
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

7 Module 7: Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving
This module is about how a solid working knowledge of psychological principles can help you to think more effectively, so you can succeed in school and life. You might be inclined to believe that—because you have been thinking for as long as you can remember, because you are able to figure out the solution to many problems, because you feel capable of using logic to argue a point, because you can evaluate whether the things you read and hear make sense—you do not need any special training in thinking. But this, of course, is one of the key barriers to helping people think better. If you do not believe that there is anything wrong, why try to fix it?
The human brain is indeed a remarkable thinking machine, capable of amazing, complex, creative, logical thoughts. Why, then, are we telling you that you need to learn how to think? Mainly because one major lesson from cognitive psychology is that these capabilities of the human brain are relatively infrequently realized. Many psychologists believe that people are essentially “cognitive misers.” It is not that we are lazy, but that we have a tendency to expend the least amount of mental effort necessary. Although you may not realize it, it actually takes a great deal of energy to think. Careful, deliberative reasoning and critical thinking are very difficult. Because we seem to be successful without going to the trouble of using these skills well, it feels unnecessary to develop them. As you shall see, however, there are many pitfalls in the cognitive processes described in this module. When people do not devote extra effort to learning and improving reasoning, problem solving, and critical thinking skills, they make many errors.
As is true for memory, if you develop the cognitive skills presented in this module, you will be more successful in school. It is important that you realize, however, that these skills will help you far beyond school, even more so than a good memory will. Although it is somewhat useful to have a good memory, ten years from now no potential employer will care how many questions you got right on multiple choice exams during college. All of them will, however, recognize whether you are a logical, analytical, critical thinker. With these thinking skills, you will be an effective, persuasive communicator and an excellent problem solver.
The module begins by describing different kinds of thought and knowledge, especially conceptual knowledge and critical thinking. An understanding of these differences will be valuable as you progress through school and encounter different assignments that require you to tap into different kinds of knowledge. The second section covers deductive and inductive reasoning, which are processes we use to construct and evaluate strong arguments. They are essential skills to have whenever you are trying to persuade someone (including yourself) of some point, or to respond to someone’s efforts to persuade you. The module ends with a section about problem solving. A solid understanding of the key processes involved in problem solving will help you to handle many daily challenges.
7.1. Different kinds of thought
7.2. Reasoning and Judgment
7.3. Problem Solving
READING WITH PURPOSE
Remember and understand.
By reading and studying Module 7, you should be able to remember and describe:
- Concepts and inferences (7.1)
- Procedural knowledge (7.1)
- Metacognition (7.1)
- Characteristics of critical thinking: skepticism; identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; reasoning and problem solving skills (7.1)
- Reasoning: deductive reasoning, deductively valid argument, inductive reasoning, inductively strong argument, availability heuristic, representativeness heuristic (7.2)
- Fixation: functional fixedness, mental set (7.3)
- Algorithms, heuristics, and the role of confirmation bias (7.3)
- Effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
By reading and thinking about how the concepts in Module 6 apply to real life, you should be able to:
- Identify which type of knowledge a piece of information is (7.1)
- Recognize examples of deductive and inductive reasoning (7.2)
- Recognize judgments that have probably been influenced by the availability heuristic (7.2)
- Recognize examples of problem solving heuristics and algorithms (7.3)
Analyze, Evaluate, and Create
By reading and thinking about Module 6, participating in classroom activities, and completing out-of-class assignments, you should be able to:
- Use the principles of critical thinking to evaluate information (7.1)
- Explain whether examples of reasoning arguments are deductively valid or inductively strong (7.2)
- Outline how you could try to solve a problem from your life using the effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
7.1. Different kinds of thought and knowledge
- Take a few minutes to write down everything that you know about dogs.
- Do you believe that:
- Psychic ability exists?
- Hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness?
- Magnet therapy is effective for relieving pain?
- Aerobic exercise is an effective treatment for depression?
- UFO’s from outer space have visited earth?
On what do you base your belief or disbelief for the questions above?
Of course, we all know what is meant by the words think and knowledge . You probably also realize that they are not unitary concepts; there are different kinds of thought and knowledge. In this section, let us look at some of these differences. If you are familiar with these different kinds of thought and pay attention to them in your classes, it will help you to focus on the right goals, learn more effectively, and succeed in school. Different assignments and requirements in school call on you to use different kinds of knowledge or thought, so it will be very helpful for you to learn to recognize them (Anderson, et al. 2001).
Factual and conceptual knowledge
Module 5 introduced the idea of declarative memory, which is composed of facts and episodes. If you have ever played a trivia game or watched Jeopardy on TV, you realize that the human brain is able to hold an extraordinary number of facts. Likewise, you realize that each of us has an enormous store of episodes, essentially facts about events that happened in our own lives. It may be difficult to keep that in mind when we are struggling to retrieve one of those facts while taking an exam, however. Part of the problem is that, in contradiction to the advice from Module 5, many students continue to try to memorize course material as a series of unrelated facts (picture a history student simply trying to memorize history as a set of unrelated dates without any coherent story tying them together). Facts in the real world are not random and unorganized, however. It is the way that they are organized that constitutes a second key kind of knowledge, conceptual.
Concepts are nothing more than our mental representations of categories of things in the world. For example, think about dogs. When you do this, you might remember specific facts about dogs, such as they have fur and they bark. You may also recall dogs that you have encountered and picture them in your mind. All of this information (and more) makes up your concept of dog. You can have concepts of simple categories (e.g., triangle), complex categories (e.g., small dogs that sleep all day, eat out of the garbage, and bark at leaves), kinds of people (e.g., psychology professors), events (e.g., birthday parties), and abstract ideas (e.g., justice). Gregory Murphy (2002) refers to concepts as the “glue that holds our mental life together” (p. 1). Very simply, summarizing the world by using concepts is one of the most important cognitive tasks that we do. Our conceptual knowledge is our knowledge about the world. Individual concepts are related to each other to form a rich interconnected network of knowledge. For example, think about how the following concepts might be related to each other: dog, pet, play, Frisbee, chew toy, shoe. Or, of more obvious use to you now, how these concepts are related: working memory, long-term memory, declarative memory, procedural memory, and rehearsal? Because our minds have a natural tendency to organize information conceptually, when students try to remember course material as isolated facts, they are working against their strengths.
One last important point about concepts is that they allow you to instantly know a great deal of information about something. For example, if someone hands you a small red object and says, “here is an apple,” they do not have to tell you, “it is something you can eat.” You already know that you can eat it because it is true by virtue of the fact that the object is an apple; this is called drawing an inference , assuming that something is true on the basis of your previous knowledge (for example, of category membership or of how the world works) or logical reasoning.
Procedural knowledge
Physical skills, such as tying your shoes, doing a cartwheel, and driving a car (or doing all three at the same time, but don’t try this at home) are certainly a kind of knowledge. They are procedural knowledge, the same idea as procedural memory that you saw in Module 5. Mental skills, such as reading, debating, and planning a psychology experiment, are procedural knowledge, as well. In short, procedural knowledge is the knowledge how to do something (Cohen & Eichenbaum, 1993).
Metacognitive knowledge
Floyd used to think that he had a great memory. Now, he has a better memory. Why? Because he finally realized that his memory was not as great as he once thought it was. Because Floyd eventually learned that he often forgets where he put things, he finally developed the habit of putting things in the same place. (Unfortunately, he did not learn this lesson before losing at least 5 watches and a wedding ring.) Because he finally realized that he often forgets to do things, he finally started using the To Do list app on his phone. And so on. Floyd’s insights about the real limitations of his memory have allowed him to remember things that he used to forget.
All of us have knowledge about the way our own minds work. You may know that you have a good memory for people’s names and a poor memory for math formulas. Someone else might realize that they have difficulty remembering to do things, like stopping at the store on the way home. Others still know that they tend to overlook details. This knowledge about our own thinking is actually quite important; it is called metacognitive knowledge, or metacognition . Like other kinds of thinking skills, it is subject to error. For example, in unpublished research, one of the authors surveyed about 120 General Psychology students on the first day of the term. Among other questions, the students were asked them to predict their grade in the class and report their current Grade Point Average. Two-thirds of the students predicted that their grade in the course would be higher than their GPA. (The reality is that at our college, students tend to earn lower grades in psychology than their overall GPA.) Another example: Students routinely report that they thought they had done well on an exam, only to discover, to their dismay, that they were wrong (more on that important problem in a moment). Both errors reveal a breakdown in metacognition.
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
In general, most college students probably do not study enough. For example, using data from the National Survey of Student Engagement, Fosnacht, McCormack, and Lerma (2018) reported that first-year students at 4-year colleges in the U.S. averaged less than 14 hours per week preparing for classes. The typical suggestion is that you should spend two hours outside of class for every hour in class, or 24 – 30 hours per week for a full-time student. Clearly, students in general are nowhere near that recommended mark. Many observers, including some faculty, believe that this shortfall is a result of students being too busy or lazy. Now, it may be true that many students are too busy, with work and family obligations, for example. Others, are not particularly motivated in school, and therefore might correctly be labeled lazy. A third possible explanation, however, is that some students might not think they need to spend this much time. And this is a matter of metacognition. Consider the scenario that we mentioned above, students thinking they had done well on an exam only to discover that they did not. Justin Kruger and David Dunning examined scenarios very much like this in 1999. Kruger and Dunning gave research participants tests measuring humor, logic, and grammar. Then, they asked the participants to assess their own abilities and test performance in these areas. They found that participants in general tended to overestimate their abilities, already a problem with metacognition. Importantly, the participants who scored the lowest overestimated their abilities the most. Specifically, students who scored in the bottom quarter (averaging in the 12th percentile) thought they had scored in the 62nd percentile. This has become known as the Dunning-Kruger effect . Many individual faculty members have replicated these results with their own student on their course exams, including the authors of this book. Think about it. Some students who just took an exam and performed poorly believe that they did well before seeing their score. It seems very likely that these are the very same students who stopped studying the night before because they thought they were “done.” Quite simply, it is not just that they did not know the material. They did not know that they did not know the material. That is poor metacognition.
In order to develop good metacognitive skills, you should continually monitor your thinking and seek frequent feedback on the accuracy of your thinking (Medina, Castleberry, & Persky 2017). For example, in classes get in the habit of predicting your exam grades. As soon as possible after taking an exam, try to find out which questions you missed and try to figure out why. If you do this soon enough, you may be able to recall the way it felt when you originally answered the question. Did you feel confident that you had answered the question correctly? Then you have just discovered an opportunity to improve your metacognition. Be on the lookout for that feeling and respond with caution.
concept : a mental representation of a category of things in the world
Dunning-Kruger effect : individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
inference : an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
metacognition : knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
Critical thinking
One particular kind of knowledge or thinking skill that is related to metacognition is critical thinking (Chew, 2020). You may have noticed that critical thinking is an objective in many college courses, and thus it could be a legitimate topic to cover in nearly any college course. It is particularly appropriate in psychology, however. As the science of (behavior and) mental processes, psychology is obviously well suited to be the discipline through which you should be introduced to this important way of thinking.
More importantly, there is a particular need to use critical thinking in psychology. We are all, in a way, experts in human behavior and mental processes, having engaged in them literally since birth. Thus, perhaps more than in any other class, students typically approach psychology with very clear ideas and opinions about its subject matter. That is, students already “know” a lot about psychology. The problem is, “it ain’t so much the things we don’t know that get us into trouble. It’s the things we know that just ain’t so” (Ward, quoted in Gilovich 1991). Indeed, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain wrong. Randolph Smith (2002) wrote a book about critical thinking in psychology called Challenging Your Preconceptions, highlighting this fact. On the other hand, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain right! But wait, how do you know which of your preconceptions are right and which are wrong? And when you come across a research finding or theory in this class that contradicts your preconceptions, what will you do? Will you stick to your original idea, discounting the information from the class? Will you immediately change your mind? Critical thinking can help us sort through this confusing mess.
But what is critical thinking? The goal of critical thinking is simple to state (but extraordinarily difficult to achieve): it is to be right, to draw the correct conclusions, to believe in things that are true and to disbelieve things that are false. We will provide two definitions of critical thinking (or, if you like, one large definition with two distinct parts). First, a more conceptual one: Critical thinking is thinking like a scientist in your everyday life (Schmaltz, Jansen, & Wenckowski, 2017). Our second definition is more operational; it is simply a list of skills that are essential to be a critical thinker. Critical thinking entails solid reasoning and problem solving skills; skepticism; and an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. Excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills contribute to critical thinking. So, you can consider the subject matter of sections 7.2 and 7.3 to be part of critical thinking. Because we will be devoting considerable time to these concepts in the rest of the module, let us begin with a discussion about the other aspects of critical thinking.
Let’s address that first part of the definition. Scientists form hypotheses, or predictions about some possible future observations. Then, they collect data, or information (think of this as making those future observations). They do their best to make unbiased observations using reliable techniques that have been verified by others. Then, and only then, they draw a conclusion about what those observations mean. Oh, and do not forget the most important part. “Conclusion” is probably not the most appropriate word because this conclusion is only tentative. A scientist is always prepared that someone else might come along and produce new observations that would require a new conclusion be drawn. Wow! If you like to be right, you could do a lot worse than using a process like this.
A Critical Thinker’s Toolkit
Now for the second part of the definition. Good critical thinkers (and scientists) rely on a variety of tools to evaluate information. Perhaps the most recognizable tool for critical thinking is skepticism (and this term provides the clearest link to the thinking like a scientist definition, as you are about to see). Some people intend it as an insult when they call someone a skeptic. But if someone calls you a skeptic, if they are using the term correctly, you should consider it a great compliment. Simply put, skepticism is a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided. People from Missouri should recognize this principle, as Missouri is known as the Show-Me State. As a skeptic, you are not inclined to believe something just because someone said so, because someone else believes it, or because it sounds reasonable. You must be persuaded by high quality evidence.
Of course, if that evidence is produced, you have a responsibility as a skeptic to change your belief. Failure to change a belief in the face of good evidence is not skepticism; skepticism has open mindedness at its core. M. Neil Browne and Stuart Keeley (2018) use the term weak sense critical thinking to describe critical thinking behaviors that are used only to strengthen a prior belief. Strong sense critical thinking, on the other hand, has as its goal reaching the best conclusion. Sometimes that means strengthening your prior belief, but sometimes it means changing your belief to accommodate the better evidence.
Many times, a failure to think critically or weak sense critical thinking is related to a bias , an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice. Everybody has biases, but many people are unaware of them. Awareness of your own biases gives you the opportunity to control or counteract them. Unfortunately, however, many people are happy to let their biases creep into their attempts to persuade others; indeed, it is a key part of their persuasive strategy. To see how these biases influence messages, just look at the different descriptions and explanations of the same events given by people of different ages or income brackets, or conservative versus liberal commentators, or by commentators from different parts of the world. Of course, to be successful, these people who are consciously using their biases must disguise them. Even undisguised biases can be difficult to identify, so disguised ones can be nearly impossible.
Here are some common sources of biases:
- Personal values and beliefs. Some people believe that human beings are basically driven to seek power and that they are typically in competition with one another over scarce resources. These beliefs are similar to the world-view that political scientists call “realism.” Other people believe that human beings prefer to cooperate and that, given the chance, they will do so. These beliefs are similar to the world-view known as “idealism.” For many people, these deeply held beliefs can influence, or bias, their interpretations of such wide ranging situations as the behavior of nations and their leaders or the behavior of the driver in the car ahead of you. For example, if your worldview is that people are typically in competition and someone cuts you off on the highway, you may assume that the driver did it purposely to get ahead of you. Other types of beliefs about the way the world is or the way the world should be, for example, political beliefs, can similarly become a significant source of bias.
- Racism, sexism, ageism and other forms of prejudice and bigotry. These are, sadly, a common source of bias in many people. They are essentially a special kind of “belief about the way the world is.” These beliefs—for example, that women do not make effective leaders—lead people to ignore contradictory evidence (examples of effective women leaders, or research that disputes the belief) and to interpret ambiguous evidence in a way consistent with the belief.
- Self-interest. When particular people benefit from things turning out a certain way, they can sometimes be very susceptible to letting that interest bias them. For example, a company that will earn a profit if they sell their product may have a bias in the way that they give information about their product. A union that will benefit if its members get a generous contract might have a bias in the way it presents information about salaries at competing organizations. (Note that our inclusion of examples describing both companies and unions is an explicit attempt to control for our own personal biases). Home buyers are often dismayed to discover that they purchased their dream house from someone whose self-interest led them to lie about flooding problems in the basement or back yard. This principle, the biasing power of self-interest, is likely what led to the famous phrase Caveat Emptor (let the buyer beware) .
Knowing that these types of biases exist will help you evaluate evidence more critically. Do not forget, though, that people are not always keen to let you discover the sources of biases in their arguments. For example, companies or political organizations can sometimes disguise their support of a research study by contracting with a university professor, who comes complete with a seemingly unbiased institutional affiliation, to conduct the study.
People’s biases, conscious or unconscious, can lead them to make omissions, distortions, and assumptions that undermine our ability to correctly evaluate evidence. It is essential that you look for these elements. Always ask, what is missing, what is not as it appears, and what is being assumed here? For example, consider this (fictional) chart from an ad reporting customer satisfaction at 4 local health clubs.
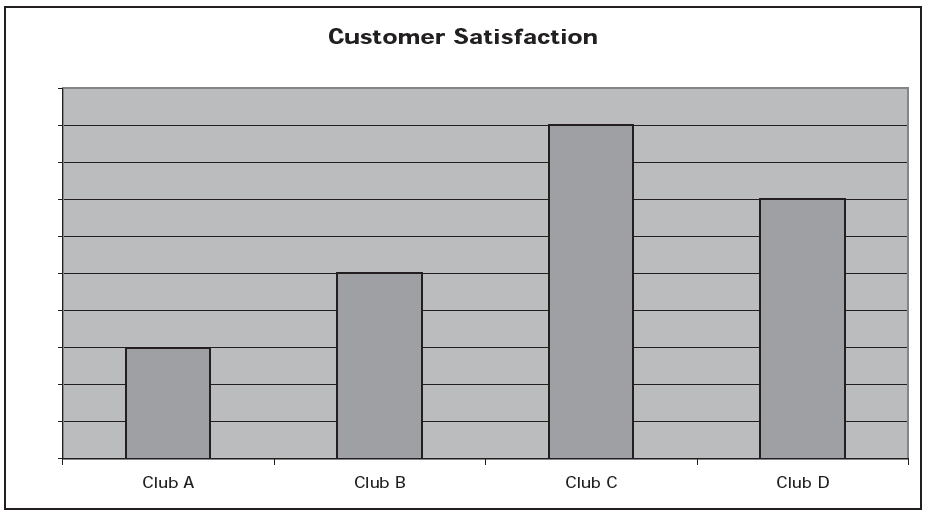
Clearly, from the results of the chart, one would be tempted to give Club C a try, as customer satisfaction is much higher than for the other 3 clubs.
There are so many distortions and omissions in this chart, however, that it is actually quite meaningless. First, how was satisfaction measured? Do the bars represent responses to a survey? If so, how were the questions asked? Most importantly, where is the missing scale for the chart? Although the differences look quite large, are they really?
Well, here is the same chart, with a different scale, this time labeled:
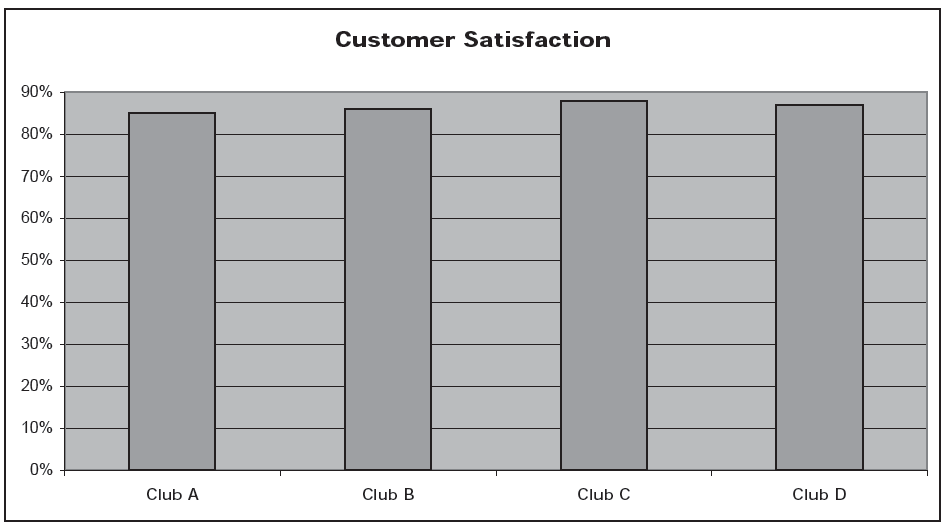
Club C is not so impressive any more, is it? In fact, all of the health clubs have customer satisfaction ratings (whatever that means) between 85% and 88%. In the first chart, the entire scale of the graph included only the percentages between 83 and 89. This “judicious” choice of scale—some would call it a distortion—and omission of that scale from the chart make the tiny differences among the clubs seem important, however.
Also, in order to be a critical thinker, you need to learn to pay attention to the assumptions that underlie a message. Let us briefly illustrate the role of assumptions by touching on some people’s beliefs about the criminal justice system in the US. Some believe that a major problem with our judicial system is that many criminals go free because of legal technicalities. Others believe that a major problem is that many innocent people are convicted of crimes. The simple fact is, both types of errors occur. A person’s conclusion about which flaw in our judicial system is the greater tragedy is based on an assumption about which of these is the more serious error (letting the guilty go free or convicting the innocent). This type of assumption is called a value assumption (Browne and Keeley, 2018). It reflects the differences in values that people develop, differences that may lead us to disregard valid evidence that does not fit in with our particular values.
Oh, by the way, some students probably noticed this, but the seven tips for evaluating information that we shared in Module 1 are related to this. Actually, they are part of this section. The tips are, to a very large degree, set of ideas you can use to help you identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. If you do not remember this section, we strongly recommend you take a few minutes to review it.
skepticism : a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
bias : an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
- Which of your beliefs (or disbeliefs) from the Activate exercise for this section were derived from a process of critical thinking? If some of your beliefs were not based on critical thinking, are you willing to reassess these beliefs? If the answer is no, why do you think that is? If the answer is yes, what concrete steps will you take?
7.2 Reasoning and Judgment
- What percentage of kidnappings are committed by strangers?
- Which area of the house is riskiest: kitchen, bathroom, or stairs?
- What is the most common cancer in the US?
- What percentage of workplace homicides are committed by co-workers?
An essential set of procedural thinking skills is reasoning , the ability to generate and evaluate solid conclusions from a set of statements or evidence. You should note that these conclusions (when they are generated instead of being evaluated) are one key type of inference that we described in Section 7.1. There are two main types of reasoning, deductive and inductive.
Deductive reasoning
Suppose your teacher tells you that if you get an A on the final exam in a course, you will get an A for the whole course. Then, you get an A on the final exam. What will your final course grade be? Most people can see instantly that you can conclude with certainty that you will get an A for the course. This is a type of reasoning called deductive reasoning , which is defined as reasoning in which a conclusion is guaranteed to be true as long as the statements leading to it are true. The three statements can be listed as an argument , with two beginning statements and a conclusion:
Statement 1: If you get an A on the final exam, you will get an A for the course
Statement 2: You get an A on the final exam
Conclusion: You will get an A for the course
This particular arrangement, in which true beginning statements lead to a guaranteed true conclusion, is known as a deductively valid argument . Although deductive reasoning is often the subject of abstract, brain-teasing, puzzle-like word problems, it is actually an extremely important type of everyday reasoning. It is just hard to recognize sometimes. For example, imagine that you are looking for your car keys and you realize that they are either in the kitchen drawer or in your book bag. After looking in the kitchen drawer, you instantly know that they must be in your book bag. That conclusion results from a simple deductive reasoning argument. In addition, solid deductive reasoning skills are necessary for you to succeed in the sciences, philosophy, math, computer programming, and any endeavor involving the use of logic to persuade others to your point of view or to evaluate others’ arguments.
Cognitive psychologists, and before them philosophers, have been quite interested in deductive reasoning, not so much for its practical applications, but for the insights it can offer them about the ways that human beings think. One of the early ideas to emerge from the examination of deductive reasoning is that people learn (or develop) mental versions of rules that allow them to solve these types of reasoning problems (Braine, 1978; Braine, Reiser, & Rumain, 1984). The best way to see this point of view is to realize that there are different possible rules, and some of them are very simple. For example, consider this rule of logic:
therefore q
Logical rules are often presented abstractly, as letters, in order to imply that they can be used in very many specific situations. Here is a concrete version of the of the same rule:
I’ll either have pizza or a hamburger for dinner tonight (p or q)
I won’t have pizza (not p)
Therefore, I’ll have a hamburger (therefore q)
This kind of reasoning seems so natural, so easy, that it is quite plausible that we would use a version of this rule in our daily lives. At least, it seems more plausible than some of the alternative possibilities—for example, that we need to have experience with the specific situation (pizza or hamburger, in this case) in order to solve this type of problem easily. So perhaps there is a form of natural logic (Rips, 1990) that contains very simple versions of logical rules. When we are faced with a reasoning problem that maps onto one of these rules, we use the rule.
But be very careful; things are not always as easy as they seem. Even these simple rules are not so simple. For example, consider the following rule. Many people fail to realize that this rule is just as valid as the pizza or hamburger rule above.
if p, then q
therefore, not p
Concrete version:
If I eat dinner, then I will have dessert
I did not have dessert
Therefore, I did not eat dinner
The simple fact is, it can be very difficult for people to apply rules of deductive logic correctly; as a result, they make many errors when trying to do so. Is this a deductively valid argument or not?
Students who like school study a lot
Students who study a lot get good grades
Jane does not like school
Therefore, Jane does not get good grades
Many people are surprised to discover that this is not a logically valid argument; the conclusion is not guaranteed to be true from the beginning statements. Although the first statement says that students who like school study a lot, it does NOT say that students who do not like school do not study a lot. In other words, it may very well be possible to study a lot without liking school. Even people who sometimes get problems like this right might not be using the rules of deductive reasoning. Instead, they might just be making judgments for examples they know, in this case, remembering instances of people who get good grades despite not liking school.
Making deductive reasoning even more difficult is the fact that there are two important properties that an argument may have. One, it can be valid or invalid (meaning that the conclusion does or does not follow logically from the statements leading up to it). Two, an argument (or more correctly, its conclusion) can be true or false. Here is an example of an argument that is logically valid, but has a false conclusion (at least we think it is false).
Either you are eleven feet tall or the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth.
You are not eleven feet tall
Therefore the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth
This argument has the exact same form as the pizza or hamburger argument above, making it is deductively valid. The conclusion is so false, however, that it is absurd (of course, the reason the conclusion is false is that the first statement is false). When people are judging arguments, they tend to not observe the difference between deductive validity and the empirical truth of statements or conclusions. If the elements of an argument happen to be true, people are likely to judge the argument logically valid; if the elements are false, they will very likely judge it invalid (Markovits & Bouffard-Bouchard, 1992; Moshman & Franks, 1986). Thus, it seems a stretch to say that people are using these logical rules to judge the validity of arguments. Many psychologists believe that most people actually have very limited deductive reasoning skills (Johnson-Laird, 1999). They argue that when faced with a problem for which deductive logic is required, people resort to some simpler technique, such as matching terms that appear in the statements and the conclusion (Evans, 1982). This might not seem like a problem, but what if reasoners believe that the elements are true and they happen to be wrong; they will would believe that they are using a form of reasoning that guarantees they are correct and yet be wrong.
deductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
argument : a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
deductively valid argument : an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
Inductive reasoning and judgment
Every day, you make many judgments about the likelihood of one thing or another. Whether you realize it or not, you are practicing inductive reasoning on a daily basis. In inductive reasoning arguments, a conclusion is likely whenever the statements preceding it are true. The first thing to notice about inductive reasoning is that, by definition, you can never be sure about your conclusion; you can only estimate how likely the conclusion is. Inductive reasoning may lead you to focus on Memory Encoding and Recoding when you study for the exam, but it is possible the instructor will ask more questions about Memory Retrieval instead. Unlike deductive reasoning, the conclusions you reach through inductive reasoning are only probable, not certain. That is why scientists consider inductive reasoning weaker than deductive reasoning. But imagine how hard it would be for us to function if we could not act unless we were certain about the outcome.
Inductive reasoning can be represented as logical arguments consisting of statements and a conclusion, just as deductive reasoning can be. In an inductive argument, you are given some statements and a conclusion (or you are given some statements and must draw a conclusion). An argument is inductively strong if the conclusion would be very probable whenever the statements are true. So, for example, here is an inductively strong argument:
- Statement #1: The forecaster on Channel 2 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #2: The forecaster on Channel 5 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #3: It is very cloudy and humid.
- Statement #4: You just heard thunder.
- Conclusion (or judgment): It is going to rain today.
Think of the statements as evidence, on the basis of which you will draw a conclusion. So, based on the evidence presented in the four statements, it is very likely that it will rain today. Will it definitely rain today? Certainly not. We can all think of times that the weather forecaster was wrong.
A true story: Some years ago psychology student was watching a baseball playoff game between the St. Louis Cardinals and the Los Angeles Dodgers. A graphic on the screen had just informed the audience that the Cardinal at bat, (Hall of Fame shortstop) Ozzie Smith, a switch hitter batting left-handed for this plate appearance, had never, in nearly 3000 career at-bats, hit a home run left-handed. The student, who had just learned about inductive reasoning in his psychology class, turned to his companion (a Cardinals fan) and smugly said, “It is an inductively strong argument that Ozzie Smith will not hit a home run.” He turned back to face the television just in time to watch the ball sail over the right field fence for a home run. Although the student felt foolish at the time, he was not wrong. It was an inductively strong argument; 3000 at-bats is an awful lot of evidence suggesting that the Wizard of Ozz (as he was known) would not be hitting one out of the park (think of each at-bat without a home run as a statement in an inductive argument). Sadly (for the die-hard Cubs fan and Cardinals-hating student), despite the strength of the argument, the conclusion was wrong.
Given the possibility that we might draw an incorrect conclusion even with an inductively strong argument, we really want to be sure that we do, in fact, make inductively strong arguments. If we judge something probable, it had better be probable. If we judge something nearly impossible, it had better not happen. Think of inductive reasoning, then, as making reasonably accurate judgments of the probability of some conclusion given a set of evidence.
We base many decisions in our lives on inductive reasoning. For example:
Statement #1: Psychology is not my best subject
Statement #2: My psychology instructor has a reputation for giving difficult exams
Statement #3: My first psychology exam was much harder than I expected
Judgment: The next exam will probably be very difficult.
Decision: I will study tonight instead of watching Netflix.
Some other examples of judgments that people commonly make in a school context include judgments of the likelihood that:
- A particular class will be interesting/useful/difficult
- You will be able to finish writing a paper by next week if you go out tonight
- Your laptop’s battery will last through the next trip to the library
- You will not miss anything important if you skip class tomorrow
- Your instructor will not notice if you skip class tomorrow
- You will be able to find a book that you will need for a paper
- There will be an essay question about Memory Encoding on the next exam
