How to Write Limitations of the Study (with examples)
This blog emphasizes the importance of recognizing and effectively writing about limitations in research. It discusses the types of limitations, their significance, and provides guidelines for writing about them, highlighting their role in advancing scholarly research.
Updated on August 24, 2023

No matter how well thought out, every research endeavor encounters challenges. There is simply no way to predict all possible variances throughout the process.
These uncharted boundaries and abrupt constraints are known as limitations in research . Identifying and acknowledging limitations is crucial for conducting rigorous studies. Limitations provide context and shed light on gaps in the prevailing inquiry and literature.
This article explores the importance of recognizing limitations and discusses how to write them effectively. By interpreting limitations in research and considering prevalent examples, we aim to reframe the perception from shameful mistakes to respectable revelations.

What are limitations in research?
In the clearest terms, research limitations are the practical or theoretical shortcomings of a study that are often outside of the researcher’s control . While these weaknesses limit the generalizability of a study’s conclusions, they also present a foundation for future research.
Sometimes limitations arise from tangible circumstances like time and funding constraints, or equipment and participant availability. Other times the rationale is more obscure and buried within the research design. Common types of limitations and their ramifications include:
- Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study.
- Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data.
- Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data.
- Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of the findings.
- Ethical: limits the access, consent, or confidentiality of the data.
Regardless of how, when, or why they arise, limitations are a natural part of the research process and should never be ignored . Like all other aspects, they are vital in their own purpose.
Why is identifying limitations important?
Whether to seek acceptance or avoid struggle, humans often instinctively hide flaws and mistakes. Merging this thought process into research by attempting to hide limitations, however, is a bad idea. It has the potential to negate the validity of outcomes and damage the reputation of scholars.
By identifying and addressing limitations throughout a project, researchers strengthen their arguments and curtail the chance of peer censure based on overlooked mistakes. Pointing out these flaws shows an understanding of variable limits and a scrupulous research process.
Showing awareness of and taking responsibility for a project’s boundaries and challenges validates the integrity and transparency of a researcher. It further demonstrates the researchers understand the applicable literature and have thoroughly evaluated their chosen research methods.
Presenting limitations also benefits the readers by providing context for research findings. It guides them to interpret the project’s conclusions only within the scope of very specific conditions. By allowing for an appropriate generalization of the findings that is accurately confined by research boundaries and is not too broad, limitations boost a study’s credibility .
Limitations are true assets to the research process. They highlight opportunities for future research. When researchers identify the limitations of their particular approach to a study question, they enable precise transferability and improve chances for reproducibility.
Simply stating a project’s limitations is not adequate for spurring further research, though. To spark the interest of other researchers, these acknowledgements must come with thorough explanations regarding how the limitations affected the current study and how they can potentially be overcome with amended methods.
How to write limitations
Typically, the information about a study’s limitations is situated either at the beginning of the discussion section to provide context for readers or at the conclusion of the discussion section to acknowledge the need for further research. However, it varies depending upon the target journal or publication guidelines.
Don’t hide your limitations
It is also important to not bury a limitation in the body of the paper unless it has a unique connection to a topic in that section. If so, it needs to be reiterated with the other limitations or at the conclusion of the discussion section. Wherever it is included in the manuscript, ensure that the limitations section is prominently positioned and clearly introduced.
While maintaining transparency by disclosing limitations means taking a comprehensive approach, it is not necessary to discuss everything that could have potentially gone wrong during the research study. If there is no commitment to investigation in the introduction, it is unnecessary to consider the issue a limitation to the research. Wholly consider the term ‘limitations’ and ask, “Did it significantly change or limit the possible outcomes?” Then, qualify the occurrence as either a limitation to include in the current manuscript or as an idea to note for other projects.
Writing limitations
Once the limitations are concretely identified and it is decided where they will be included in the paper, researchers are ready for the writing task. Including only what is pertinent, keeping explanations detailed but concise, and employing the following guidelines is key for crafting valuable limitations:
1) Identify and describe the limitations : Clearly introduce the limitation by classifying its form and specifying its origin. For example:
- An unintentional bias encountered during data collection
- An intentional use of unplanned post-hoc data analysis
2) Explain the implications : Describe how the limitation potentially influences the study’s findings and how the validity and generalizability are subsequently impacted. Provide examples and evidence to support claims of the limitations’ effects without making excuses or exaggerating their impact. Overall, be transparent and objective in presenting the limitations, without undermining the significance of the research.
3) Provide alternative approaches for future studies : Offer specific suggestions for potential improvements or avenues for further investigation. Demonstrate a proactive approach by encouraging future research that addresses the identified gaps and, therefore, expands the knowledge base.
Whether presenting limitations as an individual section within the manuscript or as a subtopic in the discussion area, authors should use clear headings and straightforward language to facilitate readability. There is no need to complicate limitations with jargon, computations, or complex datasets.
Examples of common limitations
Limitations are generally grouped into two categories , methodology and research process .
Methodology limitations
Methodology may include limitations due to:
- Sample size
- Lack of available or reliable data
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic
- Measure used to collect the data
- Self-reported data

The researcher is addressing how the large sample size requires a reassessment of the measures used to collect and analyze the data.
Research process limitations
Limitations during the research process may arise from:
- Access to information
- Longitudinal effects
- Cultural and other biases
- Language fluency
- Time constraints

The author is pointing out that the model’s estimates are based on potentially biased observational studies.
Final thoughts
Successfully proving theories and touting great achievements are only two very narrow goals of scholarly research. The true passion and greatest efforts of researchers comes more in the form of confronting assumptions and exploring the obscure.
In many ways, recognizing and sharing the limitations of a research study both allows for and encourages this type of discovery that continuously pushes research forward. By using limitations to provide a transparent account of the project's boundaries and to contextualize the findings, researchers pave the way for even more robust and impactful research in the future.
Charla Viera, MS
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Limitations in Research
Limitations in research refer to the factors that may affect the results, conclusions , and generalizability of a study. These limitations can arise from various sources, such as the design of the study, the sampling methods used, the measurement tools employed, and the limitations of the data analysis techniques.
Types of Limitations in Research
Types of Limitations in Research are as follows:
Sample Size Limitations
This refers to the size of the group of people or subjects that are being studied. If the sample size is too small, then the results may not be representative of the population being studied. This can lead to a lack of generalizability of the results.
Time Limitations
Time limitations can be a constraint on the research process . This could mean that the study is unable to be conducted for a long enough period of time to observe the long-term effects of an intervention, or to collect enough data to draw accurate conclusions.
Selection Bias
This refers to a type of bias that can occur when the selection of participants in a study is not random. This can lead to a biased sample that is not representative of the population being studied.
Confounding Variables
Confounding variables are factors that can influence the outcome of a study, but are not being measured or controlled for. These can lead to inaccurate conclusions or a lack of clarity in the results.
Measurement Error
This refers to inaccuracies in the measurement of variables, such as using a faulty instrument or scale. This can lead to inaccurate results or a lack of validity in the study.
Ethical Limitations
Ethical limitations refer to the ethical constraints placed on research studies. For example, certain studies may not be allowed to be conducted due to ethical concerns, such as studies that involve harm to participants.
Examples of Limitations in Research
Some Examples of Limitations in Research are as follows:
Research Title: “The Effectiveness of Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Customer Behavior”
Limitations:
- The study only considered a limited number of machine learning algorithms and did not explore the effectiveness of other algorithms.
- The study used a specific dataset, which may not be representative of all customer behaviors or demographics.
- The study did not consider the potential ethical implications of using machine learning algorithms in predicting customer behavior.
Research Title: “The Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance in Computer Science Courses”
- The study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have affected the results due to the unique circumstances of remote learning.
- The study only included students from a single university, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other institutions.
- The study did not consider the impact of individual differences, such as prior knowledge or motivation, on student performance in online learning environments.
Research Title: “The Effect of Gamification on User Engagement in Mobile Health Applications”
- The study only tested a specific gamification strategy and did not explore the effectiveness of other gamification techniques.
- The study relied on self-reported measures of user engagement, which may be subject to social desirability bias or measurement errors.
- The study only included a specific demographic group (e.g., young adults) and may not be generalizable to other populations with different preferences or needs.
How to Write Limitations in Research
When writing about the limitations of a research study, it is important to be honest and clear about the potential weaknesses of your work. Here are some tips for writing about limitations in research:
- Identify the limitations: Start by identifying the potential limitations of your research. These may include sample size, selection bias, measurement error, or other issues that could affect the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Be honest and objective: When describing the limitations of your research, be honest and objective. Do not try to minimize or downplay the limitations, but also do not exaggerate them. Be clear and concise in your description of the limitations.
- Provide context: It is important to provide context for the limitations of your research. For example, if your sample size was small, explain why this was the case and how it may have affected your results. Providing context can help readers understand the limitations in a broader context.
- Discuss implications : Discuss the implications of the limitations for your research findings. For example, if there was a selection bias in your sample, explain how this may have affected the generalizability of your findings. This can help readers understand the limitations in terms of their impact on the overall validity of your research.
- Provide suggestions for future research : Finally, provide suggestions for future research that can address the limitations of your study. This can help readers understand how your research fits into the broader field and can provide a roadmap for future studies.
Purpose of Limitations in Research
There are several purposes of limitations in research. Here are some of the most important ones:
- To acknowledge the boundaries of the study : Limitations help to define the scope of the research project and set realistic expectations for the findings. They can help to clarify what the study is not intended to address.
- To identify potential sources of bias: Limitations can help researchers identify potential sources of bias in their research design, data collection, or analysis. This can help to improve the validity and reliability of the findings.
- To provide opportunities for future research: Limitations can highlight areas for future research and suggest avenues for further exploration. This can help to advance knowledge in a particular field.
- To demonstrate transparency and accountability: By acknowledging the limitations of their research, researchers can demonstrate transparency and accountability to their readers, peers, and funders. This can help to build trust and credibility in the research community.
- To encourage critical thinking: Limitations can encourage readers to critically evaluate the study’s findings and consider alternative explanations or interpretations. This can help to promote a more nuanced and sophisticated understanding of the topic under investigation.
When to Write Limitations in Research
Limitations should be included in research when they help to provide a more complete understanding of the study’s results and implications. A limitation is any factor that could potentially impact the accuracy, reliability, or generalizability of the study’s findings.
It is important to identify and discuss limitations in research because doing so helps to ensure that the results are interpreted appropriately and that any conclusions drawn are supported by the available evidence. Limitations can also suggest areas for future research, highlight potential biases or confounding factors that may have affected the results, and provide context for the study’s findings.
Generally, limitations should be discussed in the conclusion section of a research paper or thesis, although they may also be mentioned in other sections, such as the introduction or methods. The specific limitations that are discussed will depend on the nature of the study, the research question being investigated, and the data that was collected.
Examples of limitations that might be discussed in research include sample size limitations, data collection methods, the validity and reliability of measures used, and potential biases or confounding factors that could have affected the results. It is important to note that limitations should not be used as a justification for poor research design or methodology, but rather as a way to enhance the understanding and interpretation of the study’s findings.
Importance of Limitations in Research
Here are some reasons why limitations are important in research:
- Enhances the credibility of research: Limitations highlight the potential weaknesses and threats to validity, which helps readers to understand the scope and boundaries of the study. This improves the credibility of research by acknowledging its limitations and providing a clear picture of what can and cannot be concluded from the study.
- Facilitates replication: By highlighting the limitations, researchers can provide detailed information about the study’s methodology, data collection, and analysis. This information helps other researchers to replicate the study and test the validity of the findings, which enhances the reliability of research.
- Guides future research : Limitations provide insights into areas for future research by identifying gaps or areas that require further investigation. This can help researchers to design more comprehensive and effective studies that build on existing knowledge.
- Provides a balanced view: Limitations help to provide a balanced view of the research by highlighting both strengths and weaknesses. This ensures that readers have a clear understanding of the study’s limitations and can make informed decisions about the generalizability and applicability of the findings.
Advantages of Limitations in Research
Here are some potential advantages of limitations in research:
- Focus : Limitations can help researchers focus their study on a specific area or population, which can make the research more relevant and useful.
- Realism : Limitations can make a study more realistic by reflecting the practical constraints and challenges of conducting research in the real world.
- Innovation : Limitations can spur researchers to be more innovative and creative in their research design and methodology, as they search for ways to work around the limitations.
- Rigor : Limitations can actually increase the rigor and credibility of a study, as researchers are forced to carefully consider the potential sources of bias and error, and address them to the best of their abilities.
- Generalizability : Limitations can actually improve the generalizability of a study by ensuring that it is not overly focused on a specific sample or situation, and that the results can be applied more broadly.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Limitations of the Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the interpretation of the findings from your research. Study limitations are the constraints placed on the ability to generalize from the results, to further describe applications to practice, and/or related to the utility of findings that are the result of the ways in which you initially chose to design the study or the method used to establish internal and external validity or the result of unanticipated challenges that emerged during the study.
Price, James H. and Judy Murnan. “Research Limitations and the Necessity of Reporting Them.” American Journal of Health Education 35 (2004): 66-67; Theofanidis, Dimitrios and Antigoni Fountouki. "Limitations and Delimitations in the Research Process." Perioperative Nursing 7 (September-December 2018): 155-163. .
Importance of...
Always acknowledge a study's limitations. It is far better that you identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor and have your grade lowered because you appeared to have ignored them or didn't realize they existed.
Keep in mind that acknowledgment of a study's limitations is an opportunity to make suggestions for further research. If you do connect your study's limitations to suggestions for further research, be sure to explain the ways in which these unanswered questions may become more focused because of your study.
Acknowledgment of a study's limitations also provides you with opportunities to demonstrate that you have thought critically about the research problem, understood the relevant literature published about it, and correctly assessed the methods chosen for studying the problem. A key objective of the research process is not only discovering new knowledge but also to confront assumptions and explore what we don't know.
Claiming limitations is a subjective process because you must evaluate the impact of those limitations . Don't just list key weaknesses and the magnitude of a study's limitations. To do so diminishes the validity of your research because it leaves the reader wondering whether, or in what ways, limitation(s) in your study may have impacted the results and conclusions. Limitations require a critical, overall appraisal and interpretation of their impact. You should answer the question: do these problems with errors, methods, validity, etc. eventually matter and, if so, to what extent?
Price, James H. and Judy Murnan. “Research Limitations and the Necessity of Reporting Them.” American Journal of Health Education 35 (2004): 66-67; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation. Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com.
Descriptions of Possible Limitations
All studies have limitations . However, it is important that you restrict your discussion to limitations related to the research problem under investigation. For example, if a meta-analysis of existing literature is not a stated purpose of your research, it should not be discussed as a limitation. Do not apologize for not addressing issues that you did not promise to investigate in the introduction of your paper.
Here are examples of limitations related to methodology and the research process you may need to describe and discuss how they possibly impacted your results. Note that descriptions of limitations should be stated in the past tense because they were discovered after you completed your research.
Possible Methodological Limitations
- Sample size -- the number of the units of analysis you use in your study is dictated by the type of research problem you are investigating. Note that, if your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to find significant relationships from the data, as statistical tests normally require a larger sample size to ensure a representative distribution of the population and to be considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred. Note that sample size is generally less relevant in qualitative research if explained in the context of the research problem.
- Lack of available and/or reliable data -- a lack of data or of reliable data will likely require you to limit the scope of your analysis, the size of your sample, or it can be a significant obstacle in finding a trend and a meaningful relationship. You need to not only describe these limitations but provide cogent reasons why you believe data is missing or is unreliable. However, don’t just throw up your hands in frustration; use this as an opportunity to describe a need for future research based on designing a different method for gathering data.
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic -- citing prior research studies forms the basis of your literature review and helps lay a foundation for understanding the research problem you are investigating. Depending on the currency or scope of your research topic, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic. Before assuming this to be true, though, consult with a librarian! In cases when a librarian has confirmed that there is little or no prior research, you may be required to develop an entirely new research typology [for example, using an exploratory rather than an explanatory research design ]. Note again that discovering a limitation can serve as an important opportunity to identify new gaps in the literature and to describe the need for further research.
- Measure used to collect the data -- sometimes it is the case that, after completing your interpretation of the findings, you discover that the way in which you gathered data inhibited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results. For example, you regret not including a specific question in a survey that, in retrospect, could have helped address a particular issue that emerged later in the study. Acknowledge the deficiency by stating a need for future researchers to revise the specific method for gathering data.
- Self-reported data -- whether you are relying on pre-existing data or you are conducting a qualitative research study and gathering the data yourself, self-reported data is limited by the fact that it rarely can be independently verified. In other words, you have to the accuracy of what people say, whether in interviews, focus groups, or on questionnaires, at face value. However, self-reported data can contain several potential sources of bias that you should be alert to and note as limitations. These biases become apparent if they are incongruent with data from other sources. These are: (1) selective memory [remembering or not remembering experiences or events that occurred at some point in the past]; (2) telescoping [recalling events that occurred at one time as if they occurred at another time]; (3) attribution [the act of attributing positive events and outcomes to one's own agency, but attributing negative events and outcomes to external forces]; and, (4) exaggeration [the act of representing outcomes or embellishing events as more significant than is actually suggested from other data].
Possible Limitations of the Researcher
- Access -- if your study depends on having access to people, organizations, data, or documents and, for whatever reason, access is denied or limited in some way, the reasons for this needs to be described. Also, include an explanation why being denied or limited access did not prevent you from following through on your study.
- Longitudinal effects -- unlike your professor, who can literally devote years [even a lifetime] to studying a single topic, the time available to investigate a research problem and to measure change or stability over time is constrained by the due date of your assignment. Be sure to choose a research problem that does not require an excessive amount of time to complete the literature review, apply the methodology, and gather and interpret the results. If you're unsure whether you can complete your research within the confines of the assignment's due date, talk to your professor.
- Cultural and other type of bias -- we all have biases, whether we are conscience of them or not. Bias is when a person, place, event, or thing is viewed or shown in a consistently inaccurate way. Bias is usually negative, though one can have a positive bias as well, especially if that bias reflects your reliance on research that only support your hypothesis. When proof-reading your paper, be especially critical in reviewing how you have stated a problem, selected the data to be studied, what may have been omitted, the manner in which you have ordered events, people, or places, how you have chosen to represent a person, place, or thing, to name a phenomenon, or to use possible words with a positive or negative connotation. NOTE : If you detect bias in prior research, it must be acknowledged and you should explain what measures were taken to avoid perpetuating that bias. For example, if a previous study only used boys to examine how music education supports effective math skills, describe how your research expands the study to include girls.
- Fluency in a language -- if your research focuses , for example, on measuring the perceived value of after-school tutoring among Mexican-American ESL [English as a Second Language] students and you are not fluent in Spanish, you are limited in being able to read and interpret Spanish language research studies on the topic or to speak with these students in their primary language. This deficiency should be acknowledged.
Aguinis, Hermam and Jeffrey R. Edwards. “Methodological Wishes for the Next Decade and How to Make Wishes Come True.” Journal of Management Studies 51 (January 2014): 143-174; Brutus, Stéphane et al. "Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations." Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Senunyeme, Emmanuel K. Business Research Methods. Powerpoint Presentation. Regent University of Science and Technology; ter Riet, Gerben et al. “All That Glitters Isn't Gold: A Survey on Acknowledgment of Limitations in Biomedical Studies.” PLOS One 8 (November 2013): 1-6.
Structure and Writing Style
Information about the limitations of your study are generally placed either at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so the reader knows and understands the limitations before reading the rest of your analysis of the findings, or, the limitations are outlined at the conclusion of the discussion section as an acknowledgement of the need for further study. Statements about a study's limitations should not be buried in the body [middle] of the discussion section unless a limitation is specific to something covered in that part of the paper. If this is the case, though, the limitation should be reiterated at the conclusion of the section.
If you determine that your study is seriously flawed due to important limitations , such as, an inability to acquire critical data, consider reframing it as an exploratory study intended to lay the groundwork for a more complete research study in the future. Be sure, though, to specifically explain the ways that these flaws can be successfully overcome in a new study.
But, do not use this as an excuse for not developing a thorough research paper! Review the tab in this guide for developing a research topic . If serious limitations exist, it generally indicates a likelihood that your research problem is too narrowly defined or that the issue or event under study is too recent and, thus, very little research has been written about it. If serious limitations do emerge, consult with your professor about possible ways to overcome them or how to revise your study.
When discussing the limitations of your research, be sure to:
- Describe each limitation in detailed but concise terms;
- Explain why each limitation exists;
- Provide the reasons why each limitation could not be overcome using the method(s) chosen to acquire or gather the data [cite to other studies that had similar problems when possible];
- Assess the impact of each limitation in relation to the overall findings and conclusions of your study; and,
- If appropriate, describe how these limitations could point to the need for further research.
Remember that the method you chose may be the source of a significant limitation that has emerged during your interpretation of the results [for example, you didn't interview a group of people that you later wish you had]. If this is the case, don't panic. Acknowledge it, and explain how applying a different or more robust methodology might address the research problem more effectively in a future study. A underlying goal of scholarly research is not only to show what works, but to demonstrate what doesn't work or what needs further clarification.
Aguinis, Hermam and Jeffrey R. Edwards. “Methodological Wishes for the Next Decade and How to Make Wishes Come True.” Journal of Management Studies 51 (January 2014): 143-174; Brutus, Stéphane et al. "Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations." Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Ioannidis, John P.A. "Limitations are not Properly Acknowledged in the Scientific Literature." Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007): 324-329; Pasek, Josh. Writing the Empirical Social Science Research Paper: A Guide for the Perplexed. January 24, 2012. Academia.edu; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation. Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Writing Tip
Don't Inflate the Importance of Your Findings!
After all the hard work and long hours devoted to writing your research paper, it is easy to get carried away with attributing unwarranted importance to what you’ve done. We all want our academic work to be viewed as excellent and worthy of a good grade, but it is important that you understand and openly acknowledge the limitations of your study. Inflating the importance of your study's findings could be perceived by your readers as an attempt hide its flaws or encourage a biased interpretation of the results. A small measure of humility goes a long way!
Another Writing Tip
Negative Results are Not a Limitation!
Negative evidence refers to findings that unexpectedly challenge rather than support your hypothesis. If you didn't get the results you anticipated, it may mean your hypothesis was incorrect and needs to be reformulated. Or, perhaps you have stumbled onto something unexpected that warrants further study. Moreover, the absence of an effect may be very telling in many situations, particularly in experimental research designs. In any case, your results may very well be of importance to others even though they did not support your hypothesis. Do not fall into the trap of thinking that results contrary to what you expected is a limitation to your study. If you carried out the research well, they are simply your results and only require additional interpretation.
Lewis, George H. and Jonathan F. Lewis. “The Dog in the Night-Time: Negative Evidence in Social Research.” The British Journal of Sociology 31 (December 1980): 544-558.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Sample Size Limitations in Qualitative Research
Sample sizes are typically smaller in qualitative research because, as the study goes on, acquiring more data does not necessarily lead to more information. This is because one occurrence of a piece of data, or a code, is all that is necessary to ensure that it becomes part of the analysis framework. However, it remains true that sample sizes that are too small cannot adequately support claims of having achieved valid conclusions and sample sizes that are too large do not permit the deep, naturalistic, and inductive analysis that defines qualitative inquiry. Determining adequate sample size in qualitative research is ultimately a matter of judgment and experience in evaluating the quality of the information collected against the uses to which it will be applied and the particular research method and purposeful sampling strategy employed. If the sample size is found to be a limitation, it may reflect your judgment about the methodological technique chosen [e.g., single life history study versus focus group interviews] rather than the number of respondents used.
Boddy, Clive Roland. "Sample Size for Qualitative Research." Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal 19 (2016): 426-432; Huberman, A. Michael and Matthew B. Miles. "Data Management and Analysis Methods." In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 428-444; Blaikie, Norman. "Confounding Issues Related to Determining Sample Size in Qualitative Research." International Journal of Social Research Methodology 21 (2018): 635-641; Oppong, Steward Harrison. "The Problem of Sampling in qualitative Research." Asian Journal of Management Sciences and Education 2 (2013): 202-210.
- << Previous: 8. The Discussion
- Next: 9. The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
What are the limitations in research and how to write them?
Learn about the potential limitations in research and how to appropriately address them in order to deliver honest and ethical research.
It is fairly uncommon for researchers to stumble into the term research limitations when working on their research paper. Limitations in research can arise owing to constraints on design, methods, materials, and so on, and these aspects, unfortunately, may have an influence on your subject’s findings.
In this Mind The Graph’s article, we’ll discuss some recommendations for writing limitations in research , provide examples of various common types of limitations, and suggest how to properly present this information.
What are the limitations in research?
The limitations in research are the constraints in design, methods or even researchers’ limitations that affect and influence the interpretation of your research’s ultimate findings. These are limitations on the generalization and usability of findings that emerge from the design of the research and/or the method employed to ensure validity both internally and externally.
Researchers are usually cautious to acknowledge the limitations of their research in their publications for fear of undermining the research’s scientific validity. No research is faultless or covers every possible angle. As a result, addressing the constraints of your research exhibits honesty and integrity .
Why should include limitations of research in my paper?
Though limitations tackle potential flaws in research, commenting on them at the conclusion of your paper, by demonstrating that you are aware of these limitations and explaining how they impact the conclusions that may be taken from the research, improves your research by disclosing any issues before other researchers or reviewers do .
Additionally, emphasizing research constraints implies that you have thoroughly investigated the ramifications of research shortcomings and have a thorough understanding of your research problem.
Limits exist in any research; being honest about them and explaining them would impress researchers and reviewers more than disregarding them.
Remember that acknowledging a research’s shortcomings offers a chance to provide ideas for future research, but be careful to describe how your study may help to concentrate on these outstanding problems.
Possible limitations examples
Here are some limitations connected to methodology and the research procedure that you may need to explain and discuss in connection to your findings.
Methodological limitations
Sample size.
The number of units of analysis used in your study is determined by the sort of research issue being investigated. It is important to note that if your sample is too small, finding significant connections in the data will be challenging, as statistical tests typically require a larger sample size to ensure a fair representation and this can be limiting.
Lack of available or reliable data
A lack of data or trustworthy data will almost certainly necessitate limiting the scope of your research or the size of your sample, or it can be a substantial impediment to identifying a pattern and a relevant connection.
Lack of prior research on the subject
Citing previous research papers forms the basis of your literature review and aids in comprehending the research subject you are researching. Yet there may be little if any, past research on your issue.
The measure used to collect data
After finishing your analysis of the findings, you realize that the method you used to collect data limited your capacity to undertake a comprehensive evaluation of the findings. Recognize the flaw by mentioning that future researchers should change the specific approach for data collection.
Issues with research samples and selection
Sampling inaccuracies arise when a probability sampling method is employed to choose a sample, but that sample does not accurately represent the overall population or the relevant group. As a result, your study suffers from “sampling bias” or “selection bias.”
Limitations of the research
When your research requires polling certain persons or a specific group, you may have encountered the issue of limited access to these interviewees. Because of the limited access, you may need to reorganize or rearrange your research. In this scenario, explain why access is restricted and ensure that your findings are still trustworthy and valid despite the constraint.
Time constraints
Practical difficulties may limit the amount of time available to explore a research issue and monitor changes as they occur. If time restrictions have any detrimental influence on your research, recognize this impact by expressing the necessity for a future investigation.
Due to their cultural origins or opinions on observed events, researchers may carry biased opinions, which can influence the credibility of a research. Furthermore, researchers may exhibit biases toward data and conclusions that only support their hypotheses or arguments.
The structure of the limitations section
The limitations of your research are usually stated at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so that the reader is aware of and comprehends the limitations prior to actually reading the rest of your findings, or they are stated at the end of the discussion section as an acknowledgment of the need for further research.
The ideal way is to divide your limitations section into three steps:
1. Identify the research constraints;
2. Describe in great detail how they affect your research;
3. Mention the opportunity for future investigations and give possibilities.
By following this method while addressing the constraints of your research, you will be able to effectively highlight your research’s shortcomings without jeopardizing the quality and integrity of your research.
Present your research or paper in an innovative way
If you want your readers to be engaged and participate in your research, try Mind The Graph tool to add visual assets to your content. Infographics may improve comprehension and are easy to read, just as the Mind The Graph tool is simple to use and offers a variety of templates from which you can select the one that best suits your information.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags

Writing Limitations of Research Study — 4 Reasons Why It Is Important!
It is not unusual for researchers to come across the term limitations of research during their academic paper writing. More often this is interpreted as something terrible. However, when it comes to research study, limitations can help structure the research study better. Therefore, do not underestimate significance of limitations of research study.
Allow us to take you through the context of how to evaluate the limits of your research and conclude an impactful relevance to your results.
Table of Contents
What Are the Limitations of a Research Study?
Every research has its limit and these limitations arise due to restrictions in methodology or research design. This could impact your entire research or the research paper you wish to publish. Unfortunately, most researchers choose not to discuss their limitations of research fearing it will affect the value of their article in the eyes of readers.
However, it is very important to discuss your study limitations and show it to your target audience (other researchers, journal editors, peer reviewers etc.). It is very important that you provide an explanation of how your research limitations may affect the conclusions and opinions drawn from your research. Moreover, when as an author you state the limitations of research, it shows that you have investigated all the weaknesses of your study and have a deep understanding of the subject. Being honest could impress your readers and mark your study as a sincere effort in research.

Why and Where Should You Include the Research Limitations?
The main goal of your research is to address your research objectives. Conduct experiments, get results and explain those results, and finally justify your research question . It is best to mention the limitations of research in the discussion paragraph of your research article.
At the very beginning of this paragraph, immediately after highlighting the strengths of the research methodology, you should write down your limitations. You can discuss specific points from your research limitations as suggestions for further research in the conclusion of your thesis.
1. Common Limitations of the Researchers
Limitations that are related to the researcher must be mentioned. This will help you gain transparency with your readers. Furthermore, you could provide suggestions on decreasing these limitations in you and your future studies.
2. Limited Access to Information
Your work may involve some institutions and individuals in research, and sometimes you may have problems accessing these institutions. Therefore, you need to redesign and rewrite your work. You must explain your readers the reason for limited access.
3. Limited Time
All researchers are bound by their deadlines when it comes to completing their studies. Sometimes, time constraints can affect your research negatively. However, the best practice is to acknowledge it and mention a requirement for future study to solve the research problem in a better way.
4. Conflict over Biased Views and Personal Issues
Biased views can affect the research. In fact, researchers end up choosing only those results and data that support their main argument, keeping aside the other loose ends of the research.
Types of Limitations of Research
Before beginning your research study, know that there are certain limitations to what you are testing or possible research results. There are different types that researchers may encounter, and they all have unique characteristics, such as:
1. Research Design Limitations
Certain restrictions on your research or available procedures may affect your final results or research outputs. You may have formulated research goals and objectives too broadly. However, this can help you understand how you can narrow down the formulation of research goals and objectives, thereby increasing the focus of your study.
2. Impact Limitations
Even if your research has excellent statistics and a strong design, it can suffer from the influence of the following factors:
- Presence of increasing findings as researched
- Being population specific
- A strong regional focus.
3. Data or statistical limitations
In some cases, it is impossible to collect sufficient data for research or very difficult to get access to the data. This could lead to incomplete conclusion to your study. Moreover, this insufficiency in data could be the outcome of your study design. The unclear, shabby research outline could produce more problems in interpreting your findings.
How to Correctly Structure Your Research Limitations?
There are strict guidelines for narrowing down research questions, wherein you could justify and explain potential weaknesses of your academic paper. You could go through these basic steps to get a well-structured clarity of research limitations:
- Declare that you wish to identify your limitations of research and explain their importance,
- Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices.
- Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future.
In this section, your readers will see that you are aware of the potential weaknesses in your business, understand them and offer effective solutions, and it will positively strengthen your article as you clarify all limitations of research to your target audience.
Know that you cannot be perfect and there is no individual without flaws. You could use the limitations of research as a great opportunity to take on a new challenge and improve the future of research. In a typical academic paper, research limitations may relate to:
1. Formulating your goals and objectives
If you formulate goals and objectives too broadly, your work will have some shortcomings. In this case, specify effective methods or ways to narrow down the formula of goals and aim to increase your level of study focus.
2. Application of your data collection methods in research
If you do not have experience in primary data collection, there is a risk that there will be flaws in the implementation of your methods. It is necessary to accept this, and learn and educate yourself to understand data collection methods.
3. Sample sizes
This depends on the nature of problem you choose. Sample size is of a greater importance in quantitative studies as opposed to qualitative ones. If your sample size is too small, statistical tests cannot identify significant relationships or connections within a given data set.
You could point out that other researchers should base the same study on a larger sample size to get more accurate results.
4. The absence of previous studies in the field you have chosen
Writing a literature review is an important step in any scientific study because it helps researchers determine the scope of current work in the chosen field. It is a major foundation for any researcher who must use them to achieve a set of specific goals or objectives.
However, if you are focused on the most current and evolving research problem or a very narrow research problem, there may be very little prior research on your topic. For example, if you chose to explore the role of Bitcoin as the currency of the future, you may not find tons of scientific papers addressing the research problem as Bitcoins are only a new phenomenon.
It is important that you learn to identify research limitations examples at each step. Whatever field you choose, feel free to add the shortcoming of your work. This is mainly because you do not have many years of experience writing scientific papers or completing complex work. Therefore, the depth and scope of your discussions may be compromised at different levels compared to academics with a lot of expertise. Include specific points from limitations of research. Use them as suggestions for the future.
Have you ever faced a challenge of writing the limitations of research study in your paper? How did you overcome it? What ways did you follow? Were they beneficial? Let us know in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Setting limitations in our study helps to clarify the outcomes drawn from our research and enhance understanding of the subject. Moreover, it shows that the author has investigated all the weaknesses in the study.
Scope is the range and limitations of a research project which are set to define the boundaries of a project. Limitations are the impacts on the overall study due to the constraints on the research design.
Limitation in research is an impact of a constraint on the research design in the overall study. They are the flaws or weaknesses in the study, which may influence the outcome of the research.
1. Limitations in research can be written as follows: Formulate your goals and objectives 2. Analyze the chosen data collection method and the sample sizes 3. Identify your limitations of research and explain their importance 4. Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices 5. Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future
Excellent article ,,,it has helped me big
This is very helpful information. It has given me an insight on how to go about my study limitations.
Good comments and helpful
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Addressing Barriers in Academia: Navigating unconscious biases in the Ph.D. journey
In the journey of academia, a Ph.D. marks a transitional phase, like that of a…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Unraveling Research Population and Sample: Understanding their role in statistical inference
Research population and sample serve as the cornerstones of any scientific inquiry. They hold the…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
What Is a Research Problem Statement? A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and…
How to Develop a Good Research Question? — Types & Examples
5 Effective Ways to Avoid Ghostwriting for Busy Researchers
Top 5 Key Differences Between Methods and Methodology

