For a better experience, please use a modern browser like Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Edge.

London Business School Publishing
- Create a profile

- Browse cases
- How to order
Preview case
Click Preview case to review the first page of this case
The Rise and Fall of Nokia
By julian birkinshaw , lisa duke.
The case describes Nokia’s spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company’s handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010.During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia’s focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation. It was acknowledged as the first smartphone manufacturer. Through the early-mid 2000s it was the undisputed leader in the global mobile phone business. The case traces the first signs of trouble and the company’s subsequent decline over the period 2005 to 2010. Pressure in the early 2000s from low-end competitors led to early signs of problems. Then of course the game changed in 2007 with Apple’s iPhone and a year later with phones powered by Google’s Android operating system from HTC, Samsung and others. Nokia was initially dismissive of these new offerings but its proprietary OS, Symbian, was ageing badly and its App store (Ovi) was no match for Apple’s. In September 2010 it was announced that American Stephen Elop, formerly of Microsoft, would become CEO. Not long afterwards a partnership with Microsoft was signed which subsequently led to Nokia’s handset business being sold to Microsoft.
Learning objectives
- Understand why good companies go bad; in other words, see how the assets that enable companies to succeed can also be liabilities when the market turns against them.
- Provide insight into the nature of disruption in an established industry and why incumbent firms struggle to adapt.
- Examine the different paths companies should take to respond to disruptive forces.
- Understand the leadership challenge for executives when their performance starts to decline2. To understand the dynamics of change in a fast-changing industry.
- Identify strategies companies can use to adapt quickly to disruptive changes.
Other cases in Strategy

- Entrepreneurship
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Management Science and Operations
- Organisational Behaviour
- Organizational Behaviour and Strategy’
- Sustainability
Privacy Overview
Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia’s Mobile Phone Business
- First Online: 30 July 2018
Cite this chapter

