- Learning Tips
- Exam Guides
- School Life

How to write a Counterclaim Paragraph, Sentence or Rebuttal
- by Joseph Kenas
- January 18, 2024

If you are writing an argumentative essay, you will find yourself including counterclaims. In this guide, we guide you on how to write a good counterclaim in an essay and how to frame your counterclaim sentence and paragraph in rebuttal.
Counterclaims are mostly included in an argumentative essay where you are required to convince your readers to agree with your arguments and point of view concerning the topic in question.
What is a Counterclaim in an Essay?
A counterclaim can be regarded as the argument or arguments that oppose the thesis statement in your essay. Within the introduction, you introduce the topic and create a thesis statement in the last sentence that makes it clear to your audience the point(s) you want to prove and the strategy you will use to prove it.
The counterclaim demonstrates to the reader that you have put into consideration the perspectives of the opposing side and you find such perspectives to be weak.
As such, a counterclaim will allow you to respond to the potential arguments of your readers before they complete reading the essay.
Additionally, a counterclaim demonstrates that both sides of the debate have been put into consideration, hence strengthening your position.
Difference Between a Claim and a Counterclaim
There is a big difference between a claim and a counterclaim. When writing essays, one may need to include both in the same essay, especially when presenting an argumentative topic.
The difference between a claim and a counterclaim lies in their assertion. A claim is a statement that demonstrates the position of argument or the assertion of a fact or a truth. On the other hand, a counterclaim is an argument that negates a specific claim by rebutting it. While a claim asserts the writer’s argument, a counterclaim rebuts.
When writing an essay, particularly an argumentative essay, you will have a topic and a thesis statement that will show the readers the points you are going to prove and how you will prove them.

Most of your paper will be dedicated to proving your claim to the reader so that they can agree with your point of view.
A good claim should be arguable and at times controversial to allow the readers to think otherwise about your perspectives as the writer.
It can also come up with their interpretations concerning the topic.
Because of this, the essay will be based on the claim and you will demonstrate why your claim is accepted. On the other hand, a counterclaim is a statement of opposition that will allow the readers to perceive the whole picture of the arguments.
Though this is the case, the counterclaim demonstrates that the writer has anticipated arguments against their claim and has provided proof, through the counterclaim, that the readers’ perspectives are false or weak.
As such, when the counterclaim is stated, it is addressed concerning its weaknesses or limitations. This enhances the claim’s strength.
How to Write a Good Counterclaim in an Essay
If you wish to write a good counterclaim, make sure that it takes the form of two stages.

The first stage is where you go against your claim or argument so that you can challenge it and the second stage is where you turn back to your claim or argument to re-affirm it.
When writing a good counterclaim, you imagine that some of your readers will be skeptical and you have to make them agree with you.
For example, if you want to present a counterclaim showing that there was a problem with how you demonstrated your claims, like an unwarranted assumption, certain evidence was played down or ignored, and so on, you can support the counterclaim by presenting the disadvantages or drawbacks of the issues with the presentation. Then, give an alternative proposal or alternative that would make more sense to the readers.
To refute the counterclaim, you announce with words like ‘yet’, ‘but’, ‘however’, ‘still’, or ‘nevertheless’ to indicate that you are about to show why the counterclaim is wrong. Acknowledge that it is a good claim but demonstrate that yours might help the argument more.
Where to Write a Counterclaim in an Essay
A counterclaim can be included anywhere within the body of the essay except the conclusion. There are some cases where you can write a counterclaim at the second last sentence of the introduction paragraph followed by the thesis statement which acts as the refutation.
You can also write a counterargument after the introduction to show the anticipated reaction to your point of view before moving forward with writing your actual claims.
Moving forward, the reason why you cannot place the counterclaim within the conclusion is that you have to include a rebuttal paragraph or statements after you have written the counterclaim. Therefore, a counterclaim located at the conclusion will miss the rebuttal paragraph or statements.
However, argumentative essays can take different structures. Even though such essays will have a basic structure of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, the differences will occur within the body paragraphs. Such differences dictate where the counterclaim(s) are located.
There is a structure where the counterclaims are located within all the body paragraphs. In this case, you will write your claim, followed by a counterclaim, and then a rebuttal. This means that for every claim you present to support your thesis, there will be a counterclaim and a rebuttal.
The most common structure is where you present your claims and present the counterclaim(s) before the conclusion. The counterclaim is immediately followed by a rebuttal.
Dos and Don’ts of Writing a Counterclaim
When it comes to the dos of writing a counterclaim, always ensure that it is followed by a rebuttal to demonstrate that your claims are superior to it. Secondly, courteously present your counterclaims to avoid upsetting the reader.

Acknowledge the anticipated arguments from the readers.
Demonstrate that the readers’ points of view are valid but your perspective makes more sense.
Finally, appeal to the logic of the readers through the use of valid evidence.
Concerning the don’ts when writing a counterclaim, do not include a counterargument just for the sake of it.
Make sure that the counterargument is valid in its own right and it is verifiable through evidence.
This is because your readers will also use logic and evidence when thinking about your claims. Secondly, do not use a disrespectful or uncourteous tone when addressing the other side of the argument.
Examples of Counterclaims
A counterclaim in a separate paragraph.
Counterclaim: “Opponents argue that after-school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries (Bancroft, 2018). Even minor injuries sustained from participation in after-school sports increase absent rates and the expense of creating injury reports for students (Sizemore, 2019)” .
Refutation: “Although students do suffer both serious and minor injuries in after-school sports, these injuries are quite rare (Kinney, 2016) .
Embedded Within a Paragraph
“Without free after-school sports programs, many students would still play sports without adult supervision and even more injuries would result”. Counterclaim : “However, some people would argue that after-school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries (Sizemore 2019)”. Refutation: “Although students do suffer both serious and minor injuries in after-school sports, without school-sponsored sports, the likelihood of more injuries from less supervised recreational leagues or privately sponsored leagues with fewer safety regulations would be much worse” .
How Long Should a Counterclaim Be?
A counterclaim can be as long as a paragraph if it appears after the introduction paragraph or at the end of the body before the conclusion. However, if a counterclaim is located within a paragraph, it can be a few sentences long (2-3).
However, the length of a counterclaim depends on the length of a claim in general. You can learn more about how to write a claim paragraph in that guide so that you can learn the two in general.
How many Counterclaims can you Put?
This depends on the structure of the essay. If the counterclaim appears after the introduction or before the conclusion, then it will only be one. However, if it is embedded within paragraphs, then they will be as many as the supportive augments.
This is because they will be used to refute every claim made within the body paragraph. If your supporting claims are 5 then the counterclaims will be 5 and so on.
Check out how to write college essays in our guide that we hope will lead you to score well.

Joseph is a freelance journalist and a part-time writer with a particular interest in the gig economy. He writes about schooling, college life, and changing trends in education. When not writing, Joseph is hiking or playing chess.
Consider the following thesis for a short paper that analyzes different approaches to stopping climate change:
Climate activism that focuses on personal actions such as recycling obscures the need for systemic change that will be required to slow carbon emissions.
The author of this thesis is promising to make the case that personal actions not only will not solve the climate problem but may actually make the problem more difficult to solve. In order to make a convincing argument, the author will need to consider how thoughtful people might disagree with this claim. In this case, the author might anticipate the following counterarguments:
- By encouraging personal actions, climate activists may raise awareness of the problem and encourage people to support larger systemic change.
- Personal actions on a global level would actually make a difference.
- Personal actions may not make a difference, but they will not obscure the need for systemic solutions.
- Personal actions cannot be put into one category and must be differentiated.
In order to make a convincing argument, the author of this essay may need to address these potential counterarguments. But you don’t need to address every possible counterargument. Rather, you should engage counterarguments when doing so allows you to strengthen your own argument by explaining how it holds up in relation to other arguments.
How to address counterarguments
Once you have considered the potential counterarguments, you will need to figure out how to address them in your essay. In general, to address a counterargument, you’ll need to take the following steps.
- State the counterargument and explain why a reasonable reader could raise that counterargument.
- Counter the counterargument. How you grapple with a counterargument will depend on what you think it means for your argument. You may explain why your argument is still convincing, even in light of this other position. You may point to a flaw in the counterargument. You may concede that the counterargument gets something right but then explain why it does not undermine your argument. You may explain why the counterargument is not relevant. You may refine your own argument in response to the counterargument.
- Consider the language you are using to address the counterargument. Words like but or however signal to the reader that you are refuting the counterargument. Words like nevertheless or still signal to the reader that your argument is not diminished by the counterargument.
Here’s an example of a paragraph in which a counterargument is raised and addressed.
Image version

The two steps are marked with counterargument and “counter” to the counterargument: COUNTERARGUMENT/ But some experts argue that it’s important for individuals to take action to mitigate climate change. In “All That Performative Environmentalism Adds Up,” Annie Lowery argues that personal actions to fight climate change, such as reducing household trash or installing solar panels, matter because change in social behavior can lead to changes in laws. [1]
COUNTER TO THE COUNTERARGUMENT/ While Lowery may be correct that individual actions can lead to collective action, this focus on individual action can allow corporations to receive positive publicity while continuing to burn fossil fuels at dangerous rates.
Where to address counterarguments
There is no one right place for a counterargument—where you raise a particular counterargument will depend on how it fits in with the rest of your argument. The most common spots are the following:
- Before your conclusion This is a common and effective spot for a counterargument because it’s a chance to address anything that you think a reader might still be concerned about after you’ve made your main argument. Don’t put a counterargument in your conclusion, however. At that point, you won’t have the space to address it, and readers may come away confused—or less convinced by your argument.
- Before your thesis Often, your thesis will actually be a counterargument to someone else’s argument. In other words, you will be making your argument because someone else has made an argument that you disagree with. In those cases, you may want to offer that counterargument before you state your thesis to show your readers what’s at stake—someone else has made an unconvincing argument, and you are now going to make a better one.
- After your introduction In some cases, you may want to respond to a counterargument early in your essay, before you get too far into your argument. This is a good option when you think readers may need to understand why the counterargument is not as strong as your argument before you can even launch your own ideas. You might do this in the paragraph right after your thesis.
- Anywhere that makes sense As you draft an essay, you should always keep your readers in mind and think about where a thoughtful reader might disagree with you or raise an objection to an assertion or interpretation of evidence that you are offering. In those spots, you can introduce that potential objection and explain why it does not change your argument. If you think it does affect your argument, you can acknowledge that and explain why your argument is still strong.
[1] Annie Lowery, “All that Performative Environmentalism Adds Up.” The Atlantic . August 31, 2020. https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2020/08/your-tote-bag-can-mak…
- picture_as_pdf Counterargument
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
How To Write A Counterclaim For A Successful Result

