Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Guides • Understanding Publishing
Last updated on Feb 14, 2023

10 Types of Creative Writing (with Examples You’ll Love)
A lot falls under the term ‘creative writing’: poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is , it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at examples that demonstrate the sheer range of styles and genres under its vast umbrella.
To that end, we’ve collected a non-exhaustive list of works across multiple formats that have inspired the writers here at Reedsy. With 20 different works to explore, we hope they will inspire you, too.
People have been writing creatively for almost as long as we have been able to hold pens. Just think of long-form epic poems like The Odyssey or, later, the Cantar de Mio Cid — some of the earliest recorded writings of their kind.
Poetry is also a great place to start if you want to dip your own pen into the inkwell of creative writing. It can be as short or long as you want (you don’t have to write an epic of Homeric proportions), encourages you to build your observation skills, and often speaks from a single point of view .
Here are a few examples:
“Ozymandias” by Percy Bysshe Shelley
Nothing beside remains. Round the decay Of that colossal Wreck, boundless and bare The lone and level sands stretch far away.
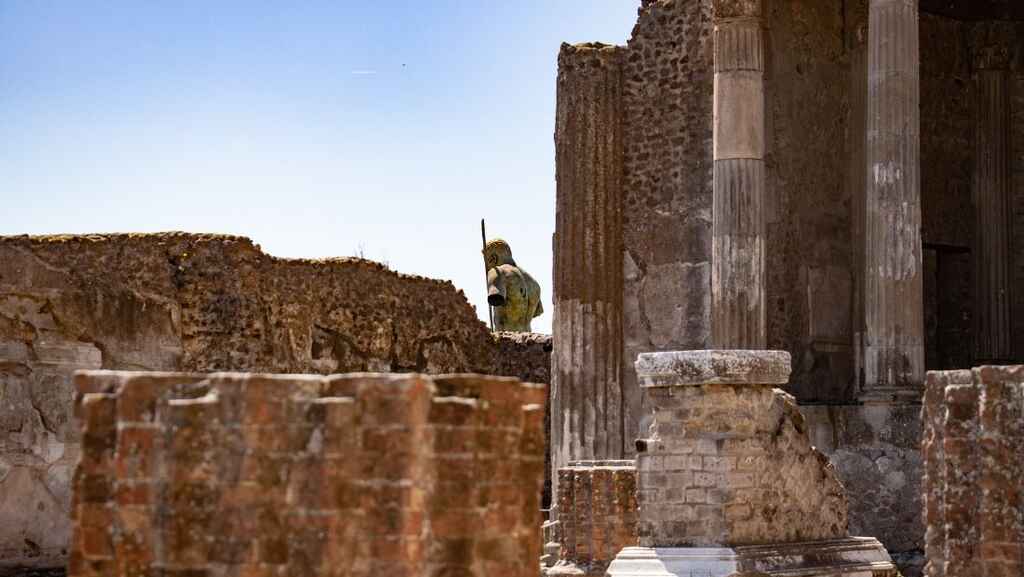

This classic poem by Romantic poet Percy Shelley (also known as Mary Shelley’s husband) is all about legacy. What do we leave behind? How will we be remembered? The great king Ozymandias built himself a massive statue, proclaiming his might, but the irony is that his statue doesn’t survive the ravages of time. By framing this poem as told to him by a “traveller from an antique land,” Shelley effectively turns this into a story. Along with the careful use of juxtaposition to create irony, this poem accomplishes a lot in just a few lines.
“Trying to Raise the Dead” by Dorianne Laux
A direction. An object. My love, it needs a place to rest. Say anything. I’m listening. I’m ready to believe. Even lies, I don’t care.
Poetry is cherished for its ability to evoke strong emotions from the reader using very few words which is exactly what Dorianne Laux does in “ Trying to Raise the Dead .” With vivid imagery that underscores the painful yearning of the narrator, she transports us to a private nighttime scene as the narrator sneaks away from a party to pray to someone they’ve lost. We ache for their loss and how badly they want their lost loved one to acknowledge them in some way. It’s truly a masterclass on how writing can be used to portray emotions.
If you find yourself inspired to try out some poetry — and maybe even get it published — check out these poetry layouts that can elevate your verse!
Song Lyrics
Poetry’s closely related cousin, song lyrics are another great way to flex your creative writing muscles. You not only have to find the perfect rhyme scheme but also match it to the rhythm of the music. This can be a great challenge for an experienced poet or the musically inclined.
To see how music can add something extra to your poetry, check out these two examples:
“Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
You say I took the name in vain I don't even know the name But if I did, well, really, what's it to ya? There's a blaze of light in every word It doesn't matter which you heard The holy or the broken Hallelujah
Metaphors are commonplace in almost every kind of creative writing, but will often take center stage in shorter works like poetry and songs. At the slightest mention, they invite the listener to bring their emotional or cultural experience to the piece, allowing the writer to express more with fewer words while also giving it a deeper meaning. If a whole song is couched in metaphor, you might even be able to find multiple meanings to it, like in Leonard Cohen’s “ Hallelujah .” While Cohen’s Biblical references create a song that, on the surface, seems like it’s about a struggle with religion, the ambiguity of the lyrics has allowed it to be seen as a song about a complicated romantic relationship.
“I Will Follow You into the Dark” by Death Cab for Cutie
If Heaven and Hell decide that they both are satisfied Illuminate the no's on their vacancy signs If there's no one beside you when your soul embarks Then I'll follow you into the dark

You can think of song lyrics as poetry set to music. They manage to do many of the same things their literary counterparts do — including tugging on your heartstrings. Death Cab for Cutie’s incredibly popular indie rock ballad is about the singer’s deep devotion to his lover. While some might find the song a bit too dark and macabre, its melancholy tune and poignant lyrics remind us that love can endure beyond death.
Plays and Screenplays
From the short form of poetry, we move into the world of drama — also known as the play. This form is as old as the poem, stretching back to the works of ancient Greek playwrights like Sophocles, who adapted the myths of their day into dramatic form. The stage play (and the more modern screenplay) gives the words on the page a literal human voice, bringing life to a story and its characters entirely through dialogue.
Interested to see what that looks like? Take a look at these examples:
All My Sons by Arthur Miller
“I know you're no worse than most men but I thought you were better. I never saw you as a man. I saw you as my father.”
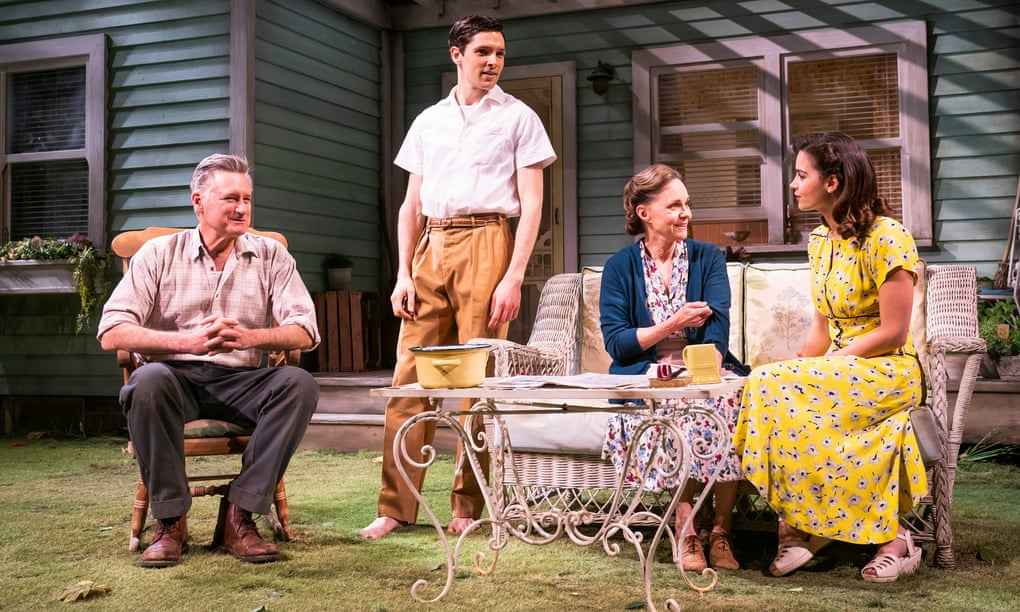

Arthur Miller acts as a bridge between the classic and the new, creating 20th century tragedies that take place in living rooms and backyard instead of royal courts, so we had to include his breakout hit on this list. Set in the backyard of an all-American family in the summer of 1946, this tragedy manages to communicate family tensions in an unimaginable scale, building up to an intense climax reminiscent of classical drama.
💡 Read more about Arthur Miller and classical influences in our breakdown of Freytag’s pyramid .
“Everything is Fine” by Michael Schur ( The Good Place )
“Well, then this system sucks. What...one in a million gets to live in paradise and everyone else is tortured for eternity? Come on! I mean, I wasn't freaking Gandhi, but I was okay. I was a medium person. I should get to spend eternity in a medium place! Like Cincinnati. Everyone who wasn't perfect but wasn't terrible should get to spend eternity in Cincinnati.”
A screenplay, especially a TV pilot, is like a mini-play, but with the extra job of convincing an audience that they want to watch a hundred more episodes of the show. Blending moral philosophy with comedy, The Good Place is a fun hang-out show set in the afterlife that asks some big questions about what it means to be good.
It follows Eleanor Shellstrop, an incredibly imperfect woman from Arizona who wakes up in ‘The Good Place’ and realizes that there’s been a cosmic mixup. Determined not to lose her place in paradise, she recruits her “soulmate,” a former ethics professor, to teach her philosophy with the hope that she can learn to be a good person and keep up her charade of being an upstanding citizen. The pilot does a superb job of setting up the stakes, the story, and the characters, while smuggling in deep philosophical ideas.
Personal essays
Our first foray into nonfiction on this list is the personal essay. As its name suggests, these stories are in some way autobiographical — concerned with the author’s life and experiences. But don’t be fooled by the realistic component. These essays can take any shape or form, from comics to diary entries to recipes and anything else you can imagine. Typically zeroing in on a single issue, they allow you to explore your life and prove that the personal can be universal.
Here are a couple of fantastic examples:
“On Selling Your First Novel After 11 Years” by Min Jin Lee (Literary Hub)
There was so much to learn and practice, but I began to see the prose in verse and the verse in prose. Patterns surfaced in poems, stories, and plays. There was music in sentences and paragraphs. I could hear the silences in a sentence. All this schooling was like getting x-ray vision and animal-like hearing.

This deeply honest personal essay by Pachinko author Min Jin Lee is an account of her eleven-year struggle to publish her first novel . Like all good writing, it is intensely focused on personal emotional details. While grounded in the specifics of the author's personal journey, it embodies an experience that is absolutely universal: that of difficulty and adversity met by eventual success.
“A Cyclist on the English Landscape” by Roff Smith (New York Times)
These images, though, aren’t meant to be about me. They’re meant to represent a cyclist on the landscape, anybody — you, perhaps.
Roff Smith’s gorgeous photo essay for the NYT is a testament to the power of creatively combining visuals with text. Here, photographs of Smith atop a bike are far from simply ornamental. They’re integral to the ruminative mood of the essay, as essential as the writing. Though Smith places his work at the crosscurrents of various aesthetic influences (such as the painter Edward Hopper), what stands out the most in this taciturn, thoughtful piece of writing is his use of the second person to address the reader directly. Suddenly, the writer steps out of the body of the essay and makes eye contact with the reader. The reader is now part of the story as a second character, finally entering the picture.
Short Fiction
The short story is the happy medium of fiction writing. These bite-sized narratives can be devoured in a single sitting and still leave you reeling. Sometimes viewed as a stepping stone to novel writing, that couldn’t be further from the truth. Short story writing is an art all its own. The limited length means every word counts and there’s no better way to see that than with these two examples:
“An MFA Story” by Paul Dalla Rosa (Electric Literature)
At Starbucks, I remembered a reading Zhen had given, a reading organized by the program’s faculty. I had not wanted to go but did. In the bar, he read, "I wrote this in a Starbucks in Shanghai. On the bank of the Huangpu." It wasn’t an aside or introduction. It was two lines of the poem. I was in a Starbucks and I wasn’t writing any poems. I wasn’t writing anything.

This short story is a delightfully metafictional tale about the struggles of being a writer in New York. From paying the bills to facing criticism in a writing workshop and envying more productive writers, Paul Dalla Rosa’s story is a clever satire of the tribulations involved in the writing profession, and all the contradictions embodied by systemic creativity (as famously laid out in Mark McGurl’s The Program Era ). What’s more, this story is an excellent example of something that often happens in creative writing: a writer casting light on the private thoughts or moments of doubt we don’t admit to or openly talk about.
“Flowering Walrus” by Scott Skinner (Reedsy)
I tell him they’d been there a month at least, and he looks concerned. He has my tongue on a tissue paper and is gripping its sides with his pointer and thumb. My tongue has never spent much time outside of my mouth, and I imagine it as a walrus basking in the rays of the dental light. My walrus is not well.
A winner of Reedsy’s weekly Prompts writing contest, ‘ Flowering Walrus ’ is a story that balances the trivial and the serious well. In the pauses between its excellent, natural dialogue , the story manages to scatter the fear and sadness of bad medical news, as the protagonist hides his worries from his wife and daughter. Rich in subtext, these silences grow and resonate with the readers.
Want to give short story writing a go? Give our free course a go!

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
Perhaps the thing that first comes to mind when talking about creative writing, novels are a form of fiction that many people know and love but writers sometimes find intimidating. The good news is that novels are nothing but one word put after another, like any other piece of writing, but expanded and put into a flowing narrative. Piece of cake, right?
To get an idea of the format’s breadth of scope, take a look at these two (very different) satirical novels:
Convenience Store Woman by Sayaka Murata
I wished I was back in the convenience store where I was valued as a working member of staff and things weren’t as complicated as this. Once we donned our uniforms, we were all equals regardless of gender, age, or nationality — all simply store workers.

Keiko, a thirty-six-year-old convenience store employee, finds comfort and happiness in the strict, uneventful routine of the shop’s daily operations. A funny, satirical, but simultaneously unnerving examination of the social structures we take for granted, Sayaka Murata’s Convenience Store Woman is deeply original and lingers with the reader long after they’ve put it down.
Erasure by Percival Everett
The hard, gritty truth of the matter is that I hardly ever think about race. Those times when I did think about it a lot I did so because of my guilt for not thinking about it.
Erasure is a truly accomplished satire of the publishing industry’s tendency to essentialize African American authors and their writing. Everett’s protagonist is a writer whose work doesn’t fit with what publishers expect from him — work that describes the “African American experience” — so he writes a parody novel about life in the ghetto. The publishers go crazy for it and, to the protagonist’s horror, it becomes the next big thing. This sophisticated novel is both ironic and tender, leaving its readers with much food for thought.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction is pretty broad: it applies to anything that does not claim to be fictional (although the rise of autofiction has definitely blurred the boundaries between fiction and nonfiction). It encompasses everything from personal essays and memoirs to humor writing, and they range in length from blog posts to full-length books. The defining characteristic of this massive genre is that it takes the world or the author’s experience and turns it into a narrative that a reader can follow along with.
Here, we want to focus on novel-length works that dig deep into their respective topics. While very different, these two examples truly show the breadth and depth of possibility of creative nonfiction:
Men We Reaped by Jesmyn Ward
Men’s bodies litter my family history. The pain of the women they left behind pulls them from the beyond, makes them appear as ghosts. In death, they transcend the circumstances of this place that I love and hate all at once and become supernatural.
Writer Jesmyn Ward recounts the deaths of five men from her rural Mississippi community in as many years. In her award-winning memoir , she delves into the lives of the friends and family she lost and tries to find some sense among the tragedy. Working backwards across five years, she questions why this had to happen over and over again, and slowly unveils the long history of racism and poverty that rules rural Black communities. Moving and emotionally raw, Men We Reaped is an indictment of a cruel system and the story of a woman's grief and rage as she tries to navigate it.
Cork Dork by Bianca Bosker
He believed that wine could reshape someone’s life. That’s why he preferred buying bottles to splurging on sweaters. Sweaters were things. Bottles of wine, said Morgan, “are ways that my humanity will be changed.”
In this work of immersive journalism , Bianca Bosker leaves behind her life as a tech journalist to explore the world of wine. Becoming a “cork dork” takes her everywhere from New York’s most refined restaurants to science labs while she learns what it takes to be a sommelier and a true wine obsessive. This funny and entertaining trip through the past and present of wine-making and tasting is sure to leave you better informed and wishing you, too, could leave your life behind for one devoted to wine.
Illustrated Narratives (Comics, graphic novels)
Once relegated to the “funny pages”, the past forty years of comics history have proven it to be a serious medium. Comics have transformed from the early days of Jack Kirby’s superheroes into a medium where almost every genre is represented. Humorous one-shots in the Sunday papers stand alongside illustrated memoirs, horror, fantasy, and just about anything else you can imagine. This type of visual storytelling lets the writer and artist get creative with perspective, tone, and so much more. For two very different, though equally entertaining, examples, check these out:
Calvin & Hobbes by Bill Watterson
"Life is like topography, Hobbes. There are summits of happiness and success, flat stretches of boring routine and valleys of frustration and failure."
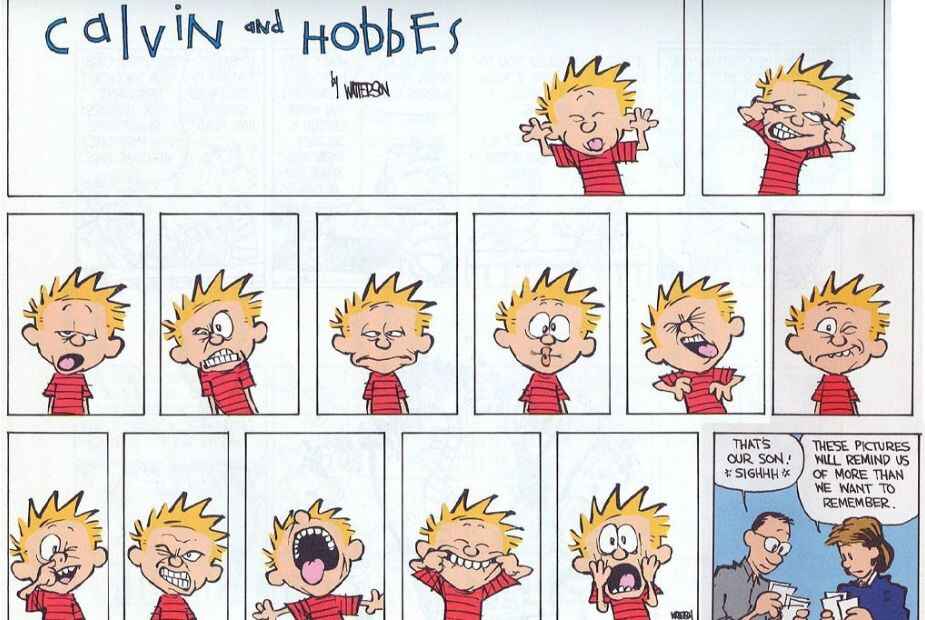

This beloved comic strip follows Calvin, a rambunctious six-year-old boy, and his stuffed tiger/imaginary friend, Hobbes. They get into all kinds of hijinks at school and at home, and muse on the world in the way only a six-year-old and an anthropomorphic tiger can. As laugh-out-loud funny as it is, Calvin & Hobbes ’ popularity persists as much for its whimsy as its use of humor to comment on life, childhood, adulthood, and everything in between.
From Hell by Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell
"I shall tell you where we are. We're in the most extreme and utter region of the human mind. A dim, subconscious underworld. A radiant abyss where men meet themselves. Hell, Netley. We're in Hell."
Comics aren't just the realm of superheroes and one-joke strips, as Alan Moore proves in this serialized graphic novel released between 1989 and 1998. A meticulously researched alternative history of Victorian London’s Ripper killings, this macabre story pulls no punches. Fact and fiction blend into a world where the Royal Family is involved in a dark conspiracy and Freemasons lurk on the sidelines. It’s a surreal mad-cap adventure that’s unsettling in the best way possible.
Video Games and RPGs
Probably the least expected entry on this list, we thought that video games and RPGs also deserved a mention — and some well-earned recognition for the intricate storytelling that goes into creating them.
Essentially gamified adventure stories, without attention to plot, characters, and a narrative arc, these games would lose a lot of their charm, so let’s look at two examples where the creative writing really shines through:
80 Days by inkle studios
"It was a triumph of invention over nature, and will almost certainly disappear into the dust once more in the next fifty years."

