-hand!” Furthermore, using a touch of urgency, like “Offer expires soon!”, can nudge your audience to act promptly.
Final Impressions and Professionalism
Your closing statement is a chance to solidify your professional image and leave a positive impression. It’s important to display confidence and poise. Consider thanking your audience for their time and offering to answer any questions. Make sure to end on a high note by summarizing your message in a concise and memorable way. If your topic was on renewable energy, you might conclude by saying, “Let’s take a leap towards a greener future by adopting these solutions today.” This reinforces your main points and encourages your listeners to think or act differently when they leave.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some creative strategies for ending a presentation memorably.
To end your presentation in a memorable way, consider incorporating a call to action that engages your audience to take the next step. Another strategy is to finish with a thought-provoking question or a surprising fact that resonates with your listeners.
Can you suggest some powerful quotes suitable for concluding a presentation?
Yes, using a quote can be very effective. For example, Maya Angelou’s “People will forget what you said, people will forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel,” can reinforce the emotional impact of your presentation.
What is an effective way to write a conclusion that summarizes a presentation?
An effective conclusion should recap the main points succinctly, highlighting what you want your audience to remember. A good way to conclude is by restating your thesis and then briefly summarizing the supporting points you made.
As a student, how can I leave a strong impression with my presentation’s closing remarks?
To leave a strong impression, consider sharing a personal anecdote related to your topic that demonstrates passion and conviction. This helps humanize your content and makes the message more relatable to your audience.
How can I appropriately thank my audience at the close of my presentation?
A simple and sincere expression of gratitude is always appropriate. You might say, “Thank you for your attention and engagement today,” to convey appreciation while also acknowledging their participation.
What are some examples of a compelling closing sentence in a presentation?
A compelling closing sentence could be something like, “Together, let’s take the leap towards a greener future,” if you’re presenting on sustainability. This sentence is impactful, calls for united action, and leaves your audience with a clear message.
- How to Build Rapport: Effective Techniques
- Active Listening (Techniques, Examples, Tips)
- Effective Nonverbal Communication in the Workplace (Examples)
- What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
- 2 Examples of an Effective and Warm Letter of Welcome
- 8 Examples of Effective Interview Confirmation Emails
What Is the Difference Between a Speech & a Presentation?
by Barbara Bean-Mellinger
Published on 22 Oct 2018
Many people use the words "speech" and "presentation" interchangeably since both involve speaking in front of a group. It's true that both can be dreaded for that very reason. Others note the difference is that speakers in a presentation use visual aids, while those in a speech typically don't. While that's true enough, there are many other distinct differences between the two.
Formal or Not So Formal
Don't tell the speaker giving a presentation in front of the company CEO and other bigwigs that it isn't a formal occurrence. His sweaty palms say otherwise. But, nervousness aside, presentations are given many times throughout the year in business, from sales meetings to conferences, while speeches are reserved for high profile, public events and special occasions like retirement parties and company mergers. Because of this, speeches are more formal. Not that the speaker has to wear formal attire; if only it were that simple to pull off a great speech! Also, the audience is more interested in what your presentation will show them, than they are in you and how you present. Whereas in a speech, it’s just you up there, so all eyes and ears are on you.
Emotional or Just the Facts?
If you think speeches tug at the listeners' emotions while presentations present the facts with visual backup, you're partially right. Speeches make use of anecdotes that pull you in. As you listen you may be thinking, "That's happened to me too!" Or, if the story is unique or outlandish, it leaves you feeling amazed that such a thing happened to the speaker. Stories people can relate to can help presentations, too, but they're not as critical and they can even be distracting. You're already talking and showing visuals; adding stories can seem like too much of a diversion.
Caring Versus Passion
Caring about your work always makes it better. But in a presentation, you can and should dazzle people with your visuals. They're not your backup; they're as critical to your presentation as your explanations. It's a lot like show-and-tell. Without the things to show, you'd have nothing to tell. If you make sure all the charts and graphs you show are easy to understand, your audience will get your messages. A speech, on the other hand, is just you. This is where your passion really comes through, or your lack of it turns your speech into a dud. It's important to decide what your speech's core message is, then build out from that with quotes, anecdotes and humor to convey your message in a memorable way.
Speech and Presentation and More
You may be wondering about other types of public speaking. What's the difference between a seminar and a presentation; or a speech and a lecture? How about the difference between a speech and a debate?
A seminar is different from a presentation in that it's more interactive. While a presentation is given by one person, a seminar involves the participants in some way. It could include small group discussions or a panel. Since seminars are typically several hours in length, they often have many parts that vary in structure to keep people interested.
A lecture is similar to a speech because both are rather formal and one person is doing the talking. Lectures are more often used to teach something, particularly in a college class. Since lectures are typically given during every class period, they aren't expected to be as dramatic or dynamic as a speech, though it might be more motivating if they were!
A debate differs from both a speech and a presentation because it's between two sides that are equally involved. Each side usually takes an opposing view on the debate question or subject. It's often like a contest where, at the end of it, a vote is taken to decide who won the debate.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

What is Coaching?
Types of Coaching
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

6 presentation skills and how to improve them

Jump to section
What are presentation skills?
The importance of presentation skills, 6 presentation skills examples, how to improve presentation skills.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
Learn how to captivate an audience with ease
Capturing an audience’s attention takes practice.
Over time, great presenters learn how to organize their speeches and captivate an audience from start to finish. They spark curiosity, know how to read a room , and understand what their audience needs to walk away feeling like they learned something valuable.
Regardless of your profession, you most likely use presentation skills on a monthly or even weekly basis. Maybe you lead brainstorming sessions or host client calls.
Developing effective presentation skills makes it easier to contribute ideas with confidence and show others you’re someone to trust. Although speaking in front of a crowd sometimes brings nerves and anxiety , it also sparks new opportunities.
Presentation skills are the qualities and abilities you need to communicate ideas effectively and deliver a compelling speech. They influence how you structure a presentation and how an audience receives it. Understanding body language , creating impactful visual aids, and projecting your voice all fall under this umbrella.
A great presentation depends on more than what you say. It’s about how you say it. Storytelling , stage presence, and voice projection all shape how well you express your ideas and connect with the audience. These skills do take practice, but they’re worth developing — especially if public speaking makes you nervous.
Engaging a crowd isn’t easy. You may feel anxious to step in front of an audience and have all eyes and ears on you.
But feeling that anxiety doesn’t mean your ideas aren’t worth sharing. Whether you’re giving an inspiring speech or delivering a monthly recap at work, your audience is there to listen to you. Harness that nervous energy and turn it into progress.
Strong presentation skills make it easier to convey your thoughts to audiences of all sizes. They can help you tell a compelling story, convince people of a pitch , or teach a group something entirely new to them. And when it comes to the workplace, the strength of your presentation skills could play a part in getting a promotion or contributing to a new initiative.
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it’s helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop:
1. Active listening
Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone. When you have strong active listening skills, you can listen to others effectively and observe their nonverbal cues . This helps you assess whether or not your audience members are engaged in and understand what you’re sharing.
Great public speakers use active listening to assess the audience’s reactions and adjust their speech if they find it lacks impact. Signs like slouching, negative facial expressions, and roaming eye contact are all signs to watch out for when giving a presentation.
2. Body language
If you’re researching presentation skills, chances are you’ve already watched a few notable speeches like TED Talks or industry seminars. And one thing you probably noticed is that speakers can capture attention with their body language.
A mixture of eye contact, hand gestures , and purposeful pacing makes a presentation more interesting and engaging. If you stand in one spot and don’t move your body, the audience might zone out.

3. Stage presence
A great stage presence looks different for everyone. A comedian might aim for more movement and excitement, and a conference speaker might focus their energy on the content of their speech. Although neither is better than the other, both understand their strengths and their audience’s needs.
Developing a stage presence involves finding your own unique communication style . Lean into your strengths, whether that’s adding an injection of humor or asking questions to make it interactive . To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides.
4. Storytelling
According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out . But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer. Include a narrative they’ll want to listen to, and tell a story as you go along.
Shaping your content to follow a clear narrative can spark your audience’s curiosity and entice them to pay careful attention. You can use anecdotes from your personal or professional life that take your audience along through relevant moments. If you’re pitching a product, you can start with a problem and lead your audience through the stages of how your product provides a solution.
5. Voice projection
Although this skill may be obvious, you need your audience to hear what you’re saying. This can be challenging if you’re naturally soft-spoken and struggle to project your voice.
Remember to straighten your posture and take deep breaths before speaking, which will help you speak louder and fill the room. If you’re talking into a microphone or participating in a virtual meeting, you can use your regular conversational voice, but you still want to sound confident and self-assured with a strong tone.
If you’re unsure whether everyone can hear you, you can always ask the audience at the beginning of your speech and wait for confirmation. That way, they won’t have to potentially interrupt you later.
Ensuring everyone can hear you also includes your speed and annunciation. It’s easy to speak quickly when nervous, but try to slow down and pronounce every word. Mumbling can make your presentation difficult to understand and pay attention to.

