We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Microgreens Business
Back to All Business Ideas

Growing Green: Starting a Microgreens Business
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 25, 2022 Updated on July 12, 2024

Investment range
$1,830 - $4,600
Revenue potential
$36,000 - $145,000 p.a.
Time to build
1 – 3 months
Profit potential
$30,000 - $130,000 p.a.
Industry trend
Important elements to think about when starting your microgreens business are outlined here:
- Location — Set up a suitable growing space, such as a greenhouse, indoor grow room, or dedicated area in your home. Ensure it has adequate lighting, ventilation, and humidity control.
- Equipment — Invest in high-quality growing equipment , such as trays, soil or hydroponic systems, grow lights, and irrigation systems. Consider using organic soil and seeds to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
- Environmental control — Implement systems to control temperature, humidity, and light exposure to optimize growing conditions for your microgreens.
- Licenses and permits — Get the necessary permits and licenses required by local, state, and federal authorities to operate a microgreens business. This may include a business license, agricultural permits, and food handling permits .
- Selection — Choose a variety of microgreens to grow, such as arugula, basil, cilantro, kale, and radish. Consider factors like growth rate, yield, and market demand.
- Seed suppliers — Establish relationships with reliable seed suppliers to ensure a steady supply of high-quality seeds.
- Register your business — A limited liability company (LLC) is the best legal structure for new businesses because it is fast and simple. Form your business immediately using ZenBusiness LLC formation service or hire one of the best LLC services on the market.
- Legal business aspects — Register for taxes, open a business bank account, and get an EIN .
- Packaging — Invest in eco-friendly packaging materials to keep your microgreens fresh during transportation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
- Sales channels — Explore various sales channels, such as farmers’ markets, local grocery stores, restaurants, and online sales. Build relationships with local chefs and food retailers to secure regular orders.
Interactive Checklist at your fingertips—begin your microgreens business today!
You May Also Wonder:
How profitable is a microgreens business?
It costs very little to grow microgreens, and you can sell them for about $20 per tray. How much you can make will just depend on how much space you have to grow.
How much can I sell microgreens for?
Microgreens sell for about $2 per ounce, and each tray should produce about 10 ounces, so you’ll probably get about $20 per tray. If you grow unusual microgreens that are more rare, you may be able to sell them for a little more.
How do I find customers for microgreens?
To find customers for microgreens, consider selling to local restaurants, farmers markets, grocery stores, and through online platforms, and leverage social media and word-of-mouth marketing to raise awareness about your microgreens and target health-conscious consumers.
What microgreens are most profitable?
The profitability of microgreens can vary, but some commonly profitable varieties include sunflower, pea shoots, radish, and basil microgreens due to their popularity, fast growth, and higher market demand.
How much does 1 tray of microgreens produce?
The yield of 1 tray of microgreens depends on the variety and density of the seeds, but on average, a tray measuring around 10×20 inches can produce approximately 8 to 12 ounces of microgreens.
What is the most popular microgreen?
While preferences may vary, some popular microgreens include sunflower, pea shoots, broccoli, radish, and kale microgreens due to their versatility, nutritional value, and appealing flavors.
How can I differentiate my microblading business from competitors in the market?
Differentiate your microblading business by focusing on specialized techniques or styles, offering personalized consultations to understand clients’ desired outcomes, showcasing before-and-after photos of satisfied clients, investing in quality pigments and tools, providing excellent customer service, and staying updated with industry trends and training to ensure you offer the latest microblading techniques.

Step 1: Decide if the Business Is Right for You
Pros and cons.
Starting a microgreens business has pros and cons to consider before deciding if it’s right for you.
- Low Startup Costs – Seeds, trays, and basic equipment are inexpensive
- Simplicity – Easy to grow, easy to maintain
- Flexibility – Not much time needed, run the business from home
- Boost Health – Microgreens offer real health benefits
- Space Needed – Adequate space in your home is necessary
- Low Revenue – Prices are low; large growing volume is essential to make money
Microgreens Industry trends
Industry size and growth.
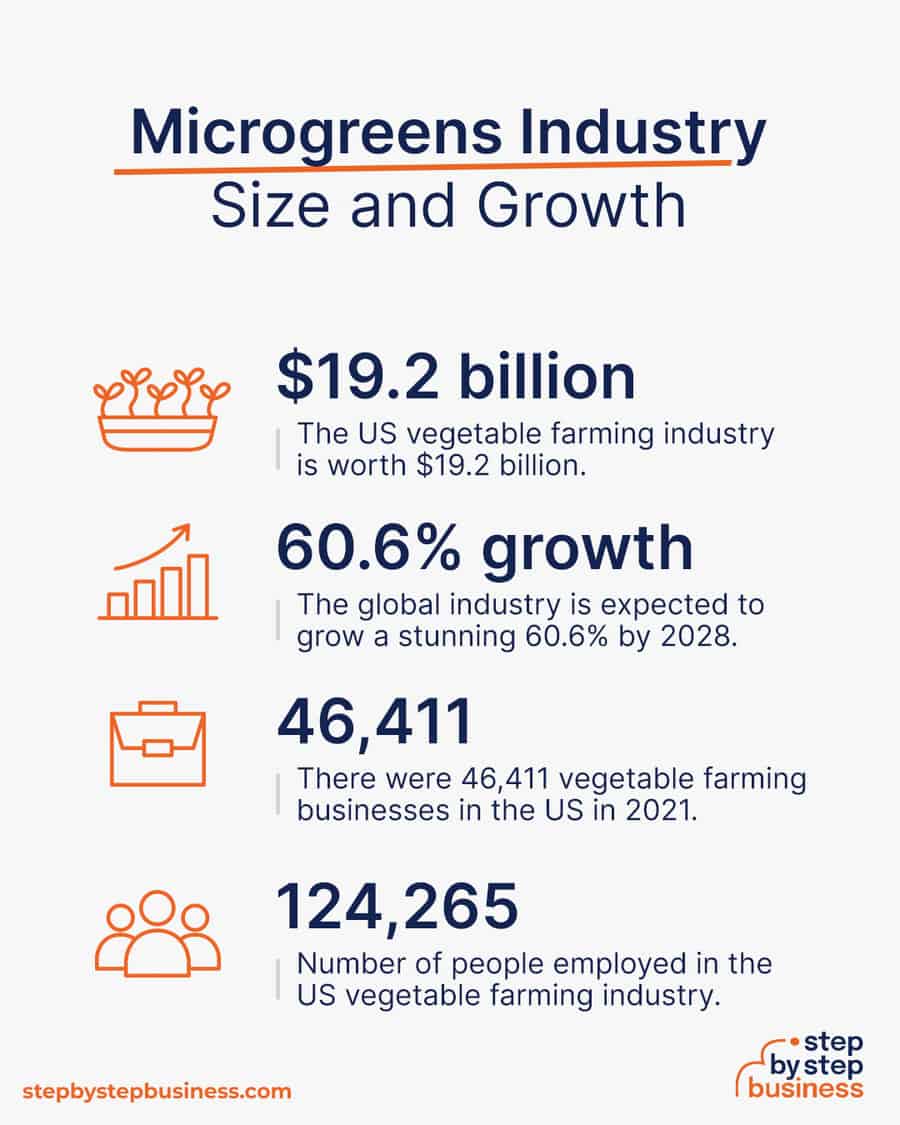
- Industry size and past growth – The US vegetable farming industry is worth $19.2 billion and has dipped slightly in recent years.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/market-size/vegetable-farming-united-states/ ))
- Growth forecast – The global microgreens industry is expected to grow a stunning 60.6% by 2028.(( https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/microgreens-market-A08733 ))
- Number of businesses – There were 46,411 vegetable farming businesses in the US in 2021.
- Number of people employed – There were 124,265 people employed by the US vegetable farming industry in 2021.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/united-states/market-research-reports/vegetable-farming-industry/ ))
Trends and challenges

