This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
We are experiencing sporadically slow performance in our online tools, which you may notice when working in your dashboard. Our team is fully engaged and actively working to improve your online experience. If you are experiencing a connectivity issue, we recommend you try again in 10-15 minutes. We will update this space when the issue is resolved.

Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., guide to the ap english language and composition exam.

Can you apply the rhetorical triangle to a piece of writing? Are you able to argue a position? The AP ® English Language and Composition exam tests topics and skills discussed in your Advanced Placement English Language course. If you score high enough, your AP English Language score could earn you college credit!
Check out our AP English Language Guide for what you need to know about the exam:
- Exam Overview
- Sections and Question Types
- How to Prepare
What’s on the AP English Language & Composition Exam?
The College Board is very detailed in what they require your AP teacher to cover in his or her AP English Language & Composition course. The exam tests your abilities to understand how authors use rhetoric and language to convey their purpose. Students are also expected to apply these techniques to their own writing and research projects. Some of the major skills tested include the ability to:
- Identify an author’s purpose and intended audience
- Recognize rhetorical devices and strategies in an author’s work
- Demonstrate understanding of citations in research papers
- Apply these skills and techniques to their own writing
- Create and organize an argument defended with evidence and reasoning
- Plan, write, and revise cogent, well-written essays
Check out our line of AP guides for a comprehensive content review.
AP English Language Sections & Question Types
The AP English Language & Composition exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long and consists of two sections: a multiple-choice section and a free response section.
|
|
|
| |
| Section 1 | 60 minutes | 45 multiple choice questions | 45% |
| Section 2 | 2 hours and 15 minutes | 3 free response questions | 55% |
Read More: Review for the exam with our AP English Language Crash Course
Multiple-Choice
For AP English Language multiple-choice questions, you are presented with two Reading Passages and three Writing passages. The two Reading passages are nonfiction passages taken from all sorts of works. The idea is to get you to focus on rhetorical devices, figures of speech and intended purposes, under rigid time constraints and with material you haven’t seen before. The three Writing passages are student-produced essays. The idea is to get you to revise the essay that help the writer accomplish his or her goal.
Free Response
The AP English Language section contains three essay prompts: a synthesis essay, a rhetorical analysis essay, and an argument essay.
- Synthesis essay: You’ll be given a scenario and tasked with writing a response using at least three of six or seven short accompanying sources for support.
- Rhetorical analysis essay: Asks you to analyze the techniques an author uses, and discuss how they contribute to the author’s purpose.
- Argument essay: Presents a claim or assertion in the prompt and then asks you to argue a position based on your own knowledge, experience, or reading.
How to Interpret AP English Language Scores
AP scores are reported from 1 to 5. Colleges are generally looking for a 4 or 5 on the AP English Language exam, but some may grant AP credit for a 3. Each test is curved so scores vary from year to year. Here’s how AP English Lang students scored on the May 2022 test:
|
|
|
|
| 5 | Extremely qualified | 10.4% |
| 4 | Well qualified | 21.1% |
| 3 | Qualified | 24.2% |
| 2 | Possibly qualified | 29.8% |
| 1 | No recommendation | 14.5% |
Source: College Board
How can I prepare?
AP classes are great, but for many students they’re not enough! For a thorough review of AP English Language content and strategy, pick the AP prep option that works best for your goals and learning style.
- AP Exams

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
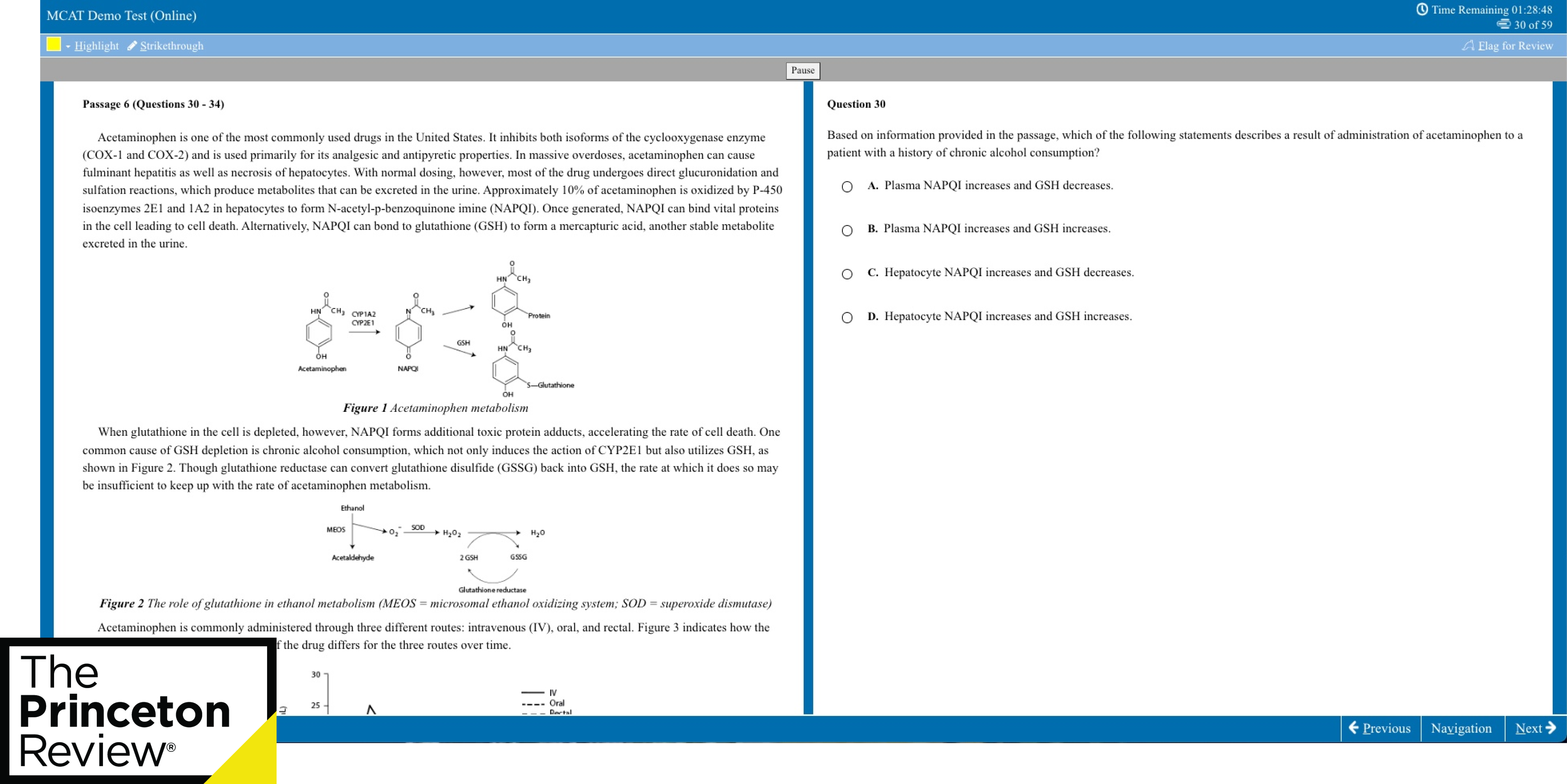
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Tackling the AP English Language and Composition essays: part 1