6. Verbal communication
Although verbal communication involves your projection and tone, it also covers the language and pacing you use to get your point across. This includes where you choose to place pauses in your speech or the tone you use to emphasize important ideas.
If you’re giving a presentation on collaboration in the workplace , you might start your speech by saying, “There’s something every workplace needs to succeed: teamwork.” By placing emphasis on the word “ teamwork ,” you give your audience a hint on what ideas will follow.
To further connect with your audience through diction, pay careful attention to who you’re speaking to. The way you talk to your colleagues might be different from how you speak to a group of superiors, even if you’re discussing the same subject. You might use more humor and a conversational tone for the former and more serious, formal diction for the latter.
Everyone has strengths and weaknesses when it comes to presenting. Maybe you’re confident in your use of body language, but your voice projection needs work. Maybe you’re a great storyteller in small group settings, but need to work on your stage presence in front of larger crowds.
The first step to improving presentation skills is pinpointing your gaps and determining which qualities to build upon first. Here are four tips for enhancing your presentation skills:
1. Build self-confidence
Confident people know how to speak with authority and share their ideas. Although feeling good about your presentation skills is easier said than done, building confidence is key to helping your audience believe in what you’re saying. Try practicing positive self-talk and continuously researching your topic's ins and outs.
If you don’t feel confident on the inside, fake it until you make it. Stand up straight, project your voice, and try your best to appear engaged and excited. Chances are, the audience doesn’t know you’re unsure of your skills — and they don’t need to.
Another tip is to lean into your slideshow, if you’re using one. Create something colorful and interesting so the audience’s eyes fall there instead of on you. And when you feel proud of your slideshow, you’ll be more eager to share it with others, bringing more energy to your presentation.

2. Watch other presentations
Developing the soft skills necessary for a good presentation can be challenging without seeing them in action. Watch as many as possible to become more familiar with public speaking skills and what makes a great presentation. You could attend events with keynote speakers or view past speeches on similar topics online.
Take a close look at how those presenters use verbal communication and body language to engage their audiences. Grab a notebook and jot down what you enjoyed and your main takeaways. Try to recall the techniques they used to emphasize their main points, whether they used pauses effectively, had interesting visual aids, or told a fascinating story.

3. Get in front of a crowd
You don’t need a large auditorium to practice public speaking. There are dozens of other ways to feel confident and develop good presentation skills.
If you’re a natural comedian, consider joining a small stand-up comedy club. If you’re an avid writer, participate in a public poetry reading. Even music and acting can help you feel more comfortable in front of a crowd.
If you’d rather keep it professional, you can still work on your presentation skills in the office. Challenge yourself to participate at least once in every team meeting, or plan and present a project to become more comfortable vocalizing your ideas. You could also speak to your manager about opportunities that flex your public speaking abilities.
4. Overcome fear
Many people experience feelings of fear before presenting in front of an audience, whether those feelings appear as a few butterflies or more severe anxiety. Try grounding yourself to shift your focus to the present moment. If you’re stuck dwelling on previous experiences that didn’t go well, use those mistakes as learning experiences and focus on what you can improve to do better in the future.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
It’s normal to feel nervous when sharing your ideas. In fact, according to a report from the Journal of Graduate Medical Education, public speaking anxiety is prevalent in 15–30% of the general population .
Even though having a fear of public speaking is common, it doesn’t make it easier. You might feel overwhelmed, become stiff, and forget what you were going to say. But although the moment might scare you, there are ways to overcome the fear and put mind over matter.
Use these tactics to reduce your stress when you have to make a presentation:
1. Practice breathing techniques
If you experience anxiety often, you’re probably familiar with breathing techniques for stress relief . Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can help you stop worrying and regulate anxious feelings.
Before a big presentation, take a moment alone to practice breathing techniques, ground yourself, and reduce tension. It’s also a good idea to take breaths throughout the presentation to speak slower and calm yourself down .
2. Get organized
The more organized you are, the more prepared you’ll feel. Carefully outline all of the critical information you want to use in your presentation, including your main talking points and visual aids, so you don’t forget anything. Use bullet points and visuals on each slide to remind you of what you want to talk about, and create handheld notes to help you stay on track.
3. Embrace moments of silence
It’s okay to lose your train of thought. It happens to even the most experienced public speakers once in a while. If your mind goes blank, don’t panic. Take a moment to breathe, gather your thoughts, and refer to your notes to see where you left off. You can drink some water or make a quick joke to ease the silence or regain your footing. And it’s okay to say, “Give me a moment while I find my notes.” Chances are, people understand the position you’re in.