You might have probably heard about a counterclaim or written one that did not go well with you, which is why you are here. We understand your frustrations and anxiety about writing counterclaims, which is why we developed this comprehensive article.
Here is what to expect:
An in-depth explanation of what a counterclaim is The necessity of a counterclaim How to write a good counterclaim Characteristics of an excellent counterclaim Structure and formatting of counterclaims
After reading this post, you will have all the information you need to craft an award-winning paper. We will not leave anything to chance until you know how to write a counterclaim like a top-class student!
Table of Contents
What is a counterclaim in writing, why is a counterclaim necessary, how to write a counterclaim from scratch, detailed guide on how to start a counterclaim paragraph, how to write rebuttal, characteristics of a good counterclaim, example of a good counterclaim.
A counterclaim refers to an argument that opposes the author’s claim. The writer presents the claim and then refutes it, giving reasons why others should not take up the contrary view and agree with their initial stand.
The counterclaim opposes the thesis statement in your essay. So, this is how a counterclaim comes about:
- You first introduce the topic in the introductory paragraph
- Create a thesis statement in the last sentence
- Write a counterclaim that rebuts the initial argument
Many students fail to appreciate the fact that there is a difference between a claim and a counterclaim. The claim demonstrates your position of argument or the assertion of a fact, whereas a counterclaim negates a specific claim by refuting it.
Any top-rated argumentative will always have a counterclaim which disagrees with and disapproves of a claim. Such a claim also provides reasoning that further clarifies a particular argument. The two main purposes of a counterclaim are as follows:
It enhances the credibility of the author: A strong argumentative essay will utilize the rhetorical appeal of ethos. With a counterclaim, a writer will prove that they researched extensively on the topic and are not trying to hide possible information from the audience. It also allows the writer to provide a rebuttal to the essay. The rebuttal is used to disprove the counterclaim within the writer’s argument.
For instance, if the claim is that the government should ban gun use, the counterclaim would be that it should not ban it because it infringes on human rights. There should always be reasons and evidence for you to have a successful counterclaim.
In the next few lines, we will provide all you need to know about starting a counterclaim and delivering the best! So stay tuned.
Every successful essay begins with thorough background research on the topic of discussion. Exploring all possible angles of your essay before embarking on the writing process is recommended—those who end up with a good counterclaim put in extra hours in research and extensive consultation.
You can read thousands of articles on how to write a counterclaim, but without the right background research strategies, that great essay might amount to nothing. So, if you want to crack your counterclaim paragraph like a guru, here are excellent tips for you:
Understand your topic Explore what previous authors have done on it Identify the knowledge gaps Seek facts to defend your claim
Once you have all the information needed for your topic, nothing will stand in the way of you writing a top-notch paper that will impress your professor. When you have factual proof of every statement you make in your essay, you will have a non-biased and credible paper. That means that the sources you use should always be credible and directly relevant to the topic of your essay.
After stating all the base knowledge you need about counterclaims, we now want to dive into the practical part of writing a counterclaim argument. Let’s explore how to write counterclaims by looking at the elements needed:
- The main counterclaim: It states an opposing argument to the claim.
- The evidence includes a previous position to show that others welcome the view.
- An explanation entails providing reasons why people hold the particular view you presented.
- A rebuttal: Here, you will explain the weakness of the counterclaim and present show why your original position is correct.
The process might be challenging initially, but with the right tools and expert advice, you will be up and running in minutes. A counterclaim is included in argumentative writing to address the opposite side of the argument and provide a rebuttal.
The process of writing an outstanding counterclaim in an argumentative essay is as follows:
Where do you put a counterclaim in an essay? Every top-ranking essay begins with a catchy intro comprising statistics or a rather dramatic intro to a particular problem. The thesis statement follows, and the then claim comes on stage. Therefore, the counterclaim comes after you have backed up your claims with evidence and further arguments. How long is the counterclaim? It depends on the number of counterclaims and the overall length of your essay. A typical counterclaim should be at least one paragraph long. Remember that you are not just stating it but explaining why it is so. That is why most guides on writing a counterclaim and rebuttal will recommend either writing them in one paragraph or separately. What different points of view do others hold? You should always understand all the possible points that may arise to counter your claim. Researching why people oppose your claim will give you room for a balanced and reliable paper. It requires a creative mind to determine how your claim goes against the common view. How to introduce a counterclaim now: The general rule is that you should present the contrary opinion fairly. You will only be ready to craft a brilliant counterclaim once you dive into the possible arguments that others who oppose your thesis make. Sincerely present the contrary opinion fairly.
Always remember to use transitions when moving on to present your counterclaim. Just like in a debate, the contrary side will come after the proposers have made their submissions. Therefore, you can begin your counterclaim paragraphs with the following:
- On the contrary, side
- Critics say that
Having presented the other side, you will detail why people also hold that view. It is where the evidence comes in to solidify your counterclaim.
It is advisable to have it in a similar paragraph where your counterclaim is, but if that is not possible, begin it in a new paragraph. However, always remember to keep it short while bringing out the following:
- How the contrary position in your counterclaim is false or weak.
- Presenting the advantages in the counterclaim but giving reasons why the opposite view may not hold water.
- Describe how your main argument outweighs the risks in the counterclaim.
After introducing the counterclaim, you have to discuss why the counterclaim is incorrect. You can start the rebuttal in several ways, such as:
Despite this information Nevertheless However
It is your opportunity to prove why the contrary view is wrong.
You cannot achieve this milestone without considering all sides of the argument first. That is why most researchers in college and university take their time before beginning the writing process. It provides a base for the facts and opinions and saves the time one will spend completing the argumentative essay.
Acknowledging the valid points of the other side is necessary for any form of argumentative writing. This practice eliminates the thought of narrow-mindedness from the reader’s point of view, which may make your essay less effective.
Instead of making your argument look weak, a counterclaim will strengthen your essay by proving that you thoughtfully considered all possible angles before writing your essay. Nobody will accuse you of bias or inadequate research when you have a formulated counterclaim.
A good counterclaim, therefore:
Acknowledges what the opposing side says Provides evidence from the opposing side Refutes the point of view and evidence
It is also crucial to state that when you have more than one claim in your paper, there is always an option of writing a counterclaim for each. You are not limited to presenting the different counterclaims in the same essay. However, follow the structure outline above in terms of length and format.
Additional characteristics of a world-class essay include:
- Objectivity in the language use
- Fairness in the diction
- Evidence to back up the counterclaim
- Fairness in the rebuttal
By validating any underlying concerns, you eliminate room for doubt or error. Remember also to explain why your argument works in that context.
Below is a brief example of what a good counterclaim can look like, from professional dissertation writers :
“On the other hand, some students say homework presents unnecessary stress and pressure. This point of view makes sense because the article states that too much homework may be overwhelming for students, which is why most of them do not complete it. However, homework does not harm the student because the article also says that homework is necessary to test students’ understanding after classroom learning. Therefore, even though homework may cause stress and pressure on the student, it does not harm the student in any way.”
From the example, you can note the following:
Phrases that can begin a counterclaim:
On the other hand, some people say Admittedly, some people say Certainly, some people say
Phrases to refer to the initial claim:
However Nevertheless On the other hand
Phrases to bring paragraph to a conclusion:
Thus Therefore As a result
A good counterclaim will always give you an edge over your competitors in any case.
Writing A Counterclaim Can Be Very Easy
Writing an all-inclusive counterclaim is not a big deal if you have all the facts rights – our writing service and master thesis help offers top-notch assistance with an incredible team of writers and research gurus. We will help you identify winning arguments and provide you with the best rebuttals.
Do not second guess what you will score in your counterclaim essay when you can try out our custom thesis writing service today. Make your pick today and improve your score effortlessly.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
How to Write an Effective Counterclaim in 5 Steps
So, you’re laboring over a killer argumentative essay — and you want to make absolutely sure that you have all your bases covered? Your essay absolutely needs at least one counterclaim with a rebuttal if you are determined to make it the best it can be.
Unless you are already an experiences essayist, however, it can prove tough to write a solid counterclaim. Watch and learn — with this guide, you’ll get ready to write a powerful counterclaim in no time!
Essay Counterclaim: The Basics
The “too long; didn’t read” version is as follows — a counterclaim is a rhetorical tool used in essay writing. You present a viewpoint for which you are not arguing in a counterclaim, and then proceed to refute it; explaining why people should disagree with the opposing argument and agree with you, instead.
As you’re writing your essay, you will inevitably make various claims. Claims can be defined as debatable statements — the views for which you are arguing in your essay. Your thesis statement will be the main, overarching, claim you make in your essay, and this can be followed by multiple further claims in favor of your argument.
Let’s see this in action:
- Thesis: “Unleashed dogs are a serious public health concern in Masonville. Policy must be amended to make it mandatory for all dogs to be leashed, at all times, and fines must be imposed on those who fail to comply.”
- Claim: “Unleashed dogs have decimated the local deer population.”
- Claim: “5 children and an elderly person have sustained serious dog bites that required medical attention in the last three years.”
- Claim: “Data from other jurisdictions shows that imposing penalties for unleashed dogs reduces incidents with dogs immensely.”
If your essay looks something like this, you’re building a compelling case. You have defined your viewpoint, offered arguments that lead to a conclusion, and you have also shared data that your proposed solution could work.
What’s missing?
To truly make a convincing argument, you have to show that you understand the subject matter you are tackling deeply — something that inevitably includes listening to the opposing side in the argument.
That is where your counterclaim comes in. A counterclaim can be defined as a claim that directly opposes yours.
If your reaction is “Wait, what!? I have to argue against myself?” right now, hold on. There are multiple strong reasons to include a counterclaim in your essay. Here’s a look:
- By including a counterclaim, or indeed multiple, you show that you don’t have tunnel vision. You have also considered the other side.
- Readers who support the other side of the argument will likely react with a “Yes, that’s right!”. This has the effect of making them feel heard, which in turn makes them more open to listening to you.
- After all that, you can — finally — respectfully and artfully refute the counterclaim. You understand the opposing viewpoint and you have deeply considered its merits, but you disagree. Lay out why, and why those who previously agreed with the opposing argument might want to consider coming over to your side, instead.
Let’s see that in action again:
Many dog owners claim that leashing dogs robs them of the ability to run around and have fun — something they consider integral to their dogs’ health and wellbeing. While it is certainly true that dogs need exercise, long leashes allow for plenty of freedom of movement. Dog parks, where dogs could run free, are another possible solution in this case.
Claim vs Counterclaim: What Is the Difference?
The difference between a claim and a counterclaim can best be summed up by saying that a claim is used to argue the position you are defending in your essay, while a counterclaim takes the opposing viewpoint. A counterclaim is an argument against your argument, in other words.
That is not the only difference between the two. To make an effective claim, a writer simply has to:
- Make the claim.
- Provide evidence or logical arguments supporting the claim.
- Where desired, follow this with rhetorical tools such as appeals to emotion or logic to further convince the audience.
A counterclaim requires more elements:
- The counterclaim itself — which states an opposing argument.
- Evidence that people in fact hold this view is very much welcomed; to make a good counterclaim, you cannot simply lay out positions that are almost never taken.
- An explanation as to why people may hold this view.
- Finally, a rebuttal, in which you explain why the counterclaim is weak, and your original position is correct.
How to Write an Effective Counterclaim: Step-by-Step
Writing an effective counterclaim — or even several, as you may be called to do in longer essays — can be challenging. That is particularly true if you fervently believe in the argument you are making, and have a hard time understanding how anyone could disagree with it.
However, it is important to remain as objective as possible as you craft a counterclaim for your essay. Here is a look at the process you may use to decide on a good counterclaim.
- Deciding Where to Place Your Counterclaim
It is typically very effective to open your essay with a compelling hook, which may consist of a powerful anecdote, statistics, or a dramatic introduction to a pressing problem. You will then want to introduce your thesis statement, and begin making claims — which you back up with evidence and further arguments.
Your counterclaim, or counter claims, should be placed after this portion of your essay. In short essays, that means it will be somewhere near the end. However, you will want to summarize your main argument succinctly and write a memorable conclusion in the paragraphs that follow your counterclaim paragraph.
- Deciding How Long Your Counterclaim Should Be
The length of a counterclaim, and indeed the number of counterclaims you decide to include, depends on the target length of your essay. You will typically require at least a short paragraph to be able to do your counterclaim justice, because you are not simply stating that some people disagree with your argument. You also want to explain why.
In some cases, you will be able to write a short rebuttal in the same paragraph. In others, you may choose to refute the counterclaim in the next paragraph.
- Researching Opposing Viewpoints
To write an effective counterclaim, it is important to understand the arguments that may be used to oppose your claims. Don’t simply turn your claim or thesis statement on its head, but research why people disagree with the argument you are making, and on what basis. Where possible, try to find out how common the view you are portraying in your counterclaim is.
- Presenting the Opposing Viewpoint Fairly
Once you immerse yourself in the types of arguments people who disagree with your thesis make, and truly understand where they are coming from, you are ready to craft a good counterclaim. Try this exercise first. Imagine what you would write if you sincerely held the opposing view, and then go ahead and do it.
- Writing Your Counterclaim Paragraph
Before presenting the counterclaim, you will need to introduce the fact that you will be doing this by making a smooth transition in your writing. Good ways to start your counterclaim paragraph include:
- “Critics have argued that…”
- “Some people may conclude that”
- “On the other side of the argument, people are concerned that…”
- “The opposing viewpoint states that…”
Once you have stated the alternative view, go ahead and describe why that view is held. Present evidence.
You can now either start a new paragraph to write a rebuttal, or — if you can keep it short — do so in the same paragraph.
A rebuttal can include:
- Reasons why the opposing view you presented in your counterclaim is weak or false.
- An acknowledgment that the views presented in the counterclaim have merit, but there is a solution that would render the concerns the opposing side has baseless.
- An explanation that the views presented in the counterclaim are exceedingly rare, or the benefits of your argument outweigh the risks the counterclaim sets forth.
Additional Tips on Writing a Counterclaim
If you have followed along so far, you are almost ready to make a very effective counterclaim, complete with a refutation. You may even have penned a draft. So far, so good, but you do have some additional things to watch out for as you write your counterclaim:
- Be objective in the language you use. Do not state that you disagree with the counterclaim, or argue that some people “erroneously believe that…”, for example. Simply present the counterclaim as an alternative opinion.
- Be fair. Do not caricature the viewpoint you are presenting in your counterclaim. Do not use condescending language. When you share the opposing argument, do so using words that those who hold that view may, in fact, use.
- Don’t forget to include evidence. Your evidence can demonstrate that a significant percentage of people hold the view you address in your counterclaim, and it should also, where possible, back up the counterclaim. In the example we used earlier, regarding the benefits of allowing dogs to run around without being leashed, you could look for studies that show that dogs need a certain amount of physical exercise.
- Be fair in your rebuttal, too. The extent to which you do this depends on your aim. If you are writing a high school or college essay, you may simply prefer to throw some hard-hitting verbal punches. If, on the other hand, you are sincerely hoping to convince people who currently hold the alternative opinion you just described that you are right, you will have to be more careful. Validate their underlying concerns or values, and explain why your argument works within that context.
Does every essay need a counterclaim?
No. There are many kinds of essays. An expository essay, for instance, simply explores a topic, and will not need a counterclaim. A narrative essay shares the writer’s personal experience, and will not require a counterclaim. Counterclaims have an important place in argumentative essays, which require the writer to demonstrate that they understand the topic thoroughly and have considered all sides.
How many counterclaims should I include?
If you make multiple claims, you may choose to write a counterclaim for each of them. Depending on the length of your essay, you may even decide to include multiple counterclaims for each claim.
Related posts:
- How to Write an Effective Claim (with Examples)
- How to Write a Counter Argument (Step-by-Step Guide)
- 14 Tips to Help you Write An Essay Fast
- Going to the Dogs - Meaning, Origin and Usage
- How to Write in the First Person Effectively
- How To Write A Movie Title In An Essay
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
A Guide to Rebuttals in Argumentative Essays