- Tuomo Peltonen 2
2091 Accesses
2 Citations
14 Altmetric
This chapter provides a wisdom-oriented reading of one of the most spectacular business failures of recent times: the collapse of Nokia mobile phones between 2007 and 2015. Using executive biographies and other published accounts of Nokia’s organisational patterns, the chapter attempts to offer a more balanced explanation of the processes behind Nokia’s inability to respond to the changing industry circumstances. The following analysis pays attention to the shaping of Nokia’s organisational culture. Company and its new leadership adopted a professional, no-nonsense approach in the aftermath of the problems of the late 1980s and early 1990s. The new generation of managers believed in a rational mindset supported by a bureaucratic organisational form. Leaning on a superior technological competence within the mobile phone sector, Nokia was capable of ultimately becoming the market leader. However, in 2007, with two major players, Apple and Google, joining the business, the established rules of competitive dynamics were irrevocably changed. Focus shifted to software and applications. Nokia’s risk-aversive and closed organisational culture could not respond in a situation where an open search for new innovations and a cooperative internal working mode were needed. An analysis of the development of Nokia’s organisational psyche following the emergence of a new generation of managers and executives highlights the role of local beliefs in using philosophical wisdom in critical circumstances. Nokia and its leadership were not able to abandon the outmoded habits and structures, as these had become integrated with the very identity of the company.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibliography
Agarwal, R., & Helfat, C. E. (2009). Strategic renewal of organizations. Organization Science, 20 (2), 281–293. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.1090.0423 .
Article Google Scholar
Alahuhta, M. (2015). Johtajuus [Leadership]. Helsinki: Bookwell.
Google Scholar
Borden, M. (2009, January 9). Nokia rocks the world: The phone King’s plan to redefine its business. Fast Company . https://www.fastcompany.com/1325729/nokia-rocks-world-phone-kings-plan-redefine-its-business . (read 1.4.2018).
Brannen, M. Y., & Doz, Y. L. (2012). Corporate languages and strategic agility: Trapped in your jargon or lost in translation? California Management Review, 54 (3), 77–97. https://doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2012.54.3.77 .
Bryman, A. (2015). Social research methods . Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781849209939 .
Cooper, R. (1986). Organization/Disorganization. Social Science Information, 25 (2), 299–335.
Cooper, R. (1997). The visibility of social systems. In K. Hetherington & R. Mundo (Eds.), Ideas of difference (pp. 32–41). Oxford: Blackwell.
Cord, D. J. (2014). The decline and fall of Nokia . Helsingfors: Schildt & Söderström.
Donaldson, L. (2001). The contingency theory of organizations . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Book Google Scholar
Häikiö, M. (2009). Nokia – matka maailman huipulle [Nokia – the journey to the top of the world] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Edita.
Heikkinen, M.-P. (2010). Mokia. Helsingin Sanomat , April 27, 2011. http://www.hs.fi/kuukausiliite/a1305875065676 (read 1.4.2018).
Insead. (2014). The decline of Nokia: Interview with former CEO Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo. Insead Knowledge , April 12, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jR5a_DBYSmI
Isaacson, W. (2011). Steve Jobs . Helsinki: Otava.
Kärppä, H. (2016). Tässä ovat 2000-luvun suurimmat irtisanomiset – kärkisijoilla Nokia ja Microsoft [The biggest layoffs during the 2000’s] (in Finnish). Helsingin Sanomat. http://www.hs.fi/talous/a1459916372158 (read 1.4.2018).
Kortteinen, M. (1992). Kunnian kenttä: suomalainen palkkatyö kulttuurisena muotona [Field of honor: Finnish work as a cultural form] (in Finnish). Hämeenlinna: Karisto.
Laamanen, T., Lamberg, J. A., & Vaara, E. (2016). Explanations of success and failure in management learning: What can we learn from Nokia’s rise and fall? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 15 (1), 2–25.
Linden, C.-G. (2015). Nokia och Finland [Nokia and Finland] (in Swedish). Helsinki: Schildt & Söderström.
March, J. G., & Sutton, R. I. (1997). Organizational performance as a dependent variable. Organization Science, 8 (6), 698–706 http://doi.org/Article .
Milne, R. (2009, March 23). Jorma Ollila: Champion of Nordic capitalism. Financial Times . http://royaldutchshellplc.com/2009/03/23/jorma-ollila-champion-of-nordic-capitalism/ (read 1.4.2018).
Nykänen, M., & Salminen, M. (2014). Operaatio Elop [Operation Elop] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Teos.
Ollila, J. (2016, Augest 29). Tervetuliaispuhe Etlan 70-vuotisjuhlaseminaarissa [Welcome speech in the 70th anniversary of Etla] (in Finnish). https://www.etla.fi/wp-content/uploads/Jorma-Ollila-Etla70.pdf (read 1.4.2018).
Ollila, J., & Saukkomaa, H. (2013). Mahdoton menestys: kasvun paikkana Nokia [Impossible success: Nokia as a place for growth] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Otava.
Ollila, J., & Saukkomaa, H. (2016). Against all odds: Leading nokia from near catastrophe to global success . Palmyra, VA: Maven House.
Palmu-Joroinen, A.-L. (2009). Nokia-vuodet [Nokia years]. Helsinki: Atena.
Ristimäki, M. (2006, October 13). Nokian ex-pomo: nykyjohtajilta puuttuu yleissivistys [Ex-Nokia boss: Current leaders are lacking general education]. Taloussanomat . http://www.iltasanomat.fi/taloussanomat/art-2000001477674.html (read 1.4.2018).
Taleb, N. N. (2007). The black swan: The impact of the highly improbable . New York: Random house.
The Editorial Staff of Ylioppilaslehti. (2004, April 9). Tuhannen ja yhden yön taistolaisuus [The Stalinism of thousand and one nights]. Ylioppilaslehti . http://ylioppilaslehti.fi/2004/04/274/ (read 1.4.2018).
Virtanen, J. (2013). Näin Nokia on irtisanonut Suomessa [This is the way Nokia has laid off employees in Finland]. Yle Uutiset . http://yle.fi/uutiset/3-6455026 (read 1.4.2018).
Vuori, T. O., & Huy, Q. N. (2016). Distributed attention and shared emotions in the innovation process: How Nokia lost the smartphone battle. Administrative Science Quarterly, 61 (1), 9–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0001839215606951 .
Weber, M. (1976). Protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism (4th ed., T. Parsons, Trans.). London: Allen & Unwin (Original work published 1930).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Business, Aalto University, Helsinki, Finland
Tuomo Peltonen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Peltonen, T. (2019). Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia’s Mobile Phone Business. In: Towards Wise Management. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91719-1_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91719-1_6
Published : 30 July 2018
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-91718-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-91719-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
What Happened To Nokia? The Rise And Fall Of A Tech Giant

