Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples

How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Step 1. Ask a question
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
| Research question | Hypothesis | Null hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| What are the health benefits of eating an apple a day? | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will result in decreasing frequency of doctor’s visits. | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will have no effect on frequency of doctor’s visits. |
| Which airlines have the most delays? | Low-cost airlines are more likely to have delays than premium airlines. | Low-cost and premium airlines are equally likely to have delays. |
| Can flexible work arrangements improve job satisfaction? | Employees who have flexible working hours will report greater job satisfaction than employees who work fixed hours. | There is no relationship between working hour flexibility and job satisfaction. |
| How effective is high school sex education at reducing teen pregnancies? | Teenagers who received sex education lessons throughout high school will have lower rates of unplanned pregnancy teenagers who did not receive any sex education. | High school sex education has no effect on teen pregnancy rates. |
| What effect does daily use of social media have on the attention span of under-16s? | There is a negative between time spent on social media and attention span in under-16s. | There is no relationship between social media use and attention span in under-16s. |
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 19, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
Independent and Dependent Variables: Differences & Examples
By Jim Frost 15 Comments

In this post, learn the definitions of independent and dependent variables, how to identify each type, how they differ between different types of studies, and see examples of them in use.
What is an Independent Variable?
Independent variables (IVs) are the ones that you include in the model to explain or predict changes in the dependent variable. The name helps you understand their role in statistical analysis. These variables are independent . In this context, independent indicates that they stand alone and other variables in the model do not influence them. The researchers are not seeking to understand what causes the independent variables to change.
Independent variables are also known as predictors, factors , treatment variables, explanatory variables, input variables, x-variables, and right-hand variables—because they appear on the right side of the equals sign in a regression equation. In notation, statisticians commonly denote them using Xs. On graphs, analysts place independent variables on the horizontal, or X, axis.
In machine learning, independent variables are known as features.
For example, in a plant growth study, the independent variables might be soil moisture (continuous) and type of fertilizer (categorical).
Statistical models will estimate effect sizes for the independent variables.
Relate post : Effect Sizes in Statistics
Including independent variables in studies
The nature of independent variables changes based on the type of experiment or study:
Controlled experiments : Researchers systematically control and set the values of the independent variables. In randomized experiments, relationships between independent and dependent variables tend to be causal. The independent variables cause changes in the dependent variable.
Observational studies : Researchers do not set the values of the explanatory variables but instead observe them in their natural environment. When the independent and dependent variables are correlated, those relationships might not be causal.
When you include one independent variable in a regression model, you are performing simple regression. For more than one independent variable, it is multiple regression. Despite the different names, it’s really the same analysis with the same interpretations and assumptions.
Determining which IVs to include in a statistical model is known as model specification. That process involves in-depth research and many subject-area, theoretical, and statistical considerations. At its most basic level, you’ll want to include the predictors you are specifically assessing in your study and confounding variables that will bias your results if you don’t add them—particularly for observational studies.
For more information about choosing independent variables, read my post about Specifying the Correct Regression Model .
Related posts : Randomized Experiments , Observational Studies , Covariates , and Confounding Variables
What is a Dependent Variable?
The dependent variable (DV) is what you want to use the model to explain or predict. The values of this variable depend on other variables. It is the outcome that you’re studying. It’s also known as the response variable, outcome variable, and left-hand variable. Statisticians commonly denote them using a Y. Traditionally, graphs place dependent variables on the vertical, or Y, axis.
For example, in the plant growth study example, a measure of plant growth is the dependent variable. That is the outcome of the experiment, and we want to determine what affects it.
How to Identify Independent and Dependent Variables
If you’re reading a study’s write-up, how do you distinguish independent variables from dependent variables? Here are some tips!
Identifying IVs
How statisticians discuss independent variables changes depending on the field of study and type of experiment.
In randomized experiments, look for the following descriptions to identify the independent variables:
- Independent variables cause changes in another variable.
- The researchers control the values of the independent variables. They are controlled or manipulated variables.
- Experiments often refer to them as factors or experimental factors. In areas such as medicine, they might be risk factors.
- Treatment and control groups are always independent variables. In this case, the independent variable is a categorical grouping variable that defines the experimental groups to which participants belong. Each group is a level of that variable.
In observational studies, independent variables are a bit different. While the researchers likely want to establish causation, that’s harder to do with this type of study, so they often won’t use the word “cause.” They also don’t set the values of the predictors. Some independent variables are the experiment’s focus, while others help keep the experimental results valid.
Here’s how to recognize independent variables in observational studies:
- IVs explain the variability, predict, or correlate with changes in the dependent variable.
- Researchers in observational studies must include confounding variables (i.e., confounders) to keep the statistical results valid even if they are not the primary interest of the study. For example, these might include the participants’ socio-economic status or other background information that the researchers aren’t focused on but can explain some of the dependent variable’s variability.
- The results are adjusted or controlled for by a variable.
Regardless of the study type, if you see an estimated effect size, it is an independent variable.
Identifying DVs
Dependent variables are the outcome. The IVs explain the variability or causes changes in the DV. Focus on the “depends” aspect. The value of the dependent variable depends on the IVs. If Y depends on X, then Y is the dependent variable. This aspect applies to both randomized experiments and observational studies.
In an observational study about the effects of smoking, the researchers observe the subjects’ smoking status (smoker/non-smoker) and their lung cancer rates. It’s an observational study because they cannot randomly assign subjects to either the smoking or non-smoking group. In this study, the researchers want to know whether lung cancer rates depend on smoking status. Therefore, the lung cancer rate is the dependent variable.
In a randomized COVID-19 vaccine experiment , the researchers randomly assign subjects to the treatment or control group. They want to determine whether COVID-19 infection rates depend on vaccination status. Hence, the infection rate is the DV.
Note that a variable can be an independent variable in one study but a dependent variable in another. It depends on the context.
For example, one study might assess how the amount of exercise (IV) affects health (DV). However, another study might study the factors (IVs) that influence how much someone exercises (DV). The amount of exercise is an independent variable in one study but a dependent variable in the other!
How Analyses Use IVs and DVs
Regression analysis and ANOVA mathematically describe the relationships between each independent variable and the dependent variable. Typically, you want to determine how changes in one or more predictors associate with changes in the dependent variable. These analyses estimate an effect size for each independent variable.
Suppose researchers study the relationship between wattage, several types of filaments, and the output from a light bulb. In this study, light output is the dependent variable because it depends on the other two variables. Wattage (continuous) and filament type (categorical) are the independent variables.
After performing the regression analysis, the researchers will understand the nature of the relationship between these variables. How much does the light output increase on average for each additional watt? Does the mean light output differ by filament types? They will also learn whether these effects are statistically significant.
Related post : When to Use Regression Analysis
Graphing Independent and Dependent Variables
As I mentioned earlier, graphs traditionally display the independent variables on the horizontal X-axis and the dependent variable on the vertical Y-axis. The type of graph depends on the nature of the variables. Here are a couple of examples.
Suppose you experiment to determine whether various teaching methods affect learning outcomes. Teaching method is a categorical predictor that defines the experimental groups. To display this type of data, you can use a boxplot, as shown below.

The groups are along the horizontal axis, while the dependent variable, learning outcomes, is on the vertical. From the graph, method 4 has the best results. A one-way ANOVA will tell you whether these results are statistically significant. Learn more about interpreting boxplots .
Now, imagine that you are studying people’s height and weight. Specifically, do height increases cause weight to increase? Consequently, height is the independent variable on the horizontal axis, and weight is the dependent variable on the vertical axis. You can use a scatterplot to display this type of data.

It appears that as height increases, weight tends to increase. Regression analysis will tell you if these results are statistically significant. Learn more about interpreting scatterplots .
Share this:

Reader Interactions
April 2, 2024 at 2:05 am
Hi again Jim
Thanks so much for taking an interest in New Zealand’s Equity Index.
Rather than me trying to explain what our Ministry of Education has done, here is a link to a fairly short paper. Scroll down to page 4 of this (if you have the inclination) – https://fyi.org.nz/request/21253/response/80708/attach/4/1301098%20Response%20and%20Appendix.pdf
The Equity Index is used to allocate only 4% of total school funding. The most advantaged 5% of schools get no “equity funding” and the other 95% get a share of the equity funding pool based on their index score. We are talking a maximum of around $1,000NZD per child per year for the most disadvantaged schools. The average amount is around $200-$300 per child per year.
My concern is that I thought the dependent variable is the thing you want to explain or predict using one or more independent variables. Choosing the form of dependent variable that gets a good fit seems to be answering the question “what can we predict well?” rather than “how do we best predict the factor of interest?” The factor is educational achievement and I think this should have been decided upon using theory rather than experimentation with the data.
As it turns out, the Ministry has chosen a measure of educational achievement that puts a heavy weight on achieving an “excellence” rating on a qualification and a much lower weight on simply gaining a qualification. My reading is that they have taken what our universities do when looking at which students to admit.
It doesn’t seem likely to me that a heavy weighting on excellent achievement is appropriate for targeting extra funding to schools with a lot of under-achieving students.
However, my stats knowledge isn’t extensive and it’s definitely rusty, so your thoughts are most helpful.
Regards Kathy Spencer
April 1, 2024 at 4:08 pm
Hi Jim, Great website, thank you.
I have been looking at New Zealand’s Equity Index which is used to allocate a small amount of extra funding to schools attended by children from disadvantaged backgrounds. The Index uses 37 socioeconomic measures relating to a child’s and their parents’ backgrounds that are found to be associated with educational achievement.
I was a bit surprised to read how they had decided on the dependent variable to be used as the measure of educational achievement, or dependent variable. Part of the process was as follows- “Each measure was tested to see the degree to which it could be predicted by the socioeconomic factors selected for the Equity Index.”
Any comment?
Many thanks Kathy Spencer
April 1, 2024 at 9:20 pm
That’s a very complex study and I don’t know much about it. So, that limits what I can say about it. But I’ll give you a few thoughts that come to mind.
This method is common in educational and social research, particularly when the goal is to understand or mitigate the impact of socioeconomic disparities on educational outcomes.
There are the usual concerns about not confusing correlation with causation. However, because this program seems to quantify barriers and then provide extra funding based on the index, I don’t think that’s a problem. They’re not attempting to adjust the socioeconomic measures so no worries about whether they’re directly causal or not.
I might have a small concern about cherry picking the model that happens to maximize the R-squared. Chasing the R-squared rather than having theory drive model selecting is often problematic. Chasing the best fit increases the likelihood that the model fits this specific dataset best by random chance rather than being truly the best. If so, it won’t perform as well outside the dataset used to fit the model. Hopefully, they validated the predicted ability of the model using other data.
However, I’m not sure if the extra funding is determined by the model? I don’t know if the index value is calculated separately outside the candidate models and then fed into the various models. Or does the choice of model affect how the index value is calculated? If it’s the former, then the funding doesn’t depend on a potentially cherry picked model. If the latter, it does.
So, I’m not really clear on the purpose of the model. I’m guessing they just want to validate their Equity Index. And maximizing the R-squared doesn’t really say it’s the best Index but it does at least show that it likely has some merit. I’d be curious how the took the 37 measures and combined them to one index. So, I have more questions than answers. I don’t mean that in a critical sense. Just that I know almost nothing about this program.
I’m curious, what was the outcome they picked? How high was the R-squared? And what were your concerns?
February 6, 2024 at 6:57 pm
Excellent explanation, thank you.
February 5, 2024 at 5:04 pm
Thank you for this insightful blog. Is it valid to use a dependent variable delivered from the mean of independent variables in multiple regression if you want to evaluate the influence of each unique independent variable on the dependent variables?
February 5, 2024 at 11:11 pm
It’s difficult to answer your question because I’m not sure what you mean that the DV is “delivered from the mean of IVs.” If you mean that multiple IVs explain changes in the DV’s mean, yes, that’s the standard use for multiple regression.
If you mean something else, please explain in further detail. Thanks!
February 6, 2024 at 6:32 am
What I meant is; the DV values used as parameters for multiple regression is basically calculated as the average of the IVs. For instance:
From 3 IVs (X1, X2, X3), Y is delivered as :
Y = (Sum of all IVs) / (3)
Then the resulting Y is used as the DV along with the initial IVs to compute the multiple regression.
February 6, 2024 at 2:17 pm
There are a couple of reasons why you shouldn’t do that.
For starters, Y-hat (the predicted value of the regression equation) is the mean of the DV given specific values of the IV. However, that mean is calculated by using the regression coefficients and constant in the regression equation. You don’t calculate the DV mean as the sum of the IVs divided by the number of IVs. Perhaps given a very specific subject-area context, using this approach might seem to make sense but there are other problems.
A critical problem is that the Y is now calculated using the IVs. Instead, the DVs should be measured outcomes and not calculated from IVs. This violates regression assumptions and produces questionable results.
Additionally, it complicates the interpretation. Because the DV is calculated from the IV, you know the regression analysis will find a relationship between them. But you have no idea if that relationship exists in the real world. This complication occurs because your results are based on forcing the DV to equal a function of the IVs and do not reflect real-world outcomes.
In short, DVs should be real-world outcomes that you measure! And be sure to keep your IVs and DV independent. Let the regression analysis estimate the regression equation from your data that contains measured DVs. Don’t use a function to force the DV to equal some function of the IVs because that’s the opposite direction of how regression works!
I hope that helps!
September 6, 2022 at 7:43 pm
Thank you for sharing.
March 3, 2022 at 1:59 am
Excellent explanation.
February 13, 2022 at 12:31 pm
Thanks a lot for creating this excellent blog. This is my go-to resource for Statistics.
I had been pondering over a question for sometime, it would be great if you could shed some light on this.
In linear and non-linear regression, should the distribution of independent and dependent variables be unskewed? When is there a need to transform the data (say, Box-Cox transformation), and do we transform the independent variables as well?
October 28, 2021 at 12:55 pm
If I use a independent variable (X) and it displays a low p-value <.05, why is it if I introduce another independent variable to regression the coefficient and p-value of Y that I used in first regression changes to look insignificant? The second variable that I introduced has a low p-value in regression.
October 29, 2021 at 11:22 pm
Keep in mind that the significance of each IV is calculated after accounting for the variance of all the other variables in the model, assuming you’re using the standard adjusted sums of squares rather than sequential sums of squares. The sums of squares (SS) is a measure of how much dependent variable variability that each IV accounts for. In the illustration below, I’ll assume you’re using the standard of adjusted SS.
So, let’s say that originally you have X1 in the model along with some other IVs. Your model estimates the significance of X1 after assessing the variability that the other IVs account for and finds that X1 is significant. Now, you add X2 to the model in addition to X1 and the other IVs. Now, when assessing X1, the model accounts for the variability of the IVs including the newly added X2. And apparently X2 explains a good portion of the variability. X1 is no longer able to account for that variability, which causes it to not be statistically significant.
In other words, X2 explains some of the variability that X1 previously explained. Because X1 no longer explains it, it is no longer significant.
Additionally, the significance of IVs is more likely to change when you add or remove IVs that are correlated. Correlated IVs is known as multicollinearity. Multicollinearity can be a problem when you have too much. Given the change in significance, I’d check your model for multicollinearity just to be safe! Click the link to read a post that wrote about that!
September 6, 2021 at 8:35 am
nice explanation
August 25, 2021 at 3:09 am
it is excellent explanation
Comments and Questions Cancel reply

Research Variables 101
Independent variables, dependent variables, control variables and more
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | January 2023
If you’re new to the world of research, especially scientific research, you’re bound to run into the concept of variables , sooner or later. If you’re feeling a little confused, don’t worry – you’re not the only one! Independent variables, dependent variables, confounding variables – it’s a lot of jargon. In this post, we’ll unpack the terminology surrounding research variables using straightforward language and loads of examples .
Overview: Variables In Research
| 1. ? 2. variables 3. variables 4. variables | 5. variables |
What (exactly) is a variable?
The simplest way to understand a variable is as any characteristic or attribute that can experience change or vary over time or context – hence the name “variable”. For example, the dosage of a particular medicine could be classified as a variable, as the amount can vary (i.e., a higher dose or a lower dose). Similarly, gender, age or ethnicity could be considered demographic variables, because each person varies in these respects.
Within research, especially scientific research, variables form the foundation of studies, as researchers are often interested in how one variable impacts another, and the relationships between different variables. For example:
- How someone’s age impacts their sleep quality
- How different teaching methods impact learning outcomes
- How diet impacts weight (gain or loss)
As you can see, variables are often used to explain relationships between different elements and phenomena. In scientific studies, especially experimental studies, the objective is often to understand the causal relationships between variables. In other words, the role of cause and effect between variables. This is achieved by manipulating certain variables while controlling others – and then observing the outcome. But, we’ll get into that a little later…
The “Big 3” Variables
Variables can be a little intimidating for new researchers because there are a wide variety of variables, and oftentimes, there are multiple labels for the same thing. To lay a firm foundation, we’ll first look at the three main types of variables, namely:
- Independent variables (IV)
- Dependant variables (DV)
- Control variables
What is an independent variable?
Simply put, the independent variable is the “ cause ” in the relationship between two (or more) variables. In other words, when the independent variable changes, it has an impact on another variable.
For example:
- Increasing the dosage of a medication (Variable A) could result in better (or worse) health outcomes for a patient (Variable B)
- Changing a teaching method (Variable A) could impact the test scores that students earn in a standardised test (Variable B)
- Varying one’s diet (Variable A) could result in weight loss or gain (Variable B).
It’s useful to know that independent variables can go by a few different names, including, explanatory variables (because they explain an event or outcome) and predictor variables (because they predict the value of another variable). Terminology aside though, the most important takeaway is that independent variables are assumed to be the “cause” in any cause-effect relationship. As you can imagine, these types of variables are of major interest to researchers, as many studies seek to understand the causal factors behind a phenomenon.
Need a helping hand?
What is a dependent variable?
While the independent variable is the “ cause ”, the dependent variable is the “ effect ” – or rather, the affected variable . In other words, the dependent variable is the variable that is assumed to change as a result of a change in the independent variable.
Keeping with the previous example, let’s look at some dependent variables in action:
- Health outcomes (DV) could be impacted by dosage changes of a medication (IV)
- Students’ scores (DV) could be impacted by teaching methods (IV)
- Weight gain or loss (DV) could be impacted by diet (IV)
In scientific studies, researchers will typically pay very close attention to the dependent variable (or variables), carefully measuring any changes in response to hypothesised independent variables. This can be tricky in practice, as it’s not always easy to reliably measure specific phenomena or outcomes – or to be certain that the actual cause of the change is in fact the independent variable.
As the adage goes, correlation is not causation . In other words, just because two variables have a relationship doesn’t mean that it’s a causal relationship – they may just happen to vary together. For example, you could find a correlation between the number of people who own a certain brand of car and the number of people who have a certain type of job. Just because the number of people who own that brand of car and the number of people who have that type of job is correlated, it doesn’t mean that owning that brand of car causes someone to have that type of job or vice versa. The correlation could, for example, be caused by another factor such as income level or age group, which would affect both car ownership and job type.
To confidently establish a causal relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable (i.e., X causes Y), you’ll typically need an experimental design , where you have complete control over the environmen t and the variables of interest. But even so, this doesn’t always translate into the “real world”. Simply put, what happens in the lab sometimes stays in the lab!
As an alternative to pure experimental research, correlational or “ quasi-experimental ” research (where the researcher cannot manipulate or change variables) can be done on a much larger scale more easily, allowing one to understand specific relationships in the real world. These types of studies also assume some causality between independent and dependent variables, but it’s not always clear. So, if you go this route, you need to be cautious in terms of how you describe the impact and causality between variables and be sure to acknowledge any limitations in your own research.

What is a control variable?
In an experimental design, a control variable (or controlled variable) is a variable that is intentionally held constant to ensure it doesn’t have an influence on any other variables. As a result, this variable remains unchanged throughout the course of the study. In other words, it’s a variable that’s not allowed to vary – tough life 🙂
As we mentioned earlier, one of the major challenges in identifying and measuring causal relationships is that it’s difficult to isolate the impact of variables other than the independent variable. Simply put, there’s always a risk that there are factors beyond the ones you’re specifically looking at that might be impacting the results of your study. So, to minimise the risk of this, researchers will attempt (as best possible) to hold other variables constant . These factors are then considered control variables.
Some examples of variables that you may need to control include:
- Temperature
- Time of day
- Noise or distractions
Which specific variables need to be controlled for will vary tremendously depending on the research project at hand, so there’s no generic list of control variables to consult. As a researcher, you’ll need to think carefully about all the factors that could vary within your research context and then consider how you’ll go about controlling them. A good starting point is to look at previous studies similar to yours and pay close attention to which variables they controlled for.
Of course, you won’t always be able to control every possible variable, and so, in many cases, you’ll just have to acknowledge their potential impact and account for them in the conclusions you draw. Every study has its limitations , so don’t get fixated or discouraged by troublesome variables. Nevertheless, always think carefully about the factors beyond what you’re focusing on – don’t make assumptions!

Other types of variables
As we mentioned, independent, dependent and control variables are the most common variables you’ll come across in your research, but they’re certainly not the only ones you need to be aware of. Next, we’ll look at a few “secondary” variables that you need to keep in mind as you design your research.
- Moderating variables
- Mediating variables
- Confounding variables
- Latent variables
Let’s jump into it…
What is a moderating variable?
A moderating variable is a variable that influences the strength or direction of the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. In other words, moderating variables affect how much (or how little) the IV affects the DV, or whether the IV has a positive or negative relationship with the DV (i.e., moves in the same or opposite direction).
For example, in a study about the effects of sleep deprivation on academic performance, gender could be used as a moderating variable to see if there are any differences in how men and women respond to a lack of sleep. In such a case, one may find that gender has an influence on how much students’ scores suffer when they’re deprived of sleep.
It’s important to note that while moderators can have an influence on outcomes , they don’t necessarily cause them ; rather they modify or “moderate” existing relationships between other variables. This means that it’s possible for two different groups with similar characteristics, but different levels of moderation, to experience very different results from the same experiment or study design.
What is a mediating variable?
Mediating variables are often used to explain the relationship between the independent and dependent variable (s). For example, if you were researching the effects of age on job satisfaction, then education level could be considered a mediating variable, as it may explain why older people have higher job satisfaction than younger people – they may have more experience or better qualifications, which lead to greater job satisfaction.
Mediating variables also help researchers understand how different factors interact with each other to influence outcomes. For instance, if you wanted to study the effect of stress on academic performance, then coping strategies might act as a mediating factor by influencing both stress levels and academic performance simultaneously. For example, students who use effective coping strategies might be less stressed but also perform better academically due to their improved mental state.
In addition, mediating variables can provide insight into causal relationships between two variables by helping researchers determine whether changes in one factor directly cause changes in another – or whether there is an indirect relationship between them mediated by some third factor(s). For instance, if you wanted to investigate the impact of parental involvement on student achievement, you would need to consider family dynamics as a potential mediator, since it could influence both parental involvement and student achievement simultaneously.

