- Defining Research Objectives: How To Write Them

Almost all industries use research for growth and development. Research objectives are how researchers ensure that their study has direction and makes a significant contribution to growing an industry or niche.
Research objectives provide a clear and concise statement of what the researcher wants to find out. As a researcher, you need to clearly outline and define research objectives to guide the research process and ensure that the study is relevant and generates the impact you want.
In this article, we will explore research objectives and how to leverage them to achieve successful research studies.

What Are Research Objectives?
Research objectives are what you want to achieve through your research study. They guide your research process and help you focus on the most important aspects of your topic.
You can also define the scope of your study and set realistic and attainable study goals with research objectives. For example, with clear research objectives, your study focuses on the specific goals you want to achieve and prevents you from spending time and resources collecting unnecessary data.
However, sticking to research objectives isn’t always easy, especially in broad or unconventional research. This is why most researchers follow the SMART criteria when defining their research objectives.
Understanding SMART Criteria in Research
Think of research objectives as a roadmap to achieving your research goals, with the SMART criteria as your navigator on the map.
SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These criteria help you ensure that your research objectives are clear, specific, realistic, meaningful, and time-bound.
Here’s a breakdown of the SMART Criteria:
Specific : Your research objectives should be clear: what do you want to achieve, why do you want to achieve it, and how do you plan to achieve it? Avoid vague or broad statements that don’t provide enough direction for your research.
Measurable : Your research objectives should have metrics that help you track your progress and measure your results. Also, ensure the metrics are measurable with data to verify them.
Achievable : Your research objectives should be within your research scope, timeframe, and budget. Also, set goals that are challenging but not impossible.
Relevant: Your research objectives should be in line with the goal and significance of your study. Also, ensure that the objectives address a specific issue or knowledge gap that is interesting and relevant to your industry or niche.
Time-bound : Your research objectives should have a specific deadline or timeframe for completion. This will help you carefully set a schedule for your research activities and milestones and monitor your study progress.
Characteristics of Effective Research Objectives
Clarity : Your objectives should be clear and unambiguous so that anyone who reads them can understand what you intend to do. Avoid vague or general terms that could be taken out of context.
Specificity : Your objectives should be specific and address the research questions that you have formulated. Do not use broad or narrow objectives as they may restrict your field of research or make your research irrelevant.
Measurability : Define your metrics with indicators or metrics that help you determine if you’ve accomplished your goals or not. This will ensure you are tracking the research progress and making interventions when needed.
Also, do use objectives that are subjective or based on personal opinions, as they may be difficult to accurately verify and measure.
Achievability : Your objectives should be realistic and attainable, given the resources and time available for your research project. You should set objectives that match your skills and capabilities, they can be difficult but not so hard that they are realistically unachievable.
For example, setting very difficult make you lose confidence, and abandon your research. Also, setting very simple objectives could demotivate you and prevent you from closing the knowledge gap or making significant contributions to your field with your research.
Relevance : Your objectives should be relevant to your research topic and contribute to the existing knowledge in your field. Avoid objectives that are unrelated or insignificant, as they may waste your time or resources.
Time-bound : Your objectives should be time-bound and specify when you will complete them. Have a realistic and flexible timeframe for achieving your objectives, and track your progress with it.
Steps to Writing Research Objectives
Identify the research questions.
The first step in writing effective research objectives is to identify the research questions that you are trying to answer. Research questions help you narrow down your topic and identify the gaps or problems that you want to address with your research.
For example, if you are interested in the impact of technology on children’s development, your research questions could be:
- What is the relationship between technology use and academic performance among children?
- Are children who use technology more likely to do better in school than those who do not?
- What is the social and psychological impact of technology use on children?
Brainstorm Objectives
Once you have your research questions, you can brainstorm possible objectives that relate to them. Objectives are more specific than research questions, and they tell you what you want to achieve or learn in your research.
You can use verbs such as analyze, compare, evaluate, explore, investigate, etc. to express your objectives. Also, try to generate as many objectives as possible, without worrying about their quality or feasibility at this stage.
Prioritize Objectives
Once you’ve brainstormed your objectives, you’ll need to prioritize them based on their relevance and feasibility. Relevance is how relevant the objective is to your research topic and how well it fits into your overall research objective.
Feasibility is how realistic and feasible the objective is compared to the time, money, and expertise you have. You can create a matrix or ranking system to organize your objectives and pick the ones that matter the most.
Refine Objectives
The next step is to refine and revise your objectives to ensure clarity and specificity. Start by ensuring that your objectives are consistent and coherent with each other and with your research questions.
Make Objectives SMART
A useful way to refine your objectives is to make them SMART, which stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Specific : Objectives should clearly state what you hope to achieve.
- Measurable : They should be able to be quantified or evaluated.
- Achievable : realistic and within the scope of the research study.
- Relevant : They should be directly related to the research questions.
- Time-bound : specific timeframe for research completion.
Review and Finalize Objectives
The final step is to review your objectives for coherence and alignment with your research questions and aim. Ensure your objectives are logically connected and consistent with each other and with the purpose of your study.
You also need to check that your objectives are not too broad or too narrow, too easy or too hard, too many or too few. You can use a checklist or a rubric to evaluate your objectives and make modifications.
Examples of Well-Written Research Objectives
Example 1- Psychology
Research question: What are the effects of social media use on teenagers’ mental health?
Objective : To determine the relationship between the amount of time teenagers in the US spend on social media and their levels of anxiety and depression before and after using social media.
What Makes the Research Objective SMART?
The research objective is specific because it clearly states what the researcher hopes to achieve. It is measurable because it can be quantified by measuring the levels of anxiety and depression in teenagers.
Also, the objective is achievable because the researcher can collect enough data to answer the research question. It is relevant because it is directly related to the research question. It is time-bound because it has a specific deadline for completion.
Example 2- Marketing
Research question : How can a company increase its brand awareness by 10%?
Objective : To develop a marketing strategy that will increase the company’s sales by 10% within the next quarter.
How Is this Research Objective SMART?
The research states what the researcher hopes to achieve ( Specific ). You can also measure the company’s reach before and after the marketing plan is implemented ( Measurable ).
The research objective is also achievable because you can develop a marketing plan that will increase awareness by 10% within the timeframe. The objective is directly related to the research question ( Relevant ). It is also time-bound because it has a specific deadline for completion.
Research objectives are a well-designed roadmap to completing and achieving your overall research goal.
However, research goals are only effective if they are well-defined and backed up with the best practices such as the SMART criteria. Properly defining research objectives will help you plan and conduct your research project effectively and efficiently.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- research goals
- research objectives
- research roadmap
- smart goals
- SMART research objectives
- Moradeke Owa

You may also like:
Subgroup Analysis: What It Is + How to Conduct It
Introduction Clinical trials are an integral part of the drug development process. They aim to assess the safety and efficacy of a new...

Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...
Projective Techniques In Surveys: Definition, Types & Pros & Cons
Introduction When you’re conducting a survey, you need to find out what people think about things. But how do you get an accurate and...
Desk Research: Definition, Types, Application, Pros & Cons
If you are looking for a way to conduct a research study while optimizing your resources, desk research is a great option. Desk research...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to Write a Marketing Research Objective
We all know the old adage: is marketing is an art or a science?
At Seer, we think it’s both. But not necessarily both at the same time. We believe the better question is: which comes first in marketing, art or science?
And if you ask us that question, we’d tell you it’s a science first.
"The science of marketing is all about using data and insights to drive your strategy. The art of marketing is how you express that strategy."
Now that we know we are starting with science, what does that mean exactly?
Well, remember when you were in school and you had to come up with your own science research experiment? Remember what came first? The objective. Why? Because without an objective, you don’t have a testable proposition. And without a testable proposition, you don’t have direction. And we all know that when research doesn’t have a direction, it typically doesn’t garner any groundbreaking takeaways.
So, what does your high school science experiment have to do with marketing research?
Similar to the traditional objective, a great marketing research plan starts with a strong objective. One that is focused, measurable, and effective. Without a clear objective, your marketing research will not be as successful.
What is a Marketing Research Objective?
[TIP] By definition, a "Research Objective" is a statement of purpose that outlines a specific result to achieve within a dedicated time frame and available resources.
Applying this logic to marketing, a marketing research objective is a statement that outlines what you want to know about your customer. Clearly defining your objective at the beginning stages will help you avoid conflicting expectations or wasted collecting irrelevant data.
How Do You Create a Marketing Research Objective?
Start at the end. I know it sounds counterintuitive, but if you start with the desired outcome, you will be able to create a more focused objective. What’s the one thing you want to be able to take away from this research? What do you plan to do with the information? What does success look like? Use this objective as your compass while you navigate your research and analysis.
Typically, it’s easiest to do this in the form of a question. Here are a few examples.
- Example 1: Which features in Product X are most important to our Enterprise customers?
This question will give you a list of features, in order of importance, for your Enterprise customer.
- Example 2: What are the different search triggers amongst our four customer segments?
This question will result in a list of common factors that result in users searching for Service Y.
When you start seeing all the data points, behaviors, and survey responses - curiosity can set in.
An abundance of data can pull you in multiple directions because each finding is interesting in its own right. That’s when your objective comes in. Know the end result you are working toward and stay on that path.
Creating a Research Objective
Once you’ve got your desired outcome, you’ll want to create your objective. A few things to consider as you create your statement:
- Where does this fit into your marketing strategy? Where does this objective fit into your larger marketing strategy? Not only is this helpful when dispersing information internally or getting buy-in, it keeps the research team focused on the higher business objectives attached to this research. Is this part of your company’s focus on brand awareness? A new product launch? An analysis of competitors? These are all very different things.
- Include your target audience. Typically, it’s difficult to understand everything with every user segment so pick which segment you plan to analyze. Is it your Enterprise customers? Customers living in a specific region? A certain demographic segment? Including this in your objective will be a helpful gut check when choosing participants.
- What will you measure? You don’t need to list out all of the data points you plan to measure, but there should be some measurable element in your objective. Is it sentiment? Are you looking for frequencies? What about behavioral trends? Including this in your objective will ensure you pick the most appropriate research methodology to acquire that measurable element.
- A behavior. What is the behavior or action that we are going to be researching? Is navigating your website? Is it purchasing a product? Is it clicking on an ad?
Let’s look at some examples:

Common Marketing Research Objective Pitfalls
While creating an objective may seem relatively straightforward, it can be easy to get wrong. Let’s go over some of the common pitfalls.
Objective is Too Broad
Now, if you follow the outline above, this shouldn’t be an issue because it forces you to get granular with your objective.
- Specific: As part of our rebranding, we are conducting a sentiment analysis with our recurring customers
- Broad: As part of our rebranding, we will ask customers how they feel about it
We want to avoid broad objectives because they can allow curiosity to get the best of us and a once seemingly clear research project can get muddied.
More Than One Objective
Every research project should have one objective and one objective only. Again, while this may seem easy enough to manage, you’d be surprised just how easy it is to sneak those secondary and tertiary objectives into your statement.
- One objective: We aim to understand what questions our customers have when considering purchasing a car
- Two objectives: We aim to understand what questions our customers have when searching for and considering a car
You see, the questions customers may have when searching for a car could be completely different than the questions they have when considering purchasing a car.
Making Assumptions
Avoid making your objective into a hypothesis with absolute statements and assumptions. Your objective should be more of a question than a prediction. That comes later.
- Objective: Uncover the purchase journey of our target demographic
- Assumption: Uncover what part search plays in the purchase journey of our target demographic
This looks unsuspecting, but in reality, we're already assuming that search plays a role in our audience's journey. That could sway the focus of the research.
Once you’ve created your objective, let it (and only it) drive the beginning stages of your marketing research.
Write it on a post-it and stick it on your desk, write it on the whiteboard at every meeting you have, keep it top of mind as you continue your research. It will serve as a compass and help you avoid being led astray by interesting data, curious colleagues, and conflicting agendas.
More Tips for Understanding Your Audience
Check back on the Seer blog for the next installment from our Audience team. Sign up for our newsletter to read the latest blogs on audience, SEO, PPC, and more.