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
How to present limitations in research
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Limitations don’t invalidate or diminish your results, but it’s best to acknowledge them. This will enable you to address any questions your study failed to answer because of them.
In this guide, learn how to recognize, present, and overcome limitations in research.
- What is a research limitation?
Research limitations are weaknesses in your research design or execution that may have impacted outcomes and conclusions. Uncovering limitations doesn’t necessarily indicate poor research design—it just means you encountered challenges you couldn’t have anticipated that limited your research efforts.
Does basic research have limitations?
Basic research aims to provide more information about your research topic. It requires the same standard research methodology and data collection efforts as any other research type, and it can also have limitations.
- Common research limitations
Researchers encounter common limitations when embarking on a study. Limitations can occur in relation to the methods you apply or the research process you design. They could also be connected to you as the researcher.
Methodology limitations
Not having access to data or reliable information can impact the methods used to facilitate your research. A lack of data or reliability may limit the parameters of your study area and the extent of your exploration.
Your sample size may also be affected because you won’t have any direction on how big or small it should be and who or what you should include. Having too few participants won’t adequately represent the population or groups of people needed to draw meaningful conclusions.
Research process limitations
The study’s design can impose constraints on the process. For example, as you’re conducting the research, issues may arise that don’t conform to the data collection methodology you developed. You may not realize until well into the process that you should have incorporated more specific questions or comprehensive experiments to generate the data you need to have confidence in your results.
Constraints on resources can also have an impact. Being limited on participants or participation incentives may limit your sample sizes. Insufficient tools, equipment, and materials to conduct a thorough study may also be a factor.
Common researcher limitations
Here are some of the common researcher limitations you may encounter:
Time: some research areas require multi-year longitudinal approaches, but you might not be able to dedicate that much time. Imagine you want to measure how much memory a person loses as they age. This may involve conducting multiple tests on a sample of participants over 20–30 years, which may be impossible.
Bias: researchers can consciously or unconsciously apply bias to their research. Biases can contribute to relying on research sources and methodologies that will only support your beliefs about the research you’re embarking on. You might also omit relevant issues or participants from the scope of your study because of your biases.
Limited access to data : you may need to pay to access specific databases or journals that would be helpful to your research process. You might also need to gain information from certain people or organizations but have limited access to them. These cases require readjusting your process and explaining why your findings are still reliable.
- Why is it important to identify limitations?
Identifying limitations adds credibility to research and provides a deeper understanding of how you arrived at your conclusions.
Constraints may have prevented you from collecting specific data or information you hoped would prove or disprove your hypothesis or provide a more comprehensive understanding of your research topic.
However, identifying the limitations contributing to your conclusions can inspire further research efforts that help gather more substantial information and data.
- Where to put limitations in a research paper
A research paper is broken up into different sections that appear in the following order:
Introduction
Methodology
The discussion portion of your paper explores your findings and puts them in the context of the overall research. Either place research limitations at the beginning of the discussion section before the analysis of your findings or at the end of the section to indicate that further research needs to be pursued.
What not to include in the limitations section
Evidence that doesn’t support your hypothesis is not a limitation, so you shouldn’t include it in the limitation section. Don’t just list limitations and their degree of severity without further explanation.
- How to present limitations
You’ll want to present the limitations of your study in a way that doesn’t diminish the validity of your research and leave the reader wondering if your results and conclusions have been compromised.
Include only the limitations that directly relate to and impact how you addressed your research questions. Following a specific format enables the reader to develop an understanding of the weaknesses within the context of your findings without doubting the quality and integrity of your research.
Identify the limitations specific to your study
You don’t have to identify every possible limitation that might have occurred during your research process. Only identify those that may have influenced the quality of your findings and your ability to answer your research question.
Explain study limitations in detail
This explanation should be the most significant portion of your limitation section.
Link each limitation with an interpretation and appraisal of their impact on the study. You’ll have to evaluate and explain whether the error, method, or validity issues influenced the study’s outcome and how.
Propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives
In this section, suggest how researchers can avoid the pitfalls you experienced during your research process.
If an issue with methodology was a limitation, propose alternate methods that may help with a smoother and more conclusive research project. Discuss the pros and cons of your alternate recommendation.
Describe steps taken to minimize each limitation
You probably took steps to try to address or mitigate limitations when you noticed them throughout the course of your research project. Describe these steps in the limitation section.
- Limitation example
“Approaches like stem cell transplantation and vaccination in AD [Alzheimer’s disease] work on a cellular or molecular level in the laboratory. However, translation into clinical settings will remain a challenge for the next decade.”
The authors are saying that even though these methods showed promise in helping people with memory loss when conducted in the lab (in other words, using animal studies), more studies are needed. These may be controlled clinical trials, for example.
However, the short life span of stem cells outside the lab and the vaccination’s severe inflammatory side effects are limitations. Researchers won’t be able to conduct clinical trials until these issues are overcome.
- How to overcome limitations in research
You’ve already started on the road to overcoming limitations in research by acknowledging that they exist. However, you need to ensure readers don’t mistake weaknesses for errors within your research design.
To do this, you’ll need to justify and explain your rationale for the methods, research design, and analysis tools you chose and how you noticed they may have presented limitations.
Your readers need to know that even when limitations presented themselves, you followed best practices and the ethical standards of your field. You didn’t violate any rules and regulations during your research process.
You’ll also want to reinforce the validity of your conclusions and results with multiple sources, methods, and perspectives. This prevents readers from assuming your findings were derived from a single or biased source.
- Learning and improving starts with limitations in research
Dealing with limitations with transparency and integrity helps identify areas for future improvements and developments. It’s a learning process, providing valuable insights into how you can improve methodologies, expand sample sizes, or explore alternate approaches to further support the validity of your findings.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

Research Limitations: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on a research journey is an exciting endeavor, but every study has its boundaries and constraints. Understanding and transparently acknowledging these limitations is a crucial aspect of scholarly work. In this guide, we'll explore the concept of research limitations, why they matter, and how to effectively address and navigate them in your academic endeavors.
1. Defining Research Limitations:
- Definition: Research limitations are the constraints or shortcomings that affect the scope, applicability, and generalizability of a study.
- Inherent in Research: Every research project, regardless of its scale or significance, possesses limitations.
2. Types of Research Limitations:
- Methodological Limitations: Constraints related to the research design, data collection methods, or analytical techniques.
- Sampling Limitations: Issues associated with the representativeness or size of the study sample.
- Contextual Limitations: Restrictions stemming from the specific time, place, or cultural context of the study.
- Resource Limitations: Constraints related to time, budget, or access to necessary resources.
3. Why Acknowledge Limitations?
- Transparency: Acknowledging limitations demonstrates transparency and honesty in your research.
- Robustness of Findings: Recognizing limitations adds nuance to your findings, making them more robust.
- Future Research Directions: Addressing limitations provides a foundation for future researchers to build upon.
4. Identifying Research Limitations:
- Reflect on Methodology: Consider the strengths and weaknesses of your research design, data collection methods, and analysis.
- Examine Sample Characteristics: Evaluate the representativeness and size of your study sample.
- Consider External Factors: Assess external factors that may impact the generalizability of your findings.
5. How to Address Limitations:
- In the Methodology Section: Clearly articulate limitations in the methodology section of your research paper.
- Offer Solutions: If possible, propose ways to mitigate or address identified limitations.
- Future Research Suggestions: Use limitations as a springboard to suggest areas for future research.
6. Common Phrases to Express Limitations:
- "This study is not without limitations."
- "One limitation of our research is..."
- "It is important to acknowledge the constraints of this study, including..."
7. Examples of Addressing Limitations:
- Example 1 (Methodological): "While our survey provided valuable insights, the reliance on self-reported data introduces the possibility of response bias."
- Example 2 (Sampling): "The small sample size of our study limits the generalizability of our findings to a broader population."
- Example 3 (Resource): "Due to budget constraints, our research was limited to a single geographical location, potentially impacting the external validity."
8. Balancing Strengths and Limitations:
- Emphasize Contributions: Highlight the contributions and strengths of your research alongside the limitations.
- Maintain a Positive Tone: Discuss limitations objectively without undermining the significance of your study.
9. Feedback and Peer Review:
- Seek Feedback: Share your research with peers or mentors to gain valuable insights.
- Peer Review: Embrace the feedback received during the peer-review process to enhance the robustness of your work.
10. Continuous Reflection:
- Throughout the Research Process: Continuously reflect on potential limitations during the entire research process.
- Adjust as Needed: Be willing to adjust your approach as you encounter unforeseen challenges.
Conclusion:
Understanding and effectively addressing research limitations is a hallmark of rigorous and responsible scholarship. By openly acknowledging these constraints, you not only enhance the credibility of your work but also contribute to the broader academic discourse. Embrace the nuances of your research journey, navigate its limitations thoughtfully, and pave the way for future investigations.
Related Guides
- How to Write the Abstract of Your Research Paper?
- Research Methods : A Comprehensive Guide
- The Art of Wringing a Research Conclusion
- Tips for Avoiding Plagiarism
- Quantitative Research Methods
- Analyze and Discuss Your Research Findings Like a Pro
21 Research Limitations Examples
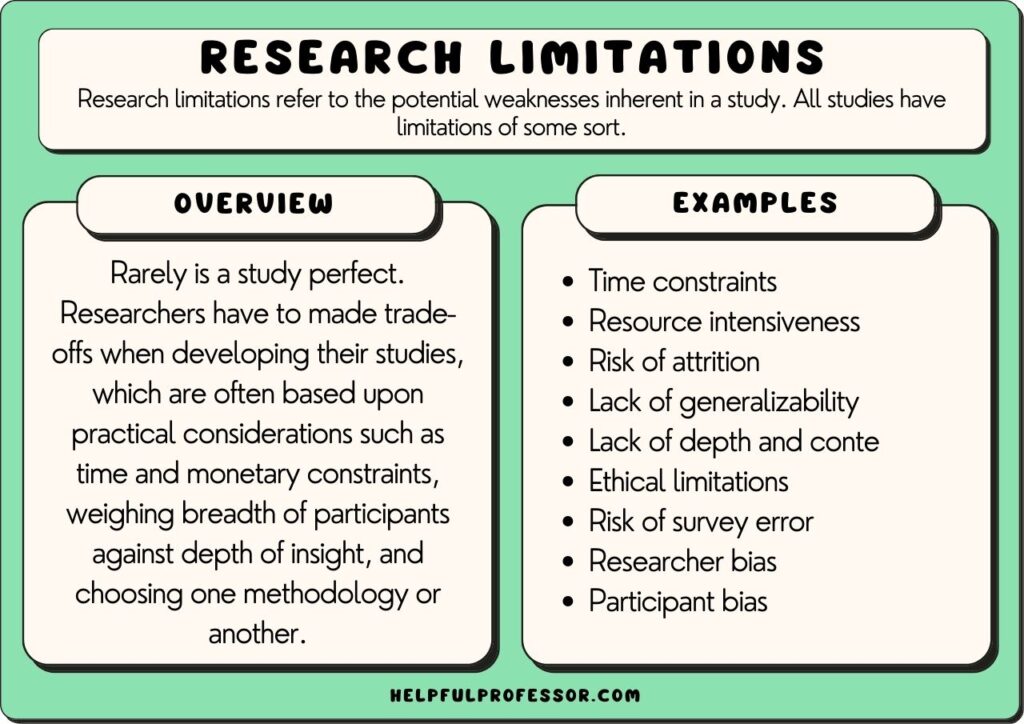
Research limitations refer to the potential weaknesses inherent in a study. All studies have limitations of some sort, meaning declaring limitations doesn’t necessarily need to be a bad thing, so long as your declaration of limitations is well thought-out and explained.
Rarely is a study perfect. Researchers have to make trade-offs when developing their studies, which are often based upon practical considerations such as time and monetary constraints, weighing the breadth of participants against the depth of insight, and choosing one methodology or another.
In research, studies can have limitations such as limited scope, researcher subjectivity, and lack of available research tools.
Acknowledging the limitations of your study should be seen as a strength. It demonstrates your willingness for transparency, humility, and submission to the scientific method and can bolster the integrity of the study. It can also inform future research direction.
Typically, scholars will explore the limitations of their study in either their methodology section, their conclusion section, or both.
Research Limitations Examples
Qualitative and quantitative research offer different perspectives and methods in exploring phenomena, each with its own strengths and limitations. So, I’ve split the limitations examples sections into qualitative and quantitative below.

