Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples

Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Amy Luo . Revised on 5 December 2022.
Discourse analysis is a research method for studying written or spoken language in relation to its social context. It aims to understand how language is used in real-life situations.
When you do discourse analysis, you might focus on:
- The purposes and effects of different types of language
- Cultural rules and conventions in communication
- How values, beliefs, and assumptions are communicated
- How language use relates to its social, political, and historical context
Discourse analysis is a common qualitative research method in many humanities and social science disciplines, including linguistics, sociology, anthropology, psychology, and cultural studies. It is also called critical discourse analysis.
Table of contents
What is discourse analysis used for, how is discourse analysis different from other methods, how to conduct discourse analysis.
Conducting discourse analysis means examining how language functions and how meaning is created in different social contexts. It can be applied to any instance of written or oral language, as well as non-verbal aspects of communication, such as tone and gestures.
Materials that are suitable for discourse analysis include:
- Books, newspapers, and periodicals
- Marketing material, such as brochures and advertisements
- Business and government documents
- Websites, forums, social media posts, and comments
- Interviews and conversations
By analysing these types of discourse, researchers aim to gain an understanding of social groups and how they communicate.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Unlike linguistic approaches that focus only on the rules of language use, discourse analysis emphasises the contextual meaning of language.
It focuses on the social aspects of communication and the ways people use language to achieve specific effects (e.g., to build trust, to create doubt, to evoke emotions, or to manage conflict).
Instead of focusing on smaller units of language, such as sounds, words, or phrases, discourse analysis is used to study larger chunks of language, such as entire conversations, texts, or collections of texts. The selected sources can be analysed on multiple levels.
Discourse analysis is a qualitative and interpretive method of analysing texts (in contrast to more systematic methods like content analysis ). You make interpretations based on both the details of the material itself and on contextual knowledge.
There are many different approaches and techniques you can use to conduct discourse analysis, but the steps below outline the basic structure you need to follow.
Step 1: Define the research question and select the content of analysis
To do discourse analysis, you begin with a clearly defined research question . Once you have developed your question, select a range of material that is appropriate to answer it.
Discourse analysis is a method that can be applied both to large volumes of material and to smaller samples, depending on the aims and timescale of your research.
Step 2: Gather information and theory on the context
Next, you must establish the social and historical context in which the material was produced and intended to be received. Gather factual details of when and where the content was created, who the author is, who published it, and whom it was disseminated to.
As well as understanding the real-life context of the discourse, you can also conduct a literature review on the topic and construct a theoretical framework to guide your analysis.
Step 3: Analyse the content for themes and patterns
This step involves closely examining various elements of the material – such as words, sentences, paragraphs, and overall structure – and relating them to attributes, themes, and patterns relevant to your research question.
Step 4: Review your results and draw conclusions
Once you have assigned particular attributes to elements of the material, reflect on your results to examine the function and meaning of the language used. Here, you will consider your analysis in relation to the broader context that you established earlier to draw conclusions that answer your research question.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Luo, A. (2022, December 05). Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/discourse-analysis-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
Case study | definition, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | guide & examples, content analysis | a step-by-step guide with examples.
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Critical discourse analysis and information and communication technology in education.
- Cheryl Brown Cheryl Brown University of Canterbury
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.794
- Published online: 28 August 2019
Critical discourse analysis (CDA) is a cross-disciplinary methodological and theoretical approach. At its core CDA explores the intersections between discourse, critique, power, and ideology which hold particular values for those teaching in developing contexts. CDA has emerged as a valuable methodological approach in cultural and media studies and has increased in prominence since the 2010s in education research where it is drawn on to explore educational policy, literacy education, and identity. This research has intersected with the field of information systems which has explored the dominant discourses and discursive practice of how information and communication technologies (ICTs) are viewed in policy and the contradictions between rhetoric and reality. It has also been drawn on in research in developing contexts to critique the role of ICTs in education. A brief historical background to CDA and overview of the key components of the approach will be provided. How CDA has been drawn on in educational studies will be examined and research on CDA will be highlighted to explore discursive practices of students and the influence of students’ digital identities on their engagement with and experience of online learning. By focusing on four key constructs of CDA—namely meaning, context, identity, and power—the potential of CDA to critically investigate how students’ are constructing their technological identity in an increasingly digital world will be demonstrated, particularly as examples of research emanating from developing contexts will be drawn.
- critical discourse analysis
- higher education
- information and communication technology
- digital world
Historical Overview
During the 1960s, the term “discourse” began to take on a more philosophical and theoretical meaning (Mills, 2004 ). In trying to provide an all-encapsulating summary of the theoretical conception of discourse, van Dijk ( 1997 ) notes that it goes beyond who uses the language to include the how, why and when. Underpinning this is a communicative event which observes that when people use language to communicate ideas, beliefs, or emotions, they do it as part of a more complex social event (i.e., within a context). Therefore, the three main dimensions of discourse analysis are language use, communication of beliefs, and interaction in social situations (van Dijk, 1997 ).
Critical approaches to discourse analysis first began to emerge as a cohesive paradigm in the early 1990s (Billig, 2003 ; Wodak & Myers, 2001 ) with the coming together of a network of scholars in Amsterdam (van Dijk, 2001 ), the launch of the journal Discourse and Society , and the “rise to fame” of various seminal, critical discourse analysis (CDA) books, such as Language and Power (Fairclough, 2001 ) and Language, Power and Ideology (Wodak, 1989 ). Billig ( 2003 ) notes the change from Fairclough’s discussion of critical approaches (in the plural) in his 1992 Discourse and Social Change to the use of the definite article in his book Critical Discourse Analysis in 1995 , which seemed to signal the recognition of a CDA that is used to refer particularly to Fairclough’s brand of discourse analysis.
CDA (as opposed to other types of discourse analysis) regards language as social practice and has been described as “at most a shared perspective on doing linguistic, semiotic and discourse analysis” (van Dijk, 1993 , p. 131) due to the “heterogeneity of methodological and theoretical approaches represented in this field of linguistics” (van Dijk, 2001 , p. 2). Its roots lie in “classical rhetoric, text linguistics and sociolinguistics as well as in applied linguistics and pragmatics,” and it still has a huge continuity with critical linguistics (van Dijk, 2001 , p. 3).
What distinguishes CDA from other sociolinguistic approaches relates primarily to the problem under investigation. Myers sums it up as “it endeavors to make explicit power relationships which are frequently hidden and thereby to derive results which are of practical relevance” (Myers, 2002 , p. 15). Because one of the central tenets of CDA is that discourses cannot be understood without reference to context, it draws on extra-linguistic factors in its research approach (Myers, 2002 ), particularly social processes and structures (Wodak & Myers, 2001 ).
CDA emerged at a time of growth in critical paradigms in other disciplines, such as critical anthropology and critical psychology (Billig, 2003 ). Billig ( 2003 , p. 37) notes that “in this context, the term ‘critical’ can be seen to mark out a specific genre of academic studies.” While most critical discourse analysts do not tend to position themselves directly with philosophers from the critical theory school, such as Kant and Popper, there are two philosophers who have had a strong influence on the development of CDA, namely Foucault and Habermas (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ).
However, even though CDA does not have a specific association with a single critical theorist, it does share the concerns and agenda of critical theorists in that it argues that language is always “part and parcel of, and partially constitutive of, specific social practices and the social practices always have implications for inherently political things like status, solidarity, the distribution of social goods and power” (Gee, 2004 , p. 23). Gee notes that when discourse analysis combines a model, grammar or textual analysis (of some kind) with sociopolitical and critical theories of society and its institutions, it becomes critical. Critical approaches always examine the implications of status, power, distribution of social goods, and solidarity.
Critical Discourse Analysis and Theory
One of the strengths of CDA is that it is multidisciplinary and essentially diverse (van Dijk, 2001 ). In fact, van Dijk ( 2001 , p. 95), who is one of its original proponents, says that good CDA scholarship seldom follows just one person or one approach but is enriched through the integration of the “best work of many people, famous or not, from different disciplines, countries, cultures and directions of research.” However, given that CDA is concerned with the critique of ideology and the effects of domination, it has clear links to critical theory. There is quite a broad range of epistemological and ontological positions that fall under the ambit of critical theory, ranging from the Frankfurt school of Habermas, Adorno, and Horkheimer, to the actor–network theory of Latour, to Marxism, to Bourdieu, to Foucault and Heidegger (Howcroft & Trauth, 2004 ). While there is no such thing as a uniform, common theory formation determining CDA (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ), it can also be argued that the plurality of theory in CDA is a positive phenomenon to which this research discipline owes its dynamics. The mediation between the social and linguistic levels of texts is highly relevant to the theory formation process of CDA (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ). The CDA viewpoint is likened to Giddens’s “duality of structure” and Bourdieu’s “structured and structuring structures”—as social systems and societies are not viewed as self-contained entities (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ). However, this flexibility within CDA has also been criticized, as lack of theoretical consistency or “indiscriminate mixing” can lead to inconsistencies that become even more acute when under the influence of grand theorists like Bourdieu and Giddens (Myers, 2002 ).
Weiss and Wodak ( 2003 ), therefore, recommend a number of steps in order to develop an integrated theoretical framework. Clarification of the theoretical assumptions regarding text, discourse, language, action, social structure, institution, and society should be done preceding analysis. This creates the framework for analytical operationalization. When using CDA, it is not about what grand theory is needed but rather which conceptual tools are relevant to solve which problem in which context. This makes the context of the discursive practice very important.
This requires the development of conceptual tools that are “capable of connecting the level of text or discourse analysis with sociological positions on institutions, actions and social structures” (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 , p. 8). These conceptual tools are analytical interfaces that allow connection between the linguistics and the sociological. They do not represent a “self contained edifice of theories” (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 , p. 8) but rather an integrated theoretical framework and mediate between “text and institution, communication and structure and discourse and society” (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 , p. 9).
The notion of discourse offers us possibilities for engaging critically with language and meaning located in the context of use (the speakers and their intentions in wider social, cultural, and political worlds).
Common Themes
While CDA has been noted as having a heterogeneity of methodological and theoretical approaches, cornerstones to the approach have been described as discourse, ideology, and power (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ; Wodak & Myers, 2001 ). CDA, like many other dominant theories of education, arose in the Global North, and whatever the opportunity for critical analyses it offers, has aimed at uncovering power relations, often focusing on disempowered groups, such as women (Adam, 2002 ; Kvasny, 2006 ; Trauth & Howcroft, 2006 ) or lower socioeconomic groups (Bozionelos, 2004 ; Lizie, Stewart, & Avila, 2004 ). This has made it a very useful approach for scholars operating in developing contexts (Brown, 2011 ; Ng’āmbi, 2008 ; Wagid & Wagid, 2016 ) and those exploring black discursive identity (Brock, 2018 ).
While the term discourse is used differently by researchers, all share the perspective that language use in speech and writing is a form of social practice (Fairclough, 2009 ) and that discursive practices—the process through which texts are produced (created) and consumed (received and interpreted)—are an important form of social practice which contribute to the constitutions of the social world (including identities and relations) (Pennycook, 2001 ).
Language is not viewed as powerful on its own but is seen to gain power by the use people make of it (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ). Discursive practices contribute to unequal power relations between social groups, namely class and gender, which have ideological effects. The research focus of CDA is therefore on the discursive practices which construct representations of the world, social subjects, and social relations (including power); and the role these have in furthering the interests of particular social groups (Fairclough, 2001 ; Pennycook, 2001 ; Wodak & Myers, 2001 ).
Differences and Points of Contention
One of the main criticisms leveled at CDA from “outside” the field is that it is an ideological interpretation and not an analysis. It has been criticized particularly for being prejudiced in favor of a particular ideological commitment (i.e., the uncovering of power imbalances and hidden meanings) and selecting texts that support this preferred interpretation (Myers, 2002 ).
However, the main response to this has been that CDA is transparent about its positions and commitments, and does not hide this bias (Myers, 2002 ). CDA is not politically neutral but is committed to social change and takes the side of oppressed social groups (Jørgenson & Phillips, 2002 ). In this, van Dijk ( 2001 ) notes that it is biased scholarship and is proud of it. He also notes that biased scholarship is not necessarily bad scholarship if based on rigorous scholarship with explicit and systematic methods that are empirically grounded.
This particular conflation of discourse and ideology has been tackled head on by Pennycook ( 2001 ), who also takes issue with the way the real world is confused with ideology in CDA and consequently adopts a more explicitly Foucauldian position on discourse that separates discourse and ideology, suggesting that the latter determines the former. Discourses are about the creation and limitation of possibilities; they are systems of power and knowledge within which subject positions are taken up. A Foucauldian analysis is not concerned with how discourses (texts) reflect social reality, but how they produce social reality (Pennycook, 2001 ).
Critical discourse researchers also openly acknowledge the diversity of theoretical and methodological approaches, publishing books that explicitly explore the multidisciplinary range of both (Weiss & Wodak, 2003 ; Wodak & Myers, 2001 ).
Critical discourse researchers are not shy of self-criticism or reflection. Billig ( 2003 ) raises the issue of subjecting the field of CDA to its own critique in an endeavor to be reflexively self-critical and aware that CDA must necessarily occur within an academic context of power and economic relations. Billig ( 2003 ) notes that academics themselves replicate power imbalances through the process of teaching, grading and passing or failing students.
Critical Discourse Analysis in Education
CDA as a multidisciplinary set of theories and methods has been adopted in educational research by scholars exploring the ideological nature of educational practices and the social, historical, and political contexts in which they emerge and are transformed.