We love helping marketers like you.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive updates and more:
Related Posts

- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Objectives
Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research . The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
Types of Research Objectives
Here are the different types of research objectives in research:
- Exploratory Objectives: These objectives are used to explore a topic, issue, or phenomenon that has not been studied in-depth before. The aim of exploratory research is to gain a better understanding of the subject matter and generate new ideas and hypotheses .
- Descriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to describe the characteristics, features, or attributes of a particular population, group, or phenomenon. Descriptive research answers the “what” questions and provides a snapshot of the subject matter.
- Explanatory Objectives : These objectives aim to explain the relationships between variables or factors. Explanatory research seeks to identify the cause-and-effect relationships between different phenomena.
- Predictive Objectives: These objectives aim to predict future events or outcomes based on existing data or trends. Predictive research uses statistical models to forecast future trends or outcomes.
- Evaluative Objectives : These objectives aim to evaluate the effectiveness or impact of a program, intervention, or policy. Evaluative research seeks to assess the outcomes or results of a particular intervention or program.
- Prescriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to provide recommendations or solutions to a particular problem or issue. Prescriptive research identifies the best course of action based on the results of the study.
- Diagnostic Objectives : These objectives aim to identify the causes or factors contributing to a particular problem or issue. Diagnostic research seeks to uncover the underlying reasons for a particular phenomenon.
- Comparative Objectives: These objectives aim to compare two or more groups, populations, or phenomena to identify similarities and differences. Comparative research is used to determine which group or approach is more effective or has better outcomes.
- Historical Objectives: These objectives aim to examine past events, trends, or phenomena to gain a better understanding of their significance and impact. Historical research uses archival data, documents, and records to study past events.
- Ethnographic Objectives : These objectives aim to understand the culture, beliefs, and practices of a particular group or community. Ethnographic research involves immersive fieldwork and observation to gain an insider’s perspective of the group being studied.
- Action-oriented Objectives: These objectives aim to bring about social or organizational change. Action-oriented research seeks to identify practical solutions to social problems and to promote positive change in society.
- Conceptual Objectives: These objectives aim to develop new theories, models, or frameworks to explain a particular phenomenon or set of phenomena. Conceptual research seeks to provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter by developing new theoretical perspectives.
- Methodological Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and improve research methods and techniques. Methodological research seeks to advance the field of research by improving the validity, reliability, and accuracy of research methods and tools.
- Theoretical Objectives : These objectives aim to test and refine existing theories or to develop new theoretical perspectives. Theoretical research seeks to advance the field of knowledge by testing and refining existing theories or by developing new theoretical frameworks.
- Measurement Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and validate measurement instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, and tests. Measurement research seeks to improve the quality and reliability of data collection and analysis by developing and testing new measurement tools.
- Design Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and refine research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and observational designs. Design research seeks to improve the quality and validity of research by developing and testing new research designs.
- Sampling Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and refine sampling techniques, such as probability and non-probability sampling methods. Sampling research seeks to improve the representativeness and generalizability of research findings by developing and testing new sampling techniques.
How to Write Research Objectives
Writing clear and concise research objectives is an important part of any research project, as it helps to guide the study and ensure that it is focused and relevant. Here are some steps to follow when writing research objectives:
- Identify the research problem : Before you can write research objectives, you need to identify the research problem you are trying to address. This should be a clear and specific problem that can be addressed through research.
- Define the research questions : Based on the research problem, define the research questions you want to answer. These questions should be specific and should guide the research process.
- Identify the variables : Identify the key variables that you will be studying in your research. These are the factors that you will be measuring, manipulating, or analyzing to answer your research questions.
- Write specific objectives: Write specific, measurable objectives that will help you answer your research questions. These objectives should be clear and concise and should indicate what you hope to achieve through your research.
- Use the SMART criteria: To ensure that your research objectives are well-defined and achievable, use the SMART criteria. This means that your objectives should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Revise and refine: Once you have written your research objectives, revise and refine them to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable. Make sure that they align with your research questions and variables, and that they will help you answer your research problem.
Example of Research Objectives
Examples of research objectives Could be:
Research Objectives for the topic of “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment”:
- To investigate the effects of the adoption of AI on employment trends across various industries and occupations.
- To explore the potential for AI to create new job opportunities and transform existing roles in the workforce.
- To examine the social and economic implications of the widespread use of AI for employment, including issues such as income inequality and access to education and training.
- To identify the skills and competencies that will be required for individuals to thrive in an AI-driven workplace, and to explore the role of education and training in developing these skills.
- To evaluate the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the use of AI for employment, including issues such as bias, privacy, and the responsibility of employers and policymakers to protect workers’ rights.
When to Write Research Objectives
- At the beginning of a research project : Research objectives should be identified and written down before starting a research project. This helps to ensure that the project is focused and that data collection and analysis efforts are aligned with the intended purpose of the research.
- When refining research questions: Writing research objectives can help to clarify and refine research questions. Objectives provide a more concrete and specific framework for addressing research questions, which can improve the overall quality and direction of a research project.
- After conducting a literature review : Conducting a literature review can help to identify gaps in knowledge and areas that require further research. Writing research objectives can help to define and focus the research effort in these areas.
- When developing a research proposal: Research objectives are an important component of a research proposal. They help to articulate the purpose and scope of the research, and provide a clear and concise summary of the expected outcomes and contributions of the research.
- When seeking funding for research: Funding agencies often require a detailed description of research objectives as part of a funding proposal. Writing clear and specific research objectives can help to demonstrate the significance and potential impact of a research project, and increase the chances of securing funding.
- When designing a research study : Research objectives guide the design and implementation of a research study. They help to identify the appropriate research methods, sampling strategies, data collection and analysis techniques, and other relevant aspects of the study design.
- When communicating research findings: Research objectives provide a clear and concise summary of the main research questions and outcomes. They are often included in research reports and publications, and can help to ensure that the research findings are communicated effectively and accurately to a wide range of audiences.
- When evaluating research outcomes : Research objectives provide a basis for evaluating the success of a research project. They help to measure the degree to which research questions have been answered and the extent to which research outcomes have been achieved.
- When conducting research in a team : Writing research objectives can facilitate communication and collaboration within a research team. Objectives provide a shared understanding of the research purpose and goals, and can help to ensure that team members are working towards a common objective.
Purpose of Research Objectives
Some of the main purposes of research objectives include:
- To clarify the research question or problem : Research objectives help to define the specific aspects of the research question or problem that the study aims to address. This makes it easier to design a study that is focused and relevant.
- To guide the research design: Research objectives help to determine the research design, including the research methods, data collection techniques, and sampling strategy. This ensures that the study is structured and efficient.
- To measure progress : Research objectives provide a way to measure progress throughout the research process. They help the researcher to evaluate whether they are on track and meeting their goals.
- To communicate the research goals : Research objectives provide a clear and concise description of the research goals. This helps to communicate the purpose of the study to other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public.
Advantages of Research Objectives
Here are some advantages of having well-defined research objectives:
- Focus : Research objectives help to focus the research effort on specific areas of inquiry. By identifying clear research questions, the researcher can narrow down the scope of the study and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Clarity : Clearly stated research objectives provide a roadmap for the research study. They provide a clear direction for the research, making it easier for the researcher to stay on track and achieve their goals.
- Measurability : Well-defined research objectives provide measurable outcomes that can be used to evaluate the success of the research project. This helps to ensure that the research is effective and that the research goals are achieved.
- Feasibility : Research objectives help to ensure that the research project is feasible. By clearly defining the research goals, the researcher can identify the resources required to achieve those goals and determine whether those resources are available.
- Relevance : Research objectives help to ensure that the research study is relevant and meaningful. By identifying specific research questions, the researcher can ensure that the study addresses important issues and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
A Roadmap to Business Research
- First Online: 15 March 2023
Cite this chapter

- Merwe Oberholzer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7180-8865 3 &
- Pieter W. Buys ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5345-3594 3
518 Accesses
This chapter seeks to constitute a roadmap or framework to guide business researchers in contextualizing and planning their research efforts. A literature study was conducted to investigate the research concept, the boundary of research, and the research process’ conceptual framework. This chapter summarized research as a systematic investigation to reveal new knowledge. In guiding industry-orientated business research, it is acknowledged that management action may solve some business problems. In contrast, higher levels of organizational issues and critical reflection of business issues may require actual research .
The framework for business research is divided into four parts: the research problem, research design, empirical evidence, and conclusion. The central part of the map is the design section that organizes the philosophic approach (theoretical foundation, research philosophy, and assumptions) on the one side and the applied research methods and techniques on the other side, with the research methodology acting as a bridge between the sides. The framework constitutes a guide when embarking on the journey to solve industry-orientated business research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
AS illustrated later, it must be noted not every business problem needs to be solved by scientific research.
Note that although conceptually four distinct elements, in actuality these ProDEC elements are highly integrated.
Note that the theoretical foundation may not be of equal importance in all paradigms, e.g., the pragmatist and design sciences paradigms where a pragmatic problem solution or artifact is the primary objective.
Abutabenjeh, S., & Jaradat, R. (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36 (3), 237–258.
Article Google Scholar
Babbie, E. (2004). The practice of social research . Thomson/ Wadsworth.
Google Scholar
Brierley, J. A. (2017). The role of a pragmatist paradigm when adopting mixed methods in behavioural accounting research. International Journal of Behavioural Accounting and Finance, 6 (2), 140–154.
Collins. (2021). Definition of research . https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/research Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. (2018). Designing and conducting mixed method research . Sage.
Davis, C., & Fisher, M. (2018). Understanding Research Paradigms. JARNA, 21 (3), 21–25.
Delen, D., & Zolbanin, H. M. (2018). The analytics paradigm in business research. Journal of Business Research, 90 , 186–195.
Department of Education and Training, Western Sydney University. 2020. Research services. https://www.westernsydney.edu.au/research/researchers/preparing_a_grant_application/dest_definition_of_research . Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Elsayed, N., & Elbardan, H. (2018). Investigating the associations between executive compensation and firm performance: Agency theory or tournament theory. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 19 (2), 245–270.
FindAPhD.com. (2021). What are the criteria for a PhD? https://www.findaphd.com/advice/finding/criteria-for-phd.aspx Date of access: 18 August 2021.
Goldkuhl, G. (2011). Design research in search for a paradigm: Pragmatism is the answer. European Design Science Symposium (pp. 84–95). Springer.
Goldkuhl, G. (2020). Design Science Epistemology: A pragmatist inquiry. Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems, 32 (1), 39–79.
Hesse-Biber, S. N., & Leavy, P. (2011). The practice of qualitative research . Sage.
Henderson, K. A. (2011). Post-positivism and the pragmatics of leisure research. Leisure Sciences, 33 (4), 341–346.
Hevner, A.R., March, S.T., Park, J. & Ram, S. (2004). Design science in information systems research. MIS quarterly : 75–105.
Kessler, E. H. (Ed.). (2013). Encyclopedia of management theory . Sage.
Kankam, P. K. (2019). The use of paradigms in information research. Library & Information Science Research, 41 (2), 85–92.
Kekeya, J. (2019, November). The commonalities and differences between research paradigms. Contemporary PNG Studies: DWU Research Journal, 31 , 26–36.
Kivunja, C. (2018). Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework: A systematic review of lessons from the field. International Journal of Higher Education, 7 (6), 44–53.
Kivunja, C., & Kuyini, A. B. (2017). Understanding and applying research paradigms in educational contexts. International Journal for Higher Education, 6 (5), 26–41.
Jansen, J. D. (2020a). What is a research question and why is it important? In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 2–14.
Jansen, J. D. (2020b). Introduction to the language of research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 16–24.
Lexico.com. (2021). Oxford English and Spanish dictionary, synonyms, and Spanish to English translator . https://www.lexico.com/definition/research Date of access: 22 July 2021.
Lincoln, Y. S., Lynham, S. A., & Guba, E. G. (2011). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences, revisited. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 97–128). Sage.
Myers, M. D. (2020). Qualitative research in business & management . Sage.
Mouton, J. (1996). Understanding social research . Van Schaik.
Mouton, J. (2011). How to succeed in your master’s & doctoral studies: A South African guide and resource book. Van Schaik.
Nieuwenhuis, J. (2020). Introducing qualitative research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 56–76.
Pandey, P. & Pandey, M. M. (2015). Research methodology: Tools and techniques . Bridge Center: Buzau.
Pietersen, J. & Maree, K. (2020). Statistical analysis II: Inferential statistics. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 242–258.
Rahi, S. (2017). Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms, sampling issues and instrument development. International Journal of Economics & Management Sciences, 6 (2), 1000403.
Rehman, A. A., & Alharthi, K. (2016). An introduction to research paradigms. International Journal of Educational Investigations, 3 (8), 51–59.
Saunders, M. N. K., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research methods for business students . Pearson.
Sein, M. K., Henfridsson, O., Purao, S., Rossi, M., & Lindgren, R. (2011). Action Design Research. MIS Quarterly, 35 (1), 37–56.
Tubey, R. J., Rotich, J. K., & Bengat, J. K. (2015). Research paradigms: Theory and practice. Research on Humanities and Social Sciences, 5 (5), 224–228.
Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (2020). Introduction to Design Science Research. In: Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (eds.), Design Science Research. Cases. Progress in IS. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46781-4_1 Date of access: 21 October 2021.
Voxco. (2022). Business research: Definition, types, and methods. https://www.voxco.com/blog/business-research-definition-types-and-methods/ Date of access: 23 May 2022.
Wilson, J. (2013). Essentials of business research: A guide to doing your research project. Sage. https://www.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-binaries/59838_Wilson_ch1.pdf Date of access: 3 June 2021.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Management Cybernetics Research Entity, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Merwe Oberholzer & Pieter W. Buys
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pieter W. Buys .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pieter W. Buys
Merwe Oberholzer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Oberholzer, M., Buys, P.W. (2023). A Roadmap to Business Research. In: Buys, P.W., Oberholzer, M. (eds) Business Research . Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Published : 15 March 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-9478-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-9479-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Business Research: It’s Meaning, Process and Objectives
Meaning of business research.
Business research is the process of studying a company’s competitors, stakeholders, and profit & loss to meet the company objectives and maximize revenue & profits.
The research involves identifying the target market, estimating their current needs & wants, and then conducting product planning to meet those demands.
The research should be unbiased and factual as they form the basis for further analysis.
Business research is neither a pre-product launch nor a post-product launch analysis. Companies continuously conduct market research relating to their political environment, social demands, technological needs, competitors’ entry, etc. so that they can keep improving their products and continue to survive even in the fiercest times.
Thus, business research is purely the collection and interpretation of external as well as internal data for a company’s better performance.
Objectives of Business Research
Understanding customer requirements.
One of the major objectives of business research is to ascertain the target customers’ requirements. This helps to conduct in-depth research relating to customers’ needs. Further, it also provides information regarding market trends, future demands of customers, and thus, pros and cons of the product being developed for them.
Defining Stakeholders
Business research helps to differentiate between potential and non-potential customers. This way the company can quantify its market reach and conduct surveys amongst some of its customers related to their tastes and type. This will help them gain feedback from their customers which they can add back as features in their products!
Pain & Gain Points
Pain points are the areas where the company lags in the market and gain points are the areas where the company can stand out in the market.
The company can list its pain points by evaluating what customers want and what they are delivering. This way, they can focus on their weaknesses and take measures to rub off or improve them.
Rival Study
The strength of a company is a threat to its competitor and the weakness of a company is the opportunity of its competitor. Therefore, the company should analyze its threats i.e., make an in-depth study of its competitors and, thus brainstorm different ways in which it can convert its threats into opportunities.
Scope of Business Research
Business Research has wide scope in deciding a particular product’s journey in the market.
Right from its launch, Business research helps sellers grab the opportunity of pulling demand, gaining investments, being tech-enabled, beating the competition, conducting SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat) and PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal environment) analysis, standing out and disrupting the entire market.
Moreover, the scope of business research is not only restricted to the product market. It also plays a crucial role in personnel management and workforce development. Research made for employee motivation, grooming, training, and promotion inculcates more coordination in the organization and also nurtures productivity amongst employees.
When they are trained and awarded, they feel empowered and they put the best of their efforts into maximizing sales and outputs.
Nature of Business Research
- The main function of business research is to define the objectives and core values of any business. It tells how the company should manage and generate leads, create sales and develop a marketing strategy.
- Business Research also deals with competitors’ pricing policies and helps in setting own costs and prices.
- It helps companies to discover new growth avenues by pinpointing the weak points of competitors.
- It assists in planning projections of the company and shows hurdles that would likely arrive and hit business cycles.
In a nutshell, it gives proposals to companies on expansion and growth in customer base.
Process of Business Research
Identification of challenge.
The first and foremost task of every research is to set an objective by defining what are the prevalent problems in the marketplace and how a company can tackle them.
Creating Research Proposal
The next step in this process is developing research plans and proposals. Plans are futuristic and require assumptions. These assumptions, in business terms, are called premises.
Therefore, the research proposal can be researched on existing demand for the product, new entrants in the market, or re-setting pricing policies.
Execution of Research
Once the plan is made and the research proposal is developed, the company can toss alternative ways they can execute the research. The company can forward with research by random sampling (mass media survey) or can rely on previously collected data too.
Interpretation of Data
The data so collected should be organized in a systematized form. It can be further used to make reports, conduct SWOT and PESTEL analyses and take necessary actions thereafter.
Action Plan
Once data is collected, interpreted, and evaluated, the last step is to execute the product planning by either launching a product, expanding existing service, or bringing changes in any other core activities around which the research revolves.
Related posts:
- Business Level Strategy: Meaning, Types, Advantages, Examples
- What is Business? Definition, Nature, Types, and Objective
- Company: Formation process, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Characteristics and Features of Business Ethics
- Business Forecasting: Types, Techniques, Need, Advantages, Limitations
- Business Ethics: Importance, Types, Function
Add CommerceMates to your Homescreen!

Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Business Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Business research: definition, types & methods.
10 min read What is business research and why does it matter? Here are some of the ways business research can be helpful to your company, whichever method you choose to carry it out.
What is business research?
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad – it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market. It could focus on customer experience and assess customer satisfaction levels. Or it could involve sizing up the competition through competitor research.
Often when carrying out business research, companies are looking at their own data, sourced from their employees, their customers and their business records. However, business researchers can go beyond their own company in order to collect relevant information and understand patterns that may help leaders make informed decisions. For example, a business may carry out ethnographic research where the participants are studied in the context of their everyday lives, rather than just in their role as consumer, or look at secondary data sources such as open access public records and empirical research carried out in academic studies.
There is also a body of knowledge about business in general that can be mined for business research purposes. For example organizational theory and general studies on consumer behavior.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
Why is business research important?
We live in a time of high speed technological progress and hyper-connectedness. Customers have an entire market at their fingertips and can easily switch brands if a competitor is offering something better than you are. At the same time, the world of business has evolved to the point of near-saturation. It’s hard to think of a need that hasn’t been addressed by someone’s innovative product or service.
The combination of ease of switching, high consumer awareness and a super-evolved marketplace crowded with companies and their offerings means that businesses must do whatever they can to find and maintain an edge. Business research is one of the most useful weapons in the fight against business obscurity, since it allows companies to gain a deep understanding of buyer behavior and stay up to date at all times with detailed information on their market.
Thanks to the standard of modern business research tools and methods, it’s now possible for business analysts to track the intricate relationships between competitors, financial markets, social trends, geopolitical changes, world events, and more.
Find out how to conduct your own market research and make use of existing market research data with our Ultimate guide to market research
Types of business research
Business research methods vary widely, but they can be grouped into two broad categories – qualitative research and quantitative research .
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative business research deals with non-numerical data such as people’s thoughts, feelings and opinions. It relies heavily on the observations of researchers, who collect data from a relatively small number of participants – often through direct interactions.
Qualitative research interviews take place one-on-one between a researcher and participant. In a business context, the participant might be a customer, a supplier, an employee or other stakeholder. Using open-ended questions , the researcher conducts the interview in either a structured or unstructured format. Structured interviews stick closely to a question list and scripted phrases, while unstructured interviews are more conversational and exploratory. As well as listening to the participant’s responses, the interviewer will observe non-verbal information such as posture, tone of voice and facial expression.
Focus groups
Like the qualitative interview, a focus group is a form of business research that uses direct interaction between the researcher and participants to collect data. In focus groups , a small number of participants (usually around 10) take part in a group discussion led by a researcher who acts as moderator. The researcher asks questions and takes note of the responses, as in a qualitative research interview. Sampling for focus groups is usually purposive rather than random, so that the group members represent varied points of view.
Observational studies
In an observational study, the researcher may not directly interact with participants at all, but will pay attention to practical situations, such as a busy sales floor full of potential customers, or a conference for some relevant business activity. They will hear people speak and watch their interactions , then record relevant data such as behavior patterns that relate to the subject they are interested in. Observational studies can be classified as a type of ethnographic research. They can be used to gain insight about a company’s target audience in their everyday lives, or study employee behaviors in actual business situations.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is an immersive design of research where one observes peoples’ behavior in their natural environment. Ethnography was most commonly found in the anthropology field and is now practices across a wide range of social sciences.
Ehnography is used to support a designer’s deeper understanding of the design problem – including the relevant domain, audience(s), processes, goals and context(s) of use.
The ethnographic research process is a popular methodology used in the software development lifecycle. It helps create better UI/UX flow based on the real needs of the end-users.
If you truly want to understand your customers’ needs, wants, desires, pain-points “walking a mile” in their shoes enables this. Ethnographic research is this deeply rooted part of research where you truly learn your targe audiences’ problem to craft the perfect solution.
Case study research
A case study is a detailed piece of research that provides in depth knowledge about a specific person, place or organization. In the context of business research, case study research might focus on organizational dynamics or company culture in an actual business setting, and case studies have been used to develop new theories about how businesses operate. Proponents of case study research feel that it adds significant value in making theoretical and empirical advances. However its detractors point out that it can be time consuming and expensive, requiring highly skilled researchers to carry it out.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research focuses on countable data that is objective in nature. It relies on finding the patterns and relationships that emerge from mass data – for example by analyzing the material posted on social media platforms, or via surveys of the target audience. Data collected through quantitative methods is empirical in nature and can be analyzed using statistical techniques. Unlike qualitative approaches, a quantitative research method is usually reliant on finding the right sample size, as this will determine whether the results are representative. These are just a few methods – there are many more.
Surveys are one of the most effective ways to conduct business research. They use a highly structured questionnaire which is distributed to participants, typically online (although in the past, face to face and telephone surveys were widely used). The questions are predominantly closed-ended, limiting the range of responses so that they can be grouped and analyzed at scale using statistical tools. However surveys can also be used to get a better understanding of the pain points customers face by providing open field responses where they can express themselves in their own words. Both types of data can be captured on the same questionnaire, which offers efficiency of time and cost to the researcher.
Correlational research
Correlational research looks at the relationship between two entities, neither of which are manipulated by the researcher. For example, this might be the in-store sales of a certain product line and the proportion of female customers subscribed to a mailing list. Using statistical analysis methods, researchers can determine the strength of the correlation and even discover intricate relationships between the two variables. Compared with simple observation and intuition, correlation may identify further information about business activity and its impact, pointing the way towards potential improvements and more revenue.
Experimental research
It may sound like something that is strictly for scientists, but experimental research is used by both businesses and scholars alike. When conducted as part of the business intelligence process, experimental research is used to test different tactics to see which ones are most successful – for example one marketing approach versus another. In the simplest form of experimental research, the researcher identifies a dependent variable and an independent variable. The hypothesis is that the independent variable has no effect on the dependent variable, and the researcher will change the independent one to test this assumption. In a business context, the hypothesis might be that price has no relationship to customer satisfaction. The researcher manipulates the price and observes the C-Sat scores to see if there’s an effect.
The best tools for business research
You can make the business research process much quicker and more efficient by selecting the right tools. Business research methods like surveys and interviews demand tools and technologies that can store vast quantities of data while making them easy to access and navigate. If your system can also carry out statistical analysis, and provide predictive recommendations to help you with your business decisions, so much the better.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry. The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.

How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.
Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Business Research: Methods, Types & Examples