So, what are the three AP Lang Essays? The College Board shares a lot of general information about these essays on its website, as well as a large number of excellent sample essays. I suggest you take the time to review all of that material, here. But here’s my primer:
On the AP Lang Exam, there are three essays to write, all in a row (during the second half of the exam, after an initial multiple-choice portion). They are:
- The Synthesis Essay: You’ll be given a general topic or question for debate (like: should public libraries continue to exist? Or: is eminent domain just?). Multiple short sources taking positions on that topic will follow the prompt. You will then be asked to write your own, short essay taking a position on the topic, citing at least three of the sources that you read.
- The Rhetoric Essay: You’ll be given a short, rhetorically interesting passage, either taking a position on a topic, telling a story, or performing some other function. You will then be asked to write a short essay analyzing this passage’s use of language/rhetorical approach.
- The Argument Essay: You will be given some position, usually stated in some brief excerpt from an author’s work. For example, you might be given an excerpt from Proust that suggests that people often regret their choices, or an excerpt from Eleanor Roosevelt praising the virtue of courage. You will then be asked to take your own position on the topic. This time, you won’t be given sources to help you make your arguments; all of your arguments must come from your own brain.
The scoring rubric for each essay is roughly similar, with six possible points awarded: there is one point for argument, four points for evidence and analysis, and one point for “sophistication.” What this means is that, in brief, you need to do three things on every essay to get a perfect score:
- Have an argument.
- Back up your argument with evidence and analyze how that evidence supports your argument.
- Have an ineffable, excellent quality to your writing, a sort of dexterity of mind and language, for which the scorers have reserved one, sacred point.
You can’t really control whether or not you can achieve #3, and a lot of that will be based on your prior level of experience writing/reading; but you can control whether or not you achieve #1-2. So, a high score is totally within your power! The TLDR version of this post is: make a clear argument and back it up with concrete, analyzed evidence. But, of course, that’s not as easy as it looks, and I have many more thoughts on how to actually achieve it, and achieve it well...
The six major components of successfully writing a timed essay on an exam are:
- Organizing your time
- Reading and Annotating
- Outlining Part 1: Thesis
- Outlining Part 2: Structure
- Writing Part 1: Paragraphs (Intro, Evidence, Analysis, Conclusion)
- Writing Part 2: Sentence by Sentence
#1 Organizing your time
On the AP Lang exam, you get a total of 2 hours and 15 minutes to write your three essays. This time is split into chunks. First, there is a 15 minute “reading period”; next, there is a 2 hour “writing period.” What this seems to imply is that the exam would like you to read all of the questions and their supplemental texts (the Synthesis Essay question and texts, the Rhetoric Essay question and passage, the Argument Essay question and short question blurb) in the 15 minute reading period, and then proceed to write the essays, in response, in the two hour writing period. This, however, is obviously an insane approach. For one thing, it’s kind of impossible: no one could keep the details of three different essay questions and associated readings together in their head all at once. For another, it’s really time inefficient: if you read all the material for all three essays first, you’re going to have to go back to it, a lot, each time you start to write a new essay, to jog your memory. Basically, no one in their right mind would (or does) advise this approach. And even the College Board seems to know it makes no sense, because they allow you to continue reading and referring to the questions and texts after the reading period.
What you should do instead? Simply treat the whole 2 hours and 15 minutes as a single time block. Divide it into three units of 45 minutes. Then, read and answer each of the three questions one after the other, giving 45 minutes to each. Start with the Synthesis Essay, followed by the Rhetoric Essay, and then the Argument Essay.
Your process should look like this: during the 15 minute reading period, begin work on the Synthesis Essay by reading the question and texts and planning that essay. Then, when the 2-hour timer starts, devote the first 30 minutes to actually writing that essay. Next, spend 45 minutes reading the Rhetoric Essay question and passage, and writing the Rhetoric Essay. Finally, spend the last 45 minutes reading the Argument Essay question/blurb and then writing the Argument Essay. The Argument Essay should actually take you less time than the first two, which means you should end up with 5-10 minutes to proofread your other essays. That said, I advise that you leave time at the end of each 45-minute block to check over each individual essay.
Now let’s talk about the Rhetoric Essay in particular. How should you organize your 45 minutes here? I suggest mapping out your time roughly like this: take about ten minutes to read the passage, take notes, and brainstorm; then, take about five minutes to make an outline for your essay; next, take about twenty to twenty-five minutes to write. Leave an extra five to seven minutes at the end to re-read and edit your work. As you practice, you might notice that slightly different divisions of time work best for you – feel free to be flexible! You don’t have to stick to your timetable exactly . BUT you should try to stick to a version of this timetable so that you have enough time for each of the steps. How? Watch the clock!
#2 Reading and Annotating
The Rhetoric Essay asks you to analyze the language or rhetoric that a passage uses to achieve its ends. In your first ten minutes of reading, you should be keeping an eye out for two things:
- What is this passage trying to achieve? Is it trying to persuade the reader of an argument (often the case)? Is it trying to entertain the reader with a story (sometimes the case)? Is it trying to make the reader laugh? Is it trying to make the reader think? Identify the passage’s main purpose.
- What rhetorical methods or devices does the passage use to achieve its aims? What exactly is it doing to achieve its aims? Yes, you should be watching out for rhetorical devices that already have fancy names, like “allusion” or “alliteration,” but you should also be using your OWN language/descriptive powers to identify the passage’s methods. You might, for example, note things like: “makes argument largely through anecdote” or “addresses counterarguments” or “lists so many absurd situations that they start to feel normal.” Try to identify not just rhetorical methods the passage uses, but also the central ones it uses.
To achieve this, I suggest proceeding as follows: read one paragraph. Once you’re done, stop, reflect, and note (in the margins) the most important rhetorical devices the passage used to achieve its aims (as far as you understand them thus far). Do this for each paragraph you read. Once you’re done, you should have a handy list in the margin of rhetorical tactics the passage uses. Which ones, looking back, seem to come up the most frequently? Which ones, even if they don’t come up frequently, seem particularly central to the passage’s aims? The tactics you identify will soon play a role in your essay’s thesis.
Next, you’ll be ready to write an outline for your essay, mapping out (as best you can) its thesis and structure. In the next blog post , we’ll begin with that step.
Related Content

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Write a Perfect Synthesis Essay for the AP Language Exam
Advanced Placement (AP)

If you're planning to take the AP Language (or AP Lang) exam , you might already know that 55% of your overall exam score will be based on three essays. The first of the three essays you'll have to write on the AP Language exam is called the "synthesis essay." If you want to earn full points on this portion of the AP Lang Exam, you need to know what a synthesis essay is and what skills are assessed by the AP Lang synthesis essay.
In this article, we'll explain the different aspects of the AP Lang synthesis essay, including what skills you need to demonstrate in your synthesis essay response in order to achieve a good score. We'll also give you a full breakdown of a real AP Lang Synthesis Essay prompt, provide an analysis of an AP Lang synthesis essay example, and give you four tips for how to write a synthesis essay.
Let's get started by taking a closer look at how the AP Lang synthesis essay works!
Synthesis Essay AP Lang: What It Is and How It Works
The AP Lang synthesis essay is the first of three essays included in the Free Response section of the AP Lang exam.
The AP Lang synthesis essay portion of the Free Response section lasts for one hour total . This hour consists of a recommended 15 minute reading period and a 40 minute writing period. Keep in mind that these time allotments are merely recommendations, and that exam takers can parse out the allotted 60 minutes to complete the synthesis essay however they choose.
Now, here's what the structure of the AP Lang synthesis essay looks like. The exam presents six to seven sources that are organized around a specific topic (like alternative energy or eminent domain, which are both past synthesis exam topics).
Of these six to seven sources, at least two are visual , including at least one quantitative source (like a graph or pie chart, for example). The remaining four to five sources are print text-based, and each one contains approximately 500 words.
In addition to six to seven sources, the AP Lang exam provides a written prompt that consists of three paragraphs. The prompt will briefly explain the essay topic, then present a claim that students will respond to in an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources provided.
Here's an example prompt provided by the College Board:
Directions : The following prompt is based on the accompanying six sources.
This question requires you to integrate a variety of sources into a coherent, well-written essay. Refer to the sources to support your position; avoid mere paraphrase or summary. Your argument should be central; the sources should support this argument .
Remember to attribute both direct and indirect citations.
Introduction
Television has been influential in United States presidential elections since the 1960's. But just what is this influence, and how has it affected who is elected? Has it made elections fairer and more accessible, or has it moved candidates from pursuing issues to pursuing image?
Read the following sources (including any introductory information) carefully. Then, in an essay that synthesizes at least three of the sources for support, take a position that defends, challenges, or qualifies the claim that television has had a positive impact on presidential elections.
Refer to the sources as Source A, Source B, etc.; titles are included for your convenience.
Source A (Campbell) Source B (Hart and Triece) Source C (Menand) Source D (Chart) Source E (Ranney) Source F (Koppel)
Like we mentioned earlier, this prompt gives you a topic — which it briefly explains — then asks you to take a position. In this case, you'll have to choose a stance on whether television has positively or negatively affected U.S. elections. You're also given six sources to evaluate and use in your response. Now that you have everything you need, now your job is to write an amazing synthesis essay.
But what does "synthesize" mean, exactly? According to the CollegeBoard, when an essay prompt asks you to synthesize, it means that you should "combine different perspectives from sources to form a support of a coherent position" in writing. In other words, a synthesis essay asks you to state your claim on a topic, then highlight the relationships between several sources that support your claim on that topic. Additionally, you'll need to cite specific evidence from your sources to prove your point.
The synthesis essay counts for six of the total points on the AP Lang exam . Students can receive 0-1 points for writing a thesis statement in the essay, 0-4 based on incorporation of evidence and commentary, and 0-1 points based on sophistication of thought and demonstrated complex understanding of the topic.
You'll be evaluated based on how effectively you do the following in your AP Lang synthesis essay:
Write a thesis that responds to the exam prompt with a defensible position
Provide specific evidence that to support all claims in your line of reasoning from at least three of the sources provided, and clearly and consistently explain how the evidence you include supports your line of reasoning
Demonstrate sophistication of thought by either crafting a thoughtful argument, situating the argument in a broader context, explaining the limitations of an argument
Make rhetorical choices that strengthen your argument and/or employ a vivid and persuasive style throughout your essay.
If your synthesis essay meets the criteria above, then there's a good chance you'll score well on this portion of the AP Lang exam!
If you're looking for even more information on scoring, the College Board has posted the AP Lang Free Response grading rubric on its website. ( You can find it here. ) We recommend taking a close look at it since it includes additional details about the synthesis essay scoring.

