The Argumentative Essay
AP Language & Composition Exam
What does the argumentative essay require of you?
- Basically, you must do three things:
- understand the nature of the position taken in the prompt;
- take a specific stand—argue, qualify, or disagree—with the assertion in the prompt; and
- clearly and logically support your claim.
Agree, Disagree, Qualify
- Do I think about this subject in the same way as the writer/speaker? (Agree)
- Do I think the writer/speaker is totally wrong? (Disagree)
- Do I think some of what is said is correct and some incorrect and do I feel lucky? (Qualify)
Plan before you write!
- Brainstorm a list of ideas, construct a chart, or create an outline…whatever it is, give yourself time to THINK about your position!
- The kinds of support you need:
- Facts/statistics - Details - Dialogue
- Quotations - Definitions - Anecdotes
- Contrast and comparison - Cause and Effect
- Appeal to authority - Examples
Does it matter what tone is taken in your argumentative essay?
- You can choose to be informal and personal, formal and objective, or even humorous and irreverent—just be certain your choice is appropriate for your purpose.
Will I be penalized for taking an unpopular, unexpected, irreverent, or bizarre position on the given issue?
- As long as you are addressing the PROMPT and appropriately supporting your position, there is no danger of losing points on your essay.
- Your essay is graded for process and mastery and manipulation of language, not for how close you come to the viewpoint of your reader.
Suggested time distribution for the argumentative essay:
- 1-3 minutes reading and working the PROMPT
- 3 minutes deciding on a position
- 10-12 minutes planning the support of your position
- 20 minutes writing the essay
- 3 minutes proofreading!
The argumentative essay prompt
In his famous “Vast Wasteland” address to the National Association of Broadcaster in May of 1961, Newton Minow, the Chairman of the Federal Communications Commission, spoke about the power of television to influence the taste, knowledge, and opinions of its viewers around the world. Carefully read the following, paying close attention to how timely it is today, especially in light of the worldwide Internet.
Minow ended his speech warning that “The power of instantaneous sight and sound is without precedent in mankind’s history. This is an awesome power. It has limitless capabilities for good—and for evil. And it carries with it awesome responsibilities—responsibilities which you and [the government] cannot escape…”
Using your own knowledge and your own experiences or reading, write a carefully constructed essay that defends, challenges, or qualifies Minow’s ideas.
Mark your copy of the prompt…take about 3 minutes.
In his famous “Vast Wasteland” address to the National Association of Broadcasters in May of 1961 , Newton Minow , the Chairman of the Federal Communications Commission , spoke about the power of television to influence the taste, knowledge, and opinions of its viewers around the world . Carefully read the following, paying close attention to how timely it is today, especially in light of the worldwide Internet.
Minow ended his speech warning that “The power of instantaneous sight and sound is without precedent in mankind’s history . This is an awesome power . It has limitless capabilities for good—and for evil . And it carries with it awesome responsibilities —responsibilities which you and [the government] cannot escape …”
Using your own knowledge and your own experiences or reading , write a carefully constructed essay that defends, challenges, or qualifies Minow’s ideas.
Developing the opening paragraph
- Refer specifically to the prompt
- Clearly state your position on the given issue
Newton Minow’s assertion to the national Association of Broadcasters that “The power of instantaneous sight and sound is . . . An awesome power . . . With capabilities for good—and for evil” is valid and true. However, placing the responsibility for this power squarely in the hands of the broadcasters and the government is in error.
Qualifies the assertion
The writer agrees with the potential of the power, but disagrees about who should take responsibility.
Imagine being gifted the limitless capability for good and evil—the ability to control the world with one’s super powers. And, what are these powers? X-ray vision? Morphability? Immortality? NO, it is the most awesome power ever devised—the instantaneous influence over the taste, knowledge and opinions of mankind around the world. Even Superman would get a headache from this kind of power! This is not a great gift, it is an “awesome responsibility” according to the Newton Minow’s 1961 warning to the National Association of Broadcasters.
Agrees with the assertion
The writer agrees with Minow’s position but treats the assertion in a lighthearted fashion. The reader can expect a humorous and possibly irreverent tone in the essay.
Nowhere is the awesome power for good and evil of modern technology more clearly seen than in the Internet’s pervasiveness and influence. Newton Minow was right on target in 1961 when he warned the National Association of Broadcasters that the power of TV has “limitless capabilities for good—and for evil.”
The writer agrees with Minow’s position, BUT has LIMITED the area of the argument to that of the Internet.
Developing the body of the essay
- After carefully reading and deconstructing the prompt, choose a way to organize your argument
- One way (for this prompt) would be to use Minow’s own three-part warning and brainstorm ideas based on those categories
Planning the essay (focus on Internet)
- Warning of dangers
- Recognition of heroes
- Involvement in humankind’s achievements
- Instant communications with family & friends
- Medical care
- Links to the world
- Entertainment
- Promote hate
- Distort reality
- Help terrorists
- Invasion of privacy
- Threats to nat’l security
- Create mass hysteria
- Exploit children
- Subvert elections
- Brainwashing
- Responsibility
- Self-censorship
- Prior restraint
- 1 st Amendment
- Financial gain
- Parental control
- Personal checks and balances
Choose those specific items you will best be able to support and develop
A sample body paragraph based on the first list:
One of the most rewarding applications of the Internet is its ability to provide instant communication between friends and family. A grandmother-to-be in New York is able to share in the moment by moment experience of her daughter’s pregnancy and her granddaughter’s birth in California through e-mail, scanned photos and quick videos . Likewise, the ability to instantly communicate with others may have saved the life of a doctor stranded at the South Pole. Her contact with medical resources and experts via the Internet enabled her to undergo surgery and treatment for breast cancer. Research and innovations in medical treatment are now available to those around the world via the “net.” Similarly, the ability for instance communication enables millions to enjoy concerts, sports events, theatrical presentations and other cultural activities without every having to leave home. These wonderful benefits are all because of the fabulous and awesome technological creation—the Internet.
Remember IDEAL ?
Analysis (explain)
One of the most rewarding applications of the Internet is its ability to provide instant communication between friends and family. A grandmother-to-be in New York is able to share in the moment by moment experience of her daughter’s pregnancy and her granddaughter’s birth in California through e-mail, scanned photos and quick videos. Likewise, the ability to instantly communicate with others may have saved the life of a doctor stranded at the South Pole. Her contact with medical resources and experts via the Internet enabled her to undergo surgery and treatment for breast cancer . Research and innovations in medical treatment are now available to those around the world via the “net.” Similarly, the ability for instance communication enables millions to enjoy concerts, sports events, theatrical presentations and other cultural activities without every having to leave home. These wonderful benefits are all because of the fabulous and awesome technological creation—the Internet.
A sample body paragraph based on the second list:
The other side of the mass communication coin has the face of evil on it. The Internet offers hate mongers unlimited access to anyone with a connection to the World Wide Web. Groups like the Neo-Nazis can spread their hate messages to susceptible minds via bright, entertaining and engaging websites. What looks like a simple, fun game can easily reinforce the group’s hate-filled philosophy to unsuspecting browsers. With the potential for millions of “hits” each week, it does not take a rocket scientist to perceive the danger here. This danger is also present with the minds and bodies of curious and vulnerable
young people. Because of its easy access and easy production, “kiddie porn” is both possible and available via the Internet and the films any number of porn sites offer for downloading with the mere click of a keyboard key. Through contacts made through e-mail and/or chat rooms on the Net, children can be easily fooled and led to contact those who would abuse their bodies and minds for a quick profit or cheap thrill. With instantaneous messaging, whether real or imagined, positive or negative, a single person or group can set into motion mass hysteria just by warning of an impending disaster, such as a flood, fire, bomb, poison, and son on. There are obviously many more possibilities floating out there in the ethernet. These are just three of the evil ones.
A sample body paragraph based on the THIRD list:
Just as there is the potential for both good and evil with regard to mass communication, so too is there the potential for both beneficial and destructive strategies related to reponsibilities. The most powerful regulator of our responsibility as individuals is our finger and its power to press a button or double click on a key and to “just say no.” With this slight pressure, we are able to exert monumental pressure on those who produce programs, websites, photos, documents, etc., which we find unacceptable. Who better to tell us what to watch, what to do, and what to think? All too
Often many people prefer to abdicate their personal responsibility and give that power to either the government or the communication industry. We must never forget that dictators target the control and censorship of mass media as the first step in the total control of the minds and hearts of the populace. The laws, which we as citizens of a democracy look to, must never impinge upon our First and Fourth Amendment rights. Each of us has the right of free speech, and each of us has the right to privacy. None of us has the right to harm others or to limit the rights of others; why, then, would we give that right to the communication industry or to the government?
The concluding paragraph
- Spend your time in planning and writing the body of your essay
- In a brief essay, you can be certain your reader can remember what you’ve already said, so there is no need to summarize your major points or to repeat the prompt.
- If you feel you MUST have a concluding statement/remark, make certain it is a FINAL remark that is of interest and is appropriate to your purpose
- You may use the last sentence of your last body paragraph as your concluding comment.
Yes, this concluding sentence IS a little on the giddy side…
Argumentative Practice Essay
- Refer to your notes
- Don’t take shortcuts
- I’ll put times up on the board
- You’ll get the whole 40 minutes to go through the entire process

- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
ESSAY WRITING FOR EXAMS
Published by Osborn Black Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "ESSAY WRITING FOR EXAMS"— Presentation transcript:

Understanding CP Writing Tasks

Writing a Report. Writing a Report – some tips ANSWER THE QUESTION PLAN your report. Make sure you have at least 5 sections You first paragraph will be.

Evaluator Identification & Preview Sign your name at the end of the essay. Review objective of the PROGRESS CHECK. Take 2 minutes to preview your peers.

Literacy Test Preparation

Strategies for Timed Writing

Argumentative Essay Standard: ELAGSE6W1

Report Writing.

Useful tips © Gerlinde Darlington MEd.Mag.phil.. Introduction Main part – consisting of a few paragraphs Conclusion Remember: poorly structured.

May 2009 Of Mice and Men Essay.

Essay Writing.

ESSAY WRITING AT LEVEL 3 How to lift your game. Analyse the question At Level 3, the questions are more complex. The question will require careful.

Developing the composition for the exam Some tips.

A woman’s place is in the home. Do you agree?

Writing Workshop Literary Analysis. The Five-Paragraph Essay Introduction Body: Supporting Paragraphs Conclusion.

31 Ways to Flavor a Composition. Consider the audience.

Writing an Analytical Essay HIMALAYA SUMMIT. 1. Understand Your Issue 2. Understand Your Question 3. Take a Position 4. Be Able to Support Your Position!

How do you end your essay in a way that leaves your reader thinking?

The Extended Response LOOK AT THE MAIN TOPIC—that is what you will be using for your idea. The other questions are guidelines for brainstorming. DO: remember.

Preparing for the College Writing Examination
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing Essays for Exams