What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable (also known as a third variable or lurking variable ) is an extraneous factor that can influence the relationship between two variables being studied. Specifically, for a variable to be considered a confounding variable, it needs to meet two criteria:
- It must be correlated with the independent variable (this can be causal or not)
- It must have a causal impact on the dependent variable (i.e., influence the DV)
Some common examples of confounding variables include demographic factors such as gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, age, education level, and health status. In addition to these, there are also environmental factors to consider. For example, air pollution could confound the impact of the variables of interest in a study investigating health outcomes.
Naturally, it’s important to identify as many confounding variables as possible when conducting your research, as they can heavily distort the results and lead you to draw incorrect conclusions . So, always think carefully about what factors may have a confounding effect on your variables of interest and try to manage these as best you can.
What is a latent variable?
Latent variables are unobservable factors that can influence the behaviour of individuals and explain certain outcomes within a study. They’re also known as hidden or underlying variables , and what makes them rather tricky is that they can’t be directly observed or measured . Instead, latent variables must be inferred from other observable data points such as responses to surveys or experiments.
For example, in a study of mental health, the variable “resilience” could be considered a latent variable. It can’t be directly measured , but it can be inferred from measures of mental health symptoms, stress, and coping mechanisms. The same applies to a lot of concepts we encounter every day – for example:
- Emotional intelligence
- Quality of life
- Business confidence
- Ease of use
One way in which we overcome the challenge of measuring the immeasurable is latent variable models (LVMs). An LVM is a type of statistical model that describes a relationship between observed variables and one or more unobserved (latent) variables. These models allow researchers to uncover patterns in their data which may not have been visible before, thanks to their complexity and interrelatedness with other variables. Those patterns can then inform hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships among those same variables which were previously unknown prior to running the LVM. Powerful stuff, we say!

Let’s recap
In the world of scientific research, there’s no shortage of variable types, some of which have multiple names and some of which overlap with each other. In this post, we’ve covered some of the popular ones, but remember that this is not an exhaustive list .
To recap, we’ve explored:
- Independent variables (the “cause”)
- Dependent variables (the “effect”)
- Control variables (the variable that’s not allowed to vary)
If you’re still feeling a bit lost and need a helping hand with your research project, check out our 1-on-1 coaching service , where we guide you through each step of the research journey. Also, be sure to check out our free dissertation writing course and our collection of free, fully-editable chapter templates .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Very informative, concise and helpful. Thank you
Helping information.Thanks
practical and well-demonstrated
Very helpful and insightful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
What Is an Independent Variable? Definition and Examples

The independent variable is the variable that is controlled or changed in a scientific experiment to test its effect on the dependent variable . It doesn’t depend on another variable and isn’t changed by any factors an experimenter is trying to measure. The independent variable is denoted by the letter x in an experiment or graph.
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE EXAMPLE
Two classic examples of independent variables are age and time. They may be measured, but not controlled. In experiments, even if measured time isn’t the variable, it may relate to duration or intensity.
For example, a scientist is testing the effect of light and dark on the behavior of moths by turning a light on and off. The independent variable is the amount of light and the moth’s reaction is the dependent variable.
For another example, say you are measuring whether amount of sleep affects test scores. The hours of sleep would be the independent variable while the test scores would be dependent variable.
A change in the independent variable directly causes a change in the dependent variable. If you have a hypothesis written such that you’re looking at whether x affects y , the x is always the independent variable and the y is the dependent variable.
GRAPHING THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
If the dependent and independent variables are plotted on a graph, the x-axis would be the independent variable and the y-axis would be the dependent variable. You can remember this using the DRY MIX acronym, where DRY means dependent or responsive variable is on the y-axis, while MIX means the manipulated or independent variable is on the x-axis.
Related Posts
If you could change one thing about college, what would it be?
Graduate faster
Better quality online classes
Flexible schedule
Access to top-rated instructors

What Are Independent and Dependent Variables?
03.17.2022 • 6 min read
Zuriel van Belle
Subject Matter Expert
This article describes what a variable is, what dependent and independent variables are, a list of examples, how they are used in psychology studies, and more.
In This Article
What Is a Variable?
Dependent variables, independent variables, examples of experiments with variables, how are dependent and independent variables used in psychology research, don't overpay for college statistics.
Take Intro to Statistics Online with Outlier.org
From the co-founder of MasterClass, earn transferable college credits from the University of Pittsburgh (a top 50 global school). The world's best online college courses for 50% less than a traditional college.

In an experiment, researchers strive to understand if (and how) one thing affects another. The elements of an experiment that might affect one another are called variables. Variables are attributes that can change.
For example, imagine you design an experiment to test whether a self-reported mood is affected by ambient noise. Your hypothesis (i.e., testable prediction) is that nature sounds will improve a self-reported mood. Your research design is relatively simple: you survey people about their mood before the experiment, then you ask them to spend 30 minutes reading a psychology textbook in a room with no added noise (just the standard whirring of fans and background noises); or you ask them to spend 30 minutes reading a psychology textbook in a room with a bird song and a babbling brook (the experimental condition).
In this case, your variables are mood and ambient noise. Both factors can be changed. Mood can stay the same, be improved, or be worsened. While ambient noise could be altered in many ways (nature sounds, white noise, talking, etc.).
Understanding what the variables are in an experiment is critical to understanding how the experiment is designed. Broadly, there are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables.
The dependent variable is the variable that a researcher measures to determine the effect of the independent variable. The dependent variable depends on the independent variable. In our experiment, the dependent variable would be the change in self-reported mood.
The independent variable is the variable that the researcher or experimenter manipulates to affect the dependent variable. It is independent of the other variables in an experiment. In other words, the independent variable causes some kind of change in the dependent variable. In our experiment, the independent variable would be the noise in the room (unaltered ambient noise, or nature sounds). If you know the independent variable definition and dependent variable definition, it’ll be easier to understand how experiments work. When designing an experiment, the goal is to ensure that the only difference between the two conditions is the independent variable.
Understanding what the variables are in an experiment is critical to understanding how the experiment is designed.
Now that we understand that the dependent variable is the variable being measured to determine the effect of the independent variable (the variable causing the effect), let’s work through a few more examples.
In this example, let’s consider the effect of an act of kindness on charitable donations. In this experiment, imagine you want to test whether being helped by someone else impacts how much money a person donates. You set up your experiment as follows: participants come to a lab. In the control condition (the baseline), the participant arrives at the lab, opens the door, and you give them $20. Then you ask them if they would like to donate any portion of their $20 before leaving the room. In the experimental condition, as the participant heads to the door of the lab, a person walking by (a confederate, or accomplice, in the experiment) goes out of their way to open the door for them. The experiment proceeds exactly as the control; the participant is given $20 and asked if they would like to donate any portion of the money.
Let’s pause for a moment. Can you identify the dependent and independent variables in this experiment?
We should begin by identifying the variables. In this experiment, the variables are:
Being helped with the door or not
How much money a participant allocates to charity
Since the dependent variable is the variable we measure, we know that, in this case, it is the amount of money allocated to charity. The dependent variable could be anywhere from $0 to $20. The independent variable, the variable that we manipulate, is whether or not we help the participant with the door.
Imagine that participants who are helped with the door, on average, donate $10 to charity, and participants who are not helped with the door on average donate $5 to charity. It might be the case that being helped with the door (the independent variable) increases the likelihood someone will donate to charity (the dependent variable). Of course, this is just an example.
To feel more confident about these results, we would need to know how many people were in the study (the sample size), and we would need to analyze the results for statistical significance.
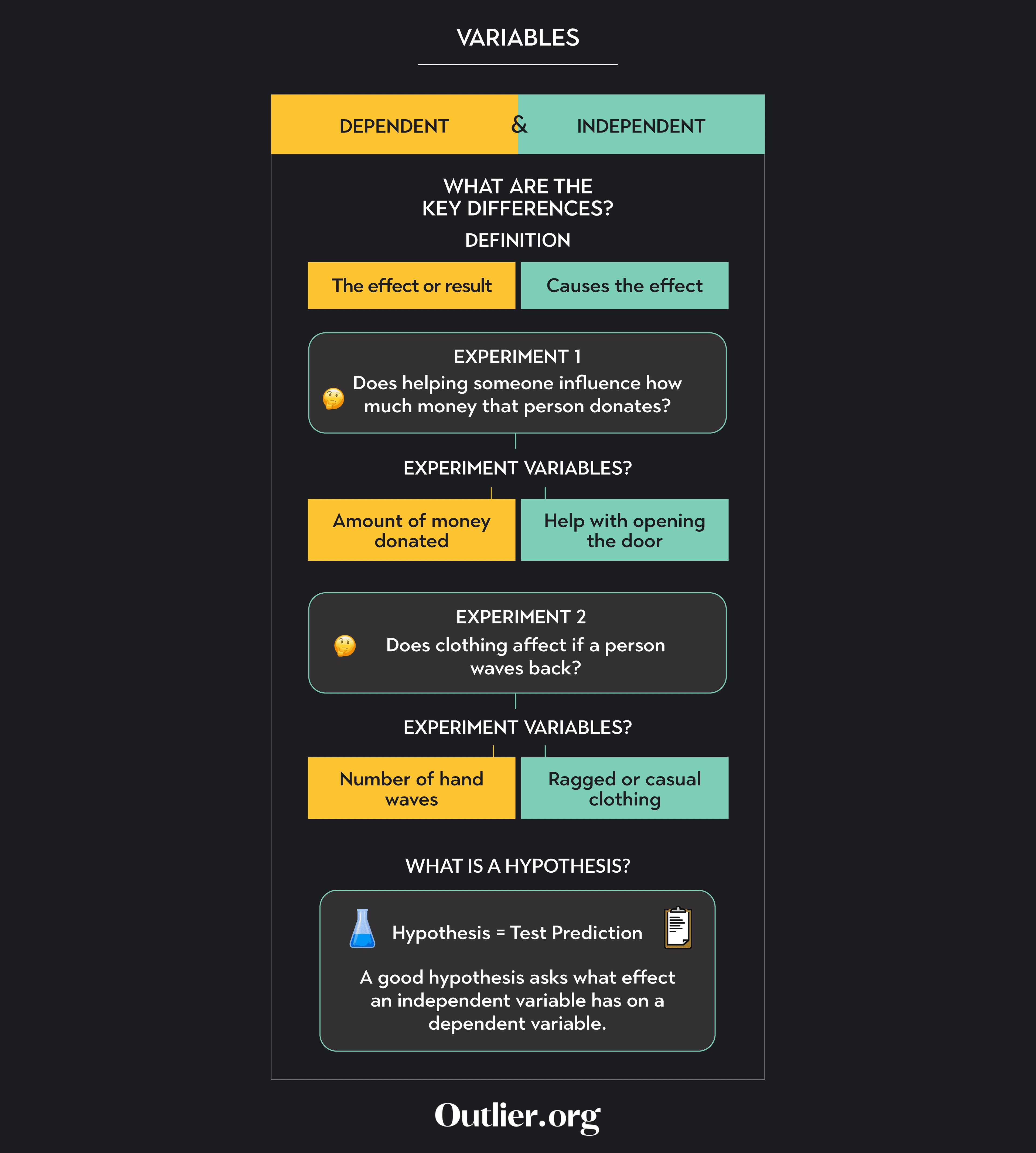
Let’s consider another example. Imagine you hypothesize that people will wave back more to you when you are wearing casual clothes than to when you are wearing ragged clothes. In this case, the variables are the number of hand waves and clothing type. Since we will be counting the number of waves, this gives us a clue that the number of waves is the dependent variable. Since we think the type of clothing will affect how many waves are given, we can determine that the type of clothing is the independent variable.
The number of waves depends on the type of clothing. If more people wave back to you when you are wearing casual clothes than when you are wearing ragged clothes, you have evidence that suggests that what you are wearing affects how people respond to you. Of course, as in the previous example, you will need to conduct a careful study with a large sample and statistical analysis to feel confident in your results.
The examples above help us understand why independent and dependent variables are so important to psychological research. In psychology, researchers often want to understand how and why people think, feel, and behave in certain ways. In order to answer questions about people’s motivation, cognition, emotions, and behavior, we often use experiments.
Whether you’re doing qualitative or quantitative research , independent and dependent variables are critical to the experimental process. Independent and dependent variables help determine cause and effect. A good hypothesis asks what effect an independent variable has on a dependent variable. Without experimental research, we would not be able to determine (with any confidence) how one variable may or may not impact another; we would not be able to determine cause and effect.
A good hypothesis asks what effect an independent variable has on a dependent variable.
Can a variable be both independent and dependent?
No, a variable cannot be both independent and dependent at the same time. You can think of the independent variable as the cause and the dependent variable as the effect. You cannot have something in an experiment that is both the cause and the effect. In other words, the independent variable must be independent of other variables and the dependent variable depends on the independent variable.
Can you include more than one independent or dependent variable in a study?
Yes, you can include more than one independent or dependent variable in a study. For example, you might have one independent variable that affects multiple dependent variables or a couple of independent variables that affect one dependent variable. Keep in mind that, generally, the more variables you have in a study, the more difficult it will be to determine cause and effect. It is generally better to have more dependent variables than independent variables in a study because, with many independent variables, it can be difficult to determine which one caused a particular effect.
What are other names for both independent and dependent variables?
We might also refer to an independent variable as a predictor variable, explanatory variable, control variable, manipulated variable, or regressor. Then we might also refer to a dependent variable as a predicted variable, response variable, responding variable, or outcome variable.
Explore Outlier's Award-Winning For-Credit Courses
Outlier (from the co-founder of MasterClass) has brought together some of the world's best instructors, game designers, and filmmakers to create the future of online college.
Check out these related courses:

Intro to Psychology
The science of the mind.

Intro to Philosophy
The big questions, examined.

The mathematics of change.
Related Articles

A Deeper Look into Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
This article should provide a comprehensive view and explanation of Jean Piaget’s theory of cognitive development.

Understanding the Difference between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
When conducting research, we can use both qualitative and quantitative methods. In this article, we’ll examine the definition of both of these approaches and look at how and when to use each of them.
Jennifer Valentine
What Are Sigmund Freud's Theories? An Explainer
As the founder and leading proponent of psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud was a central figure in 20th-century psychology. In this article, we’ll look at a number of his ideas about the human mind's inner workings, and then survey both his work’s enduring influence and the criticism it has received.
Further Reading
What is standard error statistics calculation and overview, understanding variables in statistics: types & examples, what do subsets mean in statistics, test statistics: definition, formulas & examples, what is a residual in stats, understanding sampling distributions: what are they and how do they work.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
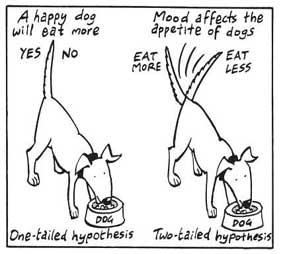
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
What Are Independent and Dependent Variables?
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Both the independent variable and dependent variable are examined in an experiment using the scientific method , so it's important to know what they are and how to use them.
In a scientific experiment, you'll ultimately be changing or controlling the independent variable and measuring the effect on the dependent variable. This distinction is critical in evaluating and proving hypotheses.
Below you'll find more about these two types of variables, along with examples of each in sample science experiments, and an explanation of how to graph them to help visualize your data.
What Is an Independent Variable?
An independent variable is the condition that you change in an experiment. In other words, it is the variable you control. It is called independent because its value does not depend on and is not affected by the state of any other variable in the experiment. Sometimes you may hear this variable called the "controlled variable" because it is the one that is changed. Do not confuse it with a control variable , which is a variable that is purposely held constant so that it can't affect the outcome of the experiment.
- What Is a Dependent Variable?
The dependent variable is the condition that you measure in an experiment. You are assessing how it responds to a change in the independent variable, so you can think of it as depending on the independent variable. Sometimes the dependent variable is called the "responding variable."
Independent and Dependent Variable Examples
- In a study to determine whether the amount of time a student sleeps affects test scores, the independent variable is the amount of time spent sleeping while the dependent variable is the test score.
- You want to compare brands of paper towels to see which holds the most liquid. The independent variable in your experiment would be the brand of paper towels. The dependent variable would be the amount of liquid absorbed by the paper towel.
- In an experiment to determine how far people can see into the infrared part of the spectrum, the wavelength of light is the independent variable and whether the light is observed (the response) is the dependent variable.
- If you want to know whether caffeine affects your appetite, the presence or absence of a given amount of caffeine would be the independent variable. How hungry you are would be the dependent variable.
- You want to determine whether a chemical is essential for rat nutrition, so you design an experiment. The presence or absence of the chemical is the independent variable. The health of the rat (whether it lives and can reproduce) is the dependent variable. If you determine the substance is necessary for proper nutrition, a follow-up experiment might determine how much of the chemical is needed. Here, the amount of the chemical would be the independent variable, and the rat's health would be the dependent variable.
How Do You Tell Independent and Dependent Variables Apart?
If you are having a hard time identifying which variable is the independent variable and which is the dependent variable, remember the dependent variable is the one affected by a change in the independent variable. If you write out the variables in a sentence that shows cause and effect, the independent variable causes the effect on the dependent variable. If you have the variables in the wrong order, the sentence won't make sense.
Independent variable causes an effect on the dependent variable.
Example : How long you sleep (independent variable) affects your test score (dependent variable).
This makes sense, but:
Example : Your test score affects how long you sleep.
This doesn't really make sense (unless you can't sleep because you are worried you failed a test, but that would be a different experiment).
How to Plot Variables on a Graph
There is a standard method for graphing independent and dependent variables. The x-axis is the independent variable, while the y-axis is the dependent variable. You can use the DRY MIX acronym to help remember how to graph variables:
D = dependent variable R = responding variable Y = graph on the vertical or y-axis
M = manipulated variable I = independent variable X = graph on the horizontal or x-axis
Test your understanding with the scientific method quiz .
Key Takeaways
- In scientific experiments, the independent variable is manipulated while the dependent variable is measured.
- The independent variable, controlled by the experimenter, influences the dependent variable, which responds to changes. This dynamic forms the basis of cause-and-effect relationships.
- Graphing independent and dependent variables follows a standard method in which the independent variable is plotted on the x-axis and the dependent variable on the y-axis.
- Difference Between Independent and Dependent Variables
- The Difference Between Control Group and Experimental Group
- How to Write a Lab Report
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Boiling Points of Ethanol, Methanol, and Isopropyl Alcohol
- Understanding Experimental Groups
- 10 Examples of Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Mixtures
- The Difference Between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
- The Difference Between Intensive and Extensive Properties
- Chemical Properties of Matter
- Examples of Physical Changes
- Commensalism Definition, Examples, and Relationships
- Acidic Solution Definition
- Understanding Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Independent Variables (Definition + 43 Examples)

Have you ever wondered how scientists make discoveries and how researchers come to understand the world around us? A crucial tool in their kit is the concept of the independent variable, which helps them delve into the mysteries of science and everyday life.
An independent variable is a condition or factor that researchers manipulate to observe its effect on another variable, known as the dependent variable. In simpler terms, it’s like adjusting the dials and watching what happens! By changing the independent variable, scientists can see if and how it causes changes in what they are measuring or observing, helping them make connections and draw conclusions.
In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of independent variables, journey through their history, examine theories, and look at a variety of examples from different fields.
History of the Independent Variable
Once upon a time, in a world thirsty for understanding, people observed the stars, the seas, and everything in between, seeking to unlock the mysteries of the universe.
The story of the independent variable begins with a quest for knowledge, a journey taken by thinkers and tinkerers who wanted to explain the wonders and strangeness of the world.
Origins of the Concept
The seeds of the idea of independent variables were sown by Sir Francis Galton , an English polymath, in the 19th century. Galton wore many hats—he was a psychologist, anthropologist, meteorologist, and a statistician!
It was his diverse interests that led him to explore the relationships between different factors and their effects. Galton was curious—how did one thing lead to another, and what could be learned from these connections?
As Galton delved into the world of statistical theories , the concept of independent variables started taking shape.
He was interested in understanding how characteristics, like height and intelligence, were passed down through generations.
Galton’s work laid the foundation for later thinkers to refine and expand the concept, turning it into an invaluable tool for scientific research.
Evolution over Time
After Galton’s pioneering work, the concept of the independent variable continued to evolve and grow. Scientists and researchers from various fields adopted and adapted it, finding new ways to use it to make sense of the world.
They discovered that by manipulating one factor (the independent variable), they could observe changes in another (the dependent variable), leading to groundbreaking insights and discoveries.
Through the years, the independent variable became a cornerstone in experimental design . Researchers in fields like physics, biology, psychology, and sociology used it to test hypotheses, develop theories, and uncover the laws that govern our universe.
The idea that originated from Galton’s curiosity had bloomed into a universal key, unlocking doors to knowledge across disciplines.

