Transcribing Interviews for Qualitative Research: Best Practices
- Serra Ardem

The long hours dedicated to transcribing interviews are now in a galaxy far far away, thanks to the developments in AI and machine learning. Qualitative research highly benefits from these advancements as AI transcription technology not only saves valuable time but also increases research efficiency and accuracy.
In this blog, we emphasize the significance of transcribing interviews for qualitative research as well as the best practices in this area. We also explain why automatic transcription offers more advantages to researchers and how to choose an interview transcription software to achieve optimal results.
Let’s begin.

What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a systematic approach to understanding and explaining social phenomena. Focused on “How?” and “Why?” questions, it is an umbrella concept that involves different research methodologies including interviews, participant observation, focus groups and so on.
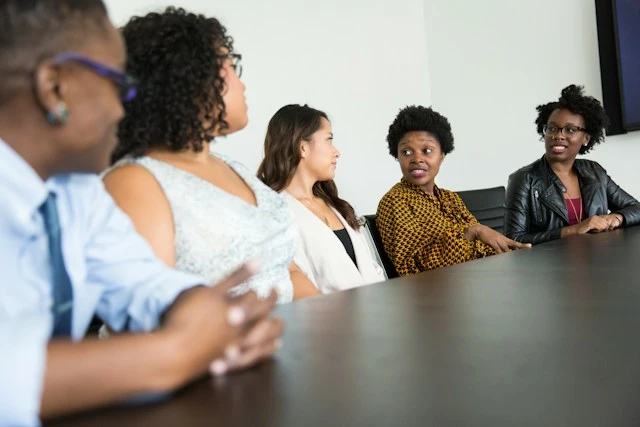

Qualitative data is based on words, behaviors and images. By analyzing these, qualitative research generates theories and hypotheses on how the social world is experienced and understood by people in everyday life. Unlike quantitative research that depends on numbers and statistics, qualitative research seeks to uncover the underlying meanings in human experiences.
Importance of Transcribing Interviews in Qualitative Research
Transcribing interviews for qualitative research offers several benefits that contribute to the overall depth and success of the research process. Here are its key advantages:
- Comprehensive analysis: Transcripts capture every word, nuance and non-verbal cue, which is a goldmine for data analysis. This allows researchers to identify themes and patterns thoroughly to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Enhanced reliability: Having the transcript for an interview will strengthen research validity by providing evidence to your argument. Plus, other researchers can review the transcription, ensuring transparency and collaboration.
- Reduced bias: Transcribing interviews will reduce bias as it minimizes the risk of misinterpreting or omitting information. Compared to note-taking, which may be influenced by the researcher’s perceptions, transcription offers a more objective representation of data.
- Increased accessibility: Via transcription , researchers can share and discuss findings with people who couldn’t participate in the interview due to language barriers. Furthermore, the practice improves accessibility for deaf and hard of hearing individuals by allowing them to engage with the findings through written text.
- Time-efficiency: No more jumping back and forth in audio files! When you transcribe the interview, you can quickly search for and navigate to specific parts, saving time during the analysis phase.
4 Types of Transcription
Transcription can be grouped into four categories: verbatim, intelligent verbatim, edited and phonetic. Let’s take a look at each one’s pros and cons, and highlight the best choice for transcribing interviews for qualitative research.
Verbatim Transcription
Verbatim transcription includes every sound in the audio recording such as coughs, doorbells and hesitations (er, mm, etc.) between sentences.
Pros: Provides the most complete and accurate record of the interview, which is essential for capturing the full context and subtle nuances.
Cons: May include unnecessary details. Can be time consuming and expensive to produce in case of manual transcription.
Primarily used in: legal proceedings, sociolinguistic research studies
Intelligent Verbatim Transcription
An intelligent verbatim transcript removes filler words and repetitions but retains key content and non-verbal cues. Its purpose is to provide a more on-point transcript.
Pros: Offers a balance between readability and details.
Cons: May sacrifice some context and require careful quality control to guarantee accuracy.
Primarily used in: qualitative research, especially in interviews and focus groups

Edited Transcription
Clarity is the main focus of an edited transcript. It corrects grammatical errors and eliminates filler words, repetitions and extraneous sounds.
Pros: More readable and concise, therefore suitable for general understanding and thematic analysis.
Cons: Risks losing some nuances and the authenticity of participants’ expressions.
Primarily used in: journalism and media contexts
Phonetic Transcription
Phonetic transcription is unorthodox as it uses symbols from the International Phonetic Association to represent sounds exactly as they are spoken. This includes accents, dialects and non-standard pronunciations.
Pros: Analyzing variations in pronunciation.
Cons: More complex and expensive than other types of transcription.
Primarily used in: linguistic studies
What is the best type for interview transcripts in qualitative research? As we’ve said above, intelligent verbatim transcription is often the best choice: It is readable and manageable for analysis, yet it also provides a detailed record of the conversation.
Still, always consider your research goals, questions, data and budget when transcribing interviews. An edited transcript might be sufficient if you want to focus on broader themes. Meanwhile, verbatim transcription can be pretty useful if details matter to you a lot.
Methods of Transcribing Interviews
There are two main methods when it comes to transcribing interviews: manual and automatic. While manual transcription involves a human transcriber typing out the spoken words in the interview, automatic transcription utilizes speech recognition technology to convert audio to text.
As in types of transcription, these two methods have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Human transcribers can better understand nuances and context. However, this method can also be pretty time consuming and it may be expensive to hire a professional transcriber.
On the other hand, automatic transcription is much faster and cost-effective. This is an important advantage in the realm of qualitative research where large amounts of interview data need to be processed and analyzed. You can definitely save time and resources by using software when transcribing interviews for research.
Moreover, automatic transcription services are getting more accurate day by day thanks to the developments in AI, machine learning and voice recognition. Current systems can handle diverse accents, linguistic variations and even contextual nuances very well. This significantly increases the reliability of the interview transcript and research results.
How to Choose an Interview Transcription Software
Decided to use an interview transcription software for research but confused on how to choose one? Look for these qualities when making your decision:
Accuracy is crucial when transcribing interviews as it directly influences the reliability of your data. Prioritize an AI-powered tool with a high accuracy rate to remain true to your original interview. We recommend you test the AI transcription software beforehand with a small sample of your interview.
Quick turnaround time is essential for researchers who work with large sums of interview data and tight deadlines. The right software must transcribe audio to text rapidly without compromising accuracy and meet the demands of an intense qualitative research process.
It is your responsibility to comply with ethical standards and protect your participants’ sensitive information. You must choose a tool that has end-to-end encryption and clear privacy policies.

Flexibility
Does the transcription software allow you to upload audio and video files in different formats? Is it easy to edit the transcript and add notes? This flexibility will help you refine interviews seamlessly, enhancing the quality of your data.
Customization
Speaker identification, timestamps and punctuation are indispensable when transcribing interviews for qualitative research. Select a software that allows you to tailor these elements to your needs.
Language Support
Make sure that the tool supports the languages spoken in your interviews. Break down the language barrier by choosing a software that transcribes multiple languages and enrich your research with global perspectives.
Transcribing Interviews with Maestra Step-by-Step
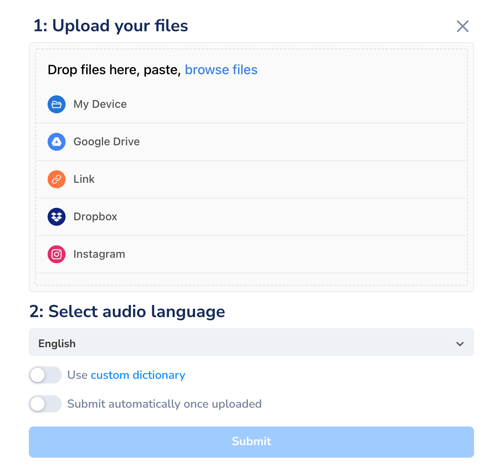
If you’re looking for a tool with all these features, then Maestra’s AI-powered interview transcription software is the right choice for you. You can get your transcript instantly by following a few simple steps.
- Upload your audio or video file. Maestra supports 125+ languages .
- Select audio language and receive the transcript in seconds.
Custom dictionary is especially beneficial when transcribing interviews for research as the audio content is more likely to include technical terminology. With this feature, you can add specific terms to your custom dictionary, assign importance values and Maestra will transcribe them as specified, ensuring accuracy.
You can also select the number of speakers during the upload phase and assign names to each speaker, making it easier to navigate the transcript.
- Click “Submit” and witness AI transcription work its magic. You will instantly receive your interview transcript with timestamps and speaker tags.
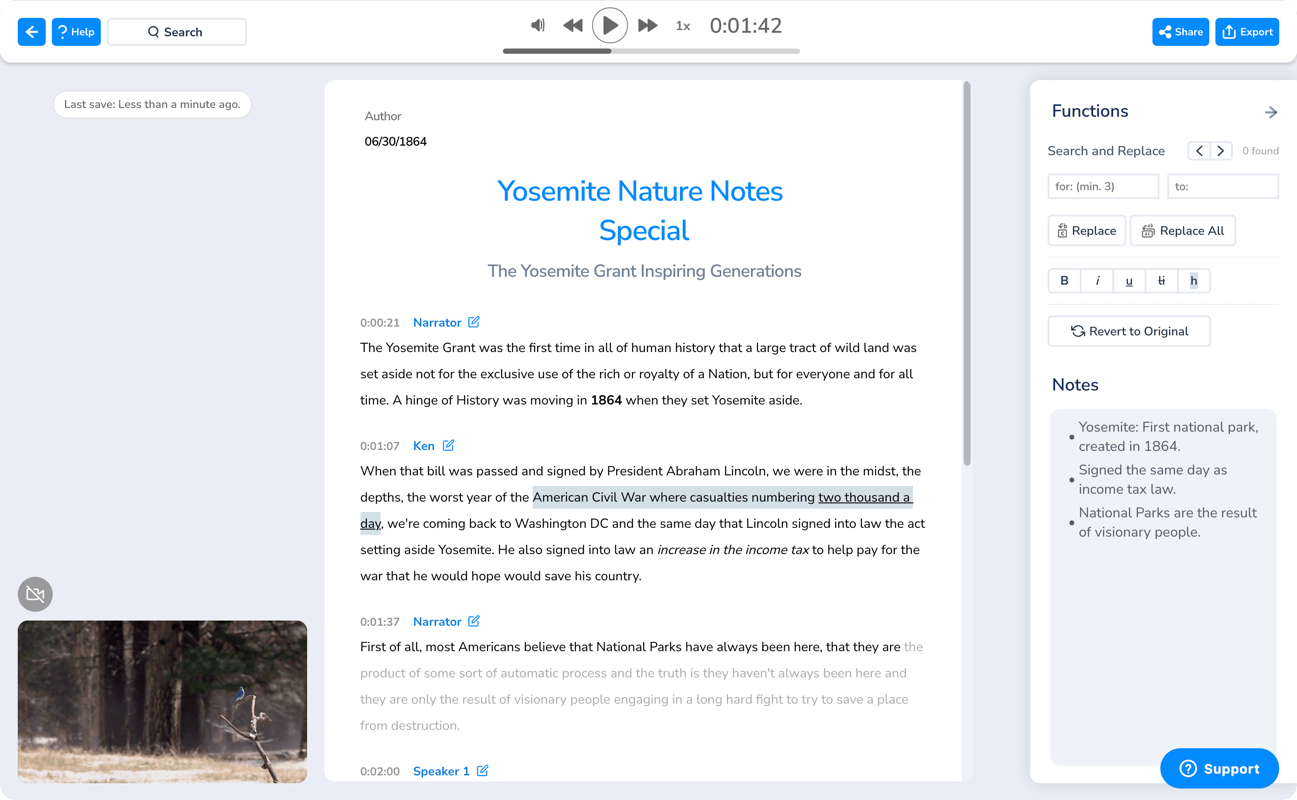
- Ta-da! You can now proofread and edit your transcript, take notes and add comments with Maestra’s built-in text editor .
Maestra has a very high accuracy rate but you can always polish your document for maximum clarity and comprehensibility.
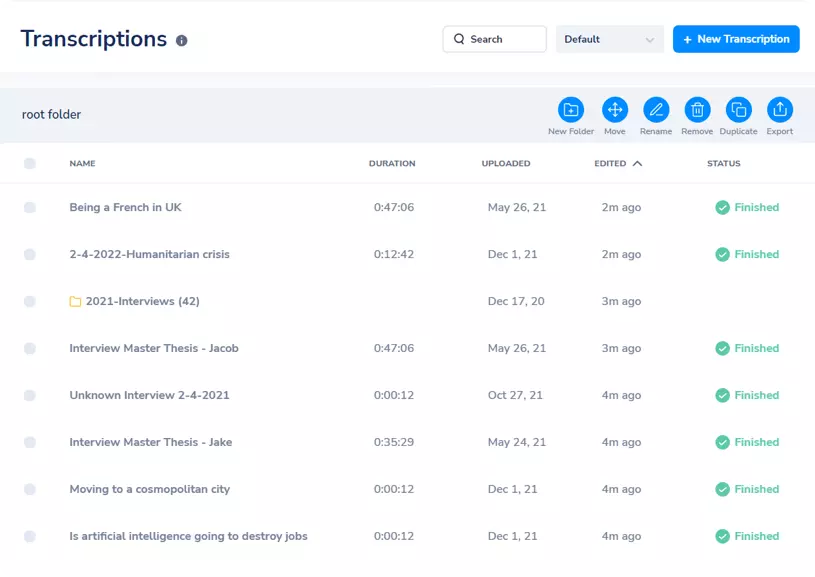
After transcribing interviews, you can safely reach and organize them via MaestraCloud . You can also store your interview recordings here as the cloud allows you to keep audio and video files of any size without time limitations.
Collaborating with fellow researchers? Maestra Teams is ready to help you. You can create team-based channels with different permission levels and edit the document with other researchers in real-time.
Tips for Transcribing Interviews for Qualitative Research
No matter your experience in qualitative research or the software you use, there are certain practices to adopt when transcribing interviews.
Use a High-Quality Recording Device
Utilizing a high-quality recording device lays a solid foundation for interview transcription. Invest in a reliable recorder with good microphone sensitivity and audio quality to capture every part of the conversation. Don’t forget to test your equipment beforehand to avoid potential technical issues during the interview.
Respect Confidentiality
Upholding confidentiality is paramount when transcribing interviews for qualitative research. Always obtain informed consent from participants for recording and transcription, and store your files securely. Avoid sharing any personally identifiable information to safeguard participant privacy and maintain the integrity of your research.
Include Speaker Identification and Time Stamps
This practice enhances the overall usability of an interview transcript by enabling easy reference to specific points. Make sure you clearly identify each speaker on the document either by name, role or pseudonym. You can use different fonts or colors to visually distinguish between speakers.

Follow the Specific Style Consistently
Choose a transcription style guide (verbatim, intelligent verbatim, etc.) and follow it consistently throughout the project. Define rules for punctuation, contractions and interruptions. This will guarantee uniformity and enhance the reliability of your findings.
Add Non-Verbal Cues and Annotations
This one is not mandatory but can provide valuable context. You can document non-verbal expressions, pauses or changes in tone to add depth to qualitative data analysis. Meanwhile, bracketed annotations can help you highlight important moments. Just remember that adding too much detail can be distracting, so only include relevant information.
Edit and Proofread the Transcript
Proofread and edit your document once transcribing an interview: correct any errors, format inconsistencies and review for readability. Double check speaker identification and timestamps for accuracy. These practices will ensure a smooth transition from transcription to analysis and publication.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is transcription necessary for qualitative research.
The necessity of transcription depends on the nature and goals of the qualitative research you conduct. For example, it is crucial for in-depth and focus group interviews but not essential for participant observation where researchers can rely on field notes.
How do you transcribe an anonymous interview?
When transcribing interviews with anonymous participants, remove any information that can directly or indirectly identify the participant such as name, nickname, location, job title and affiliations. Create neutral pseudonyms (Participant 1, Interviewee A, etc.) for the participant and use them consistently throughout the interview transcript.
How do you analyze interview transcripts in qualitative research?
First, familiarize yourself with the data through readings when analyzing an interview transcript for research . Then, assign codes to relevant segments and organize similar codes into broader recurring themes. Finally, present your findings via a structured narrative. Always maintain transparency during the process.
How do you transcribe an interview in APA format?
Transcripts of interviews are usually added to the appendix in APA format . You should use a specific header with interview details, double line spacing and speaker identifiers in the transcript.
How do you summarize an interview transcript?
Carefully read the content and identify key themes when summarizing the transcript of an interview . Organize the information logically, provide brief contextual details when necessary and use quotes to add impact. Capture the essence of the interview by keeping the summary short and sweet.
Interview transcription is particularly valuable in qualitative research, which delves deep into human experiences and perceptions. Transforming spoken words into text enables researchers to derive meaningful insights from the rich tapestry of qualitative data. It also increases the accessibility of the research, empowering scholars to collaborate with colleagues across disciplines and borders.
The advent of AI technology revolutionized the process of transcribing interviews and will continue to do so in the future. Its benefits range from increased accuracy to cost-effectiveness, providing a much refined experience for researchers. By choosing the right software and adopting the best practices for transcribing interviews, researchers can unleash the full potential of their endeavors.