Named Time Magazine ’s game of the year in 2014, this narrative adventure is based on Around the World in 80 Days by Jules Verne. The player is cast as the novel’s narrator, Passpartout, and tasked with circumnavigating the globe in service of their employer, Phileas Fogg. Set in an alternate steampunk Victorian era, the game uses its globe-trotting to comment on the colonialist fantasies inherent in the original novel and its time period. On a storytelling level, the choose-your-own-adventure style means no two players’ journeys will be the same. This innovative approach to a classic novel shows the potential of video games as a storytelling medium, truly making the player part of the story.
What Remains of Edith Finch by Giant Sparrow
"If we lived forever, maybe we'd have time to understand things. But as it is, I think the best we can do is try to open our eyes, and appreciate how strange and brief all of this is."
This video game casts the player as 17-year-old Edith Finch. Returning to her family’s home on an island in the Pacific northwest, Edith explores the vast house and tries to figure out why she’s the only one of her family left alive. The story of each family member is revealed as you make your way through the house, slowly unpacking the tragic fate of the Finches. Eerie and immersive, this first-person exploration game uses the medium to tell a series of truly unique tales.
Fun and breezy on the surface, humor is often recognized as one of the trickiest forms of creative writing. After all, while you can see the artistic value in a piece of prose that you don’t necessarily enjoy, if a joke isn’t funny, you could say that it’s objectively failed.
With that said, it’s far from an impossible task, and many have succeeded in bringing smiles to their readers’ faces through their writing. Here are two examples:
‘How You Hope Your Extended Family Will React When You Explain Your Job to Them’ by Mike Lacher (McSweeney’s Internet Tendency)
“Is it true you don’t have desks?” your grandmother will ask. You will nod again and crack open a can of Country Time Lemonade. “My stars,” she will say, “it must be so wonderful to not have a traditional office and instead share a bistro-esque coworking space.”

Satire and parody make up a whole subgenre of creative writing, and websites like McSweeney’s Internet Tendency and The Onion consistently hit the mark with their parodies of magazine publishing and news media. This particular example finds humor in the divide between traditional family expectations and contemporary, ‘trendy’ work cultures. Playing on the inherent silliness of today’s tech-forward middle-class jobs, this witty piece imagines a scenario where the writer’s family fully understands what they do — and are enthralled to hear more. “‘Now is it true,’ your uncle will whisper, ‘that you’ve got a potential investment from one of the founders of I Can Haz Cheezburger?’”
‘Not a Foodie’ by Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell (Electric Literature)
I’m not a foodie, I never have been, and I know, in my heart, I never will be.
Highlighting what she sees as an unbearable social obsession with food , in this comic Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell takes a hilarious stand against the importance of food. From the writer’s courageous thesis (“I think there are more exciting things to talk about, and focus on in life, than what’s for dinner”) to the amusing appearance of family members and the narrator’s partner, ‘Not a Foodie’ demonstrates that even a seemingly mundane pet peeve can be approached creatively — and even reveal something profound about life.
We hope this list inspires you with your own writing. If there’s one thing you take away from this post, let it be that there is no limit to what you can write about or how you can write about it.
In the next part of this guide, we'll drill down into the fascinating world of creative nonfiction.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
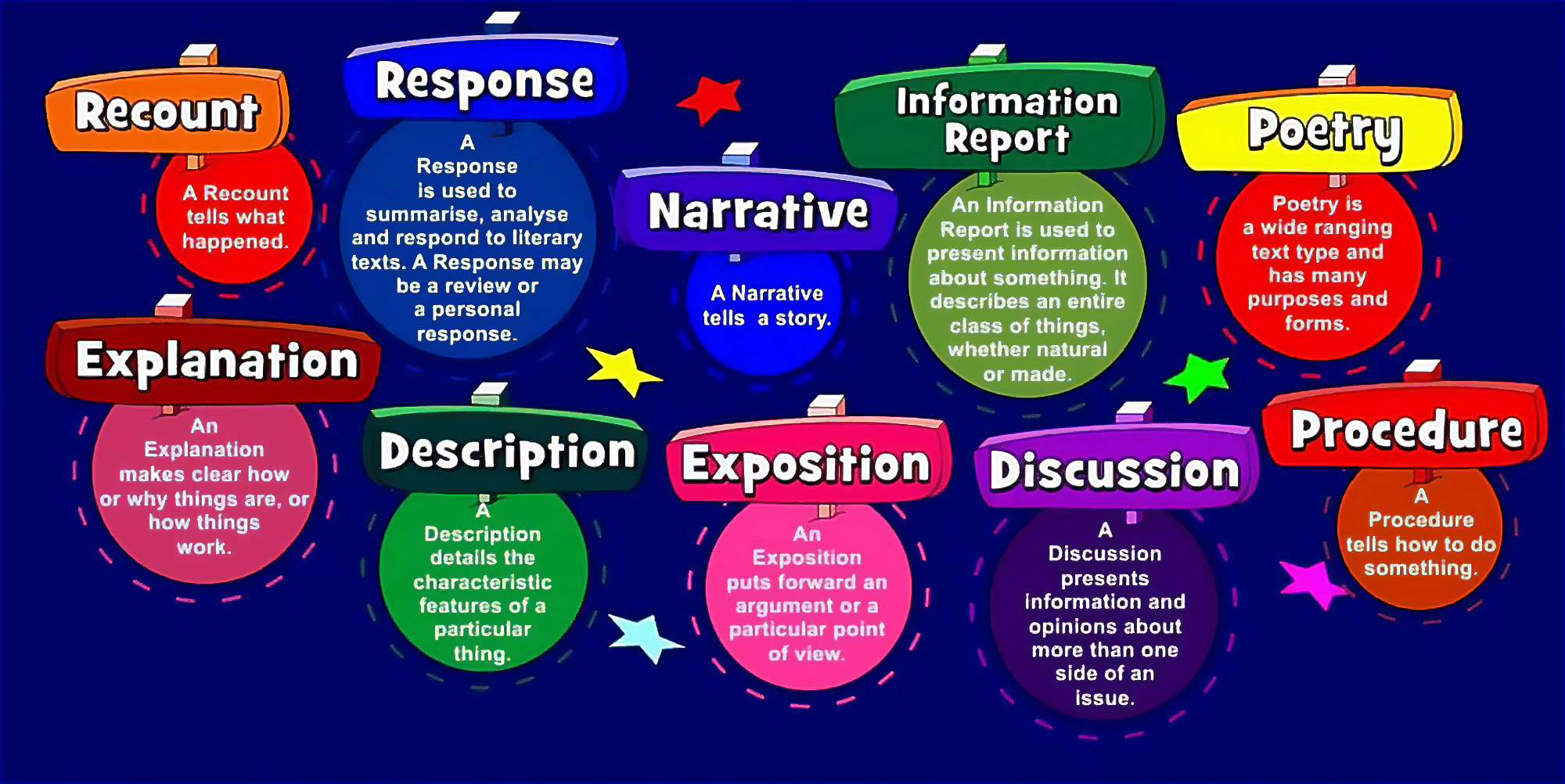
18 Text Types (with Examples) – Writing Styles Explained

Texts types, also known as genres or text forms, refer to categories of texts with different purposes. Depending on the purpose, each type of text will have have a different convention of style and structure.
It is essential to understand text types and their conventions because:
- Interpretation: It helps us understand the text’s intentions, trustworthiness, and bias
- Text Creation: It helps us to create texts that are most effective, depending upon the purpose
Below is a list of the most common text types and their key conventions, style, structure, and purpose.
Text Types Examples
1. narrative.
Purpose: A narrative text aims to tell a story to the reader. It isn’t always just about telling a story for entertainment, though. The purpose of narrative text also lies in its capacity to engage the reader’s imagination, impart a moral lesson, or just simply pass on a tale through generations. For example, narrative stories are used in folklore and folktales to pass-on cultural values and stories.
Style: The style of a narrative text is distinctive. It employs a chronological sequencing of events. Coherent, right-branching sentences, varying in length, create rhythm and draw the reader into the unfolding story. Active voice is favored to maintain directness and immediacy, bringing scenes alive.
Structure: Beginning with an orientation, it introduces characters, setting, and time. Short initial sentences establish the context. The complication, the next part, presents problems or conflicts. A series of sentences, varying in length and complexity, takes the reader through ups and downs. Ultimately, the story reaches a resolution, where the achievement or solution is laid out.
2. Descriptive
Purpose: A descriptive text is designed to describe something in a detailed manner. The writer attempts to paint a vivid image in the reader’s mind, often by intricately describing an object, person, place, experience, or situation.
Style: Adjectives play a significant role in a descriptive text. They enrich the text, adding depth to the description. Similes, metaphors, and other figurative language might also be used for more creative descriptions. The sentences can be diverse, ranging from concise statement of facts to long, detailed depictions .
Structure: A descriptive text often starts with a short, general overview of what is being described. Then, it delves into details, exploring appearance, characteristics, functions, and other aspects. It closes with a brief summary or a final remark on the described subject.
3. Expository
Purpose: The main goal of an expository text is to inform or explain. It aims to provide the reader with comprehensive information about a specific topic. This type of text gives out facts and provides deep insights, explaining complex concepts or procedures in a manner that the reader can understand.
Style: The style of an expository text is systematic and straightforward. It has an emphasis on clarity. It avoids ambiguity and confusion.
Structure: Beginning with an introduction that briefly outlines the topic, an expository text then offers a well-structured exploration of distinct aspects of the topic. Each paragraph introduces a different point related to the topic. The conclusion summarizes the main points and offers final insights.
Read More: Expository vs Argumentative Essay Writing
4. Argumentative / Persuasive
Purpose: An argumentative or persuasive text is structured to persuade the readers by presenting a point of view. It defends a position regarding an issue or topic, using reasoned arguments, facts, statistics, and real-life examples to convince readers and lure them into adopting this point of view.
Style: These texts should be precise, logical, and grounded in evidence. The use of rhetorical devices like ethos, logos, and pathos can help persuade and appeal to the reader’s sense of ethics, logic, or emotions.
Structure: Key here is to map out a clear and structured argument, often presenting the most compelling points at the beginning and end of the piece. Consider using an essay plan. Your piece may start with a clear statement of the thesis or position. Then, provide supporting evidence and arguments, section by section. Each paragraph can offer a different reason or piece of evidence supporting the thesis. A conclusion is then needed to sum up the argument, restate the thesis, and call the reader to action.
5. Instructional
Purpose: An instructional text serves to provide instructions or directions on how to do something. It aims to guide the reader through a sequence of steps to achieve a certain goal or complete a task efficiently.
Style: Unlike persuasive texts, instructional texts should not try to convince anyone of anything. Your job is to strictly provide facts. The language is direct, to-the-point, and unambiguous.
Structure: Instructional texts usually start with an overview of the task or goal, and possibly, what the end result should look like. Following that, a list of materials or requirements would come next. After this, a step-by-step guide detailing how to accomplish the task is written.
6. Procedural
Purpose: Procedural texts are designed to guide the reader through a sequence of actions or steps necessary to accomplish a specific task. These tasks might be related to cooking, science experiments, emergency procedures, or machinery operation, among others.
Style: Procedural texts are characterized by precise and unambiguous language. It is critical that the wording is exact to ensure clear communication of instructions.
Structure: Procedural texts should be written with the same goal in mind as instructional ones: begin with an overview of the task, followed by any necessary materials or preparation steps. Next, a detailed, step-by-step procedure is included. It often concludes with any necessary follow-up instructions or warnings.
Purpose: The purpose of a recount text is to retell past events, usually in chronological order. It serves to provide a detailed account of an event, experience, or historical occurrence.
Style: A recount is usually descriptive and personal, involving a chronological presentation of events, with expressive language to convey emotions or impressions that the writer felt during the events.
Structure: A typical recount text starts with the introduction, setting the scene, and often specifying the time, place, and participants involved. The series of events then unrolls in the order they occurred. Finally, it concludes with a personal comment, reflection, or evaluation of the event.
Purpose: Report texts are written to present information about a subject. The subject could range from real-world entities like animals, humans, or natural phenomena to abstract concepts like principles, theories, or ideas.
Style: Reports are communicated objectively without the use of personal pronouns or subjective language. They contain facts, statistics, and specific information related to the subject, presented in a clear, systematic manner.
Structure: A report usually begins with an introduction, defining the topic and offering a brief overview. A series of sections or subheadings then ‘chunk’ the content to make it easy to navigate, each covering different aspects of the topic. A conclusion or summary often ends the report.
9. Discussion
Purpose: A discussion text is intended to present multiple perspectives on a specific issue, allowing the reader to consider all angles before forming their own viewpoint. It aims to deepen understanding and foster a broader perspective by objectively exploring diverse opinions and arguments related to a topic.
Style: Discussion texts use neutral, unbiased language. The writer presents all sides of the argument fairly and objectively, without leaning towards supporting one over another.
Structure: The text begins with an introduction of the issue at hand. This is followed by presenting point and counterpoint for each aspect of the issue, examining arguments in favor and against it. An effective discussion text ends with a conclusion or summary that encapsulates the multiple perspectives without indicating a personal preference.
10. Response
Purpose: A response text serves to provide a personal interpretation or reaction to a piece of content, such as a book, film, article, or speech. It aims to deepen the understanding of the original content, examine its components, and express personal thoughts, feelings, and reactions to it.
Style: Response writing is subjective, reflecting the opinion and personality of the writer. Despite the writer’s personal voice being apparent, a good response should maintain an even-handed and critical approach.
Structure: Commence with an overview of the content being responded to, including its title and creator. Next, give a brief summary or description of the content. Following this, present your personal reactions, impressions, and points of critique. Lastly, conclude by summarizing your views and stating your final thoughts.
Purpose: The purpose of a poetic text is to convey emotions, experiences, concepts, and ideas using creative and imaginative language. It’s a form of verbal art that uses aesthetics and rhythmic qualities to charm and engage readers.
Style: Poetic language heavily incorporates figurative and connotative language. It frequently uses devices such as similes, metaphors, rhyme, rhythm, assonance, and alliteration to create a specific mood or emotion.
Structure: The structure of a poem can vary vastly – it may adhere to a specific form (like sonnets, haikus, or limericks) complete with rules regarding rhyme, meter, and stanza length, or it may be free verse, with no such rules.
12. Journalistic
Purpose: Journalistic texts aim to report news stories to inform readers, viewers, or listeners about events happening locally or globally. These texts provide factual information about real-world event in a balanced, fair, accurate, and comprehensive manner.
Style: Journalistic writing requires use of clear, concise, and direct language. The language is primarily factual and explanatory, striving to be impartial and unbiased.
Structure: Journalistic texts usually adopt the “inverted pyramid” structure. The most crucial information is presented first – summarizing the ‘who, what, where, when, why, and how’ of the story. Following paragraphs provide further details and context, with the least important information towards the end.
See Also: Informational Texts Examples
13. Transactional
Purpose: Transactional texts serve to communicate an intended message between individuals or organizations. Common examples include emails, reports, proposals, business letters and memos.
Style: The tone and style of transactional texts depend on their intended audience and purpose. Formality levels may vary – generally, they are written in clear, straightforward language.
Structure: Transactional texts usually start with a salutation or an introduction, followed by the body containing the key message or information. They end with a closing, which may include a call-to-action, a closing remark or a sign-off.
14. Exemplification
Purpose: Exemplification texts are those which use examples to make a point, stress a point, or clearly present a pattern or form. These texts aim to make abstract ideas concrete, clarify concepts, or provide evidence supporting statements or theories.
Style: The language of exemplification texts is straightforward and facts-based, leveraging detailed examples to make concepts clearer and more understandable.
Structure: They start with a thesis statement or main idea. Next, they introduce and elaborate various specific examples to exemplify and prove the thesis statement. Finally, a conclusion wraps up the discussion and reiterates how the examples support the main idea.
15. Compare and Contrast
Purpose: The purpose of a compare and contrast text is to examine the similarities and differences between two or more subjects, such as concepts, items, people, or events. It aids in understanding and scrutinizing the association between the subjects.
Style: This kind of writing is analytical and require a balanced and objective presentation of facts, making sure to avoid bias or favoritism.
Structure: Such texts generally follow one of two structures: block or alternating. In the block method, all about the first subject is described, followed by all about the second. In the alternating method, corresponding points about the first and second subjects are alternated for comparison.
Read More: Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
16. Cause and Effect
Purpose: Cause and effect text is written to identify and explain the reasons or causes for an event or behavior and the resulting effects or outcomes. It establishes a relationship between variables and events.
Style: Clarity is particularly important in cause and effect writing because it should aim to lucidly explain causal chains where one thing leads to another.
Structure: Generally, the text starts with an introduction to the event. This is followed by the ’cause’ section explaining its origins or reasons. Then comes the ‘effect’ section detailing the outcomes, consequences, or results. Lastly, a conclusion synthesizes the major points and may contain author’s opinion on the event.
Read More: Cause and Effect Examples
17. Diary/Journal Entry
Purpose: A diary or journal entry is written to express personal thoughts, feelings, and experiences, making them a form of autobiographical writing. The objective is self-reflection, documentation of life events or ideas, and emotional exploration.
Style: Being highly personal, these texts don’t normally adhere to strict stylistic protocols. Language is informal and conversational, representing the writer’s voice.
Structure: Diary or journal entries do not follow a strict format. They often start with the date and proceed with the entries. Entries can range from brief notes to detailed narratives.
18. Critical Review
Purpose: A critical review analyses, interprets, and appraises a text or other work (like a film or play). It’s meant to provide an evaluation of the item’s merit, significance, value, or relevance, based on careful examination and evidence-based claims.
Style: Even though a critical review presents the writer’s opinion, it should be a balanced, logical, and professional examination of the work.
Structure: A traditional critical review includes an introduction summarizing the key details of the work being reviewed, the body containing the evaluation, and a conclusion summarizing the review.
Read More: Critical Analysis Examples
Full List of Text Types and Genres
- Descriptive
- Argumentative / Persuasive
- Instructional
- Journalistic
- Transactional
- Exemplification
- Compare and Contrast
- Cause and Effect
- Diary/Journal Entry
- Critical Review
Understanding text types allows you to effectively communicate ideas and information to your target audience. It provides a structured framework that guides the writing process, enhancing clarity and coherence. Additionally, it aids in comprehension, helping readers navigate and understand the text in its intended way. Lastly, knowledge of text types helps improve critical reading skills, enabling readers to discern the underlying purpose and structure of various texts.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
1 thought on “18 Text Types (with Examples) – Writing Styles Explained”
Dear Professor Drew,
My name is Ana de Mesquita and I am from Brazil. I have been teaching English, French and Brazilian Portuguese as a second language since 2008. I really appreciated your article about texts. It is quite helpful. Best regards,
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

14 Types of Creative Writing
by Melissa Donovan | Apr 6, 2021 | Creative Writing | 20 comments

Which types of creative writing have you tried?
When we talk about creative writing, fiction and poetry often take the spotlight, but there are many other types of creative writing that we can explore.
Most writers develop a preference for one form (and genre) above all others. This can be a good thing, because you can specialize in your form and genre and become quite proficient. However, occasionally working with other types of writing is beneficial. It prevents your work from becoming stale and overladen with form- or genre-specific clichés, and it’s a good way to acquire a variety of techniques that are uncommon in your preferred form and genre but that can be used to enhance it.
Types of Creative Writing
Free writing: Open a notebook or an electronic document and just start writing. Allow strange words and images to find their way to the page. Anything goes! Also called stream-of-consciousness writing, free writing is the pinnacle of creative writing.
Journals: A journal is any written log. You could keep a gratitude journal, a memory journal, a dream journal, or a goals journal. Many writers keep idea journals or all-purpose omni-journals that can be used for everything from daily free writes to brainstorming and project planning.
Diaries: A diary is a type of journal in which you write about your daily life. Some diaries are written in letter format (“Dear Diary…”). If you ever want to write a memoir, then it’s a good idea to start keeping a diary.
Letters: Because the ability to communicate effectively is increasingly valuable, letter writing is a useful skill. There is a long tradition of publishing letters, so take extra care with those emails you’re shooting off to friends, family, and business associates. Hot tip: one way to get published if you don’t have a lot of clips and credits is to write letters to the editor of a news publication.
Memoir: A genre of creative nonfiction , memoirs are books that contain personal accounts (or stories) that focus on specific experiences. For example, one might write a travel memoir.
Essays. Essays are often associated with academic writing, but there are many types of essays, including personal essays, descriptive essays, and persuasive essays, all of which can be quite creative (and not especially academic).
Journalism: Some forms of journalism are more creative than others. Traditionally, journalism was objective reporting on facts, people, and events. Today, journalists often infuse their writing with opinion and storytelling to make their pieces more compelling or convincing.
Poetry: Poetry is a popular but under-appreciated type of writing, and it’s easily the most artistic form of writing. You can write form poetry, free-form poetry, and prose poetry.
Song Lyrics: Song lyrics combine the craft of writing with the artistry of music. Composing lyrics is similar to writing poetry, and this is an ideal type of writing for anyone who can play a musical instrument.
Scripts: Hit the screen or the stage by writing scripts for film, television, theater, or video games. Beware: film is a director’s medium, not a writer’s medium, but movies have the potential to reach a non-reading audience.
Storytelling: Storytelling is the most popular form of creative writing and is found in the realms of both fiction and nonfiction writing. Popular forms of fiction include flash fiction, short stories, novellas, and full-length novels; and there are tons of genres to choose from. True stories, which are usually firsthand or secondhand accounts of real people and events, can be found in essays, diaries, memoirs, speeches, and more. Storytelling is a tremendously valuable skill, as it can be found in all other forms of writing, from poetry to speech writing.
Speeches: Whether persuasive, inspirational, or informative, speech writing can lead to interesting career opportunities in almost any field or industry. Also, speech-writing skills will come in handy if you’re ever asked to write and deliver a speech at an important event, such as a graduation, wedding, or award ceremony.
Vignettes: A vignette is defined as “a brief evocative description, account, or episode.” Vignettes can be poems, stories, descriptions, personal accounts…anything goes really. The key is that a vignette is extremely short — just a quick snippet.
Honorable Mention: Blogs. A blog is not a type of writing; it’s a publishing platform — a piece of technology that displays web-based content on an electronic device. A blog can be used to publish any type of writing. Most blogs feature articles and essays, but you can also find blogs that contain diaries or journals, poetry, fiction, journalism, and more.
Which of these types of creative writing have you tried? Are there any forms of writing on this list that you’d like to experiment with? Can you think of any other types of creative writing to add to this list? Share your thoughts by leaving a comment, and keep writing.