4. Practice makes progress
Before presenting, rehearse in front of friends and family members you trust. This gives you the chance to work out any weak spots in your speech and become comfortable communicating out loud. If you want to go the extra mile, ask your makeshift audience to ask a surprise question. This tests your on-the-spot thinking and will prove that you can keep cool when things come up.
Whether you’re new to public speaking or are a seasoned presenter, you’re bound to make a few slip-ups. It happens to everyone. The most important thing is that you try your best, brush things off, and work on improving your skills to do better in your next presentation.
Although your job may require a different level of public speaking than your favorite TED Talk , developing presentation skills is handy in any profession. You can use presentation skills in a wide range of tasks in the workplace, whether you’re sharing your ideas with colleagues, expressing concerns to higher-ups, or pitching strategies to potential clients.
Remember to use active listening to read the room and engage your audience with an interesting narrative. Don’t forget to step outside your comfort zone once in a while and put your skills to practice in front of a crowd. After facing your fears, you’ll feel confident enough to put presentation skills on your resume.
If you’re trying to build your skills and become a better employee overall, try a communications coach with BetterUp.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
8 tips to improve your public speaking skills
The significance of written communication in the workplace, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, what is an entrepreneur understanding the different types and examples of entrepreneurship, get smart about your goals at work and start seeing results, 9 signs that you’re being pushed out of your job, goal-setting theory: why it’s important, and how to use it at work, the importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, empathic listening: what it is and how to use it, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, impression management: developing your self-presentation skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case studies
- ROI of BetterUp
- What is coaching?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Briefing
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
Presentation Definition: A Comprehensive Guide
Featured In
Table of contents, unraveling the presentation definition, what is a presentation, historical roots: from latin to modern day, types and formats of presentations, enhancing presentation skills: a guide, presentation in the digital age: multimedia and keynote, the art of visual aids: graphs and more, presentation in different languages, presentation in literature and culture, effective presentation: tips and techniques, incorporating quizzes and group activities, presentation in educational contexts, synonyms and related terms, the thesaurus and vocabulary expansion, historical and specialized types of presentations, presentation in business: introducing a new product, word of the day: presentation, key points and summarization, cultural influences and adaptations, the role of technology, eye contact and body language, the art of storytelling, innovation and new products, speechify studio.
Unraveling the Presentation DefinitionPresentation - a word frequently used in English, Spanish, Latin, French, and Arabic contexts, but what does it exactly...
Presentation - a word frequently used in English, Spanish, Latin, French, and Arabic contexts, but what does it exactly mean? In this article, we delve into the definition of presentation , exploring its various facets and applications in different fields.
The Essence of Presentation: A Definition
A presentation is the act of presenting information or ideas to a group of people in a structured and deliberate manner, often with the aid of visual aids like PowerPoint, Keynote, or multimedia tools.
Presentations are a ubiquitous part of the professional, educational, and social landscape. The act of presenting, essentially communicating information and ideas to a group of people, has evolved significantly over time. This article explores the definition of a presentation, its various formats, the skills required to make it effective, and the nuances of a great presentation, all while weaving in an eclectic mix of keywords.
The Evolution from 'Praesentātiō' to 'Presentation'
In its essence, a presentation is the act of presenting or displaying information or ideas to an audience. The Oxford English Dictionary defines it as "the action or process of presenting something to someone." In Latin, the term stems from 'praesentātiō', denoting the action of placing before or showing. This definition has broadened in modern English to encompass various methods of showcasing information, whether it's a business pitch, an academic lecture, or introducing a new product.
The term has its origins in Latin ('praesentātiō'), evolving through various languages like French and British English, symbolizing the act of presenting, displaying, or giving something to others.
Diverse Formats for Different Needs
Presentations can vary in formats - from formal PowerPoint presentations to informal Prez (an informal abbreviation of presentation) discussions, each tailored to suit specific requirements.
Mastering the Art of Presentation
Presentations come in various formats, from the traditional speech to more contemporary multimedia showcases. PowerPoint, a widely used tool, allows the integration of text, images, and graphs to create visually appealing slides. Similarly, Apple's Keynote offers tools for creating impactful multimedia presentations. The inclusion of visual aids, like graphs and charts, enhances comprehension and retention. For those interested in learning Spanish, Arabic, or French, incorporating these languages in presentations can broaden audience reach.
Effective presentation skills involve a blend of clear communication, eye contact , engaging visual aids , and a confident delivery. These skills are crucial in both business and educational settings.
Embracing Technology for Impactful Presentations
In the era of digital communication, tools like multimedia presentations and Apple's Keynote software have become indispensable for creating dynamic and interactive presentations.
Using Graphs and Visuals Effectively
Effective presentations often include graphs and other visual aids to convey complex information in an easily digestible format, enhancing the audience's understanding.
A Multilingual Perspective
The concept of presentation transcends languages, from English to Arabic , each offering unique nuances in the art of presenting.
Presentation Copy and Beyond
The term also appears in literary contexts, such as a "presentation copy" of a book, and in cultural scenarios like a "breech presentation" in childbirth, where the baby is positioned to exit the birth canal feet first.
Crafting an Impactful Presentation
An effective presentation is more than just delivering facts; it involves engaging storytelling, structured key points , and the ability to connect with the audience.
To deliver an effective presentation, certain skills are paramount. English, being a global lingua franca, is often the preferred language for presentations. However, the ability to present in multiple languages, like Spanish or French, can be a significant advantage.
Eye contact is a crucial skill, establishing a connection with the audience and making the presentation more engaging. Additionally, the ability to read the room and adjust the presentation accordingly is vital.
Interactive elements like quizzes can transform a presentation from a monologue into a dynamic group activity. They encourage participation and can be especially effective in educational settings. Quizzes can also be used in business presentations to gauge audience understanding or to introduce a new product.
Learning Through Presentations
In educational settings, presentations are used as a tool for teaching and assessment, often involving quizzes and interactive sessions to enhance learning.
Exploring Synonyms and the Thesaurus
The thesaurus offers a range of synonyms for 'presentation,' such as exhibition, demonstration, and display, each with slightly different connotations.
Utilizing a thesaurus can enrich presentation language, offering synonyms and example sentences to clarify points. The 'word of the day' concept, often found in English learning resources, can be an interesting addition to presentations, especially in multilingual contexts.
The term 'presentation' also has specialized meanings. In historical contexts, a 'presentation copy' refers to a book or manuscript gifted by the author. In obstetrics, 'breech presentation' denotes a situation where the baby is positioned to exit the birth canal feet or buttocks first. Understanding these specialized definitions enriches the overall grasp of the term.
The Role of Presentation in Business
In business contexts, presentations are crucial for scenarios like introducing a new product , persuading investors, or communicating with stakeholders.
Expanding Vocabulary with 'Presentation'
In language learning, 'presentation' can be a word of the day , helping learners understand its usage through example sentences and pronunciation (notated as /ˌprez.ənˈteɪ.ʃən/ in English).
An effective presentation distills complex information into key points, making it easier for the audience to remember the most important takeaways. Summarization skills are critical in achieving this clarity.
The concept of presentations varies across cultures. In Arabic-speaking countries, the style of presentation might differ significantly from that in English-speaking contexts. The benefice of understanding cultural nuances cannot be overstated, as it can significantly impact the effectiveness of a presentation.
Technology, particularly multimedia, plays a pivotal role in modern presentations. From PowerPoint slides to advanced software like Keynote, the use of technology has revolutionized the way information is presented. The integration of videos, sound, and interactive elements makes presentations more engaging and memorable.
In delivering a presentation, non-verbal cues like eye contact and body language are as important as the spoken content. Maintaining eye contact with the audience establishes a connection and keeps them engaged. Similarly, confident body language can convey authority and enthusiasm.
A great presentation often resembles storytelling. It's not just about relaying facts; it's about weaving a narrative that resonates with the audience. This involves understanding the audience's needs and interests and tailoring the content accordingly.
Presentations are often the first introduction of a new product to the market. The effectiveness of these presentations can make or break the product's success. Highlighting the unique features and benefits in a clear, compelling manner is crucial.
The Power of Presentation
Presentations are a powerful tool for communication and education. Whether in a formal business setting or an informal educational environment, mastering the art of presentation can lead to more effective and impactful communication.
1. Oxford English Dictionary
2. Merriam-Webster Thesaurus
3. Apple Keynote User Guide
4. Presentation Techniques in Educational Literature
Pricing: Free to try
Speechify Studio is a comprehensive creative AI suite for individuals and teams. Create stunning AI videos from text prompts, add voice overs, create AI avatars, dub videos into multiple languages, slides, and more! All projects can be used for personal or commercial content.
Top Features : Templates, text to video, real-time editing, resizing, transcription, video marketing tools.
Speechify is clearly the best option for your generated avatar videos. With seamless integration with all the products, Speechify Studio is perfect for teams of all sizes.
## Frequently Asked Questions About Presentations
### What is in a presentation?
A presentation typically includes a combination of spoken words and visual aids such as PowerPoint slides, graphs, or multimedia elements. It's an organized way to convey information or ideas to a group of people.
### What is meant by giving a presentation?
Giving a presentation refers to the act of presenting information or ideas to an audience. This act, known in various languages including English, Spanish, and French as 'presentation' (or 'praesentātiō' in Latin), involves communication skills, visual aids, and sometimes interactive elements like quizzes.
### What makes a good presentation?
A good presentation effectively communicates key points, engages the audience through eye contact and clear speech (often practiced as a 'word of the day' in English classes), uses visual aids like graphs, and is well-structured. Effective presentation skills are crucial for this.
### What are the types of presentation?
There are various types of presentations, including formal business presentations (often using PowerPoint or Keynote), educational lectures, sales pitches for a new product, and informal talks. Each type uses different formats and approaches.
### What are the 4 parts of a presentation?
The four main parts of a presentation are the introduction, the main body, the conclusion, and the Q&A session. Each part plays a vital role in delivering an effective presentation.
### What are the three things that a good presentation should do?
A good presentation should inform, engage, and persuade or inspire the audience. It's about more than just delivering facts; it's an act of communication that can change perspectives or encourage action.
### How is a presentation linked with multimedia?
Presentations often use multimedia elements like videos, audio clips, and animated graphs to enhance the viewer's understanding and engagement. Multimedia tools like PowerPoint and Keynote are widely used in creating dynamic presentations.
### How long should a presentation be?
The length of a presentation can vary, but it's typically between 15 to 30 minutes. The duration depends on the context and the amount of information to be covered. It's important to keep presentations concise to maintain the audience's attention.
These answers incorporate various aspects of presentations, including their definition, formats, and the skills required, in multiple languages and contexts, as seen in resources like Oxford dictionaries and thesaurus.
Best text to speech software
Read Aloud: Transforming the Way We Experience Text

Cliff Weitzman
Cliff Weitzman is a dyslexia advocate and the CEO and founder of Speechify, the #1 text-to-speech app in the world, totaling over 100,000 5-star reviews and ranking first place in the App Store for the News & Magazines category. In 2017, Weitzman was named to the Forbes 30 under 30 list for his work making the internet more accessible to people with learning disabilities. Cliff Weitzman has been featured in EdSurge, Inc., PC Mag, Entrepreneur, Mashable, among other leading outlets.
- Interactive Presentation
How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 April, 2024 • 9 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You're standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we'll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let's dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
| How long does it take to make a presentation? | 20 - 60 hours. |
| How can I improve my presentation writing? | Minimize text, optimize visuals, and one idea per slide. |
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you've got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?
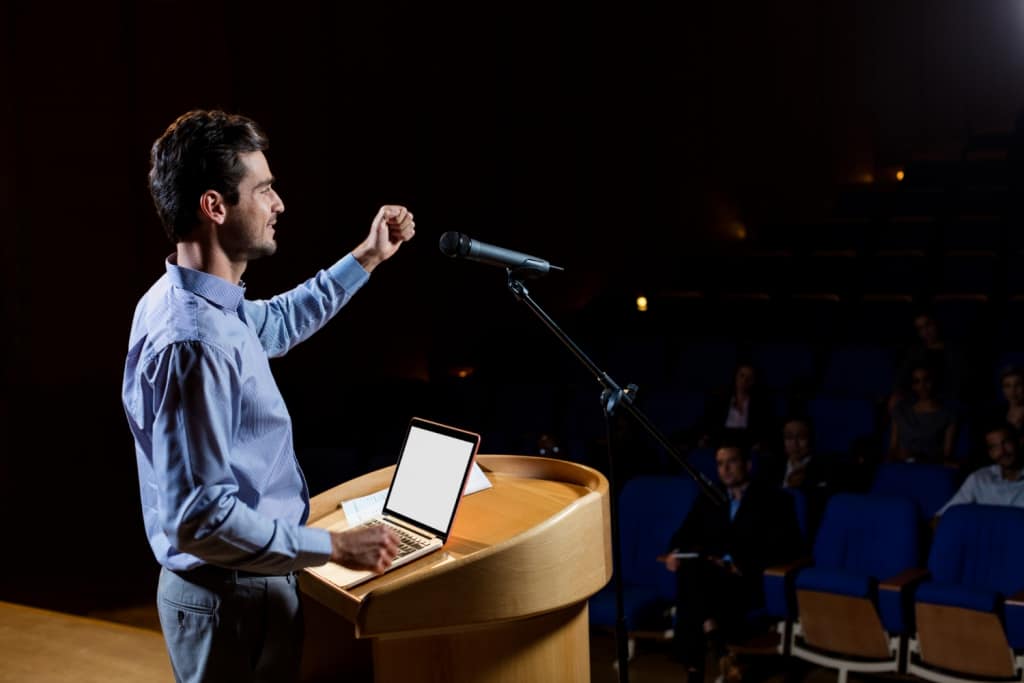

- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience's attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience's attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: "Have you ever...?"
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: "Did you know that....?"
- Use a Powerful Quote: "As Maya Angelou once said,...."
- Tell a Compelling Story : "Picture this: You're standing at...."
- Start with a Bold Statement: "In the fast-paced digital age...."
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: "In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,... Next,... Finally,.... we'll discuss...."
- Provide Background and Context: Example: "Before we dive into the details, let's understand the basics of....."
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: "To illustrate...., let's look at an example. In,....."
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: "While..., we must also consider... ."
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: "To summarize, we've... Now, let's shift our focus to..."
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: "As we conclude our presentation, it's clear that... By...., we can...."
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you've outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: "As you can see from this graph,... This demonstrates...."
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it's crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation - the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience's attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience's attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience's attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
"Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that's exactly what we'll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it's vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we'll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let's get started!"
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you're a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation's impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let's take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience's attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: "Have you ever...?" Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: "Did you know that....?" Use a Powerful Quote: "As Maya Angelou once said,...." Tell a Compelling Story : "Picture this: You're standing at...." Start with a Bold Statement: "In the fast-paced digital age...."
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience's attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Prepare for a Presentation, with Examples
February 15, 2021 - Dom Barnard
This guide covers everything you need to know to prepare for your presentation. including what you need to think about beforehand, during and after the presentation.
1. Rehearse, rehearse, rehearse (always aloud)
Once you have your presentation worked out, you will need to practice it, but even though you might think it’s the best way to have a flawless presentation, don’t memorise what you’re going to say.
That might sound like incredibly bad advice, but here’s why:
- If you memorise your speech, you’ll get stuck in thinking you can only deliver your ideas in that way, and that stifles your creativity, and the chance for new thoughts and ways to put things that come up as you speak.
Not only that, but every audience is different . Sometimes they laugh out loud, sometimes they sit and smile, and you never know which type of audience you’ll have until you’re live.
Practice Presentation Skills
Improve your public speaking and presentation skills by practicing them in realistic environments, with automated feedback on performance. Learn More
If you’re going off a memorised presentation, it’s much more difficult to break away from that to go with the flow on the day, and respond naturally to your audience.
- If you forget your speech in the middle of it, you will be thrown, and you’ll have more chance of complete brain freeze, which really will knock your confidence.
- Memorising your presentation gives you a false sense of security, which could leave you high and dry if something goes wrong. If you’ve only got your memorised speech, for example, what will you do if your PowerPoint freezes or your props break, and you can’t do what you were going to do?
Rehearse in front of colleagues, friends, a mirror, in virtual reality – always aloud. Make sure you spend plenty of time practising your presentation, it will make you feel much more relaxed if you know your material.
Courses where you can rehearse with interactive exercises:
- Essential Public Speaking
- How to Present over Video
Video showing how you can prepare for your presentation using virtual reality. Learn more about virtual reality training .
2. Memorise your opening line
Do, however, memorise your opening line. If you know how you’re going to begin, you’ll get a strong start and that will build your confidence.
Many speakers and stage actors find that the minute they’ve actually delivered their first line, the nerves are gone and they’re well into their stride.
3. Practise your speech from written notes
Writing your presentation out in your own handwriting will help you clarify your ideas and may well bring you new ones.
- How to Write a Speech to Engage your Audience
4. Practise presentation flow
As well as practising for the ideas and what you want to say, practise how you want your presentation to flow. Think of it almost as a symphony, with high points, slow movements and crescendos. If it’s important, think about how you want your audience to feel, what emotions you want them to have, and when.
5. The power of silence
Don’t be afraid to pause and use the power of silence. A good pause can have a huge emotional impact. It allows people to really absorb what you are saying and react, and it’s vital to pause if you’re using humour so that the next part of your presentation doesn’t get lost underneath people’s laughter.
For more on the ‘Power of the Pause’, watch this short from video Brian Tracy: The Power of the Pause
- 10 Effective Ways to use Pauses in your Speech
6. Have a backup
There’s nothing worse than the projector dying or finding that your laptop won’t communicate with the projector for some reason. If you know you have a backup, even if it’s only a pre-prepared flip chart, you’ll feel better, and you’ll be more confident.
7. Arrive early
Following on from that, arrive at least half an hour early so you aren’t feeling rushed, and so you have time to check your equipment and get your notes laid out ready to go. That gives you time to breathe and relax before you go on, knowing everything is as set as it can be.
8. Use physical props for a demo
Use physical props, if possible, for a demo. This can make you stand out and be more memorable among all the other speakers who only use PowerPoint, and it can add greatly to the impact of your presentation.
Video showing an example of using physical props during a live demo.
9. Structure your presentation
First, find out how much time you have to present, is it 10 minutes, 15, an hour? Prepare enough material for this time and have a couple of extra slides as backup – we tend to speak much quicker when nervous so you might find you finish your presentation too early. At some large conference events, timings may change on the day, be aware of this have a shorter version of your presentation in mind (i.e. know which slides to skip over).
- How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
- Examples of Corporate Presentation Structures
10. Prepare for questions
Have a few backup slides for questions you think will arise from your presentation. It is sometime a tactic to explain a section briefly in your speech, so that you get a question about it afterwards. If you don’t understand the question, ask for it to be rephrased.
If there are no questions, it is not an indication how good or bad your presentation was. You many have explain your material extremely well, or simply that people are tired at the end of the day and want to go home.
- Guide for Handling Questions after a Presentation
11. Prepare for where you are presenting
If you can, go to the room you are speaking in before the actual event. It gives you an idea of furniture layout, podium height, location, room size, audience size and lighting. You can then visualise the room while practising and avoid the shock of suddenly being faced with a huge room when you expected a tiny one.
Ask the organiser if you need any particular props, for example a table to help with your live demo.
Additional planning to think about before your presentation:
1. Purpose – what outcome are we trying to achieve? How can results be measured? What will success look like?
2. Topic – Novelty? Complexity? Technical?
3. People – Who should attend? What do they already know? How are they going to help?
4. Timing – When will it happen and how long will the presentation take?
5. Location – Where will the presentation be held? Do you have access to the correct facilities for the presentation?
6. Papers – Who is keeping minutes? Do you need to send out an agenda before the presentation? Background information required?
7. Visual aids – Is a projector required ? Boards?
8. Style – Structure or unstructured, discussion style? How assertive should you be? How should the meeting items be organised?
12. Choose the signals to give to your audience
Before the presentation, think about these 5 topics:
- Eye contact
- Facial gestures
- Body language
Decide how you will use each of these to reinforce your message. Use the table below for help.
| Passive | Aggressive | Assertive | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat, monotonous, trails off, shaky, hesitant. | Sharp, cold, loud, shouts, abrupt, clipped, fast. | Controlled, firm, warm, rich, clear, even, loud. | |
| Ers and ums, jerky, too slow, too fast. | Fast, emphatic, blameful, abrupt, erratic, hurried. | Steady and controlled, changes easily. | |
| Evasive, looking down, darting, low eye contact. | Stares and glaring, dominating, fixed gaze, threatening. | Firm not fixed, natural and relaxed. | |
| Fixed smile, apology facial gestures, blinking, blushing, chewing lip. | Set face, few smiles, clenched jaw, frowning, chin forward, lips tight, gritted teeth. | Open, varied and congruent expressions, calm, jaw relaxed, few blinks, smiles. | |
| Hunched, hand over mouth, arms crossed, head down, slumping, legs crossed, stands awkwardly, soft handshake. | Thumping, clenched fists, pointing, pacing, leaning forward, sharp and rapid movements, crushing handshake. | Open hand and arm movements, head upright, calm, emphatic gestures, relaxed, head nodding to show attention, firm handshake. |
Additional courses to help you prepare for your presentation:
- Presentation Skills Training Courses
Example from Steve Jobs
Think about these 10 techniques while you are preparing your presentation..

- Planning in Analog. Tell a story, create stunning visuals and videos to complement video, use demonstrations and other speakers, keep the audience engaged.
- Creating a Twitter-Friendly Description Single description sentence, condensed his message into 140 characters.
- Introduce the Enemy Story needs villains or a problem to be solved. Jobs highlighted IBM and useless mobile phones (during iPhone release) as his villains.
- Focusing on Benefits Keep reinforcing the benefits of your product, create top 10 lists, understand this is what customers care about.
- Sticking to Rule of Three Classic Literary technique, things are best remembered and reinforced in threes. Read this article on Literary Techniques for more detail.
- Sell Dreams, Not Products Create a vision people believe in, create a vision which will make people’s lives better
- Create Visual Slides Use as few words as possible and use colourful graphics on the slide to highlight points.
- Make Numbers Meaningful Compare large numbers to things people understand.
- Use Plain English Use easy to say and easy to remember words, keep it simple.
- Large Reveals Due to Apple secrecy, Jobs was able to deliver unexpected products to the world at his product launches.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Public Speaking and Presentations