Qualitative Research Limitations
Qualitative research seeks to understand phenomena in-depth and in context. It focuses on the ‘why’ and ‘how’ questions.
It’s often used to explore new or complex issues, and it provides rich, detailed insights into participants’ experiences, behaviors, and attitudes. However, these strengths also create certain limitations, as explained below.
1. Subjectivity
Qualitative research often requires the researcher to interpret subjective data. One researcher may examine a text and identify different themes or concepts as more dominant than others.
Close qualitative readings of texts are necessarily subjective – and while this may be a limitation, qualitative researchers argue this is the best way to deeply understand everything in context.
Suggested Solution and Response: To minimize subjectivity bias, you could consider cross-checking your own readings of themes and data against other scholars’ readings and interpretations. This may involve giving the raw data to a supervisor or colleague and asking them to code the data separately, then coming together to compare and contrast results.
2. Researcher Bias
The concept of researcher bias is related to, but slightly different from, subjectivity.
Researcher bias refers to the perspectives and opinions you bring with you when doing your research.
For example, a researcher who is explicitly of a certain philosophical or political persuasion may bring that persuasion to bear when interpreting data.
In many scholarly traditions, we will attempt to minimize researcher bias through the utilization of clear procedures that are set out in advance or through the use of statistical analysis tools.
However, in other traditions, such as in postmodern feminist research , declaration of bias is expected, and acknowledgment of bias is seen as a positive because, in those traditions, it is believed that bias cannot be eliminated from research, so instead, it is a matter of integrity to present it upfront.
Suggested Solution and Response: Acknowledge the potential for researcher bias and, depending on your theoretical framework , accept this, or identify procedures you have taken to seek a closer approximation to objectivity in your coding and analysis.
3. Generalizability
If you’re struggling to find a limitation to discuss in your own qualitative research study, then this one is for you: all qualitative research, of all persuasions and perspectives, cannot be generalized.
This is a core feature that sets qualitative data and quantitative data apart.
The point of qualitative data is to select case studies and similarly small corpora and dig deep through in-depth analysis and thick description of data.
Often, this will also mean that you have a non-randomized sample size.
While this is a positive – you’re going to get some really deep, contextualized, interesting insights – it also means that the findings may not be generalizable to a larger population that may not be representative of the small group of people in your study.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that take a quantitative approach to the question.
4. The Hawthorne Effect
The Hawthorne effect refers to the phenomenon where research participants change their ‘observed behavior’ when they’re aware that they are being observed.
This effect was first identified by Elton Mayo who conducted studies of the effects of various factors ton workers’ productivity. He noticed that no matter what he did – turning up the lights, turning down the lights, etc. – there was an increase in worker outputs compared to prior to the study taking place.
Mayo realized that the mere act of observing the workers made them work harder – his observation was what was changing behavior.
So, if you’re looking for a potential limitation to name for your observational research study , highlight the possible impact of the Hawthorne effect (and how you could reduce your footprint or visibility in order to decrease its likelihood).
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight ways you have attempted to reduce your footprint while in the field, and guarantee anonymity to your research participants.
5. Replicability
Quantitative research has a great benefit in that the studies are replicable – a researcher can get a similar sample size, duplicate the variables, and re-test a study. But you can’t do that in qualitative research.
Qualitative research relies heavily on context – a specific case study or specific variables that make a certain instance worthy of analysis. As a result, it’s often difficult to re-enter the same setting with the same variables and repeat the study.
Furthermore, the individual researcher’s interpretation is more influential in qualitative research, meaning even if a new researcher enters an environment and makes observations, their observations may be different because subjectivity comes into play much more. This doesn’t make the research bad necessarily (great insights can be made in qualitative research), but it certainly does demonstrate a weakness of qualitative research.
6. Limited Scope
“Limited scope” is perhaps one of the most common limitations listed by researchers – and while this is often a catch-all way of saying, “well, I’m not studying that in this study”, it’s also a valid point.
No study can explore everything related to a topic. At some point, we have to make decisions about what’s included in the study and what is excluded from the study.
So, you could say that a limitation of your study is that it doesn’t look at an extra variable or concept that’s certainly worthy of study but will have to be explored in your next project because this project has a clearly and narrowly defined goal.
Suggested Solution and Response: Be clear about what’s in and out of the study when writing your research question.
7. Time Constraints
This is also a catch-all claim you can make about your research project: that you would have included more people in the study, looked at more variables, and so on. But you’ve got to submit this thing by the end of next semester! You’ve got time constraints.
And time constraints are a recognized reality in all research.
But this means you’ll need to explain how time has limited your decisions. As with “limited scope”, this may mean that you had to study a smaller group of subjects, limit the amount of time you spent in the field, and so forth.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will build on your current work, possibly as a PhD project.
8. Resource Intensiveness
Qualitative research can be expensive due to the cost of transcription, the involvement of trained researchers, and potential travel for interviews or observations.
So, resource intensiveness is similar to the time constraints concept. If you don’t have the funds, you have to make decisions about which tools to use, which statistical software to employ, and how many research assistants you can dedicate to the study.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will gain more funding on the back of this ‘ exploratory study ‘.
9. Coding Difficulties
Data analysis in qualitative research often involves coding, which can be subjective and complex, especially when dealing with ambiguous or contradicting data.
After naming this as a limitation in your research, it’s important to explain how you’ve attempted to address this. Some ways to ‘limit the limitation’ include:
- Triangulation: Have 2 other researchers code the data as well and cross-check your results with theirs to identify outliers that may need to be re-examined, debated with the other researchers, or removed altogether.
- Procedure: Use a clear coding procedure to demonstrate reliability in your coding process. I personally use the thematic network analysis method outlined in this academic article by Attride-Stirling (2001).
Suggested Solution and Response: Triangulate your coding findings with colleagues, and follow a thematic network analysis procedure.
10. Risk of Non-Responsiveness
There is always a risk in research that research participants will be unwilling or uncomfortable sharing their genuine thoughts and feelings in the study.
This is particularly true when you’re conducting research on sensitive topics, politicized topics, or topics where the participant is expressing vulnerability .
This is similar to the Hawthorne effect (aka participant bias), where participants change their behaviors in your presence; but it goes a step further, where participants actively hide their true thoughts and feelings from you.
Suggested Solution and Response: One way to manage this is to try to include a wider group of people with the expectation that there will be non-responsiveness from some participants.
11. Risk of Attrition
Attrition refers to the process of losing research participants throughout the study.
This occurs most commonly in longitudinal studies , where a researcher must return to conduct their analysis over spaced periods of time, often over a period of years.
Things happen to people over time – they move overseas, their life experiences change, they get sick, change their minds, and even die. The more time that passes, the greater the risk of attrition.
Suggested Solution and Response: One way to manage this is to try to include a wider group of people with the expectation that there will be attrition over time.
12. Difficulty in Maintaining Confidentiality and Anonymity
Given the detailed nature of qualitative data , ensuring participant anonymity can be challenging.
If you have a sensitive topic in a specific case study, even anonymizing research participants sometimes isn’t enough. People might be able to induce who you’re talking about.
Sometimes, this will mean you have to exclude some interesting data that you collected from your final report. Confidentiality and anonymity come before your findings in research ethics – and this is a necessary limiting factor.
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight the efforts you have taken to anonymize data, and accept that confidentiality and accountability place extremely important constraints on academic research.
13. Difficulty in Finding Research Participants
A study that looks at a very specific phenomenon or even a specific set of cases within a phenomenon means that the pool of potential research participants can be very low.
Compile on top of this the fact that many people you approach may choose not to participate, and you could end up with a very small corpus of subjects to explore. This may limit your ability to make complete findings, even in a quantitative sense.
You may need to therefore limit your research question and objectives to something more realistic.
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight that this is going to limit the study’s generalizability significantly.
14. Ethical Limitations
Ethical limitations refer to the things you cannot do based on ethical concerns identified either by yourself or your institution’s ethics review board.
This might include threats to the physical or psychological well-being of your research subjects, the potential of releasing data that could harm a person’s reputation, and so on.
Furthermore, even if your study follows all expected standards of ethics, you still, as an ethical researcher, need to allow a research participant to pull out at any point in time, after which you cannot use their data, which demonstrates an overlap between ethical constraints and participant attrition.
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight that these ethical limitations are inevitable but important to sustain the integrity of the research.
For more on Qualitative Research, Explore my Qualitative Research Guide
Quantitative Research Limitations
Quantitative research focuses on quantifiable data and statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s often used to test hypotheses, assess relationships and causality, and generalize findings across larger populations.
Quantitative research is widely respected for its ability to provide reliable, measurable, and generalizable data (if done well!). Its structured methodology has strengths over qualitative research, such as the fact it allows for replication of the study, which underpins the validity of the research.
However, this approach is not without it limitations, explained below.
1. Over-Simplification
Quantitative research is powerful because it allows you to measure and analyze data in a systematic and standardized way. However, one of its limitations is that it can sometimes simplify complex phenomena or situations.
In other words, it might miss the subtleties or nuances of the research subject.
For example, if you’re studying why people choose a particular diet, a quantitative study might identify factors like age, income, or health status. But it might miss other aspects, such as cultural influences or personal beliefs, that can also significantly impact dietary choices.
When writing about this limitation, you can say that your quantitative approach, while providing precise measurements and comparisons, may not capture the full complexity of your subjects of study.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest a follow-up case study using the same research participants in order to gain additional context and depth.
2. Lack of Context
Another potential issue with quantitative research is that it often focuses on numbers and statistics at the expense of context or qualitative information.
Let’s say you’re studying the effect of classroom size on student performance. You might find that students in smaller classes generally perform better. However, this doesn’t take into account other variables, like teaching style , student motivation, or family support.
When describing this limitation, you might say, “Although our research provides important insights into the relationship between class size and student performance, it does not incorporate the impact of other potentially influential variables. Future research could benefit from a mixed-methods approach that combines quantitative analysis with qualitative insights.”
3. Applicability to Real-World Settings
Oftentimes, experimental research takes place in controlled environments to limit the influence of outside factors.
This control is great for isolation and understanding the specific phenomenon but can limit the applicability or “external validity” of the research to real-world settings.
For example, if you conduct a lab experiment to see how sleep deprivation impacts cognitive performance, the sterile, controlled lab environment might not reflect real-world conditions where people are dealing with multiple stressors.
Therefore, when explaining the limitations of your quantitative study in your methodology section, you could state:
“While our findings provide valuable information about [topic], the controlled conditions of the experiment may not accurately represent real-world scenarios where extraneous variables will exist. As such, the direct applicability of our results to broader contexts may be limited.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will engage in real-world observational research, such as ethnographic research.
4. Limited Flexibility
Once a quantitative study is underway, it can be challenging to make changes to it. This is because, unlike in grounded research, you’re putting in place your study in advance, and you can’t make changes part-way through.
Your study design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques need to be decided upon before you start collecting data.
For example, if you are conducting a survey on the impact of social media on teenage mental health, and halfway through, you realize that you should have included a question about their screen time, it’s generally too late to add it.
When discussing this limitation, you could write something like, “The structured nature of our quantitative approach allows for consistent data collection and analysis but also limits our flexibility to adapt and modify the research process in response to emerging insights and ideas.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will use mixed-methods or qualitative research methods to gain additional depth of insight.
5. Risk of Survey Error
Surveys are a common tool in quantitative research, but they carry risks of error.
There can be measurement errors (if a question is misunderstood), coverage errors (if some groups aren’t adequately represented), non-response errors (if certain people don’t respond), and sampling errors (if your sample isn’t representative of the population).
For instance, if you’re surveying college students about their study habits , but only daytime students respond because you conduct the survey during the day, your results will be skewed.
In discussing this limitation, you might say, “Despite our best efforts to develop a comprehensive survey, there remains a risk of survey error, including measurement, coverage, non-response, and sampling errors. These could potentially impact the reliability and generalizability of our findings.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will use other survey tools to compare and contrast results.
6. Limited Ability to Probe Answers
With quantitative research, you typically can’t ask follow-up questions or delve deeper into participants’ responses like you could in a qualitative interview.
For instance, imagine you are surveying 500 students about study habits in a questionnaire. A respondent might indicate that they study for two hours each night. You might want to follow up by asking them to elaborate on what those study sessions involve or how effective they feel their habits are.
However, quantitative research generally disallows this in the way a qualitative semi-structured interview could.
When discussing this limitation, you might write, “Given the structured nature of our survey, our ability to probe deeper into individual responses is limited. This means we may not fully understand the context or reasoning behind the responses, potentially limiting the depth of our findings.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that engage in mixed-method or qualitative methodologies to address the issue from another angle.
7. Reliance on Instruments for Data Collection
In quantitative research, the collection of data heavily relies on instruments like questionnaires, surveys, or machines.
The limitation here is that the data you get is only as good as the instrument you’re using. If the instrument isn’t designed or calibrated well, your data can be flawed.
For instance, if you’re using a questionnaire to study customer satisfaction and the questions are vague, confusing, or biased, the responses may not accurately reflect the customers’ true feelings.
When discussing this limitation, you could say, “Our study depends on the use of questionnaires for data collection. Although we have put significant effort into designing and testing the instrument, it’s possible that inaccuracies or misunderstandings could potentially affect the validity of the data collected.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will use different instruments but examine the same variables to triangulate results.
8. Time and Resource Constraints (Specific to Quantitative Research)
Quantitative research can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially when dealing with large samples.
It often involves systematic sampling, rigorous design, and sometimes complex statistical analysis.
If resources and time are limited, it can restrict the scale of your research, the techniques you can employ, or the extent of your data analysis.
For example, you may want to conduct a nationwide survey on public opinion about a certain policy. However, due to limited resources, you might only be able to survey people in one city.
When writing about this limitation, you could say, “Given the scope of our research and the resources available, we are limited to conducting our survey within one city, which may not fully represent the nationwide public opinion. Hence, the generalizability of the results may be limited.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will have more funding or longer timeframes.
How to Discuss Your Research Limitations
1. in your research proposal and methodology section.
In the research proposal, which will become the methodology section of your dissertation, I would recommend taking the four following steps, in order:
- Be Explicit about your Scope – If you limit the scope of your study in your research question, aims, and objectives, then you can set yourself up well later in the methodology to say that certain questions are “outside the scope of the study.” For example, you may identify the fact that the study doesn’t address a certain variable, but you can follow up by stating that the research question is specifically focused on the variable that you are examining, so this limitation would need to be looked at in future studies.
- Acknowledge the Limitation – Acknowledging the limitations of your study demonstrates reflexivity and humility and can make your research more reliable and valid. It also pre-empts questions the people grading your paper may have, so instead of them down-grading you for your limitations; they will congratulate you on explaining the limitations and how you have addressed them!
- Explain your Decisions – You may have chosen your approach (despite its limitations) for a very specific reason. This might be because your approach remains, on balance, the best one to answer your research question. Or, it might be because of time and monetary constraints that are outside of your control.
- Highlight the Strengths of your Approach – Conclude your limitations section by strongly demonstrating that, despite limitations, you’ve worked hard to minimize the effects of the limitations and that you have chosen your specific approach and methodology because it’s also got some terrific strengths. Name the strengths.
Overall, you’ll want to acknowledge your own limitations but also explain that the limitations don’t detract from the value of your study as it stands.
2. In the Conclusion Section or Chapter
In the conclusion of your study, it is generally expected that you return to a discussion of the study’s limitations. Here, I recommend the following steps:
- Acknowledge issues faced – After completing your study, you will be increasingly aware of issues you may have faced that, if you re-did the study, you may have addressed earlier in order to avoid those issues. Acknowledge these issues as limitations, and frame them as recommendations for subsequent studies.
- Suggest further research – Scholarly research aims to fill gaps in the current literature and knowledge. Having established your expertise through your study, suggest lines of inquiry for future researchers. You could state that your study had certain limitations, and “future studies” can address those limitations.
- Suggest a mixed methods approach – Qualitative and quantitative research each have pros and cons. So, note those ‘cons’ of your approach, then say the next study should approach the topic using the opposite methodology or could approach it using a mixed-methods approach that could achieve the benefits of quantitative studies with the nuanced insights of associated qualitative insights as part of an in-study case-study.
Overall, be clear about both your limitations and how those limitations can inform future studies.
In sum, each type of research method has its own strengths and limitations. Qualitative research excels in exploring depth, context, and complexity, while quantitative research excels in examining breadth, generalizability, and quantifiable measures. Despite their individual limitations, each method contributes unique and valuable insights, and researchers often use them together to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon being studied.
Attride-Stirling, J. (2001). Thematic networks: an analytic tool for qualitative research. Qualitative research , 1 (3), 385-405. ( Source )
Atkinson, P., Delamont, S., Cernat, A., Sakshaug, J., & Williams, R. A. (2021). SAGE research methods foundations . London: Sage Publications.
Clark, T., Foster, L., Bryman, A., & Sloan, L. (2021). Bryman’s social research methods . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Köhler, T., Smith, A., & Bhakoo, V. (2022). Templates in qualitative research methods: Origins, limitations, and new directions. Organizational Research Methods , 25 (2), 183-210. ( Source )
Lenger, A. (2019). The rejection of qualitative research methods in economics. Journal of Economic Issues , 53 (4), 946-965. ( Source )
Taherdoost, H. (2022). What are different research approaches? Comprehensive review of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method research, their applications, types, and limitations. Journal of Management Science & Engineering Research , 5 (1), 53-63. ( Source )
Walliman, N. (2021). Research methods: The basics . New York: Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Research Limitations
It is for sure that your research will have some limitations and it is normal. However, it is critically important for you to be striving to minimize the range of scope of limitations throughout the research process. Also, you need to provide the acknowledgement of your research limitations in conclusions chapter honestly.
It is always better to identify and acknowledge shortcomings of your work, rather than to leave them pointed out to your by your dissertation assessor. While discussing your research limitations, don’t just provide the list and description of shortcomings of your work. It is also important for you to explain how these limitations have impacted your research findings.
Your research may have multiple limitations, but you need to discuss only those limitations that directly relate to your research problems. For example, if conducting a meta-analysis of the secondary data has not been stated as your research objective, no need to mention it as your research limitation.
Research limitations in a typical dissertation may relate to the following points:
1. Formulation of research aims and objectives . You might have formulated research aims and objectives too broadly. You can specify in which ways the formulation of research aims and objectives could be narrowed so that the level of focus of the study could be increased.
2. Implementation of data collection method . Because you do not have an extensive experience in primary data collection (otherwise you would not be reading this book), there is a great chance that the nature of implementation of data collection method is flawed.
3. Sample size. Sample size depends on the nature of the research problem. If sample size is too small, statistical tests would not be able to identify significant relationships within data set. You can state that basing your study in larger sample size could have generated more accurate results. The importance of sample size is greater in quantitative studies compared to qualitative studies.
4. Lack of previous studies in the research area . Literature review is an important part of any research, because it helps to identify the scope of works that have been done so far in research area. Literature review findings are used as the foundation for the researcher to be built upon to achieve her research objectives.
However, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic if you have focused on the most contemporary and evolving research problem or too narrow research problem. For example, if you have chosen to explore the role of Bitcoins as the future currency, you may not be able to find tons of scholarly paper addressing the research problem, because Bitcoins are only a recent phenomenon.
5. Scope of discussions . You can include this point as a limitation of your research regardless of the choice of the research area. Because (most likely) you don’t have many years of experience of conducing researches and producing academic papers of such a large size individually, the scope and depth of discussions in your paper is compromised in many levels compared to the works of experienced scholars.
You can discuss certain points from your research limitations as the suggestion for further research at conclusions chapter of your dissertation.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline. John Dudovskiy


