

The Research Problem & Statement
What they are & how to write them (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Very interesting. Thank you. Please I need a PhD topic in climate change in relation to health.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
How to Write the Statement of the Problem in Research

Do you want to write a dissertation problem statement for your academic paper? In this case, you probably know already that the dissertation problem statement is the first step towards writing the research proposal. And yes, it is a very important part of your dissertation. Truth be told, everyone working on a complex paper such as a dissertation, that requires extensive research, should start with a dissertation problem statement. You will learn why in just a bit. For now, let’s explain what problem statements really are, how you write them and then show you a couple of excellent examples. We believe that you will be able to do a far better job writing the problem statement if you read a couple of examples.
What Is the Dissertation Problem Statement?
How to write a problem statement for a dissertation: the 4 steps, three dissertation problem statement examples, final word on problem statement.
First, we would like to make sure you understand what a problem statement is and what it is used for. Basically, the dissertation problem statement is a short paragraph of condensed ideas that show your readers how your research project will solve a problem. In other words, you will need to briefly state the current problem or problems, and then explain how your work solves them. You need to clearly define the problem and show how you will address it, in a very clear and concise manner. You can then use this statement to write the research proposal. Of course, you can also integrate it into the introduction of your dissertation. The bottom line, the research statement, is considered by many academics and thesis writers to be the heart of your dissertation.
Now that you know what the problem statement is and why it is so important for your dissertation, it’s time to go on to the next step. Let’s show you how to write a problem statement for a dissertation in just 4 steps. Our experienced dissertation writers have put together this guide to help you compose your statement as fast as possible. After all, you have plenty of work to do with research, analysis, writing, editing, etc. We advise you to check our tips to learn more about these steps. Without further ado, the 4 steps to write a problem statement for a dissertation:
- Think about the ideal situation or the desired goal. Start the statement with how things should be, in an ideal case.
- Think about what prevents this ideal situation. This is the problem you want to solve! Describe what is preventing the goal from being achieved and what stands in the way. In other words, use the second part of the statement to show your reader the problem you will be solving with your dissertation research and with your work.
- Enumerate all the consequences of your solution (if the solution works, of course). How will your work improve the situation? What do you aim to achieve? This is the last part of the statement; the part where you show your readers the benefits of your work.
- Read everything out loud and make sure it flows. The logic behind the statement must be strong and everything should be very clearly stated. Avoid ambiguity and don’t be afraid to cut our sections that don’t add value to the statement!
This is how a statement of the problem in the thesis generally looks like. To make things even easier for you, we have 3 examples for you.
Here are three dissertation problem statement examples that should make it clear how your statement should be organized:
- According to various studies, university students are more focused and more efficient when their dorms are equipped with modern facilities (Ideal Situation). Students in Dorm B currently don’t have AC units and temperatures are exceeding 90 degrees Fahrenheit during the summer months (Problem). My study plans to discover if students become more focused after AC units are installed in their dorm rooms (Solution).
- All children must feel safe on the playground, regardless of where the playground is located in the city (Ideal Situation). Yet children in the northern part of the city fear playing on the playground after 6 PM because of hooligans (Problem). My research shows that proper policing around playgrounds after 6 PM greatly decreases violence against children (Solution).
- Nonprofits need adequate funding and a supporting legal system to be able to help communities (Ideal Situation). The lack of funds and severe legal requirements are preventing certain foundations in the city from providing help to specific populations (Problem). My research demonstrates that softening regulations and increasing funding helps nonprofits provide assistance to 30% more people (Solution).
You can use any of the examples above as a thesis proposal template. Keep in mind that the problem statement for the dissertation must put the problem in context, describe all the details of the problem, show why the problem is important, and then clearly show what your research demonstrates. In other words, clearly and concisely show your audience why the problem is serious and how your research uncovers the best solution.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

How to Write an Effective Problem Statement for Your Research Paper
- 4 minute read
Table of Contents
The problem statement usually appears at the beginning of an article, making it one of the first things readers encounter. An excellent problem statement not only explains the relevance and importance of the research but also helps readers quickly determine if the article aligns with their interests by clearly defining the topic. Therefore, the problem statement plays a unique role in the widespread dissemination of the paper and enhancing the researcher’s academic influence.
In this article, we will focus on writing ideas, structure, and practical examples of the problem statement, helping researchers easily write an excellent problem statement.
Basic Writing Strategies for the Problem Statement
The problem statement aims to highlight the pressing issue the research intends to address. It should be concise and to the point. Researchers can follow a two-step approach: first, think about the content of the problem statement, and then organize the writing framework.
Before writing, clarify the following points¹ :
- What is the reader’s level of understanding of the research topic?
- How can the significance of the research be effectively conveyed to the reader?
After addressing these two questions, you can organize the content according to the following structure:
- Clarify what you aim to achieve with your research.
- Explore why the problem exists and explain how solving it helps reach the goal.
- Outline the potential impact of the research, such as possible outcomes, challenges, and benefits.
- Recommend a plan for your experiment that follows the rules of science.
- Explain the potential consequences if the problem is not resolved (if applicable).
Three Important Parts of the Problem Statement
The content and length of the problem statement can vary depending on the type of research. Although there’s no fixed format, it’s helpful to include these three key parts:
Research Background:
Explain clearly what problem your research focuses on. Describe how things would be better if this problem didn’t exist. Also, talk about what other researchers have tried to do about this problem and what still needs to be figured out.
Research Significance:
Clarify the impact of the problem on the research field and society, and analyze the cause of the problem. Explain who will benefit from solving the problem, thus demonstrating the relevance of the research and its contribution to the existing research system.² To illustrate the relevance, consider aspects such as the geographical location or process where the problem occurs, the time period during which it exists, and the severity of the problem.
Solution:
Describe the research objective and the expected solution or results.
Understanding the Writing Method Through Examples
To further explore the writing method of the problem statement, let’s look at the following case.
Research Topic:
The benefits of vitamin D supplementation on the immune system.
Problem Statement:
- Review existing research on the role of vitamin D in the immune system, emphasizing the potential impacts of vitamin D deficiency on the human body.
- List the obstacles encountered when trying to increase vitamin D levels in the body through supplements, and briefly mention the physiological or molecular mechanisms behind these obstacles.
- Clarify feasible ways to overcome these obstacles, such as new methods to promote the absorption of vitamin D in the intestine. Then, focus on the benefits of these methods, such as helping postmenopausal women with breast cancer improve their blood vitamin D levels.
Points to Note:
When crafting your problem statement, focus on essential details and avoid unnecessary information. Additionally, absolute terms such as “must” should be avoided.
( The examples in this article are used only to illustrate writing points, and the academic views contained therein are not for reference. )
By mastering these techniques and methods, you can enhance the clarity and impact of their problem statements. This not only makes the articles more engaging for reviewers and readers but also increases the likelihood of broader dissemination.
For efficient and professional assistance, consider reaching out to Elsevier Language Services. Our team of expert editors, who are native English speakers across various disciplines, can help refine every aspect of your article, including the problem statement. Our goal is to ensure your research achieves efficient publication and has wide-reaching impact, supporting your academic journey in the long term.
Type in wordcount for Plus Total: USD EUR JPY Follow this link if your manuscript is longer than 9,000 words. Upload
References:
- SURF Workshop Resources: Problem Statements – Purdue OWL® – Purdue University. (n.d.). https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_the_purdue_surf_program/surf_workshop_resources_problem_statements/index.html
- Problem Statement | A practical guide to delivering results. (n.d.). Copyright (C)2024 a Practical Guide to Delivering Results. All Rights Reserved. https://deliveringresults.leeds.ac.uk/delivering-results-lifecycle/problem-statement/

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Craft a Strong Research Hypothesis

How to Use Tables and Figures effectively in Research Papers
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How to write a dissertation problem statement, published by steve tippins on may 7, 2020 may 7, 2020.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 03:07 am
Your Problem Statement is one of the most important sections of your dissertation.
Let that sink in for a moment.
(Breathe. Say an om. Try to fend off the existential anxiety that is a natural part of the dissertation-writing process).
Okay, ready to know more?
The reason why it’s so important is that your study is essentially a response to a problem. Your Purpose Statement arises from the problem. So, essentially, your problem statement dictates what your entire dissertation will be about.
Fortunately for you, it also has some pretty specific requirements, and if you follow these, you’ll nail your problem statement and write a strong dissertation proposal.
That’s why I wrote this article: to help you understand the specific requirements of a dissertation problem statement so that you can write one effectively.

How to Find a Research Problem for your Dissertation
Before you can write your dissertation’s problem statement, you have to find the research problem.
Your problem statement arises from a gap in literature . When there’s something that hasn’t been studied, and when also a good reason to study it, that constitutes a problem. At its essence, a problem statement is essentially saying, “We don’t know enough about X, and we really should because of Y.”
So how do you find a research problem? There are several commonly-accepted approaches.
Literature Review

Oftentimes, the easiest and most direct way to discover a research problem is through a review of the literature. You will have to conduct a literature review anyway as part of your proposal, so make sure to write notes as you go along.
Make sure you’re familiar with seminal texts, but the real gold is often found in more recent studies. The “Recommendations for Further Research” section may explicitly state gaps in research that need to be filled, leading to your problem.
Personal Experience
Another excellent way of discovering a problem is through personal experience. Perhaps you’ve worked in a field and noticed a persistent problem that nobody has found an effective answer to. Make sure to familiarize yourself with the literature, though, before taking it too far–it could be somebody has already studied it (in which case you could still build off their study).
Discussion with Experts
Asking experts in the field is not only an expedient way to discover a research problem, it often leads to the most interesting problems as well. Those who have worked in the field for a long time have a depth and breadth of knowledge, and also often work at the frontier of knowledge in their field. They can provide a perspective that even a complete literature review on its own won’t be able to.
Discussion with Colleagues

The old over-used phrase “synergy” applies here. Sometimes, even when two people have roughly the same level of knowledge and expertise in a subject, coming together in dialogue may produce ideas that neither could have found on their own. Or maybe your colleague has just read something interesting that leads you to your research problem. Either way, getting another perspective is always helpful.
Research Agendas
An advisor or group of faculty may already be working with an established research agenda. While your scope will be limited, you may also benefit from contributing to a larger research effort.
Contradictory Evidence
Look at the literature (or ask your advisors) with an eye towards contradicting evidence. If similar studies have contradicting results, the area must be explored more. This is related to “provocative exception,” when a consistent and accepted conclusion is contradicted by the appearance of a new finding. Keeping a key eye on the research can aid your awareness of these instances.
What Makes a Good Research Problem?