Tversky and Kahneman (1983) recognized that there are two general ways that we might make these judgments; they termed them extensional (i.e., following the laws of probability) and intuitive (i.e., using shortcuts or heuristics, see below). We will use a similar distinction between Type 1 and Type 2 thinking, as described by Keith Stanovich and his colleagues (Evans and Stanovich, 2013; Stanovich and West, 2000). Type 1 thinking is fast, automatic, effortful, and emotional. In fact, it is hardly fair to call it reasoning at all, as judgments just seem to pop into one’s head. Type 2 thinking , on the other hand, is slow, effortful, and logical. So obviously, it is more likely to lead to a correct judgment, or an optimal decision. The problem is, we tend to over-rely on Type 1. Now, we are not saying that Type 2 is the right way to go for every decision or judgment we make. It seems a bit much, for example, to engage in a step-by-step logical reasoning procedure to decide whether we will have chicken or fish for dinner tonight.
Many bad decisions in some very important contexts, however, can be traced back to poor judgments of the likelihood of certain risks or outcomes that result from the use of Type 1 when a more logical reasoning process would have been more appropriate. For example:
Statement #1: It is late at night.
Statement #2: Albert has been drinking beer for the past five hours at a party.
Statement #3: Albert is not exactly sure where he is or how far away home is.
Judgment: Albert will have no difficulty walking home.
Decision: He walks home alone.
As you can see in this example, the three statements backing up the judgment do not really support it. In other words, this argument is not inductively strong because it is based on judgments that ignore the laws of probability. What are the chances that someone facing these conditions will be able to walk home alone easily? And one need not be drunk to make poor decisions based on judgments that just pop into our heads.
The truth is that many of our probability judgments do not come very close to what the laws of probability say they should be. Think about it. In order for us to reason in accordance with these laws, we would need to know the laws of probability, which would allow us to calculate the relationship between particular pieces of evidence and the probability of some outcome (i.e., how much likelihood should change given a piece of evidence), and we would have to do these heavy math calculations in our heads. After all, that is what Type 2 requires. Needless to say, even if we were motivated, we often do not even know how to apply Type 2 reasoning in many cases.
So what do we do when we don’t have the knowledge, skills, or time required to make the correct mathematical judgment? Do we hold off and wait until we can get better evidence? Do we read up on probability and fire up our calculator app so we can compute the correct probability? Of course not. We rely on Type 1 thinking. We “wing it.” That is, we come up with a likelihood estimate using some means at our disposal. Psychologists use the term heuristic to describe the type of “winging it” we are talking about. A heuristic is a shortcut strategy that we use to make some judgment or solve some problem (see Section 7.3). Heuristics are easy and quick, think of them as the basic procedures that are characteristic of Type 1. They can absolutely lead to reasonably good judgments and decisions in some situations (like choosing between chicken and fish for dinner). They are, however, far from foolproof. There are, in fact, quite a lot of situations in which heuristics can lead us to make incorrect judgments, and in many cases the decisions based on those judgments can have serious consequences.
Let us return to the activity that begins this section. You were asked to judge the likelihood (or frequency) of certain events and risks. You were free to come up with your own evidence (or statements) to make these judgments. This is where a heuristic crops up. As a judgment shortcut, we tend to generate specific examples of those very events to help us decide their likelihood or frequency. For example, if we are asked to judge how common, frequent, or likely a particular type of cancer is, many of our statements would be examples of specific cancer cases:
Statement #1: Andy Kaufman (comedian) had lung cancer.
Statement #2: Colin Powell (US Secretary of State) had prostate cancer.
Statement #3: Bob Marley (musician) had skin and brain cancer
Statement #4: Sandra Day O’Connor (Supreme Court Justice) had breast cancer.
Statement #5: Fred Rogers (children’s entertainer) had stomach cancer.
Statement #6: Robin Roberts (news anchor) had breast cancer.
Statement #7: Bette Davis (actress) had breast cancer.
Judgment: Breast cancer is the most common type.
Your own experience or memory may also tell you that breast cancer is the most common type. But it is not (although it is common). Actually, skin cancer is the most common type in the US. We make the same types of misjudgments all the time because we do not generate the examples or evidence according to their actual frequencies or probabilities. Instead, we have a tendency (or bias) to search for the examples in memory; if they are easy to retrieve, we assume that they are common. To rephrase this in the language of the heuristic, events seem more likely to the extent that they are available to memory. This bias has been termed the availability heuristic (Kahneman and Tversky, 1974).
The fact that we use the availability heuristic does not automatically mean that our judgment is wrong. The reason we use heuristics in the first place is that they work fairly well in many cases (and, of course that they are easy to use). So, the easiest examples to think of sometimes are the most common ones. Is it more likely that a member of the U.S. Senate is a man or a woman? Most people have a much easier time generating examples of male senators. And as it turns out, the U.S. Senate has many more men than women (74 to 26 in 2020). In this case, then, the availability heuristic would lead you to make the correct judgment; it is far more likely that a senator would be a man.
In many other cases, however, the availability heuristic will lead us astray. This is because events can be memorable for many reasons other than their frequency. Section 5.2, Encoding Meaning, suggested that one good way to encode the meaning of some information is to form a mental image of it. Thus, information that has been pictured mentally will be more available to memory. Indeed, an event that is vivid and easily pictured will trick many people into supposing that type of event is more common than it actually is. Repetition of information will also make it more memorable. So, if the same event is described to you in a magazine, on the evening news, on a podcast that you listen to, and in your Facebook feed; it will be very available to memory. Again, the availability heuristic will cause you to misperceive the frequency of these types of events.
Most interestingly, information that is unusual is more memorable. Suppose we give you the following list of words to remember: box, flower, letter, platypus, oven, boat, newspaper, purse, drum, car. Very likely, the easiest word to remember would be platypus, the unusual one. The same thing occurs with memories of events. An event may be available to memory because it is unusual, yet the availability heuristic leads us to judge that the event is common. Did you catch that? In these cases, the availability heuristic makes us think the exact opposite of the true frequency. We end up thinking something is common because it is unusual (and therefore memorable). Yikes.
The misapplication of the availability heuristic sometimes has unfortunate results. For example, if you went to K-12 school in the US over the past 10 years, it is extremely likely that you have participated in lockdown and active shooter drills. Of course, everyone is trying to prevent the tragedy of another school shooting. And believe us, we are not trying to minimize how terrible the tragedy is. But the truth of the matter is, school shootings are extremely rare. Because the federal government does not keep a database of school shootings, the Washington Post has maintained their own running tally. Between 1999 and January 2020 (the date of the most recent school shooting with a death in the US at of the time this paragraph was written), the Post reported a total of 254 people died in school shootings in the US. Not 254 per year, 254 total. That is an average of 12 per year. Of course, that is 254 people who should not have died (particularly because many were children), but in a country with approximately 60,000,000 students and teachers, this is a very small risk.
But many students and teachers are terrified that they will be victims of school shootings because of the availability heuristic. It is so easy to think of examples (they are very available to memory) that people believe the event is very common. It is not. And there is a downside to this. We happen to believe that there is an enormous gun violence problem in the United States. According the the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 39,773 firearm deaths in the US in 2017. Fifteen of those deaths were in school shootings, according to the Post. 60% of those deaths were suicides. When people pay attention to the school shooting risk (low), they often fail to notice the much larger risk.
And examples like this are by no means unique. The authors of this book have been teaching psychology since the 1990’s. We have been able to make the exact same arguments about the misapplication of the availability heuristics and keep them current by simply swapping out for the “fear of the day.” In the 1990’s it was children being kidnapped by strangers (it was known as “stranger danger”) despite the facts that kidnappings accounted for only 2% of the violent crimes committed against children, and only 24% of kidnappings are committed by strangers (US Department of Justice, 2007). This fear overlapped with the fear of terrorism that gripped the country after the 2001 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and US Pentagon and still plagues the population of the US somewhat in 2020. After a well-publicized, sensational act of violence, people are extremely likely to increase their estimates of the chances that they, too, will be victims of terror. Think about the reality, however. In October of 2001, a terrorist mailed anthrax spores to members of the US government and a number of media companies. A total of five people died as a result of this attack. The nation was nearly paralyzed by the fear of dying from the attack; in reality the probability of an individual person dying was 0.00000002.
The availability heuristic can lead you to make incorrect judgments in a school setting as well. For example, suppose you are trying to decide if you should take a class from a particular math professor. You might try to make a judgment of how good a teacher she is by recalling instances of friends and acquaintances making comments about her teaching skill. You may have some examples that suggest that she is a poor teacher very available to memory, so on the basis of the availability heuristic you judge her a poor teacher and decide to take the class from someone else. What if, however, the instances you recalled were all from the same person, and this person happens to be a very colorful storyteller? The subsequent ease of remembering the instances might not indicate that the professor is a poor teacher after all.
Although the availability heuristic is obviously important, it is not the only judgment heuristic we use. Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman examined the role of heuristics in inductive reasoning in a long series of studies. Kahneman received a Nobel Prize in Economics for this research in 2002, and Tversky would have certainly received one as well if he had not died of melanoma at age 59 in 1996 (Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously). Kahneman and Tversky demonstrated repeatedly that people do not reason in ways that are consistent with the laws of probability. They identified several heuristic strategies that people use instead to make judgments about likelihood. The importance of this work for economics (and the reason that Kahneman was awarded the Nobel Prize) is that earlier economic theories had assumed that people do make judgments rationally, that is, in agreement with the laws of probability.
Another common heuristic that people use for making judgments is the representativeness heuristic (Kahneman & Tversky 1973). Suppose we describe a person to you. He is quiet and shy, has an unassuming personality, and likes to work with numbers. Is this person more likely to be an accountant or an attorney? If you said accountant, you were probably using the representativeness heuristic. Our imaginary person is judged likely to be an accountant because he resembles, or is representative of the concept of, an accountant. When research participants are asked to make judgments such as these, the only thing that seems to matter is the representativeness of the description. For example, if told that the person described is in a room that contains 70 attorneys and 30 accountants, participants will still assume that he is an accountant.
inductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
inductively strong argument : an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
availability heuristic : judging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
representativeness heuristic: judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
Type 1 thinking : fast, automatic, and emotional thinking.
Type 2 thinking : slow, effortful, and logical thinking.
- What percentage of workplace homicides are co-worker violence?
Many people get these questions wrong. The answers are 10%; stairs; skin; 6%. How close were your answers? Explain how the availability heuristic might have led you to make the incorrect judgments.
- Can you think of some other judgments that you have made (or beliefs that you have) that might have been influenced by the availability heuristic?
7.3 Problem Solving
- Please take a few minutes to list a number of problems that you are facing right now.
- Now write about a problem that you recently solved.
- What is your definition of a problem?
Mary has a problem. Her daughter, ordinarily quite eager to please, appears to delight in being the last person to do anything. Whether getting ready for school, going to piano lessons or karate class, or even going out with her friends, she seems unwilling or unable to get ready on time. Other people have different kinds of problems. For example, many students work at jobs, have numerous family commitments, and are facing a course schedule full of difficult exams, assignments, papers, and speeches. How can they find enough time to devote to their studies and still fulfill their other obligations? Speaking of students and their problems: Show that a ball thrown vertically upward with initial velocity v0 takes twice as much time to return as to reach the highest point (from Spiegel, 1981).
These are three very different situations, but we have called them all problems. What makes them all the same, despite the differences? A psychologist might define a problem as a situation with an initial state, a goal state, and a set of possible intermediate states. Somewhat more meaningfully, we might consider a problem a situation in which you are in here one state (e.g., daughter is always late), you want to be there in another state (e.g., daughter is not always late), and with no obvious way to get from here to there. Defined this way, each of the three situations we outlined can now be seen as an example of the same general concept, a problem. At this point, you might begin to wonder what is not a problem, given such a general definition. It seems that nearly every non-routine task we engage in could qualify as a problem. As long as you realize that problems are not necessarily bad (it can be quite fun and satisfying to rise to the challenge and solve a problem), this may be a useful way to think about it.
Can we identify a set of problem-solving skills that would apply to these very different kinds of situations? That task, in a nutshell, is a major goal of this section. Let us try to begin to make sense of the wide variety of ways that problems can be solved with an important observation: the process of solving problems can be divided into two key parts. First, people have to notice, comprehend, and represent the problem properly in their minds (called problem representation ). Second, they have to apply some kind of solution strategy to the problem. Psychologists have studied both of these key parts of the process in detail.
When you first think about the problem-solving process, you might guess that most of our difficulties would occur because we are failing in the second step, the application of strategies. Although this can be a significant difficulty much of the time, the more important source of difficulty is probably problem representation. In short, we often fail to solve a problem because we are looking at it, or thinking about it, the wrong way.
problem : a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
problem representation : noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
Defining and Mentally Representing Problems in Order to Solve Them
So, the main obstacle to solving a problem is that we do not clearly understand exactly what the problem is. Recall the problem with Mary’s daughter always being late. One way to represent, or to think about, this problem is that she is being defiant. She refuses to get ready in time. This type of representation or definition suggests a particular type of solution. Another way to think about the problem, however, is to consider the possibility that she is simply being sidetracked by interesting diversions. This different conception of what the problem is (i.e., different representation) suggests a very different solution strategy. For example, if Mary defines the problem as defiance, she may be tempted to solve the problem using some kind of coercive tactics, that is, to assert her authority as her mother and force her to listen. On the other hand, if Mary defines the problem as distraction, she may try to solve it by simply removing the distracting objects.
As you might guess, when a problem is represented one way, the solution may seem very difficult, or even impossible. Seen another way, the solution might be very easy. For example, consider the following problem (from Nasar, 1998):
Two bicyclists start 20 miles apart and head toward each other, each going at a steady rate of 10 miles per hour. At the same time, a fly that travels at a steady 15 miles per hour starts from the front wheel of the southbound bicycle and flies to the front wheel of the northbound one, then turns around and flies to the front wheel of the southbound one again, and continues in this manner until he is crushed between the two front wheels. Question: what total distance did the fly cover?
Please take a few minutes to try to solve this problem.
Most people represent this problem as a question about a fly because, well, that is how the question is asked. The solution, using this representation, is to figure out how far the fly travels on the first leg of its journey, then add this total to how far it travels on the second leg of its journey (when it turns around and returns to the first bicycle), then continue to add the smaller distance from each leg of the journey until you converge on the correct answer. You would have to be quite skilled at math to solve this problem, and you would probably need some time and pencil and paper to do it.
If you consider a different representation, however, you can solve this problem in your head. Instead of thinking about it as a question about a fly, think about it as a question about the bicycles. They are 20 miles apart, and each is traveling 10 miles per hour. How long will it take for the bicycles to reach each other? Right, one hour. The fly is traveling 15 miles per hour; therefore, it will travel a total of 15 miles back and forth in the hour before the bicycles meet. Represented one way (as a problem about a fly), the problem is quite difficult. Represented another way (as a problem about two bicycles), it is easy. Changing your representation of a problem is sometimes the best—sometimes the only—way to solve it.
Unfortunately, however, changing a problem’s representation is not the easiest thing in the world to do. Often, problem solvers get stuck looking at a problem one way. This is called fixation . Most people who represent the preceding problem as a problem about a fly probably do not pause to reconsider, and consequently change, their representation. A parent who thinks her daughter is being defiant is unlikely to consider the possibility that her behavior is far less purposeful.
Problem-solving fixation was examined by a group of German psychologists called Gestalt psychologists during the 1930’s and 1940’s. Karl Dunker, for example, discovered an important type of failure to take a different perspective called functional fixedness . Imagine being a participant in one of his experiments. You are asked to figure out how to mount two candles on a door and are given an assortment of odds and ends, including a small empty cardboard box and some thumbtacks. Perhaps you have already figured out a solution: tack the box to the door so it forms a platform, then put the candles on top of the box. Most people are able to arrive at this solution. Imagine a slight variation of the procedure, however. What if, instead of being empty, the box had matches in it? Most people given this version of the problem do not arrive at the solution given above. Why? Because it seems to people that when the box contains matches, it already has a function; it is a matchbox. People are unlikely to consider a new function for an object that already has a function. This is functional fixedness.
Mental set is a type of fixation in which the problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past, even though the solution may no longer be useful. It is commonly seen when students do math problems for homework. Often, several problems in a row require the reapplication of the same solution strategy. Then, without warning, the next problem in the set requires a new strategy. Many students attempt to apply the formerly successful strategy on the new problem and therefore cannot come up with a correct answer.
The thing to remember is that you cannot solve a problem unless you correctly identify what it is to begin with (initial state) and what you want the end result to be (goal state). That may mean looking at the problem from a different angle and representing it in a new way. The correct representation does not guarantee a successful solution, but it certainly puts you on the right track.
A bit more optimistically, the Gestalt psychologists discovered what may be considered the opposite of fixation, namely insight . Sometimes the solution to a problem just seems to pop into your head. Wolfgang Kohler examined insight by posing many different problems to chimpanzees, principally problems pertaining to their acquisition of out-of-reach food. In one version, a banana was placed outside of a chimpanzee’s cage and a short stick inside the cage. The stick was too short to retrieve the banana, but was long enough to retrieve a longer stick also located outside of the cage. This second stick was long enough to retrieve the banana. After trying, and failing, to reach the banana with the shorter stick, the chimpanzee would try a couple of random-seeming attempts, react with some apparent frustration or anger, then suddenly rush to the longer stick, the correct solution fully realized at this point. This sudden appearance of the solution, observed many times with many different problems, was termed insight by Kohler.
Lest you think it pertains to chimpanzees only, Karl Dunker demonstrated that children also solve problems through insight in the 1930s. More importantly, you have probably experienced insight yourself. Think back to a time when you were trying to solve a difficult problem. After struggling for a while, you gave up. Hours later, the solution just popped into your head, perhaps when you were taking a walk, eating dinner, or lying in bed.
fixation : when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
functional fixedness : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
mental set : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
insight : a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
Solving Problems by Trial and Error
Correctly identifying the problem and your goal for a solution is a good start, but recall the psychologist’s definition of a problem: it includes a set of possible intermediate states. Viewed this way, a problem can be solved satisfactorily only if one can find a path through some of these intermediate states to the goal. Imagine a fairly routine problem, finding a new route to school when your ordinary route is blocked (by road construction, for example). At each intersection, you may turn left, turn right, or go straight. A satisfactory solution to the problem (of getting to school) is a sequence of selections at each intersection that allows you to wind up at school.
If you had all the time in the world to get to school, you might try choosing intermediate states randomly. At one corner you turn left, the next you go straight, then you go left again, then right, then right, then straight. Unfortunately, trial and error will not necessarily get you where you want to go, and even if it does, it is not the fastest way to get there. For example, when a friend of ours was in college, he got lost on the way to a concert and attempted to find the venue by choosing streets to turn onto randomly (this was long before the use of GPS). Amazingly enough, the strategy worked, although he did end up missing two out of the three bands who played that night.
Trial and error is not all bad, however. B.F. Skinner, a prominent behaviorist psychologist, suggested that people often behave randomly in order to see what effect the behavior has on the environment and what subsequent effect this environmental change has on them. This seems particularly true for the very young person. Picture a child filling a household’s fish tank with toilet paper, for example. To a child trying to develop a repertoire of creative problem-solving strategies, an odd and random behavior might be just the ticket. Eventually, the exasperated parent hopes, the child will discover that many of these random behaviors do not successfully solve problems; in fact, in many cases they create problems. Thus, one would expect a decrease in this random behavior as a child matures. You should realize, however, that the opposite extreme is equally counterproductive. If the children become too rigid, never trying something unexpected and new, their problem solving skills can become too limited.
Effective problem solving seems to call for a happy medium that strikes a balance between using well-founded old strategies and trying new ground and territory. The individual who recognizes a situation in which an old problem-solving strategy would work best, and who can also recognize a situation in which a new untested strategy is necessary is halfway to success.
Solving Problems with Algorithms and Heuristics
For many problems there is a possible strategy available that will guarantee a correct solution. For example, think about math problems. Math lessons often consist of step-by-step procedures that can be used to solve the problems. If you apply the strategy without error, you are guaranteed to arrive at the correct solution to the problem. This approach is called using an algorithm , a term that denotes the step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution. Because algorithms are sometimes available and come with a guarantee, you might think that most people use them frequently. Unfortunately, however, they do not. As the experience of many students who have struggled through math classes can attest, algorithms can be extremely difficult to use, even when the problem solver knows which algorithm is supposed to work in solving the problem. In problems outside of math class, we often do not even know if an algorithm is available. It is probably fair to say, then, that algorithms are rarely used when people try to solve problems.
Because algorithms are so difficult to use, people often pass up the opportunity to guarantee a correct solution in favor of a strategy that is much easier to use and yields a reasonable chance of coming up with a correct solution. These strategies are called problem solving heuristics . Similar to what you saw in section 6.2 with reasoning heuristics, a problem solving heuristic is a shortcut strategy that people use when trying to solve problems. It usually works pretty well, but does not guarantee a correct solution to the problem. For example, one problem solving heuristic might be “always move toward the goal” (so when trying to get to school when your regular route is blocked, you would always turn in the direction you think the school is). A heuristic that people might use when doing math homework is “use the same solution strategy that you just used for the previous problem.”
By the way, we hope these last two paragraphs feel familiar to you. They seem to parallel a distinction that you recently learned. Indeed, algorithms and problem-solving heuristics are another example of the distinction between Type 1 thinking and Type 2 thinking.
Although it is probably not worth describing a large number of specific heuristics, two observations about heuristics are worth mentioning. First, heuristics can be very general or they can be very specific, pertaining to a particular type of problem only. For example, “always move toward the goal” is a general strategy that you can apply to countless problem situations. On the other hand, “when you are lost without a functioning gps, pick the most expensive car you can see and follow it” is specific to the problem of being lost. Second, all heuristics are not equally useful. One heuristic that many students know is “when in doubt, choose c for a question on a multiple-choice exam.” This is a dreadful strategy because many instructors intentionally randomize the order of answer choices. Another test-taking heuristic, somewhat more useful, is “look for the answer to one question somewhere else on the exam.”
You really should pay attention to the application of heuristics to test taking. Imagine that while reviewing your answers for a multiple-choice exam before turning it in, you come across a question for which you originally thought the answer was c. Upon reflection, you now think that the answer might be b. Should you change the answer to b, or should you stick with your first impression? Most people will apply the heuristic strategy to “stick with your first impression.” What they do not realize, of course, is that this is a very poor strategy (Lilienfeld et al, 2009). Most of the errors on exams come on questions that were answered wrong originally and were not changed (so they remain wrong). There are many fewer errors where we change a correct answer to an incorrect answer. And, of course, sometimes we change an incorrect answer to a correct answer. In fact, research has shown that it is more common to change a wrong answer to a right answer than vice versa (Bruno, 2001).
The belief in this poor test-taking strategy (stick with your first impression) is based on the confirmation bias (Nickerson, 1998; Wason, 1960). You first saw the confirmation bias in Module 1, but because it is so important, we will repeat the information here. People have a bias, or tendency, to notice information that confirms what they already believe. Somebody at one time told you to stick with your first impression, so when you look at the results of an exam you have taken, you will tend to notice the cases that are consistent with that belief. That is, you will notice the cases in which you originally had an answer correct and changed it to the wrong answer. You tend not to notice the other two important (and more common) cases, changing an answer from wrong to right, and leaving a wrong answer unchanged.
Because heuristics by definition do not guarantee a correct solution to a problem, mistakes are bound to occur when we employ them. A poor choice of a specific heuristic will lead to an even higher likelihood of making an error.
algorithm : a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
problem solving heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
confirmation bias : people’s tendency to notice information that confirms what they already believe
An Effective Problem-Solving Sequence
You may be left with a big question: If algorithms are hard to use and heuristics often don’t work, how am I supposed to solve problems? Robert Sternberg (1996), as part of his theory of what makes people successfully intelligent (Module 8) described a problem-solving sequence that has been shown to work rather well:
- Identify the existence of a problem. In school, problem identification is often easy; problems that you encounter in math classes, for example, are conveniently labeled as problems for you. Outside of school, however, realizing that you have a problem is a key difficulty that you must get past in order to begin solving it. You must be very sensitive to the symptoms that indicate a problem.
- Define the problem. Suppose you realize that you have been having many headaches recently. Very likely, you would identify this as a problem. If you define the problem as “headaches,” the solution would probably be to take aspirin or ibuprofen or some other anti-inflammatory medication. If the headaches keep returning, however, you have not really solved the problem—likely because you have mistaken a symptom for the problem itself. Instead, you must find the root cause of the headaches. Stress might be the real problem. For you to successfully solve many problems it may be necessary for you to overcome your fixations and represent the problems differently. One specific strategy that you might find useful is to try to define the problem from someone else’s perspective. How would your parents, spouse, significant other, doctor, etc. define the problem? Somewhere in these different perspectives may lurk the key definition that will allow you to find an easier and permanent solution.
- Formulate strategy. Now it is time to begin planning exactly how the problem will be solved. Is there an algorithm or heuristic available for you to use? Remember, heuristics by their very nature guarantee that occasionally you will not be able to solve the problem. One point to keep in mind is that you should look for long-range solutions, which are more likely to address the root cause of a problem than short-range solutions.
- Represent and organize information. Similar to the way that the problem itself can be defined, or represented in multiple ways, information within the problem is open to different interpretations. Suppose you are studying for a big exam. You have chapters from a textbook and from a supplemental reader, along with lecture notes that all need to be studied. How should you (represent and) organize these materials? Should you separate them by type of material (text versus reader versus lecture notes), or should you separate them by topic? To solve problems effectively, you must learn to find the most useful representation and organization of information.
- Allocate resources. This is perhaps the simplest principle of the problem solving sequence, but it is extremely difficult for many people. First, you must decide whether time, money, skills, effort, goodwill, or some other resource would help to solve the problem Then, you must make the hard choice of deciding which resources to use, realizing that you cannot devote maximum resources to every problem. Very often, the solution to problem is simply to change how resources are allocated (for example, spending more time studying in order to improve grades).
- Monitor and evaluate solutions. Pay attention to the solution strategy while you are applying it. If it is not working, you may be able to select another strategy. Another fact you should realize about problem solving is that it never does end. Solving one problem frequently brings up new ones. Good monitoring and evaluation of your problem solutions can help you to anticipate and get a jump on solving the inevitable new problems that will arise.
Please note that this as an effective problem-solving sequence, not the effective problem solving sequence. Just as you can become fixated and end up representing the problem incorrectly or trying an inefficient solution, you can become stuck applying the problem-solving sequence in an inflexible way. Clearly there are problem situations that can be solved without using these skills in this order.
Additionally, many real-world problems may require that you go back and redefine a problem several times as the situation changes (Sternberg et al. 2000). For example, consider the problem with Mary’s daughter one last time. At first, Mary did represent the problem as one of defiance. When her early strategy of pleading and threatening punishment was unsuccessful, Mary began to observe her daughter more carefully. She noticed that, indeed, her daughter’s attention would be drawn by an irresistible distraction or book. Fresh with a re-representation of the problem, she began a new solution strategy. She began to remind her daughter every few minutes to stay on task and remind her that if she is ready before it is time to leave, she may return to the book or other distracting object at that time. Fortunately, this strategy was successful, so Mary did not have to go back and redefine the problem again.
Pick one or two of the problems that you listed when you first started studying this section and try to work out the steps of Sternberg’s problem solving sequence for each one.
a mental representation of a category of things in the world
an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
Thinking like a scientist in your everyday life for the purpose of drawing correct conclusions. It entails skepticism; an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; and excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills.
a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
fast, automatic, and emotional thinking
slow, effortful, and logical thinking
a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
udging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
The tendency to notice and pay attention to information that confirms your prior beliefs and to ignore information that disconfirms them.
a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Ken Gray; Elizabeth Arnott-Hill; and Or'Shaundra Benson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Mental Health
What Is Cognitive Psychology?