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is a well written answer to an essay question?
Well Focused
Be sure to answer the question completely, that is, answer all parts of the question. Avoid "padding." A lot of rambling and ranting is a sure sign that the writer doesn't really know what the right answer is and hopes that somehow, something in that overgrown jungle of words was the correct answer.
Well Organized
Don't write in a haphazard "think-as-you-go" manner. Do some planning and be sure that what you write has a clearly marked introduction which both states the point(s) you are going to make and also, if possible, how you are going to proceed. In addition, the essay should have a clearly indicated conclusion which summarizes the material covered and emphasizes your thesis or main point.
Well Supported
Do not just assert something is true, prove it. What facts, figures, examples, tests, etc. prove your point? In many cases, the difference between an A and a B as a grade is due to the effective use of supporting evidence.
Well Packaged
People who do not use conventions of language are thought of by their readers as less competent and less educated. If you need help with these or other writing skills, come to the Writing Lab
How do you write an effective essay exam?
- Read through all the questions carefully.
- Budget your time and decide which question(s) you will answer first.
- Underline the key word(s) which tell you what to do for each question.
- Choose an organizational pattern appropriate for each key word and plan your answers on scratch paper or in the margins.
- Write your answers as quickly and as legibly as you can; do not take the time to recopy.
- Begin each answer with one or two sentence thesis which summarizes your answer. If possible, phrase the statement so that it rephrases the question's essential terms into a statement (which therefore directly answers the essay question).
- Support your thesis with specific references to the material you have studied.
- Proofread your answer and correct errors in spelling and mechanics.
Specific organizational patterns and "key words"
Most essay questions will have one or more "key words" that indicate which organizational pattern you should use in your answer. The six most common organizational patterns for essay exams are definition, analysis, cause and effect, comparison/contrast, process analysis, and thesis-support.
Typical questions
- "Define X."
- "What is an X?"
- "Choose N terms from the following list and define them."
Q: "What is a fanzine?"
A: A fanzine is a magazine written, mimeographed, and distributed by and for science fiction or comic strip enthusiasts.
Avoid constructions such as "An encounter group is where ..." and "General semantics is when ... ."
- State the term to be defined.
- State the class of objects or concepts to which the term belongs.
- Differentiate the term from other members of the class by listing the term's distinguishing characteristics.
Tools you can use
- Details which describe the term
- Examples and incidents
- Comparisons to familiar terms
- Negation to state what the term is not
- Classification (i.e., break it down into parts)
- Examination of origins or causes
- Examination of results, effects, or uses
Analysis involves breaking something down into its components and discovering the parts that make up the whole.
- "Analyze X."
- "What are the components of X?"
- "What are the five different kinds of X?"
- "Discuss the different types of X."
Q: "Discuss the different services a junior college offers a community."
A: Thesis: A junior college offers the community at least three main types of educational services: vocational education for young people, continuing education for older people, and personal development for all individuals.
Outline for supporting details and examples. For example, if you were answering the example question, an outline might include:
- Vocational education
- Continuing education
- Personal development
Write the essay, describing each part or component and making transitions between each of your descriptions. Some useful transition words include:
- first, second, third, etc.
- in addition
Conclude the essay by emphasizing how each part you have described makes up the whole you have been asked to analyze.
Cause and Effect
Cause and effect involves tracing probable or known effects of a certain cause or examining one or more effects and discussing the reasonable or known cause(s).
Typical questions:
- "What are the causes of X?"
- "What led to X?"
- "Why did X occur?"
- "Why does X happen?"
- "What would be the effects of X?"
Q: "Define recession and discuss the probable effects a recession would have on today's society."
A: Thesis: A recession, which is a nationwide lull in business activity, would be detrimental to society in the following ways: it would .......A......., it would .......B......., and it would .......C....... .
The rest of the answer would explain, in some detail, the three effects: A, B, and C.
Useful transition words:
- consequently
- for this reason
- as a result
Comparison-Contrast
- "How does X differ from Y?"
- "Compare X and Y."
- "What are the advantages and disadvantages of X and Y?"
Q: "Which would you rather own—a compact car or a full-sized car?"
A: Thesis: I would own a compact car rather than a full-sized car for the following reasons: .......A......., .......B......., .......C......., and .......D....... .
Two patterns of development:
- Full-sized car
Disadvantages
- Compact car
Useful transition words
- on the other hand
- unlike A, B ...
- in the same way
- while both A and B are ..., only B ..
- nevertheless
- on the contrary
- while A is ..., B is ...
- "Describe how X is accomplished."
- "List the steps involved in X."
- "Explain what happened in X."
- "What is the procedure involved in X?"
Process (sometimes called process analysis)
This involves giving directions or telling the reader how to do something. It may involve discussing some complex procedure as a series of discrete steps. The organization is almost always chronological.
Q: "According to Richard Bolles' What Color Is Your Parachute?, what is the best procedure for finding a job?"
A: In What Color Is Your Parachute?, Richard Bolles lists seven steps that all job-hunters should follow: .....A....., .....B....., .....C....., .....D....., .....E....., .....F....., and .....G..... .
The remainder of the answer should discuss each of these seven steps in some detail.
- following this
- after, afterwards, after this
- subsequently
- simultaneously, concurrently
Thesis and Support
- "Discuss X."
- "A noted authority has said X. Do you agree or disagree?"
- "Defend or refute X."
- "Do you think that X is valid? Defend your position."
Thesis and support involves stating a clearly worded opinion or interpretation and then defending it with all the data, examples, facts, and so on that you can draw from the material you have studied.
Q: "Despite criticism, television is useful because it aids in the socializing process of our children."
A: Television hinders rather than helps in the socializing process of our children because .......A......., .......B......., and .......C....... .
The rest of the answer is devoted to developing arguments A, B, and C.
- it follows that
A. Which of the following two answers is the better one? Why?
Question: Discuss the contribution of William Morris to book design, using as an example his edition of the works of Chaucer.
a. William Morris's Chaucer was his masterpiece. It shows his interest in the Middle Ages. The type is based on medieval manuscript writing, and the decoration around the edges of the pages is like that used in medieval books. The large initial letters are typical of medieval design. Those letters were printed from woodcuts, which was the medieval way of printing. The illustrations were by Burn-Jones, one of the best artists in England at the time. Morris was able to get the most competent people to help him because he was so famous as a poet and a designer (the Morris chair) and wallpaper and other decorative items for the home. He designed the furnishings for his own home, which was widely admired among the sort of people he associated with. In this way he started the arts and crafts movement.
b. Morris's contribution to book design was to approach the problem as an artist or fine craftsman, rather than a mere printer who reproduced texts. He wanted to raise the standards of printing, which had fallen to a low point, by showing that truly beautiful books could be produced. His Chaucer was designed as a unified work of art or high craft. Since Chaucer lived in the Middle Ages, Morris decided to design a new type based on medieval script and to imitate the format of a medieval manuscript. This involved elaborate letters and large initials at the beginnings of verses, as well as wide borders of intertwined vines with leaves, fruit, and flowers in strong colors. The effect was so unusual that the book caused great excitement and inspired other printers to design beautiful rather than purely utilitarian books.
From James M. McCrimmon, Writing with a Purpose , 7th ed. (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1980), pp. 261-263.
B. How would you plan the structure of the answers to these essay exam questions?
1. Was the X Act a continuation of earlier government policies or did it represent a departure from prior philosophies?
2. What seems to be the source of aggression in human beings? What can be done to lower the level of aggression in our society?
3. Choose one character from Novel X and, with specific references to the work, show how he or she functions as an "existential hero."
4. Define briefly the systems approach to business management. Illustrate how this differs from the traditional approach.
5. What is the cosmological argument? Does it prove that God exists?
6. Civil War historian Andy Bellum once wrote, "Blahblahblah blahed a blahblah, but of course if blahblah blahblahblahed the blah, then blahblahs are not blah but blahblah." To what extent and in what ways is the statement true? How is it false?
For more information on writing exam essays for the GED, please visit our Engagement area and go to the Community Writing and Education Station (CWEST) resources.
No Frills Study Skills
From the skills team at the university library, assessed presentation learn from your essay structure.
Many students panic when they first have to create an assessed presentation. For some this is because they are unfamiliar with the software needed, but for many it is because they are unsure how to structure a presentation and what makes effective slides.
In this post we look at the similarities in structure between presentations and essays – which for many are a more familiar prospect.
Overall structure
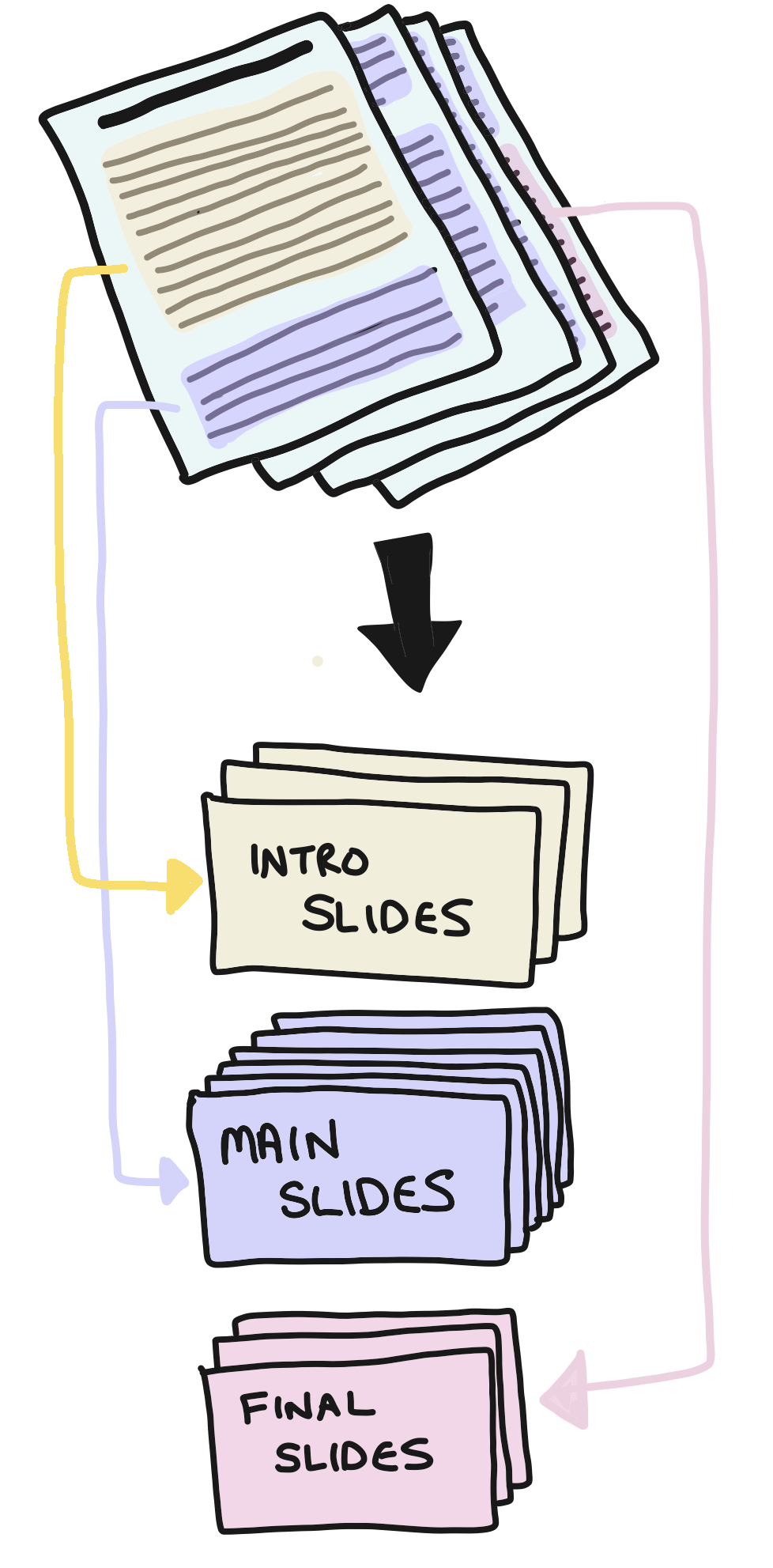
The basic structure of an essay is an introduction, followed by a main body and finishing with a conclusion. Presentations are just the same. Your first few slides should be an introduction, the bulk of your presentation represents the main body and then the final few slides are bringing everything together just like a conclusion.
Presentation introduction
We have already written a blog post all about what goes into an essay introduction so you should see some similarities.
Here is a breakdown of a typical presentation introduction:
- A really well designed title slide that grabs the attention
- A slide that gives the audience the big picture
- A slide that shows what you will be focusing on
- A slide that tells the audience what is to come in your presentation (its structure)
- A slide that uses the word ‘you’ or ‘your’ in the title to connect with the audience