It has increased in prominence in educational research over the past 20 years, particularly in countries where English is the primary language: the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, or Canada (Rogers et al., 2016 ). In a review of CDA and education-related literature between 2004 and 2016 , Rogers et al. ( 2016 ) noted that the majority of studies were situated in the higher education contest (including teacher education and professional development), but were also scattered across early childhood right through middle and high school settings to include community and adult education. Nearly half of the studies included a focus on cultural and linguistic diversity of students or teachers, or an emphasis on local, state, or national ideologies. Although the study of global technologies in CDA research increased (20%), Rogers et al. ( 2016 , p. 24) noted a paucity of CDA research in the area of online learning and became interested by the lack of critical examination of digital data sources, commenting that CDA was “amply prepared to inquire into how meanings are made in an increasingly digital world.”
Rogers ( 2004 ) notes that Gee is one of the few examples where discourse theories have been applied to matters of learning. It is therefore not surprising that many of the applications of his research have a firm base in the areas of education. In addition, because of his explicit link between Discourses and identities, Gee’s ( 2000 ) approach to discourses has been utilized by various researchers across many different contexts (e.g., fan fiction writing, internationalization of universities, and science learning) to examine how individuals use language and text to identify aspects of their identity when traditional markers of identity are unavailable. Gee’s concept of big D Discourse encompasses more than just the use of language (what he refers to as little d discourse); it includes ways of being (thinking, acting, and interacting) (Gee, 2005 ) that take on socially meaningful identities in various situations or contexts.
For example, Black ( 2008 ) looks at the world of online gaming and how individuals use language and text to identify aspects of their identity when traditional markers of identity are unavailable. She examines the sort of roles an individual occupies compared to the one ascribed to them by society. Brown, Reveles, and Kelly ( 2005 ) examine how the relationship between language, identity, and classroom learning can provide insights into how students learn to become literate members of a scientific community. They note that, in every discursive exchange, speakers and listeners are co-constructing meaning through interactions that position them as certain types of people. Their examples focus on students’ demonstrations of themselves as experts, willing participants in the discourse, and outsiders.
Gee’s notion of D(d)iscourse has been drawn on to better understand the way in which groups of students construct science knowledge in an engineering context. Kittleson and Southerland ( 2004 ) did not find much evidence of competing discourses and attributed this to the unusual homogeneity of the students’ group, but they did note that the disciplinary discourse of engineering was an important element in structuring the groups’ interactions. In order to understand their work on a project, students had to be aware of the ways in which they actualized their understanding of being engineers and doing engineering.
The contradictions between different types of discourses were also explored in an Australian education context where primary school girls struggled with discourses of ethnicity in a Studies of Asia curriculum project (Hamston, 2006 ). Here Fairclough’s earlier textually oriented discourse analysis (TODA) was complemented by Bakhtin’s theory of dialogue. This enabled a micro-linguistic description of the data, which was foundational to the students’ struggle with discourses and their framing of it within the curriculum and an exploration of the shift toward the individual nature of the struggle occurring at a micro level within the classroom. The flexibility of CDA to work alongside other approaches enabled foregrounding of both the larger social discourses at play as well as the individual internalized discourses.
Discourses and Information and Communication Technologies
In the field of information systems CDA has played a role in understanding people’s interaction with ICTs generally, which has aided in interpreting hidden meaning about ICTs and in understanding what ICTs are, how they can be used, and how different understandings affect use (Stahl, 2004 ).
Examples of this include analysis of media discourses about technology projects and applications in Canada and South Africa (Chigona & Chigona, 2008 ; Chigona, Mjali, & Denzl, 2007 ; Cukier, Bauer, & Middleton, 2004 ; Cukier, Ngwenyama, Bauer, & Middleton, 2009 ), and the exploration of contradictions between rhetoric and reality in Egyptian ICT policy (Stahl, 2004 , 2008 ). This has been extended into the education context with a CDA analysis of specifically ICT educational policy in Cameroon (Ndenge, 2013 ), Zambia (Konayuma, 2012 ), and Rwanda (Byungara et al., 2016 ). The research concludes that CDA was useful in understanding the particular historical, social, and political contexts, and some of the contradictions between these in terms of the perceived and actual role of ICTs in education in developing contexts.
Building on CDA research of discursive practice and genres in relation to global or national ICT policy (Roode, Speight, Pollock, & Webber, 2004 ; Thompson, 2004 ), Ng’ambi ( 2008 ) explored social practices (text messages) in a community of online learners in the South African higher education context. He highlighted the tension between perceptions of inflexibility of traditional teaching practices and student demands for flexible learning. In Pakistan Perveen ( 2015 ) evaluated discursive practice in online discussion forums and noted how a virtual context (which lacks explicit social context as it is anonymous and devoid of usual demographic details) enables a neutrality that can be very empowering for learners as it does not explicitly reproduce sociopolitical hierarchies. Rambe ( 2012 ) analyzed academic relations in social media sites such as Facebook using CDA in the South African higher education context. He noted less formal, more liberating discourses, and a nascent developing networked learning culture (although one where learning was still regarded as shallow rather than deep, and that has not achieved its transformational potential). CDA was also used as an analytical tool to engage secondary school students deliberately and critically to explore social, political, and cultural issues using Facebook as a social media platform (Waghid & Waghid, 2016 ).
Using CDA to explore interactions in a virtual learning environments, Giles ( 2017 ) examined how learners use discourse devices to portray identities and how this can contribute to their learning in the higher education context in Mexico. She foregrounds the complexity of multiple identities and their role in creating a social presence which is essential for effective learning in a virtual context. In the South African higher education context, Brown explored discursive practices using CDA to expose hidden assumptions about power and implicit ideologies related to technology in education. The dominant Discourse around learning was about efficiency rather than effectiveness of learning with some students viewing technology as a liberator with access to information equating to knowledge (in their mind). However, they lacked the critical digital literacy abilities that are needed to transform their learning. There is also a small but significant group who feel alienated by technology. These students are marginalized and face enormous challenges in using technology effectively for their learning (Brown, 2012 ; Brown & Hart, 2012 ).
Similarly, but with a focus on instructors this time, the discursive practices around online learning were explored at open universities in two countries where cultural norms meant the relationship between students and teachers were viewed quite differently (Lee & Brett, 2014 ). The prevailing rhetorical discourse was shown to be one of interactivity (or lack of it). Like Brown, Lee noted this had the potential to marginalize particular groups of students and urged researchers not to have a single-minded focus on developing more effective interactive distance education practices as the only response to online education ( 2014 ).
Discourses about Information and Communication Technologies and Education
Research on discourses of ICTs in education has revealed a variety of themes across educational settings, and while researchers have named these differently and noted varying levels of dominance across their contexts, these can generically be categorized as technological optimism, disembodiment, liberation, imperialism/globalization (digital divide), and productivity (Brown, 2012 ; Budd, 2005 ; Sasseville, 2004 ).
Technological optimism privileged technology, seeing it as a “force to which all things must respond and adapt” (Budd, 2005 ), as having “no choice but to follow technological evolution” and from the teachers’ point of view, as essential for today’s job market (Sasseville, 2004 ), and being essential for the working world since “nowadays wherever a person is working, a computer is needed” (Brown, 2012 , p. 50).
The invisible space or disembodiment in the virtual space due to a lack of physical presence offered both positive dimensions to learning, namely anonymity and potential empowerment for marginal groups (Budd, 2005 ), and negative ones as learners feel disconnected: “a person can depend too much on using ICTS & not even use their own mind to think & study from books” (Brown, 2012 , p. 51).
The myth of freedom of information and notions of liberation through the availability of free information ignores the reality that information is commodified and controlled. Sasseville notes that having access to so much information changes the way students think ( 2004 ) while Brown ( 2012 ) notes both opportunities this offers students in terms of furthering themselves in their studies and in contrast new forms of discrimination.
The discourse on imperialism, which Budd ( 2005 ) notes, acknowledges social divisions and yet still “sells” ICTs to the world as potentially liberating for development, which contributes to reinforce the myth of the global marketplace and neoliberal education. Brown ( 2012 ) notes that students in developing contexts often view this as “the privilege of having access to and using these new technologies” (p. 50).
Productivity discourses viewed ICTs as having a strong imperative and helping students to get things done better, faster, and to keep up with the fast pace of life. However, teachers in Sasseville’s study ( 2004 ) were also aware of the challenges of learning to use new technologies and were principally concerned with the lack of time at their disposal.
Value of Critical Discourse Analysis as an Approach to Information and Communication Technologies in Education
Avgerou and Madon ( 2004 ) note that it is necessary to understand new technologies (i.e., the Internet and the mobile phone), which can only be achieved by taking into account their symbolic meaning in everyday life. One of the ways of examining meaning is to look at identity, as identity also acts as a source of meaning and experience for people (Koc, 2006 ). It is not just about how the technology is adopted, but also about the way it is integrated into people’s lives (Cushman & McLean, 2008 ). However, critical research involves a shift away from just individual situations and local meanings to the system of relations which make these meanings possible (Trauth & Howcroft, 2006 ). Thus, context is critical if we are to understand how ICTs are used, especially in developing countries (Avgerou & Madon, 2004 ).
Issues of power surface when people’s freedom to set and pursue their own goals and interests or achieve their personally constructed life projects are curtailed (Cushman & McLean, 2008 ; Zheng & Walsham, 2008 ). That is, where local actors are not able to shape ICTs to their interests and appropriate their functionality.
Consequently, Brown ( 2011 ) foregrounded four key analytical concepts which she believed were key to exploring the relationship between ICTs and learning in a resource constrained context. These were identity and meaning (which were considered essential in understanding how new technologies were appropriated), context (which was necessary to examine the system as a whole), and power (as this influenced what was possible within the context the actors operated within).
One of the key elements of discourse analysis (critical or not) is the relationship between form (the hard structures of the linguistic system, i.e., the words, nouns, adjectives, verbs, etc.) and the function (the soft structures; i.e., the communicative purpose or, as Gee [ 2004 , 2005 ] phrases it, the “meaning potential”) (Rogers, 2004 ). Gee’s ( 1994 ) premise is that literacy in and of itself does not lead to any higher level cognitive skill, but that literacy acquisition is a form of socialization into a mainstream way of taking meanings, of making sense of experiences, and that, as students participate in different literacy practices, they begin to partake of this set of values and norms, of this worldview.
Given that higher education institutions are expected to produce students who are computer proficient and have 21st-century skills, the importance of having a positive attitude toward computers and high computer self-efficacy is critical to students learning (Kilfoil, 2015 ; Schlebusch, 2017 ). It is therefore not surprising that students are so positive about ICTs and their role in education. How can they not be? In Brown’s ( 2011 ) research students were positive about the global opportunities ICTs enable, the value of ICTs for learning, the access to information offered, and the efficiencies ICTs offered them in life. However, by excavating beneath the surface of the Discourse and endeavoring to uncover hidden meanings, it became clear that “discursive mechanisms” limited what could be said, in what forms, and what was counted as worth knowing or remembering (Mills, 2004 ). Using this concept of hidden meanings, one can see how hard it is for students to say anything negative about computers and technology. Their overwhelmingly positive attitudes are not necessarily a true reflection of what they think. It is a consequence of operating in a larger context where negativity with regard to ICTs is perceived to be associated with ignorance which is then associated with backwardness (Brown, 2011 ).
CDA has been noted by Ainsworth and Hardy ( 2004 , p. 225) as being “regularly used to study identity.” For Gee ( 1996 ), capital “D” Discourses are a sort of identity kit. They are the combination of what people say, do, think, feel, and value. Each community or social group masters a home-based discourse that integrates words, actions, values, feelings, attitudes, and thinking in specific and distinctive ways. Each of these discourses is connected to a particular social group’s way of being in the world, its “form of life,” its very identity it regards itself as having (Gee, 1996 ). Discourses are acquired through enculturation into a social practice and they cannot be taught (Gee, 1996 ).
Each discourse incorporates a usually taken-for-granted and tacit theory of what counts as a normal person and the right way to think, feel, and behave. These theories crucially involve viewpoints on the distribution of social goods, like status and worth, and material goods in society (who should and should not have them). They are defined not just by what they are, but also by what they are not (i.e., often in relation to an opposing discourse).
Discourse theories are related to the distribution of social power and hierarchical structure in society and empower the groups who have the least conflict between their discourses. Sometimes people’s discourses can be conflicting. For example a discourse can be at odds with a person’s other social practices. Gee ( 2005 ) also notes that it is a great advantage when secondary discourses are compatible in words, deeds, and values with one’s primary discourse.
However, identity construction is more than the sum of an individual’s social experiences. There is an inherent tension between group affiliation and individual agency. Membership of an identity group does not determine behavior but, as Foucault notes ( 1994 ), there is an ease with which people readily accept the social groupings imposed.
Students do not just talk about technology, but also about how technology makes them feel, what values it holds for them, and what role they see for technology in their lives. These collections of ideas are a representation of an identity, in that it shows how students understand their relationship to the digital world, how that relationship is constructed across time and space, and how they understand their possibilities for the future (Norton, 2000 ). As Foucault ( 1994 ) notes, membership of an identity group does not determine one’s behavior, but there is an ease with which people readily accept the social groupings imposed on them. Many students do not exercise individual agency and move with the mainstream Discourse, feeling like outsiders, marginalized, excluded, lost, and powerless. Thus, technological identity has a role in both facilitating and constraining students’ participation and future opportunities (Brown, 2011 ).
Blommaert ( 2005 ) notes that context is a crucial methodological and theoretical issue within CDA as it comes in various shapes and sizes, and operates at different levels from very small to very big. Context is potentially everything and potentially infinite, but it can be to some extent predictable.
Another important aspect of context is Foucault’s ( 1969 ) rooting of discourse as a historical product, Gee ( 2008 , p. 162) notes that, in this regard, it is sometimes helpful to say that “it is not individuals who speak and act but rather that historically and socially defined Discourses speak to each other through individuals. The individual instantiates, gives body to a Discourse every time he or she acts or speaks, and thus carries it and ultimately changes it through time.”
In other words, discourses are systematically organized sets of statements that give expression to the meanings and values of an institution. Beyond that, they define, describe, and delimit what it is possible to say and what it is not possible to say (and by extension, what to do, and what not to do) with respect to the area of concern of that institution, whether marginally or centrally (Pennycook, 2001 ).