About Serra Ardem
Serra Ardem is a freelance writer and editor based in Istanbul. For the last 8 years, she has been collaborating with brands and businesses to tell their unique story and develop their verbal identity.
How to Analyze Interview Transcripts in Qualitative Research
Rev › Blog › Transcription Blog › How to Analyze Interview Transcripts in Qualitative Research
Studies take time, accuracy, and a drive to provide excellent information, and qualitative research is a critical part of any successful study. You may be wondering how qualitative data adds to a paper or report, given that it’s not the hard “science” we often see highlighted the most often.
How Do You Analyze Qualitative Interviews?
There are two main approaches to qualitative analysis: inductive and deductive . What’s more, there are two types of inductive qualitative analysis to choose from. These are called thematic content analysis and narrative analysis, both of which call for an unstructured approach to research.
Inductive Methods of Analyzing Interview Transcripts
A thematic content analysis begins with weeding out biases and establishing your overarching impressions of the data. Rather than approaching your data with a predetermined framework, identify common themes as you search the materials organically. Your goal is to find common patterns across the data set.
A narrative analysis involves making sense of your interview respondents’ individual stories. Use this type of qualitative data analysis to highlight important aspects of their stories that will best resonate with your readers. And, highlight critical points you have found in other areas of your research.
Deductive Approach to Qualitative Analysis
Deductive analysis , on the other hand, requires a structured or predetermined approach. In this case, the researcher will build categories in advance of their analysis. Then, they’ll map connections in the data to those specific categories.
Each of these qualitative analysis methods lends its benefits to the research effort. Inductive analyses will produce more nuanced findings. Meanwhile, deductive analyses allow the researcher to point to key themes essential to their research.
Successful qualitative research hinges on the accuracy of your data. This can be harder to achieve than with quantitative research. It’s easy to lose important facts and meaning as you transition qualitative data from the source to your published content. This makes transcription a vital tool in maintaining integrity and relaying information in an unbiased way that’s useful for readers and adds appropriate context to the journal or study.
How to Transcribe a Qualitative Interview
Accurate transcription begins early in the interview process, even before you start interviewing. Here are the steps to transcribing a qualitative interview.
1. Collect Feedback for Qualitative Research
There are dozens of ways to gather qualitative data. Recording and accurately transcribing interviews is among the best methods to avoid inaccuracies and data loss, and researchers should consider this approach over simply taking notes firsthand.
Make sure you have a reliable way to record, whether the interview takes place in person, over the phone, or as part of a video call. Depending on the interview method, you may record a video or an audio-only format. Here are some tips depending on where the interview takes place:
- These apps can also be used for over-the-phone interviews.
- For video interviews , we recommend taking advantage of one of our transcription integrations , such as Zoom. Rev also has an API available for those who want to streamline their workflow even further by integrating Rev directly into their processes and platforms.
2. Organize Your Research Recordings
You should ensure that your audio or video files are easy to save, compile, and share. To do this, be sure to adopt easy-to-remember naming conventions as well to ensure they stay organized. An example of a naming convention that is simple to remember and recreate includes “Date.LastNameofSource.Topic”.
3. Transcribe All the Interviews and Focus Group Recordings
The next critical step is transcription. Done manually, this is a long and tedious process that can add hours, days, or even months to your report-writing process. There are dozens of pitfalls when performing transcriptions manually as well, as it can be hard to pick up words spoken in a heavy dialect or quiet tone. You also want to avoid having to transcribe all the “umms” and “ems” that occur when a source is speaking naturally.
Rev provides a variety of transcription services that take the tedium and guesswork out of the research process. You can choose to edit out all of the “umms,” while ensuring that heavy accents or muffled voices are picked up by the recording service.
You can order transcripts from Rev with both audio and video recordings. Once you’ve received your professional transcripts from Rev, you can begin your qualitative analysis.
The 6 Steps of Qualitative Interview Data Analysis
Among qualitative interview data analysis methods, thematic content analysis is perhaps the most common and effective method. It can also be one of the most trustworthy , increasing the traceability and verification of an analysis when done correctly. The following are the six main steps of a successful thematic analysis of your transcripts.
1. Read the Transcripts
By now, you will have accessed your transcript files as digital files in the cloud or have downloaded them to your computer for offline viewing. Start by browsing through your transcripts and making notes of your first impressions. You will be able to identify common themes. This will help you with your final summation of the data.
Next, read through each transcript carefully. Evidence of themes will become stronger, helping you to hone in on important insights.
You must identify bias during this step as well. Biases can appear in the data, among the interviewees, and even within your objectives and methodologies. According to SAGE Publishing , researchers should “acknowledge preconceived notions and actively work to neutralize them” at this early step.
2. Annotate the Transcripts
Annotation is the process of labeling relevant words, phrases, sentences, or sections with codes. These codes help identify important qualitative data types and patterns. Labels can be about actions, activities, concepts, differences, opinions, processes, or whatever you think is relevant. Annotations will help you organize your data for dissemination .
Be generous with your annotations—don’t hold back. You will have an opportunity to eliminate or consolidate them later. It’s best to do more here, so you don’t have to come back to find more opportunities later.
3. Conceptualize the Data
Conceptualizing qualitative data is the process of aligning data with critical themes you will use in your published content. You will have identified many of these themes during your initial review of the transcripts.
To conceptualize, create categories and subcategories by grouping the codes you created during annotation. You may eliminate or combine certain codes rather than using all the codes you created. Keep only the codes you deem relevant to your analysis.
4. Segment the Data
Segmentation is the process of positioning and connecting your categories . This allows you to establish the bulk of your data cohesively. Start by labeling your categories and then describe the connections between them.
You can use these descriptions to improve your final published content.
- Create a spreadsheet to easily compile your data.
- Then, use the columns to structure important variables of your data analysis using codes as tools for reference.
- Create a separate tab for the front of the document that contains a coding table. This glossary contains important codes used in the segmentation process. This will help you and others quickly identify what the codes are referring to.
5. Analyze the Segments
You’re now ready to take a deep dive into your data segments . Start by determining if there is a hierarchy among your categories. Determine if one is more important than the other, or draw a figure to summarize the results. At this stage, you may also want to align qualitative data with any quantitative data you collected.
6. Write the Results
Your analysis of the content is complete—you’re ready to transition your findings into the real body of your content. Use your insights to build and verify theories, answer key questions in your field, and back aims and objectives. Describe your categories and how they are connected using a neutral, objective voice.
Although you will pull heavily from your own research, be sure to publish content in the context of your field. Interpret your results in light of relevant studies, theories, and concepts related to your study.
Why Use Interviews for Qualitative Data
Unlike quantitative data, which is certainly important, a qualitative analysis adds color to academic and business reports. It offers perspective and can make a report more readable, add context, and inspire thoughtful discussion beyond the report.
As we’ve observed, transcribing qualitative interviews is crucial to getting less measurable data from direct sources. They allow researchers to provide relatable stories and perspectives and even quote important contributors directly. Lots of qualitative data from interviews enables authors to avoid embellishment and maintain the integrity of their content as well.
So, how do you conduct interview data analysis on qualitative data to pull key insights and strengthen your reports? Transcribing interviews is one of the most useful tools available for this task.
As a researcher, you need to make the most of recorded interviews . Interview transcripts allow you to use the best qualitative analysis methods. Plus, you can focus only on tasks that add value to your research effort.
Transcription is Essential to Qualitative Research Analysis
Qualitative data is often elusive to researchers. Transcripts allow you to capture original, nuanced responses from your respondents. You get their response naturally using their own words—not a summarized version in your notes.
You can also go back to the original transcript at any time to see what was said as you gain new context. The editable digital transcript files are incredibly easy to work with, saving you time and giving you speaker tags, time marks, and other tools to ensure you can find what you need within a transcript quickly.
When creating a report, accuracy matters, but efficiency matters, as well. Rev offers a seamless way of doing the transcription for you, saving you time and allowing you to focus on high-quality work instead. Consider Rev as your transcription service provider for qualitative research analysis — try Rev’s AI or Human Transcription services today.
Everybody’s Favorite Speech-to-Text Blog
We combine AI and a huge community of freelancers to make speech-to-text greatness every day. Wanna hear more about it?

How to Transcribe an Interview: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn expert tips for accurate interview transcription. Master efficient techniques, tools, and best practices in this comprehensive guide.
An interview transcript is a written record of a spoken conversation, capturing every spoken word from an audio or video recording. It's an essential tool for converting spoken content into text, enabling easier analysis, sharing, and reference.
Verbatim transcripts capture every detail, including false starts, filler words, and pauses, maintaining the authenticity of the conversation.
Definition of Interview Transcript
Transcribing an interview offers numerous benefits. It helps enhance accessibility by providing a text version of audio content, making it useful for those with hearing impairments.
Additionally, it allows for thorough analysis and research, as you can easily search for specific information within the text. Transcripts also facilitate content repurposing, as you can transform spoken words into written articles, blog posts, or social media content.

Photo by Scott Graham on Unsplash
Benefits of Writing a Transcript
Before diving into the transcription process, proper preparation is key. Ensure that your audio recording is of high quality, as clear audio greatly simplifies the transcription task. Using a reliable audio recording device or software helps maintain optimal audio quality.
You can also use transcription software like Express Scribe to play and control the audio recording while typing out the transcript. For video files, extract the audio to transcribe the conversation accurately.
Consider using speaker labels and time stamps to distinguish different speakers and pinpoint specific moments in the conversation. By properly preparing for the interview and the subsequent transcription process, you'll pave the way for creating accurate and valuable interview transcripts.
Prepare Questions
Creating effective interview questions is the foundation of a successful transcription process. Craft questions that encourage detailed and informative responses, ensuring the conversation covers all relevant topics.
Clarity in your questions reduces the chances of misunderstanding during the interview, leading to accurate transcription later. Be mindful of speech patterns and potential hesitations to anticipate transcription challenges and improve the quality of the transcript.
Choose an Appropriate Location and Audio Equipment
Selecting the right environment for the interview is pivotal for accurate transcription. Opt for a quiet and controlled space to minimize background noise. Wearing noise-canceling headphones or a good pair of headphones can help the interviewer and interviewee hear each other clearly, facilitating accurate recording. A clear and accurate audio record is a foundation for creating precise and reliable transcripts.
Train Others on How to Take Notes and Record the Interview
If you're not the one conducting the interview, training others on effective note-taking and audio recording is crucial. Ensure they understand the importance of capturing both verbal and non-verbal cues.
For instance, noting John Smith speaking might help distinguish speakers in a multi-participant conversation. Teach them to recognize speech patterns, like throat clearing or pauses, to ensure these nuances are accurately transcribed.
Introducing your team to the proper tools, including transcription templates, noise-canceling headphones, or even professional transcription services, can contribute to producing accurate and polished transcripts.
Conducting the Interview
Conducting an interview skillfully is crucial for creating an accurate transcript. Ensure you introduce yourself, explain the purpose of the interview, and obtain consent for recording. Establish a comfortable atmosphere for the interviewee to open up. Pay attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues, as capturing these nuances enriches the transcript.
Introduce Yourself and Explain What You Are Doing
Begin by introducing yourself and clarifying the purpose of the interview. This not only creates a rapport but also ensures the interviewee is aware of the recording process. Let them know that their insights are valued and that their words will be transcribed for later reference. This level of transparency sets the tone for a successful and collaborative interview.
Ask Open-Ended Questions
Crafting open-ended questions promotes in-depth responses, providing valuable content for your transcript. Instead of asking yes or no questions, inquire about experiences, opinions, or explanations. Open-ended questions encourage the interviewee to express themselves freely, facilitating a comprehensive and rich transcript.
Give Time for Answers and Respond Appropriately
During the interview, allow ample time for the interviewee to respond. Avoid interrupting or finishing their sentences, as this can disrupt the natural flow of conversation. A transcript with complete answers captures the essence of the interviewee's thoughts accurately. Responding appropriately to their answers conveys your interest and encourages them to elaborate, further enhancing the transcript's depth.
Ask Follow-Up Questions
Follow-up questions help clarify responses, delve deeper into topics, and extract additional information. When an interviewee provides an intriguing insight, posing follow-up questions uncovers more details.
This enriches the content of your transcript and contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of the interviewee's perspective. Skilled transcribers can capture these nuances effectively, ensuring your transcript retains its richness and accuracy.
Once you have conducted a well-structured interview, the next step is to ensure your transcript captures every detail accurately. This might require manual effort if you're not utilizing automatic transcription tools.
Skilled transcribers, well-versed in handling various accents, non-verbal cues, and even correcting grammar errors, can ensure your transcript reflects the actual person's words with a high level of accuracy. Their expertise and attention to detail eliminate the need for extensive post-interview editing, saving you time and ensuring a polished final transcript.
End the Interview Gracefully
Concluding the interview on a positive note is essential for maintaining rapport and professionalism. Express gratitude for the interviewee's time and insights. Ask if they have any additional points to share.
Clarify any unclear responses and ensure they have a chance to ask questions. This thoughtful closure leaves a lasting impression and encourages future engagement.
Transcribing the Interview
Transcribing an interview is a meticulous process that demands attention to detail. Listening to the recording multiple times is the first step. This familiarizes you with the content and helps capture nuances. If you're aiming for accurate interview transcription, utilizing professional transcription services or tools is recommended.
Dive.io, an AI-powered transcription tool, stands out in this regard. With its accurate speaker identification and time codes, Dive.io ensures a seamless accuracy level that's crucial for maintaining the essence of the conversation.
Listen to the Recording Multiple Times
After concluding the interview, carefully transcribing the conversation is pivotal for preserving its essence. Listen to the recording multiple times, allowing you to familiarize yourself with the interview's flow, speakers' voices, and any subtleties. This attentive approach significantly enhances the accuracy of the transcription.
Use Transcription Software or Services if Necessary
For interviews demanding a high degree of accuracy, transcription software or professional services are invaluable. Dive.io, an AI -powered transcription tool, offers a solution tailored for interview transcription.
Its ability to accurately identify speakers and provide time codes ensures your transcript mirrors the original conversation's nuances. This is particularly important for qualitative research interviews and legal documents. Dive.io's effectiveness is rooted in its AI technology, which delivers seamless accuracy and saves valuable time, allowing you to focus on extracting meaningful insights .
Whether you're conducting interviews for market research in the healthcare industry, legal documents, or business decisions, accurate interview transcription is vital. Utilizing sophisticated transcription solutions like Dive.io streamlines the process, ensuring effective communication and accurate documentation of crucial conversations.
This is particularly relevant in industries like healthcare, where quality care, precise communication, and legal compliance are paramount. Dive.io emerges as a dependable tool, bridging language barriers and ensuring your transcripts reflect the interview's substance with a high degree of accuracy.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus, mi quis viverra ornare, eros dolor interdum nulla, ut commodo diam libero vitae erat. Aenean faucibus nibh et justo cursus id rutrum lorem imperdiet. Nunc ut sem vitae risus tristique posuere.
Enjoyed this read?
Stay up to date with the latest remote work insights from our research lab

October 16, 2023

September 11, 2023
Related Articles

How to Write a Perfect Meeting Purpose Statement?

The Perfect Guide to Fast and Efficient Meetings

The Best Way to Start a Meeting

A Guide to Safety Committee Meetings
Dive into your best meetings today!
Free forever plan
No credit card required
Cancel anytime

80+ Sections
Built in Canada, India, Israel, Italy, Colombia, and USA.
Transcribing interviews for qualitative research

Transcribing interviews is an important step in qualitative research, as it forms the backbone of data analysis and interpretation. In other words we can say that it acts as a vital link between those unfiltered conversations and insightful data acquired from them. But why is accurate transcription so crucial in qualitative studies?
The fundamentals of qualitative research itself provide the first justification. The depth with which linguistic expressions and emotions are communicated during interviews is crucial for this kind of research. Accurate transcription ensures that these non-verbal cues are also added for more clarity.
Transcribing interviews qualitative research is essential to ensuring the correctness of findings because it enables researchers to fully capture the range of participant replies and perspectives. Moving forward in this article we have compiled a comprehensive guide to help you get a more clear perspective on how to transcribe interviews for qualitative research.
What Is qualitative research?
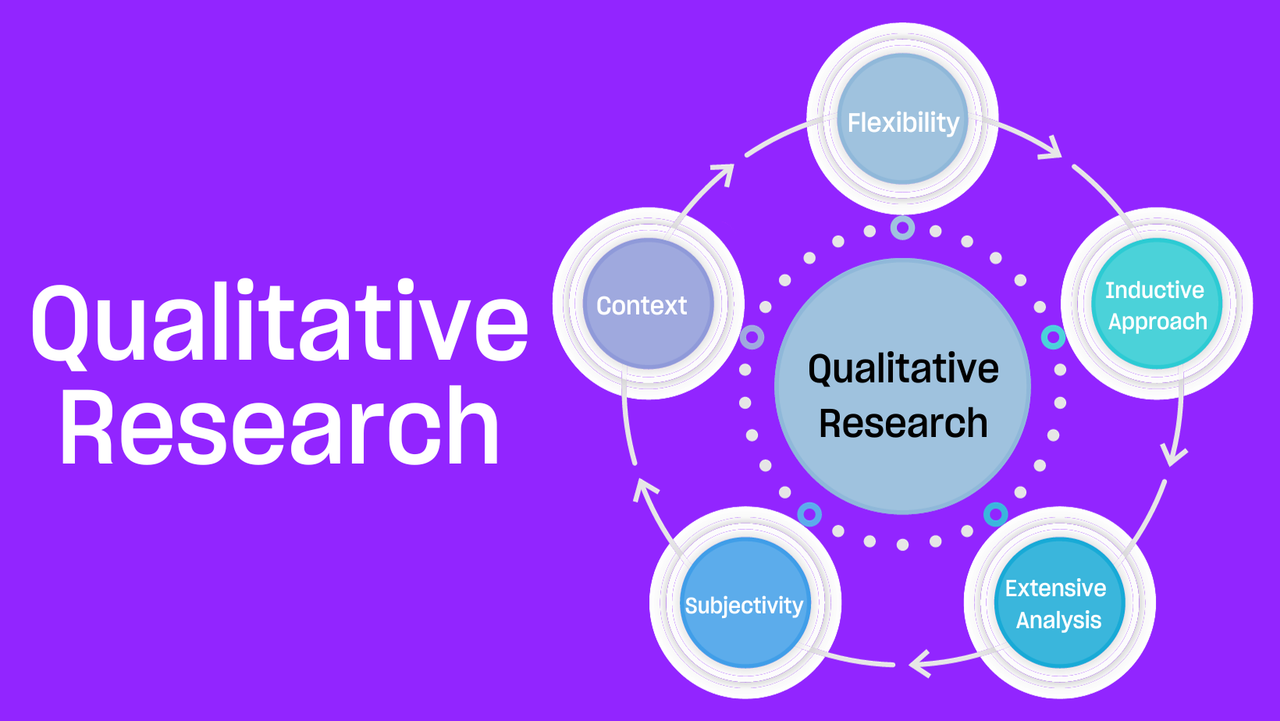
Qualitative research is one of the most commonly used research methods in the field of academia. Instead of concentrating just on the what, where, and when of decision-making, it explores the why and how by focusing on the human aspects of a specific issue or situation. It aims to comprehend people's experiences, actions, feelings, and the interpretations they place on objects.
Getting a much deeper insight into people's attitudes, actions, value systems, concerns, motives and goals is the main aim of qualitative research. It is employed to acquire a deeper comprehension of intricate occurrences that are challenging to put into numerical form.
The main characteristics of qualitative research are:
- Focus on context: It explores the context in which behaviours and events take place.
- Subjectivity: It recognises the subjective nature of the study and frequently captures the perspectives of the participants.
- Extensive analysis: This entails a thorough examination of a limited number of case studies or circumstances.
- Inductive approach: The inductive approach often begins with observations and builds theories from them.
- Flexibility in design: As the study goes on, the research question format may change. Here it is not necessary to follow the predetermined context.
Researchers use qualitative interview as their main method of data collection for this research since it allows them to interact with the subject first hand and focus on the non-verbal cues along with the information they are sharing.
Looking for support in transcribing your qualitative research interviews? Good Tape offers transcription services that can help you better understand your interviews. We're here to help make your transcription process more manageable and efficient. Explore how Good Tape can assist you in your research endeavors .
Qualitative vs quantitative interviews