You are interested in the problem. This may sound obvious, but may doctoral students have found themselves enmeshed in a research project that they have no genuine interest in because a faculty member thought they should pursue a particular topic. A dissertation is too long of a project to devote to something you’re not interested in. Plus, the quality of your research and writing will be much higher if indeed you are interested in the topic.
The scope of the problem is manageable . So many students submit problem statements that are beyond the scope of what can be explored in a single research project. Remember, the scope of the problem must be hyper-focused.
You have the time and resources to investigate the problem. This means that you can handle it with the time and resources you have now (or can count on having during the process). It’s far better to make small steps of progress than it is to bite off more than you can chew in an attempt to go in leaps and bounds.
The problem has theoretical or practical significance. This is essentially the answer to the question, “so what?” There are many problems in the world that don’t necessarily merit scientific inquiry. As I am writing at the picnic table outside, a slug appears to be trying to climb from one blade of grass to another but cannot reach the second one. This may be a problem for the slug, but doesn’t have great significance beyond this particular slug at this particular moment. Even if we were to consider the importance of this slug’s goal, it would still take longer than a day to conduct a study about how to help it, by which point I expect it will have already moved on.
It is ethical to investigate the problem. The history of scientific research is, unfortunately, marked by a trail of unethical behavior. From the scientific inquiries of the Nazis, to psychologically harmful studies here in the US, to horrific experiments that are still conducted on live animals, much harm has been done in the name of the pursuit of knowledge. As researchers, it is imperative that we consider the ethics of pursuing any research project.

Now that you’ve identified the research problem you plan to address–that is, the hyper-specific area of focus for your study– you just have to write your dissertation’s problem statement.
The Key Elements of a Dissertation Problem Statement:
Essentially, you want to establish (a) what the problem is, (b) that it matters, and (c) that it addresses a meaningful gap in the literature.
- Give some brief background information. A few sentences to help the reader understand the context of the problem.
- State the general research problem. This is one sentence that usually starts something like, “The general problem is…”
- Establish relevancy. Here’s where you’ll cite research that supports that the general problem you just stated is relevant, current, and significant to the discipline.
- Specific Problem Statement. This sentence should be worded similarly to your title and (future) purpose statement.
- Conclusion and transition. Here, you’ll include a few sentences on the impacts of the problem on society or the relevant population, and transition to the next section.
Here are some recommended ways of beginning your dissertation problem statement:
- It is not known ___
- Absent from the literature is ___
- While the literature indicates __, it is not known in ___ if
- It is not known how or to what extent ___
After reading your problem statement, someone should have a very clear answer to the questions, “So what?” or “Why does it matter?”
Tips for Writing your Problem Statement

Be concise . The wording of your problem statement should be clear and easy to follow. Avoid complexity. One of the most common mistakes students make is making their problem statement too complex. When in doubt, simplify.
Use Citations. Make sure that every claim you make is backed up by research. The vast majority of studies build on the work of previous researchers.
Focus on only one (very specific) problem. Don’t try to roll several problems into your problem statement. Also, avoid making your problem statement too broad.
Do not offer a ready solution. At most, explore possible avenues for solutions that may be tested with the help of your research.
Stay in alignment. It is also very important that your problem statement is in alignment with your title, gap in literature, purpose statement, and research questions. That means it’s saying the same thing, that it has the same hyper-specific focus.

How Long Is a Problem Statement?
While the actual General Problem Statement and Specific Problem Statement are one sentence each, the Problem Statement section can account for anywhere from a few paragraphs to a few pages. More than a few pages is usually too long. Remember, simplicity and specificity are key.

Dissertation Problem Statement Example
From Wiley :
The career development process is critical for the success of organizations. Research has shown that women managers experience career development differently from men. In addition, more and more African-American women are now joining the ranks of management, which presents new challenges and opportunities for these individuals. However, little is known about the combined effects of sex and race on the career development process of individuals, and to the extent that current career development models accurately describe the process is unclear. If career development is important for organizations and career development is viewed differently by women and men managers and more African-American women are now serving in the ranks of management, and if little is known about the combined effects of sex and race on the career development process, then more needs to be known about how African-American women perceive their career development experiences. The purpose of this study was to focus on African-American women first-line supervisors undertake and conduct a qualitative study of their career development process. *Adapted from: Cushnie, M. (1999). African-American women first-line supervisors: a qualitative study of their career development process. From Wiley
From University of Houston :
The importance of developing a constraint-free and reliable work plan has long been recognized by the [construction] industry. However, numerous construction projects are still plagued by delays and cost overruns, which can frequently be traced to ineffective identification and treatment of constraints. First, when a constraint is not properly identified during scheduling, subsequent conflicts in the field are inevitable. Today’s projects are becoming more and more technically complex and logistically challenging, which exposes construction operations to even more complex constraints. Second, the traditional scheduling methods, bar charts and Critical Path Method (CPM) which are widely used as a basis for constraint analysis, greatly limit our capability in modeling and resolving constraints during look-ahead scheduling. These methods have long been blamed for their limitations in modeling and communicating constraints, including inability to cope with non-time-related precedence constraints and difficulty to evaluate and communicate inter-dependencies at the field operation level (e.g. Sriprasert and Dawood 2002; Chua and Shen 2001). In summary, there is a need for a better understanding of constraints in construction and a structured approach in identifying and modeling constraints to ensure a constraint-free work plan. From University of Houston
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Statement of the Problem in Research