Don't be intimidated...we're going to teach you how to break down even the hardest AP synthesis essay prompt.
Full Breakdown of a Real AP Lang Synthesis Essay Prompt
In this section, we'll teach you how to analyze and respond to a synthesis essay prompt in five easy steps, including suggested time frames for each step of the process.
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt
The very first thing to do when the clock starts running is read and analyze the prompt. To demonstrate how to do this, we'll look at the sample AP Lang synthesis essay prompt below. This prompt comes straight from the 2018 AP Lang exam:
Eminent domain is the power governments have to acquire property from private owners for public use. The rationale behind eminent domain is that governments have greater legal authority over lands within their dominion than do private owners. Eminent domain has been instituted in one way or another throughout the world for hundreds of years.
Carefully read the following six sources, including the introductory information for each source. Then synthesize material from at least three of the sources and incorporate it into a coherent, well-developed essay that defends, challenges, or qualifies the notion that eminent domain is productive and beneficial.
Your argument should be the focus of your essay. Use the sources to develop your argument and explain the reasoning for it. Avoid merely summarizing the sources. Indicate clearly which sources you are drawing from, whether through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. You may cite the sources as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the descriptions in parentheses.
On first read, you might be nervous about how to answer this prompt...especially if you don't know what eminent domain is! But if you break the prompt down into chunks, you'll be able to figure out what the prompt is asking you to do in no time flat.
To get a full understanding of what this prompt wants you to do, you need to identify the most important details in this prompt, paragraph by paragraph. Here's what each paragraph is asking you to do:
- Paragraph 1: The prompt presents and briefly explains the topic that you'll be writing your synthesis essay about. That topic is the concept of eminent domain.
- Paragraph 2: The prompt presents a specific claim about the concept of eminent domain in this paragraph: Eminent domain is productive and beneficial. This paragraph instructs you to decide whether you want to defend, challenge, or qualify that claim in your synthesis essay , and use material from at least three of the sources provided in order to do so.
- Paragraph 3: In the last paragraph of the prompt, the exam gives you clear instructions about how to approach writing your synthesis essay . First, make your argument the focus of the essay. Second, use material from at least three of the sources to develop and explain your argument. Third, provide commentary on the material you include, and provide proper citations when you incorporate quotations, paraphrases, or summaries from the sources provided.
So basically, you'll have to agree with, disagree with, or qualify the claim stated in the prompt, then use at least three sources substantiate your answer. Since you probably don't know much about eminent domain, you'll probably decide on your position after you read the provided sources.
To make good use of your time on the exam, you should spend around 2 minutes reading the prompt and making note of what it's asking you to do. That will leave you plenty of time to read the sources provided, which is the next step to writing a synthesis essay.
Step 2: Read the Sources Carefully
After you closely read the prompt and make note of the most important details, you need to read all of the sources provided. It's tempting to skip one or two sources to save time--but we recommend you don't do this. That's because you'll need a thorough understanding of the topic before you can accurately address the prompt!
For the sample exam prompt included above, there are six sources provided. We're not going to include all of the sources in this article, but you can view the six sources from this question on the 2018 AP Lang exam here . The sources include five print-text sources and one visual source, which is a cartoon.
As you read the sources, it's important to read quickly and carefully. Don't rush! Keep your pencil in hand to quickly mark important passages that you might want to use as evidence in your synthesis. While you're reading the sources and marking passages, you want to think about how the information you're reading influences your stance on the issue (in this case, eminent domain).
When you finish reading, take a few seconds to summarize, in a phrase or sentence, whether the source defends, challenges, or qualifies whether eminent domain is beneficial (which is the claim in the prompt) . Though it might not feel like you have time for this, it's important to give yourself these notes about each source so you know how you can use each one as evidence in your essay.
Here's what we mean: say you want to challenge the idea that eminent domain is useful. If you've jotted down notes about each source and what it's saying, it will be easier for you to pull the relevant information into your outline and your essay.
So how much time should you spend reading the provided sources? The AP Lang exam recommends taking 15 minutes to read the sources . If you spend around two of those minutes reading and breaking down the essay prompt, it makes sense to spend the remaining 13 minutes reading and annotating the sources.
If you finish reading and annotating early, you can always move on to drafting your synthesis essay. But make sure you're taking your time and reading carefully! It's better to use a little extra time reading and understanding the sources now so that you don't have to go back and re-read the sources later.
A strong thesis will do a lot of heavy lifting in your essay. (See what we did there?)
Step 3: Write a Strong Thesis Statement
After you've analyzed the prompt and thoroughly read the sources, the next thing you need to do in order to write a good synthesis essay is write a strong thesis statement .
The great news about writing a thesis statement for this synthesis essay is that you have all the tools you need to do it at your fingertips. All you have to do in order to write your thesis statement is decide what your stance is in relationship to the topic provided.
In the example prompt provided earlier, you're essentially given three choices for how to frame your thesis statement: you can either defend, challenge, or qualify a claim that's been provided by the prompt, that eminent domain is productive and beneficial . Here's what that means for each option:
If you choose to defend the claim, your job will be to prove that the claim is correct . In this case, you'll have to show that eminent domain is a good thing.
If you choose to challenge the claim, you'll argue that the claim is incorrect. In other words, you'll argue that eminent domain isn't productive or beneficial.
If you choose to qualify, that means you'll agree with part of the claim, but disagree with another part of the claim. For instance, you may argue that eminent domain can be a productive tool for governments, but it's not beneficial for property owners. Or maybe you argue that eminent domain is useful in certain circumstances, but not in others.
When you decide whether you want your synthesis essay to defend, challenge, or qualify that claim, you need to convey that stance clearly in your thesis statement. You want to avoid simply restating the claim provided in the prompt, summarizing the issue without making a coherent claim, or writing a thesis that doesn't respond to the prompt.
Here's an example of a thesis statement that received full points on the eminent domain synthesis essay:
Although eminent domain can be misused to benefit private interests at the expense of citizens, it is a vital tool of any government that intends to have any influence on the land it governs beyond that of written law.
This thesis statement received full points because it states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning on the issue of eminent domain. It states the author's position (that some parts of eminent domain are good, but others are bad), then goes on to explain why the author thinks that (it's good because it allows the government to do its job, but it's bad because the government can misuse its power.)
Because this example thesis statement states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning, it can be elaborated upon in the body of the essay through sub-claims, supporting evidence, and commentary. And a solid argument is key to getting a six on your synthesis essay for AP Lang!

Step 4: Create a Bare-Bones Essay Outline
Once you've got your thesis statement drafted, you have the foundation you need to develop a bare bones outline for your synthesis essay. Developing an outline might seem like it's a waste of your precious time, but if you develop your outline well, it will actually save you time when you start writing your essay.
With that in mind, we recommend spending 5 to 10 minutes outlining your synthesis essay . If you use a bare-bones outline like the one below, labeling each piece of content that you need to include in your essay draft, you should be able to develop out the most important pieces of the synthesis before you even draft the actual essay.
To help you see how this can work on test day, we've created a sample outline for you. You can even memorize this outline to help you out on test day! In the outline below, you'll find places to fill in a thesis statement, body paragraph topic sentences, evidence from the sources provided, and commentary :
- Present the context surrounding the essay topic in a couple of sentences (this is a good place to use what you learned about the major opinions or controversies about the topic from reading your sources).
- Write a straightforward, clear, and concise thesis statement that presents your stance on the topic
- Topic sentence presenting first supporting point or claim
- Evidence #1
- Commentary on Evidence #1
- Evidence #2 (if needed)
- Commentary on Evidence #2 (if needed)
- Topic sentence presenting second supporting point or claim
- Topic sentence presenting three supporting point or claim
- Sums up the main line of reasoning that you developed and defended throughout the essay
- Reiterates the thesis statement
Taking the time to develop these crucial pieces of the synthesis in a bare-bones outline will give you a map for your final essay. Once you have a map, writing the essay will be much easier.
Step 5: Draft Your Essay Response
The great thing about taking a few minutes to develop an outline is that you can develop it out into your essay draft. After you take about 5 to 10 minutes to outline your synthesis essay, you can use the remaining 30 to 35 minutes to draft your essay and review it.
Since you'll outline your essay before you start drafting, writing the essay should be pretty straightforward. You'll already know how many paragraphs you're going to write, what the topic of each paragraph will be, and what quotations, paraphrases, or summaries you're going to include in each paragraph from the sources provided. You'll just have to fill in one of the most important parts of your synthesis—your commentary.
Commentaries are your explanation of why your evidence supports the argument you've outlined in your thesis. Your commentary is where you actually make your argument, which is why it's such a critical part of your synthesis essay.
When thinking about what to say in your commentary, remember one thing the AP Lang synthesis essay prompt specifies: don't just summarize the sources. Instead, as you provide commentary on the evidence you incorporate, you need to explain how that evidence supports or undermines your thesis statement . You should include commentary that offers a thoughtful or novel perspective on the evidence from your sources to develop your argument.
One very important thing to remember as you draft out your essay is to cite your sources. The AP Lang exam synthesis essay prompt indicates that you can use generic labels for the sources provided (e.g. "Source 1," "Source 2," "Source 3," etc.). The exam prompt will indicate which label corresponds with which source, so you'll need to make sure you pay attention and cite sources accurately. You can cite your sources in the sentence where you introduce a quote, summary, or paraphrase, or you can use a parenthetical citation. Citing your sources affects your score on the synthesis essay, so remembering to do this is important.