20 Comments
What is “flash” writing or stories.
Flash fiction refers to super short stories, a few hundred words or fewer.
its very helpful especially to those students like me who wasn’t capable or good in doing a creative writing
I’m glad you found this post helpful, Elena.
I also found this to be very helpful, especially because I don’t do very well at writing.
Thanks for letting me know you found this helpful. Like anything else, writing improves with practice.
Thank you Melissa. It’s very helpful!
You’re welcome!
Over all good list. Yes blogs can be publishing platforms but only if something is written first. I read what you wrote on a blog.
Thanks a lot Good job
Are these types of creaitve writing the same or different if I need to teach children’s creative writing? Can you recommend a website to teach these?
Hi Marie. Thanks for your question. I’ve come across many websites for teaching children’s creative writing. I recommend a search on Google, which will lead you to a ton of resources.
these are very helpful when it comes to getting in college or essays or just to improve my writing
Thanks, Donte. I’m glad you found this helpful.
Free writing really helps me get going. For some reason my prose are much better when I am not beholden to an overall plot or narrative with specific defined characters. I like to free writer “excerpts” on theprose.com. It allows me to practice writing and receive feedback at the same time. I am also trying to blog about writing my first novel, both for writing practice and to keep myself accountable. It really helps!
I feel the same way. Free writing is always a fun and creative experience for me.
Was trying to give an inservice on writing skills and the different types of writing.
Your wok here really helped. Thanks.
You’re welcome.
Hi, Melissa can you assist me ? I’m trying to improve my writing skills as quickly as possible. Plz send me some more tips and trick to improve my writing and communication skills.
You are welcome to peruse this website, which is packed with tips for improving your writing. I’d recommend focusing on the categories Better Writing and Writing Tips for writing improvement. You can also subscribe to get new articles send directly to your email. Thanks!
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 23 Calming Hobbies to Restore Your Energy | NunziaDreams - […] You can do a lot with creative writing. […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- How to Write Better Stories
- How to Start Writing Poetry
- Punctuation Marks: How to Use a Semicolon
- Writing Memoirs
- Do You Need a Place to Write?
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest
Discover 7 Types of Creative Writing to Spark Your Imagination
April 10, 2024

Dive into the diverse world of creative writing, exploring everything from poetry to screenwriting. Uncover strategies and techniques for compelling storytelling. Learn about the various styles, from descriptive to persuasive writing. See how AI is reshaping the creative process, offering new possibilities for writers.
Introduction
Exploring different forms of creative writing.
Creative writing is an art form that opens up worlds of possibilities, allowing writers to explore realms beyond the confines of conventional writing. It encompasses a variety of styles and formats, each offering a unique way to express thoughts, emotions, and stories. This exploration delves into the imagination and linguistic prowess that define creative writing, setting it apart from more structured forms of writing.
Understanding Creative Writing Strategies and Techniques
Mastering creative writing involves more than just a fertile imagination; it also requires a toolkit of strategies and techniques. From the initial planning stages to the final publication, each step in the writing process plays a crucial role in bringing a piece of writing to life. This section will discuss how these tools can enhance storytelling and engage readers more deeply.
Types of Creative Writing
Poetry is an intensely personal form of creative writing that allows for the expression of feelings and thoughts through rhythm, rhyme, and imagery. Poets like Emily Dickinson and Pablo Neruda have touched the hearts of many by mastering this concise, emotive form.

Fiction writing creates worlds and characters that offer escapism, reflection, and commentary on the human condition. Novels, novellas, and short stories allow writers like J.K. Rowling and George Orwell to explore complex ideas within the confines of narrative structure.
Non-Fiction
Non-fiction creative writing, such as memoirs and personal essays, allows writers to explore real events with a narrative flair. This style focuses on conveying factual information through a compelling writing style, exemplified by works like 'The Year of Magical Thinking' by Joan Didion.
Writing for theatrical performance, drama involves crafting dialogues and scenes meant to be performed in front of an audience. Playwrights like Tennessee Williams demonstrate how dialogue and stage directions intertwine to bring stories to life.
Screenplays
Screenwriting is the art of writing scripts for film or television. It combines visual elements with dialogue and requires a unique formatting style to guide production teams, as seen in classic films scripted by writers like Quentin Tarantino.
Blogs offer a more informal approach to creative writing, often blending personal insights, informational content, and a conversational tone to engage readers directly through personal or professional websites.
This form of creative writing focuses on delivering messages through spoken word, often intended to persuade, inform, or entertain an audience. Great speeches, such as those by Martin Luther King Jr., utilize rhetorical techniques to impact listeners profoundly.
Styles of Creative Writing
Creative writing can manifest in various styles, each serving a unique purpose and engaging the reader in different ways. By understanding the characteristics and aims of each style, writers can choose the most effective way to convey their message or story.
Descriptive Writing
Characteristics.
Descriptive writing aims to immerse the reader in a vividly portrayed scene, object, or feeling. It utilizes sensory details and powerful adjectives, creating a rich tapestry of images that allows the reader to visualize and experience the writer's world as if they were there.
The goal of descriptive writing is not just to describe for the sake of description but to paint a picture so real and vivid that the reader can see, feel, smell, taste, and hear the described scene or object. It enhances the reader's engagement and emotional connection with the text.
Narrative Writing
Narrative writing is the art of storytelling . It constructs a narrative with a clear beginning, middle, and end. This style is foundational in both fiction and non-fiction, involving character development, plot setting, and often reaching a climax or conclusion that resolves the tale.
The purpose of narrative writing is to tell a story that is engaging, thought-provoking, and emotionally resonant. It aims to transport the reader through time and space, offering them a glimpse into different worlds, perspectives, and experiences.
Persuasive Writing
Persuasive writing seeks to convince the reader of a particular point of view or argument. It is characterized by clear logic, emotional appeal, and the use of credible evidence to support the argument. The writer's stance is presented in a way that aims to persuade the reader to agree.
The aim here is to influence the reader's beliefs or actions. Whether it's convincing them to adopt a new perspective, make a decision, or take a specific action, persuasive writing seeks to change the way the reader thinks or behaves.
Bonus: How to ensure the Factual Accuracy of your Content?
Expository Writing
Expository writing is informative and explanatory. It presents facts, discusses ideas, or explains processes in a clear, concise manner. This style of writing is research-based , presenting a balanced analysis without the influence of the writer's personal feelings or opinions.
Its primary aim is to inform and educate the reader about a specific topic. By presenting facts and analysis, expository writing helps the reader understand complex subjects, making informed decisions or gaining new insights.
Reflective Writing
Reflective writing is introspective, exploring the writer's personal experiences, thoughts, or feelings about a particular subject or event. It allows for a deeper exploration of the writer's personal growth, understandings, and emotional journey.
The goal is to offer insights into personal development or to reflect on the significance of events and experiences. Reflective writing encourages self-awareness and critical thinking, allowing both the writer and the reader to explore deeper meanings and perspectives.
Experimental Writing
Experimental writing challenges traditional narrative forms and structures. It plays with conventional grammar, syntax, and form, often breaking the rules to create a unique reading experience. This style seeks to innovate and explore new ways of storytelling and expression.
The aim of experimental writing is to push the boundaries of how stories are told and how language is used. It seeks to engage the reader in new and unconventional ways, challenging their expectations and perceptions of what writing can be.
Incorporating AI in Creative Writing
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into creative writing represents a significant shift in how writers approach the creative process. From enhancing productivity to challenging the very notion of originality , AI tools offer both solutions and raise questions in the literary world.
Advantages and Challenges of AI in Creative Writing
- Speed and Efficiency : AI can dramatically speed up the writing process, offering assistance with data gathering, idea generation, and even the initial drafting of texts. This allows writers to focus more on refining their ideas and less on the labor-intensive aspects of writing.
- Creative Assistance : AI tools can suggest prompts, help overcome writer's block, and provide stylistic suggestions, acting as a digital muse for writers in search of inspiration or direction.
- Emotional Depth : While AI is adept at processing data and generating text, it often struggles to replicate the nuanced, deeply emotional undertones that human writers can convey. This limitation can impact the perceived authenticity and emotional resonance of AI-generated content.
- Artistic Integrity : The use of AI in creative writing brings into question issues of originality and authorship. As AI becomes more involved in the creative process, distinguishing between the writer's voice and the machine's contribution becomes increasingly complex.
Examples of AI Tools for Creative Writing
Openai's gpt models.
OpenAI's GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) models have revolutionized the field of creative writing by offering tools that can generate writing prompts, draft texts, and even suggest stylistic changes. These models leverage vast amounts of data to produce text that can mimic a wide range of writing styles, making them valuable assets for writers seeking inspiration or assistance in their creative endeavors.
LongShot AI
LongShot AI is another innovative tool designed to assist writers, particularly in the realm of content creation and enhancement. It goes beyond simple text generation, offering features tailored to the needs of content writers, such as generating article outlines, suggesting headlines, and optimizing content for search engines. LongShot AI's focus on utility and specificity makes it a powerful tool for writers looking to streamline their workflow and enhance their content's effectiveness.
Navigating the Intersection of AI and Creativity
As AI continues to evolve, its role in creative writing is likely to grow, offering new tools and technologies to aid writers. However, navigating this intersection requires a careful balance, ensuring that the essence of creativity — with its inherent unpredictability and emotional depth — remains at the heart of the writing process. The challenge lies in leveraging AI's capabilities without diminishing the personal touch and unique voice that define a writer's work.
The exploration of different creative writing styles and techniques reveals a rich landscape of expression. Each style serves a unique purpose and caters to various audiences, emphasizing the importance of choice and adaptation in creative endeavors. As writers continue to evolve and experiment, the integration of innovative tools like AI can further enhance the narrative capabilities and efficiency of creative writing.
Latest posts

AI Fact Checking: Your Ultimate Weapon Against Misinformation

Fact-Checking Fundamentals: Essential Skills for Navigating the Era of Fake News

The Science Behind AI Content Detectors: Insights into Their Methods and Accuracy

Text Types and Different Styles of Writing: The Complete Guide
A guide to understanding different types of writing and text types.
Reading and writing are complex skills that demand much from students. As they progress, we must assist them in going beyond grammar, punctuation, and spelling and understanding the conventions and structures of the various text types or genres.
By understanding the significance of each text type, educators can tailor their teaching strategies to meet the specific demands of different written contexts.
When students comprehend the purpose of an essay they have been assigned, they can approach it strategically and customize it to the intended audience.
Whether students are deciphering a Shakespearean sonnet, grappling with a scientific research paper, or crafting a persuasive argument, a nuanced understanding of text types will help them confidently navigate the intricacies of language.
In this article, we’ll explore the purpose of literary and factual text types. For greater insight, be sure to read the full guides attached to each type.
What are the main text types?
There are many ways to categorize the broad range of reading and writing materials we encounter daily. But, generally speaking, it’s helpful to think of them in terms of two overarching and broad categories: factual and literary.
We will discuss various sub-categories that fall under these two broad categories. It’s worth noting that different curricula might refer to text types in varying ways. For instance, a recount is also known as a personal narrative in certain regions, and there are several text types with multiple names.
FACTUAL TEXTS
Endeavor to inform, instruct, or persuade through the use of facts and information., literary texts, seek to entertain, enlighten, or elicit emotion through a creative use of language and structure., daily quick writes for all text types.

Our FUN DAILY QUICK WRITE TASKS will teach your students the fundamentals of CREATIVE WRITING across all text types. Packed with 52 ENGAGING ACTIVITIES
Factual Text Types
Argumentative texts.

An argumentative essay is a type of writing in which the author takes a stance on a particular issue or topic and presents arguments and evidence to support that position.
The primary goal is to persuade the reader to adopt the author’s viewpoint or consider it seriously, at the least.
Argumentative Texts are commonly assigned to students in grades three and above. They require them to critically analyze information, develop a clear thesis or main idea, and present a well-structured and reasoned argument.
Argumentative essays are used for debates, policy advocacy, public discourse, critical thinking development, research, and expressing personal views, contributing to social and intellectual dialogue.
Quick Writing Activity: An effective way to lead to writing a discussion text is to hold a discussion or debate in the classroom on a contentious issue or a topic that piques the interest of your class. For example, Should video games be considered a sport? or should homeschooling replace traditional schooling due to technology?
The style of an argumentative essay is typically formal, and the tone is persuasive. The writer should aim to engage the reader and convey the issue’s importance.
Biographies
Biographies are written accounts of people’s lives, providing a comprehensive and detailed narrative of their experiences, achievements, and societal impact. These works offer insight into the individual’s character, contributions, and the historical or cultural context in which they lived. Biographies can take various forms, including books, articles, documentaries, or online profiles, and they are valuable for preserving and sharing the stories of notable individuals.
Examples of biographies include “The Diary of Anne Frank” by Anne Frank, “Steve Jobs” by Walter Isaacson, and “The Wright Brothers” by David McCullough. Biographies play a crucial role in documenting the lives of influential individuals, preserving their stories, and inspiring readers with accounts of human achievement and resilience.
Quick Writing Activity: As a warm-up to biographical writing, St udents imagine themselves as the subject of the biography and write diary entries from that person’s perspective. This activity encourages empathy, deepens understanding of the character’s emotions, and fosters creative expression while maintaining a connection to factual information.
DISCUSSIONS

A discussion essay is a type of academic writing that presents and explores different perspectives on a given topic.
Unlike an argumentative essay, where the author takes a specific stance and argues in favour of it, a discussion essay requires the writer to consider various viewpoints, analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each, and present a well-rounded view of the issue.
The goal is not necessarily to persuade the reader to adopt a particular position but to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Discussion essays are often assigned in academic settings to assess students’ ability to analyze complex issues, consider different perspectives, and present a well-reasoned discussion. They are commonly found in subjects such as philosophy, sociology, and political science, where exploring diverse viewpoints on a topic is crucial for a comprehensive understanding
EXPOSITORY TEXTS & Explanatory ESSAYS

Explanatory texts, expository texts, or explanatory essays are written compositions that aim to provide information, clarify concepts, or explain a particular subject to the reader. The primary purpose of explanatory texts is to convey factual information in a clear, organized, and easily understandable manner. These texts can be found in various forms, including essays, articles, manuals, textbooks, and reports.
Suggested Activity: Task students with going to the library and gathering a range of explanatory texts on various topics. In groups, students go through these texts analyzing the various features they have in common. From their findings, students draw up a detailed list of criteria they can use to write their explanatory texts later.
Information Reports

Information reports, often categorized as expository or informative writing, are compositions that present factual information on a specific topic in a clear, concise, and organized manner. These reports aim to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the subject, and they are commonly found in educational, scientific, and professional contexts. Information reports follow a structured format and are characterized by their focus on delivering objective information without personal opinions or biases
Examples of information reports include scientific research papers, academic reports, technical manuals, and informational articles. These reports serve the purpose of presenting information objectively, helping readers gain insights into a specific topic, and serving as a valuable resource for reference and learning.
Suggested Activity: Students will enjoy creating an information report about their favourite animal. Providing facts and information about aspects such as appearance, habitat, movement, food and life cycle. Images and Diagrams will significantly enhance the finished product.
Procedural Texts & INSTRUCTIONAL ESSAYS

Procedural texts, also known as procedural documents or instructional texts, are written compositions that provide step-by-step guidance on how to perform a specific task or achieve a particular goal. Their primary purpose is to inform the reader about a process, procedure, or set of instructions clearly and concisely. These texts are often found in instructional manuals, recipe books, user guides, technical documents, and other contexts where a systematic set of instructions is necessary.
Procedural texts are essential for conveying information in a format that is easily accessible to individuals who need to perform specific tasks or follow a particular process.
Suggested Activity: Partner students up for this writing task. Ask the students to think of something they know how to do well. It could be anything from how to tie shoelaces to how to perform a cartwheel. It doesn’t matter what it is, as long as the student clearly understands how to do it. Students then write an explanatory text that explains how to do it. Partners swap their work with each other. They then try to perform the task exclusively following the explanation within the text. If they can’t perform the task as it’s meant to be done, then the writer needs to redraft their work until it can be done.

Persuasive Texts / OPINION WRITING

Persuasive texts cover a broad collection of opinions, and argumentative writing styles are designed to sway the reader’s opinion towards a specific viewpoint or prompt them to undertake a particular action. These texts employ language, style, and tone strategically to present compelling arguments, evidence, and reasoning, aiming to convince the audience. They are prevalent in diverse contexts, encompassing academic writing, advertising, public speeches, and opinion pieces.
Examples of persuasive texts include opinion articles in newspapers or magazines, political speeches, advertising campaigns promoting products or services, letters of recommendation, and persuasive essays within academic settings.
Suggested Activity: Distribute copies of a persuasive text to students in groups. For example, this could be an advertisement or newspaper editorial. Challenge students in their groups to identify various persuasive strategies employed within the text, whether in terms of structure, presentation, visuals, or language. Students can compare and contrast their findings between groups.
Non-chronological reports

Non-chronological reports are informative writing that presents information about a particular topic without following a strict chronological order. Unlike narratives or historical accounts that organize information based on a sequence of events over time, non-chronological reports present facts, descriptions, and details in a logical and thematic structure. These reports are commonly used in educational contexts, informational articles, and reference materials.
Examples of non-chronological reports include scientific reports, encyclopedia entries, informational articles in magazines, and educational materials. These reports are valuable for presenting information in a structured and thematic manner, making them accessible for readers seeking specific details about a particular topic.
Suggested Activity: An informational leaflet is one form of a non-chronological report. Challenge students to produce an information leaflet on something they know, such as a local attraction or historical site. When students have completed their leaflets, please encourage them to review each other’s work and offer feedback.

Recounts are a form of writing that involves retelling past events or experiences. The primary purpose of a recount is to inform or entertain the reader by providing a detailed account of what happened. Recounts can take various forms, including personal narratives, diary entries, news reports, or historical retellings. They often use a chronological structure to present events in the order in which they occurred.
Personal narratives, autobiographical accounts, eyewitness testimonies, travel diaries, and historical retellings are examples of recounts. They serve as a means of sharing personal experiences, preserving memories, and conveying information about past events in a compelling and engaging way.
Suggested Activity: In the library, challenge students to gather as many different types of recounts as possible. In their groups, students review the various recounts and compile a list of criteria for this text type. As a whole class, the groups share their results. Encourage students to pay particular attention to the range of topics that can be presented as recounts and how this can affect the language style. For example, recounting a science experiment will use more technical and formal language than the informal and personal style that might be employed to recount a travel adventure.
Literary Text Types

Poetry is a form of artistic expression that uses language to evoke emotions, convey images, and create a rhythmic and musical effect. It is a genre of literature characterized by a heightened use of language, often employing techniques such as meter, rhyme, and metaphor. Poems come in various forms and styles, each with its own unique structure and purpose. Poetry is a rich and diverse literary tradition that allows for creatively exploring themes, emotions, and perspectives.
Examples of famous poets include William Shakespeare, Emily Dickinson, Langston Hughes, and Maya Angelou. Poetry can take various forms, including sonnets, haikus, free verse, and epic poems. Its versatility allows poets to experiment with language, form, and structure to create unique and expressive works.
Suggested Activity: Find an anthology of poetry that groups poems together according to themes. Task your students to look at poems exploring a common theme. Have the students look at the features these poems have in common and the features that differ. Can the students identify the different types of poems?

A narrative is a form of writing that tells a story or recounts a series of events. Narratives can take various forms, including short stories, novels, autobiographies, and even some types of essays. The primary goal of a narrative is to engage the reader by presenting a compelling and coherent sequence of events that unfold over time using the story elements of character, setting, plot, theme and conflict.
Examples of Narratives include Charlotte’s Web by E.B. White and Charlie and the Chocolate Factory by Roald Dahl.
Narratives entertain, inform, or convey a message through the artful arrangement of events and characters in a story.
Suggested Activity: This task can be completed using novels, short stories, or even concerning movies the students are familiar with. Have the students draw an x and a y-axis on a piece of paper. Students label the x-axis time and the y-axis action. Students then plot and label the narrative’s introduction, complication, rising action, climax, and resolution. The more intense the action at each point of the story, the higher on the y-axis the point will be plotted. The points are then joined with a line. This will give the students a sense of the ‘shape’ of the story. Internalizing an understanding of this general storytelling pattern will help students immensely in their writing.