Importance in Scientific Research
Today, the independent variable stands tall as a pillar of scientific research. It helps scientists and researchers ask critical questions, test their ideas, and find answers. Without independent variables, we wouldn’t have many of the advancements and understandings that we take for granted today.
The independent variable plays a starring role in experiments, helping us learn about everything from the smallest particles to the vastness of space. It helps researchers create vaccines, understand social behaviors, explore ecological systems, and even develop new technologies.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll dive deeper into what independent variables are, how they work, and how they’re used in various fields.
Together, we’ll uncover the magic of this scientific concept and see how it continues to shape our understanding of the world around us.
What is an Independent Variable?
Embarking on the captivating journey of scientific exploration requires us to grasp the essential terms and ideas. It's akin to a treasure hunter mastering the use of a map and compass.
In our adventure through the realm of independent variables, we’ll delve deeper into some fundamental concepts and definitions to help us navigate this exciting world.
Variables in Research
In the grand tapestry of research, variables are the gems that researchers seek. They’re elements, characteristics, or behaviors that can shift or vary in different circumstances.
Picture them as the myriad of ingredients in a chef’s kitchen—each variable can be adjusted or modified to create a myriad of dishes, each with a unique flavor!
Understanding variables is essential as they form the core of every scientific experiment and observational study.
Types of Variables
Independent Variable The star of our story, the independent variable, is the one that researchers change or control to study its effects. It’s like a chef experimenting with different spices to see how each one alters the taste of the soup. The independent variable is the catalyst, the initial spark that sets the wheels of research in motion.
Dependent Variable The dependent variable is the outcome we observe and measure . It’s the altered flavor of the soup that results from the chef’s culinary experiments. This variable depends on the changes made to the independent variable, hence the name!
Observing how the dependent variable reacts to changes helps scientists draw conclusions and make discoveries.
Control Variable Control variables are the unsung heroes of scientific research. They’re the constants, the elements that researchers keep the same to ensure the integrity of the experiment.
Imagine if our chef used a different type of broth each time he experimented with spices—the results would be all over the place! Control variables keep the experiment grounded and help researchers be confident in their findings.
Confounding Variables Imagine a hidden rock in a stream, changing the water’s flow in unexpected ways. Confounding variables are similar—they are external factors that can sneak into experiments and influence the outcome , adding twists to our scientific story.
These variables can blur the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, making the results of the study a bit puzzly. Detecting and controlling these hidden elements helps researchers ensure the accuracy of their findings and reach true conclusions.
There are of course other types of variables, and different ways to manipulate them called " schedules of reinforcement ," but we won't get into that too much here.
Role of the Independent Variable
Manipulation When researchers manipulate the independent variable, they are orchestrating a symphony of cause and effect. They’re adjusting the strings, the brass, the percussion, observing how each change influences the melody—the dependent variable.
This manipulation is at the heart of experimental research. It allows scientists to explore relationships, unravel patterns, and unearth the secrets hidden within the fabric of our universe.
Observation With every tweak and adjustment made to the independent variable, researchers are like seasoned detectives, observing the dependent variable for changes, collecting clues, and piecing together the puzzle.
Observing the effects and changes that occur helps them deduce relationships, formulate theories, and expand our understanding of the world. Every observation is a step towards solving the mysteries of nature and human behavior.
Identifying Independent Variables
Characteristics Identifying an independent variable in the vast landscape of research can seem daunting, but fear not! Independent variables have distinctive characteristics that make them stand out.
They’re the elements that are deliberately changed or controlled in an experiment to study their effects on the dependent variable. Recognizing these characteristics is like learning to spot footprints in the sand—it leads us to the heart of the discovery!
In Different Types of Research The world of research is diverse and varied, and the independent variable dons many guises! In the field of medicine, it might manifest as the dosage of a drug administered to patients.
In psychology, it could take the form of different learning methods applied to study memory retention. In each field, identifying the independent variable correctly is the golden key that unlocks the treasure trove of knowledge and insights.
As we forge ahead on our enlightening journey, equipped with a deeper understanding of independent variables and their roles, we’re ready to delve into the intricate theories and diverse examples that underscore their significance.
Independent Variables in Research

