- Privacy Policy

Home » Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

Focus Group
Definition:
A focus group is a qualitative research method used to gather in-depth insights and opinions from a group of individuals about a particular product, service, concept, or idea.
The focus group typically consists of 6-10 participants who are selected based on shared characteristics such as demographics, interests, or experiences. The discussion is moderated by a trained facilitator who asks open-ended questions to encourage participants to share their thoughts, feelings, and attitudes towards the topic.
Focus groups are an effective way to gather detailed information about consumer behavior, attitudes, and perceptions, and can provide valuable insights to inform decision-making in a range of fields including marketing, product development, and public policy.
Types of Focus Group
The following are some types or methods of Focus Groups:
Traditional Focus Group
This is the most common type of focus group, where a small group of people is brought together to discuss a particular topic. The discussion is typically led by a skilled facilitator who asks open-ended questions to encourage participants to share their thoughts and opinions.
Mini Focus Group
A mini-focus group involves a smaller group of participants, typically 3 to 5 people. This type of focus group is useful when the topic being discussed is particularly sensitive or when the participants are difficult to recruit.
Dual Moderator Focus Group
In a dual-moderator focus group, two facilitators are used to manage the discussion. This can help to ensure that the discussion stays on track and that all participants have an opportunity to share their opinions.
Teleconference or Online Focus Group
Teleconferences or online focus groups are conducted using video conferencing technology or online discussion forums. This allows participants to join the discussion from anywhere in the world, making it easier to recruit participants and reducing the cost of conducting the focus group.
Client-led Focus Group
In a client-led focus group, the client who is commissioning the research takes an active role in the discussion. This type of focus group is useful when the client has specific questions they want to ask or when they want to gain a deeper understanding of their customers.
The following Table can explain Focus Group types more clearly
| Type of Focus Group | Number of Participants | Duration | Types of Questions | Geographical Area | Analysis Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | 6-12 | 1-2 hours | Open-ended | Local | Thematic Analysis |
| Mini | 3-5 | 1-2 hours | Closed-ended | Local | Content Analysis |
| Dual Moderator | 6-12 | 1-2 hours | Combination of open- and closed-ended | Regional | Discourse Analysis |
| Teleconference/Online | 6-12 | 1-2 hours | Open-ended | National/International | Conversation Analysis |
| Client-Led | 6-12 | 1-2 hours | Combination of open- and closed-ended | Local/Regional | Thematic Analy |
How To Conduct a Focus Group
To conduct a focus group, follow these general steps:
Define the Research Question
Identify the key research question or objective that you want to explore through the focus group. Develop a discussion guide that outlines the topics and questions you want to cover during the session.
Recruit Participants
Identify the target audience for the focus group and recruit participants who meet the eligibility criteria. You can use various recruitment methods such as social media, online panels, or referrals from existing customers.
Select a Venue
Choose a location that is convenient for the participants and has the necessary facilities such as audio-visual equipment, seating, and refreshments.
Conduct the Session
During the focus group session, introduce the topic, and review the objectives of the research. Encourage participants to share their thoughts and opinions by asking open-ended questions and probing deeper into their responses. Ensure that the discussion remains on topic and that all participants have an opportunity to contribute.
Record the Session
Use audio or video recording equipment to capture the discussion. Note-taking is also essential to ensure that you capture all key points and insights.
Analyze the data
Once the focus group is complete, transcribe and analyze the data. Look for common themes, patterns, and insights that emerge from the discussion. Use this information to generate insights and recommendations that can be applied to the research question.
When to use Focus Group Method
The focus group method is typically used in the following situations:
Exploratory Research
When a researcher wants to explore a new or complex topic in-depth, focus groups can be used to generate ideas, opinions, and insights.
Product Development
Focus groups are often used to gather feedback from consumers about new products or product features to help identify potential areas for improvement.
Marketing Research
Focus groups can be used to test marketing concepts, messaging, or advertising campaigns to determine their effectiveness and appeal to different target audiences.
Customer Feedback
Focus groups can be used to gather feedback from customers about their experiences with a particular product or service, helping companies improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Public Policy Research
Focus groups can be used to gather public opinions and attitudes on social or political issues, helping policymakers make more informed decisions.
Examples of Focus Group
Here are some real-time examples of focus groups:
- A tech company wants to improve the user experience of their mobile app. They conduct a focus group with a diverse group of users to gather feedback on the app’s design, functionality, and features. The focus group consists of 8 participants who are selected based on their age, gender, ethnicity, and level of experience with the app. During the session, a trained facilitator asks open-ended questions to encourage participants to share their thoughts and opinions on the app. The facilitator also observes the participants’ behavior and reactions to the app’s features. After the focus group, the data is analyzed to identify common themes and issues raised by the participants. The insights gathered from the focus group are used to inform improvements to the app’s design and functionality, with the goal of creating a more user-friendly and engaging experience for all users.
- A car manufacturer wants to develop a new electric vehicle that appeals to a younger demographic. They conduct a focus group with millennials to gather their opinions on the design, features, and pricing of the vehicle.
- A political campaign team wants to develop effective messaging for their candidate’s campaign. They conduct a focus group with voters to gather their opinions on key issues and identify the most persuasive arguments and messages.
- A restaurant chain wants to develop a new menu that appeals to health-conscious customers. They conduct a focus group with fitness enthusiasts to gather their opinions on the types of food and drinks that they would like to see on the menu.
- A healthcare organization wants to develop a new wellness program for their employees. They conduct a focus group with employees to gather their opinions on the types of programs, incentives, and support that would be most effective in promoting healthy behaviors.
- A clothing retailer wants to develop a new line of sustainable and eco-friendly clothing. They conduct a focus group with environmentally conscious consumers to gather their opinions on the design, materials, and pricing of the clothing.
Purpose of Focus Group
The key objectives of a focus group include:
Generating New Ideas and insights
Focus groups are used to explore new or complex topics in-depth, generating new ideas and insights that may not have been previously considered.
Understanding Consumer Behavior
Focus groups can be used to gather information on consumer behavior, attitudes, and perceptions to inform marketing and product development strategies.
Testing Concepts and Ideas
Focus groups can be used to test marketing concepts, messaging, or product prototypes to determine their effectiveness and appeal to different target audiences.
Gathering Customer Feedback
Informing decision-making.
Focus groups can provide valuable insights to inform decision-making in a range of fields including marketing, product development, and public policy.
Advantages of Focus Group
The advantages of using focus groups are:
- In-depth insights: Focus groups provide in-depth insights into the attitudes, opinions, and behaviors of a target audience on a specific topic, allowing researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the issues being explored.
- Group dynamics: The group dynamics of focus groups can provide additional insights, as participants may build on each other’s ideas, share experiences, and debate different perspectives.
- Efficient data collection: Focus groups are an efficient way to collect data from multiple individuals at the same time, making them a cost-effective method of research.
- Flexibility : Focus groups can be adapted to suit a range of research objectives, from exploratory research to concept testing and customer feedback.
- Real-time feedback: Focus groups provide real-time feedback on new products or concepts, allowing researchers to make immediate adjustments and improvements based on participant feedback.
- Participant engagement: Focus groups can be a more engaging and interactive research method than surveys or other quantitative methods, as participants have the opportunity to express their opinions and interact with other participants.
Limitations of Focus Groups
While focus groups can provide valuable insights, there are also some limitations to using them.
- Small sample size: Focus groups typically involve a small number of participants, which may not be representative of the broader population being studied.
- Group dynamics : While group dynamics can be an advantage of focus groups, they can also be a limitation, as dominant personalities may sway the discussion or participants may not feel comfortable expressing their true opinions.
- Limited generalizability : Because focus groups involve a small sample size, the results may not be generalizable to the broader population.
- Limited depth of responses: Because focus groups are time-limited, participants may not have the opportunity to fully explore or elaborate on their opinions or experiences.
- Potential for bias: The facilitator of a focus group may inadvertently influence the discussion or the selection of participants may not be representative, leading to potential bias in the results.
- Difficulty in analysis : The qualitative data collected in focus groups can be difficult to analyze, as it is often subjective and requires a skilled researcher to interpret and identify themes.
Characteristics of Focus Group
- Small group size: Focus groups typically involve a small number of participants, ranging from 6 to 12 people. This allows for a more in-depth and focused discussion.
- Targeted participants: Participants in focus groups are selected based on specific criteria, such as age, gender, or experience with a particular product or service.
- Facilitated discussion: A skilled facilitator leads the discussion, asking open-ended questions and encouraging participants to share their thoughts and experiences.
- I nteractive and conversational: Focus groups are interactive and conversational, with participants building on each other’s ideas and responding to one another’s opinions.
- Qualitative data: The data collected in focus groups is qualitative, providing detailed insights into participants’ attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
- Non-threatening environment: Participants are encouraged to share their thoughts and experiences in a non-threatening and supportive environment.
- Limited time frame: Focus groups are typically time-limited, lasting between 1 and 2 hours, to ensure that the discussion stays focused and productive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Ethnographic Research -Types, Methods and Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Transformative Design – Methods, Types, Guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
What is a Focus Group | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on December 10, 2021 by Tegan George . Revised on June 22, 2023.
A focus group is a research method that brings together a small group of people to answer questions in a moderated setting. The group is chosen due to predefined demographic traits, and the questions are designed to shed light on a topic of interest.

Table of contents
What is a focus group, step 1: choose your topic of interest, step 2: define your research scope and hypotheses, step 3: determine your focus group questions, step 4: select a moderator or co-moderator, step 5: recruit your participants, step 6: set up your focus group, step 7: host your focus group, step 8: analyze your data and report your results, advantages and disadvantages of focus groups, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about focus groups.
Focus groups are a type of qualitative research . Observations of the group’s dynamic, their answers to focus group questions, and even their body language can guide future research on consumer decisions, products and services, or controversial topics.
Focus groups are often used in marketing, library science, social science, and user research disciplines. They can provide more nuanced and natural feedback than individual interviews and are easier to organize than experiments or large-scale surveys .
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Focus groups are primarily considered a confirmatory research technique . In other words, their discussion-heavy setting is most useful for confirming or refuting preexisting beliefs. For this reason, they are great for conducting explanatory research , where you explore why something occurs when limited information is available.
A focus group may be a good choice for you if:
- You’re interested in real-time, unfiltered responses on a given topic or in the dynamics of a discussion between participants
- Your questions are rooted in feelings or perceptions , and cannot easily be answered with “yes” or “no”
- You’re confident that a relatively small number of responses will answer your question
- You’re seeking directional information that will help you uncover new questions or future research ideas
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, but other questions aren’t planned.
- Unstructured interviews : None of the questions are predetermined.
Differences between types of interviews
Make sure to choose the type of interview that suits your research best. This table shows the most important differences between the four types.
| Structured interview | Semi-structured interview | Unstructured interview | Focus group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed questions | ||||
| Fixed order of questions | ||||
| Fixed number of questions | ||||
| Option to ask additional questions |
Topics favorable to focus groups
As a rule of thumb, research topics related to thoughts, beliefs, and feelings work well in focus groups. If you are seeking direction, explanation, or in-depth dialogue, a focus group could be a good fit.
However, if your questions are dichotomous or if you need to reach a large audience quickly, a survey may be a better option. If your question hinges upon behavior but you are worried about influencing responses, consider an observational study .
- If you want to determine whether the student body would regularly consume vegan food, a survey would be a great way to gauge student preferences.
However, food is much more than just consumption and nourishment and can have emotional, cultural, and other implications on individuals.
- If you’re interested in something less concrete, such as students’ perceptions of vegan food or the interplay between their choices at the dining hall and their feelings of homesickness or loneliness, perhaps a focus group would be best.
Once you have determined that a focus group is the right choice for your topic, you can start thinking about what you expect the group discussion to yield.
Perhaps literature already exists on your subject or a sufficiently similar topic that you can use as a starting point. If the topic isn’t well studied, use your instincts to determine what you think is most worthy of study.
Setting your scope will help you formulate intriguing hypotheses , set clear questions, and recruit the right participants.
- Are you interested in a particular sector of the population, such as vegans or non-vegans?
- Are you interested in including vegetarians in your analysis?
- Perhaps not all students eat at the dining hall. Will your study exclude those who don’t?
- Are you only interested in students who have strong opinions on the subject?
A benefit of focus groups is that your hypotheses can be open-ended. You can be open to a wide variety of opinions, which can lead to unexpected conclusions.
The questions that you ask your focus group are crucially important to your analysis. Take your time formulating them, paying special attention to phrasing. Be careful to avoid leading questions , which can affect your responses.
Overall, your focus group questions should be:
- Open-ended and flexible
- Impossible to answer with “yes” or “no” (questions that start with “why” or “how” are often best)
- Unambiguous, getting straight to the point while still stimulating discussion
- Unbiased and neutral
If you are discussing a controversial topic, be careful that your questions do not cause social desirability bias . Here, your respondents may lie about their true beliefs to mask any socially unacceptable or unpopular opinions. This and other demand characteristics can hurt your analysis and lead to several types of reseach bias in your results, particularly if your participants react in a different way once knowing they’re being observed. These include self-selection bias , the Hawthorne effect , the Pygmalion effect , and recall bias .
- Engagement questions make your participants feel comfortable and at ease: “What is your favorite food at the dining hall?”
- Exploration questions drill down to the focus of your analysis: “What pros and cons of offering vegan options do you see?”
- Exit questions pick up on anything you may have previously missed in your discussion: “Is there anything you’d like to mention about vegan options in the dining hall that we haven’t discussed?”
It is important to have more than one moderator in the room. If you would like to take the lead asking questions, select a co-moderator who can coordinate the technology, take notes, and observe the behavior of the participants.
If your hypotheses have behavioral aspects, consider asking someone else to be lead moderator so that you are free to take a more observational role.
Depending on your topic, there are a few types of moderator roles that you can choose from.
- The most common is the dual-moderator , introduced above.
- Another common option is the dueling-moderator style . Here, you and your co-moderator take opposing sides on an issue to allow participants to see different perspectives and respond accordingly.
Depending on your research topic, there are a few sampling methods you can choose from to help you recruit and select participants.
- Voluntary response sampling , such as posting a flyer on campus and finding participants based on responses
- Convenience sampling of those who are most readily accessible to you, such as fellow students at your university
- Stratified sampling of a particular age, race, ethnicity, gender identity, or other characteristic of interest to you
- Judgment sampling of a specific set of participants that you already know you want to include
Beware of sampling bias and selection bias , which can occur when some members of the population are more likely to be included than others.
Number of participants
In most cases, one focus group will not be sufficient to answer your research question. It is likely that you will need to schedule three to four groups. A good rule of thumb is to stop when you’ve reached a saturation point (i.e., when you aren’t receiving new responses to your questions).
Most focus groups have 6–10 participants. It’s a good idea to over-recruit just in case someone doesn’t show up. As a rule of thumb, you shouldn’t have fewer than 6 or more than 12 participants, in order to get the most reliable results.
Lastly, it’s preferable for your participants not to know you or each other, as this can bias your results.
A focus group is not just a group of people coming together to discuss their opinions. While well-run focus groups have an enjoyable and relaxed atmosphere, they are backed up by rigorous methods to provide robust observations.
Confirm a time and date
Be sure to confirm a time and date with your participants well in advance. Focus groups usually meet for 45–90 minutes, but some can last longer. However, beware of the possibility of wandering attention spans. If you really think your session needs to last longer than 90 minutes, schedule a few breaks.
Confirm whether it will take place in person or online
You will also need to decide whether the group will meet in person or online. If you are hosting it in person, be sure to pick an appropriate location.
- An uncomfortable or awkward location may affect the mood or level of participation of your group members.
- Online sessions are convenient, as participants can join from home, but they can also lessen the connection between participants.
As a general rule, make sure you are in a noise-free environment that minimizes distractions and interruptions to your participants.
Consent and ethical considerations
It’s important to take into account ethical considerations and informed consent when conducting your research. Informed consent means that participants possess all the information they need to decide whether they want to participate in the research before it starts. This includes information about benefits, risks, funding, and institutional approval.
Participants should also sign a release form that states that they are comfortable with being audio- or video-recorded. While verbal consent may be sufficient, it is best to ask participants to sign a form.
A disadvantage of focus groups is that they are too small to provide true anonymity to participants. Make sure that your participants know this prior to participating.
There are a few things you can do to commit to keeping information private. You can secure confidentiality by removing all identifying information from your report or offer to pseudonymize the data later. Data pseudonymization entails replacing any identifying information about participants with pseudonymous or false identifiers.
Preparation prior to participation
If there is something you would like participants to read, study, or prepare beforehand, be sure to let them know well in advance. It’s also a good idea to call them the day before to ensure they will still be participating.
Consider conducting a tech check prior to the arrival of your participants, and note any environmental or external factors that could affect the mood of the group that day. Be sure that you are organized and ready, as a stressful atmosphere can be distracting and counterproductive.
Starting the focus group
Welcome individuals to the focus group by introducing the topic, yourself, and your co-moderator, and go over any ground rules or suggestions for a successful discussion. It’s important to make your participants feel at ease and forthcoming with their responses.
Consider starting out with an icebreaker, which will allow participants to relax and settle into the space a bit. Your icebreaker can be related to your study topic or not; it’s just an exercise to get participants talking.
Leading the discussion
Once you start asking your questions, try to keep response times equal between participants. Take note of the most and least talkative members of the group, as well as any participants with particularly strong or dominant personalities.
You can ask less talkative members questions directly to encourage them to participate or ask participants questions by name to even the playing field. Feel free to ask participants to elaborate on their answers or to give an example.
As a moderator, strive to remain neutral . Refrain from reacting to responses, and be aware of your body language (e.g., nodding, raising eyebrows) and the possibility for observer bias . Active listening skills, such as parroting back answers or asking for clarification, are good methods to encourage participation and signal that you’re listening.
Many focus groups offer a monetary incentive for participants. Depending on your research budget, this is a nice way to show appreciation for their time and commitment. To keep everyone feeling fresh, consider offering snacks or drinks as well.
After concluding your focus group, you and your co-moderator should debrief, recording initial impressions of the discussion as well as any highlights, issues, or immediate conclusions you’ve drawn.
The next step is to transcribe and clean your data . Assign each participant a number or pseudonym for organizational purposes. Transcribe the recordings and conduct content analysis to look for themes or categories of responses. The categories you choose can then form the basis for reporting your results.
Just like other research methods, focus groups come with advantages and disadvantages.
- They are fairly straightforward to organize and results have strong face validity .
- They are usually inexpensive, even if you compensate participant.
- A focus group is much less time-consuming than a survey or experiment , and you get immediate results.
- Focus group results are often more comprehensible and intuitive than raw data.
Disadvantages
- It can be difficult to assemble a truly representative sample. Focus groups are generally not considered externally valid due to their small sample sizes.
- Due to the small sample size, you cannot ensure the anonymity of respondents, which may influence their desire to speak freely.
- Depth of analysis can be a concern, as it can be challenging to get honest opinions on controversial topics.
- There is a lot of room for error in the data analysis and high potential for observer dependency in drawing conclusions. You have to be careful not to cherry-pick responses to fit a prior conclusion.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A focus group is a research method that brings together a small group of people to answer questions in a moderated setting. The group is chosen due to predefined demographic traits, and the questions are designed to shed light on a topic of interest. It is one of 4 types of interviews .
As a rule of thumb, questions related to thoughts, beliefs, and feelings work well in focus groups. Take your time formulating strong questions, paying special attention to phrasing. Be careful to avoid leading questions , which can bias your responses.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Every dataset requires different techniques to clean dirty data , but you need to address these issues in a systematic way. You focus on finding and resolving data points that don’t agree or fit with the rest of your dataset.
These data might be missing values, outliers, duplicate values, incorrectly formatted, or irrelevant. You’ll start with screening and diagnosing your data. Then, you’ll often standardize and accept or remove data to make your dataset consistent and valid.
The four most common types of interviews are:
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Focus group interviews : The questions are presented to a group instead of one individual.
It’s impossible to completely avoid observer bias in studies where data collection is done or recorded manually, but you can take steps to reduce this type of bias in your research .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, June 22). What is a Focus Group | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/focus-group/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, explanatory research | definition, guide, & examples, data collection | definition, methods & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Chapter 12. Focus Groups
Introduction.
Focus groups are a particular and special form of interviewing in which the interview asks focused questions of a group of persons, optimally between five and eight. This group can be close friends, family members, or complete strangers. They can have a lot in common or nothing in common. Unlike one-on-one interviews, which can probe deeply, focus group questions are narrowly tailored (“focused”) to a particular topic and issue and, with notable exceptions, operate at the shallow end of inquiry. For example, market researchers use focus groups to find out why groups of people choose one brand of product over another. Because focus groups are often used for commercial purposes, they sometimes have a bit of a stigma among researchers. This is unfortunate, as the focus group is a helpful addition to the qualitative researcher’s toolkit. Focus groups explicitly use group interaction to assist in the data collection. They are particularly useful as supplements to one-on-one interviews or in data triangulation. They are sometimes used to initiate areas of inquiry for later data collection methods. This chapter describes the main forms of focus groups, lays out some key differences among those forms, and provides guidance on how to manage focus group interviews.