Qualitative and quantitative interviews are different research approaches, each with a unique strategy for collecting and interpreting data. Quantitative interviews seek to measure human behaviour and experiences in a form that can be statistically examined, whereas qualitative interviews concentrate on investigating and comprehending the depth and complexity of human behaviour and experiences.
While both are extensively used in the field of research, it is important to understand where either of the two should be used. Below is a comparative table of both against which you can determine which of the two would work best in your scenario.
This table presents a clear contrast between qualitative and quantitative interviews, highlighting the differences in their technique, strategy, and study conclusions. The choice between both majorly depends on the research question at hand and the nature of the topic being studied.
How to transcribe an interview for qualitative research

For qualitative research, transcription of interviews is a painstaking procedure that needs time and close attention to detail. It requires turning spoken words from your recorded audio or video into text.
In qualitative research, this transcribing procedure is essential to data processing. Here's a step-by-step tutorial on effectively transcribing interviews, along with a few tips to make the process as easy as it can be.
Record clear audio of the interview
Select a peaceful, quiet workstation for your interviews to reduce distractions and improve focus. It is important to have a well-positioned microphone and high-quality headphones if you want to record even the minute details of speech without picking up excessive background noise.
If there are any unpleasant noises in your audio, services like Good Tape can be quite helpful. They are made to carefully pick up on all spoken and nonverbal cues, even in busy settings, and automatically transcribe all your work for you, so you won't miss any important information.
Work around your transcription
Precise transcription is essential for detailed analysis, accurately recording each word and nonverbal cue. This comprehensive approach allows for a deeper understanding of both the verbal as well as non-verbal cues in communication.
Similarly, intelligent verbatim concentrates on streamlining the text by eliminating unnecessary words and sounds to focus on the primary concepts, resulting in a transcript that is more focused and structured. Revised transcriptions enhance the material by improving clarity and fixing grammar, guaranteeing that the final transcript is accurate, comprehensible, and cohesive.
Audio transcription services such as Good Tape make accurate transcription easy with a shorter turnaround time.
Finalise the transcript
For easy navigation and the identification of important points or sensitive parts within the text, transcript formatting consistency is essential. Consistent formatting facilitates reading and improves the transcript's overall usefulness.
A further crucial stage is anonymisation, which anonymises any confidential or private data to comply with legal regulations. This also gives the interviewees peace of mind knowing that the information they provide will not be used illegally. To ensure that the transcript is correct, well-written, and presented professionally, one last review is necessary to spot any spelling, grammatical, or flow errors.
Some useful tips
Manual transcription can take a lot of time, therefore patience is essential. However, if you wish to have accurate transcripts in less time, using services such as Good Tape can cut down on the amount of time required.
It's also very important to make sure that your transcribed documents are safe. Maintaining regular backups is essential to avoiding data loss. Using services that automatically store and back up your transcribed audio might be a sensible choice if you find it difficult to remember to do backups, since they provide efficiency and peace of mind.
Why accurate transcription matters in qualitative research
Precise transcription is essential to qualitative research because it supports the accuracy and essence of the whole research process. It is the first stage of data analysis and has a direct impact on the findings and recommendations of the study. There are several reasons why accurate transcribing is important and advantageous.
Impact on data analysis
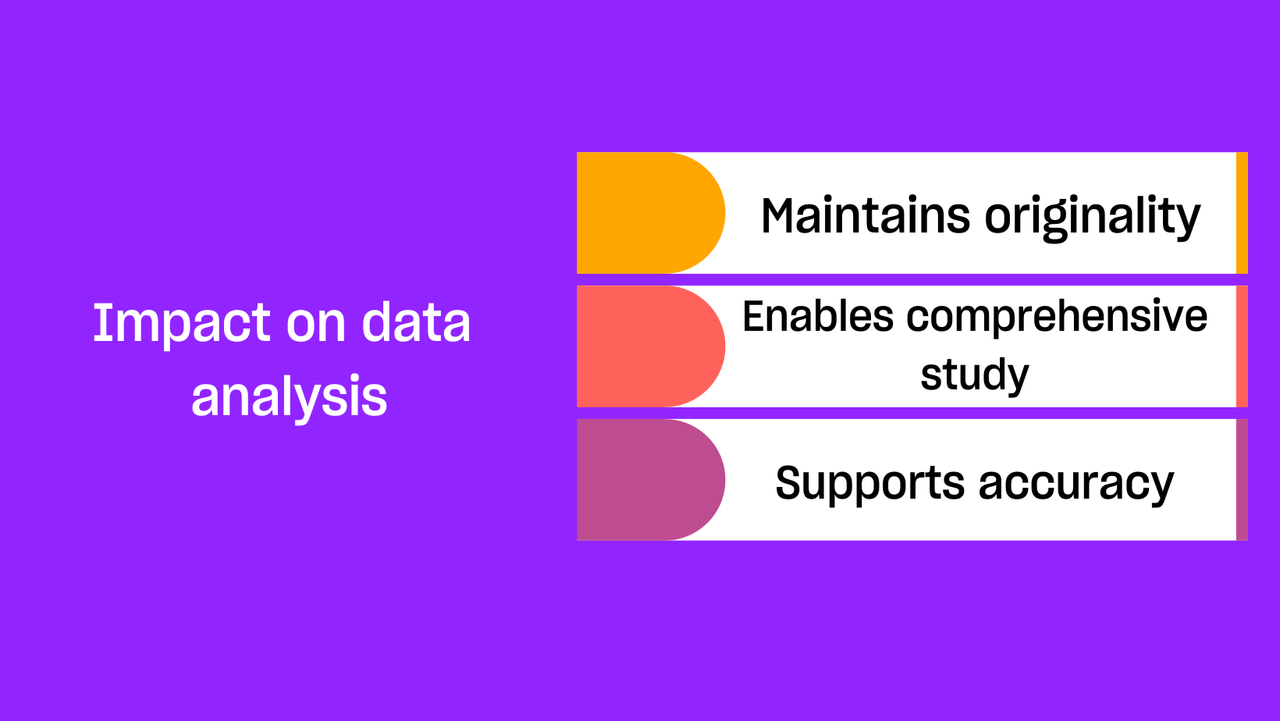
- Maintains originality: Preserving the original context of spoken words is ensured via precise transcription. For accurate interpretation of the data, this is essential.
- Enables comprehensive study: If the transcription has even minute error, it may prevent researchers from doing a thorough study of the interview data, including discourse, theme, and content analysis. Conversation analysis requires a lot of details which is possible through detailed notes of its accurate transcription.
- Supports accuracy: Data analysis in qualitative research is a very crucial step. More valid findings are produced when transcripts are accurate because they give researchers a solid foundation.
Impact on research outcomes

- Validity of findings: The reliability of the study findings is directly impacted by the quality of the transcribing. Inaccurate conclusions may result from word misinterpretation or omission.
- Reliability and reproducibility: A key component of scientific investigation is replication, which is made possible by accurate transcribing, which also increases the research's dependability.
- Reflects the voice of the participant: Accurate transcribing preserves the integrity of the participants' contributions by correctly capturing their voices.
Benefits of accurate transcription
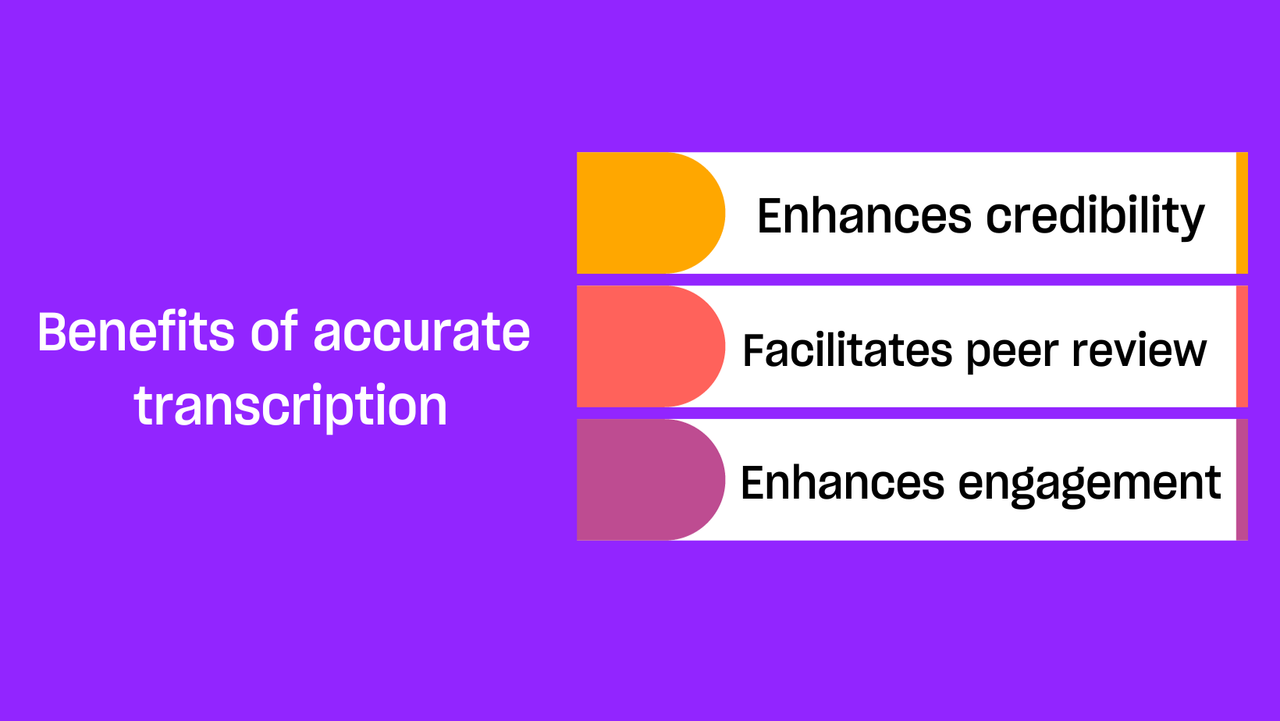
- Enhances credibility: Precisely recorded information strengthens the credibility of the study among other researchers and readers
- Facilitates peer review and cooperation: Because other researchers can comprehend and analyse the data with clarity, it makes effective peer review and cooperation possible.
- Enhances engagement with data: When data is precisely translated, researchers may interact with it at a deeper level, which results in more perceptive analysis and interpretation.
Accurate transcription plays a crucial role in maintaining the validity, reliability, and integrity of the research findings. It improves the quality and depth of data analysis, guaranteeing that the conclusions are solid, reliable, and accurate representations of the experiences and viewpoints of the participants.
Discover Good Tape’s interview transcription service
We’ve understood in depth how to transcribe interviews for qualitative research, let’s go over how you can do so accurately and quickly without having to put in much effort. Good Tape has a relatively simpler user interface which you can navigate through without any manual or instructions. Here’s what you can expect when going through the process of transcribing your audios.
- Upload your file: The first step in the process is to upload the file you need to transcribe. Make sure the file is complete and has all the information you require
- Select the language: Good Tape has a number of options when it comes to choosing the language of transcription. Select the one you want, although you can also choose the “auto-detect” option for the system to automatically identify the language in the audio.
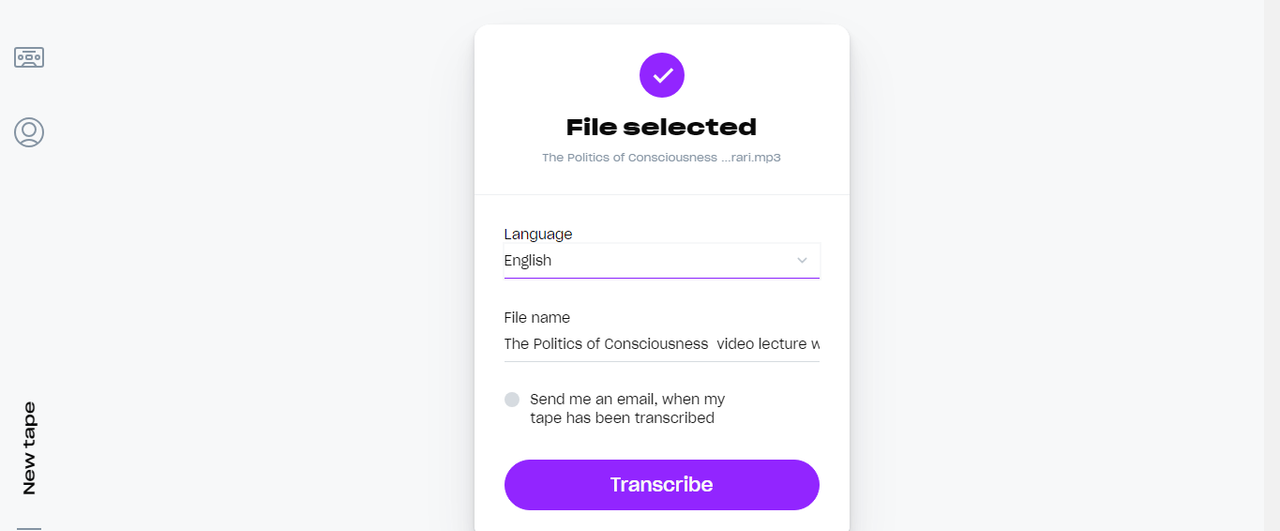
- Transcribe the text: Once the file is uploaded and the language is chosen, proceed further by clicking the “transcribe” button. Your audio transcription process starts here.

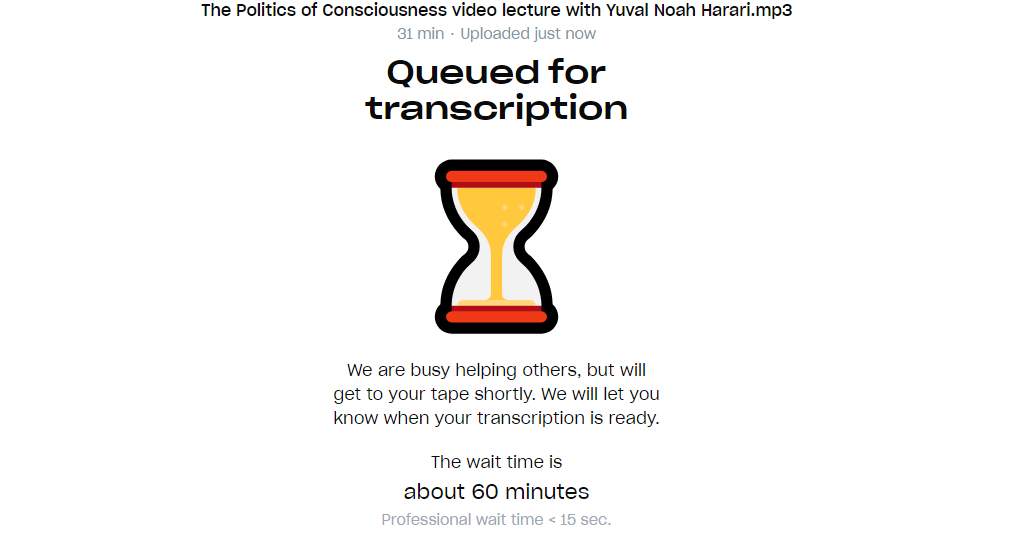
- To wait or not to wait: If you’re a casual plan user, you will have to wait for some time for your transcription to be completed due to excessive load by the users. However, if you’re a professional or a team user, you get your results ASAP! The wait time depends on the plan you’re subscribed to .
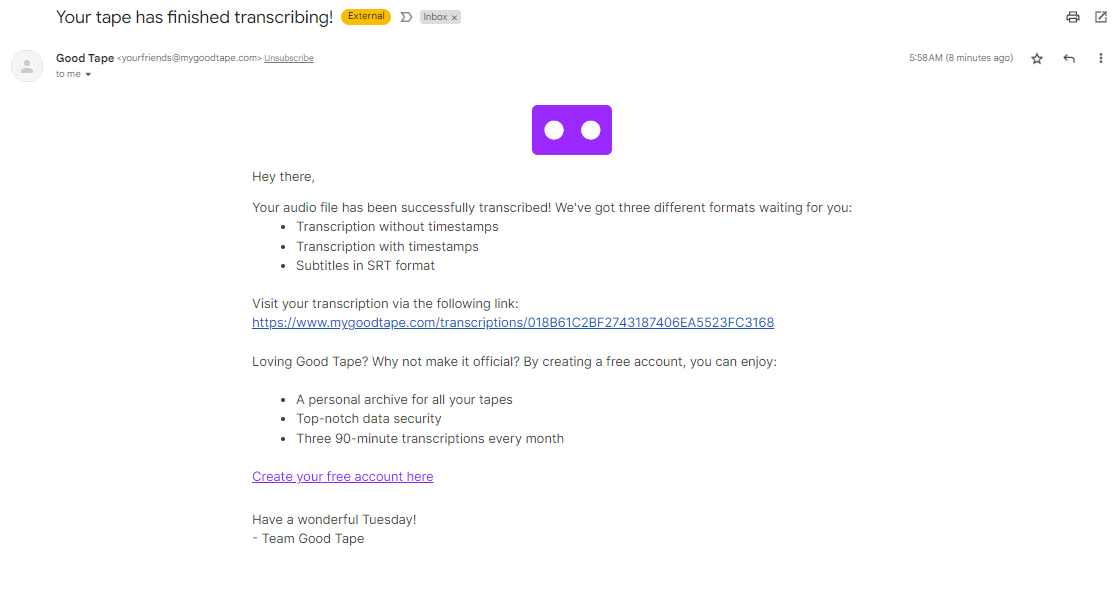
- Get notified: You will receive a notification once your transcribed document is ready. An e-mail will be sent to your inbox containing the link to access and download the document.
Looking for a good transcribing interviews qualitative research service? Try out Good Tape’s audio-to-text transcription service today and increase your work productivity. Their AI incorporated technology makes sure that every verbal and non-verbal cue is recorded, giving your qualitative data a deeper level of understanding.
More articles

Journalistic interview: How to interview someone for an article

From text to context: A complete guide to qualitative data analysis

What is verbatim transcription?