4-minute read
- 27th May 2023
Rebuttals are an essential part of a strong argument. But what are they, exactly, and how can you use them effectively? Read on to find out.
What Is a Rebuttal?
When writing an argumentative essay , there’s always an opposing point of view. You can’t present an argument without the possibility of someone disagreeing.
Sure, you could just focus on your argument and ignore the other perspective, but that weakens your essay. Coming up with possible alternative points of view, or counterarguments, and being prepared to address them, gives you an edge. A rebuttal is your response to these opposing viewpoints.
How Do Rebuttals Work?
With a rebuttal, you can take the fighting power away from any opposition to your idea before they have a chance to attack. For a rebuttal to work, it needs to follow the same formula as the other key points in your essay: it should be researched, developed, and presented with evidence.
Rebuttals in Action
Suppose you’re writing an essay arguing that strawberries are the best fruit. A potential counterargument could be that strawberries don’t work as well in baked goods as other berries do, as they can get soggy and lose some of their flavor. Your rebuttal would state this point and then explain why it’s not valid:
Read on for a few simple steps to formulating an effective rebuttal.
Step 1. Come up with a Counterargument
A strong rebuttal is only possible when there’s a strong counterargument. You may be convinced of your idea but try to place yourself on the other side. Rather than addressing weak opposing views that are easy to fend off, try to come up with the strongest claims that could be made.
In your essay, explain the counterargument and agree with it. That’s right, agree with it – to an extent. State why there’s some truth to it and validate the concerns it presents.
Step 2. Point Out Its Flaws
Now that you’ve presented a counterargument, poke holes in it . To do so, analyze the argument carefully and notice if there are any biases or caveats that weaken it. Looking at the claim that strawberries don’t work well in baked goods, a weakness could be that this argument only applies when strawberries are baked in a pie.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Step 3. Present New Points
Once you reveal the counterargument’s weakness, present a new perspective, and provide supporting evidence to show that your argument is still the correct one. This means providing new points that the opposer may not have considered when presenting their claim.
Offering new ideas that weaken a counterargument makes you come off as authoritative and informed, which will make your readers more likely to agree with you.
Summary: Rebuttals
Rebuttals are essential when presenting an argument. Even if a counterargument is stronger than your point, you can construct an effective rebuttal that stands a chance against it.
We hope this guide helps you to structure and format your argumentative essay . And once you’ve finished writing, send a copy to our expert editors. We’ll ensure perfect grammar, spelling, punctuation, referencing, and more. Try it out for free today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a rebuttal in an essay.
A rebuttal is a response to a counterargument. It presents the potential counterclaim, discusses why it could be valid, and then explains why the original argument is still correct.
How do you form an effective rebuttal?
To use rebuttals effectively, come up with a strong counterclaim and respectfully point out its weaknesses. Then present new ideas that fill those gaps and strengthen your point.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

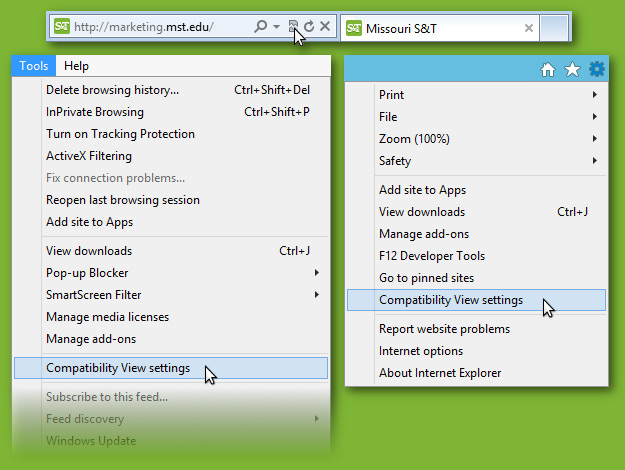
Your version of Internet Explorer is either running in "Compatibility View" or is too outdated to display this site. If you believe your version of Internet Explorer is up to date, please remove this site from Compatibility View by opening Tools > Compatibility View settings (IE11) or clicking the broken page icon in your address bar (IE9, IE10)
Missouri S&T Missouri S&T
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- writingcenter.mst.edu
- Online Resources
- Writing Guides
- Counter Arguments
Writing and Communication Center
- 314 Curtis Laws Wilson Library, 400 W 14th St Rolla, MO 65409 United States
- (573) 341-4436
- [email protected]
Counter Argument
One way to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counter arguments, or objections. By considering opposing views, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not accepting your argument. Ask yourself what someone who disagrees with you might say in response to each of the points you’ve made or about your position as a whole.
If you can’t immediately imagine another position, here are some strategies to try:
- Do some research. It may seem to you that no one could possibly disagree with the position you are taking, but someone probably has. Look around to see what stances people have and do take on the subject or argument you plan to make, so that you know what environment you are addressing.
- Talk with a friend or with your instructor. Another person may be able to play devil’s advocate and suggest counter arguments that haven’t occurred to you.
- Consider each of your supporting points individually. Even if you find it difficult to see why anyone would disagree with your central argument, you may be able to imagine more easily how someone could disagree with the individual parts of your argument. Then you can see which of these counter arguments are most worth considering. For example, if you argued “Cats make the best pets. This is because they are clean and independent,” you might imagine someone saying “Cats do not make the best pets. They are dirty and demanding.”
Once you have considered potential counter arguments, decide how you might respond to them: Will you concede that your opponent has a point but explain why your audience should nonetheless accept your argument? Or will you reject the counterargument and explain why it is mistaken? Either way, you will want to leave your reader with a sense that your argument is stronger than opposing arguments.
Two strategies are available to incorporate counter arguments into your essay:
Refutation:
Refutation seeks to disprove opposing arguments by pointing out their weaknesses. This approach is generally most effective if it is not hostile or sarcastic; with methodical, matter-of-fact language, identify the logical, theoretical, or factual flaws of the opposition.
For example, in an essay supporting the reintroduction of wolves into western farmlands, a writer might refute opponents by challenging the logic of their assumptions:
Although some farmers have expressed concern that wolves might pose a threat to the safety of sheep, cattle, or even small children, their fears are unfounded. Wolves fear humans even more than humans fear wolves and will trespass onto developed farmland only if desperate for food. The uninhabited wilderness that will become the wolves’ new home has such an abundance of food that there is virtually no chance that these shy animals will stray anywhere near humans.
Here, the writer acknowledges the opposing view (wolves will endanger livestock and children) and refutes it (the wolves will never be hungry enough to do so).
Accommodation:
Accommodation acknowledges the validity of the opposing view, but argues that other considerations outweigh it. In other words, this strategy turns the tables by agreeing (to some extent) with the opposition.
For example, the writer arguing for the reintroduction of wolves might accommodate the opposing view by writing:
Critics of the program have argued that reintroducing wolves is far too expensive a project to be considered seriously at this time. Although the reintroduction program is costly, it will only become more costly the longer it is put on hold. Furthermore, wolves will help control the population of pest animals in the area, saving farmers money on extermination costs. Finally, the preservation of an endangered species is worth far more to the environment and the ecological movement than the money that taxpayers would save if this wolf relocation initiative were to be abandoned.
This writer acknowledges the opposing position (the program is too expensive), agrees (yes, it is expensive), and then argues that despite the expense the program is worthwhile.
Some Final Hints
Don’t play dirty. When you summarize opposing arguments, be charitable. Present each argument fairly and objectively, rather than trying to make it look foolish. You want to convince your readers that you have carefully considered all sides of the issues and that you are not simply attacking or caricaturing your opponents.
Sometimes less is more. It is usually better to consider one or two serious counter arguments in some depth, rather than to address every counterargument.
Keep an open mind. Be sure that your reply is consistent with your original argument. Careful consideration of counter arguments can complicate or change your perspective on an issue. There’s nothing wrong with adopting a different perspective or changing your mind, but if you do, be sure to revise your thesis accordingly.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Organizing Your Argument