Table of Contents
The problem statement is a foundation of academic research writing , providing a precise representation of an existing gap or issue in a particular field of study.
Crafting a sharp and focused problem statement lays the groundwork for your research project.
- It highlights the research's significance .
- Emphasizes its potential to influence the broader academic community.
- Represents the initial step for you to make a meaningful contribution to your discipline.
Therefore, in this article, we will discuss what is a statement of the problem in research and how to craft a compelling research problem statement.
What is a research problem statement?
A research problem statement is a concise, clear, and specific articulation of a gap in current knowledge that your research aims to bridge. It not only sets forth the scope and direction of your research but also establishes its relevance and significance.
Your problem statement in your research paper aims to:
- Define the gap : Clearly identify and articulate a specific gap or issue in the existing knowledge.
- Provide direction : Serve as a roadmap, guiding the course of your research and ensuring you remain focused.
- Establish relevance : Highlight the importance and significance of the problem in the context of your field or the broader world.
- Guide inquiry : Formulate the research questions or hypotheses you'll explore.
- Communicate intent : Succinctly convey the core purpose of your research to stakeholders, peers, and any audience.
- Set boundaries : Clearly define the scope of your research to ensure it's focused and achievable.
When should you write a problem statement in research?
Initiate your research by crafting a clear problem statement. This should be done before any data collection or analysis, serving as a foundational anchor that clearly identifies the specific issue you aim to address.
By establishing this early on, you shape the direction of your research, ensuring it targets a genuine knowledge gap.
Furthermore, an effective and a concise statement of the problem in research attracts collaborators, funders, and supporters, resonating with its clarity and purpose. Remember, as your research unfolds, the statement might evolve, reflecting new insights and staying pertinent.
But how do you distinguish between a well-crafted problem statement and one that falls short?
Effective vs. ineffective research problem statements
Imagine a scenario where medical researchers aim to tackle a new strain of virus. Their effective problem statement wouldn't merely state the existence of the virus. Instead, it would delve into the specifics — the regions most affected, the demographics most vulnerable, and the current limitations in medical interventions.
Whereas an ineffective research problem statement is vague, overly broad, or ambiguous, failing to provide a clear direction for the research. It may not be rooted in existing literature, might lack clarity on its significance, or could be framed in a way that makes the research objectives unachievable or irrelevant.
To understand it better, let's consider the topic of “Remote work and employee productivity.”
Effective problem statement
“Over the past decade, there has been a 70% increase in organizations adopting remote work policies. While some studies suggest remote work enhances employee productivity, others indicate potential declines due to distractions at home.
However, there’s a lack of comprehensive research examining the specific factors in a remote environment that influence productivity. This study aims to identify and analyze these factors, providing organizations with actionable insights to optimize remote work policies.”
Why is this statement of a problem in research effective?
- Specificity : The statement provides a clear percentage to highlight the rise in remote work.
- Context : It acknowledges existing research and the conflicting findings.
- Clear gap identification : It points out the lack of comprehensive research on specific factors affecting productivity in remote work.
- Purpose : The statement concludes with a clear aim for the research.
Ineffective problem statement
"People are working from home a lot now, especially since there are so many internet tools. Some say it's good; others say it's not that great. This research will just look into the whole work-from-home thing and see what's up."
Why is this statement of a problem in research ineffective?
- Informal language : Phrases like "what's up" and "the whole work-from-home thing" are not suitable for academic writing.
- Vagueness : The statement doesn't provide any specific data or context about the rise of remote work.
- Lack of clear focus : It's unclear what aspect of remote work the research will address.
- Ambiguous purpose : The statement doesn't specify the research's objectives or expected outcomes.
After gaining an understanding of what an effective research problem statement looks like, let's dive deeper into how to write one.
How to write a problem statement in research?
Drafting your research problem statement at the onset of your research journey ensures that your research remains anchored. That means by defining and articulating the main issue or challenge you intend to address at the very beginning of your research process; you provide a clear focus and direction for the entire study.
Here's a detailed guide to how you can write an effective statement of the problem in research.
Identify the research area : Before addressing a specific problem, you need to know the broader domain or field of your study. This helps in contextualizing your research and ensuring it aligns with existing academic disciplines.
Example: If you're curious about the effects of digital technology on human behavior, your broader research area might be Digital Sociology or Media Studies.
Conduct preliminary literature review : Familiarize yourself with existing research related to your topic. This will help you understand what's already known and, more importantly, identify gaps or unresolved questions in the existing knowledge. This step also ensures you're advancing upon existing work rather than replicating it.
Example: Upon reviewing literature on digital technology and behavior, you find many studies on social media's impact on youth but fewer on its effects on the elderly.
Read how to conduct an effective literature review .
Define the specific problem : After thoroughly reviewing the literature, pinpoint a particular issue that your research will address. Ensure that this chosen issue is not only of substantial importance in its field but also realistically approachable given your resources and expertise. To define it precisely, you might consider:
- Highlighting discrepancies or contradictions in existing literature.
- Emphasizing the real-world implications of this gap.
- Assessing the feasibility of exploring this issue within your means and timeframe.
Example: You decide to investigate how digital technology, especially social media, affects the mental well-being of the elderly, given the limited research in this area.
Articulate clearly and concisely : Your problem statement should be straightforward and devoid of jargon. It needs to convey the essence of your research issue in a manner that's understandable to both experts and non-experts.
Example: " The impact of social media on the mental well-being of elderly individuals remains underexplored, despite the growing adoption of digital technology in this age group. "
Highlight the significance : Explain why your chosen research problem matters. This could be due to its real-world implications, its potential to fill a knowledge gap or its relevance to current events or trends.
Example: As the elderly population grows and becomes more digitally connected, understanding the psychological effects of social media on this demographic could inform digital literacy programs and mental health interventions.
Ensure feasibility : Your research problem should be something you can realistically study, given your resources, timeframe, and expertise. It's essential to ensure that you can gather data, conduct experiments, or access necessary materials or participants.
Example: You plan to survey elderly individuals in local community centers about their social media usage and perceived mental well-being, ensuring you have the means to reach this demographic.
Seek feedback : Discuss your preliminary problem statement with peers, mentors, or experts in the field. They can provide insights, point out potential pitfalls, or suggest refinements.
Example: After discussing with a gerontologist, you decide to also consider the role of digital training in moderating the effects of social media on the elderly.
Refine and Revise : Based on feedback and further reflection, revise and improve your problem statement. This iterative process ensures clarity, relevance, and precision.
Example: Your refined statement reads: Despite the increasing digital connectivity of the elderly, the effects of social media on their mental well-being, especially in the context of digital training, remain underexplored.
By following these detailed steps, you can craft a research problem statement that is both compelling and academically rigorous.
Having explored the details of crafting a research problem statement, it's crucial to distinguish it from another fundamental element in academic research: the thesis statement.
Difference between a thesis statement and a problem statement
While both terms are central to research, a thesis statement presents your primary claim or argument, whereas a problem statement describes the specific issue your research aims to address.
Think of the thesis statement as the conclusion you're driving towards, while the problem statement identifies a specific gap in current knowledge.
For instance, a problem statement might highlight the rising mental health issues among teenagers, while the thesis statement could propose that increased screen time is a significant contributor.
Refer to the comparison table between what is a thesis and a problem statement in the research below:
Aspect | Thesis Statement | Problem Statement |
Definition | A concise statement that presents the main claim or argument of the research | A clear articulation of a specific issue or gap in knowledge that the research aims to address |
Purpose | To provide readers with the primary focus or argument of the research and what it aims to demonstrate | To highlight a particular issue or gap that the research seeks to address |
Placement | Found in the introduction of a thesis or dissertation, usually within the first 1-2 pages, indicating the central argument or claim the entire work | Positioned early in research papers or proposals, it sets the context by highlighting the issue the research will address, guiding subsequent questions and methodologies |
Nature of statement | Assertive and argumentative, as it makes a claim that the research will support or refute | Descriptive and explanatory, as it outlines the issue without necessarily proposing a solution or stance |
Derived from | Research findings, data analysis, and interpretation | Preliminary literature review, observed gaps in knowledge, or identified issues in a particular field |
Word count | Typically concise, ranging from 1 sentence to a short paragraph (approximately 25-50 words) | Generally more detailed, ranging from a paragraph to a page (approximately 100-300 words) |
Common mistakes to avoid in writing statement of the problem in research
Mistakes in the research problem statement can lead to a domino effect, causing misalignment in research objectives, wasted resources, and even inconclusive or irrelevant results.
Recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls not only strengthens the foundation of your research but also ensures that your efforts concede impactful insights.
Here's a detailed exploration of frequent subjective, qualitative, quantitative and measurable mistakes and how you can sidestep them.
Being too broad or too narrow
A problem statement that's too broad can lack focus, making it challenging to derive specific research questions or objectives. Conversely, a statement that's too narrow might limit the scope of your research or make it too trivial.
Example of mistake: "Studying the effects of diet on health" is too broad, while "Studying the effects of eating green apples at 3 pm on heart health" is overly narrow.
You can refine the scope based on preliminary research. The correct way to write this problem statement will be "Studying the effects of a high-fiber diet on heart health in adults over 50." This statement is neither too broad nor too narrow, and it provides a clear direction for the research.
Using unnecessary jargon or technical language
While academic writing often involves academic terms, overloading your problem statement with jargon can alienate readers and obscure the actual problem.
Example of Mistake: "Examining the diurnal variations in macronutrient ingestion vis-à-vis metabolic homeostasis."
To ensure it’s not complicated, you can simplify and clarify. "Examining how daily changes in nutrient intake affect metabolic balance" conveys the same idea more accessible.
Not emphasizing the "Why" of the problem
It's not enough to state a problem; you must also convey its significance. Why does this problem matter? What are the implications of not addressing it?
Example of Mistake: "Many students are not engaging with online learning platforms."
You can proceed with the approach of highlighting the significance here. "Many students are not engaging with online learning platforms, leading to decreased academic performance and widening educational disparities."
Circular reasoning and lack of relevance
Your problem statement should be grounded in existing research or observed phenomena. Avoid statements that assume what they set out to prove or lack a clear basis in current knowledge.
Example of Mistake: "We need to study X because not enough research has been done on X."
Instead, try grounding your statement based on already-known facts. "While several studies have explored Y, the specific impact of X remains unclear, necessitating further research."
Being overly ambitious
While it's commendable to aim high, your problem statement should reflect a challenge that's achievable within your means, timeframe, and resources.
Example of Mistake: "This research will solve world hunger."
Here, you need to be realistic and focused. "This research aims to develop sustainable agricultural techniques to increase crop yields in arid regions."
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can craft a problem statement that is clear, relevant and sets a solid foundation for your research.
Over-reliance on outdated data
Using data that is no longer relevant can mislead the direction of your research. It's essential to ensure that the statistics or findings you reference are current and pertinent to the present scenario.
Example of Mistake: "According to a 1995 study, only 5% of the population uses the internet for daily tasks."
You always cross-check the dates and relevance of the data you're using. For a contemporary study on internet usage, you'd want to reference more recent statistics.
Not specifying the sample size or demographic
A problem statement should be clear about the population or sample size being studied, especially when making generalizations or claims.
Example of Mistake: "People prefer online shopping to in-store shopping."
Here, you would benefit from specifying the demographic or sample size when presenting data to avoid overgeneralization. " In a survey of 1,000 urban residents aged 18-35, 70% expressed a preference for online shopping over in-store shopping. "
Ignoring conflicting data
Cherry-picking data that supports your hypothesis while ignoring conflicting data can lead to a biased problem statement.
Example of Mistake: "Research shows that all students benefit from online learning."
You’ve to ensure a balanced view by considering all relevant data, even if it contradicts your hypothesis. " While many studies highlight the advantages of online learning for students, some research points to challenges such as decreased motivation and lack of face-to-face interaction. "
Making unsubstantiated predictions
Projecting future trends without solid data can weaken the credibility of your problem statement.
Example of Mistake: "The demand for electric cars will increase by 500% in the next year."
Base your predictions on current trends and reliable data sources, avoiding hyperbolic or unsupported claims. " With the current growth rate and recent advancements in battery technology, there's potential for a significant rise in the demand for electric cars. "
Wrapping Up
A well-crafted problem statement ensures that your research is focused, relevant, and contributes meaningfully to the broader academic community.
However, the consequences of an incorrect or poorly constructed problem statement can be severe. It can lead to misdirected research efforts, wasted resources, compromised credibility, and even ethical concerns. Such pitfalls underscore the importance of dedicating time and effort to craft a precise and impactful problem statement.
So, as you start your research journey , remember that a well-defined problem statement is not just a starting point; it guides your entire research journey, ensuring clarity, relevance, and meaningful contributions to your field.
Frequently Asked Questions
A problem statement is a clear, concise and specific articulation of a gap in current knowledge that your research aims to bridge.
The Problem Statement should highlight existing gaps in current knowledge and also the significance of the research. It should also include the research question and purpose of the research.
Clear articulation of the problem and establishing relevance; Working thesis (methods to solve the problem); Purpose and scope of study — are the 3 parts of the problem statement.
While the statement of the problem articulates and delineates a particular research problem, Objectives designates the aims, purpose and strategies to address the particular problem.
Here’s an example — “The study aims to identify and analyze the specific factors that impact employee productivity, providing organizations with actionable insights to optimize remote work policies.”
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Problem Statement?
A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and specific statement that describes the issue or problem that the research project addresses. It should be written in a way that is easily understandable to both experts and non-experts in the field.
To write a research problem statement, you should:
- Identify the general area of interest: Start by identifying the general area of research that interests you.
- Define the specific problem: Narrow down the general area of interest to a specific problem or issue.
- Explain the significance of the problem: Provide context for the problem by explaining why it is important to study and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
- Provide a clear and concise statement: State the problem in a clear and concise manner, making sure to use language that is easily understood by your intended audience.
- Use a scientific and objective tone: The problem statement should be written in a neutral and objective tone, avoiding any subjective language and personal bias .
An Example of a Research Problem Statement
“The increasing prevalence of obesity in children is a growing public health concern. Despite the availability of information on healthy eating and physical activity, many children are still not engaging in healthy lifestyle behaviors. The problem this study addresses is the lack of understanding of the barriers and facilitators to healthy lifestyle behaviors in children.”
When to Write a Problem Statement in Research?
A research problem statement should be written at the beginning of the research process, before any data collection or analysis takes place. This is because the statement sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the problem that the research is trying to address.
Writing a problem statement early in the research process helps to guide the research design and methodology , and ensures that the research is focused on addressing the specific problem at hand. It also helps to ensure that the research is relevant and addresses a gap in current knowledge or understanding.
In addition, a well-written problem statement effectively communicates the purpose and significance of the research to potential funders, collaborators, and other stakeholders. It also generates interest and support for the research project.
It’s also important to note that, during the research process, the statement can be refined or updated as new information is discovered or as the research progresses. This is normal and it’s a good idea to revise the statement as needed to ensure that it remains clear and concise and that it accurately reflects the current focus of the research project.
What Does a Research Problem Statement Include?
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements:
1. The research topic:
The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses.
2. The specific problem or issue:
A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address.
3. The significance of the problem:
A discussion of why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
4. The research questions:
A set of questions that the research project aims to answer, in order to address the problem or issue.
5. The research objectives:
A set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
6. The scope of the research:
A description of the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
7. The theoretical framework:
A discussion of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
8. The research design:
A description of the research methodologies that will be used to collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
It’s important to note that the problem statement is usually brief and concise, typically a few sentences or a short paragraph. But it should provide enough information to convey the main idea of the research project.
Important Features of Research Problem Statement
The problem statement should be clear and easy to understand. Write it in a way that is accessible to both experts and non-experts in the field.
2. Specificity
The statement should be specific and clearly define the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It should be narrow enough to be manageable, but broad enough to be of interest to others in the field.
3. Significance
The statement should explain why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills. It should provide context for the research project and help to justify its importance.
4. Relevance
The statement should be relevant to the field of study and address an issue that is currently of concern to researchers.