Keep reading for a real-life example of a great AP synthesis essay response!
Real-Life AP Synthesis Essay Example and Analysis
If you're still wondering how to write a synthesis essay, examples of real essays from past AP Lang exams can make things clearer. These real-life student AP synthesis essay responses can be great for helping you understand how to write a synthesis essay that will knock the graders' socks off .
While there are multiple essay examples online, we've chosen one to take a closer look at. We're going to give you a brief analysis of one of these example student synthesis essays from the 2019 AP Lang Exam below!
Example Synthesis Essay AP Lang Response
To get started, let's look at the official prompt for the 2019 synthesis essay:
In response to our society's increasing demand for energy, large-scale wind power has drawn attention from governments and consumers as a potential alternative to traditional materials that fuel our power grids, such as coal, oil, natural gas, water, or even newer sources such as nuclear or solar power. Yet the establishment of large-scale, commercial-grade wind farms is often the subject of controversy for a variety of reasons.
Carefully read the six sources, found on the AP English Language and Composition 2019 Exam (Question 1), including the introductory information for each source. Write an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources and develops your position on the most important factors that an individual or agency should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Source A (photo) Source B (Layton) Source C (Seltenrich) Source D (Brown) Source E (Rule) Source F (Molla)
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis presents a defensible position.
- Select and use evidence from at least 3 of the provided sources to support your line of reasoning. Indicate clearly the sources used through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sources may be cited as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the description in parentheses.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
Now that you know exactly what the prompt asked students to do on the 2019 AP Lang synthesis essay, here's an AP Lang synthesis essay example, written by a real student on the AP Lang exam in 2019:
[1] The situation has been known for years, and still very little is being done: alternative power is the only way to reliably power the changing world. The draw of power coming from industry and private life is overwhelming current sources of non-renewable power, and with dwindling supplies of fossil fuels, it is merely a matter of time before coal and gas fuel plants are no longer in operation. So one viable alternative is wind power. But as with all things, there are pros and cons. The main factors for power companies to consider when building wind farms are environmental boon, aesthetic, and economic factors.
[2] The environmental benefits of using wind power are well-known and proven. Wind power is, as qualified by Source B, undeniably clean and renewable. From their production requiring very little in the way of dangerous materials to their lack of fuel, besides that which occurs naturally, wind power is by far one of the least environmentally impactful sources of power available. In addition, wind power by way of gearbox and advanced blade materials, has the highest percentage of energy retention. According to Source F, wind power retains 1,164% of the energy put into the system – meaning that it increases the energy converted from fuel (wind) to electricity 10 times! No other method of electricity production is even half that efficient. The efficiency and clean nature of wind power are important to consider, especially because they contribute back to power companies economically.
[3] Economically, wind power is both a boon and a bone to electric companies and other users. For consumers, wind power is very cheap, leading to lower bills than from any other source. Consumers also get an indirect reimbursement by way of taxes (Source D). In one Texan town, McCamey, tax revenue increased 30% from a wind farm being erected in the town. This helps to finance improvements to the town. But, there is no doubt that wind power is also hurting the power companies. Although, as renewable power goes, wind is incredibly cheap, it is still significantly more expensive than fossil fuels. So, while it is helping to cut down on emissions, it costs electric companies more than traditional fossil fuel plants. While the general economic trend is positive, there are some setbacks which must be overcome before wind power can take over as truly more effective than fossil fuels.
[4] Aesthetics may be the greatest setback for power companies. Although there may be significant economic and environmental benefit to wind power, people will always fight to preserve pure, unspoiled land. Unfortunately, not much can be done to improve the visual aesthetics of the turbines. White paint is the most common choice because it "[is] associated with cleanliness." (Source E). But, this can make it stand out like a sore thumb, and make the gargantuan machines seem more out of place. The site can also not be altered because it affects generating capacity. Sound is almost worse of a concern because it interrupts personal productivity by interrupting people's sleep patterns. One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support.
[5] As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and the consequences. But, by balancing economics, efficiency, and aesthetics, power companies can create a solution which balances human impact with environmental preservation.
And that's an entire AP Lang synthesis essay example, written in response to a real AP Lang exam prompt! It's important to remember AP Lang exam synthesis essay prompts are always similarly structured and worded, and students often respond in around the same number of paragraphs as what you see in the example essay response above.
Next, let's analyze this example essay and talk about what it does effectively, where it could be improved upon, and what score past exam scorers awarded it.
To get started on an analysis of the sample synthesis essay, let's look at the scoring commentary provided by the College Board:
- For development of thesis, the essay received 1 out of 1 possible points
- For evidence and commentary, the essay received 4 out of 4 possible points
- For sophistication of thought, the essay received 0 out of 1 possible points.
This means that the final score for this example essay was a 5 out of 6 possible points . Let's look more closely at the content of the example essay to figure out why it received this score breakdown.
Thesis Development
The thesis statement is one of the three main categories that is taken into consideration when you're awarded points on this portion of the exam. This sample essay received 1 out of 1 total points.
Now, here's why: the thesis statement clearly and concisely conveys a position on the topic presented in the prompt--alternative energy and wind power--and defines the most important factors that power companies should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Evidence and Commentary
The second key category taken into consideration when synthesis exams are evaluated is incorporation of evidence and commentary. This sample received 4 out of 4 possible points for this portion of the synthesis essay. At bare minimum, this sample essay meets the requirement mentioned in the prompt that the writer incorporate evidence from at least three of the sources provided.
On top of that, the writer does a good job of connecting the incorporated evidence back to the claim made in the thesis statement through effective commentary. The commentary in this sample essay is effective because it goes beyond just summarizing what the provided sources say. Instead, it explains and analyzes the evidence presented in the selected sources and connects them back to supporting points the writer makes in each body paragraph.
Finally, the writer of the essay also received points for evidence and commentary because the writer developed and supported a consistent line of reasoning throughout the essay . This line of reasoning is summed up in the fourth paragraph in the following sentence: "One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support."
Because the writer did a good job consistently developing their argument and incorporating evidence, they received full marks in this category. So far, so good!
Sophistication of Thought
Now, we know that this essay received a score of 5 out of 6 total points, and the place where the writer lost a point was on the basis of sophistication of thought, for which the writer received 0 out of 1 points. That's because this sample essay makes several generalizations and vague claims where it could have instead made specific claims that support a more balanced argument.
For example, in the following sentence from the 5th paragraph of the sample essay, the writer misses the opportunity to state specific possibilities that power companies should consider for wind energy . Instead, the writer is ambiguous and non-committal, saying, "As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and consequences."
If the writer of this essay was interested in trying to get that 6th point on the synthesis essay response, they could consider making more specific claims. For instance, they could state the specific benefits and consequences power companies should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm. These could include things like environmental impacts, economic impacts, or even population density!
Despite losing one point in the last category, this example synthesis essay is a strong one. It's well-developed, thoughtfully written, and advances an argument on the exam topic using evidence and support throughout.

4 Tips for How to Write a Synthesis Essay
AP Lang is a timed exam, so you have to pick and choose what you want to focus on in the limited time you're given to write the synthesis essay. Keep reading to get our expert advice on what you should focus on during your exam.
Tip 1: Read the Prompt First
It may sound obvious, but when you're pressed for time, it's easy to get flustered. Just remember: when it comes time to write the synthesis essay, read the prompt first !
Why is it so important to read the prompt before you read the sources? Because when you're aware of what kind of question you're trying to answer, you'll be able to read the sources more strategically. The prompt will help give you a sense of what claims, points, facts, or opinions to be looking for as you read the sources.
Reading the sources without having read the prompt first is kind of like trying to drive while wearing a blindfold: you can probably do it, but it's likely not going to end well!
Tip 2: Make Notes While You Read
During the 15-minute reading period at the beginning of the synthesis essay, you'll be reading through the sources as quickly as you can. After all, you're probably anxious to start writing!
While it's definitely important to make good use of your time, it's also important to read closely enough that you understand your sources. Careful reading will allow you to identify parts of the sources that will help you support your thesis statement in your essay, too.
As you read the sources, consider marking helpful passages with a star or check mark in the margins of the exam so you know which parts of the text to quickly re-read as you form your synthesis essay. You might also consider summing up the key points or position of each source in a sentence or a few words when you finish reading each source during the reading period. Doing so will help you know where each source stands on the topic given and help you pick the three (or more!) that will bolster your synthesis argument.
Tip 3: Start With the Thesis Statement
If you don't start your synthesis essay with a strong thesis statement, it's going to be tough to write an effective synthesis essay. As soon as you finish reading and annotating the provided sources, the thing you want to do next is write a strong thesis statement.
According to the CollegeBoard grading guidelines for the AP Lang synthesis essay, a strong thesis statement will respond to the prompt— not restate or rephrase the prompt. A good thesis will take a clear, defensible position on the topic presented in the prompt and the sources.
In other words, to write a solid thesis statement to guide the rest of your synthesis essay, you need to think about your position on the topic at hand and then make a claim about the topic based on your position. This position will either be defending, challenging, or qualifying the claim made in the essay's prompt.
The defensible position that you establish in your thesis statement will guide your argument in the rest of the essay, so it's important to do this first. Once you have a strong thesis statement, you can begin outlining your essay.
Tip 4: Focus on Your Commentary
Writing thoughtful, original commentary that explains your argument and your sources is important. In fact, doing this well will earn you four points (out of a total of six)!
AP Lang provides six to seven sources for you on the exam, and you'll be expected to incorporate quotations, paraphrases, or summaries from at least three of those sources into your synthesis essay and interpret that evidence for the reader.
While incorporating evidence is very important, in order to get the extra point for "sophistication of thought" on the synthesis essay, it's important to spend more time thinking about your commentary on the evidence you choose to incorporate. The commentary is your chance to show original thinking, strong rhetorical skills, and clearly explain how the evidence you've included supports the stance you laid out in your thesis statement.
To earn the 6th possible point on the synthesis essay, make sure your commentary demonstrates a nuanced understanding of the source material, explains this nuanced understanding, and places the evidence incorporated from the sources in conversation with each other. To do this, make sure you're avoiding vague language. Be specific when you can, and always tie your commentary back to your thesis!

What's Next?
There's a lot more to the AP Language exam than just the synthesis essay. Be sure to check out our expert guide to the entire exam , then learn more about the tricky multiple choice section .
Is the AP Lang exam hard...or is it easy? See how it stacks up to other AP tests on our list of the hardest AP exams .
Did you know there are technically two English AP exams? You can learn more about the second English AP test, the AP Literature exam, in this article . And if you're confused about whether you should take the AP Lang or AP Lit test , we can help you make that decision, too.

Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023
Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success
Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.


AP® English Language
How to study for ap® english language and composition.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