In resource constrained contexts there exists an economic and moral dilemma with regard to using technology for learning and teaching as students come from diverse backgrounds, geographical locations, and material and technological capacities. In South African higher education this means that access to ICTs cannot be assumed (Broekman, Enslin, & Pendlebury, 2002 ; Brown & Pallitt, 2015 ; Czerniewicz & Brown, 2014 ). This dilemma is not unique to the context of developing countries. Even in contexts with high Internet penetration like New Zealand, disparities of digital access have also been observed as a consequence of socioeconomic background (Internet World Stats, 2016 ). This influences the number of digital devices in the home, the types of devices available, and whether the device(s) are shared or individually owned by students (Hartnett, 2017 ). The contextual reality is that we cannot ever assume equality, and we need to consciously choose not to disadvantage particular groups of students due to their socioeconomic or cultural contexts.
Theoretically, the concept of power is hotly contested. In a history of theoretical conceptions of power, Hindess ( 1996 ) describes three core views of power at the level of the individual. The first view of power is as a capacity to act, where people use power over things and people. In this view, there is an unequal relationship between those who use power for their own purposes and those who are subject to its effects; and power is used as an instrument of domination.
The second view of power is one where the subjugated are covertly excluded from decision-making structures and thus, while they might be exercising some voice, that voice is not heard.
The third view of power is where the subjugated are compliant in their powerlessness, failing to recognize that their interests are at risk or not making any attempts to defend these interests.
The view of power and identity as being open to change is crucial as it opens up opportunities or possibilities for interventions—a crucial aspect of critical research.
Norton ( 2000 , p. 7) comes up with a very useful succinct definition of power as the “socially constructed relations among individuals, institutions and communities through which symbolic and material resources in society are produced, distributed and validated” relations that are inevitably produced in language.
Having access and being seen to be computer or digitally literate is a big status symbol, and students perceive the opportunities afforded through digital technologies and use of ICTs as giving them higher status and more power. Interestingly, there is a contradiction though as students with empowerment also come with feelings of disempowerment. They feel they are operating in an environment with limited options and choices, hence limiting their sense of empowerment. Thus, students are encouraged to embrace technology but within its existing structures and processes, in other words, they seldom challenge it in the way described by Kvasny and Trauth ( 2002 , p. 276) as “commandeering IT to charts one’s own usage and career course.” However, there is some evidence of students who demonstrate agency and drive to achieve their goals, despite contextual challenges (Czerniewicz & Brown, 2014 ).
CDA as a theoretical and methodological approach enables researchers to systematically explore language (in whatever form it takes) and to move beyond understanding what people say to understanding meaning. This enables them to uncover hidden power dynamics, critique the status quo, and challenge dominant views. CDA places the unit of analysis at the level of the individual, and foregrounds social and cultural contexts by situating lived experiences in a landscape of culturally situated practices and by enabling a more nuanced understanding of peoples’ worlds. Research drawing on CDA to explore the intersection of ICTs and education has demonstrated its value as a lens for questioning assumptions, understanding the marginalized, and mapping contradictions between policy and practice. Yet there is still further potential to draw on this approach in educational studies in particular by exploring technological identities and practices. The type of technological identity a student holds creates both academic opportunity and obstacles for them. By understanding the act of being a student in social, economic, political, and educational terms and how students construct their technological identities and position themselves, they can benefit from better support. In their learning, viewing identities as a product of participation in communities (i.e., as contextually specific) can strengthen the investigation of how digital experiences influence individuals’ relationhships with technology.
This article has demonstrated that, although CDA has been dominated by analysis of formal texts like policy documents, there is a move to using and encouraging CDA in new emerging texts and discourses, particularly in resource constrained contexts. This is an underdeveloped opportunity for CDA to expand as a methodological approach to exploring the intersections of learning in a digital world.
- Adam, A. (2002). Exploring the gender question in critical information systems. Journal of Information Technology , 17 , 59–67.
- Ainsworth, S. , & Hardy, S. (2004). Critical discourse analysis and identity: Why bother? Critical Discourse Studies , 1 (2), 225–235.
- Avgerou, C. , & Madon, S. (2004). Framing is studies: Understanding the social context of is innovation. In C. Avgerou , C. Ciborra , & F. Land (Eds.), The social study of information and communication technology (pp. 162–182). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Billig, M. (2003). Critical discourse analysis and the rhetoric of critique. In G. Weiss & R. Wodak (Eds.), Critical discourse analysis: Theory and interdisciplinarity . New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Black, R. W. (2008). Adolescents and online fan fiction . New York, NY: Peter Lang.
- Blommaert, J. (2005). Discourse: A critical introduction . London, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Bozionelos, N. (2004). Socio-economic background and computer use: The role of computers anxiety and computer experience in their relationship. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies , 61 , 724–746.
- Brock, A. (2018). Critical technocultural discourse analysis. New Media & Society , 20 (3), 1012–1030.
- Broekman, I. , Enslin, P. , & Pendlebury, S. (2002). Distributive justice and Information Communication Technologies in higher education in South Africa. South African Journal of Higher Education , 16 (1), 29–35.
- Brown, B. A. , Reveles, J. M. , & Kelly, G. (2005). Scientific literacy and discursive identity: A theoretical framework for understanding science learning. Science Education , 89 (5), 779–802.
- Brown, C. (2011). Excavating the meaning of information and communication technology use amongst South African university students: A critical discourse analysis (Doctoral thesis). University of Cape Town, South Africa.
- Brown, C. (2012). University students as digital migrants. Language and Literacy , 14 (2), 41–61.
- Brown, C. , & Hart, M. (2012). Exploring higher education students’ technological identities using critical discourse analysis. In P. Isaias & M. B. Nunes (Eds.), Information systems research and exploring social artifacts: Approaches and methodologies . Hershey, PA: IGI Global.
- Brown, C. , & Pallitt, N. (2015). Personal mobile devices and laptops as learning tools. In W. R. Kilfoil (Ed.), Moving beyond the hype: A contextualised view of learning with technology in higher education . Pretoria: Universities South Africa.
- Budd, Y. ((2005, November 15–18). Technological discourses in education . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the International Conference on Critical Discourse Analysis: Theory into Research. University of Tasmania, Australia.
- Byungara, J.-C. , Hansson, H. , Masengesho, K. , Karunaratne, T. (2016). ICT capacity building: A critical discourse analysis of Rwandan policies from higher education perspective. European Journal of Open, Distance and e-Learning , 19 (2), 46–62.
- Chigona, A. , & Chigona, W. (2008). MXit up in the media: Media discourse analysis on a mobile instant messaging system. Southern Africa Journal of Information and Communication , 9 , 42–57.
- Chigona, W. , Mjali, P. , & Denzl, N. (2007, November 18–23). Role of ICT in national development: A critical discourse analysis of South Africa’s government statements . Paper presented at the QualIT’07 Qualitative research in IT, Wellington, New Zealand.
- Cukier, W. , Bauer, R. , & Middleton, C. (2004). Applying Habermas’ validity claims as a standard for critical discourse analysis. In B. Kaplan , D. P Truex , D. Wastell , A. T. Wood-Harper , & J. DeGross (Eds.), Information systems research: Relevant theory and informed practice (pp. 233–258). London, U.K.: Kluwer Academic.
- Cukier, W. , Ngwenyama, O. , Bauer, R. , & Middleton, C. (2009). A critical analysis of media discource on information technology: Preliminary results of a proposed method for critical discourse analysis. Information Systems Journal , 19 , 175–196.
- Cushman, M. , & McLean, R. (2008). Exclusion, inclusion and changing the face of information systems research. Information Technology & People , 21 (3), 213–221.
- Czerniewicz, L. , & Brown, C. (2014). The habitus and technological practices of rural students: A case study. South African Journal of Education , 34 (1), 1–14
- Fairclough, N. (2001). Language and power (2nd ed.). London, U.K.: Longman.
- Fairclough, N. (2009). A dialectical-relational approach to critical discourse analysis in social research. In R. Wodak & M. Myers (Eds.), Methods of critical discourse analysis (2nd rev. ed., pp. 162–186). London, U.K.: SAGE.
- Foucault, M. (1969). The archaeology of knowledge ( A. M. Sheridan Smith , Trans.). London, U.K.: Routledge.
- Foucault, M. (1994). Truth and power. In J. Faubion (Ed.), Power (pp. 111–133). New York, NY: The New Press.
- Gee, J. (1994). Orality and literacy: From the savage mind to ways with words. In J. Maybin (Ed.), Language and literacy in social practice (pp. 168–192). Clevedon, U.K.: Multilingual Matters.
- Gee, J. (1996). Social linguistics and literacies: Ideology in discourses . London, U.K.: Falmer.
- Gee, J. (2000). Identity as an analytical lens for research in education. Review of Research in Education , 25 (1), 99–125.
- Gee, J. (2004). What is critical about critical discourse analysis? In R. Rogers (Ed.), An introduction to critical discourse analysis (pp. 19–50). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Gee, J. (2005). An introduction to discourse analysis (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
- Gee, J. (2008). Social linguistics and literacies (2nd ed.). London, U.K.: Falmer.
- Giles, D. (2017). Discourse in the development of identities in an online teacher education programme . Memorias del Encuentro Internacional de Educación a Distancia , 5 (5).
- Hamston, J. (2006). Bakhtin’s theory of dialogue: A construct for pedagogy, methodology and analysis. Australian Education Researcher , 33 (1), 55–74.
- Hartnett, M. (2017). Differences in the digital home lives of young people in New Zealand. British Journal of Educational Technology , 48 (2), 642–652.
- Hindess, B. (1996). Discourses of power . Oxford, U.K.: Blackwell.
- Howcroft, D. , & Trauth, E. (2004). The choice of critical information systems research. In B. Kaplan , D. P. Truex , D. Wastell , A. T. Wood-Harper , & J. DeGross (Eds.), Relevant theory and informed practice: Looking forward from a 20 year perspective on IS research (pp. 195–211). London, U.K.: Kluwer.
- Internet World Stats . (2016). Internet world stats: Usage and population statistics .
- Jørgenson, M. , & Phillips, M. (2002). Discourse analysis as theory and method . London, U.K.: SAGE.
- Kilfoil, W. R. (Ed.) (2015). Moving beyond the hype: A contextualised view of learning with technology in higher education . Pretoria: Universities South Africa.
- Kittleson, J. , & Southerland, S. (2004). The role of discourse in group knowledge construction: A case study of engineering students. Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 41 (3), 267–293.
- Koc, M. (2006). Cultural identity crisis in the age of globalisation and technology. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology , 5 (1), 37–43.
- Konayuma, G. (2012). A critical discourse analysis of e-learning policies in education and training in Zambia . Paper presented at the ODL 12, Pretoria, South Africa.
- Kvasny, L. (2006). Let the sisters speak: Understanding Information Technology from the standpoint of the “other.” Database for Advances in Information Systems , 37 (4), 13–25.
- Kvasny, L. , & Trauth, E. (2002). The digital divide at work and at home: Discourses about power and underrepresented groups in the Information Society. In E. Whitley , E. Wynn , & J. DeGross (Eds.), Global and organizational discourse about information technology (pp. 273–294). New York, NY: Kluwer Academic.
- Lee, K. , & Brett, C. (2014). A critical discourse analysis: Reconceptualising online distance learning through a Foucauldian lens . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Networked Learning 2014.
- Lizie, A. , Stewart, C. , & Avila, G. (2004, July 24–30). Cultural dimensions of the digital divide: Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) and Brockton’s Cape Verdeans . Communication and Technology Policy Division 2004 International Association for Media and Communications Research Conference, Porto Alegre, Brazil.
- Mills, S. (2004). Discourse: The new critical idiom . London, U.K.: Routledge.
- Myers, M. (2002). Between theory, method, and politics: Positioning of the approaches to CDA. In R. Wodak & M. Myers (Eds.), Methods of critical discourse analysis (pp. 14–31). London, U.K.: SAGE.
- Ndenge, K. (2013). Analysing Cameroon government’s ICT policy documents and trainee teachers’ perception of ICT in education policy implementation using critical discourse analysis . Paper presented at the Pan-Commonwealth Forum 7 (PCF7).
- Ng’ambi, D. (2008). A critical discourse analysis of students anonymous online postings. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education , 4 (3), 31–39.
- Norton, B. (2000). Identity and language learning: Gender, ethnicity and educational change . Harlow, U.K.: Pearson Education.
- Pennycook, A. (2001). Critical applied linguistics: A critical introduction . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Perveen, A. (2015). Critical discourse analysis of moderated discussion board of abstract virtual university of Pakistan . Open Praxis , 7 (3), 243–262.
- Rambe, P. (2012). Critical discourse analysis of collaborative engagement in Facebook postings. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology , 28 (2), 295–314.
- Rogers, R. (2004). An introduction to critical discourse analysis in education . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Rogers, R. , Schaenen, I. , Schott, C. , O’Brien, K. , Trigos-Carrillo, L. , Starkey, K. , & Chasteen, C. (2016). Critical discourse analysis in education: A review of the literature, 2004 to 2012 . Review of Educational Research , 86 (4), 1192–1226.
- Roode, D. , Speight, H. , Pollock, M. , & Webber, R. (2004, June 14). Its not the digital divide—Its the socio-techno divide! Paper presented at the 12th European conference on Information Systems Turka.
- Sasseville, B. (2004). Integrating information and communication technology in the classroom: A comparative discourse analysis . Canadian Journal of Learning Technology , 30 (2).
- Schlebusch, C. L. (2017). Computer anxiety, computer self-efficacy and attitudes towards the Internt at of first year students at a South African University of Technology. African Education Review , 15 (3), 72–90.
- Stahl, B. (2004, August). Whose discourse? A comparison of the Foucauldian and Habermasian concepts of discourse in critical is research . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the tenth Americas Conference on Information Systems, New York.
- Stahl, B. (2008). Empowerment through ICT: A critical discourse analysis of the Egyptian ICT policy. In C. Avgerou , M. L. Smith , & P. van der Besselaar (Eds.), Social dimensions Of information and communication technology policy. IFIP International Federation for Information Processing (vol. 282, pp. 161–177). Boston, MA: Springer.
- Stahl, B. (2009). Critical research and ethics. In C. Brooke (Ed.), Critical research in information systems (pp. 25–40). Oxford, U.K.: Elsevier.
- Thompson, M. (2004). ICT, power, and developmental discourse: A critical view. Electronic Journal on Information Systems in Developing Countries , 20 (4), 1–25.
- Trauth, E. , & Howcroft, D. (2006). Social inclusion and the information systems field: Why now? In E. Trauth , D. Howcroft , T. Butler , B. Fitzgerald , & J. D. Gross (Eds.), Social inclusion: Societal and organisational implications for information systems (pp. 347–364). Boston, MA: Springer.
- van Dijk, T. (1993). Editor’s foreword. Discourse and Society , 4 , 131–142.
- van Dijk, T. (1997). Discourses as structure and process . London, U.K.: SAGE.
- van Dijk, T. (2001). Multidisciplinary CDA: A plea for diversity. In R. Wodak & M. Myers (Eds.), Methods of critical discourse analysis . London, U.K.: SAGE.
- Wagid, Z. , & Wagid, F. (2016). Examining digital technology for (higher) education through action research and critical discourse analysis. South African Journal of Higher Education , 30 (1), 265–284.
- Weiss, G. , & Wodak, R. (2003). Introduction: Theory, interdisciplinarity and critical discourse analysis. In G. Weiss & R. Wodak (Eds.), Critical discourse analysis: Theory and interdisciplinarity (pp. 1–34). New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Wodak, R. (1989). Language, power, and ideology: Studies in political discourse Amsterdam, The Netherlands: J. Benjamins.
- Wodak, R. , & Myers, M. (2001). Methods of critical discourse analysis . London, U.K.: SAGE.
- Zheng, Y. , & Walsham, G. (2008). Inequality of what? Social exclusion in the e-society as capability deprivation. Information Technology & People , 21 (3), 222–243.
Related Articles
- Critical Perspectives on Evaluative Research on Educational Technology Policies in Latin America
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 14 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.15.189]
- 185.66.15.189
Character limit 500 /500
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Do a Critical Discourse Analysis
Last Updated: April 7, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 90,219 times.
The field of critical discourse analysis (CDA) involves taking a deeper, qualitative look at different types of texts, whether in advertising, literature, or journalism. Analysts try to understand ways in which language connects to social, cultural, and political power structures. As understood by CDA, all forms of language and types of writing or imagery can convey and shape cultural norms and social traditions. While there is no single method that covers all types of critical discourse analyses, there are some grounding steps that you can take to ensure that your CDA is well done. [1] X Research source
Working with a Text