5. Research questions
The statement should include a set of research questions that the research project aims to answer in order to address the problem or issue.
6. Research objectives
The statement should include a set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
The statement should define the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
8. Theoretical framework
The statement should provide an overview of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
9. Research design
The statement should provide an overview of the research methodologies. This will be useful collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
Difference Between a Thesis Statement and a Problem Statement
A thesis statement and a problem statement are related but distinct elements of a research project.
A thesis statement is a statement that summarizes the central argument or claim of a research paper or essay. It presents the main idea of the paper and sets the direction for the rest of the content. It’s usually located at the end of the introduction, and it’s often one sentence.
A problem statement, on the other hand, is a statement that describes a specific problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the research problem. It is usually located at the beginning of a research paper or proposal, and is of one or a few paragraphs.
In summary, a thesis statement is a summary of the main point or key argument of the research paper. A problem statement describes the specific issue that the research project aims to address. A thesis statement is more focused on the final outcome of the research. While a problem statement is focused on the current state of knowledge and the gap in understanding that the research project aims to fill.
In Conclusion
A problem statement is a critical component of the research project, as it provides a clear and concise roadmap for the research, and helps to ensure that the research is well-designed and addresses a significant and relevant issue.
We hope this blog has clarified your doubts and confusion associated with research problem statement and helps you write an effective statement for your research project!
comprehensive contents. thanks!
Very good writing and easy to understand
WOW..its easy to understand…
This has opened up my mind, Systematically outlined steps.
Wow I’ve gained Alot from this!
WOW…This was much helpful.
Good and straightforward explanations with ease of understanding for all the students and teachers alike.
Beautiful work
I enjoy and understand every bit of the explanations on each topic. Kudos to the team.
very clear and easy to understand. i really benefited
Clear and concise piece of writing.
clear and straightforward
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
Graphical Abstracts Vs. Infographics: Best practices for using visual illustrations for increased research impact
Dr. Sarah Chen stared at her computer screen, her eyes staring at her recently published…

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…

- Trending Now
- Understanding Ethics
Understanding the Impact of Retractions on Research Integrity – A global study
As we reach the midway point of 2024, ‘Research Integrity’ remains one of the hot…
![problem statement master thesis What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Reporting Research
- AI in Academia
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
How to write a problem statement