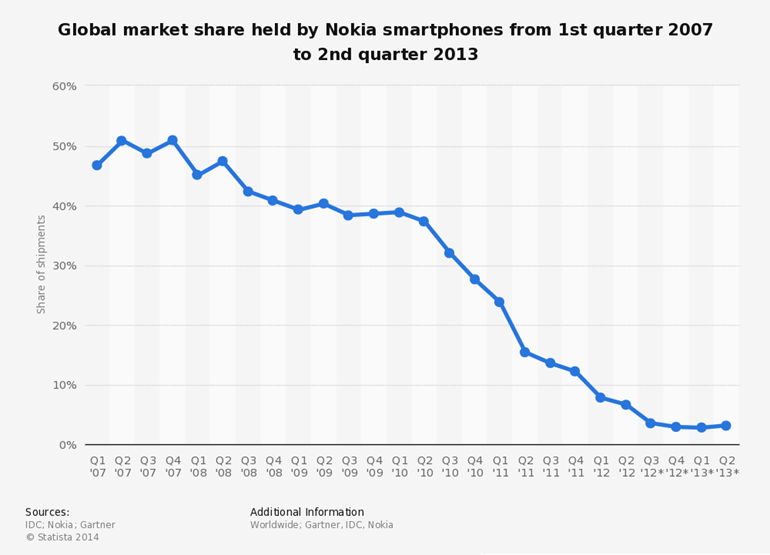
In the 2000s, everyone had a Nokia phone. Known and desired for its durability and ease of use, it became the preferred device for many worldwide. According to the BBC , Nokia's market share in 2007 was dominant, maintaining a 49.4% hold over the entire mobile phone market. While it would continue to lose market share over the subsequent years, Nokia managed to maintain the top position for over a decade before it started to decline.
Fast-forward to 2013 — just six years later — and the company made up less than 3% of the total mobile phone market and sought to exit the industry altogether. With such a meteoric rise and what seemed like complete control over the industry, it makes sense to wonder how it all went wrong.
Like most stories of massive business failures, it was likely not a result of just one poor action but a compilation of unfortunate circumstances and decisions. However, as it turns out, not everything is so dark for the company, as it still operates today.
Nokia had humble beginnings
It may surprise some to learn that Nokia didn't even start as a tech company at all. Established in 1865 in Finland, Nokia started as a pulp mill for paper manufacturing. Named after the town in which it was based, the company partnered with local companies, like Finnish Cable Works, as it expanded its operations.
Eventually, it merged with Finnish Cable Works and Finnish Rubber Works to form the Nokia Corporation. It would go on to enter and become a major factor in the electronics industry by the 1970s. While it still retained its other business lines, it would be largely known for its mobile phones. Ultimately, it would start to divest money into its rubber and paper operations and concentrate solely on tech and phones.
Nokia began its journey in the mobile phone market in the 1980s as it went on a string of acquisitions to solidify its position as a leading global tech firm. With acquisitions of Salora, Mobria, and the Information Systems division of Ericsson, the company was quickly on its way to producing its first mobile phone. This would be the 1982 Mobria Senator car phone, which would go on to influence designs for phones that we use to this day.
The early 2000s was the golden era for Nokia
The early 2000s was arguably the golden era for the company, with its best-selling cellphones, the Nokia 1100 and Nokia 1110, released in 2002 and 2005, respectively. This would result in the company's most profitable year ever, earning them $51 billion in sales in 2007, according to Statista .
This was also, coincidentally, the same year the first iPhone was released, which was considered a new and emerging technology at the time. Unfortunately, no one saw the future coming, including Nokia, as the iPhone would be one large factor in its downfall.
Nokia would continue this success to 2010, with over 30% of the market share over the entire mobile phone industry. This, however, would all come to a screeching halt within just a few short months as competitors like Samsung, HTC, and Apple began to dominate the industry. By April 2012, Samsung had taken over the top spot from Nokia . While Nokia would plan a few more product offerings, it would eventually exit the industry altogether.
Nokia refused to evolve
There were a variety of reasons that Nokia started to fall out of favor with consumers, but perhaps the biggest reason had to do with the phones themselves. While the company did dominate the mobile phone industry for over a decade, it did not dominate the smartphone industry, which was just emerging at the time with stiff competition from companies like Motorola , Samsung, and Huawei. Consumers were willing to pay for a slightly more expensive device with a good user experience and app support.
Nokia phones ran on Symbian OS, which seemed inadequate and obsolete to iPhone and Android users. In a leaked internal memo from 2011, Nokia's then-CEO, Stephen Elop, lamented that the company still did not "have a product that is close to their experience" when speaking directly about the iPhone. While a few years of floundering might not seem so devastating, it only took that short span of time for Nokia's flagship product to become obsolete.
Nokia began to adapt too late
By the time Nokia jumped on the smartphone wave, it was too late and with the wrong partner. Instead of creating devices compatible with the new and popular Android OS, Nokia instead opted to go with Microsoft and its Windows Phone 7 operating system in 2011. This would be disastrous for the company in retrospect, with Nokia posting its second quarterly loss for the first time in nearly two decades.
While the company would continue to flounder due to increased competition in the space, some of its phones, like the newer Lumia models, were actually somewhat competitive. However, it was too little, too late, and in September 2013, Nokia officially sold its mobile and devices division to Microsoft.
However, that wasn't the end for Nokia, and after a completely failed mobile launch from Microsoft — which lost at least $8 billion for the company — Nokia mobile phones would once again be sold. This time, it would be by a company founded by former Nokia employees called HMD Global. Nokia phones today are being manufactured by Foxconn subsidiary, FIH Mobile.
The future of Nokia
Nokia exists today, albeit it is concentrating on new areas of tech. Along with a recent re-brand, the company refocused its operations on telecommunications and industrial digitalization, while HMD Global still sells phones under the Nokia name. While the failings of its mobile phone branch are one of the most epic falls in the history of any global corporation, the company itself is far from a failure.
In addition to a licensing agreement with HMD Global, the company also acquired Alcatel-Lucent and Bell Labs to work on cutting-edge technology and continues to be a major patent licensor to various mobile phone vendors worldwide. The company has a line of affordable and more high-end cell phones and an affordable line of tablets that it sells online today.
Ultimately, while Nokia failed miserably after holding the top position in the mobile phone market, it was divested from the business line in time. In reality, it's Microsoft that ended up losing money in the deal and suffering from Nokia's failures. The company is now successful, boasting positive annual gross profit in the billions since 2021.
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- November 2020
- HBS Case Collection
The Rise and Fall of Nokia (Abridged)
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 24
About The Authors
Juan Alcacer
Tarun Khanna
More from the authors.
- March 2024 (Revised March 2024)
- Faculty Research
Alphabet Eyes New Frontiers (B)
- November 2023
Introduction to the RC Strategy Course 2024
Biocon biologics, 2023.
- Alphabet Eyes New Frontiers (B) By: Juan Alcácer, Raffaella Sadun and Kate Stoppiello
- Introduction to the RC Strategy Course 2024 By: Juan Alcacer
- Biocon Biologics, 2023 By: Tarun Khanna and Radhika Kak