- Texts could include things like Moby Dick , Citizen Kane , a cologne advertisement, a conversation between a doctor and their patient, or a piece of journalism describing an election.

- As a first step, circle all of the adverbs and adjectives in the text. Then, consider what they might suggest about the tone of the piece.
- Look for tone words to help you figure out what the author is trying to convey.
- For example, say you're looking at a piece of political journalism about the president. If the text describes the president as “the goofball in the Oval Office,” the attitude is sarcastic and critical.
- However, if the president is described as “the leader of the free world,” the attitude is respectful and even reverential.
- If the article simply refers to the president as “the president,” its attitude is deliberately neutral, as if the text refuses to “take sides.”

- For example, think about a news report about international immigrants coming to a country. The newscaster can create different types of community by referring to the immigrants as “strangers,” “refugees,” or “aliens.”
- The word “refugees” will prompt sympathy among listeners and will help build a community between citizens and immigrants, while “alien” will help create hostile feelings and will exclude the immigrants from the nation's community.

- For example, an 18th century short story that begins, “The savages attacked the unarmed settlers at dawn,” contains implicit interpretations and biases about indigenous populations.
- Another story that begins, “The natives and settlers made a peaceful arrangement,” has a comparatively benign interpretation of historical events.
Analyzing the Text's Form and Production

- For example, think about the difference between an author who writes a novel for money and one who writes for their own pleasure.
- The first author would want to tap into popular trends ends of the day in order to profit, while the second author would be less concerned with pleasing the public.

- For example, consider the case of a CEO delivering a speech in person to their company. The fact that they're delivering a speech and not sending an open letter shows that openness and transparency are important to the CEO and the company culture.
- If the CEO did not deliver a speech, but only sent an email to board members and top executives, the formal change would imply that the text had a very different audience. The email would make the CEO seem less personal, unconcerned about their own workers, and elitist in who they chose to address.

- For example, say that a contemporary writer opens a poem or story with: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.” Quoting Charles Dickens at once shows that the author is well-read and also grounds their writing in the English Victorian literary tradition.
Tracing Power in Social Practices

- For example, if a political speakers says, “our forefathers smile upon us today,” they are using patriarchal language.
- The term “culture” should be taken very broadly. Businesses can have cultures, as can communities of all sizes, countries, language groups, racial groups, and even hobbyists can have specific cultures.

- For example, consider 2 different magazine ads for trucks. In the first, a rugged-looking man sits in a truck below the words “The vehicle for men.” In the second, a family sits in a truck and the ad copy reads, “A truck to hold everybody.”
- The first ad seems to rely on stereotypical ideas of masculinity, while the second seems more inclusive.

- For example, imagine a politician whose slogan is “All energy should come from coal!” Because of the extremity of the stance, you may suspect that the candidate represents a fringe party that doesn't share many of the mainstream party's views.
- You could confirm this suspicion by looking at other candidates' speeches to see how they address the fringe candidate. If other candidates critique the fringe candidate, the latter is likely part of a sub-group whose views aren't shared by the main political culture.