Introduction
Choosing a problem to look into is the first step to be taken in carrying out a thesis writing . There are several problems that exist in the society, workplace, family among others. Thus, a problem statement should clearly indicates why the study in question should interest anyone, why it should be given priority among the many problem confronting an organisation. In thesis writing , stating a good problem statement is very essential because it helps to define and guide he research all through. The problem statement should be very clear and easy to understand, it should also be geared towards directing the inquiry. One has to understand the problem properly in order to have a good statement of problem. The intention of the statement of problem should be to tackle the five Ws. The five Ws are; who, what, when, where, and why. The problem statement should be able to cover these five Ws so as to create a good problem statement, which will set the basis for everything to flow well in the research and makes the research less difficult.
What is Problem Statement?
A problem statement is a short and snappy explanation of a problem that needs to be solved. Problem statement spots out the gap that exists between the present condition and the desire to achieve already set goal, which helps to tackle a present problem that needs solution. The first thing to do while trying to solve a problem is to first; understand the problem that needs to be solved, because you can’t solve what you don’t understand, before proceeding to solve the problem. A statement of problem should be in such a way that it will be able to deal with the five Ws (who, what, when, where, and why), because when a statement of problem is straight forwarded and precise it will help people to understand the issue at hand and work towards solving it. Problem statement is used in, companies, groups, institutes, academics etc, to solve a given problem. A good statement of problem can be one sentence or more depending on the number of problems you wish to address accompanied by some paragraphs to explain the problem more. The paragraph may possibly cover the current convincing point of view that makes the problem necessary to be studied, it could also contain the opinion of others like professors and also explain how the problem relates to the study.
Statement of problem could be quantitative or qualitative. A problem statement is quantitative when it deals with the populace and variables and a qualitative statement of problem is broader than a quantitative problem statement.
Types Statement of Problem
Your type of study determines the type of statement of problem you will be stating. There are two general types of statements of problem; they are quantitative statement of problem and Quantitative statement of problem
Qualitative statement of problem
Quantitative statement of problem is the type of statement of problem that identifies the population and variables that are to be considered. Quantitative problem statement also questions the relationships that exist between the variables to know whether there is a positive or a negative relationship between the variables, and also to know if there is auto-correlation or not.
Qualitative statement of problem
Qualitative statement of problem; this type of statement of problem is broader than quantitative statement of problem. While quantitative statement of problem narrows down its focus on a certain problem, the qualitative statement of problem states the general reason of the research. The focus of qualitative statement of problem may change as the research goes on.
Elements of The Statement Problem
Statements of problem normally have three elements, they are; the problem itself, the solving method and the reason, rational, and range of the research.
The problem itself should be clearly acknowledged with an adequate background detail to ascertain why the problem is necessary for study
The next element of statement of problem is the methodology adopted in solving the problem that is already stated.
Another element of statement of problem is the reason, rational, and range of the research that is being carried out, these elements should be snappy to avoid confusion on the side of the reader. You might need to read our article on Literature review
The Sources of Problem Statement
Statement of problem can come from different areas or sources, these sources include;
- Personal observation of reality or personal experience;
Review of literature
Inference from theory
Personal observation of reality or personal experience
Statement of problem could be formulated from your personal observation about reality; what peoples opinion are about the problem and what your own opinion is, how the reality is perceived, your point of view about a particular issue. Your statement of problem can come from an experience that has occurred to you before, something unclear that you need to investigate. Your personal experience and observation about a thing will help shape out your statement of problem.
While carrying out a study on a particular problem, it could be a study that has been research on before. Reviewing of literature can be to fill the gap in literature, to know the methodology adopted could be used for other studies and to know if a comparable research can be done in other areas. When reviewing the previous work on the study, read the conclusion very well, if you can discover any gap that needs to be covered. Review of literature help in constructing a statement of problem.
It communicates the inference made from societal generalization about life and in the world that the researcher is familiar with. From this inference the human character is posited in an experimental frame for suggestion during research. From a theory a researcher can create a good statement of problem conditioning the predicted result in a certain experimental circumstance.
Interviewing and directly or indirectly discussing with the experts, professionals or practitioners in the area which the research is been conducted provides some necessary information which will help in creating a good statement of problem. Interviewing or discussing with experts offers researchers the opportunity to recognize the real world problem that may not be observed in the academic group.
Purposes or Goals Of Problem Statement
- To familiarize the reader with the significance of the study.
- To propose a succinct report about the rationale of your work.
- To describe the area that will be investigated.
- To give the outline for presenting the findings.
Features of A Good Problem Statement
- It should be clear and precise.
- It should be able to identify the problem, examine the problem, its key fact and perimeter to be studied.
- It deals with the gap in information.
- The statement of problem should be short and snappy
- It should be adequately important to add to the available body of the work.
- It should lead to further research.
- The problem statement should be for the audience.
- The problem should submit itself for inquiry during the data collection.
- It should be importance to the researcher and go well with his/her skills, time, and resources
- The advance towards resolving the problem should be fair.
- The writing style should be dignified.
- Your terminologies should be well explained.
- The range of the problem statement should be kept under control.
- The problem statement should be compelling and researchable.
- It should be able to address the five Ws(who, when, why, where, and what)
Format For Writing A Problem Statement
The format for writing a problem statement is four, they include; the ideal, the reality, the consequences and the proposal. When writing a statement of problem the first section to be target is the ideal followed by the reality then the consequences and finally the proposal.
- The Ideal; this section of the statement of problem explains the chosen method to be used in the problem statement; it describes “what it is supposed to be”. This section recognizes the target of all the people that will be affected by the research. It should be able to exemplify what the anticipated situation will look like if the resolution to the problem is executed. It explains how things are supposed to be.
- The Reality; this section of the statement of problem explains the present method of what is being studied. It expresses the point of pain faced by those involved in the area that is being studied. It should also include the insights and expertise of the project team and subject matter experts provided during problem analysis. It explains the circumstance or circumstances that hinder the ideal target and aim and how the present condition falls short of the ideal goal.
- The Consequences; this section of statement of problem explains the way you should plan to advance the present circumstance. This could be time, expenditure, capital, viable benefit, efficiency, cost etc. It explains the effect the circumstance will have on those involved if not advanced, and the extent of these effects will help to decide the main concern of the research.
- The Proposal; once the ideal, reality and consequences are well understood and completed, the next line of action is to propose the possible solution, this section expresses the possible way or ways out of the problem. Proposing the solution is not just enough, it is important to also explain what the benefits of these solutions are if successfully carried out.
The Dos And Don’ts Of Problem Statement
- The problem statement should be clear and not ambiguous
- The problem statement should be compelling and not unconvincing
- It should be concise and not long winded.
- Writing of problem statement should be for the audience and not for you.
- The solution of the problem stated should be fair and not biased.
- Use a distinguished terminologies and not jargons.
Need assistance with your work, contact thesismind.com now
Bryman, Alan (2007). “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology (10) 5-20.
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg (2011).Generating Research Questions Through Problematization. Academy of Management Review (36) 247-271.
Princeton University; White, Patrick. Developing
Research Questions: A Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Palgrave McMillan, 2009
Prof. Henry M. Bwisa, Editage Insights, 2017
Kush, Max (2015). “The Statement Problem”. Quality Progress. 48(6).
Annamalai, Nagappan; Kamaruddin, Shahrul; Azid, Ishak Abdul; Yeoh, TS (2013). Importance of Problem Statement in Solving Industry Problems . Applied Mechanics and Materials. Zurich. 421 – via ProQuest.
Lindstrom, Chris (2011). “How To Write A Problem Statement”..
Shaffer, Deb (2017). “How to Write a Problem Statement” . ProProject Manager.
Shaffer, David (2015). Cooking Up Business Analysis Success”. BA Times.
Prof. Henry M. Bwisa, Editage Insights, 2018.
12 thoughts on “How to write a problem statement”
Great job thanks
Thank you for sharing your passion and knowledge with the world.
Your writing has a way of empowering and uplifting your readers.
You got a very great website, Sword lily I noticed it through yahoo.
I just couldn’t depart your site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person provide for your visitors? Is going to be back often in order to check up on new posts
I really enjoy examining on this website , it has got wonderful content. “The great secret of power is never to will to do more than you can accomplish.” by Henrik Ibsen.
I am impressed with this internet site, rattling I am a big fan .
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
I have been surfing on-line greater than 3 hours as of late, yet I by no means found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty price enough for me. Personally, if all web owners and bloggers made just right content as you probably did, the net might be a lot more useful than ever before. “Oh, that way madness lies let me shun that.” by William Shakespeare.
I am glad to be one of several visitants on this outstanding internet site (:, thanks for posting.
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
I went over this web site and I believe you have a lot of good info, saved to favorites
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
Published on 8 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
A problem statement is a concise and concrete summary of the research problem you seek to address. It should:
- Contextualise the problem. What do we already know?
- Describe the exact issue your research will address. What do we still need to know?
- Show the relevance of the problem. Why do we need to know more about this?
- Set the objectives of the research. What will you do to find out more?
Table of contents
When should you write a problem statement, step 1: contextualise the problem, step 2: show why it matters, step 3: set your aims and objectives.
Problem statement example
Frequently asked questions about problem statements
There are various situations in which you might have to write a problem statement.
In the business world, writing a problem statement is often the first step in kicking off an improvement project. In this case, the problem statement is usually a stand-alone document.
In academic research, writing a problem statement can help you contextualise and understand the significance of your research problem. It is often several paragraphs long, and serves as the basis for your research proposal . Alternatively, it can be condensed into just a few sentences in your introduction .
A problem statement looks different depending on whether you’re dealing with a practical, real-world problem or a theoretical issue. Regardless, all problem statements follow a similar process.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The problem statement should frame your research problem, giving some background on what is already known.
Practical research problems
For practical research, focus on the concrete details of the situation:
- Where and when does the problem arise?
- Who does the problem affect?
- What attempts have been made to solve the problem?
Theoretical research problems
For theoretical research, think about the scientific, social, geographical and/or historical background:
- What is already known about the problem?
- Is the problem limited to a certain time period or geographical area?
- How has the problem been defined and debated in the scholarly literature?
The problem statement should also address the relevance of the research. Why is it important that the problem is addressed?
Don’t worry, this doesn’t mean you have to do something groundbreaking or world-changing. It’s more important that the problem is researchable, feasible, and clearly addresses a relevant issue in your field.
Practical research is directly relevant to a specific problem that affects an organisation, institution, social group, or society more broadly. To make it clear why your research problem matters, you can ask yourself:
- What will happen if the problem is not solved?
- Who will feel the consequences?
- Does the problem have wider relevance? Are similar issues found in other contexts?
Sometimes theoretical issues have clear practical consequences, but sometimes their relevance is less immediately obvious. To identify why the problem matters, ask:
- How will resolving the problem advance understanding of the topic?
- What benefits will it have for future research?
- Does the problem have direct or indirect consequences for society?
Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it.
The research aim is the overall purpose of your research. It is generally written in the infinitive form:
- The aim of this study is to determine …
- This project aims to explore …
- This research aims to investigate …
The research objectives are the concrete steps you will take to achieve the aim:
- Qualitative methods will be used to identify …
- This work will use surveys to collect …
- Using statistical analysis, the research will measure …
The aims and objectives should lead directly to your research questions.
Learn how to formulate research questions
You can use these steps to write your own problem statement, like the example below.
Step 1: Contextualise the problem A family-owned shoe manufacturer has been in business in New England for several generations, employing thousands of local workers in a variety of roles, from assembly to supply-chain to customer service and retail. Employee tenure in the past always had an upward trend, with the average employee staying at the company for 10+ years. However, in the past decade, the trend has reversed, with some employees lasting only a few months, and others leaving abruptly after many years.
Step 2: Show why it matters As the perceived loyalty of their employees has long been a source of pride for the company, they employed an outside consultant firm to see why there was so much turnover. The firm focused on the new hires, concluding that a rival shoe company located in the next town offered higher hourly wages and better “perks”, such as pizza parties. They claimed this was what was leading employees to switch. However, to gain a fuller understanding of why the turnover persists even after the consultant study, in-depth qualitative research focused on long-term employees is also needed. Focusing on why established workers leave can help develop a more telling reason why turnover is so high, rather than just due to salaries. It can also potentially identify points of change or conflict in the company’s culture that may cause workers to leave.
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives This project aims to better understand why established workers choose to leave the company. Qualitative methods such as surveys and interviews will be conducted comparing the views of those who have worked 10+ years at the company and chose to stay, compared with those who chose to leave.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 08). How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/write-a-problem-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a strong hypothesis | guide & examples.

- Section 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
Defining The Problem Statement
How to write the problem statement.
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Synthesis and Analysis in Writing Support This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Research Process This link opens in a new window
- ASC Guide: Outlining and Annotating This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: RefWorks This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Copyright Information This link opens in a new window
Problem Statement
The problem needs to be very focused because everything else from the applied doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice logically flows from the problem. If the problem is too big or too vague, it will be difficult to scope out a purpose that is manageable, given the time to execute and finish the project. The problem should be the result of a practical need or an opportunity to further an applicational study or project.
Given the above, the problem statement should do four things:
Specify and describe the problem (with appropriate citations)
Provide evidence of the problem’s existence
Explain the consequences of NOT solving the problem
Identify what is not known about the problem that should be known.
What is a problem?
Example of a proper, specific, evidence-based, real-life problem: , evidence-based, what are consequences.
Consequences are negative implications experienced by a group of people, organization, profession, or industry as a result of the problem. The negative effects should be of a certain magnitude to warrant research. For example, if fewer than 1% of the stakeholders experience a negative consequence of a problem and that consequence only constitutes a minor inconvenience, research is probably not warranted. Negative consequences that can be measured weigh stronger than those that cannot be put on some kind of scale.
In the example above, a significant negative consequence is that women face much larger barriers than men when attempting to get promoted to executive jobs; or are 94% less likely than men to get to that level in Corporate America.
While a problem may be referred to as a gap in traditional research, in a doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice, the problem could be a statement of the situational condition that requires a scholar-practitioner approach. For the applied degree, this may be the part of the program or procedure that is not working.
NOTE: The applied doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice includes checklists for all sections of the document, including problem statement, purpose statement, and research questions. You should make sure you use these checklists and follow margin instructions. The present document is intended to provide additional help and examples, and also explain the importance of alignment. Alignment enables you to ensure consistency in your language and presentation of information, as well as provide a logical flow of your narrative.
Resource: Ellis, T., & Levy, Y. (2008). Framework of problem-based research: A guide for novice researchers on the development of a research-worthy problem. Informing Science , 11, 17-33. http://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db= a9h&AN=36030721&site=eds-live
- PDF Template
Option 1: Writing the Problem Statement
Do not exceed 250-300 words.
It is helpful to begin the problem statement with a sentence: “The problem to be addressed through this project is…”
Paragraph 1
The problem should be evidenced-based and focus on practice within your perspective field or domain. Then, fill out the rest of the paragraph with an elaboration of that specific problem, making sure to “document” it, as your doctoral committee will look for evidence that it is indeed a problem (emphasis also on the timeliness of the problem, supported by citations within the last 5 years). Identify the negative consequences that are occurring as a result of the problem.
Paragraph 2
Next, write a paragraph explaining the consequences of NOT solving the problem. Who will be affected? How will they be affected? How important is it to fix the problem? Again, your doctoral committee will want to see research-based citations and statistics that indicate the negative implications are significant.
Paragraph 3
In the final paragraph, you will explain what is not known that should be known. What isn’t known about the problem? Presumably, if your problem and purpose are aligned, your research will try to close or minimize this gap by investigating the problem. Have other practitioners investigated the issue? What has their research left unanswered?
Option 2: Writing the Problem Statement
Another way to tackle the statement of the problem: .
The Statement of the Problem section is a very clear, concise identification of the problem. It must stay within the template guidelines of 250-300 words but more importantly, must contain four elements as outlined below.
A worthy problem should be able to address all of the following points:
- identification of the problem itself--what is "going wrong" (Ellis & Levy, 2008)
- who is affected by the problem
- the consequences that will result from a continuation of the problem
- a brief discussion of
- at least 3 authors’ research related to the problem; and
- their stated suggestion/recommendation for further research related to the problem
Use the following to work on the Statement of the Problem by first outlining the section as follows:
One clear, concise statement that tells the reader what is not working in the profession or industry. Be specific and support it with current studies.
Tell who is affected by the problem identified in #1.
Briefly tell what will happen if the problem isn’t addressed.
Find at least 3 current studies and write a sentence or two for each study that
- briefly discusses the author(s)’ work, what they studied, and
- state their recommendation for further insight or exploration about the problem
Option 3: Writing the Problem Statement
Finally, you can follow this simple 3-part outline when writing the statement of the problem section.
Your problem statement is a short (250-300 words), 3 paragraph section, in which you:
| Context | 1. Explain context and state problem (“the problem is XYZ”), supported by statistics,and/or recent research findings, and/or the profession or industry. |
| Consequence | 2. Explain the negative consequences of the problem to stakeholders, supported by statistics and/or recent research findings and/or the profession or industry. |
| Gap | 3. Explain the gap in the research, or the part of the program or procedure that is not efficient |
Example of a problem statement that follows this 3-part outline (295 words):
| The problem to be addressed by this study is the decline of employee well-being for followers of novice mid-level managers and the corresponding rise in employee turnover faced by business leaders across the financial services industry (Oh et al., 2014). Low levels of employee well-being are toxic for morale and result in expensive turnover costs, dysfunctional work environments, anemic corporate cultures, and poor customer service (Compdata, 2018; Oh et al., 2014). According to Ufer (2017), the financial services industry suffers from one of the highest turnover rates among millennial-aged employees in all industries in the developed world, at 18.6% annually. Starkman (2015) reported that 50% of those surveyed in financial services were not satisfied with a single one of the four key workplace aspects: job, firm, pay or career path. |
| Low levels of employee well-being interrupt a financial services’ company’s ability to deliver outstanding customer service in a world increasingly dependent on that commodity (Wladawsky-Berger, 2018). Mid-level managers play an essential role in support of the success of many of top businesses today (Anicich & Hirsh, 2017). |
| The current body of literature does not adequately address the well-being issue in the financial services industry from the follower’s perspective (Uhl-Bien, Riggio, Lowe, & Carsten, 2014). Strategic direction flows top-down from senior executives and passes through mid-level leadership to individual contributors at more junior grades. The mid-level managers’ teams are tasked with the achievement of core tasks and the managers themselves are expected to maintain the workforce’s morale, motivation and welfare (Anicich & Hirsh, 2017). Unless industry leaders better understand the phenomenon of employee well-being from the follower perspective and its role in positioning employees to provide a premium client experience, they may be handicapped from preserving their most significant principal market differentiator: customer service (Wladawsky-Berger, 2018). |
- Statement of the Problem Template Use this fillable PDF to help craft your Statement of the Problem
- << Previous: Narrowing Your Topic
- Next: Purpose Statement >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1013602