Focus Groups: What Are They and When to Use Them
As interviews, focus groups can be helpfully distinguished from one-on-one interviews. The purpose of conducting a focus group is not to expand the number of people one interviews: the focus group is a different entity entirely. The focus is on the group and its interactions and evaluations rather than on the individuals in that group. If you want to know how individuals understand their lives and their individual experiences, it is best to ask them individually. If you want to find out how a group forms a collective opinion about something (whether a product or an event or an experience), then conducting a focus group is preferable. The power of focus groups resides in their being both focused and oriented to the group . They are best used when you are interested in the shared meanings of a group or how people discuss a topic publicly or when you want to observe the social formation of evaluations. The interaction of the group members is an asset in this method of data collection. If your questions would not benefit from group interaction, this is a good indicator that you should probably use individual interviews (chapter 11). Avoid using focus groups when you are interested in personal information or strive to uncover deeply buried beliefs or personal narratives. In general, you want to avoid using focus groups when the subject matter is polarizing, as people are less likely to be honest in a group setting. There are a few exceptions, such as when you are conducting focus groups with people who are not strangers and/or you are attempting to probe deeply into group beliefs and evaluations. But caution is warranted in these cases. [1]
As with interviewing in general, there are many forms of focus groups. Focus groups are widely used by nonresearchers, so it is important to distinguish these uses from the research focus group. Businesses routinely employ marketing focus groups to test out products or campaigns. Jury consultants employ “mock” jury focus groups, testing out legal case strategies in advance of actual trials. Organizations of various kinds use focus group interviews for program evaluation (e.g., to gauge the effectiveness of a diversity training workshop). The research focus group has many similarities with all these uses but is specifically tailored to a research (rather than applied) interest. The line between application and research use can be blurry, however. To take the case of evaluating the effectiveness of a diversity training workshop, the same interviewer may be conducting focus group interviews both to provide specific actionable feedback for the workshop leaders (this is the application aspect) and to learn more about how people respond to diversity training (an interesting research question with theoretically generalizable results).
When forming a focus group, there are two different strategies for inclusion. Diversity focus groups include people with diverse perspectives and experiences. This helps the researcher identify commonalities across this diversity and/or note interactions across differences. What kind of diversity to capture depends on the research question, but care should be taken to ensure that those participating are not set up for attack from other participants. This is why many warn against diversity focus groups, especially around politically sensitive topics. The other strategy is to build a convergence focus group , which includes people with similar perspectives and experiences. These are particularly helpful for identifying shared patterns and group consensus. The important thing is to closely consider who will be invited to participate and what the composition of the group will be in advance. Some review of sampling techniques (see chapter 5) may be helpful here.
Moderating a focus group can be a challenge (more on this below). For this reason, confining your group to no more than eight participants is recommended. You probably want at least four persons to capture group interaction. Fewer than four participants can also make it more difficult for participants to remain (relatively) anonymous—there is less of a group in which to hide. There are exceptions to these recommendations. You might want to conduct a focus group with a naturally occurring group, as in the case of a family of three, a social club of ten, or a program of fifteen. When the persons know one another, the problems of too few for anonymity don’t apply, and although ten to fifteen can be unwieldy to manage, there are strategies to make this possible. If you really are interested in this group’s dynamic (not just a set of random strangers’ dynamic), then you will want to include all its members or as many as are willing and able to participate.
There are many benefits to conducting focus groups, the first of which is their interactivity. Participants can make comparisons, can elaborate on what has been voiced by another, and can even check one another, leading to real-time reevaluations. This last benefit is one reason they are sometimes employed specifically for consciousness raising or building group cohesion. This form of data collection has an activist application when done carefully and appropriately. It can be fun, especially for the participants. Additionally, what does not come up in a focus group, especially when expected by the researcher, can be very illuminating.
Many of these benefits do incur costs, however. The multiplicity of voices in a good focus group interview can be overwhelming both to moderate and later to transcribe. Because of the focused nature, deep probing is not possible (or desirable). You might only get superficial thinking or what people are willing to put out there publicly. If that is what you are interested in, good. If you want deeper insight, you probably will not get that here. Relatedly, extreme views are often suppressed, and marginal viewpoints are unspoken or, if spoken, derided. You will get the majority group consensus and very little of minority viewpoints. Because people will be engaged with one another, there is the possibility of cut-off sentences, making it even more likely to hear broad brush themes and not detailed specifics. There really is very little opportunity for specific follow-up questions to individuals. Reading over a transcript, you may be frustrated by avenues of inquiry that were foreclosed early.
Some people expect that conducting focus groups is an efficient form of data collection. After all, you get to hear from eight people instead of just one in the same amount of time! But this is a serious misunderstanding. What you hear in a focus group is one single group interview or discussion. It is not the same thing at all as conducting eight single one-hour interviews. Each focus group counts as “one.” Most likely, you will need to conduct several focus groups, and you can design these as comparisons to one another. For example, the American Sociological Association (ASA) Task Force on First-Generation and Working-Class Persons in Sociology began its study of the impact of class in sociology by conducting five separate focus groups with different groups of sociologists: graduate students, faculty (in general), community college faculty, faculty of color, and a racially diverse group of students and faculty. Even though the total number of participants was close to forty, the “number” of cases was five. It is highly recommended that when employing focus groups, you plan on composing more than one and at least three. This allows you to take note of and potentially discount findings from a group with idiosyncratic dynamics, such as where a particularly dominant personality silences all other voices. In other words, putting all your eggs into a single focus group basket is not a good idea.
How to Conduct a Focus Group Interview/Discussion
Advance preparations.
Once you have selected your focus groups and set a date and time, there are a few things you will want to plan out before meeting.
As with interviews, you begin by creating an interview (or discussion) guide. Where a good one-on-one interview guide should include ten to twelve main topics with possible prompts and follow-ups (see the example provided in chapter 11), the focus group guide should be more narrowly tailored to a single focus or topic area. For example, a focus might be “How students coped with online learning during the pandemic,” and a series of possible questions would be drafted that would help prod participants to think about and discuss this topic. These questions or discussion prompts can be creative and may include stimulus materials (watching a video or hearing a story) or posing hypotheticals. For example, Cech ( 2021 ) has a great hypothetical, asking what a fictional character should do: keep his boring job in computers or follow his passion and open a restaurant. You can ask a focus group this question and see what results—how the group comes to define a “good job,” what questions they ask about the hypothetical (How boring is his job really? Does he hate getting up in the morning, or is it more of an everyday tedium? What kind of financial support will he have if he quits? Does he even know how to run a restaurant?), and how they reach a consensus or create clear patterns of disagreement are all interesting findings that can be generated through this technique.
As with the above example (“What should Joe do?”), it is best to keep the questions you ask simple and easily understood by everyone. Thinking about the sequence of the questions/prompts is important, just as it is in conducting any interviews.
Avoid embarrassing questions. Always leave an out for the “I have a friend who X” response rather than pushing people to divulge personal information. Asking “How do you think students coped?” is better than “How did you cope?” Chances are, some participants will begin talking about themselves without you directly asking them to do so, but allowing impersonal responses here is good. The group itself will determine how deep and how personal it wants to go. This is not the time or place to push anyone out of their comfort zone!
Of course, people have different levels of comfort talking publicly about certain topics. You will have provided detailed information to your focus group participants beforehand and secured consent. But even so, the conversation may take a turn that makes someone uncomfortable. Be on the lookout for this, and remind everyone of their ability to opt out—to stay silent or to leave if necessary. Rather than call attention to anyone in this way, you also want to let everyone know they are free to walk around—to get up and get coffee (more on this below) or use the restroom or just step out of the room to take a call. Of course, you don’t really want anyone to do any of these things, and chances are everyone will stay seated during the hour, but you should leave this “out” for those who need it.
Have copies of consent forms and any supplemental questionnaire (e.g., demographic information) you are using prepared in advance. Ask a friend or colleague to assist you on the day of the focus group. They can be responsible for making sure the recording equipment is functioning and may even take some notes on body language while you are moderating the discussion. Order food (coffee or snacks) for the group. This is important! Having refreshments will be appreciated by your participants and really damps down the anxiety level. Bring name tags and pens. Find a quiet welcoming space to convene. Often this is a classroom where you move chairs into a circle, but public libraries often have meeting rooms that are ideal places for community members to meet. Be sure that the space allows for food.
Researcher Note
When I was designing my research plan for studying activist groups, I consulted one of the best qualitative researchers I knew, my late friend Raphael Ezekiel, author of The Racist Mind . He looked at my plan to hand people demographic surveys at the end of the meetings I planned to observe and said, “This methodology is missing one crucial thing.” “What?” I asked breathlessly, anticipating some technical insider tip. “Chocolate!” he answered. “They’ll be tired, ready to leave when you ask them to fill something out. Offer an incentive, and they will stick around.” It worked! As the meetings began to wind down, I would whip some bags of chocolate candies out of my bag. Everyone would stare, and I’d say they were my thank-you gift to anyone who filled out my survey. Once I learned to include some sugar-free candies for diabetics, my typical response rate was 100 percent. (And it gave me an additional class-culture data point by noticing who chose which brand; sure enough, Lindt balls went faster at majority professional-middle-class groups, and Hershey’s minibars went faster at majority working-class groups.)
—Betsy Leondar-Wright, author of Missing Class , coauthor of The Color of Wealth , associate professor of sociology at Lasell University, and coordinator of staffing at the Mission Project for Class Action
During the Focus Group
As people arrive, greet them warmly, and make sure you get a signed consent form (if not in advance). If you are using name tags, ask them to fill one out and wear it. Let them get food and find a seat and do a little chatting, as they might wish. Once seated, many focus group moderators begin with a relevant icebreaker. This could be simple introductions that have some meaning or connection to the focus. In the case of the ASA task force focus groups discussed above, we asked people to introduce themselves and where they were working/studying (“Hi, I’m Allison, and I am a professor at Oregon State University”). You will also want to introduce yourself and the study in simple terms. They’ve already read the consent form, but you would be surprised at how many people ignore the details there or don’t remember them. Briefly talking about the study and then letting people ask any follow-up questions lays a good foundation for a successful discussion, as it reminds everyone what the point of the event is.
Focus groups should convene for between forty-five and ninety minutes. Of course, you must tell the participants the time you have chosen in advance, and you must promptly end at the time allotted. Do not make anyone nervous by extending the time. Let them know at the outset that you will adhere to this timeline. This should reduce the nervous checking of phones and watches and wall clocks as the end time draws near.
Set ground rules and expectations for the group discussion. My preference is to begin with a general question and let whoever wants to answer it do so, but other moderators expect each person to answer most questions. Explain how much cross-talk you will permit (or encourage). Again, my preference is to allow the group to pick up the ball and run with it, so I will sometimes keep my head purposefully down so that they engage with one another rather than me, but I have seen other moderators take a much more engaged position. Just be clear at the outset about what your expectations are. You may or may not want to explain how the group should deal with those who would dominate the conversation. Sometimes, simply stating at the outset that all voices should be heard is enough to create a more egalitarian discourse. Other times, you will have to actively step in to manage (moderate) the exchange to allow more voices to be heard. Finally, let people know they are free to get up to get more coffee or leave the room as they need (if you are OK with this). You may ask people to refrain from using their phones during the duration of the discussion. That is up to you too.
Either before or after the introductions (your call), begin recording the discussion with their collective permission and knowledge . If you have brought a friend or colleague to assist you (as you should), have them attend to the recording. Explain the role of your colleague to the group (e.g., they will monitor the recording and will take short notes throughout to help you when you read the transcript later; they will be a silent observer).
Once the focus group gets going, it may be difficult to keep up. You will need to make a lot of quick decisions during the discussion about whether to intervene or let it go unguided. Only you really care about the research question or topic, so only you will really know when the discussion is truly off topic. However you handle this, keep your “participation” to a minimum. According to Lune and Berg ( 2018:95 ), the moderator’s voice should show up in the transcript no more than 10 percent of the time. By the way, you should also ask your research assistant to take special note of the “intensity” of the conversation, as this may be lost in a transcript. If there are people looking overly excited or tapping their feet with impatience or nodding their heads in unison, you want some record of this for future analysis.
I’m not sure why this stuck with me, but I thought it would be interesting to share. When I was reviewing my plan for conducting focus groups with one of my committee members, he suggested that I give the participants their gift cards first. The incentive for participating in the study was a gift card of their choice, and typical processes dictate that participants must complete the study in order to receive their gift card. However, my committee member (who is Native himself) suggested I give it at the beginning. As a qualitative researcher, you build trust with the people you engage with. You are asking them to share their stories with you, their intimate moments, their vulnerabilities, their time. Not to mention that Native people are familiar with being academia’s subjects of interest with little to no benefit to be returned to them. To show my appreciation, one of the things I could do was to give their gifts at the beginning, regardless of whether or not they completed participating.
—Susanna Y. Park, PhD, mixed-methods researcher in public health and author of “How Native Women Seek Support as Survivors of Intimate Partner Violence: A Mixed-Methods Study”
After the Focus Group
Your “data” will be either fieldnotes taken during the focus group or, more desirably, transcripts of the recorded exchange. If you do not have permission to record the focus group discussion, make sure you take very clear notes during the exchange and then spend a few hours afterward filling them in as much as possible, creating a rich memo to yourself about what you saw and heard and experienced, including any notes about body language and interactions. Ideally, however, you will have recorded the discussion. It is still a good idea to spend some time immediately after the conclusion of the discussion to write a memo to yourself with all the things that may not make it into the written record (e.g., body language and interactions). This is also a good time to journal about or create a memo with your initial researcher reactions to what you saw, noting anything of particular interest that you want to come back to later on (e.g., “It was interesting that no one thought Joe should quit his job, but in the other focus group, half of the group did. I wonder if this has something to do with the fact that all the participants were first-generation college students. I should pay attention to class background here.”).
Please thank each of your participants in a follow-up email or text. Let them know you appreciated their time and invite follow-up questions or comments.
One of the difficult things about focus group transcripts is keeping speakers distinct. Eventually, you are going to be using pseudonyms for any publication, but for now, you probably want to know who said what. You can assign speaker numbers (“Speaker 1,” “Speaker 2”) and connect those identifications with particular demographic information in a separate document. Remember to clearly separate actual identifications (as with consent forms) to prevent breaches of anonymity. If you cannot identify a speaker when transcribing, you can write, “Unidentified Speaker.” Once you have your transcript(s) and memos and fieldnotes, you can begin analyzing the data (chapters 18 and 19).
Advanced: Focus Groups on Sensitive Topics
Throughout this chapter, I have recommended against raising sensitive topics in focus group discussions. As an introvert myself, I find the idea of discussing personal topics in a group disturbing, and I tend to avoid conducting these kinds of focus groups. And yet I have actually participated in focus groups that do discuss personal information and consequently have been of great value to me as a participant (and researcher) because of this. There are even some researchers who believe this is the best use of focus groups ( de Oliveira 2011 ). For example, Jordan et al. ( 2007 ) argue that focus groups should be considered most useful for illuminating locally sanctioned ways of talking about sensitive issues. So although I do not recommend the beginning qualitative researcher dive into deep waters before they can swim, this section will provide some guidelines for conducting focus groups on sensitive topics. To my mind, these are a minimum set of guidelines to follow when dealing with sensitive topics.
First, be transparent about the place of sensitive topics in your focus group. If the whole point of your focus group is to discuss something sensitive, such as how women gain support after traumatic sexual assault events, make this abundantly clear in your consent form and recruiting materials. It is never appropriate to blindside participants with sensitive or threatening topics .
Second, create a confidentiality form (figure 12.2) for each participant to sign. These forms carry no legal weight, but they do create an expectation of confidentiality for group members.
In order to respect the privacy of all participants in [insert name of study here], all parties are asked to read and sign the statement below. If you have any reason not to sign, please discuss this with [insert your name], the researcher of this study, I, ________________________, agree to maintain the confidentiality of the information discussed by all participants and researchers during the focus group discussion.
Signature: _____________________________ Date: _____________________
Researcher’s Signature:___________________ Date:______________________
Figure 12.2 Confidentiality Agreement of Focus Group Participants
Third, provide abundant space for opting out of the discussion. Participants are, of course, always permitted to refrain from answering a question or to ask for the recording to be stopped. It is important that focus group members know they have these rights during the group discussion as well. And if you see a person who is looking uncomfortable or like they want to hide, you need to step in affirmatively and remind everyone of these rights.
Finally, if things go “off the rails,” permit yourself the ability to end the focus group. Debrief with each member as necessary.
Further Readings
Barbour, Rosaline. 2018. Doing Focus Groups . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Written by a medical sociologist based in the UK, this is a good how-to guide for conducting focus groups.
Gibson, Faith. 2007. “Conducting Focus Groups with Children and Young People: Strategies for Success.” Journal of Research in Nursing 12(5):473–483. As the title suggests, this article discusses both methodological and practical concerns when conducting focus groups with children and young people and offers some tips and strategies for doing so effectively.
Hopkins, Peter E. 2007. “Thinking Critically and Creatively about Focus Groups.” Area 39(4):528–535. Written from the perspective of critical/human geography, Hopkins draws on examples from his own work conducting focus groups with Muslim men. Useful for thinking about positionality.
Jordan, Joanne, Una Lynch, Marianne Moutray, Marie-Therese O’Hagan, Jean Orr, Sandra Peake, and John Power. 2007. “Using Focus Groups to Research Sensitive Issues: Insights from Group Interviews on Nursing in the Northern Ireland ‘Troubles.’” International Journal of Qualitative Methods 6(4), 1–19. A great example of using focus groups productively around emotional or sensitive topics. The authors suggest that focus groups should be considered most useful for illuminating locally sanctioned ways of talking about sensitive issues.
Merton, Robert K., Marjorie Fiske, and Patricia L. Kendall. 1956. The Focused Interview: A Manual of Problems and Procedures . New York: Free Press. This is one of the first classic texts on conducting interviews, including an entire chapter devoted to the “group interview” (chapter 6).
Morgan, David L. 1986. “Focus Groups.” Annual Review of Sociology 22:129–152. An excellent sociological review of the use of focus groups, comparing and contrasting to both surveys and interviews, with some suggestions for improving their use and developing greater rigor when utilizing them.
de Oliveira, Dorca Lucia. 2011. “The Use of Focus Groups to Investigate Sensitive Topics: An Example Taken from Research on Adolescent Girls’ Perceptions about Sexual Risks.” Cien Saude Colet 16(7):3093–3102. Another example of discussing sensitive topics in focus groups. Here, the author explores using focus groups with teenage girls to discuss AIDS, risk, and sexuality as a matter of public health interest.
Peek, Lori, and Alice Fothergill. 2009. “Using Focus Groups: Lessons from Studying Daycare Centers, 9/11, and Hurricane Katrina.” Qualitative Research 9(1):31–59. An examination of the efficacy and value of focus groups by comparing three separate projects: a study of teachers, parents, and children at two urban daycare centers; a study of the responses of second-generation Muslim Americans to the events of September 11; and a collaborative project on the experiences of children and youth following Hurricane Katrina. Throughout, the authors stress the strength of focus groups with marginalized, stigmatized, or vulnerable individuals.
Wilson, Valerie. 1997. “Focus Groups: A Useful Qualitative Method for Educational Research?” British Educational Research Journal 23(2):209–224. A basic description of how focus groups work using an example from a study intended to inform initiatives in health education and promotion in Scotland.
- Note that I have included a few examples of conducting focus groups with sensitive issues in the “ Further Readings ” section and have included an “ Advanced: Focus Groups on Sensitive Topics ” section on this area. ↵
A focus group interview is an interview with a small group of people on a specific topic. “The power of focus groups resides in their being focused” (Patton 2002:388). These are sometimes framed as “discussions” rather than interviews, with a discussion “moderator.” Alternatively, the focus group is “a form of data collection whereby the researcher convenes a small group of people having similar attributes, experiences, or ‘focus’ and leads the group in a nondirective manner. The objective is to surface the perspectives of the people in the group with as minimal influence by the researcher as possible” (Yin 2016:336). See also diversity focus group and convergence focus group.
A form of focus group construction in which people with diverse perspectives and experiences are chosen for inclusion. This helps the researcher identify commonalities across this diversity and/or note interactions across differences. Contrast with a convergence focus group
A form of focus group construction in which people with similar perspectives and experiences are included. These are particularly helpful for identifying shared patterns and group consensus. Contrast with a diversity focus group .
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Glob Qual Nurs Res
- v.3; Jan-Dec 2016
Methodological Aspects of Focus Groups in Health Research
Anja p. tausch.
1 GESIS–Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences, Mannheim, Germany
Natalja Menold
Although focus groups are commonly used in health research to explore the perspectives of patients or health care professionals, few studies consider methodological aspects in this specific context. For this reason, we interviewed nine researchers who had conducted focus groups in the context of a project devoted to the development of an electronic personal health record. We performed qualitative content analysis on the interview data relating to recruitment, communication between the focus group participants, and appraisal of the focus group method. The interview data revealed aspects of the focus group method that are particularly relevant for health research and that should be considered in that context. They include, for example, the preferability of face-to-face recruitment, the necessity to allow participants in patient groups sufficient time to introduce themselves, and the use of methods such as participant-generated cards and prioritization.
Focus groups have been widely used in health research in recent years to explore the perspectives of patients and other groups in the health care system (e.g., Carr et al., 2003 ; Côté-Arsenault & Morrison-Beedy, 2005 ; Kitzinger, 2006 ). They are often included in mixed-methods studies to gain more information on how to construct questionnaires or interpret results ( Creswell & Plano Clark, 2007 ; Kroll, Neri, & Miller, 2005 ).
The fact that the group process helps people to identify and clarify their views is considered to be an important advantage of focus groups compared with individual interviews ( Kitzinger, 1995 ). The group functions as a promoter of synergy and spontaneity by encouraging the participants to comment, explain, disagree, and share their views. Thus, experiences are shared and opinions voiced that might not surface during individual interviews ( Carey, 1994 ; Stewart, Shamdasani, & Rook, 2007 ). Although focus groups allow participants to respond in their own words and to choose discussion topics themselves, they are not completely unstructured. Questions relating to the research topic are designed by the researchers and are used to guide the discussion ( Stewart et al., 2007 ). The degree of structure of the focus group depends on the openness of the research question(s). Hence, although it takes more time and effort to organize focus groups, and they cause greater logistical problems than individual interviews do, they might generate more ideas about, and yield deeper insights into, the problem under investigation ( Coenen, Stamm, Stucki, & Cieza, 2012 ; Kingry, Tiedje, & Friedman, 1990 ; Morgan, 2009 ).
Historically, focus groups were used mainly for market research before the method was adopted for application in qualitative research in the social sciences ( Morgan, 1996 ). The use of focus groups in health care research is even more recent. For this reason, methodological recommendations on using focus groups in the health care context are quite rare, and researchers rely mainly on general advice from the social sciences (e.g., Krueger, 1988 ; Morgan, 1993 ; Morgan & Krueger, 1998 ; Stewart et al., 2007 ). Even though focus groups have been used in a great variety of health research fields, such as patients’ treatments and perceptions in the context of specific illnesses (rheumatoid arthritis: for example, Feldthusen, Björk, Forsblad-d’Elia, & Mannerkorpi, 2013 ; cancer: for example, Gerber, Hamann, Rasco, Woodruff, & Lee, 2012 ; diabetes: for example, Nafees, Lloyd, Kennedy-Martin, & Hynd, 2006 ; heart failure: for example, Rasmusson et al., 2014 ), community health research (e.g., Daley et al., 2010 ; Rhodes, Hergenrather, Wilkin, Alegría-Ortega, & Montaño, 2006 ), or invention of new diagnostic or therapeutic methods (e.g., Vincent, Clark, Marquez Zimmer, & Sanchez, 2006 ), the method and its particular use in health research is rarely reflected. Methodological articles about the focus group method in health care journals mainly summarize general advice from the social sciences (e.g., Kingry et al., 1990 ; Kitzinger, 1995 , 2006 ), while field-specific aspects of the target groups (patients, doctors, other medical staff) and the research questions (not only sociological but often also medical or technical) are seldom addressed. Reports on participant recruitment and methods of conducting the focus groups are primarily episodic in nature (e.g., Coenen et al., 2012 ; Côté-Arsenault & Morrison-Beedy, 2005 ) and often focus on very specific aspects of the method (communication: for example, Lehoux, Poland, & Daudelin, 2006 ; activating methods: for example, Colucci, 2007 ) or aim at a comparison between face-to-face focus groups and other methods (individual interviews: for example, Coenen et al., 2012 ; telephone groups: for example, Frazier et al., 2010 ; Internet groups: for example, Nicholas et al., 2010 ). Thus, systematic reviews of factors influencing the results of focus groups as well as advantages, disadvantages, and pitfalls are missing. One consequence is that researchers might find it difficult to recruit enough participants or might be surprised by the communication styles of the target groups. Furthermore, in the tradition of classical clinical research, the group discussions might result in a question-and-answer situation or “resemble individual interviews done in group settings” ( Colucci, 2007 , p. 1,424), thereby missing out on the opportunity to use the group setting to activate all participants and to encourage a deeper elaboration of their ideas. Colucci, for example, proposed the use of exercises (e.g., activity-oriented questions) to focus the attention of the group on the core topic and to facilitate subsequent analyses.
Recommendations from the social sciences on using the focus group method can be subsumed under the following headings: subjects (target groups, composition of groups, recruitment), communication in the groups (discussion guide, moderator, moderating techniques), and analysis of focus groups (e.g., Morgan, 1993 ; Morgan & Krueger, 1998 ; Stewart et al., 2007 ). Specific requirements for health research can be identified in all three thematic fields: Recruitment might be facilitated by using registers of quality circles to recruit physicians or pharmacists, or by recruiting patients in outpatients departments. It might be hampered by heavy burdens on target groups—be they time burdens (e.g., clinical schedules, time-consuming therapy) or health constraints (e.g., physical fitness). With regard to communication in focus groups, finding suitable locations, identifying optimal group sizes, planning a good time line, as well as selecting suitable moderators (e.g., persons who are capable of translating medical terms into everyday language) might pose a challenge. The analysis of focus groups in health care research might also require special procedures because the focus group method is used to answer not only sociological research questions (e.g., related to the reconstruction of the perspectives of target groups) but also more specific research questions, such as user requirements with regard to written information or technical innovations.
The aim of our study was to gather more systematic methodological information for conducting focus groups in the context of health research in general and in the more specific context of the implementation of a technical innovation. To this end, we conducted interviews with focus group moderators about their experiences when planning and moderating focus groups. The groups in question were part of a research program aimed at developing and evaluating an electronic personal health record. We chose this program for several reasons: First, because it consisted of several subprojects devoted to different research topics related to the development of a personal electronic health record, it offered a variety of research content (cf. next section). Second, the focus groups were conducted to answer research questions of varying breadth, which can be regarded as typical of research in health care. Third, the focus groups comprised a variety of target groups—not only patients but also different types of health care professionals (general practitioners, independent specialists with different areas of specialization, hospital doctors, pharmacists, medical assistants, nursing staff).
In this article, we report the findings of these interviews in relation to the following questions: (a) What challenges associated with the characteristics of the target groups of health research (patients, physicians, other health care professionals) might be considered during the recruitment process? How should the specific research question relating to a technical innovation be taken into account during the recruitment process? (b) Should specific aspects of the communication styles of target groups be taken into account when planning and moderating focus groups in health care? Can additional challenges be identified in relation to the technical research question? and (c) How was the method appraised by the interviewees in their own research context?
Research Program and Description of Focus Groups
The “Information Technology for Patient-Centered Health Care” (INFOPAT) research program ( www.infopat.eu ) addresses the fact that, because patients with chronic conditions (e.g., colorectal cancer, type 2 diabetes) have complex health care needs, many personal health data are collected in different health care settings. The aim of the program is to develop and evaluate an electronic personal health record aimed at improving regional health care for chronically ill people and strengthening patients’ participation in their health care process. Subprojects are devoted, for example, to developing the personal electronic health record (Project Cluster 1), a medication platform (Project Cluster 2), and a case management system for chronically ill patients (Project Cluster 3). In the first, qualitative, phase, the researchers explored patients’ and health care professionals’ experiences with cross-sectoral health care and patient self-management, and their expectations regarding the advantages and disadvantages of a personal electronic health record. The information gathered in this phase of the program served as a basis for constructing a personal electronic health record prototype. This prototype was implemented as an intervention in a second, quantitative, phase dedicated to investigating the impact of such a record on a range of health care variables (e.g., self-management, health status, patient–doctor relationship, compliance). The University Hospital Heidelberg Ethics Committee approved the studies of the INFOPAT research program. All participants gave their written informed consent, and the participants’ anonymity and confidentiality were ensured throughout the studies according to the ethical standards of German Sociological Association. 1
Twenty-one focus groups were conducted during the qualitative phase of the program. Three groups consisted of colorectal cancer patients, four comprised type 2 diabetes patients, four were made up of physicians, three comprised physicians and pharmacists, four consisted of physicians and other health care professionals, and three consisted of other health care professionals (for more detailed information, see Tausch & Menold, 2015 ). Participants were recruited from urban and rural districts of the Rhine-Neckar region in Germany. Patients were approached in clinics, by their local general practitioners, or in self-help groups. Health care professionals were recruited in clinics, cooperating medical practices, and professional networks.
The focus groups took place at several locations at the National Center of Tumor Diseases (NCT) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the University of Heidelberg. The groups consisted of between four and seven participants and lasted between 1.5 and 2 hours. All focus groups were conducted by two researchers—a moderator and a co-moderator; a third researcher took notes. Semistructured discussion guides were used, and the groups were video- and audio recorded (cf., for example, Baudendistel et al., 2015 ; Kamradt et al., 2015 ). The researchers performed content analysis on the transcripts; the schema of categories was oriented toward the research questions. The focus groups addressed research questions of varying breadth, including, for example, individual health care experiences (comparatively broad), the expected impact of the record on the patient–doctor relationship (medium breadth), and technical requirements for such a personal health record (comparatively narrow). The variety of the research questions was important for our study because it proved to be of relevance for the interviewees’ appraisal of the usefulness of the focus group method.
Interviews With the Focus Group Moderators
We conducted qualitative interviews with nine of the 10 focus group moderators in the INFOPAT program (one moderator moved to a different department shortly after the completion of data collection and was not available for interview). The interviewees were aged between 30 and 54 years ( M age = 36 years; SD = 8.3 years). Their professions were health scientist, pharmacist, general practitioner, or medical ethicist. Their professional experience ranged from one to 23 years ( M = 7.1 years, SD = 7.7 years), and they had little or no previous experience of organizing and conducting focus groups. The moderators were interviewed in groups of one to three persons according to their project assignment (cf. Table 1 ).
Overview of Interviews and Interviewees.
| Interview | Project Cluster | Interviewees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Moderators 1, 2, and 3 |
| 2 | 1 | Moderators 4, 5, and 6 |
| 3 | 2 | Moderators 7 and 8 |
| 4 | 3 | Moderator 9 |
The interviews lasted approximately 1 hour, and the interview questions were guided by the chronological order in which a focus group is organized and conducted (recruitment, preparation, moderation, methods) and by the utilization and usefulness of the results. We tape recorded the interviews, transcribed them verbatim, and performed qualitative content analysis on the transcripts ( Elo & Kyngäs, 2008 ; Mayring, 2015 ) with the help of the program MAXQDA 10.0.
The final system of categories 2 ( Tausch & Menold, 2015 ) consisted of two types of codes: All relevant text passages were coded with respect to the content of the statement. In addition, a second type of code was required if the statement related to a specific group of participants (e.g., patients, hospital doctors, men, women).
On the basis of the research questions, the contents of interview statements were classified into the three superordinate thematic categories: recruitment, communication in the focus groups, and appraisal of the focus group method. Consequently, the reporting of the results is structured according to three main topics.
Recruitment
Statements relating to the recruitment of the participants were sorted into the main categories “factors promoting participation”, “factors preventing participation”, and “general appraisal of the recruitment process”. Figure 1 shows the subcategories that were identified under these main categories. Because many of the statements referred only to patients or only to health care professionals (physicians, other health care professionals), the subcodes shown in Figure 1 are sorted by these two types of participants.

Factors relating to the recruitment process.
Factors relevant for all target groups
As the following interviewee statement shows, addressing potential participants face-to-face (rather than in writing) proved crucial for the success of recruitment in all target groups:
Well, a really good tip when recruiting patients is . . . to address the people yourself. Not to get someone else to do it who . . . has nothing to do with [the project], because ultimately you really do have to explain a lot of things, also directly to the patient. And then it’s always good if the person [who does the recruiting] is actually involved in the project. 3
In the case of the clinicians, being addressed by a superior was even more effective for their willingness to participate: “And then top down. If the nursing director asks me, then it’s not so easy to say no.”
Furthermore, a positive response was more often achieved if the groups were scheduled at convenient times for the addressees, and they only had to choose between several alternatives. Patients welcomed times contiguous with their therapies: “And many [of the patients] said: ‘Yes, maybe we can do it after my chemotherapy, on that day when I’m in the clinic anyway?’” Whereas medical assistants were given the opportunity to take part in the groups during working hours, general practitioners preferred evening appointments on less busy weekdays (e.g., Wednesdays and Fridays):
Well, what I found quite good was to suggest a day and a time. And we concentrated on the fact that practices are often closed on Wednesday afternoons. So that’s a relatively convenient day. And then evenings for the pharmacists from seven-thirty onwards.
Interest in the topic of the discussion, or at least in research in general, was an important variable for participation. Together with lack of time, it turned out to be the main reason why sampling plans could not be realized. Among patients, men were much more interested in discussing a technical innovation such as an electronic personal health record, while women—besides their lesser interest—often declined because of family responsibilities: “Well, I’d say a higher proportion of women said: ‘I have a lot to do at home, housework and with the children, therefore I can’t do it.’”
Family physicians, physicians from cooperating medical practices, and hospital doctors showed more interest in discussing an electronic personal health record than did medical specialists in private practice, who often saw no personal gain in such an innovation. For example, one interviewee stated,
Family physicians generally have a greater willingness [to engage with] this [health] record topic. They see . . . also a personal benefit for themselves. . . . or they simply think it might be of relevance to them or they are interested in the topic for other reasons. Some of them even approached us themselves and said, “Oh, that interests me and I’d like to take part.”
In addition, because of heavy workload, private practitioners were difficult to reach (e.g., by telephone). This also lowered the participation of this target group on the focus groups.
Factors relevant only for patients
Two other variables that influenced patients’ willingness to participate were mentioned in the interviews. First, because this target group consisted of cancer patients and diabetes patients with multimorbidity, poor physical fitness also prevented several addressees from participating in the groups. The inability to climb stairs, or the general inability to leave the house, made it impossible for them to reach the location where the groups took place: “[They] immediately replied: ‘Well, no, . . . that’s really too much for me,’ and unfortunately they could not, therefore, be included in the groups.” Furthermore, unstable physical fitness often led to high drop-out rates. The moderators of the focus groups therefore proposed that up to twice as many participants as required should be recruited: “And depending on the severity of the illness, you have to expect a drop-out rate of up to fifty percent. So, if you want to have four people, you should invite eight.”
Second, moderators reported that patients’ liking for, or dislike of, talking and discussing influenced their tendency to join the groups. Participating patients were generally described as talkative. For example: “And with patients, all in all, I had the feeling that those who agreed [to participate] were all people who liked talking, because those who did not like talking refused out of hand.” Patients who refused to participate often argued that they felt uncomfortable speaking in front of a group: “And the men, when they declined they often said: ‘No, group discussion is not for me! I don’t like talking in front of a group.’”
The researchers eventually succeeded in recruiting sufficient participants. However, they were not able to realize the sampling plans according to a certain proportion of male and female patients or types of physicians. “Well, we finally managed to fill up our groups, but only as many [participants] as necessary.” Comparing the different target groups, recruiting patients was described as easier than recruiting physicians: “And that was much easier insofar as you just had to go to the clinic and each day there were five or six patients whom you could address.” However, only 10% of the patients who were addressed agreed to participate. In the health care professional group, the recruitment rates ranged between 0% and 30%, depending on the subgroup. This can be demonstrated by the following interviewee utterance:
And in the private practitioner sector it was rather . . . . Well, we tried to recruit specialists in private practice, in other words internists, gastroenterologists, and oncologists. The success [rate proved to be] extremely poor. . . . Well, on the whole, the willingness to take part, the interest, is not there. Or, well they don’t give the reasons, but they say they don’t want to take part. So that was difficult and, yes, it didn’t go too well.
Communication in the Focus Groups
With regard to the communication in the focus groups, the moderators identified factors that influenced communication in a positive or negative way. In addition, we discussed a number of factors with them that are often described in the social science literature as problematic when conducting focus groups. However, the interviewees considered that some of these factors had not influenced communication in the focus groups conducted within the framework of the INFOPAT program. In our system of categories, we also coded whether the factors in question were related to (a) the setting or (b) the moderation of the focus groups (cf. Figure 2 ).

