135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples
Completing a psychology course, studying child development, or simply analyzing social influence on teenagers? You might need to write an adolescence essay, and we are ready to help with that.

✨ Top Adolescent Psychology Topics
🏆 best adolescence topic ideas & essay examples, 📑 good research topics about adolescence, 🎓 interesting adolescent research topics, 👍 good essay topics on adolescence, ❓ research questions about adolescence.
Our Ivypanda team has collected a list of great ideas for different assignments related to the subject. So, check our adolescent research topics and essay titles to nail your academic paper.
- Ethical Issues of Social Media.
- Reaction to Physical Changes.
- Depression Among Adolescents.
- Parental vs. Social Influence.
- Must-See Youth Documentaries.
- Preventing Teenage Pregnancy.
- Dating & First Relationships.
- Reproductive Health Stigma.
- Impact of Peer Pressure on Development.
- Connection Between Mental Health & Social Media.
- Vygotsky’s Approach to the Analysis of Adolescence In Vygotsky’s view, the change in the motives of adolescence come about due to the growth of sexual desires and needs which are as a result of their ability to think logically.
- Psychology of Adolescence Development The strategy allows the examination of the significance of adolescence as a standard stage of development. However, she admits that she experienced a period of anxiety and distress upon the death of her mother when […]
- Adolescence as a Social Construct As a social construct of society, adolescence is viewed as the object of fear and anxiety by the rest of society’s members.
- Adolescence as a Period of Social Development Adolescents transition from the restricted responsibilities of childhood to the more expansive roles of adulthood through the social development process, expanding their social networks and experiencing peer influence.
- Adolescence as a Stage of the Person Development Adolescents struggle with so many things, start with, because of their physical changes that occur in their bodies and their exploration of sexual identity, most of them are not able to control their bodies and […]
- Adolescence: Behavioral Issues and Communication Strategies Despite the fact that these issues occur naturally and are frequent for the majority of the representatives of this age group, the traumas and incapability to cope with the challenges might result in adverse outcomes […]
- Family Issues and Adolescence in Crazy/Beautiful The film Crazy/Beautiful is a vivid example of relationships between teenage children and their parents: The problems and situations shown in the film are typical and timeless.
- Middle Childhood and Adolescence Periods Observation The first participant is a boy of 7, and the following series of questions will be offered to him: Do you like watching the outside world and nature changes?
- Risk-Taking Behaviors and Situations During Adolescence Risk-taking behavior in adolescents is a significant bother for the US healthcare system, as it negatively affects the health and well-being of the population.
- Adolescence: Biological and Psychosocial Perspectives Adolescence as a social construction is more complex as a concept and entails definitional vagueness regarding the beginning and the ending of adolescence, for example, social-role passages into new reference groups, perceptions of the body, […]
- Influence of Heavy Metal Music on Adolescence (Behavior, Identity, Mood, Regulation, Psychology) Accepting the potent impact of music on adolescents’ behavior, identity, and psychology leads to a deeper analysis of the influences of heavy metal music on teenagers’ development.
- Childhood, Adolescence, Young Adulthood Psychology Any intervention that can be used in the prevention of child abuse should focus on the causes of the same and the needs of children who are more prone to abuse.
- Adolescence and Adulthood Developmental Stages – Psychology The onset of adolescence marks the refinement of most individuals’ thinking abilities because at this stage the majority of individuals would have attained control in their thinking process.
- The Problem of Adolescence Pressures in Society Early adolescence start at the age of 10 to 14 while the late adolescence is from 15 to 21years in boys but girls are said to attain early maturity at the age of 19 years.
- Circumstances Causing Stress in Adolescence Hold one’s breath for many seconds and gently exhale via the mouth to evacuate the lungs, hence easing the body of stress. The more one is stressed, the more difficult and nervous it is to […]
- The Impact of Technology Development on the Adolescence Psychology The stability of the psyche in teenage society is on the minimum bar, and with few exceptions, teenagers are resistant to any criticism.
- Social Development and Adolescence: Human Services Ethics and Interventions The small circle of peer friends and the loss of a close relative provoke the feeling of loneliness and further progression of depression. A wide range of human service agencies can help Susie and her […]
- The Impact of Social Issues on the Development of Adolescence For example, boys have high esteem when they experience changes in their voices, while girls may feel shy due to the growth of their chest region.
- Depression in Adolescence and Treatment Approaches The age of adolescence, commonly referred to as children aged 10-19, is characterized by a variety of changes to one’s physical and mental health, as the child undergoes several stages of adjustment to the environment […]
- Different Stages of Adolescence Due to the rapid development, the body experiences difficulties in the work of the heart, lungs, and blood supply to the brain.
- Review of “The Legal Construction of Adolescence” Article However, as explained by Scott in The Legal Construction of Adolescence, there are several complications connected to clearly defining the end of childhood and the overall period of adolescence.
- Adolescence and Emotion Relations He attributes the occurrence of emotional problems to the overwhelming nature of the changes and demands that occur during puberty. The reaction of parents to their child’s emotional outbursts correlates to the cultivation of healthy […]
- Adolescence and Young Adulthood in Educational Psychology For Freud, it is inclusion in society, the beginning of social education, communication with peers, removing barriers in interpersonal contacts, and expanding the field of fixation of the object of attraction.
- Childhood and Adolescence Psychology One of the examples given about the effects of cultural differences in the definition of intelligence is between the Taiwanese and the Americans.
- Dating, Sex, and Romance: Adolescence and Digital Media Sexual education is significant for adolescents because, for them, the topic of sexual relations, dating, and romance is one of the most attractive ones.
- Adolescence Sexuality: Breaking Down the Myths In her work, Coming of Age in Samoa, she gave a vivid description on the variations in human behavior patterns among the adolescent girls in Samoa.
- Brain Development in Adolescence and Childhood I am going to describe the relation of moral reasoning, moral evaluations and moral behaviors in terms of worldviews approach to moral development according to Jensen. The next issue I am going to discuss is […]
- HIV and AIDS in Adolescents The teenagers in America and the world are a group that is constantly at risk of infection with the Human-Immunodeficiency-Virus and developing the Acquired-Immune-Deficiency-Syndrome, the disease condition that eventually results; this is stemming mainly from […]
- Syllabus for Life Among Adolescence This is a matter of pressure to the teenagers and this creates stress in them.”Early adulthood is the settling down period and most reproductive age.
- Adolescence and Risk Taking Analysis Studies show that children and adolescents around the world spend their maximum time watching television than they do in any other activity with an exception in the time of sleeping. The objective of this paper […]
- Adolescence Psychology: Development Early Through Late This number is approximate, because a lot of people with the disease are not aware of the symptoms and do not want to be tested on chlamydia.
- Depression and Psychotherapy in Adolescence Society needs to acknowledge that depression is a major medical problem among adolescents in the United States and measures need to be taken to address it.
- Development: Infancy Through Adolescence The evaluation of physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development in different age groups of childhood can be made due to the observation of specific subjects and conversations with them.
- Middle Childhood and Adolescence Development Children and adolescents need to be accepted by the peers, and the positive relations in groups contribute to increasing the children’s self-esteem and self-confidence.
- Psychology: Adolescence as a Developmental Stage Erik Erickson is referred to as the father of an identity crisis in that he originated with the idea of child upbringing practices and their influence on the personality of the child in later life.
- Human Development Theories: Adolescence and Adulthood In the growth and development stage of a human being, the adolescent period has been considered to be a natural stage found between childhood and adulthood.
- Addiction Occurrence and Reduction in Adolescence This implies that the earlier the start of the use of drugs, the higher the chances of the risk of becoming addicted.
- Loneliness in Adolescence as a Psychological Issue In the course of this, it will outline the background, state the hypothesis, speculate on the methods, and reflect on the conclusion which the author has arrived at.
- Adolescence: Risk, Identity and Transition There is a downside to this perspective is that it ignores the diversity in culture and differences among peers. The main problem however is that most of these youth have no experience with the real […]
- The Peculiarities of Adolescence and Puberty It is necessary to pay attention to the needs of students at risk, to the peculiarities of their interactions with other people and to the features of their awareness of themselves as personalities.
- Socioemotional Development in Adolescence Adolescence is a period that begins with the puberty, approximately at the age of 12, and ends with the early adulthood, in the 18th.
- Sexuality and Masculinity in Adolescents This is the misunderstanding which makes many teenagers behave in the way they are not to behave, to act in the way they are not to act and to act as in the result the […]
- Alcohol Consumption in Adolescence The hypotheses developed in this paper are of immense importance in guiding a study aimed at identifying credible evidence on how alcohol consumption during adolescence is associated with mental health challenges and increased STI risk […]
- Relationship Between Sleep and Depression in Adolescence Using SPSS for data analysis, the results indicate the presence of a correlation between elements of depression and sleep duration and quality.
- Attachment Dimensions and Adolescence Drug Addiction in Relation to School Counseling A meta-analysis of numerous studies relating to attachment and parental rearing behaviors have revealed that the quality of rapport between children and their caregivers is of intrinsic importance to the children’s development, and some studies, […]
- Development of Ethnic Identity During Adolescence From a study of adolescents of different racial groups in the United States, it was found out that self esteem of the groups was observed to rise among the groups of early and mid adolescents.
- Inter-Psychic Theories Adlerian Theory (In Adolescence) In his theory, social interest is identified as the need for individuals to adapt to their social environment as it is expressed subjectively in an individual’s consciousness, hence, the need to be part of society […]
- The Three D’s of Adolescence Depression There are three major types depression in teenagers: bipolar depression, major depression, and chronic depression. Parents can help their depressed adolescents by identifying the type of depression and seeking proper treatment.
- Human Development: Adolescence as the Most Important Age Range The stage is therefore very important in understanding the behavior of an individual. This is a stage when the life of an individual is either made or destroyed.
- Critical Issues in Adolescence: The Problem of Psychological Disorders It is the purpose of this paper to critically analyze how psychological disorders affect the physical, cognitive and emotional development of adolescents in contemporary times.
- A Critical Evaluation of the Behavioural Outcomes of Failure of Mylination of the Prefrontal Lobe During Adolescence It is, therefore, the purpose of this paper to evaluate the behavioural outcome of failure or impairment of mylination of the prefrontal lobe during adolescence.
- Why Do So Many Guys Seem Stuck Between Adolescence And Adulthood?
- Mental Health around Pregnancy and Child Development from Early Childhood to Adolescence
- Adolescence: Developmental Psychology and Social Work Practice
- Adolescence Sexuality Defining Sexual Self The Other Issue
- The Main Problems That Comes with Adolescence
- Working and Studying in Rural Latin America: Critical Decisions of Adolescence
- The Sense of Self in Adolescence: Teenager Movies
- The Ups and Downs of Adolescence in The Perks of Being a Wallflower Directed by Stephen Chbosky
- Understanding the Adolescence and Behaviorism in Psychology
- The Influence of Parent and Peer Attachments on Life Satisfaction in Middle Childhood and Early Adolescence
- What Are Some Of The Most Common Mental Disorders In Adolescence
- The Rite of Passage from Adolescence to Adulthood in Teen Films
- Gender Roles And Socialization In Adolescence
- The Middle Adolescence Stage Of Development
- Adolescence Is A Critical Time For A Human
- Adolescence In The Bell Jar And Catcher In The Rye
- The Reduction in Criminal Offences After Adolescence
- Weight and Blood Pressure Management in Adolescence Population
- The Relationship Between Divorce And Adolescence
- Relationship Between Adolescence and Horror Films
- Narratives of Adolescence Explored Through the Harry Potter
- Prenatal Adolescence And Early Adulthood Period
- The Pros and Cons of Internet as the Primary Source of Globalization of Adolescence
- Adolescence Is The Most Difficult Stage Of Our Lives
- The Theme of Adolescence in Melanie Rae Thon’s Iona Moon
- The Importance of Adolescence in Creating Successful Adults
- The Physiological Changes of Boys and Girls During Adolescence
- Sports Participation and Social Capital Formation During Adolescence
- The Physical and Psychological Changes that Occur During Adolescence
- Value Driven Attentional Capture Of Adolescence
- Treating Non-Malignant Pain in Adolescence with Medical Marijuana
- The Psychological And Physical Aspects Of Drug Abuse In Today’s Adolescence
- The Woman’s Natural Journey From Adolescence To Menopause
- Sexism and Aggression in Adolescence—How Do They Relate to Perceived Academic Achievement
- Understanding Sexuality During the Adolescence Stage of Our Lives
- Theories Of Child Development As They Pertain To Middle Childhood And Adolescence
- Peer Affiliation, Social Behavior, And Callous Unemotional Traits In Adolescence
- The Major Hormonal Changes That Occur During Adolescence
- Personality and Optimal Experience in Adolescence: Implications for Well-Being and Development
- An Analysis of the Concept of Adolescence and the Juvenile Delinquency
- Adolescence Is A Period Of Storm And Stress
- Child Sexual Development: Infancy, Early Childhood, Adolescence
- Mass Media and Adolescence: How Mass Media Influence Teens in Their Sexual Behavior
- The Role Of Nature And Nurture : Adolescence Eating Disorders
- Does Fruit and Vegetable Consumption During Adolescence Predict Adult Depression?
- How Does Frayn Show Stephen’s Mental Progression From Childhood to Adolescence?
- Does Periodontal Inflammation Affect Type 1 Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence?
- What Leads Subjective Well-Being to Change Throughout Adolescence?
- Is Abortion Beneficial or Harmful to a Teenager?
- How to Recognize the Signs of Depression in Young People?
- Which Role Models Do Teenagers Follow Today?
- Who Is Responsible for Sexual Education: School or Family?
- What Changes Happen During Adolescence?
- How Do Teenagers Leave Their Homes and Why They Never Come Back? Which Social Groups Have Higher Rates of Such Cases?
- Appearance as a Tool of Self-Expression. Which Elements of Style Are Used by Teenagers Today?
- How Did Communication With Parents Change Over the Past Ten Years?
- Do Technological Advances Facilitate Better Studying Among Young People or Distract From It?
- Have the Youth Become More Involved Socially, or Are They Becoming More Individualist?
- What Influences the Youth of Today?
- How Does an Adolescent Develop Intellectually?
- Are Teenagers More Religious as Compared to the Recent Past?
- What Are the Major Challenges That Adolescence Facing?
- How Does Society Affect Adolescent Development?
- What Is the Most Important Thing We Need to Know During Adolescence?
- Why Adolescent Stage Is the Most Crucial Stage?
- What Are Emotional Changes in Adolescence?
- Can Adolescent Development Change According to Culture and Upbringing?
- What Social Changes Happen in Adolescence?
- Why Is Knowledge About Changes During Adolescence Important?
- How Do Physical Changes Affect Adolescents?
- Why Is Adolescent Development Especially Challenging?
- What Are the Problems With Defining the Start and End of Adolescence? Why Do These Problems Exist?
- How Does Family Affect Adolescent Development?
- Why Is Healthy Behavior During Adolescence Important?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adolescence-essay-topics/
"135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adolescence-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adolescence-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adolescence-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "135 Adolescence Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adolescence-essay-topics/.
- Psychology Questions
- Emotional Development Questions
- Personal Identity Paper Topics
- Self Esteem Research Ideas
- Family Relationships Research Ideas
- Peer Pressure Research Topics
- Role Model Research Topics
- Personality Development Ideas
Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study (ABCD Study®)

Landmark study of adolescent brain development renews for additional seven years
With nearly $290M of new funding for seven years to research institutions around the country, the National Institutes of Health renewed its commitment to the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development SM Study (ABCD Study ® ) the largest long-term study of brain development and child health ever conducted in the United States.
“The next phase of the ABCD study will help us understand the effects of substance use, as well as environmental, social, genetic, and other biological factors on the developing adolescent brain,” said NIDA Director Nora D. Volkow, M.D. “Since the participants are now in their vulnerable middle school years or are beginning high school, this is a critical time to learn more about what enhances or disrupts a young person’s life trajectory.” Read the Press Release .
2023 ABCD Annual Curated Data Release 5.0
ABCD Data Release 5.0 has been shared. The ABCD Study® and NDA have changed the way tabulated data are downloaded for the 5.0 release. The imaging and non-imaging tabulated data are packaged as a single .zip file containing all of the relevant tables for the domain. To obtain the data you must be logged into NDA (authenticated). Visit https://nda.nih.gov/study.html?id=2147 and select the “ABCD 5.0 Tabulated Release Data” file in the Results section to download all tabulated imaging and non-imaging 5.0 data. As in past releases, neuroimaging and other file-based data (e.g., genomics; raw behavioral data) are accessible via the NDA download manager tool.
All data access information is documented on the NDA ABCD Featured Dataset page and includes pointers to an external ABCD Study wiki where data release notes and general information about the data resource are provided. All users should review the release notes for detailed information on the released data. Note that with the change to how release notes are made available, they will be updated regularly and thus users are advised to check https://wiki.abcdstudy.org/release-notes/start-page.html for the most up-to-date information. Release notes for qualified users only (i.e., non-public) are available at https://nda.nih.gov/study.html?id=2147 . The 5.0 data ontology and dictionary can be viewed at https://data-dict.abcdstudy.org/ .
The table below highlights key differences between the 4.0 and 5.0 data releases. Note that the Data Exploration and Analysis Portal (DEAP) has been decommissioned as of June 1, 2023. In addition, study creation no longer works with how the data are shared this year. We anticipate reinstating it with the 6.0 data release.
Data Release 5.0 contains early longitudinal data on the full participant cohort, including 2-year follow-up neuroimaging data (second imaging timepoint), as well as phenotypic data through the 3-year follow-up visits. Interim data are available for the 4-year follow-up visit, including some of the neuroimaging data. Also available are ABCD derived scores from linked external school performance and environmental data, including the Stanford Education Data Archive, EPA Smart Location Database, American Community Survey Area Deprivation Index, FBI’s Uniform Crime Report, lead exposure risk and air pollution indices, among others. Smokescreen genotyping array data with TOPMed imputations are available as well. These include common variations, as well as variations associated with addiction, smoking behavior, and nicotine metabolism.

ChildArt ABCD Issue
This special issue of ChildArt introduces the intersection of the arts and neuroscience through an overview of the ABCD Study ® . It presents some of the data from the study, as well as other research looking at the impact of the arts on child development. The issue combines the work of experts in neuroscience, world renowned artists, specialists in child development, and others. Topics covered include the juncture between the arts and human culture, the developing adolescent brain, the interaction between cultural and biological processes and artistic creation, the interface of the arts and science as a multisensory experience, insights from the neuroscience of dance and music, and more. We hope that this special issue will stimulate creativity and innovation in research on the impact of the arts on child development as well as encourage researchers to leverage the ABCD Study data to advance research on a wide range of other topics.