The essential transcription services for qualitative research
We believe everyone should have access to top-quality automatic trancriptions.
That's why Good Tape is completely free to use . No credit card required.
Why is it free?
How to Do Interview Transcription for a Dissertation?

Transkriptor 2024-04-23
Interview transcription is a key step in the dissertation process, transforming audio or video interviews into written text. This step allows researchers to closely analyze their data, providing a solid base for their findings.
Accurate transcription is vital in the dissertation process, turning spoken words from interviews into a written format that forms the backbone of qualitative research. It allows researchers to engage deeply with their data, marking significant sections and swiftly navigating through insights, thereby reinforcing the foundational evidence required for a compelling dissertation.
Meet Transkriptor , a leading speech-to-text tool designed to elevate the transcription process for researchers. This tool stands out for its ability to deliver precise, efficient transcriptions, making it an indispensable asset for dissertation work. By leveraging Transkriptor, researchers can ensure that their transcription process is not only faster but also more accurate.
The 6 steps to do interview transcription for a dissertation are listed below.
- Sign Up/Log in to Transkriptor: Create a new account or access an existing one.
- Upload/Record the Interview: Either upload audio/video files from your device or directly record the interview within Transkriptor for transcription.
- Start Transcribing Interview: Choose the language of the recording and let Transkriptor's AI technology accurately transcribe the speech to text.
- Review and Edit: Review and make adjustments to the transcription, ensuring it accurately reflects the interview content.
- Download or Share: After finalizing the transcript, download it in formats like TXT, SRT, or Word, or share it directly from the platform.
- Use the Transcriptions for Analysis: Utilize the accurate and detailed transcripts for in-depth analysis, identifying patterns, themes, and insights in your research.
Step 1: Sign Up/Log In to Transkriptor
The first step for researchers is to either sign up for a new account or log into an existing one on Transkriptor. This platform caters specifically to the needs of academic transcription, providing a streamlined interface for ease of use. Researchers can create an account using their Google accounts or an email address.
Upon completing this initial step, access to Transkriptor's dashboard is granted, allowing for immediate start on transcription tasks. This simple and straightforward process ensures that researchers can quickly begin their work, leveraging the platform's capabilities to facilitate their dissertation transcription needs.
Step 2: Upload/Record the Interview
After logging in, researchers have the capability to upload or record their audio or video files to Transkriptor. Simply click on the “Record” button to start recording. The platform supports a wide range of file formats, including but not limited to MP3, MP4, WAV, and MOV, accommodating virtually any type of audio or video recording used in academic research. Uploading is made flexible through options to drag and drop files directly into the platform or import them from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive or OneDrive. This feature ensures a seamless and secure upload process, allowing researchers to quickly proceed with their transcription tasks without worrying about compatibility or access issues.
Also, consider using Meetingtor . It attends and records the meetings in your calendar and stores them. With one click on the platform, users can get transcriptions via Transkriptor.

Step 3: Start Transcribing Interview
After uploading, researchers start the transcription process on Transkriptor by selecting the recording's language with one click. The platform's AI technology then accurately transcribes speech to text, supporting a broad range of languages to meet diverse research requirements. This ensures precise capture of spoken words, essential for qualitative analysis.
Step 4: Review and Edit
Transkriptor offers an editing feature that allows researchers to review and tweak the transcript while it's being created. This means immediate corrections can be made, helping to make sure the transcript matches the original recording closely. Being able to edit on the go is crucial for catching important details and ensuring the transcript accurately reflects the interview.
This process not only makes work easier but also improves the quality of the final transcript, which is important for research that relies on detailed and accurate data. Through Transkriptor, researchers can be confident that their transcripts are both precise and true to their source material.
Step 5: Download or Share
After editing their transcript, researchers can add details like speaker names and timestamps for clarity. Transkriptor allows downloading in various formats such as TXT, SRT, or Word , suiting different needs. For sharing, the platform enables direct distribution, making it simple to collaborate with others or submit work. This feature ensures transcripts are easily accessible and ready for any next steps in the research process.
Step 6: Use the Transcription for Analysis
Researchers proceed to analysis by coding and organizing data based on the dissertation's methodological framework after completing transcription. This involves identifying patterns and themes and providing meaningful insights from the interview content.
Moreover, researchers can leverage Transkriptor's AI chat feature for additional support during their analysis. This innovative tool assists in interpreting and organizing transcribed data. By integrating AI chat assistance with traditional analysis methods, researchers can navigate the coding process with greater accuracy and generate robust, meaningful outcomes in their research endeavors, making Transkriptor an invaluable ally in qualitative research.
Why is Transcription Crucial for Dissertation Interviews?
Transcription plays a crucial role in dissertation interviews. It accurately captures and preserves spoken words, ensuring data integrity and reliability. Researchers prefer working with transcripts for analysis despite the accessibility of audio and video recordings. This preference arises from easily handling tangible transcripts, facilitating quick access and annotation.
Digital recorders and cameras make recording easy, but transcripts remain more manageable for detailed analyses. Researchers find it advantageous to shuffle pages and mark transcripts with a pencil. The familiarity and convenience of working with paper transcripts persist, even with the availability of qualitative data analysis software. Traditional transcription methods remain the norm for interviews and recordings involving people.

How to Prepare Before Transcribing Dissertation Interviews?
Researchers prepare before transcribing dissertation interviews by considering essential factors. This phase involves organizing recordings, investing in quality equipment, and setting up an efficient workspace.
The steps to prepare before transcribing dissertation interviews are listed below.
- Review Interview Objectives: Gain a clear understanding of the research aims and contextual details.
- Ensure Good Quality Recordings: Focus on acquiring clear and crisp audio, minimizing background noise, and addressing technical glitches.
- Create a Comfortable Workspace: Establish an environment that promotes focus, concentration, and optimal listening.
- Understand Ethical Guidelines: Be aware of confidentiality requirements and relevant data protection rules.
Review Interview Objectives
Researchers initiate transcription by thoroughly reviewing the interview objectives. This involves gaining a clear understanding of the research aims and contextual details. Aligning transcription efforts with these goals ensures purposeful and insightful outcomes. Researchers must delve into key themes, critical topics, and specific study objectives for a detailed transcription decision-making process, fostering a deeper analysis.
Ensure Good Quality Recordings
Prioritizing high-quality audio recordings is essential for effective transcription. Researchers focus on acquiring clear and crisp audio, minimizing background noise, and addressing technical glitches. Checking for audio clarity involves evaluating factors like background noise and potential distortions. Starting with a high-quality recording establishes a reliable foundation for accurate transcription, ensuring an authentic representation of the interview content.
Create a Comfortable Workspace
Crafting a dedicated and comfortable workspace is crucial for the transcription process. Researchers establish an environment that promotes focus, concentration, and optimal listening. A well-designed workspace minimizes distractions, enhancing the ability to immerse in interview content. Consider lighting, seating arrangements, and equipment placement to optimize the workspace for transcription demands.
Understand Ethical Guidelines
Researchers engaging in transcription activities must possess a profound understanding of ethical guidelines. This involves being aware of confidentiality requirements and relevant data protection rules. Upholding ethical standards ensures the responsible treatment of interview participants and their sensitive information.
The commitment to ethical transcription practices includes obtaining informed consent, preserving anonymity, and safeguarding data confidentiality, contributing to the overall integrity of the research process.

What are the Challenges in Transcribing Interviews?
Researchers face critical challenges when preparing for the transcription process. Various hurdles impact accuracy and efficiency, requiring a keen understanding of effective mitigation strategies.
The challenges in transcribing interviews are listed below.
- Poor Audio Quality: Prioritize addressing poor audio quality for accurate transcription.
- Fast-Paced Speech Challenge: Fast-paced speech is difficult to follow and transcribe. Use transcription software or slow down the playback.
- Accents and Dialect Challenge: Navigating the variability introduced by accents and dialects in spoken language requires researchers to adopt specific approaches.
- Background Noise Challenge: Background noise hinders the transcription process, emphasizing the need to create an optimal recording environment.
- Technical Jargon Challenge: Researching technical or unfamiliar terms is essential for grasping their meanings for an accurate transcription.
Poor Audio Quality
Researchers must prioritize addressing poor audio quality for accurate transcription. High-quality recording equipment is pivotal in this process. Investing in noise-canceling software further enhances the clarity of the recorded content, ensuring the faithful representation of spoken words and eliminating potential discrepancies introduced by subpar audio.
Fast-Paced Speech Challenge
Fast-paced speech in transcription demands specific strategies. Utilizing transcription software with adjustable playback speed proves valuable. Slowing down the playback without altering the pitch lets researchers meticulously capture each spoken word. This detailed approach significantly improves transcription accuracy, especially with rapid speech patterns.
Accents and Dialects Challenge
Navigating the variability introduced by accents and dialects in spoken language requires researchers to adopt specific approaches. Familiarize yourself with the specific linguistic characteristics to overcome challenges related to unfamiliar accents. Seeking assistance from individuals proficient in the accent or dialect provides valuable insights, ensuring accurate transcription that reflects the intended communication.
Background Noise Challenge
Background noise hinders the transcription process, emphasizing the need to create an optimal recording environment. Conducting interviews in quiet settings minimizes external disturbances. Additionally, transcription software with noise reduction features proves instrumental in mitigating unwanted sounds during transcription. This dual approach significantly contributes to the overall accuracy of the transcription.
Technical Jargon Challenge
Ensuring accurate transcription when dealing with technical jargon requires a proactive approach. Thoroughly researching unfamiliar terms is essential for grasping their meanings. Alternatively, consulting with the interviewee or subject matter experts provides valuable insights and clarification. This meticulous approach guarantees the transcription captures the intended meaning, even when confronted with specialized language or terminology. Researchers navigate the intricacies of technical content with precision and clarity.
To Overcome Interview Transcription Challenges: Transkriptor
Transcription challenges such as poor audio quality, fast-paced speech, accents, background noise, and technical jargon can significantly hinder the accuracy and efficiency of the transcription process. To overcome these challenges, Transkriptor stands out as a robust solution, employing advanced AI algorithms for precise and reliable transcriptions, minimizing errors.
Transkriptor not only ensures that the transcribed text represents the spoken words but also streamlines the entire process, making it a comprehensive solution for enhancing dissertation transcription accuracy. Try it for free!
Frequently Asked Questions
It depends on your time, budget, and the level of accuracy required. Transcribing interviews yourself can be time-consuming but offers closer engagement with your data. Professional services, like Transkriptor, can save time and provide high-quality transcripts, but at a cost.
The format depends on your research needs. Verbatim transcription captures every word and sound, which is useful for detailed analysis.
Mark these sections with a standard notation (e.g., [inaudible] or [unclear]) and the timestamp. If possible, ask the interviewee for clarification on these parts. Consistency in handling these sections is key for accurate analysis.
Follow your academic institution's guidelines for citing primary research data. Typically, you would reference the interviewee (as per your ethics agreement), the date of the interview, and possibly a transcript reference number or page number.
Speech to Text
Transkriptor
Convert your audio and video files to text
Audio to Text
Video Transcription
Transcription Service
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service

Contact Information
© 2024 Transkriptor

Transcript Example (with Microsoft Word and PDF Templates)
This resource includes a transcript example from an interview, formatted in several different ways:
- Clean verbatim style
- True verbatim style
- Timestamps at regular intervals
- Timestamps at speaker or paragraph intervals
I made these .docx and PDF example transcripts for university students, educators, non-profits, journalists, podcasters, filmmakers, and transcriptionists.
Quick tip: If you’re not using it already, you can install free transcription software like Express Scribe to help you manually transcribe interviews much faster. The software lets you control audio playback using hotkeys so you don’t have to keep starting and stopping audio with your mouse.
If you want to go really fast, I also recommend getting a transcription foot pedal (I use the Infinity pedal ). Together, these two tools will save you hours upon hours of transcription time. (Or learn more about our interview transcription services .)
If you’re a professional content creator, you may also be interested in our posts about AI-powered tools for scaling up your audio and video production workflow:
- Best AI Video Upscaling Software
- Best AI Video Generators
- Best AI Video Editors
Now, on to the transcript examples!
This post may contain affiliate links. See my disclosure for more info.
Interview transcription format sample for Microsoft Word
Download this transcription format template for Microsoft Word for use with interviews and qualitative research projects:
Interview Transcription Template – Word (.docx)
Clean verbatim vs. true verbatim transcript examples
There are two main styles of transcription used in interviews and qualitative research:
- Clean verbatim (also called intelligent verbatim or non-verbatim).
- True verbatim (also called strict verbatim, or simply “verbatim”).
A clean verbatim transcript is a lightly edited version of the original audio. Typically, the following elements are removed:
- Filler speech, including “um,” “uh,” etc.
- Most non-speech sounds, including coughing and throat clearing
- False starts
A true verbatim transcript, on the other hand, attempts to capture every utterance of the speakers. These include stutters, meaningless filler speech, and false starts. Verbatim style may also include non-speech and background sounds, such as coughing and sneezing or a door closing.
While each transcription style is useful under certain circumstances, clean verbatim is used most often because the transcripts cost less and are easier to read.
However, true verbatim may be desirable for certain qualitative and market research projects and legal investigations, where it’s necessary to study not only what was said, but also the manner in which something was said.
Below, I’ve included examples of an interview transcribed in both verbatim and clean verbatim fashion.
Example transcript in true verbatim style
Here’s a sample interview transcript that demonstrates the true verbatim style:

Download the PDF version here: Interview Transcript Example – True Verbatim (PDF)
Example transcript in clean verbatim style
And here’s the same conversation from above, transcribed in clean verbatim:

Download the PDF version here: Interview Transcript Example – Clean Verbatim (PDF)
We made the following changes to the second (clean verbatim) transcript:
- We edited out stutters, partial words, and short incomplete sentences.
- We removed meaningless instances of words like “so” at the start of sentences, and “like” when used as filler speech. (However, we left in the word “like” where removing it would have made the meaning literal when it wasn’t intended to be – i.e., when Brad refers to his “like, two” Facebook friends.)
- We chose to leave in the laughter, as it helps capture the overall tone of the interview and the banter occurring between the speakers. We also left in nonsense exclamations like “Uh … phew,” because it helps set the context for what follows. However, we removed other non-speech sounds like coughing and throat clearing that do not contribute anything useful to the content.
- In this particular example, we opted to remove repetitive instances of the word “actually” spoken by Brad, the interviewee. Normally we leave longer words in, but in this case we felt it was a speaker idiosyncrasy that distracted from the content of the interview.
Clean verbatim style is not an exact science, and sometimes there may be overlap between non-verbatim and verbatim styles in a transcript. All in all, the changes we made here make for a cleaner, less distracting, and more valuable interview – without detracting anything meaningful from the original.
Sample transcript with timestamps at regular intervals
Some projects require timestamps to be placed at regular intervals in the transcript so the audio can be easily referenced later.
Below is an example of an interview transcript with timestamps:

Download the PDF version here: Interview Transcript Example – Timestamps at Regular Intervals (PDF)
Sample transcript with timestamps at speaker intervals
Another way to timestamp a document is to place the timecode markup at speaker or paragraph intervals, like in the following interview transcript sample:

Download the PDF version here: Interview Transcript Example – Timestamps at Speaker Intervals (PDF)
Transcript format tips
There are several formatting elements common to most transcripts. These include speaker labels, timestamps, inaudible and crosstalk tags, and markup for external sounds. Let’s look at how to handle each of these:
Speaker labels. Speakers are typically identified by first name, full name, title, or role. They can also be identified by generic descriptors, like “Male” or “Female,” when other information isn’t available.
In the above examples, the speakers’ names have been offset from the rest of the transcript for better readability. To use this formatting in your own transcripts, download the .docx template at the top of this article.
Timestamps. Timestamps, e.g. [01:27] , can be placed at regular intervals such as every 15 or 30 seconds, or they may be placed at the beginning or end of each paragraph or speaker. Examples of each style are shown above.
Inaudible tags. When words or phrases are unclear, mark them out with a timecode; e.g., [inaudible 00:27] . You can also include guesses (phonetic or otherwise) as to what was said – for example, [wing yard 00:27] .
Crosstalk tags. When two or more speakers are talking at the same time and it’s impossible to hear what’s being said, use a crosstalk tag, e.g. [crosstalk 01:27] .
Sounds. Non-speech and background sounds are notated in brackets; for example, [laughing] or [door slams] . No timestamp is necessary.
Finally, a note on consistency and style: It’s best to follow a style guide to ensure consistency among elements like numerals, dates, titles of works, etc. We generally follow AP style . Other common style methods include APA , MLA , and The Chicago Manual of Style .
If you’re thinking of starting a career in transcription, check out my complete guide on how to become a transcriptionist . I also recently posted this list of 75+ transcription jobs for beginners and pros.
If you have any questions about using the example transcripts above, leave a comment and I’ll do my best to help!
Similar Posts
![thesis interview transcript 6 Best AI Video Editor Tools [Ranked and Reviewed]](https://www.mondayroadmap.com/wp-content/uploads/ai-video-editors-768x480.png)
6 Best AI Video Editor Tools [Ranked and Reviewed]

4 Best Transcription Foot Pedals for Professional Audio Transcribers

7 Best AI Video Generator Tools (Text to Video)

15 Best Podcast Analytics Tools to Measure Your Show’s Growth

6 Best Private Streaming Platforms for Securely Broadcasting Live Events
![thesis interview transcript 6 Best AI Video Upscaling Software [Free and Paid]](https://www.mondayroadmap.com/wp-content/uploads/ai-video-upscaling-768x480.png)
6 Best AI Video Upscaling Software [Free and Paid]
23 comments.
thanks a lot for this. I appreciate th above lessons. at the moment lets keep the above into practice.
You’re very welcome! I’m glad you found it useful.
Very very helpful. For sure, God bless you.
Thank you. I’ve recently launched my own company in ghostwriting & editing, and typing & transcription services. These tips are GREAT reminders. God bless you.
Thank you, Mrs. Owens!
Handy for a beginner like me.
Thank you very much, really help me to do my assignment
I’m glad to hear that!
Hello, I don’t know how to thank you ,these instructions are very helpful and useful and real ,and how to contact you if I need any help.
I’m so happy you enjoyed the post! While I’m not always available to respond directly to questions, I always appreciate receiving suggestions about what kind of content you’d like to see me write about in the future. So if there’s a particular topic you have in mind, please feel free to reply and let me know. Thanks so much for commenting!
Your information is very valuable. My problem is, I need to find a resource that tells me how to set up the formatting in MSWord 2016. Setting the speaker tags and margins so it all lines up. If you have any link you could direct me to, or if you can explain how you do that, I would be forever grateful. Thanks, Lorri
I’ve been meaning to get a refresher on formatting myself and recently bookmarked this comprehensive tutorial on MS Word 2016: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TxLuuNprjXg
I haven’t watched it yet, but there’s a clickable table of contents in the video description and it has some sections on formatting and adjusting margins. I hope it helps!
how to name an interview transcript document?
If you’re doing the transcript for a client or professor, you should typically give the document the exact same name as its corresponding audio file; for example, “Interview with Sahar.mp3” would be titled “Interview with Sahar.docx”.
If you’re recording the audio yourself and there are a lot of files, it’s best practice to use some kind of file naming convention to keep everything organized. One easy way to do this is to use a date prefix; for example, 2019-05-30_Interview_with_Sahar.mp3.
I hope this helps!
Thank you so much for this guide. I am just about to embark on Transcription services as a full time activity and will be grateful for any mentoring and encouragement
You’re very welcome! Since you’re just getting started, I recommend visiting the following resources:
My complete guide on how to become a transcriptionist: https://www.mondayroadmap.com/how-to-become-a-transcriptionist/
My list of 75+ companies that hire work-from-home transcribers: https://www.mondayroadmap.com/online-transcription-jobs/
All the best in your new transcription career!
Thank you, this was very helpful.
Glad to hear it, Cony! Thanks for commenting.
This was really really helpful. Thank you so much.
Thank you for reading!
Hi, I’m just getting started transcribing hours of interviews. This article is a life saver. Really helpful, accessible, clear and the .pdfs are really useful allowing me to see what the finished transcription should look like. Thank you so very much.
You’re so welcome, Shaz! Thank you for reading!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
Published on 6 May 2022 by Raimo Streefkerk .
Transcribing is converting speech to text word for word. Transcribing is a common practice when conducting interviews because it enables you to perform analysis.
How to transcribe an interview in five steps:
- Choose your preferred transcription method.
- Transcribe the audio (using transcription software ).
- Add speaker designation and time stamps.
- Clarify the transcript where needed.
- Proofread the transcript.
Transcription software comparison
Table of contents
Transcription methods, altering the transcript, example transcript, analysing interview transcripts, transcription software.
Before you start transcribing, you first need to determine what transcription method you want to use. The best method depends on the goal of your transcription.
Verbatim transcription
Write down every single word, including pauses, the expression of emotions such as laughter, stuttering, and hesitations such as ‘uh’.
This type of transcription is mostly used in the legal profession or in research where you’re not only interested in what is said but also how it is said.
Intelligent verbatim transcription (most common)
Write down every word, but without irrelevant fillers like ‘um’, ‘yeah’, and ‘you know’. To improve readability, you can also fix grammar mistakes, broken sentences, and long paragraphs.
This method is more readable than verbatim transcription, but some data – such as emotions, pauses and hesitation – is lost in the process.
Edited transcription
A summarised and edited version of an intelligent verbatim transcript. In addition to omitting fillers like ‘you know’, irrelevant sentences can be omitted if it doesn’t change the meaning of the story.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
If the audio quality is bad or the conversation itself needs clarification, you are allowed to make changes in the transcript. For instance:
- Adding a clarifying comment: ‘I showed him that this option [raising prices] would be beneficial for profitability.’
- Marking unclear or missing audio with ellipses: ‘I showed him … would be beneficial for profitability.’
- Emphasising words: ‘ Increasing prices is needed for profitability.’
There are no rules for formatting and structuring a transcript. However, most transcripts contain the following information:
- Names of the interviewer and interviewee (can be anonymised)
- Date and time when the interview took place
- Location of the interview
- Speaker designation (who says what?)
- Line numbers and time stamps (optional)
After transcribing the interview(s) it is time to start analysing. There are several techniques for doing this – coding and categorising is one of them.
This means that you link keywords (e.g., ‘understanding customer’) to the answers you’ve received to your questions. Based on these keywords you are able to find connections between the answers of different respondents.
You can also use methods such as content analysis , thematic analysis , or discourse analysis .
If you quote from an interview in your paper, make sure you correctly cite the source. Learn how to cite an interview in MLA and APA .
Transcribing interviews takes a lot of time, but luckily transcription software is developing quickly. Using transcription software can help you speed up the process.
Most software is able to accurately convert English speech to text. However, the audio quality must be good in order for the software to work. That means a noise-free background, no over-talk, clear accents and good microphones.
If the audio quality is too poor for automatic transcription, you unfortunately have to dictate it or transcribe it manually.
We tested and reviewed the transcription software below using the audio of a YouTube video in which Bill Gates is interviewed . The audio meets all the criteria listed above.
Happy Scribe
- Speaker recognition
- Clean and intuitive editor
- Omits ‘uhs’ and stuttering
- Correct capitalisation and use of full stops
- 25% student discount
- Doesn’t insert punctuation (except for full stops)
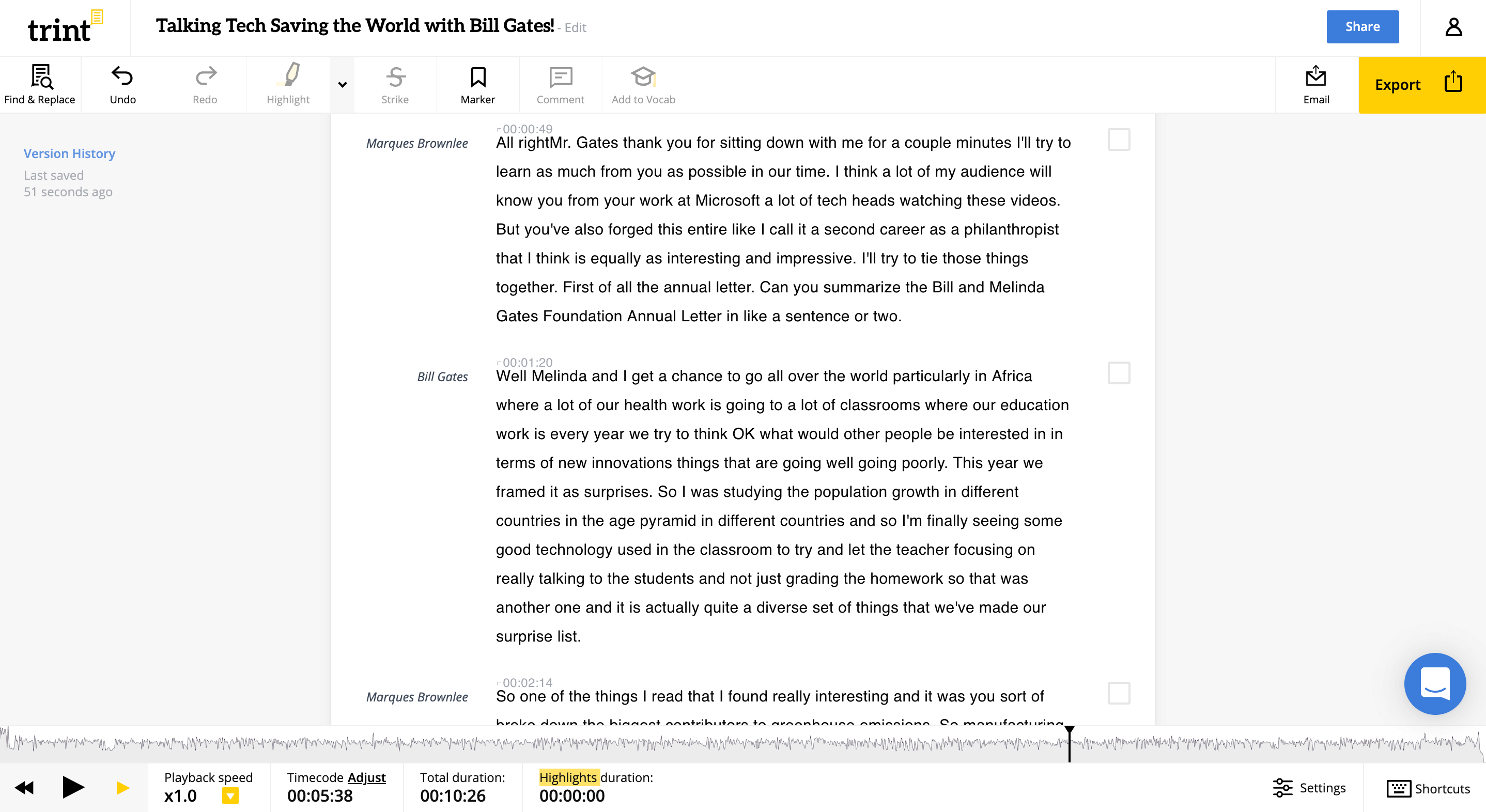
- Good speaker recognition
- Simple but powerful interface
- Comment and highlight feature
- Ignores intro music from video
- Easy to keep track of reviewing progress
- Some missing spaces
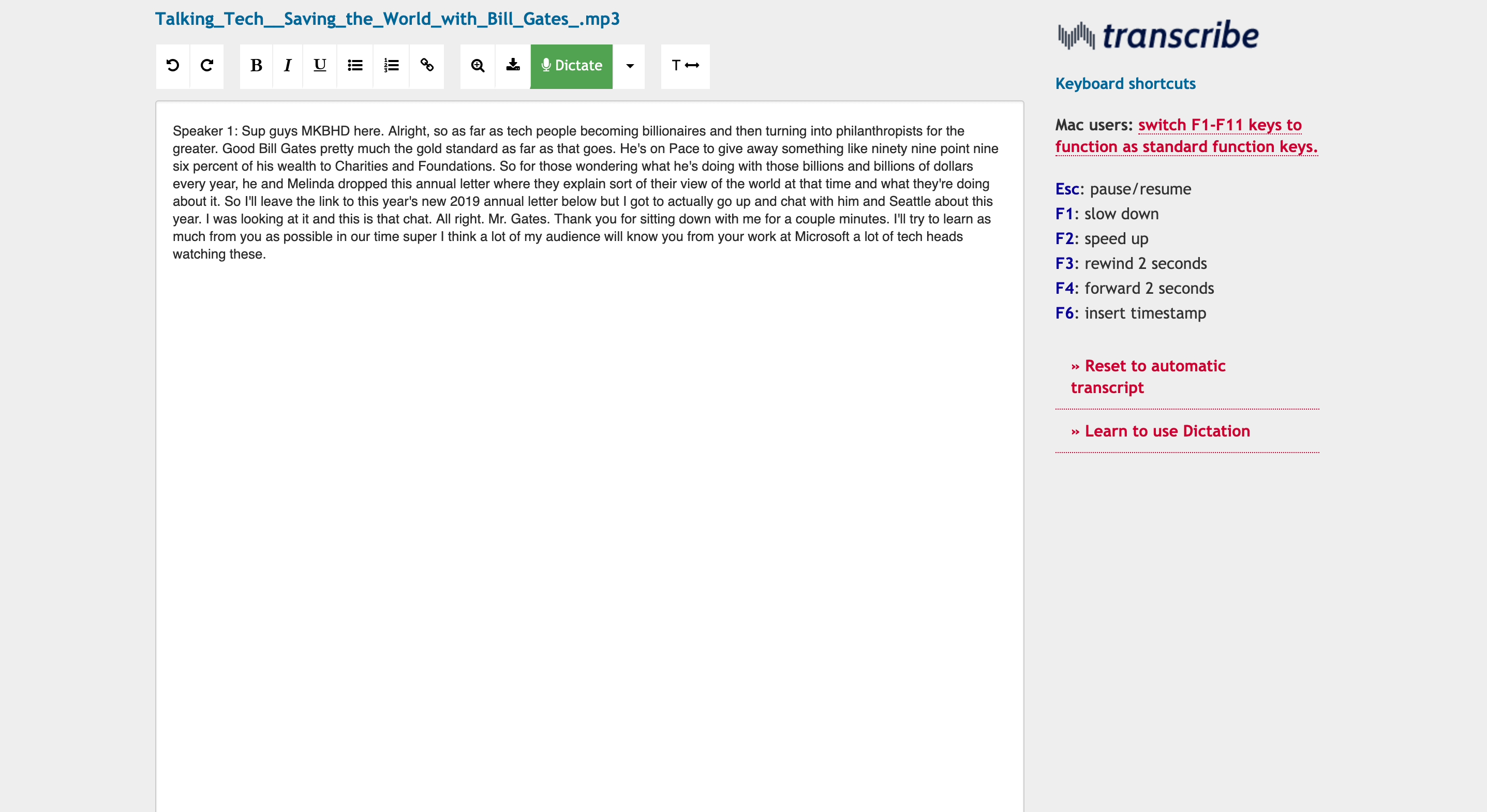
- Solid speaker recognition
- Very good capitalisation and punctuation (including commas)
- Much cheaper than other transcription software
- Just a 1-minute trial
- Dated editor with limited functionality
- Doesn’t connect audio and transcript
- $20 (approx. £16.25) annual licence fee
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2022, May 06). Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/transcribing-an-interview/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, doing survey research | a step-by-step guide & examples, types of interviews in research | guide & examples, structured interview | definition, guide & examples.