Influences on and characteristics of the focus group discussion.
Factors relating to the setting
As Figure 2 shows, communication was reported to be positively influenced by small group size, location, provision of food and beverages, and conducting the focus group without a break. In contrast to general recommendations on focus groups in the context of sociological research, the moderators in the INFOPAT program considered a smaller group size of between four and six participants to be ideal. With regard to location, the interviewees reported that, depending on the target group, different places were perceived as positive. Patients preferred locations inside the clinic because they were easy to reach and caused no additional effort. Furthermore, because these locations were familiar to them, they facilitated an atmosphere of security and ease, which was seen as an important prerequisite for an open and honest discussion. This is clear from the following quotation:
Well, the patient focus groups were all located at the clinic. We chose this location on purpose to make it easier for them, because they come to the clinic anyway for their therapy. And they know the place and they feel comfortable and in good hands.
By contrast, the clinician groups benefited from being located outside the clinic. In contrast to other common addressees of focus groups, these professionals were not only accustomed to participating in groups outside their familiar surroundings but also this location helped them to distance themselves from their professional duties and to engage more deeply in the discussion, as shown by the following quotation:
Yes, one was located at the O-Center. We chose this location on purpose so that the clinicians had to leave the hospital. It’s not too far, only a few yards away. But we wanted them to leave the clinic, and not to run back to the ward when they were called. And, well, I liked this location.
Food and beverages were welcome in all the groups and also helped to create a positive and trusting atmosphere. And finally, the interviewees found that it was better to omit the break, thereby avoiding the interruption of the ongoing discussion. This is reasonable considering the comparatively short duration of the focus group session (between 1.5 and 2 hours). Statements relating to a break might have been different in the case of longer focus group durations.
The interviewees reported that the size and temperature of the room and time pressure on the participants or the moderator had a negative impact on communication. Some of the focus groups in the project took place in midsummer and had to be held in rooms without blinds or air conditioning. The moderators of these groups had to work hard to maintain the participants’ (and their own) attention and concentration. Time pressure on the participants (e.g., the clinicians) led to an unwillingness to engage in active discussion and created a question-and-answer situation, as shown by the following statement:
And in one group of physicians . . . we never reached the point where they joined in fully. During the whole discussion they never completely arrived. And they had already cut the time short in advance. They were under so much time pressure that they were not able to discuss in an open manner.
Moderators reported that they, too, had experienced time pressure—namely, in situations where they did not have enough time to prepare the room and the recording devices. This had caused them to be nervous and stressed at the beginning of the discussion, which had negatively affected the mood of the participants, thereby rendering an honest and open discussion particularly difficult.
Factors relating to the moderation
Many of the positive factors reported by the interviewees have already been described for focus groups in general—for example, using open questions, directly addressing quiet participants, and handling the discussion guide in a flexible way. Furthermore, by showing interest in every statement, and by generating a feeling of security in every participant, moderators fostered a fruitful discussion:
I believe that another important point is that you are calm yourself. That you give the people the feeling “you can feel safe with me, you don’t have to worry that I will make fun of you . . . or that I won’t take you seriously.”
Interviewees also considered that building a bridge between the technical innovation under discussion (a web-based electronic personal health record) and everyday life (e.g., online banking) was an important factor in getting all participants to contribute to the discussion. As one interviewee noted,
We tried to anchor it in their everyday lives. And . . . the example that always worked was when we said: “Think of it as if it were a kind of online banking.” Everyone understands what online banking is. It’s about important data on the internet; they’re safe there somehow. I have my password. And people understood that. Well, it’s important to anchor it in their reality . . . because otherwise the topic is simply far too abstract.
In this context, the fact that the groups were moderated by the researchers themselves proved very helpful because they were able to answer all questions relating to the research topic. As the following quote shows, this was an important prerequisite for opinion formation on the part of participants:
Well, I think that a really important quality criterion . . . is that you have completely penetrated [the topic]. If you only know the process from the outside . . . and you then conduct the focus group about it. . . . Somewhere, at some stage, [one discussion] narrowly missed the point. . . . You simply have to be totally immersed in the topic, well, I believe that [someone who is totally immersed in the topic] is the ideal person for the job. And in our case the thinking was, okay, so I’m a doctor, but on balance it’s more important that both [moderators] are absolutely well informed because it’s a complex topic.
The more specific the research question was, the more useful the moderating strategy of inviting one participant after the other to express their opinion appeared to be. By using this strategy, the moderators ensured that every participant contributed to the discussion.
A point that was strongly emphasized by the interviewees was the duration of the round of introductions at the beginning of the focus group session. In the patient groups, introductions took much more time than the researchers had expected. Patients had a high need to express themselves and to tell the others about their illness and their experiences with the health system. Although this left less time to work through the topics in the discussion guide, the researchers came to realize that there were several good reasons not to limit these contributions: First, the introductions round proved important for helping the participants to “arrive” at the focus group, for creating a basis of trust, and for building up a sense of community among the participants. Second, the interviewees reported that, because many topics in the discussion guide (e.g., participants’ experiences with coordinating visits to different medical specialists) had already been brought up in the round of introductions, they did not have to be discussed further at a later stage:
And that is the crux of this general exchange of experiences at the beginning. Sure, it costs you a lot of time, but I almost think that if you don’t give them that time, you won’t get what you want from them, in the sense that you say: “I want to hear your frank opinion or attitude.” You don’t want them to simply answer you because they think that’s what you want to hear. You have to create an atmosphere in which they really forget where they are. I’m relatively convinced that you wouldn’t achieve that without such [a round of introductions].
The moderators’ experience in the physician groups was different. These groups benefited from having a rather short round of introductions. Giving participants too much time to introduce themselves meant that they presented their expertise rather than reporting their experiences. In contrast to the patient groups, this did not substantially contribute to the discussion of the research topics.
Depending on the context, status differences between the moderators and the participants, or among the participants, were appraised differently by interviewees. In one group comprising physicians and medical assistants, the moderators observed that status differences had a negative influence on communication. Very young female medical assistants, in particular, did not feel free to express their opinions in the presence of their superiors. By contrast, presumed differences in status between family doctors, hospital doctors, and medical specialists in private practice did not have any negative impact on communication. Nor did different forms of address (some participants in these groups were addressed by their first name and some by their last name, depending on the relationship between the moderator and the participants). Status differences between moderators (if medical doctors) and participants (patients) had an impact on communication when patients regarded doctors as an important source of information (e.g., about the meaning of their blood values) or as representatives of the health care system to whom complaints about the system should be addressed. The latter case was the subject of the following interview statement by a moderator who is a physician by profession:
And a lot [was said about] the kind of experiences they had had here at the NCT. And of course, when the patients have been treated here for many years—or even for not so many [years], but they have had many experiences—they sometimes reported at length. And I had the feeling that this had a bit of a feedback function, quite generally, for the NCT. Also the somehow frustrating experiences they had had, or a lot of things that had not gone that well in conversational exchanges [with the staff]. There was a relatively large amount of feedback that didn’t have a lot to do with the topic because I was, of course, involved as a senior physician and I am not an external researcher, but rather someone who is also seen as being jointly responsible, or at least as someone who can channel criticism.
Finally, because most of the moderators were not medical professionals, they did not experience the translation of medical or technical terms into everyday language as problematic. Rather, they automatically used terms that were also familiar to the participants.
Characteristics of the discussion
The factors described above resulted in focus group discussions that might be interpreted as characteristic of health research. The patient focus groups were characterized by a strong need to talk and a high need for information. In the health care professional focus groups, researchers experienced a greater variety of communication styles. Because of a lack of time, or because they falsely expected a question-and-answer situation, some groups demonstrated a low degree of willingness to engage in discussion:
Although, I believe that was partly due . . . well there was one [woman] who was very demanding; she wanted to know straight away: “Yes, what’s the issue here? What do I have to say to you?” Well, the three who came from the one practice, I think they really had the feeling that we would ask them questions and they would bravely answer them and then they could go home again. So, for them this principle that they were supposed to engage in a discussion, for them that was somehow a bit, I don’t know . . . disconcerting. . . . They really thought: “Okay, well we want to know now what this is all about. And they’ll ask us the questions and then we’ll say yes, no, don’t know, maybe. And then we’ll go home again.” Well, at least that was my impression.
Other groups, especially those consisting of different types of health care professionals (e.g., physicians with different areas of specialization, or physicians and pharmacists), were characterized by lively discussion and a great variety of opinions.
Appraisal of the Focus Group Method
We classified moderators’ statements relating to the appraisal of the focus group method into four main categories: “advantages of the method”, “disadvantages of the method”, “recommendations for other researchers in related research areas”, and “statements on how they used the results” (cf. Figure 3 ).

Appraisal of the focus group method.
The researchers reported that the focus group method yielded a rich blend of perspectives and opinions, brought forth, in particular, by the interaction between the participants:
But for this question and the topic, and for our lack of knowledge, that was . . . a lot of new information . . . and very many good ideas and critical remarks that you naturally read in the literature from time to time. But, let’s say, because of the complexity of the participants’ reactions and the weight they attached to things, it’s different than reading in a literature review that [this or that] could be taken into account.
The results of the focus groups further enriched the researchers’ work by relating it to everyday life: “Well, what was nice was that the topic was related to the participants’ lives. That people said: ‘Now the topic is important for me.’” Furthermore, the method yielded information about which aspects were most important and how the variety of opinions should be prioritized. This was achieved, in particular, by using participant-generated cards:
And with regard to prioritization, we incorporated it using participant-generated cards. We said: “Look: If you could develop this record now, what would be the three most important things that must absolutely be taken into consideration, from your point of view, no matter what they relate to.” And they wrote them down on the cards. And after that they were asked to carry out their own prioritization—that is, what was most important to them personally. One person wrote “data protection” first, while another [wrote] “sharing with my wife.” . . . That was good. . . . That helped a lot because it was simply clear once again what things were important to them.
In cases where concrete questions had to be answered or decisions had to be made, the interviewees also welcomed the opportunity to use structuring methods such as presentations, flip-charts, and participant-generated cards to obtain the relevant information:
. . . Well, the aim was that at the end we [would] have a set of requirements for the engineering [people]. And the engineering [people] don’t so much want to know about experiences and desires and barriers, but rather they want to know should the button be green or red and can you click on it. And that’s why I thought at the beginning it will be difficult with a focus group and an open discussion. Now, if you say that one can also interpret a focus group the way we did, partly with very specific questions and these participant-generated cards, then I think it is indeed possible to answer such questions as well.
Disadvantages
The main disadvantages of the focus group method were seen in the considerable organizational effort and expenditure of time involved. A question raised by some of the interviewees was whether comparable results could have been achieved using less time-consuming and organizationally demanding methods.
It’s true to say that you lose time. Well, you could implement [the innovation] straight away and see whether it’s better. Maybe, in this case you’re wrong and you just think it’s better or in any case not worse than before. You basically lose a year on this whole focus groups thing.
Moreover, in some cases, the discussion went in an unwanted direction and the moderators never fully succeeded in bringing the group back to the intended topics.
Furthermore, like many other medical research projects, INFOPAT included quite specific research questions. In this connection, the moderators emphasized that open focus group discussions would not have succeeded in answering those questions. Only by using methods such as participant-generated cards and prioritization was it possible to answer at least some of them. Nonetheless, some interviewees did not consider the focus group method to be really suitable for this type of research questions:
Of course we also have our engineers as counterparts who . . . need very specific requirements at some point. The question is whether such a focus group . . . . [It] can’t answer that in detail in this first stage. It’s simply not practicable.
Recommendations
As described under the “Communication in the Focus Groups” section above, the round of introductions in the patient groups lasted much longer than planned, thereby shortening the time available for other topics in the discussion guide. As a result, the moderators decided to choose a different thematic focus in each group so that every topic was discussed more deeply in at least one group.
What we usually did was to consider what hadn’t been addressed that much in the previous focus group. That [topic] was given more room in the next focus group because the guide, well it was quite a lot. You could have easily gone on discussing for another hour or two.
Using the results
On the whole, the researchers were satisfied with the number of groups that were conducted and the results that they yielded. They did not agree that more groups would have led to better, or different, results—with one possible exception, namely, in the case of specific target groups (e.g., migrants). Only one group had been composed of patients with a migrant background, and, as one interviewee stated, “I just thought, the patients with a migrant background . . . now that was [only] one group, it by no means covers the whole range.”
In cases where the results of the focus groups were perceived as not being concrete enough to proceed to the next research step (e.g., formulating a specification sheet for the construction of the electronic personal health record), the researchers planned to bring experts together in a roundtable format to make decisions on the basis of the priorities, agreements, and disagreements that had emerged from the focus groups. Following the construction of a prototype, they intended to conduct further focus groups to validate or adapt the usability of the electronic personal health record system.
Our analysis of interviews with focus group moderators yielded considerable insights into methodological aspects of conducting focus groups in health research. Our first research question related to characteristics of the target groups that should be considered during the recruitment process. We identified face-to-face contact as an important factor promoting focus group participation. The interviewees considered this type of contact to be better suited to answering target persons’ questions and explaining the method and aims of the focus groups. Moreover, they felt that addressees might find it more difficult to decline a face-to-face invitation than a written one. With regard to health care professionals, an invitation issued by a hierarchically higher person was most effective, even though ethical aspects should be considered in this case, and voluntary participation should nevertheless be ensured. Otherwise, the order to participate might prevent an atmosphere of open communication and might lead to a lower quantity or to more negative statements.
Furthermore, whereas physicians are usually accustomed to discussing topics with others, an important characteristic that influenced willingness to participate on the part of members of other target groups (other health care professionals, patients) was a liking for, or a dislike of, talking. Researchers might take account of this fact by explaining the method in more detail, by developing arguments to overcome fears, or, as suggested, for example, by Colucci (2007) , by convincing the addressees with other activities implemented in the focus groups. Other relevant personal characteristics—be they related to the research topic (e.g., technical interest in the case of an electronic innovation) or to the specific target group (e.g., physical fitness on the part of patients or lack of time on the part of health care professionals)—should be anticipated when planning recruitment. These characteristics might be taken into account by preparing arguments, providing incentives, giving thought to favorable dates and times, and choosing easily accessible locations. An interesting finding was that, depending on the target group, different locations were considered to have a positive influence on the discussion. Whereas locations inside the clinic were preferred in the case of the patient focus groups because of familiarity and easy accessibility, hospital doctors were more engaged in the discussion when the focus group site was located at least some yards away from their workplace.
Finally, the experience of our researchers that up to 50% of the patients had to cancel at short notice because of health problems does not appear to be uncommon in this research context. That overrecruitment is an effective strategy—particularly in health care research—has been reported by other authors (e.g., Coenen et al., 2012 ).
With our second research question, we focused on aspects of communication in the focus groups. The interviews revealed several factors specific to research topics and addressees of health care studies that influenced the discussions. Consequently, in addition to considering general recommendations regarding the organization and moderation of focus groups (e.g., choosing adequate rooms with a pleasant atmosphere, serving food and beverages, using open questions, showing interest in all contributions, and directly addressing quiet participants), these health care specific aspects should be taken into account. Relevant factors that should be addressed when moderating focus groups in this context are (a) the strong need to talk and the high need for information in the patient groups, (b) status differences between the participants or between the moderators and the participants, (c) the size of the focus group, and (d) the specificity of the topic of discussion. The interview data revealed that these factors influenced the discussions and thus the results achieved with the groups. In addition, the following four possibilities of addressing these factors were identified:
First, the moderators had to devote more time to the round of introductions in the patient groups, which served as a warm-up, created an atmosphere of fellowship and openness, and accommodated this target group’s strong need to talk. Second, with respect to status differences between the moderator and the participants, no definite recommendations can be derived from the interviews. The interviewees found that it was less favorable when the moderator was perceived not only in that role but also in other roles (e.g., physician), because this might hamper a goal-oriented discussion. However, they considered deep insight into the research topic on the part of the moderators to be beneficial, at least for certain research topics. Thus, one should carefully weigh up whether it is more advantageous or more disadvantageous when the group moderator is a physician. Interviewees considered status differences between participants to be disadvantageous only in one case, where—because of organizational constraints—medical assistants and their superiors joined the same focus group, which gave rise to some reticence on the part of the young assistants. Similar problems have been reported by other authors, for example, Côté-Arsenault and Morrison-Beedy (2005 ; see also Hollander, 2004 ). However, interviewees did not experience as problematic status differences between physicians with different areas of specialization.
Third, with respect to group size, interviewees found comparatively small focus groups appropriate to give all participants enough time to tell their stories. In contrast to social science research, where groups of between eight and 20 participants are recommended, our interviewees considered groups of between four and six persons to be optimal. This is in line with Côté-Arsenault and Morrison-Beedy (2005) , who recommended small groups for health research, especially when sensitive topics are discussed. Our interview data revealed that this recommendation might also be useful for other health research topics.
Fourth, with regard to the topic of the discussion, interviewees found it helpful to structure different phases of the discussion in different ways, depending on the specificity of the research questions. In contrast to social science research, certain types of research questions in health research require comparatively specific answers. Some of the focus groups in our study were aimed at collecting participants’ expectations regarding an electronic personal health record or—even more specifically—at developing a product specifications document. Conducting focus groups during the development of a technical innovation is a method that is being increasingly used in health care research. Hence, the experiences of the interviewees with regard to these aspects of their research might be relevant for many other research programs. For this type of research questions, it proved useful to include more structured parts in the discussion, for example, having certain questions answered by each participant in turn, or using methods such as participant-generated cards and prioritization. This made it easier to obtain the opinion of each participant and to cover as many concerns and expectations as possible. This finding is in line with recommendations by Colucci (2007) , who proposed the use of activity-oriented questions for health research topics as an enrichment of data collection and a means of making it easier to talk about sensitive and complex topics.
All the moderators found that their discussion guides contained too many questions and too many topics. This might have been due, at least partly, to a desire to determine all relevant aspects in advance—a tendency that might be typical of health research. However, Morgan (1995) also addressed this phenomenon in relation to social research in general: “A common error in focus group question guidelines is too much emphasis on what is of interest to the researcher and not enough emphasis on what is of interest to the participants” (p. 520).
With our third research question, we addressed the appraisal of the focus group method in the interviewees’ research context. Our results show that one should think carefully before using focus groups in the field of health research. The impression that they are quick and easy to conduct might be a misconception, especially in this research context. In fact, the appraisal of the method by the moderators revealed both advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages were the rich blend of perspectives and opinions obtained and the opportunity to have them prioritized by the target groups. For their research topics, the interviewees saw a further important advantage in the fact that they were able to relate their scientific research to everyday life, a point that might be of general importance for a number of research questions in health research, especially those that refer to new medical diagnostics or technical innovations.
The interviewees considered that the main disadvantages of focus groups were the substantial organizational effort and expenditure of time they required. They raised the question whether comparable results could have been achieved using less costly methods. Fortunately, we conducted our interviews with researchers from a research program aimed at answering research questions of different degrees of specificity. As a result, the moderators were able to compare the usefulness of focus groups for different types of research questions. Their statements revealed that they were satisfied with the results relating to more open research questions such as experiences with cross-sectoral health care. For more specific research questions, the interviewees valued the possibility of organizing the discussions in a more structured way and using methods that activated all participants (e.g., participant-generated cards, prioritizations). Nonetheless, they considered meetings of experts to be a necessary intermediate step, for example, on the way to a product specifications document. We recommend that, depending on the specificity of the results that are projected, consideration should be given to including such intermediate steps in the planning stage.
Limitations of the Study
Our analysis of the interviews with the focus group moderators revealed a number of methodological problems that typically occur when focus groups are used in a health research context and yielded recommendations on using such groups in this context. However, some limitations of the present study should also be discussed: First, we conducted our research with focus group moderators, all of whom worked in the same research program. Even though the INFOPAT program consists of several subprojects, they all deal to a greater or lesser extent with the advantages and disadvantages of an electronic support system (electronic personal health record). Furthermore, the moderators were mainly health scientists and had little or no experience with conducting focus groups. This might also have been specific for the research program in which our study was conducted. In other health care programs, focus groups might be moderated mainly by physicists or lay persons (e.g., in participatory health research). Consequently, had we also conducted interviews with focus group moderators from other research areas or included moderators with other professions or more focus group experience, this might have led to different results. However, our research project is rather typical for applied qualitative research in medical science when developing new technologies. Here, focus groups are used by the researchers to find out the potential requirements for the new technology. The researchers are often experts in a specific scientific topic and have no or only limited experience in conducting qualitative research in terms of focus groups. Therefore, our findings are of a particular importance for the researchers with little experiences in conducting focus groups, which can apply to every research, conducted first time. In addition, the little experience of our focus group moderators was a special advantage and strength of the study. More experienced moderators would have prevented some of the problems our moderators—as other unexperienced moderators—faced. As a result, the moderators would not have named these potential problems in the interviews and given no advice for preventing them.
Second, the study was conducted in Germany and thus represents problems and challenges of the German health care system. In other countries, physicians might have different work-shifts or there might be different possibilities in the health care system to reach the target groups. Therefore, more research on the methodology of focus groups in the context of the development of new technologies in health care in other countries and cultures with a consideration of additional relevant groups is needed.
Third, in our interviews, we focused mainly on the organization and conducting of focus groups. For two reasons, we did not address the aspect of data analysis: First, we conducted the interviews shortly after the focus groups had been completed, at a time when data analysis was still in progress. Second, analysis of qualitative data can be carried out in many different ways, depending on research questions and preferences of researchers, and some of the recommended methods are very complex. Had we discussed them in detail, it would have been too time-consuming in the interviews.
Concluding Remarks
Our results revealed a number of methodological challenges that might be typical of conducting focus groups in health research. We hope that our findings will be of use to researchers in similar research fields. Furthermore, we encourage other researchers who are interested in health research topics to gather more information about methodological aspects specific to this research field. Our results were achieved in the context of the development of a technical innovation. It might be interesting to endeavor to replicate them in other health care research projects dealing with technical innovations. Moreover, we would encourage researchers of other topics in health research to interview focus group moderators about their experiences in their specific research context. We hope that our results will serve as a useful basis for comparing results in different areas of health research.
Acknowledgments
We thank the focus group moderators in the INFOPAT program for their great willingness to share their experiences and for their openness during the interviews.
Author Biographies
Anja P. Tausch , PhD, is senior researcher at GESIS–Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences, Mannheim, Germany.
Natalja Menold , PhD, is senior researcher and head of the Survey Instruments Unit at GESIS–Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences, Mannheim, Germany.
1. http://www.soziologie.de/en/gsa/ethik-kommission/code-of-ethics.html , retrieved on 05/10/2015.
2. The language of the research project, focus groups, and interviews was German. The scheme was developed in German on the basis of the German text material from the transcribed interviews. The scheme and the citations were translated for the purpose of international publication by an experienced, qualified, and fully bilingual translator, whose mother tongue is English and who also has an MA in sociology from a German university. A German version of the full categorial system can be found in Tausch and Menold (2015) .
3. All citations included in this publication were translated from German.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; FKZ 01KQ1003D).
- Baudendistel I., Winkler E., Kamradt M., Brophy S., Längst G., Eckrich F., . . .Ose D. (2015). The patients’ active role in managing a personal electronic health record: A qualitative analysis . Supportive Care in Cancer , 23 , 2613-2621. doi: 10.1007/s00520-015-2620-1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carey M. A. (1994). The group effect in focus groups: Planning, implementing, and interpreting focus group research . In Morse J. M. (Ed.), Critical issues in qualitative research methods (pp. 225–241). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carr A., Hewlett S., Hughes R., Mitchell H., Ryan S., Carr M., Kirwan J. (2003). Rheumatology outcomes: The patient’s perspective . The Journal of Rheumatology , 30 , 880–883. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coenen M., Stamm T., Stucki G., Cieza A. (2012). Individual interviews and focus groups in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A comparison of two qualitative methods . Quality of Life Research , 21 , 359–370. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Colucci E. (2007). “Focus groups can be fun”: The use of activity-oriented questions in focus group discussions . Qualitative Health Research , 17 , 1422–1433. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Côté-Arsenault D., Morrison-Beedy D. (2005). Maintaining your focus in focus groups: Avoiding common mistakes . Research in Nursing & Health , 28 , 172–179. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W., Plano Clark V. L. (2007). Designing and conducting mixed methods research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Daley C. M., James A. S., Ulrey E., Joseph S., Talawyma A., Choi W. S., . . .Coe M. K. (2010). Using focus groups in community-based participatory research: Challenges and resolutions . Qualitative Health Research , 20 , 697–706. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elo S., Kyngäs H. (2008). The qualitative content analysis process . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 62 , 107–115. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feldthusen C., Björk M., Forsblad-d’Elia H., Mannerkorpi K. (2013). Perception, consequences, communication, and strategies for handling fatigue in persons with rheumatoid arthritis of working age—A focus group study . Clinical Rheumatology , 32 , 557–566. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Frazier L. M., Miller V. A., Horbelt D. V., Delmore J. E., Miller B. E., Paschal A. M. (2010). Comparison of focus groups on cancer and employment conducted face to face or by telephone . Qualitative Health Research , 20 , 617–627. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gerber D. E., Hamann H. A., Rasco D. W., Woodruff S., Lee S. J. C. (2012). Patient comprehension and attitudes toward maintenance chemotherapy for lung cancer . Patient Education and Counseling , 89 , 102–108. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hollander J. A. (2004). The social contexts of focus groups . Journal of Contemporary Ethnography , 33 , 602–637. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kamradt M., Baudendistel I., Längst G., Kiel M., Eckrich F., Winkler E., Ose D. (2015). Collaboration and communication in colorectal cancer care: A qualitative study of the challenges experienced by patients and health care professionals . Family Practice , 32 , 686-696. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmv069 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kingry M. J., Tiedje L. B., Friedman L. L. (1990). Focus groups: A research technique for nursing . Nursing Research , 39 , 124–125. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kitzinger J. (1995). Qualitative research: Introducing focus groups . British Medical Journal , 311 , 299–302. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kitzinger J. (2006). Chapter 3: Focus groups . In Pope C., Mays N. (Eds.), Qualitative research in health care (3rd ed., pp. 21–31). Malden, MA: Blackwell. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kroll T., Neri M. T., Miller K. (2005). Using mixed methods in disability and rehabilitation research . Rehabilitation Nursing , 30 , 106–113. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krueger R. A. (1988). Focus groups: A practical guide for applied research . Newbury Park, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lehoux P., Poland B. D., Daudelin G. (2006). Focus group research and “the patient’s view.” Social Science & Medicine , 63 , 2091–2104. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayring P. (2015). Qualitative Inhaltsanalyse [Qualitative content analysis] (12th ed.). Weinheim, Germany: Beltz. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L. (Ed.). (1993). Successful focus groups: Advancing the state of the art . Newbury Park, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L. (1995). Why things (sometimes) go wrong in focus groups . Qualitative Health Research , 5 , 516–523. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L. (1996). Focus groups . Annual review of sociology , 22 , 129–152. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L. (2009). Focus groups as qualitative research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L., Krueger R. A. (Eds.). (1998). Focus group kit . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nafees B., Lloyd A., Kennedy-Martin T., Hynd S. (2006). How diabetes and insulin therapy affects the lives of people with type 1 diabetes . European Diabetes Nursing , 3 , 92–97. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nicholas D. B., Lach L., King G., Scott M., Boydell K., Sawatzky B. J., . . .Young N. L. (2010). Contrasting internet and face-to-face focus groups for children with chronic health conditions: Outcomes and participant experiences . International Journal of Qualitative Methods , 9 , 105–121. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rasmusson K., Lappe D., Roberts C., Croasdell S., Meegan S., Budge D. (2014). Heart failure patient perspectives: Learning from focus groups to improve care . Heart & Lung , 43 , 382–383. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rhodes S. D., Hergenrather K. C., Wilkin A., Alegría-Ortega J., Montaño J. (2006). Preventing HIV infection among young immigrant Latino men: Results from focus groups using community-based participatory research . Journal of the National Medical Association , 98 , 564–573. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stewart D. W., Shamdasani P. N., Rook D. W. (2007). Focus groups: Theory and practice (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tausch A., Menold N. (2015). Methodische Aspekte der Durchführung von Fokusgruppen in der Gesundheitsforschung - Welche Anforderungen ergeben sich aufgrund der besonderen Zielgruppen und Fragestellungen? [Methodological aspects of conducting focus groups in health research - which requirements result from the particular target groups and research questions?]. GESIS Papers , 2015 ( 12 ). Retrieved from http://www.gesis.org/fileadmin/upload/forschung/publikationen/gesis_reihen/gesis_papers/GESIS-Papers_2015-12.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Vincent D., Clark L., Marquez Zimmer L., Sanchez J. (2006). Using focus groups to develop a culturally competent diabetes self-management program for Mexican Americans . The Diabetes Educator , 32 , 89–97. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
What Is a Focus Group?
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
A focus group is a qualitative research method that involves facilitating a small group discussion with participants who share common characteristics or experiences that are relevant to the research topic. The goal is to gain insights through group conversation and observation of dynamics.