The main difference is the last point mentioned above (this doesn’t have to be the last slide in your introduction by the way, it often works best after the ‘focusing on’ slide). By having a slide that uses the word ‘you’ or ‘your’ in its title you show why the people in front of you should bother paying attention. Unlike an essay, it is a lot more noticeable if they stop doing so and it can really affect your confidence – so you want to do everything you can to maximise their engagement. Here are a couple of examples from my own presentations:

Presentation main body
The slides in the main body of your presentation should take a lesson directly from essay paragraph structure. In essays, we emphasis PEEL structure – Point, Evidence, Explanation and Link. This exact same structure works perfectly for presentation slides:

To look at each of these elements in a little more detail:
Making a point
Just like the ‘point’ sentence in an essay paragraph, the heading of every slide should actually assert something – giving information rather than just introducing a topic. Look at the example below:

Providing evidence
In an essay, you would normally follow your point by providing evidence from your reading that backs it up. On a slide, it is best if the evidence that supports or illustrates the point is visual because presentations are in essence a form of visual communication. Still working with the slide from the previous example, you can see how this works:

Explain it to the audience
Detail can go into your verbal narration. For example, the written information on the above slide is not needed on the slide itself because you can verbally give it in the narration.
This is very important, first because it stops you putting too much text and detail on the slide (we don’t need more bullet points!); and secondly, because it is actually impossible to listen and read simultaneously – so by taking the text away, your audience may actually listen to what you are saying.
Your narration is a crucial and integral part of your presentation, just like your critical explanations are essential throughout your essays.
A good essay paragraph will either end by linking the point back to the essay question or link it to the following paragraph. In the same way, part of your presenatation narration could show why the point of the current slide is important to the presentation as a whole and/or make a link to the next slide.
Presentation conclusions
As with introductions, you can look at our previous blog post on essay conclusions and see similarities with what is here.
You should always reserve the last few slides of your presentation to conclude things satisfactorily. You will need at least:
- one slide that summarises your main points
- one slide that connects your presentation back to the wider topic
- one slide containing the most important point of your presentation

I usually make the ‘most important point’ slide the final one in the presentation. The final slide is on screen as you answer questions so it is searing itself into your audience’s conscience for a long time and should stay with them when you have finished.