- For example, companies like Ikea, Emirate Airlines, and McDonald's have strong cultures and norms that exist internationally.
Expert Q&A
- In an academic setting, CDA isn't tied to 1 single field or discipline. Instead, CDA helps students in a variety of fields understand ways in which the production of texts carries cultural meaning. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- As with any other theoretical field, there are many different ways to perform critical discourse analyses. However, they're largely the same at the core: the models all examine ways in which texts at the smallest (word-based) and the largest (social and cultural) levels have an impact on how communities are formed and what readers believe about the world. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0


You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.history.ac.uk/1807commemorated/media/methods/critical.html
- ↑ https://pages.gseis.ucla.edu/faculty/kellner/ed270/Luke/SAHA6.html#4
- ↑ https://study.com/academy/lesson/interpreting-literary-meaning-how-to-use-text-to-guide-your-interpretation.html
- ↑ https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/discourse-analysis/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/3w_5riFCMGA?t=378
- ↑ https://youtu.be/3w_5riFCMGA?t=669
- ↑ https://www.uv.es/gimenez/Recursos/criticaldiscourse.pdf
- ↑ https://youtu.be/3w_5riFCMGA?t=358
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Andrew Boyle
Jul 6, 2020
Did this article help you?

Oct 23, 2020
Aliyu Muhammad
Nov 29, 2022
SK Chakraborty
Apr 16, 2022
Aug 2, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Dissertations / Theses on the topic 'Critical Discourse Analysis/Discourse Analysis'
Create a spot-on reference in apa, mla, chicago, harvard, and other styles.
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Critical Discourse Analysis/Discourse Analysis.'
Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver, etc.
You can also download the full text of the academic publication as pdf and read online its abstract whenever available in the metadata.
Browse dissertations / theses on a wide variety of disciplines and organise your bibliography correctly.
Lillian, Donna L. "Canadian neo-conservative discourse a critical discourse analysis /." Thesis, National Library of Canada = Bibliothèque nationale du Canada, 2001. http://www.collectionscanada.ca/obj/s4/f2/dsk3/ftp05/NQ66355.pdf.
Thornborrow, Joanna. "Discourse, power and ideology : some explorations in critical discourse analysis." Thesis, University of Strathclyde, 1991. http://oleg.lib.strath.ac.uk:80/R/?func=dbin-jump-full&object_id=21500.
Flobakk, Fride Røe. "Educational Neuroscience - A Critical Discourse Analysis." Thesis, Norges teknisk-naturvitenskapelige universitet, Pedagogisk institutt, 2011. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:no:ntnu:diva-13057.
Tyrwhitt-Drake, Hugh. "A critique of critical discourse analysis." Thesis, University of Reading, 2005. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.424028.
Brodscholl, Per Christian. "Negotiating sustainability in the media: critical perspectives on the popularisation of environmental concerns." Curtin University of Technology, Faculty of Media, Society and Culture, 2003. http://espace.library.curtin.edu.au:80/R/?func=dbin-jump-full&object_id=13600.
Gillies, Donald. "Critical discourse analysis and current education policy." Thesis, University of Strathclyde, 2009. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.501919.
Michael, Michael. "Ordinary explanations as discourse : a critical analysis." Thesis, Durham University, 1986. http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/7059/.
Donno, Julian. "Make America Exceptional Again - Critical Discourse Analysis." Thesis, Malmö universitet, Fakulteten för kultur och samhälle (KS), 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:mau:diva-21045.
Foung, Kin Wai Dennis. "A critical discourse analysis of political speeches." HKBU Institutional Repository, 2008. https://repository.hkbu.edu.hk/etd_ra/979.
Wennberg, Alex. "Intuitivity in HCI : A critical discourse analysis." Thesis, KTH, Skolan för datavetenskap och kommunikation (CSC), 2017. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kth:diva-215274.
Aleshire, Seth Peter. "The Spectrum of Discourse: A Case Study Utilizing Critical Race Theory and Critical Discourse Analysis." Diss., The University of Arizona, 2014. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/338708.
Temple, Codruta. "Teaching and learning mathematical discourse in a Romanian classroom : a critical discourse analysis." Related electronic resource: Current Research at SU : database of SU dissertations, recent titles available, full text:, 2008. http://wwwlib.umi.com/cr/syr/main.
Frissa, Merertu Mogga. "Reproduction of Power: A Critical Discourse Analysis on Female Circumcision." Thèse, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2011. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/19962.
Marko, Georg. "Penetrating language a critical discourse analysis of pornography." Tübingen Narr, 2005. http://d-nb.info/986878383/04.
Widdowson, Henry George. "Text, context, pretext : critical issues in discourse analysis /." Oxford : Blackwell, 2004. http://catalogue.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/cb41322428h.
Hill, Heather L. Budd John. "Outsourcing the public library a critical discourse analysis /." Diss., Columbia, Mo. : University of Missouri--Columbia, 2009. http://hdl.handle.net/10355/6126.
Weber, Jean Jacques. "Critical analysis of fiction : essays in discourse stylistics /." Amsterdam ; Atlanta (Ga.) : Rodopi, 1992. http://catalogue.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/cb356957750.
Gomez, John-Paul. "Critical Discourse Analysis of Sexual Enhancement Medication Ads." ScholarWorks@UNO, 2004. http://scholarworks.uno.edu/td/179.
Lemoine, Hannah. "Editorial Framing. Critical Discourse Analysis of Swedish Editorials." Thesis, Malmö högskola, Fakulteten för kultur och samhälle (KS), 2016. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:mau:diva-23756.
Chan, Lit-chung. "Discourse of justice in Hong Kong." Click to view the E-thesis via HKUTO, 2006. http://sunzi.lib.hku.hk/HKUTO/record/B3955871X.
Liu, Shubo. "Advertising greenness in China : a critical discourse analysis of the corporate online advertising discourse." Thesis, University of Edinburgh, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/1842/11738.
Ho, Hong Wai. "The discourse of gaming : a critical discourse analysis of casino promotional materials in Macau." Thesis, University of Macau, 2010. http://umaclib3.umac.mo/record=b2456334.
Lahlali, El Mustapha. "Morroccan classroom discourse and critical discourse analysis : the impact of social and cultural practice." Thesis, University of Leeds, 2003. http://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/451/.
Bernard, Taryn. "Justificatory discourse of the perpetrator in TRC testimonies : a discourse-historical analysis." Thesis, Stellenbosch : University of Stellenbosch, 2009. http://hdl.handle.net/10019.1/1571.
DiAngelo, Robin J. "Whiteness in racial dialogue : a discourse analysis /." Thesis, Connect to this title online; UW restricted, 2004. http://hdl.handle.net/1773/7867.
Yates, Mark Timothy. "Congressional Debates Over Prisoner Education: A Critical Discourse Analysis." Digital Archive @ GSU, 2009. http://digitalarchive.gsu.edu/eps_diss/39.
HAIG, EDWARD. "Some Observations on the Critique of Critical Discourse Analysis." 名古屋大学大学院国際言語文化研究科, 2004. http://hdl.handle.net/2237/7888.
Doncaster, Katherine. "Making meaning in research interviews : a critical discourse analysis." Thesis, Lancaster University, 1995. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.260280.
Yates, Mark T. "Congressional debates over prisoner education a critical discourse analysis /." unrestricted, 2009. http://etd.gsu.edu/theses/available/etd-06092009-204218/.
Oliver, Hannah, and Hannah Oliver. "Politics of Climate Action Plans: A Critical Discourse Analysis." Thesis, University of Oregon, 2012. http://hdl.handle.net/1794/12424.
Johnson, Ayala Monique. "Ideology in home economics education : a critical discourse analysis." Thesis, University of British Columbia, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/2429/53523.
Fotiadou, Maria. "The discourse of careers services : a corpus-based critical discourse analysis of UK university websites." Thesis, University of Sunderland, 2017. http://sure.sunderland.ac.uk/10127/.
Davies, Alison. "Conceptions of 'talent' in official and student discourses within a music conservatoire : a critical discourse analysis." Thesis, Birmingham City University, 2002. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.272089.
Berlinger, Randi S. "Negotiating Identities Through Langauge,Learning, and Conversation." Diss., The University of Arizona, 2007. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/194420.
Petitclerc, Adèle. "Le postulat critique au coeur de l'analyse de discours. Introduction critique aux bases méthodologiques et épistémologiques des Critical Discourse Studies." Thesis, Besançon, 2014. http://www.theses.fr/2014BESA1017/document.
Chan, Lit-chung, and 陳烈忠. "Discourse of justice in Hong Kong." Thesis, The University of Hong Kong (Pokfulam, Hong Kong), 2006. http://hub.hku.hk/bib/B3955871X.
Haig, Edward. "A Critical Discourse Analysis of Discourse Strategies in Reports of Youth Crime in UK Radio News." 名古屋大学大学院国際言語文化研究科, 2008. http://hdl.handle.net/2237/10138.
Dogan, Oguzhan. "Upper Elementary Mathematics Curriculum In Turkey: A Critical Discourse Analysis." Phd thesis, METU, 2012. http://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/12614470/index.pdf.
Haber, Rebecca. "Urban revitalization and healthy public spaces, a critical discourse analysis." Thesis, University of British Columbia, 2011. http://hdl.handle.net/2429/33817.
Tsang, Y. S. "Ideology and curriculum a critical analysis of school administrators' discourse /." Click to view the E-thesis via HKUTO, 2005. http://sunzi.lib.hku.hk/hkuto/record/B31679353.
Provencher, Laura Elizabeth. "A Critical Analysis of the Islamic Discourse of Interfaith Dialogue." Thesis, The University of Arizona, 2010. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/193449.
Attar, Mohammed Arif. "A critical discourse analysis of the 'GM Nation?' public debate." Thesis, University of Newcastle Upon Tyne, 2012. http://hdl.handle.net/10443/1399.
Baker-Beall, Christopher. "The European Union's fight against terrorism : a critical discourse analysis." Thesis, Loughborough University, 2011. https://dspace.lboro.ac.uk/2134/8964.
曾宇新 and Y. S. Tsang. "Ideology and curriculum: a critical analysis of school administrators' discourse." Thesis, The University of Hong Kong (Pokfulam, Hong Kong), 2005. http://hub.hku.hk/bib/B31679353.
Jerkins, Jae. "Resplendent Ares: Critical Analysis of the Modernist Discourse of Mars." Honors in the Major Thesis, University of Central Florida, 2006. http://digital.library.ucf.edu/cdm/ref/collection/ETH/id/1228.
MacLeod, Nicola Joan. "Police interviews with women reporting rape : A critical discourse analysis." Thesis, Aston University, 2010. http://publications.aston.ac.uk/15206/.
Peralta, Adriane Kayoko. "A Critical Discourse Analysis of the Obama Administration’s Education Speeches." Digital Commons at Loyola Marymount University and Loyola Law School, 2012. https://digitalcommons.lmu.edu/etd/241.
Santy, Fertiana. "Representation of Muslim women in French jurisprudence : critical discourse analysis." Thesis, Aix-Marseille, 2019. http://www.theses.fr/2019AIXM0293.
Wallace, Alexandra. "Sustaining Patriarchy? : A Critical Discourse Analysis of Sustainable Urban Development." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Institutionen för geovetenskaper, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-416636.
Brokensha, Steven. "Psychosocial discourse and the "new" reproductive technologies : a critical analysis." Master's thesis, University of Cape Town, 1989. http://hdl.handle.net/11427/14320.