Podcast: With Neuroimaging, Large NIH Study Could Shine a Light on the Adolescent Brain
JAMA, August 14, 2019: Audio 25 min 18 sec
In this Medical News podcast , Jennifer Abbasi interviews the director of the ABCD study, Gaya Dowling, PhD, about this long-term study of brain development and child health in the United States.
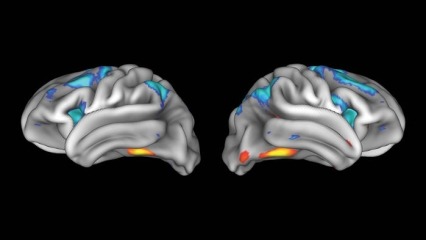
Science Magazine, January 3, 2018 Huge study of teen brains could reveal roots of mental illness, impacts of drug abuse
CBS - 60 Minutes, December 9th, 2018
Please note: The ABCD study is assessing brain development in children throughout adolescence, while tracking social, behavioral, physical and environmental factors that may affect brain development and other health outcomes. Screen time is only one of many measures evaluated as part of the study protocol.
- Watch video (12:55)
- For additional articles about the ABCD study, visit https://abcdstudy.org/news/
- View all NIDA press releases related to the ABCD Study
Study Enrollment Completed
ABCD Study Enrollment has completed as of 10/21/18 - The total enrollment stands at 11,880
- See announcement - ABCD study completes enrollment, announces opportunities for scientific engagement (12/3/18)
What Is the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study SM (ABCD Study ® )?
ABCD is a landmark study on brain development and child health supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This project will increase our understanding of environmental, social, genetic, and other biological factors that affect brain and cognitive development and that can enhance or disrupt a young person’s life trajectory.
For an overview of how the ABCD study got started, see article co-authored by NIDA Director Dr. Nora Volkow, NIAAA Director Dr. George Koob, NINDS Director Dr. Walter Koroshetz, and other NIH scientists: The conception of the ABCD study: From substance use to a broad NIH collaboration , published in Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience.
How Will the ABCD Study ® Be Implemented?
Unique in its scope and duration, the ABCD study will:
- Recruit 11,900 healthy children, ages 9 to 10 across the United States, with the goal of retaining 10,000 into early adulthood.
- Use advanced brain imaging to observe brain growth with unprecedented precision.
- Examine how biology and environment interact and relate to developmental outcomes such as physical health, mental health, and life achievements including academic success.
Why Do We Need the ABCD Study ® ?
Adolescence is a period of dramatic brain development in which children are exposed to all sorts of experiences. Yet, our understanding of precisely how these experiences interact with each other and a child’s biology to affect brain development and, ultimately, social, behavioral, health, and other outcomes, is still incomplete. As the only study of its kind, the ABCD study will yield critical insights into the foundational aspects of adolescence that shape a person’s future.
What Will We Learn from the ABCD Study ® ?
The size and scope of the study will allow scientists to:
- Identify individual developmental trajectories (e.g., brain, cognitive, emotional, academic) and the factors that can affect them.
- Understand the role of genetic vs. environmental factors on development.
- Examine the effects of physical activity, screen time, and sleep, as well as sports and other injuries, on brain development and other outcomes.
- Study the onset and progression of mental disorders.
- Determine how exposure to substances (e.g., alcohol, marijuana, nicotine, caffeine) and new ways of taking them (e.g., vaping, dabbing) affect developmental outcomes and vice versa.
- Understand the impact of changing state and local policies and laws (e.g., marijuana, tobacco, alcohol) on youth drug use and related health and development.
Scientific publications authored by ABCD Study investigators, collaborators, and other researchers can be found at https://abcdstudy.org/scientists-publications.html .
Who Is Leading the ABCD Study ® ?
The ABCD study is led by the Collaborative Research on Addiction at NIH (CRAN):
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
- National Cancer Institute (NCI)
In partnership with:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- National Institute of Minority Health and Health Disparities (NIMHD)
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- NIH Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research (OBSSR)
- NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health (ORWH)
For additional information on ABCD, please contact: Dr. Gaya Dowling, Director, ABCD Project at 301-443-4877 or at [email protected] or visit abcdstudy.org
For more information for researchers, visit: https://www.addictionresearch.nih.gov/abcd-study
Download : Flyer on the ABCD Study (PDF, 2.7MB)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 07 May 2024
Mechanisms linking social media use to adolescent mental health vulnerability
- Amy Orben ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2937-4183 1 ,
- Adrian Meier ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8191-2962 2 ,
- Tim Dalgleish ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7304-2231 1 &
- Sarah-Jayne Blakemore 3 , 4
Nature Reviews Psychology ( 2024 ) Cite this article
3828 Accesses
123 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Psychiatric disorders
- Science, technology and society
Research linking social media use and adolescent mental health has produced mixed and inconsistent findings and little translational evidence, despite pressure to deliver concrete recommendations for families, schools and policymakers. At the same time, it is widely recognized that developmental changes in behaviour, cognition and neurobiology predispose adolescents to developing socio-emotional disorders. In this Review, we argue that such developmental changes would be a fruitful focus for social media research. Specifically, we review mechanisms by which social media could amplify the developmental changes that increase adolescents’ mental health vulnerability. These mechanisms include changes to behaviour, such as sharing risky content and self-presentation, and changes to cognition, such as modifications in self-concept, social comparison, responsiveness to social feedback and experiences of social exclusion. We also consider neurobiological mechanisms that heighten stress sensitivity and modify reward processing. By focusing on mechanisms by which social media might interact with developmental changes to increase mental health risks, our Review equips researchers with a toolkit of key digital affordances that enables theorizing and studying technology effects despite an ever-changing social media landscape.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Loneliness trajectories over three decades are associated with conspiracist worldviews in midlife
Determinants of behaviour and their efficacy as targets of behavioural change interventions
Adults who microdose psychedelics report health related motivations and lower levels of anxiety and depression compared to non-microdosers
Introduction.
Adolescence is a period marked by profound neurobiological, behavioural and environmental changes that facilitate the transition from familial dependence to independent membership in society 1 , 2 . This critical developmental stage is also characterized by diminished well-being and increased vulnerability to the onset of mental health conditions 3 , 4 , 5 , particularly socio-emotional disorders such as depression, and eating disorders 4 , 6 (Fig. 1 ). Notable symptoms of socio-emotional disorders include heightened negative affect, mood dysregulation and an increased focus on distress or challenges concerning interpersonal relationships, including heightened sensitivity to peers or perceptions of others 6 . Although some risk factors for socio-emotional disorders do not necessarily occur in adolescence (including genetic predispositions, adverse childhood experiences and poverty 7 , 8 , 9 ), the unique developmental characteristics of this period of life can interact with pre-existing vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of disorder onset 10 .
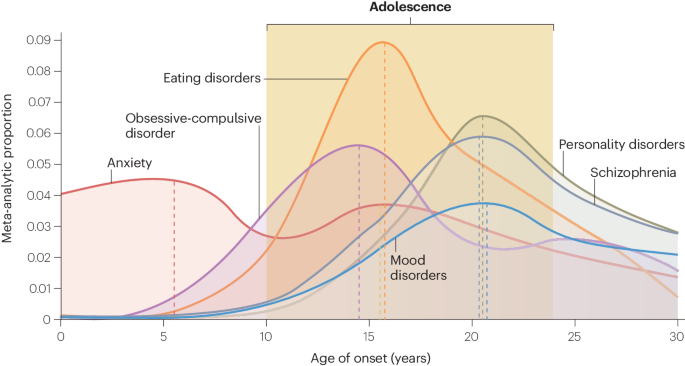
Meta-analytic proportion of age of onset of anxiety (red), obsessive-compulsive disorder (purple), eating disorders (orange), personality disorders (green), schizophrenia (grey) and mood disorders (blue). The peak age of onset (dotted lines) is 5.5 and 15.5 years for anxiety, 14.5 years for obsessive-compulsive disorder, 15.5 years for eating disorders and 20.5 years for personality disorders, schizophrenia and mood disorders. Adapted from ref. 258 , CC BY 4.0 ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Over the past decade, declines in adolescent mental health have become a great concern 11 , 12 . The prevalence of socio-emotional disorders has increased in the adolescent age range (10–24 years 2 ) 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , leading to mounting pressures on child and adolescent mental health services 16 , 21 , 22 . This increase has not been as pronounced among other age groups when compared with adolescents 20 , 22 , 23 (measured in ref. 20 , ref. 22 and ref. 23 as age 12–25 years, 12–20 years and 18–25 years, respectively), even if some studies have found increases across the entire lifespan 24 , 25 . Although these trends might not be generalizable across the world 26 or to subclinical indicators of distress 15 , similar trends have been found in a range of countries 27 . Declines in adolescent mental health, especially socio-emotional problems, are consistent across datasets and researchers have argued that they are not solely driven by changes in social attitudes, stigma or reporting of distress 28 , 29 .
Concurrently, adolescents’ lives have become increasingly digital, with most young people using social media platforms throughout the day 30 . Ninety-five per cent of UK adolescents aged 15 years use social media 31 , and 50% of US adolescents aged 13–17 years report being almost constantly online 32 . The social media environment impacts adolescent and adult life across many domains (for example, by enabling social communication or changing the way news is accessed) and influences individuals, dyads and larger social systems 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 . Because social media is inherently social and relational 37 , it potentially overlaps and interacts with the developmental changes that make adolescents vulnerable to the onset of mental health problems 38 , 39 (Fig. 2 ). Thus, it has been intensely debated whether the increase in social media use during the past decade has a causal role in the decline of adolescent mental health 40 . Indeed, rapid changes to the environment experienced before and during adolescence might be a fruitful area to explore when examining current mental health trends 41 .
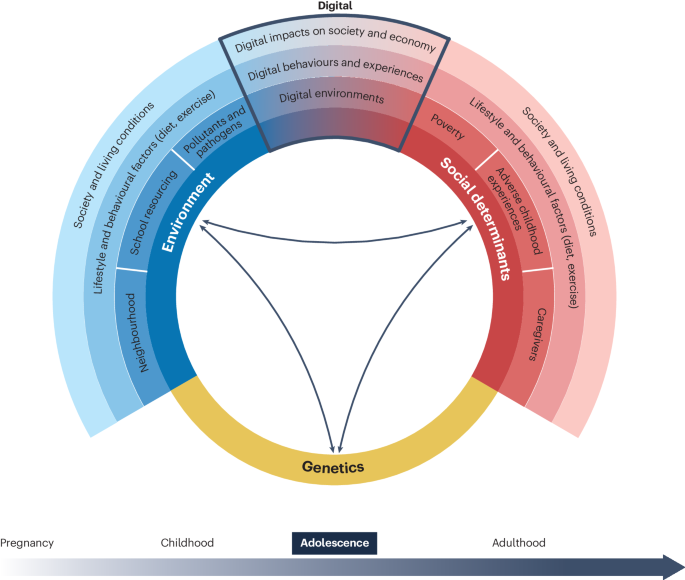
During adolescence, the interaction between genetic programming (yellow), social determinants (red) and environmental factors (blue), as well as the developmental changes discussed in this Review, increases the risk for onset of mental health conditions. Digital environments, mediated behaviours and experiences, and the impact that this technology has on society and economy more generally, are one aspect of the complex forces that might lead to the declines in adolescent mental health observed in the last decade. Adapted from ref. 259 , Springer Nature Limited.
Although there are many environmental changes that could be relevant, a substantial body of research has emerged to investigate the potential link between social media use and declines in adolescent mental health 42 , 43 using various research approaches, including cross-sectional studies 44 , longitudinal observational data analyses 45 , 46 , 47 and experimental studies 48 , 49 . However, the scientific results have been mixed and inconclusive (for reviews, see refs. 43 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ), which has made it difficult to establish evidence-based recommendations, regulations and interventions aimed at ensuring that social media use is not harmful to adolescents 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 .
Many researchers attribute the mixed results to insufficient study specificity. For instance, the relationship between social media use and mental health varies notably across individuals 45 , 58 and developmental time windows 59 . Yet studies often examine adolescents without differentiating them based on age or developmental stage 60 , which prevents systematic accounts of individual and subgroup differences. Additionally, most studies only rely on self-reported measures of time spent on social media 61 , 62 , and overlook more nuanced aspects of social media use such as the nature of the activities 63 and the content or features that users engage with 52 . These factors need to be considered to unpack any broader relationships 35 , 64 , 65 , 66 . Furthermore, the measurement of mental health often conflates positive and negative mental health outcomes as well as various mental health conditions, which could all be differentially related to social media use 52 , 67 .
This research space presents substantial complexity 68 . There is an ever-increasing range of potential combinations of social media predictors, well-being and mental health outcomes and participant groups of varying backgrounds and demographics that can become the target of scientific investigation. However, the pressure to deliver policy and public-facing recommendations and interventions leaves little time to investigate comprehensively each of these combinations. Researchers need to be able to pinpoint quickly the research programmes with the maximum potential to create translational and real-world impact for adolescent mental health.
In this Review, we aim to delineate potential avenues for future research that could lead to concrete interventions to improve adolescent mental health by considering mechanisms at the nexus between pre-existing processes known to increase adolescent mental health vulnerability and digital affordances introduced by social media. First, we describe the affordance approach to understanding the effects of social media. We then draw upon research on adolescent development, mental health and social media to describe behavioural, cognitive and neurobiological mechanisms by which social media use might amplify changes during adolescent development to increase mental health vulnerability during this period of life. The specific mechanisms within each category were chosen because they have a strong evidence base showing that they undergo substantive changes during adolescent development, are implicated in mental health risk and can be modulated by social media affordances. Although the ways in which social media can also improve mental health resilience are not the focus of our Review and therefore are not reviewed fully here, they are briefly discussed in relation to each mechanism. Finally, we discuss future research focused on how to systematically test the intersection between social media and adolescent mental health.
Social media affordances
To study the impact of social media on adolescent mental health, its diverse design elements and highly individualized uses must be conceptualized. Initial research predominately related access to or time spent on social media to mental health outcomes 46 , 69 , 70 . However, social media is not similar to a toxin or nutrient for which each exposure dose has a defined link to a health-related outcome (dose–response relationship) 56 . Social media is a diverse environment that cannot be summarized by the amount of time one spends interacting with it 71 , 72 , and individual experiences are highly varied 45 .
Previous psychological reviews often focused on social media ‘features’ 73 and ‘affordances’ 74 interchangeably. However, these terms have distinct definitions in communication science and information systems research. Social media features are components of the technology intentionally designed to enable users to perform specific actions, such as liking, reposting or uploading a story 75 , 76 . By contrast, affordances describe the perceptions of action possibilities users have when engaging with social media and its features, such as anonymity (the difficulty with which social media users can identify the source of a message) and quantifiability (how countable information is).
The term ‘affordance’ came from ecological psychology and visuomotor research, and was described as mainly determined by human perception 77 . ‘Affordance’ was later adopted for design and human–computer interaction contexts to refer to the action possibilities that are suggested to the user by the technology design 78 . Communication research synthesizes both views. Affordances are now typically understood as the perceived — and therefore flexible — action possibilities of digital environments, which are jointly shaped by the technology’s features and users’ idiosyncratic perceptions of those features 79 .
Latent action possibilities can vary across different users, uses and technologies 79 . For example, ‘stories’ are a feature of Instagram designed to share content between users. Stories can also be described in terms of affordances when users perceive them as a way to determine how long their content remains available on the platform (persistence) or who can see that content (visibility) 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 . Low persistence (also termed ephemerality) and comparatively low visibility can be achieved through a technology feature (Instagram stories), but are not an outcome of technology use itself; they are instead perceived action possibilities that can vary across different technologies, users and designs 79 .
The affordances approach is particularly valuable for theorizing at a level above individual social media apps or specific features, which makes this approach more resilient to technological changes or shifts in platform popularity 79 , 85 . However, the affordances approach can also be related back to specific types of social media by assessing the extent to which certain affordances are ‘built into’ a particular platform through feature design 35 . Furthermore, because affordances depend on individuals’ perceptions and actions, they are more aligned than features with a neurocognitive and behavioural perspective to social media use. Affordances, similar to neurocognitive and behavioural research, emphasize the role of the user (how the technology is perceived, interpreted and used) rather than technology design per se. In this sense, the affordances approach is essential to overcome technological determinism of mental health outcomes, which overly emphasizes the role of technology as the driver of outcomes but overlooks the agency and impact of the people in question 86 . This flexibility and alignment with psychological theory has contributed to the increasing popularity of the affordance approach 35 , 73 , 74 , 85 , 87 and previous reviews have explored relevant social media affordances in the context of interpersonal communication among adults and adolescents 35 , 88 , 89 , adolescent body image concerns 73 and work contexts 33 . Here, we focus on the affordances of social media that are relevant for adolescent development and its intersection with mental health (Table 1 ).
Behavioural mechanisms
Adolescents often use social media differently to adults, engaging with different platforms and features and, potentially, perceiving or making use of affordances in distinctive ways 35 . These usage differences might interact with developmental characteristics and changes to amplify mental health vulnerability (Fig. 3 ). We examine two behavioural mechanisms that might govern the impact of social media use on mental health: risky posting behaviours and self-presentation.
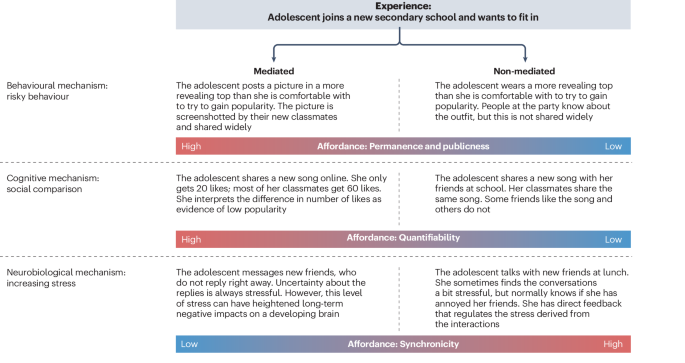
Social media affordances can amplify the impact that common adolescent developmental mechanisms (behavioural, cognitive and neurobiological) have on mental health. At the behavioural level (top), affordances such as permanence and publicness lead to an increased impact of risk-taking behaviour on mental health compared with similar behaviours in non-mediated environments. At the cognitive level (middle), high quantifiability influences the effects of social comparison. At the neurobiological level (bottom), low synchronicity can amplify the effects of stress on the developing brain.
Risky posting behaviour
Sensation-seeking peaks in adolescence and self-regulation abilities are still not fully developed in this period of life 90 . Thus, adolescents often engage in more risky behaviours than other age groups 91 . Adolescents are more likely to take risks in situations involving peers 92 , 93 , perhaps because they are motivated to avoid social exclusion 94 , 95 . Whether adolescent risk-taking behaviour is inherently adaptive or maladaptive is debated. Although some risk-taking behaviours can be adaptive and part of typical development, others can increase mental health vulnerability. For example, data from a prospective UK panel study of more than 5,500 young people showed that engaging in more risky behaviours (including social and health risks) at age 16 years increases the odds of a range of adverse outcomes at age 18 years, such as depression, anxiety and substance abuse 96 .
Social media can increase adolescents’ engagement in risky behaviours both in non-mediated and mediated environments (environments in which the behaviour is executed in or through a technology, such as a mobile phone and social media). First, affordances such as quantifiability in conjunction with visibility and association (the degree with which links between people, between people and content or between a presenter and their audience can be articulated) can promote more risky behaviours in non-mediated environments and in-person social interactions. For example, posts from university students containing references to alcohol gain more likes than posts not referencing alcohol and liking such posts predicts an individual’s subsequent drinking habits 97 . Users expecting likes from their audience are incentivized to engage in riskier posting behaviour (such as more frequent or more extreme posts containing references to alcohol). The relationship between risky online behaviour and offline behaviour is supported by meta-analyses that found a positive correlation between adolescents’ social media use and their engagement in behaviours that might expose them to harm or risk of injury (for example, substance use or risky sexual behaviours) 98 . Further, affordances such as persistence and visibility can mean that risky behaviours in mediated and non-mediated environments remain public for long periods of time, potentially influencing how an adolescent is perceived by peers over the longer term 39 , 99 .
Adolescence can also be a time of more risky social media use. For most forms of semi-public and public social media use, users typically do not know who exactly will be able to see their posts. Thus, adolescents need to self-present to an ‘imagined audience’ 100 and avoid posting the wrong kind of content as the boundaries between different social spheres collapse (context collapse 101 ). However, young people can underestimate the risks of disclosing revealing information in a social media environment 102 . Affordances such as visibility, replicability (social media posts remain in the system and can be screenshotted and shared even if they are later deleted 39 ), association and persistence could heighten the risk of experiencing cyberbullying, victimization and online harassment 103 . For example, adolescents can forward privately received sexual images to larger friendship groups, increasing the risk of online harassment over the subject of the sexual images 104 . Further, low bandwidth (a relative lack of socio-emotional cues) and high anonymity have the potential to disinhibit interactions between users and make behaviours and reactions more extreme 105 , 106 . For example, anonymity was associated with more trolling behaviours during an online group discussion in an experiment with 242 undergraduate students 107 .
Thus, social media might drive more risky behaviours in both mediated and non-mediated contexts, increasing mental health vulnerability. However, the evidence is still not clear cut and often discounts adolescent agency and understanding. For example, mixed-methods research has shown that young people often understand the risks of posting private or sexual content and use social media apps that ensure that posts are deleted and inaccessible after short periods of time to counteract them 39 (even though posts can still be captured in the meantime). Future work will therefore need to investigate how adolescents understand and balance such risks and how such processes relate to social media’s impact on mental health.
Self-presentation and identity
The adolescent period is characterized by an abundance of self-presentation activities on social media 74 , where the drive to present oneself becomes a fundamental motivation for engagement 108 . These activities include disclosing, concealing and modifying one’s true self, and might involve deception, to convey a desired impression to an audience 109 . Compared with adults, adolescents more frequently take part in self-presentation 102 , which can encompass both realistic and idealized portrayals of themselves 110 . In adults, authentic self-presentation has been associated with increased well-being, and inauthentic presentation (such as when a person describes themselves in ways not aligned with their true self) has been associated with decreased well-being 111 , 112 , 113 .
Several social media affordances shape the self-presentation behaviours of adolescents. For example, the editability of social media profiles enables users to curate their online identity 84 , 114 . Editability is further enhanced by highly visible (public) self-presentations. Additionally, the constant availability of social media platforms enables adolescents to access and engage with their profiles at any time, and provides them with rapid quantitative feedback about their popularity among peers 89 , 115 . People receive more direct and public feedback on their self-presentation on social media than in other types of environment 116 , 117 . The affordances associated with self-presentation can have a particular impact during adolescence, a period characterized by identity development and exploration.
Social media environments might provide more opportunities than offline environments for shaping one’s identity. Indeed, public self-presentation has been found to invoke more prominent identity shifts (substantial changes in identity) compared with private self-presentation 118 , 119 . Concerns have been raised that higher Internet use is associated with decreased self-concept clarity. Only one study of 101 adolescents as well as adults reviewed in a 2021 meta-analysis 120 showed that the intensity of Facebook use (measured by the Facebook Intensity Scale) predicted a longitudinal decline in self-concept clarity 3 months later, but the converse was not the case and changes in self-concept clarity did not predict Facebook use 121 . This result is still not enough to show a causal relationship 121 . Further, the affordances of persistence and replicability could also curtail adolescents’ ability to explore their identity freely 122 .
By contrast, qualitative research has highlighted that social media enables adolescents to broaden their horizons, explore their identity and identify and reaffirm their values 123 . Social media can help self-presentation by enabling adolescents to elaborate on various aspects of their identity, such as ethnicity and race 124 or sexuality 125 . Social media affordances such as editability and visibility can also facilitate this process. Adolescents can modify and curate self-presentations online, try out new identities or express previously undisclosed aspects of their identity 126 , 127 . They can leverage social media affordances to present different facets of themselves to various social groups by using different profiles, platforms and self-censorship and curation of posts 128 , 129 . Presenting and exploring different aspects of one’s identity can have mental health implications for minority teens. Emerging research shows a positive correlation between well-being and problematic Internet use in transgender, non-binary and gender-diverse adolescents (age 13–18 years), and positive sentiment has been associated with online identity disclosures in transgender individuals with supportive networks (both adolescent and adult) 130 , 131 .
Cognitive mechanisms
Adolescents and adults might experience different socio-cognitive impacts from the same social media activity. In this section, we review four cognitive mechanisms via which social media and its affordances might influence the link between adolescent development and mental health vulnerabilities (Fig. 3 ). These mechanisms (self-concept development, social comparison, social feedback and exclusion) roughly align with a previous review that examined self-esteem and social media use 115 .
Self-concept development
Self-concept refers to a person’s beliefs and evaluations about their own qualities and traits 132 , which first develops and becomes more complex throughout childhood and then accelerates its development during adolescence 133 , 134 , 135 . Self-concept is shaped by socio-emotional processes such as self-appraisal and social feedback 134 . A negative and unstable self-concept has been associated with negative mental health outcomes 136 , 137 .
Perspective-taking abilities also develop during adolescence 133 , 138 , 139 , as does the processing of self-relevant stimuli (measured by self-referential memory tasks, which assess memory for self-referential trait adjectives 140 , 141 ). During adolescence, direct self-evaluations and reflected self-evaluations (how someone thinks others evaluate them) become more similar. Further, self-evaluations have a distinct positive bias during childhood, but this positivity bias decreases in adolescence as evaluations of the self are integrated with judgements of other people’s perspectives 142 . Indeed, negative self-evaluations peak in late adolescence (around age 19 years) 140 .
The impact of social media on the development of self-concept could be heightened during adolescence because of affordances such as personalization of content 143 (the degree to which content can be tailored to fit the identity, preferences or expectations of the receiver), which adapts the information young people are exposed to. Other affordances with similar impacts are quantifiability, availability (the accessibility of the technology as well as the user’s accessibility through the technology) and public visibility of interactions 89 , which render the evaluations of others more prominent and omnipresent. The prominence of social evaluation can pose long-term risks to mental health under certain conditions and for some users 144 , 145 . For example, receiving negative evaluations from others or being exposed to cyberbullying behaviours 146 , 147 can, potentially, have heightened impact at times of self-concept development.
A pioneering cross-sectional study of 150 adolescents showed that direct self-evaluations are more similar to reflected self-evaluations, and self-evaluations are more negative, in adolescents aged 11–21 years who estimate spending more time on social media 148 . Further, longitudinal data have shown bidirectional negative links between social media use and satisfaction with domains of the self (such as satisfaction with family, friends or schoolwork) 47 .
Although large-scale evidence is still unavailable, these findings raise the interesting prospect that social media might have a negative influence on perspective-taking and self-concept. There is less evidence for the potential positive influence of social media on these aspects of adolescent development, demonstrating an important research gap. Some researchers hypothesize that social media enables self-concept unification because it provides ample opportunity to find validation 89 . Research has also discussed how algorithmic curation of personalized social media feeds (for example, TikTok algorithms tailoring videos viewed to the user’s interests) enables users to reflect on their self-concept by being exposed to others’ experiences and perspectives 143 , an area where future research can provide important insights.
Social comparison
Social comparison (thinking about information about other people in relation to the self 149 ) also influences self-concept development and becomes particularly important during adolescence 133 , 150 . There are a range of social media affordances that can amplify the impact of social comparison on mental health. For example, quantifiability enables like or follower counts to be easily compared with others as a sign of status, which facilitates social ranking 151 , 152 , 153 , 154 . Studies of older adolescents and adults aged, on average, 20 years have also found that the number of likes or reactions received predict, in part, how successful users judge their self-presentation posts on Facebook 155 . Furthermore, personalization enables the content that users see on social media to be curated so as to be highly relevant and interesting for them, which should intensify comparisons. For example, an adolescent interested in sports and fitness content will receive personalized recommendations fitting those interests, which should increase the likelihood of comparisons with people portrayed in this content. In turn, the affordance of association can help adolescents surround themselves with similar peers and public personae online, enhancing social comparison effects 63 , 156 . Being able to edit posts (via the affordance of editability) has been argued to contribute to the positivity bias on social media: what is portrayed online is often more positive than the offline experience. Thus, upward comparisons are more likely to happen in online spaces than downward or lateral comparisons 157 . Lastly, the verifiability of others’ idealized self-presentations is often low, meaning that users have insufficient cues to gauge their authenticity 158 .
Engaging in comparisons on social media has been associated with depression in correlational studies 159 . Furthermore, qualitative research has shown that not receiving as many positive evaluations as expected (or if positive evaluations are not provided quickly enough) increases negative emotions in children and adolescents aged between age 9 and 19 years 39 . This result aligns with a reinforcement learning modelling study of Instagram data, which found that the likes a user receives on their own posts become less valuable and less predictive of future posting behaviour if others in their network receive more likes on their posts 160 . Although this study did not measure mood or mental health, it shows that the value of the likes are not static but inherently social; their impact depends on how many are typically received by other people in the same network.
Among the different types of social comparison that adolescents engage in (comparing one’s achievements, social status or lifestyle), the most substantial concerns have been raised about body-related comparisons. One review suggested that social media affordances create a ‘perfect storm’ for body image concerns that can contribute to both socio-emotional and eating disorders 73 . Social media affordances might increase young people’s focus on other people’s appearances as well as on their own appearance by showing idealized, highly edited images, providing quantified feedback and making the ability to associate and compare oneself with peers constantly available 161 , 162 . The latter puts adolescents who are less popular or receive less social support at particular risk of low self-image and social distress 35 .
Affordances enable more prominent and explicit social comparisons in social media environments relative to offline environments 158 , 159 , 163 , 164 , 165 . However, this association could have a positive impact on mental health 164 , 166 . Initial evidence suggests beneficial outcomes of upward comparisons on social media, which can motivate behaviour change and yield positive downstream effects on mental health 164 , 166 . Positive motivational effects (inspiration) have been observed among young adults for topics such as travelling and exploring nature, as well as fitness and other health behaviours, which can all improve mental health 167 . Importantly, inspiration experiences are not a niche phenomenon on social media: an experience sampling study of 353 Dutch adolescents (mean age 13–15 years) found that participants reported some level of social media-induced inspiration in 33% of the times they were asked to report on this over the course of 3 weeks 168 . Several experimental and longitudinal studies show that inspiration is linked to upward comparison on social media 157 , 164 , 166 . However, the positive, motivating side of social comparison on social media has only been examined in a few studies and requires additional investigation.
Social feedback
Adolescence is also a period of social reorientation, when peers tend to become more important than family 169 , peer acceptance becomes increasingly relevant 170 , 171 , 172 and young people spend increasing amounts of time with peers 173 . In parallel, there is a heightened sensitivity to negative socio-emotional or self-referential cues 140 , 174 , higher expectation of being rejected by others 175 and internalization of such rejection 142 , 176 compared with other phases in life development. A meta-analysis of both adolescents and adults found that oversensitivity to social rejection is moderately associated with both depression and anxiety 177 .
Social media affordances might amplify the potential impact of social feedback on mental health. Wanting to be accepted by peers and increased susceptibility to social rewards could be a motivator for using social media in the first place 178 . Indeed, receiving likes as social reward activated areas of the brain (such as the nucleus accumbens) that are also activated by monetary reward 179 . Quantifiability amplifies peer acceptance and rejection (via like counts), and social rejection has been linked to adverse mental health outcomes 170 , 180 , 181 , 182 . Social media can also increase feelings of being evaluated, the risk of social rejection and rumination about potential rejection due to affordances such as quantifiability, synchronicity (the degree to which an interaction happens in real time) and variability of social rewards (the degree to which social interaction and feedback occur on variable time schedules). For example, one study of undergraduate students found that active communication such as messaging was associated with feeling better after Facebook use; however, this was not the case if the communication led to negative feelings such as rumination (for example, after no responses to the messages) 183 .
In a study assessing threatened social evaluation online 184 , participants were asked to record a statement about themselves and were told their statements would be rated by others. To increase the authenticity of the threat, participants were asked to rate other people’s recordings. Threatened social evaluation online in this study decreased mood, most prominently in people with high sensitivity to social rejection. Adolescents who are more sensitive to social rejection report more severe depressive symptoms and maladaptive ruminative brooding in both mediated and non-mediated social environments, and this association is most prominent in early adolescence 185 . Not receiving as much online social approval as peers led to more severe depressive symptoms in a study of American ninth-grade adolescents (between age 14 and 15 years), especially those who were already experiencing peer victimization 153 . Furthermore, individuals with lower self-esteem post more negative and less positive content than individuals with higher self-esteem. Posted negative content receives less social reward and recognition from others than positive content, possibly creating a vicious cycle 186 . Negative experiences pertaining to social exclusion and status are also risk factors for socio-emotional disorders 180 .
The impact of social media experiences on self-esteem can be very heterogeneous, varying substantially across individuals. As a benefit, positive social feedback obtained via social media can increase users’ self-esteem 115 , an association also found among adolescents 187 . For instance, receiving likes on one’s profile or posted photographs can bolster self-esteem in the short term 144 , 188 . A study linking behavioural data and self-reports from Facebook users found that receiving quick responses on public posts increased a sense of social support and decreased loneliness 189 . Furthermore, a review of reviews consistently documented that users who report more social media use also perceive themselves to have more social resources and support online 52 , although this association has mostly been studied among young adults using social network sites such as Facebook. Whether such social feedback benefits extend to adolescents’ use of platforms centred on content consumption (such as TikTok or Instagram) is an open question.
Social inclusion and exclusion
Adolescents are more sensitive to the negative emotional impacts of being excluded than are adults 170 , 190 . It has been proposed that, as the importance of social affiliation increases during this period of life 134 , 191 , 192 , adolescents are more sensitive to a range of social stimuli, regardless of valence 193 . These include social feedback (such as compliments or likes) 95 , 194 , negative socio-emotional cues (such as negative facial expressions or social exclusion) 174 and social rejection 172 , 185 . By contrast, social inclusion (via friendships in adolescence) is protective against emotional disorders 195 and more social support is related to higher adolescent well-being 196 .
Experiencing ostracism and exclusion online decreases self-esteem and positive emotion 197 . This association has been found in vignette experiments where participants received no, only a few or a lot of likes 198 , or experiments that used mock-ups of social media sites where others received more likes than participants 153 . Being ostracized (not receiving attention or feedback) or rejected through social media features (receiving dislikes and no likes) is also associated with a reduced sense of belonging, meaningfulness, self-esteem and control 199 . Similar results were found when ostracism was experienced over messaging apps, such as not receiving a reply via WhatsApp 200 .
Evidence on whether social media also enables adolescents to experience positive social inclusion is mostly indirect and mixed. Some longitudinal surveys have found that prosocial feedback received on social media during major life events (such as university admissions) helps to buffer against stress 201 . Adult participants of a longitudinal study reported that social media offered more informational support than offline contexts, but offline contexts more often offered emotional or instrumental support 202 . Higher social network site use is, on average, associated with a perception of having more social resources and support in adults (for an overview of meta-analyses, see ref. 52 ). However, most of these studies have not investigated social support among adolescents, and it is unclear whether early findings (for example, on Facebook or Twitter) generalize to a social media landscape more strongly characterized by content consumption than social interaction (such as Instagram or TikTok).
Still, a review of social media use and offline interpersonal outcomes among adolescents documents both positive (sense of belonging and social capital) and negative (alienation from peers and perceived isolation) correlates 203 . Experience sampling research on emotional support among young adults has further shown that online social support is received and perceived as effective, and its perceived effectiveness is similar to in-person social support 204 . Social media use also has complex associations with friendship closeness among adolescents. For example, one experience sampling study found that greater use of WhatsApp or Instagram is associated with higher friendship closeness among adolescents; however, within-person examinations over time showed small negative associations 205 .
Neurobiological mechanisms
The long-term impact of environmental changes such as social media use on mental health might be amplified because adolescence is a period of considerable neurobiological development 95 (Fig. 3 ). During adolescence, overall cortical grey matter declines and white matter increases 206 , 207 . Development is particularly protracted in brain regions associated with social cognition and executive functions such as planning, decision-making and inhibiting prepotent responses. The changes in grey and white matter are thought to reflect axonal growth, myelination and synaptic reorganization, which are mechanisms of neuroplasticity influenced by the environment 208 . For example, research in rodents has demonstrated that adolescence is a sensitive period for social input, and that social isolation in adolescence has unique and more deleterious consequences for neural, behavioural and mental health development than social isolation before puberty or in adulthood 206 , 209 . There is evidence that brain regions involved in motivation and reward show greater activation to rewarding and motivational stimuli (such as appetitive stimuli and the presence of peers) in early and/or mid adolescence compared with other age groups 210 , 211 , 212 , 213 , 214 .
Little is known about the potential links between social media and neurodevelopment due to the paucity of research investigating these associations. Furthermore, causal chains (for example, social media increasing stress, which in turn influences the brain) have not yet been accurately delineated. However, it would be amiss not to recognize that brain development during adolescence forms part of the biological basis of mental health vulnerability and should therefore be considered. Indeed, the brain is proposed to be particularly plastic in adolescence and susceptible to environmental stimuli, both positive and negative 208 . Thus, even if adults and adolescents experienced the same affective consequences from social media use (such as increases in peer comparison or stress), these consequences might have a greater impact in adolescence.
A cross-sectional study (with some longitudinal elements) suggested that habitual checking of social media (for example, checking for rewards such as likes) might exacerbate reward sensitivity processes, leading to long-term hypersensitization of the reward system 215 . Specifically, frequently checking social media was associated with reduced activation in brain regions such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the amygdala in response to anticipated social feedback in young people. Brain activation during the same social feedback task was measured over subsequent years. Upon follow-up, anticipating feedback was associated with increased activation of the same brain regions among the individuals who checked social media frequently initially 215 . Although longitudinal brain imaging measurements enabled trajectories of brain development to be specified, the measures of social media use were only acquired once in the first wave of data collection. The study therefore cannot account for confounds such as personality traits, which might influence both social media checking behaviours and brain development. Other studies of digital screen use and brain development have found no impact on adolescent functional brain organization 216 .
Brain development and heightened neuroplasticity 208 render adolescence a particularly sensitive period with potentially long-term impacts into adulthood. It is possible that social media affordances that underpin increased checking and reward-seeking behaviours (such as quantifiability, variability of social rewards and permanent availability of peers) might have long-term consequences on reward processing when experienced during adolescence. However, this suggestion is still speculative and not backed up by evidence 217 .
Stress is another example of the potential amplifying effect of social media on adolescent mental health vulnerability due to neural development. Adolescents show higher stress reactivity because of maturational changes to, and increased reactivity in, the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis 218 , 219 . Compared with children and adults, adolescents experience an increase in self-consciousness and associated emotional states such as self-reported embarrassment and related physiological measures of arousal (such as skin conductance), and heightened neural response patterns compared with adults, when being evaluated or observed by peers 220 . Similarly, adolescents (age 13–17 years) show higher stress responses (higher levels of cortisol or blood pressure) compared with children (age 7–12 years) when they perform in front of others or experience social rejection 221 .
Such changes in adolescence might confer heightened risk for the onset of mental health conditions, especially socio-emotional disorders 6 . Both adolescent rodents and humans show prolonged hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal activation after experiencing stress compared with conspecifics of different ages 218 , 219 . In animal models, stress during adolescence has been shown to result in increased anxiety levels in adulthood 222 and alterations in emotional and cognitive development 223 . Furthermore, human studies have linked stress in adolescence to a higher risk of mental health disorder onset 218 and reviews of cross-species work have illustrated a range of brain changes due to adolescent stress 224 , 225 .
There is still little conclusive neurobiological evidence about social media use and stress, and a lack of understanding about which affordances might be involved (although there has been a range of work studying digital stress; Box 1 ). Studies of changes in cortisol levels or hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal functioning and their relation to social media use have been mixed and inconclusive 226 , 227 . These results could be due to the challenge of studying stress responses in adolescents, particularly as cortisol fluctuates across the day and one-point readings can be unreliable. However, the increased stress sensitivity during the adolescent developmental period might mean that social media use can have a long-term influence on mental health due to neurobiological mechanisms. These processes are therefore important to understand in future research.
Box 1 Digital stress
Digital stress is not a unified construct. Thematic content analyses have categorized digital stress into type I stressors (for example, mean attacks, cyberbullying or shaming) and type II stressors (for example, interpersonal stress due to pressure to stay available) 260 . Other reviews have noted its complexity, and categorized digital stress into availability stress (stress that results from having to be constantly available), approval anxiety (anxiety regarding others’ reaction to their own profile, posts or activities online), fear of missing out (stress about being absent from or not experiencing others’ rewarding experiences) and communication overload (stress due to the scale, intensity and frequency of online communication) 261 .
Digital stress has been systematically linked to negative mental health outcomes. Higher digital stress was longitudinally associated with higher depressive symptoms in a questionnaire study 262 . Higher social media stress was also longitudinally related to poorer sleep outcomes in girls (but not boys) 263 . Studies and reviews have linked cyberbullying victimization (a highly stressful experience) to decreased mental health outcomes such as depression, and psychosocial outcomes such as self-esteem 103 , 146 , 147 , 264 , 265 . A systematic review of both adolescents and adults found a medium association ( r = 0.26–0.34) between different components of digital stress and psychological distress outcomes such as anxiety, depression or loneliness, which was not moderated by age or sex (except for connection overload) 266 . However, the causal structure giving rise to such results is still far from clear. For example, surveys have linked higher stress levels to more problematic social media use and fear of missing out 267 , 268 .
Thus, the impact of digital stress on mental health is probably complex and influenced by the type of digital stressor and various affordances. For example, visibility and availability increase fear of negative public evaluation 269 and high availability and a social norm of responding quickly to messages drive constant monitoring in adolescents due to a persistent fear of upsetting friends 270 .
A range of relevant evidence from qualitative and quantitative studies documents that adolescents often ruminate about online interactions and messages. For example, online salience (constantly thinking about communication, content or events happening online) was positively associated with stress on both between-person and within-person levels in a cross-sectional quota sample of adults and three diary studies of young adults 271 , 272 . Online salience has also been associated with lower well-being in a pre-registered study of momentary self-reports from young adults with logged online behaviours. However, this study also noted that positive thoughts were related to higher well-being 273 . Furthermore, although some studies found no associations between the amount of communication and digital stress 272 , a cross-sectional study found that younger users’ (age 14–34 years and 35–49 years) perception of social pressure to be constantly available was related to communication load (measured by questions about the amount of use, as well as the urge to check email and social media) and Internet multitasking, whereas this was not the case for older users aged 50–85 years 274 . By contrast, communication load and perceived stress were associated only among older users.
Summary and future directions
To help to understand the potential role of social media in the decline of adolescent mental health over the past decade, researchers should study the mechanisms linking social media, adolescent development and mental health. Specifically, social media environments might amplify the socio-cognitive processes that render adolescents more vulnerable to mental health conditions in the first place. We outline various mechanisms at three levels of adolescent development — behavioural, cognitive and neurobiological — that could be involved in the decline of adolescent mental health as a function of social media engagement. To do so, we delineate specific social media affordances, such as quantification of social feedback or anonymity, which can also have positive impacts on mental health.
Our Review sets out clear recommendations for future research on the intersection of social media and adolescent mental health. The foundation of this research lies in the existing literature investigating the underlying processes that heighten adolescents’ risk of developing socio-emotional disorders. Zooming in on the potential mechanistic targets impacted by social media uses and affordances will produce specific research questions to facilitate controlled and systematic scientific inquiry relevant for intervention and translation. This approach encourages researchers to pinpoint the mechanisms and levels of explanation they want to include and will enable them to identify what factors to additionally consider, such as participants’ age 60 , the specific mental health outcomes being measured, the types of social media being examined and the populations under study 52 , 228 . Targeted and effective research should prioritize the most promising areas of study and acknowledge that all research approaches have inherent limitations 229 . Researchers must embrace methodological diversity, which in turn will facilitate triangulation. Surveys, experience sampling designs in conjunction with digital trace data, as well as experimental or neuroimaging paradigms and computational modelling (such as reinforcement learning) can all be used to address research questions comprehensively 230 . Employing such a multi-method approach enables the convergence of evidence and strengthens the reliability of findings 231 .
Mental health and developmental research can also become more applicable to the study of social media by considering how studies might already be exploring features of the digital environment, such as its design features and perceived affordances. Many cognitive neuroscience studies that investigate social processes and mental health during adolescence necessarily design tasks that can be completed in controlled experimental or brain scanning environments. Consequently, they tend to focus on digitally mediated interactions. However, researchers conceptualize and generalize their results to face-to-face interactions. For example, it is common across the discipline to not explicitly describe the interactions under study as being about social processes in digital environments (such as studies that assess social feedback based on the number of ‘thumbs up’ or ‘thumbs down’ received in social media 232 ). Considering whether cognitive neuroscience studies include key affordances of mediated (or non-mediated) environments, and discussing these in published papers, will make studies searchable within the field of social media research, enabling researchers to broaden the impact of their work and systematically specify generalizations to offline environments 233 .
To bridge the gap between knowledge about mediated and non-mediated social environments, it is essential to directly compare the two 233 . It is often assumed that negative experiences online have a detrimental impact on mental health. However, it remains unclear whether this mechanism is present in both mediated and non-mediated spaces or whether it is specific to the mediated context. For instance, our Review highlights that the quantification of social feedback through likes is an important affordance of social media 160 . Feedback on social media platforms might therefore elicit a greater sense of certainty because it is quantified compared with the more subjective and open-to-interpretation feedback received face to face 151 . Conducting experiments in which participants receive feedback that is more or less quantified and uncertain, specifically designed to compare mediated and non-mediated environments, would provide valuable insights. Such research efforts could also establish connections with computational neuroscience studies demonstrating that people tend to learn faster from stimuli that are less uncertain 234 .