Content Index
Business research: Definition
Quantitative research methods, qualitative research methods, advantages of business research, disadvantages of business research, importance of business research.
Business research is a process of acquiring detailed information on all the areas of business and using such information to maximize the sales and profit of the business. Such a study helps companies determine which product/service is most profitable or in demand. In simple words, it can be stated as the acquisition of information or knowledge for professional or commercial purposes to determine opportunities and goals for a business.
Business research can be done for anything and everything. In general, when people speak about business research design , it means asking research questions to know where the money can be spent to increase sales, profits, or market share. Such research is critical to make wise and informed decisions.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
For example: A mobile company wants to launch a new model in the market. But they are not aware of what are the dimensions of a mobile that are in most demand. Hence, the company conducts business research using various methods to gather information, and the same is then evaluated, and conclusions are drawn as to what dimensions are most in demand.
This will enable the researcher to make wise decisions to position his phone at the right price in the market and hence acquire a larger market share.
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
Business research: Types and methodologies
Business research is a part of the business intelligence process. It is usually conducted to determine whether a company can succeed in a new region, to understand its competitors, or simply select a marketing approach for a product. This research can be carried out using steps in qualitative research methods or quantitative research methods.
Quantitative research methods are research methods that deal with numbers. It is a systematic empirical investigation using statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques . Such methods usually start with data collection and then proceed to statistical analysis using various methods. The following are some of the research methods used to carry out business research.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Management Framework
Survey research
Survey research is one of the most widely used methods to gather data, especially for conducting business research. Surveys involve asking various survey questions to a set of audiences through various types like online polls, online surveys, questionnaires, etc. Nowadays, most of the major corporations use this method to gather data and use it to understand the market and make appropriate business decisions.
Various types of surveys, like cross-sectional studies , which need to collect data from a set of audiences at a given point of time, or longitudinal surveys which are needed to collect data from a set of audiences across various time durations in order to understand changes in the respondents’ behavior are used to conduct survey research. With the advancement in technology, surveys can now be sent online through email or social media .
For example: A company wants to know the NPS score for their website i.e. how satisfied are people who are visiting their website. An increase in traffic to their website or the audience spending more time on a website can result in higher rankings on search engines which will enable the company to get more leads as well as increase its visibility.
Hence, the company can ask people who visit their website a few questions through an online survey to understand their opinions or gain feedback and hence make appropriate changes to the website to increase satisfaction.
Learn More: Business Survey Template
Correlational research
Correlational research is conducted to understand the relationship between two entities and what impact each one of them has on the other. Using mathematical analysis methods, correlational research enables the researcher to correlate two or more variables .
Such research can help understand patterns, relationships, trends, etc. Manipulation of one variable is possible to get the desired results as well. Generally, a conclusion cannot be drawn only on the basis of correlational research.
For example: Research can be conducted to understand the relationship between colors and gender-based audiences. Using such research and identifying the target audience, a company can choose the production of particular color products to be released in the market. This can enable the company to understand the supply and demand requirements of its products.
Causal-Comparative research
Causal-comparative research is a method based on the comparison. It is used to deduce the cause-effect relationship between variables. Sometimes also known as quasi-experimental research, it involves establishing an independent variable and analyzing the effects on the dependent variable.
In such research, data manipulation is not done; however, changes are observed in the variables or groups under the influence of the same changes. Drawing conclusions through such research is a little tricky as independent and dependent variables will always exist in a group. Hence all other parameters have to be taken into consideration before drawing any inferences from the research.
LEARN ABOUT: Causal Research
For example: Research can be conducted to analyze the effect of good educational facilities in rural areas. Such a study can be done to analyze the changes in the group of people from rural areas when they are provided with good educational facilities and before that.
Another example can be to analyze the effect of having dams and how it will affect the farmers or the production of crops in that area.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research trends
Experimental research
Experimental research is based on trying to prove a theory. Such research may be useful in business research as it can let the product company know some behavioral traits of its consumers, which can lead to more revenue. In this method, an experiment is carried out on a set of audiences to observe and later analyze their behavior when impacted by certain parameters.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
For example: Experimental research was conducted recently to understand if particular colors have an effect on consumers’ hunger. A set of the audience was then exposed to those particular colors while they were eating, and the subjects were observed. It was seen that certain colors like red or yellow increase hunger.
Hence, such research was a boon to the hospitality industry. You can see many food chains like Mcdonalds, KFC, etc., using such colors in their interiors, brands, as well as packaging.
Another example of inferences drawn from experimental research, which is used widely by most bars/pubs across the world, is that loud music in the workplace or anywhere makes a person drink more in less time. This was proven through experimental research and was a key finding for many business owners across the globe.
Online research / Literature research
Literature research is one of the oldest methods available. It is very economical, and a lot of information can be gathered using such research. Online research or literature research involves gathering information from existing documents and studies, which can be available at Libraries, annual reports, etc.
Nowadays, with the advancement in technology, such research has become even more simple and accessible to everyone. An individual can directly research online for any information that is needed, which will give him in-depth information about the topic or the organization.
Such research is used mostly by marketing and salespeople in the business sector to understand the market or their customers. Such research is carried out using existing information that is available from various sources. However, care has to be taken to validate the sources from where the information is going to be collected.
For example , a salesperson has heard a particular firm is looking for some solution that their company provides. Hence, the salesperson will first search for a decision maker from the company, investigate what department he is from, and understand what the target company is looking for and what they are into.
Using this research, he can cater his solution to be spot on when he pitches it to this client. He can also reach out to the customer directly by finding a means to communicate with him by researching online.’
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Qualitative research is a method that has a high importance in business research. Qualitative research involves obtaining data through open-ended conversational means of communication. Such research enables the researcher to not only understand what the audience thinks but also why he thinks it.
In such research, in-depth information can be gathered from the subjects depending on their responses. There are various types of qualitative research methods, such as interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, content analysis, and case study research, that are widely used.
Such methods are of very high importance in business research as they enable the researcher to understand the consumer. What motivates the consumer to buy and what does not is what will lead to higher sales, and that is the prime objective for any business.
Following are a few methods that are widely used in today’s world by most businesses.
Interviews are somewhat similar to surveys, like sometimes they may have the same types of questions used. The difference is that the respondent can answer these open-ended questions at length, and the direction of the conversation or the questions being asked can be changed depending on the response of the subject.
Such a method usually gives the researcher detailed information about the perspective or opinions of its subject. Carrying out interviews with subject matter experts can also give important information critical to some businesses.
For example: An interview was conducted by a telecom manufacturer with a group of women to understand why they have less number of female customers. After interviewing them, the researcher understood that there were fewer feminine colors in some of the models, and females preferred not to purchase them.
Such information can be critical to a business such as a telecom manufacturer and hence it can be used to increase its market share by targeting women customers by launching some feminine colors in the market.
Another example would be to interview a subject matter expert in social media marketing. Such an interview can enable a researcher to understand why certain types of social media advertising strategies work for a company and why some of them don’t.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
Focus groups
Focus groups are a set of individuals selected specifically to understand their opinions and behaviors. It is usually a small set of a group that is selected keeping in mind the parameters for their target market audience to discuss a particular product or service. Such a method enables a researcher with a larger sample than the interview or a case study while taking advantage of conversational communication.
Focus group is also one of the best examples of qualitative data in education . Nowadays, focus groups can be sent online surveys as well to collect data and answer why, what, and how questions. Such a method is very crucial to test new concepts or products before they are launched in the market.
For example: Research is conducted with a focus group to understand what dimension of screen size is preferred most by the current target market. Such a method can enable a researcher to dig deeper if the target market focuses more on the screen size, features, or colors of the phone. Using this data, a company can make wise decisions about its product line and secure a higher market share.
Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is one of the most challenging research but can give extremely precise results. Such research is used quite rarely, as it is time-consuming and can be expensive as well. It involves the researcher adapting to the natural environment and observing its target audience to collect data. Such a method is generally used to understand cultures, challenges, or other things that can occur in that particular setting.
For example: The world-renowned show “Undercover Boss” would be an apt example of how ethnographic research can be used in businesses. In this show, the senior management of a large organization works in his own company as a regular employee to understand what improvements can be made, what is the culture in the organization, and to identify hard-working employees and reward them.
It can be seen that the researcher had to spend a good amount of time in the natural setting of the employees and adapt to their ways and processes. While observing in this setting, the researcher could find out the information he needed firsthand without losing any information or any bias and improve certain things that would impact his business.
LEARN ABOUT: Workforce Planning Model
Case study research
Case study research is one of the most important in business research. It is also used as marketing collateral by most businesses to land up more clients. Case study research is conducted to assess customer satisfaction and document the challenges that were faced and the solutions that the firm gave them.
These inferences are made to point out the benefits that the customer enjoyed for choosing their specific firm. Such research is widely used in other fields like education, social sciences, and similar. Case studies are provided by businesses to new clients to showcase their capabilities, and hence such research plays a crucial role in the business sector.
For example: A services company has provided a testing solution to one of its clients. A case study research is conducted to find out what were the challenges faced during the project, what was the scope of their work, what objective was to be achieved, and what solutions were given to tackle the challenges.
The study can end with the benefits that the company provided through its solutions, like reduced time to test batches, easy implementation or integration of the system, or even cost reduction. Such a study showcases the capability of the company, and hence it can be stated as empirical evidence of the new prospect.
Website visitor profiling/research
Website intercept surveys or website visitor profiling/research is something new that has come up and is quite helpful in the business sector. It is an innovative approach to collect direct feedback from your website visitors using surveys. In recent times a lot of business generation happens online, and hence it is important to understand the visitors of your website as they are your potential customers.
Collecting feedback is critical to any business, as without understanding a customer, no business can be successful. A company has to keep its customers satisfied and try to make them loyal customers in order to stay on top.
A website intercept survey is an online survey that allows you to target visitors to understand their intent and collect feedback to evaluate the customers’ online experience. Information like visitor intention, behavior path, and satisfaction with the overall website can be collected using this.
Depending on what information a company is looking for, multiple forms of website intercept surveys can be used to gather responses. Some of the popular ones are Pop-ups, also called Modal boxes, and on-page surveys.
For example: A prospective customer is looking for a particular product that a company is selling. Once he is directed to the website, an intercept survey will start noting his intent and path. Once the transaction has been made, a pop-up or an on-page survey is provided to the customer to rate the website.
Such research enables the researcher to put this data to good use and hence understand the customers’ intent and path and improve any parts of the website depending on the responses, which in turn would lead to satisfied customers and hence, higher revenues and market share.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
- Business research helps to identify opportunities and threats.
- It helps identify research problems , and using this information, wise decisions can be made to tackle the issue appropriately.
- It helps to understand customers better and hence can be useful to communicate better with the customers or stakeholders.
- Risks and uncertainties can be minimized by conducting business research in advance.
- Financial outcomes and investments that will be needed can be planned effectively using business research.
- Such research can help track competition in the business sector.
- Business research can enable a company to make wise decisions as to where to spend and how much.
- Business research can enable a company to stay up-to-date with the market and its trends, and appropriate innovations can be made to stay ahead in the game.
- Business research helps to measure reputation management
- Business research can be a high-cost affair
- Most of the time, business research is based on assumptions
- Business research can be time-consuming
- Business research can sometimes give you inaccurate information because of a biased population or a small focus group.
- Business research results can quickly become obsolete because of the fast-changing markets
Business research is one of the most effective ways to understand customers, the market, and competitors. Such research helps companies to understand the demand and supply of the market. Using such research will help businesses reduce costs and create solutions or products that are targeted to the demand in the market and the correct audience.
In-house business research can enable senior management to build an effective team or train or mentor when needed. Business research enables the company to track its competitors and hence can give you the upper hand to stay ahead of them.
Failures can be avoided by conducting such research as it can give the researcher an idea if the time is right to launch its product/solution and also if the audience is right. It will help understand the brand value and measure customer satisfaction which is essential to continuously innovate and meet customer demands.
This will help the company grow its revenue and market share. Business research also helps recruit ideal candidates for various roles in the company. By conducting such research, a company can carry out a SWOT analysis , i.e. understand the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. With the help of this information, wise decisions can be made to ensure business success.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research industry
Business research is the first step that any business owner needs to set up his business to survive or to excel in the market. The main reason why such research is of utmost importance is that it helps businesses to grow in terms of revenue, market share, and brand value.
MORE LIKE THIS