Cognitive psychology is the branch of psychology dedicated to studying how people think. The cognitive perspective in psychology focuses on how the interactions of thinking, emotion, creativity, and problem-solving abilities affect how and why you think the way you do. Cognitive psychology attempts to measure different types of intelligence, determine how you organize your thoughts, and compare different components of cognition.
What Does a Cognitive Psychologist Do?
Cognitive psychologists do clinical research, training, education, and clinical practice. They use the insights gained from studying how people think and process information to help people develop new ways of dealing with problem behaviors and live better lives. Cognitive psychologists have special knowledge of applied behavior analysis, behavior therapy, learning theories, and emotional processing theories.
They know how to apply this knowledge to the human condition and use it in the treatment of:
- Anxiety disorders
- Academic performance
- Personality disorders
- Substance abuse
- Depressive disorders
- Relationship problems
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Emotional regulation
The History of Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology gained popularity in the 1950s to 1970s as researchers became more interested in how thinking affects behavior. This period is called the "cognitive revolution" and represented a shift in thinking and focus for psychologists. Before this time, the behaviorist approach dominated psychology. The behaviorists only studied external behavior that could be measured.
Behaviorists believed it was pointless to try to study the mind because there was no way to see or objectively measure what happened in someone's thoughts. The mind was seen as a black box that couldn't be measured.
The cognitive approach gave rise to the idea that internal mental behavior could be studied using experiments. Cognitive psychology assumes that there is an internal process that occurs between when a stimulus happens and when you respond to it.
These processes are called mediational processes and can involve memory, perception, attention, problem-solving, or other processes. Cognitive psychologists believe if you want to understand behavior, you have to understand the mediational processes that cause it.
Cognitive Psychology Examples
Some examples of studies and work in cognitive psychology include:
Experts think differently. Beginners think literally when they try to solve a problem. They tend to focus on the surface details when they're presented with an unfamiliar situation. Experts are able to see the underlying connections and think of the problem more abstractly.
Short-term memory. Your short-term memory is probably a lot shorter than you think. A classic study in cognitive psychology found that participants in a study could only recall 10% of random three-letter strings after 18 seconds. After 3 seconds, the participants could recall 80% of the letter strings, so there was a significant drop after 15 additional seconds.
Mapping the brain. Some cognitive psychologists are working on the BRAIN (Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies) Initiative. This project has been compared to the human genome project. It's an attempt to learn more about the 100 billion brain cells, including the connections between them and how they relate to behavior and health.
Cognitive Psychology Perspective in Practice
Cognitive psychology perspectives can be used to improve many areas of life, including how children learn. Researchers Pooja K. Agarwal and Henry L. Roediger III used insights from their cognitive psychology studies to develop better practices to encourage learning in the classroom. They used experiments to determine how students learn and apply their knowledge as well as disprove outdated theories.
Experts used to believe that memory could be improved with practice, a theory that has been disproven. Another popular theory that has been debunked is that errors interfere with learning. The opposite is actually true. You learn from your mistakes, so making errors improves your ability to learn. While most educators have moved beyond those theories, there are still some unproven ones that linger, like the notion that different people have different learning styles.
In addition to disproving theories that don't work, cognitive psychology shines a light on theories that do work. After combing through over 100 years of studies, researchers found four different practices that increased students' ability to learn:
- Retrieval practice, which is quickly bringing the information you're learning to mind
- Getting feedback that lets you know what you don't know
- Spaced practice, which is returning to the material periodically over time
- Interleaving, which is practicing a mix of skills
Careers in Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychologists can work at universities doing research or teaching. They can also work in the private sector in organizational psychology, software development, or human-computer interaction. Another option for cognitive psychologists is working in a clinical setting treating patients for issues related to mental processes, like:
- Alzheimer's disease
- Speech problems
- Memory issues
- Sensory difficulties
You can work in some entry-level jobs with a bachelor's degree in cognitive psychology, but most opportunities will be available to people with a master's or doctorate degree. Most research done by people with master's degrees is supervised by cognitive psychologists with doctorate degrees.

Top doctors in ,
Find more top doctors on, related links.
- Mental Health Home
- Mental Health News & Features
- Mental Health Reference
- Mental Health Quizzes
- Mental Health Slideshows
- Mental Health Blogs
- Mental Health Videos
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Anxiety & Panic Disorders
- Bipolar Disorder
- Crisis Assistance
- Eating Disorders
- Health & Balance
- Personality Disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Social Media and Mental Health
- Stress Management
- Substance Abuse & Addiction
- More Related Topics
What Is the Cognitive Psychology Approach? 12 Key Theories

Maintaining focus on the oncoming traffic is paramount, yet I am barely aware of the seagulls flying overhead.
These noisy birds only receive attention when I am safely walking up the other side of the road, their cries reminding me of childhood seaside vacations.
Cognitive psychology focuses on the internal mental processes needed to make sense of the environment and decide on the next appropriate action (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
This article explores the cognitive psychology approach, its origins, and several theories and models involved in cognition.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.
This Article Contains:
What is the cognitive psychology approach, a brief history of cognitive psychology, cognitive psychology vs behaviorism, 12 key theories, concepts, and models, fascinating research experiments, a look at positive cognitive psychology, interesting resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
The upsurge of research into the mysteries of the human brain and mind has been considerable in recent decades, with recognition of the importance of cognitive process in clinical psychology and social psychology (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
As a result, cognitive psychology has profoundly affected the field of psychology and our understanding of what it is to be human.
Perhaps more surprisingly, it has had such an effect without clear boundaries, an integrated set of assumptions and concepts, or a recognizable spokesperson (Gross, 2020).
So, what exactly is the cognitive psychology approach?
Cognitive psychology attempts to understand human cognition by focusing on what appear to be cognitive tasks that require little effort (Goldstein, 2011).
Let’s return to our example of walking down the road. Imagine now that we are also taking a call. We’re now combining several concurrent cognitive tasks:
- Perceiving the environment Distinguishing cars from traffic signals and discerning their direction and speed on the road as well as the people ahead standing, talking, and blocking the sidewalk.
- Paying attention Attending to what our partner is asking us on the phone, above the traffic noise.
- Visualizing Forming a mental image of items in the house, responding to the question, “Where did you leave your car keys?”
- Comprehending and producing language Understanding the real question (“I need to take the car. Where are your keys?”) from what is said and formulating a suitable reply.
- Problem-solving Working out how to get to the next appointment without the car.
- Decision-making Concluding that the timing of one meeting will not work and choosing to push it to another day.
While cognitive psychologists initially focused firmly on an analogy comparing the mind to a computer, their understanding has moved on.
There are currently four approaches, often overlapping and frequently combined, that science uses to understand human cognition (Eysenck & Keane, 2015):
- Cognitive psychology The attempt to “understand human cognition by using behavioral evidence” (Eysenck & Keane, 2015, p. 2).
- Cognitive neuropsychology Understanding ‘normal’ cognition through the study of patients living with a brain injury.
- Cognitive neuroscience Combining evidence from the brain with behavior to form a more complete picture of cognition.
- Computational cognitive science Using computational models to understand and test our understanding of human cognition.
Cognitive psychology plays a massive and essential role in understanding human cognition and is stronger because of its close relationships and interdependencies with other academic disciplines (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).

In 1868, a Dutch physiologist, Franciscus Donders, began to measure reaction time – something we would now see as an experiment in cognitive psychology (Goldstein, 2011).
Donders recognized that mental responses could not be measured directly but could be inferred from behavior. Not long after, Hermann Ebbinghaus began examining the nature and inner workings of human memory using nonsense syllables (Goldstein, 2011).
By the late 1800s, Wilhelm Wundt had set up the first laboratory dedicated to studying the mind scientifically. His approach became known as structuralism . His bold aim was to build a periodic table of the mind , containing all the sensations involved in creating any experience (Goldstein, 2011).
However, the use of analytical introspection to uncover hidden mental processes was gradually dropped when John Watson proposed a new psychological approach that became known as behaviorism (Goldstein, 2011).
Watson rejected the introspective approach and instead focused on observable behavior. His idea of classical conditioning – the connection of a new stimulus with a previously neutral one – was later surpassed by B. F. Skinner’s idea of operant conditioning , which focused on positive reinforcement (Goldstein, 2011).
Both theories sought to understand the relationship between stimulus and response rather than the mind’s inner workings (Goldstein, 2011).
Prompted by a scathing attack by linguist and cognitive scientist Noam Chomsky, by the 1950s behaviorism as the dominant psychological discipline was in decline. The introduction of the digital computer led to the information-processing approach , inspiring psychologists to think of the mind in terms of a sequence of processing stages (Goldstein, 2011).

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Moore (1996) recognized the tensions of the paradigm shift from behaviorism to cognitive psychology.
While research into cognitive psychology, cognitive neuropsychology, cognitive neuroscience , and computational cognitive science is now widely accepted as the driving force behind understanding mental processes (such as memory, perception, problem-solving, and attention), this was not always the case (Gross, 2020).
Moore (1996) highlighted the relationship between behaviorism and the relatively new field of cognitive psychology, and the sometimes mistaken assumptions regarding the nature of the former approach:
- Behaviorism is typically only associated with studying publicly observable behavior. Unlike behaviorism, cognitive psychology is viewed as free of the restrictions of logical positivism, which rely on verification through observation.
Since then, modern cognitive psychology has incorporated findings from many other disciplines, including evolutionary psychology , computer science, artificial intelligence , and neuroscience (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
- Unlike behaviorism, cognitive psychology is theoretical and explanatory. Behaviorism is often considered merely descriptive, while cognitive psychology is seen as being able to explain what is behind behavior.
Particular ongoing advances in cognitive psychology include perception, language comprehension and production, and problem-solving (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
- Behaviorism cannot incorporate theoretical terms. While challenged by some behaviorists at the time, it was argued that behaviorism could not incorporate theoretical terms unless related to directly observable behavior.
At the time, cognitive psychologists also argued that it was wrong of behaviorists to interpret mental states in terms of brain states.
Neuroscience advances, such as new imaging techniques like functional MRI, continue to offer fresh insights into the relationship between the brain and mental states (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Clearly, the relationship between behaviorism and the developing field of cognitive psychology has been complex. However, cognitive psychology has grown into a school of thought that has led to significant advances in understanding cognition, especially when teamed up with other developments in computing and neuroscience.
This may not have been possible without the shift in the dominant schools of thought in psychology (Gross, 2020; Goldstein, 2011; Eysenck & Keane, 2015).

And while it is beyond the scope of this article to cover the full breadth or depth of the areas of research, we list several of the most important and fascinating specialties and theories below.
It is hardly possible to imagine a world in which attention doesn’t play an essential role in how we interact with the environment, and yet, we rarely give it a thought.
According to cognitive psychology, attention is most active when driven by an individual’s expectations or goals, known as top-down processing . On the other hand, it is more passive when controlled by external stimuli, such as a loud noise, referred to as bottom-up processing (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
A further distinction exists between focused attention (selective) and divided attention . Research into the former explores how we are able to focus on one item (noise, image, etc.) when there are several. In contrast, the latter looks at how we can maintain attention on two or more stimuli simultaneously.
Donald Broadbent proposed the bottleneck model to explain how we can attend to just one message when several are presented, for example, in dichotic listening experiments, where different auditory stimuli are presented to each ear. Broadbent’s model suggests multiple processing stages, each one progressively restricting the information flow (Goldstein, 2011).
As with all other areas of cognition, perception is far more complicated than we might first imagine. Take, for example, vision. While a great deal of research has “involved presenting a visual stimulus and assessing aspects of its processing,” there is also the time aspect to consider (Eysenck & Keane, 2015, p. 121).
We need to not only perceive objects, but also make sense of their movement and detect changes in the visual environment over time (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Research suggests perception, like attention, combines bottom-up and top-down processing. Bottom-up processing involves neurons that fire in response to specific elements of an image – perhaps aspects of a face, nose, eyebrows, jawline, etc. Top-down processing considers how the knowledge someone brings with them affects their perception.
Bottom-down processing helps explain why two people, presented with the same stimuli, experience different perceptions as a result of their expectations and prior knowledge (Goldstein, 2011).
Combining bottom-up and top-down processing also enables the individual to make sense of both static and moving images when limited information is available; we can track a person walking through a crowd or a plane disappearing in and out of clouds (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
The mirror neuron system is incredibly fascinating and is proving valuable in our attempts to understand biological motion. Observing actions activates similar areas of the brain as performing them. The model appears to explain how we can imitate the actions of another person – crucial to learning (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Language comprehension
Whether written or spoken, understanding language involves a high degree of multi-level processing (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Comprehension begins with an initial analysis of sentence structure (larger language units require additional processing). Beyond processing syntax (the rules for building and analyzing sentences), analysis of sentence meaning ( semantics ) is necessary to understand if the interpretation should be literal or involve irony, metaphor, or sarcasm (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Pragmatics examines intended meaning. For example, shouting, “That’s the doorbell!” is not likely to be a simple observation, but rather a request to answer the door (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Several models have been proposed to understand the analysis and comprehension of sentences, known as parsing , including (Eysenck & Keane, 2015):
- Garden-path model This model attempts to explain why some sentences are ambiguous (such as, “The horse raced past the barn fell.”). It suggests they are challenging to comprehend because the analysis is performed on each individual unit of the sentence with little feedback, and correction is inhibited.
- Constraint-based model The interpretations of a sentence may be limited by several constraints, including syntactic, semantic, and general world knowledge.
- Unrestricted race model This model combines the garden-path and constraint-based model, and suggests all sources of information inform syntactic structure. One such interpretation is selected until it is discarded, with good reason, for another.
- Good-enough representation This model proposes that parsing provides a ‘good-enough’ interpretation rather than something detailed, accurate, and complete.
The research and theories above hint at the vast complexity of human cognition and explain why so many models and concepts attempt to answer what happens when it works and, equally important, when it doesn’t.
A level of psychology: the cognitive approach – Atomi
There are many research experiments in cognitive psychology that highlight the successes and failings of human cognition. Each of the following three offers insight into the mental processes behind our thinking and behavior.
Cocktail party phenomenon
Selective attention – or in this case, selective listening – is often exemplified by what has become known as the cocktail party phenomenon (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Even in a busy room and possibly mid-conversation, we can often hear if someone else mentions our name. It seems we can filter out surrounding noise by combining bottom-up and top-down processing to create a “winner takes it all” situation where the processing of one high-value auditory input suppresses the brain activity of all others (Goldstein, 2011).
While people may believe that the speed of hand movement allows magicians to trick us, research suggests the main factor is misdirection (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
A 2010 study of a trick involving the disappearance of a lighter identified that when the lighter was dropped (to hide it from a later hand-opening finale), it was masked by directing attention from the fixation point – known as covert attention – with surprising effectiveness.
However, subjects were able to identify the drop when their attention was directed to the fixation point – known as overt attention (Kuhn & Findlay, 2010).
In a thought-provoking study exploring freewill, participants were asked to consciously decide whether to move their finger left or right while a functional MRI scanner monitored their prefrontal cortex and parietal cortex (Soon, Brass, Heinze, & Haynes, 2008).
Brain activity predicted the direction of movement a full seven seconds before they consciously became aware of their decision. While follow-up research has challenged some of the findings, it appears that brain activity may come before conscious thinking (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).

Associations have been found between positive emotions, creative thinking, and overall wellbeing, suggesting environmental changes that may benefit staff productivity and innovation in the workplace (Yuan, 2015).
Factors explored include creating climates geared toward creativity, boosting challenge, trust, freedom, risk taking, low conflict, and even the beneficial effects of humor.
Undoubtedly, further innovation will be seen from marrying the two powerful and compelling new fields of positive psychology and cognitive psychology.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
We have many tools, worksheets, and exercises to explore and improve attention, problem-solving, and the ability to regulate emotions.
Why not download our free emotional intelligence pack and try out the powerful tools contained within?
- Building Emotional Awareness In this exercise, we foster emotional intelligence by mindfully attending to existing emotional states.
- Identifying False Beliefs About Emotions Our beliefs often operate outside of conscious awareness. This exercise addresses clients’ basic and often unconscious assumptions about their emotions.
Other free resources include:
- Skills for Regulating Emotion We can learn to manage our emotions by focusing on more positive experiences than negative ones.
- Emotional Repetition and Attention Remodeling Identifying phrases used to describe ourselves can help desensitize negative feelings .
More extensive versions of the following tools are available with a subscription to the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , but here is a brief overview:
- Creating Savoring Rituals It’s possible to increase positive emotions by sharpening our sensory perceptions via savoring.
Learning to focus can help.
Step one – Identify everyday activities that bring you pleasure. Step two – Focus on experiencing pleasure as it happens when doing these activities.
At the end of the week, take some time to record your reflections on creating savoring rituals.
- Extracting Strengths From Problems Surprisingly, using our strengths too much can harm our problem-solving ability.
In this exercise, we examine an existing issue in a client’s life:
Step one – Describe a current problem. Step two – Identify the problematic context or life domain. Step three – Identify the problematic behavior in yourself. Step four – Recognize your underlying strength. Step five – Identify what you can do to remedy the problem.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others enhance their wellbeing, check out this signature collection of 17 validated positive psychology tools for practitioners. Use them to help others flourish and thrive.
Cognitive psychology is crucial in our search for understanding how we interact with and make sense of a constantly changing and potentially harmful environment.
Not only that, it offers insight into what happens when things go wrong and the likely impact on our wellbeing and ability to cope with life events.
Cognitive psychology’s strength is its willingness to embrace research findings from many other disciplines, combining them with existing psychological theory to create new models of cognition.
The tasks we appear to carry out unconsciously are a great deal more complex than they might first appear. Perception, attention, problem-solving, language comprehension and production, and decision-making often happen without intentional thought and yet have enormous consequences on our lives.
Use this article as a starting point to explore the many and diverse aspects of cognitive psychology. Consider their relationships with associated research fields and reflect on the importance of understanding cognition in helping clients overcome complex events or circumstances.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Eysenck, M. W., & Keane, M. T. (2015). Cognitive psychology: A student’s handbook . Psychology Press.
- Goldstein, E. B. (2011). Cognitive psychology . Wadsworth, Cengage Learning.
- Gross, R. D. (2020). Psychology: The science of mind and behaviour . Hodder and Stoughton.
- Kuhn, G., & Findlay, J. M. (2010). Misdirection, attention and awareness: Inattentional blindness reveals temporal relationship between eye movements and visual awareness. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology , 63 (1), 136–146.
- Moore, J. (1996). On the relation between behaviorism and cognitive psychology. Journal of Mind and Behavior , 17 (4), 345–367
- Soon, C. S., Brass, M., Heinze, H., & Haynes, J. (2008). Unconscious determinants of free decisions in the human brain. Nature Neuroscience , 11 (5), 543–545.
- Yuan, L. (2015). The happier one is, the more creative one becomes: An investigation on inspirational positive emotions from both subjective well-being and satisfaction at work. Psychology , 6 , 201–209.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
As a widowed Mother and Grandmother, whom was recently told by an adult child that maybe I should have “cognitive” testing done, I found this article to be very informative and refreshing. Having the ability to read and and learn about cognitive psychology is interesting as their are so many ways our brains are affected from the time we are born until the time we reach each and every stage in life. I have spent time with my grandchildren who are from age 19 months, through 15 years old , and spend time with children who are 35, 34, and 32, and my parents who are 88 and 84. I appreciate your article and your time in writing it. Sincerely,
Cognitive Psychology creates & build human capacity to push physical and mental limits. My concept of cognition in human behavior was judged by the most time I met my lawyer or the doctor. Most of the time while listening a pause, oh I see and it is perpetual transition to see. Cognition emergence is very vital support as we see & perceive. My practices in engineering solution are base on my cognitive sensibilities.You article provokes the same perceptions. Thank you
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Hierarchy of Needs: A 2024 Take on Maslow’s Findings
One of the most influential theories in human psychology that addresses our quest for wellbeing is Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. While Maslow’s theory of [...]

Emotional Development in Childhood: 3 Theories Explained
We have all witnessed a sweet smile from a baby. That cute little gummy grin that makes us smile in return. Are babies born with [...]