You’re not the first student who has been here – panic mode, one month before the AP® English Language and Composition Exam. Whether you’re a straight-A student or the kid who sits in the back of class and hasn’t figured out what “composition” means yet, you need a PLAN. You need to know what to study, when and how to study it, and how the AP® English Language exam is structured.
Structure of the AP® English Language Exam
You will have 3 hours and 15 minutes allotted to complete the test – 1 hour for multiple choice questions, 15 minutes to read the sources for your synthesis essay and to plan how you are going to write that essay, and 2 hours to complete all three essays: the synthesis, the argument, and the rhetorical analysis. The multiple choice questions count for 45% of the final score, and the three essays count for the other 55%.
All these numbers make the test seem scarier than it really is, so before you dive into studying, take a deep breath and try to calm your nerves. Many students make unnecessary errors due to nervousness or failure to understand test instructions, even when they know the information well.
Every student will need to develop an individualized calming technique, but everyone reading this can begin by thinking about how well he or she will know the structure of the exam and how to study for AP® English Language . The following articles will serve as a sort of map of the test, so that you can’t get lost in the AP® English Language Exam, no matter how impossible it may seem.
How to Study For AP® English Language
There are four main things you need to study and practice for – the multiple choice section, the synthesis essay, the argument essay, and the rhetorical analysis essay . Since there are about four weeks in a month, you can use one week to work on each section by doing sample questions, talking to your teacher or study group, etc. You can also check out our article “5 Must Reads for Getting a 5 on AP® English Language” and try to read or at least learn about one or two of the books listed there each week.
This plan is flexible, so to make the best of your time, be self-aware! Know your own strengths and weaknesses so that you can work harder on trouble areas and not waste too much time on what you already know – although you shouldn’t ever entirely skip studying for any area of the AP® English Language Exam.
General Tips for Taking the AP® English Language Exam
Keep these 7 tips in mind as you study and as you take the test:
- In your essays, be as specific as you can. Reference the names and definitions of rhetorical techniques whenever possible, as well as specific sections in your passages.
- Don’t write down anything you can’t back up logically, especially any kind of broad generalizations – the AP® English Language examiners hate those.
- Think critically and eliminate easy-to-fix problems. Cross out any answers that you know are wrong for a multiple choice question . Don’t spend too much time “fluffing up” your essay – stick to what’s relevant.
- Use all the resources you have at hand – the articles available on this site, other Internet guides on how best to study, and books such as Fast Track to a 5 . Best of all, free sample questions (taken from previous years’ tests) are available for all sections of the AP® English Language and Composition Exam at AP® Central and Albert.io .
- Don’t stick too hard to formulas you learned in middle school or earlier high-school classes on essay questions – although there are conventions you can follow, the AP® readers will respect creativity as long as it is focused.
- Read passages twice if possible – the first reading being a skim for the main ideas and the second a full reading.
- Don’t let your nerves beat you. Practice staying calm during the test itself; the more you prepare the easier it will be. The test, although it is important, is not the end-all-be-all of your life, and should never be treated as such. Go in ready to take it seriously, but also with confidence in yourself. You know how to study for study for AP® English Language – you know how to succeed on the exam too.
Looking for AP® English Language practice?
Kickstart your AP® English Language prep with Albert. Start your AP® exam prep today .
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
All Subjects
Argument Essay: Evidence
8 min read • june 18, 2024
Stephanie Kirk
We aren’t sure where it started, but many teachers use REHUGO to help students find evidence on the Argument FRQ . This acronym provides a quick check that can help you build logical evidence that supports your claim .
- R - Reading - Something you have read, fiction or nonfiction, that connects the given topic.
- E - Entertainment - A movie or song with dialogue or lyrics that present related ideas.
- H - History - An event, document, speech, or person from history that aligns with the given topic.
- U - Universal Truths - A common maxim or socially-accepted quote people tend to accept as truth.
- G - Government - A national or international current event or governmental situation related to the topic.
- O - Observations - Any cultural, technical, or societal trend that relates to the topic.
Suggested Guided Questions for the Argument FRQ
Now that you have a better understanding of the Argument FRQ’s expectations and scoring, let’s visit a sample prompt and add a few guided questions that you can use to help plan your own writings.
| In his book Canadian journalist Malcolm Gladwell (born 1963) writes: “To assume the best about another is the trait that has created modern society. Those occasions when our trusting nature gets violated are tragic. But the alternative—to abandon trust as a defense against predation and deception—is worse.”Write an essay that argues your position on the importance of . |
Guided Question 1: What does the prompt say? 📝
- Why do I do this? Understanding the concept or idea presented by the prompt is vital to planning a response that thoroughly addresses the prompt and stays on topic throughout. This is where you are going to BAT the PROMPT .
- Background : Gladwell asserts that society should trust each other in order to continue to be productive. Assuming the best about each other presents a better outcome than assuming the worst about each other.
- Advice : The new stable prompt wording does not give much advice, but you should revisit advice you learned in class or from us as Fiveable -- things like using Toulmin to plan your response and planning modes of development that help progress your reasoning.
- Task : Write an essay giving your position about the importance of trust. Specifically, is Gladwell right or wrong? And why? 🎥 Watch: AP Lang - Argumentation, Part I: It's a Trap!
Rhetorical Situation : When writing for AP Lang, it is important to consider the rhetorical situation and write in a manner that demonstrates an understanding of all elements of that situation.
- Context - the historical, social, and cultural movements in the time of the text
- Exigence - the urgency that leads to an action
- Purpose - the goal the speaker wants to achieve and the desired audience movement
- Persona - the “mask” shown to his/her audience