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024

12 Best Employee Survey Tools for Organizational Excellence
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Market Research Objectives
Market research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that organizations set when conducting research to gather information about their target markets, customers, competitors, and industry trends. These objectives serve as a roadmap, guiding the research process and ensuring that efforts are focused and results are relevant to the organization’s needs.
Table of Contents
Key Characteristics of Market Research Objectives
Market research objectives possess several key characteristics:
- Specific: Objectives should be clearly defined and specific in terms of what information is sought, who the target audience is, and what the research aims to achieve.
- Measurable: Objectives should be quantifiable, allowing for the measurement of progress and success.
- Achievable: Objectives should be realistic and attainable within the constraints of available resources, such as time and budget.
- Relevant: Objectives should align with the organization’s overall goals and be relevant to its current situation or challenges.
Importance of Market Research Objectives
Market research objectives play a pivotal role in the success of businesses and organizations for several reasons:
1. Focus and Direction:
- They provide a clear sense of purpose and direction for the research effort, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
2. Alignment with Business Goals:
- Objectives help align market research with broader business goals, ensuring that the insights gained contribute to strategic decision-making.
3. Measurement of Success:
- Objectives serve as benchmarks for success, allowing organizations to evaluate the effectiveness of their research efforts.
4. Resource Optimization:
- By defining specific objectives, organizations can allocate resources, such as time and budget, more effectively to achieve their research goals.
5. Competitive Advantage:
- Well-defined research objectives enable organizations to gain a competitive advantage by making informed, data-driven decisions.
Types of Market Research Objectives
Market research objectives can vary based on the specific needs and goals of an organization. Some common types of market research objectives include:
1. Exploratory Objectives:
- These objectives aim to gain a deeper understanding of a market, its dynamics, and potential opportunities or challenges.
2. Descriptive Objectives:
- Descriptive objectives seek to provide a comprehensive overview of a market’s characteristics, such as demographics, preferences, and behaviors.
3. Causal Objectives:
- Causal objectives focus on understanding cause-and-effect relationships, such as how changes in pricing impact consumer purchasing decisions.
4. Predictive Objectives:
- Predictive objectives aim to forecast future market trends, allowing organizations to proactively respond to changing conditions.
5. Diagnostic Objectives:
- Diagnostic objectives seek to identify the root causes of specific issues or challenges within a market.
Setting Market Research Objectives
The process of setting market research objectives.
Setting effective market research objectives involves a systematic process:
- Identify Information Needs:
- Begin by identifying the specific information needs of the organization. What questions or challenges does the research aim to address?
- Define Clear Objectives:
- Transform information needs into clear and specific objectives. Objectives should answer the “what,” “who,” and “why” of the research.
- Prioritize Objectives:
- Prioritize objectives based on their importance and relevance to the organization’s goals and decision-making processes.
- Specify Metrics and Measurements:
- Determine how each objective will be measured and what metrics or data points are relevant to assess success.
- Consider Constraints:
- Account for constraints, such as budget and timeline, when setting objectives to ensure feasibility.
- Align with Stakeholders:
- Collaborate with relevant stakeholders to ensure that objectives align with their expectations and needs.
- Document Objectives:
- Document the objectives in a clear and concise manner, ensuring that they are accessible to all involved in the research process.
Real-World Examples of Market Research Objectives
To better understand how market research objectives are applied in practice, here are some real-world examples:
Example 1: Product Launch
Objective: To determine the market demand and potential acceptance of a new smartphone model among consumers aged 18-34 in the United States.
Metrics: Measure the projected sales volume, customer feedback on product features, and brand perception among the target demographic.
Example 2: Competitive Analysis
Objective: To assess the competitive landscape in the fast-food industry within a specific region and identify opportunities for market entry.
Metrics: Analyze market share data, conduct mystery shopping evaluations, and assess consumer preferences for various fast-food chains.
Example 3: Customer Satisfaction
Objective: To evaluate customer satisfaction with the company’s recent customer service initiatives and identify areas for improvement.
Metrics: Collect and analyze customer feedback through surveys, assess customer retention rates, and track changes in Net Promoter Score (NPS).
Example 4: Market Expansion
Objective: To explore the feasibility of expanding into international markets and identify potential entry strategies.
Metrics: Analyze market size, assess regulatory barriers, and conduct competitor analysis in selected international markets.
Best Practices for Market Research Objectives
Setting effective market research objectives requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some best practices to follow:
1. Start with Clear Information Needs:
- Ensure that objectives are driven by specific questions or challenges that the organization needs to address.
2. Make Objectives SMART:
- Follow the SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) to create well-defined objectives.
3. Prioritize Objectives:
- Recognize that not all objectives are of equal importance. Focus on the most critical ones that will have the greatest impact.
4. Involve Stakeholders:
5. document objectives:.
- Clearly document objectives in a format that is accessible to all involved in the research process.
6. Review and Update Objectives:
- Regularly review and update objectives as the research progresses to account for changing circumstances or emerging insights.
Market research objectives are the cornerstone of any successful research effort. They provide clarity, focus, and direction to organizations seeking to gain insights into their target markets, customers, and competitors. By setting clear and well-defined objectives that align with their goals, businesses can make informed decisions, stay competitive, and thrive in dynamic market environments. Whether it’s launching a new product, assessing customer satisfaction, or expanding into new markets, effective market research objectives are the compass that guides organizations toward success.
Key Highlights:
- Market research objectives provide direction and focus to research efforts, ensuring relevance and alignment with organizational goals.
- Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, and relevant to the organization’s needs.
- They help in focusing efforts, aligning with business goals, measuring success, optimizing resources, and gaining a competitive advantage.
- Exploratory, descriptive, causal, predictive, and diagnostic objectives cater to different research needs and goals.
- The process involves identifying information needs, defining clear objectives, prioritizing, specifying metrics, considering constraints, aligning with stakeholders, and documenting objectives.
- Examples include assessing demand for a new product, analyzing the competitive landscape, evaluating customer satisfaction, and exploring market expansion opportunities.
- Start with clear information needs, make objectives SMART, prioritize, involve stakeholders, document objectives, and review/update as needed.
- Market research objectives serve as a roadmap for organizations, guiding research efforts to yield valuable insights that drive informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Connected Analysis Frameworks
Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

Business Valuation

Paired Comparison Analysis

Monte Carlo Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

CATWOE Analysis

VTDF Framework

Pareto Analysis

Comparable Analysis

SWOT Analysis

PESTEL Analysis

Business Analysis

Financial Structure

Financial Modeling

Value Investing

Buffet Indicator

Financial Analysis

Post-Mortem Analysis

Retrospective Analysis

Root Cause Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Break-even Analysis

Decision Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

STEEP Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Activity-Based Management

PMESII-PT Analysis

SPACE Analysis

Lotus Diagram

Functional Decomposition

Multi-Criteria Analysis

Stakeholder Analysis

Strategic Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced Scorecard , OKR , Agile Methodology , Value Proposition , VTDF Framework , BCG Matrix , GE McKinsey Matrix , Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model .
Main Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Business Model Innovation
- Platform Business Models
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Digital Business Models
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
21 Research Objectives Examples (Copy and Paste)

Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve.
These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected by the researcher to present a clear intention or course of action for his or her qualitative or quantitative study.
Research objectives are typically nested under one overarching research aim. The objectives are the steps you’ll need to take in order to achieve the aim (see the examples below, for example, which demonstrate an aim followed by 3 objectives, which is what I recommend to my research students).
Research Objectives vs Research Aims
Research aim and research objectives are fundamental constituents of any study, fitting together like two pieces of the same puzzle.
The ‘research aim’ describes the overarching goal or purpose of the study (Kumar, 2019). This is usually a broad, high-level purpose statement, summing up the central question that the research intends to answer.
Example of an Overarching Research Aim:
“The aim of this study is to explore the impact of climate change on crop productivity.”
Comparatively, ‘research objectives’ are concrete goals that underpin the research aim, providing stepwise actions to achieve the aim.
Objectives break the primary aim into manageable, focused pieces, and are usually characterized as being more specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Examples of Specific Research Objectives:
1. “To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.” 2. “To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).” 3. “To analyze the impact of changing weather patterns on crop diseases within the same timeframe.”
The distinction between these two terms, though subtle, is significant for successfully conducting a study. The research aim provides the study with direction, while the research objectives set the path to achieving this aim, thereby ensuring the study’s efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Write Research Objectives
I usually recommend to my students that they use the SMART framework to create their research objectives.
SMART is an acronym standing for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It provides a clear method of defining solid research objectives and helps students know where to start in writing their objectives (Locke & Latham, 2013).
Each element of this acronym adds a distinct dimension to the framework, aiding in the creation of comprehensive, well-delineated objectives.
Here is each step:
- Specific : We need to avoid ambiguity in our objectives. They need to be clear and precise (Doran, 1981). For instance, rather than stating the objective as “to study the effects of social media,” a more focused detail would be “to examine the effects of social media use (Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter) on the academic performance of college students.”
- Measurable: The measurable attribute provides a clear criterion to determine if the objective has been met (Locke & Latham, 2013). A quantifiable element, such as a percentage or a number, adds a measurable quality. For example, “to increase response rate to the annual customer survey by 10%,” makes it easier to ascertain achievement.
- Achievable: The achievable aspect encourages researchers to craft realistic objectives, resembling a self-check mechanism to ensure the objectives align with the scope and resources at disposal (Doran, 1981). For example, “to interview 25 participants selected randomly from a population of 100” is an attainable objective as long as the researcher has access to these participants.
- Relevance : Relevance, the fourth element, compels the researcher to tailor the objectives in alignment with overarching goals of the study (Locke & Latham, 2013). This is extremely important – each objective must help you meet your overall one-sentence ‘aim’ in your study.
- Time-Bound: Lastly, the time-bound element fosters a sense of urgency and prioritization, preventing procrastination and enhancing productivity (Doran, 1981). “To analyze the effect of laptop use in lectures on student engagement over the course of two semesters this year” expresses a clear deadline, thus serving as a motivator for timely completion.
You’re not expected to fit every single element of the SMART framework in one objective, but across your objectives, try to touch on each of the five components.
Research Objectives Examples
1. Field: Psychology
Aim: To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.
- Objective 1: To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.
- Objective 2: To investigate the relationship between class grades and reported sleep duration.
- Objective 3: To survey student perceptions and experiences on how sleep deprivation affects their cognitive capabilities.
2. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To understand the effects of urban green spaces on human well-being in a metropolitan city.
- Objective 1: To assess the physical and mental health benefits of regular exposure to urban green spaces.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the social impacts of urban green spaces on community interactions.
- Objective 3: To examine patterns of use for different types of urban green spaces.
3. Field: Technology
Aim: To investigate the influence of using social media on productivity in the workplace.
- Objective 1: To measure the amount of time spent on social media during work hours.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the perceived impact of social media use on task completion and work efficiency.
- Objective 3: To explore whether company policies on social media usage correlate with different patterns of productivity.
4. Field: Education
Aim: To examine the effectiveness of online vs traditional face-to-face learning on student engagement and achievement.
- Objective 1: To compare student grades between the groups exposed to online and traditional face-to-face learning.
- Objective 2: To assess student engagement levels in both learning environments.
- Objective 3: To collate student perceptions and preferences regarding both learning methods.
5. Field: Health
Aim: To determine the impact of a Mediterranean diet on cardiac health among adults over 50.
- Objective 1: To assess changes in cardiovascular health metrics after following a Mediterranean diet for six months.
- Objective 2: To compare these health metrics with a similar group who follow their regular diet.
- Objective 3: To document participants’ experiences and adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
6. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To analyze the impact of urban farming on community sustainability.
- Objective 1: To document the types and quantity of food produced through urban farming initiatives.
- Objective 2: To assess the effect of urban farming on local communities’ access to fresh produce.
- Objective 3: To examine the social dynamics and cooperative relationships in the creating and maintaining of urban farms.
7. Field: Sociology
Aim: To investigate the influence of home offices on work-life balance during remote work.
- Objective 1: To survey remote workers on their perceptions of work-life balance since setting up home offices.
- Objective 2: To conduct an observational study of daily work routines and family interactions in a home office setting.
- Objective 3: To assess the correlation, if any, between physical boundaries of workspaces and mental boundaries for work in the home setting.
8. Field: Economics
Aim: To evaluate the effects of minimum wage increases on small businesses.
- Objective 1: To analyze cost structures, pricing changes, and profitability of small businesses before and after minimum wage increases.
- Objective 2: To survey small business owners on the strategies they employ to navigate minimum wage increases.
- Objective 3: To examine employment trends in small businesses in response to wage increase legislation.
9. Field: Education
Aim: To explore the role of extracurricular activities in promoting soft skills among high school students.
- Objective 1: To assess the variety of soft skills developed through different types of extracurricular activities.
- Objective 2: To compare self-reported soft skills between students who participate in extracurricular activities and those who do not.
- Objective 3: To investigate the teachers’ perspectives on the contribution of extracurricular activities to students’ skill development.
10. Field: Technology
Aim: To assess the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on the tourism industry.
- Objective 1: To document the types and popularity of VR experiences available in the tourism market.
- Objective 2: To survey tourists on their interest levels and satisfaction rates with VR tourism experiences.
- Objective 3: To determine whether VR tourism experiences correlate with increased interest in real-life travel to the simulated destinations.
11. Field: Biochemistry
Aim: To examine the role of antioxidants in preventing cellular damage.
- Objective 1: To identify the types and quantities of antioxidants in common fruits and vegetables.
- Objective 2: To determine the effects of various antioxidants on free radical neutralization in controlled lab tests.
- Objective 3: To investigate potential beneficial impacts of antioxidant-rich diets on long-term cellular health.
12. Field: Linguistics
Aim: To determine the influence of early exposure to multiple languages on cognitive development in children.
- Objective 1: To assess cognitive development milestones in monolingual and multilingual children.
- Objective 2: To document the number and intensity of language exposures for each group in the study.
- Objective 3: To investigate the specific cognitive advantages, if any, enjoyed by multilingual children.
13. Field: Art History
Aim: To explore the impact of the Renaissance period on modern-day art trends.
- Objective 1: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
- Objective 2: To analyze modern art pieces for the influence of the Renaissance style.
- Objective 3: To survey modern-day artists for their inspirations and the influence of historical art movements on their work.
14. Field: Cybersecurity
Aim: To assess the effectiveness of two-factor authentication (2FA) in preventing unauthorized system access.
- Objective 1: To measure the frequency of unauthorized access attempts before and after the introduction of 2FA.
- Objective 2: To survey users about their experiences and challenges with 2FA implementation.
- Objective 3: To evaluate the efficacy of different types of 2FA (SMS-based, authenticator apps, biometrics, etc.).
15. Field: Cultural Studies
Aim: To analyze the role of music in cultural identity formation among ethnic minorities.
- Objective 1: To document the types and frequency of traditional music practices within selected ethnic minority communities.
- Objective 2: To survey community members on the role of music in their personal and communal identity.
- Objective 3: To explore the resilience and transmission of traditional music practices in contemporary society.
16. Field: Astronomy
Aim: To explore the impact of solar activity on satellite communication.
- Objective 1: To categorize different types of solar activities and their frequencies of occurrence.
- Objective 2: To ascertain how variations in solar activity may influence satellite communication.
- Objective 3: To investigate preventative and damage-control measures currently in place during periods of high solar activity.
17. Field: Literature
Aim: To examine narrative techniques in contemporary graphic novels.
- Objective 1: To identify a range of narrative techniques employed in this genre.
- Objective 2: To analyze the ways in which these narrative techniques engage readers and affect story interpretation.
- Objective 3: To compare narrative techniques in graphic novels to those found in traditional printed novels.
18. Field: Renewable Energy
Aim: To investigate the feasibility of solar energy as a primary renewable resource within urban areas.
- Objective 1: To quantify the average sunlight hours across urban areas in different climatic zones.
- Objective 2: To calculate the potential solar energy that could be harnessed within these areas.
- Objective 3: To identify barriers or challenges to widespread solar energy implementation in urban settings and potential solutions.
19. Field: Sports Science
Aim: To evaluate the role of pre-game rituals in athlete performance.
- Objective 1: To identify the variety and frequency of pre-game rituals among professional athletes in several sports.
- Objective 2: To measure the impact of pre-game rituals on individual athletes’ performance metrics.
- Objective 3: To examine the psychological mechanisms that might explain the effects (if any) of pre-game ritual on performance.
20. Field: Ecology
Aim: To investigate the effects of urban noise pollution on bird populations.
- Objective 1: To record and quantify urban noise levels in various bird habitats.
- Objective 2: To measure bird population densities in relation to noise levels.
- Objective 3: To determine any changes in bird behavior or vocalization linked to noise levels.
21. Field: Food Science
Aim: To examine the influence of cooking methods on the nutritional value of vegetables.
- Objective 1: To identify the nutrient content of various vegetables both raw and after different cooking processes.
- Objective 2: To compare the effect of various cooking methods on the nutrient retention of these vegetables.
- Objective 3: To propose cooking strategies that optimize nutrient retention.
The Importance of Research Objectives
The importance of research objectives cannot be overstated. In essence, these guideposts articulate what the researcher aims to discover, understand, or examine (Kothari, 2014).
When drafting research objectives, it’s essential to make them simple and comprehensible, specific to the point of being quantifiable where possible, achievable in a practical sense, relevant to the chosen research question, and time-constrained to ensure efficient progress (Kumar, 2019).
Remember that a good research objective is integral to the success of your project, offering a clear path forward for setting out a research design , and serving as the bedrock of your study plan. Each objective must distinctly address a different dimension of your research question or problem (Kothari, 2014). Always bear in mind that the ultimate purpose of your research objectives is to succinctly encapsulate your aims in the clearest way possible, facilitating a coherent, comprehensive and rational approach to your planned study, and furnishing a scientific roadmap for your journey into the depths of knowledge and research (Kumar, 2019).
Kothari, C.R (2014). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques . New Delhi: New Age International.
Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners .New York: SAGE Publications.
Doran, G. T. (1981). There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Management review, 70 (11), 35-36.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2013). New Developments in Goal Setting and Task Performance . New York: Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Business Research: Types, Methods, Examples
- Updated on
- Jan 29, 2024