Written drama, often known as a play or script, is a form of literature designed for performance on stage. It involves creating characters, dialogue, and a plot structure to convey a narrative through the characters’ interactions and conflicts.
Written drama incorporates dramatic elements, such as setting, conflict, climax, and resolution, to engage an audience emotionally and intellectually.
Playwrights employ unique techniques, including dialogue, stage directions, and sometimes monologues, to bring their stories to life in a theatrical context, offering a distinct blend of literary and performative artistry.
Suggested Activity: Students can explore the different conventions, similarities, and differences between prose and drama by taking a story written in a prose genre, such as a fable, short story, etc., and converting it into a script for a drama.
A COMPLETE YEAR OF WRITING FOR STUDENTS – 1000+ PAGES

This HUGE BUNDLE offers over 1000 PAGES of COMPLETE UNITS of work that would easily fill a year of writing, all created with STRUCTURE, INSIGHT AND KNOWLEDGE to improve student writing skills. EDITABLE / DIGITAL & PRINT formats. No preparation is required.
In Conclusion
Understanding the various aspects of the different writing genres will help students navigate writing that serves a wide range of purposes.
It will also help students with their own text compositions. Understanding the various underlying text structures will provide students with an effective means of organizing their work, helping to ensure their writing is fit for purpose.
Exposing your students to as many different genres as possible and providing opportunities to explore how these text types operate will go a long way to helping them develop into adaptive and organized readers and writers in the future.

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES FROM LITERACYIDEAS.COM


Elements of Creative Writing
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
Navigation is good.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page

Ebooks, Publishing, and Everything in Between
- Downloads & Pricing
- Advertising
Exploring the Different Types of Creative Writing
- on Sep 26, 2022
- in Writing Tips
- Last update: November 16th, 2023
Writing comes in all forms and sizes. But in order for a work to be considered creative writing, it must come from a place of imagination and emotion.
This is something many people pursuing a creative writing degree online at first struggle to get a handle on. Take for example what Franz Kafa said about creative writing, “Don’t bend; don’t water it down; don’t try to make it logical; don’t edit your own soul according to the fashion. Rather, follow your most intense obsessions mercilessly.”
Many authors who choose to follow Kafka’s advice—to write “mercilessly” and from the soul—find it comforting that their writing doesn’t have to conform to one style. But this variety of types and forms might leave some writers a bit confused.
That’s why, in this article, we are going to walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, with some great examples from authors who absolutely rocked their respective forms.

In this article:
- Creative Writing Definition
- Creative Writing Techniques
- Free Writing
- Journal Diaries
- Personal Essays
- Short Fiction
- Novels/Novellas
What Is Creative Writing?
Think of creative writing as a form of artistic expression. Authors bring this expression to life using their imagination, personal writing style, and personality.
Creative writing is also different from straightforward academic or technical writing. For instance, an economics book like Khalid Ikram’s The Political Economy of Reforms in Egypt is an academic monograph. This means that readers would rightfully expect it to contain analytic rather than creative writing.
So what are some elements that make a written piece more creative than analytic?
Popular Techniques Used in Creative Writing
Despite the fact that creative writing can be “freer” and less traditional than academic writing, it is likely to contain one or more of the following six elements:
1. Literary Devices
Many creative writers use literary devices to convey the meaning and themes of their work. Some common literary devices are allegories , metaphors and similes , foreshadowing , and imagery . These all serve to make the writing more vivid and descriptive .
2. Narrative
Authors often use this technique to engage readers through storytelling. Narrative isn’t limited to novels and short stories; poems, autobiographies, and essays can be considered narratives if they tell a story. This can be fiction (as in novels) or nonfiction (as in memoirs and essays).
3. Point of View
All creative writing must have a point of view; that’s what makes it imaginative and original. The point of view is the perspective from which the author writes a particular piece. Depending on the type of work, the point of view can be first person, third person omniscient, third person limited , mixed (using third- and first-person writing), or—very rarely—second person.
4. Characterization
Characterization is the process by which authors bring their characters to life by assigning them physical descriptions, personality traits, points of view, background and history, and actions. Characterization is key in creative writing because it helps drive the plot forward.
5. Dialogue
An important element used in many creative writing works is dialogue . Assigning
dialogue to characters is a way for authors to show their characters’ different traits without explicitly listing them.
Dialogue also immerses readers in the narrative’s action by highlighting the emotions and tensions between characters. Like characterization, it also helps drive the plot forward.
6. Plot
The plot is the sequence of events that make up a narrative and establish the themes and conflicts of a work . Plots will usually include an exp osi tion (the introduction), rising action (the complications), climax (the peak in action and excitement), falling action (the revelations and slowing down of events), and denouement (the conclusion).

The Main Types of Creative Writing (With Examples)
What’s great about creative writing is that there are so many types to choose from. In this section, we’ll walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, along with some examples.
Type 1: Free writing
Free writing, also known as stream-of-consciousness writing, is a technique that allows words and images to spill onto the page without giving thought to logic, sequence, or grammar. Although authors often use it as an exercise to get rid of the infamous writer’s block , free writing is also useful within a larger work.
For instance, let’s take a look at this excerpt from Toni Morrison’s novel Beloved.
Beloved by Toni Morrison [an excerpt]
the air is heavy I am not dead I am not there is a house there is what she whispered to me I am where she told me I am not dead I sit the sun closes my eyes when I open them I see the face I lost Sethe’s is the face that left me Sethe sees me see her and I see the smile her smiling face is the place for me it is the face I lost she is my face smiling at me
Note how the author uses free writing to convey the character’s disjointed and agitated thoughts. Even punctuation has been set aside here, adding to the rush of the character’s fear and confusion. The imagery is powerful (“the sun closes my eyes”; “her smiling face is the place for me”) and relies on repetitions like “I am not dead” and “I see” to immerse the readers in the character’s disturbed mental state.
Type 2: Journals and Diaries
A journal is a written account of an author’s experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently.
Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events. For instance, if a diary entry discusses how the writer ran into an old friend, it might include details of the writer’s emotions and probably use literary devices to convey these feelings.
It’s almost impossible to read the word “diary” and not think of Anne Frank. Let’s look at this excerpt from her work The Diary of a Young Girl .
Anne Frank: The Diary of a Young Girl [an excerpt]
Saturday, 20 June, 1942: I haven’t written for a few days, because I wanted first of all to think about my diary. It’s an odd idea for someone like me to keep a diary; not only because I have never done so before, but because it seems to me that neither I—nor for that matter anyone else—will be interested in the unbosomings of a thirteen-year-old schoolgirl. Still, what does that matter? I want to write, but more than that, I want to bring out all kinds of things that lie buried deep in my heart.
In the extract above, Anne adopts a reflective tone. She uses the rhetorical question “what does that matter?” to illustrate how she arrived at the conclusion that this diary will help bring out what is “buried deep in her heart.”
In this way, the diary serves as a log of events that happened in Anne’s life, but also as a space for Anne to reflect on them, and to explore her resulting emotions.
Type 3: Memoir
Although they might seem similar at first, memoirs and diaries are two different creative writing types. While diaries offer a log of events recorded at frequent intervals, memoirs allow the writer to select key moments and scenes that help shed light on the writer’s life.
Let’s examine this excerpt from the memoir of Roxanne Gay, author of Bad Feminist .
Hunger: A Memoir of (My) Body by Roxanne Gay:
I ate and ate and ate in the hopes that if I made myself big, my body would be safe. I buried the girl I was because she ran into all kinds of trouble. I tried to erase every memory of her, but she is still there, somewhere . . . I was trapped in my body, one that I barely recognized or understood, but at least I was safe.
Roxanne Gay offers readers a powerful work on anxiety, food, and body image by taking them on a journey through her past . Using evocative imagery in the excerpt above (“I buried the girl I was”; “I was trapped in my body”) the author shares her psychological trauma and resulting tumultuous relationship with food.
As with most memoirs—and diaries—this one is intimate, allowing readers into the dark crevices of the author’s mind. However, unlike a diary, this memoir does not provide an account of the writer’s day-to-day life, but rather focuses on certain events—big and small—that the author feels made her who she is today.
Type 4: Letters
Unlike diary and journal entries—which usually don’t have a specific recipient—letters address one target reader. Many famous authors have had collections of their letters published, revealing a side of them that isn’t visible in other works.
Letter writing uncovers the nature of the relationship between sender and recipient, and can include elements of creative writing such as imagery, opinion, humor, and feeling.
Here is an excerpt from a letter by Truman Capote, author of Breakfast at Tiffany’s and In Cold Blood .
Too Brief a Treat: The Letters of Truman Capote , edited by Gerald Clarke
Dear Bob; Have come, am here, am slowly freezing to death; my fingers are pencils of ice. But really, all told, I think this is quite a place, at least so far. The company is fairly good… I have a bedroom in the mansion (there are bats circulating in some of the rooms, and Leo keeps his light on all night, for the wind blows eerily, doors creak, and the faint cheep cheep of the bats cry in the towers above: no kidding.
In his letter to editor and friend Robert “Bob” Linscott, Truman paints a scene of his new setting . He uses hyperbole (“freezing to death”) and a powerful metaphor (“my fingers are pencils of ice”) to convey the discomforting cold weather. Truman also uses sound imagery (“doors creak”; “wind blows eerily”; “cheep cheep of the bats”) to communicate the creepy, sinister mood to his reader.
Type 5: Personal Essays
Many of us don’t normally think of essays as creative writing, but that’s probably because our minds go to academic research essays. However, there are many types of essays that require creative rather than analytic writing, including discursive essays, descriptive essays, and personal essays.
A personal essay, also known as a narrative essay, is a piece of nonfiction work that offers readers a story drawn from the author’s personal experience. This is different from a memoir, in which the primary focus is on the author and their multiple experiences.
A personal essay, on the other hand, focuses on a message or theme , and the author’s personal experience is there to communicate that theme using memorable characters and setting , as well as engaging events . These, of course, all have to be true, otherwise the personal essay would turn into a fictional short story.
Here is an excerpt from a personal essay by writers Chantha Nguon and Kim Green.
The Gradual Extinction of Softness by Chantha Nguon and Kim Green
In 1975, the Khmer Rouge informed the Cambodian people that we had no history, but we knew it was a lie. Cambodia has a rich past, a mosaic of flavors from near and far: South Indian traders gave us Buddhism and spicy curries; China brought rice noodles and astrology; and French colonizers passed on a love of strong coffee, flan, and a light, crusty baguette. We lifted the best tastes from everywhere and added our own.
The opening of this paragraph establishes the author’s strong and unwavering opinion : “we knew it was a lie.” Instead of providing a history of Cambodia, she demonstrates the country’s rich past by discussing its diverse “flavors”: “spicy curries”; “strong coffee”; “light, crusty baguette”, etc.
Using gustatory imagery , which conveys a sense of taste , the authors reveal their personal version of what makes Cambodia wonderful. The writer communicates the essay’s theme of food and memories through a story of her childhood.
Type 6: Poetry
Robert Frost once wrote: “Poetry is when an emotion has found its thought and the thought has found words.” Good poetry is effective because it uses the power of imagery to convey what it is to be human. Every word in a poem counts, and the best poems are those that evoke the reader’s emotions without unpacking too much.
As one of the most diverse types of creative writing, poetry can come in many forms. Some poets prefer to write in the more traditional forms such as sonnets , villanelles , and haikus , where you have particular structures, rhyme, and rhythm to follow. And others prefer the freedom of free verse and blackout poetry .
Let’s take a look at this excerpt from Maya Angelou’s powerful lyric poem , “Still I Rise.”
“Still I Rise” from And Still I Rise: A Book of Poems by Maya Angelou
Out of the huts of history’s shame I rise Up from a past that’s rooted in pain I rise I’m a black ocean, leaping and wide, Welling and swelling I bear in the tide. Leaving behind nights of terror and fear I rise Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear I rise Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave, I am the dream and the hope of the slave. I rise I rise I rise.
Packed with powerful language, this excerpt from Angelou’s poem gives us absolute
chills! The refrain “I rise” is repeated 7 times in these two verses alone,
hammering home the idea that the speaker cannot be defeated.
The imagery, repetition, and rhyme scheme all work together to convey the emotions of pride and resilience. Both verses also rely heavily on metaphors (“I’m a black ocean”; “I am the dream and the hope of the slave”) to convey the speaker’s power. She is not like an ocean or a dream; she is both, and she is unstoppable.
Type 7: Song Lyrics
Song lyrics are in many ways similar to poems, except that lyrics are meant to be sung . They are a form of creative writing that allows writers to surpass the rules of grammar and punctuation in favor of creating rhyme and rhythm . This means that the creativity of a song lyricist is free from the traditional restrictions of language.
Type 8: Scripts
Scriptwriting is a form of creative writing that relies heavily on character dialogue , stage directions , and setting . Scripts are written for films and TV shows (known as screenplays and teleplays), stage plays, commercials, and radio and podcast programs.
Like song lyrics, scripts are written with the intention of reaching a non-reading audience. In other words, scriptwriters must bear in mind how their writing will be 1) interpreted by other storytellers , such as directors, designers, etc., and 2) performed by actors.
Let’s examine the iconic opening scene from the screenplay of the film Forrest Gump .
Forrest Gump , screenplay by Eric Roth [an excerpt]
THE MAN Hello, I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump. She nods, not much interested. He takes an old candy kiss out of his pocket. Offering it to her: FORREST (cont’d) Do you want a chocolate? She shakes “no.” He unwraps it, popping it in his mouth. FORREST (cont’d) I could eat about a million and a half of these. Mama said, “Life was just a box of chocolates. You never know what you gonna get.”
From the dialogue and stage directions in this opening scene, the audience can see that there is something innocent, kind-hearted, and simple about the character Forrest Gump. This is conveyed through the way he introduces himself with a slight repetition (“I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump.”) to a complete stranger, and the way he quotes his mother to her.
Moreover, the action of Forrest “popping” the candy in his mouth is almost childlike , and that the stranger is reluctant to communicate with him foreshadows the fact that the people Forrest meets are initially suspicious of him and his innocence. Thus, the pauses and silences in the scene are just as important to the work as what is explicitly said.
Type 9: Short Fiction
Short fiction is a form of creative fiction writing that typically falls between 5,000 to 10,000 words ; however, there is definitely room to go lower than 5,000 words, depending on the topic.
For instance, flash fiction is a form of short fiction that can be 1,000 words or less. In the case of flash fiction, the author unpacks the “skeleton” of a story in as few words as possible. For instance, legend has it that Ernest Hemingway wrote a 6-word “story”:
For sale: baby shoes, never worn.
In just six words, the reader is led to understand that this is a story of death and loss.
Nevertheless, the average short story is usually structured around the following elements: characterization , setting , plot , and conflict . Many fiction authors start out writing short fiction because it enables them to nail all the essential elements, which they can then expand upon in longer works.
Let’s look at an excerpt from Janet Frame’s short story, “The Bath”
“The Bath” by Janet Frame [an excerpt]
She leaned forward, feeling the pain in her back and shoulder. She grasped the rim of the bath but her fingers slithered from it almost at once. She would not pancic, she told herself; she would try gradually, carefully, to get out. Again she leaned forward; again her grip loosened as if iron hands had deliberately uncurled her stiffened blue fingers from their trembling hold. Her heart began to beat faster, her breath came more quickly, her mouth was dry. She moistened her lips. If I shout for help, she thought, no-one will hear me. No-one in the world will hear me. No-one will know I’m in the bath and can’t get out.
In this paragraph, there is an image of a frail, old woman, physically unable to get out of her bathtub. The diction , or word choice, serves to convey the woman’s sense of fear and helplessness. For instance, words like “grasped,” “slithered,” “uncurled,” and “stiffened,” demonstrate the immense effort it takes for her to try to get out.
The image of her “moistening” her lips illustrates that fear has turned her mouth dry. And the repetition of “no-one” in the last few sentences highlights the woman’s loneliness and entrapment —two of the story’s main themes. Indeed, the bath symbolizes the unavoidable obstacles brought about by old age.
Type 10: Novellas / Novels
Novels are one of the most popular forms of creative writing. Though they vary in length, depending on the subject, they’re generally considered a long form of fiction , typically divided into chapters .
Novellas, on the other hand, are shorter than novels but longer than short stories. Like short stories, novels, and novellas contain characters , plot , dialogue , and setting ; however, their longer forms allow writers a chance to delve much deeper into those elements.
Type 11: Speeches
Speeches are a form of writing similar to essays in that both forms are non-fiction , and both usually entail a discussion of the writer’s personal experiences and include engaging events and a particular theme.
However, speeches differ from essays in that the former are meant to be recited (usually in front of an audience), and tend to be persuasive and inspirational. For instance, think of the purpose of graduation speeches and political speeches: they aim to inspire and move listeners.
One of the most well-known speeches from the 20th century is Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream”. Let’s examine the excerpt below:
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King [an excerpt]
Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice. Now is the time to lift our nation from the quicksands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood. Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God’s children.
What immediately catches the eye (and ear) in this paragraph is the speaker’s usage of anaphora : the repetition of the phrase “now is the time” serves to emphasize the urgency of the matter being discussed (i.e. the prevalence of racial injustice).
The speaker’s repetition of the pronoun “our” is an appeal to his audience’s emotions and their sense of unity. Both he and they are in this together, and thus he is motivating them to take on the challenge as one.
Moreover, the use of figurative language is abundant here and can be found in similar inspirational and motivational styles of creative writing. The imagery created by the metaphor and alliteration in “the d ark and d esolate valley of segregation,” and its juxtaposition with “sunlit path of racial justice,” together aim to convey the speaker’s main message. Segregation has brought nothing but darkness and ruin to American society, but there is hope and light on the path toward racial equality.
Final Thoughts
Creative writing acts as a medium for artistic expression. It can come in a variety of forms, from screenplays and speeches to poetry and flash fiction. But what groups all of these different types of creative writing under the “creative” umbrella, regardless of form, is their display of a writer’s imagination, creativity, and linguistic prowess.
How to Write the Best Book Introduction
Making Use of Humor in Writing
4 Different Types of Writing You Need to Understand
I appreciate you offering such a thought-provoking perspective. It should be useful for academic writing in addition to creative writing, in my opinion. Each method you listed is pertinent and appropriate.
You’re absolutely right! Many of these writing methods can be applied to both creative and academic writing, enhancing the depth and effectiveness of communication.
Robert smith enago
Thank you for sharing this enlightening blog post on the various types of creative writing. Your exploration of different writing methods and styles provides an inspiring perspective on the boundless possibilities within the realm of creativity.
It is remarkable to see how creative writing encompasses an array of forms, each with its unique allure and artistic essence. From poetry, fiction, and drama to screenwriting, creative nonfiction, and even songwriting, each avenue offers writers a chance to express their thoughts, emotions, and imagination in captivating ways.
We truly appreciate your kind words! Creative writing is indeed a vast and fascinating world with endless opportunities for self-expression 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.