We have chosen not to make recommendations concerning interventions targeting social media use to improve adolescent mental health for several reasons. First, we did not fully consider the bidirectional interactions between environment and development 35 , 235 , or the factors modulating adolescents’ differential susceptibility to the effects of social media 45 , 58 . For example, mental health status also influences how social media is used 47 , 58 , 59 , 236 , 237 (Box 2 ). These bidirectional interactions could be addressed using network or complexity science approaches 238 . Second, we do not yet know how the potential mechanisms by which social media might increase mental health vulnerability compare in magnitude, importance, scale and ease and/or cost of intervention with other factors and mechanisms that are already well known to influence mental health, such as poverty or loneliness. Last, social media use will probably interact with these predictors in ways that have not been delineated and can also support mental health resilience (for example, through social support or online self-help programmes). These complexities should be considered in future research, which will need to pinpoint not just the existence of mechanisms but their relative importance, to identify policy and intervention priorities.
Our Review has used a broad definition of mental health. Focusing on specific diagnostic or transdiagnostic symptomatology might reveal different mechanisms of interest. Furthermore, our Review is limited to mechanisms related to behaviour and neurocognitive development, disregarding other levels of explanation (such as genetics and culture) 34 , and also studying predominately Western-centric samples 239 . Mechanisms do not operate solely in linear pathways but exist within networks of interacting risk and resilience factors, characterized by non-linear and complex dynamics across diverse timescales 9 . Mechanisms and predisposing factors can interact and combine, amplifying mental health vulnerability. Mental health can be considered a dynamic system in which gradual changes to external conditions can have substantial downstream consequences due to system properties such as feedback loops 240 , 241 , 242 . These consequences are especially prominent in times of change and pre-existing vulnerability, such as adolescence 10 .
Indeed, if social media is a contributing factor to the current decline in adolescent mental health, as is commonly assumed, then it is important to identify and investigate mechanisms that are specifically tailored to the adolescent age range and make the case for why they matter. Without a thorough examination of these mechanisms and policy analysis to indicate whether they should be a priority to address, there is insufficient evidence to support the hypothesis that social media is the primary — or even just an influential and important — driver of mental health declines. Researchers need to stop studying social media as monolithic and uniform, and instead study its features, affordances and outcomes by leveraging a range of methods including experiments, questionnaires, qualitative research and industry data. Ultimately, this comprehensive approach will enhance researchers’ ability to address the potential challenges that the digital era poses on adolescent mental health.
Box 2 Effects of mental health on social media use
Although a lot of scientific discussion has focused on the impact of social media use on mental health, cross-sectional studies cannot differentiate between whether social media use is influencing mental health or mental health is influencing social media use, or a third factor is influencing both 51 . It is likely that mental health status influences social media use creating reinforcing cycles of behaviour, something that has been considered in the communication sciences literature under the term ‘transactional media effects’ 58 , 236 , 237 . According to communication science models, media use and its consequences are components of reciprocal processes 275 .
There are similar models in mental health research. For example, people’s moods influence their judgements of events, which can lead to self-perpetuating cycles of negativity (or positivity); a mechanism called ‘mood congruency’ 276 . Behavioural studies have also shown that people experiencing poor mental health behave in ways that decrease their opportunity to experience environmental reward such as social activities, maintaining poor mental health 277 , 278 . Although for many people these behaviours are a form of coping (for example, by avoiding stressful circumstances), they often worsen symptoms of mental health conditions 279 .
Some longitudinal studies found that a decrease in adolescent well-being predicted an increase in social media use 1 year later 47 , 59 . However, other studies have found no relationships between well-being and social media use over long-term or daily time windows 45 , 46 . One reason behind the heterogeneity of the results could be that how mental health impacts social media use is highly individual 45 , 280 .
Knowledge on the impact of mental health on social media use is still in its infancy and studies struggle to reach coherent conclusions. However, findings from the mental health literature can be used to generate hypotheses about how aspects of mental health might impact social media use. For example, it has been repeatedly found that young people with anxiety or eating disorders engage in more social comparisons than individuals without these disorders 281 , 282 , and adolescents with depression report more unfavourable social comparisons on social media than adolescents without depression 283 . Similar results have been found for social feedback seeking (for example, reassurance), including in social media environments 159 . Specifically, depressive symptoms were more associated with social comparison and feedback seeking, and these associations were stronger in women and in adolescents who were less popular. Individuals from the general population with lower self-esteem post more negative and less positive content than individuals with higher self-esteem, which in turn is associated with receiving less positive feedback from others 185 . There are therefore a wide range of possible ways in which diverse aspects of mental health might influence specific facets of how social media is used — and, in turn, how it ends up impacting the user.
Savin-Williams, R. Adolescence: An Ethological Perspective (Springer, 1987).
Sawyer, S. M., Azzopardi, P. S., Wickremarathne, D. & Patton, G. C. The age of adolescence. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2 , 223–228 (2018).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Paus, T., Keshavan, M. & Giedd, J. N. Why do many psychiatric disorders emerge during adolescence? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9 , 947–957 (2008).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Solmi, M. et al. Age at onset of mental disorders worldwide: large-scale meta-analysis of 192 epidemiological studies. Mol. Psychiatry 27 , 281–295 (2022).
Orben, A., Lucas, R. E., Fuhrmann, D. & Kievit, R. A. Trajectories of adolescent life satisfaction. R. Soc. Open. Sci. 9 , 211808 (2022).
Rapee, R. M. et al. Adolescent development and risk for the onset of social-emotional disorders: a review and conceptual model. Behav. Res. Ther. 123 , 103501 (2019). This review describes why adolescence is a sensitive period for mental health vulnerability.
Arango, C. et al. Risk and protective factors for mental disorders beyond genetics: an evidence‐based atlas. World Psychiatry 20 , 417–436 (2021).
Ioannidis, K., Askelund, A. D., Kievit, R. A. & van Harmelen, A.-L. The complex neurobiology of resilient functioning after childhood maltreatment. BMC Med. 18 , 32 (2020).
Kraemer, H. C., Stice, E., Kazdin, A., Offord, D. & Kupfer, D. How do risk factors work together? Mediators, moderators, and independent, overlapping, and proxy risk factors. AJP 158 , 848–856 (2001).
Article Google Scholar
Hankin, B. L. & Abramson, L. Y. Development of gender differences in depression: an elaborated cognitive vulnerability–transactional stress theory. Psychol. Bull. 127 , 773–796 (2001).
Collishaw, S., Maughan, B., Natarajan, L. & Pickles, A. Trends in adolescent emotional problems in England: a comparison of two national cohorts twenty years apart: twenty-year trends in emotional problems. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 51 , 885–894 (2010).
Pitchforth, J. M., Viner, R. M. & Hargreaves, D. S. Trends in mental health and wellbeing among children and young people in the UK: a repeated cross-sectional study, 2000–14. Lancet 388 , S93 (2016).
Coley, R. L., O’Brien, M. & Spielvogel, B. Secular trends in adolescent depressive symptoms: growing disparities between advantaged and disadvantaged schools. J. Youth Adolescence 48 , 2087–2098 (2019).
Patalay, P. & Gage, S. H. Changes in millennial adolescent mental health and health-related behaviours over 10 years: a population cohort comparison study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 48 , 1650–1664 (2019).
Pitchforth, J. M. et al. Mental health and well-being trends among children and young people in the UK, 1995–2014: analysis of repeated cross-sectional national health surveys. Psychol. Med. 49 , 1275–1285 (2019).
Plana‐Ripoll, O. et al. Temporal changes in sex‐ and age‐specific incidence profiles of mental disorders—a nationwide study from 1970 to 2016. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 145 , 604–614 (2022).
Twenge, J. M., Cooper, A. B., Joiner, T. E., Duffy, M. E. & Binau, S. G. Age, period, and cohort trends in mood disorder indicators and suicide-related outcomes in a nationally representative dataset, 2005–2017. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 128 , 185–199 (2019).
van Vuuren, C. L., Uitenbroek, D. G., van der Wal, M. F. & Chinapaw, M. J. M. Sociodemographic differences in 10-year time trends of emotional and behavioural problems among adolescents attending secondary schools in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 27 , 1621–1631 (2018).
Collishaw, S. Annual research review: secular trends in child and adolescent mental health. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 56 , 370–393 (2015).
Goodwin, R. D. et al. Trends in U.S. depression prevalence from 2015 to 2020: the widening treatment gap. Am. J. Prev. Med. 63 , 726–733 (2022).
Mojtabai, R. & Olfson, M. National trends in mental health care for US adolescents. JAMA Psychiatry 77 , 703 (2020).
Mojtabai, R., Olfson, M. & Han, B. National trends in the prevalence and treatment of depression in adolescents and young adults. Pediatrics 138 , e20161878 (2016).
Goodwin, R. D., Weinberger, A. H., Kim, J. H., Wu, M. & Galea, S. Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008–2018: rapid increases among young adults. J. Psychiatr. Res. 130 , 441–446 (2020).
Beerten, S. G. et al. Trends in the registration of anxiety in Belgian primary care from 2000 to 2021: a registry-based study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 73 , e460–e467 (2022).
Walrave, R. et al. Trends in the epidemiology of depression and comorbidities from 2000 to 2019 in Belgium. BMC Prim. Care 23 , 163 (2022).
Vuorre, M. & Przybylski, A. K. Global well-being and mental health in the internet age. Clin. Psychol. Sci . https://doi.org/10.1177/21677026231207791 (2023).
Steffen, A., Thom, J., Jacobi, F., Holstiege, J. & Bätzing, J. Trends in prevalence of depression in Germany between 2009 and 2017 based on nationwide ambulatory claims data. J. Affect. Disord. 271 , 239–247 (2020).
Ford, T. Editorial Perspective: why I am now convinced that emotional disorders are increasingly common among young people in many countries. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatr. 61 , 1275–1277 (2020).
McElroy, E., Tibber, M., Fearon, P., Patalay, P. & Ploubidis, G. B. Socioeconomic and sex inequalities in parent‐reported adolescent mental ill‐health: time trends in four British birth cohorts. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 64 , 758–767 (2022).
OECD. Society at a Glance 2019: OECD Social Indicators (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, 2019).
Ofcom. Online Nation (2021). Ofcom.org.uk https://www.ofcom.org.uk/research-and-data/online-research/online-nation (2022).
Anderson, M. & Jiang, J. Teens’ Social Media Habits and Experiences (Pew Research Center, 2018).
McFarland, L. A. & Ployhart, R. E. Social media: a contextual framework to guide research and practice. J. Appl. Psychol. 100 , 1653–1677 (2015).
Büchi, M. Digital well-being theory and research. N. Media Soc. 26 , 172–189 (2024).
Nesi, J., Choukas-Bradley, S. & Prinstein, M. J. Transformation of adolescent peer relations in the social media context: part 1—a theoretical framework and application to dyadic peer relationships. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 21 , 267–294 (2018). This landmark paper applies the idea of affordances to understanding the impact of social media on adolescent social relationships.
Taffel, S. Perspectives on the postdigital: beyond rhetorics of progress and novelty. Convergence 22 , 324–338 (2016).
Papacharissi, Z. We have always been social. Soc. Media + Society 1 , 205630511558118 (2015).
Google Scholar
Crone, E. A. & Konijn, E. A. Media use and brain development during adolescence. Nat. Commun. 9 , 1–10 (2018). This article describes adolescent cognitive and neural development and its intersection with new types of technology.
Weinstein, E. & James, C. Behind Their Screens: What Teens Are Facing (and Adults Are Missing) (MIT Press, 2022).
Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L. & Martin, G. N. Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 6 , 3–17 (2017).
Gunnell, D., Kidger, J. & Elvidge, H. Adolescent mental health in crisis. BMJ 361 , k2608 (2018).
Odgers, C. L., Schueller, S. M. & Ito, M. Screen time, social media use, and adolescent development. Annu. Rev. Dev. Psychol. 2 , 485–502 (2020).
Valkenburg, P. M., Meier, A. & Beyens, I. Social media use and its impact on adolescent mental health: an umbrella review of the evidence. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 44 , 58–68 (2022).
Kreski, N. et al. Social media use and depressive symptoms among United States adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 68 , 572–579 (2020).
Beyens, I., Pouwels, J. L., van Driel, I. I., Keijsers, L. & Valkenburg, P. M. The effect of social media on well-being differs from adolescent to adolescent. Sci. Rep. 10 , 10763 (2020). This landmark paper highlights that the impacts of social media on well-being are highly individual.
Jensen, M., George, M. J., Russell, M. R. & Odgers, C. L. Young adolescents’ digital technology use and mental health symptoms: little evidence of longitudinal or daily linkages. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 7 , 1416–1433 (2019).
Orben, A., Dienlin, T. & Przybylski, A. K. Social media’s enduring effect on adolescent life satisfaction. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116 , 10226–10228 (2019).
Allcott, H., Braghieri, L., Eichmeyer, S. & Gentzkow, M. The welfare effects of social media. Am. Economic Rev. 110 , 629–676 (2020).
Nassen, L.-M., Vandebosch, H., Poels, K. & Karsay, K. Opt-out, abstain, unplug. A systematic review of the voluntary digital disconnection literature. Telemat. Inform. 81 , 101980 (2023).
Dienlin, T. & Johannes, N. The impact of digital technology use on adolescent well-being. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 22 , 135–142 (2020).
Odgers, C. L. & Jensen, M. R. Annual research review: adolescent mental health in the digital age: facts, fears, and future directions. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 61 , 336–348 (2020).
Meier, A. & Reinecke, L. Computer-mediated communication, social media, and mental health: a conceptual and empirical meta-review. Commun. Res. 48 , 1182–1209 (2021). This review provides a hierarchical taxonomy of the levels of analysis at which social media can be conceptualized and measured.
Orben, A. Teenagers, screens and social media: a narrative review of reviews and key studies. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 55 , 407–414 (2020).
Bell, V., Bishop, D. V. M. & Przybylski, A. K. The debate over digital technology and young people. BMJ 351 , h3064 (2015).
Online Safety Act 2023. legislation.gov.uk , https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2023/50/enacted (2023).
Hawkes, N. CMO report is unable to shed light on impact of screen time and social media on children’s health. BMJ 364 , l643 (2019).
US Department of Health and Human Services. Social Media and Youth Mental Health: The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory (2023).
Valkenburg, P. M. & Peter, J. The differential susceptibility to media effects model: differential susceptibility to media effects model. J. Commun. 63 , 221–243 (2013). This landmark paper examines how the impact of media is influenced by individual differences.
Orben, A., Przybylski, A. K., Blakemore, S.-J. & Kievit, R. A. Windows of developmental sensitivity to social media. Nat. Commun. 13 , 1649 (2022). This large-scale data analysis shows that adolescent development potentially influences how social media impacts well-being.
Orben, A. & Blakemore, S.-J. How social media affects teen mental health: a missing link. Nature 614 , 410–412 (2023).
Shaw, H. et al. Quantifying smartphone “use”: choice of measurement impacts relationships between “usage” and health. Technol. Mind Behav . 1 , https://doi.org/10.1037/tmb0000022 (2020).
Parry, D. A. et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of discrepancies between logged and self-reported digital media use. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 1535–1547 (2021).
Verduyn, P., Gugushvili, N. & Kross, E. Do social networking sites influence well-being? The extended active-passive model. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 31 , 62–68 (2022).
Davidson, B. I., Shaw, H. & Ellis, D. A. Fuzzy constructs in technology usage scales. Comput. Hum. Behav. 133 , 107206 (2022).
Shaw, D. J., Kaye, L. K., Ngombe, N., Kessler, K. & Pennington, C. R. It’s not what you do, it’s the way that you do it: an experimental task delineates among passive, reactive and interactive styles of behaviour on social networking sites. PLoS ONE 17 , e0276765 (2022).
Griffioen, N., Van Rooij, M., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A. & Granic, I. Toward improved methods in social media research. Technol. Mind Behav . 1 , https://doi.org/10.1037/tmb0000005 (2020).
Valkenburg, P. M. Social media use and well-being: what we know and what we need to know. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 45 , 101294 (2022).
Yang, C., Holden, S. M. & Ariati, J. Social media and psychological well-being among youth: the multidimensional model of social media use. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 24 , 631–650 (2021).
Kelly, Y., Zilanawala, A., Booker, C. & Sacker, A. Social media use and adolescent mental health: findings from the UK Millennium Cohort Study. EClinicalMedicine 6 , 59–68 (2019).
Orben, A. & Przybylski, A. K. The association between adolescent well-being and digital technology use. Nat. Hum. Behav. 3 , 173–182 (2019).
Sultan, M., Scholz, C. & van den Bos, W. Leaving traces behind: using social media digital trace data to study adolescent wellbeing. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 10 , 100281 (2023).
Kaye, L., Orben, A., Ellis, D., Hunter, S. & Houghton, S. The conceptual and methodological mayhem of “screen time”. IJERPH 17 , 3661 (2020).
Choukas-Bradley, S., Roberts, S. R., Maheux, A. J. & Nesi, J. The perfect storm: a developmental–sociocultural framework for the role of social media in adolescent girls’ body image concerns and mental health. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 25 , 681–701 (2022). This review focuses on how social media can influence adolescent development of body image.
Moreno, M. A. & Uhls, Y. T. Applying an affordances approach and a developmental lens to approach adolescent social media use. Digital Health 5 , 205520761982667 (2019).
Smock, A. D., Ellison, N. B., Lampe, C. & Wohn, D. Y. Facebook as a toolkit: a uses and gratification approach to unbundling feature use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 27 , 2322–2329 (2011).
Bayer, J. B., Triêu, P. & Ellison, N. B. Social media elements, ecologies, and effects. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 71 , 471–497 (2020).
Gibson, J. J. The Scological Approach to Visual Perception (Houghton Mifflin, 1979).
Norman, D. A. The Psychology of Everyday Things (Basic Books, 1988).
Evans, S. K., Pearce, K. E., Vitak, J. & Treem, J. W. Explicating affordances: a conceptual framework for understanding affordances in communication research. J. Comput. Mediat. Commun. 22 , 35–52 (2017).
Bayer, J. B., Ellison, N. B., Schoenebeck, S. Y. & Falk, E. B. Sharing the small moments: ephemeral social interaction on Snapchat. Information . Commun. Soc. 19 , 956–977 (2016).
Fox, J. & McEwan, B. Distinguishing technologies for social interaction: the perceived social affordances of communication channels scale. Commun. Monogr. 84 , 298–318 (2017).
Kreling, R., Meier, A. & Reinecke, L. Feeling authentic on social media: subjective authenticity across instagram stories and posts. Soc. Media + Society 8 , 205630512210862 (2022).
Leonardi, P. M. Social media, knowledge sharing, and innovation: toward a theory of communication visibility. Inf. Syst. Res. 25 , 796–816 (2014).
Treem, J. W. & Leonardi, P. M. Social media use in organizations: exploring the affordances of visibility, editability, persistence, and association. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 36 , 143–189 (2013).
Ellison, N. B., Pyle, C. & Vitak, J. Scholarship on well-being and social media: a sociotechnical perspective. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 46 , 101340 (2022).
Orben, A. The Sisyphean cycle of technology panics. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 15 , 1143–1157 (2020).
Granic, I., Morita, H. & Scholten, H. Beyond screen time: identity development in the digital age. Psychol. Inq. 31 , 195–223 (2020). This perspective discusses how adolescent identity development might be impacted by digital platforms including social media and video games.
Lieberman, A. & Schroeder, J. Two social lives: how differences between online and offline interaction influence social outcomes. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 31 , 16–21 (2020).
Valkenburg, P. M. & Peter, J. Online communication among adolescents: an integrated model of its attraction, opportunities, and risks. J. Adolesc. Health 48 , 121–127 (2011).
Steinberg, L. et al. Around the world, adolescence is a time of heightened sensation seeking and immature self-regulation. Dev. Sci. 21 , e12532 (2018).
Blakemore, S.-J. & Robbins, T. W. Decision-making in the adolescent brain. Nat. Neurosci. 15 , 1184–1191 (2012).
Steinberg, L. A social neuroscience perspective on adolescent risk-taking. Dev. Rev. 28 , 78–106 (2008).
Chein, J., Albert, D., O’Brien, L., Uckert, K. & Steinberg, L. Peers increase adolescent risk taking by enhancing activity in the brain’s reward circuitry: peer influence on risk taking. Dev. Sci. 14 , F1–F10 (2011).
Blakemore, S.-J. Avoiding social risk in adolescence. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 27 , 116–122 (2018).
Blakemore, S.-J. & Mills, K. L. Is adolescence a sensitive period for sociocultural processing? Annu. Rev. Psychol. 65 , 187–207 (2014). This review presents adolescence as an important stage of development characterized by changes to social cognition.
Campbell, R. et al. Multiple risk behaviour in adolescence is associated with substantial adverse health and social outcomes in early adulthood: findings from a prospective birth cohort study. Prev. Med. 138 , 106157 (2020).
Kurten, S. et al. Like to drink: dynamics of liking alcohol posts and effects on alcohol use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 129 , 107145 (2022).
Vannucci, A., Simpson, E. G., Gagnon, S. & Ohannessian, C. M. Social media use and risky behaviors in adolescents: a meta‐analysis. J. Adolesc. 79 , 258–274 (2020).
Eichhorn, K. The End of Forgetting: Growing up with Social Media (Harvard Univ. Press, 2019).
Litt, E. & Hargittai, E. The imagined audience on social network sites. Soc. Media + Society 2 , 205630511663348 (2016).
Vitak, J. The impact of context collapse and privacy on social network site disclosures. J. Broadcast. Electron. Media 56 , 451–470 (2012).
Livingstone, S. Taking risky opportunities in youthful content creation: teenagers’ use of social networking sites for intimacy, privacy and self-expression. N. Media Soc. 10 , 393–411 (2008).
Marciano, L., Schulz, P. J. & Camerini, A.-L. Cyberbullying perpetration and victimization in youth: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 25 , 163–181 (2020).
Mori, C., Temple, J. R., Browne, D. & Madigan, S. Association of sexting with sexual behaviors and mental health among adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 173 , 770 (2019).
Suler, J. The online disinhibition effect. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 7 , 321–326 (2004).
Wright, M. F., Harper, B. D. & Wachs, S. The associations between cyberbullying and callous-unemotional traits among adolescents: the moderating effect of online disinhibition. Pers. Individ. Differ. 140 , 41–45 (2019).
Nitschinsk, L., Tobin, S. J. & Vanman, E. J. The disinhibiting effects of anonymity increase online trolling. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 25 , 377–383 (2022).
Nadkarni, A. & Hofmann, S. G. Why do people use Facebook? Pers. Individ. Differ. 52 , 243–249 (2012).
Leary, M. R. & Kowalski, R. M. Impression management: a literature review and two-component model. Psychol. Bull. 107 , 34–47 (1990).
Zhao, S., Grasmuck, S. & Martin, J. Identity construction on Facebook: digital empowerment in anchored relationships. Comput. Hum. Behav. 24 , 1816–1836 (2008).
Bij de Vaate, N. A. J. D., Veldhuis, J. & Konijn, E. A. How online self-presentation affects well-being and body image: a systematic review. Telemat. Inform. 47 , 101316 (2020).
Reinecke, L. & Trepte, S. Authenticity and well-being on social network sites: a two-wave longitudinal study on the effects of online authenticity and the positivity bias in SNS communication. Comput. Hum. Behav. 30 , 95–102 (2014).
Twomey, C. & O’Reilly, G. Associations of self-presentation on Facebook with mental health and personality variables: a systematic review. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 20 , 587–595 (2017).
Vanden Abeele, M., Schouten, A. P. & Antheunis, M. L. Personal, editable, and always accessible: an affordance approach to the relationship between adolescents’ mobile messaging behavior and their friendship quality. J. Soc. Personal. Relatsh. 34 , 875–893 (2017).
Krause, H.-V., Baum, K., Baumann, A. & Krasnova, H. Unifying the detrimental and beneficial effects of social network site use on self-esteem: a systematic literature review. Media Psychol. 24 , 10–47 (2021).
Carr, C. T. & Foreman, A. C. Identity shift III: effects of publicness of feedback and relational closeness in computer-mediated communication. Media Psychol. 19 , 334–358 (2016).
Walther, J. B. et al. The effect of feedback on identity shift in computer-mediated communication. Media Psychol. 14 , 1–26 (2011).
Gonzales, A. L. & Hancock, J. T. Identity shift in computer-mediated environments. Media Psychol. 11 , 167–185 (2008).
Kelly, A. E. & Rodriguez, R. R. Publicly committing oneself to an identity. Basic. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 28 , 185–191 (2006).
Petre, C. E. The relationship between Internet use and self-concept clarity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cyberpsychology 15 , https://doi.org/10.5817/CP2021-2-4 (2021).
Appel, M., Schreiner, C., Weber, S., Mara, M. & Gnambs, T. Intensity of Facebook use is associated with lower self-concept clarity: cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence. J. Media Psychol. 30 , 160–172 (2018).
Talaifar, S. & Lowery, B. S. Freedom and constraint in digital environments: implications for the self. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 18 , 544–575 (2022).
West, M., Rice, S. & Vella-Brodrick, D. Mid-adolescents’ social media use: supporting and suppressing autonomy. J. Adolesc. Res . https://doi.org/10.1177/07435584231168402 (2023).
Grasmuck, S., Martin, J. & Zhao, S. Ethno-racial identity displays on Facebook. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 15 , 158–188 (2009).
DeVito, M. A., Walker, A. M. & Birnholtz, J. ‘Too Gay for Facebook’: presenting LGBTQ+ identity throughout the personal social media ecosystem. Proc. ACM Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2 , 1–23 (2018).
Ellison, N., Heino, R. & Gibbs, E. Managing impressions online: self-presentation processes in the online dating environment. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun . 11 , https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2006.00020.x (2006).
Hancock, J. T. in Oxford Handbook of Internet Psychology (eds Joinson, A. et al.) 287–301 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2009).
Davidson, B. I. & Joinson, A. N. Shape shifting across social media. Soc. Media + Society 7 , 205630512199063 (2021).
Davis, J. L. Triangulating the self: identity processes in a connected era: triangulating the self. Symbolic Interaction 37 , 500–523 (2014).
Allen, B. J., Stratman, Z. E., Kerr, B. R., Zhao, Q. & Moreno, M. A. Associations between psychosocial measures and digital media use among transgender youth: cross-sectional study. JMIR Pediatr. Parent. 4 , e25801 (2021).
Haimson, O. L. Mapping gender transition sentiment patterns via social media data: toward decreasing transgender mental health disparities. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 26 , 749–758 (2019).
Harter, S. The Construction of the Self: Developmental and Sociocultural Foundations (Guilford Press, 2012).
Crone, E. A., Green, K. H., van de Groep, I. H. & van der Cruijsen, R. A neurocognitive model of self-concept development in adolescence. Annu. Rev. Dev. Psychol. 4 , 273–295 (2022). This extensive review discusses how adolescence is an important time for self-concept development.
Pfeifer, J. H. & Peake, S. J. Self-development: integrating cognitive, socioemotional, and neuroimaging perspectives. Deve. Cognit. Neurosci. 2 , 55–69 (2012).
Sebastian, C., Burnett, S. & Blakemore, S.-J. Development of the self-concept during adolescence. Trends Cognit. Sci. 12 , 441–446 (2008).
Crocetti, E., Rubini, M., Luyckx, K. & Meeus, W. Identity formation in early and middle adolescents from various ethnic groups: from three dimensions to five statuses. J. Youth Adolesc. 37 , 983–996 (2008).
Morita, H., Griffioen, N. & Granic, I. in Handbook of Adolescent Digital Media Use and Mental Health (eds Nesi, J., Telzer, E. H. & Prinstein, M. J.) 63–84 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2022).
Dumontheil, I., Apperly, I. A. & Blakemore, S.-J. Online usage of theory of mind continues to develop in late adolescence. Dev. Sci. 13 , 331–338 (2010).
Weil, L. G. et al. The development of metacognitive ability in adolescence. Conscious. Cogn. 22 , 264–271 (2013).
Moses-Payne, M. E., Chierchia, G. & Blakemore, S.-J. Age-related changes in the impact of valence on self-referential processing in female adolescents and young adults. Cognit. Dev. 61 , 101128 (2022).
Scheuplein, M. et al. Perspective taking and memory for self- and town-related information in male adolescents and young adults. Cognit. Dev. 67 , 101356 (2023).
Rodman, A. M., Powers, K. E. & Somerville, L. H. Development of self-protective biases in response to social evaluative feedback. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114 , 13158–13163 (2017).
Lee, A. Y., Mieczkowski, H., Ellison, N. B. & Hancock, J. T. The algorithmic crystal: conceptualizing the self through algorithmic personalization on TikTok. Proc. ACM Hum.–Comput. Interact. 6 , 1–22 (2022).
Thomaes, S. et al. I like me if you like me: on the interpersonal modulation and regulation of preadolescents’ state self-esteem. Child. Dev. 81 , 811–825 (2010).
Valkenburg, P. M., Peter, J. & Schouten, A. P. Friend networking sites and their relationship to adolescents’ well-being and social self-esteem. CyberPsychol. Behav. 9 , 584–590 (2006).
Kwan, I. et al. Cyberbullying and children and young people’s mental health: a systematic map of systematic reviews. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 23 , 72–82 (2020).
Przybylski, A. K. & Bowes, L. Cyberbullying and adolescent well-being in England: a population-based cross-sectional study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 1 , 19–26 (2017).
Peters, S. et al. Social media use and the not-so-imaginary audience: behavioral and neural mechanisms underlying the influence on self-concept. Dev. Cognit. Neurosci. 48 , 100921 (2021).
Wood, J. V. What is social comparison and how should we study it? Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 22 , 520–537 (1996).
Dahl, R. E., Allen, N. B., Wilbrecht, L. & Suleiman, A. B. Importance of investing in adolescence from a developmental science perspective. Nature 554 , 441–450 (2018).
Ferguson, A. M., Turner, G. & Orben, A. Social uncertainty in the digital world. Trends Cognit. Sci. 28 , 286–289 (2024).
Blease, C. R. Too many ‘friends,’ too few ‘likes’? Evolutionary psychology and ‘Facebook depression’. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 19 , 1–13 (2015).
Lee, H. Y. et al. Getting fewer “likes” than others on social media elicits emotional distress among victimized adolescents. Child. Dev. 91 , 2141–2159 (2020).
Nesi, J. & Prinstein, M. J. In search of likes: longitudinal associations between adolescents’ digital status seeking and health-risk behaviors. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 48 , 740–748 (2019).
Carr, C. T., Hayes, R. A. & Sumner, E. M. Predicting a threshold of perceived Facebook post success via likes and reactions: a test of explanatory mechanisms. Commun. Res. Rep. 35 , 141–151 (2018).
Noon, E. J. & Meier, A. Inspired by friends: adolescents’ network homophily moderates the relationship between social comparison, envy, and inspiration on instagram. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 22 , 787–793 (2019).
Schreurs, L., Meier, A. & Vandenbosch, L. Exposure to the positivity bias and adolescents’ differential longitudinal links with social comparison, inspiration and envy depending on social media literacy. Curr. Psychol . https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03893-3 (2022).
Meier, A. & Krause, H.-V. Does passive social media use harm well-being? An adversarial review. J. Media Psychol. 35 , 169–180 (2023).
Nesi, J. & Prinstein, M. J. Using social media for social comparison and feedback-seeking: gender and popularity moderate associations with depressive symptoms. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 43 , 1427–1438 (2015).
Lindström, B. et al. A computational reward learning account of social media engagement. Nat. Commun. 12 , 1311 (2021).
Fardouly, J., Diedrichs, P. C., Vartanian, L. R. & Halliwell, E. Social comparisons on social media: the impact of Facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. Body Image 13 , 38–45 (2015).
Scully, M., Swords, L. & Nixon, E. Social comparisons on social media: online appearance-related activity and body dissatisfaction in adolescent girls. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 40 , 31–42 (2023).
Appel, H., Gerlach, A. L. & Crusius, J. The interplay between Facebook use, social comparison, envy, and depression. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 9 , 44–49 (2016).
Meier, A. & Johnson, B. K. Social comparison and envy on social media: a critical review. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 45 , 101302 (2022).
Verduyn, P., Gugushvili, N., Massar, K., Täht, K. & Kross, E. Social comparison on social networking sites. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 36 , 32–37 (2020).
Meier, A., Gilbert, A., Börner, S. & Possler, D. Instagram inspiration: how upward comparison on social network sites can contribute to well-being. J. Commun. 70 , 721–743 (2020).
Vaterlaus, J. M., Patten, E. V., Roche, C. & Young, J. A. #Gettinghealthy: the perceived influence of social media on young adult health behaviors. Comput. Hum. Behav. 45 , 151–157 (2015).
Valkenburg, P. M., Beyens, I., Pouwels, J. L., Van Driel, I. I. & Keijsers, L. Social media browsing and adolescent well-being: challenging the “passive social media use hypothesis”. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcmc/zmab015 (2022).
Larson, R. W., Richards, M. H., Moneta, G., Holmbeck, G. & Duckett, E. Changes in adolescents’ daily interactions with their families from ages 10 to 18: disengagement and transformation. Dev. Psychol. 32 , 744–754 (1996).
Sebastian, C., Viding, E., Williams, K. D. & Blakemore, S.-J. Social brain development and the affective consequences of ostracism in adolescence. Brain Cogn. 72 , 134–145 (2010).
Sebastian, C. et al. Developmental influences on the neural bases of responses to social rejection: implications of social neuroscience for education. NeuroImage 57 , 686–694 (2011).
Somerville, L. H. The teenage brain: sensitivity to social evaluation. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 22 , 121–127 (2013).
Larson, R. W. & How, U. S. Children and adolescents spend time: what it does (and doesn’t) tell us about their development. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 10 , 160–164 (2001).
Thomas, L. A., De Bellis, M. D., Graham, R. & LaBar, K. S. Development of emotional facial recognition in late childhood and adolescence. Dev. Sci. 10 , 547–558 (2007).
Gunther Moor, B., van Leijenhorst, L., Rombouts, S. A. R. B., Crone, E. A. & Van der Molen, M. W. Do you like me? Neural correlates of social evaluation and developmental trajectories. Soc. Neurosci. 5 , 461–482 (2010).
Silk, J. S. et al. Peer acceptance and rejection through the eyes of youth: pupillary, eyetracking and ecological data from the Chatroom Interact task. Soc. Cognit. Affect. Neurosci. 7 , 93–105 (2012).
Gao, S., Assink, M., Cipriani, A. & Lin, K. Associations between rejection sensitivity and mental health outcomes: a meta-analytic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 57 , 59–74 (2017).
Prinstein, M. J., Nesi, J. & Telzer, E. H. Commentary: an updated agenda for the study of digital media use and adolescent development—future directions following Odgers & Jensen (2020). J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatr. 61 , 349–352 (2020).
Meshi, D., Morawetz, C. & Heekeren, H. R. Nucleus accumbens response to gains in reputation for the self relative to gains for others predicts social media use. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7 , 1–11 (2013).
Crone, E. A. & Dahl, R. E. Understanding adolescence as a period of social–affective engagement and goal flexibility. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13 , 636–650 (2012).
Platt, B., Kadosh, K. C. & Lau, J. Y. F. The role of peer rejection in adolescent depression. Depress. Anxiety 30 , 809–821 (2013).
Will, G.-J., Rutledge, R. B., Moutoussis, M. & Dolan, R. J. Neural and computational processes underlying dynamic changes in self-esteem. eLife 6 , e28098 (2017).
Macrynikola, N. & Miranda, R. Active Facebook use and mood: when digital interaction turns maladaptive. Comput. Hum. Behav. 97 , 271–279 (2019).
Grunewald, K., Deng, J., Wertz, J. & Schweizer, S. The effect of online social evaluation on mood and cognition in young people. Sci. Rep. 12 , 20999 (2022).
Andrews, J. L., Khin, A. C., Crayn, T., Humphreys, K. & Schweizer, S. Measuring online and offline social rejection sensitivity in the digital age. Psychol. Assess. 34 , 742–751 (2022).
Forest, A. L. & Wood, J. V. When social networking is not working: individuals with low self-esteem recognize but do not reap the benefits of self-disclosure on Facebook. Psychol. Sci. 23 , 295–302 (2012).
Valkenburg, P. M., Koutamanis, M. & Vossen, H. G. M. The concurrent and longitudinal relationships between adolescents’ use of social network sites and their social self-esteem. Comput. Hum. Behav. 76 , 35–41 (2017).
Burrow, A. L. & Rainone, N. How many likes did I get? purpose moderates links between positive social media feedback and self-esteem. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 69 , 232–236 (2017).
Seo, M., Kim, J. & Yang, H. Frequent interaction and fast feedback predict perceived social support: using crawled and self-reported data of Facebook users. J. Comput.-Mediat. Comm. 21 , 282–297 (2016).
Fuhrmann, D., Casey, C. S., Speekenbrink, M. & Blakemore, S.-J. Social exclusion affects working memory performance in young adolescent girls. Dev. Cognit. Neurosci. 40 , 100718 (2019).
Blakemore, S.-J. & Choudhury, S. Development of the adolescent brain: implications for executive function and social cognition. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiat 47 , 296–312 (2006).
Dreyfuss, M. et al. Teens impulsively react rather than retreat from threat. Dev. Neurosci. 36 , 220–227 (2014).
Guyer, A. E., Choate, V. R., Pine, D. S. & Nelson, E. E. Neural circuitry underlying affective response to peer feedback in adolescence. Soc. Cognit. Affect. Neurosci. 7 , 81–92 (2012).
Sherman, L. E., Payton, A. A., Hernandez, L. M., Greenfield, P. M. & Dapretto, M. The power of the like in adolescence: effects of peer influence on neural and behavioral responses to social media. Psychol. Sci. 27 , 1027–1035 (2016).
van Harmelen, A.-L. et al. Adolescent friendships predict later resilient functioning across psychosocial domains in a healthy community cohort. Psychol. Med. 47 , 2312–2322 (2017).
Chu, P. S., Saucier, D. A. & Hafner, E. Meta-analysis of the relationships between social support and well-being in children and adolescents. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 29 , 624–645 (2010).
Schneider, F. M. et al. Social media ostracism: the effects of being excluded online. Comput. Hum. Behav. 73 , 385–393 (2017).
Reich, S., Schneider, F. M. & Heling, L. Zero likes—symbolic interactions and need satisfaction online. Comput. Hum. Behav. 80 , 97–102 (2018).
Lutz, S. & Schneider, F. M. Is receiving dislikes in social media still better than being ignored? The effects of ostracism and rejection on need threat and coping responses online. Media Psychol. 24 , 741–765 (2021).
Lutz, S. Why don’t you answer me? Exploring the effects of (repeated exposure to) ostracism via messengers on users’ fundamental needs, well-being, and coping motivation. Media Psychol. 26 , 113–140 (2023).
Rodríguez-Hidalgo, C. T., Tan, E. S. H., Verlegh, P. W. J., Beyens, I. & Kühne, R. Don’t stress me now: assessing the regulatory impact of face-to-face and online feedback prosociality on stress during an important life event. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 25 , 307–327 (2020).
Trepte, S., Dienlin, T. & Reinecke, L. Influence of social support received in online and offline contexts on satisfaction with social support and satisfaction with life: a longitudinal study. Media Psychol. 18 , 74–105 (2015).
Dredge, R. & Schreurs, L. Social media use and offline interpersonal outcomes during youth: a systematic literature review. Mass. Commun. Soc. 23 , 885–911 (2020).
Colasante, T., Lin, L., De France, K. & Hollenstein, T. Any time and place? Digital emotional support for digital natives. Am. Psychol. 77 , 186–195 (2022).
Pouwels, J. L., Valkenburg, P. M., Beyens, I., Van Driel, I. I. & Keijsers, L. Social media use and friendship closeness in adolescents’ daily lives: an experience sampling study. Dev. Psychol. 57 , 309–323 (2021).
Mills, K. L. et al. Structural brain development between childhood and adulthood: convergence across four longitudinal samples. NeuroImage 141 , 273–281 (2016).
Tamnes, C. K. et al. Development of the cerebral cortex across adolescence: a multisample study of inter-related longitudinal changes in cortical volume, surface area, and thickness. J. Neurosci. 37 , 3402–3412 (2017).
Larsen, B. & Luna, B. Adolescence as a neurobiological critical period for the development of higher-order cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 94 , 179–195 (2018).
Petanjek, Z. et al. Extraordinary neoteny of synaptic spines in the human prefrontal cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108 , 13281–13286 (2011).
Cohen, J. R. et al. A unique adolescent response to reward prediction errors. Nat. Neurosci. 13 , 669–671 (2010).
Ernst, M. et al. Amygdala and nucleus accumbens in responses to receipt and omission of gains in adults and adolescents. NeuroImage 25 , 1279–1291 (2005).
Galván, A. & McGlennen, K. M. Enhanced striatal sensitivity to aversive reinforcement in adolescents versus adults. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 25 , 284–296 (2013).
Braams, B. R., Van Duijvenvoorde, A. C. K., Peper, J. S. & Crone, E. A. Longitudinal changes in adolescent risk-taking: a comprehensive study of neural responses to rewards, pubertal development, and risk-taking behavior. J. Neurosci. 35 , 7226–7238 (2015).
Schreuders, E. et al. Contributions of reward sensitivity to ventral striatum activity across adolescence and early adulthood. Child. Dev. 89 , 797–810 (2018).
Maza, M. T. et al. Association of habitual checking behaviors on social media with longitudinal functional brain development. JAMA Pediatr. 177 , 160–167 (2023).
Miller, J., Mills, K. L., Vuorre, M., Orben, A. & Przybylski, A. K. Impact of digital screen media activity on functional brain organization in late childhood: evidence from the ABCD study. Cortex 169 , 290–308 (2023).
Flayelle, M. et al. A taxonomy of technology design features that promote potentially addictive online behaviours. Nat. Rev. Psychol. 2 , 136–150 (2023).
Lupien, S. J., McEwen, B. S., Gunnar, M. R. & Heim, C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10 , 434–445 (2009).
Gunnar, M. R., Wewerka, S., Frenn, K., Long, J. D. & Griggs, C. Developmental changes in hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal activity over the transition to adolescence: normative changes and associations with puberty. Dev. Psychopathol. 21 , 69–85 (2009).
Somerville, L. H. et al. The medial prefrontal cortex and the emergence of self-conscious emotion in adolescence. Psychol. Sci. 24 , 1554–1562 (2013).
Stroud, L. R. et al. Stress response and the adolescent transition: performance versus peer rejection stressors. Dev. Psychopathol. 21 , 47–68 (2009).
Avital, A. & Richter-Levin, G. Exposure to juvenile stress exacerbates the behavioural consequences of exposure to stress in the adult rat. Int. J. Neuropsychopharm. 8 , 163–173 (2005).
McCormick, C. M., Mathews, I. Z., Thomas, C. & Waters, P. Investigations of HPA function and the enduring consequences of stressors in adolescence in animal models. Brain Cogn. 72 , 73–85 (2010).
Eiland, L. & Romeo, R. D. Stress and the developing adolescent brain. Neuroscience 249 , 162–171 (2013).
Romeo, R. D. The teenage brain. Curr. Direc. Psychol. Sci. 22 , 140–145 (2013).
Afifi, T. D., Zamanzadeh, N., Harrison, K. & Acevedo Callejas, M. WIRED: the impact of media and technology use on stress (cortisol) and inflammation (interleukin IL-6) in fast paced families. Comput. Hum. Behav. 81 , 265–273 (2018).
Morin-Major, J. K. et al. Facebook behaviors associated with diurnal cortisol in adolescents: is befriending stressful? Psychoneuroendocrinology 63 , 238–46 (2016).
Ghai, S. It’s time to reimagine sample diversity and retire the WEIRD dichotomy. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 971–972 (2021).
Munafò, M. R. & Davey Smith, G. Robust research needs many lines of evidence. Nature 553 , 399–401 (2018).
Dale, R., Warlaumont, A. S. & Johnson, K. L. The fundamental importance of method to theory. Nat. Rev. Psychol. 2 , 55–66 (2022).
Parry, D. A., Fisher, J. T., Mieczkowski, H., Sewall, C. J. R. & Davidson, B. I. Social media and well-being: a methodological perspective. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 45 , 101285 (2022).
Will, G.-J. et al. Neurocomputational mechanisms underpinning aberrant social learning in young adults with low self-esteem. Transl. Psychiatry 10 , 96 (2020).
Walther, J. B. Affordances, effects, and technology errors. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 36 , 190–193 (2013).
Piray, P. & Daw, N. D. A model for learning based on the joint estimation of stochasticity and volatility. Nat. Commun. 12 , 6587 (2021).
Bronfenbrenner, U. The Ecology of Human Development: Experiments by Nature and Design (Harvard Univ. Press, 1979).
Slater, M. D. Reinforcing spirals: the mutual influence of media selectivity and media effects and their impact on individual behavior and social identity. Commun. Theory 17 , 281–303 (2007).
Valkenburg, P. M., Peter, J. & Walther, J. B. Media effects: theory and research. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 67 , 315–338 (2016).
Aalbers, G., McNally, R. J., Heeren, A., De Wit, S. & Fried, E. I. Social media and depression symptoms: a network perspective. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 148 , 1454–1462 (2019).
Ghai, S., Fassi, L., Awadh, F. & Orben, A. Lack of sample diversity in research on adolescent depression and social media use: a scoping review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 11 , 759–772 (2023).
Cramer, A. O. J. et al. Major depression as a complex dynamic system. PLoS ONE 11 , e0167490 (2016).
Kendler, K. S., Zachar, P. & Craver, C. What kinds of things are psychiatric disorders? Psychol. Med. 41 , 1143–1150 (2011).
van de Leemput, I. A. et al. Critical slowing down as early warning for the onset and termination of depression. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 111 , 87–92 (2014).
Trepte, S. The social media privacy model: privacy and communication in the light of social media affordances. Commun. Theory 31 , 549–570 (2021).
Reinecke, L. et al. Permanently online and permanently connected: development and validation of the Online Vigilance Scale. PLoS ONE 13 , e0205384 (2018).
Trieu, P., Bayer, J. B., Ellison, N. B., Schoenebeck, S. & Falk, E. Who likes to be reachable? Availability preferences, weak ties, and bridging social capital. Inform. Commun. Soc. 22 , 1096–1111 (2019).
Daft, R. L. & Lengel, R. H. Organizational information requirements, media richness and structural design. Manag. Sci. 32 , 554–571 (1986).
Rhee, L., Bayer, J. B., Lee, D. S. & Kuru, O. Social by definition: how users define social platforms and why it matters. Telemat. Inform. 59 , 101538 (2021).
Valkenburg, P. M. Understanding self-effects in social media: self-effects in social media. Hum. Commun. Res. 43 , 477–490 (2017).
Thorson, K. & Wells, C. Curated flows: a framework for mapping media exposure in the digital age: curated flows. Commun. Theor. 26 , 309–328 (2016).
Zhao, H. & Wagner, C. How TikTok leads users to flow experience: investigating the effects of technology affordances with user experience level and video length as moderators. INTR 33 , 820–849 (2023).
Carr, C. T., Wohn, D. Y. & Hayes, R. A. As social support: relational closeness, automaticity, and interpreting social support from paralinguistic digital affordances in social media. Comput. Hum. Behav. 62 , 385–393 (2016).
Rice, R. E. et al. Organizational media affordances: operationalization and associations with media use: organizational media affordances. J. Commun. 67 , 106–130 (2017).
Scissors, L., Burke, M. & Wengrovitz, S. in Proc. 19th ACM Conf. Computer-Supported Cooperative Work & Social Computing—CSCW ’16 1499–1508 (ACM Press, 2016).
Boyd, D. M. in A Networked Self: Identity, Community and Culture in Social Networking Sites (ed. Papacharissi, Z.) 35–58 (Routledge, 2011).
Valkenburg, P. M. in Handbook of Adolescent Digital Media Use and Mental Health (eds Nesi, J., Telzer, E. H. & Prinstein, M. J.) 39–60 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2022).
Dennis, Fuller & Valacich, Media Tasks, and communication processes: a theory of media synchronicity. MIS Q. 32 , 575 (2008).
DeAndrea, D. C. Advancing warranting theory: advancing warranting theory. Commun. Theor. 24 , 186–204 (2014).
Uhlhaas, P. J. et al. Towards a youth mental health paradigm: a perspective and roadmap. Mol. Psychiatry 28 , 3171–3181 (2023).
Kachuri, L. et al. Principles and methods for transferring polygenic risk scores across global populations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 25 , 8–25 (2024).
Weinstein, E. C. & Selman, R. L. Digital stress: adolescents’ personal accounts. N. Media Soc. 18 , 391–409 (2016).
Steele, R. G., Hall, J. A. & Christofferson, J. L. Conceptualizing digital stress in adolescents and young adults: toward the development of an empirically based model. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 23 , 15–26 (2020).
Nick, E. A. et al. Adolescent digital stress: frequencies, correlates, and longitudinal association with depressive symptoms. J. Adolesc. Health 70 , 336–339 (2022).
Van Der Schuur, W. A., Baumgartner, S. E. & Sumter, S. R. Social media use, social media stress, and sleep: examining cross-sectional and longitudinal relationships in adolescents. Health Commun. 34 , 552–559 (2019).
Fabio, S. & Sonja, P. Is cyberbullying worse than traditional bullying? Examining the differential roles of medium, publicity, and anonymity for the perceived severity of bullying. J. Youth Adolesc. 42 , 739–750 (2013).
Tokunaga, R. S. Following you home from school: a critical review and synthesis of research on cyberbullying victimization. Comput. Hum. Behav. 26 , 277–287 (2010).
Khetawat, D. & Steele, R. G. Examining the association between digital stress components and psychological wellbeing: a meta-analysis. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 26 , 957–974 (2023).
Beyens, I., Frison, E. & Eggermont, S. “I don’t want to miss a thing”: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput. Hum. Behav. 64 , 1–8 (2016).
Wartberg, L., Thomasius, R. & Paschke, K. The relevance of emotion regulation, procrastination, and perceived stress for problematic social media use in a representative sample of children and adolescents. Comput. Hum. Behav. 121 , 106788 (2021).
Winstone, L., Mars, B., Haworth, C. M. A. & Kidger, J. Types of social media use and digital stress in early adolescence. J. Early Adolescence 43 , 294–319 (2023).
West, M., Rice, S. & Vella-Brodrick, D. Exploring the “social” in social media: adolescent relatedness—thwarted and supported. J. Adolesc. Res . https://doi.org/10.1177/07435584211062158 (2021).
Gilbert, A., Baumgartner, S. E. & Reinecke, L. Situational boundary conditions of digital stress: goal conflict and autonomy frustration make smartphone use more stressful. Mob. Media Commun . https://doi.org/10.1177/20501579221138017 (2022).
Freytag, A. et al. Permanently online—always stressed out? The effects of permanent connectedness on stress experiences. Hum. Commun. Res. 47 , 132–165 (2021).
Johannes, N. et al. The relationship between online vigilance and affective well-being in everyday life: combining smartphone logging with experience sampling. Media Psychol. 24 , 581–605 (2021).
Reinecke, L. et al. Digital stress over the life span: the effects of communication load and internet multitasking on perceived stress and psychological health impairments in a german probability sample. Media Psychol. 20 , 90–115 (2017).
Schönbach, K. in The International Encyclopedia of Media Effects (eds Rössler, P., Hoffner, C. A. & Zoonen, L.) 1–11 (Wiley, 2017).
Mayer, J. D., Gaschke, Y. N., Braverman, D. L. & Evans, T. W. Mood-congruent judgment is a general effect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 63 , 119–132 (1992).
Ferster, C. B. A functional analysis of depression. Am. Psychol. 28 , 857–870 (1973).
Carvalho, J. P. & Hopko, D. R. Behavioral theory of depression: reinforcement as a mediating variable between avoidance and depression. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 42 , 154–162 (2011).
Helbig-Lang, S. & Petermann, F. Tolerate or eliminate? A systematic review on the effects of safety behavior across anxiety disorders. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 17 , 218–233 (2010).
Marciano, L., Driver, C. C., Schulz, P. J. & Camerini, A.-L. Dynamics of adolescents’ smartphone use and well-being are positive but ephemeral. Sci. Rep. 12 , 1316 (2022).
Rao, P. A. et al. Social anxiety disorder in childhood and adolescence: descriptive psychopathology. Behav. Res. Ther. 45 , 1181–1191 (2007).
Corning, A. F., Krumm, A. J. & Smitham, L. A. Differential social comparison processes in women with and without eating disorder symptoms. J. Couns. Psychol. 53 , 338–349 (2006).
Radovic, A., Gmelin, T., Stein, B. D. & Miller, E. Depressed adolescents’ positive and negative use of social media. J. Adolesc. 55 , 5–15 (2017).
Download references
Acknowledgements
A.O. and T.D. were funded by the Medical Research Council (MC_UU_00030/13). A.O. was funded by the Jacobs Foundation and a UKRI Future Leaders Fellowship (MR/X034925/1). S.-J.B. is funded by Wellcome (grant numbers WT107496/Z/15/Z and WT227882/Z/23/Z), the MRC, the Jacobs Foundation, the Wellspring Foundation and the University of Cambridge.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Medical Research Council Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Amy Orben & Tim Dalgleish
School of Business, Economics and Society, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen–Nürnberg, Nürnberg, Germany
Adrian Meier
Department of Psychology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Sarah-Jayne Blakemore
Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience, University College London, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.O. conceptualized the manuscript; A.O and A.M wrote the original draft; A.O., A.M., T.D. and S.-J.B. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed substantially to discussion of the content, and reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Amy Orben .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Psychology thanks Emily Weinstein, who co-reviewed with Beck Tench; Nastasia Griffioen; and Margarita Panayiotou for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Orben, A., Meier, A., Dalgleish, T. et al. Mechanisms linking social media use to adolescent mental health vulnerability. Nat Rev Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-024-00307-y
Download citation
Accepted : 02 April 2024
Published : 07 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-024-00307-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Articles on Adolescents
Displaying 1 - 20 of 142 articles.