21 Great Examples of Discourse Analysis
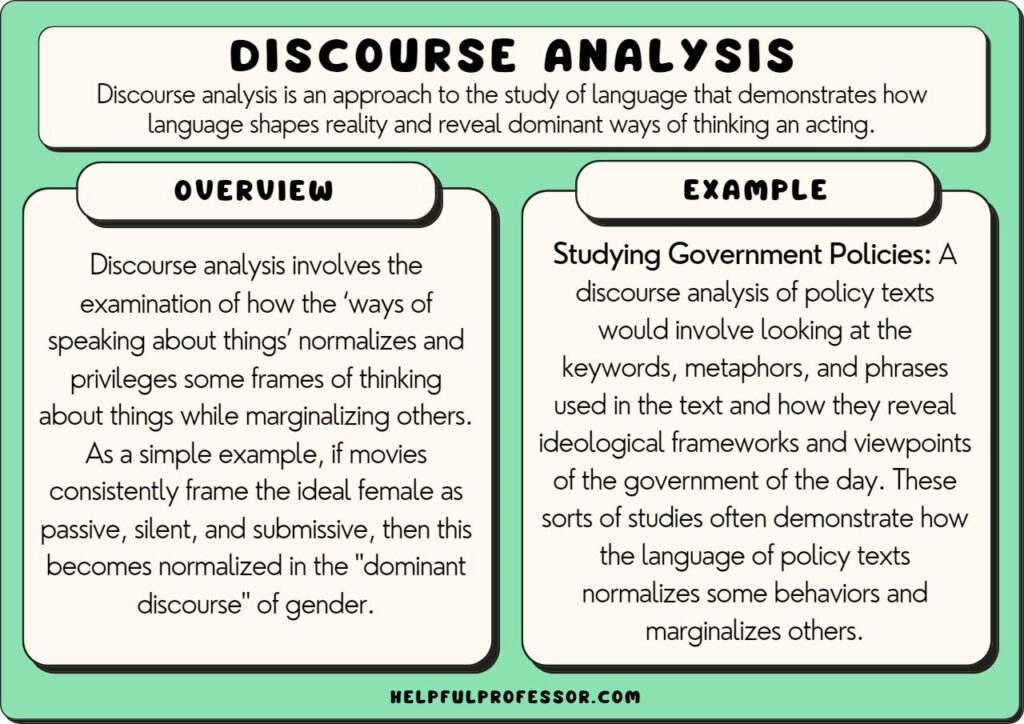
Discourse analysis is an approach to the study of language that demonstrates how language shapes reality. It usually takes the form of a textual or content analysis .
Discourse is understood as a way of perceiving, framing, and viewing the world.
For example:
- A dominant discourse of gender often positions women as gentle and men as active heroes.
- A dominant discourse of race often positions whiteness as the norm and colored bodies as ‘others’ (see: social construction of race )
Through discourse analysis, scholars look at texts and examine how those texts shape discourse.
In other words, it involves the examination of how the ‘ways of speaking about things’ normalizes and privileges some frames of thinking about things while marginalizing others.
As a simple example, if movies consistently frame the ideal female as passive, silent, and submissive, then society comes to think that this is how women should behave and makes us think that this is normal , so women who don’t fit this mold are abnormal .
Instead of seeing this as just the way things are, discourse analysts know that norms are produced in language and are not necessarily as natural as we may have assumed.
Examples of Discourse Analysis
1. language choice in policy texts.
A study of policy texts can reveal ideological frameworks and viewpoints of the writers of the policy. These sorts of studies often demonstrate how policy texts often categorize people in ways that construct social hierarchies and restrict people’s agency .
Examples include:
2. Newspaper Bias
Conducting a critical discourse analysis of newspapers involves gathering together a quorum of newspaper articles based on a pre-defined range and scope (e.g. newspapers from a particular set of publishers within a set date range).
Then, the researcher conducts a close examination of the texts to examine how they frame subjects (i.e. people, groups of people, etc.) from a particular ideological, political, or cultural perspective.
3. Language in Interviews
Discourse analysis can also be utilized to analyze interview transcripts. While coding methods to identify themes are the most common methods for analyzing interviews, discourse analysis is a valuable approach when looking at power relations and the framing of subjects through speech.
4. Television Analysis
Discourse analysis is commonly used to explore ideologies and framing devices in television shows and advertisements.
Due to the fact advertising is not just textual but rather multimodal , scholars often mix a discourse analytic methodology (i.e. exploring how television constructs dominant ways of thinking) with semiotic methods (i.e. exploration of how color, movement, font choice, and so on create meaning).
I did this, for example, in my PhD (listed below).
5. Film Critique
Scholars can explore discourse in film in a very similar way to how they study discourse in television shows. This can include the framing of sexuality gender, race, nationalism, and social class in films.
A common example is the study of Disney films and how they construct idealized feminine and masculine identities that children should aspire toward.
6. Analysis of Political Speech
Political speeches have also been subject to a significant amount of discourse analysis. These studies generally explore how influential politicians indicate a shift in policy and frame those policy shifts in the context of underlying ideological assumptions.
9. Examining Marketing Texts
Advertising is more present than ever in the context of neoliberal capitalism. As a result, it has an outsized role in shaping public discourse. Critical discourse analyses of advertising texts tend to explore how advertisements, and the capitalist context that underpins their proliferation, normalize gendered, racialized, and class-based discourses.
11. Analyzing Lesson Plans
As written texts, lesson plans can be analyzed for how they construct discourses around education as well as student and teacher identities. These texts tend to examine how teachers and governing bodies in education prioritize certain ideologies around what and how to learn. These texts can enter into discussions around the ‘history wars’ (what and whose history should be taught) as well as ideological approaches to religious and language learning.
12. Looking at Graffiti
One of my favorite creative uses of discourse analysis is in the study of graffiti. By looking at graffiti, researchers can identify how youth countercultures and counter discourses are spread through subversive means. These counterdiscourses offer ruptures where dominant discourses can be unsettled and displaced.
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
The Origins of Discourse Analysis
1. foucault.
French philosopher Michel Foucault is a central thinker who shaped discourse analysis. His work in studies like Madness and Civilization and The History of Sexuality demonstrate how our ideas about insanity and sexuality have been shaped through language.
The ways the church speaks about sex, for example, shapes people’s thoughts and feelings about it.
The church didn’t simply make sex a silent taboo. Rather, it actively worked to teach people that desire was a thing of evil, forcing them to suppress their desires.
Over time, society at large developed a suppressed normative approach to the concept of sex that is not necessarily normal except for the fact that the church reiterates that this is the only acceptable way of thinking about the topic.
Similarly, in Madness and Civilization , a discourse around insanity was examined. Medical discourse pathologized behaviors that were ‘abnormal’ as signs of insanity. Were the dominant medical discourse to change, it’s possible that abnormal people would no longer be seen as insane.
One clear example of this is homosexuality. Up until the 1990s, being gay was seen in medical discourse as an illness. Today, most of Western society sees that this way of looking at homosexuality was extremely damaging and exclusionary, and yet at the time, because it was the dominant discourse, people didn’t question it.
2. Norman Fairclough
Fairclough (2013), inspired by Foucault, created some key methodological frameworks for conducting discourse analysis.
Fairclough was one of the first scholars to articulate some frameworks around exploring ‘text as discourse’ and provided key tools for scholars to conduct analyses of newspaper and policy texts.
Today, most methodology chapters in dissertations that use discourse analysis will have extensive discussions of Fairclough’s methods.
Discourse analysis is a popular primary research method in media studies, cultural studies, education studies, and communication studies. It helps scholars to show how texts and language have the power to shape people’s perceptions of reality and, over time, shift dominant ways of framing thought. It also helps us to see how power flows thought texts, creating ‘in-groups’ and ‘out-groups’ in society.
Key examples of discourse analysis include the study of television, film, newspaper, advertising, political speeches, and interviews.
Al Kharusi, R. (2017). Ideologies of Arab media and politics: a CDA of Al Jazeera debates on the Yemeni revolution. PhD Dissertation: University of Hertfordshire.
Alaazi, D. A., Ahola, A. N., Okeke-Ihejirika, P., Yohani, S., Vallianatos, H., & Salami, B. (2021). Immigrants and the Western media: a CDA of newspaper framings of African immigrant parenting in Canada. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies , 47 (19), 4478-4496. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/1369183X.2020.1798746
Al-Khawaldeh, N. N., Khawaldeh, I., Bani-Khair, B., & Al-Khawaldeh, A. (2017). An exploration of graffiti on university’s walls: A corpus-based discourse analysis study. Indonesian Journal of Applied Linguistics , 7 (1), 29-42. Doi: https://doi.org/10.17509/ijal.v7i1.6856
Alsaraireh, M. Y., Singh, M. K. S., & Hajimia, H. (2020). Critical DA of gender representation of male and female characters in the animation movie, Frozen. Linguistica Antverpiensia , 104-121.
Baig, F. Z., Khan, K., & Aslam, M. J. (2021). Child Rearing and Gender Socialisation: A Feminist CDA of Kids’ Popular Fictional Movies. Journal of Educational Research and Social Sciences Review (JERSSR) , 1 (3), 36-46.
Barker, M. E. (2021). Exploring Canadian Integration through CDA of English Language Lesson Plans for Immigrant Learners. Canadian Journal of Applied Linguistics/Revue canadienne de linguistique appliquée , 24 (1), 75-91. Doi: https://doi.org/10.37213/cjal.2021.28959
Coleman, B. (2017). An Ideological Unveiling: Using Critical Narrative and Discourse Analysis to Examine Discursive White Teacher Identity. AERA Online Paper Repository .
Drew, C. (2013). Soak up the goodness: Discourses of Australian childhoods on television advertisements, 2006-2012. PhD Dissertation: Australian Catholic University. Doi: https://doi.org/10.4226/66/5a9780223babd
Fairclough, N. (2013). Critical discourse analysis: The critical study of language . London: Routledge.
Foucault, M. (1990). The history of sexuality: An introduction . London: Vintage.
Foucault, M. (2003). Madness and civilization . New York: Routledge.
Hahn, A. D. (2018). Uncovering the ideologies of internationalization in lesson plans through CDA. The New English Teacher , 12 (1), 121-121.
Isti’anah, A. (2018). Rohingya in media: CDA of Myanmar and Bangladesh newspaper headlines. Language in the Online and Offline World , 6 , 18-23. Doi: http://repository.usd.ac.id/id/eprint/25962
Khan, M. H., Adnan, H. M., Kaur, S., Qazalbash, F., & Ismail, I. N. (2020). A CDA of anti-Muslim rhetoric in Donald Trump’s historic 2016 AIPAC policy speech. Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs , 40 (4), 543-558. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/13602004.2020.1828507
Louise Cooper, K., Luck, L., Chang, E., & Dixon, K. (2021). What is the practice of spiritual care? A CDA of registered nurses’ understanding of spirituality. Nursing Inquiry , 28 (2), e12385. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/nin.12385
Mohammadi, D., Momeni, S., & Labafi, S. (2021). Representation of Iranians family’s life style in TV advertising (Case study: food ads). Religion & Communication , 27 (58), 333-379.
Munro, M. (2018) House price inflation in the news: a CDA of newspaper coverage in the UK. Housing Studies, 33(7), pp. 1085-1105. doi: 10.1080/02673037.2017.1421911
Ravn, I. M., Frederiksen, K., & Beedholm, K. (2016). The chronic responsibility: a CDA of Danish chronic care policies. Qualitative Health Research , 26 (4), 545-554. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1049732315570133
Sengul, K. (2019). Critical discourse analysis in political communication research: a case study of right-wing populist discourse in Australia. Communication Research and Practice , 5 (4), 376-392. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/22041451.2019.1695082
Serafis, D., Kitis, E. D., & Archakis, A. (2018). Graffiti slogans and the construction of collective identity: evidence from the anti-austerity protests in Greece. Text & Talk , 38 (6), 775-797. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/text-2018-0023
Suphaborwornrat, W., & Punkasirikul, P. (2022). A Multimodal CDA of Online Soft Drink Advertisements. LEARN Journal: Language Education and Acquisition Research Network , 15 (1), 627-653.
Symes, C., & Drew, C. (2017). Education on the rails: a textual ethnography of university advertising in mobile contexts. Critical Studies in Education , 58 (2), 205-223. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17508487.2016.1252783
Thomas, S. (2005). The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis. Critical Studies in Education , 46 (2), 25-44. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17508480509556423