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

ARTICLE: Problem Statement Development: How to Write a Problem Statement in A Dissertation

Most researchers and doctoral students have considerable trouble writing a problem statement with their research projects dissertations, and theses. We have to ask ourselves, why that is? Why are we encountering doctoral students and researchers that have trouble writing the problem statement? Why the disconnect? This is a common occurrence with doctoral students. We would think the required research methods course would address this. However, that is not case. Thus, this article addresses, discusses and illustrates how to develop a problem statement. This article will provide a model and template for developing a problem statement. As basis for a research study, it is important the researcher and doctoral student know how to construct a problem statement. First, this article discusses the problem statement. Second, this article provides a model as a for developing a problem statement. Last, the article provides examples of problem statements using the conceptual template. Doctoral Student Workshop: Problem Statement Development and Strategies
Related Papers
International Journal of Doctoral Studies
shardul pandya
Aim/Purpose: Provide methodology suggesting steps to doctoral mentors to work with students in constructing their research problem statement in their dissertation. Background: Doctoral students face difficulties writing their dissertation and they begin by writing the research problem statement. Methodology: This paper uses a framework widely used to describe student adjustment to graduate studies in general and to doctoral program in particular. Contribution: This study provides a framework to mentors/advisors that is helpful in guiding the students to writing their research problem statement. Findings: Writing a research problem statement is difficult by itself. Following a methodological approach suggested in this study could help with writing it. Recommendations for Practitioners: A methodological approach in writing the dissertation is helpful to mitigate the difficulties of writing the dissertation. Our study tackles difficulties with writing the research problem statement. Re...
InSITE Conference
Aim/Purpose: Develop instructional rubrics that help in writing and evaluating the doctoral dissertation research problem statement. Background: This is a follow-up study. In the first paper, we introduced a model for writing a research problem statement that takes the students through four phases to complete their writing. In this paper, we introduce an instructional rubric to be used for helping to write the research problem statement. Methodology: This paper builds on the previous model and adds Socratic questions to trigger critical thinking to help with writing the research problem statement. Contribution: Developing the instructional rubrics is the contribution of this study. The instructional rubrics can help with writing the research problem statement. Findings: Writing a research problem statement is difficult by itself. Following the methodological approach suggested in this study will help students with the task of writing their own. Following this instructional rubric wi...
A publication of the Department of Public Administration, Federal University Wukari, Taraba State. April 2024, 7(2), 35-46
Dr. Usman Bappi
This research aims to investigate the challenges encountered in formulating effective problem statements in research and proposes strategies for improvement. The statement of the problem is a critical component of any research study, and its quality influences the overall success of the research. The study will identify common problems, such as lack of clarity, scope issues, and insufficient justification, observed in existing research problem statements. Through a detailed analysis of literature and case studies, the research will explore the impact of these problems on the research process and outcomes. Additionally, the study will propose practical and theoretical frameworks to guide researchers in crafting more effective and impactful problem statements. The findings will contribute to enhancing the quality of research by providing actionable insights for researchers, educators, and practitioners to overcome challenges in formulating problem statements and improve the overall rigor of their studies.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series
Mahyuddin K. M. Nasution
This paper aims to provide an understanding of designing a problem statement that must be present in every research proposal or other scientific work. A study, from proposals to scientific papers, requires a problem statement. The design of the program statement is basically always present from research interests. Objectives as a translation of the problem statement will be described through a methodology that matches the answers to be given to the interests. In the industry 4.0 era, problem statement in research prioritize innovation or change to improve welfare.
Leo Andrew B . Diego
Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them.
Manu Mathew
Dr. Md Inaam Akhtar
Aptisi Transactions on Management (ATM)
Eka Purnama Harahap
Basically in conducting a study there are problems that can be used as a means toachieve a goal or goal in the study. Everyone who conducts research must have their ownmethod, concept, or method in formulating the problem that is the object of the research. In thispaper will explain the techniques or ways that can be done in relation to formulating problems inresearch including determining a topic to be discussed in research, making backgroundproblems, explaining problem identification, limiting the scope of research, determiningproblems that are worthy of research, making questions in research, and determine the goals,benefits, and uses of the research. With the concept of planning and mature thinking toformulate and determine the formulation of the problem, it is expected that the research that willbe conducted will be focused and directed so that it does not extend to the discussion that is notthe topic of his research. With the formulation of this problem also the reader becomes...
Princy Jain
Edupedia Publications
Research is an investigation or experimentation that is aimed at a discovery and interpretation of facts, revision of theories or laws or practical application of the new or revised theories or laws. Identification of research problem leads in conducting a research. To initiate a research, the necessity for the research, to be carried out should be generated.The ideas and topics are developed while consulting literatures, discussions with experts and continuation of activities related to the subject matter. These ideas/topics generally called research problems and are statements about areas of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. A research problem does not state how to do something, offer a vague or broad proposition, or present a value question. The problem must be significant researchable lead to further research and suitable for the researcher. Formulation of the problem should lead to empirical investigation. Formulation of research problem should depict what is to be determined and scope of the study.It also involves key concept definitions questions to be asked. The objective of the present paper highlights the above stated issues.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
International Journal of Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences
IJHASS Journal
Razieh Tadayon Nabavi
Vinicius M. Netto
Dr Dare E Ajayi
Serafin Talisayon
Augustine Akhidime
BOUKEZZOULA, M. (2019). A Plea for a Focus on the Contrasts between Two Paradigms and Their Implications for Problem Statement. Arab World English Journal, 10 (3) 448-469.
mohammed boukezzoula
Abdilahi Adam Mohamoud
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Masood Hassan
Scientific Research Publishing: Creative Education
Dr. Qais Faryadi
ZAHRA TARVIRDIZADEH
Vikalpa: The Journal for Decision Makers
Vivek Patkar
The Teachers College Record
Abdul Hakeem
Moses Adeleke ADEOYE
Luis Alberto Ibarra Díaz
Jaime Alfredo Cabrera
Nie Tagarao II
Scientific Research Publishing: Creative Education.
EURO Journal on Decision Processes
ALBERTO FRANCO
Families in Society: The Journal of Contemporary Social Services
Joanne Riebschleger
Sharmaine Espejo
John E Horsfield
The Qualitative Report
Glenn A Bowen
Dayana Mastura, FCCA(UK), MBA
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Problem Statement – When to Use it & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