Trends in the microgreens industry include:
- The most popular microgreens and the best to grow in containers are arugula, broccoli, beets, kale, collards, radish, red cabbage, sunflowers, wheatgrass, and, in particular, pea shoots.
- Microgreens have been used in salads for some time, but now they’re being used as drink garnishes, in juices and smoothies, as soup seasonings, on pizzas and more.
- New evidence shows microgreens are high in antioxidants, which reduce the risk of many diseases, as well as vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Challenges in the microgreens industry include:
- Microgreens dehydrate quickly so they must be sold while fresh.
- Mold and mildew can be an issue when growing microgreens, increasing the need for proper ventilation and drainage.
Demand hotspots
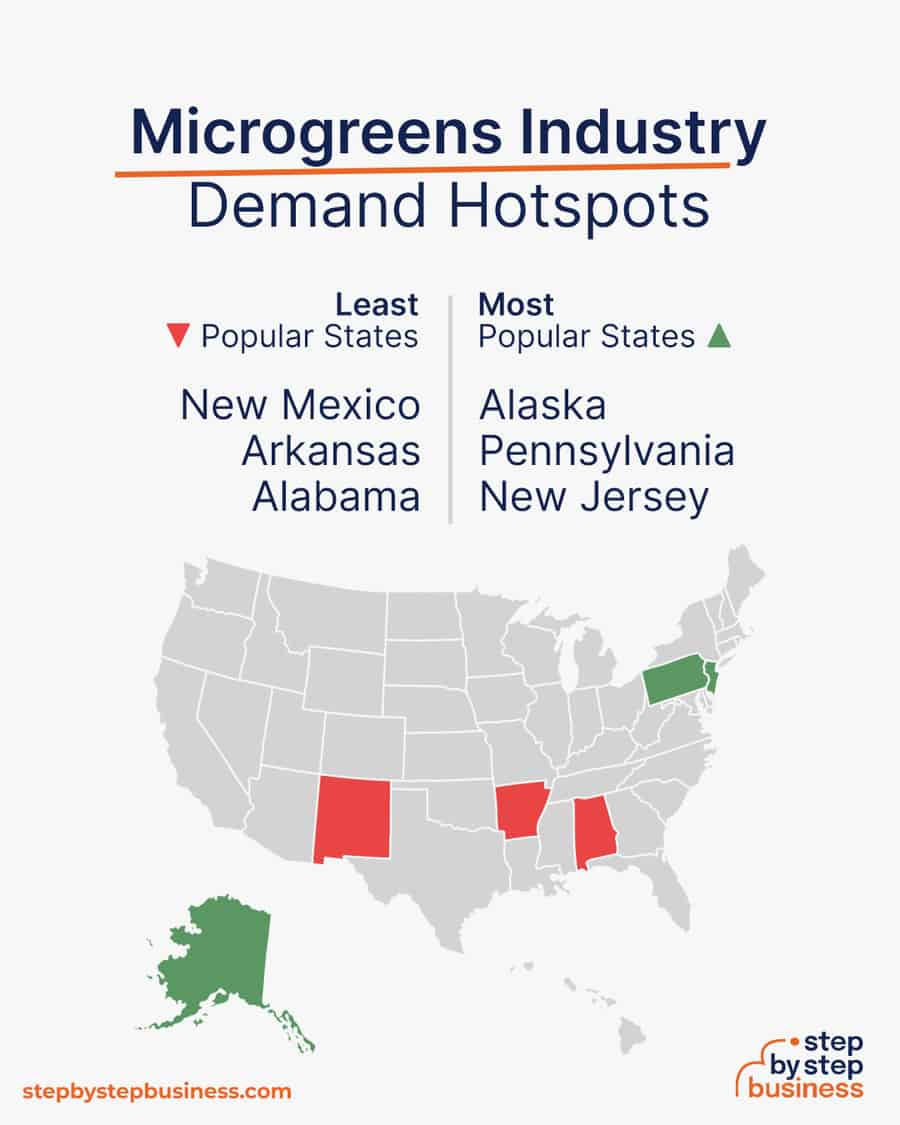
- Most popular states – The most popular states for growing in greenhouses or indoors are Alaska, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey.(( https://www.zippia.com/grower-jobs/best-states/ ))
- Least popular states – The least popular states for growing in greenhouses or indoors are New Mexico, Arkansas, and Alabama.
What kind of people work in Microgreens?
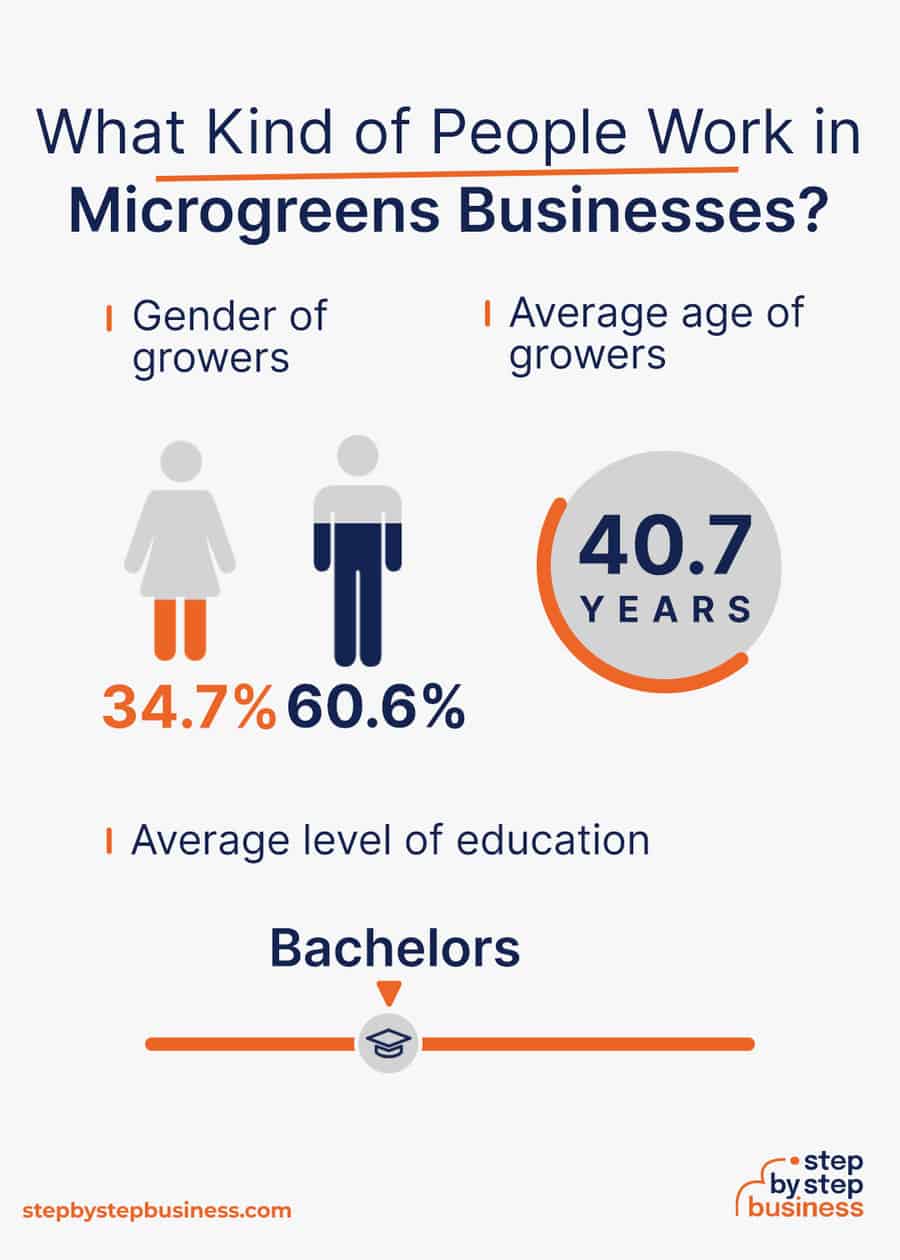
- Gender – 34.7% of growers are female, while 60.6% are male.(( https://www.zippia.com/grower-jobs/demographics/ ))
- Average level of education – The average grower has a bachelor’s degree.
- Average age – The average grower in the US is 40.7 years old.
How much does it cost to start a microgreens business?
Startup costs for a microgreens business range from $1,800 to $4,500. The largest expense is for a website to market your business. Other expenses include seeds, trays, and equipment. If you need to brush up on your indoor gardening skills, you can take a microgreens course on Udemy for less than $20.
You’ll need a handful of items to successfully launch your microgreens business, including:
- Growing lights
- Growing mats
- Packaging supplies
| Start-up Costs | Ballpark Range | Average |
|---|---|---|
| Setting up a business name and corporation | $150 - $200 | $175 |
| Business licenses and permits | $100 - $300 | $200 |
| Insurance | $100-$300 | $200 |
| Business cards and brochures | $200 - $300 | $250 |
| Website setup | $1,000 - $3,000 | $2,000 |
| Seeds | $80 - $100 | $90 |
| Trays, growing mats | $100 - $200 | $150 |
| Grow lights | $100 - $200 | $150 |
| Total | $1,830 - $4,600 | $3,215 |
How much can you earn from a microgreens business?
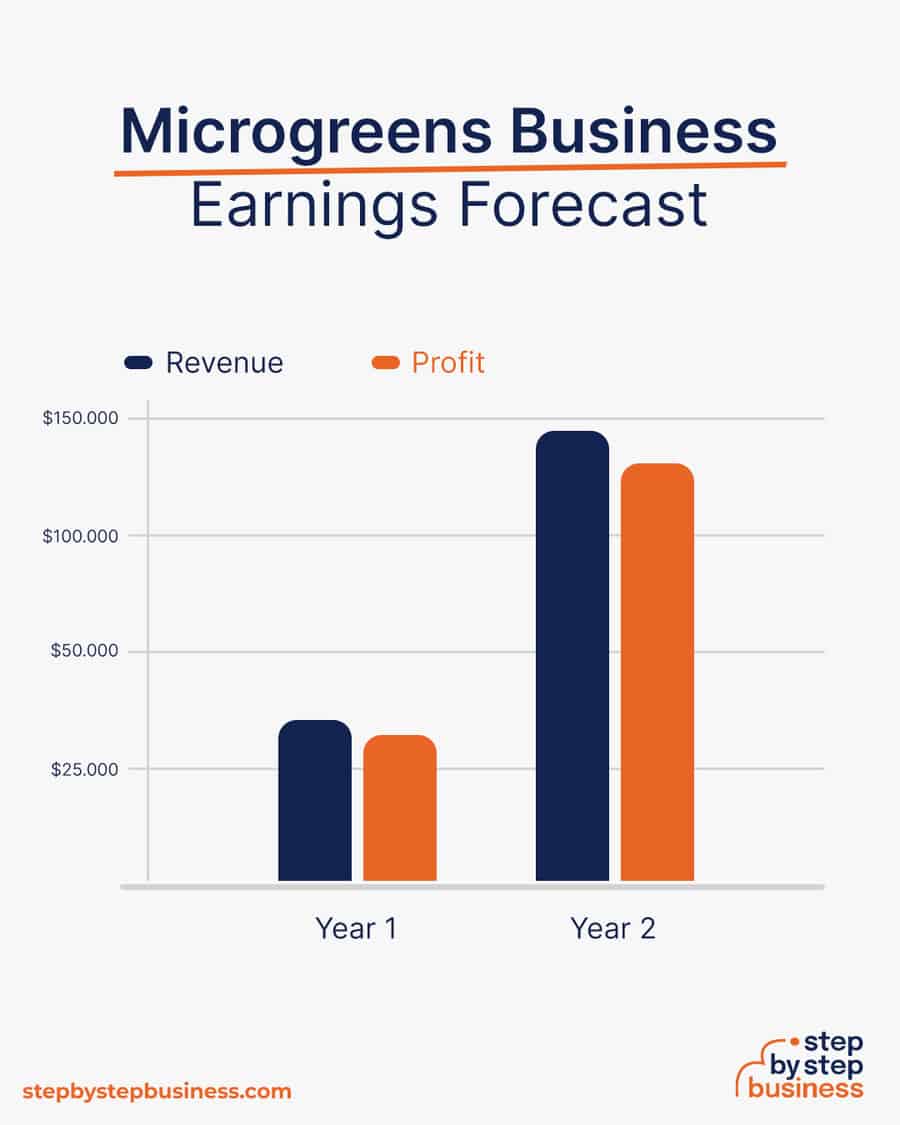
You should make about $20 per tray of microgreens, so your revenue will depend on how many trays you can fit in your space. Most microgreens grow in 2-3 weeks, so you should be able to average 1.5 grows per tray per month. Your profit margin will be about 90%.
In your first year or two, if you can sell 150 trays per month, you’ll bring in $36,000 in annual revenue. This would mean more than $30,000 in profit, assuming that 90% margin. As your business gains traction, you may be able to build a small greenhouse and sales could climb to 600 trays per month. With annual revenue of approaching $145,000, you’d make a tidy profit of $130,000.
What barriers to entry are there?
There are a few barriers to entry for a microgreens business. Your biggest challenges will be:
- Having ample space to grow enough to make money
- Building relationships with grocery stores and restaurants to make sales
Related Business Ideas