How To Transcribe an Interview for Dissertation – Part 2
“[I]t is a truism to note that all transcription is in some sense interpretation …” (Cook, 1990, p.12)
In the first post (please read!) of this 2 part series on how to transcribe an interview for dissertation, I gave you on overview of the transcription process, equipment you’ll need, 3 ways to transcribe your interviews and made a few remarks on accuracy of the transcripts, and recording high quality interviews (check out this post on choosing a voice recorder for your data collection).
In this second and final post in this series on how to transcribe academic interviews for dissertation I get into the minutia of transcription. How do you transcribe? What are the different ways you can transcribe your thesis interviews (with examples)?
How do you transcribe interviews for dissertation?
Speaker identification.
How do you transcribe, what do you do when you are transcribing? Things you need to think about as you transcribe are first the names of respondents. It is useful to just use a standard format for entering the names. I suggested some of them here.
You can put the person’s actual name and perhaps the initials letter of their surnames. So for Mary Clark, you can write Mary C on your transcript. Learn to be consistent, every time Mary talks you have the same letters in front of those speech. You can also identify the interviewee simply as “Interviewee” or “Respondent” or even “Resp”. Again be consistent.
For the interviewer you might have “I” for interviewer or IV, or INT or Intvr. You can put your name on it if you like, G for Gandalf and so on. But be consistent, so you use the same name all the time on the transcript to identify when the interviewer speaks.
At weloty we use Intvr: and Resp: as our default speaker identifiers.
You also need to think about the formatting of the speaker designation. The most common approach is have the name/identifier, and then you have the colon, and then indented text. In other cases some transcribers put the name of the speaker on a separate line. So there will be an identifier and then the next line the speech starts. You might also want to bold or italize the interviewer or the interviewee to make it easier for you to identify who is speaking. Here are some examples:
Jane= interviewer, Paul =interviewee
Tell me how you came to be a transcriber?
Well, it’s a funny story, I started transcribing when I was…
Intvr: Oh
Resp: Yes, and they keep referring their fellow students to my transcription site.
Intvr: Last question, what do you find to be the most challenging part when transcribing interviews?
Resp: That’s a difficult one. Most of the time it’s the audio quality of the interview that is..
Now, which format you use might depend on what software you plan to use for analysis. There are different standards for different kinds of software. So you think need to think about that. For instance, Atlas-ti or Nvivo require that their transcripts be formatted differently. But again read the manuals that come with the software. That there was no single best way of doing it, one program wants it done one way, one program another way. And some QDAs will accept different formats than others.
Anonymization
Anonymization of your transcripts is very important. As far as possible make sure that if anything is published when you do the research the name should be anonymized so that the names of people and contextual names like the organizations they work for, the towns they work in and so on, all of those are anonymized.
But you will need to keep the original names themselves. It’s common practice to keep the names on the transcripts during the analysis. So I have the original data with the original names on it. But when it is published then it gets anonymized at that stage.
On the other hand you might decide it is better anonymize it right from the start. The problem with that is you lose the context in your mind. For instance if you anonymized Mary to you respondent 2 or, June or something like that, so you have to remember June was actually Mary or respondent 2 was Mary.
Makes it slightly harder for you to think about what you are doing and what you can remember you have used there. So, that is why I prefer to keep it un-anonymised until the last minute, which you will need to do that eventually. But remember to publish only anonymized versions.
Checking for Accuracy
Checking for accuracy. What if you can’t hear things? Then use a standard thing like this square brackets 3 dots square brackets […], to indicate something missing. Something was said, but none of us can work out, the typist can’t, I can’t, we can’t work out what was said, just can’t remember it. So it is missing.
Other possibilities, [bribery?] Did the person actually say bribery? I am not really sure. So put it is in square brackets put question mark, just to indicate that you are not quite sure about what is being said. In this instances it might also be really helpful to insert timestamps. So […][00:05:34] to clearly indicate where the missing part is in the audio or [bribery?] [00:08:32].
Also printing with wider margins, because you are going to be writing on things. The idea is that when you start to code and work with this material you do write on it a lot. So double spacing or a spacing and a half, between the lines and wide margins to write in on the side of the page are really helpful, because you need space to write in those notes. You don’t always have to use them all the time. But you know some bits will be very detailed and lots of lines, lots of comments on the side, so leave space for them.
Transcript Format
Structure the transcripts. Two things I want to talk about here, 1) is to do with the software and a lot of these things depend on what software you are using. Some of it you simply do it consistently, so if you have got a structured questionnaire, where everybody gets asked the same questions, then make sure you use something like Q1, Q2 and the question perhaps, and always using exactly the same wording on everyone’s transcripts. So you can always be consistent about how do you find things, and how you search for things.
If you are going to use NVivo, put those questions headings in a heading style. Very similar to styles in Word. So NVivo uses the same style as word. So putting the Heading 1 style, when you upload the transcripts into NVivo, you could automatically code those headings as codes in the programs. Please contact us to discuss your NVivo transcription requirements, so we can decide what the best fit is for you.
Section format is another issue particularly if you are doing NVivo or Atlas-ti. Some software allow some use of automatic coding. For instance, I’ve formatted transcripts so that there were 2 kinds of returns between the speeches.
The speech was always the lawyer asking a question, and the witness replied. I had 2 returns, then the lawyer asking the questions, then a single return, then the witness replying and then 2 returns. I did that because the software the client was using automatically assign each of those speakers interchanges as a paragraph.
So again it needs reading the computer manuals to check, what is going on and how you can then set things up for what you need.
Styles of Transcription
I talked a little about this in Part 1 of this series, but let’s have a deeper discussion about the styles of transcription.
The problem is people don’t speak in whole sentences. They repeat themselves, they hesitate, they stutter, they talk in very long sentences. There are no fullstops in speech. They use contractions like don’t, coz, I’m and so on. And they use filler words as they hesitate, you know, I mean, err, mmh and so on, all sorts of different sounds.

The question is do you transcribe all those things that people do?
Do you spend time with all these issues, repetitions, hesitations and so on?
Now for some purposes you do do that. If you are doing conversation analysis then this is the kind of detail you need to transcribe.
So the question is how much of the interview interaction do we want to capture? I think there are 3 different ways of transcribing: what I call the intelligent verbatim approach, the (strict) verbatim approach, and finally Discourse or the Conversation Analysis, CA.
Deciding which approach to use largely depends on your research questions and the intent of the study. As an important step in data management and analysis, the process of thesis transcription must be congruent with the methodological design and theoretical underpinnings of each investigation.
Let me show you some examples of each of these approaches.
Intelligent Verbatim Approach
To begin with the intelligent verbatim approach. Now, I plan to pen Here’s a detailed guide on intelligent verbatim transcription . so keep your eyes peeled out for it .
Intelligent Verbatim Transcript Example.
Frank: True, it’s going to be the greatest in the history of the world.
Jon: I’d expect no less. I think it will put an end to the conflict in the Middle East, I mean quite possibly.
Frank: That’s true.
Jon: No, no I’m confusing that with a nuclear bomb. I’m sorry, yours is not going to bomb. Yours is actually going to do really well. But let’s share some ideas I want to run by you and then if I can get some information from you it’s going to help a whole lot.
This is snippet from a interview transcript between Jon and Frank. The purpose of the interview was to gather information on a product that’s being launched. So the intelligent verbatim approach works really well in this particular case. It reads fairly easily and from the transcript you can quickly get the information you need. This type of transcription is perfect for researchers using the grounded approach or analyzing for themes and categories.
Verbatim Transcription Approach
I have written a couple of detailed posts on verbatim transcription. The first is a general overview of verbatim transcription and the other a detailed verbatim transcription guide for psychotherapy interviews and sessions . Please refer to those posts for a more detailed guide on how to create verbatim transcripts. A short example.
Verbatim Transcription Example.
Frank: Oh true, it’s going to be the greatest in the history of the world.
Jon: I I I would expect no less. I think it will put an end to um to the conflict in the Middle East I mean quite possibly.
Frank: [CT] That’s true.
Jon: No, no way I’m I’m I’m confusing that with a nuclear bomb. I’m sorry, that’s that’s, yours is not going to bomb. Yours is actually gonna do really well. But ah [chuckles] let’s ah let’s share some, I guess I guess some ideas I wanna run by you and then if we can talk through um, if I can get some um information from you it’s gonna help a whole lot.
Same interview, different transcript. As you can see, there’s more detail of the interview interaction in the verbatim transcript as opposed to the intelligent verbatim transcript. Verbatim transcripts are great if you interested in the dynamics of the interview.
Discourse or the Conversation Analysis
Conversation analysis (CA) is a “unique” (ten HAVE 1990) form of qualitative social research. Books have been written about this approach to transcription = there is no enough space on this blog for me to adequately cover conversational transcription convections. But, I’ll provide you with a few references that you can use. Jefferson, Gail (1985). ‘An exercise in the transcription and analysis of laughter’ is a great starting point and a valuable entry point into learning more about the Jeffersonian CA transcription notation. I’d also recommend Ochs, Elinor (1979) ‘Transcription as theory’. Even for us non-discourse analysis researchers, it’s a great read. And for a critique: Ashmore and Reed (2000) Innocence and Nostalgia in Conversation Analysis.
Discourse Analysis Transcript Example.

Here is an image of a discourse analysis transcript. There are many symbols used conversational analysis transcription and creating an appendix of what each symbol denotes is the first thing you do before you begin transcription.
If you are going to use a conversation analysis approach you do need this kind of level of transcription of the data. But for most of us this is not relevant, even if you are doing discourse analysis, this is not relevant. Verbatim approach should get you what you want.
Dissertation Transcript Cover Page
As you transcribe interviews it is useful to have with them information about the interview itself, or about the case if there are separate interviews perhaps. So it is common to have a document headers sheet with the data. Again if you are doing it in software, then you keep it in a certain place. In NVivo document properties is a place where you keep this information.
Typically things you would have here are, choose the names. If you anonymize the interviewee’s name, use this cover sheet or document header sheet keep the pseudonym, you can separate it after the interview if you want to.
You can also add information about location, time, topic and circumstance, and add your interview notes. Also include the name of the interview, if you are in a team of people it might be useful to name who is interviewing the person.
If you are taking field notes as well, and I certainly would advice that if you are doing interviews to take notes as well recording the interview, you take notes about important things that you think about, or things that happen, or ideas that occur to you as you interview the people. So again link it or have the name of the document on the cover sheet.
Here’s a sample dissertation interview cover page you can use.
Interviewee: [Name of interviewee] [Pseudonym]
Interviewer: [Name of interviewer]
Date and Time: [mm/dd/yyyy][00:00]
Location: [Place interview was conducted]
Audio file information: [Name][Duration]
Link to field notes:
Link to follow up interview transcript:
Additional Notes:
That’s it on this series on how to transcribe your interviews for dissertation. If you have any burning questions post them below and I’ll be more than happy to answer them. And if you find transcribing your dissertation interviews to be a chore – get in touch . We’ll be glad to transcribe them for you.
References.
Ashmore, Malcolm & Reed, Darren (2000). Innocence and Nostalgia in Conversation Analysis: The Dynamic Relations of Tape and Transcript . Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 1(3), Art. 3.
Cook, Guy (1990). Transcribing infinity: Problems of context presentation. Journal of Pragmatics, 14, 1-24.
Have, Paul ten (1990). Methodological issues in conversation analysis. Bulletin de Méthodologie Sociologique, 27 (June), 23-51.
Jefferson, Gail (1985). An exercise in the transcription and analysis of laughter. In T. Van Dijk (Ed.), Handbook of Discourse Analysis, Vol. 3: Discourse and Dialogue (pp.25-34). London, UK: Academic Press.
Ochs, Elinor (1979). Transcription as theory. In E. Ochs & B. Schieffelin (Eds.), Developmental Pragmatics. New York: Academic Press.
Heĺlo I am doing a research which has some interviews. Now i want to write the interview in the dissertation. Hiw can you help ne, please. Thank you, shahab.
Shahab, for to be able to assist you, I’ll need to know more about your research methodology. For instance, have you conducted and recorded the interview? How do you plan to analyze the data you collect…?
Regards, Isaac
Can you provide a sample interview transcription chapter for the dissertation. I’m going to have a chapter where I include all of my interview transcripts, but I haven’t yet found a sample chapter.
And you are unlikely to find one. I’ve yet to come across a dissertation that has all the interview transcripts. I’ve seen dissertations with samples of the transcripts in the Appendices, or in an attached CD (most research project transcripts number hundred of pages). Common practice is to reference the transcripts (snippets/quotes) in your results chapter and just leave it at that – talk to your supervisor. If you do plan to include all your interview transcripts, you’ll have to consider consent (get additional consent from the participants to share the transcripts + IRB review) and data anonyminization (not an easy feat – as Nancy Scheper-Hughes found out).
thanks for the guidance. but if I want to include all of the interviews in my dissertation and my study is qualitative so wouldn’t be too lengthy to write those 10 interview transcripts? or should I prefer some other way to include that interview data in my dissertation.
Rarely do researchers include all of the transcripts in their dissertation. And unless there’s a good methodological reason, it’s not recommended. So yes, you should consider other ways to “illustrate” your findings in your results chapter. But first you’ll need to analyze the interviews; here’s a great post on a few how to books.
Hi Isaac, thank you for this post it is immensely useful, and I have been grateful for the guide.
In my interview, I was initially interviewing one person, an author, however, it began as a conversation in an informal setting after lunch and I felt I could not ask the other family members to leave. This meant that my interview began with one interviewee, however, when I directed her the questions, the other family members often interjected or answered on her behalf.
I have attempted to explain this in the Introduction, in the Additional Notes section you have on the Interview cover page.
Do you have any more advice? For example, under ‘Interviewee’ should I add: ‘others present: ______’ ?
Best wishes,
Yeah, I’d add any relevant information to the cover page and maybe consider the interview a group interview. It is interesting what participants say/don’t say when they are alone and in a group. You’ll have to take that into consideration when analyzing the interview.
Hi,that was really nice and helpful I am wondering if i could speak with you in more details as i need some advises
Hi, happy to answer any questions you may have. Just post them in the comment section so that we can also assist other researchers that might have similar questions. KR Isaac
Great Post. Actually i was looking for transcription blogs and ended up here and found some helpful tips. Thanks for sharing.
My pleasure.
Doctoral Support FAQs
- Capella FAQs Home
- Capella FAQs
- Doctoral Support
Q: How do I format interview transcripts in my dissertation?
- Career Center
- Disability Support
- Learner Records
- Military Support
- Office of Research & Scholarship
- Quantitative Skills Center
- Scholarships & Grants
- Technical Support
- Writing Center
- 3 Academic Planning
- 12 Capstone
- 7 CITI training
- 1 Comprehensive Exam
- 2 Conflict of Interest
- 7 DHA Capstone
- 42 Dissertation
- 15 Dissertation Writing
- 7 DNP Capstone
- 7 DrPH Capstone
- 7 DSW Capstone
- 7 EdD Capstone
- 2 Feasibility
- 16 Format Editing
- 4 Informed Consent
- 5 Instruments
- 19 IRB Forms, Templates, and Handbooks
- 18 IRB Review
- 17 IRBManager
- 9 Milestone Completion
- 3 Privacy and Confidentality
- 2 Published Dissertation
- 8 Recruitment
- 4 Research Misconduct
- 7 Research Plan
- 2 Review Status
- 1 Risks to Participants
- 7 Scientific Merit Review
- 17 Site Permissions
Search Doctoral Support FAQs
Search All FAQs
Answer Last Updated: Jul 08, 2016 Views: 1617
There is no set style or rule for the presentation of interview transcripts. Purpose and readability should drive the presentation. That being said, the following recommendations are provided:
- Do not include verbatim question-by-question transcripts in the manuscript. Rather, extract key, relevant quotations or synthesize the responses.
- Always review the quotations for any information that may accidentally reveal participants, his or her immediate community (e.g., family, clients, coworkers), or location.
- Use single-spacing for interview transcripts.
- Do not italicize participant quotations.
- Use block-style formatting for interview transcripts.
- Set quotations of fewer than 40 words off with quotation marks.
- Set the speaker’s name in parentheses at the end, as in (Participant 1).
- Unless you are doing a Delphi study, do not include the date of the interview.
- Participant quotations are considered data, so never refer to them as “personal communication.”
- For traditional “script-style” transcripts, with questions from the interviewer and answers from the participants, use a colon after the speaker’s designation and indent the first line of all new paragraphs.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 0
Further Resources
Check out our resources on Campus (iGuide):
Doctoral Resources and Support
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
Related Topics
- Format Editing
- Dissertation Writing
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A method of analysing interview transcripts in qualitative research

1991, Nurse education today
Related Papers
luci paulson
Chief Editor
Kelly M Tucker
Qualitative research remains central to the enhancement and intellectual development of the social sciences. Sociologists use this umbrella term in reference to a variety of research methodologies including sensory data, participant observation, and interviewing. This paper provides an in-depth exploration of qualitative interviewing, endeavouring to highlight theoretical and practical elements of consideration to be sought within the data collection and analysis procedure, drawing upon potential strategies for broaching these issues should they arise. Empirical examples presented will demonstrate the appropriate use of interviewing as a tool to elicit valid, relevant, and insightful information for sociological analysis. Latterly, the use of material objects as elicitation devices will be examined as part of an effective strategy for enhancing interview quality.
Maria Fortes
Psychological Thought
Stanislava Stoyanova
Shannon Oltmann
Interviews are a staple method used in qualitative research. Many authors hold face-to-face interviews to be the gold standard, or the assumed best mode in which to conduct interviews. However, a large number of research projects are based on conducting interviews via telephone. While some scholars have addressed the advantages and disadvantages of using telephones to conduct interviews, this work is scattered across multiple disciplines and lacks a cohesive, comprehensive framework. The current article seeks to rectify this gap in the literature, by explicitly developing the constructs of the interviewer context and the respondent context. By examining key components in each of these contexts, the qualitative interviewer can make an informed, reflective decision about the best interview mode to use for a particular project.
Glen Lekgau
Jeanne Marecek
Baczoni Levente
RELATED PAPERS
Chistera 264
Jorge Sepulvudeda
Canrea Journal: Food Technology, Nutritions, and Culinary Journal
Journal of Biological Chemistry
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering
Acta Agrobotanica
Agnieszka Klimek-Kopyra
Archivi digitali di Sapienza Itinerari culturali per la conoscenza
Emanuela Chiavoni
Medicina Clínica
Eduardo Verde
Sustainability
Lena Smidfelt Rosqvist
Revista Vértices
Flávio Antônio Zagotta Vital
Bethany Walker
International Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Management (IJIREM)
IJIREM JOURNAL
Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America
Chrissie Mtali
Carmelle Fajutrao Valles
Elena Cattelino
Leprosy Review
nisha kurian
Kekal Abadi
Janaki Sinnasamy
Le Centre pour la Communication Scientifique Directe - HAL - Aix-Marseille Université
Iman Mersal
International Journal of Aquatic Biology
Javid Imanpour Namin
Physical Education Theory and Methodology
asmadi ishak
Wilson Quarterly
Carl Elliott
Acta Geophysica
Paweł Wiejacz
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Instructions for Written Work
- Suomeksi This link opens in a new window
- Introduction
- Support for the thesis writing This link opens in a new window
- Table of contents
- Text settings and formats
- Figures, pictures , tables and formulae
- Use of punctuation
- Bibliography and appendices
- Critism and evaluation
- Notable deviations from the basic rules of APA 7
- Author-oriented citing
- Subject-orinted citing
- Citation covering one sentence only
- Citation covering two or more sentences
- Publication with several authors
- Citing several publications by the same author
- Citing publications by several authors
- Information not received from a primary source
- Publications with no author data
- Publications with no publication date
- Personal communications and organizations' internal data sources
- Online sources and other type of sources
- Pictures and pictorial collages
- Page numbers
- Direct quotations
Interview transcript
- Article in an edited volume
- Articles (journals, magazines, newspapers, conferences)
- Audiovisual media (photography, podcast, PowerPoint slides, webinar, video, map)
- Books (printed book, e-book, audiobook, multivolume book)
- Dictionaries and encyclopedias
- Expert interviews, personal communications and organizations’ internal data sources
- Lectures and online courses
- Legal references
- Mobile appilications, computer softwares, artificial intelligence (AI) applications
- Reports and serials
- Social media (blog post, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter)
- Standards, patents, RT-cards and technical instructions
- Statistics and research data
- Sources published in another language
- Bibliography and other literature
Both brief and long utterances are indented and their line spacing is reduced. This is a deviation from the recommendation of APA 7. Neither quotation marks nor italics are used, but the utterance is consistently written in the style of a Quotation , even if the utterance were brief. This way, the interview transcript stands out from other data. It is recommended that quotes be linked content-wise to the body text so that utterances do not remain disjointed and the context completely to be figured out by the reader. Excerpts of data can be coded by a combination of a letter and number (such as H1, H2).
If there is a direct quote from the interview transcript in the middle of the text, it is separated with quotes. Interview data are not included in the bibliography.
- << Edellinen | Previous: Direct quotations
- Seuraava | Next: Making a bibliography (general instructions, bibliography example) >>
- Sivua päivitetty | Last updated: Apr 16, 2024 2:03 PM
- URL: https://seamk.libguides.com/instructionsforwrittenwork
- Tulosta sivu | Print page
Accessibility Statement

How to Transcribe Interviews Automatically: Turn Your Audio & Video Content Into Text
Interview transcripts help make your content more accessible, discoverable, and offer ways to get more from every interview. Here's how to create interview transcripts automatically with best-in-class tools.