Organizing Academic Research Papers: Limitations of the Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the application or interpretation of the results of your study. They are the constraints on generalizability and utility of findings that are the result of the ways in which you chose to design the study and/or the method used to establish internal and external validity.
Importance of...
Always acknowledge a study's limitations. It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor and be graded down because you appear to have ignored them.
Keep in mind that acknowledgement of a study's limitations is an opportunity to make suggestions for further research. If you do connect your study's limitations to suggestions for further research, be sure to explain the ways in which these unanswered questions may become more focused because of your study.
Acknowledgement of a study's limitations also provides you with an opportunity to demonstrate to your professor that you have thought critically about the research problem, understood the relevant literature published about it, and correctly assessed the methods chosen for studying the problem. A key objective of the research process is not only discovering new knowledge but also to confront assumptions and explore what we don't know.
Claiming limitiations is a subjective process because you must evaluate the impact of those limitations . Don't just list key weaknesses and the magnitude of a study's limitations. To do so diminishes the validity of your research because it leaves the reader wondering whether, or in what ways, limitation(s) in your study may have impacted the findings and conclusions. Limitations require a critical, overall appraisal and interpretation of their impact. You should answer the question: do these problems with errors, methods, validity, etc. eventually matter and, if so, to what extent?
Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation . Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com.
Descriptions of Possible Limitations
All studies have limitations . However, it is important that you restrict your discussion to limitations related to the research problem under investigation. For example, if a meta-analysis of existing literature is not a stated purpose of your research, it should not be discussed as a limitation. Do not apologize for not addressing issues that you did not promise to investigate in your paper.
Here are examples of limitations you may need to describe and to discuss how they possibly impacted your findings. Descriptions of limitations should be stated in the past tense.
Possible Methodological Limitations
- Sample size -- the number of the units of analysis you use in your study is dictated by the type of research problem you are investigating. Note that, if your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to find significant relationships from the data, as statistical tests normally require a larger sample size to ensure a representative distribution of the population and to be considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred.
- Lack of available and/or reliable data -- a lack of data or of reliable data will likely require you to limit the scope of your analysis, the size of your sample, or it can be a significant obstacle in finding a trend and a meaningful relationship. You need to not only describe these limitations but to offer reasons why you believe data is missing or is unreliable. However, don’t just throw up your hands in frustration; use this as an opportunity to describe the need for future research.
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic -- citing prior research studies forms the basis of your literature review and helps lay a foundation for understanding the research problem you are investigating. Depending on the currency or scope of your research topic, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic. Before assuming this to be true, consult with a librarian! In cases when a librarian has confirmed that there is a lack of prior research, you may be required to develop an entirely new research typology [for example, using an exploratory rather than an explanatory research design]. Note that this limitation can serve as an important opportunity to describe the need for further research.
- Measure used to collect the data -- sometimes it is the case that, after completing your interpretation of the findings, you discover that the way in which you gathered data inhibited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results. For example, you regret not including a specific question in a survey that, in retrospect, could have helped address a particular issue that emerged later in the study. Acknowledge the deficiency by stating a need in future research to revise the specific method for gathering data.
- Self-reported data -- whether you are relying on pre-existing self-reported data or you are conducting a qualitative research study and gathering the data yourself, self-reported data is limited by the fact that it rarely can be independently verified. In other words, you have to take what people say, whether in interviews, focus groups, or on questionnaires, at face value. However, self-reported data contain several potential sources of bias that should be noted as limitations: (1) selective memory (remembering or not remembering experiences or events that occurred at some point in the past); (2) telescoping [recalling events that occurred at one time as if they occurred at another time]; (3) attribution [the act of attributing positive events and outcomes to one's own agency but attributing negative events and outcomes to external forces]; and, (4) exaggeration [the act of representing outcomes or embellishing events as more significant than is actually suggested from other data].
Possible Limitations of the Researcher
- Access -- if your study depends on having access to people, organizations, or documents and, for whatever reason, access is denied or otherwise limited, the reasons for this need to be described.
- Longitudinal effects -- unlike your professor, who can literally devote years [even a lifetime] to studying a single research problem, the time available to investigate a research problem and to measure change or stability within a sample is constrained by the due date of your assignment. Be sure to choose a topic that does not require an excessive amount of time to complete the literature review, apply the methodology, and gather and interpret the results. If you're unsure, talk to your professor.
- Cultural and other type of bias -- we all have biases, whether we are conscience of them or not. Bias is when a person, place, or thing is viewed or shown in a consistently inaccurate way. It is usually negative, though one can have a positive bias as well. When proof-reading your paper, be especially critical in reviewing how you have stated a problem, selected the data to be studied, what may have been omitted, the manner in which you have ordered events, people, or places and how you have chosen to represent a person, place, or thing, to name a phenomenon, or to use possible words with a positive or negative connotation. Note that if you detect bias in prior research, it must be acknowledged and you should explain what measures were taken to avoid perpetuating bias.
- Fluency in a language -- if your research focuses on measuring the perceived value of after-school tutoring among Mexican-American ESL [English as a Second Language] students, for example, and you are not fluent in Spanish, you are limited in being able to read and interpret Spanish language research studies on the topic. This deficiency should be acknowledged.
Brutus, Stéphane et al. Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations. Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Senunyeme, Emmanuel K. Business Research Methods . Powerpoint Presentation. Regent University of Science and Technology.
Structure and Writing Style
Information about the limitations of your study are generally placed either at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so the reader knows and understands the limitations before reading the rest of your analysis of the findings, or, the limitations are outlined at the conclusion of the discussion section as an acknowledgement of the need for further study. Statements about a study's limitations should not be buried in the body [middle] of the discussion section unless a limitation is specific to something covered in that part of the paper. If this is the case, though, the limitation should be reiterated at the conclusion of the section.
If you determine that your study is seriously flawed due to important limitations , such as, an inability to acquire critical data, consider reframing it as a pilot study intended to lay the groundwork for a more complete research study in the future. Be sure, though, to specifically explain the ways that these flaws can be successfully overcome in later studies.
But, do not use this as an excuse for not developing a thorough research paper! Review the tab in this guide for developing a research topic . If serious limitations exist, it generally indicates a likelihood that your research problem is too narrowly defined or that the issue or event under study is too recent and, thus, very little research has been written about it. If serious limitations do emerge, consult with your professor about possible ways to overcome them or how to reframe your study.
When discussing the limitations of your research, be sure to:
- Describe each limitation in detailed but concise terms;
- Explain why each limitation exists;
- Provide the reasons why each limitation could not be overcome using the method(s) chosen to gather the data [cite to other studies that had similar problems when possible];
- Assess the impact of each limitation in relation to the overall findings and conclusions of your study; and,
- If appropriate, describe how these limitations could point to the need for further research.
Remember that the method you chose may be the source of a significant limitation that has emerged during your interpretation of the results [for example, you didn't ask a particular question in a survey that you later wish you had]. If this is the case, don't panic. Acknowledge it, and explain how applying a different or more robust methodology might address the research problem more effectively in any future study. A underlying goal of scholarly research is not only to prove what works, but to demonstrate what doesn't work or what needs further clarification.
Brutus, Stéphane et al. Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations. Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Ioannidis, John P.A. Limitations are not Properly Acknowledged in the Scientific Literature. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007): 324-329; Pasek, Josh. Writing the Empirical Social Science Research Paper: A Guide for the Perplexed . January 24, 2012. Academia.edu; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation . Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Writing Tip
Don't Inflate the Importance of Your Findings! After all the hard work and long hours devoted to writing your research paper, it is easy to get carried away with attributing unwarranted importance to what you’ve done. We all want our academic work to be viewed as excellent and worthy of a good grade, but it is important that you understand and openly acknowledge the limitiations of your study. Inflating of the importance of your study's findings in an attempt hide its flaws is a big turn off to your readers. A measure of humility goes a long way!
Another Writing Tip
Negative Results are Not a Limitation!
Negative evidence refers to findings that unexpectedly challenge rather than support your hypothesis. If you didn't get the results you anticipated, it may mean your hypothesis was incorrect and needs to be reformulated, or, perhaps you have stumbled onto something unexpected that warrants further study. Moreover, the absence of an effect may be very telling in many situations, particularly in experimental research designs. In any case, your results may be of importance to others even though they did not support your hypothesis. Do not fall into the trap of thinking that results contrary to what you expected is a limitation to your study. If you carried out the research well, they are simply your results and only require additional interpretation.
Yet Another Writing Tip
A Note about Sample Size Limitations in Qualitative Research
Sample sizes are typically smaller in qualitative research because, as the study goes on, acquiring more data does not necessarily lead to more information. This is because one occurrence of a piece of data, or a code, is all that is necessary to ensure that it becomes part of the analysis framework. However, it remains true that sample sizes that are too small cannot adequately support claims of having achieved valid conclusions and sample sizes that are too large do not permit the deep, naturalistic, and inductive analysis that defines qualitative inquiry. Determining adequate sample size in qualitative research is ultimately a matter of judgment and experience in evaluating the quality of the information collected against the uses to which it will be applied and the particular research method and purposeful sampling strategy employed. If the sample size is found to be a limitation, it may reflect your judgement about the methodological technique chosen [e.g., single life history study versus focus group interviews] rather than the number of respondents used.
Huberman, A. Michael and Matthew B. Miles. Data Management and Analysis Methods. In Handbook of Qualitative Research. Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 428-444.
- << Previous: 8. The Discussion
- Next: 9. The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Gen Intern Med
- v.37(1); 2022 Jan

Methods for Identifying Health Research Gaps, Needs, and Priorities: a Scoping Review
Eunice c. wong.
1 RAND Corporation, Santa Monica, CA USA
Alicia R. Maher
Aneesa motala.
2 Department of Population and Public Health Sciences, University of Southern California Gehr Family Center for Health Systems Science & Innovation, Los Angeles, USA
Rachel Ross
Olamigoke akinniranye, jody larkin, susanne hempel, associated data.
Well-defined, systematic, and transparent processes to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are vital to ensuring that available funds target areas with the greatest potential for impact.
The purpose of this review is to characterize methods conducted or supported by research funding organizations to identify health research gaps, needs, or priorities.
We searched MEDLINE, PsycINFO, and the Web of Science up to September 2019. Eligible studies reported on methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities that had been conducted or supported by research funding organizations. Using a published protocol, we extracted data on the method, criteria, involvement of stakeholders, evaluations, and whether the method had been replicated (i.e., used in other studies).
Among 10,832 citations, 167 studies were eligible for full data extraction. More than half of the studies employed methods to identify both needs and priorities, whereas about a quarter of studies focused singularly on identifying gaps (7%), needs (6%), or priorities (14%) only. The most frequently used methods were the convening of workshops or meetings (37%), quantitative methods (32%), and the James Lind Alliance approach, a multi-stakeholder research needs and priority setting process (28%). The most widely applied criteria were importance to stakeholders (72%), potential value (29%), and feasibility (18%). Stakeholder involvement was most prominent among clinicians (69%), researchers (66%), and patients and the public (59%). Stakeholders were identified through stakeholder organizations (51%) and purposive (26%) and convenience sampling (11%). Only 4% of studies evaluated the effectiveness of the methods and 37% employed methods that were reproducible and used in other studies.
To ensure optimal targeting of funds to meet the greatest areas of need and maximize outcomes, a much more robust evidence base is needed to ascertain the effectiveness of methods used to identify research gaps, needs, and priorities.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s11606-021-07064-1.
Well-defined, systematic, and transparent methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are vital to ensuring that available funds target areas with the greatest potential for impact. 1 , 2 As defined in the literature, 3 , 4 research gaps are defined as areas or topics in which the ability to draw a conclusion for a given question is prevented by insufficient evidence. Research gaps are not necessarily synonymous with research needs , which are those knowledge gaps that significantly inhibit the decision-making ability of key stakeholders, who are end users of research, such as patients, clinicians, and policy makers. The selection of research priorities is often necessary when all identified research gaps or needs cannot be pursued because of resource constraints. Methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities (from herein referred to as gaps, needs, priorities) can be multi-varied and there does not appear to be general consensus on best practices. 3 , 5
Several published reviews highlight the diverse methods that have been used to identify gaps and priorities. In a review of methods used to identify gaps from systematic reviews, Robinson et al. noted the wide range of organizing principles that were employed in published literature between 2001 and 2009 (e.g., care pathway, decision tree, and patient, intervention, comparison, outcome framework,). 6 In a more recent review spanning 2007 to 2017, Nyanchoka et al. found that the vast majority of studies with a primary focus on the identification of gaps (83%) relied solely on knowledge synthesis methods (e.g., systematic review, scoping review, evidence mapping, literature review). A much smaller proportion (9%) relied exclusively on primary research methods (i.e., quantitative survey, qualitative study). 7
With respect to research priorities, in a review limited to a PubMed database search covering the period from 2001 to 2014, Yoshida documented a wide range of methods to identify priorities including the use of not only knowledge synthesis (i.e., literature reviews) and primary research methods (i.e., surveys) but also multi-stage, structured methods such as Delphi, Child Health and Nutrition Research Initiative (CHNRI), James Lind Alliance Priority Setting Partnership (JLA PSP), and Essential National Health Research (ENHR). 2 The CHNRI method, originally developed for the purpose of setting global child health research priorities, typically employs researchers and experts to specify a long list of research questions, the criteria that will be used to prioritize research questions, and the technical scoring of research questions using the defined criteria. 8 During the latter stages, non-expert stakeholders’ input are incorporated by using their ratings of the importance of selected criteria to weight the technical scores. The ENHR method, initially designed for health research priority setting at the national level, involves researchers, decision-makers, health service providers, and communities throughout the entire process of identifying and prioritizing research topics. 9 The JLA PSP method convenes patients, carers, and clinicians to equally and jointly identify questions about healthcare that cannot be answered by existing evidence that are important to all groups (i.e., research needs). 10 The identified research needs are then prioritized by the groups resulting in a final list (often a top 10) of research priorities. Non-clinical researchers are excluded from voting on research needs or priorities but can be involved in other processes (e.g., knowledge synthesis). CHNRI, ENHR, and JLA PSP usually employ a mix of knowledge synthesis and primary research methods to first identify a set of gaps or needs that are then prioritized. Thus, even though CHNRI, ENHR, and JLA PSP have been referred to as priority setting methods, they actually consist of a gaps or needs identification stage that feeds into a research prioritization stage.
Nyanchoka et al.’s review found that the majority of studies focused on the identification of gaps alone (65%), whereas the remaining studies focused either on research priorities alone (17%) or on both gaps and priorities (19%). 7 In an update to Robinson et al.’s review, 6 Carey et al. reviewed the literature between 2010 and 2011 and observed that the studies conducted during this latter period of time focused more on research priorities than gaps and had increased stakeholder involvement, and that none had evaluated the reproducibility of the methods. 11
The increasing development and diversity of formal processes and methods to identify gaps and priorities are indicative of a developing field. 2 , 12 To facilitate more standardized and systematic processes, other important areas warrant further investigation. Prior reviews did not distinguish between the identification of gaps versus research needs. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence-based Practice Center (AHRQ EPC) Program issued a series of method papers related to establishing research needs as part of comparative effectiveness research. 13 – 15 The AHRQ EPC Program defined research needs as “evidence gaps” identified within systematic reviews that are prioritized by stakeholders according to their potential impact on practice or care. 16 Furthermore, Nyanchoka et al. relied on author designations to classify studies as focusing on gaps versus research priorities and noted that definitions of gaps varied across studies, highlighting the need to apply consistent taxonomy when categorizing studies in reviews. 7 Given the rise in the use of stakeholders in both gaps and prioritization exercises, a greater understanding of the range of practices involving stakeholders is also needed. This includes the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders (e.g., consultants versus final decision-makers), the composition of stakeholders (e.g., non-research clinicians, patients, caregivers, policymakers), and the methods used to recruit stakeholders. The lack of consensus of best practices also highlights the importance of learning the extent to which evaluations to determine the effectiveness of gaps, needs, and prioritization exercises have been conducted, and if so, what were the resultant outcomes.
To better inform efforts and organizations that fund health research, we conducted a scoping review of methods used to identify gaps, needs, and priorities that were linked to potential or actual health research funding decision-making. Hence, this scoping review was limited to studies in which the identification of health research gaps, needs, or priorities was supported or conducted by funding organizations to address the following questions 1 : What are the characteristics of methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities? and 2 To what extent have evaluations of the impact of these methods been conducted? Given that scoping reviews may be executed to characterize the ways an area of research has been conducted, 17 , 18 this approach is appropriate for the broad nature of this study’s aims.
Protocol and Registration
We employed methods that conform to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews. 19 See Appendix A in the Supplementary Information. The scoping review protocol is registered with the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/5zjqx/ ).
Eligibility Criteria
Studies published in English that described methods to identify health research gaps, needs, or priorities that were supported or conducted by funding organizations were eligible for inclusion. We excluded studies that reported only the results of the exercise (e.g., list of priorities) absent of information on the methods used. We also excluded studies involving evidence synthesis (e.g., literature or systematic reviews) that were solely descriptive and did not employ an explicit method to identify research gaps, needs, or priorities.
Information Sources and Search Strategy
We searched the following electronic databases: MEDLINE, PsycINFO, and Web of Science. Our database search also included an update of the Nyanchoka et al. scoping review, which entailed executing their database searches for the time period following 2017 (the study’s search end date). 7 Nyanchoka et al. did not include database searches for research needs. The electronic database search and scoping review update were completed in August and September 2019, respectively . The search strategy employed for each of the databases is presented in Appendix B in the Supplementary Information.
Selection of Sources of Evidence and Data Charting Process
Two reviewers screened titles and abstracts and full-text publications. Citations that one or both reviewers considered potentially eligible were retrieved for full-text review. Relevant background articles and scoping and systematic reviews were reference mined to screen for eligible studies. Full-text publications were screened against detailed inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data was extracted by one reviewer and checked by a second reviewer. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion by the review team.
Information on study characteristics were extracted from each article including the aims of the exercise (i.e., gaps, needs, priorities, or a combination) and health condition (i.e., physical or psychological). Based on definitions in the literature, 3 – 5 the aims of the exercise were coded according to the activities that were conducted, which may not have always corresponded with the study authors’ labeling of the exercises. For instance, the JLA PSP method is often described as a priority exercise but we categorized it as a needs and priority exercise. Priority exercises can be preceded by exercises to identify gaps or needs, which then feed into the priority exercise such as in JLA PSP; however, standalone priority exercises can also be conducted (e.g., stakeholders prioritize an existing list of emerging diseases).
For each type of exercise, information on the methods were recorded. An initial list of methods was created based on previous reviews. 9 , 12 , 20 During the data extraction process, any methods not included in the initial list were subsequently added. If more than one exercise was reported within an article (e.g., gaps and priorities), information was extracted for each exercise separately. Reviewers extracted the following information: methods employed (e.g., qualitative, quantitative), criteria used (e.g., disease burden, importance to stakeholders), stakeholder involvement (e.g., stakeholder composition, method for identifying stakeholders), and whether an evaluation was conducted on the effectiveness of the exercise (see Appendix C in the Supplementary Information for full data extraction form).
Synthesis of results entailed quantitative descriptives of study characteristics (e.g., proportion of studies by aims of exercise) and characteristics of methods employed across all studies and by each type of study (e.g., gaps, needs, priorities).
The electronic database search yielded a total of 10,548 titles. Another 284 articles were identified after searching the reference lists of full-text publications, including three systematic reviews 21 – 23 and one scoping review 24 that had met eligibility criteria. Moreover, a total of 99 publications designated as relevant background articles were also reference mined to screen for eligible studies. We conducted full-text screening for 2524 articles, which resulted in 2344 exclusions (440 studies were designated as background articles). A total of 167 exercises related to the identification of gaps, needs, or priorities that were supported or conducted by a research funding organization were described across 180 publications and underwent full data extraction. See Figure Figure1 1 for the flow diagram of our search strategy and reasons for exclusion.