In a focus group:
- A moderator asks questions and leads a group of typically 6 to 12 pre-screened participants through a discussion focused on a particular topic.
- Group members are encouraged to talk with one another, exchange anecdotes, comment on each others’ experiences and points of view, and build on each others’ responses.
- The goal is to create a candid, natural conversation that provides insights into the participants’ perceptions, attitudes, beliefs, and opinions on the topic.
- Focus groups capitalize on group dynamics to elicit multiple perspectives in a social environment as participants are influenced by and influence others through open discussion.
- The interactive responses allow researchers to quickly gather more contextual, nuanced qualitative data compared to surveys or one-on-one interviews.
Focus groups allow researchers to gather perspectives from multiple people at once in an interactive group setting. This group dynamic surfaces richer responses as participants build on each other’s comments, discuss issues in-depth, and voice agreements or disagreements.
It is important that participants feel comfortable expressing diverse viewpoints rather than being pressured into a consensus.
Focus groups emerged as an alternative to questionnaires in the 1930s over concerns that surveys fostered passive responses or failed to capture people’s authentic perspectives.
During World War II, focus groups were used to evaluate military morale-boosting radio programs. By the 1950s focus groups became widely adopted in marketing research to test consumer preferences.
A key benefit K. Merton highlighted in 1956 was grouping participants with shared knowledge of a topic. This common grounding enables people to provide context to their experiences and allows contrasts between viewpoints to emerge across the group.
As a result, focus groups can elicit a wider range of perspectives than one-on-one interviews.
Step 1 : Clarify the Focus Group’s Purpose and Orientation
Clarify the purpose and orientation of the focus group (Tracy, 2013). Carefully consider whether a focus group or individual interviews will provide the type of qualitative data needed to address your research questions.
Determine if the interactive, fast-paced group discussion format is aligned with gathering perspectives vs. in-depth attitudes on a topic.
Consider incorporating special techniques like extended focus groups with pre-surveys, touchstones using creative imagery/metaphors to focus the topic, or bracketing through ongoing conceptual inspection.
For example
A touchstone in a focus group refers to using a shared experience, activity, metaphor, or other creative technique to provide a common reference point and orientation for grounding the discussion.
The purpose of Mulvale et al. (2021) was to understand the hospital experiences of youth after suicide attempts.
The researchers created a touchstone to focus the discussion specifically around the hospital visit. This provided a shared orientation for the vulnerable participants to open up about their emotional journeys.
In the example from Mulvale et al. (2021), the researchers designated the hospital visit following suicide attempts as the touchstone. This means:
- The visit served as a defining shared experience all youth participants could draw upon to guide the focus group discussion, since they unfortunately had this in common.
- Framing questions around recounting and making meaning out of the hospitalization focused the conversation to elicit rich details about interactions, emotions, challenges, supports needed, and more in relation to this watershed event.
- The hospital visit as a touchstone likely resonated profoundly across youth given the intensity and vulnerability surrounding their suicide attempts. This deepened their willingness to open up and established group rapport.
So in this case, the touchstone concentrated the dialogue around a common catalyst experience enabling youth to build understanding, voice difficulties, and potentially find healing through sharing their journey with empathetic peers who had endured the same trauma.
Step 2 : Select a Homogeneous Grouping Characteristic
Select a homogeneous grouping characteristic (Krueger & Casey, 2009) to recruit participants with a commonality, like shared roles, experiences, or demographics, to enable meaningful discussion.
A sample size of between 6 to 10 participants allows for adequate mingling (MacIntosh 1993).
More members may diminish the ability to capture all viewpoints. Fewer risks limited diversity of thought.
Balance recruitment across income, gender, age, and cultural factors to increase heterogeneity in perspectives. Consider screening criteria to qualify relevant participants.
Choosing focus group participants requires balancing homogeneity and diversity – too much variation across gender, class, profession, etc., can inhibit sharing, while over-similarity limits perspectives. Groups should feel mutual comfort and relevance of experience to enable open contributions while still representing a mix of viewpoints on the topic (Morgan 1988).
Mulvale et al. (2021) determined grouping by gender rather than age or ethnicity was more impactful for suicide attempt experiences.
They fostered difficult discussions by bringing together male and female youth separately based on the sensitive nature of topics like societal expectations around distress.
Step 3 : Designate a Moderator
Designate a skilled, neutral moderator (Crowe, 2003; Morgan, 1997) to steer productive dialogue given their expertise in guiding group interactions. Consider cultural insider moderators positioned to foster participant sharing by understanding community norms.
Define moderator responsibilities like directing discussion flow, monitoring air time across members, and capturing observational notes on behaviors/dynamics.
Choose whether the moderator also analyzes data or only facilitates the group.
Mulvale et al. (2021) designated a moderator experienced working with marginalized youth to encourage sharing by establishing an empathetic, non-judgmental environment through trust-building and active listening guidance.
Step 4 : Develop a Focus Group Guide
Develop an extensive focus group guide (Krueger & Casey, 2009). Include an introduction to set a relaxed tone, explain the study rationale, review confidentiality protection procedures, and facilitate a participant introduction activity.
Also include guidelines reiterating respect, listening, and sharing principles both verbally and in writing.
Group confidentiality agreement
The group context introduces distinct ethical demands around informed consent, participant expectations, confidentiality, and data treatment. Establishing guidelines at the outset helps address relevant issues.
Create a group confidentiality agreement (Berg, 2004) specifying that all comments made during the session must remain private, anonymous in data analysis, and not discussed outside the group without permission.
Have it signed, demonstrating a communal commitment to sustaining a safe, secure environment for honest sharing.
Berg (2004) recommends a formal signed agreement prohibiting participants from publicly talking about anything said in the focus group without permission. This reassures members their personal disclosures are safeguarded.
Develop questions starting general then funneling down to 10-12 key questions on critical topics. Integrate think/pair/share activities between question sets to encourage inclusion. Close with a conclusion to summarize key ideas voiced without endorsing consensus.
Krueger and Casey (2009) recommend structuring focus group questions in five stages:
Opening Questions:
- Start with easy, non-threatening questions to make participants comfortable, often related to their background and experience with the topic.
- Get everyone talking and open up initial dialogue.
- Example: “Let’s go around and have each person share how long you’ve lived in this city.”
Introductory Questions:
- Transition to the key focus group objectives and main topics of interest.
- Remain quite general to provide baseline understanding before drilling down.
- Example: “Thinking broadly, how would you describe the arts and cultural offerings in your community?”
Transition Questions:
- Serve as a logical link between introductory and key questions.
- Funnel participants toward critical topics guided by research aims.
- Example: “Specifically related to concerts and theatre performances, what venues in town have you attended events at over the past year?”
Key Questions:
- Drive at the heart of study goals, and issues under investigation.
- Ask 5-10 questions that foster organic, interactive discussion between participants.
- Example: “What enhances or detracts from the concert-going experience at these various venues?”
Ending Questions:
- Provide an opportunity for final thoughts or anything missed.
- Assess the degree of consensus on key topics.
- Example: “If you could improve just one thing about the concert and theatre options here, what would you prioritize?”
It is vital to extensively pilot test draft questions to hone the wording, flow, timing, tone and tackle any gaps to adequately cover research objectives through dynamic group discussion.
Step 5 : Prepare the focus group room
Prepare the focus group room (Krueger & Casey, 2009) attending to details like circular seating for eye contact, centralized recording equipment with backup power, name cards, and refreshments to create a welcoming, affirming environment critical for participants to feel valued, comfortable engaging in genuine dialogue as a collective.
Arrange seating comfortably in a circle to facilitate discussion flow and eye contact among members. Decide if space for breakout conversations or activities like role-playing is needed.
Refreshments
- Coordinate snacks or light refreshments to be available when focus group members arrive, especially for longer sessions. This contributes to a welcoming atmosphere.
- Even if no snacks are provided, consider making bottled water available throughout the session.
- Set out colorful pens and blank name tags for focus group members to write their preferred name or pseudonym when they arrive.
- Attaching name tags to clothing facilitates interaction and expedites learning names.
- If short on preparation time, prepare printed name tags in advance based on RSVPs, but blank name tags enable anonymity if preferred.
Krueger & Casey (2009) suggest welcoming focus group members with comfortable, inclusive seating arrangements in a circle to enable eye contact. Providing snacks and music sets a relaxed tone.
Step 6 : Conduct the focus group
Conduct the focus group utilizing moderation skills like conveying empathy, observing verbal and non-verbal cues, gently redirecting and probing overlooked members, and affirming the usefulness of knowledge sharing.
Use facilitation principles (Krueger & Casey, 2009; Tracy 2013) like ensuring psychological safety, mutual respect, equitable airtime, and eliciting an array of perspectives to expand group knowledge. Gain member buy-in through collaborative review.
Record discussions through detailed note-taking, audio/video recording, and seating charts tracking engaged participation.
The role of moderator
The moderator is critical in facilitating open, interactive discussion in the group. Their main responsibilities are:
- Providing clear explanations of the purpose and helping participants feel comfortable
- Promoting debate by asking open-ended questions
- Drawing out differences of opinion and a range of perspectives by challenging participants
- Probing for more details when needed or moving the conversation forward
- Keeping the discussion focused and on track
- Ensuring all participants get a chance to speak
- Remaining neutral and non-judgmental, without sharing personal opinions
Moderators need strong interpersonal abilities to build participant trust and comfort sharing. The degree of control and input from the moderator depends on the research goals and personal style.
With multiple moderators, roles, and responsibilities should be clear and consistent across groups. Careful preparation is key for effective moderation.
Mulvale et al. (2021) fostered psychological safety for youth to share intense emotions about suicide attempts without judgment. The moderator ensured equitable speaking opportunities within a compassionate climate.
Krueger & Casey (2009) advise moderators to handle displays of distress empathetically by offering a break and emotional support through active listening instead of ignoring reactions. This upholds ethical principles.
Advantages and disadvantages of focus groups
Focus groups efficiently provide interactive qualitative data that can yield useful insights into emerging themes. However, findings may be skewed by group behaviors and still require larger sample validation through added research methods. Careful planning is vital.
- Efficient way to gather a range of perspectives in participants’ own words in a short time
- Group dynamic encourages more complex responses as members build on others’ comments
- Can observe meaningful group interactions, consensus, or disagreements
- Flexibility for moderators to probe unanticipated insights during discussion
- Often feels more comfortable sharing as part of a group rather than one-on-one
- Helps participants recall and reflect by listening to others tell their stories
Disadvantages
- Small sample size makes findings difficult to generalize
- Groupthink: influential members may discourage dissenting views from being shared
- Social desirability bias: reluctance from participants to oppose perceived majority opinions
- Requires highly skilled moderators to foster inclusive participation and contain domineering members
- Confidentiality harder to ensure than with individual interviews
- Transcriptions may have overlapping talk that is difficult to capture accurately
- Group dynamics adds layers of complexity for analysis beyond just the content of responses
Goss, J. D., & Leinbach, T. R. (1996). Focus groups as alternative research practice: experience with transmigrants in Indonesia. Area , 115-123.
Kitzinger, J. (1994). The methodology of focus groups: the importance of interaction between research participants . Sociology of health & illness , 16 (1), 103-121.
Kitzinger J. (1995). Introducing focus groups. British Medical Journal, 311 , 299-302.
Morgan D.L. (1988). Focus groups as qualitative research . London: Sage.
Mulvale, G., Green, J., Miatello, A., Cassidy, A. E., & Martens, T. (2021). Finding harmony within dissonance: engaging patients, family/caregivers and service providers in research to fundamentally restructure relationships through integrative dynamics . Health Expectations , 24 , 147-160.
Powell, R. A., Single, H. M., & Lloyd, K. R. (1996). Focus groups in mental health research: enhancing the validity of user and provider questionnaires . International Journal of Social Psychiatry , 42 (3), 193-206.
Puchta, C., & Potter, J. (2004). Focus group practice . Sage.
Redmond, R. A., & Curtis, E. A. (2009). Focus groups: principles and process. Nurse researcher , 16 (3).
Smith, J. A., Scammon, D. L., & Beck, S. L. (1995). Using patient focus groups for new patient services. The Joint Commission Journal on Quality Improvement , 21 (1), 22-31.
Smithson, J. (2008). Focus groups. The Sage handbook of social research methods , 357-370.
White, G. E., & Thomson, A. N. (1995). Anonymized focus groups as a research tool for health professionals. Qualitative Health Research , 5 (2), 256-261.
Download PDF slides of the presentation ‘ Conducting Focus Groups – A Brief Overview ‘
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Mixed Methods Research

Conversation Analysis

Discourse Analysis

Phenomenology In Qualitative Research

Ethnography In Qualitative Research

Narrative Analysis In Qualitative Research
Qualitative study design: Focus groups
- Qualitative study design
- Phenomenology
- Grounded theory
- Ethnography
- Narrative inquiry
- Action research
- Case Studies
- Field research
- Focus groups
- Observation
- Surveys & questionnaires
- Study Designs Home
Focus Groups
Focus groups bring individuals from the study population together in a specific setting in order to discuss an issue as a group. The discussion generates research data.
Focus groups typically have these features:
- Four to ten participants meeting for up to two hours
- A facilitator or facilitators to guide discussion using open-ended questions
- An emphasis on the group talking among itself rather than to the facilitator
- Discussion is recorded and then transcribed for analysis by researchers
Researchers conduct several individual focus group meetings to produce a series. The number of focus groups in the series depends on the study’s aim, methods and resources.
Focus groups use a group setting to generate data different to that obtained in a one-to-one interview. The group context may allow for better examination of beliefs, attitudes, values, perspectives, knowledge and ideas.
Focus groups can be useful in action research methodology and other study designs which seek to empower research participants. Focus groups are also useful in multimethod studies utilising different forms of data collection.
- Quick way to collect data from several people
- Produces data unique to group setting (e.g. teasing, arguing and non-verbal behaviour) due to the interaction between participants. This is a unique feature of focus groups.
- Unlike written questionnaires, focus groups don’t rely on participant literacy to generate data
- Can encourage participation from marginalised groups
- Can facilitate discussion of stigmatised or counter-cultural topics due to feeling of mutual support among focus group participants
- Can generate more critical comments than individual interviews. This is valuable for research aimed at improving products or services.
- Can be used to validate findings from quantitative research methods by providing a deeper understanding that statistics cannot.
Limitations
- Individual perspectives that dissent from the focus group’s majority may remain hidden due to overriding behavioural or cultural norms, or a desire to be seen as conforming.
- Confidentiality of individual responses is compromised due to the existence of the group
- Only applicable when the population of interest has shared social and cultural experience or share common areas of concern.
- Group discussion does not provide enough depth for researchers to understand experiences, especially in comparison to in-depth interviews.
- Data is representative of the range of views in a population, not the prevalence of such views.
- The facilitator has a strong effect on the focus groups behaviour and can therefore influence the extent to which issues or views are explored.
- Data analysis is usually very time consuming due to the quantity produced.
Example questions
- What are the experiences, needs and wishes of mothers who received midwifery care at tertiary hospitals in Victoria, Australia?
- How useful is the patient perspective for the creation of an information information booklet for patients with liver cancer?
- What factors influence nursing students' development of end-of-life communication skills?
Example studies
Harrison, M., Ryan, T., Gardiner, C., & Jones, A. (2017). Psychological and emotional needs, assessment, and support post-stroke: a multi-perspective qualitative study . Top Stroke Rehabil, 24 (2), 119-125. doi: 10.1080/10749357.2016.1196908
Shilubane, H. N., Ruiter, R. A., Bos, A. E., Reddy, P. S., & van den Borne, B. (2014). High school students' knowledge and experience with a peer who committed or attempted suicide: a focus group study . BMC Public Health, 14 , 1081. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-1081
Wiles, J. L., Leibing, A., Guberman, N., Reeve, J., & Allen, R. E. (2012). The meaning of "aging in place" to older people . Gerontologist , 52(3), 357-366. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnr098
Kitzinger, J. (1995). Qualitative research: introducing focus groups . BMJ, 311 (7000), 299. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7000.299
Rice, P. L., & Ezzy, D. (1999). Qualitative research methods: a health focus . South Melbourne, Australia: Oxford University Press.
- << Previous: Methods
- Next: Observation >>
- Last Updated: Jun 13, 2024 10:34 AM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/qualitative-study-designs
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 05 October 2018
Interviews and focus groups in qualitative research: an update for the digital age
- P. Gill 1 &
- J. Baillie 2
British Dental Journal volume 225 , pages 668–672 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
30k Accesses
51 Citations
20 Altmetric
Metrics details
Highlights that qualitative research is used increasingly in dentistry. Interviews and focus groups remain the most common qualitative methods of data collection.
Suggests the advent of digital technologies has transformed how qualitative research can now be undertaken.
Suggests interviews and focus groups can offer significant, meaningful insight into participants' experiences, beliefs and perspectives, which can help to inform developments in dental practice.
Qualitative research is used increasingly in dentistry, due to its potential to provide meaningful, in-depth insights into participants' experiences, perspectives, beliefs and behaviours. These insights can subsequently help to inform developments in dental practice and further related research. The most common methods of data collection used in qualitative research are interviews and focus groups. While these are primarily conducted face-to-face, the ongoing evolution of digital technologies, such as video chat and online forums, has further transformed these methods of data collection. This paper therefore discusses interviews and focus groups in detail, outlines how they can be used in practice, how digital technologies can further inform the data collection process, and what these methods can offer dentistry.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others

Interviews in the social sciences

Professionalism in dentistry: deconstructing common terminology
A review of technical and quality assessment considerations of audio-visual and web-conferencing focus groups in qualitative health research, introduction.
Traditionally, research in dentistry has primarily been quantitative in nature. 1 However, in recent years, there has been a growing interest in qualitative research within the profession, due to its potential to further inform developments in practice, policy, education and training. Consequently, in 2008, the British Dental Journal (BDJ) published a four paper qualitative research series, 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 to help increase awareness and understanding of this particular methodological approach.
Since the papers were originally published, two scoping reviews have demonstrated the ongoing proliferation in the use of qualitative research within the field of oral healthcare. 1 , 6 To date, the original four paper series continue to be well cited and two of the main papers remain widely accessed among the BDJ readership. 2 , 3 The potential value of well-conducted qualitative research to evidence-based practice is now also widely recognised by service providers, policy makers, funding bodies and those who commission, support and use healthcare research.
Besides increasing standalone use, qualitative methods are now also routinely incorporated into larger mixed method study designs, such as clinical trials, as they can offer additional, meaningful insights into complex problems that simply could not be provided by quantitative methods alone. Qualitative methods can also be used to further facilitate in-depth understanding of important aspects of clinical trial processes, such as recruitment. For example, Ellis et al . investigated why edentulous older patients, dissatisfied with conventional dentures, decline implant treatment, despite its established efficacy, and frequently refuse to participate in related randomised clinical trials, even when financial constraints are removed. 7 Through the use of focus groups in Canada and the UK, the authors found that fears of pain and potential complications, along with perceived embarrassment, exacerbated by age, are common reasons why older patients typically refuse dental implants. 7
The last decade has also seen further developments in qualitative research, due to the ongoing evolution of digital technologies. These developments have transformed how researchers can access and share information, communicate and collaborate, recruit and engage participants, collect and analyse data and disseminate and translate research findings. 8 Where appropriate, such technologies are therefore capable of extending and enhancing how qualitative research is undertaken. 9 For example, it is now possible to collect qualitative data via instant messaging, email or online/video chat, using appropriate online platforms.
These innovative approaches to research are therefore cost-effective, convenient, reduce geographical constraints and are often useful for accessing 'hard to reach' participants (for example, those who are immobile or socially isolated). 8 , 9 However, digital technologies are still relatively new and constantly evolving and therefore present a variety of pragmatic and methodological challenges. Furthermore, given their very nature, their use in many qualitative studies and/or with certain participant groups may be inappropriate and should therefore always be carefully considered. While it is beyond the scope of this paper to provide a detailed explication regarding the use of digital technologies in qualitative research, insight is provided into how such technologies can be used to facilitate the data collection process in interviews and focus groups.
In light of such developments, it is perhaps therefore timely to update the main paper 3 of the original BDJ series. As with the previous publications, this paper has been purposely written in an accessible style, to enhance readability, particularly for those who are new to qualitative research. While the focus remains on the most common qualitative methods of data collection – interviews and focus groups – appropriate revisions have been made to provide a novel perspective, and should therefore be helpful to those who would like to know more about qualitative research. This paper specifically focuses on undertaking qualitative research with adult participants only.
Overview of qualitative research
Qualitative research is an approach that focuses on people and their experiences, behaviours and opinions. 10 , 11 The qualitative researcher seeks to answer questions of 'how' and 'why', providing detailed insight and understanding, 11 which quantitative methods cannot reach. 12 Within qualitative research, there are distinct methodologies influencing how the researcher approaches the research question, data collection and data analysis. 13 For example, phenomenological studies focus on the lived experience of individuals, explored through their description of the phenomenon. Ethnographic studies explore the culture of a group and typically involve the use of multiple methods to uncover the issues. 14
While methodology is the 'thinking tool', the methods are the 'doing tools'; 13 the ways in which data are collected and analysed. There are multiple qualitative data collection methods, including interviews, focus groups, observations, documentary analysis, participant diaries, photography and videography. Two of the most commonly used qualitative methods are interviews and focus groups, which are explored in this article. The data generated through these methods can be analysed in one of many ways, according to the methodological approach chosen. A common approach is thematic data analysis, involving the identification of themes and subthemes across the data set. Further information on approaches to qualitative data analysis has been discussed elsewhere. 1
Qualitative research is an evolving and adaptable approach, used by different disciplines for different purposes. Traditionally, qualitative data, specifically interviews, focus groups and observations, have been collected face-to-face with participants. In more recent years, digital technologies have contributed to the ongoing evolution of qualitative research. Digital technologies offer researchers different ways of recruiting participants and collecting data, and offer participants opportunities to be involved in research that is not necessarily face-to-face.
Research interviews are a fundamental qualitative research method 15 and are utilised across methodological approaches. Interviews enable the researcher to learn in depth about the perspectives, experiences, beliefs and motivations of the participant. 3 , 16 Examples include, exploring patients' perspectives of fear/anxiety triggers in dental treatment, 17 patients' experiences of oral health and diabetes, 18 and dental students' motivations for their choice of career. 19
Interviews may be structured, semi-structured or unstructured, 3 according to the purpose of the study, with less structured interviews facilitating a more in depth and flexible interviewing approach. 20 Structured interviews are similar to verbal questionnaires and are used if the researcher requires clarification on a topic; however they produce less in-depth data about a participant's experience. 3 Unstructured interviews may be used when little is known about a topic and involves the researcher asking an opening question; 3 the participant then leads the discussion. 20 Semi-structured interviews are commonly used in healthcare research, enabling the researcher to ask predetermined questions, 20 while ensuring the participant discusses issues they feel are important.
Interviews can be undertaken face-to-face or using digital methods when the researcher and participant are in different locations. Audio-recording the interview, with the consent of the participant, is essential for all interviews regardless of the medium as it enables accurate transcription; the process of turning the audio file into a word-for-word transcript. This transcript is the data, which the researcher then analyses according to the chosen approach.
Types of interview
Qualitative studies often utilise one-to-one, face-to-face interviews with research participants. This involves arranging a mutually convenient time and place to meet the participant, signing a consent form and audio-recording the interview. However, digital technologies have expanded the potential for interviews in research, enabling individuals to participate in qualitative research regardless of location.
Telephone interviews can be a useful alternative to face-to-face interviews and are commonly used in qualitative research. They enable participants from different geographical areas to participate and may be less onerous for participants than meeting a researcher in person. 15 A qualitative study explored patients' perspectives of dental implants and utilised telephone interviews due to the quality of the data that could be yielded. 21 The researcher needs to consider how they will audio record the interview, which can be facilitated by purchasing a recorder that connects directly to the telephone. One potential disadvantage of telephone interviews is the inability of the interviewer and researcher to see each other. This is resolved using software for audio and video calls online – such as Skype – to conduct interviews with participants in qualitative studies. Advantages of this approach include being able to see the participant if video calls are used, enabling observation of non-verbal communication, and the software can be free to use. However, participants are required to have a device and internet connection, as well as being computer literate, potentially limiting who can participate in the study. One qualitative study explored the role of dental hygienists in reducing oral health disparities in Canada. 22 The researcher conducted interviews using Skype, which enabled dental hygienists from across Canada to be interviewed within the research budget, accommodating the participants' schedules. 22
A less commonly used approach to qualitative interviews is the use of social virtual worlds. A qualitative study accessed a social virtual world – Second Life – to explore the health literacy skills of individuals who use social virtual worlds to access health information. 23 The researcher created an avatar and interview room, and undertook interviews with participants using voice and text methods. 23 This approach to recruitment and data collection enables individuals from diverse geographical locations to participate, while remaining anonymous if they wish. Furthermore, for interviews conducted using text methods, transcription of the interview is not required as the researcher can save the written conversation with the participant, with the participant's consent. However, the researcher and participant need to be familiar with how the social virtual world works to engage in an interview this way.
Conducting an interview
Ensuring informed consent before any interview is a fundamental aspect of the research process. Participants in research must be afforded autonomy and respect; consent should be informed and voluntary. 24 Individuals should have the opportunity to read an information sheet about the study, ask questions, understand how their data will be stored and used, and know that they are free to withdraw at any point without reprisal. The qualitative researcher should take written consent before undertaking the interview. In a face-to-face interview, this is straightforward: the researcher and participant both sign copies of the consent form, keeping one each. However, this approach is less straightforward when the researcher and participant do not meet in person. A recent protocol paper outlined an approach for taking consent for telephone interviews, which involved: audio recording the participant agreeing to each point on the consent form; the researcher signing the consent form and keeping a copy; and posting a copy to the participant. 25 This process could be replicated in other interview studies using digital methods.
There are advantages and disadvantages of using face-to-face and digital methods for research interviews. Ultimately, for both approaches, the quality of the interview is determined by the researcher. 16 Appropriate training and preparation are thus required. Healthcare professionals can use their interpersonal communication skills when undertaking a research interview, particularly questioning, listening and conversing. 3 However, the purpose of an interview is to gain information about the study topic, 26 rather than offering help and advice. 3 The researcher therefore needs to listen attentively to participants, enabling them to describe their experience without interruption. 3 The use of active listening skills also help to facilitate the interview. 14 Spradley outlined elements and strategies for research interviews, 27 which are a useful guide for qualitative researchers:
Greeting and explaining the project/interview
Asking descriptive (broad), structural (explore response to descriptive) and contrast (difference between) questions
Asymmetry between the researcher and participant talking
Expressing interest and cultural ignorance
Repeating, restating and incorporating the participant's words when asking questions
Creating hypothetical situations
Asking friendly questions
Knowing when to leave.
For semi-structured interviews, a topic guide (also called an interview schedule) is used to guide the content of the interview – an example of a topic guide is outlined in Box 1 . The topic guide, usually based on the research questions, existing literature and, for healthcare professionals, their clinical experience, is developed by the research team. The topic guide should include open ended questions that elicit in-depth information, and offer participants the opportunity to talk about issues important to them. This is vital in qualitative research where the researcher is interested in exploring the experiences and perspectives of participants. It can be useful for qualitative researchers to pilot the topic guide with the first participants, 10 to ensure the questions are relevant and understandable, and amending the questions if required.
Regardless of the medium of interview, the researcher must consider the setting of the interview. For face-to-face interviews, this could be in the participant's home, in an office or another mutually convenient location. A quiet location is preferable to promote confidentiality, enable the researcher and participant to concentrate on the conversation, and to facilitate accurate audio-recording of the interview. For interviews using digital methods the same principles apply: a quiet, private space where the researcher and participant feel comfortable and confident to participate in an interview.
Box 1: Example of a topic guide
Study focus: Parents' experiences of brushing their child's (aged 0–5) teeth
1. Can you tell me about your experience of cleaning your child's teeth?
How old was your child when you started cleaning their teeth?
Why did you start cleaning their teeth at that point?
How often do you brush their teeth?
What do you use to brush their teeth and why?
2. Could you explain how you find cleaning your child's teeth?
Do you find anything difficult?
What makes cleaning their teeth easier for you?
3. How has your experience of cleaning your child's teeth changed over time?
Has it become easier or harder?
Have you changed how often and how you clean their teeth? If so, why?
4. Could you describe how your child finds having their teeth cleaned?
What do they enjoy about having their teeth cleaned?
Is there anything they find upsetting about having their teeth cleaned?
5. Where do you look for information/advice about cleaning your child's teeth?
What did your health visitor tell you about cleaning your child's teeth? (If anything)
What has the dentist told you about caring for your child's teeth? (If visited)
Have any family members given you advice about how to clean your child's teeth? If so, what did they tell you? Did you follow their advice?
6. Is there anything else you would like to discuss about this?
Focus groups
A focus group is a moderated group discussion on a pre-defined topic, for research purposes. 28 , 29 While not aligned to a particular qualitative methodology (for example, grounded theory or phenomenology) as such, focus groups are used increasingly in healthcare research, as they are useful for exploring collective perspectives, attitudes, behaviours and experiences. Consequently, they can yield rich, in-depth data and illuminate agreement and inconsistencies 28 within and, where appropriate, between groups. Examples include public perceptions of dental implants and subsequent impact on help-seeking and decision making, 30 and general dental practitioners' views on patient safety in dentistry. 31
Focus groups can be used alone or in conjunction with other methods, such as interviews or observations, and can therefore help to confirm, extend or enrich understanding and provide alternative insights. 28 The social interaction between participants often results in lively discussion and can therefore facilitate the collection of rich, meaningful data. However, they are complex to organise and manage, due to the number of participants, and may also be inappropriate for exploring particularly sensitive issues that many participants may feel uncomfortable about discussing in a group environment.
Focus groups are primarily undertaken face-to-face but can now also be undertaken online, using appropriate technologies such as email, bulletin boards, online research communities, chat rooms, discussion forums, social media and video conferencing. 32 Using such technologies, data collection can also be synchronous (for example, online discussions in 'real time') or, unlike traditional face-to-face focus groups, asynchronous (for example, online/email discussions in 'non-real time'). While many of the fundamental principles of focus group research are the same, regardless of how they are conducted, a number of subtle nuances are associated with the online medium. 32 Some of which are discussed further in the following sections.
Focus group considerations
Some key considerations associated with face-to-face focus groups are: how many participants are required; should participants within each group know each other (or not) and how many focus groups are needed within a single study? These issues are much debated and there is no definitive answer. However, the number of focus groups required will largely depend on the topic area, the depth and breadth of data needed, the desired level of participation required 29 and the necessity (or not) for data saturation.
The optimum group size is around six to eight participants (excluding researchers) but can work effectively with between three and 14 participants. 3 If the group is too small, it may limit discussion, but if it is too large, it may become disorganised and difficult to manage. It is, however, prudent to over-recruit for a focus group by approximately two to three participants, to allow for potential non-attenders. For many researchers, particularly novice researchers, group size may also be informed by pragmatic considerations, such as the type of study, resources available and moderator experience. 28 Similar size and mix considerations exist for online focus groups. Typically, synchronous online focus groups will have around three to eight participants but, as the discussion does not happen simultaneously, asynchronous groups may have as many as 10–30 participants. 33
The topic area and potential group interaction should guide group composition considerations. Pre-existing groups, where participants know each other (for example, work colleagues) may be easier to recruit, have shared experiences and may enjoy a familiarity, which facilitates discussion and/or the ability to challenge each other courteously. 3 However, if there is a potential power imbalance within the group or if existing group norms and hierarchies may adversely affect the ability of participants to speak freely, then 'stranger groups' (that is, where participants do not already know each other) may be more appropriate. 34 , 35
Focus group management
Face-to-face focus groups should normally be conducted by two researchers; a moderator and an observer. 28 The moderator facilitates group discussion, while the observer typically monitors group dynamics, behaviours, non-verbal cues, seating arrangements and speaking order, which is essential for transcription and analysis. The same principles of informed consent, as discussed in the interview section, also apply to focus groups, regardless of medium. However, the consent process for online discussions will probably be managed somewhat differently. For example, while an appropriate participant information leaflet (and consent form) would still be required, the process is likely to be managed electronically (for example, via email) and would need to specifically address issues relating to technology (for example, anonymity and use, storage and access to online data). 32
The venue in which a face to face focus group is conducted should be of a suitable size, private, quiet, free from distractions and in a collectively convenient location. It should also be conducted at a time appropriate for participants, 28 as this is likely to promote attendance. As with interviews, the same ethical considerations apply (as discussed earlier). However, online focus groups may present additional ethical challenges associated with issues such as informed consent, appropriate access and secure data storage. Further guidance can be found elsewhere. 8 , 32
Before the focus group commences, the researchers should establish rapport with participants, as this will help to put them at ease and result in a more meaningful discussion. Consequently, researchers should introduce themselves, provide further clarity about the study and how the process will work in practice and outline the 'ground rules'. Ground rules are designed to assist, not hinder, group discussion and typically include: 3 , 28 , 29
Discussions within the group are confidential to the group
Only one person can speak at a time
All participants should have sufficient opportunity to contribute
There should be no unnecessary interruptions while someone is speaking
Everyone can be expected to be listened to and their views respected
Challenging contrary opinions is appropriate, but ridiculing is not.
Moderating a focus group requires considered management and good interpersonal skills to help guide the discussion and, where appropriate, keep it sufficiently focused. Avoid, therefore, participating, leading, expressing personal opinions or correcting participants' knowledge 3 , 28 as this may bias the process. A relaxed, interested demeanour will also help participants to feel comfortable and promote candid discourse. Moderators should also prevent the discussion being dominated by any one person, ensure differences of opinions are discussed fairly and, if required, encourage reticent participants to contribute. 3 Asking open questions, reflecting on significant issues, inviting further debate, probing responses accordingly, and seeking further clarification, as and where appropriate, will help to obtain sufficient depth and insight into the topic area.
Moderating online focus groups requires comparable skills, particularly if the discussion is synchronous, as the discussion may be dominated by those who can type proficiently. 36 It is therefore important that sufficient time and respect is accorded to those who may not be able to type as quickly. Asynchronous discussions are usually less problematic in this respect, as interactions are less instant. However, moderating an asynchronous discussion presents additional challenges, particularly if participants are geographically dispersed, as they may be online at different times. Consequently, the moderator will not always be present and the discussion may therefore need to occur over several days, which can be difficult to manage and facilitate and invariably requires considerable flexibility. 32 It is also worth recognising that establishing rapport with participants via online medium is often more challenging than via face-to-face and may therefore require additional time, skills, effort and consideration.
As with research interviews, focus groups should be guided by an appropriate interview schedule, as discussed earlier in the paper. For example, the schedule will usually be informed by the review of the literature and study aims, and will merely provide a topic guide to help inform subsequent discussions. To provide a verbatim account of the discussion, focus groups must be recorded, using an audio-recorder with a good quality multi-directional microphone. While videotaping is possible, some participants may find it obtrusive, 3 which may adversely affect group dynamics. The use (or not) of a video recorder, should therefore be carefully considered.
At the end of the focus group, a few minutes should be spent rounding up and reflecting on the discussion. 28 Depending on the topic area, it is possible that some participants may have revealed deeply personal issues and may therefore require further help and support, such as a constructive debrief or possibly even referral on to a relevant third party. It is also possible that some participants may feel that the discussion did not adequately reflect their views and, consequently, may no longer wish to be associated with the study. 28 Such occurrences are likely to be uncommon, but should they arise, it is important to further discuss any concerns and, if appropriate, offer them the opportunity to withdraw (including any data relating to them) from the study. Immediately after the discussion, researchers should compile notes regarding thoughts and ideas about the focus group, which can assist with data analysis and, if appropriate, any further data collection.
Qualitative research is increasingly being utilised within dental research to explore the experiences, perspectives, motivations and beliefs of participants. The contributions of qualitative research to evidence-based practice are increasingly being recognised, both as standalone research and as part of larger mixed-method studies, including clinical trials. Interviews and focus groups remain commonly used data collection methods in qualitative research, and with the advent of digital technologies, their utilisation continues to evolve. However, digital methods of qualitative data collection present additional methodological, ethical and practical considerations, but also potentially offer considerable flexibility to participants and researchers. Consequently, regardless of format, qualitative methods have significant potential to inform important areas of dental practice, policy and further related research.
Gussy M, Dickson-Swift V, Adams J . A scoping review of qualitative research in peer-reviewed dental publications. Int J Dent Hygiene 2013; 11 : 174–179.
Article Google Scholar
Burnard P, Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B . Analysing and presenting qualitative data. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 429–432.
Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B . Methods of data collection in qualitative research: interviews and focus groups. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 291–295.
Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B . Conducting qualitative interviews with school children in dental research. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 371–374.
Stewart K, Gill P, Chadwick B, Treasure E . Qualitative research in dentistry. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 235–239.
Masood M, Thaliath E, Bower E, Newton J . An appraisal of the quality of published qualitative dental research. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2011; 39 : 193–203.
Ellis J, Levine A, Bedos C et al. Refusal of implant supported mandibular overdentures by elderly patients. Gerodontology 2011; 28 : 62–68.
Macfarlane S, Bucknall T . Digital Technologies in Research. In Gerrish K, Lathlean J (editors) The Research Process in Nursing . 7th edition. pp. 71–86. Oxford: Wiley Blackwell; 2015.
Google Scholar
Lee R, Fielding N, Blank G . Online Research Methods in the Social Sciences: An Editorial Introduction. In Fielding N, Lee R, Blank G (editors) The Sage Handbook of Online Research Methods . pp. 3–16. London: Sage Publications; 2016.
Creswell J . Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five designs . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1998.
Guest G, Namey E, Mitchell M . Qualitative research: Defining and designing In Guest G, Namey E, Mitchell M (editors) Collecting Qualitative Data: A Field Manual For Applied Research . pp. 1–40. London: Sage Publications, 2013.
Chapter Google Scholar
Pope C, Mays N . Qualitative research: Reaching the parts other methods cannot reach: an introduction to qualitative methods in health and health services research. BMJ 1995; 311 : 42–45.
Giddings L, Grant B . A Trojan Horse for positivism? A critique of mixed methods research. Adv Nurs Sci 2007; 30 : 52–60.
Hammersley M, Atkinson P . Ethnography: Principles in Practice . London: Routledge, 1995.
Oltmann S . Qualitative interviews: A methodological discussion of the interviewer and respondent contexts Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2016; 17 : Art. 15.
Patton M . Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002.
Wang M, Vinall-Collier K, Csikar J, Douglas G . A qualitative study of patients' views of techniques to reduce dental anxiety. J Dent 2017; 66 : 45–51.
Lindenmeyer A, Bowyer V, Roscoe J, Dale J, Sutcliffe P . Oral health awareness and care preferences in patients with diabetes: a qualitative study. Fam Pract 2013; 30 : 113–118.
Gallagher J, Clarke W, Wilson N . Understanding the motivation: a qualitative study of dental students' choice of professional career. Eur J Dent Educ 2008; 12 : 89–98.
Tod A . Interviewing. In Gerrish K, Lacey A (editors) The Research Process in Nursing . Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006.
Grey E, Harcourt D, O'Sullivan D, Buchanan H, Kipatrick N . A qualitative study of patients' motivations and expectations for dental implants. Br Dent J 2013; 214 : 10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.1178.
Farmer J, Peressini S, Lawrence H . Exploring the role of the dental hygienist in reducing oral health disparities in Canada: A qualitative study. Int J Dent Hygiene 2017; 10.1111/idh.12276.
McElhinney E, Cheater F, Kidd L . Undertaking qualitative health research in social virtual worlds. J Adv Nurs 2013; 70 : 1267–1275.
Health Research Authority. UK Policy Framework for Health and Social Care Research. Available at https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/policies-standards-legislation/uk-policy-framework-health-social-care-research/ (accessed September 2017).
Baillie J, Gill P, Courtenay P . Knowledge, understanding and experiences of peritonitis among patients, and their families, undertaking peritoneal dialysis: A mixed methods study protocol. J Adv Nurs 2017; 10.1111/jan.13400.
Kvale S . Interviews . Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage, 1996.
Spradley J . The Ethnographic Interview . New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1979.
Goodman C, Evans C . Focus Groups. In Gerrish K, Lathlean J (editors) The Research Process in Nursing . pp. 401–412. Oxford: Wiley Blackwell, 2015.
Shaha M, Wenzell J, Hill E . Planning and conducting focus group research with nurses. Nurse Res 2011; 18 : 77–87.
Wang G, Gao X, Edward C . Public perception of dental implants: a qualitative study. J Dent 2015; 43 : 798–805.
Bailey E . Contemporary views of dental practitioners' on patient safety. Br Dent J 2015; 219 : 535–540.
Abrams K, Gaiser T . Online Focus Groups. In Field N, Lee R, Blank G (editors) The Sage Handbook of Online Research Methods . pp. 435–450. London: Sage Publications, 2016.
Poynter R . The Handbook of Online and Social Media Research . West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
Kevern J, Webb C . Focus groups as a tool for critical social research in nurse education. Nurse Educ Today 2001; 21 : 323–333.
Kitzinger J, Barbour R . Introduction: The Challenge and Promise of Focus Groups. In Barbour R S K J (editor) Developing Focus Group Research . pp. 1–20. London: Sage Publications, 1999.
Krueger R, Casey M . Focus Groups: A Practical Guide for Applied Research. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE; 2009.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Senior Lecturer (Adult Nursing), School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University,
Lecturer (Adult Nursing) and RCBC Wales Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University,
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to P. Gill .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gill, P., Baillie, J. Interviews and focus groups in qualitative research: an update for the digital age. Br Dent J 225 , 668–672 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2018.815
Download citation
Accepted : 02 July 2018
Published : 05 October 2018
Issue Date : 12 October 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2018.815
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Focus Groups 101