Starting a Plant Nursery Business

From Spores to Sales: Starting a Mushroom Farm

Your Guide to Starting a Greenhouse Business
Step 2: hone your idea.
Now that you know what’s involved in starting a microgreens business, it’s a good idea to hone your concept in preparation to enter a competitive market.
Market research will give you the upper hand, even if you’re already positive that you have a perfect product or service. Conducting market research is important, because it can help you understand your customers better, who your competitors are, and your business landscape.
Why? Identify an opportunity
Research microgreens businesses online and in your area to examine their products, price points, and customer reviews. You’re looking for a market gap to fill. For instance, maybe the local market is missing a business that sells pea shoots.
You might consider targeting a niche market by specializing in a certain aspect of your industry, such as pea shoots.
This could jumpstart your word-of-mouth marketing and attract clients right away.
What? Determine your microgreens offerings
You’ll need to determine which microgreens to grow and sell. Your best bet might be to go to local restaurants, particularly high-end restaurants, to ask what microgreens they use, and which they might be looking for. You could also go to high-end grocery stores.
How much should you charge for microgreens?
Prices for microgreens average $2 per ounce, and each microgreen tray should produce about 10 ounces, for a total of $20. Your ongoing costs will be limited to seeds and supplies, so you should aim for a profit margin of 90%.
Once you know your costs, you can use this Step By Step profit margin calculator to determine your mark-up and final price points. Remember, the prices you use at launch should be subject to change if warranted by the market.
Who? Identify your target market
Your target market will be mainly high-end restaurants and grocery stores. You can find their owners and managers on LinkedIn, and find the businesses on Google or Yelp. You could also set up a farmer’s market stand to sell direct to consumers.
Where? Choose your business premises
If you have adequate space, you can probably always run your business from home, and perhaps even build a small greenhouse in your backyard. If you don’t have space, you could rent a growing space. Find commercial space to rent in your area on sites such as Craigslist , Crexi , and Instant Offices .
When choosing a commercial space, you may want to follow these rules of thumb:
- Central location accessible via public transport
- Ventilated and spacious, with good natural light
- Flexible lease that can be extended as your business grows
- Ready-to-use space with no major renovations or repairs needed
Step 3: Brainstorm a Microgreens Business Name
Here are some ideas for brainstorming your business name:
- Short, unique, and catchy names tend to stand out
- Names that are easy to say and spell tend to do better
- Name should be relevant to your product or service offerings
- Ask around — family, friends, colleagues, social media — for suggestions
- Including keywords, such as “microgreens” or “organic microgreens”, boosts SEO
- Name should allow for expansion, for ex: “Green Oasis” over “Superfood Sprouts”
- A location-based name can help establish a strong connection with your local community and help with the SEO but might hinder future expansion
Once you’ve got a list of potential names, visit the website of the US Patent and Trademark Office to make sure they are available for registration and check the availability of related domain names using our Domain Name Search tool. Using “.com” or “.org” sharply increases credibility, so it’s best to focus on these.
Find a Domain
Powered by GoDaddy.com
Finally, make your choice among the names that pass this screening and go ahead with domain registration and social media account creation. Your business name is one of the key differentiators that sets your business apart. Once you pick your company name, and start with the branding, it is hard to change the business name. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider your choice before you start a business entity.
Step 4: Create a Microgreens Business Plan
Here are the key components of a business plan:
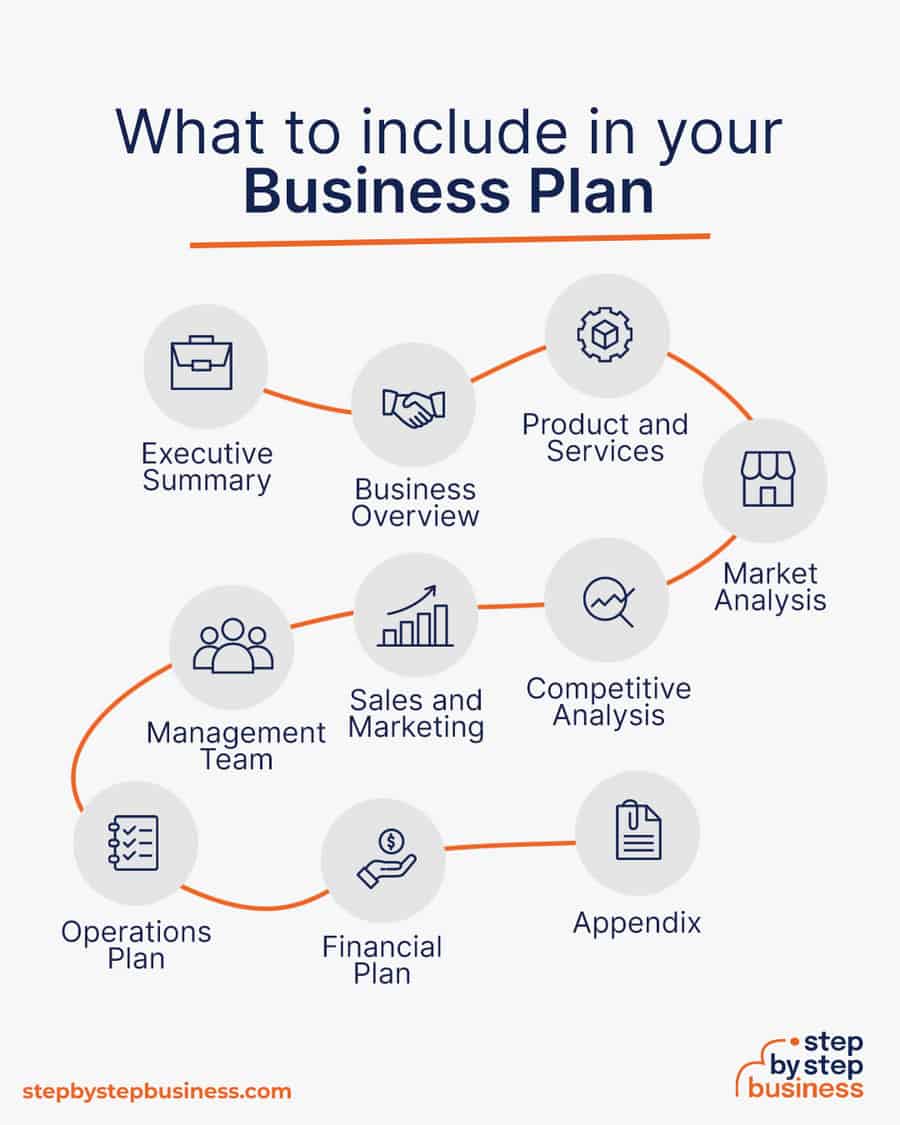
- Executive Summary : A brief overview of the microgreens business plan, highlighting its key aspects and objectives.
- Business Overview : A concise description of the microgreens business, including its mission, vision, and location.
- Product and Services : Details about the specific microgreens products and services offered, their unique features, and benefits.
- Market Analysis : Insights into the microgreens market, including target customer demographics, size, and growth potential.
- Competitive Analysis : Examination of competitors in the microgreens industry, their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning.
- Sales and Marketing : Strategies for promoting and selling microgreens, encompassing marketing and sales tactics.
- Management Team : Information about the individuals leading the microgreens business, their roles, and qualifications.
- Operations Plan : A plan outlining the day-to-day operations of the microgreens business, from sourcing to distribution.
- Financial Plan : Projections and financial details, including revenue, expenses, and funding requirements.
- Appendix : Supplementary documents and information that support the microgreens business plan, such as resumes, research data, and additional references.
If you’ve never created a business plan, it can be an intimidating task. You might consider hiring a business plan specialist to create a top-notch business plan for you.
Step 5: Register Your Business
Registering your business is an absolutely crucial step — it’s the prerequisite to paying taxes, raising capital, opening a bank account, and other guideposts on the road to getting a business up and running.
Plus, registration is exciting because it makes the entire process official. Once it’s complete, you’ll have your own business!
Choose where to register your company
Your business location is important because it can affect taxes, legal requirements, and revenue. Most people will register their business in the state where they live, but if you’re planning to expand, you might consider looking elsewhere, as some states could offer real advantages when it comes to microgreens businesses.
If you’re willing to move, you could really maximize your business! Keep in mind, it’s relatively easy to transfer your business to another state.
Choose your business structure
Business entities come in several varieties, each with its pros and cons. The legal structure you choose for your microgreens business will shape your taxes, personal liability, and business registration requirements, so choose wisely.
Here are the main options:
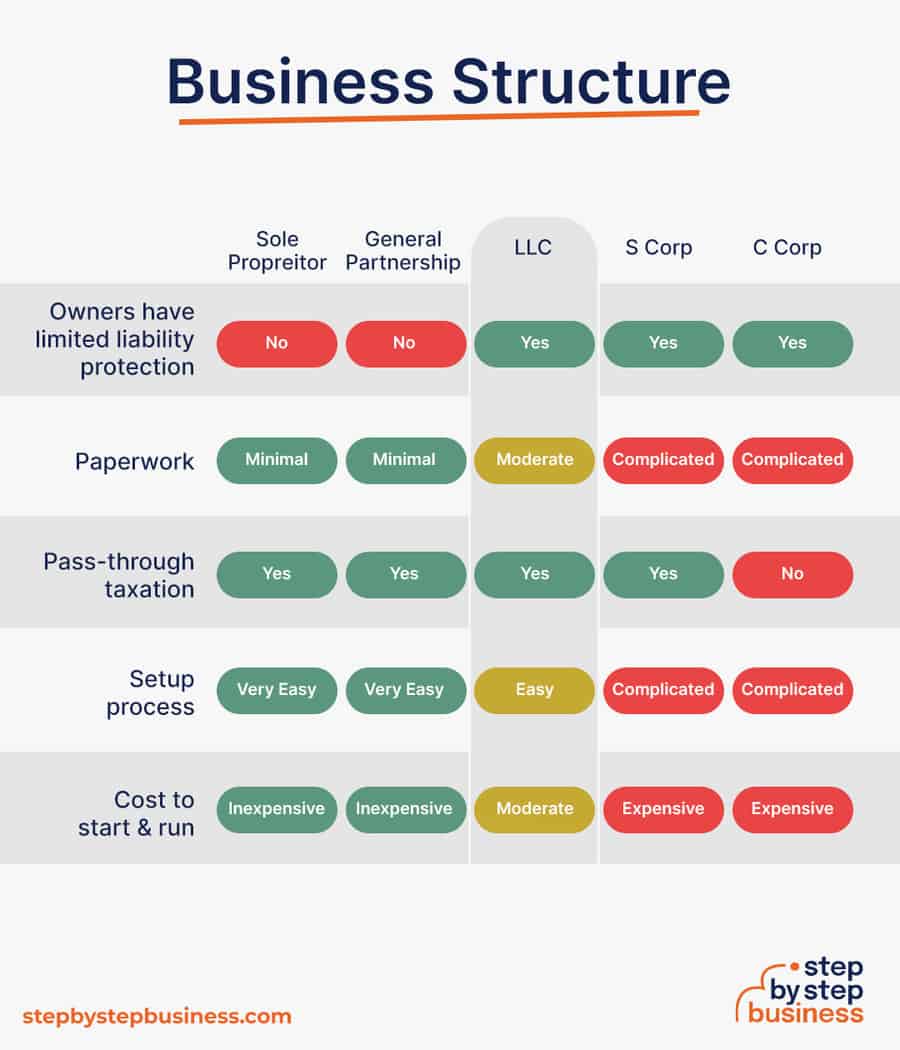
- Sole Proprietorship – The most common structure for small businesses makes no legal distinction between company and owner. All income goes to the owner, who’s also liable for any debts, losses, or liabilities incurred by the business. The owner pays taxes on business income on his or her personal tax return.
- General Partnership – Similar to a sole proprietorship, but for two or more people. Again, owners keep the profits and are liable for losses. The partners pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC) – Combines the characteristics of corporations with those of sole proprietorships or partnerships. Again, the owners are not personally liable for debts.
- C Corp – Under this structure, the business is a distinct legal entity and the owner or owners are not personally liable for its debts. Owners take profits through shareholder dividends, rather than directly. The corporation pays taxes, and owners pay taxes on their dividends, which is sometimes referred to as double taxation.
- S Corp – An S-Corporation refers to the tax classification of the business but is not a business entity. An S-Corp can be either a corporation or an LLC , which just need to elect to be an S-Corp for tax status. In an S-Corp, income is passed through directly to shareholders, who pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
We recommend that new business owners choose LLC as it offers liability protection and pass-through taxation while being simpler to form than a corporation. You can form an LLC in as little as five minutes using an online LLC formation service. They will check that your business name is available before filing, submit your articles of organization , and answer any questions you might have.
Form Your LLC
Choose Your State
We recommend ZenBusiness as the Best LLC Service for 2024