Kotobee is the complete end-to-end ebook solution for you and your business. Export multiple formats. Deliver securely.
Create, publish, and sell ebooks with ease
Kotobee es la solución completa de ebooks de extremo a extremo para usted y su empresa.
Cree, publique y venda libros electrónicos con facilidad

Recent Posts
- How to Edit a Book for Publishing: Tips & Best Practices
- Book Royalties: What They Are and How to Earn the Best Rates
- Game-Based Learning: What It Is, and How to Apply It
- How to Publish a Book for Free and Maximize Your Profit
- How to Become a Best-Selling Author: 5 Secrets for Success
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 4 writing styles: how to identify and use them.
General Education

A piece’s writing style can help you figure out what kind of writing it is, what its purpose is, and how the author’s voice is unique. With so many different types of writing, you may think it’s difficult to figure out the specific writing style of a piece or you'll need to search through a long list of writing styles.
However, there are actually just four main types of writing styles, and together they cover practically all the writing you see, from textbooks to novels, to billboards and more. Whether you’re studying writing styles for class or trying to develop your own writing style and looking for information, we’ve got you covered.
In this guide, we explain the four styles of writing, provide examples for each one, go over the one thing you need to know to identify writing style, and give tips to help you develop your own unique style of writing.
The 4 Types of Writing
There are four main different styles of writing. We discuss each of them below, list where you’re likely to see them, and include an example so you can see for yourself what each of the writing styles looks like.
Writers who use the narrative style are telling a story with a plot and characters. It’s the most common writing style for fiction, although nonfiction can also be narrative writing as long as its focus is on characters, what they do, and what happens to them.
Common Places You’d See Narrative Writing
- Biography or autobiography
- Short stories
- Journals or diaries
“We had luncheon in the dining-room, darkened too against the heat, and drank down nervous gayety with the cold ale. ‘What’ll we do with ourselves this afternoon?’ cried Daisy, ‘and the day after that, and the next thirty years?’ ‘Don’t be morbid,’ Jordan said. ‘Life starts all over again when it gets crisp in the fall.’ ‘But it’s so hot,’ insisted Daisy, on the verge of tears, ‘and everything’s so confused. Let’s all go to town!’ - The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
You can quickly tell that this passage from the novel The Great Gatsby is an example of narrative writing because it has the two key traits: characters and a plot. The group is discussing eating and drinking while trying to decide what to do for the rest of the day.
As in this example, narrative writing often has extended dialogue scenes since the dialogue is used to move the plot along and give readers greater insight into the characters.
Writers use the expository style when they are trying to explain a concept. Expository writing is fact-based and doesn’t include the author’s opinions or background. It’s basically giving facts from the writer to the reader.
Common Places You’d See Expository Writing
- Newspaper articles
- Academic journals
- Business memos
- Manuals for electronics
- How-to books and articles
“The 1995/1996 reintroduction of gray wolves (Canis lupus) into Yellowstone National Park after a 70 year absence has allowed for studies of tri-trophic cascades involving wolves, elk (Cervus elaphus), and plant species such as aspen (Populus tremuloides), cottonwoods (Populus spp.), and willows (Salix spp.). To investigate the status of this cascade, in September of 2010 we repeated an earlier survey of aspen and measured browsing and heights of young aspen in 97 stands along four streams in the Lamar River catchment of the park’s northern winter range. We found that browsing on the five tallest young aspen in each stand decreased from 100% of all measured leaders in 1998 to means of <25% in the uplands and <20% in riparian areas by 2010. Correspondingly, aspen recruitment (i.e., growth of seedlings/sprouts above the browse level of ungulates) increased as browsing decreased over time in these same stands.” -”Trophic cascades in Yellowstone: The first 15 years after wolf reintroduction” by William J. Ripple and Robert L. Beschta
This abstract from an academic journal article is clearly expository because it only focuses on facts. The authors aren’t giving their opinion of wolves of Yellowstone, they’re not telling a story about the wolves, and the only descriptions are number of trees, streams, etc. so readers can understand the study better.
Because expository writing is focused on facts, without any unnecessary details or stories, the writing can sometimes feel dense and dry to read.
Descriptive
Descriptive writing is, as you may guess, when the author describes something. The writer could be describing a place, person, or an object, but descriptive writing will always include lots of details so the reader can get a clear and complete idea of what is being written about.
Common Places You’d See Descriptive Writing
- Fiction passages that describe something
“In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit. Not a nasty, dirty, wet hole, filled with the ends of worms and an oozy smell, nor yet a dry, bare sandy hole with nothing in it to sit down on or eat: it was a hobbit hole and that means comfort. It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted...” - The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien
This is the opening passage of the novel The Hobbit . While The Hobbit is primarily an example of narrative writing, since it explores the adventures of the hobbit and his companions, this scene is definitely descriptive. There is no plot or action going on in this passage; the point is to explain to readers exactly what the hobbit’s home looks like so they can get a clear picture of it while they read. There are lots of details, including the color of the door and exactly where the doorknob is placed.
You won’t often find long pieces of writing that are purely descriptive writing, since they’d be pretty boring to read (nothing would happen in them), instead many pieces of writing, including The Hobbit , will primarily be one of the other writing styles with some descriptive writing passages scattered throughout.
When you’re trying to persuade the reader to think a certain way or do a certain thing, you’ll use persuasive writing to try to convince them. Your end goal could be to get the reader to purchase something you’re selling, give you a job, give an acquaintance of yours a job, or simply agree with your opinion on a topic.
Common Places You’d See Persuasive Writing
- Advertisements
- Cover letters
- Opinion articles/letters to the editor
- Letters of recommendation
- Reviews of books/movies/restaurants etc.
- Letter to a politician
“What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink by the lights of perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves, that if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, ‘This was their finest hour.’ - “This was their finest hour” by Winston Churchill
In this excerpt from his famous “Their finest hour” speech, Prime Minister Winston Churchill is clearing trying to convince his audience to see his viewpoint, and he lays out the actions he thinks they should take. In this case, Churchill is speaking to the House of Commons (knowing many other British people would also hear the speech), and he’s trying to prepare the British for the coming war and convince them how important it is to fight.
He emphasizes how important the fight will be (“Upon this battle depends the survival of the Christian civilization.” and clearly spells out what he thinks his audience should do (“Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties…”).

Common Writing Styles to Know
Each of the four main types of writing styles has multiple subsets of styles within it. Here are nine of the most common and important types of writing you’ll see.
Narrative Writing
Character voice.
Character voice is a common writing style in novels. Instead of having an unknown narrator, the audience knows who is telling the story. This first-person narrator can help the reader relate more both to the narrator and the storyline since knowing who is telling a story can help the reader feel more connected to it. Sometimes the narrator is completely truthful in telling what happens, while other times they are an unreliable narrator and will mislead or outright lie to readers to make themselves look better.
To Kill a Mockingbird (Scout is the narrator) and The Hunger Games (Katniss is the narrator) are two examples of this writing style.
Stream-of-Consciousness
This writing style attempts to emulate the thought process of the character. Instead of only writing about what the character says or does, stream-of-consciousness will include all or most of the characters thoughts, even if they jump from one topic to another randomly or include incomplete thoughts.
For example, rather than writing “I decided to take a walk to the ice cream shop,” an author using the stream-of-consciousness writing style could write, “It’s pretty hot out, and I feel like I should eat something, but I’m not really that hungry. I wonder if we have leftovers of the burgers Mom made last night? Is Mom staying late at work tonight? I can’t remember if she said. Ice cream would be a good choice, and not too filling. I can’t drive there though because my car is still in for repairs. Why is the repair shop taking so long? I should have listened when David said to check for reviews online before choosing a place. I should text David later to see how he is. He’ll think I’m mad at him if I don’t. I guess I’ll just have to walk to the shop.”
James Joyce and William Faulkner are two of the most well-known writers to have regularly used the stream-of-consciousness writing style.
Epistolary writing uses a series of documents, such as letters, diary entries, newspaper articles, or even text messages to tell a story. They don’t have a narrator, there’s just whoever purportedly gathered the documents together. This writing style can provide different points of view because a different person can be the author of each document.
Well-known examples of epistolary writing include the novels Dracula (written as a series of letters, newspaper articles, and diary entries) and Frankenstein (written as a series of letters).
Expository Writing
You’ll find this style in textbooks or academic journal articles. It’ll focus on teaching a topic or discussing an experiment, be heavy on facts, and include any sources it cited to get the information. Academic writing often assumes some previous knowledge of the topic and is more focused on providing information than being entertaining, which can make it difficult to read and understand at times.
Business writing refers to the writing done in a workplace. It can include reports, memos, and press releases. Business writing typically has a formal tone and standard formatting rules. Because employees are presumably very busy at work, business writing is very concise and to the point, without any additional flourishes intended to make the writing more interesting.
You’ll see this writing style most commonly in newspaper articles. It focuses on giving the facts in a concise, clear, and easy-to-understand way. Journalists often try to balance covering all the key facts, keeping their articles brief, and making the audience interested in the story.
This writing style is used to give information to people in a specific field, such as an explanation of a new computer programming system to people who work in software, a description of how to install pipes within a house for plumbers, or a guide to new gene modifications for microbiologists.
Technical writing is highly specialized for a certain occupational field. It assumes a high level of knowledge on the topic, and it focuses on sharing large amounts of information with the reader. If you’re not in that field, technical writing can be nearly impossible to understand because of the jargon and references to topics and facts you likely don’t know.

Descriptive Writing
Poetry is one of the most challenging styles of writing to define since it can come in many forms. In general, poems use rhythmic language and careful word choice to express an idea. A poem can be an example of descriptive writing or narrative writing, depending on whether it’s describing something or telling a story. Poetry doesn’t need to rhyme, and it often won’t follow standard grammatical or structural rules. Line breaks can, and often do, occur in the middle of sentences.
Persuasive Writing
Copywriting.
Copywriting is writing that is done for advertising or marketing purposes. It’s attempting to get the reader to buy whatever the writer is trying to sell. Examples of copywriting include catalogs, billboards, ads in newspapers or magazines, and social media ads.
In an attempt to get the reader to spend their money, copywriters may use techniques such as descriptive language (“This vanilla was harvested from the lush and exotic island of Madagascar"), exciting language (Stop what you’re doing and learn about this new product that will transform your life!”) and exaggeration (“This is the best cup of coffee you will ever taste!”).
Opinion
People write opinion pieces for the purpose of stating their beliefs on a certain topic and to try to get readers to agree with them. You can see opinion pieces in newspaper opinion sections, certain blog posts, and some social media posts. The quality of opinion writing can vary widely. Some papers or sites will only publish opinion pieces if all the facts in them can be backed up by evidence, but other opinion pieces, especially those that are self-published online, don't go through any fact-checking process and can include inaccuracies and misinformation.
What If You’re Unsure of a Work’s Writing Style?
If you’re reading a piece of writing and are unsure of its main writing style, how can you figure which style it is? The best method is to think about what the purpose or main idea of the writing is. Each of the four main writing styles has a specific purpose:
- Descriptive: to describe things
- Expository: to give facts
- Narrative: to tell a story
- Persuasive: to convince the reader of something
Here’s an example of a passage with a somewhat ambiguous writing style:
It can be tricky to determine the writing style of many poems since poetry is so varied and can fit many styles. For this poem, you might at first think it has a narrative writing style, since it begins with a narrator mentioning a walk he took after church. Character + plot = narrative writing style, right?
Before you decide, you need to read the entire passage. Once you do, it’ll become clear that there really isn’t much narrative. There’s a narrator, and he’s taking a walk to get a birch from another man, but that’s about all we have for character development and plot. We don’t know anything about the narrator or his friend’s personality, what’s going to happen next, what his motivations are, etc.
The poem doesn’t devote any space to that, instead, the majority of the lines are spent describing the scene. The narrator mentions the heat, scent of sap, the sound of frogs, what the ground is like, etc. It’s clear that, since the majority of the piece is dedicated to describing the scene, this is an example of descriptive writing.

How Can You Develop Your Own Writing Style?
A distinctive writing style is one of the hallmarks of a good writer, but how can you develop your own? Below are four tips to follow.
Read Many Different Styles of Writing
If you don’t read lots of different kinds of writing, you won’t be able to write in those styles, so before you try to get your own writing style, read different writing styles than what you’re used to. This doesn’t mean that, if you mostly read novels, you suddenly need to shift to reading computer manuals. Instead, you can try to read novels that use unreliable narrators, stream-of-consciousness writing, etc.
The more you read, the more writing styles you’ll be exposed to, and the easier it’ll be able to combine some of those into your own writing style.
Consider Combining Multiple Types of Writing Styles
There’s no rule that you can only use one style for a piece of writing. In fact, many longer works will include multiple styles. A novel may be primarily narrative, but it can also contain highly descriptive passages as well as expository parts when the author wants the readers to understand a new concept.
However, make sure you don’t jump around too much. A paper or book that goes from dense academic text to impassioned plea for a cause to a story about your childhood and back again will confuse readers and make it difficult for them to understand the point you’re trying to make.
Find a Balance Between Comfort and Boundary-Pushing
You should write in a style that feels natural to you, since that will be what comes most easily and what feels most authentic to the reader. An academic who never ventures outside the city trying to write a book from the perspective of a weathered, unschooled cowboy may end up with writing that seems fake and forced.
A great way to change up your writing and see where it can be improved is to rewrite certain parts in a new writing style. If you’ve been writing a novel with narrative voice, change a few scenes to stream-of-consciousness, then think about how it felt to be using that style and if you think it improved your writing or gave you any new ideas. If you’re worried that some writing you did is dull and lacking depth, add in a few passages that are purely descriptive and see if they help bring the writing to life.
You don’t always need to do this, and you don’t need to keep the new additions in what you wrote, but trying new things will help you get a better idea of what you want your own style to be like.
The best way to develop your own writing style is to expose yourself to numerous types of writing, both through reading and writing. As you come into contact with more writing styles and try them out for yourself, you’ll naturally begin to develop a writing style that you feel comfortable with.
Summary: The 4 Different Styles of Writing
There are four main writing styles, and each has a different purpose:
If you’re struggling to figure out the writing style of a piece, ask yourself what its purpose is and why the author wants you to read it.
To develop your own writing style, you should:
- Read widely
- Consider mixing styles
- Balance writing what you know and trying new things
What's Next?
Literary devices are also an important part of understanding writing styles. Learn the 24 literary devices you must know by reading our guide on literary devices.
Writing a research paper for school but not sure what to write about? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Are you reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing

Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
404 Not found
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Writing Tips Oasis - A website dedicated to helping writers to write and publish books.
21 Top Examples of Creative Writing
By Rofida Khairalla

Let’s be practical: anyone can be a writer.
Sure, practicing the skill and perfecting the art takes a certain modicum of natural interest in the profession.
But the thing that so many people can often overlook is that being a “writer” isn’t defined by how much you write.
So many times we can get hung up on trying to write a bestselling novel or groundbreaking book that we can forget that there are so many other types of writing out there.
Take a step back for a moment and think about it this way:
Whether you have a blog, a social media page, or spend all day texting that special someone, there’s probably an inner literary genius inside you waiting to burst out on the page.
Maybe you don’t have the time or the patience to write a novel, and that’s okay. There are plenty of different types of writing out there and you can most likely find one category, or several, that allow you to get your thoughts on paper in a way that works for you.
If you’re curious to know more, or are just interested in trying out a new writing genre, we’ve made it easier for you by compiling a list of the top 21 examples of creative writing.
1. Novel Writing
A novel is probably the most popular example of creative writing out there. When you think “creative writing” an image of Stephen King typing madly at his computer is probably the first thing that pops into your head. And that’s okay. Given that novels have been a popular form of entertainment for centuries, it’s not surprising. Typically what distinguishes a novel from other forms of writing is that novels are usually works of fiction that are longer in length and follow a set of characters and plot structure.
2. Short Stories
When it comes to examples of imaginative writing, not unlike its longer counterpart, the novel, short stories also follow a set plot and typically feature one character or a selection of characters. However, the thing to keep in mind about short stories is that they typically resolve in fewer than 50 pages.

3. Flash Fiction
If you’re up for a real challenge, try your hand at some flash fiction . This type is similar to a short story or novel in the sense that it follows some form of a plot. However, flash fiction usually resolves within a few hundred words or less. There are a few kinds of flash fiction that exist: the six word story, the 50 word story, and the hundred word story. Additionally, flash fiction also has another faction known as sudden fiction, which usually tells a full story in about 750 words.
As an example of imaginative writing, the incredible thing about poetry is that there are so many kinds. From narrative to lyrical and even language poetry there’s so many different ways you can express yourself through a poem. You might be especially interested in pursuing poetry if you enjoy word play or experimenting with the musicality behind words.
Although rap is somewhat of a subcategory of poetry, it’s one of the few forms of poetry that can often get over looked in academic classes. However, it’s probably one of the more contemporary types of poetry available while still sticking to many of the classical rules (or tools) of poetry, including rhyme. Also, it’s one of the areas where the best writers are really produced. The reason for that is because rap forces writers to think on their feet in a way that many other genres don’t.
Playwriting is another great writing style to experiment with, especially if you enjoy the idea of seeing your work come to life. Typically, playwriting involves developing a script that both clearly sets the setting, plot, and characters while also minimizing the amount of description used. One of the key elements of a play is that it’s a collaboration of minds, even though they often don’t work together at the same time. Yet the final product, the performance, is always the end result of work done by the playwright as well as the director, actors and even set designers.
7. Scripts (T.V./Movies)
Like traditional plays, movie or T.V. scripts are often the result of collaboration between a team of people including the cast and crew. However, the big difference is that when you’re writing a T.V. or movie script , you’re often working together with the director and the actors as part of the production team.
Not a fiction writer? No problem! You probably have a unique story worth sharing: it’s called your life. Here’s the deal when it comes to memoirs: the biggest thing to remember is that not everything in your life is considered readership-worthy. In fact, most things probably aren’t. But, most likely, there is a unique angle or perspective that you can take when examining your life.
For example, if you have a really distinctive family history and you’re looking into exploring it, that could be a great subject for a memoir. Maybe you have a really interesting job that exposes you to lots of different people and events on a regular basis; you could write a book about your experiences in that field. The key to writing a good memoir is knowing what angle to take on any subject.
9. Non-Fiction Narratives
Of course, a memoir is just a subsection of a category known as the non-fiction narrative. But not all non-fiction narratives are memoirs. Take for example author Tim Hernandez, who wrote the book Mañana means Heaven . Hernandez writes in a style that is inherently descriptive and interesting, despite the fact that the book’s narrative is mostly based on research and interviews.
10. Songs/Lyrics
Another sector of poetry, songs and lyrics are also a great place where you can express your thoughts and emotions not only through words, but also through music. Whether you’re writing a love ballad or a hymn, there are lots of reasons to enjoy working in this genre. While a lot of this genre is relatively unrestrictive in terms of what you can create, it’s a really good idea to get familiar with the basics of song writing. Especially in an era where so much of the music we hear is impacted by technology, the more you know about the art of song writing, the freer you will be to experiment.
11. Speeches
Speech writing is another great way to express yourself and also reach a wider audience. The thing about speeches is that they are both a form of oral and written text, so the key to writing a really good speech is to take into consideration your phrasing, word choice and syntax. More importantly, the way a speech is delivered can really make or break its success. Practice strong enunciation, confident body language and invoking a clear voice.
12. Greeting Cards
You might hear a lot about greeting cards when people talk about how to make easy money as a writer. But the truth is, being a greeting card writer is anything but easy. You have to be able to keep the greeting card expressions short, catchy and, in a lot of cases, funny. However, if you’ve got the chops to try your hand at a few greeting cards, practice writing limericks and other forms of short poetry. More importantly, read lots of greeting cards to get an idea of how the best writers go about creating the really fun cards that you enjoy purchasing.
It used to be that blogs were the place where teenagers could go to express their teenage angst. But nowadays, blogs are also a great place to be if you’re a writer. There are an unlimited amount of topics you can successfully blog on that will garner attention from audiences. You can use your blog as a forum to share your writing or even reflect on current events, the stock market—really anything! The possibilities are endless, but the key is finding a subject and sticking to it. For example, if you decide to start a blog dedicated to rock music, stick to rock music. Avoid long tangents about politics or other unrelated subjects.
14. Feature Journalism
Feature Journalism is a great place to start if you want to get your feet wet if you’re interested in reporting. Why? Because there are a lot more creative aspects to feature journalism compared to news journalism. Feature stories typically allow you more flexibility with the kinds of details you put into the article, as well as more room for creativity in your lede.
15. Column Writing
If you like the idea of journalism but feel you could never be a journalist in light of your strong opinions, column writing is another avenue you can take. The thing about columns is that they’re typically based in ideas and opinions rather than fact. Yet, because columnists are considered experts in their respective fields, their opinion tends to hold more sway with readers.
As part of the non-fiction narrative family, the personal essay, or even the academic essay, has plenty of elements that are creative. Whether you’re writing about personal experiences or a science project, there are lots of opportunities you have to be creative and hook your reader. Even the most mundane reports have the opportunity to become interesting if you know how to present your topic. As with a lot of non-fiction writing, the secret to writing a good essay is all about your framing. When you begin writing, think about explaining the issue in the most engaging way possible. Just because your writing should cut to the chase doesn’t mean that it should be bland, boring or bogged down in technical jargon. Use anecdotes, clear and concise language, and even humor to express your findings.
17. Twitter Stories
With only 140 characters, how can you tell a story? Well, when you use Twitter, that’s exactly what you’re doing. However, a new phenomenon that’s currently taking over the site is a type of flash fiction called Twitterature, where writers tell a full story or write a poem in 140 characters or less.
18. Comic Strips
If you have a knack for writing and drawing, then you might be especially interested in working on a comic strip. Comic strips are harder project to tackle because they require a lot of preplanning before you start writing. Before you begin drafting you need to know the plot and have a strong outline for how the graphics will look.
19. Collaboration
This is typically a writing exercise that writers do with other writers to expand on their creativity. Essentially the way the exercise works is that one writer will start a story and another will finish it. You might be especially familiar with this kind of work if you’ve ever read the work of an author that was completed AFTER their death. However, collaboration is just another way you can bounce ideas off another person. You can also collaborate with other writers for world building , character development and even general brainstorming.
20. Novella
An example of creative writing, a novella is essentially the love child of a short story and a novel. Although the novella does feature a plot, the plot is typically less complicated compared to that of a novel. Usually novellas are about 50 pages.
21. Genre Writing
Another type of writing that fiction writers can do is genre writing. If you think of popular writers like Stephen King, Nora Roberts and James Patterson, then you’re probably familiar with genre writing. Essentially, genre writing is when a writer explores different stories in one particular genre, like romance, fantasy, or mystery. There’s a huge market out there for genre fiction, which makes it definitely worth pursuing if you a have preference for a particular kind of literature.
The important thing to keep in mind as a writer is that experimentation is never a bad idea. If you’re genuinely curious about one or more items on this list, give it a go! Some of the best literary works were created by accident.
What did you think of our list of 21 creative writing examples? Do you have experience in any of these types of creative writing? Do you know of any other creative writing examples? Please tell us more in the comments box below!
21 Top Examples of Creative Writing is an article from Writing Tips Oasis . Copyright © 2014-2017 Writing Tips Oasis All Rights Reserved
As a graduate from the University of Arizona in English and Creative Writing, Rofida Khairalla’s love for classical literature and post-modern fiction extends beyond the realm of books. She has provided her services independently as a freelance writer, and wrote on the news desk for the student-run newspaper, The Daily Wildcat. As an aspiring children’s book author, she’s refined her craft amongst the grand saguaros of the Southwest, and enjoys playing with her German Shepherd on the slopes of Mount Lemmon.
Home › Study Tips › Creative Writing Resources For Secondary School Students
What Is Creative Writing? Is It Worth Studying?
- Published October 31, 2022