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Public Speaking and Presentations: Tips for Success
This resource includes tips and suggestions for improving your public speaking skills.
Even if you’ve never spoken in front of a large group before, chances are you will encounter public speaking sometime during your life. Whether you’re giving a presentation for your classmates or addressing local politicians at a city council meeting, public speaking allows you to convey your thoughts and feelings in clear ways. Having the right tools can prepare you for successful public speaking and equip you with high-quality communication skills.
Know Your Audience
Different audiences require different modes of public speaking. How you address a room full of preschoolers will vary from how you address a group of professors at an academic conference. Not only will your vocabulary change, but you might alter your pacing and tone as well.
Knowing your audience also helps you decide the content of your speech. For example, if you’re presenting research to a group of scientists, you might not need to define all your scientific language. However, if you present that same research to a group of individuals who are unfamiliar with your scientific field, you may need to define your terms or use simpler language.
Recognizing the extent to which your audience is familiar with your topic helps you center your presentation around the most important elements and avoid wasting time on information your audience either 1) already knows or 2) does not need to know for the purpose of your speech.
Knowing your audience also means tailoring your information to them. Try to keep things straight and to the point; leave out extraneous anecdotes and irrelevant statistics.
Establish Your Ethos and Feel Confident in Your Subject
It’s important to let your audience know what authority you have over your subject matter. If it’s clear you are familiar with your subject and have expertise, your audience is more likely to trust what you say.
Feeling confident in your subject matter will help establish your ethos. Rather than simply memorizing the content on your PowerPoint slides or your note cards, consider yourself a “mini expert” on your topic. Read up on information related to your topic and anticipate questions from the audience. You might want to prepare a few additional examples to use if people ask follow-up questions. Being able to elaborate on your talking points will help you stay calm during a Q & A section of your presentation.
Stick to a Few Main Points
Organizing your information in a logical way not only helps you keep track of what you’re saying, but it helps your audience follow along as well. Try to emphasize a few main points in your presentation and return to them before you conclude. Summarizing your information at the end of your presentation allows your audience to walk away with a clear sense of the most important facts.
For example, if you gave a presentation on the pros and cons of wind energy in Indiana, you would first want to define wind energy to make sure you and your audience are on the same page. You might also want to give a brief history of wind energy to give context before you go into the pros and cons. From there, you could list a few pros and a few cons. Finally, you could speculate on the future of wind energy and whether Indiana could provide adequate land and infrastructure to sustain wind turbines. To conclude, restate a few of the main points (most likely the pros and cons) and end with the most important takeaway you want the audience to remember about wind energy in Indiana.
Don't be Afraid to Show Your Personality
Delivering information without any sort of flourish or style can be boring. Allowing your personality to show through your speaking keeps you feeling relaxed and natural. Even if you’re speaking about something very scientific or serious, look for ways to let your personality come through your speech.
For example, when Jeopardy! host Alex Trebek announced in March of 2019 that he had stage 4 pancreatic cancer, he still let his trademark dignity and professionalism set the tone for his address. He began his announcement by saying “it’s in keeping with my long-time policy of being open and transparent with our Jeopardy! fan base.” Later, he joked that he would need to overcome his illness in order to fulfill his contract, whose terms required him to host the show for three more years. Though the nature of Trebek's announcement could easily have justified a grim, serious tone, the host instead opted to display the charm that has made him a household name for almost thirty-five years. In doing so, he reminded his audience precisely why he is so well-loved.
Use Humor (When Appropriate)
Using humor at appropriate moments can keep your audience engaged and entertained. While not all occasions are appropriate for humor, look for moments where you can lighten the mood and add some humor.
For example, just two months after the assassination attempt on Ronald Reagan, Reagan was in the middle of giving a speech when a balloon loudly popped while he was speaking. Reagan paused his speech to say “missed me,” then immediately continued speaking. This off-the-cuff humor worked because it was appropriate, spontaneous, and did not really distract from his message.
Similarly, at the end of his final White House Correspondents Dinner, Barack Obama concluded his speech by saying “Obama out” and dropping the mic. Once again, the humor did not distract from his message, but it did provide a light-hearted shift in his tone.
Don't Let Visual Aids Distract From Your Presentation
Visual aids, such as PowerPoints or handouts, often go alongside presentations. When designing visual aids, be sure they do not distract from the content of your speech. Having too many pictures or animations can cause audience members to pay more attention to the visuals rather than what you’re saying.
However, if you present research that relies on tables or figures, having many images may help your audience better visualize the research you discuss. Be aware of the ways different types of presentations demand different types of visual aids.
Be Aware of Your Body Language
When it comes to giving a presentation, nonverbal communication is equally as important as what you’re saying. Having the appropriate posture, gestures, and movement complement the spoken element of your presentation. Below are a few simple strategies to make you appear more confident and professional.
Having confident posture can make or break a presentation. Stand up straight with your shoulders back and your arms at your sides. Slouching or crossing your arms over your chest makes you appear smaller and more insecure. However, be sure you’re not too rigid. Just because you’re standing up tall does not mean you cannot move around.
Eye contact
Making eye contact with your audience not only makes them feel connected to you but it also lets you gauge their response to you. Try to look around the room and connect with different audience members so you’re not staring at the same people the whole time. If you notice your audience starting to nod off, it might be a good time to change your tone or up your energy.
Avoid distracting or compulsive gestures
While hand gestures can help point out information in a slide or on a poster, large or quick gestures can be distracting. When using gestures, try to make them feel like a normal part of your presentation.
It’s also easy to slip into nervous gestures while presenting. Things like twirling your hair or wringing your hands can be distracting to your audience. If you know you do something like this, try to think hard about not doing it while you’re presenting.
Travel (if possible)
If you are presenting on a stage, walking back and forth can help you stay relaxed and look natural. However, be sure you’re walking slowly and confidently and you’re using an appropriate posture (described above). Try to avoid pacing, which can make you appear nervous or compulsive.
Rehearse (if Possible)
The difference between knowing your subject and rehearsing comes down to how you ultimately present your information. The more you rehearse, the more likely you are to eliminate filler words such as like and um . If possible, try practicing with a friend and have them use count the filler words you use. You can also record yourself and play back the video. The more you rehearse, the more confident you will feel when it comes time to actually speak in front of an audience.
Finally, Relax!
Although public speaking takes time and preparation, perhaps one of the most important points is to relax while you’re speaking. Delivering your information in a stiff way prevents you from appearing natural and letting your personality come through. The more relaxed you feel, the more confident your information will come across.
Before your next presentation or speech, here’s the first thing you must think about
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