Teens see social media algorithms as accurate reflections of themselves, study finds
Nora McDonald , George Mason University

Talking to teens about sex: advice for parents on when, how, what to say and why it’s so important
Ayobami Precious Adekola , University of South Africa

Vaping now more common than smoking among young people – and the risks go beyond lung and brain damage
Amira Guirguis , Swansea University

Cannabis legalization has led to a boom in potent forms of the drug that present new hazards for adolescents
Ty Schepis , Texas State University

Online child safety laws could help or hurt – 2 pediatricians explain what’s likely to work and what isn’t
Megan Moreno , University of Wisconsin-Madison and Jenny Radesky , University of Michigan

How teens benefit from being able to read ‘disturbing’ books that some want to ban
Gay Ivey , University of North Carolina – Greensboro

New research shows some gains but fresh difficulties in combating child sexual abuse
Ben Mathews , Queensland University of Technology and Chanel Contos , Australian National University
Breaking the curve: A call for comprehensive scoliosis awareness and care
Sanja Schreiber , University of Alberta and Emily Somers , University of Michigan

Students could get more sleep and learn better if school started a little later
Joanna Fong-Isariyawongse , University of Pittsburgh

Teens don’t know everything − and those who acknowledge that fact are more eager to learn
Tenelle Porter , Rowan University

Teens and screens: 7 ways tried-and -true parenting approaches can help navigate family conflict
Tom Hollenstein , Queen's University, Ontario and Katie Faulkner , Queen's University, Ontario

I think my teen is depressed. How can I get them help and what are the treatment options?
Louise Birrell , University of Sydney ; Andrew Baillie , University of Sydney ; Erin Kelly , University of Sydney , and Maree Teesson , University of Sydney

7 red flags your teen might be in an abusive relationship – and 6 signs it’s escalating
Carmel Hobbs , University of Tasmania

Too many young people who’ve been in detention die prematurely. They deserve better
Lucas Calais Ferreira , The University of Melbourne ; Alex Brown , Australian National University ; Stuart Kinner , Curtin University , and Susan M Sawyer , The University of Melbourne

Fixing the global childhood obesity epidemic begins with making healthy choices the easier choices – and that requires new laws and policies
Kathleen Trejo Tello , College of Charleston

Sex or social media? The sacrifices we’re willing to make to stay online
Paige Coyne , University of Windsor ; Bailey Csabai , University of Windsor , and Sarah Woodruff , University of Windsor

Better bipolar diagnosis may reduce suicide rates in boys – new research
Adrian Desai Boström , Karolinska Institutet and Peter Andersson , Karolinska Institutet

How can I help my teen quit vaping?
Michelle Jongenelis , The University of Melbourne

TB kills 75,000 children in Africa every year: how this can stop
Graeme Hoddinott , Stellenbosch University

Protecting children from exploitation means rethinking how we approach online behaviour
Jan Kietzmann , University of Victoria and Dionysios Demetis , University of Hull
Related Topics
- Adolescence
- Adolescent health
- Mental health
Top contributors
Professor, Canada Research Chair in Determinants of Child Development, Owerko Centre at the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, University of Calgary
Research Fellow, Centre for Alcohol Policy Research, La Trobe University
Senior Research Fellow, UNSW Sydney
Professor of Demography and Social Statistics., Obafemi Awolowo University
Professor of Psychology, Texas State University
Research fellow, UNSW Sydney
Assistant professor, School of Psychology, Scientist, Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, L’Université d’Ottawa/University of Ottawa
Senior Lecturer in Māori Language Revitalisation, Auckland University of Technology
PhD student in Clinical Psychology, University of Calgary
Behavioural Scientist, Centre for the AIDS Program of Research in South Africa (CAPRISA)
Professor of Adolescent Health Research, The University of Melbourne
Professor of Disability and Health, Melbourne School of Population and Global Health, The University of Melbourne
NHMRC Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Murdoch Children's Research Institute
Professor of Clinical Psychology, University of Liverpool
Professor emeritus, The University of Melbourne
- X (Twitter)
- Unfollow topic Follow topic
108 Adolescence Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on adolescence, ✍️ adolescence essay topics for college, 🎓 most interesting adolescence research titles, 💡 simple adolescence essay ideas, ❓ questions about adolescence.
- Mental Disorders in Infancy, Childhood, Adolescence
- Substance Abuse Prevention in Adolescence
- Adolescence: Contemporary Issues and Resources
- The Effect of Adolescence on Development
- Adolescence: Developmental Theories
- The Effect of Social Media during Adolescence
- Adolescence: Developmental Changes
- Escaping the Endless Adolescence’ by Joseph Allen In their book “Escaping the endless adolescent: How we can help our teenagers grow up before they grow old” J.Allen and C.Allen address the issue of prepared for adult life.
- Obesity in Adolescence as a Social Problem The paper states that adolescence is one of the most crucial developmental phases of human life during which the issue of obesity must be solved.
- The Beginning of Life (Conception) Through Adolescence Conception is the process by which a spermatozoon, which is a male germ cell, released from testis penetrates the ovum released from the ovary of a female.
- Adolescence Songs: “A Teenager in Love” by Dion DiMucci “A Teenager in Love” by Dion DiMucci was a famous song during my adolescent years. Some of the most crucial lyrics are “Each time we have a quarrel / It almost breaks my heart.”
- Adolescence and the Social Determinants of Health Today, adolescents face a number of health risks that could impact their further life. However, most of these health risks are preventable.
- Transition from Adolescence to Adulthood The 27-year old interviewee might need psychological assistance to deal with the process of transition from adolescence to adulthood as sociocultural concerns indicate.
- Identity Establishment in Adolescence and Its Relation to Conflict The adolescent development of a new identity can cause conflict with their parents. An essential aspect of identity is a commitment, which adolescents may change.
- Adolescence and Sexuality: Girls’ and Boys’ Sexual and Emotional Experiences The paper aims to discuss girls’ and boys’ sexual and emotional experiences and how social and gender norms influence adolescent behavior and personal identity.
- Adolescence Perception in Nancy Lesko’s Study The ways to the problem of adolescence change over time and Nancy Lesko provides a provocative analysis of the issue, which became an accepted approach to observing adolescents.
- The Social Problem of Obesity in Adolescence The social worker should be the bridge uniting obese individuals and society advertising social changes, and ending injustice and discrimination.
- Suicide in Adolescence: Warning Signs and Causes Adolescence is a life stage that precedes reaching psychological maturity and social independence. It involves the risks of extreme reactions to negative experiences.
- Adolescence to Emerging Adulthood It is widely believed that developing one’s physical talents can also assist in developing one’s personal and social skills.
- Adolescence as a Stage of Psychological Development Adolescence is an important stage of cognitive, physical, and social development. Piaget, Freud, and Erikson each focused on different aspects.
- Depression in Adolescence: Causes and Treatment Depression amongst young adults at the puberty stage comes in hand with several causes that one cannot imagine, and depression happens or is triggered by various reasons.
- Anorexia Nervosa Among Eating Disorders in Adolescence Anorexia nervosa is characterized by an incessant desire to be thin, hence the unhealthy eating behaviors that include starving.
- Adolescence in “Dangerous Laughter” by Millhauser In Millhauser’s short story “Dangerous Laughter,” a group of adolescents congregate at gatherings and laugh irrationally until the laughing obscures prudence and rationality.
- Sexuality and Gender-Related Behavior During Adolescence The paper analyzes identity development in adolescence, the neurological shifts that occur at this age, as well as other changes characteristic.
- The Perspectives of Adolescence: Examining the Insights From Two Generations Different perspectives on the teenage years can be especially valuable for reminiscing on the past and assessing its value for the subsequent establishment of one’s personality.
- Obesity in Adolescence in the Hispanic Community The health risks linked to Hispanic community adolescent obesity range from diabetes, heart problems, sleep disorders, asthma, and joint pain.
- Impact of Social Media on Adolescence The paper argues there is a need for adolescents to regulate their time spent on social media platforms to eliminate the growing impacts of social media.
- Adolescence Substance Abuse: Over The Counter Inhalants And Cough Syrup Over-the-counter drugs, commonly known as OTC, refer to the prescription of drugs that are not meant for medical use.
- Self-Esteem in the Adolescence Period According to Kail and Cavanaugh, self-esteem can be explained to mean the general perception of an individual and individual views in the eyes of society.
- Adolescence and Human Development Challenges There are various questions about how puberty affects adolescents concerning the fact that not all people are impacted in the same way.
- Depression in Adolescence as a Contemporary Issue Depression in adolescents is not medically different from adult depression but is caused by developmental and social challenges young people encounter.
- Adolescence from Developmental Perspective The adolescent period is notable for the development of formal cognitive operations that allow adolescents to construct the so-called “contrary to fact” propositions.
- Homosexuality and Adolescence Development This report discusses issues related to transgender disorders and homosexuality and considers social, cognitive, and physical development in adolescence.
- Conduct Disorder in Adolescence Conduct disorder refers to a collection of antisocial behaviors exhibited by adolescents that infringe on the rights of other people and that defy societal norms.
- Does Alcohol Consumption Reinforce Mental Problems in Adolescence?
- Adolescence and Its Effects on Adult Behavior
- Mass Media and Adolescence: How Mass Media Influence Teens in Their Sexual Behavior
- Childhood and Adolescence During the Middle Ages
- Peer Effects, Unobserved Factors, and Risk Behaviors in Adolescence
- Adolescence and Its Transitional Stages of Physical and Mental Development
- Body Image and Eating Disorders in Adolescence
- Low and Decreasing Self-Esteem During Adolescence
- Adolescence and the Factors That Help Lead Us Through It
- Eating Behavior and Social Interactions From Adolescence to Adulthood
- Cognitive Function Impairments Linked to Alcohol and Cannabis Use During Adolescence
- Adolescence: Developmental Psychology and Social Work Practice
- Metacognition and Headache: Which Is the Role in Childhood and Adolescence?
- Coping With Autonomy: The Challenge of Adolescence
- Adolescence, Maturity and Public Life in Dublin in the Short Story “Araby” by James Joyce
- New Directions for Preventing Dating Violence in Adolescence
- Child Sexual Development: Infancy, Early Childhood, Adolescence
- Parental Factors Associated With Rumination-Related Metacognitive Beliefs in Adolescence
- Adolescence: Stress, Depression, and Suicide
- Crises and Psychological Development in Adolescence and Adulthood
- Attachment, Social Value Orientation, Sensation Seeking, and Bullying in Early Adolescence
- Current Trends and Issues on Pregnancy in Adolescence
- Girls’ Development During Adolescence: Diminishment of Self
- Adolescence and the Common Identity Crisis
- Early Parenting and the Reduction of Educational Inequality in Childhood and Adolescence
- Parenting, Family Care, and Adolescence in East and Southern Africa
- Bullying Perpetration and Narcissistic Personality Traits Across Adolescence: Joint Trajectories and Childhood Risk Factors
- Family Instability and Locus of Control in Adolescence
- Emotional and Moral Development in Childhood and Adolescence
- Adolescence: Physical and Cognitive Development
- How Mass Media Affects the Image of Adolescence?
- Changes Through Adolescence and Its Effects
- Attachment Styles and Suicide-Related Behaviors in Adolescence: The Mediating Role of Self-Criticism and Dependency
- Muscle and Tendon Adaptation in Adolescence: Elite Volleyball Athletes Compared to Untrained Boys and Girls
- Attention Matters: Pitch vs. Pattern Processing in Adolescence
- Family Dynamics and the Changing Home Environment: Infancy Through Adolescence
- Critical Periods During Childhood and Adolescence
- Parasocial Interactions and Relationships in Early Adolescence
- Gender Roles and Socialization in Adolescence
- Adolescence Relationships With Parents and Peers
- Obesity Among Hispanic Adolescents: Culture and Eating Habits
- Children’s and Parents’ Time-Use Choices and Cognitive Development During Adolescence
- Politics and Prejudice: How Political Discussion With Peers Is Related to Attitudes About Immigrants During Adolescence
- Adolescence: Transition Stage Between Childhood and Adulthood
- What Is the Difference Between Puberty and Adolescence?
- Why Is Adolescence Not Necessarily Just the Teen Years?
- What Is the Motivation for the Academic Achievement Among Adolescent Students?
- What Are the Positive Aspects of Peer Groups During Adolescence?
- How Is Brain Development Related to Adolescent Impulsivity?
- What Is the Contrast in Physical Development Between the Genders at the Beginning of Adolescence?
- What Are the Characteristics of Adolescence?
- What Are the Reasons for the Formation of Egocentrism in Adolescence?
- During Which Years Does Early Adolescence Usually Occur?
- Why Did Erik Erikson Describe Adolescence as a Crucial Period?
- What Are the Social Tasks and Challenges of Adolescence?
- What Are the Changes That Occur in the Brain During Adolescence?
- What Are the Stereotypes About Adolescence?
- What Is Cognitive Development in Adolescence?
- What Did Piaget Call the Reasoning That Characterizes Adolescence?
- How Does Self-Esteem Change in Adolescence?
- How Does Identity Develop in Adolescents?
- What Is the “Pruning” Process in Brain Development During Adolescence?
- What Are the Developmental Milestones During Late Adolescence?
- What Is an Example of an Issue Surrounding the Physical Changes During Adolescence?
- What Moral Conflicts Do Adolescents Face?
- What Is the Change in Roles and Expectations During Adolescence in the Context of Family and School?
- How Can External Factors Affect Student Learning Throughout Adolescence?
- How Does Cognitive Development Influence the Characteristics of Adolescence?
- What Is Considered the Stormy Part of Adolescence According to Erik Erikson?
- What Are the Factors That Affect Adolescent Development?
- What Are Some Factors That Influence Emotional Changes Throughout Adolescence?
- What Are the Changes in the Parent-Child Relationship During Adolescence?
- What Is the Impact of Peer Relationships in Adolescence?
- What Is Adolescent Idealism?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, October 26). 108 Adolescence Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/adolescence-essay-topics/
"108 Adolescence Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 26 Oct. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/adolescence-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '108 Adolescence Essay Topics'. 26 October.
1. StudyCorgi . "108 Adolescence Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/adolescence-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "108 Adolescence Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/adolescence-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "108 Adolescence Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/adolescence-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Adolescence were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 5, 2024 .