Literature flow
Characteristics of Sources of Evidence
Among the published exercises, the majority of studies (152/167) conducted gaps, need, or prioritization exercises related to physical health, whereas only a small fraction of studies focused on psychological health (12/167) (see Appendix D in the Supplementary Information).
Methods for Identifying Gaps, Needs, and Priorities
As seen in Table Table1, 1 , only about a quarter of studies involved a singular type of exercise with 7% focused on the identification of gaps only (i.e., areas with insufficient information to draw a conclusion for a given question), 6% on needs only (i.e., knowledge gaps that inhibit the decision-making of key stakeholders), and 14% priorities only (i.e., ranked gaps or needs often because of resource constraints). Studies more commonly conducted a combination of multiple types of exercises with more than half focused on the identification of both research needs and priorities, 14% on gaps and priorities, 3% gaps, needs, and priorities, and 3% gaps and needs.
Methods for Identifying Health Research Gaps, Needs, and Priorities
JLA PSP , James Lind Alliance Priority Setting Partnerships; ENHR , Essential National Health Research; CHNRI , Child Health and Nutrition Research Initiative. Numbers in columns may add up to more than the total N or 100% since some studies employed more than one method
Across the 167 studies, the three most frequently used methods were the convening of workshops/meetings/conferences (37%), quantitative methods (32%), and the JLA PSP approach (28%). This was followed by methods involving literature reviews (17%), qualitative methods (17%), consensus methods (13%), and reviews of source materials (15%). Other methods included the CHNRI process (7%), reviews of in-progress data (7%), consultation with (non-researcher) stakeholders (4%), applying a framework tool (4%), ENHR (1%), systematic reviews (1%), and evidence mapping (1%).
The criterion most widely applied across the 167 studies was the importance to stakeholders (72%) (see Table Table2). 2 ). Almost one-third (29%) considered the potential value and 18% feasibility as criteria. Burden of disease (9%), addressing inequities (8%), costs (6%), alignment with organization’s mission (3%), and patient centeredness (2%) were adopted as criteria to a lesser extent.
Criteria for Identifying Health Research Gaps, Needs, and Priorities
Numbers in columns may add up to more than the total N or 100% since some studies employed more than one criterion
About two-thirds of the studies included researchers (66%) and clinicians (69%) as stakeholders (see Appendix E in the Supplementary Information). Patients and the public were involved in 59% of the studies. A smaller proportion included policy makers (20%), funders (13%), product makers (8%), payers (5%), and purchasers (2%) as stakeholders. Nearly half of the studies (51%) relied on stakeholder organizations to identify stakeholders (see Appendix F in the Supplementary Information). A quarter of studies (26%) used purposive sampling and some convenience sampling (11%). Few (9%) used snowball sampling to identify stakeholders. Only a minor fraction of studies, seven of the 167 (4%), reported some type of effectiveness evaluation. 25 – 31
Our scoping review revealed that approaches to identifying gaps, needs, and priorities are less likely to occur as discrete processes and more often involve a combination of exercises. Approaches encompassing multiple exercises (e.g., gaps and needs) were far more prevalent than singular standalone exercises (e.g., gaps only) (73% vs. 27%). Findings underscore the varying importance placed on gaps, needs, and priorities, which reflect key principles of the Value of Information approach (i.e., not all gaps are important, addressing gaps do not necessarily address needs nor does addressing needs necessarily address priorities). 32
Findings differ from Nyanchoka et al.’s review in which studies involving the identification of gaps only outnumbered studies involving both gaps and priorities. 7 However, Nyanchoka et al. relied on author definitions to categorize exercises, whereas our study made designations based on our review of the activities described in the article and applied definitions drawn from the literature. 3 , 4 Lack of consensus on definitions of gaps and priority setting has been noted in the literature. 33 , 34 To the authors’ knowledge, no prior scoping review has focused on methods related to the identification of “research needs.” Findings underscore the need to develop and apply more consistent taxonomy to this growing field of research.
More than 40% of studies employed methods with a structured protocol including JLA PSP, ENHR, CHRNI, World Café, and the Dialogue model. 10 , 35 – 40 The World Café and Dialogue models particularly value the experiential perspectives of stakeholders. The World Café centers on creating a special environment, often modeled after a café, in which rounds of multi-stakeholder, small group, conversations are facilitated and prefaced with questions designed for the specific purpose of the session. Insights and results are reported and shared back to the entire group with no expectation to achieve consensus, but rather diverse perspectives are encouraged. 36 The Dialogue model is a multi-stakeholder, participatory, priority setting method involving the following phases: exploratory (informal discussions), consultation (separate stakeholder consultations), prioritization (stakeholder ratings), and integration (dialog between stakeholders). 39 Findings may indicate a trend away from non-replicable methods to approaches that afford greater transparency and reproducibility. 41 For instance, of the 17 studies published between 2000 and 2009, none had employed CHNRI and 6% used JLA PSP compared to the 141 studies between 2010 and 2019 in which 8% applied CHNRI and 32% JLA PSP. However, notable variations in implementing CHNRI and JLA PSP have been observed. 41 – 43 Though these protocols help to ensure a more standardized process, which is essential when testing the effectiveness of methods, such evaluations are infrequent but necessary to establish the usefulness of replicable methods.
Convening workshops, meetings, or conferences was the method used by the greatest proportion of studies (37%). The operationalization of even this singular method varied widely in duration (e.g., single vs. multi-day conferences), format (e.g., expert panel presentations, breakout discussion groups), processes (e.g., use of formal/informal consensus methods), and composition of stakeholders. The operationalization of other methods (e.g., quantitative, qualitative) also exhibited great diversity.
The use of explicit criteria to determine gaps, needs, or priorities is a key component of certain structured protocols 40 , 44 and frameworks. 9 , 45 In our scoping review, the criterion applied most frequently across studies (71%) was “importance to stakeholders” followed by potential value (31%) and feasibility (18%). Stakeholder values are being incorporated into the identification of gaps, needs, and exercises across a significant proportion of studies, but how this is operationalized varies widely across studies. For instance, the CHNRI typically employs multiple criteria that are scored by technical experts and these scores are then weighted based on stakeholder ratings of their relative importance. Other studies totaled scores across multiple criteria, whereas JLA PSP asks multiple stakeholders to rank the top ten priorities. The importance of involving stakeholders, especially patients and the public, in priority setting is increasingly viewed as vital to ensuring the needs of end users are met, 46 , 47 particularly in light of evidence demonstrating mismatches between the research interests of patients and researchers and clinicians. 48 – 50 In our review, clinicians (69%) and researchers (66%) were the most widely represented stakeholder groups across studies. Patients and the public (e.g., caregivers) were included as stakeholders in 59% of the studies. Only a small fraction of studies involved exercises in which stakeholders were limited to researchers only. Patients and the public were involved as stakeholders in 12% of studies published between 2000 and 2009 compared to 60% of studies between 2010 and 2019. Findings may reflect a trend away from researchers traditionally serving as one of the sole drivers of determining which research topics should be pursued.
More than half of the studies reported relying on stakeholder organizations to identify participants. Partnering with stakeholder organizations has been noted as one of the primary methods for identifying stakeholders for priority setting exercises. 34 Purposive sampling was the next most frequently used stakeholder identification method. In contrast, convenience sampling (e.g., recommendations by study team) and snowball sampling (e.g., identified stakeholders refer other stakeholders who then refer additional stakeholders) were not as frequently employed, but were documented as common methods in a prior review conducted almost a decade ago. 14 The greater use of stakeholder organizations than convenience or snowball sampling may be partly due to the more recent proliferation of published studies using structured protocols like JLA PSP, which rely heavily on partnerships with stakeholder organizations. Though methods such as snowball sampling may introduce more bias than random sampling, 14 there are no established best practices for stakeholder identification methods. 51 Nearly a quarter of studies provided either unclear or no information on stakeholder identification methods, which has been documented as a barrier to comparing across studies and assessing the validity of research priorities. 34
Determining the effectiveness of gaps, needs, and priority exercises is challenging given that outcome evaluations are rarely conducted. Only seven studies reported conducting an evaluation. 25 – 31 Evaluations varied with respect to their focus on process- (e.g., balanced stakeholder representation, stakeholder satisfaction) versus outcome-related impact (e.g., prioritized topics funded, knowledge production, benefits to health). There is no consensus on what constitutes optimal outcomes, which has been found to vary by discipline. 52
More than 90% of studies involved exercises related to physical health in contrast to a minor portfolio of work being dedicated to psychological health, which may be an indication of the low priority placed on psychological health policy research. Understanding whether funding decisions for physical versus psychological health research are similarly or differentially governed by more systematic, formal processes may be important to the extent that this affects the effective targeting of funds.
Limitations
By limiting studies to those supported or conducted by funding organizations, we may have excluded global, national, or local priority setting exercises. In addition, our scoping review categorized approaches according to the actual exercises conducted and definitions provided in the scientific literature rather than relying on the terminology employed by studies. This resulted in instances in which the category assigned to an exercise within our scoping review could diverge from the category employed by the study authors. Lastly, this study’s findings are subject to limitations often characteristic of scoping reviews such as publication bias, language bias, lack of quality assessment, and search, inclusion, and extraction biases. 53
Conclusions
The diversity and growing establishment of formal processes and methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are characteristic of a developing field. Even with the emergence of more structured and systematic approaches, the inconsistent categorization and definition of gaps, needs, and priorities inhibit efforts to evaluate the effectiveness of varied methods and processes, such efforts are rare and sorely needed to build an evidence base to guide best practices. The immense variation occurring within structured protocols, across different combinations of disparate methods, and even within singular methods, further emphasizes the importance of using clearly defined approaches, which are essential to conducting investigations of the effectiveness of these varied approaches. The recent development of reporting guidelines for priority setting for health research may facilitate more consistent and clear documentation of processes and methods, which includes the many facets of involving stakeholders. 34 To ensure optimal targeting of funds to meet the greatest areas of need and maximize outcomes, a much more robust evidence base is needed to ascertain the effectiveness of methods used to identify research gaps, needs, and priorities.
(PDF 1205 kb)
Acknowledgements
This scoping review is part of research that was sponsored by Defense Centers of Excellence for Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury (now Psychological Health Center of Excellence).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
APA Citation Generator
MLA Citation Generator
Chicago Citation Generator
Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Present the Limitations of the Study Examples
What are the limitations of a study?
The limitations of a study are the elements of methodology or study design that impact the interpretation of your research results. The limitations essentially detail any flaws or shortcomings in your study. Study limitations can exist due to constraints on research design, methodology, materials, etc., and these factors may impact the findings of your study. However, researchers are often reluctant to discuss the limitations of their study in their papers, feeling that bringing up limitations may undermine its research value in the eyes of readers and reviewers.
In spite of the impact it might have (and perhaps because of it) you should clearly acknowledge any limitations in your research paper in order to show readers—whether journal editors, other researchers, or the general public—that you are aware of these limitations and to explain how they affect the conclusions that can be drawn from the research.
In this article, we provide some guidelines for writing about research limitations, show examples of some frequently seen study limitations, and recommend techniques for presenting this information. And after you have finished drafting and have received manuscript editing for your work, you still might want to follow this up with academic editing before submitting your work to your target journal.
Why do I need to include limitations of research in my paper?
Although limitations address the potential weaknesses of a study, writing about them toward the end of your paper actually strengthens your study by identifying any problems before other researchers or reviewers find them.
Furthermore, pointing out study limitations shows that you’ve considered the impact of research weakness thoroughly and have an in-depth understanding of your research topic. Since all studies face limitations, being honest and detailing these limitations will impress researchers and reviewers more than ignoring them.

Where should I put the limitations of the study in my paper?
Some limitations might be evident to researchers before the start of the study, while others might become clear while you are conducting the research. Whether these limitations are anticipated or not, and whether they are due to research design or to methodology, they should be clearly identified and discussed in the discussion section —the final section of your paper. Most journals now require you to include a discussion of potential limitations of your work, and many journals now ask you to place this “limitations section” at the very end of your article.
Some journals ask you to also discuss the strengths of your work in this section, and some allow you to freely choose where to include that information in your discussion section—make sure to always check the author instructions of your target journal before you finalize a manuscript and submit it for peer review .
Limitations of the Study Examples
There are several reasons why limitations of research might exist. The two main categories of limitations are those that result from the methodology and those that result from issues with the researcher(s).
Common Methodological Limitations of Studies
Limitations of research due to methodological problems can be addressed by clearly and directly identifying the potential problem and suggesting ways in which this could have been addressed—and SHOULD be addressed in future studies. The following are some major potential methodological issues that can impact the conclusions researchers can draw from the research.
Issues with research samples and selection
Sampling errors occur when a probability sampling method is used to select a sample, but that sample does not reflect the general population or appropriate population concerned. This results in limitations of your study known as “sample bias” or “selection bias.”
For example, if you conducted a survey to obtain your research results, your samples (participants) were asked to respond to the survey questions. However, you might have had limited ability to gain access to the appropriate type or geographic scope of participants. In this case, the people who responded to your survey questions may not truly be a random sample.
Insufficient sample size for statistical measurements
When conducting a study, it is important to have a sufficient sample size in order to draw valid conclusions. The larger the sample, the more precise your results will be. If your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to identify significant relationships in the data.
Normally, statistical tests require a larger sample size to ensure that the sample is considered representative of a population and that the statistical result can be generalized to a larger population. It is a good idea to understand how to choose an appropriate sample size before you conduct your research by using scientific calculation tools—in fact, many journals now require such estimation to be included in every manuscript that is sent out for review.
Lack of previous research studies on the topic
Citing and referencing prior research studies constitutes the basis of the literature review for your thesis or study, and these prior studies provide the theoretical foundations for the research question you are investigating. However, depending on the scope of your research topic, prior research studies that are relevant to your thesis might be limited.
When there is very little or no prior research on a specific topic, you may need to develop an entirely new research typology. In this case, discovering a limitation can be considered an important opportunity to identify literature gaps and to present the need for further development in the area of study.
Methods/instruments/techniques used to collect the data
After you complete your analysis of the research findings (in the discussion section), you might realize that the manner in which you have collected the data or the ways in which you have measured variables has limited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results.
For example, you might realize that you should have addressed your survey questions from another viable perspective, or that you were not able to include an important question in the survey. In these cases, you should acknowledge the deficiency or deficiencies by stating a need for future researchers to revise their specific methods for collecting data that includes these missing elements.
Common Limitations of the Researcher(s)
Study limitations that arise from situations relating to the researcher or researchers (whether the direct fault of the individuals or not) should also be addressed and dealt with, and remedies to decrease these limitations—both hypothetically in your study, and practically in future studies—should be proposed.
Limited access to data
If your research involved surveying certain people or organizations, you might have faced the problem of having limited access to these respondents. Due to this limited access, you might need to redesign or restructure your research in a different way. In this case, explain the reasons for limited access and be sure that your finding is still reliable and valid despite this limitation.
Time constraints
Just as students have deadlines to turn in their class papers, academic researchers might also have to meet deadlines for submitting a manuscript to a journal or face other time constraints related to their research (e.g., participants are only available during a certain period; funding runs out; collaborators move to a new institution). The time available to study a research problem and to measure change over time might be constrained by such practical issues. If time constraints negatively impacted your study in any way, acknowledge this impact by mentioning a need for a future study (e.g., a longitudinal study) to answer this research problem.
Conflicts arising from cultural bias and other personal issues
Researchers might hold biased views due to their cultural backgrounds or perspectives of certain phenomena, and this can affect a study’s legitimacy. Also, it is possible that researchers will have biases toward data and results that only support their hypotheses or arguments. In order to avoid these problems, the author(s) of a study should examine whether the way the research problem was stated and the data-gathering process was carried out appropriately.
Steps for Organizing Your Study Limitations Section
When you discuss the limitations of your study, don’t simply list and describe your limitations—explain how these limitations have influenced your research findings. There might be multiple limitations in your study, but you only need to point out and explain those that directly relate to and impact how you address your research questions.
We suggest that you divide your limitations section into three steps: (1) identify the study limitations; (2) explain how they impact your study in detail; and (3) propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives. By following this sequence when discussing your study’s limitations, you will be able to clearly demonstrate your study’s weakness without undermining the quality and integrity of your research.
Step 1. Identify the limitation(s) of the study
- This part should comprise around 10%-20% of your discussion of study limitations.
The first step is to identify the particular limitation(s) that affected your study. There are many possible limitations of research that can affect your study, but you don’t need to write a long review of all possible study limitations. A 200-500 word critique is an appropriate length for a research limitations section. In the beginning of this section, identify what limitations your study has faced and how important these limitations are.
You only need to identify limitations that had the greatest potential impact on: (1) the quality of your findings, and (2) your ability to answer your research question.