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Critical Discourse Analysis Compare & Contrast Essay
Introduction, defining discourse analysis, defining critical discourse analysis, the difference between critical discourse analysis and discourse analysis.
Language may be used in different contexts and texts to create different meanings. To understand the sign, vocal, or even written language, a form of analysis is crucial in establishing both the intended and implied meanings.
This paper discusses discourse examination and critical discourse analysis (CDA) as two important approaches to analysing language use in vocal, sign, and written forms. Its main concern is to demonstrate the difference between the perspectives of language use in written and text forms.
Discourse analysis (DA) is a general term that is applied to various paradigms that are deployed in the study of the sign, vocal, written, and any other language semiotics. Objects that are used in the analysis under this approach are defined in terms of an individual’s consistency in the application of prepositions, use of sentences, tongue, and even turns-at-talk (Ross & Nightingale 2003).
Opposed to traditional approaches to linguistic analysis, discourse analysis focuses on studying not only the usage of language outside the limits of sentences use, but also analysing language in its conventional usage, rather than utilising invented examples.
This claim suggests a close relationship between discourse analysis and text analysis. However, the two concepts are different since discourse analysis also objects to identify various socio-psychological traits of people, rather than just the structure of the texts (Keller 2011).
As Bryman (2008) confirms, discourse analysis may find application in various social sciences among them being linguistics, social work, cultural studies, and communications disciplines. However, in each of the disciplines, its application is subject to assumptions, methodologies of studies, and analysis approaches that guide it. Discourse analysis covers a variety of topics that are of interest to different analysts.
They include sounds, language syntax, rhetoric, meanings, gesture, interaction, and acts of speech among others. It can take different genres, including business, politics, and science among others. Discourse analysts are interested in topics such as the relationship between context and texts, discourse and power, and interaction and the discourse.
From the above discussions, the term discourse analysis simply means studies on different ways in which languages are deployed in different texts and contexts.
In a more interactive definition, as Blommaert (2005, p.97) informs, ‘it concerns itself with the use of language in a running discourse, continued over a number of sentences, and involving the interaction of a speaker, writer, auditor, or a reader in a specific situational context, and within a framework of social cultural conventions’. Indeed, it is not just concerned with the methodology.
Its studies include the nature of usage of language and its relationship with key issues that scholars encounter in social science studies (Ritchie & Lewis 2003).
In particular, discourse analysis relates to the gathering of different perspectives of discourse. Such approaches relate to both data collection practices and theoretical assumptions together with meta-theoretical postulations that guide research approaches (Wood & Kroger 2000).
Discourse analysis differs from the grammatical analysis. Grammatical data involves one sentence or a collection of many sentences that demonstrate a given aspect of the language under study. In the process of analysis, a grammatical analyst will compile different sentences that he or she deploys as examples.
This approach differs from discourse analysis. Its primary interest is on the morphological productivity of different people as opposed to the forecaster. Discourse analysis data is adopted from recordings or written texts. Such data is hardly derived from one sentence.
Discourse analysis interconnects with rhetoric studies. Indeed, Eisenhart and Barbara (2008) reveal how discourse researches are interrelated classes of oratory, symphony, and practical morphology. Studies on speech making have been expanding. They comprise rhetoric of politics, popular culture, and informal arguments. A new pedagogy has been established concerning personal identity rhetoric.
These changes call for the expansion traditional approaches to language analysis and talks and texts in new mechanisms that reflect material and socio-cultural discourse contexts. This observation suggests that the discipline of rhetoric studies is now closely interlinked with discourse analysis.
Consequently, as Gee (2005) reveals, discourse analysis is a means of engaging in an incredibly crucial human task, which entails thinking deeply on meanings that are attached to words that people utter for the world to become a humane living place.
Critical discourse analysis is a sub-discipline of discourse analysis. It approaches discourses from a political motive. Conversely compared to campaigners and or politicians, decisive dissertation examination extends past grave matters. Analysts in critical discourses have a structural understanding and knowledge, which supersedes general insights on politically motivated issues (Renkema 2004).
They examine basic sources, the circumstances, and even the consequences of different concerns. Hence, as opposed to political scientists, critical discourse analysts have an interest in arriving at a scholarly sound contribution, which includes an in-depth insight into specific pressing politicised issues in the society.
The critical dissertation is perhaps the hardest test that discourse forecasters encounter. It demands a multidisciplinary understanding together with intricate understanding of relationships that occur in texts, power, culture, talks, and even the society. Indeed, its criterion for adequacy does not merely depend on descriptive, explanatory, or observational skills (Renkema 2004).
Success in the critical discourse analysis rests on the platform of the relevance and effectiveness of the contribution of analysis in creating change.
This situation requires modesty. Indeed, under critical discourses, educational involvement may be trivial in times of transformation, particularly if individuals who are closely engaged with reference to their conduct are successful transformation agents. This position is perhaps well evidenced by the transformation procedures that involve liberalisation, feminist campaigns, the battle for public privileges, and class campaigns.
One of the most significant concerns of critical discourse analysis involves developing an understanding of the relationship between languages, dominance, and social power. Such an understanding helps in predicting the contribution of discourse on the reproduction of various power differences.
While discussing social power, critical discourse analysis ignores powers that individuals portray, unless under circumstances in which the powers contribute to the development of productive relationships between different social groups.
Social power may be manifested in the form of accessibility to various valuable resources in social platforms, including wealth, education, skills, knowledge, and even status. Under critical discourse analysis, accessibility to different forms of power from the context of communication and discourse is a crucial resource of power.
In critical discourse analysis, political motive forms its basic tenet, which involves power struggles. Authority is a means of being in charge of one assembly of people over members of another assembly. It limits people’s cognition and actions. Hence, it influences people’s minds and their freedom of action.
Power is enacted through acts of persuasion, manipulation through talks, and dissimulation. The goal is to alter people’s cognitions and thinking processes in an effort to align them with those of the influential social groups. To this extent, critical discourse analysis helps in the management of other people’s minds via texts and talks.
Critical discourse analysts garner different topics that require analysis before proceeding to collect large amounts of texts. However, the corpus of texts does not comprise the only methodology for critical discourse analysis.
Different researchers grant the right to apply all methods that permit the generation of insights to ideologies that the discourses promote. The critical discourse analysis investigates different text echelons that range from micro, macro, and meso levels of text to identify political motives in them.
Critical discourse analysis involves the utilisation of different techniques of studying language and texts as a cultural and social practice (Seale 2004). It draws its tenets from the poststructuralist pedagogy that investigates the functions of all institutional sites.
It also contends that language and texts play important roles in the development of human ideologies and identities (Eisenhart & Barbara 2008). Similar to the concerns of Bourdieu’s sociology, critical discourse analysis holds that texts and/or interactions with them utilise embodied approaches that operate in different social fields (Seale 2004).
Critical discourse also draws some of its facets from the ideologies of the neo-Marxist theory of culture, which assumes that discourses are created and utilised in the political economy. This observation perhaps explains its particular focus on political motives. Thus, it is different from discourse analysis to the extent that it has specific areas of interest.
Discourse analysis focuses on a variety of genres, including phonology, pragmatics, communication ethnography, conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, rhetoric, text linguistics, and functional grammar amongst others (Bromley 2001; Crang & Cook 2007). Hence, critical discourse analysis is a genre of discourse analysis.
Considering that discourse analysis has a variety of genres, including critical discourse analysis, the difference between the two concepts is clear with reference to the structures and the main concerns of the critical discourse analysis. Practice techniques that are deployed in critical discourse analysis are borrowed from interdisciplinary fields.
For example, just like in the case of pragmatics, the theory of speech acts, and narratology, which are advanced in discourse analysis, critical discourse analysis holds that texts comprise a complex mechanism for social actions, which take place in sophisticated contexts on a social platform (Gee 2005).
Functional linguistics studies depict the manner in which language forms can relate to achieve ideological functions. The theory is used in the critical discourse analysis as an analytic tool for establishing the relations between culture, politics, gender, and social classes.
Critical discourse analysis acknowledges the existence of asymmetries in resources and power among different speakers, including people who listen to them. It holds that writers and readers have unequal accessibility to social and linguistic resources, a situation that reveals their differences in social contexts.
From the paradigms of discourse analysis, discussion combines with languages to influence the ideologies of people’s daily affairs and hence the asymmetry that is evident between textual portrayals and the relations of power. The CDA is both constructive and deconstructive.
From the paradigms of power and textual portrayals, in a deconstructive approach, CDA renders power relationship themes problematic in a society as expressed through written texts and talks. In a constructive approach, it advocates the increased development of critical skills that are necessary for the analysis of discourses and various social relations to ensure equity in terms of resource distribution (Keller 2011).
Discourse analysis deploys text as its main unit of analysis. This approach differs from discourse analysis, which can use a sound and its patterns, textual frameworks, and rhetoric in the analysis. CDA considers texts social actions that form meaningful and reasoned printed and verbal language.
However, it does not consider textual forms random in nature. Specific types of texts do certain things within various social institutions. They can help to predict material effects in qualitative researches (Denzin & Lincoln 2005). Under critical discourses, studies are dynamic. They continue undergoing processes of reinvention and innovations.
From the paradigms of discourse analysis, all genres can be adequately analysed via studying language structures such as prepositions and microstructures of the texts. The discourse reveals how written and verbal languages possess various identifiable segments and movements. For example, a scientific text can be interpreted as a series of actions that have been joined by a set of chains.
CDA can focus on word-level and sentence-level analysis. It does this by using analysis approaches derived from functional linguistics studies. Halliday and Matthiessen (2004) support this assertion by adding that grammatical combined with various lexical textual features possess different identifiable functionalities. They can explain the natural and social world.
They create different effects on social relations through the conventions that form coherency in texts that are deployed in a given media. Critical discourse analysis focuses on identifying these effects.
Under discourse examination, verbal texts depict some chosen perspectives of the natural world to help in explaining the social world. Therefore, through texts, people can position others to align with identifiable relations that are consistent with power differences that exist among them.
Language employment in writing and speech (discourse) constitutes a social practice. Discursive events shape social structures and/or institutions. This claim suggests that discourse is socially conditioned and that may be socially constitutive. Since it reproduces the status quo, it contributes to its transformation.
Discursive events also play the role of reproducing varying power relations among different classes of people in the society (Fairclough 2000).
Depending on the academic culture under investigation, different linguistic scholars can use the term discourse in different contexts. For example, German linguistic scholars distinguish discourses from texts, depending on the relationship between traditional text linguistics and language rhetoric. However, in English-speaking nations, discourses imply oral communication and written texts.
It is possible to consider a transcript a tangible comprehension of conceptual structures of knowledge. However, amid these differences, discourses encompass a form of memory and knowledge bases that are manifested in the form of power differences that are witnessed in talks and in written texts (Reisigl & Wodak 2001). However, critical discourse analysis focuses on structures of talks and written texts.
Dominance reproduction is a major aim of CDA. Dominance has reception together with reproduction as two important perspectives in its contribution to power differences. This observation suggests that CDA analysis focuses on the legitimisation and the expression of dominance in different structures of talks and texts.
Reproduction of various discursive events in CDA emanates from power differences that are manifested in the form of social cognition power among some groups over others. As studied from the paradigms of discourse analysis, discourse structures translate into social cognitions while social cognitions in CDA produce power imbalances.
Therefore, under the two approaches, researchers struggle with establishing the relationships between cognition and the discourses. However, under both CDA and discourse analysis, discourse structures play the role of mediation. Thus, they are mechanisms for reproducing dominance in written texts and speeches.
In the context of dominance, CDA differs from DA in its emphasis on power variations among different groups of people who interact in social contexts through talk and written texts. To this extent, Fairclough (2000, p.103) reckon, ‘members of less powerful groups may also otherwise be more or less dominated in discourse’. This claim implies that in all levels of talks and texts, participants who possess influential power control freedom.
Consequently, in CDA, language does not possess any power of its own. It acquires it when it interacts with high-ranking people. This observation perhaps reveals why CDA conducts the analysis of discourse from the perspective of distinguished people. Such people carry the load when it comes to inequality issues. They solely have the ability to improve social conditions.
Discourse, which denotes language use in talk and written texts, can be studied from the paradigm of discourse analysis (DA) and critical discourse analysis (CDA).
Discourse analysis constitutes a variety of genres such as phonology, pragmatics, and critical discourse analysis among many other genres that study language use in social contexts. CDA is a genre of DA. CDA focuses on political motives in language use, which is manifested through power differences that create the dominance of different groups in social communication contexts.
Blommaert, J 2005, Discourse , Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Bromley, D 2001, Toward reflexive ethnography , JAI, London.
Bryman, A 2008, Social research methods, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Crang, M & Cook, I 2007, Doing ethnographies, Sage, London.
Denzin, N & Lincoln, Y 2005, The SAGE handbook of qualitative research, Sage, London.
Eisenhart, C & Barbara, J 2008, Discourse Analysis and Rhetorical Studies: Rhetoric in Detail: Discourse Analyses of Rhetorical Talk and Text , John Benjamins Publishers, New York, NY.
Fairclough, N 2000, The discourse of social exclusion: Approaches in Critical Discourse Analysis , Passagen Verlag, Vienna.
Gee, J 2005, An Introduction to Discourse Analysis , Routledge, London.
Halliday, M & Matthiessen, C 2004, An Introduction to Functional Grammar , Arnold, London.
Keller, R 2011, ‘The Sociology of Knowledge Approach to Discourse (SKAD)’, Human Studies, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 43-65.
Reisigl, M & Wodak, R 2001, Discourse and Discrimination , Routledge, London.
Renkema, J 2004, Introduction to Discourse Studies , Benjamins, Amsterdam.
Ritchie, J & Lewis, J 2003, Qualitative research practice: A guide for social science students and researchers, Sage, London.
Ross, K & Nightingale, V 2003, Media and Audiences New Perspectives , Open University Press, Virginia.
Seale, C 2004, Social research methods: a reader , Routledge, London.
Silverman, D 2005, Doing qualitative research: a practical handbook, Sage, London.
Wood, L & Kroger, R 2000, Doing Discourse Analysis , Sage Publishers, London.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 15). Critical Discourse Analysis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-discourse-analysis/
"Critical Discourse Analysis." IvyPanda , 15 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/critical-discourse-analysis/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Critical Discourse Analysis'. 15 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Critical Discourse Analysis." December 15, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-discourse-analysis/.
1. IvyPanda . "Critical Discourse Analysis." December 15, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-discourse-analysis/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Critical Discourse Analysis." December 15, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-discourse-analysis/.
- The Internet and Freedom of Speech: Ethics and Restrictions
- Colgate Brand's Promotional Strategy
- English Literature Impact on Racism Among Africans
- Problem of Racial Slurs in Australia
- "Immigrant Workers Cleaning and Caring in the Shadows of Affluence" by Pierrette Hondagneu-Sotelo
- Women in Asian Literature in The Tale of Kieu by Du Nguyen and the play The love suicide at Amijima
- Magical Realism: Garcia Marquez
- Bamako: Movie Concept and Theme
The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader
This essay about the pivotal role of essay readers in academia and beyond. It highlights how essay readers decode complex texts, foster critical dialogue, and uphold the integrity of written communication. They serve as interpreters, guiding scholars and shaping scholarly discourse. Beyond academia, they play crucial roles in ensuring quality and integrity in publishing, media, and legal realms. Ultimately, essay readers enrich scholarly discourse, foster critical thinking, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge and understanding.
How it works
Essay writing is a craft that demands not only the art of expression but also the skill of interpretation. As such, the role of the essay reader becomes pivotal in the academic landscape. Beyond merely evaluating the coherence and structure of an essay, essay readers delve into the nuances of language, argumentation, and critical thinking. In this discourse, we explore the multifaceted responsibilities of essay readers, shedding light on their integral role in shaping scholarly discourse.
At the heart of the essay reader’s task lies the art of comprehension.
Beyond surface-level understanding, essay readers must decipher the underlying messages, themes, and arguments embedded within the text. This requires a keen eye for detail, an astute grasp of language, and an ability to discern implicit meanings. Whether analyzing a literary masterpiece or a scientific treatise, essay readers serve as custodians of interpretation, unraveling the layers of meaning woven into the fabric of the text.
Furthermore, essay readers play a pivotal role in fostering critical dialogue within academic circles. Through their feedback and assessments, they not only provide guidance to aspiring scholars but also challenge established paradigms and perspectives. By engaging with essays thoughtfully and constructively, essay readers contribute to the continuous evolution of knowledge, pushing the boundaries of inquiry and discourse.
Moreover, the role of the essay reader extends beyond the confines of academia, permeating various spheres of society. In professional settings, such as publishing houses and media outlets, essay readers serve as gatekeepers of quality and integrity, ensuring that only the most rigorous and compelling works reach the public domain. Similarly, in legal and governmental contexts, essay readers scrutinize documents and reports, offering invaluable insights that inform decision-making processes.
In conclusion, the role of the essay reader is both nuanced and indispensable in the realm of academia and beyond. By embracing the responsibilities of comprehension, critique, and engagement, essay readers enrich scholarly discourse, foster critical thinking, and uphold the integrity of written communication. As we navigate the complex terrain of interpretation, let us recognize and celebrate the profound contributions of essay readers to the advancement of knowledge and understanding.
Cite this page
The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-intricacies-of-interpretation-the-role-of-the-essay-reader/
"The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-intricacies-of-interpretation-the-role-of-the-essay-reader/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-intricacies-of-interpretation-the-role-of-the-essay-reader/ [Accessed: 14 May. 2024]
"The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-intricacies-of-interpretation-the-role-of-the-essay-reader/
"The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-intricacies-of-interpretation-the-role-of-the-essay-reader/. [Accessed: 14-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Intricacies of Interpretation: the Role of the Essay Reader . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-intricacies-of-interpretation-the-role-of-the-essay-reader/ [Accessed: 14-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