Table of Contents
As loose as the definition of Creative Writing is, it’s not always easy to understand. Sure, writing a story is Creative Writing. What about poems or personal essays?
Also, how does Creative Writing even help one succeed in university and career life? We empower our Creative Writing summer school students to grasp the power of creative writing and how to use it.
How? By giving them access to personalised tutorials with expert Creative Writing tutors from prestigious universities such as the University of Oxford and Cambridge.
Creative Writing doesn’t have to be confusing or intimidating. In this article, we’ll take you through a simple explanation of what Creative Writing is and why it’s helpful and relevant.
What is Creative Writing?
The simplest description of Creative Writing is what it’s not: it doesn’t revolve around facts like technical writing.
Technical Writing vs Creative Writing
You encounter technical writing in your daily life. You’ll find it in newspapers, journal articles, and textbooks. Do you notice how the presentation of accurate information is necessary in each of these mediums?
Because the goal of technical writing is to explain or relay information as it is .
But in creative writing, such is not the case. The primary goal of Creative Writing is not to present complex information for the sake of educating the audience.
Instead, the goal is to express yourself. Should you want to share information via Creative Writing, the objective becomes persuading your readers to think about it as you do.
Hence, if you contrast Technical Writing and Creative Writing within this context,
- Technical Writing: share information without biases
- Creative Writing: self-expression of how one feels or thinks about said information.
If reducing personal opinion in Technical Writing is virtuous, in creative writing, it is criminal .
Self-Expression in Creative Writing
One must express oneself in Creative Writing to entertain, captivate, or persuade readers. Since Creative Writing involves one’s imagination and self-expression, it’s common for Creative Writers to say that they “poured a part of themselves” into their work.
What are the different ways you can express yourself in Creative Writing?
Types of Creative Writing: 2 Major Types
The two major umbrellas of Creative Writing are Creative Nonfiction and Creative Fiction.
1. Creative Nonfiction
“Nonfiction” means writing based on actual events, persons, and experiences. Some forms of creative nonfiction include:
- Personal Essay – here, the writer shares their personal thoughts, beliefs, or experiences.
- Memoir – captures the writer’s memories and experiences of a life-changing past event.
- Narrative Nonfiction – a factual event written in a story format.
2. Creative Fiction
The bulk of Creative Writing literature is found under the Creative Fiction category, such as:
- Short Story – shorter than a novel, containing only a few scenes and characters.
- Novel – a full-blown plot line with multiple scenes, characters, and subplots.
- Poem – uses specific rhythm and style to express ideas or feelings
- Play – contains dialogue and stage directions for theatre performances.
- Screenplay – script to be used for film production (e.g. movies, video games.)
In short, Creative Fiction involves stories . Do you want more specific examples of Creative Writing? Then, you may want to read this article called “Creative Writing Examples.”
Why Is It Important to Learn Creative Writing?
It’s essential to learn Creative Writing because of the following reasons:
1. Creative Writing is a valuable skill in school and work
As a student, you know well why Creative Writing is important. You submit written work in various situations, such as writing essays for assignments and exams. Or when you have to write a Personal Statement to apply for University.
In these situations, your chances of getting higher grades depend on your ability to write creatively. (Even your chances of getting accepted into a top ranked creative writing university of your dreams!)
What about when you graduate? Do you use Creative Writing in your career? Convincing a recruiter to hire you via cover letters is an example of creative writing.
Once you’re hired, you’ll find that you need to write something up. It depends on your line of work and how often and complex your writing should be.
But mundane tasks such as writing an email response, coming up with a newsletter, or making a PowerPoint presentation involve creative writing.
So when you’ve practised your Creative Writing skills, you’ll find these tasks manageable. Even enjoyable! If you want to study creative writing at university, we put together what a-levels you need for creative writing .
2. Creative Writing enhances several essential skills.
Do you know that writing is thinking? At least that’s what the American Historian and two-time winner of the Pulitzer Prize, David McCullough said.
Many people find Creative Writing challenging because it requires a combination of the following skills:
- Observation
- Critical thinking and analysis
- Reasoning skills
- Communication
Many of these skills make you a valuable employee in many industries. In fact, Forbes reports that:
- Critical Thinking
- and Emotional Intelligence
are three of the Top 10 most in-demand skills for the next decade. That’s why Creative Writing is a valuable endeavour and if you take it at university there are some great creative writing degree career prospects .
3. Creative Writing Is Therapeutic
Do you know that Creative Writing has a significant beneficial effect on your mental and emotional health?
A 2021 study in the Counselling & Psychotherapy Research reports that Creative Writing brought significant health benefits to nine people who worked in creative industries. Writing helped them in their cognitive processing of emotional difficulty.
Result? Improved mood and mental well-being.
A plethora of studies over the decades found the same results. Expressing yourself via creative writing, especially by writing in your daily journal, is beneficial for your mental and emotional health.
4. You may want to work in a Creative Writing-related Career
Creative employment in the UK grows 2x faster than the rest of the economy. In fact, did you know that jobs in the creative industry grew by 30.6% from 2011 to 2018?
Compare that to the average UK growth of 10.1% during the same period, and you can see the potential.
How about in the US? The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates a 4% increase in employment for authors and writers from 2021 to 2031. Resulting in about 15,200 job openings yearly over the next 10 years.
The median yearly salary? It was at $69,510 as of May 2021.
So if you’re considering a Creative Writing career, now would be a great time to do so!
How To Be A Creative Writer?
You want to be a Creative Writer but don’t know where to start. Don’t worry! The best way to start is to learn from Creative Writing experts .
That’s why we ensure our Creative Writing summer school students have access to 1:1 personalised tutorials with expert Creative Writing tutors.
Our Creative Writing tutors come from world-renowned universities such as the University of Cambridge and Oxford. So you’re in excellent hands!
Here you’ll learn creative writing tips and techniques , such as character creation and plot mapping. But the best part is, you’ll come out of the course having experienced what a Creative Writer is like!
Because by then, you’ll have a Written Portfolio to show for your efforts. Which you presented to your tutor and peers for receiving constructive feedback.
Another surefire way to start becoming a Creative Writer is by practising. Check out this article called “ Creative Writing Exercises .” You’ll begin building a writing routine if you practice these exercises daily.
And trust us, every great writer has a solid writing routine!
Creative Writing is a form of self-expression that allows you to use your imagination and creativity. It can be in the form of personal essays, short stories, or poems. It is often used as an outlet for emotions and experiences. Start with creative writing by reading through creative writing examples to help get you in the mood. Then, just let the words flow daily, and you’re on the road to becoming an excellent Creative Writer!
Related Content
Tackling homework anxiety: your guide to a calmer study life.
Types of Writing Styles
There are four main types of writing: expository, descriptive, persuasive, and narrative. Each of these writing styles is used for a specific purpose. A single text may include more than one writing style.
Expository writing is one of the most common types of writing. When an author writes in an expository style, all they are trying to do is explain a concept, imparting information from themselves to a wider audience. Expository writing does not include the author’s opinions, but focuses on accepted facts about a topic, including statistics or other evidence.
Examples of Expository Writing
- How-to articles
- News stories (not editorials or Op-Eds)
- Business, technical, or scientific writing
Descriptive
Descriptive writing is often found in fiction, though it can make an appearance in nonfiction as well (for example, memoirs, first-hand accounts of events, or travel guides). When an author writes in a descriptive style, they are painting a picture in words of a person, place, or thing for their audience. The author might employ metaphor or other literary devices in order to describe the author’s impressions via their five senses (what they hear, see, smell, taste, or touch). But the author is not trying to convince the audience of anything or explain the scene – merely describe things as they are.
Examples of Descriptive Writing
- Journal/diary writing
- Descriptions of Nature
- Fictional novels or plays
Persuasive writing is the main style of writing you will use in academic papers. When an author writes in a persuasive style, they are trying to convince the audience of a position or belief. Persuasive writing contains the author’s opinions and biases, as well as justifications and reasons given by the author as evidence of the correctness of their position. Any “argumentative” essay you write in school should be in the persuasive style of writing.
Examples of Persuasive Writing
- Cover letters
- Op-Eds and Editorial newspaper articles
- Reviews of items
- Letters of complaint
- Advertisements
- Letters of recommendation
Narrative writing is used in almost every longer piece of writing, whether fiction or nonfiction. When an author writes in a narrative style, they are not just trying to impart information, they are trying to construct and communicate a story, complete with characters, conflict, and settings.
Examples of Narrative Writing
- Oral histories
- Novels/Novellas
- Poetry (especially epic sagas or poems)
- Short Stories
About Writing: A Guide Copyright © 2015 by Robin Jeffrey is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
12 Types of Creative Writing to Explore
Kate is an experienced writer who has written hundreds of articles for publication.
Learn about our Editorial Policy .
Creative writing isn't just limited to novels, short stories, and poems; in fact, this type of writing encompasses at least a dozen different types, each suited to specific situations and kinds of personal expression. Try them all to find out which ones you enjoy the most.
You may think of writing a song as a purely musical form of creative expression, but if your song has lyrics, you'll also be doing some creative writing. Lyrics are similar to poetry in that they can have many forms, although some type of rhyme scheme is common. See examples of some of the most popular song lyrics at MetroLyrics .
- 14 Mood Ring Color Meanings Decoded: What They Say About You
- Mercury Retrograde: What It Is, When It Is, & How It Affects You
From haiku to sonnets, there are dozens of different poetic forms to try. In general, the key to writing poetry is to create evocative images and make every word count. You can write about anything, from nature to love to your family . You can even write poems for specific occasions, such as a wedding ceremony or a funeral .
3. Vignettes
Vignettes are a short form of fiction or creative non-fiction that sets up a scene for the reader. There may not be a central conflict to drive the story forward, and there may not even be characters. Length can range from a single paragraph to a few pages. Generally, the entire piece takes place in one location. Ernest Hemingway's In Our Time features several examples of vignettes.
4. Short Fiction
Short fiction offers more of a "story" than a vignette. It includes short stories and even modern fan fiction. Writing a short story is a great way to learn about how fiction is structured, including plot, characters, conflict, and setting. You can even make money writing short fiction. A great example of this genre is A&P by John Updike.
5. Novellas
Longer than a short story but not quite as long as a novel, a novella goes into great detail about all the elements of the story. It may or may not have chapters. Joseph Conrad's Heart of Darkness is a good example of a novella.
Novels are perhaps the best known form of fiction, and you'll see them in many genres, including romance, thrillers, and science fiction. In this long form of fiction, you have time to explore the plot, characters, and other elements more fully. Writing a novel is a huge undertaking and a great way to improve your skills as a writer. If you're considering such a project, look at what works in some of the best novels of all time.
Scripts, for everything from TV commercials to radio programs and even movies, are another form of creative writing. The length can vary significantly, but the key is that the words you write will be recited by actors and recorded. An audience will view or listen to the piece later. Find movie scripts to review as examples of this form of writing.
Like a script in that the dialogue you write will be recited by actors, plays are designed to be performed in front of an audience. They are usually divided into several acts, although short, one-act plays are also popular. Writing a play is a great way to see your story ideas come to life. Arthur Miller's Death of a Salesman is a good example if you're looking for inspiration.
9. Personal Essays
Not all creative writing is made up. In fact, creative non-fiction comes in several important forms. One of these is the personal essay in which the writer explores his or her own life experiences or opinions. Writing an essay on yourself isn't always easy, but it's an important skill to have for everything from college applications to family history.
10. Journals and Diaries
More than just a therapeutic exercise or a way to record the day's events, journals can also be a type of creative writing. This is especially true if you infuse your entries with your emotions and personal experiences. Take some time to read journal writing prompts and try your hand at this creative writing form.
11. Memoirs
A longer form of the personal essay or journal, a memoir is a type of creative nonfiction that explores a person's life or experiences. You can focus on a single period or your entire life. This is different from an autobiography in that it includes feelings and thoughts - not just the facts of what happened. There are even websites with examples of memoirs and tips for writing your own.
12. Letters
Because they contain more than a basic reporting of the facts, letters can also be a type of creative writing. This is especially true if they discuss emotion or opinion. Even love letters can be creative.
Try All the Forms
There are many more forms of writing that can become creative if they expand beyond the basic facts. For instance, some blogs and literary journalism articles are very creative too. There are so many types of creative writing to explore that it makes sense to try them all. You're sure to find one (or several) that you love.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
EveryWriter
A New Community of Writers
Types of Writing and Styles
November 23, 2023 by Richard Leave a Comment
Types of Writing
There are many types of writing and styles that can take to serve different purposes. Whether you want to inform, persuade, entertain or express yourself, aligning your writing style with your goals is key for effectively reaching your audience. This comprehensive guide covers over 25 major categories and examples of writing types.
From creative fiction, scripts, and humor to technical manuals, academic papers, business writing and more, discover the spectrum of writing styles you can leverage. Learn how expository, descriptive, persuasive, and professional writing each engage readers differently. See how narrative, journalism, legal writing, interviews and other genres apply specialized conventions and techniques.
Understand the unique objectives and elements that characterize satirical, scientific, marketing and interpretive writing. Expand your writing skills by considering which types best fit your objectives and message. With various formats from essays, editorials and blog posts to speeches, research reports and screenplays examined, the extensive range of writing varieties and techniques here will inspire you to broaden your writing horizons.
Writing is a means of communication that allows us to share information, tell stories, express ideas, and document events. There are many types of writing and styles that serve different purposes. Here are some of the main categories of writing. Take a look at these types of writing and see which type of writing your work falls into. These definitions of types of writing will should help inform you on what kinds of writing are out there, and what kind of writing you may want to try.
Writing Types and Styles
- Expository (essays, reports, articles, textbooks)
- Narrative (fiction, memoirs, biographies)
- Persuasive (advertising, editorials, reviews)
- Descriptive (travel, nature, character sketches)
- Technical (instruction manuals, specifications)
- Creative (fiction, poetry, humor)
- Professional (emails, business plans, linkedIn profiles)
- Academic (research papers, literary analyses)
- Journalism (news articles, features)
- Scripts (plays, movies, comedy)
- Marketing (blog posts, social media, sales letters)
- Science/Tech (lab reports, patents, academic texts)
- Business (presentations, project proposals)
- Transactional (cover letters, thank you notes)
- Interviews (profiles, Q&As, investigative)
- Interpretive (analyses, editorials, translations)
- Legal (contracts, briefs, judicial opinions)
- Satirical/Humorous (parody, essays, comics)
Expository Writing
Expository writing aims to inform, explain, or describe something to the reader. The purpose is to educate or convey information accurately. Types of expository writing include:
- Essays – Often short compositions that inform or persuade on a certain topic. Academic essays have a clear structure with an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Articles – Found in publications like magazines, newspapers, or online. News articles report on events or topics while other articles can explain or analyze a subject.
- Textbooks – Present factual information on academic subjects in a structured way. The writing is objective and focuses on conveying the facts.
- How-To Guides – Provide step-by-step instructions on how to do something. The writing is clear, detailed, and puts things in logical order.
- Reports – Document factual information with research and data on a specific topic. Business, scientific, and technical reports present data analysis and conclusions.
Narrative Writing
Narrative writing tells a story or recounts an event. The purpose is to engage the reader in an experience. Types of narrative writing include:
- Fiction – Novels, short stories, and plays explore imaginary people, places, and events. Creative fiction writing transports readers into a scene using detailed characters, setting, and plot.
- Memoirs – First-person narratives about past events in the writer’s life. Memoirs focus on personal experience and emotion.
- Personal Essays – Also written in first-person, these essays relate an event or share a perspective based on the writer’s experience.
- Biographies – The story of a real person’s life written by someone else in narrative form.
- Poetry – Literary writing that conveys meaning through style, rhythm, imagery, and structure rather than just plot.
Persuasive Writing
Persuasive writing aims to convince the reader of a certain point of view or to take a specific action. Types of persuasive writing include:
- Advertisements – Creative copy and imagery encourages purchase of products or services.
- Editorials – Opinion-based articles that take a position and persuade readers on current events or issues.
- Reviews – Combine opinion and information to evaluate and recommend products or experiences.
- Political Speeches – Public speaking to persuade citizens, colleagues, or opponents to support a policy, party, or candidate.
- Personal Statements – For academia or job applications, these essays convince why the writer is right for opportunity.
Descriptive Writing
Descriptive writing uses vivid sensory details to paint a picture and create an experience for the reader. Types of descriptive writing include:
- Travel Writing – Describes places and cultures the writer has visited to transport readers there.
- Nature Writing – Vividly describes landscapes, animals, and natural phenomena.
- Descriptive Poems – Use lyrical language and imagery to bring a scene or subject to life.
- Setting Descriptions – In fiction writing, detailed descriptions of setting establish place and atmosphere.
- Character Sketches – Detailed physical and personality descriptions of characters in stories.
Technical Writing
Technical writing communicates complex information to a specific audience through clear, accurate writing and visuals. Types include:
- Instruction Manuals – Provide step-by-step instructions on how to assemble or operate a device or complete a process.
- Specification Documents – Outline detailed technical specifications for engineers and manufacturers.
- User Guides – Help consumers understand how to use a software application or perform tasks.
- Legal Writing – Precise language like court briefs, patents, and legislative documents.
- Medical Writing – Clear descriptions of medical procedures, health conditions, and pharmaceuticals.
Creative Writing
Creative writing expresses ideas and thoughts in an imaginative, subjective, and artistic way. Types include:
- Fiction Writing – Novels, short stories, poetry, and creative nonfiction.
- Screenwriting – Scripts and teleplays for television, film, and theater.
- Humor Writing – Comedy that entertains through funny observations, exaggeration, and wit.
- Songwriting – Uses rhythm, melody, and rhyme to create narrative songs.
There are so many forms writing can take to engage audiences and serve different purposes. The key is aligning the writing style with your objective and intended reader.
Reflective Writing
Reflective writing analyzes experiences, events, or new information to make sense of them. Types include:
- Journals – First-person accounts of daily experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
- Reflective Essays – Draw personal insights from experiences like travel, volunteering, reading books, etc.
- Response/Reaction Papers – Respond to insights personally and analytically to express what was learned.
Professional Writing
Professional writing clearly communicates complex information between colleagues, businesses, and organizations. Types include:
- Emails/Memos – Clear, concise messages to colleagues about work activities.
- Business Plans – Detailed plans describing objectives and predicted growth of a company.
- Grant Proposals – Persuade funders or nonprofits to provide resources for projects.
- White Papers – Authoritative reports to inform readers or make recommendations.
- LinkedIn Profiles – Summarize professional background, skills, and accomplishments.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction uses literary techniques to tell factual stories. Types include:
- Literary Journalism – Immersive, vivid stories about real events and people like Truman Capote’s In Cold Blood.
- Personal Essays – First-person stories about real-life experiences of the author.
- Memoirs – First-person nonfiction stories about the author’s life.
- Biographies – Nonfiction accounts of a real person’s life story.
Script Writing
Script writing involves writing content for performance and visual media. Types include:
- Plays – Dramas performed live on stage. Play scripts contain dialogue and stage directions.
- Movie Scripts – Visual stories for film. Movie scripts focus on action and dialogue.
- Television Scripts – Episodes for broadcast television. Teleplays structurally divide acts separated by commercial breaks.
- Speech Writing – Prepared content for speeches and presentations. Good speechwriting techniques include personal anecdotes, repetition, and clear messaging.
- Standup Comedy Scripts – Written comedic material for live performances. Comedy scripts may just outline jokes or fully script an act.
Academic Writing
Academic writing is formal writing produced in an academic setting. Types include:
- Research Papers – Reports that analyze information from academic sources on a particular topic. Research papers follow standard formatting styles like MLA or APA.
- Literary Analysis – Essays that closely examine and evaluate works of poetry, prose, or drama.
- Annotated Bibliographies – Citations of academic sources with short descriptive paragraphs summarizing each work.
- Theses and Dissertations – Extensive research papers completed to earn a graduate level degree.
- Abstracts – Brief overviews summarizing longer works of research or analysis.
Advertising and Marketing Writing
Writing designed to promote products, services, or ideas. Types include:
- Blog Posts – Entertaining or informative articles promoting a business, organization, or cause.
- Social Media Posts – Bite-sized content designed for platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Sales Letters – Persuasive letters promoting products or services to potential customers.
- Press Releases – Announcements about business achievements, products, or events to media outlets.
- Product Descriptions – Details product features and benefits for websites, catalogs, or packaging.
- Taglines and Slogans – Short, memorable phrases that capture a brand. Examples are “Just Do It” (Nike) and “Think Different” (Apple).
Technical and Scientific Writing
Writing that accurately communicates complex technical or scientific information. Types include:
- Research Articles – Reports of original research and findings in science and academia.
- Lab Reports – Documentation of experimental procedures, data, analysis, and conclusions.
- Manuals – Instructions on how to operate technical or electronic equipment.
- Medical Documentation – Records patient health information for medical, regulatory, or insurance purposes.
- Patent Applications – Legal documents describing processes or inventions seeking patent protection.
- Academic Textbooks – Books presenting authoritative research and information on scholarly subjects.
Business Writing
Writing for the workplace and business communication. Types include:
- Emails – Quick, professional communication for collaborating, sharing information, and making requests.
- Meeting Minutes & Notes – Documents discussions, decisions, and action items from business meetings.
- Policy & Procedure Documents – Clearly outline company protocols and operations.
- Presentations – Slide decks that inform or persuade coworkers or stakeholders.
- Project Proposals – Formal proposals to management recommending new initiatives or workflows.
- Case Studies – In-depth analysis of a business situation used for research or education.
Transactional Writing
Writing with the aim of communicating straightforward information or requests. Types include:
- Cover Letters – Introduce qualifications to potential employers when submitting resumes.
- Thank You Notes – Express gratitude or appreciation for gifts, time, or opportunities.
- RSVP Messages – Confirm attendance for events or decline invitations.
- Reminders – Brief notes prompting people about upcoming deadlines, tasks, appointments.
- Apology Letters – Express regret and take responsibility for mistakes or offenses.
- Congratulatory Messages – Sentiments praising accomplishments like graduations, promotions, or awards.
Interview Writing
Writing related to conducting and publishing interviews. Types include:
- Informational Interviews – Discuss a person’s career path and industry insights.
- Profile Interviews – Reveal a person’s background, personality, and experiences.
- Investigative Interviews – Seek information or accountability related to scandals, corruption, etc.
- Guest Interviews – Q&A style discussions with TV show guests about their lives and work.
- Research Interviews – Gather firsthand knowledge from experts for articles, books, or documentaries.
- Transcripts – Documents that exactly record audio or video interview content.
Interpretive Writing
Writing that explains, analyzes, or translates complex concepts. Types include:
- Literature Reviews – Survey and distill current academic knowledge on a research topic.
- Critical Analysis – Close interpretation and commentary on texts, art, or music.
- Editorials – Opinion pieces that explain events and issues to readers.
- Translation – Accurately converting texts from one language to another.
- Paraphrasing – Restating information from one source in your own words.
I’ve covered a wide variety of major writing categories and styles. Please let me
Legal Writing
Writing related to the law and legal field. Types include:
- Legislation – Documents that codify laws and regulations.
- Legal Briefs – Documents that provide a summary and arguments in a legal case.
- Contracts – Binding agreements between parties setting terms.
- Wills and Trusts – Legal documents outlining assets and inheritance wishes.
- Judicial Opinions – Written explanations of court rulings and precedents.
Satirical/Humorous Writing
Writing that critiques through humor, irony, and exaggeration. Types include:
- Parody – Imitates or exaggerates other works to be funny and critical.
- Satirical Essays – Wryly poke fun at societal behaviors and norms.
- Spoofs – Lighthearted mockery of genres like movies, ads, or books.
- Comic Strips/Cartoons – Images and captions conveying jokes and humor.
Here are the major writing types. I hope this guide helps you find something new about types of writing. We have many other articles about writing on our site . Also, if you have questions, comments or concerns please leave them in the comments below.
Related posts:
- 10 Reasons to Keep a Writing Journal
- 10 Things You Can Do To Improve Your Writing
- Writing Characters: Know Them Well
- Writing Horror
- 50 Common Simple Writing Mistakes to Avoid
About Richard
Richard Everywriter (pen name) has worked for literary magazines and literary websites for the last 25 years. He holds degrees in Writing, Journalism, Technology and Education. Richard has headed many writing workshops and courses, and he has taught writing and literature for the last 20 years.
In writing and publishing he has worked with independent, small, medium and large publishers for years connecting publishers to authors. He has also worked as a journalist and editor in both magazine, newspaper and trade publications as well as in the medical publishing industry. Follow him on Twitter, and check out our Submissions page .
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Tone in Writing: 42 Examples of Tone For All Types of Writing
by Joe Bunting | 0 comments
Free Book Planning Course! Sign up for our 3-part book planning course and make your book writing easy . It expires soon, though, so don’t wait. Sign up here before the deadline!
What is tone in writing and why does it matter?
Tone is key to all communication. Think of the mother telling her disrespectful child, “Watch your tone, young man.” Or the sarcastic, humorous tone of a comedian performing stand up. Or the awe filled way people speak about their favorite musician, author, or actor. Or the careful, soft tones that people use with each other when they first fall in love.
Tone is communication, sometimes more than the words being used themselves.