Step 2. Explain these study limitations in detail
- This part should comprise around 60-70% of your discussion of limitations.
After identifying your research limitations, it’s time to explain the nature of the limitations and how they potentially impacted your study. For example, when you conduct quantitative research, a lack of probability sampling is an important issue that you should mention. On the other hand, when you conduct qualitative research, the inability to generalize the research findings could be an issue that deserves mention.
Explain the role these limitations played on the results and implications of the research and justify the choice you made in using this “limiting” methodology or other action in your research. Also, make sure that these limitations didn’t undermine the quality of your dissertation .
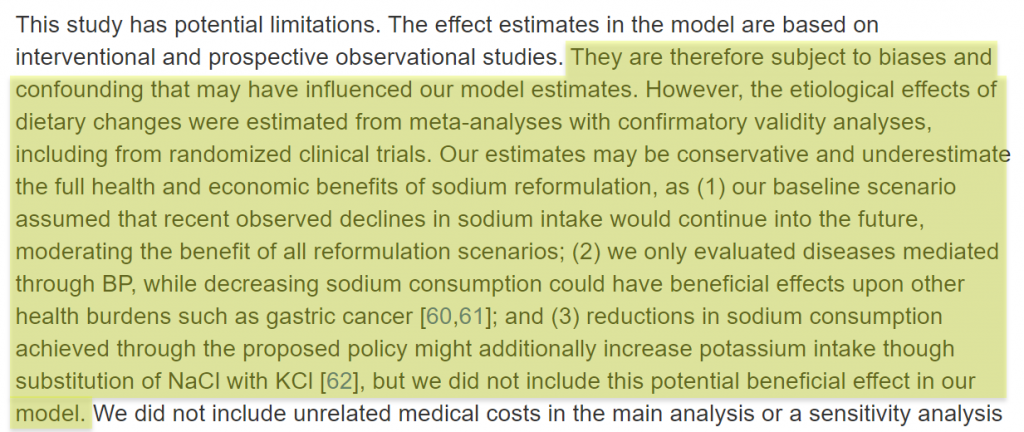
Step 3. Propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives (optional)
- This part should comprise around 10-20% of your discussion of limitations.
After acknowledging the limitations of the research, you need to discuss some possible ways to overcome these limitations in future studies. One way to do this is to present alternative methodologies and ways to avoid issues with, or “fill in the gaps of” the limitations of this study you have presented. Discuss both the pros and cons of these alternatives and clearly explain why researchers should choose these approaches.
Make sure you are current on approaches used by prior studies and the impacts they have had on their findings. Cite review articles or scientific bodies that have recommended these approaches and why. This might be evidence in support of the approach you chose, or it might be the reason you consider your choices to be included as limitations. This process can act as a justification for your approach and a defense of your decision to take it while acknowledging the feasibility of other approaches.
P hrases and Tips for Introducing Your Study Limitations in the Discussion Section
The following phrases are frequently used to introduce the limitations of the study:
- “There may be some possible limitations in this study.”
- “The findings of this study have to be seen in light of some limitations.”
- “The first is the…The second limitation concerns the…”
- “The empirical results reported herein should be considered in the light of some limitations.”
- “This research, however, is subject to several limitations.”
- “The primary limitation to the generalization of these results is…”
- “Nonetheless, these results must be interpreted with caution and a number of limitations should be borne in mind.”
- “As with the majority of studies, the design of the current study is subject to limitations.”
- “There are two major limitations in this study that could be addressed in future research. First, the study focused on …. Second ….”
For more articles on research writing and the journal submissions and publication process, visit Wordvice’s Academic Resources page.
And be sure to receive professional English editing and proofreading services , including paper editing services , for your journal manuscript before submitting it to journal editors.
Wordvice Resources
Proofreading & Editing Guide
Writing the Results Section for a Research Paper
How to Write a Literature Review
Research Writing Tips: How to Draft a Powerful Discussion Section
How to Captivate Journal Readers with a Strong Introduction
Tips That Will Make Your Abstract a Success!
APA In-Text Citation Guide for Research Writing
Additional Resources
- Diving Deeper into Limitations and Delimitations (PhD student)
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Limitations of the Study (USC Library)
- Research Limitations (Research Methodology)
- How to Present Limitations and Alternatives (UMASS)
Article References
Pearson-Stuttard, J., Kypridemos, C., Collins, B., Mozaffarian, D., Huang, Y., Bandosz, P.,…Micha, R. (2018). Estimating the health and economic effects of the proposed US Food and Drug Administration voluntary sodium reformulation: Microsimulation cost-effectiveness analysis. PLOS. https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002551
Xu, W.L, Pedersen, N.L., Keller, L., Kalpouzos, G., Wang, H.X., Graff, C,. Fratiglioni, L. (2015). HHEX_23 AA Genotype Exacerbates Effect of Diabetes on Dementia and Alzheimer Disease: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. PLOS. Retrieved from https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1001853

Managing Multiple Organizational Goals in Turbulent Environments pp 177–185 Cite as
Limitations and Future Research Directions
- Feifei Yang 4 ,
- Mirjam Goudsmit 5 &
- George Shinkle 6
- First Online: 01 September 2022
252 Accesses
Research is often conducted progressively. Acknowledging limitations helps to define what is yet to be investigated and can provide avenues for future research. This chapter presents the limitations of this research and suggests ideas for future research directions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Aguinis, H., Boyd, B. K., Pierce, C. A., & Short, J. C. (2011). Walking new avenues in management research methods and theories: Bridging micro and macro domains. Journal of Management, 37 (2), 395–403.
Article Google Scholar
Ansoff, H. I. (1979). Strategic management . Macmillan.
Book Google Scholar
Ansoff, H. I. (1984). Implanting strategic management . Prentice Hall.
Google Scholar
Ansoff, H. I. (1987). The emerging paradigm of strategic behavior. Strategic Management Journal, 8 (6), 501–515.
Bagozzi, R., & Phillips, L. (1982). Representing and testing organizational theories: A holistic construal. Administrative Science Quarterly, 27 , 459–489.
Barnard, C. I. (1938). The functions of the executive . Harvard University Press.
Bascle, G. (2008). Controlling for endogeneity with instrumental variables in strategic management research. Strategic Organization, 6 (3), 285–327.
Bluedorn, A. C., Kalliath, T. J., Strube, M. J., & Martin, G. D. (1999). Polychronicity and the inventory of polychronic values (IPV) the development of an instrument to measure a fundamental dimension of organizational culture. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 14 (3/4), 205–231.
Cardinal, L. B. (2001). Technological innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: The use of organizational control in managing research and development. Organization Science, 12 (1), 19–3.
Cardinal, L. B., Sitkin, S. B., & Long, C. P. (2004). Balancing and rebalancing in the creation and evolution of organizational control. Organization Science, 15 (4), 411–431.
Cyert, R. M., & March, J. G. (1963). A behavioral theory of the firm . Prentice Hall.
Dess, G. G., Newport, S., & Rasheed, A. M. A. (1993). Configuration research in strategic management: Key issues and suggestions. Journal of Management, 19 (4), 775–795.
Eckert, C., & Hohberger, J. (2022). Addressing endogeneity without instrumental variables: An evaluation of the Gaussian Copula approach for management research. Journal of Management , forthcoming.
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1985). Control: Organizational and economic approaches. Management Science, 31 (2), 134–149.
Eisenhardt, K. M., Furr, N. R., & Bingham, C. B. (2010). Microfoundations of performance: Balancing efficiency and flexibility in dynamic environments. Organization Science, 21 (6), 1263–1273.
Evans, K. R., Landry, T. D., Li, P. C., & Zou, S. (2007). How sales controls affect job-related outcomes: The role of organizational sales-related psychological climate perceptions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 35 (3), 445–459.
Evans, M. G. (1985). A Monte Carlo study of the effects of correlated method variance in moderated multiple regression analysis. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 36 (3), 305–323.
Fayol, H. (1949). General and industrial management . Pitman Publishing.
Fiegenbaum, A., Hart, S., & Schendel, D. (1996). Strategic reference point theory. Strategic Management Journal, 17 (3), 219–235.
Fischer, R. (2004). Standardization to account for cross-cultural response bias a classification of score adjustment procedures and review of research in JCCP. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 35 (3), 263–282.
Frey, B. S., Homberg, F., & Osterloh, M. (2013). Organizational control systems and pay-for-performance in the public service. Organization Studies, 34 (7), 949–972.
Gaba, V., & Greve, H. R. (2019). Safe or profitable? The pursuit of conflicting goals. Organization Science, 30 (4), 647–667.
Gagné, M., & Deci, E. L. (2005). Self-determination theory and work motivation. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 26 (4), 331–362.
Govindarajan, V. (1988). A contingency approach to strategy implementation at the business-unit level: Integrating administrative mechanisms with strategy. Academy of Management Journal, 31 (4), 828–853.
Govindarajan, V., & Fisher, J. (1990). Strategy, control systems, and resource sharing: Effects on business-unit performance. Academy of Management Journal, 33 (2), 259–285.
Greckhamer, T., Furnari, S., Fiss, P. C., & Aguilera, R. V. (2018). Studying configurations with qualitative comparative analysis: Best practices in strategy and organization research. Strategic Organization, 16 (4), 482–495.
Harris, M. L., Collins, R. W., & Hevner, A. R. (2009). Control of flexible software development under uncertainty. Information Systems Research, 20 (3), 400–419.
Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P. (1996). The balanced scorecard: Translating strategy into action . Harvard Business School Press.
Kirsch, L. J. (1996). The management of complex tasks in organizations: Controlling the systems development process. Organization Science, 7 (1), 1–21.
Kreutzer, M., Cardinal, L. B., Walter, J., & Lechner, C. (2016). Formal and Informal control as complement or substitute? The role of the task environment. Strategy Science, 1 (4), 235–255.
Kreutzer, M., Walter, J., & Cardinal, L. B. (2015). Organizational control as antidote to politics in the pursuit of strategic initiative performance. Strategic Management Journal, 36 (9), 1317–1337.
Levinthal, D. A., & Rerup, C. (2020). The plural of goal: Learning in a world of ambiguity. Organization Science, 32 (3), 527–543.
Li, H., & Zhang, Y. (2007). The role of managers political networking and functional experience in new venture performance: Evidence from Chinas transition economy. Strategic Management Journal, 28 (8), 791.
Lindenberg, S., & Foss, N. J. (2011). Managing joint production motivation: The role of goal framing and governance mechanisms (article). Academy of Management Review, 36 (3), 500–525.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (1990). A theory of goal setting and task performance . Prentice Hall.
Locke, E. A., Shaw, K. N., Saari, L. M., & Latham, G. P. (1981). Goal setting and task performance: 1969–1980. Psychological Bulletin, 90 (1), 125.
Marginson, D. E. W. (2002). Management control systems and their effects on strategy formation at middle-management levels: evidence from a U.K. organization. Strategic Management Journal , 23(11), 1019–1031.
Misangyi, V. F., Greckhamer, T., Furnari, S., Fiss, P. C., Crilly, D., & Aguilera, R. (2017). Embracing causal complexity: The emergence of a neo-configurational perspective. Journal of Management, 42 (1), 255–282.
Ouchi, W. G. (1977). The relaionship between organizational structure and organizational control. Academy of Management Journal, 22 (1), 95–113.
Papalexandris, A., Ioannou, G., Prastacos, G., & Soderquist, K. E. (2005). An integrated methodology for putting the balanced scorecard into action. European Management Journal, 23 (2), 214–227.
Phillips, L. W. (1981). Assessing measurement error in key informant reports: A methodological note on organizational analysis in marketing. Journal of Marketing Research, 18 (4), 395–415.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88 (5), 879.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55 (1), 68–78.
Shinkle, G. A., Kriauciunas, A. P., & Hundley, G. (2013). Why pure strategies may be wrong for transition economy firms. Strategic Management Journal, 34 (10), 1244–1254.
Shinkle, G. A., Yang, M. M., Yang, F., Elshaw, J., & Schleicher, D. J. (2021). Enacting formal controls in information system development: Process guidance and goal importance. Information & Management, 58 , 103430.
Short, J. C., Payne, G. T., & Ketchen, D. J. (2008). Research on organizational configurations: Past accomplishments and future challenges. Journal of Management, 34 (6), 1053–1079.
Siemsen, E., Roth, A., & Oliveira, P. (2010). Common method bias in regression models with linear, quadratic, and interaction effects. Organizational Research Methods, 13 (3), 456–476.
Simon, H. A. (1947). Administrative behavior: A study of decision-making processes in administrative organizations . Macmillan.
Sitkin, S. B., Cardinal, L. B., & Bijlsma-Frankema, K. M. (2010). Organizational control . Cambridge University Press.
Snell, S. A. (1992). Control theory in strategic human resource management: The mediating effect of administrative information. Academy of Management Journal, 35 (2), 292–327.
Turner, K. L., & Makhija, M. V. (2006). The role of organizational controls in managing knowledge. Academy of Management Review, 31 (1), 197–217.
Weber, M. (1947). Theory of social and economic organization . Free Press.
Weibel, A. (2007). Formal Control and Trustworthiness Shall the Twain Never Meet? Group & Organization Management, 32 (4), 500–517.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Asia Europe Business School, Faculty of Economics and Management, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
Feifei Yang
Nijmegen School of Management, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Mirjam Goudsmit
UNSW-Sydney Business School, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
George Shinkle
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Feifei Yang .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Yang, F., Goudsmit, M., Shinkle, G. (2022). Limitations and Future Research Directions. In: Managing Multiple Organizational Goals in Turbulent Environments. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5319-4_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5319-4_10
Published : 01 September 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-5318-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-5319-4
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Diving Deeper into Limitations and Delimitations