Using Classical Conditioning for Treating Phobias & Disorders
Does the name Pavlov ring a bell? Classical conditioning, a psychological phenomenon first discovered by Ivan Pavlov in the late 19th century, has proven to [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (54)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (27)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (46)
- Optimism & Mindset (35)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (23)
- Positive Education (48)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (20)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (22)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (35)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
3 Positive Psychology Tools (PDF)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Thinking, Language, and Problem Solving
What is the best way to solve a problem? How does a person who has never seen or touched snow in real life develop an understanding of the concept of snow? How do young children acquire the ability to learn language with no formal instruction? Psychologists who study thinking explore questions like these and are called cognitive psychologists.
In other chapters, we discussed the cognitive processes of perception, learning, and memory. In this chapter, we will focus on high-level cognitive processes. As a part of this discussion, we will consider thinking and briefly explore the development and use of language. We will also discuss problem solving and creativity. After finishing this chapter, you will have a greater appreciation of the higher-level cognitive processes that contribute to our distinctiveness as a species.
Table of Contents
7.1 What is Cognition? 7.2 Language 7.3 Problem Solving
7.1 What is Cognition?
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe cognition
- Distinguish concepts and prototypes
- Explain the difference between natural and artificial concepts
- Describe how schemata are organized and constructed
Imagine all of your thoughts as if they were physical entities, swirling rapidly inside your mind. How is it possible that the brain is able to move from one thought to the next in an organized, orderly fashion? The brain is endlessly perceiving, processing, planning, organizing, and remembering—it is always active. Yet, you don’t notice most of your brain’s activity as you move throughout your daily routine. This is only one facet of the complex processes involved in cognition . Simply put, cognition is thinking, and it encompasses the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgment, language, and memory. Scientists who study cognition are searching for ways to understand how we integrate, organize, and utilize our conscious cognitive experiences without being aware of all of the unconscious work that our brains are doing (for example, Kahneman, 2011).
Upon waking each morning, you begin thinking—contemplating the tasks that you must complete that day. In what order should you run your errands? Should you go to the bank, the cleaners, or the grocery store first? Can you get these things done before you head to class or will they need to wait until school is done? These thoughts are one example of cognition at work. Exceptionally complex, cognition is an essential feature of human consciousness, yet not all aspects of cognition are consciously experienced.
Cognitive psychology is the field of psychology dedicated to examining how people think. It attempts to explain how and why we think the way we do by studying the interactions among human thinking, emotion, creativity, language, and problem solving, in addition to other cognitive processes. Cognitive psychologists strive to determine and measure different types of intelligence, why some people are better at problem solving than others, and how emotional intelligence affects success in the workplace, among countless other topics. They also sometimes focus on how we organize thoughts and information gathered from our environments into meaningful categories of thought, which will be discussed later.
Concepts and Prototypes
The human nervous system is capable of handling endless streams of information. The senses serve as the interface between the mind and the external environment, receiving stimuli and translating it into nervous impulses that are transmitted to the brain. The brain then processes this information and uses the relevant pieces to create thoughts, which can then be expressed through language or stored in memory for future use. To make this process more complex, the brain does not gather information from external environments only. When thoughts are formed, the mind synthesizes information from emotions and memories ( Figure 7.2 ). Emotion and memory are powerful influences on both our thoughts and behaviors.
Concepts are informed by our semantic memory (you will learn more about semantic memory in a later chapter) and are present in every aspect of our lives; however, one of the easiest places to notice concepts is inside a classroom, where they are discussed explicitly. When you study United States history, for example, you learn about more than just individual events that have happened in America’s past. You absorb a large quantity of information by listening to and participating in discussions, examining maps, and reading first-hand accounts of people’s lives. Your brain analyzes these details and develops an overall understanding of American history. In the process, your brain gathers details that inform and refine your understanding of related concepts like democracy, power, and freedom.
Concepts can be complex and abstract, like justice, or more concrete, like types of birds. Some concepts, like tolerance, are agreed upon by many people, because they have been used in various ways over many years. Other concepts, like the characteristics of your ideal friend or your family’s birthday traditions, are personal and individualized. In this way, concepts touch every aspect of our lives, from our many daily routines to the guiding principles behind the way governments function.
Another technique used by your brain to organize information is the identification of prototypes for the concepts you have developed. A prototype is the best example or representation of a concept. For example, what comes to your mind when you think of a dog? Most likely your early experiences with dogs will shape what you imagine. If your first pet was a Golden Retriever, there is a good chance that this would be your prototype for the category of dogs.
Natural and Artificial Concepts
In psychology, concepts can be divided into two categories, natural and artificial. Natural concepts are created “naturally” through your experiences and can be developed from either direct or indirect experiences. For example, if you live in Essex Junction, Vermont, you have probably had a lot of direct experience with snow. You’ve watched it fall from the sky, you’ve seen lightly falling snow that barely covers the windshield of your car, and you’ve shoveled out 18 inches of fluffy white snow as you’ve thought, “This is perfect for skiing.” You’ve thrown snowballs at your best friend and gone sledding down the steepest hill in town. In short, you know snow. You know what it looks like, smells like, tastes like, and feels like. If, however, you’ve lived your whole life on the island of Saint Vincent in the Caribbean, you may never have actually seen snow, much less tasted, smelled, or touched it. You know snow from the indirect experience of seeing pictures of falling snow—or from watching films that feature snow as part of the setting. Either way, snow is a natural concept because you can construct an understanding of it through direct observations, experiences with snow, or indirect knowledge (such as from films or books) ( Figure 7.3 ).
An artificial concept , on the other hand, is a concept that is defined by a specific set of characteristics. Various properties of geometric shapes, like squares and triangles, serve as useful examples of artificial concepts. A triangle always has three angles and three sides. A square always has four equal sides and four right angles. Mathematical formulas, like the equation for area (length × width) are artificial concepts defined by specific sets of characteristics that are always the same. Artificial concepts can enhance the understanding of a topic by building on one another. For example, before learning the concept of “area of a square” (and the formula to find it), you must understand what a square is. Once the concept of “area of a square” is understood, an understanding of area for other geometric shapes can be built upon the original understanding of area. The use of artificial concepts to define an idea is crucial to communicating with others and engaging in complex thought. According to Goldstone and Kersten (2003), concepts act as building blocks and can be connected in countless combinations to create complex thoughts.
A schema (plural: schemata) is a mental construct consisting of a cluster or collection of related concepts (Bartlett, 1932). There are many different types of schemata, and they all have one thing in common: schemata are a method of organizing information that allows the brain to work more efficiently. When a schema is activated, the brain makes immediate assumptions about the person or object being observed.
There are several types of schemata. A role schema makes assumptions about how individuals in certain roles will behave (Callero, 1994). For example, imagine you meet someone who introduces himself as a firefighter. When this happens, your brain automatically activates the “firefighter schema” and begins making assumptions that this person is brave, selfless, and community-oriented. Despite not knowing this person, already you have unknowingly made judgments about him. Schemata also help you fill in gaps in the information you receive from the world around you. While schemata allow for more efficient information processing, there can be problems with schemata, regardless of whether they are accurate: Perhaps this particular firefighter is not brave, he just works as a firefighter to pay the bills while studying to become a children’s librarian.
An event schema , also known as a cognitive script , is a set of behaviors that can feel like a routine. Think about what you do when you walk into an elevator ( Figure 7.4 ). First, the doors open and you wait to let exiting passengers leave the elevator car. Then, you step into the elevator and turn around to face the doors, looking for the correct button to push. You never face the back of the elevator, do you? And when you’re riding in a crowded elevator and you can’t face the front, it feels uncomfortable, doesn’t it? Interestingly, event schemata can vary widely among different cultures and countries. For example, while it is quite common for people to greet one another with a handshake in the United States, in Tibet, you greet someone by sticking your tongue out at them, and in Belize, you bump fists (Cairns Regional Council, n.d.)
Because event schemata are automatic, they can be difficult to change. Imagine that you are driving home from work or school. This event schema involves getting in the car, shutting the door, and buckling your seatbelt before putting the key in the ignition. You might perform this script two or three times each day. As you drive home, you hear your phone’s ring tone. Typically, the event schema that occurs when you hear your phone ringing involves locating the phone and answering it or responding to your latest text message. So without thinking, you reach for your phone, which could be in your pocket, in your bag, or on the passenger seat of the car. This powerful event schema is informed by your pattern of behavior and the pleasurable stimulation that a phone call or text message gives your brain. Because it is a schema, it is extremely challenging for us to stop reaching for the phone, even though we know that we endanger our own lives and the lives of others while we do it (Neyfakh, 2013) ( Figure 7.5 ).
Remember the elevator? It feels almost impossible to walk in and not face the door. Our powerful event schema dictates our behavior in the elevator, and it is no different with our phones. Current research suggests that it is the habit, or event schema, of checking our phones in many different situations that makes refraining from checking them while driving especially difficult (Bayer & Campbell, 2012). Because texting and driving has become a dangerous epidemic in recent years, psychologists are looking at ways to help people interrupt the “phone schema” while driving. Event schemata like these are the reason why many habits are difficult to break once they have been acquired. As we continue to examine thinking, keep in mind how powerful the forces of concepts and schemata are to our understanding of the world.
7.2 LAnguage
- Define language and demonstrate familiarity with the components of language
- Understand the development of language
- Explain the relationship between language and thinking
Language is a communication system that involves using words and systematic rules to organize those words to transmit information from one individual to another. While language is a form of communication, not all communication is language. Many species communicate with one another through their postures, movements, odors, or vocalizations. This communication is crucial for species that need to interact and develop social relationships with their conspecifics. However, many people have asserted that it is language that makes humans unique among all of the animal species (Corballis & Suddendorf, 2007; Tomasello & Rakoczy, 2003). This section will focus on what distinguishes language as a special form of communication, how the use of language develops, and how language affects the way we think.
Components of Language
Language, be it spoken, signed, or written, has specific components: a lexicon and lexicon grammar . Lexicon refers to the words of a given language. Thus, lexicon is a language’s vocabulary. Grammar refers to the set of rules that are used to convey meaning through the use of the lexicon (Fernández & Cairns, 2011). For instance, English grammar dictates that most verbs receive an “-ed” at the end to indicate past tense.
Words are formed by combining the various phonemes that make up the language. A phoneme (e.g., the sounds “ah” vs. “eh”) is a basic sound unit of a given language, and different languages have different sets of phonemes. For example, the phoneme English speakers associate with the letter ‘L’ is not used in the Japanese language. Similarly, many Southern African languages use phonemes, sometimes referred to as ‘click consonants’ that are not used in English.
Phonemes are combined to form morphemes , which are the smallest units of language that convey some type of meaning. Some words are morphemes, but not all morphemes are words. For example, “-ed” is a morpheme used to convey the past-tense in English, but it is not a word. The word “review” contains two morphemes: re- (meaning to do something again) and view (to see). Finally, some words like “I” and “a” are both a phonemes and morphemes.
We use semantics and syntax to construct language. Semantics and syntax are part of a language’s grammar. Semantics refers to the process by which we derive meaning from morphemes and words by connecting those morphemes and words to stored concepts. Syntax refers to the way words are organized into sentences (Chomsky, 1965; Fernández & Cairns, 2011). For example, you would never say “the dog walked I today” to let someone know you took your dog for a walk–that sentence does not obey English syntax and is therefore difficult to make sense of.
We apply the rules of grammar to organize the lexicon in novel and creative ways, which allow us to communicate information about both concrete and abstract concepts. We can talk about our immediate and observable surroundings as well as the surface of unseen planets. We can share our innermost thoughts, our plans for the future, and debate the value of a college education. We can provide detailed instructions for cooking a meal, fixing a car, or building a fire. Through our use of words and language, we are able to form, organize, and express ideas, schema, and artificial concepts.
Language Development
Given the remarkable complexity of a language, one might expect that mastering a language would be an especially arduous task; indeed, for those of us trying to learn a second language as adults, this might seem to be true. However, young children master language very quickly with relative ease. B. F. Skinner (1957) proposed that language is learned through reinforcement. Noam Chomsky (1965) criticized this behaviorist approach, asserting instead that the mechanisms underlying language acquisition are biologically determined. The use of language develops in the absence of formal instruction and appears to follow a very similar pattern in children from vastly different cultures and backgrounds. It would seem, therefore, that we are born with a biological predisposition to acquire a language (Chomsky, 1965; Fernández & Cairns, 2011). Moreover, it appears that there is a critical period for language acquisition, such that this proficiency at acquiring language is maximal early in life; generally, as people age, the ease with which they acquire and master new languages diminishes (Johnson & Newport, 1989; Lenneberg, 1967; Singleton, 1995).
Children begin to learn about language from a very early age ( Table 7.1 ). In fact, it appears that this is occurring even before we are born. Newborns show preference for their mother’s voice and appear to be able to discriminate between the language spoken by their mother and other languages. Babies are also attuned to the languages being used around them and show preferences for videos of faces that are moving in synchrony with the audio of spoken language versus videos that do not synchronize with the audio (Blossom & Morgan, 2006; Pickens, 1994; Spelke & Cortelyou, 1981).
| Stages of Language and Communication Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stage | Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
| 1 | 0–3 months | Reflexive communication |
| 2 | 3–8 months | Reflexive communication; interest in others |
| 3 | 8–13 months | Intentional communication; sociability |
| 4 | 12–18 months | First words |
| 5 | 18–24 months | Simple sentences of two words |
| 6 | 2–3 years | Sentences of three or more words |
| 7 | 3–5 years | Complex sentences; has conversations |
DIG DEEPER: The Case of Genie
In the fall of 1970, a social worker in the Los Angeles area found a 13-year-old girl who was being raised in extremely neglectful and abusive conditions. The girl, who came to be known as Genie, had lived most of her life tied to a potty chair or confined to a crib in a small room that was kept closed with the curtains drawn. For a little over a decade, Genie had virtually no social interaction and no access to the outside world. As a result of these conditions, Genie was unable to stand up, chew solid food, or speak (Fromkin, Krashen, Curtiss, Rigler, & Rigler, 1974; Rymer, 1993). The police took Genie into protective custody.
Genie’s abilities improved dramatically following her removal from her abusive environment, and early on, it appeared she was acquiring language—much later than would be predicted by critical period hypotheses that had been posited at the time (Fromkin et al., 1974). Genie managed to amass an impressive vocabulary in a relatively short amount of time. However, she never developed a mastery of the grammatical aspects of language (Curtiss, 1981). Perhaps being deprived of the opportunity to learn language during a critical period impeded Genie’s ability to fully acquire and use language.
You may recall that each language has its own set of phonemes that are used to generate morphemes, words, and so on. Babies can discriminate among the sounds that make up a language (for example, they can tell the difference between the “s” in vision and the “ss” in fission); early on, they can differentiate between the sounds of all human languages, even those that do not occur in the languages that are used in their environments. However, by the time that they are about 1 year old, they can only discriminate among those phonemes that are used in the language or languages in their environments (Jensen, 2011; Werker & Lalonde, 1988; Werker & Tees, 1984).
After the first few months of life, babies enter what is known as the babbling stage, during which time they tend to produce single syllables that are repeated over and over. As time passes, more variations appear in the syllables that they produce. During this time, it is unlikely that the babies are trying to communicate; they are just as likely to babble when they are alone as when they are with their caregivers (Fernández & Cairns, 2011). Interestingly, babies who are raised in environments in which sign language is used will also begin to show babbling in the gestures of their hands during this stage (Petitto, Holowka, Sergio, Levy, & Ostry, 2004).
Generally, a child’s first word is uttered sometime between the ages of 1 year to 18 months, and for the next few months, the child will remain in the “one word” stage of language development. During this time, children know a number of words, but they only produce one-word utterances. The child’s early vocabulary is limited to familiar objects or events, often nouns. Although children in this stage only make one-word utterances, these words often carry larger meaning (Fernández & Cairns, 2011). So, for example, a child saying “cookie” could be identifying a cookie or asking for a cookie.
As a child’s lexicon grows, she begins to utter simple sentences and to acquire new vocabulary at a very rapid pace. In addition, children begin to demonstrate a clear understanding of the specific rules that apply to their language(s). Even the mistakes that children sometimes make provide evidence of just how much they understand about those rules. This is sometimes seen in the form of overgeneralization . In this context, overgeneralization refers to an extension of a language rule to an exception to the rule. For example, in English, it is usually the case that an “s” is added to the end of a word to indicate plurality. For example, we speak of one dog versus two dogs. Young children will overgeneralize this rule to cases that are exceptions to the “add an s to the end of the word” rule and say things like “those two gooses” or “three mouses.” Clearly, the rules of the language are understood, even if the exceptions to the rules are still being learned (Moskowitz, 1978).
Language and Thought
When we speak one language, we agree that words are representations of ideas, people, places, and events. The given language that children learn is connected to their culture and surroundings. But can words themselves shape the way we think about things? Psychologists have long investigated the question of whether language shapes thoughts and actions, or whether our thoughts and beliefs shape our language. Two researchers, Edward Sapir and Benjamin Lee Whorf, began this investigation in the 1940s. They wanted to understand how the language habits of a community encourage members of that community to interpret language in a particular manner (Sapir, 1941/1964). Sapir and Whorf proposed that language determines thought. For example, in some languages there are many different words for love. However, in English we use the word love for all types of love. Does this affect how we think about love depending on the language that we speak (Whorf, 1956)? Researchers have since identified this view as too absolute, pointing out a lack of empiricism behind what Sapir and Whorf proposed (Abler, 2013; Boroditsky, 2011; van Troyer, 1994). Today, psychologists continue to study and debate the relationship between language and thought.
WHAT DO YOU THINK? The Meaning of Language
Think about what you know of other languages; perhaps you even speak multiple languages. Imagine for a moment that your closest friend fluently speaks more than one language. Do you think that friend thinks differently, depending on which language is being spoken? You may know a few words that are not translatable from their original language into English. For example, the Portuguese word saudade originated during the 15th century, when Portuguese sailors left home to explore the seas and travel to Africa or Asia. Those left behind described the emptiness and fondness they felt as saudade ( Figure 7.6 ) . The word came to express many meanings, including loss, nostalgia, yearning, warm memories, and hope. There is no single word in English that includes all of those emotions in a single description. Do words such as saudade indicate that different languages produce different patterns of thought in people? What do you think??
One group of researchers who wanted to investigate how language influences thought compared how English speakers and the Dani people of Papua New Guinea think and speak about color. The Dani have two words for color: one word for light and one word for dark . In contrast, the English language has 11 color words. Researchers hypothesized that the number of color terms could limit the ways that the Dani people conceptualized color. However, the Dani were able to distinguish colors with the same ability as English speakers, despite having fewer words at their disposal (Berlin & Kay, 1969). A recent review of research aimed at determining how language might affect something like color perception suggests that language can influence perceptual phenomena, especially in the left hemisphere of the brain. You may recall from earlier chapters that the left hemisphere is associated with language for most people. However, the right (less linguistic hemisphere) of the brain is less affected by linguistic influences on perception (Regier & Kay, 2009)
7.3 Problem Solving
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving and decision making
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( Table 7.2 ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
| Problem-Solving Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Method | Description | Example |
| Trial and error | Continue trying different solutions until problem is solved | Restarting phone, turning off WiFi, turning off bluetooth in order to determine why your phone is malfunctioning |
| Algorithm | Step-by-step problem-solving formula | Instruction manual for installing new software on your computer |
| Heuristic | General problem-solving framework | Working backwards; breaking a task into steps |
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
EVERYDAY CONNECTION: Solving Puzzles
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( Figure 7.7 ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( Figure 7.8 ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. Duncker (1945) conducted foundational research on functional fixedness. He created an experiment in which participants were given a candle, a book of matches, and a box of thumbtacks. They were instructed to use those items to attach the candle to the wall so that it did not drip wax onto the table below. Participants had to use functional fixedness to solve the problem ( Figure 7.10 ). During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in Table 7.3 .
| Summary of Decision Biases | |
|---|---|
| Bias | Description |
| Anchoring | Tendency to focus on one particular piece of information when making decisions or problem-solving |
| Confirmation | Focuses on information that confirms existing beliefs |
| Hindsight | Belief that the event just experienced was predictable |
| Representative | Unintentional stereotyping of someone or something |
| Availability | Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty |
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure 7.9 ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in Figure 7.7 and Figure 7.8 ? Here are the answers ( Figure 7.11 ).
Chapter Summary
7.1 what is cognition.
In this section, you were introduced to cognitive psychology, which is the study of cognition, or the brain’s ability to think, perceive, plan, analyze, and remember. Concepts and their corresponding prototypes help us quickly organize our thinking by creating categories into which we can sort new information. We also develop schemata, which are clusters of related concepts. Some schemata involve routines of thought and behavior, and these help us function properly in various situations without having to “think twice” about them. Schemata show up in social situations and routines of daily behavior.
7.2 Language
Language is a communication system that has both a lexicon and a system of grammar. Language acquisition occurs naturally and effortlessly during the early stages of life, and this acquisition occurs in a predictable sequence for individuals around the world. Language has a strong influence on thought, and the concept of how language may influence cognition remains an area of study and debate in psychology.
Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
thinking; or, all of the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgement, language, and memory.
A modern school of psychological thought that empirically examines mental processes such as perception, memory, language, and judgement.
a category or grouping of linguistic information, images, ideas or memories, such as life experiences.
knowledge about words, concepts, and language-based knowledge and facts
the best example or representation of a concept, specific to an individual
concepts developed through direct or indirect experiences with the world
a concept defined by a specific set of characteristics.
a mental construct consisting of a cluster of related concepts
a set of ideas relating to how individuals in certain roles will behave.
also known as a cognitive script; a set of behaviors associated with a particular place or event
also known as an event schema; a set of behaviors associated with a particular place or event
a communication system that involves using words and systematic rules to organize those words to transmit information from one individual to another.
the words of a language
the rules of a language used to convey meaning through the use of the lexicon
the basic sounds that make up a language
the smallest unit of language that conveys meaning
the process by which we derive meaning from morphemes and words
the rules guiding the organization of morphemes into words and words into sentences.
Psychology 2e Copyright © 2020 by Openstax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Last updated 09/07/24: Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > The Psychology of Problem Solving
- > Feeling and Thinking: Implications for Problem Solving

Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Contributors
- PART I INTRODUCTION
- PART II RELEVANT ABILITIES AND SKILLS
- PART III STATES AND STRATEGIES
- 8 Motivating Self-Regulated Problem Solvers
- 9 Feeling and Thinking: Implications for Problem Solving
- 10 The Fundamental Computational Biases of Human Cognition: Heuristics That (Sometimes) Impair Decision Making and Problem Solving
- 11 Analogical Transfer in Problem Solving
- PART IV CONCLUSION AND INTEGRATION
9 - Feeling and Thinking: Implications for Problem Solving
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 June 2012
INTRODUCTION
Consistent with the classic juxtaposition of reason and emotion, moods and emotions have long been assumed to interfere with problem solving. Recent advances in psychology's understanding of the interplay of feeling and thinking suggest a more complex story: Positive as well as negative moods and emotions can facilitate as well as inhibit problem solving, depending on the nature of the task. Moreover, the same feeling may have differential effects at different stages of the problem-solving process. In addition, nonaffective feelings, such as bodily sensations and cognitive experiences (e.g., fluency of recall or perception), may also influence problem solving, often paralleling the effects observed for affective feelings. This chapter summarizes key lessons learned about the interplay of feeling and thinking and addresses their implications for problem solving. To set the stage, we begin with a summary of key elements of the problem-solving process.
ELEMENTS OF PROBLEM SOLVING
In the most general sense, “a problem arises when we have a goal – a state of affairs that we want to achieve – and it is not immediately apparent how the goal can be attained” (Holyoak, 1995, p. 269). Consistent with the spatial metaphors of ordinary language use, where we “search for a way to reach the goal,” “get lost” in a problem, meet “roadblocks” or have to “backtrack,” problem solving is typically conceptualized as search through a metaphorical space (Duncker, 1945).
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- Feeling and Thinking: Implications for Problem Solving
- By Norbert Schwarz , University of Michigan, Ian Skurnik , University of Michigan
- Edited by Janet E. Davidson , Lewis and Clark College, Portland , Robert J. Sternberg , Yale University, Connecticut
- Book: The Psychology of Problem Solving
- Online publication: 05 June 2012
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511615771.010
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Cognitive Approach in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of the mind as an information processor. It concerns how we take in information from the outside world, and how we make sense of that information.
Cognitive psychology studies mental processes, including how people perceive, think, remember, learn, solve problems, and make decisions.
Cognitive psychologists try to build cognitive models of the information processing that occurs inside people’s minds, including perception, attention, language, memory, thinking, and consciousness.
Cognitive psychology became of great importance in the mid-1950s. Several factors were important in this:
- Dissatisfaction with the behaviorist approach in its simple emphasis on external behavior rather than internal processes.
- The development of better experimental methods.
- Comparison between human and computer processing of information . Using computers allowed psychologists to try to understand the complexities of human cognition by comparing it with computers and artificial intelligence.
The emphasis of psychology shifted away from the study of conditioned behavior and psychoanalytical notions about the study of the mind, towards the understanding of human information processing using strict and rigorous laboratory investigation.

Summary Table
| Key Features |
|---|
| • Mediation processes • Information processing approach • Reductionism (breaks behavior down) • (studies the group) • Schemas (re: Kohlberg & Piaget) |
| Methodology |
|---|
| • Controlled Experiments • Physical measures (e.g., neuroimaging) • Case studies (cognitive neuroscience) • Behavioral measures (e.g., reaction time) |
| Assumptions |
|---|
| • Psychology should be studied scientifically. • Information received from our senses is processed by the brain, and this processing directs how we behave. • The mind/brain processes information like a computer. We take information in, and then it is subjected to mental processes. There is input, processing, and then output. • Mediational processes (e.g., thinking, memory) occur between stimulus and response. |
| Strengths |
|---|
| • Objective measurement, which can be replicated and peer-reviewed • Real-life applications (e.g., CBT) • Clear predictions that can be can be scientifically tested |
| Limitations |
|---|
| • Reductionist (e.g., ignores biology) • Experiments have low ecological validity • Behaviourism – can’t objectively study unobservable internal behavior |
Theoretical Assumptions
Mediational processes occur between stimulus and response:
The behaviorist approach only studies external observable (stimulus and response) behavior that can be objectively measured.
They believe that internal behavior cannot be studied because we cannot see what happens in a person’s mind (and therefore cannot objectively measure it).
However, cognitive psychologists consider it essential to examine an organism’s mental processes and how these influence behavior.
Cognitive psychology assumes a mediational process occurs between stimulus/input and response/output.