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How can I effectively present my argument?
In order for your argument to be persuasive, it must use an organizational structure that the audience perceives as both logical and easy to parse. Three argumentative methods —the Toulmin Method , Classical Method , and Rogerian Method — give guidance for how to organize the points in an argument.
Note that these are only three of the most popular models for organizing an argument. Alternatives exist. Be sure to consult your instructor and/or defer to your assignment’s directions if you’re unsure which to use (if any).
Toulmin Method
The Toulmin Method is a formula that allows writers to build a sturdy logical foundation for their arguments. First proposed by author Stephen Toulmin in The Uses of Argument (1958), the Toulmin Method emphasizes building a thorough support structure for each of an argument's key claims.
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows:
Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument.
Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
Warrant (Bridge): In this section, you explain why or how your data supports the claim. As a result, the underlying assumption that you build your argument on is grounded in reason.
Backing (Foundation): Here, you provide any additional logic or reasoning that may be necessary to support the warrant.
Counterclaim: You should anticipate a counterclaim that negates the main points in your argument. Don't avoid arguments that oppose your own. Instead, become familiar with the opposing perspective. If you respond to counterclaims, you appear unbiased (and, therefore, you earn the respect of your readers). You may even want to include several counterclaims to show that you have thoroughly researched the topic.
Rebuttal: In this section, you incorporate your own evidence that disagrees with the counterclaim. It is essential to include a thorough warrant or bridge to strengthen your essay’s argument. If you present data to your audience without explaining how it supports your thesis, your readers may not make a connection between the two, or they may draw different conclusions.
Example of the Toulmin Method:
Claim: Hybrid cars are an effective strategy to fight pollution.
Data1: Driving a private car is a typical citizen's most air-polluting activity.
Warrant 1: Due to the fact that cars are the largest source of private (as opposed to industrial) air pollution, switching to hybrid cars should have an impact on fighting pollution.
Data 2: Each vehicle produced is going to stay on the road for roughly 12 to 15 years.
Warrant 2: Cars generally have a long lifespan, meaning that the decision to switch to a hybrid car will make a long-term impact on pollution levels.
Data 3: Hybrid cars combine a gasoline engine with a battery-powered electric motor.
Warrant 3: The combination of these technologies produces less pollution.
Counterclaim: Instead of focusing on cars, which still encourages an inefficient culture of driving even as it cuts down on pollution, the nation should focus on building and encouraging the use of mass transit systems.
Rebuttal: While mass transit is an idea that should be encouraged, it is not feasible in many rural and suburban areas, or for people who must commute to work. Thus, hybrid cars are a better solution for much of the nation's population.
Rogerian Method
The Rogerian Method (named for, but not developed by, influential American psychotherapist Carl R. Rogers) is a popular method for controversial issues. This strategy seeks to find a common ground between parties by making the audience understand perspectives that stretch beyond (or even run counter to) the writer’s position. Moreso than other methods, it places an emphasis on reiterating an opponent's argument to his or her satisfaction. The persuasive power of the Rogerian Method lies in its ability to define the terms of the argument in such a way that:
- your position seems like a reasonable compromise.
- you seem compassionate and empathetic.
The basic format of the Rogerian Method is as follows:
Introduction: Introduce the issue to the audience, striving to remain as objective as possible.
Opposing View : Explain the other side’s position in an unbiased way. When you discuss the counterargument without judgement, the opposing side can see how you do not directly dismiss perspectives which conflict with your stance.
Statement of Validity (Understanding): This section discusses how you acknowledge how the other side’s points can be valid under certain circumstances. You identify how and why their perspective makes sense in a specific context, but still present your own argument.
Statement of Your Position: By this point, you have demonstrated that you understand the other side’s viewpoint. In this section, you explain your own stance.
Statement of Contexts : Explore scenarios in which your position has merit. When you explain how your argument is most appropriate for certain contexts, the reader can recognize that you acknowledge the multiple ways to view the complex issue.
Statement of Benefits: You should conclude by explaining to the opposing side why they would benefit from accepting your position. By explaining the advantages of your argument, you close on a positive note without completely dismissing the other side’s perspective.
Example of the Rogerian Method:
Introduction: The issue of whether children should wear school uniforms is subject to some debate.
Opposing View: Some parents think that requiring children to wear uniforms is best.
Statement of Validity (Understanding): Those parents who support uniforms argue that, when all students wear the same uniform, the students can develop a unified sense of school pride and inclusiveness.
Statement of Your Position : Students should not be required to wear school uniforms. Mandatory uniforms would forbid choices that allow students to be creative and express themselves through clothing.
Statement of Contexts: However, even if uniforms might hypothetically promote inclusivity, in most real-life contexts, administrators can use uniform policies to enforce conformity. Students should have the option to explore their identity through clothing without the fear of being ostracized.
Statement of Benefits: Though both sides seek to promote students' best interests, students should not be required to wear school uniforms. By giving students freedom over their choice, students can explore their self-identity by choosing how to present themselves to their peers.
Classical Method
The Classical Method of structuring an argument is another common way to organize your points. Originally devised by the Greek philosopher Aristotle (and then later developed by Roman thinkers like Cicero and Quintilian), classical arguments tend to focus on issues of definition and the careful application of evidence. Thus, the underlying assumption of classical argumentation is that, when all parties understand the issue perfectly, the correct course of action will be clear.
The basic format of the Classical Method is as follows:
Introduction (Exordium): Introduce the issue and explain its significance. You should also establish your credibility and the topic’s legitimacy.
Statement of Background (Narratio): Present vital contextual or historical information to the audience to further their understanding of the issue. By doing so, you provide the reader with a working knowledge about the topic independent of your own stance.
Proposition (Propositio): After you provide the reader with contextual knowledge, you are ready to state your claims which relate to the information you have provided previously. This section outlines your major points for the reader.
Proof (Confirmatio): You should explain your reasons and evidence to the reader. Be sure to thoroughly justify your reasons. In this section, if necessary, you can provide supplementary evidence and subpoints.
Refutation (Refuatio): In this section, you address anticipated counterarguments that disagree with your thesis. Though you acknowledge the other side’s perspective, it is important to prove why your stance is more logical.
Conclusion (Peroratio): You should summarize your main points. The conclusion also caters to the reader’s emotions and values. The use of pathos here makes the reader more inclined to consider your argument.
Example of the Classical Method:
Introduction (Exordium): Millions of workers are paid a set hourly wage nationwide. The federal minimum wage is standardized to protect workers from being paid too little. Research points to many viewpoints on how much to pay these workers. Some families cannot afford to support their households on the current wages provided for performing a minimum wage job .
Statement of Background (Narratio): Currently, millions of American workers struggle to make ends meet on a minimum wage. This puts a strain on workers’ personal and professional lives. Some work multiple jobs to provide for their families.
Proposition (Propositio): The current federal minimum wage should be increased to better accommodate millions of overworked Americans. By raising the minimum wage, workers can spend more time cultivating their livelihoods.
Proof (Confirmatio): According to the United States Department of Labor, 80.4 million Americans work for an hourly wage, but nearly 1.3 million receive wages less than the federal minimum. The pay raise will alleviate the stress of these workers. Their lives would benefit from this raise because it affects multiple areas of their lives.
Refutation (Refuatio): There is some evidence that raising the federal wage might increase the cost of living. However, other evidence contradicts this or suggests that the increase would not be great. Additionally, worries about a cost of living increase must be balanced with the benefits of providing necessary funds to millions of hardworking Americans.
Conclusion (Peroratio): If the federal minimum wage was raised, many workers could alleviate some of their financial burdens. As a result, their emotional wellbeing would improve overall. Though some argue that the cost of living could increase, the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Healthy Happy Teacher
Helping hardworking teachers stay healthy and happy.
How to Write a Counterclaim [Explained Simply!]
Counterclaims are an essential part of a top-notch argumentative essay. After all, they show that you’ve thoroughly researched and considered both sides of the issue before deciding on your particular stance.
There’s just one problem: they can be a little tricky to write without weakening your main argument, as you may already be aware!
That’s why we put together this guide on writing a counterclaim that will only enhance your position in an argumentative essay and not take anything away from it.
By the end of this article, you’ll be writing counterclaims like a pro – and get that grade you deserve on your next paper. Let’s get started!
What Is a Counterclaim in Writing?
Before we get into how to write one, let’s clarify what we mean by “counterclaim.” In writing, a counterclaim is an opposing argument that goes against the thesis statement of a paper.
It shows your audience that you have researched the topic thoroughly by looking into both sides of the issue and that you’re not trying to hide any important information that refutes your thesis.
Not only that, a well-written counterclaim can even help you win over those who don’t agree with your main claim or argument – especially when you make some good points in your rebuttal paragraph (which we will get into as well).
For example, let’s say you’re writing an argumentative essay on the use of cellphones in schools. If your claim is that they should be allowed at all times because they can help support learning, then the counterclaim could be that they’re more distracting than anything else.
How to Write a Counterclaim
The key to excellent argumentative writing is to make your position convincing and clear while acknowledging – not to mention rebutting – the counterarguments. Fortunately, you can break down the process of crafting a great counterclaim into four simple steps:
1. Research, Research, Research
Of course, a thorough understanding of your position on the topic is essential, but you should also have a good grasp of the main arguments of your opponents.
It’s not enough to just know what the arguments are – you need to know why other people feel this way.
For example, going back to our cellphone paper. If one of the main counterclaims is that cellphones are distracting in schools, you need to find out what is driving these opinions. Are there facts to back it up, or is this purely based on anecdotal evidence?
Once you feel like you have a firm grasp on the opposing view, you can move on to the next step.
2. Determine Where to Put the Counterclaim
A well-written essay typically starts with a few introductory sentences to capture the reader’s attention. Next comes the thesis and the claims (backed with plenty of research and evidence, of course).
By this point, your stance on the issue should be clear, so it’s usually safe to start including your counterclaims in the body of the essay.
As to where exactly you should include your counterclaims, two of the best options include the following:
- In the paragraphs. If your paper has several claims you want to counter, then you may address each one in the paragraphs. This is often most effective right after supporting your claims with evidence and arguments.
- Before the conclusion. This is often the preferred place for counterclaims, especially in shorter essays. It’s a good option because your reader should have a firm grasp of your position at this point, so the counterclaims shouldn’t really weaken your main arguments.
Remember that your counterclaim paragraph(s) should be separate from your introduction and conclusion. As long as it’s outside these areas, your counterclaim should be in a perfectly acceptable position in the paper.
3. Figure Out How Long Your Counterclaim Should Be
It isn’t time to start writing yet! Now that you’ve identified your counterclaim or counterclaims, you need to figure out how much space to devote to it in your essay.
You’ll want to cover the opposing side as concisely as possible, as you don’t want to give them more space than your claims. This is especially important if you have a specific word count; dragging out a counterclaim argument for too long may not leave enough room for you to argue your position properly.
In most cases, one short paragraph per counterclaim should do the trick. Just remember that you need to explain the opposing argument and why others feel this way.
4. Consider How to Present the Counterclaim Fairly
Before you officially start typing things out, one of the most important things to consider is how you will present your counterclaim fairly. You don’t want to present the opposing view with an obvious bias, as it may take away from the credibility of your paper.
And besides, you shouldn’t have to put the other viewpoint down to clarify your stance!
You should have already put lots of strong evidence and arguments in favor of your position throughout your paper, so trying to understand and present the opposing viewpoint fairly shouldn’t weaken your claims too much.
5. Write Your Counterclaim
You’re finally ready to write your counterclaim! The first thing you need to do is include an appropriate transition to help with the flow of your paper.
Some good transitions include:
- Critics have argued that…
- On the other side of the argument, people are concerned that…
- The contrasting viewpoint indicates that…
Once you have chosen an appropriate transition and stated the opposing viewpoint, you can describe why people feel this way. And don’t forget your evidence! As with your claims, you need to show that you’ve done the research to support this position.
From here, you can write your rebuttal explaining any issues or weaknesses with the counterclaim. This is essential to solidifying your original position.
Some suggestions for a good rebuttal include:
- Detailing the particular weaknesses with the counterclaim
- Acknowledging that while these viewpoints have some merit, there is a solution that renders it baseless
- Showing that the benefits of your claims outweigh the risks of the counterclaims
- Pointing out that the benefits of the counterclaim are exceedingly rare
Tips on Writing a Great Counterclaim
Want to make a good counterclaim even better? Remember these tips when writing:
- Objectivity is key. As passionately as you may feel about your position, do your best to remain objective when presenting a counterclaim. For example, avoid saying things like “critics mistakenly believe that…”
- Don’t leave out information on purpose. If you find evidence for your counterclaim supported by research, don’t leave it out of your paper to avoid weakening your argument. Instead, explain why it is weaker than your claims.
- Read through other essays. If you’re still unsure what a good counterclaim looks like, read professional-level papers to see how others have done it.
- A second set of eyes is always helpful! If you can, get someone to read through your paper to make sure your counterclaim is clear, objective, and concise. You may also want their opinion on whether your rebuttal is effective enough to dispute the main points of your counterclaim.
The Bottom Line
Though it may seem daunting, writing an effective counterclaim doesn’t have to be difficult.
Just remember to do your research, avoid putting it in the introduction and conclusion, keep it to a paragraph, present it fairly, and transition into it appropriately.
And most of all, do your best to put any biases aside and remain objective.
By following these tips, writing counterclaims will become second nature to you in no time. Good luck with your next paper!
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Disclosure, disclaimer & privacy policy
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Center Quick Guides
- Citation Resources
- Helpful Links
- Video Resources
- Login or Register
- Graduate Writing Consultations
- Thesis and Dissertation Consultations
- Weekly Write-Ins
- ESOL Graduate Peer Feedback Groups
- Setting Up Your Own Writing Group
- Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- Support for Multilingual Students
- ESOL Opt-In Program
- About Our Consulting Services
- Promote Us to Your Students
- Recommend Consultants
All About Counterarguments
So, you’ve been assigned a paper about counterarguments....
Or, maybe a paper that just requires you to think about the opposition to your argument. Never fear! Counter-arguments can help you to better understand your own argument. This type of assignment allows you the opportunity to think about the issue or problem as a whole rather than just your piece of the whole.
What is a counterargument?
A counterargument is an argument that goes against your thesis and that expresses the perspective of someone with an opposite point of view from your own. While it may seem that acknowledging your opponent’s argument would undermine your own argument, if done well, a counterargument actually fortifies your point. With a counterargument, you have an opportunity to acknowledge and respond to any objections from the opposition, giving you the advantage since the response comes from you. Usage of a counterargument also demonstrates that you’re a rational and fair arguer who is well-versed in your issue since you acknowledge both sides of the argument.

How to start:
First, start as early as possible. Part of utilizing a counterargument is in knowing your argument well, and knowing any subject well takes time.
To find your subject, think about what you’re interested in, but also something that you’re not necessarily emotionally, politically, or personally tied to. That way, you can consider both points in a fair and unbiased way, allowing for equal arguments for both sides of the issue, even though eventually you’ll only take one side of the issue. Start by looking up information about your topic.
Use online databases, looking up both sides of the issue. Remember to that the library has access to hundreds of online databases housing scholarly articles that you can access for free! The university pays for the resources, so be sure to take advantage of them.
Be open to what you find! Even if you initially take one side of the issue, you might find that your stance has changed. This is not necessarily a bad thing! Consider which side feels more compelling based on the research that you find.
How to present your counterargument:
It may be tempting to just write a sentence or two explaining your opponent’s argument and then spend paragraphs refuting that argument, but a good counter-argument is fair in the assessment of the opponent’s position.
Here are some tips:
Provide a few fair reasons why someone could possibly have the perspective of your opposition.
Communicate the counter-point objectively without bias. Look for any words that communicate feelings specific (especially negative) emotions or feelings concerning the argument. Those probably aren’t fair or unbiased. A reader can usually tell that you’re being unfair and might not want to continue reading.
Consider this: would the person who holds this opposite perspective be okay with your method of explaining their side of the issue? If not, then you’re probably not being fair.
How to actually write and implement a counter-argument:
Identify or explain opposing viewpoints. Use phrases like “on the other hand...” or “it is often perceived that...” or “critics may argue...” or “although...” or “some people may think” or (invoking the viewpoint of an expert/group) “according to...”
Summarize their stance in your own words.
Concede. Explain what aspects of your opponent’s argument have validity (but only if you really feel this way because if you don’t, the reader can tell).
Respond. Bring the reader back to your argument and its strengths. Refute your opponent’s argument by explaining how your point works better, is more logically sound, or makes more sense.

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How Counterclaim Your Position in an Argumentative Essay
by Antony W
April 7, 2022

When it comes to an argumentative essay , you have to consider both sides of the argument.
Sure, the goal of the assignment is to take a side on an issue and give evidence to support your stand.
However, if you fail to focus on both sides of the argument, you’ll appear narrowly minded and your essay will be less effective.
So to write a good argumentative essay that can convince your audience or instructor to keep reading to learn more about the issue under investigation, you should include a counterclaim in the paper.
A counterclaim is one of the elements of an argument that shows you invested your time and effort to investigate the two sides of an issue before taking your own stand on the topic.
What is a Counterclaim in an Argumentative Essay?
A counterclaim is simply one or more arguments that oppose the thesis statement of your argument.
Before you arrive at a counterclaim, you need to make sure your thesis explains what you claim you want to prove and how you’d like to do it.
You don’t include a counterclaim in the thesis part. Rather, the thesis should explicitly explain that you’ve done your research and you're convinced that the viewpoint of the opposing side is either invalid or weak.
By including a counterclaim in your essay, you create for yourself an opportunity to give a solid response to a reader’s arguments even before they finish reading the paper.
You end up with an essay that’s not only interesting to read but also one that strengthen your position.
How to Deal With Counterclaims in Your Essay
Counterclaims can be quite challenging to write.
On the one hand, you have your position to defend and you have to do so using all the evidences that you can use.
On the other hand, you have the opposing view to consider and include in the essay.
The question is, how do you consider the counterclaims without weakening your position ?
You can do so in two ways.
The first option is to note and point out the obvious flaws in the opposing arguments. This will show that, while you recognize the opposing views, they have a weakness that your point of view is trying to address.
By identifying the obvious flaws in a counterclaim, you’ll strengthen your own point of view on the issue. The second option is where you agree with the counter argument, but you take this a step further by providing a new evidence that can either weaken or contradict the counterargument.
Again, this will go a long way to strengthen your position and convince your audience to agree with you even if the subject in question is sensitive or controversial.
The Common Types of Counter Arguments in Argumentative Essays
There are 5 types of counterclaims that you’ll encounter as you work on your argumentative essay.
It’s important to understand each before we look at how you can respond to the counter claims.
- Your audience (your reader) may come up with an evidence that could potentially weaken your position. Find out what the evidence can be. Cite and examine the evidence and then conclude by responding to it.
- You can have a situation where an audience draws a different conclusion from the examples you present. If so, you should find a unique conclusion and then respond to it accordingly.
- Sometimes a reader is highly likely to question the claim of your argument . In such a situation, it’s best to identify those claims, explain, and then give a solid response.
- You can have an instance where someone disagrees with your claim. If this is the case, you should explain their perspective in your argument and then give a reasonable response.
- If a reader can give a different explanation for an issue, you should figure out what that explanation might be and then give a completely different explanation yourself.
With that out of the way, let us look at how you can respond to a counterclaim in a way that makes your essay stand a chance to win an argument.
How to Respond to Counterclaims
There are a few response strategies that you can use to respond to counterclaims, but you don’t have to use all of them in the same paper.
The most important thing to do is to choose a strategy that makes the most sense for a particular counterargument.
- If you find yourself nodding in agreement with some of the arguments that your reader or audience present, present their points and then give a challenge to oppose their points.
- There may be an instance where a counterclaim provides an evidence different from what you have in your own argument. In such a case, it would be best if you give the reader a reason not to accept the evidence that the counter argument presents.
- Some arguers will come up with counterclaims that threaten to weaken your argument. In this case, you need to give a thorough explanation on the how or why the evidence they’ve presented doesn’t interfere with or invalidate your claim.
Hire Our Team to Write Your Argumentative Essay
While counterclaims are expected in an argument, responding to them can be quite challenging. So if you feel like the task is too overwhelming to handle even after reading this guide, feel free to get in touch with us and we’ll help you write a high quality argumentative essay fast.
Get in touch with your professional team of writers and get your argumentative essay completed on time
At Help for Assessment, our goal is to see you excel in your academics.
Part of contributing to that vision is by helping you write essays that grab attention, spike reading interest, and earn you the grades that you deserve.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