Ever wondered what it takes to build a flourishing business ? Aiming to provide maximum sales and profit, business research helps you to gather comprehensive information about your business and accordingly make relevant changes if required. So, in this process of being successful, we gather all types of data to better define our strategies and understand what products or services customers want. And in case, you’re planning to expand your business, research can help you determine your odds of positive results. In this blog, we’ll help you understand the basics of research and analysis .
“Whoever gets closer to the customer, wins.” – Bernadette Jiwa
This Blog Includes:
What is business research, business research example, importance of business research, types & methods, focus groups , case study research , ethnographic research, survey , correlation research , experimental research , advantages and disadvantages of business research, scope of business research, role of business research, business research books, business research report, top 10 tools for business research, business research partners, top 10 business research topics, career prospects , [bonus] best mba colleges in the world.
Business Research can be simply defined as a process of gathering comprehensive data and information on all the areas of business and incorporating this information for sales and profit maximization. If you are wondering what is Business Research, it is a systematic management activity helping companies to determine which product will be most profitable for companies to produce. Also, there are multiple steps in conducting research, with each thoroughly reviewed to ensure that the best decision is made for the company as a whole.
Also Read: Scope of MBA in International Business
Let’s say there’s an automobile company that is planning to launch a car that runs on CNG. To promote cleaner fuel, the company will be involved in developing different plans and strategies to identify the demand for the car they intend to launch. Other than this, the company will also look for competitors, and the target audience, keeping in mind the distribution of CNG in India. Hence the research is conducted on various ideas to formulate a sustainable and more efficient design.
When it comes to the question of why Business Research is important, it has an essential role to play in varied areas of business. Here are some of the reasons describing the importance of Business Research:
- It helps businesses gain better insights into their target customer’s preferences, buying patterns, pain points, as well as demographics.
- Business Research also provides businesses with a detailed overview of their target markets, what’s in trend, as well as market demand.
- By studying consumers’ buying patterns and preferences as well as market trends and demands with the help of business research, businesses can effectively and efficiently curate the best possible plans and strategies accordingly.
- The importance of business research also lies in highlighting the areas where unnecessary costs can be minimized and those areas in a business which need more attention and can bring in more customers and hence boost profits.
- Businesses can constantly innovate as per their customers’ preferences and interests and keep their attention on the brand.
- Business Research also plays the role of a catalyst as it helps businesses thrive in their markets by capturing all the available opportunities and also meeting the needs and preferences of their customers.
Also Read: Business Analyst vs Data Analyst