Now that we’re acquainted with the basic concepts and have the tools to identify independent variables, let’s dive into the fascinating ocean of theories and frameworks.
These theories are like ancient scrolls, providing guidelines and blueprints that help scientists use independent variables to uncover the secrets of the universe.
Scientific Method
What is it and How Does it Work? The scientific method is like a super-helpful treasure map that scientists use to make discoveries. It has steps we follow: asking a question, researching, guessing what will happen (that's a hypothesis!), experimenting, checking the results, figuring out what they mean, and telling everyone about it.
Our hero, the independent variable, is the compass that helps this adventure go the right way!
How Independent Variables Lead the Way In the scientific method, the independent variable is like the captain of a ship, leading everyone through unknown waters.
Scientists change this variable to see what happens and to learn new things. It’s like having a compass that points us towards uncharted lands full of knowledge!
Experimental Design
The Basics of Building Constructing an experiment is like building a castle, and the independent variable is the cornerstone. It’s carefully chosen and manipulated to see how it affects the dependent variable. Researchers also identify control and confounding variables, ensuring the castle stands strong, and the results are reliable.
Keeping Everything in Check In every experiment, maintaining control is key to finding the treasure. Scientists use control variables to keep the conditions consistent, ensuring that any changes observed are truly due to the independent variable. It’s like ensuring the castle’s foundation is solid, supporting the structure as it reaches for the sky.
Hypothesis Testing
Making Educated Guesses Before they start experimenting, scientists make educated guesses called hypotheses . It’s like predicting which X marks the spot of the treasure! It often includes the independent variable and the expected effect on the dependent variable, guiding researchers as they navigate through the experiment.
Independent Variables in the Spotlight When testing these guesses, the independent variable is the star of the show! Scientists change and watch this variable to see if their guesses were right. It helps them figure out new stuff and learn more about the world around us!
Statistical Analysis
Figuring Out Relationships After the experimenting is done, it’s time for scientists to crack the code! They use statistics to understand how the independent and dependent variables are related and to uncover the hidden stories in the data.
Experimenters have to be careful about how they determine the validity of their findings, which is why they use statistics. Something called "experimenter bias" can get in the way of having true (valid) results, because it's basically when the experimenter influences the outcome based on what they believe to be true (or what they want to be true!).
How Important are the Discoveries? Through statistical analysis, scientists determine the significance of their findings. It’s like discovering if the treasure found is made of gold or just shiny rocks. The analysis helps researchers know if the independent variable truly had an effect, contributing to the rich tapestry of scientific knowledge.
As we uncover more about how theories and frameworks use independent variables, we start to see how awesome they are in helping us learn more about the world. But we’re not done yet!
Up next, we’ll look at tons of examples to see how independent variables work their magic in different areas.
Examples of Independent Variables
Independent variables take on many forms, showcasing their versatility in a range of experiments and studies. Let’s uncover how they act as the protagonists in numerous investigations and learning quests!
Science Experiments
1) plant growth.
Consider an experiment aiming to observe the effect of varying water amounts on plant height. In this scenario, the amount of water given to the plants is the independent variable!
2) Freezing Water
Suppose we are curious about the time it takes for water to freeze at different temperatures. The temperature of the freezer becomes the independent variable as we adjust it to observe the results!
3) Light and Shadow
Have you ever observed how shadows change? In an experiment, adjusting the light angle to observe its effect on an object’s shadow makes the angle of light the independent variable!
4) Medicine Dosage
In medical studies, determining how varying medicine dosages influence a patient’s recovery is essential. Here, the dosage of the medicine administered is the independent variable!
5) Exercise and Health
Researchers might examine the impact of different exercise forms on individuals’ health. The various exercise forms constitute the independent variable in this study!
6) Sleep and Wellness
Have you pondered how the sleep duration affects your well-being the following day? In such research, the hours of sleep serve as the independent variable!
7) Learning Methods
Psychologists might investigate how diverse study methods influence test outcomes. Here, the different study methods adopted by students are the independent variable!
8) Mood and Music
Have you experienced varied emotions with different music genres? The genre of music played becomes the independent variable when researching its influence on emotions!
9) Color and Feelings
Suppose researchers are exploring how room colors affect individuals’ emotions. In this case, the room colors act as the independent variable!
Environment
10) rainfall and plant life.
Environmental scientists may study the influence of varying rainfall levels on vegetation. In this instance, the amount of rainfall is the independent variable!
11) Temperature and Animal Behavior
Examining how temperature variations affect animal behavior is fascinating. Here, the varying temperatures serve as the independent variable!
12) Pollution and Air Quality
Investigating the effects of different pollution levels on air quality is crucial. In such studies, the pollution level is the independent variable!
13) Internet Speed and Productivity
Researchers might explore how varying internet speeds impact work productivity. In this exploration, the internet speed is the independent variable!
14) Device Type and User Experience
Examining how different devices affect user experience is interesting. Here, the type of device used is the independent variable!
15) Software Version and Performance
Suppose a study aims to determine how different software versions influence system performance. The software version becomes the independent variable!
16) Teaching Style and Student Engagement
Educators might investigate the effect of varied teaching styles on student engagement. In such a study, the teaching style is the independent variable!
17) Class Size and Learning Outcome
Researchers could explore how different class sizes influence students’ learning. Here, the class size is the independent variable!
18) Homework Frequency and Academic Achievement
Examining the relationship between the frequency of homework assignments and academic success is essential. The frequency of homework becomes the independent variable!
19) Telescope Type and Celestial Observation
Astronomers might study how different telescopes affect celestial observation. In this scenario, the telescope type is the independent variable!
20) Light Pollution and Star Visibility
Investigating the influence of varying light pollution levels on star visibility is intriguing. Here, the level of light pollution is the independent variable!
21) Observation Time and Astronomical Detail
Suppose a study explores how observation duration affects the detail captured in astronomical images. The duration of observation serves as the independent variable!
22) Community Size and Social Interaction
Sociologists may examine how the size of a community influences social interactions. In this research, the community size is the independent variable!
23) Cultural Exposure and Social Tolerance
Investigating the effect of diverse cultural exposure on social tolerance is vital. Here, the level of cultural exposure is the independent variable!
24) Economic Status and Educational Attainment
Researchers could explore how different economic statuses impact educational achievements. In such studies, economic status is the independent variable!
25) Training Intensity and Athletic Performance
Sports scientists might study how varying training intensities affect athletes’ performance. In this case, the training intensity is the independent variable!
26) Equipment Type and Player Safety
Examining the relationship between different sports equipment and player safety is crucial. Here, the type of equipment used is the independent variable!
27) Team Size and Game Strategy
Suppose researchers are investigating how the size of a sports team influences game strategy. The team size becomes the independent variable!
28) Diet Type and Health Outcome
Nutritionists may explore the impact of various diets on individuals’ health. In this exploration, the type of diet followed is the independent variable!
29) Caloric Intake and Weight Change
Investigating how different caloric intakes influence weight change is essential. In such a study, the caloric intake is the independent variable!
30) Food Variety and Nutrient Absorption
Researchers could examine how consuming a variety of foods affects nutrient absorption. Here, the variety of foods consumed is the independent variable!
Real-World Examples of Independent Variables
Isn't it fantastic how independent variables play such an essential part in so many studies? But the excitement doesn't stop there!
Now, let’s explore how findings from these studies, led by independent variables, make a big splash in the real world and improve our daily lives!
Healthcare Advancements
31) treatment optimization.
By studying different medicine dosages and treatment methods as independent variables, doctors can figure out the best ways to help patients recover quicker and feel better. This leads to more effective medicines and treatment plans!
32) Lifestyle Recommendations
Researching the effects of sleep, exercise, and diet helps health experts give us advice on living healthier lives. By changing these independent variables, scientists uncover the secrets to feeling good and staying well!
Technological Innovations
33) speeding up the internet.
When scientists explore how different internet speeds affect our online activities, they’re able to develop technologies to make the internet faster and more reliable. This means smoother video calls and quicker downloads!
34) Improving User Experience
By examining how we interact with various devices and software, researchers can design technology that’s easier and more enjoyable to use. This leads to cooler gadgets and more user-friendly apps!
Educational Strategies
35) enhancing learning.
Investigating different teaching styles, class sizes, and study methods helps educators discover what makes learning fun and effective. This research shapes classrooms, teaching methods, and even homework!
36) Tailoring Student Support
By studying how students with diverse needs respond to different support strategies, educators can create personalized learning experiences. This means every student gets the help they need to succeed!
Environmental Protection
37) conserving nature.
Researching how rainfall, temperature, and pollution affect the environment helps scientists suggest ways to protect our planet. By studying these independent variables, we learn how to keep nature healthy and thriving!
38) Combating Climate Change
Scientists studying the effects of pollution and human activities on climate change are leading the way in finding solutions. By exploring these independent variables, we can develop strategies to combat climate change and protect the Earth!
Social Development
39) building stronger communities.
Sociologists studying community size, cultural exposure, and economic status help us understand what makes communities happy and united. This knowledge guides the development of policies and programs for stronger societies!
40) Promoting Equality and Tolerance
By exploring how exposure to diverse cultures affects social tolerance, researchers contribute to fostering more inclusive and harmonious societies. This helps build a world where everyone is respected and valued!
Enhancing Sports Performance
41) optimizing athlete training.
Sports scientists studying training intensity, equipment type, and team size help athletes reach their full potential. This research leads to better training programs, safer equipment, and more exciting games!
42) Innovating Sports Strategies
By investigating how different game strategies are influenced by various team compositions, researchers contribute to the evolution of sports. This means more thrilling competitions and matches for us to enjoy!
Nutritional Well-Being
43) guiding healthy eating.
Nutritionists researching diet types, caloric intake, and food variety help us understand what foods are best for our bodies. This knowledge shapes dietary guidelines and helps us make tasty, yet nutritious, meal choices!
44) Promoting Nutritional Awareness
By studying the effects of different nutrients and diets, researchers educate us on maintaining a balanced diet. This fosters a greater awareness of nutritional well-being and encourages healthier eating habits!
As we journey through these real-world applications, we witness the incredible impact of studies featuring independent variables. The exploration doesn’t end here, though!
Let’s continue our adventure and see how we can identify independent variables in our own observations and inquiries! Keep your curiosity alive, and let’s delve deeper into the exciting realm of independent variables!
Identifying Independent Variables in Everyday Scenarios
So, we’ve seen how independent variables star in many studies, but how about spotting them in our everyday life?
Recognizing independent variables can be like a treasure hunt – you never know where you might find one! Let’s uncover some tips and tricks to identify these hidden gems in various situations.
1) Asking Questions
One of the best ways to spot an independent variable is by asking questions! If you’re curious about something, ask yourself, “What am I changing or manipulating in this situation?” The thing you’re changing is likely the independent variable!
For example, if you’re wondering whether the amount of sunlight affects how quickly your laundry dries, the sunlight amount is your independent variable!
2) Making Observations
Keep your eyes peeled and observe the world around you! By watching how changes in one thing (like the amount of rain) affect something else (like the height of grass), you can identify the independent variable.
In this case, the amount of rain is the independent variable because it’s what’s changing!
3) Conducting Experiments
Get hands-on and conduct your own experiments! By changing one thing and observing the results, you’re identifying the independent variable.
If you’re growing plants and decide to water each one differently to see the effects, the amount of water is your independent variable!
4) Everyday Scenarios
In everyday scenarios, independent variables are all around!
When you adjust the temperature of your oven to bake cookies, the oven temperature is the independent variable.
Or if you’re deciding how much time to spend studying for a test, the study time is your independent variable!
5) Being Curious
Keep being curious and asking “What if?” questions! By exploring different possibilities and wondering how changing one thing could affect another, you’re on your way to identifying independent variables.
If you’re curious about how the color of a room affects your mood, the room color is the independent variable!
6) Reviewing Past Studies
Don’t forget about the treasure trove of past studies and experiments! By reviewing what scientists and researchers have done before, you can learn how they identified independent variables in their work.
This can give you ideas and help you recognize independent variables in your own explorations!
Exercises for Identifying Independent Variables
Ready for some practice? Let’s put on our thinking caps and try to identify the independent variables in a few scenarios.
Remember, the independent variable is what’s being changed or manipulated to observe the effect on something else! (You can see the answers below)
Scenario One: Cooking Time
You’re cooking pasta for dinner and want to find out how the cooking time affects its texture. What is the independent variable?
Scenario Two: Exercise Routine
You decide to try different exercise routines each week to see which one makes you feel the most energetic. What is the independent variable?
Scenario Three: Plant Fertilizer
You’re growing tomatoes in your garden and decide to use different types of fertilizer to see which one helps them grow the best. What is the independent variable?
Scenario Four: Study Environment
You’re preparing for an important test and try studying in different environments (quiet room, coffee shop, library) to see where you concentrate best. What is the independent variable?
Scenario Five: Sleep Duration
You’re curious to see how the number of hours you sleep each night affects your mood the next day. What is the independent variable?
By practicing identifying independent variables in different scenarios, you’re becoming a true independent variable detective. Keep practicing, stay curious, and you’ll soon be spotting independent variables everywhere you go.
Independent Variable: The cooking time is the independent variable. You are changing the cooking time to observe its effect on the texture of the pasta.
Independent Variable: The type of exercise routine is the independent variable. You are trying out different exercise routines each week to see which one makes you feel the most energetic.
Independent Variable: The type of fertilizer is the independent variable. You are using different types of fertilizer to observe their effects on the growth of the tomatoes.
Independent Variable: The study environment is the independent variable. You are studying in different environments to see where you concentrate best.
Independent Variable: The number of hours you sleep is the independent variable. You are changing your sleep duration to see how it affects your mood the next day.
Whew, what a journey we’ve had exploring the world of independent variables! From understanding their definition and role to diving into a myriad of examples and real-world impacts, we’ve uncovered the treasures hidden in the realm of independent variables.
The beauty of independent variables lies in their ability to unlock new knowledge and insights, guiding us to discoveries that improve our lives and the world around us.
By identifying and studying these variables, we embark on exciting learning adventures, solving mysteries and answering questions about the universe we live in.