9 Reasons Why Nokia Failed After Enjoying Unrivaled Dominance

Devashish Shrivastava , Akshat Hawelia
In the annals of mobile phone history, Nokia once reigned supreme with its robust devices and iconic brand. However, as the smartphone revolution took hold, Nokia's fortunes took a sharp turn, leading to a notable decline in its market share and influence. The fall of such a prominent industry leader begs the question: What were the reasons behind Nokia's failure?
This post focuses on the reasons why Nokia failed after enjoying unrivaled dominance in the mobile segment for several years. The ferocious and mighty telecom giant Nokia was well known for its products' hardware and battery life. By understanding the lessons from Nokia's journey, we can gain valuable insights into the rapidly evolving landscape of the technology industry and the critical importance of adaptation and innovation.
For years, it was the talk of the town. User satisfaction with Nokia’s mobiles was globally recognized. The company launched the first internet-enabled phone in 1996, and by the start of the millennium, Nokia had also released a touch-screen mobile prototype.
This was the start of a revolution in the mobile phone industry. The Finnish giant was the largest cell phone maker in 1998. Nokia overtook Motorola, a move that was hard to predict. So, what led to the downfall of Nokia? It wasn’t a single factor but a myriad of reasons, most of which resulted from Nokia's resistance to change. We present to you the six main reasons behind Nokia's failure.

List of Courses Curated By Top Marketing Professionals in the Industry
These are the courses curated by Top Marketing Professionals in the Industry who have spent 100+ Hours reviewing the Courses available in the market. These courses will help you to get a job or upgrade your skills.
Reasons for Nokia Failure: Case Study
The resistance to smartphone evolution, the deal with microsoft, nokia's failed marketing strategies, moving too slow with the industry, overestimation of strength, lack of innovation in products, organizational restructuring at nokia, the symbian vs. meego os dilemma at nokia, failure to adapt and reposition.

In the fast-paced world of technology, companies that fail to adapt to changing trends and consumer demands can quickly find themselves left behind. Nokia, once synonymous with mobile phone supremacy, experienced a significant downfall due to its resistance to smartphone evolution. As competitors embraced the shift towards smartphones, Nokia's reluctance to fully embrace this revolution became one of the key reasons for its failure.
Nokia failed to take advantage of the Android bandwagon. When mobile phone manufacturers were busy improving and working on their smartphones, Nokia remained stubborn. Samsung soon launched its Android-based range of phones that were cost-effective and user-friendly.
Nokia's management was under the impression that people wouldn’t accept touchscreen phones and would continue with the QWERTY keypad layout. This misapprehension was the start of its downfall. Nokia never considered Android as an advancement and neither wanted to adopt the Android operating system.
After realizing the market trends, Nokia introduced its Symbian operating system, which was used in its smartphones. It faced usability issues and lacked the app support and developer ecosystem that rival platforms like iOS and Android offered. The clunky user experience and limited app selection hampered Nokia's ability to compete effectively. Also, it was too late by then, with Apple and Samsung having cemented their positions. It was difficult for the Symbian operating system to make any inroads. This is the biggest reason behind Nokia's downfall.
Nokia was slow to recognize the potential of smartphones and the shift from feature phones to touchscreen devices. They failed to anticipate the demand for devices with advanced capabilities, such as app ecosystems and touch interfaces. This led to a loss of market share to competitors like Apple's iPhone and Android-based smartphones.
Another reason for Nokia's failure was the ill-timed deal with the tech giant Microsoft . The company sold itself to Microsoft at a time when the software behemoth was fraught with losses.
Nokia's sales screamed the mobile phone maker's inability to survive on its own. At the same time, Apple and Samsung were making significant strides in innovation and technological developments.
It was too late for Nokia to adapt to the dynamic and rigorous changes in the market. Microsoft’s acquisition of Nokia is considered to be one of the biggest blunders and wasn't fruitful for either side.
The partnership limited Nokia's ability to differentiate itself and left it dependent on Microsoft's success in the mobile industry . The Windows Phone platform struggled to gain traction, further impacting Nokia's market position. This case study provides valuable lessons for businesses considering similar alliances and emphasizes the importance of aligning visions, complementary strengths, and adaptable strategies.