So then how do you use tone in writing, and how does tone influence the meaning of a writing piece?
In this article, you'll learn everything you need to know about how to use tone in all types of writing, from creative writing to academic and even business writing. You'll learn what tone actually is in writing and how it's conveyed. You'll learn the forty-two types of tone in writing, plus even have a chance to test your tone recognition with a practice exercise.
Ready to become a tone master? Let's get started.
Why You Should Listen To Me?
I've been a professional writer for more than a decade, writing in various different formats and styles. I've written formal nonfiction books, descriptive novels, humorous memoir chapters, and conversational but informative online articles (like this one!).
Which is all to say, I earn a living in part by matching the right tone to each type of writing I work on. I hope you find the tips on tone below useful!
Table of Contents
Definition of Tone in Writing Why Tone Matters in Writing 42 Types of Tone Plus Tone Examples How to Choose the Right Tone for Your Writing Piece Tone Writing Identification Exercise Tone Vs. Voice in Writing The Role of Tone in Different Types of Writing
Tone in Creative Writing Tone in Academic Writing Tone in Business Writing Tone in Online Writing
Conclusion: How to Master Tone Practice Exercise
Definition of Tone in Writing
Examples of tone can be formal, informal, serious, humorous, sarcastic, optimistic, pessimistic, and many more (see below for all forty-two examples)
Why Does Tone Matter in Writing
I once saw a version of Shakespeare's A Midsummer Night's Dream in which the dialogue had been completely translated into various Indian dialects, including Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, and more. And yet, despite not knowing any of those languages, I was amazed to find that I could follow the story perfectly, infinitely better than the average Shakespeare in the park play.
How could I understand the story so well despite the fact that it was in another language? In part, it was the skill of the actors and their body language. But one of the biggest ways that the actors communicated meaning was one thing.
Their tone of voice.
Tone is one of the most important ways we grasp the meaning of what someone is saying. If someone says, “I love you,” in an angry, sneering way, it doesn't matter what their words are saying, the meaning will be completely changed by their tone.
In the same way, tone is crucial in writing because it significantly influences how readers interpret and react to the text. Here are a few reasons why tone is important:
- Tone conveys feeling. The tone reflects the writer's attitude toward the subject and the audience, helping to shape readers' perceptions and emotional responses.
- Tone can help readers understand the meaning of the text. A well-chosen tone can clarify meaning, making it easier for readers to understand the writer's intent and message.
- Tone is engaging! As humans, we are designed to respond to emotion and feeling! Tone can help to engage or disengage readers. A relatable or compelling tone can draw readers in, while an off-putting tone can push them away.
- Tone sets the mood. Tone can set the mood or atmosphere of a piece of writing, influencing how readers feel as they go through the text.
- Tone persuades. In persuasive writing, tone plays a significant role in influencing how convincing or compelling your arguments are.
- Tone reflects professionalism. In professional or academic contexts, maintaining an appropriate tone is crucial to uphold the writer's authority.
42 Types of Tone in Writing Plus Examples of Tone
Tone is about feeling—the feeling of a writer toward the topic and audience. Which means that nearly any attitude or feeling can be a type of tone, not just the forty-two listed below.
However, you have to start somewhere, so here a list of common tones that can be used in writing, with an example for each type:
- Example : “Upon analysis of the data, it's evident that the proposed hypothesis is substantiated.”
- Example : “Hey folks, today we'll be chatting about the latest trends in tech.”
- Example : “The implications of climate change on our future generations cannot be overstated.”
- Example : “Why don't scientists trust atoms? Because they make up everything!”
- Example : “Oh great, another diet plan. Just what I needed!”
- Example : “Despite the setbacks, we remain confident in our ability to achieve our goals.”
- Example : “Given the declining economy, it's doubtful if small businesses can survive.”
- Example : “We must act now! Every moment we waste increases the danger.”
- Example : “The experiment concluded with the subject showing a 25% increase in performance.”
- Example : “I've always found the taste of coffee absolutely heavenly.”
- Example : “We owe our success to the ceaseless efforts of our esteemed team.”
- Example : “So much for their ‘revolutionary' product. It's as exciting as watching paint dry.”
- Example : “The film's plot was so predictable it felt like a tiresome déjà vu.”
- Example : “Every setback is a setup for a comeback. Believe in your potential.”
- Example : “A politician making promises? Now there's something new.”
- Example : “We must fight to protect our planet—it's the only home we have.”
- Example : “Whether it rains or shines tomorrow, it makes little difference to me.”
- Example : “As the doors creaked open, a chilling wind swept through the abandoned mansion.”
- Example : “She gazed at the fading photograph, lost in the echoes of a time long past.”
- Example : “The fire station caught on fire—it's almost poetic, isn't it?”
- Example : “I can understand how challenging this period has been for you.”
- Example : “His excuse for being late was as pathetic as it was predictable.”
- Example : “Our feline companion has gone to pursue interests in a different locale” (meaning: the cat ran away).
- Example : “Your report is due by 5 PM tomorrow, no exceptions.”
- Example : “So, you've got a hankering to learn about star constellations—well, you're in the right place!”
- Example : “She tiptoed down the dim hallway, every shadow pulsating with the mysteries of her childhood home.”
- Example : “With the approaching footsteps echoing in his ears, he quickly hid in the dark alcove, heart pounding.”
- Example : “His eyes were a stormy sea, and in their depths, she found an anchor for her love.”
- Example : “In the heart of the mystical forest, nestled between radiant will-o'-the-wisps, was a castle spun from dreams and starlight.”
- Example : “The quantum mechanical model posits that electrons reside in orbitals, probabilistic regions around the nucleus, rather than fixed paths.”
- Example : “When constructing a thesis statement, it's crucial to present a clear, concise argument that your paper will substantiate.”
- Example : “The juxtaposition of light and dark imagery in the novel serves to illustrate the dichotomy between knowledge and ignorance.”
- Example : “Upon deconstructing the narrative, one can discern the recurrent themes of loss and redemption.”
- Example : “One must remember, however, that the epistemological underpinnings of such an argument necessitate a comprehensive understanding of Kantian philosophy.”
- Example : “The ephemeral nature of existence prompts us to contemplate the purpose of our pursuits and the value of our accomplishments.”
- Example : “She left the room.”
- Example : “Global warming is a major issue that needs immediate attention.”
- Example : “Maybe she’ll come tomorrow, I thought, watching the cars pass by, headlights blurring in the rain—oh, to be somewhere else, anywhere, the beach maybe, sand between my toes, the smell of the sea…”
- Example : “In the quiet solitude of the night, I grappled with my fears, my hopes, my dreams—how little I understood myself.”
- Example : “The autumn leaves crunched underfoot, their vibrant hues of scarlet and gold painting a brilliant tapestry against the crisp, cerulean sky.”
- Example : “Looking back on my childhood, I see a time of joy and innocence, a time when the world was a playground of endless possibilities.”
- Example : “Gazing up at the star-studded sky, I was struck by a sense of awe; the universe's vast expanse dwarfed my existence, reducing me to a speck in the cosmic canvas.”
- Example : “His unwavering determination in the face of adversity serves as a shining beacon for us all, inspiring us to strive for our dreams, no matter the obstacles.”
Any others that we forgot? Leave a comment and let us know!
Remember, tone can shift within a piece of writing, and a writer can use more than one tone in a piece depending on their intent and the effect they want to create.
The tones used in storytelling are particularly broad and flexible, as they can shift and evolve according to the plot's developments and the characters' arcs.
How do you choose the right tone for your writing piece?
The tone of a piece of writing is significantly determined by its purpose, genre, and audience. Here's how these three factors play a role:
- Purpose: The main goal of your writing guides your tone. If you're trying to persuade someone, you might adopt a passionate, urgent, or even a formal tone, depending on the subject matter. If you're trying to entertain, a humorous, dramatic, or suspenseful tone could be suitable. For educating or informing, an objective, scholarly, or didactic tone may be appropriate.
- Genre: The type of writing also influences the tone. For instance, academic papers often require a formal, objective, or scholarly tone, while a personal blog post might be more informal and conversational. Similarly, a mystery novel would have a suspenseful tone, a romance novel a romantic or passionate tone, and a satirical essay might adopt an ironic or sarcastic tone.
- Audience: Understanding your audience is crucial in setting the right tone. Professional audiences may expect a formal or respectful tone, while a younger audience might appreciate a more conversational or even irreverent tone. Furthermore, if your audience is familiar with the topic, you can use a more specialized or cerebral tone. In contrast, for a general audience, a clear and straightforward tone might be better.
It's also worth mentioning that the tone can shift within a piece of writing. For example, a novel might mostly maintain a dramatic tone, but could have moments of humor or melancholy. Similarly, an academic paper could be mainly objective but might adopt a more urgent tone in the conclusion to emphasize the importance of the research findings.
In conclusion, to choose the right tone for your writing, consider the intent of your piece, the expectations of the genre, and the needs and preferences of your audience. And don't forget, maintaining a consistent tone is key to ensuring your message is received as intended.
How to Identify Tone in Writing
How do you identify the tone in various texts (or even in your own writing)? What are the key indicators that help you figure out what tone a writing piece is?
Identifying the tone in a piece of writing can be done by focusing on a few key elements:
- Word Choice (Diction): The language an author uses can give you strong clues about the tone. For instance, formal language with lots of technical terms suggests a formal or scholarly tone, while casual language with slang or contractions suggests an informal or conversational tone.
- Sentence Structure (Syntax): Longer, complex sentences often indicate a formal, scholarly, or descriptive tone. Shorter, simpler sentences can suggest a more direct, informal, or urgent tone.
- Punctuation: The use of punctuation can also impact tone. Exclamation marks may suggest excitement, urgency, or even anger. Question marks might indicate confusion, curiosity, or sarcasm. Ellipsis (…) can suggest suspense, uncertainty, or thoughtfulness.
- Figurative Language: The use of metaphors, similes, personification, and other literary devices can help set the tone. For instance, an abundance of colorful metaphors and similes could suggest a dramatic, romantic, or fantastical tone.
- Mood: The emotional atmosphere of the text can give clues to the tone. If the text creates a serious, somber mood, the tone is likely serious or melancholic. If the mood is light-hearted or amusing, the tone could be humorous or whimsical.
- Perspective or Point of View: First-person narratives often adopt a subjective, personal, or reflective tone. Third-person narratives can have a range of tones, but they might lean towards being more objective, descriptive, or dramatic.
- Content: The subject matter itself can often indicate the tone. A text about a tragic event is likely to have a serious, melancholic, or respectful tone. A text about a funny incident will probably have a humorous or light-hearted tone.
By carefully analyzing these elements, you can determine the tone of a text. In your own writing, you can use these indicators to check if you're maintaining the desired tone consistently throughout your work.
Tone Writing Exercise: Identify the tone in each of the following sentences
Let’s do a little writing exercise by identifying the tones of the following example sentences.
- “The participants in the study displayed a significant improvement in their cognitive abilities post intervention.”
- “Hey guys, just popping in to share some cool updates from our team!”
- “The consequences of climate change are dire and demand immediate attention from world leaders.”
- “I told my wife she should embrace her mistakes. She gave me a hug.”
- “Despite the challenges we've faced this year, I'm confident that brighter days are just around the corner.”
- “Given the state of the economy, it seems unlikely that we'll see any significant improvements in the near future.”
- “No mountain is too high to climb if you believe in your ability to reach the summit.”
- “As she stepped onto the cobblestone streets of the ancient city, the echoes of its rich history whispered in her ears.”
- “Oh, you're late again? What a surprise.”
- “The methodology of this research hinges upon a quantitative approach, using statistical analysis to derive meaningful insights from the collected data.”
Give them a try. I’ll share the answers at the end!
Tone Versus Voice in Writing
Tone and voice in writing are related but distinct concepts:
Voice is the unique writing style or personality of the writing that makes it distinct to a particular author. It's a combination of the author's syntax, word choice, rhythm, and other stylistic elements.
Voice tends to remain consistent across different works by the same author, much like how people have consistent speaking voices.
For example, the voice in Ernest Hemingway's work is often described as minimalist and straightforward, while the voice in Virginia Woolf's work is more stream-of-consciousness and introspective.
Tone , on the other hand, refers to the attitude or emotional qualities of the writing. It can change based on the subject matter, the intended audience, and the purpose of the writing.
In the same way that someone's tone of voice can change based on what they're talking about or who they're talking to, the tone of a piece of writing can vary. Using the earlier examples, a work by Hemingway might have a serious, intense tone, while a work by Woolf might have a reflective, introspective tone.
So, while an author's voice remains relatively consistent, the tone they use can change based on the context of the writing.
Tone and voice are two elements of writing that are closely related and often work hand in hand to create a writer's unique style. Here's how they can be used together:
- Consistency: A consistent voice gives your writing a distinctive personality, while a consistent tone helps to set the mood or attitude of your piece. Together, they create a uniform feel to your work that can make your writing instantly recognizable to your readers.
- Audience Engagement: Your voice can engage readers on a fundamental level by giving them a sense of who you are or the perspective from which you're writing. Your tone can then enhance this engagement by setting the mood, whether it's serious, humorous, formal, informal, etc., depending on your audience and the purpose of your writing.
- Clarity of Message: Your voice can express your unique perspective and values, while your tone can help convey your message clearly by fitting the context. For example, a serious tone in an academic research paper or a casual, friendly tone in a personal blog post helps your audience understand your purpose and message.
- Emotional Impact: Voice and tone together can create emotional resonance. A distinctive voice can make readers feel connected to you as a writer, while the tone can evoke specific emotions that align with your content. For example, a melancholic tone in a heartfelt narrative can elicit empathy from the reader, enhancing the emotional impact of your story.
- Versatility: While maintaining a consistent overall voice, you can adjust your tone according to the specific piece you're writing. This can show your versatility as a writer. For example, you may have a generally conversational voice but use a serious tone for an important topic and a humorous tone for a lighter topic.
Remember, your unique combination of voice and tone is part of what sets you apart as a writer. It's worth taking the time to explore and develop both.
The Role of Tone in Different Types of Writing
Just as different audiences require different tones of voice, so does your tone change depending on the audience of your writing.
Tone in Creative Writing
Tone plays a crucial role in creative writing, shaping the reader's experience and influencing their emotional response to the work. Here are some considerations for how to use tone in creative writing:
- Create Atmosphere: Tone is a powerful tool for creating a specific atmosphere or mood in a story. For example, a suspenseful tone can create a sense of tension and anticipation, while a humorous tone can make a story feel light-hearted and entertaining.
- Character Development: The tone of a character's dialogue and thoughts can reveal a lot about their personality and emotional state. A character might speak in a sarcastic tone, revealing a cynical worldview, or their internal narrative might be melancholic, indicating feelings of sadness or regret.
- Plot Development: The tone can shift with the plot, reflecting changes in the story's circumstances. An initially optimistic tone might become increasingly desperate as a situation worsens, or a serious tone could give way to relief and joy when a conflict is resolved.
- Theme Expression: The overall tone of a story can reinforce its themes. For instance, a dark and somber tone could underscore themes of loss and grief, while a hopeful and inspirational tone could enhance themes of resilience and personal growth.
- Reader Engagement: A well-chosen tone can engage the reader's emotions, making them more invested in the story. A dramatic, high-stakes tone can keep readers on the edge of their seats, while a romantic, sentimental tone can make them swoon.
- Style and Voice: The tone is part of the writer's unique voice and style. The way you blend humor and seriousness, or the balance you strike between formal and informal language, can give your work a distinctive feel.
In creative writing, it's important to ensure that your tone is consistent, unless a change in tone is intentional and serves a specific purpose in your story. An inconsistent or shifting tone can be jarring and confusing for the reader. To check your tone, try reading your work aloud, as this can make shifts in tone more evident.
Tone in Academic Writing
In academic writing, the choice of tone is crucial as it helps to establish credibility and convey information in a clear, unambiguous manner. Here are some aspects to consider about tone in academic writing:
- Formal: Academic writing typically uses a formal tone, which means avoiding colloquialisms, slang, and casual language. This helps to maintain a level of professionalism and seriousness that is appropriate for scholarly work. For instance, instead of saying “experts think this is really bad,” a more formal phrasing would be, “scholars have identified significant concerns regarding this matter.”
- Objective: The tone in academic writing should usually be objective, rather than subjective. This means focusing on facts, evidence, and logical arguments rather than personal opinions or emotions. For example, instead of saying “I believe that climate change is a major issue,” an objective statement would be, “Research indicates that climate change poses substantial environmental risks.”
- Precise: Precision is crucial in academic writing, so the tone should be specific and direct. Avoid vague or ambiguous language that might confuse the reader or obscure the meaning of your argument. For example, instead of saying “several studies,” specify the exact number of studies or name the authors if relevant.
- Respectful: Even when critiquing other scholars' work, it's essential to maintain a respectful tone. This means avoiding harsh or judgmental language and focusing on the intellectual content of the argument rather than personal attacks.
- Unbiased: Strive for an unbiased tone by presenting multiple perspectives on the issue at hand, especially when it's a subject of debate in the field. This shows that you have a comprehensive understanding of the topic and that your conclusions are based on a balanced assessment of the evidence.
- Scholarly: A scholarly tone uses discipline-specific terminology and acknowledges existing research on the topic. However, it's also important to explain any complex or specialized terms for the benefit of readers who may not be familiar with them.
By choosing an appropriate tone, you can ensure that your academic writing is professional, credible, and accessible to your intended audience. Remember, the tone can subtly influence how your readers perceive your work and whether they find your arguments convincing.
Tone in Business Writing
In business writing, your tone should be professional, clear, and respectful. Here are some aspects to consider:
- Professional and Formal: Just like in academic writing, business writing typically uses a professional and formal tone. This ensures that the communication is taken seriously and maintains an air of professionalism. However, remember that “formal” doesn't necessarily mean “stiff” or “impersonal”—a little warmth can make your writing more engaging.
- Clear and Direct: Your tone should also be clear and direct. Ambiguity can lead to misunderstanding, which can have negative consequences in a business setting. Make sure your main points are obvious and not hidden in jargon or overly complex sentences.
- Respectful: Respect is crucial in business communication. Even when addressing difficult topics or delivering bad news, keep your tone courteous and considerate. This fosters a positive business relationship and shows that you value the other party.
- Concise: In the business world, time is often at a premium. Therefore, a concise tone—saying what you need to say as briefly as possible—is often appreciated. This is where the minimalist tone can shine.
- Persuasive: In many situations, such as a sales pitch or a negotiation, a persuasive tone is beneficial. This involves making your points convincingly, showing enthusiasm where appropriate, and using language that motivates the reader to act.
- Neutral: In situations where you're sharing information without trying to persuade or express an opinion, a neutral tone is best. For example, when writing a business report or summarizing meeting minutes, stick to the facts without letting personal bias influence your language.
By adapting your tone based on these guidelines and the specific context, you can ensure your business writing is effective and appropriate.
Tone in Online Writing
Online writing can vary greatly depending on the platform and purpose of the content. However, some common considerations for tone include:
- Conversational and Informal: Online readers often prefer a more conversational, informal tone that mimics everyday speech. This can make your writing feel more personal and relatable. Blogs, social media posts, and personal websites often employ this tone.
- Engaging and Enthusiastic: With so much content available online, an engaging and enthusiastic tone can help grab readers' attention and keep them interested. You can express your passion for a topic, ask questions, or use humor to make your writing more lively and engaging.
- Clear and Direct: Just like in business and academic writing, clarity is key in online writing. Whether you're writing a how-to article, a product description, or a blog post, make your points clearly and directly to help your readers understand your message.
- Descriptive and Vivid: Because online writing often involves storytelling or explaining complex ideas, a descriptive tone can be very effective. Use vivid language and sensory details to help readers visualize what you're talking about.
- Authoritative: If you're writing content that's meant to inform or educate, an authoritative tone can help establish your credibility. This involves demonstrating your knowledge and expertise on the topic, citing reliable sources, and presenting your information in a confident, professional manner.
- Optimistic and Inspirational: Particularly for motivational blogs, self-help articles, or other content meant to inspire, an optimistic tone can be very effective. This involves looking at the positive side of things, encouraging readers, and offering hope.
Remember, the best tone for online writing depends heavily on your audience, purpose, and platform. Always keep your readers in mind, and adapt your tone to suit their needs and expectations.
How to Master Tone
Tone isn't as hard as you think.
If you've ever said something with feeling in your voice or with a certain attitude, you know how it works.
And while mastering the word choice, syntax, and other techniques to use tone effectively can be tricky, just by choosing a tone, being aware of tone in your writing, and making a concerted effort to practice it will add depth and style to your writing, heightening both the meaning and your audiences enjoyment.
Remember, we all have tone. You just need to practice using it. Happy writing!
What tone do you find yourself using the most in your writing ? Let us know in the comments .
Here are two writing exercises for you to practice tone.
Exercise 1: Identify the Tone
Using the ten identification examples above, write out the tones for each of the examples. Then use this answer guide to check your work.
- Pessimistic
- Inspirational
How many did you get correctly? Let me know in the comments .
Exercise 2: Choose One Tone and Write
Choose one of the tones above, set a timer for fifteen minutes, then free write in that tone.
When your time's up, post your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop here (and if you’re not a member yet, you can join here ), and share feedback with a few other writers.
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Types of Writing Genres: A Short Guide