In the process of crafting a research proposal , the problem statement holds paramount importance as it captures the reader’s attention from the get-go. Thus, it is imperative to comprehend its essence and what it encompasses. This article offers a thorough set of guidelines for determining and articulating a well-defined problem statement in the research process . Further, it emphasizes that an effective problem statement can not only frame the study but also serve as a foundation for the subsequent research steps.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Problem Statement – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Problem statement
- 3 When is a problem statement required?
- 4 1. Contextualize the problem statement
- 5 2. Why does the problem statement matter?
- 6 3. Objectives and aims for the problem statement
Problem Statement – In a Nutshell
- The problem statement is a description of the topic or issue that a researcher will explore.
- The statement should feature four primary elements: context, precise problem, relevance, and objectives.
- Problem statements may differ in theoretical and practical research.
Definition: Problem statement
A problem statement is a research proposal or paper description that explains what the research will address and why the issue needs to be addressed.
The statement is important in research and business proposals because it is one of the first things your instructor, colleagues, or potential customers will read in your document.
Once you have recognized the problem you want to explore in your project, you can come up with a problem statement by asking the questions below:
- What information is currently available about the problem? (Give context)
- What should we know about the topic? (Explain the precise issue)
- Why is this topic important? (Explain its relevance)
- What do you intend to do to find out more about the issue? (Explain the research objectives)
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
When is a problem statement required?
A problem statement is applicable in various situations. Also, you can use the statement when dealing with a practical or theoretical problem, like in science.
In each case, the problem statement will look different. However, the basic principles for writing it are constant.
A problem statement is required in:
| • The statement here helps readers, including your instructor, to understand your research problem and its significance. • It gives a contextual overview of your research subject. • The problem statement in academic research can feature several paragraphs, as long as they are relevant and serve as a basis for your project. • You can condense the statement into a few sentences and include it in your thesis paper’s introduction. | |
| • The problem statement here is a significant element in proposals for improvement projects. • It explains the issues that need to be addressed in a business or institution and the most effective solutions. • It provides an overview of how the solutions can be implemented. • In businesses and institutions, the problem statement is usually an independent document. |
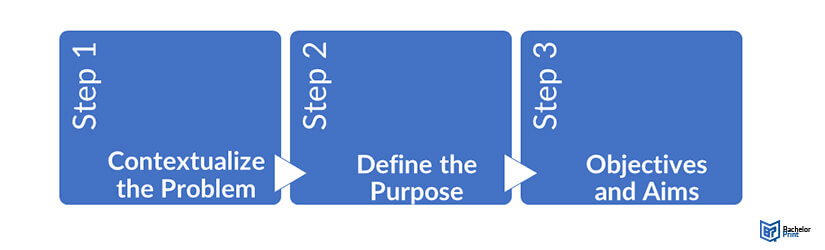
1. Contextualize the problem statement
The first thing you should do when preparing a problem statement is to contextualize the problem. Here, you should give some background about the issue and what is already known.
For instance, you can quote findings from a previous study about the issue. The approach may differ depending on the problem.
Practical problem statement
A practical problem involves everyday issues arising in institutions, businesses, and lives.
In such cases, your problem statement should answer the following questions:
- Who does the problem affect?
- Where does the problem arise?
- When does it happen?
- What steps have been made to resolve the issue?
The number of college dropouts in Texas has been increasing rapidly over the past decade compared to other states in the US. Studies show that around 1/5 of students that enroll in colleges do not see their studies through to graduation. The state has tried making colleges a friendlier environment to resolve the issue. However, this approach has not provided the expected results.
Theoretical problem statements
A theoretical problem results from abstract thinking and does not necessarily apply to everyday life. Theoretical research usually applies to scientific, historical, and geographical subjects. Therefore, your approach to theoretical research is usually different from a practical one.
When writing the problem statement for theoretical research problems, you should answer the questions below:
- What existing knowledge is there about the problem?
- Is the problem restricted to a specific period?
- Is the problem restricted to a specific geographical region?
- Is there scholarly literature that defines or debates the problem?
Over the past decade, social media “influencing” has become a significant element in the marketing sector. Research indicates that most people between 13 and 45 years old are likely to respond better to product marketing via public figures than traditional methods. Therefore, research on effective marketing schemes has shifted its focus to social media and the internet. However, little has been done to explore why this shift is happening and whether it is positive or negative.
2. Why does the problem statement matter?
Another significant element of the statement is the relevance of the research. In other words, why is the research problem worth exploring?
In practical research, you can explain the relevance of the problem by answering the questions below:
- What will transpire if the issue is not addressed?
- Who will be affected the most?
- Do similar issues exist in other contexts?
The high college dropout rate has already adversely affected Texas’ economy. However, if the issue is not addressed, students will no longer see the need to join colleges. Also, it may trickle down to the high school level as the value of education decreases among students. Besides the students, parents will also be affected by the dropouts because of increased crime rates and the declining economy. Therefore, addressing this issue will benefit Texas and other states.
Theoretical problem statement
For theoretical research, you can explain the relevance of the problem by asking the following questions:
- How will the problem’s resolution advance the comprehension of the subject?
- What benefits will the research have in future studies?
- Does the issue impact society directly or indirectly?
The social media “influencing” era can be viewed as positive or negative. In-depth research is required to fully understand why this generation responds to influences from social media. Expounding on social media habits may help develop more theories regarding the influences of the internet and social media on the current generation. It will also help with policy development.
3. Objectives and aims for the problem statement
After explaining the context of the research problem and its relevance, the next step is describing how you aim to address it.
The overall goal of any research is to find conclusive solutions for a specific problem and suggest the best ways to implement the solutions. However, you can only achieve this by determining the causes or reasons for the issue.
- I intend to investigate (the dropout rates in Texas).
- This project seeks to explore (the increasing college dropout rates in Texas).
- I purpose to determine (the causes of the increased college dropout rates in Texas).
The objectives are slightly different from the aims. Instead, objectives are steps you intend to apply to achieve your aim.
- I will use surveys to gather data (on the reasons students drop out of college in Texas).
- Using qualitative procedures, this research will identify (the number of college dropouts in the past decade).
- Statistical analysis will be applied to identify (the rates of college acceptance in Texas).
This project seeks to understand students’ college experiences and factors contributing to the increasing dropout rates in Texas. I will use statistical analysis to gather insight into the rates of college acceptances and graduations in the region.
This study intends to investigate the impact of the social media “influencing” era on the marketing sector and what practitioners can expect. Qualitative methods will be applied to identify the impact of social media and the success rates of social media marketing.
What is a problem statement?
A problem statement is a precise explanation of the issues a research project pursues to address. It includes:
- Precise issue
- Relevance of the study
When should you write a problem statement?
This statement is necessary for academic projects by university or college students.
However, businesses and institutions also need project statements (independent documents) when recommending improvement projects.
What is the value of a problem statement?
This statement provides readers with an overview of your project.
It also serves as a communication tool for those working on the project (it helps them know issues they should address).
What are the key fundamentals of a statement problem?
The key elements of a statement problem are:
- Precise problem identification
Therefore, your statement should explain each of these elements.
Bachelor Print is the most amazing company ever to print or bind academic work...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint

Thesis Problem Statement
Ai generator.

Writing a research has always been a tough process that enables a researcher to increase current knowledge and discover new things. One of the most important step in doing your research is to identify your research problem. It refers to what the researcher wants to solve and other areas of concern contained in the research. Although there are a lot of ways to solve a problem, difficulties may still arise.
Have you ever heard of a problem statement ? Perhaps, you do. It is a very essential part of every research that outlines the problem in your study. It answers the question, “what is the problem that your research study addresses?”
6+ Thesis Problem Statement Examples
1. thesis problem statement template.

Size: 157 KB
2. Sample Thesis Problem Statement

Size: 307 KB
3. Thesis Problem Statement Example

Size: 125 KB
4. Students and Thesis Problem Statement

Size: 309 KB
5. Printable Thesis Problem Statement

Size: 143 KB
6. Basic Thesis Problem Statement

Size: 89 KB
7. Thesis Problem Statement in PDF

Size: 20 KB
What is a Thesis Problem Statement?
A problem statement is a type of statement that points out a specific problem. It requires action to improve a particular situation. This statement is purely objective which focuses on the problem itself disregarding any subjective views. They are usually answered by questions starting with who, when, what, why and where. Through this, it will be easier to make the problem more comprehensive and solvable.
Why is a Problem Statement Important?
A problem statement is considered as a communication tool that businesses and other entities develop something for the purpose of improvement. It also helps in defining a problem and its corresponding solution. They provide information that is essential in the decision-making process for a particular project or business activity.
How to Write a Problem Statement?
There are a few elements that you need to have in mind. We might not know that this will be capable of providing a positive impact to the outcome.
You must be able to describe how things would work – provide a particular context that will help you understand the problem better. You may start doing so by describing or letting your readers know how to make things work. This refers to the process that functions effectively.
You should be able to explain the problem – the statement of the problem shows what the problem is, why it is being referred to as a problem, and why it is important to solve the problem. You may also try to consider the attempts you made to fix the problem.
You should be able to provide an explanation regarding the financial cost – money is considered as the language of every business. It is said that it would be easy to frame a problem and look for a solution if it has something to do with the financial cost.
You should be able to back up your claims – you must prepare a supporting claim with evidence every time you encounter costing problems. The best advise would be do some research, provide a text reference of the one you have researched and present a data.
You should be able to propose a solution to the problem – you should see first the cause of the problem before you start looking for a solution. Propose approaches that are considered as practical. Make sure that it is understandable. Do not forget to state the objectives of your research and provide plans that are already organized.
You should be able to explain the benefits of the solution you provided – present why the solution will work. Focus on its efficiency and the impact. This should fit into a single paragraph.
You should be able to provide a conclusion that summarizes the problem and its solution – this part should consist of the problem itself, the reason why it has to be fixed, and the summary as to why your solution is the best.
What are the key characteristics of a statement of the problem?
A good problem statement should be able to lead to further research, contribute to the existing research and should render itself for investigation by means of collecting data.
When can you say that it is an effective problem statement?
Effective problem statements would describe the issue precisely, show its relevance and set objectives based on your research.
When should you write a problem statement?
It is when you felt the need to outline the negative issues that arise regarding a current situation. After that, you provide an explanation as to why it matters.
Every problem statement will look entirely different. It varies on what research you are dealing with. It may be a real situation or a scientific issue. These problem statements may have several paragraphs long, but it is always important that the researcher should be able to keep the focus of stating the main problem and its solution alone.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What a Thesis Paper is and How to Write One

From choosing a topic and conducting research to crafting a strong argument, writing a thesis paper can be a rewarding experience.
It can also be a challenging experience. If you've never written a thesis paper before, you may not know where to start. You may not even be sure exactly what a thesis paper is. But don't worry; the right support and resources can help you navigate this writing process.
What is a Thesis Paper?