Step 6: Register for Taxes
The final step before you’re able to pay taxes is getting an Employer Identification Number , or EIN. You can file for your EIN online or by mail or fax: visit the IRS website to learn more. Keep in mind, if you’ve chosen to be a sole proprietorship you can simply use your social security number as your EIN.
Once you have your EIN, you’ll need to choose your tax year. Financially speaking, your business will operate in a calendar year (January–December) or a fiscal year, a 12-month period that can start in any month. This will determine your tax cycle, while your business structure will determine which taxes you’ll pay.
The IRS website also offers a tax-payers checklist , and taxes can be filed online.
It is important to consult an accountant or other professional to help you with your taxes to ensure you’re completing them correctly.
Step 7: Fund your Business
Securing financing is your next step and there are plenty of ways to raise capital:
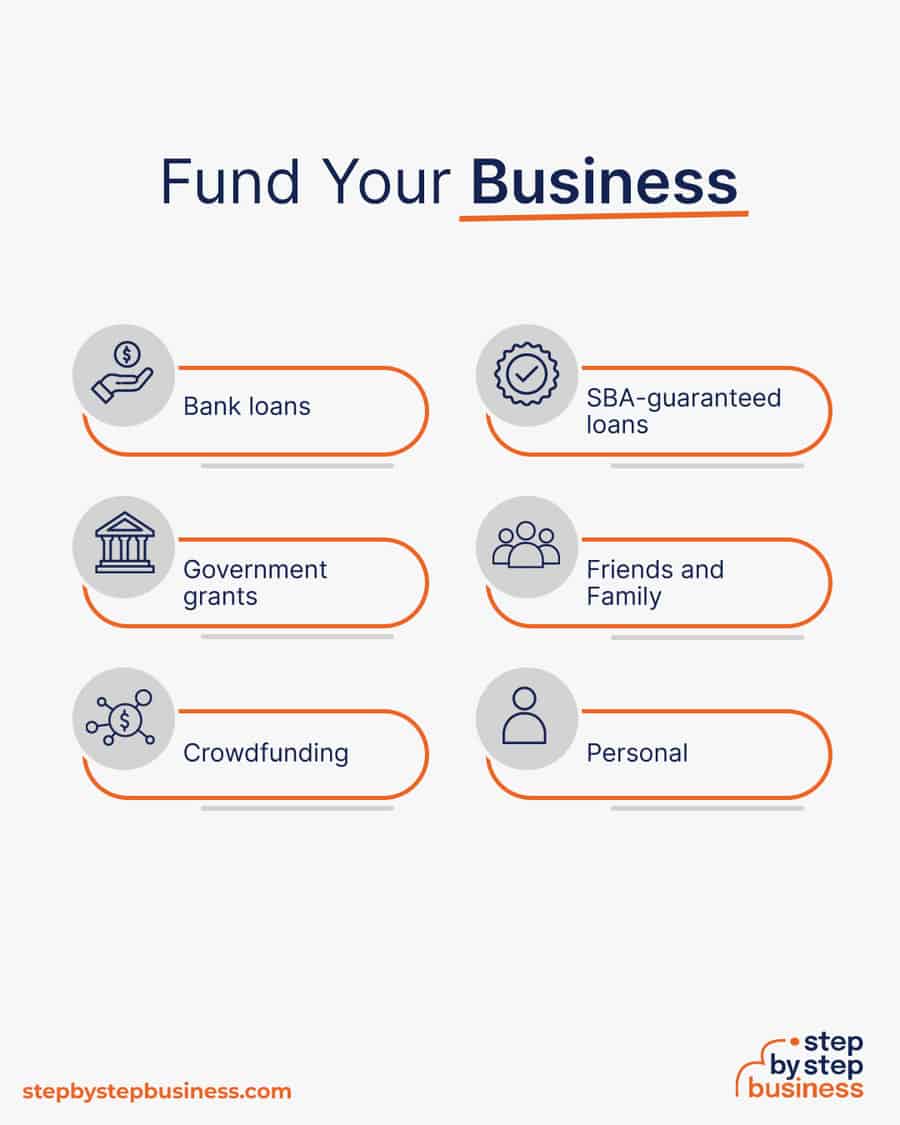
- Bank loans : This is the most common method but getting approved requires a rock-solid business plan and strong credit history.
- SBA-guaranteed loans: The Small Business Administration can act as guarantor, helping gain that elusive bank approval via an SBA-guaranteed loan .
- Government grants : A handful of financial assistance programs help fund entrepreneurs. Visit Grants.gov to learn which might work for you.
- Friends and Family : Reach out to friends and family to provide a business loan or investment in your concept. It’s a good idea to have legal advice when doing so because SEC regulations apply.
- Crowdfunding : Websites like Kickstarter and Indiegogo offer an increasingly popular low-risk option, in which donors fund your vision. Entrepreneurial crowdfunding sites like Fundable and WeFunder enable multiple investors to fund your business.
- Personal : Self-fund your business via your savings or the sale of property or other assets.
Bank and SBA loans are probably the best option, other than friends and family, for funding a microgreens business. You might also try crowdfunding if you have an innovative concept.
Step 8: Apply for Microgreens Business Licenses and Permits
Starting a microgreens business requires obtaining a number of licenses and permits from local, state, and federal governments.
Federal regulations, licenses, and permits associated with starting your business include doing business as (DBA), health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ), trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual properties, as well as industry-specific licenses and permits.
You may also need state-level and local county or city-based licenses and permits. The license requirements and how to obtain them vary, so check the websites of your state, city, and county governments or contact the appropriate person to learn more.
You could also check this SBA guide for your state’s requirements, but we recommend using MyCorporation’s Business License Compliance Package . They will research the exact forms you need for your business and state and provide them to ensure you’re fully compliant.
This is not a step to be taken lightly, as failing to comply with legal requirements can result in hefty penalties.
If you feel overwhelmed by this step or don’t know how to begin, it might be a good idea to hire a professional to help you check all the legal boxes.
Step 9: Open a Business Bank Account
Before you start making money, you’ll need a place to keep it, and that requires opening a bank account .
Keeping your business finances separate from your personal account makes it easy to file taxes and track your company’s income, so it’s worth doing even if you’re running your microgreens business as a sole proprietorship. Opening a business bank account is quite simple, and similar to opening a personal one. Most major banks offer accounts tailored for businesses — just inquire at your preferred bank to learn about their rates and features.
Banks vary in terms of offerings, so it’s a good idea to examine your options and select the best plan for you. Once you choose your bank, bring in your EIN (or Social Security Number if you decide on a sole proprietorship), articles of incorporation, and other legal documents and open your new account.
Step 10: Get Business Insurance
Business insurance is an area that often gets overlooked yet it can be vital to your success as an entrepreneur. Insurance protects you from unexpected events that can have a devastating impact on your business.
Here are some types of insurance to consider:
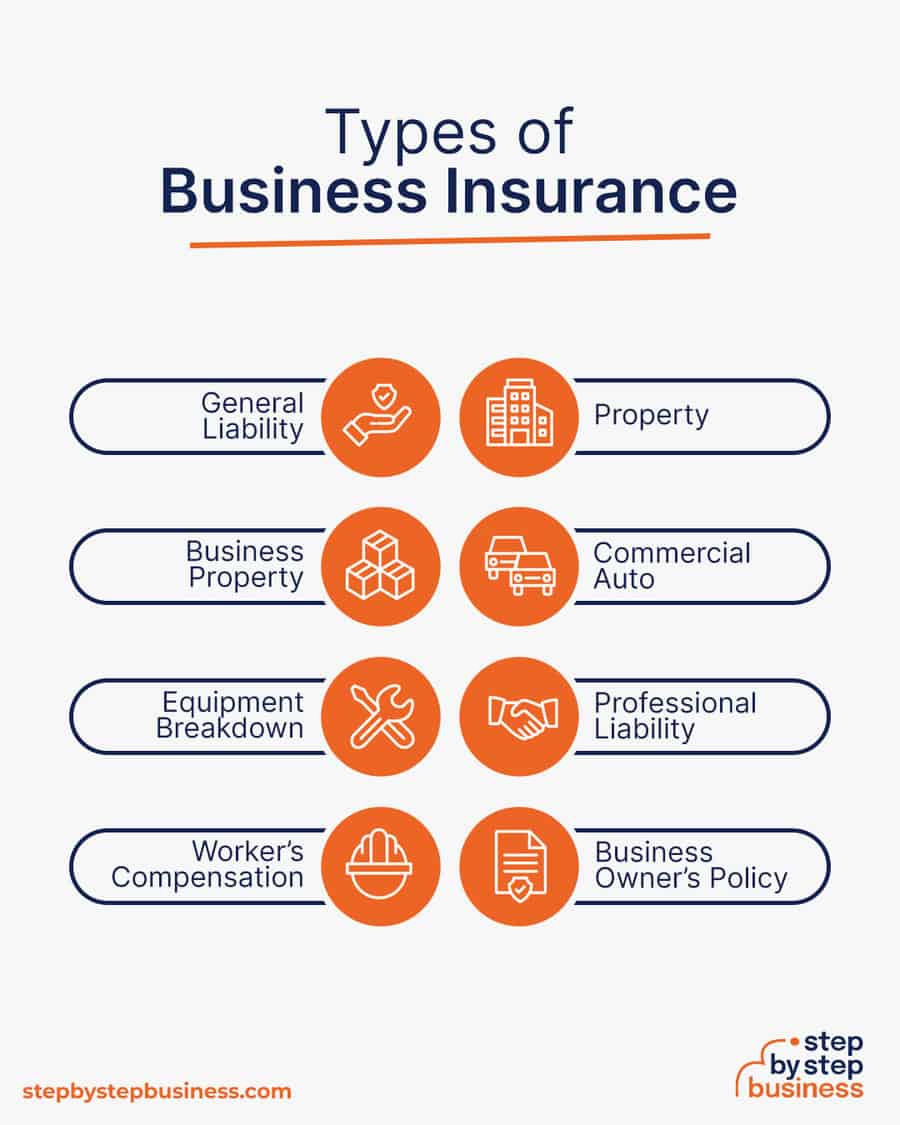