Don’t waste your final slide with “Any questions” or “Thanks for listening”. These can just be verbal, they don’t need illustrating and would be a waste of your most important slide.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
| Essay type | Skills tested | Example prompt |
|---|---|---|
| Has the rise of the internet had a positive or negative impact on education? | ||
| Explain how the invention of the printing press changed European society in the 15th century. | ||
| Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself. | ||
| Describe an object that has sentimental value for you. |
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
- Academic Leaders
- Faculty and Instructors
- Graduate Students and Postdocs
Center for Educational Innovation
- Campus and Collegiate Liaisons
- Pedagogical Innovations Journal Club
- Teaching Enrichment Series
- Recorded Webinars
- Video Series
- All Services
- Teaching Consultations
- Student Feedback Facilitation
- Instructional Media Production
- Curricular and Educational Initiative Consultations
- Educational Research and Evaluation
- Thank a Teacher
- All Teaching Resources
- Aligned Course Design
- Active Learning
- Team Projects
- Active Learning Classrooms
- Leveraging the Learning Sciences
- Inclusive Teaching at a Predominantly White Institution
- Strategies to Support Challenging Conversations in the Classroom
- Assessments
- Online Teaching and Design
- AI and ChatGPT in Teaching
- Documenting Growth in Teaching
- Early Term Feedback
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Writing Your Teaching Philosophy
- All Programs
- Assessment Deep Dive
- Designing and Delivering Online Learning
- Early Career Teaching and Learning Program
- International Teaching Assistant (ITA) Program
- Preparing Future Faculty Program
- Teaching with Access and Inclusion Program
- Teaching for Student Well-Being Program
- Teaching Assistant and Postdoc Professional Development Program
- Essay Exams
Essay exams provide opportunities to evaluate students’ reasoning skills such as the ability to compare and contrast concepts, justify a position on a topic, interpret cases from the perspective of different theories or models, evaluate a claim or assertion with evidence, design an experiment, and other higher level cognitive skills. They can reveal if students understand the theory behind course material or how different concepts and theories relate to each other.
+ Advantages and Challenges of essay exams
Advantages:
- Can be used to measure higher order cognitive skills
- Takes relatively less time to write questions
- Difficult for respondents to get correct answers by guessing
Challenges:
- Can be time consuming to administer and to score
- Can be challenging to identify measurable, reliable criteria for assessing student responses
- Limited range of content can be sampled during any one testing period
- Timed exams in general add stress unrelated to a student's mastery of the material
+ Creating an essay exam
- Limit the use of essay questions to learning aims that require learners to share their thinking processes, connect and analyze information, and communicate their understanding for a specific purpose.
- Write each item so that students clearly understand the specific task and what deliverables are required for a complete answer (e.g. diagram, amount of evidence, number of examples).
- Indicate the relative amount of time and effort students should spend on each essay item, for example “2 – 3 sentences should suffice for this question”.
- Consider using several narrowly focused items rather than one broad item.
- Consider offering students choice among essay questions, while ensuring that all learning aims are assessed.
When designing essay exams, consider the reasoning skills you want to assess in your students. The following table lists different skills to measure with example prompts to guide assessment questions.
| Skill to Assess | Possible Question Stems |
|---|---|
| Comparing | |
| Relating Cause and Effect | |
| Justifying | |
| Summarizing | |
| Generalizing | |
| Inferring | |
| Classifying | |
| Creating | |
| Applying | |
| Analyzing | |
| Synthesizing | |
+ Preparing students for an essay exam
Adapted from Piontek, 2008