July 31, 2022 2022-07-31
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
It is no secret that the field of user experience often favors objective, observational research methods over subjective, attitudinal methods. After all, when something is observed, with proof that it has actually happened, it can be hard to argue against it. However, it takes more than observational research to truly empathize and understand the full complexity of a person’s experience, which includes emotional experiences, mindsets, values, and belief systems. Since there is no other way to gather this data (at the writing of this article, mind reading with neural implants is not possible) researchers must use attitudinal methods to solicit the thoughts and opinions of target customers. A focus group is one of these methods.
In This Article:
What is a focus group, limitations and risks of focus groups, benefits of focus groups, you can run an effective focus group.
Definition: A focus group is a qualitative, attitudinal research method in which a facilitator conducts a meeting or workshop (typically about 1–2 hours long) with a group of 6–9 people to discuss issues and concerns about their experiences with a product or service. The term “focus” relates to the role of the facilitator, who maintains the group’s focus on certain topics during discussions.
Traditionally, focus groups have been a market-research method, used to get a sense of some aspect of a product, service, or concept. In these settings, the focus would typically be on certain words, graphics, videos, or other noninteractive media. All participants are presented with the media as a group and then prompted to provide their thoughts to the facilitator and the rest of the group.
Generally speaking, focus groups can provide useful information about your customers’ overall opinions and their impressions of a product or service.
Focus groups are notoriously problematic and often improperly used. Here are some of their limitations:
- They do not provide detailed insights on usability. People will comment on what is shown or remembered and offer opinions, so, by their nature, focus groups cannot provide any objective information on behavior when using a product or service. Thus, they cannot provide detailed usability insights, which would be best found with a usability test or field study . Even if there are some usability insights uncovered when presenting a design, products are almost never used by a whole committee; they’re used individually.
- People don’t always know what they will do or what will MOST benefit them in the future. In many focus groups, participants are asked whether they would use a particular product. But users do not always do what they say they will do. So, while it’s helpful to listen to customers’ concerns, preferences, or requests for features or product offerings — especially to uncover unmet user needs — the requests themselves are not always going to be the best solutions to address customers’ needs in a systematic and prioritized way.
- Negativity bias often results in people more readily recalling what was bad about an experience (particularly if it was not a great one), which can skew the discussion negatively for everyone else.
- The peak-end rule can cause people to overly focus on the most memorable and most recent moments, at the expense of other possibly more-meaningful ones.
- Priming can cause participants to overemphasize an aspect of their experience, because it so happened that someone else mentioned it and made them remember it.
- Group dynamics may impact how much (or how little) people share. Strong personalities in the group may affect what and how much is shared. Depending on the focus group’s format, it may disproportionately represent the opinions of those who are more talkative or quick to answer. Groupthink is also more likely to occur in these settings if only verbal contributions are given attention. To paraphrase my colleague Sarah Gibbons : a poorly run focus group can be a great way to pay 9 people for the opinions of three.
Given these limitations, focus groups should NOT be utilized in the following contexts:
- Evaluating a design’s usability
- Evaluating workflows
- Creating a list of design requirements
- Determining a UI’s impact on emotions
- Quantifying satisfaction or other sentiments
Despite these shortcomings, there are some good reasons to consider a focus group:
- Participants with similar goals or perspectives can build on each other’s responses or recall experiences in greater detail. Sometimes during interviews, a participant might have trouble recalling all the details of an experience. However, hearing another participant mention something related may trigger the recollection of an important detail, which would otherwise get skimmed over in an interview.
- They can help teams clarify users’ mental models and language (vocabulary) around the problem space during discovery phases , before conducting further research. While you should generally run a pilot study for most research studies anyway, a focus group can help researchers rework a research plan or facilitator guide with language that could be more user-centered.
- They are a time-efficient method for the researcher. Rather than dedicate 9–12 hours interviewing 6–9 individual participants, a researcher can dedicate 1–2 hours to gather the perspectives of 6–9 people at the same time. It can be a quick way to learn from many people and perspectives (and certainly a 100% improvement to conducting no research at all). These can be especially time-efficient if the researcher is facilitating the focus group online rather than in person.
- When run properly, they can yield rich qualitative insights due to a format similar to semistructured interviews . Unlike questionnaires — which can sometimes limit the level of detail covered — focus groups give facilitators the flexibility to explore topics in which the participants are interested. This format is especially useful if the team is still in early stages of product development and trying to discover new information about the problem space.
Given these benefits, focus groups are BEST utilized in the following contexts:
- Early discovery research to gauge customer familiarity or interest in a concept and initial impressions
- Understanding users’ mental models and expectations
- Cocreation workshops with sponsored customers
It’s fair to say that focus groups are often unfairly maligned, considering the many benefits they can yield with relatively less time commitment compared to other methods. The key to reaping these benefits and mitigating limitations is to use a combination of other research methods (like other behavioral or attitudinal methods), and having a strong research plan.
Here are the key things to consider when planning your focus group:
1. Recruit participants that are representative of your target audience(s).
Who do you want to learn about? What specific segment of users are you interested in? Even if your user is “everybody,” use personas , archetypes , or jobs-to-be-done to identify key recruiting criteria . Recruiting is a tricky balance of finding similar user motivations and goals (not demographics) while inviting a mix of backgrounds to reduce bias from other sources — such as having an overly westernized sample when studying a global offering.
2. Note potential sources of bias from the focus group’s structure.
Note who is not included, and why, for consideration during analysis and when strategizing future research. Is it a different segment that’s intentionally excluded? Lack of response? Lack of interest/trust? Bias is difficult to totally eliminate, but awareness of sources of bias can help during analysis and might inform future research. For example:
- With online focus groups, there may be potential participants who are excluded from participating (be it due to a poor internet connection, lack of a desktop device, or low literacy in certain digital tools). Thus, they may not be able join a video chat or, if they do join, they may be less likely to participate when using an unfamiliar online-meeting tool or whiteboard platform for the first time.
- With in-person focus groups, it’s fair to assume that the study will only involve participants from the immediate commutable vicinity (i.e., within the city or state), especially if travel is not funded by the study or if insufficient notice is provided for those commuting from further distances.
- Is your focus group accessible? This is relevant for both in-person and online focus groups. Can disabled participants get into the facility and participate readily? Can nonverbal participants contribute?
3. Treat your focus group like a workshop . Make participants comfortable with participating, verbally or nonverbally.
As you plan your agenda for the focus group, remember that most of your participants likely do not know each other and will be asked to speak honestly, potentially revealing information that may make them feel vulnerable or unlike others. Some people may do it, others may not. Consider having the following in your focus group:
- It gives a structured way for participants to build rapport with the facilitator and with each other.
- It builds participants’ confidence, in themselves and in the format (particularly if you’re using online-meeting tools or digital whiteboards). Note: Do not “break the ice” with highly personal or sensitive topics, which will likely cause participants to withdraw instead. (In fact, those types of answers are probably not going to come easily in a focus-group format, even with the most “warmed up” group. These types of questions are better suited to 1:1 interviews).
- Both written and verbal participation opportunities As with any other UX workshop , offer multiple methods of engagement (verbal and nonverbal) to encourage maximum participation and contribution. This ensures that less vocal or nonnative speakers feel comfortable contributing. You can also use the diverge–converge technique to maximize participation while decreasing bias potential. Note: If covering sensitive topics, offer an anonymous way to contribute (or, again, consider a different, more-private method altogether).
4. Have a (written) plan and guide.
Construct your prompts in advance to avoid leading or biasing participants. As with semistructured interviews, focus-group questions should use the funnel technique : be open-ended and broad at the beginning and progressively build detail and specificity with concepts as the conversation progresses. On a related note: remember to frame followup questions both positively and negatively to avoid leading participants, particularly when the conversation may naturally skew in one of these directions.
Focus groups don’t accurately predict future behavior. However, they can help gauge attitudes and guide future exploration, thus avoiding wasted research time. Still, they should be considered a starting point to further research, rather than a validation step. The good news? If your focus-group participants are willing, not only will you have their input to guide your further research, you may also have a group of customers willing and able to test what you create to further guide your design.

Related Courses
User research methods: from strategy to requirements to design.
Pick the best UX research method for each stage in the design process
User Interviews
Uncover in-depth, accurate insights about your users
ResearchOps: Scaling User Research
Orchestrate and optimize research to amplify its impact
Related Topics
- Research Methods Research Methods
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RP0JIQorMxI
Level Up Your Focus Groups

Frequency ≠ Importance in Qualitative Data
Tanner Kohler · 3 min

Therese Fessenden · 4 min

Deductively Analyzing Qualitative Data
Related Articles:
Obtaining Consent for User Research
Therese Fessenden · 8 min
Data Is More than Numbers: Why Qualitative Data Isn’t Just Opinions
Page Laubheimer · 9 min
6 Mistakes When Crafting Interview Questions
Maria Rosala · 5 min
Should You Run a Survey?
Maddie Brown · 6 min
Why 5 Participants Are Okay in a Qualitative Study, but Not in a Quantitative One
Raluca Budiu · 7 min
How Many Participants for a UX Interview?
Maria Rosala · 6 min
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Qualitative Research:...
Qualitative Research: Introducing focus groups
- Related content
- Peer review
- Jenny Kitzinger , research fellow a
- a Glasgow University Media Group, Department of Sociology, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8LF
This paper introduces focus group methodology, gives advice on group composition, running the groups, and analysing the results. Focus groups have advantages for researchers in the field of health and medicine: they do not discriminate against people who cannot read or write and they can encourage participation from people reluctant to be interviewed on their own or who feel they have nothing to say.
This is the fifth in a series of seven articles describing non-quantitative techniques and showing their value in health research
**FIGURE OMITTED**
Rationale and uses of focus groups
Focus groups are a form of group interview that capitalises on communication between research participants in order to generate data. Although group interviews are often used simply as a quick and convenient way to collect data from several people simultaneously, focus groups explicitly use group interaction as part of the method. This means that instead of the researcher asking each person to respond to a question in turn, people are encouraged to talk to one another: asking questions, exchanging anecdotes and commenting on each other's experiences and points of view. 1 The method is particularly useful for exploring people's knowledge and experiences and can be used to examine not only what people think but how they think and why they think that way.
Focus groups were originally used within communication studies to explore the effects of films and television programmes, 2 and are a popular method for assessing health education messages and examining public understandings of illness and of health behaviours. 3 4 5 6 7 They are widely used to examine people's experiences of disease and of health services. 8 9 and are an effective technique for exploring the attitudes and needs of staff. 10 11
The idea behind the focus group method is that group processes can help people to explore and …
Log in using your username and password
BMA Member Log In
If you have a subscription to The BMJ, log in:
- Need to activate
- Log in via institution
- Log in via OpenAthens
Log in through your institution
Subscribe from £184 *.
Subscribe and get access to all BMJ articles, and much more.
* For online subscription
Access this article for 1 day for: £33 / $40 / €36 ( excludes VAT )
You can download a PDF version for your personal record.
Buy this article
Focus group research: 8 essential steps
Last updated
20 March 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Learn the essential steps to focus group research on getting the most accurate insights from your participants.
Analyze focus group sessions
Dovetail streamlines focus group research to help you understand the responses and find patterns faster
- Step 1: Choose your topic of interest
Topics favorable to focus groups
A favorable topic for focus groups is exploring the participant's beliefs, feelings, attitudes, and thoughts. Examples of topics that focus groups can explore include:
What are people's perceptions of a particular brand?
What are their thoughts on a new service?
How do they feel about the current trends?
Differences between types of interviews
In focus group research, interviews are used to explore the topic more in-depth. The three kinds of interviews used are: unstructured, semi-structured, and structured. The differences are discussed as follows:
Unstructured interviews are used to establish rapport with the participants. As a result, they often have few questions.
Semi-structured interviews involve the use of a guide throughout the process. This allows the researcher to probe the participant for additional information.
Structured interviews adhere strictly to an interview protocol. As a result, it limits the chance to explore topics further.
Primarily, focus group research uses semi-structured interviews.
- Step 2: Define your research scope and hypotheses
This step is crucial because it defines how the subsequent steps will proceed. A rule of thumb is to be as specific as possible when defining the scope so that the questions you ask your participants from the discussion guide will be adequately answered. When clear scope is set, the focus groups become successful. In addition, by defining the research scope, you know what is expected from the focus group as well as:
Purpose of the focus group research
Types of questions to be asked
Specific information required
The outcome of the information being sought
A research scope helps highlight what will be covered in the focus group. It also helps in giving an estimate of the expenses and time needed to complete the study. To help you define your research scope, here are some preliminary questions that can be helpful.
Why is the research information needed?
Who is interested in the results of the focus group research?
What is the exact topic of interest?
Why does the client need the study to be done?
The next step is to formulate a hypothesis. This is a statement that predicts the outcome of the study and gives a relationship between variables.
When writing a hypothesis , ensure that it satisfies the following characteristics:
Clear and concise
Can be tested
Predicts the results or outcome of the study
Is relevant to the research study
- Step 3: Determine your focus group questions
Questions asked in focus group discussions are crucial in collecting findings. Determining the right questions for the focus group is vital for collecting actionable findings. The questions should have a good questioning route. This means they flow logically and naturally, moving from a general concern to a more specific topic.
There are three categories of questions to ask a focus group. These are:
Engagement questions , which are used to get the participants to feel comfortable
Exploration questions, which are those that focus on the major areas of concern
Exit questions , which bring the discussion session to a close
The question should be appropriately formulated so that accurate responses are collected. In addition, good questions should be natural and conversational. Also, ensure that the questions are:
Unambiguous
Not leading
- Step 4: Select a moderator or co-moderator
A moderator is responsible for leading the group in engaging discussions. A co-moderator is an assistant to the primary facilitator. Moderating a focus group requires adequate skills, expertise, and competency. Therefore, while selecting a moderator, consider one who has the following qualities:
An observer
Uses non-verbal communication cues
Restrains from expressing biased views
Has people skills
Is knowledgeable
- Step 5: Recruit your participants
The next step is to recruit participants. An important step in conducting focus groups is the process of recruiting participants. The most common criterion for selecting participants is choosing individuals with adequate subject knowledge.
Number of participants
Most focus groups have five to 10 members. This is the ideal size for the moderator to manage the group and facilitate effective discussions. The participants of a focus group should be homogeneous. This means that they share common characteristics and behavior. For instance, recruit participants that have the same occupation, gender, age, and family characteristics or have used the service under study in the past.
- Step 6: Set up your focus group
Confirm a time and date
When developing focus group research, the two good rules of thumb are to allow six to eight weeks of preparation time and create a schedule to help the planner stay on track. Make a schedule that is convenient for everyone.
Confirm whether it will take place in person or online
Be sure to inform the participants if the session will occur online or face-to-face. If the discussions are conducted virtually, send out reminders for the online event. In-person discussions will require a location that is accessible to all participants. To ensure high attendance rates, follow the steps outlined below.
Set an appropriate location, date, and time for the discussion.
Make contact with the participants via personal visits or phone calls.
Send a follow-up invitation to the participants. The invitation should have the proposed agenda, time, and date.
Call potential members before the actual date and remind them to attend.
Consent and ethical considerations
All the participants must provide informed consent. This includes being aware of what the focus group is about, the risks of participating, and having the right to withdraw from participating at any time. The stakeholders should also take the necessary measures to protect the participants' confidentiality and privacy.
Preparation prior to participation
Before the set date:
Select a location that is free from noise and can accommodate the members of the groups.
Ensure that the venue has bathrooms and refreshments to make the participants comfortable.
Arrange chairs so that all the participants can see each other.
Set in place an audio or video recorder to record the session.
Ensure that there are name tags for participants to wear.
Create forum brochures with a welcome note, agenda of the discussions, and ground rules.
- Step 7: Host your focus group
Starting the focus group
Focus group discussions should be scheduled to last between 60 to 90 minutes. This ensures that the participants remain active and contribute to the discussion. Before starting the session, the moderator should welcome the members. Also, engaging in small talk will make the process easier for shy participants.
Leading the discussion
After the pre-session, explain the purpose of conducting the discussion by giving an overview of the agenda. Then proceed to ask the predetermined set of questions. While asking questions, the moderator should allocate equal time to each participant to give their responses. Some of the valuable tips to make the discussion successful include the use of the following:
Pauses, including giving participants a chance to add feedback
Probes, ensuring that the answers are explored more. It may include asking follow-up questions such as "Can you tell us more about that?"
Non-verbal communication, including the use of eye contact and hand signals to encourage engagement
During the discussion, the co-moderator can help with note-taking. Once the main tasks of the session have been completed, the moderator can give a closing summary and thank the participants for their time.
- Step 8: Analyze your data and report your results
This last step involves examining, tabulating, and recombining evidence collected during the session. The sources to be analyzed include:
Moderator's notes
Audio tape recordings
Since the collected data is mainly descriptive and not measurable, it has to be converted into forms that can be analyzed. The moderator’s notes will capture the key points that will be analyzed. The audio recordings can be converted into abridged text documents (transcripts).
To gather information from memory, aided recall and directed cues are effective. Data analysis will then involve indexing, managing, and interpreting collected data.
Indexing refers to transcribing the transcripts or notes and assigning unique codes to each. The codes link together pieces of text that represent a similar perspective related to the focus group questions.
Management will involve collecting all pieces of text with the same code.
Interpretation will involve generating a summary statement that applies to each piece of text. These statements become the key themes that will be recorded in the research report.
When the analysis is completed, a report is written and discussed with the top stakeholders of the research study. The written report should include the aim of the study, a description of the methodology used, a summary of results, and recommendations.
- Advantages of focus groups
A focus group is a research method that involves bringing together a small group of people to discuss a particular topic or issue.
Here are some advantages of using a focus group:
In-depth insights
Focus groups allow for a detailed exploration of a particular topic or issue. The group members can provide rich, in-depth insights into their experiences, opinions, and attitudes related to the topic being discussed.
Interactive discussion
A focus group encourages an interactive discussion among the group members. Participants can bounce ideas off each other, challenge each other's opinions, and explore different perspectives. This can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the topic being discussed.
Group dynamics
Group dynamics can provide valuable information about how people interact with each other and how they form opinions. For example, a focus group can reveal how group members influence each other's opinions or how certain individuals dominate the conversation.
Flexibility
Focus groups are a flexible research method that can be adapted to different research objectives. For example, focus groups can be used to explore new ideas, test product concepts, or evaluate advertising campaigns.
Cost-effective
Compared to other research methods, focus groups can be a cost-effective way to gather data from multiple participants. This is because data can be collected from a group of people at once rather than individually.
Focus groups can quickly generate data, especially when compared to more traditional research methods such as surveys or experiments. This can be especially useful when time is of the essence, such as when evaluating a new product or service.
- Disadvantages of focus groups
The following are some disadvantages of using focus groups.
Limited sample size
Focus groups typically involve few participants, meaning the findings may not be generalized to the broader population.
Moderator bias
Moderator bias affects the outcome of the results. Facilitators may inject explicit bias or allocate unequal response times to the participants. For example, the moderator may force participants to answer questions in a certain way. This significantly impacts the outcome of the research.
Time-consuming
Conducting focus groups can be time-consuming and expensive, particularly if they involve recruiting participants, paying incentives, and renting a space for the session.
The group dynamics can also impact the quality of the data collected. Some participants may be more dominant and vocal, while others may be quieter or reluctant to share their opinions.
Biased responses
Group thinking may influence the opinions of participants. For instance, participants may agree with the responses of fellow group members and avoid sharing their honest views. In addition, desirability bias is common. Participants may also be influenced by social desirability bias, which can lead them to provide responses that they believe are more socially acceptable rather than their true opinions.
Sensitive topics
Sensitive topics may be avoided. Some participants may be uncomfortable discussing sensitive issues that may concern the public.
Difficulty in analyzing data
Analyzing focus group data can be challenging, as the data can be subjective and open to interpretation. Additionally, the data may be difficult to quantify or summarize meaningfully.
Why is a focus group the best method?
Focus groups allow the researcher to gather in-depth information on a specific topic from all participants at once.
Is the focus group quantitative or qualitative?
Focus groups are a qualitative data collection technique since collected results are mostly descriptive rather than statistical and measurable.
What is the sample size in the focus group?
The sample size is defined as the total number of participants in the research study. The ideal sample size for a focus group is six to ten participants.
What type of data collection is a focus group?
A focus group is a qualitative data collection technique in which the researcher learns and understands people's motivations for certain actions.
How do you find people for a focus group?
Several ways to recruit participants in focus groups to include nominations, convenience sampling, random selection, or open calls. Online forums, social media, and social media interest groups can be a source to recruit participants. Consider also discussion boards and professional networks. Last but not least, you can use the services of a recruitment agency which will arrange a sample of representative participants.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Communities
Focus group: What It Is & How to Conduct It + Examples