- General liability : The most comprehensive type of insurance, acting as a catch-all for many business elements that require coverage. If you get just one kind of insurance, this is it. It even protects against bodily injury and property damage.
- Business Property : Provides coverage for your equipment and supplies.
- Equipment Breakdown Insurance : Covers the cost of replacing or repairing equipment that has broken due to mechanical issues.
- Worker’s compensation : Provides compensation to employees injured on the job.
- Property : Covers your physical space, whether it is a cart, storefront, or office.
- Commercial auto : Protection for your company-owned vehicle.
- Professional liability : Protects against claims from a client who says they suffered a loss due to an error or omission in your work.
- Business owner’s policy (BOP) : This is an insurance plan that acts as an all-in-one insurance policy, a combination of the above insurance types.
Step 11: Prepare to Launch
As opening day nears, prepare for launch by reviewing and improving some key elements of your business.
Essential software and tools
Being an entrepreneur often means wearing many hats, from marketing to sales to accounting, which can be overwhelming. Fortunately, many websites and digital tools are available to help simplify many business tasks.
You may want to use industry-specific software, such as Fancom , Hectre , or Si , to manage your growing, harvesting, billing, and costs.
- Popular web-based accounting programs for smaller businesses include Quickbooks , Freshbooks , and Xero .
- If you’re unfamiliar with basic accounting, you may want to hire a professional, especially as you begin. The consequences for filing incorrect tax documents can be harsh, so accuracy is crucial.
Develop your website
Website development is crucial because your site is your online presence and needs to convince prospective clients of your expertise and professionalism.
You can create your own website using services like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace . This route is very affordable, but figuring out how to build a website can be time-consuming. If you lack tech-savvy, you can hire a web designer or developer to create a custom website for your business.
They are unlikely to find your website, however, unless you follow Search Engine Optimization ( SEO ) practices. These are steps that help pages rank higher in the results of top search engines like Google.
Launching a microgreens business requires creative and strategic marketing to stand out in a competitive market. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Local Farmers Markets and Food Festivals : Attend these events regularly to showcase your products. It’s a great way to interact directly with potential customers, get immediate feedback, and build a loyal local customer base.
- Social Media Marketing : Use platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Pinterest to showcase your microgreens through high-quality images and videos. Highlight the freshness, health benefits, and ways to use them in cooking. Engaging content like ‘behind-the-scenes’ farming processes or recipe ideas can attract a broader audience.
- Collaborations with Local Restaurants and Chefs : Partner with them to include your microgreens in their dishes. This not only provides a steady business but also acts as a testament to the quality of your product.
- Subscription Services : Offer a subscription model where customers receive a regular supply of fresh microgreens. This ensures a consistent revenue stream and builds customer loyalty.
- Workshops and Educational Sessions : Host events where you teach about the benefits of microgreens, how to grow them at home, and their nutritional value. This positions you as an expert in the field and can attract health-conscious consumers.
- Target Health and Wellness Platforms : Collaborate with health bloggers, dieticians, and wellness platforms to feature your microgreens. This can help you reach an audience that is already interested in healthy eating.
- Sampling and In-Store Promotions : If your microgreens are sold in local stores, arrange for sampling sessions. This allows potential customers to taste the quality firsthand, increasing the likelihood of purchase.
- Leverage Customer Reviews and Testimonials : Encourage your customers to share their experiences and feedback. This can be showcased on your social media and used as a powerful tool for attracting new customers.
- Offer Diverse and Unique Varieties : Experiment with and offer a range of microgreens that are not commonly available. This uniqueness can set you apart from competitors.
- Participate in Community Events : Engage in local community events to increase brand visibility and connect with potential customers in a more personal setting.
Focus on USPs