English Current
ESL Lesson Plans, Tests, & Ideas
- North American Idioms
- Business Idioms
- Idioms Quiz
- Idiom Requests
- Proverbs Quiz & List
- Phrasal Verbs Quiz
- Basic Phrasal Verbs
- North American Idioms App
- A(n)/The: Help Understanding Articles
- The First & Second Conditional
- The Difference between 'So' & 'Too'
- The Difference between 'a few/few/a little/little'
- The Difference between "Other" & "Another"
- Check Your Level
- English Vocabulary
- Verb Tenses (Intermediate)
- Articles (A, An, The) Exercises
- Prepositions Exercises
- Irregular Verb Exercises
- Gerunds & Infinitives Exercises
- Discussion Questions
- Speech Topics
- Argumentative Essay Topics
- Top-rated Lessons
- Intermediate
- Upper-Intermediate
- Reading Lessons
- View Topic List
- Expressions for Everyday Situations
- Travel Agency Activity
- Present Progressive with Mr. Bean
- Work-related Idioms
- Adjectives to Describe Employees
- Writing for Tone, Tact, and Diplomacy
- Speaking Tactfully
- Advice on Monetizing an ESL Website
- Teaching your First Conversation Class
- How to Teach English Conversation
- Teaching Different Levels
- Teaching Grammar in Conversation Class
- Members' Home
- Update Billing Info.
- Cancel Subscription
- North American Proverbs Quiz & List
- North American Idioms Quiz
- Idioms App (Android)
- 'Be used to'" / 'Use to' / 'Get used to'
- Ergative Verbs and the Passive Voice
- Keywords & Verb Tense Exercises
- Irregular Verb List & Exercises
- Non-Progressive (State) Verbs
- Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Present Simple vs. Present Progressive
- Past Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Subject Verb Agreement
- The Passive Voice
- Subject & Object Relative Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns Where/When/Whose
- Commas in Adjective Clauses
- A/An and Word Sounds
- 'The' with Names of Places
- Understanding English Articles
- Article Exercises (All Levels)
- Yes/No Questions
- Wh-Questions
- How far vs. How long
- Affect vs. Effect
- A few vs. few / a little vs. little
- Boring vs. Bored
- Compliment vs. Complement
- Die vs. Dead vs. Death
- Expect vs. Suspect
- Experiences vs. Experience
- Go home vs. Go to home
- Had better vs. have to/must
- Have to vs. Have got to
- I.e. vs. E.g.
- In accordance with vs. According to
- Lay vs. Lie
- Make vs. Do
- In the meantime vs. Meanwhile
- Need vs. Require
- Notice vs. Note
- 'Other' vs 'Another'
- Pain vs. Painful vs. In Pain
- Raise vs. Rise
- So vs. Such
- So vs. So that
- Some vs. Some of / Most vs. Most of
- Sometimes vs. Sometime
- Too vs. Either vs. Neither
- Weary vs. Wary
- Who vs. Whom
- While vs. During
- While vs. When
- Wish vs. Hope
- 10 Common Writing Mistakes
- 34 Common English Mistakes
- First & Second Conditionals
- Comparative & Superlative Adjectives
- Determiners: This/That/These/Those
- Check Your English Level
- Grammar Quiz (Advanced)
- Vocabulary Test - Multiple Questions
- Vocabulary Quiz - Choose the Word
- Verb Tense Review (Intermediate)
- Verb Tense Exercises (All Levels)
- Conjunction Exercises
- List of Topics
- Business English
- Games for the ESL Classroom
- Pronunciation
- Teaching Your First Conversation Class
- How to Teach English Conversation Class
Argumentative Essays: The Counter-Argument & Refutation
An argumentative essay presents an argument for or against a topic. For example, if your topic is working from home , then your essay would either argue in favor of working from home (this is the for side) or against working from home.
Like most essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction that ends with the writer's position (or stance) in the thesis statement .
Introduction Paragraph
(Background information....)
- Thesis statement : Employers should give their workers the option to work from home in order to improve employee well-being and reduce office costs.
This thesis statement shows that the two points I plan to explain in my body paragraphs are 1) working from home improves well-being, and 2) it allows companies to reduce costs. Each topic will have its own paragraph. Here's an example of a very basic essay outline with these ideas:
- Background information
Body Paragraph 1
- Topic Sentence : Workers who work from home have improved well-being .
- Evidence from academic sources
Body Paragraph 2
- Topic Sentence : Furthermore, companies can reduce their expenses by allowing employees to work at home .
- Summary of key points
- Restatement of thesis statement
Does this look like a strong essay? Not really . There are no academic sources (research) used, and also...
You Need to Also Respond to the Counter-Arguments!
The above essay outline is very basic. The argument it presents can be made much stronger if you consider the counter-argument , and then try to respond (refute) its points.
The counter-argument presents the main points on the other side of the debate. Because we are arguing FOR working from home, this means the counter-argument is AGAINST working from home. The best way to find the counter-argument is by reading research on the topic to learn about the other side of the debate. The counter-argument for this topic might include these points:
- Distractions at home > could make it hard to concentrate
- Dishonest/lazy people > might work less because no one is watching
Next, we have to try to respond to the counter-argument in the refutation (or rebuttal/response) paragraph .
The Refutation/Response Paragraph
The purpose of this paragraph is to address the points of the counter-argument and to explain why they are false, somewhat false, or unimportant. So how can we respond to the above counter-argument? With research !
A study by Bloom (2013) followed workers at a call center in China who tried working from home for nine months. Its key results were as follows:
- The performance of people who worked from home increased by 13%
- These workers took fewer breaks and sick-days
- They also worked more minutes per shift
In other words, this study shows that the counter-argument might be false. (Note: To have an even stronger essay, present data from more than one study.) Now we have a refutation.
Where Do We Put the Counter-Argument and Refutation?
Commonly, these sections can go at the beginning of the essay (after the introduction), or at the end of the essay (before the conclusion). Let's put it at the beginning. Now our essay looks like this:
Counter-argument Paragraph
- Dishonest/lazy people might work less because no one is watching
Refutation/Response Paragraph
- Study: Productivity increased by 14%
- (+ other details)
Body Paragraph 3
- Topic Sentence : In addition, people who work from home have improved well-being .
Body Paragraph 4
The outline is stronger now because it includes the counter-argument and refutation. Note that the essay still needs more details and research to become more convincing.

Working from home may increase productivity.
Extra Advice on Argumentative Essays
It's not a compare and contrast essay.
An argumentative essay focuses on one topic (e.g. cats) and argues for or against it. An argumentative essay should not have two topics (e.g. cats vs dogs). When you compare two ideas, you are writing a compare and contrast essay. An argumentative essay has one topic (cats). If you are FOR cats as pets, a simplistic outline for an argumentative essay could look something like this:
- Thesis: Cats are the best pet.
- are unloving
- cause allergy issues
- This is a benefit > Many working people do not have time for a needy pet
- If you have an allergy, do not buy a cat.
- But for most people (without allergies), cats are great
- Supporting Details
Use Language in Counter-Argument That Shows Its Not Your Position
The counter-argument is not your position. To make this clear, use language such as this in your counter-argument:
- Opponents might argue that cats are unloving.
- People who dislike cats would argue that cats are unloving.
- Critics of cats could argue that cats are unloving.
- It could be argued that cats are unloving.
These underlined phrases make it clear that you are presenting someone else's argument , not your own.
Choose the Side with the Strongest Support
Do not choose your side based on your own personal opinion. Instead, do some research and learn the truth about the topic. After you have read the arguments for and against, choose the side with the strongest support as your position.
Do Not Include Too Many Counter-arguments
Include the main (two or three) points in the counter-argument. If you include too many points, refuting these points becomes quite difficult.
If you have any questions, leave a comment below.
- Matthew Barton / Creator of Englishcurrent.com
Additional Resources :
- Writing a Counter-Argument & Refutation (Richland College)
- Language for Counter-Argument and Refutation Paragraphs (Brown's Student Learning Tools)
EnglishCurrent is happily hosted on Dreamhost . If you found this page helpful, consider a donation to our hosting bill to show your support!
24 comments on “ Argumentative Essays: The Counter-Argument & Refutation ”
Thank you professor. It is really helpful.
Can you also put the counter argument in the third paragraph
It depends on what your instructor wants. Generally, a good argumentative essay needs to have a counter-argument and refutation somewhere. Most teachers will probably let you put them anywhere (e.g. in the start, middle, or end) and be happy as long as they are present. But ask your teacher to be sure.
Thank you for the information Professor
how could I address a counter argument for “plastic bags and its consumption should be banned”?
For what reasons do they say they should be banned? You need to address the reasons themselves and show that these reasons are invalid/weak.
Thank you for this useful article. I understand very well.
Thank you for the useful article, this helps me a lot!
Thank you for this useful article which helps me in my study.
Thank you, professor Mylene 102-04
it was very useful for writing essay
Very useful reference body support to began writing a good essay. Thank you!
Really very helpful. Thanks Regards Mayank
Thank you, professor, it is very helpful to write an essay.
It is really helpful thank you
It was a very helpful set of learning materials. I will follow it and use it in my essay writing. Thank you, professor. Regards Isha
Thanks Professor
This was really helpful as it lays the difference between argumentative essay and compare and contrast essay.. Thanks for the clarification.
This is such a helpful guide in composing an argumentative essay. Thank you, professor.
This was really helpful proof, thankyou!
Thanks this was really helpful to me
This was very helpful for us to generate a good form of essay
thank you so much for this useful information.
Thank you so much, Sir. This helps a lot!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Claim vs. Counterclaim
What's the difference.
Claim and counterclaim are two essential components of argumentative writing. A claim is a statement that asserts a position or viewpoint on a particular issue, while a counterclaim is a statement that presents an opposing viewpoint or challenges the validity of the original claim. Both claim and counterclaim are necessary in order to present a well-rounded argument and consider multiple perspectives on a topic. By acknowledging and addressing counterclaims, writers can strengthen their own arguments and demonstrate a deeper understanding of the complexities of the issue at hand.
| Attribute | Claim | Counterclaim |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A statement or assertion that something is true or valid | A statement or assertion that contradicts or opposes the claim |
| Evidence | Supporting facts, data, or examples used to back up the claim | Supporting facts, data, or examples used to back up the counterclaim |
| Purpose | To persuade or convince the audience of a particular viewpoint | To challenge or question the validity of the opposing viewpoint |
| Strength | The degree of persuasiveness or credibility of the claim | The degree of persuasiveness or credibility of the counterclaim |
Further Detail
Introduction.
When engaging in a debate or argument, it is essential to understand the concepts of claim and counterclaim. Both play crucial roles in presenting and defending a particular viewpoint. While a claim asserts a position or belief, a counterclaim challenges or opposes that assertion. In this article, we will explore the attributes of claim and counterclaim, highlighting their differences and similarities.
Definition and Purpose
A claim is a statement that asserts a particular position or viewpoint. It is the main argument that a person or party is trying to prove or support. Claims are typically supported by evidence, reasoning, or examples to persuade others of their validity. On the other hand, a counterclaim is a statement that challenges or opposes a claim. It presents an alternative viewpoint or argument that contradicts the original assertion. The purpose of a counterclaim is to provide a different perspective and challenge the validity of the claim.
Evidence and Support
Claims are typically supported by evidence, reasoning, or examples to strengthen their validity. Evidence can come in various forms, such as statistics, research studies, expert opinions, or personal experiences. The quality and relevance of the evidence play a crucial role in convincing others of the claim's validity. On the contrary, a counterclaim also requires evidence and support to challenge the original assertion effectively. Counterclaims may use similar types of evidence to refute the claim or present contrasting evidence to support the opposing viewpoint.
Strength and Weakness
The strength of a claim lies in its ability to persuade others of the validity of a particular viewpoint. A strong claim is supported by compelling evidence, sound reasoning, and logical arguments. It effectively addresses the issue at hand and convinces others of its truth. However, a weak claim lacks sufficient evidence, reasoning, or support to convince others of its validity. It may be easily refuted or challenged by counterclaims that present stronger arguments or evidence. On the other hand, the strength of a counterclaim lies in its ability to challenge the original assertion effectively. A strong counterclaim presents a compelling alternative viewpoint supported by evidence and reasoning. It raises doubts about the validity of the claim and forces others to consider different perspectives. Conversely, a weak counterclaim fails to provide sufficient evidence or reasoning to challenge the claim effectively. It may be easily dismissed or refuted by the original assertion.
Relevance and Impact
The relevance of a claim lies in its ability to address the issue at hand and persuade others of a particular viewpoint. A relevant claim is directly related to the topic of discussion and provides valuable insights or arguments. It contributes to the overall understanding of the issue and influences others' opinions. Conversely, an irrelevant claim fails to address the topic effectively or provide meaningful insights. It may distract from the main issue or confuse others with irrelevant information. On the other hand, the relevance of a counterclaim lies in its ability to challenge the original assertion effectively. A relevant counterclaim presents a valid alternative viewpoint that adds depth to the discussion and forces others to consider different perspectives. It highlights weaknesses in the original claim and encourages critical thinking. However, an irrelevant counterclaim fails to address the main issue or provide meaningful insights. It may detract from the discussion or confuse others with irrelevant arguments.
In conclusion, claims and counterclaims play essential roles in presenting and defending different viewpoints in debates or arguments. While claims assert a particular position or belief, counterclaims challenge or oppose that assertion. Both require evidence, reasoning, and support to strengthen their validity and persuade others. Understanding the attributes of claim and counterclaim is crucial for effectively engaging in debates and discussions, as it allows individuals to present and defend their viewpoints convincingly.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Pennington Publishing Blog
- Grammar/Mechanics
- Literacy Centers
- Spelling/Vocabulary
- Study Skills
- Uncategorized
Where to Put the Essay Counterclaim