Prior to the essay exam
- Administer a formative assessment that asks students to do a brief write on a question similar to one you will use on an exam and provide them with feedback on their responses.
- Provide students with examples of essay responses that do and do not meet your criteria and standards.
- Provide students with the learning aims they will be responsible for mastering to help them focus their preparation appropriately.
- Have students apply the scoring rubric to sample essay responses and provide them with feedback on their work.
Resource video : 2-minute video description of a formative assessment that helps prepare students for an essay exam.
+ Administering an essay exam
- Provide adequate time for students to take the assessment. A strategy some instructors use is to time themselves answering the exam questions completely and then multiply that time by 3-4.
- Endeavor to create a distraction-free environment.
- Review the suggestions for informal accommodations for multilingual learners , which may be helpful in setting up an essay exam for all learners.
+ Grading an essay exam
To ensure essays are graded fairly and without bias:
- Outline what constitutes an acceptable answer (criteria for knowledge and skills).
- Select an appropriate scoring method based on the criteria.
- Clarify the role of writing mechanics and other factors independent of the learning aims being measured.
- Share with students ahead of time.
- Use a systematic process for scoring each essay item. For instance, score all responses to a single question in one setting.
- Anonymize student work (if possible) to ensure fairer and more objective feedback. For example students could use their student ID number in place of their name.
+ References & Resources
- For more information on setting criteria, preparing students, and grading essay exams read: Boye, A. (2019) Writing Better Essay Exams , IDEA paper #76.
- For more detailed descriptions of how to develop and score essay exams read: Piontek, M.E. (2008). Best Practices for Designing and Grading Exams, CRLT Occasional Paper # 24.
Web resources
- Designing Effective Writing Assignments (Teaching with Writing Program - UMNTC )
- Writing Assignment Checklist (Teaching with Writing Program - UMNTC)
- Designing and Using Rubrics (Center for Writing - UMTC)
- Caroline Hilk
- Research and Resources
- Why Use Active Learning?
- Successful Active Learning Implementation
- Addressing Active Learning Challenges
- Why Use Team Projects?
- Project Description Examples
- Project Description for Students
- Team Projects and Student Development Outcomes
- Forming Teams
- Team Output
- Individual Contributions to the Team
- Individual Student Understanding
- Supporting Students
- Wrapping up the Project
- Addressing Challenges
- Course Planning
- Working memory
- Retrieval of information
- Spaced practice
- Active learning
- Metacognition
- Definitions and PWI Focus
- A Flexible Framework
- Class Climate
- Course Content
- An Ongoing Endeavor
- Learn About Your Context
- Design Your Course to Support Challenging Conversations
- Design Your Challenging Conversations Class Session
- Use Effective Facilitation Strategies
- What to Do in a Challenging Moment
- Debrief and Reflect On Your Experience, and Try, Try Again
- Supplemental Resources
- Align Assessments
- Multiple Low Stakes Assessments
- Authentic Assessments
- Formative and Summative Assessments
- Varied Forms of Assessments
- Cumulative Assessments
- Equitable Assessments
- Multiple Choice Exams and Quizzes
- Academic Paper
- Skill Observation
- Alternative Assessments
- Assessment Plan
- Grade Assessments
- Prepare Students
- Reduce Student Anxiety
- SRT Scores: Interpreting & Responding
- Student Feedback Question Prompts
- Research Questions and Design
- Gathering data
- Publication
- GRAD 8101: Teaching in Higher Education
- Finding a Practicum Mentor
- GRAD 8200: Teaching for Learning
- Proficiency Rating & TA Eligibility
- Schedule a SETTA
- TAPD Webinars
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Constructing Essay Tests
Related Papers
UNIAFRICA JOURNAL OF EDUCATION
Chinelo Blessing Oribhabor
The need for teachers to adopt good essay construction and marking/scoring techniques is imperative. The concern for reliability of students' assessment data necessitated this article. When teachers construct essay questions and score students' responses in test or examination unskillfully, unreliable scores are generated. Decisions made using such scores are decisions made on false data which may have far reaching implications on the education system and the society at large. This paper therefore discusses the advantages of essay test; disadvantages of essay test; measures to overcome the disadvantages of essay questions; and guidelines for constructing and scoring essay questions. The causes of delays and poor marking of students' scripts are highlighted and suggestions made which include the use of point score method of marking as it is preferred over the holistic method. Teachers should also be encouraged to mark one number across scripts instead of scripts by scripts.
Journal of Basic Writing
Carol Haviland
Current Developments in English for Academic and Occupational Purposes
Kibiwott P Kurgatt
Most literature on writing assessment offers a lot of guidance on design and validation of measures and items in essays and examination questions (e.g. Alderson and North 1991, Bachman 1990, Hamp-Lyons 1988). Most of this literature, however, seems to be oriented towards language tests and not to how information concerning exam questions is interpreted in the academic contexts for which most students work in. Nevertheless, the most extensive analysis of prompts in subject-specific contexts can be rightly attributed to Horowitz (1986a and 1986b), Canseco and Byrd 1989 and Braine (1989). These studies also make suggestions concerning implications of the analysis to the teaching of English for Academic Purposes. The concern of the present paper was to seek to build on these earlier studies by looking at the types of prompts found in essay and examination questions in an ESL context in Africa. In particular it attempts to find out: a) The general features of first year undergraduate essay and examination questions b) What these features tell us about what students need to know c) What are the features of format and/or content of which students need to be aware d) Whether there is significance in the nature of the distribution of prompts (specific or general) across disciplines or courses. This paper starts with looking at the general features of the questions including the marks allocated to different types of questions per department. Subsequently, the questions are then classified according to the categories and subcategories of prompts as proposed by Horowitz. The nature of these prompts is then discussed and a summary of the results and conclusions is then presented.
karen gabinete
Journal of Research in Science Teaching
Gordon Warren
Journal of Baltic Science Education
Çetin DOGAR
Putu Febry Valentina Griadhi
Febry Valentina
Assessment is the systematic and ongoing process of acquiring, evaluating, and applying data from measured outcomes to evaluate, quantify, and document many elements of learning, such as academic preparedness, learning progress, skill acquisition, and students' educational needs. It refers to the act of judging or deciding the amount, value, quality, or significance of anything, as well as the judgment or decision made. Assessments in the educational setting can take many different forms and are intended to measure specific aspects of learning, identify individual student shortcomings and strengths, and inform educational programming. There are three types of assessments, which are summative assessment, formative assessment, and diagnostic assessment. Summative assessment is a type of evaluation that is used at the end of a unit or course to assess a student's understanding and learning by comparing performance to a standard. Formative assessment refers to a wide range of approaches used by teachers to assess student comprehension, learning progress, and academic support during a lesson, unit, or course. Diagnostic assessment is a type of pre-assessment or pre-test used by teachers to evaluate students' strengths, weaknesses, knowledge, and skills before instruction, usually at the start of a course, grade level, unit, or lesson. These tests are intended to discover learning gaps, clarify misconceptions, and guide instructional tactics. Diagnostic tests are often low-stakes and do not contribute toward a student's grade. Assessment is important for instruction because it pushes teaching by promoting critical thinking, reasoning, and reflection, providing a high-quality learning environment, and allowing teachers to quantify the efficacy of their instruction by relating student performance to specific learning objectives. It also aids in the monitoring of students' progress, gives diagnostic feedback, and informs teaching methods, resulting in greater learning and the enhancement of teaching approaches. Assessment of student learning is an essential component of a good education, it influences grade, placement, advancement, instructional requirements, curriculum, and, in certain situations, making decisions. Both cognitive and non-cognitive diagnostic assessments must be used to ensure that students accomplish their learning objectives. A well-rounded assessment strategy also includes the implementation of higher-order thinking skills (HOTS), numeracy literacy, culturally responsive pedagogy, reflection, differentiated assessment, assessment instruments, and technological integration. This essay intends to demonstrate the importance of assessment procedures in understanding student learning and ensuring equitable opportunities for academic success through an observational study of assessment procedures in a Singaraja secondary school.
Education. Innovation. Diversity.
Sandija Gabdulļina
This scientific research explores the potential of using essays as a formative assessment tool in the context of the competencies approach. The competencies approach emphasises the importance of focusing on learning progress and needs to promote successful learning, thus formative assessment plays a pivotal role in facilitating effective learning. The study highlights the significance of essay writing in promoting critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-directed learning. However, students often perceive essays solely as a means of summative assessment, lacking a comprehensive understanding of the assessment criteria. To address this issue, the research emphasizes the importance of involving students in the learning process by collectively defining outcomes, establishing assessment criteria, and providing constructive feedback. Clear objectives and feedback are crucial in fostering self-regulated learning and lifelong learning. The study highlights the need for student-teacher ...
Gazi Medical Journal
CHANDNI GUPTA
Assessing Writing
Catherine Trapani
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Applied Psychological Measurement
Terry Ackerman
aynur Yürekli
Jennifer Kobrin
Bioscience Education
Cjr Willmott
Sharifah Khairol Musairah Syed Abdul Mutalib
Dirasat, Educational Sciences
Yahya Nassar
Behavior Research Methods
Joe Magliano
Alexander Maxwell
College Board
Medical Teacher
ETS Research Report Series
Sandip Sinharay
Donald Weasenforth
martha martha
Juntendo Medical Journal
Rie Koizumi
Edd Pitt , James Adie
Jamil Asghar
LAUTARO ALEJANDRO MANRIQUEZ MANQUEHUAL
Yin Ling Cheung
James Elander
Cindy Hendricks
Higher Education Studies
lotfollah Karimi
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Elena Melekhina
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Essay Examination
Dec 09, 2023
0 likes | 1 Views
>>> How to write an essay? Order on the website: HelpWriting.Net <<< Examination of the Newborn Essay, Essay on School Examinations Should Be Abolished, Advantages and Disadvantages of Examination, Essay on My Examination as a Writer, Examination Should Not Be Abolished, An Examination of Standardized Testing Essay, Essay on History and Physical Examination Case 4, Essay about Examination of Clinical Psychology, Exam Week Essay, Preparing for and taking tests Essay example, Examination Malpractice, Breast Self Examination ( Bse ), Disadvantages Of Examination Malpractice, Examination Malpracti
Share Presentation

Presentation Transcript
- More by User

ENG-101 Essay Examination Samples
ENG-101 Essay Examination Samples.
555 views • 9 slides

Self-Examination or no Self-Examination
To Shanghai we must go. Randomized Trial of Breast Self-Examination in Shanghai: Final Results David B. Thomas, Dao Li Gao, Roberta M. Ray, Wen Wan Wang, Charlene J. Allison, Fan Liang Chen, Peggy Porter, Yong Wei Hu, Guan Lin Zhao, Lei Da Pan, Wenjin Li, Chunyuan Wu, Zakia Coriaty, Ilonka Evans, M
454 views • 25 slides