Unique selling propositions, or USPs, are the characteristics of a product or service that sets it apart from the competition. Customers today are inundated with buying options, so you’ll have a real advantage if they are able to quickly grasp how your microgreens business meets their needs or wishes. It’s wise to do all you can to ensure your USPs stand out on your website and in your marketing and promotional materials, stimulating buyer desire.
Global pizza chain Domino’s is renowned for its USP: “Hot pizza in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.” Signature USPs for your microgreens business could be:
- Organic , home-grown microgreens – can’t get any fresher than that!
- Fresh pea shoots, great taste and great for your health!
- Boost your immunity with antioxidant-rich microgreens
You may not like to network or use personal connections for business gain. But your personal and professional networks likely offer considerable untapped business potential. Maybe that Facebook friend you met in college is now running a microgreens business, or a LinkedIn contact of yours is connected to dozens of potential clients. Maybe your cousin or neighbor has been in microgreens for years and can offer invaluable insight and industry connections.
The possibilities are endless, so it’s a good idea to review your personal and professional networks and reach out to those with possible links to or interest in microgreens. You’ll probably generate new customers or find companies with which you could establish a partnership.
Step 12: Build Your Team
You will probably never need any employees unless you want to hire a salesperson to visit restaurants and grocery stores for you.
Free-of-charge methods to recruit employees include posting ads on popular platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, or Jobs.com. You might also consider a premium recruitment option, such as advertising on Indeed , Glassdoor , or ZipRecruiter . Further, if you have the resources, you could consider hiring a recruitment agency to help you find talent.
Step 13: Run a Microgreens Business – Start Making Money!
Microgreens are booming and you can get in on the action, help people live healthier lives and make a good living with your very own microgreens business. It’s easy, low-cost, and requires minimal labor. Now that you’ve done your business homework, it’s time to get your seeds and supplies and start walking down the garden path of entrepreneurial success.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Decide if the Business Is Right for You
- Hone Your Idea
- Brainstorm a Microgreens Business Name
- Create a Microgreens Business Plan
- Register Your Business
- Register for Taxes
- Fund your Business
- Apply for Microgreens Business Licenses and Permits
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get Business Insurance
- Prepare to Launch
- Build Your Team
- Run a Microgreens Business - Start Making Money!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.

19 Profitable Farming and Agriculture Ventures
David Lepeska
Published on November 4, 2022
Many young people today think it’s not cool to go into agriculture so they shy away from anything related to farms. Well, they’re missing a lot. ...

11 Sustainable Vegan Business Ideas for Eco-Friendly Ventures
Natalie Fell
Published on August 11, 2022
If you’re a vegan looking for a business idea that aligns with your diet, you’ve got more options than you might think. You could start abakery, ...

24 Green Business Ideas for Environmental Entrepreneurs
Published on July 12, 2022
Looking to help save the world? There are countless eco-friendly business ideas to help you create a greener earth while also making a good living.B ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.