Guided Question 2: What do I think? 💡
Why do I do this? Taking a moment to brainstorm ideas can help organize thoughts and build an outline that you can revisit if you lose your train of thought in the stress of timed writing.
What does it look like? This might just be stream-of-consciousness in your head, cloud diagrams, or even bulleted notes on the side of your prompt, but it needs to end with a clear position statement you can use for your thesis statement . For example: Trust is important. It does suck to get betrayed though but having a positive outlook creates positive results. Thinking the worst makes people act negatively because they project in a way that leads toward the worst response. ⬇️
- Thesis Statement: Although some people believe humanity seems self-interested, a trusting nature enables individuals to focus on the positive and treat others with the respect that foster positive interrelationships.
Guided Question 3: What evidence can I use? 🤔
- Why do I do this? Revisit REHUGO and use Toulmin to plan your body paragraphs based on the thesis statement you came to when brainstorming ideas.
- Modes of Development: When writing, it is helpful to arrange the overall essay and its parts in a way that aligns with the purpose. Consider these basic modes and how you might use them in writing an argumentative essay.- Cause and Effect attempt to follow the chain of events and establish causation. The description brings imagery and details into a text so that it set up the tone and ensures the reader can follow the mood.- Classification allows the speaker to categorize things in a way that guides the reader to follow the line of reasoning.- Comparison , looking at the similarities and differences, helps to analyze the intricate details of a given topic. Because this describes differing elements, it may be structured by the element or by the characteristic.- Definition works to explain what something is or is not. By defining the subject being discussed, the speaker is able to control the thinking about that subject. Because this helps to clarify the topic, it is generally used in the introductory section of argumentation.- Exemplification is used when explaining the topic or situation by giving examples to help lead the audience to the desired conclusion.- Narration tells a story or gives an anecdote to help illustrate the point.- Process Analysis serves to explain the process by which something is done.
- What does it look like? I always use a version of the T-chart because one side is my evidence and the other side helps me consider multiple perspectives. You may not have an idea in all areas, and you may have multiple ideas in one area. Try to time yourself so that you get plenty of strong evidence without wasting too much time. | Supports 🏗️ | Thoughts 💭 | | --- | --- | | ~ R - Trust in Society by Cook points out that we only realize the importance of trust when there’s a breakdown.~ R - Essay “Importance of Trust” from class said that trust is not easy but it is what builds the foundation of a relationship and drives all actions between sides.~ E - The 2011 movie Trust shows that too much trust can get you hurt or killed.~ E - The media has so much bias it can’t be trusted… ~ H - Revolutionary War - trusted founding fathers and God’s position resulting in breaking free from Britain~ U - Trust - People should be trusted until proven otherwise~ G - A criminal escaped in our town and was on the loose; we trusted police to do their job rather than resort to vigilante justice~ G - Trust the president will have our best interests at heart -- most appear to have done that~ O - App-based dating - relies on trusting the person you meet online before meeting in person | > relationships between couples> trust in contractual agreements? Moral obligation for trust?> Counter?> Relied on trust and won with not much else to go ob> Ex, Parents, Teachers, Siblings > Trust helped keep us safe; job was well done when we were out of the way> Obvious exceptions; System of impeachment |
🎥 Watch: AP Lang - Review: Argument Body Paragraphs
PRO TIP: What if you have more evidence for the other side? Well, you haven’t started writing just yet, so it isn’t too late to go back and revise the thesis statement. Sometimes this happens in looking for evidence, and that’s perfectly okay. In fact, many times students will say they wrote an essay using evidence that went completely against what they felt in their head or heart just because they couldn’t put a logical argument on paper without getting too emotional. Know your audience, and build your argument.
Guided Question 4: How should I effectively organize my response? 📈
- Why do I do this? This step helps to outline the response so that your ideas are organized before you start writing. The general advice is to follow the structure of Classical Argumentation , but there is no rule saying that must be done to score well on the rubric. 💯
- What does it look like? One way of doing this would be to mark numbers by ideas tracked and written in the brainstorm, but some do take a moment to build an outline with topic sentences.
- Modes of Development: When writing, it is helpful to arrange the overall essay and its parts in a way that aligns with the purpose. Consider these basic modes and how you might use them in writing an argumentative essay.- Cause and Effect attempt to follow the chain of events and establish causation. The description brings imagery and details into a text so that it set up the tone and ensures the reader can follow the mood.- Classification allows the speaker to categorize things in a way that guides the reader to follow the line of reasoning.- Comparison , looking at the similarities and differences, helps to analyze the intricate details of a given topic. Because this describes differing elements, it may be structured by the element or by the characteristic.- Definition works to explain what something is or is not. By defining the subject being discussed, the speaker is able to control the thinking about that subject. Because this helps to clarify the topic, it is generally used in the introductory section of argumentation.- Exemplification is used when explaining the topic or situation by giving examples to help lead the audience to the desired conclusion.- Narration tells a story or gives an anecdote to help illustrate the point.- Process Analysis serves to explain the process by which something is done.
- Start by creating Toulmin Position Statements that can be used for topic sentences and then move into a writing plan. Here’s a sample for this prompt:
Sample Outline:
- Revised Thesis: Although some people believe trust must be earned, maintaining a trusting nature is important because it enables society to focus on positivity and create positive interrelationships that lead to positive outcomes.
- Universal truth
- Observation
- Entertainment - refute
- Conclude: When considering the value of trust in society, it is clear that the benefits of granting trust far outweigh the consequences of withholding it.
Key Terms to Review ( 35 )
© 2024 fiveable inc. all rights reserved., ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..
AP English Language and Composition Writing Study Skills
Writing is central to the AP English courses and exams. Both courses have two goals: to provide you with opportunities to become skilled, mature, critical readers, and to help you to develop into practiced, logical, clear, and honest writers. In AP English, writing is taught as “process”—that is, thinking, planning, drafting the text, then reviewing, discussing, redrafting, editing, polishing, and finishing it. It’s also important that AP students learn to write “on call” or “on demand.” Learning to write critical or expository essays on call takes time and practice.
Here are some key guidelines to remember in learning to write a critical essay:
- Take time to organize your ideas.
- Make pertinent use of the text given to you to analyze.
- Quote judiciously from the text to support your observations.
- Be logical in your exposition of ideas.
If you acquire these skills—organizing ideas, marshalling evidence, being logical in analysis, and using the text judiciously—you should have little trouble writing your essays on the AP Exam. Practice in other kinds of writing—narrative, argument, exposition, and personal writing—all have their place alongside practice in writing on demand.
As you study and practice writing, consider the following points.
Reading directly influences writing skills and habits.
Reading and writing are intertwined. When you read what published authors have written you are immersed not just in their ideas, but in the pulsing of their sentences and the aptness of their diction. The more you read, the more that the rhythm of the English language will be available to influence your writing. Reading is not a substitute for writing, but it does help lay the foundation that makes good writing possible.
Writing is fun.
When you have penned what you think is a great sentence or a clean, logical paragraph, read it over to yourself out loud. Enjoy it. Delight in the ideas, savor the diction, and let the phrases and clauses roll around in your mind. Claim it as part of yourself. You may discover you have a voice worthy of respect.
A tip from E. M. Forster
He is reputed to have said that he never knew clearly what it was he thought until he spoke it; and once he had said it, he never knew clearly what it was that he said until he had written it down. Then, Forster noted, he could play with it and give it final form. Be like Forster: think, speak, write, analyze your writing, then give it final shape.
Write purposefully with rhetorical awareness.
When you write, fashion your text with awareness of key rhetorical elements. What is the message of your text? How do you intend to convey your message to your particular audience? Give shape to your thinking with language that enlightens your readers and lets you achieve your aims.
Pay close attention to the task verbs used in the free-response questions. Each one directs you to complete a specific type of response. Here are the task verbs you’ll see on the exam:
- Analyze: Examine methodically and in detail the structure of the topic of the question for purposes of interpretation and explanation.
- Argue your position: Formulate a claim and support it with evidence.
- Read: Look at or view printed directions and provided passages.
- Synthesize: Combine different perspectives from sources to form a support of a coherent position.
- Write: Produce a response in writing.
Get the Reddit app
No matter what course you are taking, we are a community that helps students earn college credit!
AP Lang exam tips you may not have heard
Hello everybody! The UWorld English team is a group of former AP teachers and AP readers. We talked together and came up with this short list of tips that might help you for your exam.
Reading MCQs
People think the answers are subjective; they're not. Right answers are completely supported by evidence, while wrong answers are sort of supported or not at all.
Don't waste time studying a bunch of terms. Instead, make sure you know these words: exigence, qualify/qualification, ambiguous, underscore, and undermine (not the same thing).
Answer questions about specific lines/paragraphs first. Answer questions about the overall passage last.
Pay attention to how the questions/ answers actually help you understand the passage.
Writing MCQs
You got these. Fuhgeddaboudit. But if you do need help, think about these ideas.
Biggest tip: Writing MCQs are really reading questions in disguise. Read the whole draft.
You can get away with not reading the writing passages on the SAT, but not here. They won't ask about punctuation or grammar; they are primarily asking about coherency and support. That means you have to know what direction the draft is going so you can choose the best organization and support for its claims.
Transition questions: Identify what the information after the transition does (3 basic categories). Does it...
contrast the info that came before it?
give more of the same as what came before it?
clarify the information that came before?
Choose the transition word/phrase that accurately communicates what the info does.
Style questions: To choose the best word or to decide whether to keep/delete a word, consider these two things:
How formal or casual is the language in the draft?
Is the tone more positive or negative?
The right answer will be as formal/casual as the rest of the language and will likely match the positivity/negativity of the rest of the draft.
Bias questions: Pick the answer that has no bias (prejudice).
Look at connotations and pick the answer that's most neutral. (eg. Calling someone a "health nut" makes them sound a little crazy = biased. Saying someone is a "health-conscious consumer" is neither good nor bad = unbiased.)
Crediting a source questions : Pick the most specific answer.
The right answer gives specific info about who/what the source is and why it can be trusted. (eg. My dad says he makes the best cookies. = So? Prove it. My dad, Tim Casey, the CEO of Mrs. Fields' Cookies, says he makes the best cookies. = Ok, he's got cred.)
Add/Keep/Delete questions : Whether a sentence stays or goes, it's all about picking the right reason for it.
Decide if the info in question actually does what the answer choice claims. (eg. Keep it, because it provides evidence from a scientific study ( does it? ) that supports the claim that ants are more intelligent than humans ( does the evidence actually support that claim? )
Synthesis essay
Easiest essay IMO. Don't read all 6-7 sources. No need.
This essay, like the Arg essay, will use a topic that there's not a clear yes/no, good/bad opinion on. It will have complexity; everybody's perspective will have something positive and negative about it. Acknowledge that, but write in a more opinionated way about one perspective than the other = 70% your opinion, 30% opposition's point of view. Do NOT write a 50/50 essay.
Pick 2 pieces of evidence to support your argument and 1 from the opposition to use as a concession or to refute. That gets you points for using 3 pieces of evidence and lets you write a couple of good body paragraphs.
Rhetorical analysis essay
If the passage is more modern, it's the second easiest essay.
Consider these questions: How does the speaker make the topic sound? How did you know? That's really the crux of the entire essay.
Remember, nearly anything a writer does in the text can be a strategy, and it's ok if there's not an official "literary" name for it. For example, using we/us = unifying language. Talking about his background = building credibility. Shaming the audience = guilt trip. The first paragraph is a good place to look for strategies because writers have to work hard to engage their audience.
Top essay score is a 6. You can make an easy 4. Here's how:
ALWAYS write a thesis = 1 point.
The most common point split for Evidence and Commentary is between a 2 and 3. Don't summarize the passage; that only earns you a point. Pick something specific the speaker does to get his purpose across and explain how the speaker makes it work = 2 points. Do it again = 3 points. Anything beyond that is gravy.
Don't worry about the Sophistication point. It will either come out of your pen or it won't.
Argument essay
Hardest one. If you're stuck for ideas, try using the "ripple effect." Start close and venture out. Think of a personal example, an example from someone you know/ something you've seen, then something/someone famous, influential, or historical. Valid examples can come from art, science, sports, music, gaming, and entertainment. They don't always have to come from a textbook.
Same general tips apply as in the RA essay. Must write thesis = 1 point. Explain how one example proves your point = 2 points. Explain how two examples prove your point = 3 points. More than two examples = o7
Caution: Don't get lost in telling all the details of your example. Just focus on the parts that tie into the point you're making and spend your energy explaining how your example proves it.
Remember that the best thing you can do for your MCQ score is to practice questions with comprehensive explanations. We have hundreds of questions like this here .
Good luck on your studies!
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
What is the ap lang rhetorical essay, tips for writing the ap lang rhetorical essay.
- AP Lang Rhetorical Essay Example
How Will AP Scores Affect College Chances?
The AP English Language Exam is one of the most common AP exams you can take. However, the average score on the exam in 2020 was a 2.96 out of 5. While this may seem a bit low, it is important to note that over 550,000 students take the exam annually. With some preparation and knowing how to study, it is totally possible to do well on this AP exam.
The AP Lang Rhetorical Essay is one section of the AP English Language Exam. The exam itself is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, and is broken into two sections. The first part of the exam is a 60 minute, 45-question multiple-choice section. The questions on this part of the exam will test your ability to read a passage and then interpret its meaning, style, and overall themes. After the multiple-choice section, there is a section lasting 2 hours and 15 minutes with three “free response” essays. This includes the synthesis essay, the rhetorical analysis essay, and the argument essay.
- In the synthesis essay , you will have to develop an argument using pieces of evidence provided to you.
- The argumentative essay will have you pick a side in a debate and argue for or against it.
- The rhetorical essay requires that you discuss how an author’s written passage contributes to a greater meaning or theme.
The rhetorical essay is perhaps the most unique of all AP Lang exam essays because it requires the test taker to analyze and interpret the deeper meanings of the passage and connect them to the author’s writing style and writing syntax in only 40 minutes. This essay can be the trickiest because it requires you to have knowledge of rhetorical strategies and then apply them to a passage you’ve never seen before.
1. Outline Your Essay Before Writing
One of the most important parts of the AP Lang essays is structuring your essay so that it makes sense to the reader. This is just as important as having good content. For this essay in particular, you’ll want to read the passage first and write a brief outline of your points before you begin the essay. This is because you will want to write the essay using the passage chronologically, which will be discussed in detail below.
2. Understand Rhetorical Strategies
If you feel like you don’t know where to start as you prepare to study for the rhetorical essay portion of the exam, you aren’t alone. It is imperative that you have a grasp on what rhetorical strategies are and how you can use them in your essay. One definition of rhetoric is “language carefully chosen and arranged for maximum effect.” This can include types of figurative language (metaphor, simile, personification, pun, irony, etc.) elements of syntax (parallelism, juxtaposition, anthesis, anaphora, etc), logical fallacies, or persuasive appeals. Overall, there are many elements that you can analyze in an essay and having a good grasp on them through practice and memorization is important.
3. Keep the Essay Well Structured
Even if you understand the various rhetorical strategies you can use, where do you begin? First of all, you’ll want to write a strong introduction that outlines the purpose of the piece. At the end of this introduction, you will write a thesis statement that encapsulates all the rhetorical strategies you discuss. Perhaps these are style elements, tone, or syntax. Be sure to be specific as you list these.
Next, you will create your body paragraphs. As you discuss the rhetorical elements in the piece and tie them back to the work’s meanings, be sure to discuss the points in chronological order. You don’t have to discuss every single strategy, but just pick the ones that are most important. Be sure to cite the line where you found the example. At the end of the essay, write a short conclusion that summarizes the major points above.
4. Be Sure to Explain Your Examples
As you write the essay, don’t just list out your examples and say something like “this is an example of ethos, logos, pathos.” Instead, analyze how the example shows that rhetoric device and how it helps the author further their argument. As you write the rhetorical essay, you’ll want to be as specific and detail-focused as possible.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Below is a prompt and example for a rhetorical essay, along with its score and what the writer did well and could have improved:
The passage below is an excerpt from “On the Want of Money,” an essay written by nineteenth-century author William Hazlitt. Read the passage carefully. Then write an essay in which you analyze the rhetorical strategies Hazlitt uses to develop his position about money.