Business research plays an important role in the business intelligence process. This is usually conducted to determine if a company can succeed in a new region through competitive analyses and a better marketing approach. Due to this, this broad field has been distinguished into two types namely, Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research Method.
Here are the most important types of Business Research :
Qualitative Research Methods
It involves putting open-ended questions to the audience through different channels of communication to understand why researchers think in a particular manner. Stress is laid on understanding the intent, attitude, and beliefs to figure out the behaviour and response of the customers. Moreover, the goal of Qualitative Business Research is to get in-depth knowledge about the subjects of the research. Moreover, qualitative research enables us to put the perspective of the consumer in front of the researcher so that we can understand and see the alignment of the ideas between the market and the business.
The data collected in this type of business research is by the following methods:
- Interviews
- Case Study
- Ethnographic Research
- Website Visitor Profiling
- Content Analysis
Also Read: Study MBA in Music Business at Berklee College of Music!
Let us take a detailed look at some of the ways-
Interviews and surveys are similar. The only difference lies in the fact that the responder can put a question in an interview whilst it is not possible during a survey. Through interviews, it is easier to understand the detailed perspective of the person concerning the subject of research. A mobile brand researched to understand why certain colours are preferred by male and female customers. The research revealed that since red is assumed to be a feminine colour, it is more preferred by females than males.
Focus groups are a type of business research that involves only a set of individuals. Each selected individual represents a particular category of the target market. The major difference between interviews and focus groups is the number of people that it involves. To launch a new product for a particular group of society, focus groups prove to be the best way to understand the needs of the local audience.
For example, Tesla decides to launch their latest car model in India. The company, therefore, will require feedback from the Indian audience only.
Did you know? Amazon, the internet giant changed its payment strategy to enter the Indian market. Since the Indian economy was not entirely ready for online modes of payment, amazon introduced a new payment method and came up with ‘ cash on delivery ’ to gain consumers’ trust.
One of the most effective ways for business research is conducting case studies. With the motive to understand customer satisfaction, challenges that usually the customers face while using the product and hence, providing them with the right solution can be achieved by analysing data secured through data secured by case studies. Case study researchers are conducted in many fields of business that ultimately aid organisations in improving their products or services.
Ethnographic Research refers to understanding people as a whole. One must be able to grok their consumers or target audience which will help identify patterns, flaws, etc. Ethnography is a branch of anthropology that is the study of what elements or features make us humans. How did people live? What aspect made us so dependent on smartphones and technology? Why would people buy one product over the other? It refers to asking questions about lifestyle, communities, etc., and trying to gain insight into consumer behaviour and buying patterns.
For example, consider a random product. Are people looking for that product? Do they need it? Is it a necessity or a luxury? Which class of people are most likely to buy it? People often cannot comprehend what they are looking for. Gaining different perceptions can help us tailor our products accordingly to the consumers. Who would have thought that the majority of humans will need face masks for survival?
Also Read: How to Become a Research Analyst?
Quantitative Research Methods
With the employment of mathematical, statistical and computational techniques, quantitative research is carried out to deal with numbers. This systematical empirical investigation starts with the acquisition of the data and then moves on to analyzing it with the help of different tools. The goal is to identify clientele and then meet the targets of the audience. As the method of business research employs a questionnaire to determine the audience’s response, the questions are built around the idea that the audience knows about the product or the services that the firm offers. Some of the key questions answered in quantitative research methods include, who is connected with your network, how they qualify for the ‘product’ or how regularly they visit your website.
The data is collected based on the following research:
- Correlational
- Online
- Casual Comparative
- Experimental
It is the most common method under quantitative research via which a huge amount of data can be collected concerning a product or service. A common set of questions are asked to the people and they are asked to provide their inputs. To understand the nature of the market in-depth, this method is massively used by leading organisations all across the globe. Analysing data recorded through service helps organisations make suitable decisions.
Under this research, usually two entities are put together to examine the impact they create on each other. As suggested by the name it is the best process to understand patterns, relationships and trends. the data grasped through correlation research is generally combined with other tools as one cannot achieve a firm conclusion using this type of business research.
Experimental research is purely based on proving a particular theory that is pre-assumed. True experimental research companies can understand varied behavioural traits of the customers that further assist them in generating more revenue. Exposing a set of audience to common parameters, their behaviour is recorded and hence analysed. This can be understood as the main basis of the experimental research.
Also Read: Scope of Operation Research
There are certain pros and cons of business research that you must know about. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of Business Research.
Advantages of Business Research
- Business Research plays the role of a catalyst in identifying potential threats, issues as well as opportunities .
- It provides a detailed analysis of customers and the target audience , thus helping in building better relationships with one’s audience and capturing the areas which we might be missing out on.
- It also anticipates future problems thus the enterprise is able to tackle those uncertainties and prepare for them beforehand.
- It keeps a continuous track of competition in the market and gives businesses the scope to come up with better strategies to tackle their competitors.
- Business Research also conducts a thorough cost analysis thus helping the company efficiently manage resources and allocate them in an optimal manner.
- It keeps you updated with the latest trends and competitor analysis .
Disadvantages of Business Research
- Business Research can be expensive and time-consuming .
- It also has the danger of being assumptive and imprecise at times , because the focus groups might be small or can be highly based on assumptions.
- The market is ever-changing and ever-evolving and capturing the right trends or anticipating them can constitute a complicated process for business research.
Also Read: Types of Research Design
The process of business research can be as comprehensive and as detailed as a business wants it to be. Generally, a company takes up research with a certain aim or hypothesis in order to figure out the issues, opportunities and trends and how they can be leveraged in the best way.
Here is the step-by-step process of Business Research:
- Identifying the Opportunity or Problem – To begin with the research, we first need to know what is the problem or the opportunity we would be leveraging on. It can be a popular trend or a common problem that a business is facing and can potentially become the headstart for the research process. Once you know the problem or the opportunity, go ahead with giving an understandable statement of what it’s about, what the hypothesis of the research will be as well as its objectives.
- Decide and Plan the Research Design – The next step in the business research process to find the right research design which suits the objectives and overall plan of the research. The most popular research designs are Quantitative and Qualitative Research.
- Determining the Research Method – The research design is closely connected to the research method since both qualitative and quantitative research designs have different methods for data collection, analysis, amongst others. So, once you have put a finger on what the right research design will be, go ahead with finding the right research method as per the plan, types of data collection, objective, costs involved, and other determining factors.
- Collect Data – Utilizing the research method and design, the next step in the business research process is to collect data and assimilate it.
- Data Analysis and Evaluation – After assimilating the data required, the data analysis will take place to gather all the observations and findings.
- Communicate Results – The presentation of the business research report is the concluding step of this procedure after which the higher management works upon the best techniques and strategies to leverage the opportunity or tackle the issue.
Also Read: MBA in Business Analytics
The scope of Business Research is multifarious and reaches out to many specialisations and areas. Let’s take a look the scope of business research across various specialisations:
- Marketing Management When it comes to business research, becomes an important part of marketing management that analyses consumer behaviour, target audiences, competition, price policy, promotional plans and much more.
- Financial Management It also plays an essential role in budgeting, financial planning, cost allocation, capital raising, tackling fluctuations with international currency as well as taking finance-related decisions.
- Production Management Production Management also includes business research as it helps in product development, planning out for a newer one, finalizing the right technologies for production, and so on.
- Materials Management Business Research is an important aspect of checking the best materials and carrying out its production, supply chain management , logistics , as well as shortlisting negotiation strategies.
There is an incremental role of business research as its importance is across every aspect of the business. Let’s take a look at the role of business research in an enterprise:
- The most primary role of business research is that it helps across every decision in the business, from product innovation to marketing and promotional planning.
- Business Research also helps in forecasting a business, whether in terms of competition or any other types of problems it will be facing.
- Another key area where this plays a bigger role is ensuring consumer satisfaction as through research, we can carry out research and highlight areas where we can efficiently serve our target audience.
- Business research also helps in implementing cost-effectiveness in a business as it can assist in cutting costs wherever needed and investing more in those areas, where profit is coming from.
Want to understand and learn more about business research? Here are some of the books that will make you a pro in this field. Check out the list of business research books:
Also Read: Is It Possible to Study MBA in Europe Without GMAT?
The purpose of a report is to inform the other members, junior and subordinates of the team to provide information on the specific topic. There is a specific format of a business report which makes it look more professional and presentable. There should be a title with the date and nature. The second section includes the introduction, body, and then conclusion. Reports help to identify the issues and helps in resolving them at earlier stages. It can include graphs, surveys, interviews, flow, and piecharts also.
Are you wondering why is there a need to do business research? Business is not stable and it is vital to stay up to date with all the data and developments. It is also important to make business-related decisions, and keep track of competitors, customer feedback, and market changes. The basic objective of business research is to identify the issues and evaluate a plan to resolve them for better managerial functioning.
Now that you are familiar with the objective, importance, and advantages the next important step is to know how to conduct research. There are numerous tools available for free while for some advanced tools there is a membership. Check out the list of top 10 tools:
- Google Keyword Tools
- Google Analytics
- Google Trends
The one thing constant in a business is market changes. A new trend or change comes every time you blink an eye. To keep track of everything externally and internally a research partner comes helpful. There are a few things to keep in mind that will help you in choosing the right business partner. The first thing to keep in mind is that the person should have relevant work experience and expertise in that particular field. An experienced partner can help businesses reach new heights. Look for a partner that can provide well-curated solutions and not the generic ideas that every enterprise follows. Last but not least is that your business research partner should have knowledge of the latest tools and techniques.
Also Read: MBA in Sustainable Development: Courses & Universities
Is your big presentation coming up or your report is due on Monday but you still haven’t finalized your business research topic? Here are some of the trendiest research topics for you:
- How advertisements influence consumer behaviour?
- Does incentive motivation increase employee productivity?
- How to handle crises in the business?
- How to create a work-life balance in the organization?
- What are the things a small business owner has to face?
- How to expand the company globally?
- How is digital marketing helping every business type?
- How to maintain the quality and quantity of products?
- What are the struggles entrepreneurs of a start-up face?
- How to create a budget and maintain company finances?
In order to build a career in Research , you can simply grab a degree in the field of Management , Business or Administration. So, students with an understanding of the core concepts of business and an inclination for research can consider it as a go-to option. Other suitable programs can be Master in Management , MBA Business Analytics , and MBA Data Analytics , to name a few.
To know more, check out Qualitative Research Methods !
It can simply mean researching every area of a business and using the provided information and data to ensure profit maximization.
There are different types of business research such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, correlational research, ethnographic research, case study research, and quantitative research methods, amongst others.
It is essentially important for various aspects of a business such as profit maximization, cost-cutting, financial management , personnel management, consumer behaviour, etc.
The process of research depends upon the type of research design you are opting for. To start with, we first need to determine the aim or objective of the research, then plan out the whole process which includes the types of methods we will be using, then the actual research that takes place followed by the data found that helps in understanding the key observations and how they can be implemented to actualize research hypothesis.
If you’re thinking to start a product line in your existing business or planning a startup, business research is a fundamental process that helps you to navigate the opportunities and obstacles in the marketplace. Knowing your strengths and weaknesses can help you come up with advanced and powerful research techniques that will make it easier to manage. Are you planning to take your higher education abroad? Then, you can quickly book a counselling session with the experts at Leverage Edu and we can help you build the right platform for you to grow in the corporate world.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Great article! Your content is beneficial. Thank you, and Keep Sharing.
Thank you, Sophia!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
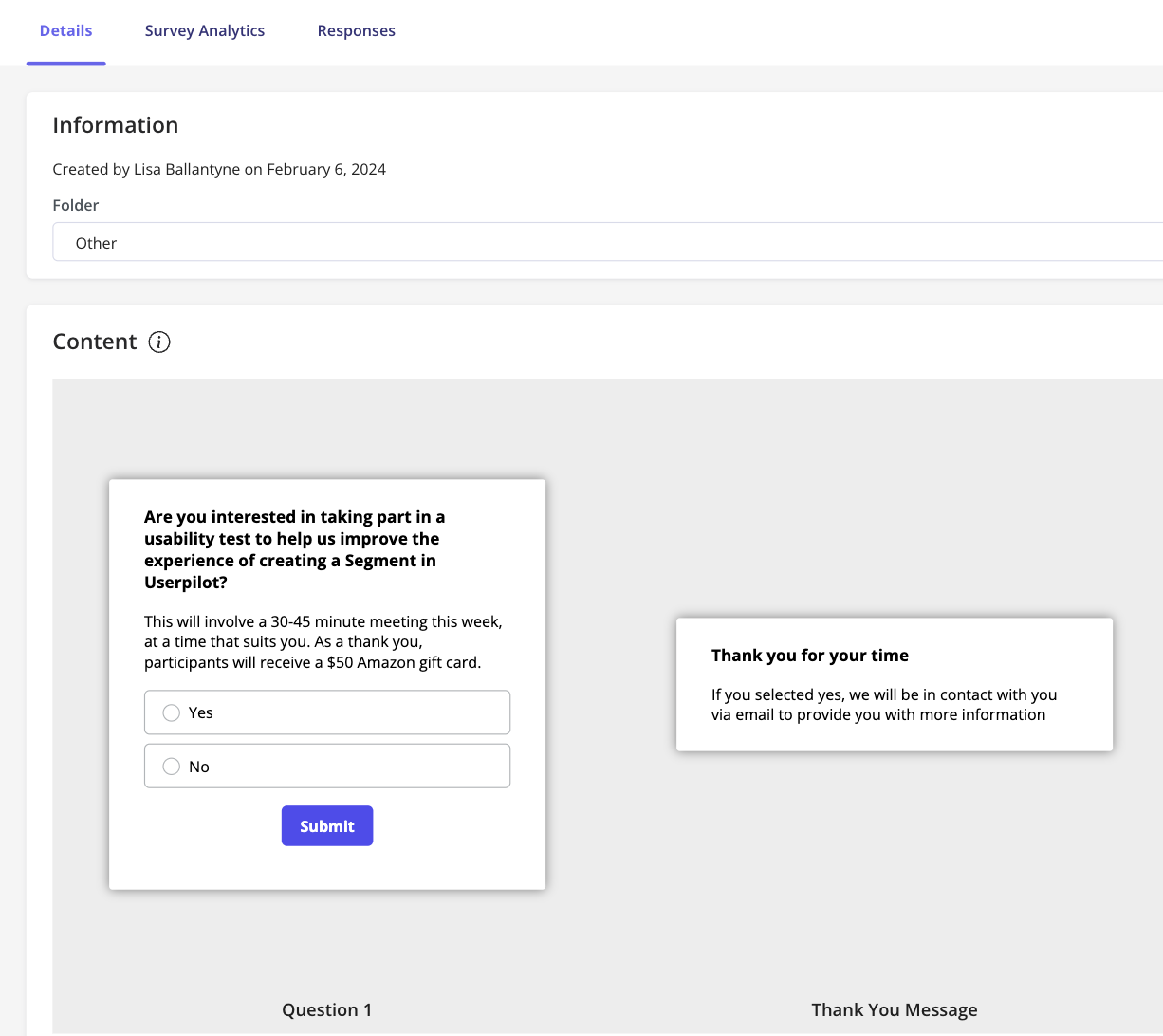
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
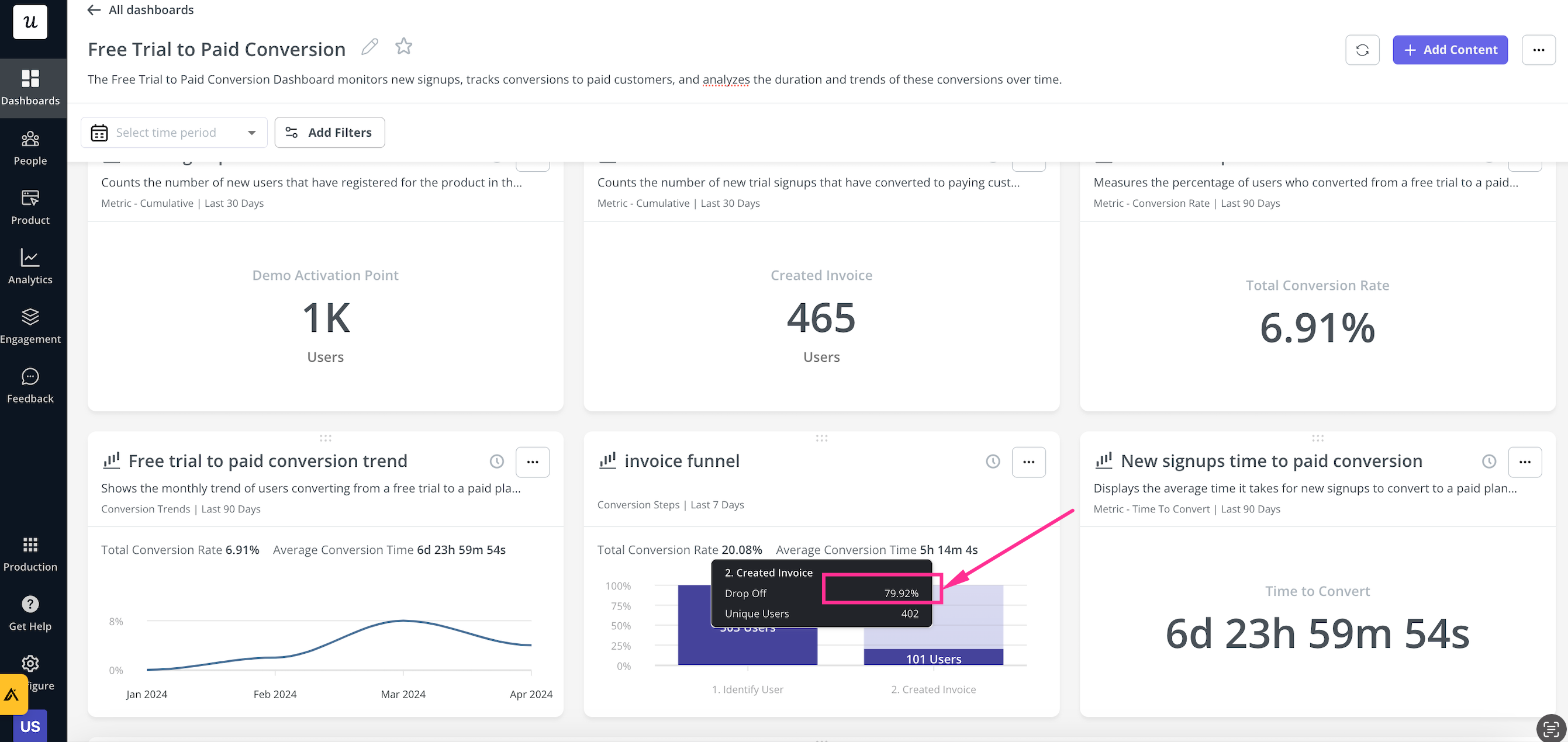
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
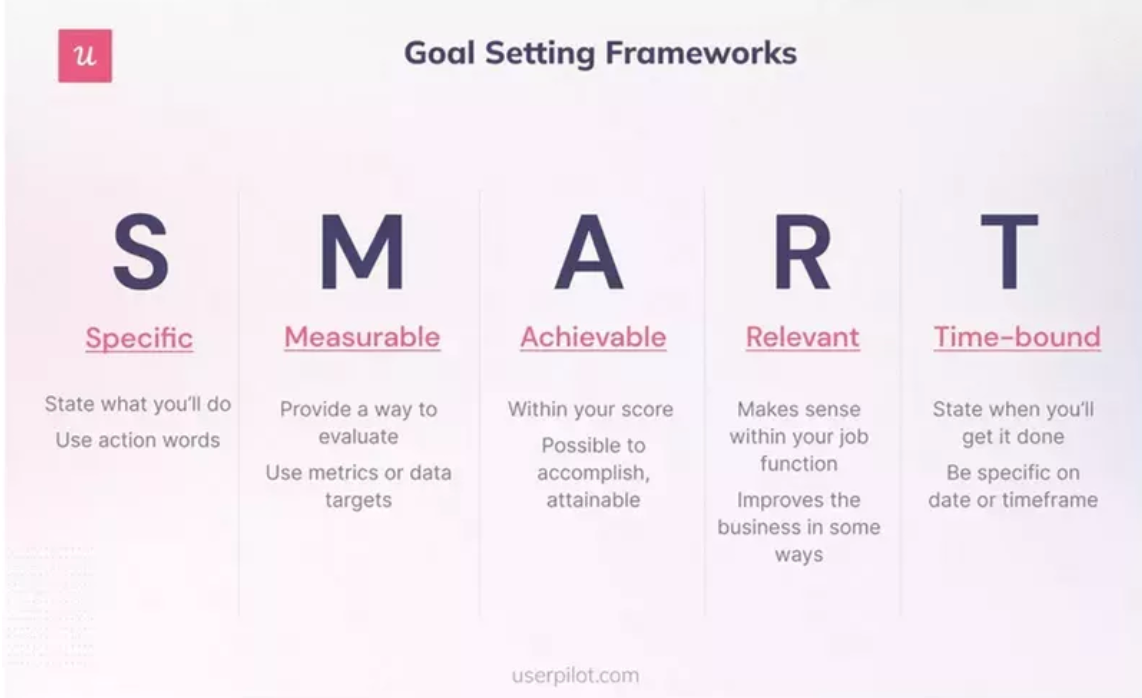
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Funnel marketing: definition and strategies that work for saas, how to do market research: a step-by-step guide.