Microgreens Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Microgreens Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their microgreens farms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a microgreens business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Microgreens Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your microgreens business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Microgreens Business
If you’re looking to start a microgreens business or grow your existing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your microgreens business in order to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Microgreen Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a microgreens business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings is the other most common form of funding for a microgreen business.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a microgreens farm.
If you want to start a microgreens business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The microgreens business plan template below provides a guide to what you should in each section of your own business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of microgreens business you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a microgreens business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of microgreen businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the microgreens industry. Discuss the type of microgreens business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of microgreens business you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of microgreens businesses:
- Organic Microgreens : this type of business grows only organic plants, which means starting with organic seeds and avoiding pesticides or herbicides in the growing process.
- Hydroponic Microgreens: this type of business grows plants from water instead of soil.
- Soil Grown Microgreens: this type of business is where microgreens are grown in soil.
In addition to explaining the type of microgreens business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of customers served, number of positive reviews, number of wholesale contracts, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the microgreens industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the microgreens industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section:
- How big is the microgreens industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your microgreens business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: restaurants, local grocery stores, farmer’s markets and CSAs.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of microgreens business you operate. Clearly, restaurants would respond to different marketing promotions than residents at farmer’s markets, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most microgreens businesses primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Microgreens Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other microgreens businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes plant nurseries, co-ops and CSAs. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other microgreens businesses with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be microgreens businesses located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of microgreens do they grow and sell?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regard to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide a better product or a wider product variety?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a microgreens business, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of microgreens company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to microgreens, will you provide delivery services, wholesaling or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your microgreens company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your microgreens business located in your home, a greenhouse, or an industrial facility with room for packaging operations and expansion, etc.? Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your microgreens marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your business, including cultivating plants, harvesting, packaging, making deliveries and meeting with potential customers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to reach X pounds of plant sales, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your microgreens business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your microgreens business’ ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing microgreens businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing microgreens operations or successfully running small businesses.

Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you gain one new customer per month or per quarter? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your microgreens business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a microgreens business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your facility location lease or blueprints of the growing operation you are working on.
Putting together a business plan for your microgreens business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will have an expert microgreens business plan; download it to PDF to show banks and investors. You will really understand the microgreens industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful microgreens business.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Microgreens business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Microgreens Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Microgreens Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Microgreens business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Microgreens businesses.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Microgreens business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Tara’s Greens is a startup microgreens farm located in Portland, Oregon. The company is founded by Tara Harper, an experienced horticulturist who has gained valuable knowledge on how to grow microgreens while working for another microgreens farm in the area. She started her career as a planting associate and worked her way up into an upper management position. Now that Tara has experienced managing a microgreens farm, she is ready to start her own company, Tara’s Greens. Tara is confident that her microgreens skills, combined with her understanding of business management, will enable her to run a profitable microgreens company of her own.
Tara’s Greens will provide a wide selection of microgreens for grocery stores, restaurants, and individual consumers. Tara’s Greens will be the go-to microgreens farm in Portland for fresh produce available all year round. The company will be the ultimate choice for customer service while offering the best prices in the area.
Product Offering
Tara’s Greens will offer a large selection of microgreens for grocery stores, restaurants, and individuals to buy. Some of these microgreens include kale, spinach, basil, watercress, and cabbage. Consumers can buy our products in grocery stores, at farmers markets, on our website, or directly at our facility.
Customer Focus
Tara’s Greens will primarily target grocery stores and restaurants located in the Portland, Oregon area. The company will also target customers including farmers market shoppers and customers who come directly to the farm to purchase microgreens.
Management Team
Tara’s Greens will be owned and operated by Tara Harper. Tara is a graduate of Oregon University with a degree in Horticulture. She has over ten years of experience working as an planting associate, grower, and facility manager at another local microgreens farm. Her education and experience are the company’s most valuable assets and will ensure that our farm is a success.
Success Factors
Tara’s Greens will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Skilled team of growers and horticulture experts who will oversee the growing process and conduct inspections daily to ensure all microgreen produce is of the highest quality.
- Tara’s Greens offer multiple ways for customers to shop with us. They can buy our microgreens online through our website, directly at our facility, or at local grocery stores and farmers markets.
- The company offers competitive pricing and discounts for regular customers.
Financial Highlights
Tara’s Greens is seeking $550,000 in debt financing to launch its microgreens business. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the facility and purchasing farm equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff and marketing expenses. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Facility build-out: $200,000
- Equipment, supplies, and materials: $100,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $50,000
- Working capital: $50,000
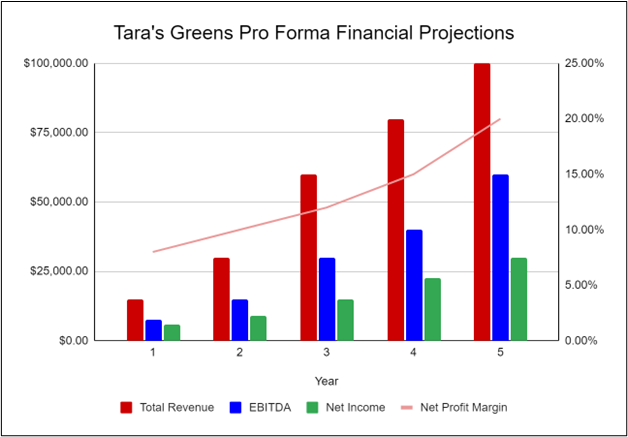
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Tara’s Greens.
Company Overview
Who is tara’s greens.
Tara’s Greens is a newly established microgreens company in Portland, Oregon. We aim to be the first choice for local grocers, restaurants, and consumers in Portland and the surrounding communities for fresh microgreens all year round. We will sell our products in grocery stores, at farmers markets, on our website, and directly from our farm.
Tara’s Greens will be able to guarantee the freshness, quality, and availability of its produce all year round thanks to the latest and most innovative microgreens technology and a stringent quality control process. We will use a vertical farming system to ensure we have the space to grow as many microgreens as possible. Customers can take a tour of our farm to learn how we grow our microgreens and to pick fresh microgreens directly from our facility.
Tara’s Greens’ History
Tara’s Greens is owned and operated by Tara Harper, an experienced horticulturist who has gained valuable knowledge during her ten year tenure working for another local microgreens farm. Now that Tara has gained the experience and knowledge of how to manage a microgreens farm, she is ready to start one of her own. Tara incorporated Tara’s Greens on June 1st, 2023.
Since incorporation, Tara’s Greens has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Tara’s Greens to transact business in the state of Oregon.
- Found a potential location and signed a letter of intent to lease it.
- Reached out to numerous contacts to include local restaurants, grocers, and farmers markets to start getting vendor contracts.
- Began recruiting a staff of technicians, growers, maintenance workers, and sales personnel to work at Tara’s Greens.
Tara’s Greens’ Services
Tara’s Greens will sell a wide variety of microgreens and herbs, including the following:
Industry Analysis
The global microgreens industry was valued at an estimated $1.3 billion in 2019 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.1% to reach $2.2 billion by 2028. This growth is led by increased spending on premium produce and healthy foods. The popularity of microgreens is also due to increased awareness of the importance of eating greens and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The industry’s growth is also influenced by the implementation of vertical farming, greenhouse farming, and similar technologies.
The microgreens market is highly fragmented with a handful of major players and an expanding global market for emerging companies making up the rest of the market share. Industry operators can achieve a competitive advantage by selling high quality, in-demand microgreens, effective marketing campaigns, and keeping up with local food trends.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Tara’s Greens will primarily target grocery stores and restaurants located in the Portland, Oregon area. The company will also target customers including farmers market shoppers and customers who come directly to the farm to purchase produce.
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,680,988 | 100% |
| Male | 838,675 | 49.9% |
| Female | 842,313 | 50.1% |
| 20 to 24 years | 114,872 | 6.8% |
| 25 to 34 years | 273,588 | 16.3% |
| 35 to 44 years | 235,946 | 14.0% |
| 45 to 54 years | 210,256 | 12.5% |
| 55 to 59 years | 105,057 | 6.2% |
| 60 to 64 years | 87,484 | 5.2% |
| 65 to 74 years | 116,878 | 7.0% |
| 75 to 84 years | 52,524 | 3.1% |
Customer Segmentation
Tara’s Greens will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Grocery stores
- Restaurants
- Farmers market shoppers
- Individuals looking for fresh herbs and microgreens
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Tara’s Greens will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Organic Microgreens
Organic Microgreens is one of the most popular microgreens farms in the Portland metro area. The company grows a wide variety of microgreens including cilantro, cress, fennel, kale, and sorrel. All of the company’s microgreens are grown organically and the company has a very stringent growing and quality control process to ensure each plant meets their standards of quality. Though Organic Microgreens is very popular, their high prices prevent many people in the Portland area from purchasing their products. Consumers looking for the same quality microgreens for an affordable price will be more eager to buy their microgreens from Tara’s Greens.
PDX Microgreens
PDX Microgreens is a small microgreens farm catering to local restaurants, grocers, and farmers markets in Portland, Oregon and surrounding areas. PDX Microgreens provide fresh microgreens including parsley, cabbage, celery, and arugula all year round. The company provides tours of the facility to local schools for a nominal fee. The owners of PDX Microgreens are former restaurant managers and farm-to-table supporters so they understand how important it is to the community for restaurants to have fresh produce and microgreens that are locally grown.
Tiny Greens
Tiny Greens is a trusted Portland, Oregon-based microgreens farm that provides superior produce to consumers in Portland and the surrounding areas. The company is able to provide a wide variety of microgreens using vertical farming and state-of-the-art equipment. Tiny Greens serve local grocers, specialty stores, and individual consumers with guaranteed fresh microgreens all year round.
Competitive Advantage
Tara’s Greens will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Tara’s Greens will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Tara’s Greens offers the best microgreens in town. All of our microgreens are organic and grown with great care.
- Our microgreens are priced competitively and the company offers discounts for regular customers.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Tara’s Greens is as follows:
Social Media Marketing
The company’s marketing director will create accounts on social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and YouTube.Shewill ensure Tara’s Greens maintains an active social media presence with regular daily updates and fun content to get customers excited about our microgreens.
Word of Mouth/Referrals
Tara’s Greens will encourage word-of-mouth marketing from loyal and satisfied clients. The company will incentivize its existing customer base to encourage their friends and colleagues to try its range of microgreens.
Print Advertising
Tara’s Greens will invest in professionally designed print ads to display in programs or flyers at industry networking events. The company will also send direct mailers to local restaurants and grocery stores.
Website/SEO Marketing
Tara’s Greens will utilize the in-house marketing director that designed the print ads to also design the company website. The website will be well organized, informative, and list all the produce that Tara’s Greens is able to provide. The website will also list information on the company’s events and guided tours.
The pricing of Tara’s Greens will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive value when purchasing the company’s produce.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Tara’s Greens. Operation Functions:
- Tara Harper will be the CEO and Head Farmer of Tara’s Greens. She will oversee the staff, production process, and general operations of the company. Tara will spend the next several months recruiting the following staff:
- Chief Operating Officer who will manage the budgeting, vendor relationships, and logistics.
- Staff Accountant/Bookkeeper will provide all accounting, tax payments, and monthly financial reporting.
- Marketing Director who will oversee all marketing strategies for the company and manage the website, social media, and outreach.
- Several growers and farm hands who will grow microgreens and ensure they meet our standards of quality.
Milestones:
Tara’s Greens will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
- 8/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease property.
- 9/1/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the Tara’s Greens management team.
- 10/1/202X – Begin build-out of the facility, purchase equipment, and start production.
- 11/1/202X – Begin networking at industry events and implement the marketing plan.
- 12/1/202X – Finalize contracts for initial grocery, farmers market, and restaurant vendors.
- 1/1/202X – Tara’s Greens officially opens its facility up to customers and starts shipping out online orders.
Though Tara has never run a business of her own, she has worked in the industry long enough to gain an in-depth knowledge of the operations (e.g., running day-to-day operations) and the business (e.g., staffing, marketing, etc.) sides of running a microgreens business. She will also hire several professionals to help her run other aspects of the business she is unfamiliar with.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Tara’s Greens are the fees charged to customers in exchange for the company’s products. When it comes to pricing, the company will monitor production costs, average prices charged by competitors, and product availability in the market to ensure its prices will generate a healthy profit margin.
The cost drivers will include the overhead costs, labor costs, cost of the equipment and supplies, and marketing expenses.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Pounds of microgreens sold per month: 1000
- Overhead costs per year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Microgreens Business Plan FAQs
What is a microgreens business plan.
A microgreens business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your microgreens business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Microgreens business plan using our Microgreens Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Microgreens Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of microgreens businesses , some examples include: Organic Microgreens, Hydroponic Microgreens, and Soil Grown Microgreens.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Microgreens Business Plan?
Microgreens businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Microgreens Business?
Starting a microgreens business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Microgreens Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed microgreens business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your microgreens business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your microgreens business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Microgreens Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your microgreens business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your microgreens business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Microgreens Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your microgreens business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your microgreens business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful microgreens business:
- How to Open a Microgreens Business