Adolescent Literacy Topics A-Z
AdLit offers lots of articles, expert Q&A, video, research and reports, and additional resources that provide research-based information for educators, families, and others who want to help young people become better readers and writers. Browse the topics below to learn more.

About Teaching Reading

Achievement

Afterschool & Summer Programs

Assessment & Evaluation

Background Knowledge

College Readiness

Community Literacy Programs

Comprehension
Content-Area Literacy

Curriculum & Instruction

Dropout Prevention

English Language Learners

Families & Schools

Federal Research and Reports

Gender & Diversity Issues

Intervention


Learning Disabilities

Motivation and Engagement

Parent Tips

Phonics, Word Study & Decoding

Policy, Legislation & Initiatives

Professional Development

School-Wide Reform

Service Learning
Social emotional learning.

Special Education

Tutoring & Volunteering

Liked it? Share it!
Visit our sister websites:, reading rockets launching young readers (opens in a new window), start with a book read. explore. learn (opens in a new window), colorín colorado helping ells succeed (opens in a new window), ld online all about learning disabilities (opens in a new window), reading universe all about teaching reading and writing (opens in a new window).
- Call to +1 844 889-9952
102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples
📝 adolescence research papers examples, 🏆 best adolescence essay titles, 🎓 simple research topics about adolescence, ❓ adolescence research questions.
- American Adolescence. Teenage Problems Psychology essay sample: There are those psychological problems that youngsters cannot omit simply because of the society they currently live in.
- Psychological Development: Adolescence Psychology essay sample: Adolescence is a stage of development whereby people experience interpersonal, emotional, and cognitive changes.
- Risk-Taking Behavior in Adolescence Psychology essay sample: Adolescence has always been linked to problematic times and hot-tempered feelings among young people. Even the great philosophers of ancient Greece have addressed this issue.
- Lifespan Development: Adolescence to Early Adulthood Psychology essay sample: The paper examined all the physical, cognitive, and socio-emotional aspects of development between adolescence and adulthood.
- Cognitive Development in Adolescence: Fundamental Concepts Psychology essay sample: The development of teenagers requires a lot of commitment and understanding to help parents and teachers appreciate the values.
- Conflicts Experienced in Adolescence and Related Parenting Challenge Psychology essay sample: This paper evaluates a treatment process when dealing with conflicts that arise because of changes experienced in adolescence and the relative parenting challenges.
- Social Development in Adolescence Psychology essay sample: This paper examines social development in adolescence by reviewing its aspects, such as identity development, self-concept, etc., and applying different perspectives and concepts.
- Suicide in Adolescence Psychology essay sample: In the paper psychoeducational intervention for adolescents is developed and evaluated to improve suicide-related outcomes for high-risk students.
- Aspects of Puberty in Adolescence Psychology essay sample: The book “Exploring Lifespan Development” provides a detailed analysis of the psychological and physical conditions of adolescence.
- David Elkind's Theory of Adolescence Psychology essay sample: An unnecessarily long fixation on the specified stage of one’s development may be viewed as a significant problem in the psychological growth of a person.
- Adolescence in the Identity Development Context Psychology essay sample: Identity is one of the essential components of the personality of any person. In the context of identity development, adolescence is the most critical moment in a person's life.
- Adolescence as a Stage of Human Development Psychology essay sample: Adolescence marks the end of society's influence on a person without them criticizing it. In contrast with a child, teenagers reflect on matters being suggested or instilled in them.
- G. Stanley Hall: Adolescence and the Teenage Mind Psychology essay sample: Granville Stanley Hall, who is frequently referred to as G. Stanley Hall, warrants mentioning among the fathers of American psychology in general.
- Developmental Analysis: Personal Introduction of Childhood – Adolescence Psychology essay sample: This paper presents a personal introduction of childhood – adolescence, and theoretical perspectives of development (Freud’s, Erikson’s, Piaget’s theories).
- Stages of Child Development Psychology essay sample: Egocentrism - the inability or unwillingness of a person to look at what is happening from the point of view of other people, to put himself in the place of another person.
- Freud's Psychosexual Theory vs. Erikson's Psychosocial Theory Psychology essay sample: Freud's theory focused on the significance of individuals’ biological forces and their basic needs. On the other hand, Erikson's model emphasized ecological and social issues.
- Adolescent Mental and Suicide Issues Psychology essay sample: This paper discusses four websites that provide information related to the topic of adolescent mental and suicide issues.
- Why Adolescents Engage in Risk-Taking Behaviors Psychology essay sample: It is common knowledge among psychologists and neuroscientists that adolescence is a period of heightened reported and observed risk-taking.
- Developmental Perceptions of Death Anxiety Psychology essay sample: From early childhood until late adulthood, people’s understanding of death evolves. Age, cultural views, and familial duties, influence how people see death.
- Cognitive and Emotional Maturity of Teenagers Psychology essay sample: Sex hormones, in combination with other factors, interact with brain development and evoke typical behaviors of teenagers during the emotional and cognitive maturity process.
- "Development, Psychology, and Adolescence" by David Moshman Psychology essay sample: The paper states that the timeframe of adolescence is not that easy to identify since it is not always clear which parameters characterize this period.
- Adolescent Identity: Needs, Desires, Requirements Psychology essay sample: Adolescence remains one of the most psychologically and physically challenging and turbulent times in the life of people. This paper discusses adolescent identity.
- Adolescent Transition Period: Difficulties and Changes Psychology essay sample: This paper states that adolescent idealism, criticism, personal fable, and the imaginary audience may persist in adult life if the child is not given proper attention.
- Narrative Therapy: Patient Case Psychology essay sample: The narrative approach would be the most useful for the described case conceptualization, as it allows the person to separate the context and see these stories as situational.
- The Importance of Parent-Adolescent Relationship Psychology essay sample: Adolescence is a difficult period that allows the child to transition from being a parent-reliant individual to an independent person.
- Erik Erikson’s and Sigmund Freud’s Psychological Theories Comparison Psychology essay sample: This paper compares and contrasts Erik Erikson’s psychosocial theory and Sigmund Freud’s psychosexual theory and how psychotherapists can use this knowledge.
- Causes and Effects of Anxiety in Children Psychology essay sample: This work not only systematizes the findings of the causes of anxiety in children but also provides arguments from various authors about how to help the target population.
- Biological, Psychological, and Social Changes in Teenage Boys Psychology essay sample: During adolescence, there's an incredible variation in the rate of changes that occur as a boy enters his teenage years.
- Anxiety and Depression During Childhood and Adolescence Psychology essay sample: Attachment can be defined as the bond shared between two or more persons. People may have emotional closeness with one another.
- Human Development from Infancy to Death Psychology essay sample: The paper discusses the stages of human development. It includes infancy, early childhood, middle to late childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and death.
- Adolescence in Erikson's Developmental Theory Psychology essay sample: Erikson's theory of the development stages states that identity is formed during adolescence, which affects self-esteem and the determination of own place in life.
- Factors That Influence Personality Development Psychology essay sample: Although the notion concerning the remarkable role of prenatal development does not directly contradict the approach to the crucial role of adolescence, the emphasis is different.
- Effects of Depression Among Adolescents Psychology essay sample: Depression is a problem that affects all demographics, but this paper focuses on adolescents as its main point of discussion. Depression is a major cause of mental health.
- Analyzing the Role of Developmental Factors in Two Families Psychology essay sample: This paper analyzes the developmental factors for the personal and case scenario families, compares these factors, and develops strategies to solve the issues.
- Adolescence Egocentrism: Examples Psychology essay sample: This paper explores the concept of egocentrism during adolescence and its impact on the interpersonal relationships and development of teenagers.
- Personality Disorder: The Development of Antisocial Behavior Psychology essay sample: Antisocial behavior refers to a set of actions that result from a person's lack of the ability to respect other people's rights. Examples of these actions include setting fires.
- The Science Behind Adolescent Brain Development and Its Impact on Behavior
- Understanding the Emotional Rollercoaster of Adolescence
- The Role of Peer Pressure in Adolescent Dating
- Navigating Peer Pressure: Tips for Teens and Parents
- Social Media and Adolescence: The Effects on Self-Esteem and Mental Health
- Art, Music, and Dance in Therapeutic Treatment The paper reviews music, art, and dance as separate elements and their combination, as an important option for the treatment of disability problems.
- Navigating First Love: Tips for Parents
- Hormonal Changes in Adolescence: What Every Teen Should Know
- Navigating the Challenges of Peer Pressure During the Teenage Years
- Balancing Academic and Work Responsibilities: Tips for Teenagers
- The Power of Self-Expression: Creative Outlets for Adolescents
- The Role of Family Dynamics in Shaping Adolescent Behavior
- Adolescent Obesity in the United States The purpose of this paper is to review the issue of adolescent obesity in the contemporary environment and potential support options.
- Mental Health Awareness: Recognizing Depression and Anxiety in Adolescents
- Addressing Conflict and Resolving Differences Within the Family Unit
- Coping With Academic Stress: Strategies for Adolescents and Parents
- The Importance of Healthy Relationships During Adolescence
- The Adolescent Brain Development: Understanding the Teenage Mind
- Exploring Identity: Self-Discovery and Self-Expression in Adolescence
- Adolescence: Contemporary Issues and Resources Due to multiple changes experienced during adolescence as the transitioning period from childhood to adulthood, teenagers are quite vulnerable to stress.
- The Importance of Resilience and Coping Skills in Teenage Years
- Building Healthy Boundaries in Teenage Relationships
- Understanding Teenage Love: Hormones and Emotions
- Substance Abuse and Adolescents: Warning Signs and Prevention
- The Influence of Music and Art on Adolescent Brain Development
- Navigating the Emotional Roller Coaster: Coping Strategies for Adolescents
- LGBTQ+ Adolescents: Understanding and Supporting Gender and Sexual Identity
- Teenage and Issues Associated with Social Media Use The current essay aims to address those issues associated with the adolescence period and social media networks.
- The Evolution of Family Dynamics During the Adolescent Years
- Overcoming Procrastination and Time Management Challenges in Adolescent Work
- Body Image and Adolescence: Navigating the Pressures of Physical Appearance
- The Impact of Technology on Adolescent Development
- Transitioning to Adulthood: Life Skills Every Adolescent Should Learn
- The Impact of Social Media on Teen Dating Trends
- Single Mothers’ Experiences of Relationships with Their Adolescent Sons A generic qualitative design was applied in the study to investigate the experiences of single African American mothers and their relationships with their adolescent sons.
- The Impact of After-School Jobs on Adolescent Social Development
- Balancing Academics and Dating in Adolescence
- The Science of Adolescent Brain Development: Understanding the Teenage Mind
- Supporting Adolescents Through Transitions: From Middle School to High School
- The Connection Between Social Media and Adolescent Mental Health
- Addressing the Prevalence of Stress and Anxiety in Adolescents
- The Impact of Role Models and Mentors in Shaping Adolescent Identity
- High School and Its Purpose for Adolescents
- Setting Healthy Boundaries With Your Teen: Balancing Freedom and Responsibility
- The Impact of Peer Pressure on Adolescent Work Ethic and Performance
- Exploring the Benefits of Part-Time Work for Adolescents
- How to Help Your Teenager Cope With Heartbreak?
- How Adolescents in the Workplace Can Adapt and Grow?
- What the Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Academic Achievement in Adolescents?
- How Adolescents Can Cultivate Professional Relationships in the Workplace?
- How to Adjust to the Transformations of Family Life During Adolescence?
- How to Recognize Adolescents With Anxiety and Depression?
- How to Thrive as a Young Professional in the Modern Workplace?
- How to Finding Balance as an Adolescent?
- How Adolescent Work Experiences Shape Career Trajectories?
- What the Psychological Development of Adolescents in the Workplace?
- Time Management Skills for Adolescents: Practical Advice for Teenagers on How to Effectively Manage Their Time for Studying and Other Activities.
- Why Emotional Intelligence Matters for Adolescent Employees?
- What the Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Development?
- How to Help Teenagers Develop Good Study Habits and Improve Academic Performance?
- What the Relationship Between Sleep, Cognitive Function, and Academic Performance in Teenagers?
- What the Role of Parents in Supporting Their Adolescent’s Studies and Fostering Open Communication?
- How to Foster Positive Body Image in Adolescents?
- How Neurological Development Impacts Learning and Behavior?
- What the Impact of Anxiety and Stress in Adolescents?
- How to Prepare Adolescents for Independence and Responsibility?
Cite this page
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
PsychologyWriting. (2024, May 12). 102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/adolescence-research-topics/
"102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples." PsychologyWriting , 12 May 2024, psychologywriting.com/topics/adolescence-research-topics/.
PsychologyWriting . (2024) '102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples'. 12 May.
PsychologyWriting . 2024. "102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples." May 12, 2024. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/adolescence-research-topics/.
1. PsychologyWriting . "102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples." May 12, 2024. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/adolescence-research-topics/.
Bibliography
PsychologyWriting . "102 Adolescence Research Topics & Essay Examples." May 12, 2024. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/adolescence-research-topics/.

Psychology Research Guide
Child & adolescent development.
“Child development”, or “child and adolescent development” refers to the process of growth and maturation of the human individual from conception to adulthood. The term “adolescence” has particular connotations in particular cultural and social contexts. Child & Adolescent Psychology focuses on understanding the physical, social, psychological, and cognitive needs of young human beings. You can read more about the focus of Child & Adolescent Development on the American Psychological Association's Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology website This link opens in a new window . To find ideas for paper/research topics within child & adolescent development, visit these sites:
APA Psychology Topics This link opens in a new window (Try Bullying; Children; Education; Kids & the Media; Learning & Memory; Parenting; Teens)
Child & Adolescent Development Databases
Research in child & adolescent psychology utilizes core psychology resources, as well as resources in child & family development and sociology. You may find it helpful to search the following databases for your child & adolescent development topics or research questions, in addition to the core resources listed on the home page.
Child & Adolescent Development Subject Headings
You may find it helpful to take advantage of predefined subjects or subject headings in Shapiro Databases. These subjects are applied to articles and books by expert catalogers to help you find materials on your topic.
- Learn more about Subject Searching
Consider using databases to perform subject searches, or incorporating words from applicable subjects into your keyword searches. Here are some social psychology subjects to consider:
- adopted children
- Attachment Theory
- child abuse
- child behavior
- children of alcoholics
- cognitive development
- developmental stages
- early childhood development
- emotional development
- family relations
- middle school/junior high school/high school students
- parent child relations
- peer pressure
- personality
Child & Adolescent Development Organization Websites
- American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) This link opens in a new window A national professional medical association dedicated to treating and improving the quality of life for children, adolescents, and families affected by mental, behavioral, or developmental disorders.
- Child & Adolescent Development course module (UNHCR) This link opens in a new window This Resource Pack published by the United Nations High Commissioner on Refugees' Action for the Rights of Children (ARC) is a training module for those working with children and teen refugees. It covers major areas of child development acknowledging that " the concept of childhood is understood differently in different cultural and social contexts."
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development (NICHD) This link opens in a new window NICHD’s mission is to lead research and training to understand human development, improve reproductive health, enhance the lives of children and adolescents, and optimize abilities for all.
- Society of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology (APA Division) This link opens in a new window The Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology is Division 53 of the American Psychological Association. Its purpose is to encourage the development and advancement of clinical child and adolescent psychology through integration of its scientific and professional aspects.
- Child Welfare Information Gateway - Understanding Adolescent Development This link opens in a new window United States Health & Human Services Children's Bureau Child Welfare Information Gateway has extensive resources on child & adolescent development. This link leads to their "Understanding Adolescent Development" resources page.
- << Previous: Applied Psychology
- Next: Forensic Psychology >>
Loneliness in Emerging Adulthood: A Scoping Review
- Open access
- Published: 09 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Emma M. Kirwan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8536-023X 1 , 2 ,
- Annette Burns 3 ,
- Páraic S. O’Súilleabháin 1 , 2 ,
- Sarah Summerville 1 ,
- Máire McGeehan 1 , 2 ,
- Jennifer McMahon 1 , 2 ,
- Ashweeja Gowda 4 &
- Ann-Marie Creaven 1 , 2
271 Accesses
12 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Loneliness is prevalent during emerging adulthood (approximately 18–25 years) and is an important issue given it has been linked to poorer physical and mental health outcomes. This preregistered scoping review aimed to provide an overview of the literature on loneliness in emerging adulthood, including the (a) conceptualization and measurement of loneliness, (b) loneliness theories used, (c) risk factors and outcomes examined, (d) sex-gender differences observed, and (e) characteristics of emerging adult samples previously researched. Following the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) guidelines, seven electronic databases were searched for articles focused on loneliness published from 2016 to 2021, where the mean age of participants was ≥ 18 and ≤ 25 years. Of the 4068 papers screened, 201 articles were included in the final review. Findings suggest the need for a clearer consensus in the literature regarding the conceptualization of loneliness for emerging adults and more qualitative work exploring emerging adults’ subjective experiences of loneliness. Results highlight an over-reliance on cross-sectional studies. Over two thirds of articles described their sample as university students and the median percentage of females was 63.30%. Therefore, fewer cross-sectional studies using convenience samples and more population-based, longitudinal research is needed to understand the factors predicting loneliness over time, and the downstream impact of loneliness for emerging adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
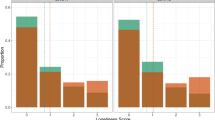
Estimating the prevalence of social and emotional loneliness across the adult lifespan
“where are all the lonely people” a population-based study of high-risk groups across the life span.