Interviews are the lifeblood of good marketing. Interviews help you understand customers and the market at large, and they're also an important part of building a reliable content engine, especially if you rely on expert opinions, customer proof, and content repurposing. And these days, who doesn't?
Running a great interview is hard enough, so we don't want to make transcribing the interview itself any harder than it needs to be. Fortunately, we're in the age of AI-powered transcription software and it has never been easier to get a highly accurate transcript in just a few seconds—but you need the right tools.
Below, we'll share a step-by-step tutorial for automatically generating and revising an interview transcript, along with other more manual approaches, best practices for transcripts, and all the ways transcripts can be used to power your marketing. Let's start with defining what we mean and getting a transcript made quickly.
What's an interview transcript?
An interview transcript is a written record of a conversation where the dialogue from an audio or video recording is converted into text. These transcripts are often verbatim and include all of the questions and responses in a conversation, but they're sometimes lightly edited or summarized.
Interview transcripts are used in many different ways but are most commonly used for:
- Accessibility. Transcripts are especially valuable to users with hearing or other disabilities, or for users who simply prefer to get the information via text.
- Discoverability. A video’s metadata helps Google index, classify, and surface it to searchers. Transcripts and subtitles/captions add lots of metadata to videos that would otherwise not exist.
- Repurposing. Want to turn your interview into a blog post, email, or other text content? Getting more value from interviews starts with getting the transcript.
- Localization. Translating audio and videos also begins with a detailed transcript that can then be localized to the target region via subtitles, voice overs, or dubbing.
- Reference. Transcripts create a detailed record of the conversation and are typically easier to store and archive than long video or audio interviews; they're also easier to search.
How to transcribe interviews automatically
Though we'll cover other, more manual ways to transcribe an interview, let's start with the fastest and easiest way: using an AI-powered tool to automatically create a word-by-word transcript. Here's how to transcribe an interview using this approach:
1. Play back your interview
The first step is actually to play back your interview and check the recording quality. If there's an excessive amount of background noise, or if the audio quality could simply be clearer, try a tool like Kapwing's Clean Audio or Adobe's speech enhancer before you begin transcribing.
Doing audio cleanup now will save valuable time as you begin to transcribe your interview because you'll have fewer manual edits to make—the clearer your audio, the better AI-powered transcribers are at returning accurate transcripts.
📚 Learn more: How to Remove Silences from Podcast Audio with AI
2. Upload your interview file
Head over to Kapwing's Transcription tool and click "Start transcribing." You'll then be Kapwing and upload your interview file, whether it's audio or video.
Select the "Transcript" tab from the left sidebar in Kapwing, then click on "Trim with Transcript." You'll then be able to select your language—the language the speakers are talking in—and from there you can click on the big "Generate transcript" button. Your word-by-word transcript will start being created.
What's useful about Kapwing's transcript tool is that you can edit your transcript like a text document to edit your audio or video interview. Just remove a section in the transcript and that portion of the interview will be removed as well.
Make any edits you need, try advanced tools like Remove Filler Words, or apply more hands-on edits via Kapwing's traditional timeline editor before moving on to the next step.
3. Export your transcript
Now it's time to export your transcript and download it to any device. When you're ready, select the "Download transcript" option just above the transcript editor. Your transcript will download as a plain .txt file which can be used almost anywhere.
If you used your transcript along with our Subtitle Generator , you'll also be able to download subtitle files in .srt and .vtt as well.
4. Proofread and publish
We've mentioned that although auto-generated transcripts are highly accurate, it's worth planning on at least one round of revisions to avoid any obvious mistakes and ensure your transcript is as accurate as possible. Depending on your industry or the context of the transcript, you may require additional reviews, too.
At the bare minimum, we recommend considering the following steps as you proofread your transcript and prepare it to be fit to publish:
- Let an editor proofread your transcript. The editor can just be someone else on your team. Fresh eyes on a transcript will often help catch obvious misspellings or mistakes that will stick out to anyone reading your transcript.
- Review your transcript with AI. No time for review? Then head over to Grammarly or ProWritingAid for a quick AI-powered grammar check. These tools may not catch misuse of industry terms or other niche-specific mistakes, but they'll help you clean up the basics.
- Add Custom Spelling for future interviews. "Ca-poing?" It's Kapwing! Transcription tools are known for misinterpreting brand names and terms, so we've built a Custom Spelling tool that will automatically catch and fix common misspellings you notice in your transcripts.
Other ways to transcribe interviews
The reason we recommend using automatic transcription software is that these tools have become much more accurate over recent years. Many popular providers of hand-written transcription services have introduced AI-based transcriptions as part of their offering for this reason.
AI-powered transcription plus a human review and quick edit is the way to go for most creatives. But if you want to keep all of your options open, here are the two other ways to transcribe an interview:
1. Hire a transcription service
Hand-written transcription services still exist, but they're going to cost you a pretty penny in comparison to software. In terms of the typical expense, Rev, a leading provider of human-written transcripts, starts pricing at $1.50 USD per minute of audio/video. That's a palatable $18 for a 12-minute transcript for a YouTube video —so long as you don't add extras—but a tougher-to-justify $105 for a 70-minute webinar.
So, what do you get in return for the cost? Most service providers we saw promised "98-99% accuracy" for human-written transcriptions and, from experience, are usually able to deliver. Specialty services can also accommodate transcription work that needs to e.g. meet HIPAA compliance or be structured in a specific or unique way, such as for legal services.
Human transcriptions are also useful for extraordinarily long interviews with multiple speakers. If that's the case for your interview, you should also know that there are usually a few levels of service that you can request from transcription providers:
- Verbatim transcripts. Every word, sound, and expression ("uh, um") will be transcribed without edits. Useful if you need everything in an interview or prefer to make editorial decisions yourself.
- Intelligent transcripts. Verbatim transcripts minus filler words, filler words, and sections where a speaker stumbles over their words or repeats themselves.
- Edited transcripts. Transcripts where editorial judgment is applied, including the removal of sections that are superfluous or simply not valuable to your audience.
Depending on which of these options (and more) you've selected, turnaround times can vary widely but typically range from 6-48 hours. Note that any human-written transcript that is word-by-word and guarantees 99% accuracy is going to take at least a few hours. Popular providers for these services include Rev , GoTranscript , TranscribeMe! , and Scribie .
2. Manually transcribe your interview
If you can avoid it, we strongly recommend not taking this approach. But, if you're resource-strapped or must manually transcribe your interview for other industry or company-specific reasons, let's look at the steps to take.
- Prepare to transcribe. All this really means is to grab a pair of headphones, sit in a (reasonably) quiet room, open a text editor, and then load up your audio or video interview.
- Listen from start to finish. If time allows, listen to the entire interview front to back to understand the full context before you begin transcribing. If there isn't time, skip to the next step.
- Break the interview into sections. Separate the audio into manageable segments that you can listen to in sequential order. You don't have to do this inside of your editing tool or word document; you can just pick stopping points e.g. 15-minute segments for a 60-minute interview.
- Slow down the playback. If needed, use software or your playback device to slow down the audio without altering its pitch for clarity. This can often be faster than having to re-listen to segments over and over.
- Transcribe a verbatim OR intelligent draft. You can either transcribe everything that you hear including filler words and false starts or make small editorial decisions as you go such as removing "uhs" and "ums" in your first pass.
- Review and edit. Read through the entire transcript to correct obvious errors and mispronunciations that turned into misspellings, along with any other factual or grammatical errors.
- Proofread and publish. Listen to the recording again while reading the transcript to ensure accuracy. Double-check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Then, ship it!
Benefits of creating an interview transcript
As fast as it may be to transcribe an interview with software, there's still work involved in exporting, reviewing, and formatting a transcript so that it's ready to go live.
Since it takes time, there needs to be upside—and we think there's plenty. Here are just a few of the benefits of converting your audio to text , for interviews and more.
1. Caption your audio/video interview
Transcripts are a frequent first step toward getting word-by-word video subtitles, which are a must-have for videos published online. The number of people who use subtitles is surprisingly high and the preference to watch subtitled videos with sound off is only growing among younger viewers.
Captioning your interview is obviously useful for video podcasts or other video formats, but interview transcripts can also be used to create the popular podcast audiograms that are so frequently found on social media. With subtitles & captions or audiograms, interviews can help fill your social media feed with useful and engaging multimedia content.
2. Repurpose interviews into written content
Well-constructed interviews with an expert guest or interesting customer can be the source for multiple new blog articles, emails, or social media posts. Taking just one interview and generating a podcast transcript could, all by itself, lead to 2-3 new search-driven blog posts—all built from the advice and insight from a single conversation.
Interviews are particularly valuable in industries that are complex or especially technical, such as developer products or cybersecurity. For these topics, you frequently need to interview subject matter experts to help answer a challenge your customers have; interviews are the bedrock of your content strategy. And with interview transcripts, you can get lots of mileage from these conversations for all forms of marketing content.
📚 Learn more: How to Transcribe a Podcast and Turn It Into a Blog Post
3. Improve the SEO for your audio/video assets
Audio and video files, just like web pages, rely on metadata to be crawled and surfaced by search engines like Google. Transcripts provide lots of relevant text-based content for audio or video interviews that search engines are efficient at crawling, which makes it easier to understand and index the content.
And that's just for the audio/video asset itself; as covered above, transcripts can also be used to create companion blog posts or other text-based web pages that can rank on Google web search with the multimedia content embedded. For example, you could transcribe an interview you hosted on YouTube and turn the transcription into a blog post while also embedding the interview inside the blog post. If the blog article then ranks in search, that also helps with visibility for your interview.
4. Turn transcripts into testimonials & case studies
Customer success is abundant in any good product, but customer proof is contingent on getting those perfect quotes from happy customers during a spur-of-the-moment chat. Transcripts are critical for capturing and surfacing these hidden gems that might otherwise disappear after the call ends.
A single great testimonial can go a long way. For more in-depth customer proof points, like case studies, you definitely need the entire transcript to create a clear Problem → Solution → Outcome story that helps other users see how your product can make them successful.
5. Edit your transcript to edit your video
Tools like Trim with Transcript allow you to automatically generate a transcript and then edit the text to edit your video. This means you can edit a rough cut just by removing words, sentences, and sections from the transcript.
Text-based editing is one of the fastest ways to rough cut a video because it's so straightforward—it's also one of the easiest ways to edit a video or audio file for marketers or anyone who isn't that familiar with timeline-based editors.
📚 Learn more: How to Quickly Transcribe Audio to Text with AI Tools
Effective examples of interview transcripts
So, who's going the extra mile with interview transcripts? To help answer that question, we collected a pair of transcripts that go much further than "plain text pasted to a blog." Use these as your inspiration.
Shopify Masters podcast transcript
What's in this interview transcript? This transcript example comes from Shopify Masters , a podcast hosted by Shopify on running a successful ecommerce business. This particular transcript is based on an interview with David Gaylord, who is the CEO of a direct-to-consumer company called Bushbalm.
Why we like this interview transcript: Shopify's podcast is a good example of what I'd call a "Transcript Plus" for marketing content. The story above is based on a transcript, to be sure, but it's also highly edited and includes original photography, inline images, pull quotes, and more. The transcript was ultimately a foundation for a really good piece of editorial content—along with the original interview.
Inside Intercom interview transcript
What's in this interview transcript? This transcript example comes from a roundtable discussion on Inside Intercom , an interview-style show produced by the customer support platform Intercom. In this particular interview, the Intercom team speaks to journalists, lecturers, and entertainers about the history of telephone support.
Why we like this interview transcript: This interview juggles multiple speakers quite well and is formatted in a clean and easy-to-navigate structure. Small editorial details like pull quotes and subheadings also make this transcript much easier to browse. Lastly, the conversations are organized in a coherent way so that ideas build on top of each other as new interviewees are introduced.
FAQs on Interview Transcripts
What is the easiest way to transcribe an interview.
Generating a word-by-word transcript with AI-powered transcription software is the fastest and easiest way to transcribe an interview. AI-generated transcripts are now highly accurate and require minimal editing. Tools like Kapwing, Rev, and Happy Scribe all offer software to automatically transcribe audio or video interviews.
What does an interview transcript look like?
Interview transcripts are typically plain text records of a conversation between two or more people. The text can either be unformatted entirely, or it can be lightly formatted and edited with speaker notes, slight revisions, or even inline assets such as if the transcript is repurposed to a blog article.
Is there an app that transcribes interviews?
Yes, Kapwing features a transcript generator that converts any audio or video file into text. Transcripts are available in minutes and can be downloaded as a .txt file, turned into subtitles, or even used to edit your video itself with Kapwing's text-based video editor.

5 Free Templates for Effective LinkedIn Video Ads

How to Make an Old-Fashioned Video Online

How to Make a Video Look Vintage


Interview Transcript
Get your transcript in minutes
From 0,33€/Min.
Start Free Trial
DSGVO-compliant + ISO certified
Edited by professionals
39 languages are available
Done within 24 hours
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Interview Transcript In A Nutshell
- 2 Save Time With Digital Help
- 3 Amberscript
- 4 Automatic transcription
- 5 Manual transcription
- 6 What Is The Process Of An Interview Transcript?
- 8 Any Questions Left?
Interview Transcript In A Nutshell
An interview transcript is common in journalism, medicine, law, and even among students, especially when submitting their thesis. An interview transcript should be accurate. Manual transcription can be hard. However, software packages are available: some are free, others are commercial, some are offline and others can only be used online. All the same, the software gives an accurate interview transcript, saves time, and is stress-free to use.
- Upload your file and save time The transcription online supports the following formats: MP3, MP4, WAV, M4A, M4V, MOV, WMA, AAC, OPUS, FLAC, MPG, MPEG, TS, VOB, WebM, GSM, 3GP, AVI, FLV, MXF, WMV. The maximum file size is 6 GB.
- Pick your interview transcript You can opt for a free as well as a commercial package. There are transcribers that can only be used online, but also ones that function offline.
- Export the final interview transcript You can receive your interview transcript with just one click.
Save Time With Digital Help
An interview transcript is a practical and effective method for capturing data for academic or professional purposes, but it’s more than meets the eye. Learning about their methods and benefits can be very helpful if you’re pressed for time.
Because of this, we recommend:
Amberscript
What is offered to me by amberscript.
You can easily transcribe your audio files with the professional interview transcripts offered by Amberscript.
Automatic transcription
What's included.
Your files are safely stored
Transcript in a few minutes
Over 39 languages are supported
With an accuracy of up to 85%
Online editor to edit transcripts
You can contact us by email
Manual transcription
Files can be exported in any format
Your data is safeguarded
Personal contact is available on demand
Always a 100% accuracy
Differentiation between multiple speakers
What Is The Process Of An Interview Transcript?
There are rules for every type of transcription. These completely depend on your topic and for what you need the interview transcript. This is why it’s so important to answer the following questions beforehand:
What is the purpose of your research?
Are there any additional requirements for the transcript, beyond the voice text, what additional information is needed.