Marketing plays a crucial role in shaping a brand's success and perception. In the case of Nokia, its decline can be attributed, in part, to failed marketing strategies that hindered its ability to compete effectively in the mobile phone market.
One notable misstep in Nokia's marketing approach was its unsuccessful implementation of umbrella branding . Companies like Apple and Samsung successfully adopted the umbrella branding model, with flagship products like the iPhone and Samsung Galaxy series acting as the focal point for expanding their product lines. However, Nokia failed to follow suit and capitalize on the umbrella branding strategy, missing out on the opportunity to create a cohesive and recognizable brand identity.
Additionally, Nokia's marketing efforts struggled to maintain the user trust that the company had built over the years. Inefficient selling and distribution methods further eroded consumer confidence and made it difficult for Nokia to reach its target audience effectively.
While Nokia attempted to regain momentum by introducing hardware and software innovations, these offerings were often late to the market and lacked the uniqueness that would have set them apart from competitors. Rivals had already released similar features and devices, diminishing Nokia's ability to capture consumers' attention and regain market share.
The failure of Nokia's marketing and distribution strategies played a significant role in its ultimate decline and exit from the mobile industry market. Without a strong brand identity, effective distribution channels, and timely innovations, Nokia struggled to compete with rivals who had successfully aligned their marketing strategies with evolving consumer preferences and market dynamics.
Nokia's failure to keep pace with changing technology and trends played a significant role in its decline. While the company had earned a reputation for its hardware, it didn't prioritize its software lineup, which proved to be a crucial oversight.
Initially, Nokia was cautious about embracing technical advancements in order to mitigate the risks associated with introducing innovative features to its phones. However, this approach hindered the company's ability to adapt to the rapidly evolving market.
The business needed diversification, but it was too late by the time Nokia realized this. Instead of being amongst the early initiators, Nokia transitioned when almost every major brand had already started producing awesome phones.
This case study shows Nokia's failure to keep up with changing technology and its delayed response to industry trends significantly contributed to its downfall.
Nokia overestimated its brand value. The company believed that even after the late launch of its smartphones, people would still flock to stores and purchase Nokia-manufactured phones. This turned out to be a misconception, as consumer preferences had shifted towards other brands.
People still make predictions that Nokia will retain the market leadership if it uses better software at its core. However, this is far from the truth, as seen today.
The company got stuck with its software system, which is known to have several bugs and clunks. Nokia felt its previous glory would help alleviate any sort of trouble. Unfortunately, things didn’t play out that way.
Unfortunately, the market dynamics had changed, and consumers were no longer willing to overlook the shortcomings of Nokia's software. Competitors had surpassed Nokia in terms of user experience and software innovation, leaving Nokia struggling to regain its position.
Nokia's lack of innovation in its products significantly contributed to its failure case study. While brands like Samsung and Apple came up with advanced phones every year, Nokia simply launched the Windows phone with basic features, failing to keep up with the industry's rapid progress..
The Nokia Lumia series was a jump-start measure, but even that collapsed due to a lack of innovation. The unattractive and dull features didn’t help. In the era of 4G, Nokia didn’t even have 3G-enabled phones. Nokia also came up with the Asha series, but it was game over by then.
Wrong decisions and risk aversion brought about the decline of the mobile giant. Nokia refrained from adopting the latest tech. Nokia's failure became a powerful case study that made organizations realize the importance of continuous evolution and enhancements. The journey of what was once the world’s best mobile phone company to losing it all by 2013 is quite tragic. Nokia's failure was not solely due to its lack of innovation but also its shortcomings in leadership and guidance. These factors, combined with its inability to adapt to market demands and technological advancements, sealed the company's fate.

Want to Work in Top Gobal & Indian Startups or Looking For Remote/Web3 Jobs - Join angel.co
Angel.co is the best Job Searching Platform to find a Job in Your Preferred domain like tech, marketing, HR etc.
Nokia underwent a sudden and significant organizational shift by adopting a matrix structure driven by enhancing agility within the company. However, this abrupt change resulted in dissatisfaction among stakeholders, particularly as key individuals in top management departed from the organization. These individuals, who had played instrumental roles in establishing Nokia as a leading company, were no longer part of the decision-making process .
The shift to a matrix structure also brought about internal challenges, as stability in top management, a crucial element for organizational coherence, was disrupted. Over just five years, Nokia experienced two CEO replacements , preventing employees from fully adapting to new leadership goals and visions. The frequent changes in leadership created instability and hindered consistent strategic direction. The lack of continuity in leadership contributed to employee dissatisfaction and impacted the overall cohesiveness of the organization. Employees and other stakeholders found it challenging to align with successive CEOs, leading to a breakdown in communication and a sense of disconnect within the company.
Nokia Changes their Logo After 60 Years
Nokia's problem arose when its R&D division underwent a split, with one faction dedicated to enhancing the Symbian operating system and the other focused on developing MeeGo. The competing claims of superiority between the two teams led to internal friction, causing delays in the release of new phones. The company grappled with the challenge of harmonizing divergent technological directions, impacting its ability to bring innovative products to market in a timely manner. This internal competition within the R&D division created a complex dynamic, hindering Nokia's efficiency and potentially affecting its competitive edge in the rapidly evolving smartphone market.