Where is the best place to put the essay counterclaim? The short and sweet answer? David Oldham, professor at Shoreline Community College, states, “The short answer is a counter-argument (counterclaim) can go anywhere except the conclusion. This is because there has to be a rebuttal paragraph after the counter-argument, so if the counter-argument is in the conclusion, something has been left out.”
The counterclaim is the opposing point of view to one’s thesis and is also known as the counterargument. The counterclaim is always accompanied by a refutation, sometimes referred to as a rebuttal. The Common Core State Standards include the counterclaim in Writing Standards 1.0 for grades 7-12. These Standards reference the organization of the counterclaim in terms of clear relationships and logical sequencing. See the boldface phrases in the following grades 7-12 Standards.

Common Core State Standards
Seventh Grade: Introduce claim(s), acknowledge alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence logically.
Eighth Grade: Introduce claim(s), acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence logically.
Ninth and Tenth Grade: Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence.
Eleventh and Twelfth Grade: Introduce precise, knowledgeable claim(s), establish the significance of the claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that logically sequences claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence.
Placement Options
1. Writers can place a separate counterclaim paragraph with refutation as the last body paragraph prior to the conclusion paragraph.
Separate Paragraph Example #1
COUNTERCLAIM Opponents argue that after school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries. Specifically, health professionals suggest that life-threatening concussions occur at frightening rates for student athletes participating in such popular after school sports as football, soccer, basketball, and wrestling (Bancroft 22, 23). Even minor injuries sustained from participation in after school sports increase absent rates and the expense of creating injury reports for students (Sizemore 3). REFUTATION Although students do suffer both serious and minor injuries in after school sports, these injuries are quite rare. The organization, supervision, and safety measures of school-sponsored sports are superior to those of alternative fee-based community-sponsored recreational leagues or even privately sponsored sports organizations (Kinney 2). Additionally, without free after school sports programs, many students would still play sports without adult supervision and even more injuries would result.
2. Writers can place a separate counterclaim paragraph without refutation as the first body paragraph following the thesis statement to anticipate objections prior to providing evidence to prove the claim of the thesis statement.
Separate Paragraph Example #2
COUNTERCLAIM Those who favor eliminating after school sports argue that after school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries. Specifically, health professionals suggest that life-threatening concussions occur at frightening rates for student athletes participating in such popular after school sports as football, soccer, basketball, and wrestling (Bancroft 22, 23). Even minor injuries sustained from participation in after school sports increase absent rates and the expense of creating injury reports for students (Sizemore 3). Additionally, youth and adolescents are not developmentally ready to play contact sports. Key components of the brain and skeletal structure have not yet formed (Mays 14), and injuries can have lasting damage to young people.
3. Writers can embed a counterclaim and refutation within a body paragraph.
Embedded within Paragraph Example
After school sports provide safe and free programs for students who might otherwise not be able to participate in individual or team sports. The organization, supervision, and safety measures of school-sponsored sports are superior to those of alternative fee-based community-sponsored recreational leagues or even privately sponsored sports organizations (Kinney 2). Additionally, without free after school sports programs, many students would still play sports without adult supervision and even more injuries would result. COUNTERCLAIM However, some people would argue that after school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries and resulting absences with the added expenses of creating injury reports for students (Sizemore 3). REFUTATION Although students do suffer both serious and minor injuries in after school sports and there are resulting absences and injury reports, without school-sponsored sports the likelihood of more injuries from less supervised recreational leagues or privately sponsored leagues with fewer safety regulations would, no doubt, be much worse.
4. Writers can embed a counterclaim and refutation within a sentence or sentences found in a body paragraph.
Embedded within Sentences Example
After school sports provide safe and free programs for students who might otherwise not be able to participate in individual or team sports. COUNTERCLAIM Even so, some would question the safety of these programs, citing the numbers of life-threatening concussions from after school sports such as football, REFUTATION but these statistics are misleading. According to the highly respected Youth in Sports report, fewer serious injuries occur to students playing after school sports as compared to students not playing after school sports (Green 22).
5. Writers can embed a counterclaim within the introductory paragraph and use the thesis statement as refutation.
Introductory Paragraph Example
After school sports are extra-curricular activities included in most elementary, middle school, and high schools throughout the world. COUNTERCLAIM Some would argue that schools can no longer afford these programs and the expenses of lawsuits resulting from sports-related injuries. REFUTATION AS THESIS STATEMENT On the contrary, schools can and should invest in well-supervised after school sports to promote health and minimize sports-related injuries.
Each of these counterclaim placements has merit, depending upon the nature of the argumentative essay. Help students develop the writing flexibility and dexterity they need by applying each of these strategies in the draft and revision stages. As always, show models of counterclaims and refutations, teach a variety of types of evidence , and help students avoid the pitfalls of fallacious reasoning .
In addition to Where to Put the Essay Counterclaim, writing teachers may also be interested in these related articles: Counterclaim and Refutation Sentence Frames , What is the Essay Counterclaim? , and Why Use an Essay Counterclaim?

TEACHING ESSAYS BUNDLE
The author’s TEACHING ESSAYS BUNDLE includes the three printable and digital resources students need to master the CCSS W.1 argumentative and W.2 informational/explanatory essays. Each no-prep resource allows students to work at their own paces via mastery learning. How to Teach Essays includes 42 skill-based essay strategy worksheets (fillable PDFs and 62 Google slides), beginning with simple 3-word paragraphs and proceeding step-by-step to complex multi-paragraph essays. One skill builds upon another. The Essay Skills Worksheets include 97 worksheets (printables and 97 Google slides) to help teachers differentiate writing instruction with both remedial and advanced writing skills. The Eight Writing Process Essays (printables and 170 Google slides) each feature an on-demand diagnostic essay assessment, writing prompt with connected reading, brainstorming, graphic organizer, response, revision, and editing activities. Plus, each essay includes a detailed analytical (not holistic) rubric for assessment-based learning.
Grammar/Mechanics , Literacy Centers , Study Skills , Writing argument essay , argumentative essay , claims , common core writing standards , Counterarguments , Counterclaims , essay argument , essay strategies , Mark Pennington , Opposing Claims , rebut , Rebuttal , Refutation , refute , Teaching Essay Strategies , types of evidence
- No comments yet.
- No trackbacks yet.
Links to Programs and Resources
- About the Author/Contact Us
- Free Reading/ELA Assessments
- Free Articles and Resources
- Testimonials
Join the SOR Literacy Hub - Resource Sharing FB Group
https://www.facebook.com/groups/sorliteracyhub
Recent Articles
- FREE Diagnostic Literacy Assessments August 28, 2024
- FREE Transition Worksheets August 28, 2024
- FREE Interactive Morphology Walls August 27, 2024
- Middle School Reading Intervention June 16, 2024
- Phonics Lesson for Reading Intervention May 30, 2024
- Phonemic Awareness for Older Students May 29, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | ELL January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | SPED January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | High School January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | Middle School January 2, 2024
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Dianna Radcliff
Teaching Upper Elementary & more
How to Teach Claims, Counterclaims and Rebuttals in Writing!
July 29, 2019 by Dianna Radcliff

Teaching claims, counterclaims and rebuttals in writing can improve a students opinion or argumentative essay.
This post will explain how I teach claims, counterclaims and rebuttals in writing.
To begin, let’s clarify the meaning of the following terms when giving instruction:
- Counterclaim

What is a Counterclaim?
A counterclaim is a claim used to rebut a previous claim.
A claim is the main argument. A counterclaim is the opposite of the claim, or argument.
What is a Rebuttal?
A rebuttal is when you address and challenge a claim by disapproving it.
After you have stated your counterclaim in an argument, you add your rebuttal to why you disapprove it. The goal is to weaken the main argument with your reasons and evidence.
What is a Reason?
A reason tells why a claim is made. Followed by supporting evidence.
What is Evidence?
Evidence is the facts or research to support the claim and reason.
Mini Lesson:
What to Prepare in advance:
- Download, print, cut, laminate and attach to sticks the FREE resource below.
- Write or type examples of a claim, counterclaim and rebuttal then cut up. This is for the acting out part. (see image below as an example)
- Find additional examples via student work pieces, articles or in texts to share and color code. You can share on another anchor chart, display on your SmartBoard or simply read aloud.

- Introduce the lesson by creating an anchor chart. (See below example or search online.)
- Using the colors in my example below, or your own colors, share examples from student pieces, articles or in texts you have found. You can share these examples on another anchor chart, display on your SmartBoard or simply read aloud.
- Using the stick bubbles in the FREE resource below, have 3 volunteers come up to demonstrate. Line students up in order and have them read their part holding up the stick bubble when speaking.

Anchor Chart Examples:
***Click on the Anchor Chart images to find more anchor charts you can use in your classroom!

Where to insert a Counterclaim?
When modeling, show students examples of inserting a counterclaim inside a body paragraph following reasons and evidence.
Where to insert a Rebuttal?
When modeling, show students examples of inserting a rebuttal following a counterclaim inside a body paragraph. Always use reasons and evidence.
Free Resource to Download:
More Helpful Essay Writing Resources:
- FREE Essay Planning Pages
- FREE Paragraph Writing Rubric
- FREE Paragraph Writing for an Essay Graphic Organizers (Color Coded)
- FREE Essay Writing Timing Slides
- Essay Writing Test Prep PowerPoint
- Essay Writing Sources and Prompts
***Click HERE or on the photo below to Download your FREE Resource! Simply print on colored paper (or cardstock) and then laminate!
Thank you for subscribing!

Share this:


Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
How to write counterclaim: essential guide.
October 20, 2021
Are you trying to address your opinion and convince someone of your point of view? A counterclaim is what you need! A claim is an idea or an opinion that someone stands by. A counterclaim, however, is an opposing point of view about the concept. A strategic argumentative essay defines what the other side may say and explains why their claim is wrong; this is a counterclaim.