3 Benefits Of An Interview Transcript
There are many benefits to using software for your interview transcript as discussed here.
An interview transcript software transcribes in the shortest time in comparison to a manual kind.
High quality
Software is the best bet when it comes to the production of a high-quality interview transcript with the utmost accuracy and efficiency.
Stress free
All the different steps of an interview transcript can be tasking, and it may even take days or weeks to achieve the desired results.
Do I need an interview transcript?
If you’re considering transcription, there are many online transcription services and transcription programs to assist you. Follow the link to start transcription today.
An interview transcript is necessary because it makes work easier. It is easy to read a transcribed piece of work instead of picking up your earphones every time you need to write down something from the recorded interview.
How do I transcribe audio?
Ideally, you should be able to show when different speakers talk as well as time stamps. Each new idea is often written as a new paragraph. Since interviews are usually in a question-and-answer format, make sure to write each question asked as well as the answer given by the respondent. When transcribing, accuracy has to be maintained so that no data gets lost in the process. If this sounds like a lot of work, you should consider an online transcription program .
How do you transcribe an interview faster?
Creating an interview transcript requires attention to detail. As such, make sure that you have a conducive working environment. Furthermore, invest in quality headsets that minimize background noises. You can also use software to help you transcribe. Most importantly, you need to practice your typing speed and accuracy.
When should I have my dissertation audio transcribed?
Numerous factors should be considered before deciding when to convert your recorded interview into an interview transcript. For instance, if you are on a tight budget, and you need to hire a professional transcriber, then you should give yourself enough time because the urgency determines the cost. Or, perhaps you’d rather use an online transcription software . Another factor is the number of audio hours you need to transcribe, and most importantly, the style of transcription you want, something that is often dictated by your area of study.
Is my data safe if I outsource to a professional transcriber?
If you have time, you can transcribe your audio, however, an online transcription program would save time. Nevertheless, if time is not on your side, you can choose to outsource your work. Before you decide on where to outsource, you have to ask the transcriber about the transcription software they use or even about the safety of your data and personal information. Most legitimate transcribers do not use clients’ data to their benefit.
Any Questions Left?
Please refer to the contact page of our partner for further details!
To Amberscript
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
How to Analyze Interview Transcripts with AI Tools
Home » How to Analyze Interview Transcripts with AI Tools

AI-powered Interview Analysis at scale
Interview transcripts come in handy for all sorts of purposes these days. They give you a full record of what was said during a conversation, which lets you really dig into the details and extract meaningful insights. Whether you’re doing market research, getting customer feedback, or picking the brains of experts, having transcripts means you’ve got a rich dataset for qualitative analysis.
Transcripts capture the real-life perspectives, experiences, and nuances that you need to understand in order to make smart decisions. With a verbatim record, you can thoroughly examine everything that was discussed and zero in on the key takeaways.
While quantitative data provides important metrics to knowledge professionals, qualitative data adds depth, context, and human perspective to decision making. This is why many teams rely on AI-powered tools like Insight7 for efficient interview transcription and analysis.
In this article, we’ll explore how to use the latest AI technology to obtain thematic analysis from interview transcripts and we’ll explain its benefits. We’ll also share some of the top tools you can find for implementation.
Understanding the Basics of Interview Transcripts
Interview transcripts are written records of conversations between an interviewer and one or more participants. These transcripts serve as a valuable tool in qualitative customer research, where in-depth understanding and analysis of interviews are essential. The purpose of interview transcripts is to document and preserve the content and context of interviews, making it easier for researchers, to review, analyze, and draw insights from the information collected during the interview process.
There are dozens of ways to do qualitative research but recording and accurately transcribing interviews is among the best methods to avoid inaccuracies and data loss. A recording is a highly successful method for interviews and focus groups. It allows respondents the freedom to be open in how they respond.
Researchers should consider this approach over simply taking notes firsthand.
Recording and transcribing interviews is the best way to collect feedback. Make sure you have a reliable way to record, whether the interview takes place in person, over the phone, or as part of a video call. Depending on the interview method, you may record a video or an audio-only format.
Each interview method will have its own tools, but transcribing and analyzing them can be done with Insight7 , which is AI-powered and easy to use. An easy way to do this is by uploading your interview recordings to the tool and it analyzes your recordings in seconds.
Types of Interview Transcripts
1. structured interview transcripts:.
In a structured interview, the questions are pre-determined and asked in a fixed order to all participants. The transcripts for structured interviews typically follow a standardized format, making it easier to compare responses across participants.
2. Unstructured Interview Transcripts:
Unstructured interviews allow more flexibility in the questioning process. Interviewers have the freedom to explore topics in depth and adapt their questions based on the participant’s responses. Unstructured interview transcripts often reflect a more conversational tone and can be valuable in capturing rich, detailed insights.
3. Semi-Structured Interview Transcripts:
These transcripts combine elements of both structured and unstructured interviews. While certain questions are predetermined to maintain consistency, interviewers can also ask follow-up questions and delve deeper into specific areas of interest, allowing for more in-depth responses.
Key Components of a Typical Interview Transcript
- Identification and Metadata: The transcript typically begins with information about the interview, including the date, location, interviewer, interviewee(s) names or pseudonyms, and any relevant context or background information.
- Timestamps: Some interview transcripts include timestamps, noting the time at which each question or response occurred. Timestamps help researchers and analysts to locate specific moments in the interview quickly and efficiently.
- Questions and Prompts: The interview questions or prompts are included in the transcript, indicating what the interviewer asked the participant(s). In structured interviews, the questions are predetermined, while in unstructured or semi-structured interviews, the questions may vary.
- Responses: The interviewees’ responses are recorded verbatim or slightly edited for clarity and readability. These responses form the core of the transcript and provide valuable data for analysis and interpretation.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Interview transcripts may also capture non-verbal cues, such as pauses, laughter, sighs, or any other non-verbal communication that might convey additional meaning or emotions.
- Annotations and Observations: Researchers may include annotations or observational notes in the transcript. These annotations can provide context, identify themes, or offer initial insights.
Benefits of AI-Powered Interview Transcript Analysis
Interviews offer a goldmine of rich data – if you ask the right questions and analyze it properly. People tend to open up and reveal their authentic thoughts and emotions in those open-ended conversations. With an AI-driven approach, organizations across industries can model to revamp how they gather and interpret audience feedback. It is not easier and faster to collect and analyze massive volumes of qualitative data much faster than traditional methods.
Whether studying customers, constituents, or stakeholders, AI empowers you to finally hear the unfiltered voice of your audience. The insights are there – you just need the right tools to accurately capture and understand them.
Eliminating human bias effectively
One of the most significant advantages of utilizing AI tools for interview analysis is their potential for providing unbiased and objective insights. Human analysts may unknowingly bring their preconceived notions, beliefs, and interpretations to the data analysis process, which can introduce bias and affect the objectivity of the results. On the other hand, AI tools operate purely on algorithms and data-driven patterns, ensuring a neutral and impartial analysis.
By eliminating human biases, AI tools can offer a more accurate and impartial interpretation of the interview data. This objectivity becomes particularly crucial when dealing with sensitive or controversial topics where personal biases could inadvertently skew the analysis. Researchers can have more confidence in the credibility and reliability of the insights generated by AI-powered systems.
Furthermore, AI tools can process and analyze data at a significantly faster pace than manual methods. What might have taken weeks or even months for human analysts to complete can now be accomplished in a fraction of the time.
Choosing the Right AI Tool For Interview Transcript Analysis
When it comes to interview analysis, leveraging AI-powered tools can greatly enhance efficiency and accuracy. However, with numerous options available, it is essential to select the most suitable AI tool based on specific research requirements. Let’s explore the different types of AI tools available, the importance of tailored selection, and key factors to consider while choosing these tools for analysis.
Different Types of AI Tools for Interview Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis Tools: These tools focus on understanding the emotional tone of participants’ responses. They can identify sentiments such as positivity, negativity, or neutrality, providing valuable insights into participants’ feelings and opinions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Tools: NLP tools are versatile and can perform various tasks, including language comprehension, topic modeling, and keyword extraction. They excel at extracting meaningful information from unstructured interview data.
- Topic Modeling Tools: These tools aim to identify the key themes and topics present in the interview transcripts. By clustering related responses together, they help researchers understand the prevalent issues discussed during the interviews.
- Keyword Extraction Tools: Keyword extraction tools identify and extract significant keywords or phrases from the transcripts. These keywords can serve as important indicators of the primary focus areas of the interviews.
Interestingly, a tool such as Insight7 possesses all these elements.
Importance of Selecting an Tool Based on Specific Requirements
Each research project comes with unique objectives and needs. Therefore, selecting an AI tool that aligns with specific requirements is critical for a successful analysis. Relying on a tool that doesn’t cater to the project’s needs may result in inaccurate or irrelevant insights.
Different projects may demand different levels of accuracy, the depth of analysis, or focus on specific aspects. For instance, sentiment analysis might be essential for a study on customer feedback, while topic and theme modeling may be crucial for deeper brand development research.
Key Factors to Consider when selecting an AI tool for interview analysis
- Accuracy : Accuracy is paramount in interview analysis. Look for AI tools that have been extensively tested and have a proven track record of delivering reliable results.
- Language Support : If the interviews are conducted in multiple languages, ensure the AI tool supports all relevant languages to ensure accurate analysis across the entire dataset.
- Customization Options : Flexibility is essential when analyzing interview data as each project may require unique parameters and criteria for analysis. Choose a tool that allows customization to adapt to specific your research needs.
- Cost : Consider the budget for the research project and compare the costs of different AI tools. Strike a balance between affordability and the tool’s capabilities.
Here are some great tools for analyzing interview transcripts in 2023
- Insight7.io
- Raven’s Eye Compare
- Gotranscript.com
How Insight7 Helps Automate Interview Transcript Analysis
Among the many AI tools available for interview analysis, Insight7 stands out as a powerful and user-friendly solution for research and knowledge teams. With its intuitive interface and advanced features, Insight7 streamlines the analysis process and delivers valuable insights in seconds.
Insight7 simplifies the process of analyzing interview transcripts by offering a seamless upload feature. If you have recorded interviews that need transcribing, the app can automatically transcribe the audio recordings for you. This saves significant time and effort, eliminating the need for manual transcription or relying on third-party services.
Once the transcripts are ready, Insight7 automatically processes the text data to generate insightful analysis. Its natural language processing capabilities enable it to understand the context, emotions, and sentiment behind each response.
Understanding the sentiment and emotions expressed by interview participants is crucial for gauging their reactions, opinions, and behaviors. Insight7 excels in this aspect, offering automated sentiment analysis of the interview transcripts. The AI-powered tool can determine whether the responses carry a positive, negative, or neutral sentiment, allowing researchers to grasp the participants’ emotional responses accurately.
Time is often of the essence in research projects, and Insight7 recognizes this necessity. With its advanced algorithms, Insight7 can rapidly process the data and generate insights within seconds. This swift turnaround enables teams to promptly delve into the results, draw conclusions, and identify critical trends or patterns in the interview data.
If a UX researcher already has the interview transcripts ready, they can easily upload them to Insight7 for analysis. The app’s adaptability ensures that it can accommodate a variety of transcript formats, making the process even more convenient. Whether the data is in a structured or unstructured format, Insight7 can effectively analyze it and produce meaningful insights.
Challenges and Limitations of AI Tools
AI-powered interview analysis tools offer significant benefits, but they come with specific challenges and limitations that users must be mindful of. One crucial aspect is accuracy. While AI algorithms have advanced, they may still make errors in understanding complex nuances present in human language, leading to misinterpretations of interview data.
Bias is another concern. AI tools learn from existing data, and if that data is biased, the analysis can perpetuate and amplify those biases. This may result in skewed insights and recommendations, affecting the objectivity of the research.
Human intervention remains essential. While AI can expedite data processing, human judgment is irreplaceable when it comes to interpreting subtle emotions, contexts, and underlying meanings in interviews. Users should supplement AI analyses with their expertise to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the data.
Therefore, it’s crucial for users to be aware of these limitations and approach AI tools as aids rather than complete replacements. Relying solely on AI-powered analysis without human oversight can lead to erroneous conclusions. Instead, users should leverage AI tools to augment their research efforts, enhance efficiency, and identify potential patterns, but also remain cautious and actively engage in the analysis process themselves. By combining AI capabilities with human expertise, researchers can maximize the utility of these tools while ensuring the integrity and accuracy of their findings.
AI-powered tools have transformed interview transcript analysis, offering teams a faster and more efficient way to extract valuable insights. With benefits such as improved efficiency, unbiased analysis, and the ability to handle large datasets, AI is revolutionizing research and data analysis.
By carefully selecting the right AI tool and combining it with human expertise, teams can elevate the quality and depth of their interview analysis, driving new discoveries and advancements in various fields. Click here to analyze your interview transcript in seconds.
Customer Sentiment: How To Measure With AI
Related posts, how to analyze in-depth interviews with ai tools.
How to Generate Automatic Transcription With AI Tools in 2024
How to transcribe audio recording to text with ai tools.
Unlock Insights from Interviews 10x faster
- Request demo
- Get started for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Transcribing is a common practice when conducting interviews because it enables you to perform analysis. How to transcribe an interview in five steps: Choose your preferred transcription method. Transcribe the audio (using transcription software) Add speaker designation and time stamps. Clarify the transcript where needed.
Carefully read the content and identify key themes when summarizing the transcript of an interview. Organize the information logically, provide brief contextual details when necessary and use quotes to add impact. Capture the essence of the interview by keeping the summary short and sweet.
Interview transcripts allow you to use the best qualitative analysis methods. Plus, you can focus only on tasks that add value to your research effort. Transcription is Essential to Qualitative Research Analysis. Qualitative data is often elusive to researchers. Transcripts allow you to capture original, nuanced responses from your respondents.
Conducting an interview skillfully is crucial for creating an accurate transcript. Ensure you introduce yourself, explain the purpose of the interview, and obtain consent for recording. Establish a comfortable atmosphere for the interviewee to open up. Pay attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues, as capturing these nuances enriches the ...
The aim of interview transcription is to allow easy data analysis in research using techniques like coding and categorizing, content analysis, and thematic analysis. ... Formatting the transcript (adding the speaker designation and time stamps) Clarifying the text; Proofreading; Use the final format revision to perfect your thesis. Revise your ...
Qualitative Interview. Quantitative Interview. Purpose. To understand people's experiences, ideas, and feelings on a deeper level. To quantify information and generalise findings to a wider audience. Nature of d ata c ollection. Textual, d escriptive. Numerical, s tatistics. Data c ollection m ethod. Open-ended questions and unstructured interviews
In this first post of a 2 part series on how to transcribe an interview for dissertation, I'll start with a brief overview of the thesis transcription process. Then discuss 3 ways to transcribe your research interviews. And finally make a few remarks on accuracy of the transcripts and audio quality. Why Transcripts
Step 3: Start Transcribing Interview. After uploading, researchers start the transcription process on Transkriptor by selecting the recording's language with one click. The platform's AI technology then accurately transcribes speech to text, supporting a broad range of languages to meet diverse research requirements.
The purpose of summaries is to gather key basic information about the circumstances of the interview and give a concise guide to its contents. Summaries need to include names, places, events and topics appearing in each interview, with indications of how substantial the reference is and where in the course of the interview the reference appears.
How to transcribe an interview for your thesis. A bachelor or master thesis refers to a research proposal or academic study in which a student's theories and findings are contained in. The thesis must contain factual evidence which will support the findings and theories. ... This will ensure consistency between the transcript and the uploaded ...
Download the PDF version here: Interview Transcript Example - Clean Verbatim (PDF) We made the following changes to the second (clean verbatim) transcript: We edited out stutters, partial words, and short incomplete sentences. We removed meaningless instances of words like "so" at the start of sentences, and "like" when used as filler ...
1. In my PhD, I ran an experiment falling within the grounded theory framework, based on interviews I conducted. I transcripted them, tagged them, etc. This "enhanced transcription" is about 130 pages long (with pretty narrow margins). I am now writing my thesis and I wonder if I should include these transcription in appendix of my PhD thesis.
Transcribing is a common practice when conducting interviews because it enables you to perform analysis. How to transcribe an interview in five steps: Choose your preferred transcription method. Transcribe the audio (using transcription software ). Add speaker designation and time stamps. Clarify the transcript where needed.
Here's a sample dissertation interview cover page you can use. Interviewee: [Name of interviewee] [Pseudonym] Interviewer: [Name of interviewer] Date and Time: [mm/dd/yyyy][00:00] Location: [Place interview was conducted] Audio file information: [Name][Duration] Link to field notes: Link to follow up interview transcript: Additional Notes:
Transcription. Translation. Recording. Our ultimate guide to transcribe interviews for qualitative research. 1. Decide the important interview information. 2. Confirm what kind of transcript you need. 3. Have your tools ready.
Here is a common example of an interview transcript: Interviewee: Michael Stowfield, 555-4242, m.stowfield@abccompany. Interviewer: Lincoln Burnnos, 555-7788, l.burnnos@xyzcompany Date: Wednesday, July 23 Meeting place: Room N102. Attendees: MS = Michael Stowfield (interviewer), LB = Lincoln Burnnos (interviewee) MS: Welcome back, Lincoln.
Use block-style formatting for interview transcripts. Set quotations of fewer than 40 words off with quotation marks. Set the speaker's name in parentheses at the end, as in (Participant 1). Unless you are doing a Delphi study, do not include the date of the interview. Participant quotations are considered data, so never refer to them as ...
that is said in an interview Merely what was said. A crude example as follows. Here, the bracketed Stage eight Each transcript cut out to leave a phrase is worked through and sub-headings ing to the list of categories highlighting between with the list of and 'coded' accordheadings.
This way, the interview transcript stands out from other data. It is recommended that quotes be linked content-wise to the body text so that utterances do not remain disjointed and the context completely to be figured out by the reader. Excerpts of data can be coded by a combination of a letter and number (such as H1, H2).
2. Upload your interview file. Head over to Kapwing's Transcription tool and click "Start transcribing." You'll then be Kapwing and upload your interview file, whether it's audio or video. During this tutorial, I'm going to transcribe an interview we recently hosted with John Collins, a content marketing consultant.
An interview transcript is common in journalism, medicine, law, and even among students, especially when submitting their thesis. An interview transcript should be accurate. Manual transcription can be hard. However, software packages are available: some are free, others are commercial, some are offline and others can only be used online.
Types of Interview Transcripts 1. Structured Interview Transcripts: In a structured interview, the questions are pre-determined and asked in a fixed order to all participants. The transcripts for structured interviews typically follow a standardized format, making it easier to compare responses across participants. 2. Unstructured Interview ...