Nokia's downfall can be attributed to its failure to analyze market trends and adjust its strategy accordingly. The company neglected the burgeoning smartphone market, ultimately missing a significant opportunity for growth. Rather than capitalizing on this evolving landscape, Nokia could have revitalized its position by enhancing its existing software, such as Symbian. Unfortunately, the lack of strategic foresight and adaptability led to a missed chance to stay competitive in the dynamic tech industry.
Moreover, the oversight in market analysis and strategic planning eroded Nokia's market share and diminished its relevance in the rapidly changing consumer electronics landscape. The company's reluctance to pivot and innovate in response to market dynamics ultimately contributed to its decline in the face of evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements.
The fall of Nokia can be attributed to a combination of factors that hindered its ability to adapt, innovate, and stay competitive in the mobile phone market. The resistance to smartphone evolution, missed opportunities, ineffective marketing strategies, and the deal with Microsoft all contributed to its downfall. Ultimately, Nokia's decline serves as a reminder of the importance of staying agile, embracing change, and continuously evolving to meet consumer demands.
Why did Nokia fail?
Not switching to Android, lack of innovation, not upgrading the software, and overestimating the brand value were some of the reasons that led to Nokia's failure.
What is Nokia?
Nokia is a consumer electronics company popular for its mobile phones. It is one of the largest mobile phone manufacturers in the world.
Is the Nokia company closed?
No, the company is still running, but it has shut down some of its plants.
What happened to Nokia?
Once a dominant force, Nokia clung to outdated software, allowing Android and iOS to surge ahead, leaving the brand lagging. Despite its focus on new technologies, Nokia's legacy now lives on in the realm of Android.
Why did Nokia fail to compete with Samsung and Apple?
Nokia didn't adopt Android and focused on its hardware more than its software, which is why it failed to compete against Samsung and Apple.
Are there any new Nokia smartphones coming in the near future?
Though Nokia might seem dominant on the phone front, the company occasionally comes up with some new phones/smartphone devices. Here are some of the Nokia smartphones that are likely to be launched in 2022:
- Nokia 2760 Flip 4G
- Nokia C21 Plus
- Nokia Suzume
- Nokia C2 2nd Edition
Who took over Nokia?
Nokia phones were robust and dependable companions of the pre-smartphone era. However, Nokia's Java and Windows phones failed to stand out in the market dominated by Apple and Android phones. The Android phone manufacturing companies like Samsung, LG, HTC, Sony, Motorola, and other Chinese smartphone developers like MI, Realme, Oppo, Vivo, and the Apple IOS devices took over Nokia in the mobile sector.
What lessons can other businesses learn from Nokia's failure?
Nokia's failure highlights the importance of embracing change, anticipating market trends, and continuously innovating to meet customer expectations. It underscores the need for effective marketing strategies, strategic partnerships, and an unwavering commitment to adaptation and innovation in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Was Nokia's lack of innovation a significant factor in its decline?
Yes, Nokia's lack of innovation in its product lineup played a significant role in its downfall. The company failed to keep pace with rivals who consistently introduced advanced devices and embraced evolving market demands, which resulted in Nokia losing its competitive edge.
Why did Nokia go out of business?
Nokia lost its phone industry dominance by sticking to outdated software, missing the smartphone revolution, and experiencing a significant sell-off. Despite not going out of business, Nokia's cautionary tale highlights the vital role of innovation in a rapidly evolving tech landscape, with the company still present in network tech and patents.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Payment Gateway- Razorpay
- Spy on your Competitors- Adspyder
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
How to Craft an Impressive Internship Resume: Step-by-Step Guide
This article has been contributed by Mr. Rajat Vashishta, Career Coach & Founder, Resumod. The job market has become quite competitive and an internship is the stepping stone for a successful career. As you are applying for your dream internship, your resume should create a good impression on the recruiter. Although,
The Business Behind Free Apps: How They Make Money Without Charging You
Free apps are ubiquitous on our phones and tablets. From social media giants to addictive games, these seemingly free offerings dominate the app stores. But how exactly do these apps make money if they don't charge upfront? The answer lies in a sophisticated web of monetization strategies designed to leverage
How Mobicule Utilise AI to Improve Debt Collection Process
This article has been contributed by Siddharth Agarwal, Founder and Managing Director, Mobicule Technologies Pvt Ltd. The recovery of loans is frequently the top priority for lenders in the field of lending because the risk of defaulting is constant. Lenders are increasingly using technology-driven solutions to help in the recovery
Groww: How It Is Changing the Traditional Ways of Investing
Company Profile is an initiative by StartupTalky to publish verified information on different startups and organizations. Investing a decade ago entailed a lot of paperwork, many bank visits, long queues, and application processing that used to take days. When you add in a dearth of knowledge about financial products and
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Real Cause of Nokia’s Crisis
- Michael Schrage
Nokia’s technology isn’t a root cause of its current crisis. Don’t blame its engineers and designers either. The company still knows how to innovate. There’s a simpler and more strategic explanation for why this once-perennial market leader became second-rate. Nokia ignored America. The company simply refused to compete energetically, ingeniously and respectfully in the U.S. […]
Nokia’s technology isn’t a root cause of its current crisis. Don’t blame its engineers and designers either. The company still knows how to innovate . There’s a simpler and more strategic explanation for why this once-perennial market leader became second-rate.
- MS Michael Schrage , a research fellow at MIT Sloan School’s Center for Digital Business, is the author of the books Serious Play (HBR Press), Who Do You Want Your Customers to Become? (HBR Press) and The Innovator’s Hypothesis (MIT Press).
Partner Center
The Brand Hopper
All Brand Stories At One Place
The Rise and Fall of Nokia – Why and How Nokia Failed?