The Importance Of Research Objectives
Imagine you’re a student planning a vacation in a foreign country. You’re on a tight budget and need to draw…

Imagine you’re a student planning a vacation in a foreign country. You’re on a tight budget and need to draw up a pocket-friendly plan. Where do you begin? The first step is to do your research.
Before that, you make a mental list of your objectives—finding reasonably-priced hotels, traveling safely and finding ways of communicating with someone back home. These objectives help you focus sharply during your research and be aware of the finer details of your trip.
More often than not, research is a part of our daily lives. Whether it’s to pick a restaurant for your next birthday dinner or to prepare a presentation at work, good research is the foundation of effective learning. Read on to understand the meaning, importance and examples of research objectives.
Why Do We Need Research?
What are the objectives of research, what goes into a research plan.
Research is a careful and detailed study of a particular problem or concern, using scientific methods. An in-depth analysis of information creates space for generating new questions, concepts and understandings. The main objective of research is to explore the unknown and unlock new possibilities. It’s an essential component of success.
Over the years, businesses have started emphasizing the need for research. You’ve probably noticed organizations hiring research managers and analysts. The primary purpose of business research is to determine the goals and opportunities of an organization. It’s critical in making business decisions and appropriately allocating available resources.
Here are a few benefits of research that’ll explain why it is a vital aspect of our professional lives:
Expands Your Knowledge Base
One of the greatest benefits of research is to learn and gain a deeper understanding. The deeper you dig into a topic, the more well-versed you are. Furthermore, research has the power to help you build on any personal experience you have on the subject.
Keeps You Up To Date
Research encourages you to discover the most recent information available. Updated information prevents you from falling behind and helps you present accurate information. You’re better equipped to develop ideas or talk about a topic when you’re armed with the latest inputs.
Builds Your Credibility
Research provides you with a good foundation upon which you can develop your thoughts and ideas. People take you more seriously when your suggestions are backed by research. You can speak with greater confidence because you know that the information is accurate.
Sparks Connections
Take any leading nonprofit organization, you’ll see how they have a strong research arm supported by real-life stories. Research also becomes the base upon which real-life connections and impact can be made. It even helps you communicate better with others and conveys why you’re pursuing something.
Encourages Curiosity
As we’ve already established, research is mostly about using existing information to create new ideas and opinions. In the process, it sparks curiosity as you’re encouraged to explore and gain deeper insights into a subject. Curiosity leads to higher levels of positivity and lower levels of anxiety.
Well-defined objectives of research are an essential component of successful research engagement. If you want to drive all aspects of your research methodology such as data collection, design, analysis and recommendation, you need to lay down the objectives of research methodology. In other words, the objectives of research should address the underlying purpose of investigation and analysis. It should outline the steps you’d take to achieve desirable outcomes. Research objectives help you stay focused and adjust your expectations as you progress.
The objectives of research should be closely related to the problem statement, giving way to specific and achievable goals. Here are the four types of research objectives for you to explore:
General Objective
Also known as secondary objectives, general objectives provide a detailed view of the aim of a study. In other words, you get a general overview of what you want to achieve by the end of your study. For example, if you want to study an organization’s contribution to environmental sustainability, your general objective could be: a study of sustainable practices and the use of renewable energy by the organization.
Specific Objectives
Specific objectives define the primary aim of the study. Typically, general objectives provide the foundation for identifying specific objectives. In other words, when general objectives are broken down into smaller and logically connected objectives, they’re known as specific objectives. They help define the who, what, why, when and how aspects of your project. Once you identify the main objective of research, it’s easier to develop and pursue a plan of action.
Let’s take the example of ‘a study of an organization’s contribution to environmental sustainability’ again. The specific objectives will look like this:
To determine through history how the organization has changed its practices and adopted new solutions
To assess how the new practices, technology and strategies will contribute to the overall effectiveness
Once you’ve identified the objectives of research, it’s time to organize your thoughts and streamline your research goals. Here are a few effective tips to develop a powerful research plan and improve your business performance.
Set SMART Goals
Your research objectives should be SMART—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time-constrained. When you focus on utilizing available resources and setting realistic timeframes and milestones, it’s easier to prioritize objectives. Continuously track your progress and check whether you need to revise your expectations or targets. This way, you’re in greater control over the process.
Create A Plan
Create a plan that’ll help you select appropriate methods to collect accurate information. A well-structured plan allows you to use logical and creative approaches towards problem-solving. The complexity of information and your skills are bound to influence your plan, which is why you need to make room for flexibility. The availability of resources will also play a big role in influencing your decisions.
Collect And Collate
After you’ve created a plan for the research process, make a list of the data you’re going to collect and the methods you’ll use. Not only will it help make sense of your insights but also keep track of your approach. The information you collect should be:
Logical, rigorous and objective
Can be reproduced by other people working on the same subject
Free of errors and highlighting necessary details
Current and updated
Includes everything required to support your argument/suggestions
Analyze And Keep Ready
Data analysis is the most crucial part of the process and there are many ways in which the information can be utilized. Four types of data analysis are often seen in a professional environment. While they may be divided into separate categories, they’re linked to each other.
Descriptive Analysis:
The most commonly used data analysis, descriptive analysis simply summarizes past data. For example, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) use descriptive analysis. It establishes certain benchmarks after studying how someone has been performing in the past.
Diagnostic Analysis:
The next step is to identify why something happened. Diagnostic analysis uses the information gathered through descriptive analysis and helps find the underlying causes of an outcome. For example, if a marketing initiative was successful, you deep-dive into the strategies that worked.
Predictive Analysis:
It attempts to answer ‘what’s likely to happen’. Predictive analysis makes use of past data to predict future outcomes. However, the accuracy of predictions depends on the quality of the data provided. Risk assessment is an ideal example of using predictive analysis.
Prescriptive Analysis:
The most sought-after type of data analysis, prescriptive analysis combines the insights of all of the previous analyses. It’s a huge organizational commitment as it requires plenty of effort and resources. A great example of prescriptive analysis is Artificial Intelligence (AI), which consumes large amounts of data. You need to be prepared to commit to this type of analysis.
Review And Interpret
Once you’ve collected and collated your data, it’s time to review it and draw accurate conclusions. Here are a few ways to improve the review process:
Identify the fundamental issues, opportunities and problems and make note of recurring trends if any
Make a list of your insights and check which is the most or the least common. In short, keep track of the frequency of each insight
Conduct a SWOT analysis and identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
Write down your conclusions and recommendations of the research
When we think about research, we often associate it with academicians and students. but the truth is research is for everybody who is willing to learn and enhance their knowledge. If you want to master the art of strategically upgrading your knowledge, Harappa Education’s Learning Expertly course has all the answers. Not only will it help you look at things from a fresh perspective but also show you how to acquire new information with greater efficiency. The Growth Mindset framework will teach you how to believe in your abilities to grow and improve. The Learning Transfer framework will help you apply your learnings from one context to another. Begin the journey of tactful learning and self-improvement today!
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics related to the THINK Habit such as Learning From Experience , Critical Thinking & What is Brainstorming to think clearly and rationally.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8. Identify the research problem. Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
Example: Research aim. To examine contributory factors to muscle retention in a group of elderly people. Example: Research objectives. To assess the relationship between sedentary habits and muscle atrophy among the participants. To determine the impact of dietary factors, particularly protein consumption, on the muscular health of the ...
Research objectives are how researchers ensure that their study has direction and makes a significant contribution to growing an industry or niche. Research objectives provide a clear and concise statement of what the researcher wants to find out. As a researcher, you need to clearly outline and define research objectives to guide the research ...
A research objective is defined as a clear and concise statement of the specific goals and aims of a research study. It outlines what the researcher intends to accomplish and what they hope to learn or discover through their research. Research objectives are crucial for guiding the research process and ensuring that the study stays focused and ...
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
That comes later. Objective: Uncover the purchase journey of our target demographic. Assumption: Uncover what part search plays in the purchase journey of our target demographic. This looks unsuspecting, but in reality, we're already assuming that search plays a role in our audience's journey. That could sway the focus of the research.
Research Objectives. Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research.The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.
The previous chapter provided some introductory guidance into the objective of this book, which aims to provide business researchers with enough academically sound knowledge to navigate the complex maze of scientific business research. This chapter seeks to constitute a roadmap or framework to guide business researchers in contextualizing and planning their research efforts and guide the ...
Business Research The purpose of business research is to gather information in order to aid business-related decision-making. Business research is defined as 'the systematic and objective process of collecting, recording, analyzing and interpreting data for aid in solving managerial problems'.
Meaning of Business Research. Business research is the process of studying a company's competitors, stakeholders, and profit & loss to meet the company objectives and maximize revenue & profits. The research involves identifying the target market, estimating their current needs & wants, and then conducting product planning to meet those demands.
Business research is one of the most useful weapons in the fight against business obscurity, since it allows companies to gain a deep understanding of buyer behavior and stay up to date at all times with detailed information on their market. ... Quantitative research focuses on countable data that is objective in nature. It relies on finding ...
Monitor and adapt. Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let's delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here's a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts. 1. Set clear objectives.
Summary. The importance of research aims and objectives cannot be over-stressed. It is vital to have a very clear understanding of what the research is about and what you are actually trying to achieve. You need to know this. And you need to be able to communicate it to others. Carrying out a research project is rather like going on a journey.
Here are three simple steps that you can follow to identify and write your research objectives: 1. Pinpoint the major focus of your research. The first step to writing your research objectives is to pinpoint the major focus of your research project. In this step, make sure to clearly describe what you aim to achieve through your research.
The objective of this article is to present a step-by-step guide that research students may follow to save their valuable time reading through plethora of books on business research. The authors have recently conducted an in-depth case study in the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) industry of New Zealand.
Business research: Definition. Business research is a process of acquiring detailed information on all the areas of business and using such information to maximize the sales and profit of the business. Such a study helps companies determine which product/service is most profitable or in demand. In simple words, it can be stated as the acquisition of information or knowledge for professional or ...
Before you start your research and analysis, determine your objectives. Decide what you want to learn from the process. It will guide the data you search for and how you use it, so be specific.
Market research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that organizations set when conducting research to gather information about their target markets, customers, competitors, and industry trends. These objectives serve as a roadmap, guiding the research process and ensuring that efforts are focused and results are relevant to the organization's needs. Key Characteristics ...
Examples of Specific Research Objectives: 1. "To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.". 2. "To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).". 3.
Define Research Objectives. The first step in market research is to clearly define the research objectives. This involves identifying the specific information needed, the target audience, and the desired outcomes of the research. ... Pricing Market Research: A business is considering introducing a new product or service and wants to determine ...
The basic objective of business research is to identify the issues and evaluate a plan to resolve them for better managerial functioning. Top 10 Tools for Business Research. Now that you are familiar with the objective, importance, and advantages the next important step is to know how to conduct research. There are numerous tools available for ...
Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
An in-depth analysis of information creates space for generating new questions, concepts and understandings. The main objective of research is to explore the unknown and unlock new possibilities. It's an essential component of success. Over the years, businesses have started emphasizing the need for research.