“It’s a feeling of complete disconnection”: experiences of existential loneliness from youth to older adulthood
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Loneliness is commonly defined as the unpleasant feeling that accompanies the experience of perceiving the quantity or quality of one’s social relationships as inadequate (Perlman & Peplau, 1981 ). While loneliness is common across the lifespan, it is particularly prevalent in young, or emerging adults (Barreto et al., 2021 ; Hawkley et al., 2022 ). Prevalence estimates from the United Kingdom suggest up to 31% of emerging adults experience loneliness at least some of the time, and 5–7% feel lonely often (Matthews et al., 2019 ). In the United States, about 24% of emerging adults report feeling lonely “a lot of the day” (Witters, 2023 ), and almost one in three (32.6%) emerging adults in India report high levels of loneliness (Banerjee & Kohli, 2022 ). Emerging adult loneliness has been independently associated with indictors of poorer physical and mental health, including hypertension, anxiety and depressive symptoms, alcohol problems, and long-term mental illness (Christiansen et al., 2021 ). Therefore, loneliness is an important issue in emerging adulthood and good quality research is a key step in offsetting this potential harm. However, the literature is lacking a review that summarizes important aspects of the research in emerging adulthood, including how loneliness is conceptualized and measured, which loneliness theories are used, which risk factors and outcomes of loneliness have been examined, if there are sex-gender differences in loneliness, and the characteristics of emerging adults previously included in research in this area. This information is needed to provide a basis for rigorous loneliness research for this group. Therefore, this scoping review addresses this gap.
Loneliness in Emerging Adulthood
The transition from adolescence to full-fledged adulthood in developed countries is longer and more challenging to define than in previous points in history. This is primarily due to engaging in traditional markers of adulthood such as marriage and parenthood at later ages, and the widespread uptake of education beyond secondary school (Arnett, 2024 ). Arnett’s theory of emerging adulthood ( 2000 , 2024 ) describes a distinct life-stage, from late teens through mid-to-late twenties. When age ranges are needed to describe emerging adulthood, ages 18–25 years are considered a conservative estimate, as few 18–25-year-olds have entered stable adulthood (Arnett, 2024 ). However, the specific age of the beginning and end of this life stage is variable, and critics have noted that the concept of emerging adulthood is heavily influenced by cultural, socioeconomic, and educational factors (Shanahan & Longest, 2009 ). Culture plays an important role in variation in the length and content of emerging adulthood, and the markers of established adulthood (Arnett, 2024 ). For instance, in keeping with the Chinese tradition of collectivism, a key marker of adulthood for Chinese emerging adults is the ability to financially support their parents, whereas this is not typically endorsed in the United States (Nelson & Luster, 2015 ).
Despite these critiques, there is general agreement that the prolonged entry into adulthood has resulted in significant developmental challenges (Côté, 2014 ). Typical features of emerging adulthood include identity exploration and greater self-focus, which may lead to instability in emerging adults’ social networks (Arnett & Mitra, 2020 ). Major social transitions occurring during young, or emerging, adulthood include moving out of the parental home, or beginning university or employment (Arnett, 2024 ). An age-normative perspective suggests that the timing of ongoing physical and psychological changes, unique societal expectations, and key social transitions places emerging adults at increased risk of loneliness (Qualter et al., 2015 ). Given the vulnerability to loneliness in this age group, robust research is needed to understand loneliness in emerging adulthood.
Recognizing that emerging adults are at particular risk for loneliness emphasizes the need to consider factors associated with loneliness in this group. However, the research priorities in relation to examining risk factors and outcomes of loneliness in emerging adulthood are unclear. One existing scoping review explored the literature on loneliness in youth (aged 15–24 years; Adib & Sabharwal, 2023 ); however, the review was limited in scope with a specific focus on social support and relationship factors like parenting bonds, both of which were inversely associated with loneliness. The extent to which other factors that may be associated with loneliness, for example mental health issues and technology use (Matthews et al., 2019 ), are focused on in the literature with emerging adults have not been reviewed. Additionally, gender differences in loneliness are important for understanding who is most vulnerable to loneliness. While one comprehensive meta-analysis suggested that young adult males were lonelier than females (Maes et al., 2019 ), this study considered a much wider age range (21–40 years) as young adulthood. Therefore, summarizing sex-gender differences in emerging adulthood merits consideration. Finally, persistent sampling bias issues mean that loneliness research generalized to emerging adults may be based on convenience samples of university undergraduates which may not represent diverse groups (Nielsen et al., 2017 ). It is unclear to what extent specific groups who disproportionately experience loneliness, such as migrants and people with poor health (Barreto et al., 2023 ), are focused on in the literature. Understanding who we study when we study emerging adults is of importance; therefore, a summary of the characteristics of emerging adults included in loneliness research is needed to support robust research in this area.
A key aspect of understanding loneliness in emerging adulthood is a clear conceptualization and distinction from related concepts. Loneliness is a subjective and emotional experience that is related to, but distinct from social isolation, which is the objective count of social contacts (Wigfield et al., 2022 ). Across all ages, loneliness is only weakly associated with measures of social contact (Luhmann & Hawkley, 2016 ). In other words, it is not the mere absence of social contact that impacts lonely individuals, but rather the perceived discrepancy between one’s desired and actual social relationships (Perlman & Peplau, 1981 ). Loneliness is also distinct from solitude in that loneliness is an unwanted experience, whereas solitude, or being alone, is a conscious choice that is often described as positive (Weinstein et al., 2023 ). The fact that loneliness and related concepts have been conflated or confused underscores the importance of a clear conceptual understanding of loneliness (Wigfield et al., 2022 ). Defining and measuring constructs of interest are a foundational part of rigorous research (Flake & Fried, 2020 ), yet no review has summarized how loneliness has been conceptualized and measured in research with emerging adults.
While loneliness has often been considered unidimensional, there has long been a conceptualization of loneliness as multidimensional. For example, Weiss’ ( 1973 ) interactionist approach proposed that relationship-specific types of loneliness arise as the result of deficits in two types of social needs; the need for close attachment figures (emotional loneliness) and the need for a meaningful social network (social loneliness). Social and emotional loneliness are distinct, but correlated, states that arise from different events in a person’s life; emotional loneliness might occur as the result of a romantic relationship breakup, whereas social loneliness can occur after moving to a new town. Recent research demonstrated distinct developmental trajectories for social and emotional loneliness across emerging adulthood (von Soest et al., 2020 ) and midlife (Manoli et al., 2022 ). Emotional loneliness levels moderately increase across emerging adulthood, whereas social loneliness substantially decreases throughout emerging adulthood (von Soest et al., 2020 ), suggesting that multidimensional conceptualizations of loneliness warrant consideration.
The complex nature of loneliness means that several other theories have conceptualized loneliness. Prominent approaches include the cognitive discrepancy model (Peplau & Perlman, 1982 ), the evolutionary theory (Cacioppo et al., 2006 ), the psychodynamic theory (Reichmann, 1959 ), and the existential approach (Moustakas, 1961 ). Although theoretical approaches to loneliness may overlap in their definitions, they can differ in proposed causes of loneliness. For example, the cognitive discrepancy model considers the influence of personality, cultural, and situational factors and proposes that loneliness is caused by a person appraising a deficiency in their social relationships (Peplau & Perlman, 1982 ). The evolutionary theory of loneliness suggests that loneliness arises as a signal of social pain to motivate reconnection and is transient for most individuals (Cacioppo et al., 2006 ; Spithoven et al., 2019 ). Other theories, such as the socio-cognitive model, focus on the mechanisms through which loneliness persists and impacts health (Cacioppo & Hawkley, 2009 ). However, no review has summarized how loneliness has been conceptualized and what theories of loneliness have been used in the emerging adult literature.
Current Study
Although there has been an acceleration of research on loneliness in emerging adulthood and recognition that loneliness is an important issue for young people’s health, there is no existing scoping review summarizing key aspects of this literature. The goal of this preregistered scoping review was to provide a descriptive overview of the existing literature on loneliness in emerging adulthood to inform future research. This review was guided by the following research question: What is known from the available literature about loneliness in emerging adults? The research sub-questions included how has loneliness been conceptualized and measured in research in emerging adults (Research Question 1)?, what loneliness theories have been used in research on loneliness in emerging adulthood (Research Question 2)?, what risk factors and outcomes for loneliness have been previously examined in emerging adulthood (Research Question 3)?, what is the evidence on sex-gender differences in loneliness in emerging adults (Research Question 4)?, and what are the characteristics of emerging adults included in previous loneliness research (Research Question 5)?.
Given the focus on loneliness in emerging adulthood, a topic with increasing and disparate literature, a scoping review, rather than a systematic review, was considered most appropriate (Munn et al., 2018 ). This scoping review was informed by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) framework for scoping reviews (Peters et al., 2015 ) and Arksey and O’Malley’s ( 2005 ) seminal work. The reporting of results was guided by Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR; Tricco et al., 2018 ). This review was preregistered on Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/c7ke9 ). To complete a feasible review, some amendments to the protocol were necessary and are outlined below (labelled as Amendment to Protocol 1–4).
Identifying Relevant Studies
Following preliminary searches of two databases (PsycInfo and Medline) to become familiar with key terms, the following electronic databases were searched in June 2021; Scopus, PubMed, PsycArticles, PsycInfo, Medline, ScienceDirect, and Applied Social Sciences Index and Abstracts (ASSIA). The search was updated in April 2022 to source articles published until the end of 2021. The search terms describe the concepts loneliness and young, or emerging, adults (see Table 1 ). The search was tailored to the specific requirements of each electronic database (see Supplementary Material 1 for example of a database search).
Initially, the search included peer-reviewed journal articles published between the years 2000–2021. Given that Arnett’s ( 2000 ) seminal work on emerging adulthood was published in the year 2000, it was expected to yield more research on the target population after this year. Using this year limit, 313 articles were eligible for inclusion in the review. However, following discussion among the authors, a consensus was reached that given the large volume of relevant literature, a year limit of 2016–2021 was sufficient for a feasible narrative summary of the recent literature on loneliness in emerging adulthood (Amendment to Protocol 1). The increase in research interest on loneliness in emerging adulthood in 2016 is shown in Fig. 1 .
The number of articles eligible for inclusion by year of publication. Note Solid vertical line indicates the cut off from 2016 to 2021 following Amendment to Protocol 1
Grey literature in the form of difficult-to-locate studies or reports by organizations interested in youth mental health (e.g., Jigsaw, SpunOut. i.e., National Youth Council of Ireland) were searched for by posting general requests (in October 2021) for relevant information on Twitter and mentioning relevant youth and research network organizations (“@organization”) in such tweets to encourage reposting (Adams et al., 2016 ). Additionally, a large loneliness research network placed a request for literature in their newsletter distributed to experts in the field (in December 2021). No additional eligible articles that had not already been identified were located.
The study protocol outlined the aim for an additional search for reports by relevant organizations interested in youth mental health by identifying organization websites using a search engine like Google. After a preliminary search for this type of grey literature, consensus was reached that following grey literature search strategies outlined by others (i.e., Adams et al., 2016 ) was a satisfactory search for grey literature (Amendment to Protocol 2). Grey literature was a complementary part of the search strategy and considering the large volume of identified peer-reviewed articles, peer-reviewed literature was prioritized in this review. This decision was also influenced by the consideration that when using search engines like Google, even if the search engine search was replicable, other researchers may not retrieve the same results on replication, as Google indexes websites based on several predictors: geographical location, previous search history, popularity, and so on (Bates, 2011 ).
Study Selection
Research where loneliness was a key focus of the work was included. This was determined by the inclusion of loneliness in an aim, objective, research question, or hypothesis. Quantitative studies that reported on loneliness under a broader term were included; for example, studies measuring or reporting on the construct of loneliness but describing it in the aims or objectives under broader terms like “psychological well-being”, “mental health”, or similar. Following preliminary screening, additional inclusion criteria outlined that where it was difficult to determine if loneliness was a key focus of quantitative research, articles must have reported analysis beyond the prevalence of loneliness to be included. With regards to qualitative research, if it was unclear if loneliness was a key focus of the work, articles must have discussed loneliness as a key concept in the introduction to be included (Amendment to Protocol 3).
To identify the types of available evidence in the area (Munn et al., 2018 ), qualitative, quantitative, mixed-methods, systematic reviews, and meta-synthesis articles were included.
Articles where the age of participants was ≥ 18 and ≤ 25 years were included. Articles that included a wider age range but reported a mean age ≥ 18 and ≤ 25 years were included. Following preliminary screening, further clarification was added to the inclusion criteria detailing where studies were longitudinal in design, included studies must report loneliness for age ≥ 18 and ≤ 25 years at least one time point (Amendment to Protocol 4).
Included research articles were not limited by population groups, specific life-events, specific samples, setting, or geographical location.
Included articles were not limited by measure of loneliness.
Included articles were published in English (the researchers’ only language).
Narrative reviews and loneliness scale development articles were excluded, as well as editorials, commentaries, opinion pieces, dissertations, and book chapters (labelled as “wrong article type or study design” in Fig. 2 ). Figure 2 summarizes the study selection process. In total, 8,863 articles were retrieved from the electronic database search. EndNote X9 software was used to manage references and facilitate duplicate record removal. Following duplicate record removal, 4,068 articles were screened by title and abstract on Rayyan ( https://rayyan.ai/ , Ouzzani et al., 2016 ). Fifty percent of titles and abstracts were blindly screened by a second reviewer (SS), inter-rater agreement was 98.00%. After title and abstract screening, 754 articles were included for full text screening. During full-text screening, EK contacted authors via ResearchGate to request their full-text articles and 13 of these requests were unsuccessful. Second reviewers (SS, MMG, AG) screened 50% of full-text articles. Inter-rater agreement for full-text articles was 94.19%. All disagreements were resolved through discussion; a further reviewer (AMC) was consulted on six (0.79%) decisions during full text screening.
PRISMA flow chart of the study selection
Data Charting
Data charting was conducted for all included articles by one reviewer (EK) by entering information into Microsoft Excel tables. The data charting form was pre-piloted on a random selection of articles and was refined to ensure all relevant information was extracted. A proportion of data charting (10%) was checked by a second reviewer (MMcG) for accuracy. The data charting form included (a) bibliographic information, (b) key study and subject matter information, (c) the conceptualization and measurement of loneliness, (d) the loneliness theories included, (e) the examined predictors and outcomes for loneliness, (f) sex-gender differences, and (g) characteristics of emerging adult samples included. The detailed list of information for which data were charted can be found in Supplementary Material 2.
Summarizing, and Reporting the Findings
Given that the aim of this review was to provide a descriptive summary of the available literature on loneliness in emerging adulthood, the quality of included studies was not assessed. All findings were included in the narrative review. Checks were completed to ensure the findings of the included systematic review were not duplicated in the results. Tables and narrative summaries were generated for each research sub-question to present a descriptive overview of the research on loneliness in emerging adulthood (Peters et al., 2015 ).
Study Context and Characteristics
After eligibility screening, 201 articles were included in the final scoping review. The publication year of included articles ranged from 2016 to 2021 (see Fig. 1 ). A small number of articles identified in the original search that were published online in 2020 or 2021 but were assigned to a journal issue in 2022 (e.g., Arslan et al., 2022 ; Hopmeyer et al., 2022 ) were retained. Research on loneliness in emerging adulthood represents a growing area of research, with almost half (47.26%) of the included articles published in 2020 and 2021.
The sample sizes within original research articles ranged from 4 to 71,988. Studies using quantitative analysis had sample sizes ranging from 35 to 71,988. Qualitative and mixed-method studies conducting qualitative analysis had sample sizes ranging from 4 to 686. The sole included systematic review and meta-analysis (Buecker et al., 2021 ) included data from 124,855 participants.
Included original articles were conducted in 44 countries across five continents. Thirteen (6.47%) articles included samples from more than one country. Almost half (49.25%) of the articles included samples from Western countries where English is the primary language. The breakdown of how many articles included samples from each country are as follows: USA ( k = 66, 32.84%), China ( k = 21, 10.45%), UK ( k = 18, 8.96%), Turkey ( k = 12, 5.97%), Poland ( k = 11, 5.47%), Australia ( k = 9, 4.48%), Germany ( k = 5, 2.49%), Denmark ( k = 4, 1.99%). The Netherlands, South Korea, Canada, Hungary, South Africa, and Spain were each included in three (1.49%) articles. Singapore, Greece, Republic of Ireland, Israel, and Bangladesh were each included in two (1.00%) articles. Finland, Italy, Northern Ireland, Norway, Slovakia, Austria, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, Sweden, Thailand, Malaysia, and Nigeria were each included in one (0.50%) article. Included original research articles had a general community or university setting (including online surveys) ( k = 186, 92.54%), or were conducted in a clinical or laboratory setting (e.g., an outpatient clinic) ( k = 13, 6.47%).
Study Design
Included articles were quantitative ( k = 190, 94.53%), mixed method ( k = 8, 3.98%), qualitative ( k = 1, 0.50%), systematic review and meta-analyses ( k = 1, 0.50%), and qualitative protocol ( k = 1, 0.50%) studies. The following study designs were included; cross-sectional ( k = 151, 75.12%), longitudinal ( k = 44, 21.89%), and experimental ( k = 4, 1.99%).
Covid-19 Related Studies
Thirty (14.93%) articles explored loneliness in relation to the Covid-19 pandemic. Most studies ( k = 23) explored the prevalence of loneliness or the association of loneliness with factors such as life satisfaction, mental health, quality of life during pandemic restrictions, or in the broader context of Covid-19 pandemic. For example, one study compared the reported prevalence of mental health issues and loneliness in emerging adults in the UK and China during the pandemic (Liu et al., 2021 ), reporting higher loneliness levels in the UK. Some studies ( k = 3) examined specific Covid-19 related factors, such as “Covid-19 worry” (Mayorga et al., 2021 ) and “Coronavirus anxiety” (Arslan et al., 2022 ), in relation to loneliness. Merolla et al. ( 2021 ) used experience sampling and nightly diary surveys to examine how pandemic related anxiety and depressive symptoms manifested in daily perceptions of loneliness; Covid-19 related anxiety was independently associated with greater loneliness. Other studies ( k = 2) focused on emerging adults’ relocations during the pandemic (Conrad et al., 2021 ; Fanari & Segrin, 2021 ). For example, a longitudinal examination of the extent to which the stressor of forced re-entry from studying abroad during the Covid-19 pandemic was predictive of loneliness in U.S. emerging adults (Fanari & Segrin, 2021 ). Lastly, one study conducted during the Covid-19 pandemic evaluated two interventions for depression and loneliness (Cruwys et al., 2021 ).
Research Question 1: Conceptualization and Measurement of Loneliness
Over half ( k = 112; 55.72%) of the articles included an explicit definition of loneliness, while another five (2.49%) articles did not formally define loneliness beyond describing it as “perceived social isolation”. Although there was some variation in the way loneliness was defined, for example, describing loneliness as thwarted belongingness (Chu et al., 2016 ), or as the response to the absence of a relationship (Andangsari & Dhowi, 2016 ), loneliness was mostly defined as an emotionally unpleasant subjective experience that occurs when a person perceives their social relationships to be inadequate (Perlman & Peplau, 1981 ). While most ( k = 187, 93.03%) articles did not explicitly articulate multiple dimensions of loneliness, 14 (6.97%) articles considered a multidimensional conceptualization of loneliness referring to: social and emotional loneliness ( k = 6, 2.98%); social, romantic, and family loneliness ( k = 6, 2.98%); isolation, relational connectedness, and collective connectedness ( k = 1, 0.50%); romantic loneliness ( k = 1, 0.50%).
In total, this scoping review identified 16 measures of loneliness in included articles. The University of California Los Angeles (UCLA; Russell et al., 1980 ) Loneliness scale was the most employed measure with 161 (80.10%) included articles using a version of this scale. Twelve (5.97%) studies employed a single-item direct measure of loneliness, such as “How lonely did you feel in the past week?”. See Supplementary Material 3 for a full summary of measures of loneliness in included articles.
Most qualitative or mixed-method studies employed semi-structured interviews to explore loneliness ( k = 4). Others used open ended survey responses ( k = 2), free association task ( k = 1), or group discussions and reflective journal responses ( k = 1).
Research Question 2: Loneliness Theories
Of the 201 included articles, 29 (14.43%) articles explicitly referenced a loneliness theory in their introduction. While it is possible that some articles implicitly used loneliness theory, articles were considered to have explicitly stated use of loneliness theory if a loneliness theory was referenced in the introduction or aims of the article. Some articles referred to more than one loneliness theory. Seven loneliness theories (see Table 2 for summary) were clearly articulated in loneliness research on emerging adults.
Research Question 3: Risk Factors and Outcomes
A wide range of risk factors and outcomes were examined in association with loneliness in quantitative or mixed-method studies (see Supplementary Material 4 for detail). Most articles examining factors associated with loneliness were cross-sectional in design; longitudinal studies mostly examined loneliness risk factors ( k = 25, 12.44%), outcomes were examined in 13 (6.47%) longitudinal studies. Of the longitudinal research examining predictors of loneliness, family and social relationship factors, such as perceived social support, were the most studied risk factors ( k = 7). Whereas mental health outcomes, like depression, were the most examined loneliness outcomes in longitudinal studies ( k = 6).
Only two longitudinal studies examined within- and between-person variances in loneliness development and the risk and outcome factors associated with changes; one explored the interindividual differences in loneliness development and mental health outcomes in emerging adulthood (Hutten et al., 2021 ). Another examined longitudinal within- and between-person associations of substance use, social influences, and loneliness among emerging adults who use drugs (Bonar et al., 2022 ).
Research Question 4: Sex-Gender Differences in Loneliness
In total, 48 (23.88%) studies explored sex-gender differences in loneliness; 40 reported no statistically significant ( p > 0.05) difference between male and female loneliness scores, whereas there were eight reports of a significant ( p < 0.05) sex-gender difference. Of those that reported significant sex-gender differences, six studies reported higher female loneliness scores and two studies reported higher male loneliness scores. Most studies ( k = 4) reporting significant sex-gender differences measured loneliness using the 20-item UCLA Loneliness Scale (Russell et al., 1980 ), others ( k = 2) used the Social and Emotional Loneliness Scale for Adults (SELSA; DiTommaso & Spinner, 1993 ), one used the Loneliness in Context Questionnaire for College Students (Asher & Weeks, 2014 ), and one used a direct single-item measure. See Table 3 for a complete summary of results.
Research Question 5: Characteristics of Emerging Adult Samples Included in Loneliness Research
The minimum mean age of included studies was 18.00 years, the maximum mean age was 24.78 years. The gender split of included studies ranged from 0% female to 100% female. The median percentage of females in included samples was 63.30%. Over two thirds ( k = 137, 68.16%) of articles described their sample as either all or mostly (> 80% of sample) university students. The remaining articles included: general community samples ( k = 24, 11.94%), specific samples (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease patients, see Supplementary Material 5 for full details of articles including specific emerging adult samples) ( k = 20, 9.95%), population representative samples ( k = 11, 5.47%), high school students ( k = 6, 2.94%). Some articles ( k = 3, 1.49%) did not report information on their sample or sample information was not applicable.
Despite an increase of research interest in loneliness in younger age groups and recognition that loneliness is an important issue for emerging adults’ health (Christiansen et al., 2021 ), there was no existing scoping review summarizing the key aspects of this literature. Reviews can reduce research waste by identifying priority research questions and key gaps in the literature, mapping existing methodological approaches, and clarifying terms and concepts used in the literature (Khalil et al., 2022 ). Therefore, a scoping review was most appropriate to provide an overview of the literature and identify priorities for future research on loneliness in emerging adulthood.
Three key issues are apparent from this review. First, there was a lack of clear conceptualization of loneliness and prioritization of unidimensional conceptualizations of loneliness in emerging adults, which may be related to the measure of loneliness used. Second, despite the volume of research identified, there was a lack of qualitative research exploring the subjective experience of loneliness. This suggests that the relevance of existing conceptualizations of loneliness for emerging adults who have experienced it remains unclear. Third, while a range of risk factors and outcomes for loneliness have been examined in the literature, research tends to be cross-sectional in design and based on convenience samples of university students. Some additional considerations are noted. Relatively few articles explicitly articulated the use of loneliness theory in their research. Relatively few articles reported on sex-gender differences in loneliness; those that did reported mixed results. Finally, loneliness in emerging adulthood is a growing area of research, with some of this growth due to a focus on loneliness in the context of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Definitions of loneliness in included articles tended to align with Perlman and Peplau’s ( 1981 ) widely used definition. Definitions acknowledged both the affective (i.e., the negative emotional experience) and cognitive (i.e., the discrepancy between one’s actual and desired social relations) components of loneliness. A few articles did not explain what is meant by loneliness beyond describing it as perceived social isolation, which does not account for the more complex affective and cognitive aspects of loneliness. While there may be general agreement that loneliness is a subjective emotional experience, the finding that just over half of all articles included a formal definition of loneliness leaves open the possibility that the conceptualization is implicit, poorly understood, or even that loneliness is akin to separate constructs like chosen solitude or objective social isolation. The distinction between concepts like social isolation and loneliness is critical given that across age groups, loneliness is only weakly associated with objective measures of contact with friends and family (Luhmann & Hawkley, 2016 ). A lack of clear definition of loneliness and conflation with other distinct, but related, terms contribute to conceptual confusion which can have practical implications; for example, policy responses designed for lonely people often aim to increase their social connections, therefore reducing social isolation rather than focusing on reducing experiences of subjective loneliness (Wigfield et al., 2022 ).
Other loneliness distinctions potentially relevant for understanding loneliness in emerging adulthood include a multi-dimensional conceptualization of social and emotional loneliness (von Soest et al., 2020 ). These facets are proposed to differentially develop depending on the type of social relationship a person perceives to be inadequate (Weiss, 1973 ). In addition, existential loneliness was described in recent qualitative work as occurring particularly during young adulthood for some individuals (McKenna-Plumley et al., 2023 ). A lack of transparent reporting on the conceptualization of loneliness has important implications for its measurement (Flake & Fried, 2020 ). The finding that few included articles considered different aspects of loneliness, and most did not explicitly discuss whether loneliness was unidimensional or multidimensional, suggests that a unidimensional conceptualization of loneliness is implicit. This is reflected in the frequent use of the UCLA Loneliness Scale (Russell et al., 1980 ), originally designed as a unidimensional measure. Although the UCLA includes items considered to align with social (11 items) and emotional (7 items) loneliness (Maes et al., 2022 ), there is no agreed multi-factorial structure of this measure, and using UCLA subscales may not be the best way of measuring multidimensional loneliness; given studies that report the same number of factors differ in terms of the items that are allocated to which factors and the interpretation of the factors (Maes et al., 2022 ). Additionally, although single-item loneliness measures have shown adequate reliability (Mund et al., 2022 ) and may be useful as brief screening measures in large-scale surveys (Reinwarth et al., 2023 ), few articles reported the use of direct single-item loneliness measures; perhaps because of concerns of potential socially desirable responding. Loneliness measurement is central to the validity of studies examining the risk factors and consequences of the experience in emerging adults (Flake & Fried, 2020 ). Therefore, future research should clearly report the conceptualization and measurement of loneliness.
One approach to achieving consensus on conceptualizations of loneliness in emerging adulthood is through more inductive and exploratory qualitative methods. The only qualitative study eligible for inclusion here focused on young adults living in London’s most deprived areas who described loneliness as being linked to feeling excluded, social media, sadness, and low self-worth (Fardghassemi & Joffe, 2021 ). While this study gives an insight into loneliness in this demographic, the experiences of loneliness for emerging adults more broadly are lacking in the literature. Further, there is a lack of qualitative research exploring the complexities of the life stage more generally (Schwab & Syed, 2015 ). Loneliness is an inherently subjective experience. Qualitative methods allow individuals to describe their experience in their own words and are ideally suited for examining how relevant existing conceptualizations of loneliness are for emerging adults. Exploring the meaning of loneliness for those who have experienced it should be a key research priority; a gap which has been addressed among early adolescents (Verity et al., 2021 ). Although the major features of emerging adulthood may vary between cultures, it is a distinct developmental period of the lifespan (Arnett, 2024 ). To assume emerging adults share the same social roles, developmental tasks, and societal expectations as adolescents underestimates the increased independence, self-focus, and instability (Arnett et al., 2014 ) that may be central to loneliness during this stage. Therefore, qualitative research focused on understanding loneliness within the complexities of the life-stage of emerging adulthood is needed.
Of the articles that explicitly considered loneliness theory, most considered approaches that typically focus on individual level characteristics that may increase a person’s risk for loneliness. For example, the evolutionary theory of loneliness (Cacioppo et al., 2006 ), suggests that younger age groups, due to ongoing development of brain regions associated with cognitive control, may be more sensitive to their social environment and more prone to loneliness beyond the typical features of emerging adulthood (Wong et al., 2018 ). However, societal, and cultural factors are also likely to contribute to loneliness by influencing a person’s social norms (van Staden & Coetzee, 2010 ). The cognitive discrepancy theory emphasizes the role of individual attributes, as well as wider cultural norms in how a person perceives their social relationships (Peplau & Perlman, 1982 ). Theories of loneliness are not mutually exclusive; developing a causal understanding of loneliness in emerging adulthood likely requires the integration of theory. For example, McHugh Power et al. ( 2018 ) synthesized model of loneliness considers both interindividual factors, such as the role of culture in shaping social norms about emerging adults’ social lives, and intraindividual factors, such as changes in the brain regions responsible for social processes, in the development of loneliness. Further, loneliness can be explored within broader theoretical frameworks not specific to loneliness. Developmental approaches can inform research on specific life events and developmental tasks during a particular life stage that may increase a person’s risk of loneliness. For example, employing Erikson’s ( 1968 ) psychosocial theory in research exploring the link between identity formation and loneliness in adolescents and emerging adults (Lindekilde et al., 2018 ).
An age-normative life span perspective suggests that different factors drive loneliness at different ages (Luhmann & Hawkley, 2016 ). For example, peer relations may be more strongly associated with loneliness during adolescence and emerging adulthood, where friendships are their primary social connections, as opposed to older age groups (Qualter et al., 2015 ). This aligns with the finding that family and social relationship factors, such as perceived social support from peers, were the most examined risk factors for loneliness in emerging adulthood in longitudinal studies. Perhaps unsurprisingly, aspects of mental health were the most examined outcomes of loneliness. It is also plausible that poorer mental health predicts or has a reciprocal relationship with loneliness during emerging adulthood; emerging adults with depressive symptoms may withdraw from their social relationships or perceive more social rejection (Achterbergh et al., 2020 ). Despite examining a range of loneliness risk factors and outcomes, included studies were mostly cross-sectional and conducted in Western countries with convenience samples comprising university students. Therefore, the third key issue with this literature highlights the persistent sampling bias and lack of representation and diversity in the field (Nielsen et al., 2017 ).
Sex-gender differences are also important for understanding who is vulnerable to loneliness. Most studies reported no significant difference. A small number reported a significant difference, mostly reporting higher loneliness among females. Gender differences in loneliness have been hypothesized to emerge in adolescence, where females may be more at risk of adolescent-onset internalizing problems (Martel, 2013 ). However, a meta-analysis reported a significant, but small, effect of gender on loneliness in young adulthood, finding greater loneliness in males (Maes et al., 2019 ). The variation of findings in studies examining sex-gender differences have long been attributed to differences in how loneliness is assessed (Borys & Perlman, 1985 ). Given that few a-priori hypotheses on gender differences in loneliness have been proposed (Maes et al., 2019 ), future research should report analysis examining sex-gender differences to determine whether sex-gender represents a vulnerability factor for loneliness.
Finally, the findings suggest that loneliness in emerging adulthood is a fast-growing area of research; almost half of all included articles were published in the years 2020 and 2021. Some of this growth was due to the Covid-19 pandemic making the issue of loneliness in younger age groups even more salient than before (Holt-Lunstad, 2021 ). Although not all who are socially isolated are lonely (Luhmann & Hawkley, 2016 ), this increased focus on loneliness is unsurprising considering that response measures aimed at mitigating the spread of Covid-19, like social distancing orders, and remote work and education, resulted in less social contact and greater social isolation. One systematic review comparing loneliness before and during the Covid-19 pandemic found an increase in loneliness in younger participant groups (Ernst et al., 2022 ). However, this increase was from studies including only university student samples; how the pandemic has impacted loneliness during emerging adulthood more generally remains unclear. The theory of emerging adulthood describes a range of developmental transitions to achieve adulthood, such as moving out of the parental home (Arnett, 2024 ). For some emerging adults, Covid-19 measures may have halted or even reversed steps towards adulthood, resulting in increased loneliness. For example, emerging adults forced to relocate from college campuses to live with parents and guardians experienced greater loneliness than those who did not relocate (Conrad et al., 2021 ). Life events that impact the achievement of normative social transitions and result in some emerging adults feeling out of sync may be important to consider in the development of loneliness during emerging adulthood.
Strengths and Limitations
The strengths of this review included preregistration of the protocol on Open Science Framework and rigorous methodology following well-established scoping review guidelines (Peters et al., 2015 ). One potential limitation is the inclusion criteria that articles needed to report a mean age of 18–25 years. This age range is sometimes extended to age 29; however, 18–25 years is appropriate when conservative age ranges are required to describe emerging adulthood (Arnett, 2024 ). Although a large volume of articles was included, the year limit and lack of grey literature means that there is a possibility that relevant research was not included in this review. While articles were not excluded based on geographical location, included articles were limited to those published in or translated to the English language only, potentially influencing this review’s results.
Future Research
Based on these findings, future studies should provide a clear conceptualization of loneliness, including articulation of loneliness as a uni- or multi-dimensional construct. Studies should specify the theoretical approach (if any) that is informing the research. To generate a clearer understanding of sex-gender differences, these should be reported.
Regarding broad research priorities for loneliness, given the skew towards cross-sectional convenience samples of Western, educated emerging adults, longitudinal research that is population-based or focuses on under-studied cohorts should be prioritized. The current literature does not adequately explore the emergence of specific forms of loneliness, the predictors of loneliness development, and the long-term outcomes of emerging adult loneliness. Developmental trends, the stability of loneliness, and the factors associated with interindividual differences in loneliness during emerging adulthood appear to have also been neglected. Previous research underscores the importance of identifying the characteristics of emerging adults more likely to develop loneliness and the factors that, when changed, correspond to changes in loneliness (Mund et al., 2020 ). Therefore, longitudinal research should seek to identify emerging adults most at risk of developing sustained or intensely felt loneliness in response to common life events, like finishing school. Also, identifying emerging adults who are at risk of loneliness due to developmental transitions being halted or reversed is a consideration for future longitudinal research. Given potential cultural differences in the markers of adulthood and developmental tasks of emerging adulthood (Nelson & Luster, 2015 ), research should consider cultural norms in the relationship between social transitions and loneliness during this life stage.
The high prevalence of loneliness during emerging adulthood indicates that loneliness is an issue of importance requiring good quality research. However, no review has provided an overview of key aspects of the literature on loneliness in emerging adulthood. This scoping review provided a descriptive summary of 201 articles on loneliness in emerging adulthood and serves as an initial step highlighting issues with the current research and identifying priorities for future research. Specifically, findings suggest the need for a clearer consensus in the literature regarding the conceptualization of loneliness during emerging adulthood. Second, this review highlights the need for more qualitative work exploring young people’s subjective experiences of loneliness, which is key for understanding the complexities of loneliness during emerging adulthood. Finally, the results indicate that this literature needs fewer cross-sectional studies using convenience samples and more population-based, longitudinal research to understand the factors predicting loneliness over time, and the downstream impact of loneliness for emerging adults.
Data Availability
All data collected for this study were obtained from published peer-review literature. Data extracted to inform this review are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Articles included in the scoping review are marked with (•)
•Aakvaag, H. F., Strøm, I. F., & Thoresen, S. (2018). But were you drunk? Intoxication during sexual assault in Norway. European Journal of Psychotraumatology, 9 (1), 1539059. https://doi.org/10.1080/20008198.2018.1539059
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Achterbergh, L., Pitman, A., Birken, M., Pearce, E., Sno, H., & Johnson, S. (2020). The experience of loneliness among young people with depression: A qualitative meta-synthesis of the literature. BMC Psychiatry, 20 , 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-020-02818-3
Article Google Scholar
•Adamczyk, K. (2016). An investigation of loneliness and perceived social support among single and partnered young adults. Current Psychology, 35 , 674–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-015-9337-7
Article PubMed Google Scholar
•Adamczyk, K. (2017). Voluntary and involuntary singlehood and young adults’ mental health: An investigation of mediating role of romantic loneliness. Current Psychology, 36 (4), 888–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-016-9478-3
•Adamczyk, K. (2018). Direct and indirect effects of relationship status through unmet need to belong and fear of being single on young adults’ romantic loneliness. Personality and Individual Differences, 124 , 124–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.12.011
Adams, J., Hillier-Brown, F. C., Moore, H. J., Lake, A. A., Araujo-Soares, V., White, M., & Summerbell, C. (2016). Searching and synthesising ‘grey literature’ and ‘grey information’ in public health: Critical reflections on three case studies. Systematic Reviews, 5 (1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0337-y
•Akdoğan, R. (2017). A model proposal on the relationships between loneliness, insecure attachment, and inferiority feelings. Personality and Individual Differences, 111 , 19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.01.048
•Akdoğan, R., & Çimşir, E. (2019). Linking inferiority feelings to subjective happiness: Self-concealment and loneliness as serial mediators. Personality and Individual Differences, 149 , 14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2019.05.028
•Akhter, M. S., Islam, M. H., & Momen, M. N. (2020). Problematic internet use among university students of Bangladesh: The predictive role of age, gender, and loneliness. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment, 30 (8), 1082–1093. https://doi.org/10.1080/10911359.2020.1784346
•Al Omari, O., Al Sabei, S., Al Rawajfah, O., Abu Sharour, L., Al-Hashmi, I., Al Qadire, M., & Khalaf, A. (2021). Prevalence and predictors of loneliness among youth during the time of COVID-19: A multinational study. Journal of the American Psychiatric Nurses Association . https://doi.org/10.1177/10783903211017640
•Alvarez-Jimenez, M., Rice, S., D’Alfonso, S., Leicester, S., Bendall, S., Pryor, I., Russon, P., McEnery, C., Santesteban-Echarri, O., Da Costa, G., Gilbertson, T., Valentine, L., Solves, L., Ratheesh, A., McGorry, P. D., & Gleeson, J. (2020). A novel multimodal digital service (moderated online social therapy+) for help-seeking young people experiencing mental ill-health: pilot evaluation within a national youth e-mental health service. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 22 (8), e17155. https://doi.org/10.2196/17155
•Andangsari, E. W., & Dhowi, B. (2016). Two typology types of loneliness and problematic internet use (PIU): An Evidence of Indonesian measurement. Advanced Science Letters, 22 (5–6), 1711–1714. https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2016.6740
•Andic, S., & Batigün, A. D. (2021). Development of internet addiction scale based on DSM-5 diagnostic criteria: An evaluation in terms of internet gaming disorder. Turkish Journal of Psychiatry, 32 (1), 33. https://doi.org/10.5080/u23194
•Aparicio-Martínez, P., Ruiz-Rubio, M., Perea-Moreno, A. J., Martínez-Jiménez, M. P., Pagliari, C., Redel-Macías, M. D., & Vaquero-Abellán, M. (2020). Gender differences in the addiction to social networks in the Southern Spanish university students. Telematics and Informatics, 46 , 101304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2019.101304
Arksey, H., & O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8 (1), 19–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Arnett, J. J. (2000). Emerging adulthood: A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. American Psychologist, 55 (5), 469. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.55.5.469
Arnett, J. J. (2024). Emerging adulthood: The winding road from the late teens through the twenties (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Arnett, J. J., & Mitra, D. (2020). Are the features of emerging adulthood developmentally distinctive? A comparison of ages 18–60 in the United States. Emerging Adulthood, 8 (5), 412–419. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696818810073
Arnett, J. J., Žukauskienė, R., & Sugimura, K. (2014). The new life stage of emerging adulthood at ages 18–29 years: Implications for mental health. The Lancet Psychiatry, 1 (7), 569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(14)00080-7
•Arroyo, A., Segrin, C., & Curran, T. M. (2016). Maternal care and control as mediators in the relationship between mothers’ and adult children’s psychosocial problems. Journal of Family Communication, 16 (3), 216–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/15267431.2016.1170684
•Arslan, G., Yıldırım, M., & Aytaç, M. (2022). Subjective vitality and loneliness explain how coronavirus anxiety increases rumination among college students. Death Studies, 46 (5), 1042–1051. https://doi.org/10.1080/07481187.2020.1824204
Asher, S. R., & Weeks, M. S. (2014). Loneliness and belongingness in the college years. In R. J. Coplan & J. C. Bowker (Eds.), The handbook of solitude: Psychological perspectives on social isolation, social withdrawal, and being alone (pp. 283–301). Wiley.
Google Scholar
•Babad, S., Zwilling, A., Carson, K. W., Fairchild, V., & Nikulina, V. (2022). Childhood environmental instability and social-emotional outcomes in emerging adults. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 37 (7–8), NP3875–NP3904. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260520948147
•Badcock, J. C., Barkus, E., Cohen, A. S., Bucks, R., & Badcock, D. R. (2016). Loneliness and schizotypy are distinct constructs, separate from general psychopathology. Frontiers in Psychology, 7 , 1018. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01018
•Balter, L. J., Raymond, J. E., Aldred, S., Drayson, M. T., van Zanten, J. J. V., Higgs, S., & Bosch, J. A. (2019). Loneliness in healthy young adults predicts inflammatory responsiveness to a mild immune challenge in vivo. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 82 , 298–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.08.196
Banerjee, A., & Kohli, N. (2022). Prevalence of loneliness among young adults during COVID-19 lockdown in India. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6 , 7797–7805.
•Barnett, M. D., Moore, J. M., & Edzards, S. M. (2020). Body image satisfaction and loneliness among young adult and older adult age cohorts. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 89 , 104088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2020.104088
•Barnett, M. D., Smith, L. N., Sandlin, A. M., & Coldiron, A. M. (2023). Loneliness and off-topic verbosity among young adults and older adults. Psychological Reports, 126 (2), 641–655. https://doi.org/10.1177/00332941211058045
Barreto, M., Qualter, P., & Doyle, D. (2023). Loneliness inequalities evidence review . Wales Centre for Public Policy. https://www.wcpp.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/WCPP-REPORT-Loneliness-Inequalities-Evidence-Review.pdf
Barreto, M., Victor, C., Hammond, C., Eccles, A., Richins, M. T., & Qualter, P. (2021). Loneliness around the world: Age, gender, and cultural differences in loneliness. Personality and Individual Differences, 169 , 110066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.110066
Bates, E. M. (2011). Is Google hiding my news? Onlintese-Medford, 35 , 64.
BBC Loneliness Experiment. (2018). Who feels lonely? The results of the world’s largest loneliness study. https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/articles/2yzhfv4DvqVp5nZyxBD8G23/who‐feels‐lonely‐the‐results‐of‐the‐world‐s‐largest‐loneliness‐study
•Beckmeyer, J. J., & Cromwell, S. (2019). Romantic relationship status and emerging adult well-being: Accounting for romantic relationship interest. Emerging Adulthood, 7 (4), 304–308. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696818772653
•Bernhold, Q. S., & Giles, H. (2020). The role of grandchildren’s own age-related communication and accommodation from grandparents in predicting grandchildren’s well-being. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 91 (2), 149–181. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415019852775
•Berryman, C., Ferguson, C. J., & Negy, C. (2018). Social media use and mental health among young adults. Psychiatric Quarterly, 89 , 307–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11126-017-9535-6
•Besse, R., Whitaker, W. K., & Brannon, L. A. (2022). Reducing loneliness: The impact of mindfulness, social cognitions, and coping. Psychological Reports, 125 (3), 1289–1304. https://doi.org/10.1177/0033294121997779
Binte Mohammad Adib, N. A., & Sabharwal, J. K. (2023). Experience of loneliness on well-being among young individuals: A systematic scoping review. Current Psychology . https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04445-z
•Błachnio, A., Przepiorka, A., Boruch, W., & Bałakier, E. (2016). Self-presentation styles, privacy, and loneliness as predictors of Facebook use in young people. Personality and Individual Differences, 94 , 26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.12.051
•Blachnio, A., Przepiórka, A., Wolonciej, M., Mahmoud, A. B., Holdos, J., & Yafi, E. (2018). Loneliness, friendship, and Facebook intrusion. A study in Poland, Slovakia, Syria, Malaysia, and Ecuador. Studia Psychologica, 60 (3), 183–194. https://doi.org/10.21909/sp.2018.03.761
•Bonar, E. E., Walton, M. A., Carter, P. M., Lin, L. A., Coughlin, L. N., & Goldstick, J. E. (2022). Longitudinal within-and between-person associations of substance use, social influences, and loneliness among adolescents and emerging adults who use drugs. Addiction Research & Theory, 30 (4), 262–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/16066359.2021.2009466
•Borawski, D. (2018). The loneliness of the zero-sum game loser. The balance of social exchange and belief in a zero-sum game as predictors of loneliness. Personality and Individual Differences, 135 , 270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.07.037
Borys, S., & Perlman, D. (1985). Gender differences in loneliness. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 11 , 63–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167285111006
•Bowker, J. C., Bowker, M. H., Santo, J. B., Ojo, A. A., Etkin, R. G., & Raja, R. (2019). Severe social withdrawal: Cultural variation in past hikikomori experiences of university students in Nigeria, Singapore, and the United States. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 180 (4–5), 217–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.2019.1633618
•Brown, E. G., Creaven, A. M., & Gallagher, S. (2019). Loneliness and cardiovascular reactivity to acute stress in younger adults. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 135 , 121–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2018.07.471
•Brown, S., Fite, P. J., Stone, K., & Bortolato, M. (2016). Accounting for the associations between child maltreatment and internalizing problems: The role of alexithymia. Child Abuse & Neglect, 52 , 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2015.12.008
•Bruehlman-Senecal, E., Hook, C. J., Pfeifer, J. H., FitzGerald, C., Davis, B., Delucchi, K. L., Haritatos, J., & Ramo, D. E. (2020). Smartphone app to address loneliness among college students: Pilot randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mental Health, 7 (10), e21496. https://doi.org/10.2196/21496
•Buchanan, C. M., & McDougall, P. (2021). Predicting psychosocial maladjustment in emerging adulthood from high school experiences of peer victimization. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 36 (3–4), NP1810–NP1832. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260518756115
•Buckley, C. Y., Whittle, J. C., Verity, L., Qualter, P., & Burn, J. M. (2018). The effect of childhood eye disorders on social relationships during school years and psychological functioning as young adults. The British and Irish Orthoptic Journal, 14 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.22599/bioj.111
•Buecker, S., Mund, M., Chwastek, S., Sostmann, M., & Luhmann, M. (2021). Is loneliness in emerging adults increasing over time? A preregistered cross-temporal meta-analysis and systematic review. Psychological Bulletin, 147 (8), 787. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000332
•Burger, C., & Bachmann, L. (2021). Perpetration and victimization in offline and cyber contexts: A variable-and person-oriented examination of associations and differences regarding domain-specific self-esteem and school adjustment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18 (19), 10429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph181910429
•Burke, T. J., Ruppel, E. K., & Dinsmore, D. R. (2016). Moving away and reaching out: Young adults’ relational maintenance and psychosocial well-being during the transition to college. Journal of Family Communication, 16 (2), 180–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/15267431.2016.1146724
Cacioppo, J. T., & Hawkley, L. C. (2009). Perceived social isolation and cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 13 (10), 447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2009.06.005
Cacioppo, J. T., Hawkley, L. C., & Berntson, G. G. (2003). The anatomy of loneliness. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12 (3), 71–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8721.01232
Cacioppo, J. T., Hawkley, L. C., Ernst, J. M., Burleson, M., Berntson, G. G., Nouriani, B., & Spiegel, D. (2006). Loneliness within a nomological net: An evolutionary perspective. Journal of Research in Personality, 40 (6), 1054–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2005.11.007
•Cai, L. B., Xu, F. R., Cheng, Q. Z., Zhan, J., Xie, T., Ye, Y. L., Xiong, S. Z., McCarthy, K., & He, Q. Q. (2017). Social smoking and mental health among Chinese male college students. American Journal of Health Promotion, 31 (3), 226–231. https://doi.org/10.4278/ajhp.141001-QUAN-494
•Chang, E. C. (2018). Relationship between loneliness and symptoms of anxiety and depression in African American men and women: Evidence for gender as a moderator. Personality and Individual Differences, 120 , 138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.08.035
•Chang, E. C., Chang, O. D., Martos, T., Sallay, V., Zettler, I., Steca, P., D’Addario, M., Boniwell, I., Pop, A., Tarragona, M., Slemp, G. R., Shin, J. E., de la Fuente, A., & Cardeñoso, O. (2019). The positive role of hope on the relationship between loneliness and unhappy conditions in Hungarian young adults: How pathways thinking matters! The Journal of Positive Psychology, 14 (6), 724–733. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2018.1545042
•Chang, E. C., Liu, J., Yi, S., Jiang, X., Li, Q., Wang, R., Tian, W., Gao, X., Li, M., Lucas, A. G., & Chang, O. D. (2020). Loneliness, social problem solving, and negative affective symptoms: Negative problem orientation as a key mechanism. Personality and Individual Differences, 167 , 110235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.110235
•Chang, E. C., Wan, L., Li, P., Guo, Y., He, J., Gu, Y., Wang, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Sun, Y., Batterbee, C. N., Chang, O. D., Lucas, A. G., & Hirsch, J. K. (2017). Loneliness and suicidal risk in young adults: Does believing in a changeable future help minimize suicidal risk among the lonely? The Journal of Psychology, 151 (5), 453–463. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2017.1314928
•Chen, Y. W., Wengler, K., He, X., & Canli, T. (2022). Individual differences in cerebral perfusion as a function of age and loneliness. Experimental Aging Research, 48 (1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/0361073X.2021.1929748
•Christiansen, J., Qualter, P., Friis, K., Pedersen, S. S., Lund, R., Andersen, C. M., Bekker-Jeppesen, M., & Lasgaard, M. (2021). Associations of loneliness and social isolation with physical and mental health among adolescents and young adults. Perspectives in Public Health, 141 (4), 226–236. https://doi.org/10.1177/17579139211016077
•Chu, C., Hom, M. A., Rogers, M. L., Ringer, F. B., Hames, J. L., Suh, S., & Joiner, T. E. (2016). Is insomnia lonely? Exploring thwarted belongingness as an explanatory link between insomnia and suicidal ideation in a sample of South Korean university students. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 12 (5), 647–652. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.5784
•Conrad, R. C., Koire, A., Pinder-Amaker, S., & Liu, C. H. (2021). College student mental health risks during the COVID-19 pandemic: Implications of campus relocation. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 136 , 117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.01.054
Côté, J. E. (2014). The dangerous myth of emerging adulthood: An evidence-based critique of a flawed developmental theory. Applied Developmental Science, 18 (4), 177–188. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2014.954451
•Creaven, A. M., Kirwan, E., Burns, A., & O’Súilleabháin, P. S. (2021). Protocol for a qualitative study: Exploring loneliness and social isolation in emerging adulthood (ELSIE). International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 20 , 16094069211028682. https://doi.org/10.1177/160940692110286
•Cruwys, T., Haslam, C., Rathbone, J. A., Williams, E., & Haslam, S. A. (2021). Groups 4 health protects against unanticipated threats to mental health: Evaluating two interventions during COVID-19 lockdown among young people with a history of depression and loneliness. Journal of Affective Disorders, 295 , 316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.029
•Cudo, A., Kopiś, N., & Zabielska-Mendyk, E. (2019). Personal distress as a mediator between self-esteem, self-efficacy, loneliness and problematic video gaming in female and male emerging adult gamers. PLoS ONE, 14 (12), e0226213. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226213
•Curran, T., Janovec, A., & Olsen, K. (2021). Making others laugh is the best medicine: Humor orientation, health outcomes, and the moderating role of cognitive flexibility. Health Communication, 36 (4), 468–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2019.1700438
•D’Agostino, A. E., Kattan, D., & Canli, T. (2019). An fMRI study of loneliness in younger and older adults. Social Neuroscience, 14 (2), 136–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2018.1445027
•Dalton, F., & Cassidy, T. (2021). Problematic Internet usage, personality, loneliness, and psychological well-being in emerging adulthood. Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy, 21 (1), 509–519. https://doi.org/10.1111/asap.12224
•De la Fuente, A., Chang, E. C., Cardeñoso, O., & Chang, O. D. (2018). How loneliness is associated with depressive symptoms in Spanish college students: Examining specific coping strategies as mediators. The Spanish Journal of Psychology, 21 , E54. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2018.56
•Dembińska, A., Kłosowska, J., & Ochnik, D. (2022). Ability to initiate relationships and sense of loneliness mediate the relationship between low self-esteem and excessive internet use. Current Psychology, 41 (9), 6577–6583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-01138-9
•Diehl, K., Jansen, C., Ishchanova, K., & Hilger-Kolb, J. (2018). Loneliness at universities: Determinants of emotional and social loneliness among students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15 (9), 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091865
•Dissing, A. S., Hulvej Rod, N., Gerds, T. A., & Lund, R. (2021). Smartphone interactions and mental well-being in young adults: A longitudinal study based on objective high-resolution smartphone data. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 49 (3), 325–332. https://doi.org/10.1177/1403494820920418
•Ditcheva, M., Vrshek-Schallhorn, S., & Batista, A. (2018). People who need people: Trait loneliness influences positive affect as a function of interpersonal context. Biological Psychology, 136 , 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2018.05.014
DiTommaso, E., & Spinner, B. (1993). The development and initial validation of the Social and Emotional Loneliness Scale for Adults (SELSA). Personality and Individual Differences, 14 (1), 127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8869(93)90182-3
•Dong, H., Wang, M., Zheng, H., Zhang, J., & Dong, G. H. (2021). The functional connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and supplementary motor area moderates the relationship between internet gaming disorder and loneliness. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 108 , 110154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110154
•Drake, E. C., Sladek, M. R., & Doane, L. D. (2016). Daily cortisol activity, loneliness, and coping efficacy in late adolescence: A longitudinal study of the transition to college. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 40 (4), 334–345. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025415581914
•Enez Darcin, A., Kose, S., Noyan, C. O., Nurmedov, S., Yılmaz, O., & Dilbaz, N. (2016). Smartphone addiction and its relationship with social anxiety and loneliness. Behaviour & Information Technology, 35 (7), 520–525. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2016.1158319
•Engeland, C. G., Hugo, F. N., Hilgert, J. B., Nascimento, G. G., Junges, R., Lim, H. J., Marucha, P. T., & Bosch, J. A. (2016). Psychological distress and salivary secretory immunity. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 52 , 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.08.017
Erikson, E. H. (1968). Identity: Youth and crisis . W.W. Norton Company.
Ernst, M., Niederer, D., Werner, A. M., Czaja, S. J., Mikton, C., Ong, A. D., Rosen, T., Brähler, E., & Beutel, M. E. (2022). Loneliness before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review with meta-analysis. The American psychologist, 77 (5), 660–677. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0001005
•Essau, C. A., & de la Torre-Luque, A. (2021). Adolescent psychopathological profiles and the outcome of the COVID-19 pandemic: Longitudinal findings from the UK Millennium Cohort Study. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 110 , 110330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110330
•Etkin, R. G., Bowker, J. C., & Scalco, M. D. (2016). Associations between subtypes of social withdrawal and emotional eating during emerging adulthood. Personality and Individual Differences, 97 , 239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2016.03.059
•Evans, S., Alkan, E., Bhangoo, J. K., Tenenbaum, H., & Ng-Knight, T. (2021). Effects of the COVID-19 lockdown on mental health, wellbeing, sleep, and alcohol use in a UK student sample. Psychiatry Research, 298 , 113819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2021.113819
•Fanari, A., & Segrin, C. (2021). Longitudinal effects of US students’ reentry shock on psychological health after returning home during the COVID-19 global pandemic. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 82 , 298–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2021.04.013
•Fang, J., Wang, X., Wen, Z., & Huang, J. (2020). Cybervictimization and loneliness among Chinese college students: A moderated mediation model of rumination and online social support. Children and Youth Services Review, 115 , 105085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105085
•Fardghassemi, S., & Joffe, H. (2021). Young adults’ experience of loneliness in London’s most deprived areas. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 660791. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.660791
•Fernandes, B., Uzun, B., Aydin, C., Tan-Mansukhani, R., Vallejo, A., Saldaña-Gutierrez, A., Nanda Biswas, U., & Essau, C. A. (2021). Internet use during COVID-19 lockdown among young people in low- and middle-income countries: Role of psychological wellbeing. Addictive Behaviors Reports, 14 , 100379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abrep.2021.100379
Flake, J. K., & Fried, E. I. (2020). Measurement schmeasurement: Questionable measurement practices and how to avoid them. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, 3 (4), 456–465. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515245920952393
•Flett, G. L., Goldstein, A. L., Pechenkov, I. G., Nepon, T., & Wekerle, C. (2016). Antecedents, correlates, and consequences of feeling like you don’t matter: Associations with maltreatment, loneliness, social anxiety, and the five-factor model. Personality and Individual Differences, 92 , 52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.12.014
•Fransson, M., Granqvist, P., Marciszko, C., Hagekull, B., & Bohlin, G. (2016). Is middle childhood attachment related to social functioning in young adulthood? Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 57 (2), 108–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12276
•Fumagalli, E., Dolmatzian, M. B., & Shrum, L. J. (2021). Centennials, FOMO, and loneliness: An investigation of the impact of social networking and messaging/VoIP apps usage during the initial stage of the coronavirus pandemic. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 620739. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.620739
•Gan, S. W., Ong, L. S., Lee, C. H., & Lin, Y. S. (2020). Perceived social support and life satisfaction of Malaysian Chinese young adults: The mediating effect of loneliness. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 181 (6), 458–469. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.2020.1803196
•Gonzalez Avilés, T., Finn, C., & Neyer, F. J. (2021). Patterns of romantic relationship experiences and psychosocial adjustment from adolescence to young adulthood. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 50 , 550–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01350-7
•Harriger, J. A., Joseph, N. T., & Trammell, J. (2021). Detrimental associations of cumulative trauma, COVID-19 infection indicators, avoidance, and loneliness with sleep and negative emotionality in emerging adulthood during the pandemic. Emerging Adulthood, 9 (5), 479–491. https://doi.org/10.1177/21676968211022594
Hawkley, L. C., Buecker, S., Kaiser, T., & Luhmann, M. (2022). Loneliness from young adulthood to old age: Explaining age differences in loneliness. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 46 (1), 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025420971048
•Ho, A. H. Y., Ma, S. H. X., Tan, M. K. B., & Bajpai, R. C. (2021). A Randomized waitlist-controlled trial of an intergenerational arts and heritage-based intervention in Singapore: Project ARTISAN. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 730709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.730709
•Hoffman, Y. S. G., Grossman, E. S., Bergman, Y. S., & Bodner, E. (2021). The link between social anxiety and intimate loneliness is stronger for older adults than for younger adults. Aging & Mental Health, 25 (7), 1246–1253. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2020.1774741
•Holmes, L. M., Popova, L., & Ling, P. M. (2016). State of transition: Marijuana use among young adults in the San Francisco Bay Area. Preventive Medicine, 90 , 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.06.025
Holt-Lunstad, J. (2021). A pandemic of social isolation? World Psychiatry, 20 (1), 55. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20839
•Hom, M. A., Hames, J. L., Bodell, L. P., Buchman-Schmitt, J. M., Chu, C., Rogers, M. L., & Joiner, T. E. (2017). Investigating insomnia as a cross-sectional and longitudinal predictor of loneliness: Findings from six samples. Psychiatry Research, 253 , 116–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.03.046
•Hom, M. A., Stanley, I. H., Chu, C., Sanabria, M. M., Christensen, K., Albury, E. A., & Joiner, T. E. (2019). A longitudinal study of psychological factors as mediators of the relationship between insomnia symptoms and suicidal ideation among young adults. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 15 (1), 55–63. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.7570
•Hood, M., Creed, P. A., & Mills, B. J. (2018). Loneliness and online friendships in emerging adults. Personality and Individual Differences, 133 , 96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.03.045
•Hopmeyer, A., & Medovoy, T. (2017). Emerging adults’ self-identified peer crowd affiliations, risk behavior, and social–emotional adjustment in college. Emerging Adulthood, 5 (2), 143–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696816665055
•Hopmeyer, A., Terino, B., Adamczyk, K., Corbitt Hall, D., DeCoste, K., & Troop-Gordon, W. (2022). The lonely collegiate: An examination of the reasons for loneliness among emerging adults in college in the western United States and west-central Poland. Emerging Adulthood, 10 (1), 237–248. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696820966110
•Hu, Y., & Gutman, L. M. (2021). The trajectory of loneliness in UK young adults during the summer to winter months of COVID-19. Psychiatry Research, 303 , 114064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114064
•Hudson, D. B., Campbell-Grossman, C., Kupzyk, K. A., Brown, S. E., Yates, B., & Hanna, K. M. (2016). Social support and psychosocial well-being among low-income, adolescent, African American, first-time mothers. Clinical Nurse Specialist CNS, 30 (3), 150. https://doi.org/10.1097/NUR.0000000000000202
Hughes, M. E., Waite, L. J., Hawkley, L. C., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2004). A short scale for measuring loneliness in large surveys: Results from two population-based studies. Research on Aging, 26 (6), 655–672. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027504268574
•Hutten, E., Jongen, E. M., Verboon, P., Bos, A. E., Smeekens, S., & Cillessen, A. H. (2021). Trajectories of loneliness and psychosocial functioning. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 689913. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.689913
•Jattamart, A., & Kwangsawad, A. (2021). What awareness variables are associated with motivation for changing risky behaviors to prevent recurring victims of cyberbullying? Heliyon, 7 (10), e08121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08121
•Jeong, Y., & Kim, S. H. (2021). Modification of socioemotional processing in loneliness through feedback-based interpretation training. Computers in Human Behavior, 117 , 106668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106668
•Jia, R., Ayling, K., Chalder, T., Massey, A., Broadbent, E., Morling, J. R., & Vedhara, K. (2020). Young people, mental health and COVID-19 infection: The canaries we put in the coal mine. Public Health, 189 , 158–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2020.10.018
Khalil, H., Peters, M. D., McInerney, P. A., Godfrey, C. M., Alexander, L., Evans, C., Pieper, D., Moraes, E. B., Tricco, A. C., & Munn, Z. (2022). The role of scoping reviews in reducing research waste. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 152 , 30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.09.012
•Kim, E., Cho, I., & Kim, E. J. (2017). Structural equation model of smartphone addiction based on adult attachment theory: Mediating effects of loneliness and depression. Asian Nursing Research, 11 (2), 92–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2017.05.002
•Kircaburun, K., Griffiths, M. D., Şahin, F., Bahtiyar, M., Atmaca, T., & Tosuntaş, ŞB. (2020). The mediating role of self/everyday creativity and depression on the relationship between creative personality traits and problematic social media use among emerging adults. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 18 , 77–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-018-9938-0
•Kohls, E., Baldofski, S., Moeller, R., Klemm, S. L., & Rummel-Kluge, C. (2021). Mental health, social and emotional well-being, and perceived burdens of university students during COVID-19 pandemic lockdown in Germany. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12 , 643957. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.643957
•Kokkinos, C. M., & Antoniadou, N. (2019). Cyber-bullying and cyber-victimization among undergraduate student teachers through the lens of the General Aggression Model. Computers in Human Behavior, 98 , 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.04.007
•Kokkinos, C. M., & Saripanidis, I. (2017). A lifestyle exposure perspective of victimization through Facebook among university students. Do individual differences matter? Computers in Human Behavior, 74 , 235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.04.036
•Kumar, S. A., & Mattanah, J. F. (2018). Interparental conflict, parental intrusiveness, and interpersonal functioning in emerging adulthood. Personal Relationships, 25 (1), 120–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/pere.12231
•Lai, J. C., Lee, D. Y., Leung, M. O., & Lam, Y. W. (2019). Daily hassles, loneliness, and diurnal salivary cortisol in emerging adults. Hormones and Behavior, 115 , 104558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2019.07.006
•Lai, J. C. L., Leung, M. O. Y., Lee, D. Y. H., Lam, Y. W., & Berning, K. (2018). Loneliness and diurnal salivary cortisol in emerging adults. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19 (7), 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071944
•Lapierre, M. A. (2020). Smartphones and loneliness in love: Testing links between smartphone engagement, loneliness, and relational health. Psychology of Popular Media, 9 (2), 125. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000230
•Lapierre, M. A., Zhao, P., & Custer, B. E. (2019). Short-term longitudinal relationships between smartphone use/dependency and psychological well-being among late adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65 (5), 607–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.06.001
•Lardone, A., Sorrentino, P., Giancamilli, F., Palombi, T., Simper, T., Mandolesi, L., & Galli, F. (2020). Psychosocial variables and quality of life during the COVID-19 lockdown: A correlational study on a convenience sample of young Italians. PeerJ, 8 , e10611. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10611
•Lau, J. F., Shariff, R., & Meehan, A. (2021). Are biased interpretations of ambiguous social and non-social situations a precursor, consequence or maintenance factor of youth loneliness? Behaviour Research and Therapy, 140 , 103829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2021.103829
•Lee, C. Y. S., Dik, B. J., & Barbara, L. A. (2016). Intergenerational solidarity and individual adjustment during emerging adulthood. Journal of Family Issues, 37 (10), 1412–1432. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513X14567957
•Lee, C. Y. S., & Goldstein, S. E. (2016). Loneliness, stress, and social support in young adulthood: Does the source of support matter? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45 , 568–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-015-0395-9
•Lee, C. Y. S., Goldstein, S. E., & Dik, B. J. (2018). The relational context of social support in young adults: Links with stress and well-being. Journal of Adult Development, 25 , 25–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-017-9271-z
•Li, L., Niu, Z., Griffiths, M. D., Wang, W., Chang, C., & Mei, S. (2021a). A network perspective on the relationship between gaming disorder, depression, alexithymia, boredom, and loneliness among a sample of Chinese university students. Technology in Society, 67 , 101740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101740
•Li, Q., Xiang, G., Song, S., Xiao, M., Huang, X., & Chen, H. (2021b). The association of sense of power with well-being outcomes: The mediating role of hope-agency. The Journal of Psychology, 155 (7), 624–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2021.1939246
•Li, T. M., Li, C. T., Wong, P. W., & Cao, J. (2017). Withdrawal behaviors and mental health among college students. Behavioral Psychology, 25 (1), 99–109.
•Li, W., Zhang, W., Xiao, L., & Nie, J. (2016). The association of Internet addiction symptoms with impulsiveness, loneliness, novelty seeking and behavioral inhibition system among adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Psychiatry Research, 243 , 357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.02.020
•Lim, M. H., Gleeson, J. F., Rodebaugh, T. L., Eres, R., Long, K. M., Casey, K., & Penn, D. L. (2020). A pilot digital intervention targeting loneliness in young people with psychosis. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 55 , 877–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-019-01681-2
•Lim, M. H., Rodebaugh, T. L., Eres, R., Long, K. M., Penn, D. L., & Gleeson, J. F. (2019). A pilot digital intervention targeting loneliness in youth mental health. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10 , 604. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00604
•Lin, S., Falbo, T., Qu, W., Wang, Y., & Feng, X. (2021). Chinese only children and loneliness: Stereotypes and realities. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 91 (4), 531. https://doi.org/10.1037/ort0000554
•Lindekilde, N., Lübeck, M., & Lasgaard, M. (2018). Identity formation and evaluation in adolescence and emerging adulthood: How is it associated with depressive symptoms and loneliness? Scandinavian Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychology, 6 (2), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.21307/sjcapp-2018-010
•Lippke, S., Fischer, M. A., & Ratz, T. (2021). Physical activity, loneliness, and meaning of friendship in young individuals–a mixed-methods investigation prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic with three cross-sectional studies. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 617267. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.617267
•Liu, M. B., Dufour, G., Sun, Z. E., Galante, J., Xing, C. Q., Zhan, J. Y., & Wu, L. L. (2021). The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of young people: A comparison between China and the United Kingdom. Chinese Journal of Traumatology, 24 (04), 231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.05.005
•Luhmann, M., Bohn, J., Holtmann, J., Koch, T., & Eid, M. (2016). I’m lonely, can’t you tell? Convergent validity of self-and informant ratings of loneliness. Journal of Research in Personality, 61 , 50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2016.02.002
Luhmann, M., & Hawkley, L. C. (2016). Age differences in loneliness from late adolescence to oldest old age. Developmental Psychology, 52 (6), 943–959. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000117
•MacDonald, K. B., & Schermer, J. A. (2021). Loneliness unlocked: Associations with smartphone use and personality. Acta Psychologica, 221 , 103454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2021.103454
Maes, M., Qualter, P., Lodder, G. M., & Mund, M. (2022). How (not) to measure loneliness: A review of the eight most commonly used scales. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19 (17), 10816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710816
Maes, M., Qualter, P., Vanhalst, J., Van den Noortgate, W., & Goossens, L. (2019). Gender differences in loneliness across the lifespan: A meta-analysis. European Journal of Personality, 33 (6), 642–654. https://doi.org/10.1002/per.2220
Manoli, A., McCarthy, J., & Ramsey, R. (2022). Estimating the prevalence of social and emotional loneliness across the adult lifespan. Scientific Reports, 12 (1), 21045. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24084-x
•Marchini, S., Zaurino, E., Bouziotis, J., Brondino, N., Delvenne, V., & Delhaye, M. (2021). Study of resilience and loneliness in youth (18–25 years old) during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown measures. Journal of Community Psychology, 49 (2), 468–480. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.22473
Martel, M. M. (2013). Sexual selection and sex differences in the prevalence of childhood externalizing and adolescent internalizing disorders. Psychological Bulletin, 139 (6), 1221. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032247
•Martončik, M., & Lokša, J. (2016). Do World of Warcraft (MMORPG) players experience less loneliness and social anxiety in online world (virtual environment) than in real world (offline)? Computers in Human Behavior, 56 , 127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.11.035
•Matthews, T., Caspi, A., Danese, A., Fisher, H. L., Moffitt, T. E., & Arseneault, L. (2022). A longitudinal twin study of victimization and loneliness from childhood to young adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 34 (1), 367–377. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579420001005
•Matthews, T., Danese, A., Caspi, A., Fisher, H. L., Goldman-Mellor, S., Kepa, A., Moffitt, T. E., Odgers, C. L., & Arseneault, L. (2019). Lonely young adults in modern Britain: Findings from an epidemiological cohort study. Psychological Medicine, 49 (2), 268–277. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291718000788
•Matthews, T., Danese, A., Gregory, A. M., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., & Arseneault, L. (2017). Sleeping with one eye open: Loneliness and sleep quality in young adults. Psychological Medicine, 47 (12), 2177–2186. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291717000629
•Matthews, T., Danese, A., Wertz, J., Odgers, C. L., Ambler, A., Moffitt, T. E., & Arseneault, L. (2016). Social isolation, loneliness and depression in young adulthood: A behavioural genetic analysis. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology: The International Journal for Research in Social and Genetic Epidemiology and Mental Health Services, 51 (3), 339–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-016-1178-7
•Mayorga, N. A., Smit, T., Garey, L., Gold, A. K., Otto, M. W., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2021). Evaluating the interactive effect of COVID-19 worry and loneliness on mental health among young adults. Cognitive Therapy and Research . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-021-10252-2
•McComb, S. E., Goldberg, J. O., Flett, G. L., & Rose, A. L. (2020). The double jeopardy of feeling lonely and unimportant: State and trait loneliness and feelings and fears of not mattering. Frontiers in Psychology, 11 , 563420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.563420
•McGlone, M., & Long, E. (2020). Are young adults with long-standing illness or disability at increased risk of loneliness? Evidence from the UK Longitudinal Household Study. Journal of Public Health Research, 9 (4), jphr-2020. https://doi.org/10.4081/jphr.2020.1861
McHugh Power, J. E., Dolezal, L., Kee, F., & Lawlor, B. A. (2018). Conceptualizing loneliness in health research: Philosophical and psychological ways forward. Journal of Theoretical and Philosophical Psychology, 38 (4), 219. https://doi.org/10.1037/teo0000099
•McIntyre, J. C., Worsley, J., Corcoran, R., Harrison Woods, P., & Bentall, R. P. (2018). Academic and non-academic predictors of student psychological distress: The role of social identity and loneliness. Journal of Mental Health, 27 (3), 230–239. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638237.2018.1437608
McKenna-Plumley, P. E., Turner, R. N., Yang, K., & Groarke, J. M. (2023). Experiences of loneliness across the lifespan: A systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-Being, 18 (1), 2223868. https://doi.org/10.1080/17482631.2023.2223868
•Melkman, E. P. (2017). Childhood adversity, social support networks and well-being among youth aging out of care: An exploratory study of mediation. Child Abuse & Neglect, 72 , 85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2017.07.020
•Meng, J., Hao, L., Wei, D., Sun, J., Li, Y., & Qiu, J. (2017). BDNF Val66Met polymorphism modulates the effect of loneliness on white matter microstructure in young adults. Biological Psychology, 130 , 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2017.10.002
•Merolla, A. J., Otmar, C., & Hernandez, C. R. (2021). Day-to-day relational life during the COVID-19 pandemic: Linking mental health, daily relational experiences, and end-of-day outlook. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 38 (8), 2350–2375. https://doi.org/10.1177/02654075211020137
Milner, J. S. (1986). The child abuse potential inventory: Manual (2nd ed.). Psytec.
•Moeller, R. W., & Seehuus, M. (2019). Loneliness as a mediator for college students’ social skills and experiences of depression and anxiety. Journal of Adolescence, 73 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2019.03.006
•Morse, A. M., Wax, A., Malmquist, E. J., & Hopmeyer, A. (2021). Protester, partygoer, or simply playing it down? The impact of crowd affiliations on LGBT emerging adults’ socioemotional and academic adjustment to college. Journal of Homosexuality, 68 (5), 752–776. https://doi.org/10.1080/00918369.2019.1657752
Moustakas, C. E. (1961). Loneliness . Prentice Hall.
Mund, M., Freuding, M. M., Möbius, K., Horn, N., & Neyer, F. J. (2020). The stability and change of loneliness across the life span: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 24 (1), 24–52. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088868319850738
Mund, M., Maes, M., Drewke, P. M., Gutzeit, A., Jaki, I., & Qualter, P. (2022). Would the real loneliness please stand up? The validity of loneliness scores and the reliability of Single-Item Scores. Assessment . https://doi.org/10.1177/10731911221077227
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 18 , 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
Nelson, L. J., & Luster, S. S. (2015). “Adulthood” by whose definition?: The complexity of emerging adults’ conceptions of adulthood. In J. J. Arnett (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of emerging adulthood (pp. 421–437). Oxford University Press.
Nielsen, M., Haun, D., Kärtner, J., & Legare, C. H. (2017). The persistent sampling bias in developmental psychology: A call to action. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 162 , 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2017.04.017
•Nowakowska, I. (2020). Lonely and thinking about the past: The role of time perspectives, Big Five traits and perceived social support in loneliness of young adults during COVID-19 social distancing. Current Issues in Personality Psychology, 8 (3), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.5114/cipp.2020.97289
•Nowland, R., Talbot, R., & Qualter, P. (2018). Influence of loneliness and rejection sensitivity on threat sensitivity in romantic relationships in young and middle-aged adults. Personality and Individual Differences, 131 , 185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.04.047
•Nwosu, K. C., David, E. T., & Unachukwu, G. C. (2021). Student teachers’ socio-demographic variables, internet addiction and their loneliness in the digital age. International Journal of Education and Practice, 9 (2), 272–284. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.61.2021.92.272.284
•Ohtsubo, Y., Matsunaga, M., Masuda, T., Noguchi, Y., Yamasue, H., & Ishii, K. (2022). Test of the serotonin transporter gene × early life stress interaction effect on subjective well-being and loneliness among japanese young adults. Japanese Psychological Research, 64 (2), 193–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpr.12376
•Okruszek, Ł, Aniszewska-Stańczuk, A., Piejka, A., Wiśniewska, M., & Żurek, K. (2020). Safe but lonely? Loneliness, anxiety, and depression symptoms and COVID-19. Frontiers in Psychology, 11 , 579181. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.579181
•Osman, E. R. O. L., & Cirak, N. S. (2019). Exploring the loneliness and internet addiction level of college students based on demographic variables. Contemporary Educational Technology, 10 (2), 156–172. https://doi.org/10.30935/cet.554488
Ouzzani, M., Hammady, H., Fedorowicz, Z., & Elmagarmid, A. (2016). Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Systematic Reviews, 5 , 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
•Ozden Yildirim, M. S. (2019). The relationship between loneliness, malicious envy, and cyberbullying in emerging adults. Education in the Knowledge Society: EKS . https://doi.org/10.14201/eks2019_20_a30
•Öztekin, C., & Öztekin, A. (2020). The association of depression, loneliness and internet addiction levels in patients with acne vulgaris. BioPsychoSocial Medicine, 14 , 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13030-020-00190-y
•Padmanabhanunni, A., & Pretorius, T. (2021a). The loneliness–life satisfaction relationship: The parallel and serial mediating role of hopelessness, depression and ego-resilience among young adults in south africa during covid-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18 (7), 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073613
•Padmanabhanunni, A., & Pretorius, T. B. (2021b). The unbearable loneliness of COVID-19: COVID-19-related correlates of loneliness in South Africa in young adults. Psychiatry Research, 296 , 113658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113658
•Papp, L. M., & Kouros, C. D. (2021). Effect of COVID-19 disruptions on young adults’ affect and substance use in daily life. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 35 (4), 391. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000748
Parkhurst, J., & Hopmeyer, A. (1999). Developmental change in the sources of loneliness: Contributions of attachment theory. Loneliness in Childhood and Adolescence . https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511551888.004
Peplau, L. A., & Perlman, D. (1982). Perspectives on loneliness. In Loneliness: A sourcebook of current theory, research and therapy (pp. 1–20). Wiley.
Perlman, D., & Peplau, L. A. (1981). Toward a social psychology of loneliness. Personal Relationships, 3 , 31–56.
Peters, M. D., Godfrey, C. M., Khalil, H., McInerney, P., Parker, D., & Soares, C. B. (2015). Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Implementation, 13 (3), 141–146. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050
•Phu, B., & Gow, A. J. (2019). Facebook use and its association with subjective happiness and loneliness. Computers in Human Behavior, 92 , 151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.11.020
•Piejka, A., Wiśniewska, M., Thayer, J. F., & Okruszek, Ł. (2021). Brief induction of loneliness decreases vagal regulation during social information processing. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 164 , 112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2021.03.002
•Piko, B. F., Prievara, D. K., & Mellor, D. (2017). Aggressive and stressed? Youth’s aggressive behaviors in light of their internet use, sensation seeking, stress and social feelings. Children and Youth Services Review, 77 , 55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.04.007
•Pisinger, V. S., Bloomfield, K., & Tolstrup, J. S. (2016). Perceived parental alcohol problems, internalizing problems and impaired parent—Child relationships among 71 988 young people in Denmark. Addiction, 111 (11), 1966–1974. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13508
•Pittman, M., & Reich, B. (2016). Social media and loneliness: Why an Instagram picture may be worth more than a thousand Twitter words. Computers in Human Behavior, 62 , 155–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.03.084
•Pretorius, T., & Padmanabhanunni, A. (2021). A looming mental health pandemic in the time of COVID-19? Role of fortitude in the interrelationship between loneliness, anxiety, and life satisfaction among young adults. South African Journal of Psychology, 51 (2), 256–268. https://doi.org/10.1177/0081246321991030
•Prievara, D. K., Piko, B. F., & Luszczynska, A. (2019). Problematic internet use, social needs, and social support among youth. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 17 , 1008–1019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-018-9973-x
•Putnick, D. L., Uddin, M. K., Rohner, R. P., Singha, B., & Shahnaz, I. (2020). Remembrances of parental rejection are associated with loneliness as mediated by psychological maladjustment in young Bangladeshi men but not women. International Journal of Psychology, 55 (3), 354–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijop.12609
•Qualter, P., Rouncefield-Swales, A., Bray, L., Blake, L., Allen, S., Probert, C., & Carter, B. (2021). Depression, anxiety, and loneliness among adolescents and young adults with IBD in the UK: the role of disease severity, age of onset, and embarrassment of the condition. Quality of Life Research, 30 , 497–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-020-02653-9
Qualter, P., Vanhalst, J., Harris, R., Van Roekel, E., Lodder, G., Bangee, M., Maes, M., & Verhagen, M. (2015). Loneliness across the life span. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10 (2), 250–264. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691615568999
•Rahal, D., Fales, M. R., Haselton, M. G., Slavich, G. M., & Robles, T. F. (2022). Achieving status and reducing loneliness during the transition to college: The role of entitlement, intrasexual competitiveness, and dominance. Social Development, 31 (3), 568–586. https://doi.org/10.1111/sode.12569
Reichmann, F. F. (1959). Loneliness. Psychiatry, 22 (1), 1–15.
Reinwarth, A. C., Ernst, M., Krakau, L., Brähler, E., & Beutel, M. E. (2023). Screening for loneliness in representative population samples: Validation of a single-item measure. PLoS ONE, 18 (3), e0279701. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279701
•Reissmann, A., Hauser, J., Stollberg, E., Kaunzinger, I., & Lange, K. W. (2018). The role of loneliness in emerging adults’ everyday use of facebook–An experience sampling approach. Computers in Human Behavior, 88 , 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.06.011
•Ren, L., Han, X., Li, D., Hu, F., Mo, B., & Liu, J. (2021). The association between loneliness and depression among Chinese college students: Affinity for aloneness and gender as moderators. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 18 (3), 382–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2020.1789861
•Roberson, P. N., Norona, J. C., Fish, J. N., Olmstead, S. B., & Fincham, F. (2017). Do differences matter? A typology of emerging adult romantic relationship. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 34 (3), 334–355. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407516661589
•Robustelli, B. L., Newberry, R. E., Whisman, M. A., & Mittal, V. A. (2017). Social relationships in young adults at ultra high risk for psychosis. Psychiatry Research, 247 , 345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.12.008
Russell, D., Peplau, L. A., & Cutrona, C. E. (1980). The revised UCLA Loneliness Scale: Concurrent and discriminant validity evidence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39 (3), 472.
•Sanecka, E. (2021). The role of machiavellianism and loneliness in predicting self-disclosure online. The New Educational Review, 66 , 198–208. https://doi.org/10.15804/tner.2021.66.4.16
•Satici, S. A. (2019). Facebook addiction and subjective well-being: A study of the mediating role of shyness and loneliness. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 17 (1), 41–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-017-9862-8
•Savolainen, I., Oksanen, A., Kaakinen, M., Sirola, A., & Paek, H. J. (2020). The role of perceived loneliness in youth addictive behaviors: Cross-national survey study. JMIR Mental Health, 7 (1), e14035. https://doi.org/10.2196/14035
•Say, G., & Durak Batigun, A. (2016). The assessment of the relationship between problematic Internet use and parent adolescent relationship quality, loneliness, anger, and problem solving skills. Düşünen Adam: Journal of Psychiatry and Neurological Sciences, 29 (4), 324–334. https://doi.org/10.5350/DAJPN2016290404
•Schaan, V. K., Schulz, A., Schächinger, H., & Vögele, C. (2019). Parental divorce is associated with an increased risk to develop mental disorders in women. Journal of Affective Disorders, 257 , 91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.06.071
•Schiltz, H. K., McVey, A. J., Dolan Wozniak, B., Haendel, A. D., Stanley, R., Arias, A., & Van Hecke, A. V. (2021). The role of loneliness as a mediator between autism features and mental health among autistic young adults. Autism, 25 (2), 545–555. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361320967789
Schwab, J. R., & Syed, M. (2015). Qualitative inquiry and emerging adulthood: Meta-theoretical and methodological issues. Emerging Adulthood, 3 (6), 388–399. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696815587801
•Segrin, C., McNelis, M., & Pavlich, C. A. (2018). Indirect effects of loneliness on substance use through stress. Health Communication, 33 (5), 513–518. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2016.1278507
•Segrin, C., Pavlich, C. A., & McNelis, M. (2017). Transitional instability predicts polymorphous distress in emerging adults. The Journal of Psychology, 151 (5), 496–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2017.1335687
Shanahan, M. I., & Longest, K. C. (2009). Thinking about the Transition to Adulthood. In I. Schoon & R. K. Silbereisen (Eds.), Transitions from school to work: Globalization, individualization, and patterns of diversity (pp. 30–41). Cham: Cambridge University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
•Shen, S., & Kusunoki, Y. (2019). Intimate partner violence and psychological distress among emerging adult women: A bidirectional relationship. Journal of Women’s Health, 28 (8), 1060–1067. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2018.7405
•Shen, X., & Wang, J. L. (2019). Loneliness and excessive smartphone use among Chinese college students: Moderated mediation effect of perceived stressed and motivation. Computers in Human Behavior, 95 , 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.01.012
•Siebenbruner, J. (2019). Companion animals in childhood and emerging adulthood: The relation to emerging adult development. Society & Animals, 27 (3), 235–253. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685306-12341522
•Sirola, A., Kaakinen, M., Savolainen, I., & Oksanen, A. (2019). Loneliness and online gambling-community participation of young social media users. Computers in Human Behavior, 95 , 136–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.01.023
•Skrzynski, C., Creswell, K. G., Bachrach, R. L., & Chung, T. (2018). Social discomfort moderates the relationship between drinking in response to negative affect and solitary drinking in underage drinkers. Addictive Behaviors, 78 , 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.11.009
•Smith, C. V., Lair, E. C., & O’Brien, S. M. (2019). Purposely stoic, accidentally alone? Self-monitoring moderates the relationship between emotion suppression and loneliness. Personality and Individual Differences, 149 , 286–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2019.06.012
•Smith, K. M., Cobb, K. F., Reed-Fitzke, K., Ferraro, A. J., Duncan, J. M., & Lucier-Greer, M. (2022). Connections between parental reciprocity and emerging adult depressive symptoms and loneliness: The role of peer social support. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science, 54 (1), 52. https://doi.org/10.1037/cbs0000284
•Smith, K. M., & Reed-Fitzke, K. (2023). An exploration of factors related to service utilization in emerging adults: Loneliness and psychosocial supports. Journal of American College Health, 71 (2), 440–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2021.1892699
•Snodgrass, J. G., Bagwell, A., Patry, J. M., Dengah, H. F., II., Smarr-Foster, C., Van Oostenburg, M., & Lacy, M. G. (2018). The partial truths of compensatory and poor-get-poorer internet use theories: More highly involved videogame players experience greater psychosocial benefits. Computers in Human Behavior, 78 , 10–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.09.020
Sønderby, L. C., & Wagoner, B. (2013). Loneliness: An integrative approach. Journal of Integrated Social Sciences, 3 (1), 1–29.
Spithoven, A. W., Cacioppo, S., Goossens, L., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2019). Genetic contributions to loneliness and their relevance to the evolutionary theory of loneliness. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 14 (3), 376–396. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691618812684
•Stice, L. V., & Lavner, J. A. (2019). Social connectedness and loneliness mediate the association between autistic traits and internalizing symptoms among young adults. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 49 , 1096–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3812-6
•Sun, L., Fu, Z., & Zheng, Y. (2021). Shyness and loneliness in Chinese young adults: Roles of aggression and gender. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma, 30 (1), 43–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/10926771.2020.1725209
•Sun, Q. W., Wang, C. D., & Jiang, G. R. (2017). Culture-based emotional working models of attachment, Western-based attachment, and psychosocial functioning of Chinese young adults. International Perspectives in Psychology, 6 (4), 195–208. https://doi.org/10.1037/ipp0000075
•Sun, Y., Lin, S. Y., & Chung, K. K. H. (2020). University students’ perceived peer support and experienced depressive symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic: The mediating role of emotional well-being. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17 (24), 9308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249308
•Tam, K. Y., & Chan, C. S. (2019). The effects of lack of meaning on trait and state loneliness: Correlational and experience-sampling evidence. Personality and Individual Differences, 141 , 76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.12.023
•Tam, W. W. S., Poon, S. N., Mahendran, R., Kua, E. H., & Wu, X. V. (2021). Impacts of COVID-19 and partial lockdown on family functioning, intergenerational communication and associated psychosocial factors among young adults in Singapore. BMC Psychiatry, 21 (1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-021-03599-z
•Tan, M., Barkus, E., & Favelle, S. (2021). The cross-lagged relationship between loneliness, social support, and psychotic-like experiences in young adults. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 26 (6), 379–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/13546805.2021.1960156
•Tan, M., Shallis, A., & Barkus, E. (2020). Social anhedonia and social functioning: Loneliness as a mediator. PsyCh Journal, 9 (2), 280–289. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.344
•Thoresen, S., Aakvaag, H. F., Strøm, I. F., Wentzel-Larsen, T., & Birkeland, M. S. (2018). Loneliness as a mediator of the relationship between shame and health problems in young people exposed to childhood violence. Social Science & Medicine, 211 , 183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2018.06.002
•Tian, Y., Bian, Y., Han, P., Gao, F., & Wang, P. (2017). Associations between psychosocial factors and generalized pathological internet use in Chinese university students: A longitudinal cross-lagged analysis. Computers in Human Behavior, 72 , 178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.02.048
Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., Moher, D., Peters, M. D., Horsley, T., & Weeks, L. (2018). PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Annals of Internal Medicine, 169 (7), 467–473. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850
•Turhan Gürbüz, P., Çoban, Ö. G., Erdoğan, A., Kopuz, H. Y., Adanir, A. S., & Önder, A. (2021). Evaluation of internet gaming disorder, social media addiction, and levels of loneliness in adolescents and youth with substance use. Substance Use & Misuse, 56 (12), 1874–1879. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2021.1958856
•van Roekel, E., Ha, T., Scholte, R. H., Engels, R. C., & Verhagen, M. (2016). Loneliness in the daily lives of young adults: Testing a socio-cognitive model. European Journal of Personality, 30 (1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/per.2028
•van Roekel, E., Verhagen, M., Engels, R. C., Scholte, R. H., Cacioppo, S., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2018). Trait and state levels of loneliness in early and late adolescents: Examining the differential reactivity hypothesis. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 47 (6), 888–899. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2016.1146993
Van Staden, W. C., & Coetzee, K. (2010). Conceptual relations between loneliness and culture. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 23 (6), 524–529. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0b013e32833f2ff9
•Vasileiou, K., Barnett, J., Barreto, M., Vines, J., Atkinson, M., Long, K., & Wilson, M. (2019). Coping with loneliness at university: A qualitative interview study with students in the UK. Mental Health & Prevention, 13 , 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mhp.2018.11.002
•Vaterlaus, J. M., Aylward, A., Tarabochia, D., & Martin, J. D. (2021). “A smartphone made my life easier”: An exploratory study on age of adolescent smartphone acquisition and well-being. Computers in Human Behavior, 114 , 106563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106563
•Veerman, L., Heppe, E., Gold, D., & Kef, S. (2019). Intra-and interpersonal factors in adolescence predicting loneliness among young adults with visual impairments. Journal of Visual Impairment & Blindness, 113 (1), 7–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145482X18818615
Verity, L., Schellekens, T., Adam, T., Sillis, F., Majorano, M., Wigelsworth, M., & Maes, M. (2021). Tell me about loneliness: Interviews with young people about what loneliness is and how to cope with it. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18 (22), 11904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182211904
von Soest, T., Luhmann, M., & Gerstorf, D. (2020). The development of loneliness through adolescence and young adulthood: Its nature, correlates, and midlife outcomes. Developmental Psychology, 56 (10), 1919–1934. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001102
•Vuorinen, I., Oksanen, A., Savolainen, I., Sirola, A., Kaakinen, M., Paek, H. J., & Zych, I. (2021). The mediating role of psychological distress in excessive gambling among young people: A four-country study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18 (13), 6973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136973
•Wax, A., Hopmeyer, A., Dulay, P. N., & Medovoy, T. (2019). Commuter college student adjustment: Peer crowd affiliation as a driver of loneliness, belongingness, and risk behaviors. Emerging Adulthood, 7 (5), 363–369. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696818781128
Weinstein, N., Hansen, H., & Nguyen, T. V. (2023). Definitions of solitude in everyday life. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 49 (12), 1663–1678. https://doi.org/10.1177/01461672221115941
Weiss, R. S. (1973). Loneliness: The experience of emotional and social isolation . The MIT Press.
•Weisskirch, R. S. (2018). Psychosocial intimacy, relationships with parents, and well-being among emerging adults. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 27 (11), 3497–3505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-018-1171-8
Wigfield, A., Turner, R., Alden, S., Green, M., & Karania, V. K. (2022). Developing a new conceptual framework of meaningful interaction for understanding social isolation and loneliness. Social Policy and Society, 21 (2), 172–193. https://doi.org/10.1017/S147474642000055X
Witters, D. (2023). Loneliness in U.S. subsides from pandemic high. Gallup.com. https://news.gallup.com/poll/473057/loneliness-subsides-pandemic-high.aspx
Wong, N. M. L., Yeung, P. P. S., & Lee, T. M. C. (2018). A developmental social neuroscience model for understanding loneliness in adolescence. Social Neuroscience, 13 (1), 94–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2016.1256832
•Woznicki, N., Arriaga, A. S., Caporale-Berkowitz, N. A., & Parent, M. C. (2021). Parasocial relationships and depression among LGBQ emerging adults living with their parents during COVID-19: The potential for online support. Psychology of Sexual Orientation and Gender Diversity, 8 (2), 228. https://doi.org/10.1037/sgd0000458
•Yang, C. C., Carter, M. D., Webb, J. J., & Holden, S. M. (2020). Developmentally salient psychosocial characteristics, rumination, and compulsive social media use during the transition to college. Addiction Research & Theory, 28 (5), 433–442. https://doi.org/10.1080/16066359.2019.1682137
•Yu, K., & Zheng, Y. (2020). Sexting and emotional reactions to hooking up among Chinese college students: Moderated mediation effects of loneliness and number of hookup partners. Personality and Individual Differences, 167 , 110252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.110252
•Yu, Q., Mazzoni, S., Lauzon, M., Borgatti, A., Caceres, N., Miller, S., & Salvy, S. J. (2020). Associations between social network characteristics and loneliness during pregnancy in a sample of predominantly African American, largely publicly-insured women. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 24 , 1429–1437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-020-03009-y
•Yu, S., Wu, A. M. S., & Pesigan, I. J. A. (2016). Cognitive and psychosocial health risk factors of social networking addiction. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 14 , 550–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-015-9612-8
•Yubero, S., Navarro, R., Elche, M., Larrañaga, E., & Ovejero, A. (2017). Cyberbullying victimization in higher education: An exploratory analysis of its association with social and emotional factors among Spanish students. Computers in Human Behavior, 75 , 439–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.05.037
•Zawadzki, M. J., & Gavrilova, L. (2021). All the lonely people: Comparing the effects of loneliness as a social stressor to non-lonely stress on blood pressure recovery. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 167 , 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2021.06.016
•Zhang, L., Mersky, J. P., & Topitzes, J. (2020). Adverse childhood experiences and psychological well-being in a rural sample of Chinese young adults. Child Abuse & Neglect, 108 , 104658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104658
•Zhang, N., Fan, F. M., Huang, S. Y., & Rodriguez, M. A. (2018). Mindfulness training for loneliness among Chinese college students: A pilot randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Psychology, 53 (5), 373–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijop.12394
•Zhang, Y., Huang, L., Luo, Y., & Ai, H. (2021). The relationship between state loneliness and depression among youths during COVID-19 lockdown: Coping style as mediator. Frontiers in Psychology . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.701514
•Zlomke, K., Jeter, K., & Cook, N. (2016). Recalled childhood teasing in relation to adult rejection and evaluation sensitivity. Personality and Individual Differences, 89 , 129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.10.021
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the editor of Adolescent Research Review and anonymous reviewers for their helpful feedback.
Open Access funding provided by the IReL Consortium. The first author is in receipt of an Irish Research Council Government of Ireland Postgraduate Scholarship (GOIPG/2021/345). The sponsor had no role in the study design, analysis, interpretation of the data, or writing of the article.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
Emma M. Kirwan, Páraic S. O’Súilleabháin, Sarah Summerville, Máire McGeehan, Jennifer McMahon & Ann-Marie Creaven
Health Research Institute, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
Emma M. Kirwan, Páraic S. O’Súilleabháin, Máire McGeehan, Jennifer McMahon & Ann-Marie Creaven
Institute of Public Health, Dublin, Ireland
Annette Burns
School of Psychology, University of Galway, Galway, Ireland
Ashweeja Gowda
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
EMK conceived of the study, participated in study design, coordination, and interpretation of the data, and drafted the manuscript; AB conceived of the study, participated in study design and coordination, and drafted the manuscript; PSO’S conceived of the study, participated in study design and coordination, and drafted the manuscript; SS performed data screening and drafted the manuscript; MMG performed data screening and charting, and drafted the manuscript; JMM contributed to study conceptualization, methodology, and drafted the manuscript; AG performed data screening and drafted the manuscript; AMC conceived of the study, participated in study design, coordination, and interpretation of the data, and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emma M. Kirwan .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Preregistration
This study’s aims, design, and methods were preregistered on Open Science Framework ( https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C7KE9 ).
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
The authors declare that AI or AI-assisted technologies were not used in the writing process.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 36 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kirwan, E.M., Burns, A., O’Súilleabháin, P.S. et al. Loneliness in Emerging Adulthood: A Scoping Review. Adolescent Res Rev (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-024-00240-4
Download citation
Received : 20 December 2023
Accepted : 10 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-024-00240-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Emerging adulthood
- Young adults
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
May 13, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Study shows alarming rise of electronic vaping use in US adolescents
by Florida Atlantic University