A counterclaim is included in argumentative writing and thesis to convince the reader to accept your claim. It’s essential to craft a good counterclaim to convince and get the reader on your side. The blog will provide you with complete insight into everything you need to know about writing counterclaims.
What is a Counterclaim in Writing?
A counterclaim is the other side of the argument or your original claim. In your claim, you make clear what you plan to prove. The counterclaim paragraph shows the opponent’s side of viewpoint and defines it in a way that seems weak and invalid.
The main aim behind the counterclaim is to convince the reader of your point of view. Hence, it’s essential to write a strong counterclaim paragraph to answer all the potential arguments the reader might have. A counterclaim essay, if done well, shows that the writer has considered both sides of the picture, which strengthens its position. Argumentative writing, thesis, or any other assignments that may involve convincing the audience in favor of your point of view can Use counterclaims to persuade the audience of the writer’s opinion. Any form of writing that involves more than one point of you can use claims and counterclaims to simplify the situation.
An argumentative essay is written in the following steps: Claim Counterclaim/ Counterclaims Rebuttal
Learning how to draft counterclaims is essential for every student. Individuals may need to convince the audience of their point of view when they step into real life. If you find yourself in any form of debate, you will always have a claim to fight for. You will have to create counterclaims to tell the audience about all the aspects that you have considered and then let them know the best possible option through a rebuttal.
The concept of counterclaims is also helpful for Law and business students in attaining their degrees. For law students, many cases may require a lawyer to draft a substantial counterclaim and rebuttal for the opponent in the legal issues. Likewise, in the business field, the concept of counterclaim may help the business evaluate the effectiveness of each contract. Also, considering all the contradictory aspects of your claim in any form of writing creates a good impression. The writer appears to be thoughtful, and just by considering and mentioning all the arguments, there may be present against his claim.
Claims vs. Counterclaims
| Claims | Counterclaims | |
| Goal | They have a position to be argued | They address the arguments against the claim |
| What is a good claim/counterclaim? | Strong claims are debatable, compelling, and defensible | Strong counterclaims help in building a convincing argument |
| Point of View | Clearly identifies the writer’s opinion | Identifies all the other points of view that are valid |
| Intention | Shows the direction of the writer’s thinking | Allows the reader to evaluate other valid points of views |
| Format | Claims do not have terms such as “I think” or “I feel” | The words that should be used are “It may be true, however…” |
| Example | McDonald’s is considered a healthy restaurant as they offer salad, water, fruits, and other great alternatives for breakfast. | Even though Mcdonald’s has a few healthy options on its menu, the vast majority of the options are deep fried and high in calories. |
How to Find Counterclaim?
There are a few steps and options to consider when trying to find a counterclaim:
- You need to identify the target audience that will be most affected by the claim.
- After you have identified your target audience, you can do quick questioning from an individual representing each group against their problems with your claim.
- Meanwhile, the writer should also form an idea of the possible alternative points of view the audience may have against the main claim.
- An alternative to finding a counterclaim is to note down all the disadvantages or alternative explanations that your target audience may have. However, the first option is more effective as this may allow you to find the counterclaims that may not be in your mind.
Where Do You Put A Counterclaim in an Essay?
When writing counterclaims in an essay, it’s essential to introduce the reader to the claim or the original argument. The claim is your point of view and can be argued by the reader. There is usually one main claim for which the argumentative essay revolves around. The claim is generally introduced in the introductory paragraph of your article or thesis. Right after the claim comes your counterclaim, which are the possible concerns the audience might have against your claim.
How to Introduce A Counterclaim?
There are various options you can consider on how to start a counterclaim paragraph, for example:
“On the other hand, some people say….” “Certainly, some people say….” “Admittedly, some people might say….” “A common counterpoint is often….”
You can start the counterclaim by explaining what counter-arguments the claim has. A good counterclaim paragraph will strengthen your essay and your position in the eyes of the reader.
How to Write a Counterclaim?
When writing a counterclaim, you need to imagine a skeptical reader and then draft your counterclaim paragraph. In the counterclaim, cite all the critics or sources who may resist your claim. The main aim behind the counterclaim is to address all the possible concerns of the reader to refute them. You can manage them by using the following words:
“However, some socials would certainly believe….” “Here, many feminists would argue….” “The opposing view is that….”
Moreover, it’s also vital that you evaluate your claim for all the possible problems and disadvantages that the claim may have. After introducing the counterclaim, discuss why it is incorrect. Also, use this part of the essay to think of alternate solutions that the claim may have in the following words:
“Alternatively, the issue could be viewed….” “Others may conclude….” “Despite this information….”
Explain the counterclaim as clearly and briefly as you can. It’s also an excellent strategy to prove where possible to weaken the opponent’s point of view.
How to Write A Good Counterclaim?
There are few tips that you can keep in mind when drafting a counterclaim.
- Never introduce your counterclaim in the introductory paragraph: It’s a rule you should abide by to create an effective essay. Stating a counterclaim in the introduction makes the essay look vague.
- When you start your counterclaim do not state it as right or wrong: Talk about why a counterclaim is believed instead of considering it right or wrong. Write a counterclaim in a way that the reader automatically turns in your favor.
- Always choose the best words for your counterclaim: You don’t want to sound rude to the reader so always choose the words wisely.
- It’s also essential to be just and unbiased as you write a counterclaim: To strengthen your thesis or argument you should always sound unbiased towards your opinion. The reader should know that you talking on the basis of facts and you don’t just want to implement your point of view.
- Always provide evidence that supports your counterclaim: Providing evidence where ever possible is another great way to write counterclaims. Providing evidence to support the counterclaim makes it easier to convince the reader of your claim.
What Is A Rebuttal?
Your response to the counterclaim is known as the rebuttal. In this section, you showcase the evidence that disagrees with the counterclaim. You present all your reasoning to shoot down the opponent’s disagreement and bring them to your side. The comebacks are always intense; likewise, a rebuttal paragraph should clearly explain why you support your claim. An excellent rebuttal might involve research to get the full knowledge of the facts. This will also allow you to resolve the argument in the best way.
How To Write Counterclaim And Rebuttal?
After the counterclaim argument, we come to the solution in the form of a rebuttal. In the counterclaim, the paragraph mentions the counterargument a reader might have for your claim. Then we move on to resolving the debate by writing a rebuttal. It’s crucial to sound polite as you start with your rebuttal. The tone of your essay can make a significant impact on the audience; therefore, make sure to respect the different options as you write a rebuttal. There are few examples of how you can begin your rebuttal:
“Although some people think..others understand….” “The Evidence, however, clearly supports the argument that….” “This may be an understandable concern, however….”
Moreover, provide a point-by-point reply to all the counterclaims you have outlined. Make sure not to miss out on any counterclaim otherwise, your essay will look incomplete and vague. Also, if you miss out on any counterclaim in your rebuttal, this may weaken your claim. Rebuttal marks the end of your argument, so it’s advised to finish it with friendly and positive sentences. The tone of the rebuttal will let the audience know that you have done your best to come up with the best solution to the counterclaim. Lastly, when your rebuttal is done and your argument is sorted, it’s time to review your work. Read your work from the perspective of the reviewer. Will they be satisfied by the explanations you have given? Is the text clear and easily comprehendible? If the answer to all these questions is yes, you can submit your paper or argument confidently.
Example Of Claim, Counterclaim, And Rebuttal
Claim: Cellphones should be banned from school as they distract students from learning Counterclaim: Others may say that students should carry cell phones for emergency purposes. Rebuttal: There are many other less disruptive ways parents can use to communicate with their kids.
Need Help Writing A Counterclaim?
Writing a counterclaim for your thesis can be tricky, and you may need help with your work. Our writing services offer assistance for writing counterclaims. They offer reliable and creative solutions for all your writing needs. Our writers make sure to do proper research for the content so that there is no room for error. Our researchers are well versed in the services they offer. The writing services can easily be accessed online and cater to all the assignments of college, university, and other classes. You can contact the writing services for a custom-based package if you hire them for a long-term basis. Even the professors can benefit from the writing services by getting their student’s work proofread.

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics
Counterclaim
Definition of counterclaim, what is counterclaim, counterclaim example.
Marsha has made her claim – asking for a company cell phone.
Compulsory Counterclaims and Permissive Counterclaims
(a) (1) … A pleading must state as a counterclaim any claim that—at the time of its service—the pleader has against an opposing party if the claim:
Example of Compulsory Counterclaim
Once Martin had filed his lawsuit, Adam could have filed a counterclaim, claiming that Martin had fraudulently convinced him to invest the money, and asking for his $5,000 investment to be returned. This counterclaim then requires Martin to show to the court that he had indeed been fulfilling his responsibilities according to the contract, and that he will continue to do so. In such a case, the court will hear the entire case, from both sides, before making its decision.
Frivolous Counterclaim Rejected by Court
Related legal terms and issues.

Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key things to know about U.S. election polling in 2024

Confidence in U.S. public opinion polling was shaken by errors in 2016 and 2020. In both years’ general elections, many polls underestimated the strength of Republican candidates, including Donald Trump. These errors laid bare some real limitations of polling.
In the midterms that followed those elections, polling performed better . But many Americans remain skeptical that it can paint an accurate portrait of the public’s political preferences.
Restoring people’s confidence in polling is an important goal, because robust and independent public polling has a critical role to play in a democratic society. It gathers and publishes information about the well-being of the public and about citizens’ views on major issues. And it provides an important counterweight to people in power, or those seeking power, when they make claims about “what the people want.”
The challenges facing polling are undeniable. In addition to the longstanding issues of rising nonresponse and cost, summer 2024 brought extraordinary events that transformed the presidential race . The good news is that people with deep knowledge of polling are working hard to fix the problems exposed in 2016 and 2020, experimenting with more data sources and interview approaches than ever before. Still, polls are more useful to the public if people have realistic expectations about what surveys can do well – and what they cannot.
With that in mind, here are some key points to know about polling heading into this year’s presidential election.
Probability sampling (or “random sampling”). This refers to a polling method in which survey participants are recruited using random sampling from a database or list that includes nearly everyone in the population. The pollster selects the sample. The survey is not open for anyone who wants to sign up.
Online opt-in polling (or “nonprobability sampling”). These polls are recruited using a variety of methods that are sometimes referred to as “convenience sampling.” Respondents come from a variety of online sources such as ads on social media or search engines, websites offering rewards in exchange for survey participation, or self-enrollment. Unlike surveys with probability samples, people can volunteer to participate in opt-in surveys.
Nonresponse and nonresponse bias. Nonresponse is when someone sampled for a survey does not participate. Nonresponse bias occurs when the pattern of nonresponse leads to error in a poll estimate. For example, college graduates are more likely than those without a degree to participate in surveys, leading to the potential that the share of college graduates in the resulting sample will be too high.
Mode of interview. This refers to the format in which respondents are presented with and respond to survey questions. The most common modes are online, live telephone, text message and paper. Some polls use more than one mode.
Weighting. This is a statistical procedure pollsters perform to make their survey align with the broader population on key characteristics like age, race, etc. For example, if a survey has too many college graduates compared with their share in the population, people without a college degree are “weighted up” to match the proper share.
How are election polls being conducted?
Pollsters are making changes in response to the problems in previous elections. As a result, polling is different today than in 2016. Most U.S. polling organizations that conducted and publicly released national surveys in both 2016 and 2022 (61%) used methods in 2022 that differed from what they used in 2016 . And change has continued since 2022.
One change is that the number of active polling organizations has grown significantly, indicating that there are fewer barriers to entry into the polling field. The number of organizations that conduct national election polls more than doubled between 2000 and 2022.
This growth has been driven largely by pollsters using inexpensive opt-in sampling methods. But previous Pew Research Center analyses have demonstrated how surveys that use nonprobability sampling may have errors twice as large , on average, as those that use probability sampling.
The second change is that many of the more prominent polling organizations that use probability sampling – including Pew Research Center – have shifted from conducting polls primarily by telephone to using online methods, or some combination of online, mail and telephone. The result is that polling methodologies are far more diverse now than in the past.
(For more about how public opinion polling works, including a chapter on election polls, read our short online course on public opinion polling basics .)
All good polling relies on statistical adjustment called “weighting,” which makes sure that the survey sample aligns with the broader population on key characteristics. Historically, public opinion researchers have adjusted their data using a core set of demographic variables to correct imbalances between the survey sample and the population.
But there is a growing realization among survey researchers that weighting a poll on just a few variables like age, race and gender is insufficient for getting accurate results. Some groups of people – such as older adults and college graduates – are more likely to take surveys, which can lead to errors that are too sizable for a simple three- or four-variable adjustment to work well. Adjusting on more variables produces more accurate results, according to Center studies in 2016 and 2018 .
A number of pollsters have taken this lesson to heart. For example, recent high-quality polls by Gallup and The New York Times/Siena College adjusted on eight and 12 variables, respectively. Our own polls typically adjust on 12 variables . In a perfect world, it wouldn’t be necessary to have that much intervention by the pollster. But the real world of survey research is not perfect.
Predicting who will vote is critical – and difficult. Preelection polls face one crucial challenge that routine opinion polls do not: determining who of the people surveyed will actually cast a ballot.
Roughly a third of eligible Americans do not vote in presidential elections , despite the enormous attention paid to these contests. Determining who will abstain is difficult because people can’t perfectly predict their future behavior – and because many people feel social pressure to say they’ll vote even if it’s unlikely.
No one knows the profile of voters ahead of Election Day. We can’t know for sure whether young people will turn out in greater numbers than usual, or whether key racial or ethnic groups will do so. This means pollsters are left to make educated guesses about turnout, often using a mix of historical data and current measures of voting enthusiasm. This is very different from routine opinion polls, which mostly do not ask about people’s future intentions.
When major news breaks, a poll’s timing can matter. Public opinion on most issues is remarkably stable, so you don’t necessarily need a recent poll about an issue to get a sense of what people think about it. But dramatic events can and do change public opinion , especially when people are first learning about a new topic. For example, polls this summer saw notable changes in voter attitudes following Joe Biden’s withdrawal from the presidential race. Polls taken immediately after a major event may pick up a shift in public opinion, but those shifts are sometimes short-lived. Polls fielded weeks or months later are what allow us to see whether an event has had a long-term impact on the public’s psyche.
How accurate are polls?
The answer to this question depends on what you want polls to do. Polls are used for all kinds of purposes in addition to showing who’s ahead and who’s behind in a campaign. Fair or not, however, the accuracy of election polling is usually judged by how closely the polls matched the outcome of the election.
By this standard, polling in 2016 and 2020 performed poorly. In both years, state polling was characterized by serious errors. National polling did reasonably well in 2016 but faltered in 2020.
In 2020, a post-election review of polling by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) found that “the 2020 polls featured polling error of an unusual magnitude: It was the highest in 40 years for the national popular vote and the highest in at least 20 years for state-level estimates of the vote in presidential, senatorial, and gubernatorial contests.”
How big were the errors? Polls conducted in the last two weeks before the election suggested that Biden’s margin over Trump was nearly twice as large as it ended up being in the final national vote tally.
Errors of this size make it difficult to be confident about who is leading if the election is closely contested, as many U.S. elections are .
Pollsters are rightly working to improve the accuracy of their polls. But even an error of 4 or 5 percentage points isn’t too concerning if the purpose of the poll is to describe whether the public has favorable or unfavorable opinions about candidates , or to show which issues matter to which voters. And on questions that gauge where people stand on issues, we usually want to know broadly where the public stands. We don’t necessarily need to know the precise share of Americans who say, for example, that climate change is mostly caused by human activity. Even judged by its performance in recent elections, polling can still provide a faithful picture of public sentiment on the important issues of the day.
The 2022 midterms saw generally accurate polling, despite a wave of partisan polls predicting a broad Republican victory. In fact, FiveThirtyEight found that “polls were more accurate in 2022 than in any cycle since at least 1998, with almost no bias toward either party.” Moreover, a handful of contrarian polls that predicted a 2022 “red wave” largely washed out when the votes were tallied. In sum, if we focus on polling in the most recent national election, there’s plenty of reason to be encouraged.
Compared with other elections in the past 20 years, polls have been less accurate when Donald Trump is on the ballot. Preelection surveys suffered from large errors – especially at the state level – in 2016 and 2020, when Trump was standing for election. But they performed reasonably well in the 2018 and 2022 midterms, when he was not.
During the 2016 campaign, observers speculated about the possibility that Trump supporters might be less willing to express their support to a pollster – a phenomenon sometimes described as the “shy Trump effect.” But a committee of polling experts evaluated five different tests of the “shy Trump” theory and turned up little to no evidence for each one . Later, Pew Research Center and, in a separate test, a researcher from Yale also found little to no evidence in support of the claim.
Instead, two other explanations are more likely. One is about the difficulty of estimating who will turn out to vote. Research has found that Trump is popular among people who tend to sit out midterms but turn out for him in presidential election years. Since pollsters often use past turnout to predict who will vote, it can be difficult to anticipate when irregular voters will actually show up.
The other explanation is that Republicans in the Trump era have become a little less likely than Democrats to participate in polls . Pollsters call this “partisan nonresponse bias.” Surprisingly, polls historically have not shown any particular pattern of favoring one side or the other. The errors that favored Democratic candidates in the past eight years may be a result of the growth of political polarization, along with declining trust among conservatives in news organizations and other institutions that conduct polls.
Whatever the cause, the fact that Trump is again the nominee of the Republican Party means that pollsters must be especially careful to make sure all segments of the population are properly represented in surveys.
The real margin of error is often about double the one reported. A typical election poll sample of about 1,000 people has a margin of sampling error that’s about plus or minus 3 percentage points. That number expresses the uncertainty that results from taking a sample of the population rather than interviewing everyone . Random samples are likely to differ a little from the population just by chance, in the same way that the quality of your hand in a card game varies from one deal to the next.
The problem is that sampling error is not the only kind of error that affects a poll. Those other kinds of error, in fact, can be as large or larger than sampling error. Consequently, the reported margin of error can lead people to think that polls are more accurate than they really are.
There are three other, equally important sources of error in polling: noncoverage error , where not all the target population has a chance of being sampled; nonresponse error, where certain groups of people may be less likely to participate; and measurement error, where people may not properly understand the questions or misreport their opinions. Not only does the margin of error fail to account for those other sources of potential error, putting a number only on sampling error implies to the public that other kinds of error do not exist.
Several recent studies show that the average total error in a poll estimate may be closer to twice as large as that implied by a typical margin of sampling error. This hidden error underscores the fact that polls may not be precise enough to call the winner in a close election.
Other important things to remember
Transparency in how a poll was conducted is associated with better accuracy . The polling industry has several platforms and initiatives aimed at promoting transparency in survey methodology. These include AAPOR’s transparency initiative and the Roper Center archive . Polling organizations that participate in these organizations have less error, on average, than those that don’t participate, an analysis by FiveThirtyEight found .
Participation in these transparency efforts does not guarantee that a poll is rigorous, but it is undoubtedly a positive signal. Transparency in polling means disclosing essential information, including the poll’s sponsor, the data collection firm, where and how participants were selected, modes of interview, field dates, sample size, question wording, and weighting procedures.
There is evidence that when the public is told that a candidate is extremely likely to win, some people may be less likely to vote . Following the 2016 election, many people wondered whether the pervasive forecasts that seemed to all but guarantee a Hillary Clinton victory – two modelers put her chances at 99% – led some would-be voters to conclude that the race was effectively over and that their vote would not make a difference. There is scientific research to back up that claim: A team of researchers found experimental evidence that when people have high confidence that one candidate will win, they are less likely to vote. This helps explain why some polling analysts say elections should be covered using traditional polling estimates and margins of error rather than speculative win probabilities (also known as “probabilistic forecasts”).
National polls tell us what the entire public thinks about the presidential candidates, but the outcome of the election is determined state by state in the Electoral College . The 2000 and 2016 presidential elections demonstrated a difficult truth: The candidate with the largest share of support among all voters in the United States sometimes loses the election. In those two elections, the national popular vote winners (Al Gore and Hillary Clinton) lost the election in the Electoral College (to George W. Bush and Donald Trump). In recent years, analysts have shown that Republican candidates do somewhat better in the Electoral College than in the popular vote because every state gets three electoral votes regardless of population – and many less-populated states are rural and more Republican.
For some, this raises the question: What is the use of national polls if they don’t tell us who is likely to win the presidency? In fact, national polls try to gauge the opinions of all Americans, regardless of whether they live in a battleground state like Pennsylvania, a reliably red state like Idaho or a reliably blue state like Rhode Island. In short, national polls tell us what the entire citizenry is thinking. Polls that focus only on the competitive states run the risk of giving too little attention to the needs and views of the vast majority of Americans who live in uncompetitive states – about 80%.
Fortunately, this is not how most pollsters view the world . As the noted political scientist Sidney Verba explained, “Surveys produce just what democracy is supposed to produce – equal representation of all citizens.”
- Survey Methods
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
- Voter Files