Neurological Examination
Neurological Examination. What comes first?. As with any system the first thing that should be done before commencing the examination is to ___________. For the neurological system the review questions are: Headache or facial pain? Fits, faints or funny turns? Dizziness or vertigo?
548 views • 22 slides

Examination Preparation
Examination Preparation. Objectives: . 1. List the key features of argumentative writing. . 2. Analyse the key features of argumentative writing in a response. . 3. Apply the features of argumentative writing to your own response. .
333 views • 6 slides
Laboratory Examination
Laboratory Examination. Examination of Urine. pH - will reflect the pH of the serum S pecific gravity reflects the hydration status of the patient and the concentrating ability of the kidney Proteinuria indicate intrinsic renal pathology or the presence of excess protein in the serum.
163 views • 6 slides

PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. GENERAL SURVEY. Baby is awake, comfortable, no gross malformations observed and not in cardiorespiratory distress. ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS AND VITAL SIGNS. Head Circumference: 33 cm Chest Circumference: 29 cm Abdominal Circumference: 30 cm Length: 47 cm
599 views • 10 slides

Cardiovascular Examination
Cardiovascular Examination. DAWIT AYELE (MD) INTERNIST. Dyspnea. Dyspnea an abnormally uncomfortable awareness of breathing that is easily differentiated from normal, quiet, unnoticed breathing heart failure, pulmonary edema, obstructive airway disease, and pulmonary embolism.
1.01k views • 36 slides

Knee Examination
Knee Examination. Abdulaziz Alomar, MD, MSc , FRCSC Assistant Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic and Sport Medicine Surgeon . General MSK Physical Examination P rinciples for Lower Examination. Exposure Bilateral limb examination Anterior and posterior Gait LLD NV examination
1.29k views • 28 slides

Writing the In-Class Essay Examination
Writing the In-Class Essay Examination. Writing an In-class Essay Exam:. 1. Be aware of the time!. 2. Follow the steps!. 3. Use the topic to your advantage!. 4. Don’t write more than you need!. 5. Know your strategy for the introduction and the conclusion!.
362 views • 19 slides

Tes uraian (essay examination)
Tes uraian (essay examination). Minggu ke sepuluh Evaluasi Pembelajaran Seni Rupa. Pengertian :. Tes tertulis butir-butir tesnya berupa pertanyaan-pertanyaan atau tugas yang hrs di jawab siswa dng menggunakan bahasa sendiri
308 views • 13 slides
Examination
Final. Initial. 10. 8. 6. 5. 4. 3. 7. 2. In. Weight:. Height:. Lbs. Pulse:. BPM. History. Yes. No. Yes. No. Yes. No. Birth Control Pills Hypertension Atherosclerosis History of CVA Anticoagulants. Vertigo L.O.C. Coll. W/O L.O.C. Smoking. Blurred Vision Tinnitis
213 views • 2 slides
WOUND EXAMINATION
WOUND EXAMINATION. PATIENT HISTORY. WOUND HISTORY DURATION ATTRIBUTING EVENT SYMPTOMS PAIN PARESTHESIA/ANESTHESIA. HISTORY (cont.). DOES PAIN CHANGE WITH POSITION elevation decreases pain = venous dependency increases pain in venous lesions pain with rest - severe occlusive disease
1.03k views • 49 slides
Examination :
Examination : The University shall have continuous evaluation system for each theory, practical,sessional, design and project papers. Theory Papers (a) A theory paper will have 100 percentage points. The weightage for three class tests and the end semester examinations will be as follows:
364 views • 7 slides

EXAMINATION
EXAMINATION. APA PERASAAN KITA DALAM MENGHADAPI EXAM? APA HARAPAN KITA DALAM MENGHADAPI EXAM? APA PERSEDIAAN KITA ?. KEJAYAAN. APA ITU KEJAYAAN ? SIAPAKAH YG DI KATAKAN BERJAYA?. KISAH KEHIDUPAN KITA.
429 views • 22 slides

Cardiovascular Examination. Deling Zou. Medical ppt. http://hastaneciyiz.blogspot.com. Anatomy. Inspection. 1 Precardial projection and excavation 2 Apical impulse 3 Abnormal pulsations of precardium. Inspection. 1 Precardial projection and excavation 1) Precardial projection
1.94k views • 127 slides

Knee Examination. Kathy Rainsbury February 2008. How to diagnose a knee complaint - HISTORY. 1) Patient’s age + sex 2) Does the knee swell? 3) Is there a mechanical problem?. Age + sex. Swelling?. Effusion presence of pathology which must be investigated
434 views • 18 slides

Final Examination
Final Examination. The final exam will be held in Van Allen Hall at 2:15 P.M. on Tuesday, December 16th. Classroom Assessment and Grading. Arnold the Average comic. You will fill out a Spot form for this course. Will that be a formative or summative form of assessment?
178 views • 8 slides

Examination. Listening. READ THE INSTRUCTION! Focus on task! Don’t think of other things! Before listening read the notes carefully. Try to answer during the first listening, but don’t hurry. During the second listening, focus only on topics, which are required.
297 views • 10 slides

Abdominal Examination
Abdominal Examination. H.A.Soleimani MD Gastroenterologist Adapted by Judy Gearhart, MD. Gastrointestinal History. www.rightdiagnosis.com Be a detective! Think about what all could cause this presentation. What are risk factors?. How to perform the physical examination?.
8.59k views • 113 slides

Physical examination
Physical examination. Department of Gastroenterology Ren Ji Hospital Prof. Zhi Hua Ran. Physical examination. It is the process of examining the patient’s body to determine the presence or absence of physical problems
1.4k views • 60 slides

Examination. Kunskap och teori om examination, samt hur vi kan examinera via IKT. Upplägg. Vad är kunskap? (Vad är det vi mäter) Hur mäter vi? Varför examinera? Bedömningskriterier och mål Examination och lärande i OLC (Online communities). Examination.
657 views • 39 slides
Cardiovascular Examination. Part 2. Cardiovascular Examination Part 2. Precordium. Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation. Inspection. Scars Sternotomy Valvotomy Thorocotomy Deformity Pectus excavatum kyphoscoliosis Pulsations Gynomastia Digoxin Spironolactone. Palpation.
1.22k views • 56 slides
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

An Inspector Calls PLANNING AND WRITING PPT 53 SLIDES
Subject: English
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
13 February 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