Student essay example:
In his essay, Hazlitt develops his position on money through careful use of adjectives and verbs, hypothetical situations, and images. His examples serve to impress upon the reader the highly negative consequences of being in “want of money.”
Hazlitt’s word choice in his opening phrase provides an example of his technique in the rest of the essay. It is not necessary to follow “literally” with “truly” yet his repetition of the same ideas emphasizes his point. In his next sentence, one that lasts forty-six lines, Hazlitt condignly repeats similar ideas, beating into his audience the necessity of having money in this world. The parallelism throughout that one long sentence, “it is not to be sent for to court, or asked out to dinner…it is not to have your own opinion consulted or sees rejected with contempt..” ties the many different situations Haziltt gives together. What could have become a tedious spiel instead becomes a melodious recitation, each example reminding you of one before it, either because of the similarities in structure or content. Hazlitt addresses many different negative effects of not having money but manages to tie them together with his rhetorical strategies.
The diction of the passage fully relays Hazlitt’s position about money. In every example he gives a negative situation but in most emphasizes the terrible circumstance with strong negative adjectives or verbs. “Rejected,” “contempt,” “disparaged,” “scrutinized,” “irksome,” “deprived,” “assailed” “chagrin;” the endless repetition of such discouragement shows how empathetically Hazlitt believes money is a requisite for a happy life. Even the irony of the last sentences is negative, conveying the utter hopelessness of one without money. Through one may have none in life, pitiless men will proceed to mock one’s circumstances, “at a considerable expense” after death!
In having as the body of his essay one long sentence, Hazlitt creates a flow that speeds the passage along, hardly giving the reader time to absorb one idea before another is thrown at him. The unceasing flow is synonymous with Hazlitt’s view of the life of a person without money: he will be “jostled” through life, unable to stop and appreciate the beauty around him or to take time for his own leisure.
The score on this essay was a 6 out of 6. This essay started out very strong as the student had a concrete thesis statement explaining the strategies that Hazlitt used to develop his position on money as well as Hazlitt’s belief on the topic. In the thesis statement, the student points out that adjectives, verbs, hypothetical situations, and images help prove Hazlitt’s point that wanting money can be problematic.
Next, the student broke down their points into three main subsections related to their thesis. More specifically, the student first discusses word choice of repetition and parallelism. When the student discusses these strategies, they list evidence in the paragraph that can be found chronologically in Hazlitt’s essay. The next paragraph is about diction, and the student used specific adjectives and verbs that support this idea. In the last paragraph, the student emphasized how the speed and flow of the essay helped describe Hazlitt’s viewpoint on life. This last concluding sentence is particularly thoughtful, as it goes beyond the explicit points made in the essay and discusses the style and tone of the writing.
It is important to remember that in some ways, the rhetorical essay is also an argumentative essay, as the student must prove how certain rhetorical strategies are used and their significance in the essay. The student even discussed the irony of the paragraph, which is not explicit in the passage.
Overall, this student did an excellent job organizing and structuring the essay and did a nice job using evidence to prove their points.
Now that you’ve learned about the AP Lang rhetorical essay, you may be wondering how your AP scores impact your chances of admission. In fact, your AP scores have relatively little impact on your admissions decision , and your course rigor has much more weight in the application process.
If you’d like to know your chances of admission, be sure to check out our chancing calculator! This tool takes into account your classes, extracurriculars, demographic information, and test scores to understand your chances at admission at over 600 schools. Best of all, it is completely free!
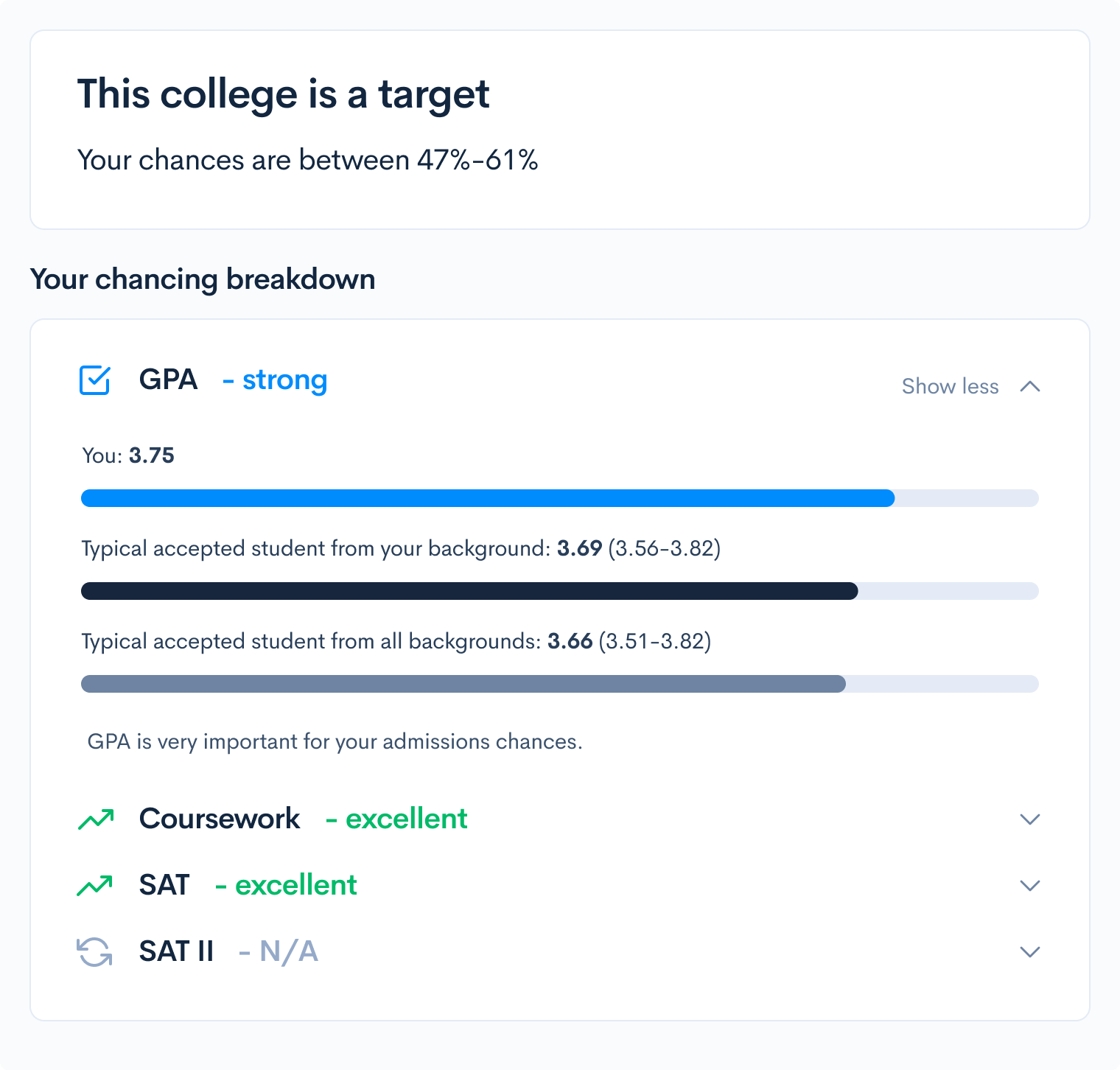
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Sharks are taking a bite out of anglers’ catch in the Gulf of Mexico, but culling isn’t likely to help
Associate Extension Professor in Marine Fisheries Ecology, Mississippi State University
Disclosure statement
James Marcus Drymon has received funding from NOAA Fisheries and the Gulf States Marine Fisheries Commission to study depredation.
Mississippi State University provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
Fishermen across the Gulf of Mexico are reporting that something is eating fish off their lines. What’s to blame? Many recreational anglers point a finger at sharks .
This conflict has caught politicians’ attention. Congress has directed the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , which regulates fishing in U.S. waters, to review shark and dolphin interactions with fisheries , and the U.S. House of Representatives recently passed the SHARKED Act , which would create a task force to address the problem.
I’ve studied this conflict, which is formally called depredation , for the past decade. While some shark populations in the Gulf of Mexico, such as bull sharks, are increasing , my colleagues and I have found evidence that human perceptions are also an important factor.
Sharky waters
The Gulf of Mexico is home to more than 70 species of sharks – and those are just the ones that scientists know about. The field of shark research has grown dramatically in recent decades , and new species are still being discovered.
For example, the American pocket shark , which is literally pocket-size, wasn’t discovered until 2019. This tiny shark lives in deep water far from shore and secretes a glowing blue fluid from small “pocket” glands near its front fins, for a purpose scientists have yet to determine.
Many other species, including bull sharks and sandbar sharks , are found in coastal waters. This creates the potential for conflict with anglers.
Shark predation on captured fish isn’t new. In Ernest Hemingway’s 1952 Pulitzer Prize-winning novella “ The Old Man and the Sea ,” an aging Cuban fisherman struggles to catch a giant marlin, only to see it eaten by sharks on his voyage home.