Electronic vapor products (EVPs), also known as e-cigarettes or vaping devices, have an allure because of their marketed image as a safer alternative to traditional cigarette smoking and for their variety of appealing flavors.
Yet, they contain many substances beyond nicotine, including propylene glycol , glycerin, flavorings and potentially harmful chemicals such as formaldehyde and metals, which could pose significant health risks such as respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Vaping also is strongly linked with a serious medical condition that damages the lungs due to the vitamin E acetate, an additive used in tetrahydrocannabinol-containing e-cigarettes.
In 2022, 6% of adults in the U.S. reported current vaping device use. Widespread use by adults has raised concerns about EVP use among adolescents.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Schmidt College of Medicine explored temporal trends in EVP use from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey for ninth through 12th grades among 57,006 subjects from 2015 (earliest available data) to 2021 (most recently available data) from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Results of the study, published online ahead of print in Ochsner Journal , show alarming statistically significant and clinically important increases of the daily use of EVPs in U.S. adolescents.
Daily use of EVPs increased from 2% in 2015 to 7.2% in 2019, greater than three-and-one-half times increase. Although the percentage decreased to 5% in 2021, it was still more than a two-and-one-half increase since 2015. The researchers speculate that the effects of COVID-19, which included lockdowns and remote schooling, may have contributed to the decrease in 2021 but cautioned that further research is warranted.
Findings also show that in 2015, the percentage of EVP use was significantly higher in boys (2.8%) than girls (1.1%). By 2021, the percentage of EVP use was higher in girls (5.6%) than boys (4.5%), a one-and-one-quarter increase.
In addition, the percentage of EVP use in 2021 was higher in whites (6.5%) than Blacks (3.1%), Asians (1.2%), and Hispanic/Latinos (3.4%) compared to 2015. However, white and Black adolescents had the highest increases of about threefold between 2015 and 2021. In all four survey years, daily EVP use was highest in grade 12 where most students are ages 17 to 18.
"EVP use increases risks of nicotine addiction, drug-seeking behavior, mood disorders and long-term risks of avoidable premature morbidities and mortality," said Charles H. Hennekens, M.D., Dr.PH, first author, first Sir Richard Doll Professor of Medicine and senior academic advisor, FAU Schmidt College of Medicine.
"In addition, compared to nonusers, adolescents and young adults who use EVPs are more likely to switch to cigarette smoking, which, despite remarkable declines in the U.S., remains the leading avoidable cause of premature death in the U.S. and worldwide."
The researchers also raise concerns about risks of short- as well as long-term use of EVPs.
"Almost 100% of e-cigarettes sold in the U.S. contain nicotine, and the use of these products by adolescents may lead to future abuse of and addiction to additional substances," said Panagiota "Yiota" Kitsantas, Ph.D., senior author and professor and chair of the Department of Population Health and Social Medicine, FAU Schmidt College of Medicine.
"EVP use is not a safer alternative to smoking but may have contributed to the decline in regular tobacco product use. EVP use also raises concerns about new health risks, including nicotine addiction."
While data indicate a substantial decline in traditional cigarette smoking among U.S. adolescents, the introduction of EVP use and their alarming increases have presented new challenges. The researchers believe that the data create clinical and public health challenges.
"These alarming trends in the use of EVPs suggest the need for targeted interventions such as mass media campaigns and peer interventions to combat the influences of social norms that promote the adoption of risky health behaviors during adolescence," said Hennekens. "Clinical interventions could include routine screening for vaping and nicotine dependence during adolescent health assessments as well as counseling and tailored cessation programs."
Study co-authors are Adedamola Adele, Department of Biomedical Science; Maria C. Mejia, M.D., professor of population health and social medicine; and Robert S. Levine, M.D., affiliate professor of family medicine, all within the Schmidt College of Medicine.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