These are mediational processes because they mediate (i.e., go-between) between the stimulus and the response. They come after the stimulus and before the response.
Instead of the simple stimulus-response links proposed by behaviorism, the mediational processes of the organism are essential to understand.
Without this understanding, psychologists cannot have a complete understanding of behavior.
The mediational (i.e., mental) event could be memory , perception , attention or problem-solving, etc.
- Perception : how we process and interpret sensory information.
- Attention : how we selectively focus on certain aspects of our environment.
- Memory : how we encode, store, and retrieve information.
- Language : how we acquire, comprehend, and produce language.
- Problem-solving and decision-making : how we reason, make judgments, and solve problems.
- Schemas : Cognitive psychologists assume that people’s prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences shape their mental processes.
For example, the cognitive approach suggests that problem gambling results from maladaptive thinking and faulty cognitions, which both result in illogical errors.
Gamblers misjudge the amount of skill involved with ‘chance’ games, so they are likely to participate with the mindset that the odds are in their favour and that they may have a good chance of winning.
Therefore, cognitive psychologists say that if you want to understand behavior, you must understand these mediational processes.
Psychology should be seen as a science:
This assumption is based on the idea that although not directly observable, the mind can be investigated using objective and rigorous methods, similar to how other sciences study natural phenomena.
Controlled experiments
The cognitive approach believes that internal mental behavior can be scientifically studied using controlled experiments . It uses the results of its investigations to make inferences about mental processes. Cognitive psychology uses highly controlled laboratory experiments to avoid the influence of extraneous variables . This allows the researcher to establish a causal relationship between the independent and dependent variables. These controlled experiments are replicable, and the data obtained is objective (not influenced by an individual’s judgment or opinion) and measurable. This gives psychology more credibility.
Operational definitions
Cognitive psychologists develop operational definitions to study mental processes scientifically. These definitions specify how abstract concepts, such as attention or memory, can be measured and quantified (e.g., verbal protocols of thinking aloud). This allows for reliable and replicable research findings.
Falsifiability
Falsifiability in psychology refers to the ability to disprove a theory or hypothesis through empirical observation or experimentation. If a claim is not falsifiable, it is considered unscientific.
Cognitive psychologists aim to develop falsifiable theories and models, meaning they can be tested and potentially disproven by empirical evidence.
This commitment to falsifiability helps to distinguish scientific theories from pseudoscientific or unfalsifiable claims.
Empirical evidence
Cognitive psychologists rely on empirical evidence to support their theories and models. They collect data through various methods, such as experiments, observations, and questionnaires, to test hypotheses and draw conclusions about mental processes.
Cognitive psychologists assume that mental processes are not random but are organized and structured in specific ways. They seek to identify the underlying cognitive structures and processes that enable people to perceive, remember, and think.
Cognitive psychologists have made significant contributions to our understanding of mental processes and have developed various theories and models, such as the multi-store model of memory , the working memory model , and the dual-process theory of thinking.
Humans are information processors:
The idea of information processing was adopted by cognitive psychologists as a model of how human thought works.
The information processing approach is based on several assumptions, including:
- Information is processed by a series of systems : The information processing approach proposes that a series of cognitive systems, such as attention, perception, and memory, process information from the environment. Each system plays a specific role in processing the information and passing it along to the next stage.
- Processing systems transform information : As information passes through these cognitive systems, it is transformed or modified in systematic ways. For example, incoming sensory information may be filtered by attention, encoded into memory, or used to update existing knowledge structures.
- Research aims to specify underlying processes and structures : The primary goal of research within the information processing approach is to identify, describe, and understand the specific cognitive processes and mental structures that underlie various aspects of cognitive performance, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Human information processing resembles computer processing : The information processing approach draws an analogy between human cognition and computer processing. Just as computers take in information, process it according to specific algorithms, and produce outputs, the human mind is thought to engage in similar processes of input, processing, and output.
Computer-Mind Analogy
The computer-brain metaphor, or the information processing approach, is a significant concept in cognitive psychology that likens the human brain’s functioning to that of a computer.
This metaphor suggests that the brain, like a computer, processes information through a series of linear steps, including input, storage, processing, and output.
According to this assumption, when we interact with the environment, we take in information through our senses (input).
This information is then processed by various cognitive systems, such as perception, attention, and memory. These systems work together to make sense of the input, organize it, and store it for later use.
During the processing stage, the mind performs operations on the information, such as encoding, transforming, and combining it with previously stored knowledge. This processing can involve various cognitive processes, such as thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
The processed information can then be used to generate outputs, such as actions, decisions, or new ideas. These outputs are based on the information that has been processed and the individual’s goals and motivations.
This has led to models showing information flowing through the cognitive system, such as the multi-store memory model.

The information processing approach also assumes that the mind has a limited capacity for processing information, similar to a computer’s memory and processing limitations.
This means that humans can only attend to and process a certain amount of information at a given time, and that cognitive processes can be slowed down or impaired when the mind is overloaded.
The Role of Schemas
A schema is a “packet of information” or cognitive framework that helps us organize and interpret information. It is based on previous experience.
Cognitive psychologists assume that people’s prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences shape their mental processes. They investigate how these factors influence perception, attention, memory, and thinking.
Schemas help us interpret incoming information quickly and effectively, preventing us from being overwhelmed by the vast amount of information we perceive in our environment.
Schemas can often affect cognitive processing (a mental framework of beliefs and expectations developed from experience). As people age, they become more detailed and sophisticated.
However, it can also lead to distortion of this information as we select and interpret environmental stimuli using schemas that might not be relevant.
This could be the cause of inaccuracies in areas such as eyewitness testimony. It can also explain some errors we make when perceiving optical illusions.
1. Behaviorist Critique
B.F. Skinner criticizes the cognitive approach. He believes that only external stimulus-response behavior should be studied, as this can be scientifically measured.
Therefore, mediation processes (between stimulus and response) do not exist as they cannot be seen and measured.
Behaviorism assumes that people are born a blank slate (tabula rasa) and are not born with cognitive functions like schemas , memory or perception .
Due to its subjective and unscientific nature, Skinner continues to find problems with cognitive research methods, namely introspection (as used by Wilhelm Wundt).
2. Complexity of mental experiences
Mental processes are highly complex and multifaceted, involving a wide range of cognitive, affective, and motivational factors that interact in intricate ways.
The complexity of mental experiences makes it difficult to isolate and study specific mental processes in a controlled manner.
Mental processes are often influenced by individual differences, such as personality, culture, and past experiences, which can introduce variability and confounds in research .

3. Experimental Methods
While controlled experiments are the gold standard in cognitive psychology research, they may not always capture real-world mental processes’ complexity and ecological validity.
Some mental processes, such as creativity or decision-making in complex situations, may be difficult to study in laboratory settings.
Humanistic psychologist Carl Rogers believes that using laboratory experiments by cognitive psychology has low ecological validity and creates an artificial environment due to the control over variables .
Rogers emphasizes a more holistic approach to understanding behavior.
The cognitive approach uses a very scientific method that is controlled and replicable, so the results are reliable.
However, experiments lack ecological validity because of the artificiality of the tasks and environment, so they might not reflect the way people process information in their everyday lives.
For example, Baddeley (1966) used lists of words to find out the encoding used by LTM.
However, these words had no meaning to the participants, so the way they used their memory in this task was probably very different from what they would have done if the words had meaning for them.
This is a weakness, as the theories might not explain how memory works outside the laboratory.
4. Computer Analogy
The information processing paradigm of cognitive psychology views the minds in terms of a computer when processing information.
However, although there are similarities between the human mind and the operations of a computer (inputs and outputs, storage systems, and the use of a central processor), the computer analogy has been criticized.
For example, the human mind is characterized by consciousness, subjective experience, and self-awareness , which are not present in computers.
Computers do not have feelings, emotions, or a sense of self, which play crucial roles in human cognition and behavior.
The brain-computer metaphor is often used implicitly in neuroscience literature through terms like “sensory computation,” “algorithms,” and “neural codes.” However, it is difficult to identify these concepts in the actual brain.
5. Reductionist
The cognitive approach is reductionist as it does not consider emotions and motivation, which influence the processing of information and memory. For example, according to the Yerkes-Dodson law , anxiety can influence our memory.
Such machine reductionism (simplicity) ignores the influence of human emotion and motivation on the cognitive system and how this may affect our ability to process information.
Early theories of cognitive approach did not always recognize physical ( biological psychology ) and environmental (behaviorist approach) factors in determining behavior.
However, it’s important to note that modern cognitive psychology has evolved to incorporate a more holistic understanding of human cognition and behavior.
1. Importance of cognitive factors versus external events
Cognitive psychology emphasizes the role of internal cognitive processes in shaping emotional experiences, rather than solely focusing on external events.
Beck’s cognitive theory suggests that it is not the external events themselves that lead to depression, but rather the way an individual interprets and processes those events through their negative schemas.
This highlights the importance of addressing cognitive factors in the treatment of depression and other mental health issues.
Social exchange theory (Thibaut & Kelly, 1959) emphasizes that relationships are formed through internal mental processes, such as decision-making, rather than solely based on external factors.
The computer analogy can be applied to this concept, where individuals observe behaviors (input), process the costs and benefits (processing), and then make a decision about the relationship (output).
2. Interdisciplinary approach
While early cognitive psychology may have neglected physical and environmental factors, contemporary cognitive psychology has increasingly integrated insights from other approaches.
Cognitive psychology draws on methods and findings from other scientific disciplines, such as neuroscience , computer science, and linguistics, to inform their understanding of mental processes.
This interdisciplinary approach strengthens the scientific basis of cognitive psychology.
Cognitive psychology has influenced and integrated with many other approaches and areas of study to produce, for example, social learning theory , cognitive neuropsychology, and artificial intelligence (AI).
3. Real World Applications
Another strength is that the research conducted in this area of psychology very often has applications in the real world.
By highlighting the importance of cognitive processing, the cognitive approach can explain mental disorders such as depression.
Beck’s cognitive theory of depression argues that negative schemas about the self, the world, and the future are central to the development and maintenance of depression.
These negative schemas lead to biased processing of information, selective attention to negative aspects of experience, and distorted interpretations of events, which perpetuate the depressive state.
By identifying the role of cognitive processes in mental disorders, cognitive psychology has informed the development of targeted interventions.
Cognitive behavioral therapy aims to modify the maladaptive thought patterns and beliefs that underlie emotional distress, helping individuals to develop more balanced and adaptive ways of thinking.
CBT’s basis is to change how people process their thoughts to make them more rational or positive.
Through techniques such as cognitive restructuring, behavioral experiments, and guided discovery, CBT helps individuals to challenge and change their negative schemas, leading to improvements in mood and functioning.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has been very effective in treating depression (Hollon & Beck, 1994), and moderately effective for anxiety problems (Beck, 1993).
Issues and Debates
Free will vs. determinism.
The cognitive approach’s position is unclear. It argues that cognitive processes are influenced by experiences and schemas, which implies a degree of determinism.
On the other hand, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) operates on the premise that individuals can change their thought patterns, suggesting a capacity for free will.
Nature vs. Nurture
The cognitive approach takes an interactionist view of the debate, acknowledging the influence of both nature and nurture on cognitive processes.
It recognizes that while some cognitive abilities, such as language acquisition, may have an innate component (nature), experiences and learning (nurture) also shape the way information is processed.
Holism vs. Reductionism
The cognitive approach tends to be reductionist in its methodology, as it often studies cognitive processes in isolation.
For example, researchers may focus on memory processes without considering the influence of other cognitive functions or environmental factors.
While this approach allows for more controlled study, it may lack ecological validity, as in real life, cognitive processes typically interact and function simultaneously.
Idiographic vs. Nomothetic
The cognitive approach is primarily nomothetic, as it seeks to establish general principles and theories of information processing that apply to all individuals.
It aims to identify universal patterns and mechanisms of cognition rather than focusing on individual differences.
History of Cognitive Psychology
- Wolfgang Köhler (1925) – Köhler’s book “The Mentality of Apes” challenged the behaviorist view by suggesting that animals could display insightful behavior, leading to the development of Gestalt psychology.
- Norbert Wiener (1948) – Wiener’s book “Cybernetics” introduced concepts such as input and output, which influenced the development of information processing models in cognitive psychology.
- Edward Tolman (1948) – Tolman’s work on cognitive maps in rats demonstrated that animals have an internal representation of their environment, challenging the behaviorist view.
- George Miller (1956) – Miller’s paper “The Magical Number 7 Plus or Minus 2” proposed that short-term memory has a limited capacity of around seven chunks of information, which became a foundational concept in cognitive psychology.
- Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon (1972) – Newell and Simon developed the General Problem Solver, a computer program that simulated human problem-solving, contributing to the growth of artificial intelligence and cognitive modeling.
- George Miller and Jerome Bruner (1960) – Miller and Bruner established the Center for Cognitive Studies at Harvard, which played a significant role in the development of cognitive psychology as a distinct field.
- Ulric Neisser (1967) – Neisser’s book “Cognitive Psychology” formally established cognitive psychology as a separate area of study, focusing on mental processes such as perception, memory, and thinking.
- Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin (1968) – Atkinson and Shiffrin proposed the Multi-Store Model of memory, which divided memory into sensory, short-term, and long-term stores, becoming a key model in the study of memory.
- Eleanor Rosch’s (1970s) research on natural categories and prototypes, which influenced the study of concept formation and categorization.
- Endel Tulving’s (1972) distinction between episodic and semantic memory, which further developed the understanding of long-term memory.
- Baddeley and Hitch’s (1974) proposal of the Working Memory Model, which expanded on the concept of short-term memory and introduced the idea of a central executive.
- Marvin Minsky’s (1975) framework of frames in artificial intelligence, which influenced the understanding of knowledge representation in cognitive psychology.
- David Rumelhart and Andrew Ortony’s (1977) work on schema theory, which described how knowledge is organized and used for understanding and remembering information.
- Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman’s (1970s-80s) research on heuristics and biases in decision making, which led to the development of behavioral economics and the study of judgment and decision-making.
- David Marr’s (1982) computational theory of vision, which provided a framework for understanding visual perception and influenced the field of computational cognitive science.
- The development of connectionism and parallel distributed processing (PDP) models in the 1980s, which provided an alternative to traditional symbolic models of cognitive processes.
- Noam Chomsky’s (1980s) theory of Universal Grammar and the language acquisition device, which influenced the study of language and cognitive development.
- The emergence of cognitive neuroscience in the 1990s, which combined techniques from cognitive psychology, neuroscience, and computer science to study the neural basis of cognitive processes.
Atkinson, R. C., & Shiffrin, R. M. (1968). Chapter: Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In Spence, K. W., & Spence, J. T. The psychology of learning and motivation (Volume 2). New York: Academic Press. pp. 89–195.
Baddeley, A. D., & Hitch, G. (1974). Working memory. In G. H. Bower (Ed.), The Psychology of Learning and Motivation: Advances in Research and Theory (Vol. 8, pp. 47-89). Academic Press.
Beck, A. T, & Steer, R. A. (1993). Beck Anxiety Inventory Manual. San Antonio: Harcourt Brace and Company.
Chomsky, N. (1986). Knowledge of Language: Its Nature, Origin, and Use . Praeger.
Gazzaniga, M. S. (Ed.). (1995). The Cognitive Neurosciences. MIT Press.
Hollon, S. D., & Beck, A. T. (1994). Cognitive and cognitive-behavioral therapies. In A. E. Bergin & S.L. Garfield (Eds.), Handbook of psychotherapy and behavior change (pp. 428—466) . New York: Wiley.
Köhler, W. (1925). An aspect of Gestalt psychology. The Pedagogical Seminary and Journal of Genetic Psychology, 32(4) , 691-723.
Marr, D. (1982). Vision: A Computational Investigation into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information . W. H. Freeman.
Miller, G. A. (1956). The magical number seven, plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychological Review , 63 (2): 81–97.
Minsky, M. (1975). A framework for representing knowledge. In P. H. Winston (Ed.), The Psychology of Computer Vision (pp. 211-277). McGraw-Hill.
Neisser, U (1967). Cognitive psychology . Appleton-Century-Crofts: New York
Newell, A., & Simon, H. (1972). Human problem solving . Prentice-Hall.
Rosch, E. H. (1973). Natural categories. Cognitive Psychology, 4 (3), 328-350.
Rumelhart, D. E., & McClelland, J. L. (1986). Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition. Volume 1: Foundations. MIT Press.
Rumelhart, D. E., & Ortony, A. (1977). The representation of knowledge in memory. In R. C. Anderson, R. J. Spiro, & W. E. Montague (Eds.), Schooling and the Acquisition of Knowledge (pp. 99-135). Erlbaum.
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1974). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science, 185 (4157), 1124-1131.
Thibaut, J., & Kelley, H. H. (1959). The social psychology of groups . New York: Wiley.
Tolman, E. C., Hall, C. S., & Bretnall, E. P. (1932). A disproof of the law of effect and a substitution of the laws of emphasis, motivation and disruption. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 15(6) , 601.
Tolman E. C. (1948). Cognitive maps in rats and men . Psychological Review. 55, 189–208
Tulving, E. (1972). Episodic and semantic memory. In E. Tulving & W. Donaldson (Eds.), Organization of Memory (pp. 381-403). Academic Press.
Wiener, N. (1948). Cybernetics or control and communication in the animal and the machine . Paris, (Hermann & Cie) & Camb. Mass. (MIT Press).
Further Reading
- Why Your Brain is Not a Computer
- Cognitive Psychology Historial Development
Thinking and Intelligence
Introduction to thinking and problem-solving, what you’ll learn to do: describe cognition and problem-solving strategies.

Imagine all of your thoughts as if they were physical entities, swirling rapidly inside your mind. How is it possible that the brain is able to move from one thought to the next in an organized, orderly fashion? The brain is endlessly perceiving, processing, planning, organizing, and remembering—it is always active. Yet, you don’t notice most of your brain’s activity as you move throughout your daily routine. This is only one facet of the complex processes involved in cognition. Simply put, cognition is thinking, and it encompasses the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgment, language, and memory. Scientists who study cognition are searching for ways to understand how we integrate, organize, and utilize our conscious cognitive experiences without being aware of all of the unconscious work that our brains are doing (for example, Kahneman, 2011).
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between concepts and prototypes
- Explain the difference between natural and artificial concepts
- Describe problem solving strategies, including algorithms and heuristics
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- What Is Cognition?. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/7-1-what-is-cognition . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- A Thinking Man Image. Authored by : Wesley Nitsckie. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/nitsckie/5507777269 . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike


6 Thinking and Intelligence
What is the best way to solve a problem? How does a person who has never seen or touched snow in real life develop an understanding of the concept of snow? How do young children acquire the ability to learn language with no formal instruction? Psychologists who study thinking explore questions like these and are called cognitive psychologists.
Cognitive psychologists also study intelligence. What is intelligence, and how does it vary from person to person? Are “street smarts” a kind of intelligence, and if so, how do they relate to other types of intelligence? What does an IQ test really measure? These questions and more will be explored in this chapter as you study thinking and intelligence.
In other chapters, we discussed the cognitive processes of perception, learning, and memory. In this chapter, we will focus on high-level cognitive processes. As a part of this discussion, we will consider thinking and briefly explore the development and use of language. We will also discuss problem solving and creativity before ending with a discussion of how intelligence is measured and how our biology and environments interact to affect intelligence. After finishing this chapter, you will have a greater appreciation of the higher-level cognitive processes that contribute to our distinctiveness as a species.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe cognition
- Distinguish concepts and prototypes
- Explain the difference between natural and artificial concepts
- Describe how schemata are organized and constructed
Imagine all of your thoughts as if they were physical entities, swirling rapidly inside your mind. How is it possible that the brain is able to move from one thought to the next in an organized, orderly fashion? The brain is endlessly perceiving, processing, planning, organizing, and remembering—it is always active. Yet, you don’t notice most of your brain’s activity as you move throughout your daily routine. This is only one facet of the complex processes involved in cognition. Simply put, cognition is thinking, and it encompasses the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgment, language, and memory. Scientists who study cognition are searching for ways to understand how we integrate, organize, and utilize our conscious cognitive experiences without being aware of all of the unconscious work that our brains are doing (for example, Kahneman, 2011).
Upon waking each morning, you begin thinking—contemplating the tasks that you must complete that day. In what order should you run your errands? Should you go to the bank, the cleaners, or the grocery store first? Can you get these things done before you head to class or will they need to wait until school is done? These thoughts are one example of cognition at work. Exceptionally complex, cognition is an essential feature of human consciousness, yet not all aspects of cognition are consciously experienced.
Cognitive psychology is the field of psychology dedicated to examining how people think. It attempts to explain how and why we think the way we do by studying the interactions among human thinking, emotion, creativity, language, and problem solving, in addition to other cognitive processes. Cognitive psychologists strive to determine and measure different types of intelligence, why some people are better at problem solving than others, and how emotional intelligence affects success in the workplace, among countless other topics. They also sometimes focus on how we organize thoughts and information gathered from our environments into meaningful categories of thought, which will be discussed later.
Concepts and Prototypes
The human nervous system is capable of handling endless streams of information. The senses serve as the interface between the mind and the external environment, receiving stimuli and translating it into nerve impulses that are transmitted to the brain. The brain then processes this information and uses the relevant pieces to create thoughts, which can then be expressed through language or stored in memory for future use. To make this process more complex, the brain does not gather information from external environments only. When thoughts are formed, the mind synthesizes information from emotions and memories ( Figure 7.2 ). Emotion and memory are powerful influences on both our thoughts and behaviors.
In order to organize this staggering amount of information, the mind has developed a “file cabinet” of sorts in the mind. The different files stored in the file cabinet are called concepts. Concepts are categories or groupings of linguistic information, images, ideas, or memories, such as life experiences. Concepts are, in many ways, big ideas that are generated by observing details, and categorizing and combining these details into cognitive structures. You use concepts to see the relationships among the different elements of your experiences and to keep the information in your mind organized and accessible.
Concepts are informed by our semantic memory (you will learn more about semantic memory in a later chapter) and are present in every aspect of our lives; however, one of the easiest places to notice concepts is inside a classroom, where they are discussed explicitly. When you study United States history, for example, you learn about more than just individual events that have happened in America’s past. You absorb a large quantity of information by listening to and participating in discussions, examining maps, and reading first-hand accounts of people’s lives. Your brain analyzes these details and develops an overall understanding of American history. In the process, your brain gathers details that inform and refine your understanding of related concepts like democracy, power, and freedom.
Concepts can be complex and abstract, like justice, or more concrete, like types of birds. In psychology, for example, Piaget’s stages of development are abstract concepts. Some concepts, like tolerance, are agreed upon by many people because they have been used in various ways over many years. Other concepts, like the characteristics of your ideal friend or your family’s birthday traditions, are personal and individualized. In this way, concepts touch every aspect of our lives, from our many daily routines to the guiding principles behind the way governments function.
Another technique used by your brain to organize information is the identification of prototypes for the concepts you have developed. A prototype is the best example or representation of a concept. For example, what comes to your mind when you think of a dog? Most likely your early experiences with dogs will shape what you imagine. If your first pet was a Golden Retriever, there is a good chance that this would be your prototype for the category of dogs.
Natural and Artificial Concepts
In psychology, concepts can be divided into two categories, natural and artificial. Natural concepts are created “naturally” through your experiences and can be developed from either direct or indirect experiences. For example, if you live in Essex Junction, Vermont, you have probably had a lot of direct experience with snow. You’ve watched it fall from the sky, you’ve seen lightly falling snow that barely covers the windshield of your car, and you’ve shoveled out 18 inches of fluffy white snow as you’ve thought, “This is perfect for skiing.” You’ve thrown snowballs at your best friend and gone sledding down the steepest hill in town. In short, you know snow. You know what it looks like, smells like, tastes like, and feels like. If, however, you’ve lived your whole life on the island of Saint Vincent in the Caribbean, you may never have actually seen snow, much less tasted, smelled, or touched it. You know snow from the indirect experience of seeing pictures of falling snow—or from watching films that feature snow as part of the setting. Either way, snow is a natural concept because you can construct an understanding of it through direct observations, experiences with snow, or indirect knowledge (such as from films or books) ( Figure 7.3 ).
An artificial concept , on the other hand, is a concept that is defined by a specific set of characteristics. Various properties of geometric shapes, like squares and triangles, serve as useful examples of artificial concepts. A triangle always has three angles and three sides. A square always has four equal sides and four right angles. Mathematical formulas, like the equation for area (length × width), are artificial concepts defined by specific sets of characteristics that are always the same. Artificial concepts can enhance the understanding of a topic by building on one another. For example, before learning the concept of “area of a square” (and the formula to find it), you must understand what a square is. Once the concept of “area of a square” is understood, an understanding of area for other geometric shapes can be built upon the original understanding of area. The use of artificial concepts to define an idea is crucial to communicating with others and engaging in complex thought. According to Goldstone and Kersten (2003), concepts act as building blocks and can be connected in countless combinations to create complex thoughts.
A schema is a mental construct consisting of a cluster or collection of related concepts (Bartlett, 1932). There are many different types of schemata, and they all have one thing in common: schemata are a method of organizing information that allows the brain to work more efficiently. When a schema is activated, the brain makes immediate assumptions about the person or object being observed.
There are several types of schemata. A role schema makes assumptions about how individuals in certain roles will behave (Callero, 1994). For example, imagine you meet someone who introduces himself as a firefighter. When this happens, your brain automatically activates the “firefighter schema” and begins making assumptions that this person is brave, selfless, and community-oriented. Despite not knowing this person, already you have unknowingly made judgments about him. Schemata also help you fill in gaps in the information you receive from the world around you. While schemata allow for more efficient information processing, there can be problems with schemata, regardless of whether they are accurate: Perhaps this particular firefighter is not brave, he just works as a firefighter to pay the bills while studying to become a children’s librarian.
An event schema , also known as a cognitive script , is a set of behaviors that can feel like a routine. Think about what you do when you walk into an elevator ( Figure 7.4 ). First, the doors open and you wait to let exiting passengers leave the elevator car. Then, you step into the elevator and turn around to face the doors, looking for the correct button to push. You never face the back of the elevator, do you? And when you’re riding in a crowded elevator and you can’t face the front, it feels uncomfortable, doesn’t it? Interestingly, event schemata can vary widely among different cultures and countries. For example, while it is quite common for people to greet one another with a handshake in the United States, in Tibet, you greet someone by sticking your tongue out at them, and in Belize, you bump fists (Cairns Regional Council, n.d.)
Because event schemata are automatic, they can be difficult to change. Imagine that you are driving home from work or school. This event schema involves getting in the car, shutting the door, and buckling your seatbelt before putting the key in the ignition. You might perform this script two or three times each day. As you drive home, you hear your phone’s ring tone. Typically, the event schema that occurs when you hear your phone ringing involves locating the phone and answering it or responding to your latest text message. So without thinking, you reach for your phone, which could be in your pocket, in your bag, or on the passenger seat of the car. This powerful event schema is informed by your pattern of behavior and the pleasurable stimulation that a phone call or text message gives your brain. Because it is a schema, it is extremely challenging for us to stop reaching for the phone, even though we know that we endanger our own lives and the lives of others while we do it (Neyfakh, 2013) ( Figure 7.5 ).
Remember the elevator? It feels almost impossible to walk in and not face the door. Our powerful event schema dictates our behavior in the elevator, and it is no different with our phones. Current research suggests that it is the habit, or event schema, of checking our phones in many different situations that make refraining from checking them while driving especially difficult (Bayer & Campbell, 2012). Because texting and driving has become a dangerous epidemic in recent years, psychologists are looking at ways to help people interrupt the “phone schema” while driving. Event schemata like these are the reason why many habits are difficult to break once they have been acquired. As we continue to examine thinking, keep in mind how powerful the forces of concepts and schemata are to our understanding of the world.
- Define language and demonstrate familiarity with the components of language
- Understand the development of language
- Explain the relationship between language and thinking
Language is a communication system that involves using words and systematic rules to organize those words to transmit information from one individual to another. While language is a form of communication, not all communication is language. Many species communicate with one another through their postures, movements, odors, or vocalizations. This communication is crucial for species that need to interact and develop social relationships with their conspecifics. However, many people have asserted that it is language that makes humans unique among all of the animal species (Corballis & Suddendorf, 2007; Tomasello & Rakoczy, 2003). This section will focus on what distinguishes language as a special form of communication, how the use of language develops, and how language affects the way we think.
Components of Language
Language, be it spoken, signed, or written, has specific components: a lexicon and grammar. Lexicon refers to the words of a given language. Thus, lexicon is a language’s vocabulary. Grammar refers to the set of rules that are used to convey meaning through the use of the lexicon (Fernández & Cairns, 2011). For instance, English grammar dictates that most verbs receive an “-ed” at the end to indicate past tense.
Words are formed by combining the various phonemes that make up the language. A phoneme (e.g., the sounds “ah” vs. “eh”) is a basic sound unit of a given language, and different languages have different sets of phonemes. Phonemes are combined to form morphemes , which are the smallest units of language that convey some type of meaning (e.g., “I” is both a phoneme and a morpheme). We use semantics and syntax to construct language. Semantics and syntax are part of a language’s grammar. Semantics refers to the process by which we derive meaning from morphemes and words. Syntax refers to the way words are organized into sentences (Chomsky, 1965; Fernández & Cairns, 2011).
We apply the rules of grammar to organize the lexicon in novel and creative ways, which allow us to communicate information about both concrete and abstract concepts. We can talk about our immediate and observable surroundings as well as the surface of unseen planets. We can share our innermost thoughts, our plans for the future, and debate the value of a college education. We can provide detailed instructions for cooking a meal, fixing a car, or building a fire. Through our use of words and language, we are able to form, organize, and express ideas, schema, and artificial concepts.
Language Development
Given the remarkable complexity of a language, one might expect that mastering a language would be an especially arduous task; indeed, for those of us trying to learn a second language as adults, this might seem to be true. However, young children master language very quickly with relative ease. B. F. Skinner (1957) proposed that language is learned through reinforcement. Noam Chomsky (1965) criticized this behaviorist approach, asserting instead that the mechanisms underlying language acquisition are biologically determined. The use of language develops in the absence of formal instruction and appears to follow a very similar pattern in children from vastly different cultures and backgrounds. It would seem, therefore, that we are born with a biological predisposition to acquire a language (Chomsky, 1965; Fernández & Cairns, 2011). Moreover, it appears that there is a critical period for language acquisition, such that this proficiency at acquiring language is maximal early in life; generally, as people age, the ease with which they acquire and master new languages diminishes (Johnson & Newport, 1989; Lenneberg, 1967; Singleton, 1995).
Children begin to learn about language from a very early age ( Table 7.1 ). In fact, it appears that this is occurring even before we are born. Newborns show a preference for their mother’s voice and appear to be able to discriminate between the language spoken by their mother and other languages. Babies are also attuned to the languages being used around them and show preferences for videos of faces that are moving in synchrony with the audio of spoken language versus videos that do not synchronize with the audio (Blossom & Morgan, 2006; Pickens, 1994; Spelke & Cortelyou, 1981).
| Stages of Language and Communication Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stage | Age | Developmental Language and Communication |
| 1 | 0–3 months | Reflexive communication |
| 2 | 3–8 months | Reflexive communication; interest in others |
| 3 | 8–13 months | Intentional communication; sociability |
| 4 | 12–18 months | First words |
| 5 | 18–24 months | Simple sentences of two words |
| 6 | 2–3 years | Sentences of three or more words |
| 7 | 3–5 years | Complex sentences; has conversations |
DIG DEEPER: The Case of Genie
In the fall of 1970, a social worker in the Los Angeles area found a 13-year-old girl who was being raised in extremely neglectful and abusive conditions. The girl, who came to be known as Genie, had lived most of her life tied to a potty chair or confined to a crib in a small room that was kept closed with the curtains drawn. For a little over a decade, Genie had virtually no social interaction and no access to the outside world. As a result of these conditions, Genie was unable to stand up, chew solid food, or speak (Fromkin, Krashen, Curtiss, Rigler, & Rigler, 1974; Rymer, 1993). The police took Genie into protective custody.
Genie’s abilities improved dramatically following her removal from her abusive environment, and early on, it appeared she was acquiring language—much later than would be predicted by critical period hypotheses that had been posited at the time (Fromkin et al., 1974). Genie managed to amass an impressive vocabulary in a relatively short amount of time. However, she never developed a mastery of the grammatical aspects of language (Curtiss, 1981). Perhaps being deprived of the opportunity to learn language during a critical period impeded Genie’s ability to fully acquire and use language.
You may recall that each language has its own set of phonemes that are used to generate morphemes, words, and so on. Babies can discriminate among the sounds that make up a language (for example, they can tell the difference between the “s” in vision and the “ss” in fission); early on, they can differentiate between the sounds of all human languages, even those that do not occur in the languages that are used in their environments. However, by the time that they are about 1 year old, they can only discriminate among those phonemes that are used in the language or languages in their environments (Jensen, 2011; Werker & Lalonde, 1988; Werker & Tees, 1984).
After the first few months of life, babies enter what is known as the babbling stage, during which time they tend to produce single syllables that are repeated over and over. As time passes, more variations appear in the syllables that they produce. During this time, it is unlikely that the babies are trying to communicate; they are just as likely to babble when they are alone as when they are with their caregivers (Fernández & Cairns, 2011). Interestingly, babies who are raised in environments in which sign language is used will also begin to show babbling in the gestures of their hands during this stage (Petitto, Holowka, Sergio, Levy, & Ostry, 2004).
Generally, a child’s first word is uttered sometime between the ages of 1 year to 18 months, and for the next few months, the child will remain in the “one word” stage of language development. During this time, children know a number of words, but they only produce one-word utterances. The child’s early vocabulary is limited to familiar objects or events, often nouns. Although children in this stage only make one-word utterances, these words often carry larger meaning (Fernández & Cairns, 2011). So, for example, a child saying “cookie” could be identifying a cookie or asking for a cookie.
As a child’s lexicon grows, she begins to utter simple sentences and to acquire new vocabulary at a very rapid pace. In addition, children begin to demonstrate a clear understanding of the specific rules that apply to their language(s). Even the mistakes that children sometimes make provide evidence of just how much they understand about those rules. This is sometimes seen in the form of overgeneralization . In this context, overgeneralization refers to an extension of a language rule to an exception to the rule. For example, in English, it is usually the case that an “s” is added to the end of a word to indicate plurality. For example, we speak of one dog versus two dogs. Young children will overgeneralize this rule to cases that are exceptions to the “add an s to the end of the word” rule and say things like “those two gooses” or “three mouses.” Clearly, the rules of the language are understood, even if the exceptions to the rules are still being learned (Moskowitz, 1978).
Language and Thought
When we speak one language, we agree that words are representations of ideas, people, places, and events. The given language that children learn is connected to their culture and surroundings. But can words themselves shape the way we think about things? Psychologists have long investigated the question of whether language shapes thoughts and actions, or whether our thoughts and beliefs shape our language. Two researchers, Edward Sapir and Benjamin Lee Whorf began this investigation in the 1940s. They wanted to understand how the language habits of a community encourage members of that community to interpret language in a particular manner (Sapir, 1941/1964). Sapir and Whorf proposed that language determines thought. For example, in some languages, there are many different words for love. However, in English, we use the word love for all types of love. Does this affect how we think about love depending on the language that we speak (Whorf, 1956)? Researchers have since identified this view as too absolute, pointing out a lack of empiricism behind what Sapir and Whorf proposed (Abler, 2013; Boroditsky, 2011; van Troyer, 1994). Today, psychologists continue to study and debate the relationship between language and thought.
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving and decision making
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe is doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( Table 7.2 ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first, you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
| Problem-Solving Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Method | Description | Example |
| Trial and error | Continue trying different solutions until problem is solved | Restarting phone, turning off WiFi, turning off bluetooth in order to determine why your phone is malfunctioning |
| Algorithm | Step-by-step problem-solving formula | Instruction manual for installing new software on your computer |
| Heuristic | General problem-solving framework | Working backwards; breaking a task into steps |
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of the five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backward is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C., and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backward heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or a long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
EVERYDAY CONNECTION: Solving Puzzles
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( Figure 7.7 ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( Figure 7.8 ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( Figure 7.9 ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. Duncker (1945) conducted foundational research on functional fixedness. He created an experiment in which participants were given a candle, a book of matches, and a box of thumbtacks. They were instructed to use those items to attach the candle to the wall so that it did not drip wax onto the table below. Participants had to use functional fixedness to solve the problem ( Figure 7.10 ). During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in Table 7.3 .
| Summary of Decision Biases | |
|---|---|
| Bias | Description |
| Anchoring | Tendency to focus on one particular piece of information when making decisions or problem-solving |
| Confirmation | Focuses on information that confirms existing beliefs |
| Hindsight | Belief that the event just experienced was predictable |
| Representative | Unintentional stereotyping of someone or something |
| Availability | Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty |
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure 7.9 ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in Figure 7.7 and Figure 7.8 ? Here are the answers ( Figure 7.11 ).
- Define intelligence
- Explain the triarchic theory of intelligence
- Identify the difference between intelligence theories
- Explain emotional intelligence
- Define creativity
Classifying Intelligence
What exactly is intelligence? The way that researchers have defined the concept of intelligence has been modified many times since the birth of psychology. British psychologist Charles Spearman believed intelligence consisted of one general factor, called g , which could be measured and compared among individuals. Spearman focused on the commonalities among various intellectual abilities and de-emphasized what made each unique. Long before modern psychology developed, however, ancient philosophers, such as Aristotle, held a similar view (Cianciolo & Sternberg, 2004).
Other psychologists believe that instead of a single factor, intelligence is a collection of distinct abilities. In the 1940s, Raymond Cattell proposed a theory of intelligence that divided general intelligence into two components: crystallized intelligence and fluid intelligence (Cattell, 1963). Crystallized intelligence is characterized as acquired knowledge and the ability to retrieve it. When you learn, remember, and recall information, you are using crystallized intelligence. You use crystallized intelligence all the time in your coursework by demonstrating that you have mastered the information covered in the course. Fluid intelligence encompasses the ability to see complex relationships and solve problems. Navigating your way home after being detoured onto an unfamiliar route because of road construction would draw upon your fluid intelligence. Fluid intelligence helps you tackle complex, abstract challenges in your daily life, whereas crystallized intelligence helps you overcome concrete, straightforward problems (Cattell, 1963).
Other theorists and psychologists believe that intelligence should be defined in more practical terms. For example, what types of behaviors help you get ahead in life? Which skills promote success? Think about this for a moment. Being able to recite all 45 presidents of the United States in order is an excellent party trick, but will knowing this make you a better person?
Robert Sternberg developed another theory of intelligence, which he titled the triarchic theory of intelligence because it sees intelligence as comprised of three parts (Sternberg, 1988): practical, creative, and analytical intelligence ( Figure 7.12 ).
Practical intelligence , as proposed by Sternberg, is sometimes compared to “street smarts.” Being practical means you find solutions that work in your everyday life by applying knowledge based on your experiences. This type of intelligence appears to be separate from the traditional understanding of IQ; individuals who score high in practical intelligence may or may not have comparable scores in creative and analytical intelligence (Sternberg, 1988).
Analytical intelligence is closely aligned with academic problem solving and computations. Sternberg says that analytical intelligence is demonstrated by an ability to analyze, evaluate, judge, compare, and contrast. When reading a classic novel for a literature class, for example, it is usually necessary to compare the motives of the main characters of the book or analyze the historical context of the story. In a science course such as anatomy, you must study the processes by which the body uses various minerals in different human systems. In developing an understanding of this topic, you are using analytical intelligence. When solving a challenging math problem, you would apply analytical intelligence to analyze different aspects of the problem and then solve it section by section.
Creative intelligence is marked by inventing or imagining a solution to a problem or situation. Creativity in this realm can include finding a novel solution to an unexpected problem or producing a beautiful work of art or a well-developed short story. Imagine for a moment that you are camping in the woods with some friends and realize that you’ve forgotten your camp coffee pot. The person in your group who figures out a way to successfully brew coffee for everyone would be credited as having higher creative intelligence.
Multiple Intelligences Theory was developed by Howard Gardner, a Harvard psychologist and former student of Erik Erikson. Gardner’s theory, which has been refined for more than 30 years, is a more recent development among theories of intelligence. In Gardner’s theory, each person possesses at least eight intelligences. Among these eight intelligences, a person typically excels in some and falters in others (Gardner, 1983). Table 7.4 describes each type of intelligence.
| Multiple Intelligences | ||
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence Type | Characteristics | Representative Career |
| Linguistic intelligence | Perceives different functions of language, different sounds and meanings of words, may easily learn multiple languages | Journalist, novelist, poet, teacher |
| Logical-mathematical intelligence | Capable of seeing numerical patterns, strong ability to use reason and logic | Scientist, mathematician |
| Musical intelligence | Understands and appreciates rhythm, pitch, and tone; may play multiple instruments or perform as a vocalist | Composer, performer |
| Bodily kinesthetic intelligence | High ability to control the movements of the body and use the body to perform various physical tasks | Dancer, athlete, athletic coach, yoga instructor |
| Spatial intelligence | Ability to perceive the relationship between objects and how they move in space | Choreographer, sculptor, architect, aviator, sailor |
| Interpersonal intelligence | Ability to understand and be sensitive to the various emotional states of others | Counselor, social worker, salesperson |
| Intrapersonal intelligence | Ability to access personal feelings and motivations, and use them to direct behavior and reach personal goals | Key component of personal success over time |
| Naturalist intelligence | High capacity to appreciate the natural world and interact with the species within it | Biologist, ecologist, environmentalist |
Gardner’s theory is relatively new and needs additional research to better establish empirical support. At the same time, his ideas challenge the traditional idea of intelligence to include a wider variety of abilities, although it has been suggested that Gardner simply relabeled what other theorists called “cognitive styles” as “intelligences” (Morgan, 1996). Furthermore, developing traditional measures of Gardner’s intelligences is extremely difficult (Furnham, 2009; Gardner & Moran, 2006; Klein, 1997).
Gardner’s inter- and intrapersonal intelligences are often combined into a single type: emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence encompasses the ability to understand the emotions of yourself and others, show empathy, understand social relationships and cues, and regulate your own emotions and respond in culturally appropriate ways (Parker, Saklofske, & Stough, 2009). People with high emotional intelligence typically have well-developed social skills. Some researchers, including Daniel Goleman, the author of Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More than IQ , argue that emotional intelligence is a better predictor of success than traditional intelligence (Goleman, 1995). However, emotional intelligence has been widely debated, with researchers pointing out inconsistencies in how it is defined and described, as well as questioning results of studies on a subject that is difficult to measure and study empirically (Locke, 2005; Mayer, Salovey, & Caruso, 2004)
The most comprehensive theory of intelligence to date is the Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) theory of cognitive abilities (Schneider & McGrew, 2018). In this theory, abilities are related and arranged in a hierarchy with general abilities at the top, broad abilities in the middle, and narrow (specific) abilities at the bottom. The narrow abilities are the only ones that can be directly measured; however, they are integrated within the other abilities. At the general level is general intelligence. Next, the broad level consists of general abilities such as fluid reasoning, short-term memory, and processing speed. Finally, as the hierarchy continues, the narrow level includes specific forms of cognitive abilities. For example, short-term memory would further break down into memory span and working memory capacity.
Intelligence can also have different meanings and values in different cultures. If you live on a small island, where most people get their food by fishing from boats, it would be important to know how to fish and how to repair a boat. If you were an exceptional angler, your peers would probably consider you intelligent. If you were also skilled at repairing boats, your intelligence might be known across the whole island. Think about your own family’s culture. What values are important for Latinx families? Italian families? In Irish families, hospitality and telling an entertaining story are marks of the culture. If you are a skilled storyteller, other members of Irish culture are likely to consider you intelligent.
Some cultures place a high value on working together as a collective. In these cultures, the importance of the group supersedes the importance of individual achievement. When you visit such a culture, how well you relate to the values of that culture exemplifies your cultural intelligence , sometimes referred to as cultural competence.
Creativity is the ability to generate, create, or discover new ideas, solutions, and possibilities. Very creative people often have intense knowledge about something, work on it for years, look at novel solutions, seek out the advice and help of other experts, and take risks. Although creativity is often associated with the arts, it is actually a vital form of intelligence that drives people in many disciplines to discover something new. Creativity can be found in every area of life, from the way you decorate your residence to a new way of understanding how a cell works.
Creativity is often assessed as a function of one’s ability to engage in divergent thinking . Divergent thinking can be described as thinking “outside the box;” it allows an individual to arrive at unique, multiple solutions to a given problem. In contrast, convergent thinking describes the ability to provide a correct or well-established answer or solution to a problem (Cropley, 2006; Gilford, 1967)
- Explain how intelligence tests are developed
- Describe the history of the use of IQ tests
- Describe the purposes and benefits of intelligence testing
While you’re likely familiar with the term “IQ” and associate it with the idea of intelligence, what does IQ really mean? IQ stands for intelligence quotient and describes a score earned on a test designed to measure intelligence. You’ve already learned that there are many ways psychologists describe intelligence (or more aptly, intelligences). Similarly, IQ tests—the tools designed to measure intelligence—have been the subject of debate throughout their development and use.
When might an IQ test be used? What do we learn from the results, and how might people use this information? While there are certainly many benefits to intelligence testing, it is important to also note the limitations and controversies surrounding these tests. For example, IQ tests have sometimes been used as arguments in support of insidious purposes, such as the eugenics movement (Severson, 2011). The infamous Supreme Court Case, Buck v. Bell , legalized the forced sterilization of some people deemed “feeble-minded” through this type of testing, resulting in about 65,000 sterilizations ( Buck v. Bell , 274 U.S. 200; Ko, 2016). Today, only professionals trained in psychology can administer IQ tests, and the purchase of most tests requires an advanced degree in psychology. Other professionals in the field, such as social workers and psychiatrists, cannot administer IQ tests. In this section, we will explore what intelligence tests measure, how they are scored, and how they were developed.
Measuring Intelligence
It seems that the human understanding of intelligence is somewhat limited when we focus on traditional or academic-type intelligence. How then, can intelligence be measured? And when we measure intelligence, how do we ensure that we capture what we’re really trying to measure (in other words, that IQ tests function as valid measures of intelligence)? In the following paragraphs, we will explore the how intelligence tests were developed and the history of their use.
The IQ test has been synonymous with intelligence for over a century. In the late 1800s, Sir Francis Galton developed the first broad test of intelligence (Flanagan & Kaufman, 2004). Although he was not a psychologist, his contributions to the concepts of intelligence testing are still felt today (Gordon, 1995). Reliable intelligence testing (you may recall from earlier chapters that reliability refers to a test’s ability to produce consistent results) began in earnest during the early 1900s with a researcher named Alfred Binet ( Figure 7.13 ). Binet was asked by the French government to develop an intelligence test to use on children to determine which ones might have difficulty in school; it included many verbally based tasks. American researchers soon realized the value of such testing. Louis Terman, a Stanford professor, modified Binet’s work by standardizing the administration of the test and tested thousands of different-aged children to establish an average score for each age. As a result, the test was normed and standardized, which means that the test was administered consistently to a large enough representative sample of the population that the range of scores resulted in a bell curve (bell curves will be discussed later). Standardization means that the manner of administration, scoring, and interpretation of results is consistent. Norming involves giving a test to a large population so data can be collected comparing groups, such as age groups. The resulting data provide norms, or referential scores, by which to interpret future scores. Norms are not expectations of what a given group should know but a demonstration of what that group does know. Norming and standardizing the test ensures that new scores are reliable. This new version of the test was called the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale (Terman, 1916). Remarkably, an updated version of this test is still widely used today.
In 1939, David Wechsler, a psychologist who spent part of his career working with World War I veterans, developed a new IQ test in the United States. Wechsler combined several subtests from other intelligence tests used between 1880 and World War I. These subtests tapped into a variety of verbal and nonverbal skills because Wechsler believed that intelligence encompassed “the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment” (Wechsler, 1958, p. 7). He named the test the Wechsler-Bellevue Intelligence Scale (Wechsler, 1981). This combination of subtests became one of the most extensively used intelligence tests in the history of psychology. Although its name was later changed to the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and has been revised several times, the aims of the test remain virtually unchanged since its inception (Boake, 2002). Today, there are three intelligence tests credited to Wechsler, the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-fourth edition (WAIS-IV), the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-V), and the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence—IV (WPPSI-IV) (Wechsler, 2012). These tests are used widely in schools and communities throughout the United States, and they are periodically normed and standardized as a means of recalibration. As a part of the recalibration process, the WISC-V was given to thousands of children across the country, and children taking the test today are compared with their same-age peers ( Figure 7.13 ).
The WISC-V is composed of 14 subtests, which comprise five indices, which then render an IQ score. The five indices are Verbal Comprehension, Visual Spatial, Fluid Reasoning, Working Memory, and Processing Speed. When the test is complete, individuals receive a score for each of the five indices and a Full Scale IQ score. The method of scoring reflects the understanding that intelligence is comprised of multiple abilities in several cognitive realms and focuses on the mental processes that the child used to arrive at his or her answers to each test item.
Interestingly, the periodic recalibrations have led to an interesting observation known as the Flynn effect. Named after James Flynn, who was among the first to describe this trend, the Flynn effect refers to the observation that each generation has a significantly higher IQ than the last. Flynn himself argues, however, that increased IQ scores do not necessarily mean that younger generations are more intelligent per se (Flynn, Shaughnessy, & Fulgham, 2012).
Ultimately, we are still left with the question of how valid intelligence tests are. Certainly, the most modern versions of these tests tap into more than verbal competencies, yet the specific skills that should be assessed in IQ testing, the degree to which any test can truly measure an individual’s intelligence, and the use of the results of IQ tests are still issues of debate (Gresham & Witt, 1997; Flynn, Shaughnessy, & Fulgham, 2012; Richardson, 2002; Schlinger, 2003).
The Bell Curve
The results of intelligence tests follow the bell curve, a graph in the general shape of a bell. When the bell curve is used in psychological testing, the graph demonstrates a normal distribution of a trait, in this case, intelligence, in the human population. Many human traits naturally follow the bell curve. For example, if you lined up all your female schoolmates according to height, it is likely that a large cluster of them would be the average height for an American woman: 5’4”–5’6”. This cluster would fall in the center of the bell curve, representing the average height for American women ( Figure 7.14 ). There would be fewer women who stand closer to 4’11”. The same would be true for women of above-average height: those who stand closer to 5’11”. The trick to finding a bell curve in nature is to use a large sample size. Without a large sample size, it is less likely that the bell curve will represent the wider population. A representative sample is a subset of the population that accurately represents the general population. If, for example, you measured the height of the women in your classroom only, you might not actually have a representative sample. Perhaps the women’s basketball team wanted to take this course together, and they are all in your class. Because basketball players tend to be taller than average, the women in your class may not be a good representative sample of the population of American women. But if your sample included all the women at your school, it is likely that their heights would form a natural bell curve.
The same principles apply to intelligence test scores. Individuals earn a score called an intelligence quotient (IQ). Over the years, different types of IQ tests have evolved, but the way scores are interpreted remains the same. The average IQ score on an IQ test is 100. Standard deviations describe how data are dispersed in a population and give context to large data sets. The bell curve uses the standard deviation to show how all scores are dispersed from the average score ( Figure 7.15 ). In modern IQ testing, one standard deviation is 15 points. So a score of 85 would be described as “one standard deviation below the mean.” How would you describe a score of 115 and a score of 70? Any IQ score that falls within one standard deviation above and below the mean (between 85 and 115) is considered average, and 68% of the population has IQ scores in this range. An IQ score of 130 or above is considered a superior level.
Only 2.2% of the population has an IQ score below 70 (American Psychological Association [APA], 2013). A score of 70 or below indicates significant cognitive delays. When these are combined with major deficits in adaptive functioning, a person is diagnosed with having an intellectual disability (American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 2013). Formerly known as mental retardation, the accepted term now is intellectual disability, and it has four subtypes: mild, moderate, severe, and profound ( Table 7.5 ). The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Psychological Disorders lists criteria for each subgroup (APA, 2013).
| Characteristics of Cognitive Disorders | ||
|---|---|---|
| Intellectual Disability Subtype | Percentage of Population with Intellectual Disabilities | Description |
| Mild | 85% | 3rd- to 6th-grade skill level in reading, writing, and math; may be employed and live independently |
| Moderate | 10% | Basic reading and writing skills; functional self-care skills; requires some oversight |
| Severe | 5% | Functional self-care skills; requires oversight of daily environment and activities |
| Profound | <1% | May be able to communicate verbally or nonverbally; requires intensive oversight |
On the other end of the intelligence spectrum are those individuals whose IQs fall into the highest ranges. Consistent with the bell curve, about 2% of the population falls into this category. People are considered gifted if they have an IQ score of 130 or higher, or superior intelligence in a particular area. Long ago, popular belief suggested that people of high intelligence were maladjusted. This idea was disproven through a groundbreaking study of gifted children. In 1921, Lewis Terman began a longitudinal study of over 1500 children with IQs over 135 (Terman, 1925). His findings showed that these children became well-educated, successful adults who were, in fact, well-adjusted (Terman & Oden, 1947). Additionally, Terman’s study showed that the subjects were above average in physical build and attractiveness, dispelling an earlier popular notion that highly intelligent people were “weaklings.” Some people with very high IQs elect to join Mensa, an organization dedicated to identifying, researching, and fostering intelligence. Members must have an IQ score in the top 2% of the population, and they may be required to pass other exams in their application to join the group.
DIG DEEPER: What’s in a Name?
In the past, individuals with IQ scores below 70 and significant adaptive and social functioning delays were diagnosed with mental retardation. When this diagnosis was first named, the title held no social stigma. In time, however, the degrading word “retard” sprang from this diagnostic term. “Retard” was frequently used as a taunt, especially among young people, until the words “mentally retarded” and “retard” became an insult. As such, the DSM-5 now labels this diagnosis as “intellectual disability.” Many states once had a Department of Mental Retardation to serve those diagnosed with such cognitive delays, but most have changed their name to the Department of Developmental Disabilities or something similar in language.
Erin Johnson’s younger brother Matthew has Down syndrome. She wrote this piece about what her brother taught her about the meaning of intelligence:
His whole life, learning has been hard. Entirely possible – just different. He has always excelled with technology – typing his thoughts was more effective than writing them or speaking them. Nothing says “leave me alone” quite like a text that reads, “Do Not Call Me Right Now.” He is fully capable of reading books up to about a third-grade level, but he didn’t love it and used to always ask others to read to him. That all changed when his nephew came along, because he willingly reads to him, and it is the most heart-swelling, smile-inducing experience I have ever had the pleasure of witnessing.
When it comes down to it, Matt can learn. He does learn. It just takes longer, and he has to work harder for it, which if we’re being honest, is not a lot of fun. He is extremely gifted in learning things he takes an interest in, and those things often seem a bit “strange” to others. But no matter. It just proves my point – he can learn. That does not mean he will learn at the same pace, or even to the same level. It also, unfortunately, does not mean he will be allotted the same opportunities to learn as many others.
Here’s the scoop. We are all wired with innate abilities to retain and apply our learning and natural curiosities and passions that fuel our desire to learn. But our abilities and curiosities may not be the same.
The world doesn’t work this way though, especially not for my brother and his counterparts. Have him read aloud a book about skunks, and you may not get a whole lot from him. But have him tell you about skunks straight out of his memory, and hold onto your hats. He can hack the school’s iPad system, but he can’t tell you how he did it. He can write out every direction for a drive to our grandparents’ home in Florida, but he can’t drive.
Society is quick to deem him disabled and use demeaning language like the r-word to describe him, but in reality, we haven’t necessarily given him opportunities to showcase the learning he can do. In my case, I can escape the need to memorize how to change the oil in my car without anyone assuming I can’t do it, or calling me names when they find out I can’t. But Matthew can’t get through a day at his job without someone assuming he needs help. He is bright. Brighter than most anyone would assume. Maybe we need to redefine what is smart.
My brother doesn’t fit in the narrow schema of intelligence that is accepted in our society. But intelligence is far more than being able to solve 525 x 62 or properly introduce yourself to another. Why can’t we assume the intelligence of someone who can recite all of a character’s lines in a movie or remember my birthday a year after I told him/her a single time? Why is it we allow a person’s diagnosis or appearance to make us not just wonder if, but entirely doubt that they are capable? Maybe we need to cut away the sides of the box we have created for people so everyone can fit.
My brother can learn. It may not be what you know. It may be knowledge you would deem unimportant. It may not follow a traditional learning trajectory. But the fact remains – he can learn. Everyone can learn. And even though it is harder for him and harder for others still, he is not a “retard.” Nobody is.
When you use the r-word, you are insinuating that an individual, whether someone with a disability or not, is unintelligent, foolish, and purposeless. This in turn tells a person with a disability that they too are unintelligent, foolish, and purposeless. Because the word was historically used to describe individuals with disabilities and twisted from its original meaning to fit a cruel new context, it is forevermore associated with people like my brother. No matter how a person looks or learns or behaves, the r-word is never a fitting term. It’s time we waved it goodbye.
Why Measure Intelligence?
The value of IQ testing is most evident in educational or clinical settings. Children who seem to be experiencing learning difficulties or severe behavioral problems can be tested to ascertain whether the child’s difficulties can be partly attributed to an IQ score that is significantly different from the mean for her age group. Without IQ testing—or another measure of intelligence—children and adults needing extra support might not be identified effectively. In addition, IQ testing is used in courts to determine whether a defendant has special or extenuating circumstances that preclude him from participating in some way in a trial. People also use IQ testing results to seek disability benefits from the Social Security Administration.
- Describe how genetics and environment affect intelligence
- Explain the relationship between IQ scores and socioeconomic status
- Describe the difference between a learning disability and a developmental disorder
High Intelligence: Nature or Nurture?
Where does high intelligence come from? Some researchers believe that intelligence is a trait inherited from a person’s parents. Scientists who research this topic typically use twin studies to determine the heritability of intelligence. The Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart is one of the most well-known twin studies. In this investigation, researchers found that identical twins raised together and identical twins raised apart exhibit a higher correlation between their IQ scores than siblings or fraternal twins raised together (Bouchard, Lykken, McGue, Segal, & Tellegen, 1990). The findings from this study reveal a genetic component to intelligence ( Figure 7.15 ). At the same time, other psychologists believe that intelligence is shaped by a child’s developmental environment. If parents were to provide their children with intellectual stimuli from before they are born, it is likely that they would absorb the benefits of that stimulation, and it would be reflected in intelligence levels.
The reality is that aspects of each idea are probably correct. In fact, one study suggests that although genetics seem to be in control of the level of intelligence, the environmental influences provide both stability and change to trigger manifestation of cognitive abilities (Bartels, Rietveld, Van Baal, & Boomsma, 2002). Certainly, there are behaviors that support the development of intelligence, but the genetic component of high intelligence should not be ignored. As with all heritable traits, however, it is not always possible to isolate how and when high intelligence is passed on to the next generation.
Range of Reaction is the theory that each person responds to the environment in a unique way based on his or her genetic makeup. According to this idea, your genetic potential is a fixed quantity, but whether you reach your full intellectual potential is dependent upon the environmental stimulation you experience, especially in childhood. Think about this scenario: A couple adopts a child who has average genetic intellectual potential. They raise her in an extremely stimulating environment. What will happen to the couple’s new daughter? It is likely that the stimulating environment will improve her intellectual outcomes over the course of her life. But what happens if this experiment is reversed? If a child with an extremely strong genetic background is placed in an environment that does not stimulate him: What happens? Interestingly, according to a longitudinal study of highly gifted individuals, it was found that “the two extremes of optimal and pathological experience are both represented disproportionately in the backgrounds of creative individuals”; however, those who experienced supportive family environments were more likely to report being happy (Csikszentmihalyi & Csikszentmihalyi, 1993, p. 187).
Another challenge to determining the origins of high intelligence is the confounding nature of our human social structures. It is troubling to note that some ethnic groups perform better on IQ tests than others—and it is likely that the results do not have much to do with the quality of each ethnic group’s intellect. The same is true for socioeconomic status. Children who live in poverty experience more pervasive, daily stress than children who do not worry about the basic needs of safety, shelter, and food. These worries can negatively affect how the brain functions and develops, causing a dip in IQ scores. Mark Kishiyama and his colleagues determined that children living in poverty demonstrated reduced prefrontal brain functioning comparable to children with damage to the lateral prefrontal cortex (Kishyama, Boyce, Jimenez, Perry, & Knight, 2009).
The debate around the foundations and influences on intelligence exploded in 1969 when an educational psychologist named Arthur Jensen published the article “How Much Can We Boost I.Q. and Achievement” in the Harvard Educational Review . Jensen had administered IQ tests to diverse groups of students, and his results led him to the conclusion that IQ is determined by genetics. He also posited that intelligence was made up of two types of abilities: Level I and Level II. In his theory, Level I is responsible for rote memorization, whereas Level II is responsible for conceptual and analytical abilities. According to his findings, Level I remained consistent among the human race. Level II, however, exhibited differences among ethnic groups (Modgil & Routledge, 1987). Jensen’s most controversial conclusion was that Level II intelligence is prevalent among Asians, then Caucasians, then African Americans. Robert Williams was among those who called out racial bias in Jensen’s results (Williams, 1970).
Obviously, Jensen’s interpretation of his own data caused an intense response in a nation that continued to grapple with the effects of racism (Fox, 2012). However, Jensen’s ideas were not solitary or unique; rather, they represented one of many examples of psychologists asserting racial differences in IQ and cognitive ability. In fact, Rushton and Jensen (2005) reviewed three decades worth of research on the relationship between race and cognitive ability. Jensen’s belief in the inherited nature of intelligence and the validity of the IQ test to be the truest measure of intelligence are at the core of his conclusions. If, however, you believe that intelligence is more than Levels I and II, or that IQ tests do not control for socioeconomic and cultural differences among people, then perhaps you can dismiss Jensen’s conclusions as a single window that looks out on the complicated and varied landscape of human intelligence.
In a related story, parents of African American students filed a case against the State of California in 1979, because they believed that the testing method used to identify students with learning disabilities was culturally unfair as the tests were normed and standardized using white children ( Larry P. v. Riles ). The testing method used by the state disproportionately identified African American children as mentally retarded. This resulted in many students being incorrectly classified as “mentally retarded.”
What are Learning Disabilities?
Learning disabilities are cognitive disorders that affect different areas of cognition, particularly language or reading. It should be pointed out that learning disabilities are not the same thing as intellectual disabilities. Learning disabilities are considered specific neurological impairments rather than global intellectual or developmental disabilities. A person with a language disability has difficulty understanding or using spoken language, whereas someone with a reading disability, such as dyslexia, has difficulty processing what he or she is reading.
Often, learning disabilities are not recognized until a child reaches school age. One confounding aspect of learning disabilities is that they most often affect children with average to above-average intelligence. In other words, the disability is specific to a particular area and not a measure of overall intellectual ability. At the same time, learning disabilities tend to exhibit comorbidity with other disorders, like attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Anywhere between 30–70% of individuals with diagnosed cases of ADHD also have some sort of learning disability (Riccio, Gonzales, & Hynd, 1994). Let’s take a look at three examples of common learning disabilities: dysgraphia, dyslexia, and dyscalculia.
Children with dysgraphia have a learning disability that results in a struggle to write legibly. The physical task of writing with a pen and paper is extremely challenging for the person. These children often have extreme difficulty putting their thoughts down on paper (Smits-Engelsman & Van Galen, 1997). This difficulty is inconsistent with a person’s IQ. That is, based on the child’s IQ and/or abilities in other areas, a child with dysgraphia should be able to write, but can’t. Children with dysgraphia may also have problems with spatial abilities.
Students with dysgraphia need academic accommodations to help them succeed in school. These accommodations can provide students with alternative assessment opportunities to demonstrate what they know (Barton, 2003). For example, a student with dysgraphia might be permitted to take an oral exam rather than a traditional paper-and-pencil test. Treatment is usually provided by an occupational therapist, although there is some question as to how effective such treatment is (Zwicker, 2005).
Dyslexia is the most common learning disability in children. An individual with dyslexia exhibits an inability to correctly process letters. The neurological mechanism for sound processing does not work properly in someone with dyslexia. As a result, dyslexic children may not understand sound-letter correspondence. A child with dyslexia may mix up letters within words and sentences—letter reversals, such as those shown in Figure 7.17 , are a hallmark of this learning disability—or skip whole words while reading. A dyslexic child may have difficulty spelling words correctly while writing. Because of the disordered way that the brain processes letters and sounds, learning to read is a frustrating experience. Some dyslexic individuals cope by memorizing the shapes of most words, but they never actually learn to read (Berninger, 2008).
Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia is difficulty in learning or comprehending arithmetic. This learning disability is often first evident when children exhibit difficulty discerning how many objects are in a small group without counting them. Other symptoms may include struggling to memorize math facts, organize numbers, or fully differentiate between numerals, math symbols, and written numbers (such as “3” and “three”).
Additional Supplemental Resources
- Use Google’s QuickDraw web app on your phone to quickly draw 5 things for Google’s artificially intelligent neural net. When you are done, the app will show you what it thought each of the drawings was. How does this relate to the psychological idea of concepts, prototypes, and schemas? Check out here. Works best in Chrome if used in a web browser
- This article lists information about a variety of different topics relating to speech development, including how speech develops and what research is currently being done regarding speech development.
- The Human intelligence site includes biographical profiles of people who have influenced the development of intelligence theory and testing, in-depth articles exploring current controversies related to human intelligence, and resources for teachers.