Hemingway himself contended with shark depredation as he attempted to land bluefin tuna in Bimini, the Bahamas. Kip Farrington, a longtime Field & Stream magazine editor and Hemingway confidante, noted that “none of these magnificent fish have ever been boated near Bimini unmarked by sharks.” Today, anglers often refer to sharks as “the tax man.”
Humans preying on sharks
Sharks have been harvested commercially in the Gulf since the 1930s. Catches increased during World War II, partly because shark livers were used in the production of Vitamin A , and declined after 1950 with the development of synthetic vitamins.
Shark catches surged again in the 1980s, encouraged by federal regulators, who saw sharks as an “ underutilized resource .” Yet within a decade, scientists determined that several stocks of Gulf sharks were overfished, including sandbar sharks and dusky sharks .
In 1993, NOAA issued the first federal fishery management plan for sharks in U.S. waters of the Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico. These regulations created a pathway to rebuild stocks by requiring permits and establishing recreational trip limits and commercial catch quotas.
Today, many of the Gulf’s overfished shark stocks are recovering . As evidence grows that sharks are an important component of healthy oceans , this is a conservation success story. However, many anglers blame increases in depredation on regulations enacted to rebuild shark populations.
Shifting baselines
Experts agree that there are more sharks in the Gulf of Mexico today than there were 30 years ago. But how do these populations compare with levels before 1989, when commercial shark fishing spiked?
Over time, this question becomes increasingly difficult to answer as people gradually accept environmental decline. Marine biologist Daniel Pauly calls this habituation “ shifting baseline syndrome .” For fisheries, each new generation of fishermen accepts the current, often reduced, status of a fish population as the baseline and forgets that there was a time when these species were much more abundant.
In this case, modern anglers are comparing increased numbers of sharks in the Gulf of Mexico to the past 30 years – a time when many shark populations were overfished.
Lifting baselines
The recovery of populations that were once overfished can create an opposite situation, known as lifting baselines , with conservation and management efforts leading to population increases.
Instances where populations have been overfished and then rebuilt can create a perception of overabundance. When the species that’s recovering is a predator, that can lead to human-wildlife conflict.
For example, recovering populations of California sea lions now compete with fishermen for their catch along the Pacific coast. Off Cape Cod, Massachusetts, the same thing happens with gray and harbor seals . The seals, in turn, are attracting white sharks .
The call to cull
Sportfishing is a popular and lucrative year-round industry across the Gulf of Mexico. As reports of depredation increase, so do calls for culling shark populations .
Similar action has been proposed elsewhere for other marine predators, including sea lions in California and goliath groupers in Florida .
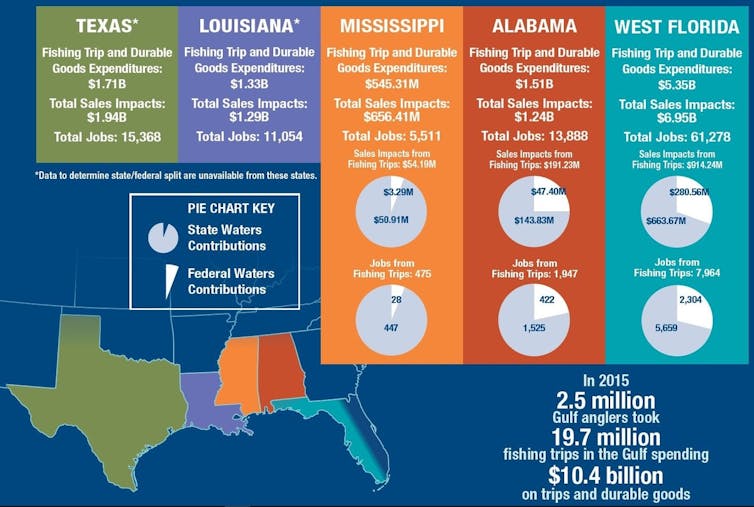
Studies show, however, that predator removal is rarely an effective strategy . It’s particularly ineffective for species such as sharks that move around a lot and will readily recolonize areas that have been culled. Predator culls also pit people with different values, such as fishing boat operators and conservationists, against each other .
Paying the tax man
Unfortunately, there is no silver-bullet solution for shark depredation. The Gulf’s sportfishing industry has grown, and it’s likely that sharks learn to associate the presence of boats with an easy meal.
Shark deterrents are available, and new versions are continually being developed. Some fishermen are changing their practices to avoid sharks – for example, shifting locations frequently and never anchoring or fishing farther offshore to avoid coastal species such as bull sharks.
NOAA-funded research has identified sandbar sharks and bull sharks as the species that prey most often on catch . The agency is analyzing ways to better measure depredation and assess stocks of these two species to understand their population trends.
In my view, measures like these, along with better data about which sharks are taxing fishermen and where, are the most promising ways to help anglers coexist with sharks in the Gulf.
- Endangered species
- Overfishing
- Human-wildlife conflict
- Gulf of Mexico
- recreational fishing

Administration and Events Assistant

Head of Evidence to Action

Supply Chain - Assistant/Associate Professor (Tenure-Track)

OzGrav Postdoctoral Research Fellow

Casual Facilitator: GERRIC Student Programs - Arts, Design and Architecture

IMAGES
COMMENTS
AP® English Language Free Response Question Review: 19 Tips 1. Spend time analyzing the question. Make sure you read the essay prompt many times and identify the key question being asked. AP® English Language questions can be tricky and demand multiple readings. Approach the question from each side of the possible argument that it poses.
If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected]. Note: The table below features a selection of free-response questions and related scoring information from the 2020 exam.
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Language and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. ... Students write essays that respond to 3 free-response prompts from the following categories: Synthesis Question: ...
Course Overview. AP English Language and Composition is an introductory college-level composition course. Students cultivate their understanding of writing and rhetorical arguments through reading, analyzing, and writing texts as they explore topics like rhetorical situation, claims and evidence, reasoning and organization, and style.
2. Pick one side of the argument, but acknowledge the other side. When you write the essay, it's best if you pick one side of the debate and stick with it for the entire essay. All your evidence should be in support of that one side. However, in your introductory paragraph, as you introduce the debate, be sure to mention any merit the ...
5 AP® English Language and Composition FRQ Study Tips. 1. Practice answering questions from The College Board's archive of past exam questions. Typically, the same skills are assessed from year to year, so practicing with released exams is a great way to brush up on your analysis skills. 2.
Step 5: Write your Essay. Use the remaining 30-35 minutes to write your essay. This should be relatively easy if you took the time to mark up the sources and have a detailed outline. Remember to add special consideration and emphasis to the commentary sections of the supporting arguments outlined in your thesis.
Format of the 2024 AP English Language and Composition exam. This year, all AP exams will cover all units and essay types. The 2024 AP English Language and Composition exam format will be: Section I: Multiple Choice - 45% of your score- - 45 questions in 1 hour. Section II: Free Response Section - 55% of your score- - 2 hours and 15 minutes for ...
The three Writing passages are student-produced essays. The idea is to get you to revise the essay that help the writer accomplish his or her goal. Free Response . The AP English Language section contains three essay prompts: a synthesis essay, a rhetorical analysis essay, and an argument essay.
The newest section of the AP® English Language and Composition Exam, the synthesis essay, is one of three essays you will be completing during the examination's 2-hour free-response period. However, you'll also have a 15-minute reading and planning period just for this essay, and if you use this time to plan effectively, you can't go wrong.
The six major components of successfully writing a timed essay on an exam are: Organizing your time. Reading and Annotating. Outlining Part 1: Thesis. Outlining Part 2: Structure. Writing Part 1: Paragraphs (Intro, Evidence, Analysis, Conclusion) Writing Part 2: Sentence by Sentence.
AP Language and Composition Score Distribution, Average Score, and Passing Rate. In 2019, 54.3% of the students who took the AP English Language and Composition exam received a score of 3 or higher. Only 9.9% of students who took the exam achieved the top score of 5, and 14.5% of students who took the exam scored a 1.
The AP English Language and Composition Multiple-Choice. The multiple-choice section tests you on two main areas. The first is how well you can read and understand nonfiction passages for their use of rhetorical devices and tools. The second is how well you can "think like a writer" and make revisions to texts in composition questions.
Typically, the AP Lang Argument Essay prompt asks you to reflect on a broad cultural, moral, or social issue that is open to debate. For evidence, you won't be asked to memorize and cite statistics or facts. Rather, you'll want to bring in real-world examples of: Historical events. Current-day events from the news.
If you're planning to take the AP Language (or AP Lang) exam, you might already know that 55% of your overall exam score will be based on three essays.The first of the three essays you'll have to write on the AP Language exam is called the "synthesis essay." If you want to earn full points on this portion of the AP Lang Exam, you need to know what a synthesis essay is and what skills are ...
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you ...
How to Study For AP® English Language. There are four main things you need to study and practice for - the multiple choice section, the synthesis essay, the argument essay, and the rhetorical analysis essay. Since there are about four weeks in a month, you can use one week to work on each section by doing sample questions, talking to your ...
It is typically based on the knowledge and experience of the person offering it. Argument FRQ: An Argument FRQ (Free Response Question) is an essay question on the AP English Language exam that requires students to construct and defend an argument using evidence and rhetorical strategies. Audience: The audience refers to the intended recipients ...
Writing is central to the AP English courses and exams. Both courses have two goals: to provide you with opportunities to become skilled, mature, critical readers, and to help you to develop into practiced, logical, clear, and honest writers. In AP English, writing is taught as "process"—that is, thinking, planning, drafting the text, then reviewing, discussing, redrafting, editing ...
The two synthesis essay questions below are examples of the question type that has been one of the three free-response questions on the AP English Language and Composition Exam as of the May 2007 exam. The synthesis question asks students to synthesize information from a variety of sources to inform their own discussion of a topic. Students are given a 15-minute reading period to accommodate ...
ADMIN MOD. AP Lang exam tips you may not have heard. Hello everybody! The UWorld English team is a group of former AP teachers and AP readers. We talked together and came up with this short list of tips that might help you for your exam. Reading MCQs. People think the answers are subjective; they're not. Right answers are completely supported ...
AP ® English Language and Composition ... Stronger essays used commentary to explain how the evidence supported the larger claim. Sample: 3A Score: 1-4-1 Thesis (0-1) points: 1 . The thesis, which is stated at the end of paragraph 1, takes a nuanced position on the value of striving for
Tips for Writing the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay. 1. Outline Your Essay Before Writing. One of the most important parts of the AP Lang essays is structuring your essay so that it makes sense to the reader. This is just as important as having good content. For this essay in particular, you'll want to read the passage first and write a brief ...
A Gulf angler races to land a fish before sharks take it. Sharky waters. The Gulf of Mexico is home to more than 70 species of sharks - and those are just the ones that scientists know about.