In 1991, marketing and psychological expert Ernest Dichter coined the name “Focus Group.” The term described meetings held with a limited group of participants with the objective of discussion.
The group’s purpose is not to arrive at a consensus or agreement on the topic. Instead, it seeks to identify and understand customer perceptions of a brand, product, or service.
We’ll cover what a focus group is, how to conduct one, and example questions and best practices below.
What is a focus group?
A focus group is best defined as a small group of carefully selected participants who contribute to open discussions for research. The hosting organization carefully selects participants for the study to represent the larger population they’re attempting to target.
The group might look at new products, feature updates, or other topics of interest to generalize the entire population’s reaction. This research includes a moderator. Their job is to ensure legitimate results and reduce bias in the discussions.
- You use a focus group in qualitative research . A group of 6-10 people, usually 8, meet to explore and discuss a topic, such as a new product. The group shares their feedback, opinions, knowledge, and insights about the topic at hand.
- Participants openly share opinions and are free to convince other participants of their ideas.
- The mediator takes notes on the discussion and opinions of group members.
- The right group members affect the results of your research, so it’s vital to be picky when selecting members.
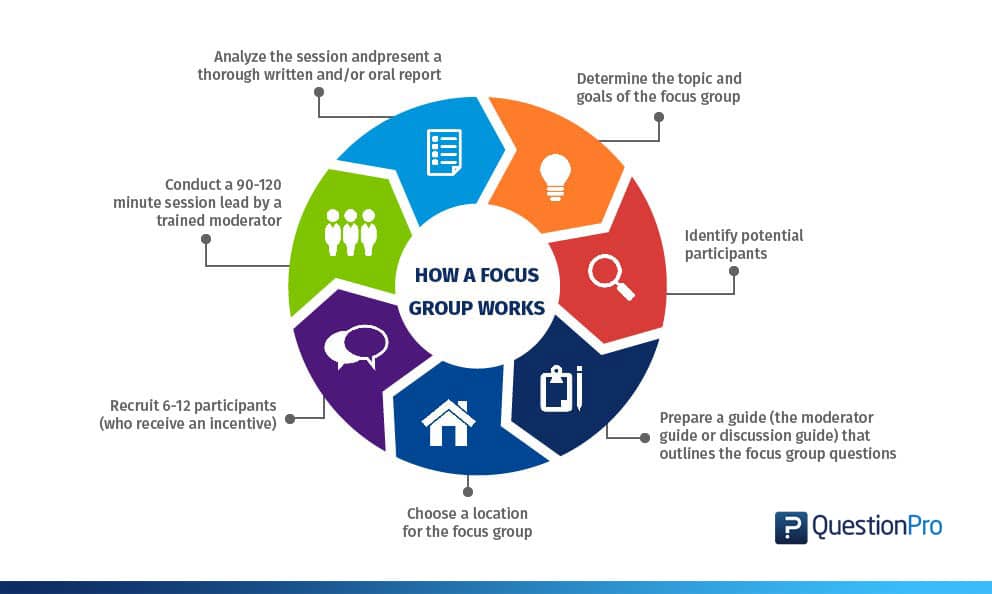
These groups possess a distinct advantage over other market research and market research methods. They capitalize on the moderator’s communication with participants and the flexibility to move the discussion. It allows you to extract meaningful insights and opinions.
Explore our latest article delving into real-world examples of qualitative data in education . Why not take a look and gather more insights from the valuable information we’ve shared?
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
Main pillars of a focus group
Participant, the role of a moderator, types of focus groups.
Your choice of focus group depends on the needs of your action research . Types include:
- Dual moderator: There are two moderators for this event. One ensures smooth execution, and the other guarantees the discussion of each question.
- Two-way: A two-way group involves two separate groups having discussions on the topic at different times. As one group conducts its study, the other group observes the discussion. In the end, the group that observed the first session performed their conversation. The second group can use insights gained from watching the first discussion to dive deeper into the topic and offer more perspective.
- Mini: This type of small group restricts participants to 4-5 members instead of the usual 6-10.
- Client-involvement: Use this group when clients ask you to conduct a focus group and invite those who ask.
- Participant-moderated: One or more participants provisionally take up the role of moderator.
- Online: These groups employ online mediums to gather opinions and feedback. There are three categories of people in an online panel : observer, moderator, and respondent.
How to conduct a focus group
A focus group is a research method or technique that is used to collect opinions and ideas regarding a concept, service, or product. Follow the below steps to conduct it:

- Recruit the right participants
A researcher must be careful while recruiting participants. Members need adequate knowledge of the topic so that they can add to the conversation.
- Choose a moderator
Your moderator should understand the topic of discussion and possess the following qualities:
- Ensures participation from all members of the group.
- Regulates dominant group members so others may speak.
- Motivates inattentive members through supportive words and positive body language.
- Makes the executive decision to end or continue a discussion should it become too heated.
Verify your moderator doesn’t know any of the participants. Existing relationships between a member and moderator cause bias and can skew your data.
- Record the meeting for future purposes
While conducting a focus group, recording the sessions or meetings is essential. A researcher can record the discussion through audio or video. You must let participants know you’re planning to record the event and get their consent.
- Write clear discussion guidelines
Before the session starts, writing down clear session guidelines is crucial. Include key questions, expectations of focus group members, whether you’re recording the discussion, and methods of sharing results. Give out the instructions in advance and request participants to comply with them.
- Conduct the session and generate a report
Once participants understand their role, the moderator leads the survey. You can ask members to fill out a feedback form to collect quantitative data from the event. Use your data collection and generate reports on the overall findings of your study.
- Use the data to make a plan of action
Share your report with stakeholders and decision-makers in your organization. According to the focus group feedback, a good report helps you design actionable plans to improve products or services. Update the group members on the changes you make and the results of those changes.
Focus Group Examples
Focus groups are common in three situations:
- Initial stages of a research study
- While creating a plan of action during research
- After the completion of the study to establish the results
For example, a laptop company needs customer feedback about an upcoming product. Focus group provides direct information about the marketing research from actual consumers.
The company chooses eight individuals representing their target market for a constructive discussion. The moderator asks questions regarding customer preference for laptop size and features. Group members discuss why they do or do not like certain aspects of a laptop. The company uses the opinions of the participants to create a product that fits customer needs and wants
Best practices for focus group research
Follow these five steps to create a market research focus group:
Have a clear plan for focus group members
With a plan in place, begin writing your focus group survey questions, schedule the time, place, and duration of the discussion, you can host it in person or through an online community, create informational brochures or forum, focus group advantages and disadvantages.
Focus group is a well-liked research technique due to its simple setup and the insightful data it can yield. It has advantages and disadvantages much, like other research techniques.
- A great complement to other mediums like online surveys and online polls . Focus groups give you access to why a customer feels a certain way about a product, and surveys help you collect supporting feedback in large batches.
- Immediate access to customer opinions, making data collection and analysis quick and convenient.
- Highly flexible to adapt to the needs and opinions of the group members.
- Easy to conduct regular discussions to eliminate inaccurate results due to current market outlooks.
- Focus groups are perfect sources to understand the true feelings and perceptions of your selected target audience.
Disadvantages
- Creating a representative sample is tough. Small-size sample makes focus groups unreliable.
- Due to the limited sample size, you cannot guarantee respondent anonymity, which may affect their willingness to speak freely.
- Getting honest opinions on sensitive topics can make the depth of analysis difficult.
- Data analysis is vulnerable to inaccuracy and observer research bias .
Focus group question examples
When using a focus group in market research , you must ask the right questions for accurate results. Good group questions have the following characteristics:
- A friendly and conversational tone
- Language or phrases that resonate with focus group participants
- Straightforward and accurate
- Each item includes one aspect and doesn’t merge multiple topics
- Clarify complex questions for more precise answers
Avoid asking questions to specific individuals to ensure the inclusion of all participants. Restrict discussion time per question to 5-20 minutes to keep the conversation efficient.
There are four categories:
1. Pr imary question: This first open-ended question initiates the entire discussion.
- We are here to discuss ____. What are your thoughts about it?
2. Probe questions: These questions dig deeper into the discussion of the primary question.
For example:
- What do you know about ____?
- How familiar are you with this organizational program?
- What do you love about our organization?
3. Questions to follow up : After establishing the overall knowledge and feelings of the group, the moderator identifies specific insights.
- What do you think are the pros and cons of this product?
- According to you, where can we improve to provide better customer service?
- Which factors prompted you to purchase our products/services?
- What is the likelihood of recommending our products to your friends and colleagues?
4. Questions for the conclusion: Review previous questions to avoid overlooking the main points. It is the time when a moderator can revisit specific topics to gather more data.
For example :
- Is there anything other than the already discussed questions you would like to talk about?
- Do you want to add to what is already spoken about?
Focus group questions to recruit participants
Here are some questions you may ask to recruit participants:
- Do you or any of your family members work in any of the following sectors?

- Select your age range:
- Kindly select your employment type:

- Please specify your level of education:

- Please state your family status:

Our focus group recruitment questionnaire template gives you a range of survey question types for maximum responses. These responses also help you make the best choice in recruiting the appropriate group members.
Best Online Focus Group Software: QuestionPro Communities
Online focus groups remove the need for a physical location. Like in-person groups, online groups involve 6-10 participants who share their opinions. Many researchers prefer online focus groups for convenience and cost-effectiveness.
QuestionPro Communities is an online focus group software . It’s a highly-effective market research tool that helps researchers find online focus groups for their research purposes, including market research.
QuestionPro Communities software includes:
- Discussions : Organizations invite participants to a moderated online discussion forum. Participants may answer questions at any time suitable to them.
- Idea Board : Idea Board allows respondents to share their ideas. Other group members can analyze, write feedback, and even vote on submissions.
- Topics : Users can submit topics, cast their votes in existing posts, and leave comments or feedback instantly.

Organizations can ensure that they gather the most valuable insights from their focus groups by carefully planning, recruiting, and conducting the sessions. The examples provided highlight the versatility of focus groups, highlighting the wide range of applications for this research method.
Organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their customers and make more informed decisions that drive success by leveraging the power of focus groups.
QuestionPro Communities is the only online focus group software available on desktop and mobile. Go mobile and take Discussions, Idea Board, and Topics anywhere your respondents go.
Start conducting online focus group surveys with participants from across the globe with QuestionPro Communities today.
Collect community feedback through our insights community software!
More like this.

When You Have Something Important to Say, You want to Shout it From the Rooftops
Jun 28, 2024

The Item I Failed to Leave Behind — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 25, 2024

Feedback Loop: What It Is, Types & How It Works?
Jun 21, 2024

QuestionPro Thrive: A Space to Visualize & Share the Future of Technology
Jun 18, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Focus group research
- Nursing standard: official newspaper of the Royal College of Nursing 29(37):44-8
- 29(37):44-8

- Independent Scholar and writer
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Brent Oliver
- Ken LaPointe
- Vincenzo Sabella