The next time you’re preparing to speak to a group, remember to keep your audience at the center of your communication, says Briar Goldberg, the director of speaker coaching at TED. One way to do this is to ask yourself: “What gift are you giving to your audience?”
TED recently partnered with Marriott Hotels to offer a special day-long seminar on public speaking for Marriott Bonvoy members. Briar Goldberg — TED’s director of speaker coaching who has helped prepare hundreds of people for the TED stage — gave them tips and tools to be better communicators in their own lives.
Below, she takes a deeper dive into one aspect of public speaking that many of us overlook when drafting our speeches and presentations: our audience.
Let’s be honest, there’s no shortage of public speaking advice out there. There are countless books, blog posts and YouTube videos offering you instructions on how to tell engaging stories, make eye contact, use hand gestures, and more. I think that’s great, although I’ll admit I’m biased. I’ve spent my career teaching public speaking and coaching executives, and since 2015, I’ve been working with TED speakers. I truly believe that everyone benefits when we communicate more effectively.
But even with so much advice available, I still see one big communication mistake made all of the time. It’s this: Most people communicate in the wrong direction .
What is the wrong direction? Too many of us write our scripts, build our decks, or compile our talking points before we think about our audience and what they need or expect to get out of our communication. This has serious consequences. When your audience doesn’t feel like your words apply to them, when they don’t understand what you’re trying to say, or, worse yet, they don’t care about your ideas, then your carefully-crafted slides, agenda or jokes simply don’t matter.
My earliest mentor in this work, Jim Wagstaffe always tells speakers to practice their ABCs: Audience Before Content. I love that acronym so much because it captures the essence of what communication is really all about — it’s not about you, the speaker; it’s always about your audience. Your audience’s needs should always be your central focus.
At TED, when we’re helping speakers prepare their talks, we ask them to identify the “gift” they’re giving the audience. In my opinion, this is what every communicator should be asking themselves before any kind of communication — whether it’s a keynote or a TED Talk or something smaller like a pitch to your boss or a statement at a community meeting. What gift are you giving the audience?
The good news is, understanding how to put your audience at the center of your communication isn’t rocket science. And when you do it correctly, I can almost guarantee that your next speech, presentation or meeting will be a success.
What does it really mean to know your audience?
You’ve probably heard the phrase “know your audience.” I’ve even seen lists floating around that offer a series of questions designed to help you do this, with queries such as: “What’s the gender breakdown of your audience?” “Are they executives or middle-managers?” “Where are they from?”
While demographic information like this is important — for example, you should probably rethink a joke about swiping right if the average age of your audience is 76 — the kind of knowledge I’m talking about goes much deeper. It goes beyond the superficial to zoom in on these two key things: “What are my audience’s goals?” and “How do they make decisions?”
How to really understand your audience’s goals
This means you’ll need to ask a different set of questions — ones that get at your audience’s needs and expectations. These include:
“Why are these people taking time out of their busy schedules to listen to me speak?”
“What do they hope (or need) to gain from this presentation/speech/address/meeting?”
“What are their expectations coming in?”
“What can I say in order to meet or exceed those expectations?”
Once you know the answers to these questions, you can craft a communication that is tailored to your audience; when you do, your audience is more likely to stay focused, remember what you said, pass on the information you shared, and remember you as a good speaker.
But what happens if your goals as a speaker don’t align with the audience’s goals?
As a communicator, you will have your own goals. Perhaps you’re an executive and you have an important message that you need the rest of the company to hear. Maybe you’ve designed a new product that you want your customers to get excited about. Getting clear on your own communication goals is important because then you can evaluate if your goals line up with your audience’s goals. If they do, that’s great — and you can start crafting your communication.
But sometimes they won’t. When this happens, it’s your job to figure out how to close the gap and persuade the audience that your goals can — and should — be their goals, too. I’m not talking about manipulation or asking you to trick people into thinking something different. What I am advocating is that you work to understand your audience well enough to know how they make decisions and what kind of information they need to have to be persuaded of their own accord.
One of the most persuasive TED Talks this year was delivered by sleep expert Matt Walker . Everyone has different goals when they decide to watch a talk about sleep. But Matt was clear on his goal: to convince people to prioritize sleep above all else. To get the audience on his side, he had to persuade them that getting enough sleep is the single most important thing they could do with our time.
Understand how your audience makes decisions
You can’t effectively persuade anyone unless you know what kind of information they need to make a decision. Think about it this way: If a salesperson was trying to sell you a new computer, you wouldn’t decide to buy it until they told you the price. With your audience, you can’t expect to influence them until you provide them with the information they need to decide if they want to change their minds.
But every audience is different. How do you know what kind of information you need to offer in order to sway them? There are entire bodies of research that cover audience persuasion strategies. But let me offer a simple framework to get you started.
In general, audiences can be broken down into three types: expert, novice and mixed. An expert audience understands your topic and they might already know you, the speaker. If you’re a real-estate broker addressing an annual meeting of the nation’s realtors, you’re speaking to an expert audience. A novice audience doesn’t know much about the topic and doesn’t know anything about you. An example of this would be a real-estate broker speaking at an open-house for community residents interested in buying a first home. But more often than not, your audience will be a mix of experts, novices and everyone in-between. The large, international TED audience is a perfect example of a mixed audience.
When you’re speaking to an expert audience: Use logical/quantitative arguments to persuade them.
In general, expert audiences are more likely to be persuaded by logical arguments and quantitative information. If you’re a real-estate broker trying to convince your expert audience to invest in a new kind of property, you’re more likely to be successful if your presentation is built around data and statistics that support this plan.
When you’re speaking to a novice audience: Lean into your own credibility.
Because a novice audience doesn’t know much about you or your topic, they tend to make decisions based on your credibility and the credibility of your sources. Therefore, it can be important to build up your reputation and credentials so they’ll trust what you’re saying and follow your recommendations.
When I’m giving a lecture on public speaking to a group who doesn’t know me, I always mention the universities I’ve taught at and some of the names of executives I’ve coached. This isn’t to brag — and let me be clear, you’ll need to use your judgement to figure out how much information to give so it doesn’t sound like you’re bragging — but it’s a quick way for me to get my audience to accept that I’m a solid source of communication advice and that they should listen to me. In some cases, I’ll tell my audience where a particular piece of information in my lecture came from. By saying “Harvard published this study last year…” I’m referencing a respected source, which reinforces my credibility as a speaker.
When you’re speaking to a mixed audience: Appeal to their emotions.
Emotional appeals can be very persuasive, especially when you’re speaking to a mixed audience. After all, everyone has made a decision based on their emotions at one point or another in their lives. Last year, TED speaker Nora McInerny shared her own experience with death to teach us about moving forward with grief. It was an A+ example of an emotional appeal.
OK great, but how do I find out all this information about my audience?
Well, that’s part of the fun. OK, maybe it’s not always fun but it is your responsibility to take a deep dive into your audience, their needs, and their motivations and — trust me — this work will pay off ten-fold. If you’re speaking at an official conference or meeting, I recommend starting with the person or organization who asked you to speak. What can they tell you about the audience? Are they willing to share any of registration information? How did they market the event? If you’re speaking on an earnings call, what about the analysts who follow your company — have you ever asked them what they need or want? If you’re speaking at your company’s town hall, can you talk to your team and find out what they expect to hear from you? If you’re speaking at an event in another country, can you find a translator or local who can help you better understand the expectations of that audience?
The information is out there — you just need to find and use it. You’ll know when you’ve done it right, because your audience will stay engaged and, when you’re done speaking, they’ll help pass your message along.
This post is part of TED’s “How to Be a Better Human” series, each of which contains a piece of helpful advice from someone in the TED community; browse through all the posts here.
About the author
Briar Goldberg is the Director of Speaker Coaching at TED.
- briar goldberg
- business advice
- communication
- public speaking
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

Feeling unseen by your boss? Here’s what you can do

Let’s stop calling them “soft skills” -- and call them “real skills” instead

There’s a know-it-all at every job — here’s how to deal

The 7 types of people you need in your life to be resilient

Perfectionism holding you back? 3 ways to shift the habit

The unseen forces that can cause your great new idea to crash and burn

Have you quietly quit? Your next step: Go to the neutral zone

6 ways to give that aren't about money

7 Zoom mistakes you might still be making -- and how to raise your video skills

The skill you need now: presentation literacy

Storytelling is a powerful communication tool — here’s how to use it, from TED

7 ways to be a better communicator -- by tweaking your body language

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.1 Four Methods of Delivery
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the four methods of speech delivery.
- Understand when to use each of the four methods of speech delivery.