- Post author By admin
- October 11, 2022
In this blog, we will discuss the different types of writing genres. Every genre of writing has its mindset and set of expectations. Genres are the tool for creativity and provide various perspectives to tell your story in different ways.
As a writer, your work will fit into a certain genre whether you want it or not, and that is purely based on what you are creating. On one side, some work may fit into one Genre. On the other hand, some may have different genres.
There are three different types of writing genres that we will take a look at in this blog. We have separated writing genres like Professional Writing, Literary Writing, and, lastly, Academic Writing.
If you’re wondering which one is right for you then this is the right place for you.
Here we will discover different writing genres that you need to know!
So, without further ado, let’s dive into it!
Table of Contents
What is the Need for Types of Writing Genres?
They Help Writers Sort Out Their Ideas and Feelings : When writers know what kind of writing they are doing, they can use the rules of that kind of writing to help them organize their writing. This can speed up the writing process and help writers make work simpler and more sense.
They Help People Know What to Expect From a Piece of Writing : When a reader knows the genre of a piece of writing, they can guess what they know about it to guess what the piece is about. This can help people read faster and better understand what they are reading.
They Help Writers Connect With the People Who Read Their Work : When writers choose the right type for their readers, their writing is easier to understand and more interesting to read. This can help writers connect with their readers and reach their goals for dialogue.
Aside From These General Benefits: there are other reasons to use different types of writing. For example, expository writing can help writers explain complicated ideas clearly, while descriptive writing can help writers paint detailed pictures in the minds of their readers. Narrative writing can help writers tell stories that entertain and teach, while persuasive writing can help writers persuade readers to do something.
They Can Help a Writer Find His or Her Voice : By trying different types of writing, writers can find the type that fits their style and attitude the best. This can help writers find their style, which will help them connect with their readers.
They Can Help Writers Come Up With Better Ideas : Writers can stretch their creative skills and develop new ideas if they try to write in different styles. This can make writers more creative and help them develop more original ideas.
They Can Help Writers Get Better at What They Do : Writers can improve their skills by learning the rules of different types of writing. This can help writers write better and make their work look more polished.
In the end, there are different types of writing because they are used for different things. If writers know the rules for each type, they can choose the right one for their purpose and audience. This will help them write in a clear, powerful, and interesting way.
What are Writing Genres?
The writing Genre is mostly called the name of Literary Genre. It is a type of narrative that can be used or written. Mostly, it is used for one purpose only to share emotions, ideas, and news with other people. Writing Genre is used to tell the story interestingly.
Writing within each Genre will reflect a whole new story and share several features like rhyme, image, and stylistic devices. The main focus of each Genre is to describe the events, theory, and several ideas in certain ways. In other words, the aim of each writing genre is how the elements are conveyed and described.
What are the Different Types of Writing Genres?
Three main types of Writing Genres are as follows:
- Professional Writing.
- Literary Writing.
- Academic Writing.
Professional Writing Genre (Types of Writing Genres)
Social media .
Social Media is a growing genre in business communication. The level of discussion in social media may vary depending on the topic and audience. Well-considered successful post on social media to help understand how it’s used to reach a wider target audience.
Business Letters
It can be both formal and informal. A perfectly written business letter shows the reader why it is important. If you want successful communication, then a structured approach is very important.
Memos
Well, Memos provide a clear summary, and the most crucial information is given at the beginning, but Paper Memos are no longer used nowadays. A positive tone is used to help the reader understand what the author is trying to say, making it appropriate for the users.
In the past, memos were considered the best business correspondence. The Main Guideline of the memo still exists, even if the median of the paper memo has been changed.
Meeting Minutes
Meeting Minutes include dates, times, attendees, and location. This is the standard format of Meeting Minutes. It is also important to record the most crucial details to avoid any misunderstanding later.
As a result, there are many ways involved in recording meeting minutes. The minutes should be uniform with the location and names. Unnecessary information should be avoided so that it can not cause any difficulty later.
This is the end of the Professional writing genre. Now we move to the Literary writing genre, and lastly, we will continue with the Academic Genre.
Literary Writing Genre (Types of Writing Genres)
Mystery .
This Genre is mostly associated with crime, mainly murder, but it does have to be. Any story which involves the unraveling of a secret or mystery would be considered within this Genre.
This Genre often describes a criminal investigation or legal case. Well, the most popular novel is The Sherlock Holmes Story. Mystery novels are a genre that typically has a problem to solve.
Category of Mystery Genre:
- Locked-room mysteries.
- Historical mysteries.
- Police procedural whodunit. ( A story about a murder in which the identity of the murderer is hidden at the end )
Literary nonfiction
Literary nonfiction is all about real events and people. Nonfiction can be found in magazines like The Atlantic, The New York, and Harper’s Magazine.
This type of Genre is associated with creating feelings of fear and dread. Some of you might think of this Genre as full of “blood and gore”. Anything which creates negative feelings about something will come under the category of Horror.
Horror is the genre of film, literature, and TV shows. The main aim of the horror genre is to create fear.
Gothic novels are an example of ancient horror literature. On the other hand, Stephen King is considered the father of modern horror literature. Well, nowadays, new writers have pushed the boundaries of horror stories. Writers include John Langan, Stephen Graham Jones, and many more.
In the Historical Genre, the story takes place in the past. Sometimes real people are included to interact with the fictional character to create a sense of realism.
Romance
This Genre deals with the love stories between two people. The element of romance can be found in many types of literature. Romance has been there since ancient times, but time travels so fast, and the paranormal romances have become more popular nowadays.
Science Fiction
As the name suggests, Science Fiction is the genre that deals with science and technology in society. Science fiction is a special type of Genre that includes elements of time travel, futuristic societies, and space. People often call Science Fiction ( Sci-Fi ) .
Magical realism
Magical realism is a type of literature in which the real world is depicted with an influence of magic and fantasy. In magical realism, the stories may occur in the real world but with some supernatural elements. Magical realism has close ties with Latin American Authors. Magical realism is used by literature from around the globe.
Fantasy novels are fiction stories that are set in imaginary universes. This Genre is inspired by folklore and mythology that is enjoyed by both children and adults
Dystopian novels are about futuristic and oppressive societies. In other words, the Dystopian novel features some political and social unrest. It can help us examine real types of fear like mass surveillance by the government.
Graphic Fiction
Graphic Fiction is the category of Graphic Novels and Comic Books.
Short Stories
Well, this type of Genre may fit into any number of genres. In Short stories, there is only one plot to it, no subplot in this Genre.
Tall Tales stories are not realistic or don’t try to become realistic.
Academic Writing Genre (Types of Writing Genres)
Analytical writing.
In Analytical writing, the author has a chance to include persuasive writing. A common layout uses the structure of methods, results, introduction, summary, and discussion.
Professional Writing
Professional Writing is a wide category that includes emails, studies, reports, business letters, and summaries. If you are writing for a client, then it is beneficial for you to follow the style rule of the company.
Argumentative Writing
Argumentative writing is a type of academic essay. In this, the writer breaks down an idea into its parts and then offers evidence for each part. This writing is mostly based on understanding and reading fiction or nonfiction texts.
Argumentative writing has three sections:
- Evidence or supporting point.
- Conclusion.
Most Common Types of Writing Genres That You Should Know
Descriptive writing .
In Descriptive writing, the author writes about every aspect of the person, place, or event and describes all aspects in detail.
Example of Descriptive Writing:
- Narrative Nonfiction.
- Fictional Stories.
Expository Writing
Expository writing is used to educate the reader. So the main goal of expository writing is to teach the reader rather than entertainment.
Example of Expository Writing:
- Technical Writing.
- Recipes writing.
Narrative Writing
Narrative Writing is used to tell people what happens somewhere or with someone. Narrative Writing includes Fiction and nonfiction. Whereas nonfiction is based on real events, and fiction writing is completely made up.
Example of Narrative Writing:
- Short-story.
- Presentations
- Speeches, and many more.
Persuasive Writing
Persuasive writing is used to convince the reader about something. This type of writing is written when the author has a strong opinion on something. It is used to encourage people to take action regarding any issue.
Example of Persuasive Writing:
- An opinion piece in the newspaper.
- Sales writing.
Read more about writing styles: Different Types Of Writing Styles
Now you know the different types of writing genres and their most used forms. So which Genre or form is close to you, and which one do you use the most. In this blog, we provide you with a short guide to types of writing genres, with the most common Genre that you should know.
I hope you like it!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1.what are the seven styles of writing.
The seven most common types of essay writing Narrative Descriptive Expository Persuasive Compare Reflective Personal
Q2. What are the three main genres of literature?
The three major genres are: Drama Poetry Prose
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (266)
- General (70)
- How To (16)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts

- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
A Creative Guide to Different Text Types
Table of Contents
Writing is a complex skill that demands knowledge and understanding of different literary devices and text types. Besides grammar, punctuation, and spelling, students must understand the conventions and structures of many different text types and genres.
This article will walk you through the text type examples along with their purpose and features.
What Are the Main Text Types?
The wide range of reading and writing materials we may encounter in a single day can be categorized in many different ways. However, it’s helpful to divide them into two broad and all-encompassing categories, which are defined below:
Factual Texts
Factual texts are primarily used to inform, instruct, or persuade someone using facts, opinions, and statistics. These texts target an audience that doesn’t want emotional or entertaining content.
They want a quick overview of facts, so the text is not elaborated, and the language is typically succinct.
Literary Texts
Literary texts are metacognition, which are the thoughts, ideas, and reflections of a more general topic. These texts are targeted for entertainment or to provoke an emotional response by using language to create mental images.
These two major groups each contain a number of subcategories. Let’s now explore in detail a few of these text types.

Factual Text Type Examples With Sub-Categories
Following are some of the subcategories that fall under factual text types:
Discussion Text
The goal of discussion texts is to explore several viewpoints on a given topic to establish an informed opinion or make a decision. Discussion texts typically begin by providing background information on the issue before introducing the main point or areas of disagreement.
Explanatory Text
Explanatory texts look at causes and reasons instead of just giving simple descriptions . They go beyond simply recounting what happened and examine the why and how of what occurred. Explanatory texts typically begin with an overarching thesis statement that introduces the subject under investigation.
Procedural or Instructional Text
Instructional and procedural texts are used to outline the rules or processes that need to be followed. They frequently come with games, home goods, or recipes, among other things.
Procedural texts might seem similar to explanatory texts, but they serve different purposes. The main difference is that procedural texts advise you on how to do something, whereas explanatory texts describe something .
Persuasive Text
The goal of a persuasive text is to convince the reader to follow a particular course of action or accept a specific viewpoint. Persuasive texts begin with an opening statement, or thesis statement, that summarizes the perspective that will be conveyed in the text.
Non-Chronological Report
Non-chronological reports provide information and detail about an event without being restricted to giving a linear narrative.
The report often groups material by category and proceeds from a general introductory statement on the issue to thorough and particular information.
Recount texts primarily focus on retelling the events and are usually aimed at informing or entertaining. It often opens with the setting of a scene or other elements that establish context. They begin by describing the events that took place , usually in chronological order.
Literary Text Type Examples With Subcategories
Following are some of the subcategories that fall under literary text types:
Poetry can be written to entertain, share knowledge, amuse, inform, pass on culture, and more. Poetry is generally structured around rhyme schemes, rhythmical patterns, grammatical patterns, and line lengths.
Narrative writings are written to tell a story. Although there are many different kinds of narrative texts, they all generally start by establishing the scene and introducing the main characters. Then a complication is added, acting as the catalyst for the subsequent occurrences.
Drama is mainly intended to entertain through storytelling, much like narrative texts. It can also be used to share culture, amuse, inform, and provide social commentary. Drama differs from prose narrative in that it makes considerable use of dialogue and stage directions.
This article is a simple guide to help students learn about the different text types. The different text type examples will help students better comprehend the concepts behind each type and their key features. This guide serves as a handbook for a more thorough understanding of text types.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Descriptive Text Articles
Effective writing tips to describe a person.
As with any piece of writing, it’s essential to paint a picture vividly and make your reader fully grasp your…
- Descriptive Text
Best Words to Describe Your Personality
There are instances when you’ll be required to describe yourself. It can be for a job interview or when introducing…
30+ Interesting Words To Describe Beauty
Beauty is the quality of being physically or visually attractive. It is the aesthetic properties of an entity, a natural…
Interesting Adjectives to Describe Movies
You might need to give a review about a movie you just watched. While you can use a few phrases…
Interesting Personality Adjectives to Describe People
What words best describe you? Funny? Determined? Hardworking? These words are adjectives. Adjectives modify one’s personality. They’re an easy and…
The Most Creative Words to Describe Smell
When depicting smell, descriptive language can help the reader have a much more vivid experience. This article explores the best…

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Style: Response writing is subjective, reflecting the opinion and personality of the writer. Despite the writer's personal voice being apparent, a good response should maintain an even-handed and critical approach. Structure: Commence with an overview of the content being responded to, including its title and creator.
Scripts: Hit the screen or the stage by writing scripts for film, television, theater, or video games. Beware: film is a director's medium, not a writer's medium, but movies have the potential to reach a non-reading audience. Storytelling: Storytelling is the most popular form of creative writing and is found in the realms of both fiction ...
Literary techniques you develop with writing plays and screenplays can include satire, motif, dramatic irony, allusion, and diction. 5. Personal essays. Focusing on the author's life and experiences, a personal essay is a form of creative non-fiction that almost acts as an autobiography.
Types of Creative Writing Poetry. Poetry is an intensely personal form of creative writing that allows for the expression of feelings and thoughts through rhythm, rhyme, and imagery. ... Pretrained Transformer) models have revolutionized the field of creative writing by offering tools that can generate writing prompts, draft texts, and even ...
ARGUMENTATIVE Texts. An argumentative essay is a type of writing in which the author takes a stance on a particular issue or topic and presents arguments and evidence to support that position. The primary goal is to persuade the reader to adopt the author's viewpoint or consider it seriously, at the least.
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
Creative writing is writing meant to evoke emotion in a reader by communicating a theme. In storytelling (including literature, movies, graphic novels, creative nonfiction, and many video games), the theme is the central meaning the work communicates. Take the movie (and the novel upon which it's based) Jaws, for instance.
Comics are strips of illustration accompanied by dialogue and some narrative text. Usually, comics are written out like scripts before they're put down in the comic strip format. A comic might be a graphic novel, which is the length of a book, or it might be a single strip in a newspaper. ... Step 1 - Pick a type of creative writing .
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
Type 2: Journals and Diaries. A journal is a written account of an author's experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently. Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events.
1. Novels. There is hardly a 21st-century teenager who hasn't laid their hands on a novel or two. A novel is one of the most well-loved examples of creative writing. It's a fictional story in prose form found in various genres, including romance, horror, Sci-Fi, Fantasy and contemporary.
The eight elements of creative writing that are used in short stories and novels are character development, setting, plot, conflict, theme, point of view, tone, and style. Some of these elements ...
Expository: to give facts. Narrative: to tell a story. Persuasive: to convince the reader of something. If you're struggling to figure out the writing style of a piece, ask yourself what its purpose is and why the author wants you to read it. To develop your own writing style, you should:
Poems. People have since writing artistic for almost as long as we have been able to press pens. Just think of long-form epic poems like The Odyssey or, later, the Cantar de Mio Cid — some of the initial recorded writings of their kind.. Poetry is additionally a great place to start if you want to dive your personal pen into the inkwell of creative writing.
An example of creative writing, a novella is essentially the love child of a short story and a novel. Although the novella does feature a plot, the plot is typically less complicated compared to that of a novel. Usually novellas are about 50 pages. 21. Genre Writing. Another type of writing that fiction writers can do is genre writing.
Creative Writing is a form of self-expression that allows you to use your imagination and creativity. It can be in the form of personal essays, short stories, or poems. It is often used as an outlet for emotions and experiences. Start with creative writing by reading through creative writing examples to help get you in the mood.
Expository writing is one of the most common types of writing. When an author writes in an expository style, all they are trying to do is explain a concept, imparting information from themselves to a wider audience. Expository writing does not include the author's opinions, but focuses on accepted facts about a topic, including statistics or ...
4. Short Fiction. Short fiction offers more of a "story" than a vignette. It includes short stories and even modern fan fiction. Writing a short story is a great way to learn about how fiction is structured, including plot, characters, conflict, and setting. You can even make money writing short fiction.
Creative writing expresses ideas and thoughts in an imaginative, subjective, and artistic way. Types include: Fiction Writing - Novels, short stories, poetry, and creative nonfiction. Screenwriting - Scripts and teleplays for television, film, and theater. Humor Writing - Comedy that entertains through funny observations, exaggeration ...
Expository Writing. The word expository contains the word expose, so the reason expository is an apt descriptor for this type of writing is that it exposes, or sets forth, facts. It is probably the most common writing genre you will come across throughout your day. In an expository piece, a topic will be introduced and laid out in a logical order without reference to the author's personal ...
Formal: This tone is professional, dignified, and somewhat detached. Example: "Upon analysis of the data, it's evident that the proposed hypothesis is substantiated.". Informal: This tone is casual, friendly, and conversational. Example: "Hey folks, today we'll be chatting about the latest trends in tech.".
Read more about writing styles: Different Types Of Writing Styles. Conclusion. Now you know the different types of writing genres and their most used forms. So which Genre or form is close to you, and which one do you use the most. In this blog, we provide you with a short guide to types of writing genres, with the most common Genre that you ...
Procedural or Instructional Text. Persuasive Text. Non-Chronological Report. Recount. Poetry. Narrative. Drama. Writing is a complex skill that demands knowledge and understanding of different literary devices and text types. Besides grammar, punctuation, and spelling, students must understand the conventions and structures of many different ...