Sow the seeds of success: microgreens business plan essentials
The global microgreens industry is flourishing, offering immense potential. As demand for fresh produce rises, health-focused consumers increasingly seek microgreens. Starting a microgreens business and succeeding in this competitive market requires a well-thought-out microgreens business plan.

Microgreens business overview
A well-prepared business plan is the backbone of success in the microgreens market. It serves as a roadmap, guiding you through every step of your entrepreneurial journey.
Benefits of a well-written business plan
Developing a comprehensive business plan offers various benefits. It ensures a deep understanding of your market, competitors, and target audience.
Meticulous market research helps identify trends, preferences, and potential opportunities.
Essential sections of a microgreens business plan template

Market research and analysis: the basis for building a business plan
With this roadmap, you can establish a strong foundation for your microgreens business. The SWOT analysis ensures you understand your business’s current state, allowing you to develop a strategic microgreens business plan.
Writing the business plan
Executive summary and company analysis.
A concise executive summary highlights your microgreens business’s core aspects and goals to attract potential investors and stakeholders. It should effectively showcase the value of your microgreens business plan through your business’s potential.
A compelling executive summary and well-presented company analysis form a strong foundation for your business plan.
Effective marketing and promotion
A marketing plan is vital to growing your microgreens business and reaching your target customers. Use effective techniques like digital platforms, local promotions, and partnerships with health-conscious communities to create brand awareness.
Operations and financial projections
To ensure financial health and sustainability of this, accurate cash flow forecasts and profit margins are vital.
Building a strong management team
Financing your successful microgreens business.
When funding your microgreens business , explore various financing sources to make informed decisions and secure the necessary capital.
You can dip into your personal savings or seek loans from banks to kickstart your microgreens business, while still retaining control over it.

Targeting customers: from local grocery stores to home cooks
When starting a microgreens business, effectively targeting and reaching your customers is a crucial challenge.
Defining your target market
Health-conscious consumers.
This group prioritizes nutritious and fresh microgreens options. Use digital marketing, social media, and health influencers to showcase microgreens’ health benefits and attract them.
Retail and wholesale
Local restaurants and specialty eateries, health food enthusiasts.
Health food stores and food delivery services seek nutrient-dense organic microgreens. Promote to them your organic microgreens and their nutritional benefits, and provide point-of-sale materials for better visibility.
Urban dwellers and home cooks
Offer starter kits and guidance for home cultivation, and provide recipe ideas and cooking tips on your website.
Maximizing ways to reach and engage your target audience
Growing and selling high-quality microgreens.
Starting a microgreens business takes more than just a savvy mind – it’s an art that demands precision, knowledge, and passion. These young and tender shoots of veggies and herbs have captured the culinary scene with their intense flavors and exceptional nutrition.
Mastering the growing process
Sourcing supplies.
Start a microgreens business with premium-quality seeds and growing mediums. Partner with reputable suppliers to obtain seeds that guarantee high germination rates and flavorful yields. Equally crucial is the choice of growing medium, as it directly impacts the nutritional density and overall quality of your microgreens.
Offering fresh and vibrant microgreens
Diverse distribution channels.
Explore various distribution channels to reach your target market. Participate in local farmers’ markets to engage with health-conscious audiences directly. Partner with nearby grocery stores and restaurants, use online platforms to cater to a broader audience, and offer doorstep delivery.
Effective sales strategies
Develop a marketing plan that tailors your messaging and offerings to different target groups, positioning your microgreens as a premium and essential ingredient in any kitchen.

Choosing among business structures for microgreens businesses
Financial planning.
Detailed financial planning, including startup costs, ongoing expenses, and revenue projections, is essential for your business strategy. This blueprint will serve as your roadmap to financial stability and growth.
Besides the obvious financial planning steps, you need to pay attention to several things that will affect and, in many cases, define the success of your venture. Let’s discuss what these things are.
Embracing financial flexibility. Be prepared to adapt and make necessary adjustments to your financial plan as your microgreens venture grows.
Consider investing in employee training – this will not only enhance productivity but also lead to improved financial performance and sustainable growth of your business.
Monitoring business performance. Regularly track key performance indicators (KPIs) like sales, expenses, and customer feedback. Analyze data to identify areas for improvement and capitalize on growth opportunities.

Is microgreens business profitable?
Is growing microgreens still profitable.
Yes, despite increased competition and market saturation, growing microgreens can still be profitable. As demand for fresh, nutritious produce continues to rise, targeting specific customer segments and employing efficient marketing strategies can help maintain profitability in the microgreens industry.
Do microgreens sell well?
How do i market my microgreens business.
To achieve success in the microgreens industry, meticulous planning and execution are essential. It all begins with a comprehensive business plan encompassing well-conducted research, impactful marketing tactics, financial forecasts, and a capable management team.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