FULLY COMPREHENSIVE LESSON ON PLANNING AND WRITING EXAM ESSAYS PPT 53 SLIDES
Explanation of the PEEL paragraph technique
PEEL Activities and Examples
Exploration of How To Plan An Essay Answer – What The Examiner Is Looking For, Example Questions, And Planning Methods
Example Plans and 3 ‘Plan An Answer’ Activities
How To Write An Essay Answer Layout, Examples and Activities
3 Writing ‘Have a Go’ Activities – Intro, Paragraphs, Conclusion
6 Multiple Choice Check Point Questions
6 Wiz Quiz Questions
5 Mini ‘5-10 minutes’ Activities
Differentiated ‘30 minute’ Challenges Blue (lower) Orange (middle) and Green (higher)
Fully PPT Animated Ready for Online or Classroom Lessons
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 50%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
AN INSPECTOR CALLS COMPLETE MODULE
FULLY COMPREHENSIVE POWERPOINT PRESENTATION (PPT) LESSONS ON: PLOT - 86 SLIDES MR BIRLING - 55 SLIDES MRS BIRLING - 54 SLIDES SHEILA BIRLING - 56 SLIDES ERIC BIRLING - 55 SLIDES GERALD CROFT - 53 SLIDES INSPECTOR GOOLE - 56 SLIDES EVA SMITH / DAISY RENTON - 59 SLIDES THEMES - 82 SLIDES CONTEXT SETTING AND STRUCTURE - 50 SLIDES PLANNING AND WRITING EXAM ESSAYS - 53 SLIDES 659 PPT SLIDES!
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay type test. Nov 28, 2013 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 109 likes • 152,502 views. AI-enhanced description. D. Dr.Shazia Zamir. The document provides information on essay tests and how to construct them. It defines essay tests as requiring students to compose lengthy responses of several paragraphs. Essay tests measure higher-level ...
ation.4. Explain and analyze the examplesYou must explain why each e. ample is relevant to the controlling idea. It shows the reader w. yo. chose the examples for your support.5. Complete the. dea and transition into the next paragraphTie up any loose ends in your paragraph and make sure your reader wi.
essat type question. MR. JAGDISH SAMBAD. 1. The document discusses essay type questions, their advantages and disadvantages as an assessment tool. 2. Essay questions allow for freedom of response but are time-consuming to score and more subjective than other assessments. 3. The document provides tips for constructing and scoring essay questions ...
5. Essay Definition:- An examination or test questions that requires an explanation and analytical answer in a sentence, paragraph, or short composition . 6. There are two major purposes for using essay questions; First purpose is to assess students' understanding of and ability to think with subject matter content.
the exam-giver expects proof that the student understands material covered in the course. follow the conventions for excellent essay writing--which you know. fol; 5 two essay test situations. objective test plus essay question or questions ; essay question(s) only ; 6 steps for answering an essay question with an objective section. turn to the ...
Taking an essay test:. How to do well on fewer than 10 cups of coffee. In this workshop, we'll talk about how to succeed at essay tests. What is an essay test?. Unlike multiple-choice or true-or-false exams, an essay test looks for more than mere correctness. Slideshow 2373614 by yehuda
1-3 minutes reading and working the PROMPT. 3 minutes deciding on a position. 10-12 minutes planning the support of your position. 20 minutes writing the essay. 3 minutes proofreading! The argumentative essay prompt. In his famous "Vast Wasteland" address to the National Association of Broadcaster in May of 1961, Newton Minow, the Chairman ...
Presentation on theme: "Writing Essays in Exam Conditions"— Presentation transcript: 1 Writing Essays in Exam Conditions This workshop will… Introduce you to common examination formats Offer a model for managing the time allocated for the exam on the day Provide tips on essay-writing techniques during an exam Louise Livesey Academic Skills Adviser 05/12/2018 Academic Skills Advice
1 ESSAY WRITING FOR EXAMS. CLAIRE WALLIS FACULTY OF LANGUAGES. 2 EXAM ESSAYS Analyze the question. Make a quick plan and stick to it. Think about useful language. Make sure you don't go off topic. Leave spaces between your paragraphs for additions and cancellations. Read it back (edit and correct)
During the Exam. Set a time schedule. Figure out how much time you have for each question. Bring a watch to keep yourself on track. Consider weighted questions. Select questions and make brief outlines for each. Always think before you write! Proofread what youve written before turning in your test. 7 How to Reduce Exam Anxiety
Essay Exam Skills Refresher. Essay Exam Skills Refresher. Jeff Minneti Associate Professor of Legal Skills and Director of Academic Success [email protected]. Objectives. Understand your job on essay exams. Appreciate the kind of essay exam questions you will face. 369 views • 19 slides
Most essay questions will have one or more "key words" that indicate which organizational pattern you should use in your answer. The six most common organizational patterns for essay exams are definition, analysis, cause and effect, comparison/contrast, process analysis, and thesis-support. Definition. Typical questions.
Overall structure. The basic structure of an essay is an introduction, followed by a main body and finishing with a conclusion. Presentations are just the same. Your first few slides should be an introduction, the bulk of your presentation represents the main body and then the final few slides are bringing everything together just like a ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Resource video: 2-minute video description of a formative assessment that helps prepare students for an essay exam. + Administering an essay exam. Provide adequate time for students to take the assessment. A strategy some instructors use is to time themselves answering the exam questions completely and then multiply that time by 3-4.
A powerpoint presentation about the Multiple Choice Test as one of the assessment strategies that can be used by teachers in assessing learners. ... This document discusses strategies for constructing effective multiple choice and essay exam questions. For multiple choice questions, key points include writing clear stems that present definite ...
This workbook is the first in a series of three workbooks designed to improve the. development and use of effective essay questions. It focuses on the writing and use of. essay questions. The second booklet in the series focuses on scoring student responses to. essay questions.
The need for teachers to adopt good essay construction and marking/scoring techniques is imperative. The concern for reliability of students' assessment data necessitated this article. When teachers construct essay questions and score students' responses in test or examination unskillfully, unreliable scores are generated.
File previews. pptx, 21.54 MB. A detailed (103 slides) PowerPoint walking pupils through: Part 1: What to expect in the exam. Part 2: How am I assessed? Part 3: What should I do before I write my essay? Part 4: How do I plan? Part 5: How do I structure my essay? Using PowerPoint transitions to animate slides when in full screen mode.
Title: Exam Essay Structure 1 Exam Essay Structure. The following notes will help you prepare yourself to write an exam essay for either a novel, or a play, or a selection of poems. Remember ; You have 50 minutes to write your answer, so its important that you use your time efficiently; 2 Exam Essay Structure Language Hints
>>> How to write an essay? Order on the website: HelpWriting.Net Slideshow 12712057 by toidistperla1985
pptx, 450.51 KB. FULLY COMPREHENSIVE LESSON ON PLANNING AND WRITING EXAM ESSAYS PPT 53 SLIDES. Explanation of the PEEL paragraph technique. PEEL Activities and Examples. Exploration of How To Plan An Essay Answer - What The Examiner Is Looking For, Example Questions, And Planning Methods. Example Plans and 3 'Plan An Answer' Activities.
Essay Test.pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The document describes an essay exam given in a government class where students had to argue for or against limiting US presidents to two consecutive terms. The exam question asked students to take a position and support it using at least three points ...