Remember, the joy of discovery doesn’t end here. The world is brimming with questions waiting to be answered and mysteries waiting to be solved.
Keep your curiosity alive, continue exploring, and who knows what incredible discoveries lie ahead.
Related posts:
- Confounding Variable in Psychology (Examples + Definition)
- 19+ Experimental Design Examples (Methods + Types)
- Variable Interval Reinforcement Schedule (Examples)
- Variable Ratio Reinforcement Schedule (Examples)
- State Dependent Memory + Learning (Definition and Examples)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Psychol Med
- v.43(2); 2021 Mar
A Student’s Guide to the Classification and Operationalization of Variables in the Conceptualization and Design of a Clinical Study: Part 1
Chittaranjan andrade.
1 Dept. of Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neurotoxicology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Students without prior research experience may not know how to conceptualize and design a study. This article explains how an understanding of the classification and operationalization of variables is the key to the process. Variables describe aspects of the sample that is under study; they are so called because they vary in value from subject to subject in the sample. Variables may be independent or dependent. Independent variables influence the value of other variables; dependent variables are influenced in value by other variables. A hypothesis states an expected relationship between variables. A significant relationship between an independent and dependent variable does not prove cause and effect; the relationship may partly or wholly be explained by one or more confounding variables. Variables need to be operationalized; that is, defined in a way that permits their accurate measurement. These and other concepts are explained with the help of clinically relevant examples.
Key Message:
This article explains the following concepts: Independent variables, dependent variables, confounding variables, operationalization of variables, and construction of hypotheses.
In any body of research, the subject of study requires to be described and understood. For example, if we wish to study predictors of response to antidepressant drugs (ADs) in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), we might select patient age, sex, age at onset of MDD, number of previous episodes of depression, duration of current depressive episode, presence of psychotic symptoms, past history of response to ADs, and other patient and illness characteristics as potential predictors. These characteristics or descriptors are called variables. Whether or not the patient responds to AD treatment is also a variable. A solid understanding of variables is the cornerstone in the conceptualization and preparation of a research protocol, and in the framing of study hypotheses. This subject is presented in two parts. This article, Part 1, explains what independent and dependent variables are, how an understanding of these is important in framing hypotheses, and what operationalization of a variable entails.
Variables are defined as characteristics of the sample that are examined, measured, described, and interpreted. Variables are so called because they vary in value from subject to subject in the study. As an example, if we wish to examine the relationship between age and height in a sample of children, age and height are the variables of interest; their values vary from child to child. In the earlier example, patients vary in age, sex, duration of current depressive episode, and response to ADs. Variables are classified as dependent and independent variables and are usually analyzed as categorical or continuous variables.
Independent and Dependent Variables
Independent variables are defined as those the values of which influence other variables. For example, age, sex, current smoking, LDL cholesterol level, and blood pressure are independent variables because their values (e.g., greater age, positive for current smoking, and higher LDL cholesterol level) influence the risk of myocardial infarction. Dependent variables are defined as those the values of which are influenced by other variables. For example, the risk of myocardial infarction is a dependent variable the value of which is influenced by variables such as age, sex, current smoking, LDL cholesterol level, and blood pressure. The risk is higher in older persons, in men, in current smokers, and so on.
There may be a cause–effect relationship between independent and dependent variables. For example, consider a clinical trial with treatment (iron supplement vs placebo) as the independent variable and hemoglobin level as the dependent variable. In children with anemia, an iron supplement will raise the hemoglobin level to a greater extent than will placebo; this is a cause–effect relationship because iron is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin. However, consider the variables teeth and weight . An alien from outer space who has no knowledge of human physiology may study human children below the age of 5 years and find that, as the number of teeth increases, weight increases. Should the alien conclude that there is a cause–effect relationship here, and that growing teeth causes weight gain? No, because a third variable, age, is a confounding variable 1 – 3 that is responsible for both increase in the number of teeth and increase in weight. In general, therefore, it is more proper to state that independent variables are associated with variations in the values of the dependent variables rather than state that independent variables cause variations in the values of the dependent variables. For causality to be asserted, other criteria must be fulfilled; this is out of the scope of the present article, and interested readers may refer to Schunemann et al. 4
As a side note, here, whether a particular variable is independent or dependent will depend on the question that is being asked. For example, in a study of factors influencing patient satisfaction with outpatient department (OPD) services, patient satisfaction is the dependent variable. But, in a study of factors influencing OPD attendance at a hospital, OPD attendance is the dependent variable, and patient satisfaction is merely one of many possible independent variables that can influence OPD attendance.
Importance of Variables in Stating the Research Objectives
Students must have a clear idea about what they want to study in order to conceptualize and frame a research protocol. The first matters that they need to address are “What are my research questions?” and “What are my hypotheses?” Both questions can be answered only after choosing the dependent variables and then the independent variables for study.
In the case of a student who is interested in studying predictors of AD outcomes in patients with MDD, treatment response is the dependent variable and patient and clinical characteristics are possible independent variables. So, the selection of dependent and independent variables helps defines the objectives of the study:
- To determine whether sociodemographic variables, such as age and sex, predict the outcome of an episode of depression in MDD patients who are treated with an AD.
- To determine whether clinical variables, such as age at onset of depression, number of previous depressive episodes, duration of current depressive episode, and the presence of soft neurological signs, predict the outcome of an episode of depression in MDD patients who are treated with an AD.
Note that in a formal research protocol, the student will need to state all the independent variables and not merely list examples. The student may also choose to include additional independent variables, such as baseline biochemical, psychophysiological, and neuroradiological measures.
Importance of Variables in Framing Hypotheses
A hypothesis is a clear statement of what the researcher expects to find in the study. As an example, a researcher may hypothesize that longer duration of current depression is associated with poorer response to ADs. In this hypothesis, the duration of the current episode of depression is the independent variable and treatment response is the dependent variable. It should be obvious, now, that a hypothesis can also be defined as the statement of an expected relationship between an independent and a dependent variable . Or, expressed visually, (independent variable) (arrow) (dependent variable) = hypothesis.
It would be a waste of time and energy to do a study to examine only one question: whether duration of current depression predicts treatment response. So, it is usual for research protocols to include many independent variables and many dependent variables in the generation of many hypotheses, as shown in Table 1 . Pairing each variable in the “independent variable” column with each variable in the “dependent variable” column would result in the generation of these hypotheses. Table 2 shows how this is done for age. Sets of hypotheses can likewise be constructed for the remaining independent and dependent variables in Table 1 . Importantly, the student must select one of these hypotheses as the primary hypothesis; the remaining hypotheses, no matter how many they are, would be secondary hypotheses. It is necessary to have only one hypothesis as the primary hypothesis in order to calculate the sample size necessary for an adequately powered study and to reduce the risk of false positive findings in the analysis. 5 In rare situations, two hypotheses may be considered equally important and may be stated as coprimary hypotheses.
Independent Variables and Dependent Variables in a Study on Sociodemographic and Clinical Prediction of Response of Major Depressive Disorder to Antidepressant Drug Treatment
| • Age • Sex • Age at onset of major depressive disorder • Number of past episodes of depression • Past history of response to antidepressant drugs • Duration of current depressive episode • Baseline severity of depression • Baseline suicidality • Baseline melancholia • Baseline psychotic symptoms • Baseline soft neurological signs • Severity of depression • Global severity of illness • Subjective well-being • Quality of life • Everyday functioning |
Combinations of Age with Dependent Variables in the Generation of Hypotheses
| 1. Older age is associated with less attenuation in the severity of depression. 2. Older age is associated with less attenuation in the global severity of illness. 3. Older age is associated with less improvement in subjective well-being. 4. Older age is associated with less improvement in quality of life. 5. Older age is associated with less improvement in everyday functioning. |
Operationalization of Variables
In Table 1 , suicidality is listed as an independent variable and severity of depression, as a dependent variable. These variables need to be operationalized; that is, stated in a way that explains how they will be measured. Table 3 presents three ways in which suicidality can be measured and four ways in which (reduction in) the severity of depression can be measured. Now, each way of measurement in the “independent variable” column can be paired with a way of measurement in the “dependent variable” column, making a total of 12 possible hypotheses. In like manner, the many variables listed in Table 1 can each be operationalized in several different ways, resulting in the generation of a very large number of hypotheses. As already stated, the student must select only one hypothesis as the primary hypothesis.
Possible Ways of Operationalization of Suicidality and Depression
| Independent Variable: Suicidality | Dependent Variable: Severity of Depression |
| • Item score on the HAM-D • Item score on the MADRS • Beck scale for Suicide ideation total score | • MADRS total score • HAM-D total score • HAM-D response rate • HAM-D remission rate |
HAM-D: Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, MADRS: Montgomery–Asberg Depression Rating Scale.
Much thought should be given to the operationalization of variables because variables that are carelessly operationalized will be poorly measured; the data collected will then be of poor quality, and the study will yield unreliable results. For example, socioeconomic status may be operationalized as lower, middle, or upper class, depending on the patient’s monthly income, on the total monthly income of the family, or using a validated socioeconomic status assessment scale that takes into consideration income, education, occupation, and place of residence. The student must choose the method that would best suit the needs of the study, and the method that has the greatest scientific acceptability. However, it is also permissible to operationalize the same variable in many different ways and to include all these different operationalizations in the study, as shown in Table 3 . This is because conceptualizing variables in different ways can help understand the subject of the study in different ways.
Operationalization of variables requires a consideration of the reliability and validity of the method of operationalization; discussions on reliability and validity are out of the scope of this article. Operationalization of variables also requires specification of the scale of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio; this is also out of the scope of the present article. Finally, operationalization of variables can also specify details of the measurement procedure. As an example, in a study on the use of metformin to reduce olanzapine-associated weight gain, we may state that we will obtain the weight of the patient but fail to explain how we will do it. Better would be to state that the same weighing scale will be used. Still better would be to state that we will use a weighing instrument that works on the principle of moving weights on a levered arm, and that the same instrument will be used for all patients. And best would be to add that we will weigh patients, dressed in standard hospital gowns, after they have voided their bladder but before they have eaten breakfast. When the way in which a variable will be measured is defined, measurement of that variable becomes more objective and uniform
Concluding Notes
The next article, Part 2, will address what categorical and continuous variables are, why continuous variables should not be converted into categorical variables and when this rule can be broken, and what confounding variables are.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
Published on 4 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 17 October 2022.
In research, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as height, age, temperature, or test scores.
Researchers often manipulate or measure independent and dependent variables in studies to test cause-and-effect relationships.
- The independent variable is the cause. Its value is independent of other variables in your study.
- The dependent variable is the effect. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable.
Your independent variable is the temperature of the room. You vary the room temperature by making it cooler for half the participants, and warmer for the other half.
Table of contents
What is an independent variable, types of independent variables, what is a dependent variable, identifying independent vs dependent variables, independent and dependent variables in research, visualising independent and dependent variables, frequently asked questions about independent and dependent variables.
An independent variable is the variable you manipulate or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. It’s called ‘independent’ because it’s not influenced by any other variables in the study.
Independent variables are also called:
- Explanatory variables (they explain an event or outcome)
- Predictor variables (they can be used to predict the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-hand-side variables (they appear on the right-hand side of a regression equation).
These terms are especially used in statistics , where you estimate the extent to which an independent variable change can explain or predict changes in the dependent variable.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
There are two main types of independent variables.
- Experimental independent variables can be directly manipulated by researchers.
- Subject variables cannot be manipulated by researchers, but they can be used to group research subjects categorically.
Experimental variables
In experiments, you manipulate independent variables directly to see how they affect your dependent variable. The independent variable is usually applied at different levels to see how the outcomes differ.
You can apply just two levels in order to find out if an independent variable has an effect at all.
You can also apply multiple levels to find out how the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
You have three independent variable levels, and each group gets a different level of treatment.
You randomly assign your patients to one of the three groups:
- A low-dose experimental group
- A high-dose experimental group
- A placebo group
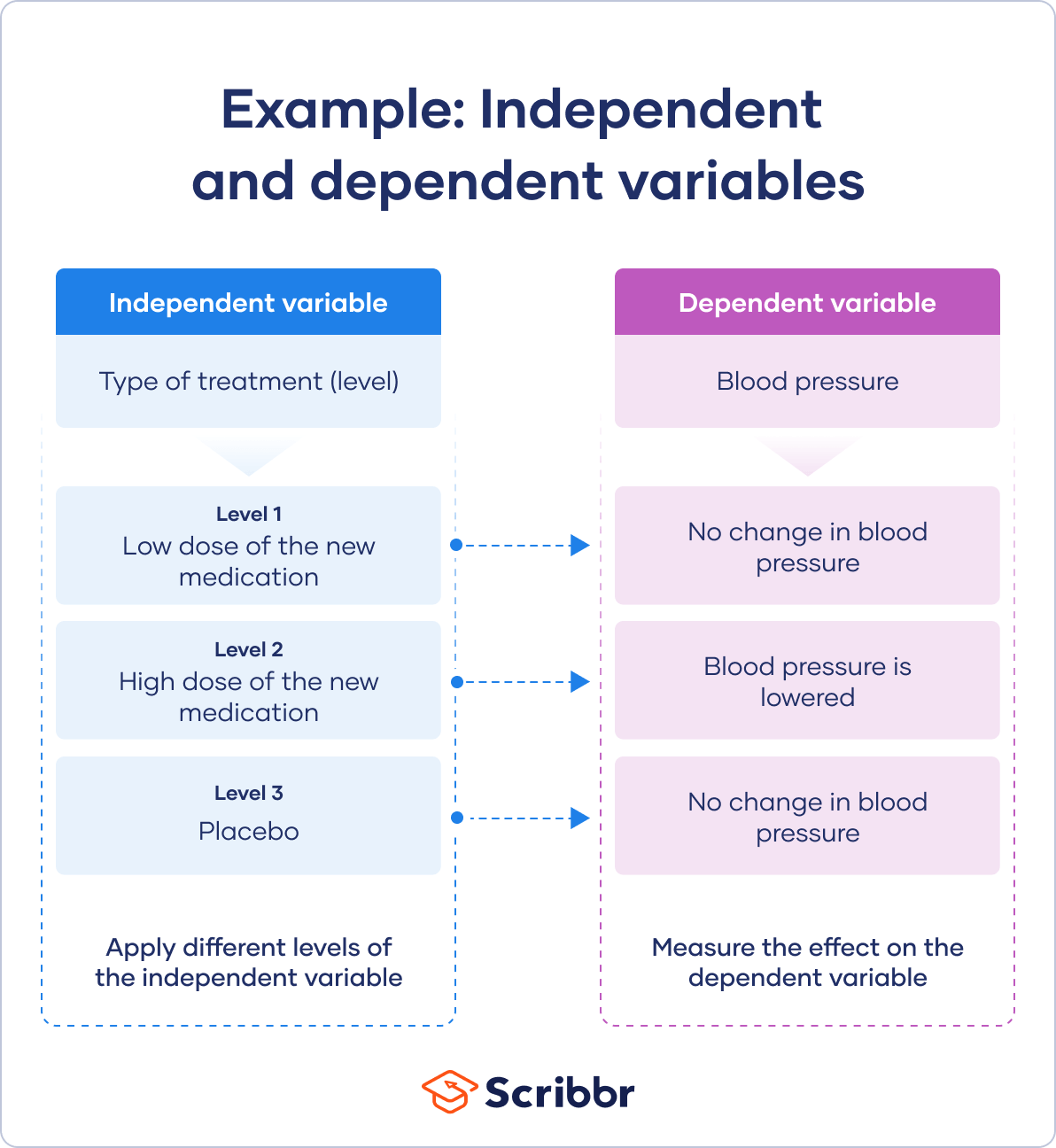
A true experiment requires you to randomly assign different levels of an independent variable to your participants.
Random assignment helps you control participant characteristics, so that they don’t affect your experimental results. This helps you to have confidence that your dependent variable results come solely from the independent variable manipulation.
Subject variables
Subject variables are characteristics that vary across participants, and they can’t be manipulated by researchers. For example, gender identity, ethnicity, race, income, and education are all important subject variables that social researchers treat as independent variables.
It’s not possible to randomly assign these to participants, since these are characteristics of already existing groups. Instead, you can create a research design where you compare the outcomes of groups of participants with characteristics. This is a quasi-experimental design because there’s no random assignment.
Your independent variable is a subject variable, namely the gender identity of the participants. You have three groups: men, women, and other.
Your dependent variable is the brain activity response to hearing infant cries. You record brain activity with fMRI scans when participants hear infant cries without their awareness.
A dependent variable is the variable that changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation. It’s the outcome you’re interested in measuring, and it ‘depends’ on your independent variable.
In statistics , dependent variables are also called:
- Response variables (they respond to a change in another variable)
- Outcome variables (they represent the outcome you want to measure)
- Left-hand-side variables (they appear on the left-hand side of a regression equation)