Scott Keeter is a senior survey advisor at Pew Research Center .

Courtney Kennedy is Vice President of Methods and Innovation at Pew Research Center .
How do people in the U.S. take Pew Research Center surveys, anyway?
How public polling has changed in the 21st century, what 2020’s election poll errors tell us about the accuracy of issue polling, a field guide to polling: election 2020 edition, methods 101: how is polling done around the world, most popular.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

Trump and Allies Forge Plans to Increase Presidential Power in 2025
The former president and his backers aim to strengthen the power of the White House and limit the independence of federal agencies.
Donald J. Trump intends to bring independent regulatory agencies under direct presidential control. Credit... Doug Mills/The New York Times
Supported by
- Share full article

By Jonathan Swan Charlie Savage and Maggie Haberman
- Published July 17, 2023 Updated July 18, 2023
Donald J. Trump and his allies are planning a sweeping expansion of presidential power over the machinery of government if voters return him to the White House in 2025, reshaping the structure of the executive branch to concentrate far greater authority directly in his hands.
Their plans to centralize more power in the Oval Office stretch far beyond the former president’s recent remarks that he would order a criminal investigation into his political rival, President Biden, signaling his intent to end the post-Watergate norm of Justice Department independence from White House political control.
Mr. Trump and his associates have a broader goal: to alter the balance of power by increasing the president’s authority over every part of the federal government that now operates, by either law or tradition, with any measure of independence from political interference by the White House, according to a review of his campaign policy proposals and interviews with people close to him.
Mr. Trump intends to bring independent agencies — like the Federal Communications Commission, which makes and enforces rules for television and internet companies, and the Federal Trade Commission, which enforces various antitrust and other consumer protection rules against businesses — under direct presidential control.
He wants to revive the practice of “impounding” funds, refusing to spend money Congress has appropriated for programs a president doesn’t like — a tactic that lawmakers banned under President Richard Nixon.
He intends to strip employment protections from tens of thousands of career civil servants, making it easier to replace them if they are deemed obstacles to his agenda. And he plans to scour the intelligence agencies, the State Department and the defense bureaucracies to remove officials he has vilified as “the sick political class that hates our country.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement

COMMENTS
There is a structure where the counterclaims are located within all the body paragraphs. In this case, you will write your claim, followed by a counterclaim, and then a rebuttal. This means that for every claim you present to support your thesis, there will be a counterclaim and a rebuttal.
The most common spots are the following: Before your conclusion. This is a common and effective spot for a counterargument because it's a chance to address anything that you think a reader might still be concerned about after you've made your main argument. Don't put a counterargument in your conclusion, however.
The 4 parts of an argumentative essay are the claim, counterclaim, reasoning, and evidence. The claim is the author's argument that they are attempting to prove in the essay. The counterclaim is ...
Create a thesis statement in the last sentence. Write a counterclaim that rebuts the initial argument. Many students fail to appreciate the fact that there is a difference between a claim and a counterclaim. The claim demonstrates your position of argument or the assertion of a fact, whereas a counterclaim negates a specific claim by refuting it.
Good ways to start your counterclaim paragraph include: "Critics have argued that…". "Some people may conclude that". "On the other side of the argument, people are concerned that…". "The opposing viewpoint states that…". Once you have stated the alternative view, go ahead and describe why that view is held. Present evidence.
Step 1. Come up with a Counterargument. A strong rebuttal is only possible when there's a strong counterargument. You may be convinced of your idea but try to place yourself on the other side. Rather than addressing weak opposing views that are easy to fend off, try to come up with the strongest claims that could be made.
Writers should state claims as fact and be as straightforward and concise as possible. In an essay or any other form of argumentative writing, the claim is usually found at the end of the first ...
Counter Argument. One way to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counter arguments, or objections. By considering opposing views, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not ...
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows: Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument. Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
When writing an argumentative essay, it is important to understand what exactly a counterargument (sometimes referred to as a counterclaim) is.In an effective argument, the writer or speaker will ...
The key to excellent argumentative writing is to make your position convincing and clear while acknowledging - not to mention rebutting - the counterarguments. Fortunately, you can break down the process of crafting a great counterclaim into four simple steps: 1. Research, Research, Research. Of course, a thorough understanding of your ...
With a counterargument, you have an opportunity to acknowledge and respond to any objections from the opposition, giving you the advantage since the response comes from you. Usage of a counterargument also demonstrates that you're a rational and fair arguer who is well-versed in your issue since you acknowledge both sides of the argument.
A thesis statement is a claim that sets up your argument. Your thesis should situate your argument within a broader discussion, which will likely involve addressing possible objections, or counter-claims. Counter-claims will help you develop a well-rounded argument by showing you've considered many possible positions on your topic.
A counterclaim is one of the elements of an argument that shows you invested your time and effort to investigate the two sides of an issue before taking your own stand on the topic. What is a Counterclaim in an Argumentative Essay? A counterclaim is simply one or more arguments that oppose the thesis statement of your argument.
An argumentative essay presents an argument for or against a topic. For example, if your topic is working from home, then your essay would either argue in favor of working from home (this is the for side) or against working from home.. Like most essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction that ends with the writer's position (or stance) in the thesis statement.
Step 1: Write a counterclaim. Write a sentence that contradicts the claim. For example, if your thesis says, "Everyone should eat chocolate ice cream," then your counterclaim might be, "Some people are allergic to chocolate.". Step 2: Explain the counterclaim. The more "real" you make the opposing position, the more "right" you ...
A claim is a statement that asserts a particular position or viewpoint. It is the main argument that a person or party is trying to prove or support. Claims are typically supported by evidence, reasoning, or examples to persuade others of their validity. On the other hand, a counterclaim is a statement that challenges or opposes a claim.
The counterclaim is the opposing point of view to one's thesis and is also known as the counterargument. The counterclaim is always accompanied by a refutation, sometimes referred to as a rebuttal. The Common Core State Standards include the counterclaim in Writing Standards 1.0 for grades 7-12. These Standards reference the organization of ...
Teaching claims, counterclaims and rebuttals in writing can improve a students opinion or argumentative essay. This post will explain how I teach claims, counterclaims and rebuttals in writing. To begin, let's clarify the meaning of the following terms when giving instruction: Counterclaim. Rebuttal. Reason.
There are various options you can consider on how to start a counterclaim paragraph, for example: "On the other hand, some people say….". "Certainly, some people say….". "Admittedly, some people might say….". "A common counterpoint is often….". You can start the counterclaim by explaining what counter-arguments the claim ...
The counterclaim is just one of the four elements of an argument, which include: Claim - to assert facts that give rise to a legally enforceable right or judicial action. Counterclaim - a claim for relief made in opposition to, or to offset another person's claim. Reasons - the rationale behind a party's claim.
Just what is a claim in writing? It's not all that far off from a claim you might make out loud. Learn more about when you're making a claim right here.
An effective argumentative essay addresses what the other side might say and explains why that point of view is wrong. This is called the counterclaim. Key Items Necessary: 1 - Transition. 2 - Evidence. 3 - Reasons. . A counterclaim is the argument (or one of the arguments) opposing your thesis statement. In your thesis paragraph, you make it ...
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the "default" enrollment option.
No one knows the profile of voters ahead of Election Day. We can't know for sure whether young people will turn out in greater numbers than usual, or whether key racial or ethnic groups will do so. This means pollsters are left to make educated guesses about turnout, often using a mix of historical data and current measures of voting enthusiasm.
The former president and his backers aim to strengthen the power of the White House and limit the independence of federal agencies.