- Sabine Bohnet-Joschko
- Eirini Bathrellou

- Breanna Crane
- Janiece L. Taylor

- Nathalie Thilly
- EUR J ONCOL NURS

- Laetitia Gimenez
- Délia Bonis
- Mathilde Morel

- Azin Alipour Tabrizi
- BASIC CLIN PHARMACOL

- Mocquard Julie

- BMC PUBLIC HEALTH

- Anne-Marie Thow

- Nurs Stand Spec Suppl

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Open access
- Published: 28 June 2024
Perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies in nursing education: a mixed methods study
- Basma Mohammed Al Yazeedi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2327-6918 1 ,
- Lina Mohamed Wali Shakman 1 ,
- Sheeba Elizabeth John Sunderraj ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9171-7239 1 ,
- Harshita Prabhakaran ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5470-7066 1 ,
- Judie Arulappan 1 ,
- Erna Judith Roach ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5817-8886 1 ,
- Aysha Al Hashmi 1 , 2 &
- Zeinab Al Azri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3376-9380 1
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 441 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
24 Accesses
Metrics details
Case analysis is a dynamic and interactive teaching and learning strategy that improves critical thinking and problem-solving skills. However, there is limited evidence about its efficacy as an assessment strategy in nursing education.
This study aimed to explore nursing students’ perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies in nursing education.
This study used a mixed methods design. Students filled out a 13-item study-advised questionnaire, and qualitative data from the four focus groups was collected. The setting of the study was the College of Nursing at Sultan Qaboos University, Oman. Descriptive and independent t-test analysis was used for the quantitative data, and the framework analysis method was used for the qualitative data.
The descriptive analysis of 67 participants showed that the mean value of the perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method was 3.20 (SD = 0.53), demonstrating an 80% agreement rate. Further analysis indicated that 78.5% of the students concurred with the acceptability of case analysis as an assessment method (mean = 3.14, SD = 0.58), and 80.3% assented its association with clinical competencies as reflected by knowledge and cognitive skills (m = 3.21, SD = 0.60). No significant difference in the perceived efficacy between students with lower and higher GPAs (t [61] = 0.05, p > 0.05) was identified Three qualitative findings were discerned: case analysis is a preferred assessment method for students when compared to MCQs, case analysis assesses students’ knowledge, and case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills.
Conclusions
This study adds a potential for the case analysis to be acceptable and relevant to the clinical competencies when used as an assessment method. Future research is needed to validate the effectiveness of case analysis exams in other nursing clinical courses and examine their effects on academic and clinical performance.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Nurses play a critical role in preserving human health by upholding core competencies [ 1 ]. Clinical competence in nursing involves a constant process of acquiring knowledge, values, attitudes, and abilities to deliver safe and high-quality care [ 2 , 3 ]. Nurses possessing such competencies can analyze and judge complicated problems, including those involving crucial patient care, ethical decision-making, and nurse-patient disputes, meeting the constantly altering health needs [ 4 , 5 ]. To optimize the readiness of the new graduates for the challenging clinical work environment needs, nurse leaders call for integrating clinical competencies into the nursing curriculum [ 6 , 7 ] In 2021, the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN) released updated core competencies for professional nursing education [ 8 ]. These competencies were classified into ten fundamental essentials, including knowledge of nursing practice and person-centered care (e.g. integrate assessment skills in practice, diagnose actual or potential health problems and needs, develop a plan of care), representing clinical core competencies.
Nursing programs emphasize clinical competencies through innovative and effective teaching strategies, including case-based teaching (CBT) [ 9 ]. CBT is a dynamic teaching method that enhances the focus on learning goals and increases the chances of the instructor and students actively participating in teaching and learning [ 10 , 11 ]. Additionally, it improves the students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills and enriches their capacity for independent study, cooperation capacity, and communication skills [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. It also broadens students’ perspectives and helps develop greater creativity in fusing theory and practice [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. As the learning environment significantly impacts the students’ satisfaction, case analysis fosters a supportive learning atmosphere and encourages active participation in learning, ultimately improving their satisfaction [ 21 , 22 ].
In addition to proper teaching strategies for clinical competencies, programs are anticipated to evaluate the students’ attainment of such competencies through effective evaluation strategies [ 23 ]. However, deploying objective assessment methods for the competencies remains challenging for most educators [ 24 ]. The standard assessment methods used in clinical nursing courses, for instance, include clinical evaluations (direct observation), skills checklists, Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE), and multiple-choice questions (MCQs) written exams [ 25 ]. MCQs tend to test the recall of factual information rather than the application of knowledge and cognitive skills, potentially leading to assessment inaccuracies [ 26 ].
Given the aforementioned outcomes of CBT, the deployment of case analysis as a clinical written exam is more closely aligned with the course’s expected competencies. A mixed methods study was conducted among forty nursing students at the University of Southern Taiwan study concluded that the unfolding case studies create a safe setting where nursing students can learn and apply their knowledge to safe patient care [ 6 ]. In a case analysis, the patient’s sickness emerges in stages including the signs and symptoms of the disease, urgent care to stabilize the patient, and bedside care to enhance recovery. Thus, unfolding the case with several scenarios helps educators track students’ attained competencies [ 27 ]. However, case analysis as an assessment method is sparsely researched [ 28 ]. A literature review over the past five years yielded no studies investigating case analysis as an assessment method, necessitating new evidence. There remains uncertainty regarding its efficacy as an assessment method, particularly from the students’ perspectives [ 29 ]. In this study, we explored the undergraduate nursing students’ perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies. Results from this study will elucidate the position of case analysis as an assessment method in nursing education. The potential benefits are improved standardization of clinical assessment and the ability to efficiently evaluate a broad range of competencies.
Research design
Mixed-method research with a convergent parallel design was adopted in the study. This approach intends to converge two data types (quantitative and qualitative) at the interpretation stage to ensure an inclusive research problem analysis [ 30 ]. The quantitative aspect of the study was implemented through a cross-sectional survey. The survey captured the perceived efficacy of using case analysis as an assessment method in clinical nursing education. The qualitative part of the study was carried out through a descriptive qualitative method using focus groups to provide an in-depth understanding of the perceived strengths experienced by the students.
Study setting
Data were collected in the College of Nursing at Sultan Qaboos University (SQU), Oman, during the Spring and Fall semesters of 2023. At the end of each clinical course, the students have a clinical written exam and a clinical practical exam, which constitute their final exam. Most clinical courses use multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in their written exam. However, the child health clinical course team initiated the case analysis as an assessment method in the clinical written exam, replacing the MCQs format.
Participants
For this study, the investigators invited undergraduate students enrolled in the child health nursing clinical course in the Spring and Fall semesters of 2023. Currently, the only course that uses case analysis is child health. Other courses use MCQs. A total enumeration sampling technique was adopted. All the students enrolled in child health nursing clinical courses in the Spring and Fall 2023 semesters were invited to participate in the study. In the Spring, 36 students registered for the course, while 55 students were enrolled in the Fall. We included students who completed the case analysis as a final clinical written exam on the scheduled exam time. Students who did not show up for the exam during the scheduled time and students not enrolled in the course during the Spring and Fall of 2023 were excluded. Although different cases were used each semester, both had the same structure and level of complexity. Further, both cases were peer-reviewed.
Case analysis format
The format presents open-ended questions related to a clinical case scenario. It comprises three main sections: Knowledge, Emergency Room, and Ward. The questions in the sections varied in difficulty based on Bloom’s cognitive taxonomy levels, as presented in Table 1 . An answer key was generated to ensure consistency among course team members when correcting the exam. Three experts in child health nursing peer-reviewed both the case analysis exam paper and the answer key paper. The students were allocated two hours to complete the exam.
Study instruments
Quantitative stage.
The researchers developed a study questionnaire to meet the study objectives. It included two parts. The first was about the demographic data, including age, gender, type of residence, year in the program, and cumulative grade point average (GPA). The second part comprised a 13-item questionnaire assessing the perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method. The perceived efficacy was represented by the acceptability of case analysis as an assessment method (Items 1–5 and 13) and the association with clinical competencies (Items 6 to 12). Acceptability involved format organization and clarity, time adequacy, alignment with course objectives, appropriateness to students’ level, and recommendation for implementation in other clinical nursing courses. Clinical competencies-related items were relevant to knowledge (motivation to prepare well for the exam, active learning, interest in topics, collaboration while studying) and cognitive skills (critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills) (The questionnaire is attached as a supplementary document).
The questionnaire is answered on a 4-point Likert scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = agree, 4 = strongly agree. Higher scores indicated better perceived efficacy and vice versa. The tool underwent content validity testing with five experts in nursing clinical education, resulting in an item-content validity index ranging from 0.7 to 1. The Cronbach alpha was 0.83 for acceptability and 0.90 for clinical competencies.
Qualitative stage
For the focus group interviews, the investigators created a semi-structured interview guide to obtain an in-depth understanding of the students’ perceived strengths of case analysis as an assessment method. See Table 2 .
Data collection
Data was collected from the students after they gave their written informed consent. Students were invited to fill out the study questionnaire after they completed the case analysis as a clinical written exam.
All students in the child health course were invited to participate in focus group discussions. Students who approached the PI to participate in the focus group discussion were offered to participate in four different time slots. So, the students chose their time preferences. Four focus groups were conducted in private rooms at the College of Nursing. Two trained and bilingual interviewers attended the focus groups, one as a moderator while the other took notes on the group dynamics and non-verbal communication. The discussion duration ranged between 30 and 60 min. After each discussion, the moderator transcribed the audio recording. The transcriptions were rechecked against the audio recording for accuracy. Later, the transcriptions were translated into English by bilingual researchers fluent in Arabic and English for the analysis.
Rigor and trustworthiness
The rigor and trustworthiness of the qualitative method were enhanced using multiple techniques. Firstly, quantitative data, literature reviews, and focus groups were triangulated. Participants validated the summary after each discussion using member checking to ensure the moderator’s understanding was accurate. Third, the principal investigator (PI) reflected on her assumptions, experiences, expectations, and feelings weekly. In addition, the PI maintained a detailed audit trail of study details and progress. The nursing faculty conducted the study with experience in qualitative research and nursing education. This report was prepared following the Standard for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) protocol [ 31 ].
Data analysis
Quantitative data were entered in SPSS version 24 and analyzed using simple descriptive analysis using means, standard deviations, and percentages. After computing the means of each questionnaire item, an average of the means was calculated to identify the perceived efficacy rate. A similar technique was used to calculate the rate of acceptability and clinical competencies. The percentage was calculated based on the mean: gained score/total score* 100. In addition, the investigators carried out an independent t-test to determine the relationship between the perceived efficacy and students’ GPA.
The qualitative data were analyzed using the framework analysis method. In our analysis, we followed the seven interconnected stages of framework analysis: (1) transcription, (2) familiarization with the interview, (3) coding, (4) developing a working analytical framework, (5) applying the analytical framework, (6) charting data into framework matrix and (7) interpreting the data [ 32 ]. Two members of the team separately analyzed the transcriptions. Then, they discussed the coding, and discrepancies were solved with discussion.
Mixed method integration
In our study, the quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed separately, and integration occurred at the interpretation level by merging the data [ 33 ]. As a measure of integration between qualitative and quantitative data, findings were assessed through confirmation, expansion, and discordance. If both data sets confirmed each other’s findings, it was considered confirmation, and if they expanded each other’s insight, it was considered expansion. Discordance was determined if the findings were contradictory.
Ethical considerations
Ethical approval was obtained from the Research and Ethics Committee of the College of Nursing, SQU (CON/NF/2023/18). Informed consent was collected, and no identifiable information was reported. For the focus group interviews, students were reassured that their grades were finalized, and their participation would not affect their grades. Also, the interviewers were instructed to maintain a non-judgmental and non-biased position during the interview. Data were saved in a locked cabinet inside a locked office room. The electronic data were saved in a password-protected computer.
The results section will present findings from the study’s quantitative and qualitative components. The integration of the two data types is described after each qualitative finding.
Quantitative findings
We analyzed the data of 67 participants, representing a 73.6% response rate. The mean age was 21.0 years old (SD 0.73) and 36.4% were male students. See Table 3 for more details.
The descriptive analysis showed that the mean value of the perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method was 3.20 (SD = 0.53), demonstrating an 80% agreement rate. Further analysis indicated that 78.5% of the students concurred the acceptability of case analysis as an assessment method (mean = 3.14, SD = 0.58) and 80.3% (m = 3.21, SD = 0.60) assented the clinical competencies associated with it.
For the items representing acceptability, 81.8% of the students agreed that the case analysis was written clearly, and 80.3% reported that it was well organized. As per the questions, 81% described they were appropriate to their level, and 79.8% agreed upon their alignment with the course objectives. Moreover, the time allocated was adequate for 74.5% of the students, and 73.5% recommend using case analysis as an evaluation strategy for other clinical written examinations.
Regarding the clinical competencies, 77.3% of students agreed that the case analysis motivated them to prepare well for the exam, 81.3% reported that it encouraged them to be active in learning, and 81.0% indicated that it stimulated their interest in the topics discussed in the course. Additionally, 76.5% of the students agreed that the case analysis encouraged them to collaborate with other students when studying for the exam. Among the students, 82.5% reported that the case analysis as an assessment method enhanced their critical thinking skills, 81.0% agreed that it helped them practice decision-making skills, and 81.8% indicated that it improved their problem-solving abilities. See Table 4 .
The independent t-test analysis revealed no significant difference in the perceived efficacy between students with lower and higher GPAs (t [61] = 0.05, p > 0.05). Further analysis showed that the means of acceptability and clinical competencies were not significantly different between the lower GPA group and higher GPA group, t [62] = 0.72, p > 0.05 and t [63] = -0.83, p > 0.05, respectively (Table 5 ).
Qualitative findings
A total of 22 had participated in four focus groups, each group had 5–6 students. The qualitative framework analysis revealed three main findings; case analysis is a preferred assessment method to students when compared to MCQs, case analysis assesses students’ knowledge, and case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills.
Qualitative Finding 1: case analysis is a preferred assessment method to students when compared to MCQs
Most of the students’ statements about the case analysis as an assessment method were positive. One student stated, “Previously, we have MCQs in clinical exams, but they look as if they are theory exams. This exam makes me deal with cases like a patient, which is good for clinical courses.” . At the same time, many students conveyed optimism about obtaining better grades with this exam format. A student stated, “Our grades, with case analysis format, will be better, … may be because we can write more in open-ended questions, so we can get some marks, in contrast to MCQs where we may get it right or wrong” . On the other hand, a few students suggested adding multiple-choice questions, deleting the emergency department section, and lessening the number of care plans in the ward section to secure better grades.
Although the case analysis was generally acceptable to students, they have repeatedly expressed a need to allocate more time for this type of exam. A student stated, “The limited time with the type of questions was a problem, …” . When further discussion was prompted to understand this challenge, we figured that students are not used to handwriting, which has caused them to be exhausted during the exam. An example is “writing is time-consuming and energy consuming in contrast to MCQs …” . These statements elucidate that the students don’t necessarily mind writing but recommend more practice as one student stated, “More experience of this type of examination is required, more examples during clinical practice are needed.” Some even recommended adopting this format with other clinical course exams by saying “It’s better to start this method from the first year for the new cohort and to apply it in all other courses.”
Mixed Methods Inference 1: Confirmation and Expansion
The abovementioned qualitative impression supports the high acceptability rate in quantitative analysis. In fact, there is a general agreement that the case analysis format surpasses the MCQs when it comes to the proper evaluation strategies for clinical courses. Expressions in the qualitative data revealed more details, such as the limited opportunities to practice handwriting, which negatively impacted the perceived adequacy of exam time.
Qualitative Finding 2: case analysis assesses students’ knowledge
Students conferred that they were reading more about the disease pathophysiology, lab values, and nursing care plans, which they did not usually do with traditional means of examination. Examples of statements include “… before we were not paying attention to the normal lab results but …in this exam, we went back and studied them which was good for our knowledge” and “we cared about the care plan. In previous exams, we were not bothered by these care plans”. Regarding the burden that could be perceived with this type of preparation, the students expressed that this has helped them prepare for the theory course exam; as one student said, “We also focus on theory lectures to prepare for this exam …. this was very helpful to prepare us for the theory final exam as well.” However, others have highlighted the risks of limiting the exam’s content to one case analysis. The argument was that some students may have not studied the case completely or been adequately exposed to the case in the clinical setting. To solve this risk, the students themselves advocated for frequent case group discussions in the clinical setting as stated by one student: “There could be some differences in the cases that we see during our clinical posting, for that I recommend that instructors allocate some time to gather all the students and discuss different cases.” Also, the participants advocated for more paper-based case analysis exercises as it is helpful to prepare them for the exams and enhance their knowledge and skills.
Mixed Methods Inferences 2: Confirmation and Expansion
The qualitative finding supports the quantitative data relevant to items 6, 7, and 8. Students’ expressions revealed more insights, including the acquisition of deeper knowledge, practicing concept mapping, and readiness for other course-related exams. At the same time, students recommended that faculty ensure all students’ exposure to common cases in the clinical setting for fair exam preparation.
Qualitative Finding 3. case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills
Several statements conveyed how the case analysis format helped the students use their critical thinking and analysis skills. One student stated, “It, the case analysis format, enhanced our critical thinking skills as there is a case with given data and we analyze the case….” . Therefore, the case analysis format as an exam is potentially a valid means to assess the student’s critical thinking skills. Students also conveyed that the case analysis format helped them link theory to practice and provided them with the platform to think like real nurses and be professional. Examples of statements are: “…we connect our knowledge gained from theory with the clinical experience to get the answers…” and “The questions were about managing a case, which is what actual nurses are doing daily.” Another interesting cognitive benefit to case analysis described by the students was holistic thinking. For example, one student said, “Case analysis format helped us to see the case as a whole and not only from one perspective.”
Mixed Methods Inferences 3: Confirmation
The quantitative data indicated mutual agreement among the students that the case analysis enhanced their critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. The students’ statements from the interviews, including critical thinking, linking theory to practice, and holistic thinking, further supported these presumptions.
This research presents the findings from a mixed methods study that explored undergraduate nursing students’ perceived efficacy of using case analysis as an assessment method. The perceived efficacy was reflected through acceptability and association with two core competencies: knowledge and cognitive skills. The study findings showed a high rate of perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method among nursing students. Additionally, three findings were extracted from the qualitative data that further confirmed the perceived efficacy: (1) case analysis is a preferred assessment method to students compared to MCQs, (2) case analysis assesses students’ knowledge, and (3) case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills. Moreover, the qualitative findings revealed details that expanded the understanding of the perceived efficacy among nursing students.
Previous literature reported students’ preference for case analysis as a teaching method. A randomized controlled study investigated student’s satisfaction levels with case-based teaching, in addition to comparing certain outcomes between a traditional teaching group and a case-based teaching group. They reported that most students favored the use of case-based teaching, whom at the same time had significantly better OSCE scores compared to the other group [ 34 ]. As noted, this favorable teaching method ultimately resulted in better learning outcomes and academic performance. Although it may be challenging since no answer options are provided, students appreciate the use of case analysis format in their exams because it aligns better with the course objectives and expected clinical competencies. The reason behind students’ preference for case analysis is that it allows them to interact with the teaching content and visualize the problem, leading to a better understanding. When case analysis is used as an assessment method, students can connect the case scenario presented in the exam to their clinical training, making it more relevant.
In this study, students recognized the incorporation of nursing knowledge in the case analysis exam. They also acknowledged improved knowledge and learning abilities similar to those observed in case-based teaching. Boney et al. (2015) reported that students perceived increased learning gains and a better ability to identify links between different concepts and other aspects of life through case-based teaching [ 35 ]. Additionally, case analysis as an exam promotes students’ in-depth acquirement of knowledge through the type of preparation it entails. Literature suggested that case-based teaching promotes self-directed learning with high autonomous learning ability [ 34 , 36 ]. Thus, better achievement in the case analysis exam could be linked with a higher level of knowledge, making it a suitable assessment method for knowledge integration in nursing care.
The findings of this study suggest that case analysis can be a useful tool for evaluating students’ cognitive skills, such as critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving. A randomized controlled study implied better problem-solving abilities among the students in the case-based learning group compared to those in the traditional teaching methods group [ 12 ]. Moreover, students in our study conveyed that case analysis as an exam was an opportunity for them to think like real nurses. Similar to our findings, a qualitative study on undergraduate nutrition students found that case-based learning helped students develop professional competencies for their future practice, in addition to higher-level cognitive skills [ 37 ]. Therefore, testing students through case analysis allows educators to assess the student’s readiness for entry-level professional competencies, including the thinking process. Also, to evaluate students’ high-level cognitive skills according to Bloom’s taxonomy (analysis, synthesis, and evaluation), which educators often find challenging.
Case analysis as an assessment method for clinical courses is partially integrated in case presentation or OSCE evaluation methods. However, the written format is considered to be more beneficial for both assessment and learning processes. A qualitative study was conducted to examine the impact of paper-based case learning versus video-based case learning on clinical decision-making skills among midwifery students. The study revealed that students paid more attention and were able to focus better on the details when the case was presented in a paper format [ 38 ]. Concurrently, the students in our study recommended more paper-based exercises, which they believed would improve their academic performance.
This study has possible limitations. The sample size was small due to the limited experience of case analysis as a clinical written exam in the program. Future studies with larger sample sizes and diverse nursing courses are needed for better generalizability.
Implications
Little evidence relates to the efficacy of case analysis as an evaluation method, suggesting the novelty of this study. Despite the scarcity of case-based assessment studies, a reader can speculate from this study’s findings that there is a potential efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method in nursing education. Future research is warranted to validate the effectiveness of case-analysis assessment methods and investigate the effects of case-analysis exams on academic and clinical performance.
Overall, our findings are in accordance with the evidence suggesting students’ perceived efficacy of case analysis as a teaching method. This study adds a potential for the case analysis to be acceptable and relevant to the clinical competencies when used as an assessment method. Future research is needed to validate the effectiveness of case analysis exams in other nursing clinical courses and examine their effects on academic and clinical performance.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available fromthe Principal Investigator (BAY) upon reasonable request.
Iriarte-Roteta A, Lopez‐Dicastillo O, Mujika A, Ruiz‐Zaldibar C, Hernantes N, Bermejo‐Martins E, Pumar‐Méndez MJ. Nurses’ role in health promotion and prevention: a critical interpretive synthesis. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(21–22):3937–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15441
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fukada M. Nursing competency: definition, structure and development. Yonago Acta Med. 2018;61(1):001–7. https://doi.org/10.33160/yam.2018.03.001
Article Google Scholar
Nabizadeh-Gharghozar Z, Alavi NM, Ajorpaz NM. Clinical competence in nursing: a hybrid concept analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;97:104728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104728
Allande-Cussó R, Fernández-García E, Porcel-Gálvez AM. Defining and characterising the nurse–patient relationship: a concept analysis. Nurs Ethics. 2021;29(2):462–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/09697330211046651
Butts JB, Rich KL. Nursing ethics: across the curriculum and into practice. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019.
Chen W, Shah UV, Brechtelsbauer C. A framework for hands-on learning in chemical engineering education—training students with the end goal in mind. Educ Chem Eng. 2019;28:25–9.
Willman A, Bjuresäter K, Nilsson J. Newly graduated registered nurses’ self-assessed clinical competence and their need for further training. Nurs Open. 2020;7(3):720–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.443
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. (2021). The essentials: Core competencies for professional nursing education. In. Retrieved from n.d.). American Association of Colleges of Nursing. https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/0/PDFs/Publications/Essentials-2021.pdf
Kaur G, Rehncy J, Kahal KS, Singh J, Sharma V, Matreja PS, Grewal H. Case-based learning as an effective tool in teaching pharmacology to undergraduate medical students in a large group setting. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520920640.
Patiraki E, Katsaragakis S, Dreliozi A, Prezerakos P. Nursing care plans based on NANDA, nursing interventions classification, and nursing outcomes classification: the investigation of the effectiveness of an educational intervention in Greece. Int J Nurs Knowl. 2017;28:88–93.
Cui C, Li Y, Geng D, Zhang H, Jin C. The effectiveness of evidence-based nursing on development of nursing students ‘critical thinking: a meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;65:46–53.
Bi M, Zhao Z, Yang J, Wang Y. Comparison of case-based learning and traditional method in teaching postgraduate students of medical oncology. Med Teach. 2019;41(10):1124–8.
Seshan V, Matua GA, Raghavan D, Arulappan J, Al Hashmi I, Roach EJ, Prince EJ. Case study analysis as an effective teaching strategy: perceptions of undergraduate nursing students from a Middle Eastern Country. SAGE Open Nurs. 2021;7:23779608211059265.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Slieman TA, Camarata T. Case-based group learning using concept maps to achieve multiple educational objectives and behavioral outcomes. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519872510.
Yu Z, Hu R, Ling S, Zhuang J, Chen Y, Chen M, Lin Y. Effects of blended versus offline case-centered learning on the academic performance and critical thinking ability of undergraduate nursing students: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Nurse Educ Pract. 2021;53:103080.
Chan AW, Chair SY, Sit JW, Wong EM, Lee DT, Fung OW. Case-based web learning versus face-to-face learning: a mixed-method study on university nursing students. J Nurs Res. 2016;24(1):31–40.
Hong S, Yu P. Comparison of the effectiveness of two styles of case-based learning implemented in lectures for developing nursing students’ critical thinking ability: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;68:16–24.
Shohani M, Bastami M, Gheshlaghi LA, Nasrollahi A. Nursing student’s satisfaction with two methods of CBL and lecture-based learning. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):1–5.
Tan KW. Using Teaching Cases for Achieving Bloom’s High-Order Cognitive Levels: An Application in Technically-Oriented Information Systems Course (2017). 2017 Proceedings. 1. http://aisel.aisnet.org/siged2017/1
Farashahi M, Tajeddin M. Effectiveness of teaching methods in business education: a comparison study on the learning outcomes of lectures, case studies and simulations. Int J Manage Educ. 2018;16(1):131–42.
Google Scholar
Farha RJA, Zein MH, Al Kawas S. Introducing integrated case-based learning to clinical nutrition training and evaluating students’ learning performance. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021;16(4):558–64.
Picciano AG. Theories and frameworks for Online Education: seeking an Integrated Model. Online Learn. 2017;213:166–90.
Bezanilla MJ, Fernández-Nogueira D, Poblete M, Galindo-Domínguez H. Methodologies for teaching-learning critical thinking in higher education: the teacher’s view. Think Skills Creativity. 2019;33:100584.
Immonen K, Oikarainen A, Tomietto M, Kääriäinen M, Tuomikoski A-M, Kaučič BM, Perez-Canaveras RM. Assessment of nursing students’ competence in clinical practice: a systematic review of reviews. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;100:103414.
Oermann MH, Gaberson KB, De Gagne JC, NPD-BC C. Evaluation and testing in nursing education. Springer Publishing Company; 2024.
McCarty T. (2020). How to Build Assessments for Clinical Learners. Roberts Academic Medicine Handbook: A Guide to Achievement and Fulfillment for Academic Faculty, 83–90.
Gholami M, Changaee F, Karami K, Shahsavaripour Z, Veiskaramian A, Birjandi M. Effects of multiepisode case-based learning (CBL) on problem-solving ability and learning motivation of nursing students in an emergency care course. J Prof Nurs. 2021;37(3):612–9.
King N. (2016, April). Case-based exams for learning and assessment: Experiences in an information systems course [ Confeence presentation]. In 2016 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) , Abu Dhabi, UAE.
Pereira D, Flores MA, Niklasson L. Assessment revisited: a review of research in Assessment and evaluation in Higher Education. Assess Evaluation High Educ. 2016;41(7):1008–32.
Creswell JW, Poth CN. Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches. SAGE; 2016.
O’Brien BC, Harris IB, Beckman TJ, Reed DA, Cook DA. Standards for reporting qualitative research. Acad Med. 2014;89(9):1245–51.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-117
Fetters MD, Curry LA, Creswell JW. Achieving integration in mixed methods designs—principles and practices. Health Serv Res. 2013;48(6pt2):2134–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/1475-6773.12117
Liu L, Li M, Zheng Q, Jiang H. The effects of case-based teaching in nursing skill education: cases do matter. INQUIRY. J Health Care Organ Provis Financing. 2020;57:004695802096442.
Bonney KM. Case study teaching methods improve student performance and perceptions of learning gains. J Microbiol Biology Educ. 2015;16(1):21–8.
Rezaee R, Mosalanejad L. The effects of case-based team learning on students’ learning, self-regulation, and self-direction. Global J Health Sci. 2015;7(4):295.
Harman T, Bertrand B, Greer A, Pettus A, Jennings J, Wall-Bassett E, Babatunde OT. Case-based learning facilitates critical thinking in undergraduate nutrition education: students describe the big picture. J Acad Nutr Dietetics. 2015;115(3):378–88.
Nunohara K, Imafuku R, Saiki T, Bridges SM, Kawakami C, Tsunekawa K, Niwa M, Fujisaki K, Suzuki Y. (2020). How does video case-based learning influence clinical decision-making by midwifery students? An exploratory study. BMC Med Educ, 20 (1).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the nursing students at SQU who voluntarily participated in this study.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sultan Qaboos University, Al Khodh 66, Muscat, 123, Oman
Basma Mohammed Al Yazeedi, Lina Mohamed Wali Shakman, Sheeba Elizabeth John Sunderraj, Harshita Prabhakaran, Judie Arulappan, Erna Judith Roach, Aysha Al Hashmi & Zeinab Al Azri
Oman College of Health Science, Norht Sharqia Branch, Ibra 66, Ibra, 124, Oman
Aysha Al Hashmi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Dr. Basma Mohammed Al Yazeedi contributed to conceptualization, methods, data collection, data analysis, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft. Ms. Lina Mohamed Wali Shakman contributed to conceptualization, data collection, data analysis, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft. Ms. Sheeba Elizabeth John Sunderraj contributed to conceptualization, methods, data collection, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft.Ms. Harshita Prabhakaran contributed to conceptualization, data collection, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft.Dr. Judie Arulappan contributed to conceptualization and reviewing the final draft.Dr. Erna Roach contributed to conceptualization writing the draft and reviewing the final draft.Ms. Aysha Al Hashmi contributed to the conceptualization and reviewing the final draft. Dr. Zeinab Al Azri contributed to data collection, data analysis, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft.All auhors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscirpt.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zeinab Al Azri .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Research and Ethics Committee of the College of Nursing, Sultan Qaboos University SQU (CON/NF/2023/18). All data was held and stored following the SQU data policy retention. Informed consent to participate was obtained from all of the participants in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1:
The questionnaire used in this study is attached as a supplementary document.
Supplementary Material 2
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Yazeedi, B.M.A., Shakman, L.M.W., Sunderraj, S.E.J. et al. Perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies in nursing education: a mixed methods study. BMC Nurs 23 , 441 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02102-9
Download citation
Received : 07 April 2024
Accepted : 17 June 2024
Published : 28 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02102-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case-analysis
- Clinical competency
- Nursing education
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 4 May 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 6 February 2023.
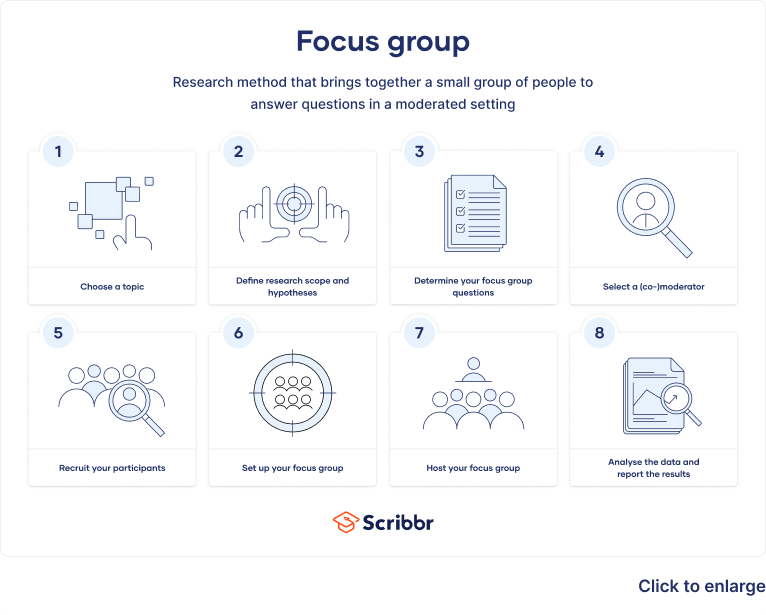
Table of contents
What is a focus group, step 1: choose your topic of interest, step 2: define your research scope and hypotheses, step 3: determine your focus group questions, step 4: select a moderator or co-moderator, step 5: recruit your participants, step 6: set up your focus group, step 7: host your focus group, step 8: analyse your data and report your results, advantages and disadvantages of focus groups, frequently asked questions about focus groups.
Focus groups are a type of qualitative research . Observations of the group’s dynamic, their answers to focus group questions, and even their body language can guide future research on consumer decisions, products and services, or controversial topics.
Focus groups are often used in marketing, library science, social science, and user research disciplines. They can provide more nuanced and natural feedback than individual interviews and are easier to organise than experiments or large-scale surveys .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Focus groups are primarily considered a confirmatory research technique . In other words, their discussion-heavy setting is most useful for confirming or refuting preexisting beliefs. For this reason, they are great for conducting explanatory research , where you explore why something occurs when limited information is available.
A focus group may be a good choice for you if:
- You’re interested in real-time, unfiltered responses on a given topic or in the dynamics of a discussion between participants
- Your questions are rooted in feelings or perceptions , and cannot easily be answered with ‘yes’ or ‘no’
- You’re confident that a relatively small number of responses will answer your question
- You’re seeking directional information that will help you uncover new questions or future research ideas
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, but other questions aren’t planned.
- Unstructured interviews : None of the questions are predetermined.
Differences between types of interviews
Make sure to choose the type of interview that suits your research best. This table shows the most important differences between the four types.
| Structured interview | Semi-structured interview | Unstructured interview | Focus group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed questions | ||||
| Fixed order of questions | ||||
| Fixed number of questions | ||||
| Option to ask additional questions |
Topics favorable to focus groups
As a rule of thumb, research topics related to thoughts, beliefs, and feelings work well in focus groups. If you are seeking direction, explanation, or in-depth dialogue, a focus group could be a good fit.
However, if your questions are dichotomous or if you need to reach a large audience quickly, a survey may be a better option. If your question hinges upon behaviour but you are worried about influencing responses, consider an observational study .
- If you want to determine whether the student body would regularly consume vegan food, a survey would be a great way to gauge student preferences.
However, food is much more than just consumption and nourishment and can have emotional, cultural, and other implications on individuals.
- If you’re interested in something less concrete, such as students’ perceptions of vegan food or the interplay between their choices at the dining hall and their feelings of homesickness or loneliness, perhaps a focus group would be best.
Once you have determined that a focus group is the right choice for your topic, you can start thinking about what you expect the group discussion to yield.
Perhaps literature already exists on your subject or a sufficiently similar topic that you can use as a starting point. If the topic isn’t well studied, use your instincts to determine what you think is most worthy of study.
Setting your scope will help you formulate intriguing hypotheses , set clear questions, and recruit the right participants.
- Are you interested in a particular sector of the population, such as vegans or non-vegans?
- Are you interested in including vegetarians in your analysis?
- Perhaps not all students eat at the dining hall. Will your study exclude those who don’t?
- Are you only interested in students who have strong opinions on the subject?
A benefit of focus groups is that your hypotheses can be open-ended. You can be open to a wide variety of opinions, which can lead to unexpected conclusions.
The questions that you ask your focus group are crucially important to your analysis. Take your time formulating them, paying special attention to phrasing. Be careful to avoid leading questions , which can affect your responses.
Overall, your focus group questions should be:
- Open-ended and flexible
- Impossible to answer with ‘yes’ or ‘no’ (questions that start with ‘why’ or ‘how’ are often best)
- Unambiguous, getting straight to the point while still stimulating discussion
- Unbiased and neutral
If you are discussing a controversial topic, be careful that your questions do not cause social desirability bias . Here, your respondents may lie about their true beliefs to mask any socially unacceptable or unpopular opinions. This and other demand characteristics can hurt your analysis and bias your results.
- Engagement questions make your participants feel comfortable and at ease: ‘What is your favourite food at the dining hall?’
- Exploration questions drill down to the focus of your analysis: ‘What pros and cons of offering vegan options do you see?’
- Exit questions pick up on anything you may have previously missed in your discussion: ‘Is there anything you’d like to mention about vegan options in the dining hall that we haven’t discussed?’
It is important to have more than one moderator in the room. If you would like to take the lead asking questions, select a co-moderator who can coordinate the technology, take notes, and observe the behaviour of the participants.
If your hypotheses have behavioural aspects, consider asking someone else to be lead moderator so that you are free to take a more observational role.
Depending on your topic, there are a few types of moderator roles that you can choose from.
- The most common is the dual-moderator , introduced above.
- Another common option is the dueling-moderator style . Here, you and your co-moderator take opposing sides on an issue to allow participants to see different perspectives and respond accordingly.
Depending on your research topic, there are a few sampling methods you can choose from to help you recruit and select participants.
- Voluntary response sampling , such as posting a flyer on campus and finding participants based on responses
- Convenience sampling of those who are most readily accessible to you, such as fellow students at your university
- Stratified sampling of a particular age, race, ethnicity, gender identity, or other characteristic of interest to you
- Judgement sampling of a specific set of participants that you already know you want to include
Beware of sampling bias , which can occur when some members of the population are more likely to be included than others.
Number of participants
In most cases, one focus group will not be sufficient to answer your research question. It is likely that you will need to schedule three to four groups. A good rule of thumb is to stop when you’ve reached a saturation point (i.e., when you aren’t receiving new responses to your questions).
Most focus groups have 6–10 participants. It’s a good idea to over-recruit just in case someone doesn’t show up. As a rule of thumb, you shouldn’t have fewer than 6 or more than 12 participants, in order to get the most reliable results.
Lastly, it’s preferable for your participants not to know you or each other, as this can bias your results.
A focus group is not just a group of people coming together to discuss their opinions. While well-run focus groups have an enjoyable and relaxed atmosphere, they are backed up by rigorous methods to provide robust observations.
Confirm a time and date
Be sure to confirm a time and date with your participants well in advance. Focus groups usually meet for 45–90 minutes, but some can last longer. However, beware of the possibility of wandering attention spans. If you really think your session needs to last longer than 90 minutes, schedule a few breaks.
Confirm whether it will take place in person or online
You will also need to decide whether the group will meet in person or online. If you are hosting it in person, be sure to pick an appropriate location.
- An uncomfortable or awkward location may affect the mood or level of participation of your group members.
- Online sessions are convenient, as participants can join from home, but they can also lessen the connection between participants.
As a general rule, make sure you are in a noise-free environment that minimises distractions and interruptions to your participants.
Consent and ethical considerations
It’s important to take into account ethical considerations and informed consent when conducting your research. Informed consent means that participants possess all the information they need to decide whether they want to participate in the research before it starts. This includes information about benefits, risks, funding, and institutional approval.
Participants should also sign a release form that states that they are comfortable with being audio- or video-recorded. While verbal consent may be sufficient, it is best to ask participants to sign a form.
A disadvantage of focus groups is that they are too small to provide true anonymity to participants. Make sure that your participants know this prior to participating.
There are a few things you can do to commit to keeping information private. You can secure confidentiality by removing all identifying information from your report or offer to pseudonymise the data later. Data pseudonymisation entails replacing any identifying information about participants with pseudonymous or false identifiers.
Preparation prior to participation
If there is something you would like participants to read, study, or prepare beforehand, be sure to let them know well in advance. It’s also a good idea to call them the day before to ensure they will still be participating.
Consider conducting a tech check prior to the arrival of your participants, and note any environmental or external factors that could affect the mood of the group that day. Be sure that you are organised and ready, as a stressful atmosphere can be distracting and counterproductive.
Starting the focus group
Welcome individuals to the focus group by introducing the topic, yourself, and your co-moderator, and go over any ground rules or suggestions for a successful discussion. It’s important to make your participants feel at ease and forthcoming with their responses.
Consider starting out with an icebreaker, which will allow participants to relax and settle into the space a bit. Your icebreaker can be related to your study topic or not; it’s just an exercise to get participants talking.
Leading the discussion
Once you start asking your questions, try to keep response times equal between participants. Take note of the most and least talkative members of the group, as well as any participants with particularly strong or dominant personalities.
You can ask less talkative members questions directly to encourage them to participate or ask participants questions by name to even the playing field. Feel free to ask participants to elaborate on their answers or to give an example.
As a moderator, strive to remain neutral. Refrain from reacting to responses, and be aware of your body language (e.g., nodding, raising eyebrows). Active listening skills, such as parroting back answers or asking for clarification, are good methods to encourage participation and signal that you’re listening.
Many focus groups offer a monetary incentive for participants. Depending on your research budget, this is a nice way to show appreciation for their time and commitment. To keep everyone feeling fresh, consider offering snacks or drinks as well.
After concluding your focus group, you and your co-moderator should debrief, recording initial impressions of the discussion as well as any highlights, issues, or immediate conclusions you’ve drawn.
The next step is to transcribe and clean your data . Assign each participant a number or pseudonym for organisational purposes. Transcribe the recordings and conduct content analysis to look for themes or categories of responses. The categories you choose can then form the basis for reporting your results.
Just like other research methods, focus groups come with advantages and disadvantages.
- They are fairly straightforward to organise and results have strong face validity .
- They are usually inexpensive, even if you compensate participant.
- A focus group is much less time-consuming than a survey or experiment , and you get immediate results.
- Focus group results are often more comprehensible and intuitive than raw data.
Disadvantages
- It can be difficult to assemble a truly representative sample. Focus groups are generally not considered externally valid due to their small sample sizes.
- Due to the small sample size, you cannot ensure the anonymity of respondents, which may influence their desire to speak freely.
- Depth of analysis can be a concern, as it can be challenging to get honest opinions on controversial topics.
- There is a lot of room for error in the data analysis and high potential for observer dependency in drawing conclusions. You have to be careful not to cherry-pick responses to fit a prior conclusion.
A focus group is a research method that brings together a small group of people to answer questions in a moderated setting. The group is chosen due to predefined demographic traits, and the questions are designed to shed light on a topic of interest. It is one of four types of interviews .
As a rule of thumb, questions related to thoughts, beliefs, and feelings work well in focus groups . Take your time formulating strong questions, paying special attention to phrasing. Be careful to avoid leading questions , which can bias your responses.
The four most common types of interviews are:
- Focus group interviews : The questions are presented to a group instead of one individual.
Social desirability bias is the tendency for interview participants to give responses that will be viewed favourably by the interviewer or other participants. It occurs in all types of interviews and surveys , but is most common in semi-structured interviews , unstructured interviews , and focus groups .
Social desirability bias can be mitigated by ensuring participants feel at ease and comfortable sharing their views. Make sure to pay attention to your own body language and any physical or verbal cues, such as nodding or widening your eyes.
This type of bias in research can also occur in observations if the participants know they’re being observed. They might alter their behaviour accordingly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2023, February 06). What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 24 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/focus-groups/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, structured interview | definition, guide & examples, semi-structured interview | definition, guide & examples, unstructured interview | definition, guide & examples.
Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
At michigan state university, investigating the conditions for a new stellar process.
A scientific research team studied how the barium-139 nucleus captures neutrons in the stellar environment in an experiment at Argonne National Laboratory ’s (ANL) CARIBU facility using FRIB’s Summing Nal (SuN) detector . The team’s goal was to lessen uncertainties related to lanthanum production. Lanthanum is a rare earth element sensitive to intermediate neutron capture process (i process) conditions. Uncovering the conditions of the i process allows scientists to determine its required neutron density and reveal potential sites where it might occur. The team recently published its findings in Physical Review Letters (“First Study of the 139Ba(𝑛,𝛾)140Ba Reaction to Constrain the Conditions for the Astrophysical i Process”).
Artemis Spyrou , professor of physics at FRIB and in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Michigan State University (MSU), and Dennis Mücher , professor of physics at the University of Cologne in Germany, led the experiment. MSU is home to FRIB, the only accelerator-based U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC) user facility on a university campus. FRIB is operated by MSU to support the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics as one of 28 DOE-SC user facilities.
Combining global collaboration and world-class educational experiences
The experiment was a collaborative effort involving more than 30 scientists and students from around the world. Participating institutions included the University of Victoria in Canada, the University of Oslo in Norway, and the University of Jyväskyla in Finland.
“The collaboration is essential because everyone comes from different backgrounds with different areas of expertise,” Spyrou said. “Together, we’re much stronger. It’s really an intellectual sharing of that knowledge and bringing new ideas to the experiment.”
The international collaboration also included five FRIB graduate and two FRIB undergraduate students. FRIB is an educational resource for the next generation of science and technical talent. Students enrolled in nuclear physics at MSU can work with scientific researchers from around the world to conduct groundbreaking research in accelerator science, cryogenic engineering, and astrophysics.
“Our students contribute to every aspect of the experiment, from transporting the instrumentation to unpacking and setting it up, then testing and calibrating it to make sure everything works,” Spyrou said. “Then, we all work together to identify what’s in the beam. Is it reasonable? Do we accept it? Once everything is set up and ready, we all take shifts.”
Measuring the i process
Producing some of the heaviest elements found on Earth, like platinum and gold, requires stellar environments rich in neutrons. Inside stars, neutrons combine with an atomic nucleus to create a heavier nucleus. These nuclear reactions, called neutron capture processes, are what create these heavy elements. Two neutron capture processes are known to occur in stars: the rapid neutron capture process ( r process) and the slow neutron capture process ( s process). Yet, neither process can explain some astronomic observations, such as unusual abundance patterns found on very old stars. A new stellar process—the i process—may help. The i process represents neutron densities that fall between those of the r and s processes.
“Through this reaction we are constraining, we discovered that compared to what theory predicted, the amount of lanthanum is actually less,” said Spyrou.
Spyrou said that combining lanthanum with other elements, like barium and europium, helps provide a signature of the i process.
“It’s a new process, and we don’t know the conditions where the i process is happening. It’s all theoretical, so unless we constrain the nuclear physics, we will never find out,” Spyrou said. “This was the first strong constraint from the nuclear physics point of view that validates that yes, the i process should be making these elements under these conditions.”
Neutron capture processes are difficult to measure directly, Spyrou said. Indirect techniques, like the beta-Oslo and shape methods, help constrain neutron capture reaction rates in exotic nuclei . These two methods formed the basis of the barium-139 nucleus experiment.
To measure the data, beams provided by ANL’s CARIBU facility produced a high-intensity beam and delivered it to the center of the SuN detector, a device that measures gamma rays emitted from decaying isotope beams. This tool was pivotal in producing strong data constraints during the study.
“I developed SuN with my group at the National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, the predecessor to FRIB,” Spyrou said. “It’s a very efficient and large detector. Basically, every gamma ray that comes out, we can detect. This is an advantage compared to other detectors, which are smaller.”
The first i process constraint paves the way for more research
Studying the barium-139 neutron capture was only the first step in discovering the conditions of the i process. Mücher is starting a new program at the University of Cologne that aims to measure some significant i process reactions directly. Spyrou said that she and her FRIB team plan to continue studying the i process through different reactions that can help constrain the production of different elements or neutron densities. They recently conducted an experiment at ANL to study the neodymium-151 neutron capture. This neutron capture is the dominant reaction for europium production.
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation.
Michigan State University operates the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) as a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC), supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics. Hosting what is designed to be the most powerful heavy-ion accelerator, FRIB enables scientists to make discoveries about the properties of rare isotopes in order to better understand the physics of nuclei, nuclear astrophysics, fundamental interactions, and applications for society, including in medicine, homeland security, and industry.
The U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of today’s most pressing challenges. For more information, visit energy.gov/science .
Understanding evacuation behavior for effective disaster preparedness: a hybrid machine learning approach
- Letter to the Editor
- Published: 27 June 2024
Cite this article