The dependent variable is what you record after you’ve manipulated the independent variable. You use this measurement data to check whether and to what extent your independent variable influences the dependent variable by conducting statistical analyses.
Based on your findings, you can estimate the degree to which your independent variable variation drives changes in your dependent variable. You can also predict how much your dependent variable will change as a result of variation in the independent variable.
Distinguishing between independent and dependent variables can be tricky when designing a complex study or reading an academic paper.
A dependent variable from one study can be the independent variable in another study, so it’s important to pay attention to research design.
Here are some tips for identifying each variable type.
Recognising independent variables
Use this list of questions to check whether you’re dealing with an independent variable:
- Is the variable manipulated, controlled, or used as a subject grouping method by the researcher?
- Does this variable come before the other variable in time?
- Is the researcher trying to understand whether or how this variable affects another variable?
Recognising dependent variables
Check whether you’re dealing with a dependent variable:
- Is this variable measured as an outcome of the study?
- Is this variable dependent on another variable in the study?
- Does this variable get measured only after other variables are altered?
Independent and dependent variables are generally used in experimental and quasi-experimental research.
Here are some examples of research questions and corresponding independent and dependent variables.
| Research question | Independent variable | Dependent variable(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Do tomatoes grow fastest under fluorescent, incandescent, or natural light? | ||
| What is the effect of intermittent fasting on blood sugar levels? | ||
| Is medical marijuana effective for pain reduction in people with chronic pain? | ||
| To what extent does remote working increase job satisfaction? |
For experimental data, you analyse your results by generating descriptive statistics and visualising your findings. Then, you select an appropriate statistical test to test your hypothesis .
The type of test is determined by:
- Your variable types
- Level of measurement
- Number of independent variable levels
You’ll often use t tests or ANOVAs to analyse your data and answer your research questions.
In quantitative research , it’s good practice to use charts or graphs to visualise the results of studies. Generally, the independent variable goes on the x -axis (horizontal) and the dependent variable on the y -axis (vertical).
The type of visualisation you use depends on the variable types in your research questions:
- A bar chart is ideal when you have a categorical independent variable.
- A scatterplot or line graph is best when your independent and dependent variables are both quantitative.
To inspect your data, you place your independent variable of treatment level on the x -axis and the dependent variable of blood pressure on the y -axis.
You plot bars for each treatment group before and after the treatment to show the difference in blood pressure.
An independent variable is the variable you manipulate, control, or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. It’s called ‘independent’ because it’s not influenced by any other variables in the study.
- Right-hand-side variables (they appear on the right-hand side of a regression equation)
A dependent variable is what changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation in experiments . It’s what you’re interested in measuring, and it ‘depends’ on your independent variable.
In statistics, dependent variables are also called:
Determining cause and effect is one of the most important parts of scientific research. It’s essential to know which is the cause – the independent variable – and which is the effect – the dependent variable.
You want to find out how blood sugar levels are affected by drinking diet cola and regular cola, so you conduct an experiment .
- The type of cola – diet or regular – is the independent variable .
- The level of blood sugar that you measure is the dependent variable – it changes depending on the type of cola.
Yes, but including more than one of either type requires multiple research questions .
For example, if you are interested in the effect of a diet on health, you can use multiple measures of health: blood sugar, blood pressure, weight, pulse, and many more. Each of these is its own dependent variable with its own research question.
You could also choose to look at the effect of exercise levels as well as diet, or even the additional effect of the two combined. Each of these is a separate independent variable .
To ensure the internal validity of an experiment , you should only change one independent variable at a time.
No. The value of a dependent variable depends on an independent variable, so a variable cannot be both independent and dependent at the same time. It must be either the cause or the effect, not both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 17). Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 19 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/independent-vs-dependent-variables/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, quasi-experimental design | definition, types & examples, types of variables in research | definitions & examples.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Definitions
Dependent Variable The variable that depends on other factors that are measured. These variables are expected to change as a result of an experimental manipulation of the independent variable or variables. It is the presumed effect.
Independent Variable The variable that is stable and unaffected by the other variables you are trying to measure. It refers to the condition of an experiment that is systematically manipulated by the investigator. It is the presumed cause.
Cramer, Duncan and Dennis Howitt. The SAGE Dictionary of Statistics . London: SAGE, 2004; Penslar, Robin Levin and Joan P. Porter. Institutional Review Board Guidebook: Introduction . Washington, DC: United States Department of Health and Human Services, 2010; "What are Dependent and Independent Variables?" Graphic Tutorial.
Identifying Dependent and Independent Variables
Don't feel bad if you are confused about what is the dependent variable and what is the independent variable in social and behavioral sciences research . However, it's important that you learn the difference because framing a study using these variables is a common approach to organizing the elements of a social sciences research study in order to discover relevant and meaningful results. Specifically, it is important for these two reasons:
- You need to understand and be able to evaluate their application in other people's research.
- You need to apply them correctly in your own research.
A variable in research simply refers to a person, place, thing, or phenomenon that you are trying to measure in some way. The best way to understand the difference between a dependent and independent variable is that the meaning of each is implied by what the words tell us about the variable you are using. You can do this with a simple exercise from the website, Graphic Tutorial. Take the sentence, "The [independent variable] causes a change in [dependent variable] and it is not possible that [dependent variable] could cause a change in [independent variable]." Insert the names of variables you are using in the sentence in the way that makes the most sense. This will help you identify each type of variable. If you're still not sure, consult with your professor before you begin to write.
Fan, Shihe. "Independent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design. Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 592-594; "What are Dependent and Independent Variables?" Graphic Tutorial; Salkind, Neil J. "Dependent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 348-349;
Structure and Writing Style
The process of examining a research problem in the social and behavioral sciences is often framed around methods of analysis that compare, contrast, correlate, average, or integrate relationships between or among variables . Techniques include associations, sampling, random selection, and blind selection. Designation of the dependent and independent variable involves unpacking the research problem in a way that identifies a general cause and effect and classifying these variables as either independent or dependent.
The variables should be outlined in the introduction of your paper and explained in more detail in the methods section . There are no rules about the structure and style for writing about independent or dependent variables but, as with any academic writing, clarity and being succinct is most important.
After you have described the research problem and its significance in relation to prior research, explain why you have chosen to examine the problem using a method of analysis that investigates the relationships between or among independent and dependent variables . State what it is about the research problem that lends itself to this type of analysis. For example, if you are investigating the relationship between corporate environmental sustainability efforts [the independent variable] and dependent variables associated with measuring employee satisfaction at work using a survey instrument, you would first identify each variable and then provide background information about the variables. What is meant by "environmental sustainability"? Are you looking at a particular company [e.g., General Motors] or are you investigating an industry [e.g., the meat packing industry]? Why is employee satisfaction in the workplace important? How does a company make their employees aware of sustainability efforts and why would a company even care that its employees know about these efforts?
Identify each variable for the reader and define each . In the introduction, this information can be presented in a paragraph or two when you describe how you are going to study the research problem. In the methods section, you build on the literature review of prior studies about the research problem to describe in detail background about each variable, breaking each down for measurement and analysis. For example, what activities do you examine that reflect a company's commitment to environmental sustainability? Levels of employee satisfaction can be measured by a survey that asks about things like volunteerism or a desire to stay at the company for a long time.
The structure and writing style of describing the variables and their application to analyzing the research problem should be stated and unpacked in such a way that the reader obtains a clear understanding of the relationships between the variables and why they are important. This is also important so that the study can be replicated in the future using the same variables but applied in a different way.
Fan, Shihe. "Independent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design. Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 592-594; "What are Dependent and Independent Variables?" Graphic Tutorial; “Case Example for Independent and Dependent Variables.” ORI Curriculum Examples. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Research Integrity; Salkind, Neil J. "Dependent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 348-349; “Independent Variables and Dependent Variables.” Karl L. Wuensch, Department of Psychology, East Carolina University [posted email exchange]; “Variables.” Elements of Research. Dr. Camille Nebeker, San Diego State University.
- << Previous: Design Flaws to Avoid
- Next: Glossary of Research Terms >>
- Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 12:13 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The independent variable is the cause. Its value is independent of other variables in your study. The dependent variable is the effect. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable. Example: Independent and dependent variables. You design a study to test whether changes in room temperature have an effect on math test scores.
In research, a variable is any characteristic, number, or quantity that can be measured or counted in experimental investigations. One is called the dependent variable, and the other is the independent variable. In research, the independent variable is manipulated to observe its effect, while the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
Example: Hypothesis Daily exposure to the sun leads to increased levels of happiness. In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun - the assumed cause. The dependent variable is the level of happiness - the assumed effect.
Treatment and control groups are always independent variables. In this case, the independent variable is a categorical grouping variable that defines the experimental groups to which participants belong. Each group is a level of that variable. In observational studies, independent variables are a bit different.
The independent variable (IV) in psychology is the characteristic of an experiment that is manipulated or changed by researchers, not by other variables in the experiment. For example, in an experiment looking at the effects of studying on test scores, studying would be the independent variable. Researchers are trying to determine if changes to ...
Here are several examples of independent and dependent variables in experiments: In a study to determine whether how long a student sleeps affects test scores, the independent variable is the length of time spent sleeping while the dependent variable is the test score. You want to know which brand of fertilizer is best for your plants.
While the independent variable is the " cause ", the dependent variable is the " effect " - or rather, the affected variable. In other words, the dependent variable is the variable that is assumed to change as a result of a change in the independent variable. Keeping with the previous example, let's look at some dependent variables ...
A change in the independent variable directly causes a change in the dependent variable. If you have a hypothesis written such that you're looking at whether x affects y, the x is always the independent variable and the y is the dependent variable. GRAPHING THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE. If the dependent and independent variables are plotted on a ...
The independent variable is the variable that the researcher or experimenter manipulates to affect the dependent variable. It is independent of the other variables in an experiment. ... A good hypothesis asks what effect an independent variable has on a dependent variable. Without experimental research, we would not be able to determine (with ...
Independent Variable Examples. Here are some examples of an independent variable. A scientist is testing the effect of light and dark on the behavior of moths by turning a light on and off. The independent variable is the amount of light (cause) and the moth's reaction is the dependent variable (the effect).
Simple hypothesis: This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.; Complex hypothesis: This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.; Null hypothesis: This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
A variable is considered dependent if it depends on an independent variable. Dependent variables are studied under the supposition or demand that they depend, by some law or rule (e.g., by a mathematical function ), on the values of other variables. Independent variables, in turn, are not seen as depending on any other variable in the scope of ...
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable. It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The independent variable is the drug, while the patient's blood pressure is the dependent variable. In some ways, this experiment resembles the one with breakfast and test scores. However, when comparing two different treatments, such as drug A and drug B, it's usual to add another variable, called the control variable. ...
The independent variable in your experiment would be the brand of paper towels. The dependent variable would be the amount of liquid absorbed by the paper towel. In an experiment to determine how far people can see into the infrared part of the spectrum, the wavelength of light is the independent variable and whether the light is observed (the ...
An independent variable is a condition or factor that researchers manipulate to observe its effect on another variable, known as the dependent variable. ... It has steps we follow: asking a question, researching, guessing what will happen (that's a hypothesis!), experimenting, checking the results, figuring out what they mean, and telling ...
In this hypothesis, the duration of the current episode of depression is the independent variable and treatment response is the dependent variable. It should be obvious, now, that a hypothesis can also be defined as the statement of an expected relationship between an independent and a dependent variable .
by Zach Bobbitt February 5, 2020. In an experiment, there are two main variables: The independent variable: the variable that an experimenter changes or controls so that they can observe the effects on the dependent variable. The dependent variable: the variable being measured in an experiment that is "dependent" on the independent variable.
The independent variable is the cause. Its value is independent of other variables in your study. The dependent variable is the effect. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable. Example: Independent and dependent variables. You design a study to test whether changes in room temperature have an effect on maths test scores.
Dependent Variable The variable that depends on other factors that are measured. These variables are expected to change as a result of an experimental manipulation of the independent variable or variables. It is the presumed effect. Independent Variable The variable that is stable and unaffected by the other variables you are trying to measure.
3 Define your variables. Once you have an idea of what your hypothesis will be, select which variables are independent and which are dependent. Remember that independent variables can only be factors that you have absolute control over, so consider the limits of your experiment before finalizing your hypothesis.
To form a solid theory, the vital first step is creating a hypothesis. See the various types of hypotheses and how they can lead you on the path to discovery. ... The independent variable can cause a change in the dependent variable, but the dependent variable cannot cause a change in the independent variable. For example:
A hypothesis is your statement of what you think will happen to a dependent variable when a change occurs in the independent variable. Your dependent variable is the result.