COMMENTS
Learn how to conduct discourse analysis, a qualitative research method for studying language in relation to its social context. Find out what discourse analysis is used for, how it differs from other methods, and how to apply it to various types of materials.
This dissertation explores how women in top business and leadership roles are represented within newspapers in the UK and U.S. using an aggregate level analysis and a critical discourse analysis. It suggests that women are often represented negatively and stereotypically within the press, despite their progression in society.
interested in using discourse analysis methods to further demystify the process of CDA for others. I have outlined in the thesis further research studies which potentially lead on from this study. Having reflected on my findings I will apply for funding to further explore under-
A Critical Discourse Analysis of Social Change in Women-related Posts on Saudi English-Language Blogs Posted between 2009 and 2012 Shrouq Hamad Al Maghlouth A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Department of Linguistics and English Language Lancaster University United Kingdom June 2017
This article presents a general critical discourse analysis (CDA) framework and illustrates its application to a literature review of CDA studies in education. CDA is a qualitative approach for examining how discourses construct and legitimize social inequalities.
Learn how to conduct discourse analysis, a qualitative method for studying language in relation to its social context. Find out the steps, levels, and techniques of discourse analysis and see examples of research questions and sources.
Critical discourse analysis is a rapidly growing, interdisciplinary field of inquiry that combines linguistic analysis and social theory to address the way power and dominance are enacted and reproduced in text. Critical discourse analysis is primarily concerned with the construction of social phenomena and involves a focus on the wider social ...
Discourse Studies is the discipline devoted to the investigation of the relationship. between form and function in verb al communication (Renkema, 2004, p.1). The notions of text and discourse ...
Critical Discourse Analysis and Theory. One of the strengths of CDA is that it is multidisciplinary and essentially diverse (van Dijk, 2001).In fact, van Dijk (2001, p. 95), who is one of its original proponents, says that good CDA scholarship seldom follows just one person or one approach but is enriched through the integration of the "best work of many people, famous or not, from different ...
The critical approach is distinctive in its view of (a) the relationship between language and society, and (b) the relationship between analysis and the practices analysed" (Wodak 1997:173). CDA states that discourse is socially constitutive as well as socially conditioned. Furthermore, discourse is an opaque power object in modem societies and ...
Critical discourse analysis (CDA) is a rapidly developing area of language study. It regards discourse as 'a form as social practice' (Fairclough & Wodak, 1997, p.258), and takes consideration of the context of language use to be crucial to discourse (Wodak, 2001). It takes particular interest in the relation between language and power.
EDUCATION POLICY AND NEWSPAPERS: A CRITICAL DISCOURSE ANALYSIS Jumana Khalifeh Follow this and additional works at: https://via.library.depaul.edu/soe_etd Part of the Education Commons Recommended Citation Khalifeh, Jumana, "EDUCATION POLICY AND NEWSPAPERS: A CRITICAL DISCOURSE ANALYSIS" (2017). College of Education Theses and Dissertations. 132.
Critical Discourse Analysis 353 be based on such insights. Theory formation, description, and explanation, also in discourse analysis, are sociopolitically "situated," whether we like it or not. Reflec-tion on the role of scholars in society and the polity thus becomes an inherent part of the discourse analytical enterprise.
Dissertation of Ciara Spencer 6 discourse analysis. Finally, the third section will set out the research objectives for this dissertation. Literature review Politics of reconciliation and the role of the media Theoretical literature in the field of peace and reconciliation, and the role the media ought to
This dissertation is a Critical Discourse Analysis of the representations of social actors within political discourse. To understand how specific discourse structures affect different mental processes or enable the development of distinct social representations, Critical Discourse Analysis endeavors to detail and explain the ways in which ...
Critical Discourse Analysis (hereafter CDA) is a cross-discipline set forth in the early 1990s by a group of scholars such as Theo van Leeuwen, Gunther Kress, Teun van Dijk, and Norman Fairclough (Wodak & Meyer, 2001). At that time, theories and methods of CDA have been formulated to differentiate this paradigm from other theories and ...
the method of analysis used as well as the limitations of the study. Finally, it offers operational definitions and an overview of the thesis. Critical Discourse Analysis as a Linguistic Research Tool Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA) has become prominent and influential over recent years.
Download Article. 1. Select a specific text that you'd like to analyze. In critical discourse analysis (CDA), the term "text" has many meanings because it applies to any type of communication, whether it's words or visuals. This includes written texts (whether literary, scientific, or journalistic), speech, and images.
A Corpus-Assisted Discourse Analysis. by Dominic Castello. A dissertation submitted to The School of Humanities of the University of Birmingham in part fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts in Applied Linguistics. This dissertation is approximately 14,986 words Supervisor: Narges Mahpeykar.
online and offline mediums. In this manner, discourse is a form of social practice that uses language to produce knowledge and subjectivity (Hall, 1997). I will use Fairclough's Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA) to challenge claims made by the media, as outlined above, in its coverage of Sen. Sanders and Mr. Trump throughout the primary process.
This thesis uses critical discourse analysis to study the discursive construction of EU counter-terrorism policy. It uses representative extracts from twenty counter-terrorism documents prepared by/or for the EU institution the European Council, across a ten-year period from November 1999 to December 2009.
Discourse analysis is an approach to the study of language that demonstrates how language shapes reality. It usually takes the form of a textual or content analysis. Discourse is understood as a way of perceiving, framing, and viewing the world. For example: A dominant discourse of gender often positions women as gentle and men as active heroes.
In critical discourse analysis, political motive forms its basic tenet, which involves power struggles. Authority is a means of being in charge of one assembly of people over members of another assembly. It limits people's cognition and actions. Hence, it influences people's minds and their freedom of action.
They serve as interpreters, guiding scholars and shaping scholarly discourse. Beyond academia, they play crucial roles in ensuring quality and integrity in publishing, media, and legal realms. Ultimately, essay readers enrich scholarly discourse, foster critical thinking, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge and understanding.