If you are working on a thesis, dissertation, or other formal research project, chances are your advisor or committee will ask you to address the delimitations of your study. When faced with this request, many students respond with a puzzled look and then go on to address what are actually the study’s limitations.
In a previous article , we covered what goes into the limitations, delimitations, and assumptions sections of your thesis or dissertation. Here, we will dive a bit deeper into the differences between limitations and delimitations and provide some helpful tips for addressing them in your research project—whether you are working on a quantitative or qualitative study.
Acknowledging Weaknesses vs. Defining Boundaries
These concepts are easy to get confused because both limitations and delimitations restrict (or limit) the questions you’ll be able to answer with your study, most notably in terms of generalizability.
However, the biggest difference between limitations and delimitations is the degree of control you have over them—that is, how much they are based in conscious, intentional choices you made in designing your study.
Limitations occur in all types of research and are, for the most part, outside the researcher’s control (given practical constraints, such as time, funding, and access to populations of interest). They are threats to the study’s internal or external validity.
Limitations may include things such as participant drop-out, a sample that isn’t entirely representative of the desired population, violations to the assumptions of parametric analysis (e.g., normality, homogeneity of variance), the limits of self-report, or the absence of reliability and validity data for some of your survey measures.
Limitations can get in the way of your being able to answer certain questions or draw certain types of inferences from your findings. Therefore, it’s important to acknowledge them upfront and make note of how they restrict the conclusions you’ll be able to draw from your study. Frequently, limitations can get in the way of our ability to generalize our findings to the larger populations or to draw causal conclusions, so be sure to consider these issues when you’re thinking about the potential limitations of your study.
Delimitations are also factors that can restrict the questions you can answer or the inferences you can draw from your findings. However, they are based on intentional choices you make a priori (i.e., as you’re designing the study) about where you’re going to draw the boundaries of your project. In other words, they define the project’s scope.
Like limitations, delimitations are a part of every research project, and this is not a bad thing. In fact, it’s very important! You can’t study everything at once. If you try to do so, your project is bound to get huge and unwieldy, and it will become a lot more difficult to interpret your results or come to meaningful conclusions with so many moving parts. You have to draw the line somewhere, and the delimitations are where you choose to draw these lines.
One of the clearest examples of a delimitation that applies to almost every research project is participant exclusion criteria. In conducting either a quantitative or a qualitative study, you will have to define your population of interest. Defining this population of interest means that you will need to articulate the boundaries of that population (i.e., who is not included). Those boundaries are delimitations.
For example, if you’re interested in understanding the experiences of elementary school teachers who have been implementing a new curriculum into their classrooms, you probably won’t be interviewing or sending a survey to any of the following people: non-teachers, high-school teachers, college professors, principals, parents of elementary school children, or the children themselves. Furthermore, you probably won’t be talking to elementary school teachers who have not yet had the experience of implementing the curriculum in question. You would probably only choose to gather data from elementary school teachers who have had this experience because that is who you’re interested in for the purposes of your study. Perhaps you’ll narrow your focus even more to elementary school teachers in a particular school district who have been teaching for a particular length of time. The possibilities can go on. These are choices you will need to make, both for practical reasons (i.e., the population you have access to) and for the questions you are trying to answer.
Of course, for this particular example, this does not mean that it wouldn’t be interesting to also know what principals think about the new curriculum. Or parents. Or elementary school children. It just means that, for the purposes of your project and your research questions, you’re interested in the experience of the teachers, so you’re excluding anyone who does not meet those criteria. Having delimitations to your population of interest also means that you won’t be able to answer any questions about the experiences of those other populations; this is ok because those populations are outside of the scope of your project . As interesting as their experiences might be, you can save these questions for another study. That is the part of the beauty of research: there will always be more studies to do, more questions to ask. You don’t have to (and can’t) do it all in one project.
Continuing with the previous example, for instance, let’s suppose that the problem you are most interested in addressing is the fact that we know relatively little about elementary school teachers’ experiences of implementing a new curriculum. Perhaps you believe that knowing more about teachers’ experiences could inform their training or help administrators know more about how to support their teachers. If the identified problem is our lack of knowledge about teachers’ experiences, and your research questions focus on better understanding these experiences, that means that you are choosing not to focus on other problems or questions, even those that may seem closely related. For instance, you are not asking how effective the new curriculum is in improving student test scores or graduation rates. You might think that would be a very interesting question, but it will have to wait for another study. In narrowing the focus of your research questions, you limit your ability to answer other questions, and again, that’s ok. These other questions may be interesting and important, but, again, they are beyond the scope of your project .
Common Examples of Limitations
While each study will have its own unique set of limitations, some limitations are more common in quantitative research, and others are more common in qualitative research.
In quantitative research, common limitations include the following:
– Participant dropout
– Small sample size, low power
– Non-representative sample
– Violations of statistical assumptions
– Non-experimental design, lack of manipulation of variables, lack of controls
– Potential confounding variables
– Measures with low (or unknown) reliability or validity
– Limits of an instrument to measure the construct of interest
– Data collection methods (e.g., self-report)
– Anything else that might limit the study’s internal or external validity
In qualitative research, common limitations include the following:
– Lack of generalizability of findings (not the goal of qualitative research, but still worth mentioning as a limitation)
– Inability to draw causal conclusions (again, not the goal of qualitative research, but still worth mentioning)
– Researcher bias/subjectivity (especially if there is only one coder)
– Limitations in participants’ ability/willingness to share or describe their experiences
– Any factors that might limit the rigor of data collection or analysis procedures
Common Examples of Delimitations
As noted above, the two most common sources of delimitations in both quantitative and qualitative research include the following:
– Inclusion/exclusion criteria (or how you define your population of interest)
– Research questions or problems you’ve chosen to examine
Several other common sources of delimitations include the following:
– Theoretical framework or perspective adopted
– Methodological framework or paradigm chosen (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods)
– In quantitative research, the variables you’ve chosen to measure or manipulate (as opposed to others)
Whether you’re conducting a quantitative or qualitative study, you will (hopefully!) have chosen your research design because it is well suited to the questions you’re hoping to answer. Because these questions define the boundaries or scope of your project and thus point to its delimitations, your research design itself will also be related to these delimitations.
Questions to Ask Yourself
As you are considering the limitations and delimitations of your project, it can be helpful to ask yourself a few different questions.
Questions to help point out your study’s limitations :
1. If I had an unlimited budget, unlimited amounts of time, access to all possible populations, and the ability to manipulate as many variables as I wanted, how would I design my study differently to be better able to answer the questions I want to answer? (The ways in which your study falls short of this will point to its limitations.)
2. Are there design issues that get in the way of my being able to draw causal conclusions?
3. Are there sampling issues that get in the way of my being able to generalize my findings?
4. Are there issues related to the measures I’m using or the methods I’m using to collect data? Do I have concerns about participants telling the truth or being able to provide accurate responses to my questions?
5. Are there any other factors that might limit my study’s internal or external validity?
Questions that help point out your study’s delimitations :
1. What are my exclusion criteria? Who did I not include in my study, and why did I make this choice?
2. What questions did I choose not to address in my study? (Of course, the possibilities are endless here, but consider related questions that you chose not to address.)
3. In what ways did I narrow the scope of my study in order to hone in on a particular issue or question?
4. What other methodologies did I not use that might have allowed me to answer slightly different questions about the same topic?
How to Write About Limitations and Delimitations
Remember, having limitations and delimitations is not a bad thing. They’re present in even the most rigorous research. The important thing is to be aware of them and to acknowledge how they may impact your findings or the conclusions you can draw.
In fact, writing about them and acknowledging them gives you an opportunity to demonstrate that you can think critically about these aspects of your study and how they impact your findings, even if they were out of your control.
Keep in mind that your study’s limitations will likely point to important directions for future research. Therefore, when you’re getting ready to write about your recommendations for future research in your discussion, remember to refer back to your limitations section!
As you write about your delimitations in particular, remember that they are not weaknesses, and you don’t have to apologize for them. Good, strong research projects have clear boundaries. Also, keep in mind that you are the researcher and you can choose whatever delimitations you want for your study. You’re in control of the delimitations. You just have to be prepared—both in your discussion section and in your dissertation defense itself—to justify the choices you make and acknowledge how these choices impact your findings.
Browse More on PhDStudent

Everything You Need to Know About References and Citations: Part 1
When you conduct your research, it is important to record the details of all the information you find to provide accurate references, …

How to Write a Proposal: For a Master’s Thesis or Dissertation
Note: Many thanks to fellow PhDStudent blogger Ryan Krone for his contributions and insight to this post. Your thesis/dissertation proposal provides an …

How to Find Free Money for Graduate School Part 2
Getting into graduate school is already a challenge on its own, and funding the program once admitted is even harder. Graduate studies …

How to Find Free Money for Graduate School
You’ve finally earned your Bachelor’s degree and have made it into graduate school. Whether you already have massive student loans from undergrad …

Part 3 of How to Pick Your Defense Committee
What strategies can a doctoral student employ to maneuver the trials and tribulations of a dissertation committee? In Part 2, we …
Best Dissertation Proofreading and Editing Tips to Make Your Work Spotless
You’ve heard this statement many times before: “the dissertation is the most important project you’ve ever worked on.” That may sound like …

Part 2 of How to Pick Your Defense Committee
Choosing a committee can be a daunting task for a doctoral student. We’ve already covered two strategies that can help you through this …

Part 1 of How to Pick Your Defense Committee
So you’re ready to pick your committee members; there are a few things to keep in mind first—after all, it is a …

Intro To Series on How to Pick Your Defense Committee
Choosing the right defense committee can potentially be the difference between a smooth transition of receiving your doctoral degree or dodging bullets …

On Babies and Dissertations: Part 3
I recently had the experience of expecting my first baby a month before I graduated. Throughout the process, I accidentally learned several …

On Babies and Dissertations: Part 2

On Babies and Dissertations: Part 1
I recently had the experience of expecting my first baby a month before I graduated and accidentally learned tips on graduating on time with a …
Click here to cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Copyright © 2024 PhDStudent.com. All rights reserved. Designed by Divergent Web Solutions, LLC .

Understanding the Limitations of Research Ethics in Management Studies
Table of Contents
As researchers, we must adhere to the highest ethical standards to ensure the integrity of our work. However, it’s important to understand the limitations of research ethics to avoid any unintentional negative consequences. In this blog, we’ll explore the limitations of research ethics in management studies and how to address them.
What are Research Ethics?
Research ethics are a set of moral principles that guide researchers on how to conduct research in an ethical manner. These principles include informed consent, confidentiality, protection of participants from harm, and the right to withdraw from the study.
Limitations of Research Ethics
Despite the importance of research ethics, there are limitations that can affect the validity and generalizability of the research findings. Some of the limitations of research ethics in management studies include:
1. Lack of diversity in the sample population
The sample population used in research studies is often limited to a specific demographic, which may not be representative of the larger population. This can result in biased findings and limit the generalizability of the research.
2. Ethnocentrism
Researchers may unknowingly impose their cultural beliefs and values on the research participants, leading to biased data collection and analysis.
3. Difficulty in obtaining informed consent
In some cases, obtaining informed consent from participants can be challenging. For example, if the participants are minors or have cognitive impairments, they may not be able to provide informed consent, which can limit the study’s validity.
4. Limited access to participants
Some populations may be difficult to access, such as incarcerated individuals or those with certain medical conditions, which can limit the generalizability of the research findings.
5. Limited funding
Research studies often require significant funding, which can limit the sample size or scope of the study. This can impact the validity and generalizability of the research.
Addressing the Limitations
To address the limitations of research ethics, researchers can take several steps. For example, they can:
- Ensure a diverse sample population that is representative of the larger population.
- Take measures to avoid ethnocentrism, such as working with a diverse team and being mindful of personal biases.
- Use alternative methods for obtaining informed consent, such as proxy consent for participants who are unable to provide informed consent.
- Work with community organizations or advocacy groups to gain access to hard-to-reach populations.
- Look for alternative sources of funding or collaborate with other researchers to increase the scope of the study.
Research ethics are crucial to ensure the integrity of our work, but it’s important to understand their limitations. By acknowledging and addressing these limitations, we can increase the validity and generalizability of our research findings. As researchers, it’s our responsibility to continuously strive for ethical and high-quality research.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Research Methodology for Management Decisions
1 Research Methodology: An Overview
- Meaning of Research
- Research Methodology
- Research Method
- Business Research Method
- Types of Research
- Importance of business research
- Role of research in important areas
2 Steps for Research Process
- Research process
- Define research problems
- Research Problem as Hypothesis Testing
- Extensive literature review in research
- Development of working hypothesis
- Preparing the research design
- Collecting the data
- Analysis of data
- Preparation of the report or the thesis
3 Research Designs
- Functions and Goals of Research Design
- Characteristics of a Good Design
- Different Types of Research Designs
- Exploratory Research Design
- Descriptive Research Design
- Experimental Research Design
- Types of Experimental Designs
4 Methods and Techniques of Data Collection
- Primary and Secondary Data
- Methods of Collecting Primary Data
- Merits and Demerits of Different Methods of Collecting Primary Data
- Designing a Questionnaire
- Pretesting a Questionnaire
- Editing of Primary Data
- Technique of Interview
- Collection of Secondary Data
- Scrutiny of Secondary Data
5 Attitude Measurement and Scales
- Attitudes, Attributes and Beliefs
- Issues in Attitude Measurement
- Scaling of Attitudes
- Deterministic Attitude Measurement Models: The Guttman Scale
- Thurstone’s Equal-Appearing Interval Scale
- The Semantic Differential Scale
- Summative Models: The Likert Scale
- The Q-Sort Technique
- Multidimensional Scaling
- Selection of an Appropriate Attitude Measurement Scale
- Limitations of Attitude Measurement Scales
6 Questionnaire Designing
- Introductory decisions
- Contents of the questionnaire
- Format of the questionnaire
- Steps involved in the questionnaire
- Structure and Design of Questionnaire
- Management of Fieldwork
- Ambiguities in the Questionnaire Methods
7 Sampling and Sampling Design
- Advantage of Sampling Over Census
- Simple Random Sampling
- Sampling Frame
- Probabilistic As pects of Sampling
- Stratified Random Sampling
- Other Methods of Sampling
- Sampling Design
- Non-Probability Sampling Methods
8 Data Processing
- Editing of Data
- Coding of Data
- Classification of Data
- Statistical Series
- Tables as Data Presentation Devices
- Graphical Presentation of Data
9 Statistical Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Nonparametric Tests
- One Sample Tests
- Two Sample Tests
- K Sample Tests
10 Multivariate Analysis of Data
- Regression Analysis
- Discriminant Analysis
- Factor Analysis
11 Ethics in Research
- Principles of research ethics
- Advantages of research ethics
- Limitations of the research ethics
- Steps involved in ethics
- What are research misconducts?
12 Substance of Reports
- Research Proposal
- Categories of Report
- Reviewing the Draft
13 Formats of Reports
- Parts of a Report
- Cover and Title Page
- Introductory Pages
- Reference Section
- Typing Instructions
- Copy Reading
- Proof Reading
14 Presentation of a Report
- Communication Dimensions
- Presentation Package
- Audio-Visual Aids
- Presenter’s Poise

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Common types of limitations and their ramifications include: Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study. Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data. Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data. Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of ...
Limitations in Research. Limitations in research refer to the factors that may affect the results, conclusions, and generalizability of a study.These limitations can arise from various sources, such as the design of the study, the sampling methods used, the measurement tools employed, and the limitations of the data analysis techniques.
The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the interpretation of the findings from your research. Study limitations are the constraints placed on the ability to generalize from the results, to further describe applications to practice, and/or related to the utility of findings ...
ings away from the null. Other limitations may have an unpredictable impact on your findings. In general, limitations that lead to a bias toward the null are considered less dangerous than limitations that cause a bias away from the null. On the other hand, limitations that lead to a conclusion that your exposure impacts your outcome when
The ideal way is to divide your limitations section into three steps: 1. Identify the research constraints; 2. Describe in great detail how they affect your research; 3. Mention the opportunity for future investigations and give possibilities. By following this method while addressing the constraints of your research, you will be able to ...
A strong regional focus. 3. Data or statistical limitations. In some cases, it is impossible to collect sufficient data for research or very difficult to get access to the data. This could lead to incomplete conclusion to your study. Moreover, this insufficiency in data could be the outcome of your study design.
Here's an example of a limitation explained in a research paper about the different options and emerging solutions for delaying memory decline. These statements appeared in the first two sentences of the discussion section: "Approaches like stem cell transplantation and vaccination in AD [Alzheimer's disease] work on a cellular or molecular level in the laboratory.
1. Defining Research Limitations: Definition: Research limitations are the constraints or shortcomings that affect the scope, applicability, and generalizability of a study. Inherent in Research: Every research project, regardless of its scale or significance, possesses limitations. 2. Types of Research Limitations: Methodological Limitations ...
Limitations generally fall into some common categories, and in a sense we can make a checklist for authors here. Price and Murnan ( 2004) gave an excellent and detailed summary of possible research limitations in their editorial for the American Journal of Health Education. They discussed limitations affecting internal and external validity ...
build reviewers' trust in you and your research, discussing every drawback, no matter how small, can give the impression that the study is irreparably flawed. For each limitation you identify, provide a sentence that refutes the limitation or that provides information to counterbalance or otherwise minimize the limitation's perceived impact.
Abstract. Study limitations represent weaknesses within a research design that may influence outcomes and conclusions of the research. Researchers have an obligation to the academic community to present complete and honest limitations of a presented study. Too often, authors use generic descriptions to describe study limitations.
In research, studies can have limitations such as limited scope, researcher subjectivity, and lack of available research tools. Acknowledging the limitations of your study should be seen as a strength. It demonstrates your willingness for transparency, humility, and submission to the scientific method and can bolster the integrity of the study.
Research Data Management (RDM) is a burgeoning field of research (Tenopir et al., 2011; ... Study limitations and recommendations for further research. This paper addressed the challenges in researcher RDM practices that impact the sharing/reusing of their research data. In this analysis we showcase RDM as consisting of (i) alignment of ...
Writing the limitations of the research papers is often assumed to require lots of effort. However, identifying the limitations of the study can help structure the research better. Therefore, do not underestimate the importance of research study limitations. 3. Opportunity to make suggestions for further research.
Research Limitations. It is for sure that your research will have some limitations and it is normal. However, it is critically important for you to be striving to minimize the range of scope of limitations throughout the research process. Also, you need to provide the acknowledgement of your research limitations in conclusions chapter honestly.
Brutus, Stéphane et al. Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations. Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Ioannidis, John P.A. Limitations are not Properly Acknowledged in the Scientific Literature. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007): 324-329; Pasek, Josh.
BACKGROUND. Well-defined, systematic, and transparent methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are vital to ensuring that available funds target areas with the greatest potential for impact. 1, 2 As defined in the literature, 3, 4 research gaps are defined as areas or topics in which the ability to draw a conclusion for a given question is prevented by insufficient evidence.
Step 1. Identify the limitation (s) of the study. This part should comprise around 10%-20% of your discussion of study limitations. The first step is to identify the particular limitation (s) that affected your study. There are many possible limitations of research that can affect your study, but you don't need to write a long review of all ...
Experimental research designs are important because they minimize threats to internal validity. Internal validity is the confidence a researcher has that a change (whether naturally occurring or due to manipulation) in the independent variable causes the observed change in the dependent variable. Although there are a number of confounding variables that may threaten internal validity, the most ...
Organizational control is a fundamental aspect of organizational management. The management literature has also long addressed the various means to control organizations (Barnard, 1938; Fayol, 1949; Simon, 1947; Weber, 1947).Built on the seminal beginnings, control-related research has developed into diverse, and distinct, research streams that frequently use different logics and terminologies.
While each study will have its own unique set of limitations, some limitations are more common in quantitative research, and others are more common in qualitative research. In quantitative research, common limitations include the following: - Participant dropout. - Small sample size, low power. - Non-representative sample.
conference, or a published research paper in an academic journal. "Limitations of Research". is a section in the standard research report (the research report is usually divided into the ...
Despite the importance of research ethics, there are limitations that can affect the validity and generalizability of the research findings. Some of the limitations of research ethics in management studies include: 1. Lack of diversity in the sample population. The sample population used in research studies is often limited to a specific ...