The Rise and Fall of Nokia – Why and How Nokia Failed? 12 min read
During the early 2000s, Nokia reigned supreme in the mobile phone market, boasting a significant global market share. Back then, Nokia faced little competition as it offered highly acclaimed and popular products like the Nokia 1280, Nokia 5300, Nokia N91, and Nokia N95. However, the brand’s fortunes took a nosedive as it witnessed a gradual decline in market share, eventually ceding ground to rivals such as Apple and Samsung. In 2014, acknowledging its inability to sustain a presence in the mobile phone market, Nokia made the decision to sell its mobile phone business to Microsoft. What led to the downfall of this once mighty mobile industry leader in a mere span of ten years? This article delves into the events that unfolded at Nokia and the valuable insights garnered from its story.
Table of Contents
The rise of Nokia
1865: nokia was found.

Established in 1865 by Fredrik Idestam, an esteemed engineer in Tempere, Finland, the company we now know as Nokia had humble beginnings. Initially, the business focused on operating a pulp mill and producing paper goods. In 1871, a second factory was opened alongside the banks of the Nokianvirta river, providing the inspiration for the company’s eventual name, Nokia Ab. It was not until 1979 that Nokia ventured into telecommunications research and manufacturing.
Initially, their offerings predominantly consisted of radio equipment, desk phones, and televisions. In the same year, Nokia made the strategic decision to merge with Salora Oy, an enterprise specializing in electrical equipment. Subsequently, the mobile device business was separated from the merged entity, establishing Nokia – Mobira Oy as a distinct entity. This significant development marked Nokia’s official entry into the mobile phone manufacturing industry.
1984: Nokia’s first mobile phone

In 1984, Nokia made its debut in the mobile phone industry by introducing the Mobira Cityman 900 to the public. This mobile phone operated on the NMT-900 network, offering improved signal strength compared to existing networks. Additionally, with a weight of only 800g, it was significantly lighter than other portable products available at the time, such as the Mobira Senator weighing 9.8kg and the Talkman weighing under 5kg. During this era, mobile phones were considered luxury devices reserved for the elite, including aristocrats and royalty. However, due to the sleek design and advancements of the Mobira Cityman 900, it quickly became highly coveted among affluent individuals.
In 1987, a noteworthy incident occurred when a reporter spotted Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev using a Mobira Cityman in Helsinki. This occurrence led to the phone earning the nickname “Gorba,” further enhancing its reputation and desirability.
Recognizing the immense potential of the mobile phone market, Nokia-Mobira Oy underwent a name change in 1989, adopting the name “Nokia Mobile Phones.” The company remained dedicated to significant investments in research and development, aiming to continuously innovate and introduce new products to the market.
The Nokia 1011 marked the next major milestone in Nokia’s journey of innovation
In 1987, Nokia achieved a significant breakthrough with the introduction of a groundbreaking phone, known as ‘The Brick’ or the Nokia 1011. This remarkable device became the first mass-produced GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) phone, catapulting Nokia to new heights in the telecommunications industry. The Nokia 1011 boasted a compact design, measuring 195 x 60 x 45 mm, which was notably smaller compared to other phones available at the time. It featured a monochrome LCD display and an expandable antenna, offering users enhanced functionality and convenience.
Moreover, the Nokia 1011 showcased innovative features, including the ability to store up to 99 phone numbers in its memory and the capability to send SMS messages. These features, along with its compact design, made the Nokia 1011 an instant success upon its release, elevating Nokia’s reputation and influence in the telephony and telecommunications market. It is worth noting that although mobile phones were not yet widely accessible during this period, the Nokia 1011 garnered substantial acclaim and contributed to Nokia’s growing prominence.
1996: Nokia 9000 Communicator & Nokia 8110

In 1996, Nokia unveiled the Nokia 9000 Communicator, a groundbreaking phone that signaled the company’s strategic advancement. Priced at $800, this product ushered in a new era of capabilities, enabling users to access email, fax, and web browsing, while also providing word processing and spreadsheet functionalities. Despite industry recognition, the Nokia 9000 Communicator faced challenges due to its less user-friendly design and suboptimal user experience. Consequently, it did not achieve significant commercial success. Nonetheless, this product stood as a testament to Nokia’s commitment to technological innovation and breakthroughs, as the industry continually values advancements that push the boundaries of possibility.
That same year, the company also released the Nokia 8110 slider phone. The product was also nicknamed the “banana phone”, appearing in the popular 1999 sci-fi action film The Matrix.
1998: Dominating the global mobile phone market

In 1988, Nokia introduced the highly anticipated Nokia 6100 series, marking the dawn of a new era in mobile phone technology. This innovative product line showcased Nokia’s prowess and propelled the company into the global spotlight. The Nokia 6100 series featured a compact design, user-friendly buttons, and an LCD screen, offering consumers a seamless and enjoyable mobile experience. Additionally, the inclusion of the legendary Snake game, pre-installed on the phones, ignited a wave of enthusiasm within the user community. The exceptional popularity of the Nokia 6100 series translated into remarkable sales figures, with nearly 41 million units sold by 1998. This exceptional achievement propelled Nokia ahead of Motorola, solidifying its position as the world’s leading mobile phone manufacturer that year.