Maryland GovPics – House of Ruth Luncheon – CC BY 2.0.
The easiest approach to speech delivery is not always the best. Substantial work goes into the careful preparation of an interesting and ethical message, so it is understandable that students may have the impulse to avoid “messing it up” by simply reading it word for word. But students who do this miss out on one of the major reasons for studying public speaking: to learn ways to “connect” with one’s audience and to increase one’s confidence in doing so. You already know how to read, and you already know how to talk. But public speaking is neither reading nor talking.
Speaking in public has more formality than talking. During a speech, you should present yourself professionally. This doesn’t mean you must wear a suit or “dress up” (unless your instructor asks you to), but it does mean making yourself presentable by being well groomed and wearing clean, appropriate clothes. It also means being prepared to use language correctly and appropriately for the audience and the topic, to make eye contact with your audience, and to look like you know your topic very well.
While speaking has more formality than talking, it has less formality than reading. Speaking allows for meaningful pauses, eye contact, small changes in word order, and vocal emphasis. Reading is a more or less exact replication of words on paper without the use of any nonverbal interpretation. Speaking, as you will realize if you think about excellent speakers you have seen and heard, provides a more animated message.
The next sections introduce four methods of delivery that can help you balance between too much and too little formality when giving a public speech.
Impromptu Speaking
Impromptu speaking is the presentation of a short message without advance preparation. Impromptu speeches often occur when someone is asked to “say a few words” or give a toast on a special occasion. You have probably done impromptu speaking many times in informal, conversational settings. Self-introductions in group settings are examples of impromptu speaking: “Hi, my name is Steve, and I’m a volunteer with the Homes for the Brave program.” Another example of impromptu speaking occurs when you answer a question such as, “What did you think of the documentary?”
The advantage of this kind of speaking is that it’s spontaneous and responsive in an animated group context. The disadvantage is that the speaker is given little or no time to contemplate the central theme of his or her message. As a result, the message may be disorganized and difficult for listeners to follow.
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you are called upon to give an impromptu speech in public.
- Take a moment to collect your thoughts and plan the main point you want to make.
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak.
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace your listeners can follow.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking.
As you can see, impromptu speeches are generally most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
Extemporaneous Speaking
Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses. The opportunity to assess is also an opportunity to restate more clearly any idea or concept that the audience seems to have trouble grasping.
For instance, suppose you are speaking about workplace safety and you use the term “sleep deprivation.” If you notice your audience’s eyes glazing over, this might not be a result of their own sleep deprivation, but rather an indication of their uncertainty about what you mean. If this happens, you can add a short explanation; for example, “sleep deprivation is sleep loss serious enough to threaten one’s cognition, hand-to-eye coordination, judgment, and emotional health.” You might also (or instead) provide a concrete example to illustrate the idea. Then you can resume your message, having clarified an important concept.
Speaking extemporaneously has some advantages. It promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible. In addition, your audience is likely to pay better attention to the message because it is engaging both verbally and nonverbally. The disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that it requires a great deal of preparation for both the verbal and the nonverbal components of the speech. Adequate preparation cannot be achieved the day before you’re scheduled to speak.
Because extemporaneous speaking is the style used in the great majority of public speaking situations, most of the information in this chapter is targeted to this kind of speaking.
Speaking from a Manuscript
Manuscript speaking is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains his or her attention on the printed page except when using visual aids.
The advantage to reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. As we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, in some circumstances this can be extremely important. For example, reading a statement about your organization’s legal responsibilities to customers may require that the original words be exact. In reading one word at a time, in order, the only errors would typically be mispronunciation of a word or stumbling over complex sentence structure.
However, there are costs involved in manuscript speaking. First, it’s typically an uninteresting way to present. Unless the speaker has rehearsed the reading as a complete performance animated with vocal expression and gestures (as poets do in a poetry slam and actors do in a reader’s theater), the presentation tends to be dull. Keeping one’s eyes glued to the script precludes eye contact with the audience. For this kind of “straight” manuscript speech to hold audience attention, the audience must be already interested in the message before the delivery begins.
It is worth noting that professional speakers, actors, news reporters, and politicians often read from an autocue device, such as a TelePrompTer, especially when appearing on television, where eye contact with the camera is crucial. With practice, a speaker can achieve a conversational tone and give the impression of speaking extemporaneously while using an autocue device. However, success in this medium depends on two factors: (1) the speaker is already an accomplished public speaker who has learned to use a conversational tone while delivering a prepared script, and (2) the speech is written in a style that sounds conversational.
Speaking from Memory
Memorized speaking is the rote recitation of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script in a stage play, television program, or movie scene. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage to memorization is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. Being free of notes means that you can move freely around the stage and use your hands to make gestures. If your speech uses visual aids, this freedom is even more of an advantage. However, there are some real and potential costs. First, unless you also plan and memorize every vocal cue (the subtle but meaningful variations in speech delivery, which can include the use of pitch, tone, volume, and pace), gesture, and facial expression, your presentation will be flat and uninteresting, and even the most fascinating topic will suffer. You might end up speaking in a monotone or a sing-song repetitive delivery pattern. You might also present your speech in a rapid “machine-gun” style that fails to emphasize the most important points. Second, if you lose your place and start trying to ad lib, the contrast in your style of delivery will alert your audience that something is wrong. More frighteningly, if you go completely blank during the presentation, it will be extremely difficult to find your place and keep going.
Key Takeaways
- There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized.
- Impromptu speaking involves delivering a message on the spur of the moment, as when someone is asked to “say a few words.”
- Extemporaneous speaking consists of delivering a speech in a conversational fashion using notes. This is the style most speeches call for.
- Manuscript speaking consists of reading a fully scripted speech. It is useful when a message needs to be delivered in precise words.
- Memorized speaking consists of reciting a scripted speech from memory. Memorization allows the speaker to be free of notes.
- Find a short newspaper story. Read it out loud to a classroom partner. Then, using only one notecard, tell the classroom partner in your own words what the story said. Listen to your partner’s observations about the differences in your delivery.
- In a group of four or five students, ask each student to give a one-minute impromptu speech answering the question, “What is the most important personal quality for academic success?”
- Watch the evening news. Observe the differences between news anchors using a TelePrompTer and interviewees who are using no notes of any kind. What differences do you observe?
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Figurative Language: Simile and Other Types of Figures of Speech
- By Judhajit Sen
- September 12, 2024
Figure of speech definition is the use of words or phrases in a way that goes beyond their everyday, actual meanings. It creates a special effect or paints a mental picture to help the reader or listener better understand or feel something. Unlike literal language, which is straightforward, figurative speech adds color and depth to writing and speech.
Different figures of speech help make complex ideas clearer, descriptions more vivid, and messages more powerful. For example, saying “time is a thief” is a metaphor that helps convey the idea that time can take away moments from us, much like a thief would steal.
Figurative language types are used in many forms of communication, from literature and poetry to everyday conversations, advertising slogans, and even newspaper headlines. It can make writing more interesting and engaging by creating emotional, visual, or sensory connections, making it easier for the listeners to relate to the content.
Key Takeaways
- Figurative Language Enhances Communication: Common figures of speech make writing more vivid and engaging by going beyond actual meanings. They help paint pictures in the reader’s mind and convey complex ideas more clearly.
- Metaphors and Similes: Similes use “like” or “as” to compare two different things, while metaphors make direct comparisons without these terms. Both techniques help create vivid imagery and deeper understanding.
- Hyperbole and Personification: Hyperbole involves exaggerated statements to emphasize a point or add humor, while personification figure of speech gives human traits to non-human elements, making descriptions more relatable and dynamic.
- Diverse Uses: Figurative language is prevalent in literature, everyday conversations, and advertising. Understanding and using these techniques can make communication more impactful and memorable.
Figurative Language: Simile, Metaphor, and Other Types of Figures of Speech