- In 2000, psychologists Sheena Iyengar and Mark Lepper from Columbia and Stanford University published a study about the paradox of choice. This is the original journal article.
- Mensa , the high IQ society, provides a forum for intellectual exchange among its members. There are members in more than 100 countries around the world. Anyone with an IQ in the top 2% of the population can join.
- This test developed in the 1950s is used to refer to some kinds of behavioral tests for the presence of mind, or thought, or intelligence in putatively minded entities such as machines.
- Your central “Hub” of information and products created for the network of Parent Centers serving families of children with disabilities.
- How have average IQ levels changed over time? Hear James Flynn discuss the “Flynn Effect” in this Ted Talk. Closed captioning available.
- We all want customized experiences and products — but when faced with 700 options, consumers freeze up. With fascinating new research, Sheena Iyengar demonstrates how businesses (and others) can improve the experience of choosing. This is the same researcher that is featured in your midterm exam.
- What does an IQ Score distribution look like? Where do most people fall on an IQ Score distribution? Find out more in this video. Closed captioning available.
- How do we solve problems? How can data help us to do this? Follow Amy Webb’s story of how she used algorithms to help her find her way to true love. Closed captioning available.
- In this Ted-Ed video, explore some of the ways in which animals communicate, and determine whether or not this communication qualifies as language. A variety of discussion and assessment questions are included with the video (free registration is required to access the questions). Closed captioning available.
- Watch this Ted-Ed video to learn more about the benefits of speaking multiple languages, including how bilingualism helps the brain to process information, strengthens the brain, and keeps the speaker more engaged in their world. A variety of discussion and assessment questions are included with the video (free registration is required to access the questions). Closed captioning available.
- This video is on how your mind can amaze and betray you includes information on topics such as concepts, prototypes, problem-solving and mistakes in thinking. Closed captioning available.
- This video on language includes information on topics such as the development of language, language theories, and brain areas involved in language, as well as language disorders. Closed captioning available.
- This video on the controversy of intelligence includes information on topics such as theories of intelligence, emotional intelligence, and measuring intelligence. Closed captioning available.
- This video on the brains vs. bias includes information on topics such as intelligence testing, testing bias, and stereotype threat. Closed captioning available.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Julie Lazzara is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Define Cognitive Psychology: Meaning and Examples
Categories Cognition
Cognitive psychology is defined as the study of internal mental processes. Such processes include thinking, decision-making, problem-solving , language, attention, and memory. The cognitive approach in psychology is often considered part of the larger field of cognitive science. This branch of psychology is also related to several other disciplines, including neuroscience, philosophy, and linguistics.
To define cognitive psychology , it is important to understand the core focus of the cognitive approach, which is to psychology is on how people acquire, process, and store information. Cognitive psychologists are interested in studying what happens inside people’s minds.
Table of Contents
How Do We Define Cognitive Psychology?
While the cognitive approach to psychology is a popular branch of psychology today, it is actually a relatively young field of study. Until the 1950s, behaviorism was the dominant school of thought in psychology.
Between 1950 and 1970, the tide began to shift against behavioral psychology to focus on topics such as attention, memory, and problem-solving.
Often referred to as the cognitive revolution, this period generated considerable research on subjects, including processing models, cognitive research methods , and the first use of the term “cognitive psychology.”
The term “cognitive psychology” was first used in 1967 by American psychologist Ulric Neisser in his book Cognitive Psychology . Neisser went on to define cognitive psychology by saying that cognition involves “all processes by which the sensory input is transformed, reduced, elaborated, stored, recovered, and used.” Neisser also suggested that given such a broad and sweeping definition, cognition was involved in anything and everything that people do.
Essentially, all psychological events are cognitive events. Today, the American Psychological Association defines cognitive psychology as the “study of higher mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, and thinking.”
Understanding How We Define Cognitive Psychology
Some factors that contributed to the rise of the cognitive approach to psychology. These include:
- Dissatisfaction with the behaviorist approach : Behaviorism largely focused on looking at external influences on behavior. What the behavioral perspective failed to account for was the internal processes that influence human behavior. The cognitive approached emerged to fill this void.
- The increased use of computers : Scientists began comparing the way the human mind works to how a computer stores information on a hard drive. The information-processing model became popular as a result.
Thanks to these influences, the cognitive approach became an increasingly important branch of psychology. Behaviorism lost its hold as a dominant perspective, and psychologists began to look more intensely at memory, learning, language, and other internal processes.
Research Methods Used in Cognitive Psychology
Psychologists who use the cognitive approach rely on rigorous scientific methods to research the human mind. In many cases, this involves using experiments to determine if changes in an independent variable result in changes in the dependent variable.
Some of the main research methods used in the cognitive approach include:
Experimental Research
This involves conducting controlled experiments to manipulate variables and observe their effects on cognitive processes. Experiments are often conducted in laboratory settings to maintain control over extraneous variables.
For example, a memory experiment might involve randomly assigning participants to take a series of memory tests to determine if a certain change in conditions led to changes in memory abilities.
By using rigorous empirical methods, psychologists can accurately determine that it is the independent variable causing the changes rather than some other factor.
Cognitive Neuropsychology
This approach studies cognitive function by examining individuals with brain injuries or neurological disorders. By observing how damage to specific brain areas affects cognitive processes, researchers can infer the functions of those areas.
Neuroimaging Techniques
Cognitive neuroscientists use techniques to examine brain activity during cognitive tasks. Some of these neuroimaging tools include:
- Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET)
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
Eye-Tracking Studies
Eye-tracking technology is used to study visual attention and perception by recording eye movements as participants view stimuli. This method provides insights into how people process visual information and allocate attention.
Areas of Study in the Cognitive Psychology
As mentioned previously, any mental event is considered a cognitive event. There are a number of larger topics that have held the interest of cognitive psychologists over the last few decades. These include:
Information-Processing
As you might imagine, studying what’s happening in a person’s thoughts is not always the easiest thing to do.
Very early in psychology’s history, Wilhelm Wundt attempted to use a process known as introspection to study what was happening inside a person’s mind. This involved training people to focus on their internal states and write down what they were feeling, thinking, or experiencing. This approach was extremely subjective, so it did not last long as a cognitive research tool.
Cognitive psychologists have developed different models of thinking to study the human mind. One of the most popular of these is the information-processing approach .
In this approach, the mind is thought of as a computer. Thoughts and memories are broken down into smaller units of knowledge. As information enters the mind through the senses, it is manipulated by the brain, which then determines what to do with it.
Some information triggers an immediate response. Other units of information are transferred into long-term memory for future use.
Units of Knowledge
Cognitive psychologists often break down the units of knowledge into three different types: concepts, prototypes, and schemas.
A concept is basically a larger category of knowledge. A broad category exists inside your mind for these concepts where similar items are grouped together. You have concepts for things that are concrete such as a dog or cat, as well as concepts for abstract ideas such as beauty, gravity, and love.
A prototype refers to the most recognizable example of a particular concept. For example, what comes to mind when you think of a chair. If a large, comfy recliner immediately springs to mind, that is your prototype for the concept of a chair. If a bench, office chair, or bar stool pops into your mind, then that would be your prototype for that concept.
A schema is a mental framework you utilize to make sense of the world around you. Concepts are essentially the building blocks that are used to construct schemas, which are mental models for what you expect from the world around you. You have schemas for a wide variety of objects, ideas, people, and situations.
So what happens when you come across information that does not fit into one of your existing schemas? In some cases, you might even encounter things in the world that challenges or completely upend the ideas you already hold.
When this happens, you can either assimilate or accommodate the information. Assimilating the information involves broadening your current schema or even creating a new one. Accommodating the information requires changing your previously held ideas altogether. This process allows you to learn new things and develop new and more complex schemas for the world around you.
The Cognitive Approach to Attention
Attention is another major topic studied in the field of cognitive psychology. Attention is a state of focused awareness of some aspect of the environment. This ability to focus your attention allows you to take in knowledge about relevant stimuli in the world around you while at the same time filtering out things that are not particularly important.
At any given moment in time, you are taking in an immense amount of information from your visual, auditory, olfactory, tactile, and taste senses. Because the human brain has a limited capacity for handling all of this information, attention is both limited and selective.
Your attentional processes allow you to focus on the things that are relevant and essential for your survival while filtering out extraneous details.
The Cognitive Approach to Memory
How people form, recall, and retain memories is another important focus in the cognitive approach. The two major types of memory that researchers tend to look at are known as short-term memory and long-term memory.
Short-Term Memory
Short-term memories are all the things that you are actively thinking about and aware of at any given moment. This type of memory is both limited and very brief.
Estimates suggest that you can probably hold anywhere from 5 to 9 items in short-term memory for approximately 20 to 30 seconds.
Long-Term Memory
If this information is actively rehearsed and attended to, it may be transferred to what is known as long-term memory. As the name suggests, this type of memory is much more durable. While these longer-lasting memories are still susceptible to forgetting , the information retained in your long-term memory can last anywhere from days to decades.
Cognitive psychologists are interested in the various processes that influence how memories are formed, stored, and later retrieved. They also look at things that might interfere with the formation and storage of memories as well as various factors that might lead to memory errors or even false memories.
The Cognitive Approach to Intelligence
Human intelligence is also a major topic of interest within cognitive psychology, but it is also one of the most hotly debated and sometimes controversial. Not only has there been considerable questioning over how intelligence is measured (or if it can even be measured), but experts also disagree on exactly how to define intelligence itself.
One survey of psychologists found that experts provided more than 70 different definitions of what made up intelligence. While exact definitions vary, many agree that two important themes include both the ability to learn and the capacity to adapt as a result of experience.
Researchers have found that more intelligent people tend to perform better on tasks that require working memory , problem-solving, selective attention , concept formation, and decision-making. When looking at intelligence, cognitive psychologists often focus on understanding the mental processes that underlie these critical abilities.
Cognitive Development
Cognitive development refers to the changes in cognitive abilities that occur over the lifespan, from infancy through old age. Cognitive psychologists study the development of perception, attention, memory, language, and reasoning skills.
Research in cognitive development explores factors that influence cognitive growth, such as genetics, environment, and social interactions.
Language is a complex cognitive ability that enables communication through the use of symbols and grammatical rules. Cognitive psychologists study the cognitive processes involved in language comprehension, production, and acquisition.
Research in language examines topics such as syntax, semantics, pragmatics, and the neurobiological basis of language processing.
Reasons to Study Cognitive Psychology
Because cognitive psychology touches on many other disciplines, this branch of psychology is frequently studied by people in different fields. Even if you are not a psychology student, learning some of the basics of cognitive psychology can be helpful.
The following are just a few of those who may benefit from studying cognitive psychology.
- Students interested in behavioral neuroscience, linguistics, industrial-organizational psychology, artificial intelligence, and other related areas.
- Teachers, curriculum designers, instructional developers, and other educators may find it helpful to learn more about how people process, learn, and remember information.
- Engineers, scientists, artists, architects, and designers can all benefit from understanding internal mental states and processes.
Key Points to Remember About Cognitive Approach
- The cognitive approach emerged during the 1960s and 70s and has become a major force in the field of psychology.
- Cognitive psychologists are interested in mental processes, including how people take in, store, and utilize information.
- The cognitive approach to psychology often relies on an information-processing model that likens the human mind to a computer.
- Findings from the field of cognitive psychology apply in many areas, including our understanding of learning, memory, moral development, attention, decision-making, problem-solving, perceptions, and therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavior therapy and rational emotive behavior therapy.
Airenti G. (2019). The place of development in the history of psychology and cognitive science . Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 895. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00895
Legg S, Hutter M. A collection of definitions of intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications . 2007;157:17-24.
Miller, G. A. (1956). The magical n u mber seven, plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information . Psychological Review, 63 (2), 81–97. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0043158
Neisser U. Cognitive Psychology . Meredith Publishing Company; 1967.
Image: Julia Freeman-Woolpert / freeimages.com

Cognitive Psychology Explores Our Mental Processes

Understanding Brain Science and Cognitive Psychology
The human brain is an amazing and powerful tool. It allows us to learn, see, remember, hear, perceive, understand and create language. Sometimes, the human brain also fails us.
Cognitive psychologists study how people acquire, perceive, process and store information. This work can range from exploring how we learn language to understanding the interplay between cognition and emotion.
New technologies like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allow researchers to see a picture of the brain at work — helping them to understand how a brain reacts to a particular stimulus or how differences in brain structure can affect a person’s health, personality or cognitive functioning.
Brain Science and Cognitive Psychology Applied
Brain science and cognitive psychology is one of the most versatile psychological specialty areas today — and one of the most in demand. All professions have a compelling interest in how the brain works. Educators, curriculum designers, engineers, scientists, judges, public health and safety officials, architects and graphic designers all want to know more about how the brain processes information. Their research and its resulting applications have become an integral part of how organizations, schools and businesses function and succeed. In clinical settings, cognitive psychologists seek to treat issues related to human mental processes, including Alzheimer’s disease, speech issues, memory loss and sensory or perception difficulties.