- Evangelos Karampotsis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6041-2301 1 ,
- Kitty Kioskli 2 , 3 ,
- Athina Tsirimpa 2 , 4 ,
- Georgios Dounias 1 &
- Amalia Polydoropoulou 2
25 Accesses
Explore all metrics
This paper delves into the pivotal role of machine learning in responding to natural disasters and understanding human behavior during crises. Natural disasters, from earthquakes to floods, have profound consequences for both the environment and society, impacting health, the economy, and mental well-being. Prevention and preparedness are key components of disaster management, yet the psychological challenges faced by affected individuals are equally significant. Psychosocial support and educational programs play a vital role in aiding individuals in their recovery. Machine learning, in this context, offers the ability to predict the evolution of natural disasters, providing early warnings that can save lives and reduce losses. It further extends to analyzing data related to human behavior during disasters, enhancing readiness for future calamities. This study specifically addresses the challenge of understanding human behavior during a snowstorm that struck Greece in 2023, employing artificial intelligence techniques to develop classification models categorizing individuals into three distinct groups based on socio-economic characteristics and is one of the few machine learning approaches that have been performed to date on data derived from corresponding questionnaire surveys. Artificial intelligence methodologies were harnessed to construct these classification models, with a focus on categorizing individuals into three specific classes: "Did not travel at all", "Traveled only as necessary", or “Did not limit travel”. The dataset employed in this study was collected through a survey conducted within the framework of the AEGIS+ research project, concentrating on assessing the mental health of individuals impacted by natural disasters. The goal was to generalize the optimal classification model and extract knowledge applicable in natural disaster scenarios. Three methodological frameworks for data analysis were proposed, incorporating combinations of Simple Logistic Regression and Inductive Decision Trees with the SMOTE data balancing method and a new data balancing method called LCC (Leveling of Cases per Class), within the context of validation procedures like “Use Train Set,” “10-fold Cross Validation,” and “Hold Out.” This paper’s contribution lies in the development of hybrid classification models, highlighting the significance of data balancing with LCC method throughout the modeling process. The results were deemed satisfactory, with the inductive decision tree method demonstrating superior performance (Classification accuracy near to 90%). This approach, offering strong classification rules, holds potential for knowledge application in natural disaster risk management. Knowledge Mining and Metadata Analysis further revealed the socio-economic characteristics influencing the decision to move during a natural disaster, including age, education, work-status, and workstyle. Crucially, this work, in addition to providing knowledge through the data mining process that can be used to estimate evacuation probability, develop targeted emergency information messages, and improve evacuation planning, is also used as a catalyst for future research efforts. It encourages the collection of relevant data, the exploration of new challenges in data analysis related to natural disasters and mental health, and the development of new data balancing methods and hybrid data analysis methodological frameworks.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Agrawal A, Viktor HL, Paquet E (2015) SCUT: multi-class imbalanced data classification using SMOTE and cluster-based undersampling. In: 2015 7th international joint conference on knowledge discovery, knowledge engineering and knowledge management (IC3K), pp 226–234. Accessed 19 Feb 2024. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7526924?casa_token=RuN4fIOHSEEAAAAA:FfW0KJeqkV4uB7VX69pyV2RPSkv72vOQtyebN2fsQOkaDLhHdGb4W1it1Lkj7EYFDhW211Ls
Ayyadevara VK (2018) Gradient boosting machine. In: Ayyadevara VK (ed) Pro machine learning algorithms: a hands-on approach to implementing algorithms in Python and R. Apress, Berkeley, pp 117–134
Chapter Google Scholar
Babić IĐ (2017) Machine Learning methods in predicting the student academic motivation. Croat Oper Res Rev 8:443–461
Article Google Scholar
Bartholomew DJ (1980) Factor analysis for categorical data. J Roy Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 42(3):293–312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1980.tb01128.x
Batista GEAPA, Prati RC, Monard MC (2004) A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data. SIGKDD Explor Newsl 6(1):20–29. https://doi.org/10.1145/1007730.1007735
Brown M, Williams R (2024) human behavior factors in emergencies: implications for emergency response and communication strategies. J Disaster Stud 21(1):12–28
Google Scholar
Buskirk TD, Kirchner A (2020) Why machines matter for survey and social science researchers. Big data meets survey science. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Hoboken, pp 9–62
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP (2002) SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res 16:321–357. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, in KDD ’16. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, pp 785–794
Chien HY, Kwok OM, Yeh YC, Sweany NW, Baek E, McIntosh W (2020) Identifying at-risk online learners by psychological variables using machine learning techniques. Online Learn 24:131–146
Dabhade P, Agarwal R, Alameen KP, Fathima AT, Sridharan R, Gopakumar G (2021) Educational data mining for predicting students’ academic performance using machine learning algorithms. Mater Today Proc 47:5260–5267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.646
Dahan H, Cohen S, Rokach L, Maimon O (2014) Proactive data mining with decision trees. SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering. Springer-Verlag, New York
De La Garza ÁG, Blanco C, Olfson M, Wall MM (2021) Identification of suicide attempt risk factors in a national US survey using machine learning. JAMA Psychiat 78:398–406. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4165
Deb K (1999) An introduction to genetic algorithms. Sadhana 24(4):293–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823145
Deng Z, Ji M (2012) Deriving rules for trip purpose identification from GPS travel survey data and land use data: a machine learning approach, pp 768–777
Dulebenets MA, Abioye OF, Ozguven EE, Moses R, Boot WR, Sando T (2019) Development of statistical models for improving efficiency of emergency evacuation in areas with vulnerable population. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 182:233–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2018.09.021
Dutton DM, Conroy GV (1997) A review of machine learning. Knowl Eng Rev 12(4):341–367. https://doi.org/10.1017/S026988899700101X
Elreedy D, Atiya AF (2019) A comprehensive analysis of synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) for handling class imbalance. Inf Sci 505:32–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.070
European Disaster Risk Management (2023) Accessed 29 Jul 2023. Available: https://civil-protection-humanitarian-aid.ec.europa.eu/what/civil-protection/european-disaster-risk-management_en
Fernandez A, Garcia S, Herrera F, Chawla NV (2018) SMOTE for learning from imbalanced data: progress and challenges, marking the 15-year anniversary. J Artif Intell Res 61:863–905. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.1.11192
Flener P, Schmid U (2008) An introduction to inductive programming. Artif Intell Rev 29(1):45–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-009-9108-7
Franke TM, Ho T, Christie CA (2012) The chi-square test: often used and more often misinterpreted. Am J Eval 33(3):448–458. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098214011426594
Freund Y, Schapire R, Abe N (1999) A short introduction to boosting. J Jpn Soc Artif Intell 14(771–780):1612
Gahegan M (2003) Is inductive machine learning just another wild goose (or might it lay the golden egg)? Int J Geogr Inf Sci 17(1):69–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/713811742
Gu B, Sheng VS, Tay KY, Romano W, Li S (2015) Incremental support vector learning for ordinal regression. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(7):1403–1416. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2342533
Gupta S, Gupta A (2019) Dealing with noise problem in machine learning datasets: a systematic review. Procedia Comput Sci 161:466–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.146
Jain S, Narayan SP, Dewang RK, Bhartiya U, Meena N, Kumar V (2019) A machine learning based depression analysis and suicidal ideation detection system using questionnaires and twitter. In: 2019 IEEE students conference on engineering and systems (SCES), Feb. 2019, pp 1–6
James G, Witten D, Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Taylor J (2023) An introduction to statistical learning: With applications in python. Springer Nature [Online]. Available: https://books.google.com/books?hl=el&lr=&id=ygzJEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR7&dq=An+Introduction+to+Statistical+Learning,+second+edition,+springer&ots=WzlbjSH_Tj&sig=s63qpVbiofehpQ4nSzsblcGSmds . Accessed 26 June 2024
Johnson R, Lee S (2023) Predictive models for identifying evacuation bottlenecks using machine learning. Disaster Prev Manag 18(1):75–90
Johnson Α, Smith J, Lee J (2022) The importance of understanding evacuation behavior: enhancing disaster preparedness and response strategies. J Emerg Manag 5:78–94
Joo J et al (2013) Agent-based simulation of affordance-based human behaviors in emergency evacuation. Simul Model Pract Theory 32:99–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2012.12.007
Kim S, Lee H-K, Lee K (2021) Which PHQ-9 items can effectively screen for Suicide? Machine learning approaches. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(7):3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073339
Kramer O (2013) K-Nearest Neighbors. In: Kramer O (ed) Dimensionality reduction with unsupervised nearest neighbors. Springer, Berlin, pp 13–23
Landwehr N, Hall M, Frank E (2005) Logistic model trees. Mach Learn 59(1):161–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-005-0466-3
Li P (2012) Robust LogitBoost and adaptive base class (ABC) LogitBoost. arXiv https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1203.3491
Lin M-R, Huang W, Huang C, Hwang H-F, Tsai L-W, Chiu Y-N (2002) The impact of the chi-chi earthquake on quality of life among elderly survivors in Taiwan—a before and after study. Qual Life Res 11(4):379–388. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015543113448
Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhang J (2012) New Machine learning algorithm: random forest. Information computing and applications. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, Berlin, pp 246–252
Liu H, Chen H, Hong R, Liu H, You W (2020) Mapping knowledge structure and research trends of emergency evacuation studies. Saf Sci 121:348–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.09.020
Lopez de Mantaras R, Armengol E (1998) Machine learning from examples: inductive and lazy method. Data Knowl Eng 25(1):99–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-023X(97)00053-0
Madrid PA, Grant R (2008) Meeting mental health needs following a natural disaster: lessons from Hurricane Katrina. Prof Psychol Res Pract 39(1):86–92. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7028.39.1.86
Maimon O, Rokach L (2010) Introduction to knowledge discovery and data mining. In: Maimon O, Rokach L (eds) Data mining and knowledge discovery handbook. Springer, Boston, pp 1–15
Mental Health Assistance to the Populations Affected by the Tsunami in Asia - Indonesia | ReliefWeb (2023) Accessed 29 Jul 2023. Available: https://reliefweb.int/report/indonesia/mental-health-assistance-populations-affected-tsunami-asia
Michalski RS (1983) A theory and methodology of inductive learning. In: Michalski RS, Carbonell JG, Mitchell TM (eds) Machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, pp 83–134
Mitchell MJ, Witman M, Taffaro C (2008) Reestablishing Mental Health Services in St. Bernard Parish, Louisiana, following Hurricane Katrina. Prof Psychol Res Pract 39(1):66–76. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7028.39.1.66
Mustapha A, Mohamed L, Ali K (2020) An overview of gradient descent algorithm optimization in machine learning: application in the ophthalmology field. In: Hamlich M, Bellatreche L, Mondal A, Ordonez C (eds) Smart applications and data analysis. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 349–359
National Meteorological Service of Greece (2024). Accessed 18 Feb 2024. Available: http://www.emy.gr/emy/el/meteorology/meteorological_news?name=2302031536
Norris FH, Phifer JF, Kaniasty K (1994) Individual and community reactions to the Kentucky floods: findings from a longitudinal study of older adults. Individual and community responses to trauma and disaster: the structure of human chaos. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 378–400
Ontivero-Ortega M, Lage-Castellanos A, Valente G, Goebel R, Valdes-Sosa M (2017) Fast Gaussian Naïve Bayes for searchlight classification analysis. Neuroimage 163:471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.001
Papanikolaou V, Adamis D, Kyriopoulos J (2012) Long term quality of life after a wildfire disaster in a rural part of Greece. Open J Psychiatry 02(02):164–170. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojpsych.2012.22022
Peng C-YJ, Lee KL, Ingersoll GM (2002) An introduction to logistic regression analysis and reporting. J Educ Res 96(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220670209598786
Perner P (2015) Decision tree induction methods and their application to big data. In: Xhafa F, Barolli L, Barolli A, Papajorgji P (eds) Modeling and processing for next-generation big-data technologies: with applications and case studies, Modeling and optimization in science and technologies. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 57–88
Peterson MJ (2023) The UN general assembly. In: International organization and global governance, 3rd edn. Routledge. ISBN: 9781003266365
Podgorelec V, Kokol P, Stiglic B, Rozman I (2002) Decision trees: an overview and their use in medicine. J Med Syst 26(5):445–463. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016409317640
Polyzotis N, Zinkevich M, Roy S, Breck E, Whang S (2019) Data validation for machine learning. Proc Mach Learn Syst 1:334–347
Quinlan JR (1987) Generating production rules from decision trees. In: IJCAI, vol 87, pp 304–307
Quinlan JR (1993) C4.5: programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington
Reyes G, Elhai JD (2004) Psychosocial interventions in the early phases of disasters. Psychother Theory Res Pract Train 41(4):399–411. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-3204.41.4.399
Robertson A, Sillén R, Norén JG (1998) Inductive analysis methods applied on questionnaires. Acta Odontol Scand 56:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/000163598428437
Article CAS Google Scholar
Sánchez-Maroño N, Alonso-Betanzos A, Fontenla-Romero O, Gary Polhill J, Craig T (2017) Empirically-derived behavioral rules in agent-based models using decision trees learned from questionnaire data. In: Alonso-Betanzos A, Sánchez-Maroño N, Oscar Fontenla-Romero J, Polhill G, Craig T, Bajo J, Corchado JM (eds) Agent-based modeling of sustainable behaviors. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 53–76
Smith J, Lee S (2023) Predictive models for optimizing evacuation routes: insights from past evacuation incidents. Disaster Prev Manag 18(3):145–160
Smith J, Johnson A, Brown M (2022) Application of deep learning algorithms for real-time analysis of evacuation behavior. J Emerg Manag 15(3):125–140
Sperandei S (2014) Understanding logistic regression analysis. Biochem Med 24(1):12–18. https://doi.org/10.11613/BM.2014.003
Sun CK, Tang YX, Liu TC, Lu CJ (2022) An integrated machine learning scheme for predicting mammographic anomalies in high-risk individuals using questionnaire-based predictors. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:9756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159756
Terano T, Ishino Y (1995) Marketing data analysis using inductive learning and genetic algorithms with interactive and automated phases. In Proceedings of 1995 IEEE international conference on evolutionary computation, vol 2, pp 771–776
Wang W et al (2022) Predicting the 10-year risk of cataract surgery using machine learning techniques on questionnaire data: findings from the 45 and up study. Br J Ophthalmol 106(11):1503–1507. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-318609
Warsini S, West C, Ed GD, Res Meth GC, Mills J, Usher K (2014) The psychosocial impact of natural disasters among adult survivors: an integrative review. Issues Mental Health Nurs 35:420–436. https://doi.org/10.3109/01612840.2013.875085
Weilnhammer V et al (2021) Extreme weather events in europe and their health consequences—a systematic review. Int J Hyg Environ Health 233:113688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113688
Wong SD (2023) Compliance, congestion, and social equity: tackling critical evacuation challenges through the sharing economy, joint choice modeling, and regret minimization. Accessed 29 Jul 2023. Available: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9b51w7h6
Xanthopoulos P, Pardalos PM, Trafalis TB (2013) Linear discriminant analysis. In: Xanthopoulos P, Pardalos PM, Trafalis TB (eds) Robust data mining. Springer, New York, pp 27–33
Yanatma S (2023) How much has climate change cost the EU in the last 40 years? Euronews. Accessed 23 Oct 2023. Available: https://www.euronews.com/green/2022/11/13/climate-change-has-cost-the-eu-almost-almost-500-billion-in-the-last-40-years
Yzermans CJ, Donker GA, Kerssens JJ, Dirkzwager AJ, Soeteman RJ, ten Veen PM (2005) Health problems of victims before and after disaster: a longitudinal study in general practice. Int J Epidemiol 34(4):820–826. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyi096
Zhao B, Wong SD (2021) Developing transportation response strategies for wildfire evacuations via an empirically supported traffic simulation of Berkeley, California. Transp Res Rec 2675(12):557–582. https://doi.org/10.1177/03611981211030271
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere gratitude to the participants for their valuable time and cooperation. They would also like to express their appreciation to The American College of Greece for their support and approval of the ethical procedures. The research described in this paper was funded by the Greek national project "Development of the 'Coastal Environmental Observatory and Crisis Management in Island Areas' Infrastructure (AEGIS+)" conducted at the University of the Aegean. Additionally, the second author (KK) would like to acknowledge the financial support provided for the following projects: ‘Collaborative, Multi- modal and Agile Professional Cybersecurity Training Program for a Skilled Workforce In the European Digital Single Market and Industries’ (CyberSecPro) project, which has received funding from the European Union’s Digital Europe Programme (DEP) programme under grant agreement No 101083594. The ‘Human-centered Trustworthiness Optimisation in Hybrid Decision Support’ (THEMIS 5.0) project, which has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Programme under grant agreement No 101121042. The ‘advaNced cybErsecurity awaReness ecOsystem for SMEs’ (NERO) project, which has received funding from the European Union’s DEP programme under grant agreement No 101127411. And ‘Fostering Artificial Intelligence Trust for Humans towards the optimization of trustworthiness through large-scale pilots in critical domains’ (FAITH) project, which has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Programme under grant agreement No 101135932. It is important to note that the views expressed in this paper solely represent the opinions of the authors and not those of the University of the Aegean, the American College of Greece, trustilio B.V., the European Commission, or the partners involved in the mentioned projects. Finally, the authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest, including any financial or personal relationships, that could be perceived as potential conflicts.
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Financial and Management Engineering, University of the Aegean, Chios, Greece
Evangelos Karampotsis & Georgios Dounias
Department of Shipping, Trade and Transport, University of the Aegean, Chios, Greece
Kitty Kioskli, Athina Tsirimpa & Amalia Polydoropoulou
Trustilio B.V., Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Kitty Kioskli
Department of Maritime Transport and Logistics, The American College of Greece, Athens, Greece
Athina Tsirimpa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: AP, AT, KK, EK; data collection, recruitment process and ethics approval: AP, AT, KK; data analysis and production of the first draft of the manuscript: EK, GD. Discussion and conclusions: AP, EK, KK, AT, GD. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Evangelos Karampotsis .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study received ethical clearance from the Institutional Review Board of the American College of Greece (reference number: 202212333). As the survey was carried out anonymously, direct assistance was not feasible for participants who obtained high scores on the psychometric tests and displayed potential indications of clinical problems. To tackle this concern, the information sheet included contact details for accessible support services.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Karampotsis, E., Kioskli, K., Tsirimpa, A. et al. Understanding evacuation behavior for effective disaster preparedness: a hybrid machine learning approach. Nat Hazards (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06759-y
Download citation
Received : 17 November 2023
Accepted : 21 June 2024
Published : 27 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06759-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Trips-related decisions
- Behavioral response
- Natural disasters
- Artificial intelligence
- Inductive machine learning
- Data mining
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition: A focus group is a qualitative research method used to gather in-depth insights and opinions from a group of individuals about a particular product, service, concept, or idea. The focus group typically consists of 6-10 participants who are selected based on shared characteristics such as demographics, interests, or experiences.
Step 1: Choose your topic of interest. Step 2: Define your research scope and hypotheses. Step 3: Determine your focus group questions. Step 4: Select a moderator or co-moderator. Step 5: Recruit your participants. Step 6: Set up your focus group. Step 7: Host your focus group. Step 8: Analyze your data and report your results.
Doing Focus Groups. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Written by a medical sociologist based in the UK, this is a good how-to guide for conducting focus groups. Gibson, Faith. 2007. "Conducting Focus Groups with Children and Young People: Strategies for Success." Journal of Research in Nursing 12(5):473-483. As the title suggests, this ...
Focus groups have been widely used in health research in recent years to explore the perspectives of patients and other groups in the health care system (e.g., Carr et al., 2003; Côté-Arsenault & Morrison-Beedy, 2005; Kitzinger, 2006 ). They are often included in mixed-methods studies to gain more information on how to construct ...
A focus group is a qualitative research method that involves facilitating a small group discussion with participants who share common characteristics or experiences that are relevant to the research topic. The goal is to gain insights through group conversation and observation of dynamics. In a focus group: A moderator asks questions and leads a group of typically 6 to 12 pre-screened ...
Focus groups use a group setting to generate data different to that obtained in a one-to-one interview. The group context may allow for better examination of beliefs, attitudes, values, perspectives, knowledge and ideas. Focus groups can be useful in action research methodology and other study designs which seek to empower research participants.
A focus group is a moderated group discussion on a pre-defined topic, for research purposes. 28,29 While not aligned to a particular qualitative methodology (for example, grounded theory or ...
Focus Groups 101. Therese Fessenden. July 31, 2022. Summary: Well-run focus groups help gather some initial feedback from a group of people. However, their bias potential makes them insufficient as a standalone research method. Workshop techniques can help maximize participation and reduce the potential for bias.
Focus Group Methodology is an introductory text which leads readers through the entire process of designing a focus group study, from conducting interviews to analysing data and presenting the findings. It also includes discussions on cross-cultural and virtual focus group. Liamputtong presents clear, practical advice in simple terms which will be appropriate for undergraduate and postgraduate ...
A focus group is a qualitative fact-finding method involving a small group of five to 10 people discussing a specific topic or issue. A moderator leads the group, poses open-ended questions, and encourages participant discussion and interaction. A focus group aims to gain insights into participants' opinions, attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors about the discussed topic.
Focus groups are a form of group interview that capitalises on communication between research participants in order to generate data. Although group interviews are often used simply as a quick and convenient way to collect data from several people simultaneously, focus groups explicitly use group interaction as part of the method.
"Successful Focus Groups is a state-of-the-art text on focus group research methods…. Successful Focus Groups is a well-written document with clearly presented reasons why researchers should follow the guide lines presented. Additionally, this text is groundbreaking in its focus on topics that will advance knowledge of focus group research methods…. an improvement over prior treatises on ...
Publication Date: 2018. Focus Groups by Richard A. Krueger; Mary Anne Casey. ISBN: 9781483365244. Publication Date: 2014-08-14. Print book available through Interlibrary Loan. Focus groups as qualitative research by David L. Morgan. ISBN: 0761903429. Focus Groups in Social Research by Michael Bloor; Jane Frankland; Michelle Thomas; Kate Stewart.
A focus group is a qualitative research method used in market research and social sciences, where a small group of people, typically 6 to 10 individuals, participate in a guided discussion about a particular topic. Learn more about focus group with examples, questions and best practices.
Is relevant to the research study. Step 3: Determine your focus group questions. Questions asked in focus group discussions are crucial in collecting findings. Determining the right questions for the focus group is vital for collecting actionable findings. ... Compared to other research methods, focus groups can be a cost-effective way to ...
What is Focus Group Research? Focus group research is defined as a qualitative research method used to gather data from a small, diverse group of people in a facilitated group discussion. This method is commonly used in marketing and social science research to gain insight into the opinions, attitudes, and perceptions of a target audience.
A focus group is a research method or technique that is used to collect opinions and ideas regarding a concept, service, or product. Follow the below steps to conduct it: A researcher must be careful while recruiting participants. Members need adequate knowledge of the topic so that they can add to the conversation.
Quantitative and Mixed Methods Perspectives on Focus Group Research. When focus groups are used within mixed or quantitative research, they tend to be employed as part of instrument development (Nagel & Williams, Citation n.d.).These focus groups are positioned as an adjunct to the quantitative data collection, and appear to be centered on task-focused aims (Department of Health and Human ...
Researchers use the focus group method in order to obtain in-depth knowledge concerning attitudes, perceptions, beliefs and opinions of individuals regarding a specific health issue. The purpose ...
a method of collecting research data. Focus groups. A focus group is usually understood as a group of people who share some common. 1. characteristic, brought together by a researcher to interact ...
Therefore, in writing the research methods the challenge lies in providing sufficient transparency on how focus groups were conducted and the methodological decisions that shaped the study process. The methods section needs to describe both the procedural detail and scientific reasoning to demonstrate the rigor of the study.
Focus groups have been used by large corporations to gather the public's opinions regarding their products. In the past 20 years the focus group method has been increasingly used in health care research in a variety of settings. Researchers use the focus group method in order to obtain in-depth knowledge concerning attitudes, perceptions ...
This study used a mixed methods design. Students filled out a 13-item study-advised questionnaire, and qualitative data from the four focus groups was collected. ... a potential for the case analysis to be acceptable and relevant to the clinical competencies when used as an assessment method. Future research is needed to validate the ...
Step 1: Choose your topic of interest. Step 2: Define your research scope and hypotheses. Step 3: Determine your focus group questions. Step 4: Select a moderator or co-moderator. Step 5: Recruit your participants. Step 6: Set up your focus group. Step 7: Host your focus group. Step 8: Analyse your data and report your results.
A mixed methods study, using an open cross-sectional online survey, followed by working groups using nominal group techniques. Participants were professionals interested in palliative care research, working as generalist/specialist palliative care providers, or palliative care research staff across areas of North West England.
The focus groups found that the combination of evidence-based knowledge, clinical viewpoint, and visibility was crucial for clinical implementation. The systematic review identified 2543 records, of which 2 syntheses of guidelines met all the inclusion criteria, but only 1 (the OxPPL guidance) used evidence-based methodology.
A scientific research team studied how the barium-139 nucleus captures neutrons in the stellar environment in an experiment at Argonne National Laboratory's (ANL) CARIBU facility using FRIB's Summing Nal (SuN) detector. The team's goal was to lessen uncertainties related to lanthanum production. Lanthanum is a rare earth element sensitive to intermediate neutron capture process (i ...
Background: Youth, aged 15 to 24 years, are more likely to experience mental health (MH) or substance use issues than other age groups. This is a critical period for intervention because MH disorders, if left unattended, may become chronic and serious and negatively affect many aspects of a young person's life. Even among those who are treated, poor outcomes will still occur for a percentage ...
This paper delves into the pivotal role of machine learning in responding to natural disasters and understanding human behavior during crises. Natural disasters, from earthquakes to floods, have profound consequences for both the environment and society, impacting health, the economy, and mental well-being. Prevention and preparedness are key components of disaster management, yet the ...
Given the limited focus on females in previous studies, this research aimed to evaluate the effects of dietary curcumin on obesity and NAFLD outcomes in naturally aged (18-month-old) female mice. Methods: Female C57BL/6 mice aged 18 months were fed a normal chow diet (NCD) and a HFHSD, with or without curcumin (0.4% w/w), for an 8-week period.