A minimal cognitive architecture reproduces control of human decision-making processes

Artificial intelligence tool detects sex-related differences in brain structure
3 hours ago

Over 20,000 people join UK search for new dementia treatments

Clinical trial: New drug makes exercise, everyday tasks easier for people with common heart condition
11 hours ago

Semaglutide can yield weight loss, lower heart issues for at least four years in non-diabetic adults with overweight
14 hours ago
Study reveals key role of glutamate tRNA fragments in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease
15 hours ago
New molecule mimics the anti-clotting action of blood-sucking organisms
Axons in female mammal brains may be more prone to concussions

Herpes cure with gene editing makes progress in laboratory studies

Breast cancer risk variants identified for women of African ancestry
16 hours ago
Related Stories

Researchers report dramatic decline in cigarette use among US teens over three decades
Jan 10, 2024

Young adults with cognitive disabilities and major depressive episodes found more likely to vape nicotine
Feb 20, 2024

US teen smoking rates have plummeted, with fewer than 1% now daily smokers

Researchers find association between vaping and asthma among US adolescents
Sep 19, 2023

New national study finds adolescent vapers much likelier to use cannabis and binge drink
May 18, 2023

Higher taxes on e-cigs likely to boost cigarette smoking among young adults
Jul 20, 2022
Recommended for you

Teenage users of high-THC cannabis varieties twice as likely to experience psychotic episodes
17 hours ago

For treating retinopathy of prematurity, research proves that ranibizumab is safe
18 hours ago

Anti-immigrant political rhetoric and action threaten Latino/a youth mental health: Study
21 hours ago

Visual experiences unique to early infancy provide building blocks of human vision, study finds
May 10, 2024

Research team introduces new tool to boost battle against childhood undernutrition

Study finds THC lingers in breastmilk with no clear peak point
May 8, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Influence of Heavy Metal Music on Adolescence (Behavior, Identity, Mood, Regulation, Psychology) Accepting the potent impact of music on adolescents' behavior, identity, and psychology leads to a deeper analysis of the influences of heavy metal music on teenagers' development. Childhood, Adolescence, Young Adulthood Psychology.
Research on adolescence has also changed dramatically. This review discusses recent developments in this literature, being cognizant of their historical underpinnings while focusing on the future. ... and 17% looked online for information about sensitive health topics, such as those related to drug use, mental health, and sex (Lenhart et al ...
Special Issue: Decade in Review. The Journal of Research on Adolescence has published a special section, A Decade Review of Adolescence Research, highlighting research conducted over the last decade.The special section features fifteen articles from experts on adolescent development on topics ranging from parenting and peers to immigrant resilience and positive youth development.
Journal of Adolescent Research (JAR) aims to publish informative and dynamic articles from a variety of disciplines focused on adolescence and early emerging adulthood development.JAR has particular interest in papers that use mixed-methods, systematically combining qualitative and quantitative data and analyses and seeks rigorous qualitative research using a variety of strategies including ...
Long-term study will produce open-access data on adolescents, including neurological development, sociocultural and psychological factors, mental and physical health, environmental exposures, substance use, academic achievement and more. ... Explore how scientific research by psychologists can inform our professional lives, family and community ...
Special Issue: Decade in Review. The Journal of Research on Adolescence has published a special section, A Decade Review of Adolescence Research, highlighting research conducted over the last decade.The special section features fifteen articles from experts on adolescent development on topics ranging from parenting and peers to immigrant resilience and positive youth development.
The past few decades have witnessed rapid growth in research centered on the period of adolescence. Several markers of that growth are now obvious, such as multidisciplinary journals dedicated to that developmental period. But, it remains to be determined, like other fields of research that often contribute to the understanding of adolescence (genetics, cognitive science, medicine), whether ...
Erikson's psychosocial development is a well-known and sound framework for adolescent development. However, despite its importance in scientific literature, the scarcity of literature reviews on Erikson's theory on adolescence calls for an up-to-date systematization. Therefore, this study's objectives are to understand the extent and nature of published research on Erikson's ...
Adolescence research must grow up. Young people get a raw deal from society. Targeted study and approaches as part of a new global effort are urgently needed to help them. Many adolescents would ...
Adolescent Research Review is a multidisciplinary journal publishing articles that review important contributions to the understanding of adolescence. Offers a quick turnaround time of typically on a few days to first decision. Advances science, practice, and policy relating to youth and adolescents through cutting edge and comprehensive ...
Jo-Anna B. Baxter, University of Toronto. Adolescence lies between childhood and adulthood, but adolescents are neither big children nor little adults. They have increased food requirements to ...
In addition to the biological changes of puberty, they experience cognitive changes that allow them to think more abstractly. They become increasingly focused on friends. And as they seek greater independence, they often come into conflict with parents. Most get through adolescence with few problems, establishing identities and preparing for ...
Topics covered include the juncture between the arts and human culture, the developing adolescent brain, the interaction between cultural and biological processes and artistic creation, the interface of the arts and science as a multisensory experience, insights from the neuroscience of dance and music, and more.
Research linking social media use and adolescent mental health has produced mixed and inconsistent findings and little translational evidence, despite pressure to deliver concrete recommendations ...
New research shows some gains but fresh difficulties in combating child sexual abuse. Ben Mathews, Queensland University of Technology and Chanel Contos, Australian National University. While ...
Members of the editorial boards of the two peer-reviewed journals related to adolescent health with the highest impact factor (Journal of Adolescent Health—2.75 and Journal of Research on Adolescence—2.51) based on Web of Science Journal Citation Reports for 2013 were included in the adolescent health: policy, health and social systems area ...
Adolescent health. Adolescence is the phase of life between childhood and adulthood, from ages 10 to 19. It is a unique stage of human development and an important time for laying the foundations of good health. Adolescents experience rapid physical, cognitive and psychosocial growth. This affects how they feel, think, make decisions, and ...
Adolescence is an important stage of cognitive, physical, and social development. Piaget, Freud, and Erikson each focused on different aspects. Depression amongst young adults at the puberty stage comes in hand with several causes that one cannot imagine, and depression happens or is triggered by various reasons.
AdLit offers lots of articles, expert Q&A, video, research and reports, and additional resources that provide research-based information for educators, families, and others who want to help young people become better readers and writers. Browse the topics below to learn more. Home. Adolescent Literacy Topics A-Z.
Adolescence as a Stage of Human Development. Psychology essay sample: Adolescence marks the end of society's influence on a person without them criticizing it. In contrast with a child, teenagers reflect on matters being suggested or instilled in them. G. Stanley Hall: Adolescence and the Teenage Mind. Psychology essay sample: Granville Stanley ...
Research in child & adolescent psychology utilizes core psychology resources, as well as resources in child & family development and sociology. You may find it helpful to search the following databases for your child & adolescent development topics or research questions, in addition to the core resources listed on the home page.
Four systematic reviews reflect interest in menstruation as a research and/or intervention topic in LMICs; none focus exclusively on young adolescents or deal with puberty. ... sexuality, or related topics. These findings may reflect an elision by researchers and/or respondents of puberty with menstruation for girls. However, puberty is a broad ...
Loneliness is prevalent during emerging adulthood (approximately 18-25 years) and is an important issue given it has been linked to poorer physical and mental health outcomes. This preregistered scoping review aimed to provide an overview of the literature on loneliness in emerging adulthood, including the (a) conceptualization and measurement of loneliness, (b) loneliness theories used, (c ...
The research into adolescence highlights several key ideas about parenting during these years: Parents, families, and other supportive adults still matter very much to use during adolescence, even as peers seem to take center stage. ... and who frequently discussed topics related to being in love, sexual relationships, and safe sex, are more ...
During adolescence the body usually experiences a growth spurt, which is a time of very rapid growth in height and weight. Puberty, which also happens during adolescence, is the time period of maturation where sexual organs mature. 1 Rapid changes in the body can be exciting, scary, and/or confusing. Some adolescents may mature early while others experience late maturation, both of which can ...
Results of the study, published online ahead of print in Ochsner Journal, show alarming statistically significant and clinically important increases of the daily use of EVPs in U.S. adolescents ...