Related books
Child Development at the Intersection ...
Clinical Neuropsychology
Essentials of Conditioning and Learning 5th
APA Handbook of Neuropsychology
Revealing the interplay of cognitive, meta-cognitive, and social processes in university students’ collaborative problem solving: a three-stage analytical framework
- Published: 11 July 2024
Cite this article

- Shuowen An 1 ,
- Si Zhang 1 ,
- Zhihui Cai 2 ,
- Wei Pan 2 ,
- Mingwei Li 1 &
- Mingwen Tong 1
23 Accesses
Explore all metrics
An in-depth analysis of collaborative problem solving (CPS) patterns contributes to understand team dynamics and effective paths to conflict resolution. However, there remains the lack of a perspective in the field of CPS research that organically combines the cognitive, meta-cognitive, and social-communicative dimensions. Moreover, the analysis of CPS sequences has primarily focused on the temporal dimension while overlooking the differences in spatial dimensions. To shed further light on the nature of CPS in computer-based environments, this study collected discourse data generated by 24 university students through an online synchronous chat tool. They were student teachers from a variety of disciplines (math, history, English, etc.) who were required to accomplish two tasks: instructional design and multimedia courseware development. Specifically, a three-stage analytical framework was proposed to code, cluster, and analyze these discourse data to further explore the differences in CPS patterns. We clustered time sequences by calculating the distance similarity metric via the dynamic time warping (DTW) method, which took into account both the spatial and temporal characteristics of the time sequences. Consequently, 16 time sequences of CPS processes were divided into 2 kinds of clusters (CPS subgroups), i.e., cluster 1 and cluster 2. From the statistical analysis, both clusters actively used the skills included in the meta-cognitive dimensions. Cluster 1 was oriented toward the solution of the problem whereas cluster 2 focused primarily on the requirements of the collaborative problem itself. From the process mining analysis, solution-driven cluster 1 tended to focus on expressing specific ideas and evaluating and summarizing them, intermittently monitoring and regulating task progress. Problem-driven cluster 2 tended to express specific ideas intermittently, and lacked the process of summarizing and evaluating different ideas to further filter out the best solutions. Finally, we summarized the implications of this study from theoretical and practical perspectives and discussed future research directions with regard to the limitations of this study.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others
When coding-and-counting is not enough: using epistemic network analysis (ENA) to analyze verbal data in CSCL research

Investigation 9. Tracing the Change in Discourse in a Collaborative Dynamic-Geometry Environment: From Visual to More Mathematical
Temporal group interaction density in collaborative problem solving: Exploring group interactions with different time granularities
Data availability.
Data will be made available on request.
Andrews-Todd, J., & Forsyth, C. (2020). Exploring social and cognitive dimensions of collaborative problem solving in an open online simulation-based task. Computers in Human Behavior, 104 , 105759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.10.025
Article Google Scholar
An, S., & Zhang, S. (2024). Effects of ability grouping on students’ collaborative problem solving patterns: Evidence from lag sequence analysis and epistemic network analysis. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 51 , 101453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2023.101453
Avry, S., Molinari, G., Bétrancourt, M., & Chanel, G. (2020). Sharing emotions contributes to regulating collaborative intentions in group problem-solving. Frontiers in Psychology, 11 , 1160. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01160
Bada, S. O., & Olusegun, S. (2015). Constructivism learning theory: A paradigm for teaching and learning. Journal of Research & Method in Education, 5 (6), 66–70.
Google Scholar
Baker, K., Greenberg, S., & Gutwin, C. (2001). Heuristic evaluation of groupware based on the mechanics of collaboration. In IFIP International Conference on Engineering for Human-Computer Interaction (pp. 123–139). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45348-2_14
Baker, R. (2010). Data mining for education. In B. McGaw, P. Peterson, & E. Baker (Eds.), International Encyclopedia of Education (3rd ed., pp. 112–118). Elsevier Science.
Chapter Google Scholar
Bannert, M., Reimann, P., & Sonnenberg, C. (2013). Process mining techniques for analysing patterns and strategies in students’ self-regulated learning. Metacognition and Learning, 9 (2), 161–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-013-9107-6
Biasutti, M., & Frate, S. (2018). Group metacognition in online collaborative learning: Validity and reliability of the group metacognition scale (GMS). Educational Technology Research and Development, 66 (6), 1321–1338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9583-0
Bozeman, B., Dietz, J. S., & Gaughan, M. (2001). Scientific and technical human capital: An alternative model for research evaluation. International Journal of Technology Management, 22 (7), 716–740.
Chen, W., & Hapgood, S. (2021). Understanding knowledge, participation and learning in L2 collaborative writing: A metacognitive theory perspective. Language Teaching Research, 25 (2), 256–281. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362168819837560
Chen, W., Tan, J. S. H., & Pi, Z. (2021). The spiral model of collaborative knowledge improvement: An exploratory study of a networked collaborative classroom. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 16 (1), 7–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-021-09338-6
Çini, A., Järvelä, S., Dindar, M., & Malmberg, J. (2023). How multiple levels of metacognitive awareness operate in collaborative problem solving. Metacognition and Learning, 18 (3), 891–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-023-09358-7
Clark, I. (2012). Formative assessment: Assessment is for self-regulated learning. Educational Psychology Review, 24 (2), 205–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-011-9191-6
Damşa, C. (2014). The multi-layered nature of small-group learning: Productive interactions in object-oriented collaboration. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 9 (3), 247–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-014-9193-8
Dindar, M., Järvelä, S., & Järvenoja, H. (2020). Interplay of metacognitive experiences and performance in collaborative problem solving. Computers & Education, 154 , 103922.
Fleiss, J. L. (1981). Statistical methods for rates and proportions (2nd ed.). John Wiley.
Gatta, R., Lenkowicz, J., Vallati, M., Rojas, E., Damiani, A., Sacchi, L., et al. (2017). pMineR: An innovative R library for performing process mining in medicine. In A. Teije, C. Popow, J. Holmes, & L. Sacchi (Eds.), Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. AIME 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (pp. 351–355 vol. 10259). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59758-4_42
Griffin, P., & Care, E. (2015). Assessment and teaching of 21st century skills . Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9395-7
Book Google Scholar
Hadwin, A., Järvelä, S., & Miller, M. (2017). Self-regulation, co-regulation, and shared regulation in collaborative learning environments. In Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 83–106). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315697048-6
He, Q., Liao, D., & Jiao, H. (2019). Clustering behavioral patterns using process data in PIAAC problem-solving items. In B. Veldkamp, & C. Sluijter (Eds.), Theoretical and Practical Advances in Computer-based Educational Measurement. Methodology of Educational Measurement and Assessment (pp. 189–212). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18480-3_10
He, Q., Borgonovi, F., & Suárez‐Álvarez, J. (2022). Clustering sequential navigation patterns in multiple‐source reading tasks with dynamic time warping method. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 39 (3), 719–736. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12748
Hesse, F., Care, E., Buder, J., Sassenberg, K., Griffin, P. (2015). A framework for teachable collaborative problem solving skills. In P. Griffin, & E. Care (Eds.), Assessment and Teaching of 21st Century Skills (pp. 37–56). Educational Assessment in an Information Age. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9395-7_2
Huang, X., & Lajoie, S. P. (2023). Social emotional interaction in collaborative learning: Why it matters and how can we measure it? Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 7 (1), 100447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2023.100447
Jiang, P., Ruan, X., Feng, Z., Jiang, Y., & Xiong, B. (2023). Research on online collaborative problem-solving in the last 10 years: Current status, hotspots, and outlook—A knowledge graph analysis based on CiteSpace. Mathematics, 11 (10), 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11102353
Laal, M., & Laal, M. (2012). Collaborative learning: What is it? Procedia: Social & Behavioral Sciences, 31 , 491dia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.12.092
Lämsä, J., Hämäläinen, R., Koskinen, P., Viiri, J., & Lampi, E. (2021). What do we do when we analyse the temporal aspects of computer-supported collaborative learning? A systematic literature review. Educational Research Review, 33 , 100387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100387
Lee, Y. (2018). Using self-organizing map and clustering to investigate problem-solving patterns in the massive open online course: An exploratory study. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57 (2), 471–490. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117753364
Lee, G., Kwon, J., Park, S., Kim, J., Kwon, H., & Park, H. (2003). Development of an instrument for measuring cognitive conflict in secondary-level science classes. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 40 (6), 585–603. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.10099
Li, C., & Liu, Z. (2017). Collaborative problem-solving behavior of 15-Year-Old Taiwanese students in science education. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 13 (10), 6677–6695. https://doi.org/10.12973/ejmste/78189
Li, D., Zhao, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Time-sequences representation and clustering approaches for sharing bike usage mining. IEEE Access, 7 , 177856–177863. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2958378
Li, S., Pöysä-Tarhonen, J., & Häkkinen, P. (2022). Patterns of action transitions in online collaborative problem solving: A network analysis approach. International Journal of Computer-supported Collaborative Learning, 17 (2), 191tional. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-022-09369-7
Liu, C. H., & Matthews, R. (2005). Vygotsky’s philosophy: Constructivism and its criticisms examined. International Education Journal, 6 (3), 386–399.
Luengo-Aravena, D., Cabello, P., & Bachino, B.R.-M. (2024). Online collaborative problem-solving as a tangible outcome of digital skills in technical and vocational higher education. Computers & Education, 218 , 105079.
Ma, Y., Zhang, H., Ni, L., & Zhou, D. (2023). Identifying collaborative problem-solver profiles based on collaborative processing time, actions and skills on a computer-based task. International Journal of Computer-supported Collaborative Learning, 18 , 465–488.
Malmberg, J., Järvelä, S., & Järvenoja, H. (2017). Capturing temporal and sequential patterns of self-, co-, and socially shared regulation in the context of collaborative learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 49 , 160–174.
OECD. (2013). Education at a glance 2013: OECD indicators. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/eag-2013-en
OECD. (2017). PISA 2015 collaborative problem solving framework. PISA 2015 assessment and analytical framework: Science, reading, mathematic, financial literacy and collaborative problem solving, 131–188. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264281820-en
Ouyang, F., & Chang, Y. H. (2019). The relationship between social participatory role and cognitive engagement level in online discussions. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50 (3), 13961414. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12647
Ouyang, F., & Dai, X. (2021). Using a three-layered social-cognitive network analysis framework for understanding online collaborative discussions. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 38 (1), 164–181. https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.7166
Ouyang, F., Xu, W., & Cukurova, M. (2023). An artificial intelligence-driven learning analytics method to examine the collaborative problem-solving process from the complex adaptive systems perspective. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 18 (1), 39–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-023-09387-z
Saint, J., Gašević, D., Matcha, W., Uzir, N. A., & Pardo, A. (2020). Combining analytic methods to unlock sequential and temporal patterns of self-regulated learning. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Analytics & Knowledge . https://doi.org/10.1145/3375462.3375487
Saint, J., Fan, Y., Singh, S., Gasevic, D., & Pardo, A. (2021). Using process mining to analyse self-regulated learning: a systematic analysis of four algorithms. In LAK21: 11th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference (LAK21) . Association for Computing Machinery, New York, 333–343. https://doi.org/10.1145/3448139.3448171
Smith, J. M., & Mancy, R. (2018). Exploring the relationship between metacognitive and collaborative talk during group mathematical problem-solving – What do we mean by collaborative metacognition? Research in Mathematics Education, 20 (1), 14–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2017.1410215
Su, Y., Li, Y., Hu, H., & Rosé, C. P. (2018). Exploring college English language learnerso self and social regulation of learning during wiki-supported collaborative reading activities. International Journal of Computer-supported Collaborative Learning, 13 (1), 35tiona. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-018-9269-y
Sun, C., Shute, V. J., Stewart, A., Yonehiro, J., Duran, N. D., & D’Mello, S. K. (2020). Towards a generalized competency model of collaborative problem solving. Computers & Education, 143 , 103672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103672
Swiecki, Z., Ruis, A. R., Farrell, C., & Shaffer, D. W. (2020). Assessing individual contributions to collaborative problem solving: A network analysis approach. Computers in Human Behavior, 104 , 105876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.01.009
Tan, J. P. L., Caleon, I. S., Jonathan, C. R., & Koh, E. (2014). A dialogic framework for assessing collective creativity in computer-supported collaborative problem-solving tasks. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 9 (3), 411–437.
Von Davier, A. A., Hao, J., Liu, L., & Kyllonen, P. C. (2017). Interdisciplinary research agenda in support of assessment of collaborative problem solving: Lessons learned from developing a collaborative science assessment prototype. Computers in Human Behavior, 76 , 631–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.04.059
Xu, W., Wu, Y., & Ouyang, F. (2023). Multimodal learning analytics of collaborative patterns during pair programming in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20 (8), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-022-00377-z
Zhang, M., & Andersson, B. (2023). Identifying problem-solving solution patterns using network analysis of operation sequences and response times. Educational Assessment, 28 (3), 172–189. https://doi.org/10.1080/10627197.2023.2222585
Zhang, S., Chen, J., Wen, Y., Chen, H., Gao, Q., & Wang, Q. (2021). Capturing regulatory patterns in online collaborative learning: A network analytic approach. International Journal of Computer-supported Collaborative Learning, 16 (1), 37–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-021-09339-5
Zhang, S., Gao, Q., Sun, M., Cai, Z., Li, H., Tang, Y., & Liu, Q. (2022). Understanding student teachers’ collaborative problem solving: Insights from an epistemic network analysis (ENA). Computers & Education, 183 , 104485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104485
Zhang, S., Li, H., Wen, Y., Zhang, Y., Guo, T., & He, X. (2023). Exploration of a group assessment model to foster student teachers’ critical thinking. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 47 , 101239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2023.101239
Zheng, Y., Bao, H., Shen, J., & Zhai, X. (2020). Investigating sequence patterns of collaborative problem-solving behavior in online collaborative discussion activity. Sustainability, 12 (20), 8522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208522
Zheng, X., Gu, X., Lai, W., Tu, Y., Hwang, G., & Wang, R. (2023). Development of the social metacognition inventory for online collaborative argumentation: Construct validity and reliability. Educational Technology Research and Development, 71 (3), 949nal Te. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-023-10220-5
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a project funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62077016). This work was conducted as part of a Research Project Supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Number CCNU22QN013).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Hubei Key Laboratory of Digital Education, Faculty of Artificial Intelligence in Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 430079, China
Shuowen An, Si Zhang, Mingwei Li & Mingwen Tong
School of Psychology, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 430079, China
Zhihui Cai & Wei Pan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Si Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1 The CPS coding framework
Skill dimension | Components | Coding categories | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Meta-cognitive skill | Reflexivity | Monitoring | Reflecting on or evaluating their own or their peers’ progress and experiences |
Planning | Planning the group’s sequence of activities, strategies and solution | ||
Regulation | Regulating own or peers’ motivation and behaviors | ||
Cognitive skill | Divergent production | Solution generation-epistemic | New ideas and possible solutions based on standards |
Solution generation-concrete | Particular or specific new ideas and possible solutions | ||
Solution generation-elaboration | Explaining or reasoning about previously presented ideas, or making connections between different ideas | ||
Premature closure (anti-divergent) | Reluctance to further consider possible solutions | ||
Convergent production | Problem defining/ establishing | Describing the problem and seeking to establish a common problem space | |
Problem analysis | Figuring out the specific details and rationale contained in a problem or task | ||
Solution evaluation acquiescence | Simply agreement with suggestions or statements about the solution | ||
Solution evaluation checking | Requiring peers to validate suggestions or statements about the solution | ||
Solution evaluation critique | Challenging or investigating the proposed solution | ||
Solution evaluation justification | Giving explicit or implicit justification for evaluation of the proposed solution | ||
Social-communicative skill | Prosocial interaction | Mutual grounding questioning | Building shared understanding with peers through questioning |
Mutual grounding responding | Giving immediate responses or information to the questions previously posed | ||
Affective | Expressing positive emotions through Emojis | ||
Cohesive-task | Expressing encouragement and praise to peers through specific discourse | ||
Cohesive-playful | Jokes unrelated to the task at hand and banter for purely social functions | ||
Dis-affective (anti-social) | Expressions of negative feelings such as the desire to disengage from the task | ||
Uncohesive (anti-social) | Negative impact on current group, e.g., lack of respect for peers, blaming rude discourse |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
An, S., Zhang, S., Cai, Z. et al. Revealing the interplay of cognitive, meta-cognitive, and social processes in university students’ collaborative problem solving: a three-stage analytical framework. Intern. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-024-09429-0
Download citation
Received : 03 March 2024
Accepted : 27 June 2024
Published : 11 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-024-09429-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Collaborative problem solving
- Collaborative learning
- Process mining
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Developing Logical Mathematical Intelligence
How to unlock your problem-solving potential
Cynthia Vinney, PhD is an expert in media psychology and a published scholar whose work has been published in peer-reviewed psychology journals.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/cynthiavinney-ec9442f2aae043bb90b1e7405288563a.jpeg)
- Characteristics and Examples
- Develop Logical Mathematical Intelligence
- Tips and Strategies
Logical mathematical intelligence is one of eight intelligences that Howard Gardner, a professor of cognition and education at Harvard University, proposed in his theory of multiple intelligences , which he outlined in his book Frames of Mind . Gardner's theory posited these types of intelligence:
- Visual-spatial
- Linguistic-verbal
- Logical-mathematical
- Body-kinesthetic
- Interpersonal
- Intrapersonal
- Naturalistic
According to Rebecca Mannis, PhD and Founder and Learning Specialist at Ivy Prep, for a long time American psychologists viewed intelligence as a single factor, typified by Lewis Terman in the early to mid-1900s, who referred to intelligence as “g.” Similarly, Kimberly Berens, PhD, CEO of Fit Learning Online and author of Blind Spots: Why Students Fail and the Science That Can Save Them , explains that intelligence is often viewed as an innate ability, but there is a lack of scientific evidence to support this.
Instead, Gardner theorized that there are a number of kinds of intelligence that we each may have, that we may vary in the degree we have of each one, and that we may have more or less of each of these throughout our lifetimes. Logical mathematical intelligence is one of the intelligences he described, and it represents the ability to use numbers effectively, to reason well, and to recognize and solve problems using logical patterns.
In this article, we’ll review the characteristics of logical mathematical intelligence, discover how to develop it, explore strategies to enhance it, and look at the benefits of this kind of intelligence.
Anchiy / E+ / Getty
Characteristics and Examples of Logical Mathematical Intelligence
People who have logical mathematical intelligence solve problems using logic, can quickly calculate math problems , and like when things are categorized in a rational way. They’re also good at understanding patterns, the relationships between things, and understanding complex ideas.
Thus, logical-mathematical intelligence encompasses the following:
- Being good with numbers
- Understanding logical concepts
- Having good reasoning skills
- Enjoying experiments
- Enjoying solving puzzles and mysteries
- Being good at manipulating numbers and operations
- Being good at understanding and applying scientific principles
According to Berens, examples of logical mathematical intelligence include “fluently solving multi-step equations, [solving] language-based math problems , interpreting and analyzing scientific findings, and designing experiments.”
Mannis explains that mastery of basic facts and concepts that leads to the ability to adapt those facts and concepts into more complex tasks and to new settings is a hallmark of logical mathematical intelligence.
For instance, Mannis gives the example of a third grader with strong logical mathematical intelligence who not only knows how to distinguish between perimeter and area but can also use those formulas for other things. The child can apply “that information to a math challenge to design a playground… where they are tasked with determining what the area of a complex shape would be if there were sections of semicircles or squares within that figure ‘cut out.’ They would also be able to then identify the cost of paving the entire play area given a particular per foot fee.”
For those of us who are more inclined toward verbal linguistics or another type of intelligence, this may seem beyond our reach, but it is possible to build your strength in the more mathematical areas of intelligence.
How to Develop Logical Mathematical Intelligence
Decades of research indicate that higher-level skills, such as those seen in logical mathematical intelligence, require the mastery of foundational skills, says Berens. As a result, “Young learners require explicit instruction and repeated practice to fluency in core math skills such as numeracy, basic computation, fractions, decimals, percents, and ratios," she says. "They also require fluent reading skills and fluent comprehension, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills.”
Mannis explains that some children are better at memorizing facts and drawing connections between concepts than others, but there are ways to develop these skills.
These methods include:
- Teacher education: According to Mannis, teachers must have a “strong understanding of how children develop these skills and methods [by] first teaching this content systematically and then gradually ‘scaffolding’ or adding complexity and integration."
- Focusing on basic math: As Berens indicates students must attain fluency in the basics before they can begin applying these core skills for mastery of highly complex skills, including algebra, geometry, and calculus.
- Engagement beyond the classroom: Encouraging children to see how mathematical concepts can be part of their real lives can help develop logical mathematical intelligence skills.
Mannis provides an example of the last point: “A child usually reads a book in four days and would like to borrow the series to read during the three weeks between the end of the school year and sleep away camp. How can they estimate how many books they will get through? How does being free of homework shift their estimate? That is an example of living math that offers a chance to systematize, use concepts such as ratios and estimating, and also encourage them to engage through creating a system to make their estimate.”
Strategies for Enhancing Logical Mathematical Intelligence
To enhance logical mathematical intelligence you first have to learn the basics, so explicit instruction and repeated practice in math skills is essential, says Berens.
Moreover, per Mannis, to enhance skills in logical mathematical intelligence further:
- Provide opportunities to create systems and patterns, and solve logic problems
- Encourage ‘metacognitive awareness,’ or being aware of how you think, and talk through this approach
- Balance learning facts and math operations with real-world problem-solving
For example, Mannis speaks of a middle school class she consulted with that timed its geometry unit so it was right before the school carnival. “After completing the basics of the course, the students were put in charge of designing, creating, and manning some of the carnival stations using” what they learned. This allowed them to use the skills they got from the course and enhance their logical mathematical intelligence.
Benefits of Logical Mathematical Intelligence
People with logical mathematical intelligence are good at rational thinking, analyzing problems logically, and thinking about issues scientifically. “Not only does mastery of high-level math skills produce long-term academic success," says Berens, "but it also gives learners access to careers in science, technology, and engineering.”
We have a lot of complex problems in these fields to solve, such as climate change, and we need people with logical mathematical intelligence to solve them, she says.
While some people may have more innate ability with logical mathematical intelligence, anyone can enhance their abilities. Developing math skills, engaging in strategy games and logic problems, explaining your thinking, and using your skills in the real world can help develop your logical mathematical intelligence and have you on your way to unlocking your problem-solving potential.
Gardner H. Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences . 10th anniversary ed. BasicBooks; 1993.
Arani HK, Mobarakeh SD. Metacognitive strategies and logical/mathematical intelligence in EFL context: Investigating possible relationships. TPLS . 2012;2(2):304-313. doi:10.4304/tpls.2.2.304-313
Šafranj J. Logical/mathematical intelligence in teaching English as a second language . Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences . 2016;232:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.10.019
By Cynthia Vinney, PhD Cynthia Vinney, PhD is an expert in media psychology and a published scholar whose work has been published in peer-reviewed psychology journals.

COMMENTS
The major cognitive processes in problem solving are representing, planning, executing, and monitoring. The major kinds of knowledge required for problem solving are facts, concepts, procedures, strategies, and beliefs. Classic theoretical approaches to the study of problem solving are associationism, Gestalt, and information processing.
As you shall see, however, there are many pitfalls in the cognitive processes described in this module. When people do not devote extra effort to learning and improving reasoning, problem solving, and critical thinking skills, they make many errors.
Cognitive psychology is the study of internal mental processes—all of the workings inside your brain, including perception, thinking, memory, attention, language, problem-solving, and learning. Learning about how people think and process information helps researchers and psychologists understand the human brain and assist people with psychological difficulties.
The cognitive perspective in psychology focuses on how the interactions of thinking, emotion, creativity, and problem-solving abilities affect how and why you think the way you do. Cognitive ...
In cognitive psychology, the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
While research into cognitive psychology, cognitive neuropsychology, cognitive neuroscience, and computational cognitive science is now widely accepted as the driving force behind understanding mental processes (such as memory, perception, problem-solving, and attention), this was not always the case (Gross, 2020).
Cognitive psychology is the field of psychology dedicated to examining how people think. It attempts to explain how and why we think the way we do by studying the interactions among human thinking, emotion, creativity, language, and problem solving, in addition to other cognitive processes. Cognitive psychologists strive to determine and ...
This chapter summarizes key lessons learned about the interplay of feeling and thinking and addresses their implications for problem solving. To set the stage, we begin with a summary of key elements of the problem-solving process.
Thinking and Problem-Solving presents a comprehensive and up-to-date review of literature on cognition, reasoning, intelligence, and other formative areas specific to this field. Written for advanced undergraduates, researchers, and academics, this volume is a necessary reference for beginning and established investigators in cognitive and ...
Simply put, cognition is thinking, and it encompasses the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgment, language, and memory. Scientists who study cognition are searching for ways to understand how we integrate, organize, and utilize our conscious cognitive experiences without being aware of all of the unconscious ...
Learn about problem-solving, a mental process that involves discovering and analyzing a problem and then coming up with the best possible solution.
The major cognitive processes in problem solving are representing, planning, executing, and monitoring. The major kinds of knowledge required for problem solving are facts, concepts, procedures, strategies, and beliefs. Classic theoretical approaches to the study of problem solving are associationism, Gestalt, and information processing.
Thinking as subject matter of cognition, is covered as a section by most texts on cognitive psychology; The Psychology of Thinking: Reasoning, Decision-Making, and Problem-Solving is aimed at studying the psychology of thinking and evaluating advanced concepts of cognition using a thinking approach.
Thinking and Problem-Solving presents a comprehensive and up-to-date review of literature on cognition, reasoning, intelligence, and other formative areas specific to this field. Written for advanced undergraduates, researchers, and academics, this volume is a necessary reference for beginning and established investigators in cognitive and educational psychology. Thinking and Problem-Solving ...
The word "cognitive" refers to thinking. So cognitive psychology is a branch of psychology that aims to understand mental processes such as perception, learning, memory, language, decision-making, and problem-solving. It also examines how these processes affect our behavior and our emotions (APA, 2023).
Cognitive psychology studies mental processes, including how people perceive, think, remember, learn, solve problems, and make decisions. Cognitive psychologists try to build cognitive models of the information processing that occurs inside people's minds, including perception, attention, language, memory, thinking, and consciousness ...
This second edition of "Thinking, Problem Solving, Cognition" retains the same goal as the first: to introduce the reader to our current understanding of the cognition side of cognitive psychology. . . . The book's intended audience is also the same: students in such courses as cognitive psychology, learning and memory, problem solving ...
Cognitive psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on studying mental processes such as thinking, perception, memory, language, problem-solving, and decision-making. It seeks to understand how humans acquire, store, process, and use information daily. Cognitive psychology explores the mind's inner workings and investigates how ...
Simply put, cognition is thinking, and it encompasses the processes associated with perception, knowledge, problem solving, judgment, language, and memory. Scientists who study cognition are searching for ways to understand how we integrate, organize, and utilize our conscious cognitive experiences without being aware of all of the unconscious ...
Cognitive psychology is the field of psychology dedicated to examining how people think. It attempts to explain how and why we think the way we do by studying the interactions among human thinking, emotion, creativity, language, and problem solving, in addition to other cognitive processes.
Cognitive psychology seeks to understand all of the mental processes involved in human thought and behavior. It focuses on cognitive processes such as decision-making, problem-solving, attention, memory, learning, and more. Keep reading to learn more about different types of cognitive processes, factors that can affect cognition, and the ...
For example, if problem solving is defined in terms of cognitive rather than neurophysiological, biological, or behavioral processes, then it makes little sense to construct a theory of problem solving at a neurophysiological, biological, or behavioral level.
Cognitive psychology is defined as the study of internal mental processes. Such processes include thinking, decision-making, problem-solving, language, attention, and memory. The cognitive approach in psychology is often considered part of the larger field of cognitive science. This branch of psychology is also related to several other ...
In clinical settings, cognitive psychologists seek to treat issues related to human mental processes, including Alzheimer's disease, speech issues, memory loss and sensory or perception difficulties. Brain science and cognitive psychology focuses on how individuals learn, process and store information.
An in-depth analysis of collaborative problem solving (CPS) patterns contributes to understand team dynamics and effective paths to conflict resolution. However, there remains the lack of a perspective in the field of CPS research that organically combines the cognitive, meta-cognitive, and social-communicative dimensions. Moreover, the analysis of CPS sequences has primarily focused on the ...
Developing math skills, engaging in strategy games and logic problems, explaining your thinking, and using your skills in the real world can help develop your logical mathematical intelligence and have you on your way to unlocking your problem-solving potential.