A simile is a figurative type of speech that compares two different things using the words “like,” “as,” or “than.” The objective is to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind by highlighting a specific characteristic that two things share. For instance, saying, “The boy was as brave as a lion in the jungle,” helps the reader picture a boy showing courage just like a lion, known for its bravery in the wild.
This type of figurative speech is common in everyday language and is used to make descriptions more colorful and engaging. For example, when you say, “The assistant was as busy as a bee,” you parallel the assistant’s activity to that of a bee, known for its hard work. Another example is, “Andrew was white as a sheet after he stepped out of the horror movie,” which vividly conveys how frightened he was.
Other such figure of speech examples include:
– “They fought like cats and dogs,” showing a fierce argument.
– “Her love for her children is as constant as the passing of time,” indicating unwavering affection.
By using comparisons, this type of figurative speech helps the audience connect with and better understand the subject being described.
A metaphor is a way of describing something by saying it is something else, without using “like” or “as.” This figure of speech makes a direct comparison between two different things to create a vivid picture or deeper understanding. For example, saying “Time is money” parallels time to money to show how valuable it is. The statement doesn’t mean that time literally equals money, but it emphasizes that time should be spent wisely, just like money.
This type of figurative speech can make writing more engaging and help readers connect with the meaning behind terms. For instance, saying “Love is a battlefield” suggests that love can be challenging and full of conflicts. Another example, “He was an onion,” shows that someone might have many layers to their personality that need to be peeled back to be understood.
Sometimes, this kind of figurative speech can stretch over several sentences or even a whole piece of writing. These are called extended metaphors. They help deepen the meaning by continuing the comparison for a longer time. For example, “The tall trees were curtains that surrounded us during our picnic” creates a picture of trees as if they were curtains, giving a sense of privacy and enclosure.
This type of expression of speech is a powerful tool in language because it enables writers and speakers to express complex ideas simply and creatively, helping the audience see things in a new light.
This figure of speech uses extreme exaggeration to emphasize a point, add emotion, or create humor. It’s so over-the-top that no one would actually believe the statement is true, but that’s what makes it effective. You likely use this type of figurative speech in everyday conversations without even realizing it.
For instance, when someone says, “I’ve told you a million times to wash the dishes,” they don’t mean a million times. They just want to stress how often they’ve made that request. This kind of figurative speech adds color and drama, making the message stand out.
Other common examples include:
– “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse.”
– “This bag weighs a ton.”
– “You snore like a freight train.”
This type of figurative speech can also bring humor or urgency to a situation. For example, saying, “If I don’t eat soon, I’m going to die of hunger,” doesn’t mean you will actually die. It just emphasizes how extremely hungry you feel.
By using this kind of figurative speech, writers and speakers can make their language more lively, vivid, and memorable.
Personification
Personification is a form of figurative speech where human characteristics are given to non-human objects, animals, or abstract ideas. This technique makes descriptions more vivid and relatable, helping readers identify with the text on a deeper level. By using this figure of speech, writers can bring life to inanimate objects or ideas, making them feel as if they have emotions, intentions, or actions like a human being.
For instance, saying “The sun greeted me when I woke up” gives the sun the human ability to greet, sparking the imagination of readers. Other examples of this kind of figurative speech include: “The car brakes screamed all through the journey,” or “The computer argued with me and refused to work.” In each case, the non-human subjects are described as if they have human traits or actions.
This figurative speech type can add color and interest to writing, allowing readers to visualize and emotionally engage with the subject matter. It makes the description more dynamic and memorable, helping to create a more engaging reading experience.
Synecdoche is a type of figurative speech where a part of something is used to represent the whole, or the whole is used to represent a part. It’s a way to make language more vivid and engaging by using familiar parts to describe something larger or vice versa.
For example, when someone says “a set of wheels,” they often mean a car. Here, “wheels,” which are just a part of the car, represent the entire vehicle. Similarly, referring to a businessman as “a suit” uses a piece of clothing to represent the person wearing it.
Other examples of synecdoche include:
– “Bread” to mean food in general or money.
– “Head” to count people or cattle.
– “Hired hands” to refer to workers.
Synecdoche can also work in the opposite way, using a whole to refer to a part. For example, when people say “New England won the game,” they are referring to the New England football team, not the entire region. Another example is “The White House issued a statement,” where the whole building represents the President or their administration.
Synecdoche adds color to language by making it more concise and imaginative, helping listeners and readers visualize and understand the context more easily.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia refers to words that mimic or resemble the sounds they describe. These terms make writing more vivid and engaging by bringing the sound of the action to life for the reader. They help create a sense of reality, making it easier to imagine the scene.
Common examples of this type of figure of speech include words like “buzz,” “bang,” “splash,” and “roar.” When you read a sentence like, “The alarm clock buzzed,” you can almost hear the annoying sound it makes. Or consider, “The water splashed all over the car” — the term “splash” mimics the sound of water hitting a surface.
Using onomatopoeia can add drama, humor, or intensity to a narrative. It brings emotions and situations to life, whether it’s the “hiss” of a fireplace, the “roar” of a truck engine, or the “grumble” of a hungry stomach. These words capture the essence of the sounds around us, enhancing the reader’s experience.
An oxymoron is a figurative language where two opposite or contradictory terms are placed together to create a new meaning or emphasize a point. It often uses an adjective followed by a noun. This combination of conflicting ideas can create a striking or memorable description.
For example, in the phrase “jumbo shrimp,” the words “jumbo” and “shrimp” seem to contradict each other. “Jumbo” suggests something large, while “shrimp” usually refers to something small. However, when paired, they create a unique meaning that catches the reader’s attention. Similarly, the expression “thoughtless idea” brings together two conflicting ideas to highlight a point in an unexpected way.
Oxymorons are commonly used in writing and speech to add depth or humor. Phrases like “loud silence,” “awfully good,” or “ever-flowing stillness” use contradiction to make a point more vividly or provoke thought. The use of oxymoron can make language more interesting and add a layer of complexity to simple statements.
Litotes is a figurative language that uses understatement to emphasize a point. It often involves using a double negative to express a positive meaning. Instead of directly stating something, this figure of speech affirms an idea by negating its opposite. This form of speech can often have a subtle, sometimes sarcastic tone.
For example, saying “I can’t say I disagree” is another way of saying “I agree.” Similarly, the phrase “She’s not unkind” means “She is kind.” Other examples include “A million dollars is no small chunk of change,” which emphasizes that a million dollars is a significant amount.
Litotes is an effective way to add emphasis or irony to a statement, making the language more interesting and engaging.
An idiom is a phrase or saying whose meaning is different from the actual meaning of the terms used. These phrases are common in everyday language and are often unique to specific cultures and languages. Idioms can be hard for language learners to understand because their true meaning isn’t obvious from the words themselves.
For example, if someone says, “I have a frog in my throat,” it doesn’t mean they actually have a frog in their throat. Instead, it means they are having trouble speaking, often due to a sore throat or hoarseness.
Other idioms include “green thumb,” which means someone is good at gardening, or “raining cats and dogs,” which describes heavy rain. Another example is “throw in the towel,” which means to give up. These expressions make language colorful but can be confusing for those who don’t know their figurative meaning.
Alliteration
Alliteration is a literary tool where the same consonant sound is repeated at the beginning of several terms close to each other. This literary device often highlights an emotion or enhances a description. It creates a rhythmic or melodic effect that can make phrases more memorable.
For example, in “She sells seashells by the seashore,” the repetition of the “s” sound makes the line catchy and engaging. Another example is “The pitter-patter of paws echoed down the hallway,” where the repetition of the “p” sound emphasizes the soft noise of the paws.
Alliteration can also be seen in tongue twisters, where the repeated sounds challenge pronunciation, like “She sells seashells by the seashore.” This device not only adds emphasis but also adds a lyrical quality to the text.
Wrap-up: Figurative Speech
Different types of figures of speech enrich our language by using words and phrases in creative ways that go beyond their literal meanings. All figurative language paints vivid pictures, clarifies complex ideas, and evokes emotions. Similes compare different things using “like” or “as” to make descriptions more engaging, while metaphors create direct comparisons to offer deeper insights. Hyperboles use exaggeration to emphasize points or add humor, and personification gives human traits to non-human elements to make descriptions more relatable.
Figurative language appears across various forms of communication, from everyday conversations to literature and advertising. It transforms ordinary speech into something more memorable and impactful, helping the audience connect more deeply with the content. By understanding and using these figures of speech, we can make our communication more dynamic and expressive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a figure of speech?
A figure of speech uses terms or phrases in ways that go beyond their actual meanings to create vivid images or emotional effects. It helps make writing and speech more engaging and expressive.
2. What is a simile?
This figurative speech type compares two things using “like” or “as.” For example, “brave as a lion” helps create a strong image of bravery.
3. What is a metaphor?
This type of figurative speech describes something by saying it is something else, without using “like” or “as.” For example, “Time is money” suggests time is valuable, like money.
4. What is hyperbole used for?
This kind of figurative speech involves extreme embellishments to emphasize a point or add humor. For example, “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse” is not literal but highlights intense hunger.
Elevate Your Communication with Figurative Speech
At Prezentium, we know that making a memorable impact goes beyond straightforward language. Figurative speech can transform your presentations into powerful tools that captivate and engage your audience. Imagine describing your latest project as “a beacon in a sea of mediocrity” or using an idiom to convey the depth of your ideas—these techniques can make your message stand out.
With our Overnight Presentations , we ensure that your key points are highlighted with the right figures of speech, tailored to your audience. Our Accelerators help you craft visuals and templates that make your comparisons and descriptions shine. And through Zenith Learning , we provide workshops that teach you to harness these expressive tools effectively.
Let Prezentium help you turn your presentations into compelling stories that resonate and inspire. Reach out today to see how our expertise can elevate your communication.
Why wait? Avail a complimentary 1-on-1 session with our presentation expert. See how other enterprise leaders are creating impactful presentations with us.
Shark Tank Presentation Tips: Winning Shark Tank Pitch Elements
Visual communication: benefits, importance, and examples, 7 public speaking tips for enhancing your public speaking abilities.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Look and Sound Confident During a Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Your audience will make up their minds about you in seconds.
How you look and sound during a speech or presentation are going to make a big impression on your audience. Within seconds, listeners will decide whether you are trustworthy, and they will do it based on your body language and vocal attributes. The good news is that there is plenty of hard evidence that explains how you can give the appearance of confidence and competence — even if you’re nervous or timid on the inside. To look confident, make eye contact, keep an open posture, and use gestures to emphasize your message. To sound confident, eliminate filler words, take time to pause before important messages, and vary your pace.
You’ve crafted the message and created the slides for your next presentation. Now it’s time to wow the audience. How you look and sound are going to make a big impression — and your audience will form opinions quickly .
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The boundaries aren't sharp. But, according to the definition, a speech is a talk or address, and a presentation is a talk with the use of some sort of visual aid. Speech vs. presentation. Why does this matter? Because giving a speech - for a lot of people - seems harder than giving a presentation. Bad slides are actually worse than no ...
A presentation speech typically follows the basic speech format that includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction lays out the context, the body conveys the main content, and the conclusion reinforces the key points. Audience; Effective presentation speeches are tailored to the needs and expectations of the audience.
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other 'speaking engagements' such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across in a video conference.
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
A speech presentation requires enough preparation for it to be effective. This would mean that the speaker must prepare an informative speech along with its supporting visual aids. But first, you must think about the purpose of the speech and the type of audience the speech will be delivered to. With this, you will be able to gather enough ...
While speech is described as "a formal talk that a person gives to an audience," a presentation is "a meeting at which something, especially a new product or idea, or piece of work, is shown to a group of people.". From the definition alone, you can see that one says 'talk' and the other says 'shown.'.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION. 2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation. This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
10. "Thank you for joining me on this journey. I look forward to our next steps.". 11. "In closing, I'd like to thank everyone for their participation.". 12. "Let's conclude with a reminder of the impact we can make together.". 13. "To wrap up our session, here's a brief summary of our discussion.".
A debate differs from both a speech and a presentation because it's between two sides that are equally involved. Each side usually takes an opposing view on the debate question or subject. It's often like a contest where, at the end of it, a vote is taken to decide who won the debate. A speech and a presentation are two very different things.
To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides. 4. Storytelling. According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out. But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer.
A presentation is the act of presenting information or ideas to a group of people in a structured and deliberate manner, often with the aid of visual aids like PowerPoint, Keynote, or multimedia tools. Presentations are a ubiquitous part of the professional, educational, and social landscape.
Speech transitions: words and phrases to connect your ideas. When delivering presentations it's important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it's all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions because these act as signposts to the audience - signalling the ...
6/ Engage Emotionally. Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning. Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
4. Practise presentation flow. As well as practising for the ideas and what you want to say, practise how you want your presentation to flow. Think of it almost as a symphony, with high points, slow movements and crescendos. If it's important, think about how you want your audience to feel, what emotions you want them to have, and when. 5.
Public Speaking and Presentations: Tips for Success. This resource includes tips and suggestions for improving your public speaking skills. Even if you've never spoken in front of a large group before, chances are you will encounter public speaking sometime during your life. Whether you're giving a presentation for your classmates or ...
My earliest mentor in this work, Jim Wagstaffe always tells speakers to practice their ABCs: Audience Before Content. I love that acronym so much because it captures the essence of what communication is really all about — it's not about you, the speaker; it's always about your audience. Your audience's needs should always be your ...
It's likely about a fear of public humiliation rather than of public speaking. Shift the spotlight from yourself to what you have to say. Reject the voice in your head trying to destroy your ...
Extemporaneous Speaking. Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses.
Frame your story (figure out where to start and where to end). Plan your delivery (decide whether to memorize your speech word for word or develop bullet points and then rehearse it—over and ...
Figure of speech definition is the use of words or phrases in a way that goes beyond their everyday, actual meanings. It creates a special effect or paints a mental picture to help the reader or listener better understand or feel something. ... Figurative speech can transform your presentations into powerful tools that captivate and engage your ...
How you look and sound during a speech or presentation are going to make a big impression on your audience. Within seconds, listeners will decide whether you are trustworthy, and they will do it ...