A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field.
“In some ways, a thesis paper can look a lot like a novella,” said Shana Chartier , director of information literacy at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU). “It’s too short to be a full-length novel, but with the standard size of 40-60 pages (for a bachelor’s) and 60-100 pages (for a master’s), it is a robust exploration of a topic, explaining one’s understanding of a topic based on personal research.”
Chartier has worked in academia for over 13 years and at SNHU for nearly eight. In her role as an instructor and director, Chartier has helped to guide students through the writing process, like editing and providing resources.
Chartier has written and published academic papers such as "Augmented Reality Gamifies the Library: A Ride Through the Technological Frontier" and "Going Beyond the One-Shot: Spiraling Information Literacy Across Four Years." Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion.
“When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated,” said Chartier. “Mapping out each step of the way, making firm and soft deadlines... and having other pairs of eyes on your work to ensure academic accuracy and clean editing are crucial to writing a successful paper.”
How Do I Choose a Topic For My Thesis Paper?

What your thesis paper is for will determine some of the specific requirements and steps you might take, but the first step is usually the same: Choosing a topic.
“Choosing a topic can be daunting," said Rochelle Attari , a peer tutor at SNHU. "But if (you) stick with a subject (you're) interested in... choosing a topic is much more manageable.”
Similar to a thesis, Attari recently finished the capstone for her bachelor’s in psychology . Her bachelor’s concentration is in forensics, and her capstone focused on the topic of using a combined therapy model for inmates who experience substance abuse issues to reduce recidivism.
“The hardest part was deciding what I wanted to focus on,” Attari said. “But once I nailed down my topic, each milestone was more straightforward.”
In her own writing experience, Attari said brainstorming was an important step when choosing her topic. She recommends writing down different ideas on a piece of paper and doing some preliminary research on what’s already been written on your topic.
By doing this exercise, you can narrow or broaden your ideas until you’ve found a topic you’re excited about. " Brainstorming is essential when writing a paper and is not a last-minute activity,” Attari said.
How Do I Structure My Thesis Paper?
Thesis papers tend to have a standard format with common sections as the building blocks.
While the structure Attari describes below will work for many theses, it’s important to double-check with your program to see if there are any specific requirements. Writing a thesis for a Master of Fine Arts, for example, might actually look more like a fiction novel.
According to Attari, a thesis paper is often structured with the following major sections:
Introduction
- Literature review
- Methods, results
Now, let’s take a closer look at what each different section should include.
Your introduction is your opportunity to present the topic of your thesis paper. In this section, you can explain why that topic is important. The introduction is also the place to include your thesis statement, which shows your stance in the paper.
Attari said that writing an introduction can be tricky, especially when you're trying to capture your reader’s attention and state your argument.
“I have found that starting with a statement of truth about a topic that pertains to an issue I am writing about typically does the trick,” Attari said. She demonstrated this advice in an example introduction she wrote for a paper on the effects of daylight in Alaska:
In the continental United States, we can always count on the sun rising and setting around the same time each day, but in Alaska, during certain times of the year, the sun rises and does not set for weeks. Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep.
In the example Attari wrote, she introduces the topic and informs the reader what the paper will cover. Somewhere in her intro, she said she would also include her thesis statement, which might be:
Twenty-four hours of daylight over an extended period does not affect sleep patterns in humans and is not the cause of daytime fatigue in northern Alaska .
Literature Review
In the literature review, you'll look at what information is already out there about your topic. “This is where scholarly articles about your topic are essential,” said Attari. “These articles will help you find the gap in research that you have identified and will also support your thesis statement."
Telling your reader what research has already been done will help them see how your research fits into the larger conversation. Most university libraries offer databases of scholarly/peer-reviewed articles that can be helpful in your search.
In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. This might include what experiment you conducted as a part of your independent research.
“For instance,” Attari said, “if you are a psychology major and have identified a gap in research on which therapies are effective for anxiety, your methods section would consist of the number of participants, the type of experiment and any other particulars you would use for that experiment.”
In this section, you'll explain the results of your study. For example, building on the psychology example Attari outlined, you might share self-reported anxiety levels for participants trying different kinds of therapies. To help you communicate your results clearly, you might include data, charts, tables or other visualizations.
The discussion section of your thesis paper is where you will analyze and interpret the results you presented in the previous section. This is where you can discuss what your findings really mean or compare them to the research you found in your literature review.
The discussion section is your chance to show why the data you collected matters and how it fits into bigger conversations in your field.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters.
Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. “You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research,” she said.
Find Your Program
Resources to help write your thesis paper.
While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn’t have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier.
If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
- Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are correct. APA , MLA and Chicago styles have all published their own guides.
- Citation Generators: There are many citation generator tools that help you to create citations. Some — like RefWorks — even let you directly import citations from library databases as you research.
- Your Library's Website: Many academic and public libraries allow patrons to access resources like databases or FAQs. Some FAQs at the SNHU library that might be helpful in your thesis writing process include “ How do I read a scholarly article? ” or “ What is a research question and how do I develop one? ”
It can also be helpful to check out what coaching or tutoring options are available through your school. At SNHU, for example, the Academic Support Center offers writing and grammar workshops , and students can access 24/7 tutoring and 1:1 sessions with peer tutors, like Attari.
"Students can even submit their papers and receive written feedback... like revisions and editing suggestions," she said.
If you are writing a thesis paper, there are many resources available to you. It's a long paper, but with the right mindset and support, you can successfully navigate the process.
“Pace yourself,” said Chartier. “This is a marathon, not a sprint. Setting smaller goals to get to the big finish line can make the process seem less daunting, and remember to be proud of yourself and celebrate your accomplishment once you’re done. Writing a thesis is no small task, and it’s important work for the scholarly community.”
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.
Meg Palmer ’18 is a writer and scholar by trade who loves reading, riding her bike and singing in a barbershop quartet. She earned her bachelor’s degree in English, language and literature at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and her master’s degree in writing, rhetoric and discourse at DePaul University (’20). While attending SNHU, she served as the editor-in-chief of the campus student newspaper, The Penmen Press, where she deepened her passion for writing. Meg is an adjunct professor at Johnson and Wales University, where she teaches first year writing, honors composition, and public speaking. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.

COMMENTS
Learn how to write a problem statement for your research project. A problem statement explains the issue you want to address and why it matters. Find out the key components and examples of a problem statement.
How can we write a problem statement for a thesis? To write a problem statement for a thesis, we must provide the context of the research, followed by the purpose of the study, then the general research procedure that includes the setting and target population, and lastly, the specific research questions that used to address the general problem.
Learn what the research problem and problem statement are and how to write them. Plain-language explanation with clear, practical examples.
Getting to the core: How to write problem statement for a thesis Before we get detailed into the question of how to write a problem statement for a dissertation, it is crucial to approach the story's core and explain the meaning and significance of the problem statement briefly.
It takes just 4 steps to write an interesting dissertation problem statement. Here are examples and a detailed guide on how to write the best statement.
The problem statement aims to highlight the pressing issue the research intends to address. It should be concise and to the point. Researchers can follow a two-step approach: first, think about the content of the problem statement, and then organize the writing framework. Before writing, clarify the following points¹:
The dissertation problem statement is one of the section most frequently requested for revision by committee members. To save time, read our primer.
Statement of the Problem in research is pivotal. Learn how to craft it effectively, avoid common mistakes, and enhance your academic study's impact.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge. Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other.
A thesis statement and a problem statement are related but distinct elements of a research project. A thesis statement is a statement that summarizes the central argument or claim of a research paper or essay.
Problem Statement Overview The dissertation problem needs to be very focused because everything else from the dissertation research logically flows from the problem. You may say that the problem statement is the very core of a dissertation research study. If the problem is too big or too vague, it will be difficult to scope out a purpose that is manageable for one person, given the time ...
"There is no study if there is no problem." These words were said to me when I wrote my Masters dissertation and are arguably the most important in all my ye...
A thesis will generally respond to an analytical question or pose a solution to a problem that you have framed for your readers (and for yourself). When you frame that question or problem for your readers, you are telling them what is at stake in your argument—why your question matters and why they should care about the answer. If you can explain to your readers why a question or problem is ...
Writing problem statement, choosing a problem to investigate is the first step in carrying out a thesis writing even before literature review
When should you write a problem statement? There are various situations in which you might have to write a problem statement. In the business world, writing a problem statement is often the first step in kicking off an improvement project. In this case, the problem statement is usually a stand-alone document.
The problem statement poses a crucial section of any dissertation, research project, and thesis, providing a concise and clear outline of the issue the study seeks to address. A well-written problem statement serves as a cornerstone in guiding the research process and sets the foundation for your methodology, findings, and research questions. This article will provide problem statement ...
Problem Statement The problem needs to be very focused because everything else from the applied doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice logically flows from the problem. If the problem is too big or too vague, it will be difficult to scope out a purpose that is manageable, given the time to execute and finish the project. The problem should be the result of a practical need or an ...
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your essay. It usually comes at the end of the introduction.
However, that is not case. Thus, this article addresses, discusses and illustrates how to develop a problem statement. This article will provide a model and template for developing a problem statement. As basis for a research study, it is important the researcher and doctoral student know how to construct a problem statement.
A problem statement is a research proposal or paper description that explains what the research will address and why the issue needs to be addressed. The statement is important in research and business proposals because it is one of the first things your instructor, colleagues, or potential customers will read in your document.
When businesses encounter obstacles that demand collaborative problem solving, key stakeholders can draft a problem statement to lay out current issues and state what needs to change. Effective problem statements can be valuable communication tools that get all team members working toward potential solutions.
Thesis Problem Statement Writing a research has always been a tough process that enables a researcher to increase current knowledge and discover new things. One of the most important step in doing your research is to identify your research problem. It refers to what the researcher wants to solve and other areas of concern contained in the research. Although there are a lot of ways to solve a ...
A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field. ... "You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and ...
The document discusses writing a problem statement for a master's thesis. Crafting an effective problem statement is one of the most challenging parts of the thesis process, as it requires clarity, a deep understanding of the research topic, and the ability to articulate the problem concisely.