Besides the Nokia 6100 series, Nokia 8810 was also launched by Nokia in the same year. This is the first flagship phone without an external antenna with a sliding chrome cover.
With two groundbreaking and commercially successful new product lines, Nokia saw a jump in business results as the company’s net revenue increased by more than 50% year-on-year, operating profit increased. nearly 75% and the stock price skyrocketed 220%, resulting in an increase in market capitalization from nearly $21 billion to about $70 billion.

2000 – 2006: King of the early digital era
The year 2000 marked a significant milestone in the global shift towards the digital era, witnessing the emergence of groundbreaking technological advancements such as digital cameras, mp3 players, CDs, DVDs, and the advent of 2G and 3G networks. Amidst this transformative period, Nokia displayed remarkable adaptability by introducing new product lines that aligned with the changing technological landscape.

The Nokia 7650 represents Nokia’s initial response to the evolving mobile phone landscape. Released in 2001, it was the company’s pioneering device featuring an integrated camera capable of capturing and storing photos, accompanied by a vibrant color screen.

In the subsequent year, 2002, Nokia further expanded its product offerings with two notable releases. The Nokia 6650 was unveiled as the company’s first 3G phone, introducing users to the capabilities of this advanced network technology. Simultaneously, Nokia introduced the Nokia 3650, marking its entry into the Symbian software phone line. Notably, the Nokia 3650 featured a built-in camera with video recording functionality, adding an exciting new dimension to mobile phone photography.

In addition to its focus on the high-end market, Nokia also aimed to capture the popular segment. This led to the introduction of the Nokia 1100 in 2003, a budget-friendly phone renowned for its compact, user-friendly, and robust design that catered to essential functionalities like calling, messaging, and reliable connectivity across various telecommunications bands worldwide. The Nokia 1100 quickly gained traction, with approximately 250 million units sold in its debut year alone. This remarkable achievement earned it a place among the world’s best-selling consumer electronics products. By 2005, the cumulative sales of the Nokia 1100 surpassed an astounding 1 billion units.

In 2005, Nokia introduced its highly anticipated flagship series consisting of the N70, N90, and N91. These devices showcased significant advancements in design, camera functionality, storage capacity, memory, battery life, and speakers. At that time, these products were widely regarded as the epitome of technological excellence.
By 2007, Nokia’s business report revealed its commanding position in the global mobile phone market, boasting a market share of nearly 50%. The company’s revenue stood at approximately $150 billion, and its workforce consisted of around one million employees.
The downfall of Nokia
2006: a major change in nokia’s leadership and business strategy.

In 2006, a significant change occurred at Nokia as Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo assumed the role of chief executive officer, succeeding Mr. Jorma Ollila. Alongside this leadership transition, several new board members were appointed. Under this new leadership structure, Nokia made the decision to consolidate its smartphone and feature phone operations, emphasizing a focus on traditional phones rather than venturing into untested technologies. This strategic shift indicated a move towards prioritizing profitability over the pursuit of groundbreaking technological innovations.
Mr. Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo himself was known for his conservative approach to business strategy, often rejecting ideas for new products and technologies in favor of safer options that could generate revenue and profit in the near term. However, this strategic direction unexpectedly led Nokia into a downward spiral in the subsequent years, a decline that the company had not anticipated.
2007: Steve Jobs introduced the first iPhone
In 2007, Apple’s launch of the iPhone, a competitor significantly trailing behind Nokia in terms of brand recognition, market share, and scale, captivated the world. The iPhone represented a revolutionary product in the mobile phone industry, signaling the end of the era of digital phones and heralding the arrival of the smartphone era. Its design diverged entirely from existing mobile phone models, featuring a minimalistic layout with only a Home button, power button, and volume controls, while all other operations were performed on a single touch screen. Powered by the innovative iOS operating system, the iPhone also introduced an application store that enabled users to easily download and install various applications via the internet.
In response to the iPhone’s remarkable success, Nokia initially responded with indifference, derision, and laughter, dismissing the new technologies of the iPhone as impractical and asserting that consumers had to pay an exorbitant price to own one.
Despite the introduction of the iPhone, Nokia initially experienced a marginal 3% loss in market share by the end of 2007. Nokia had valid reasons for its initial dismissal, such as the iPhone’s limited 2G connectivity in contrast to Nokia phones equipped with 3G connectivity. However, Nokia’s executives basked too long in their victories, leading to a series of subsequent missteps and challenges that ultimately plagued the company.
2008: Android OS was released
Following the triumphant release of the iPhone, Google made its foray into the smartphone market in 2008 with the introduction of Android, an operating system designed for mobile devices. Despite the potential opportunity to rival Apple by embracing Android, Nokia’s management remained steadfast in their confidence in the Symbian operating system. They pursued plans to develop their own operating system, MeeGo, underestimating the significance of Google and considering it to be an inconsequential player in the market.

In an effort to compete with its rivals, Nokia introduced the 5800 Express series in 2018, featuring a spacious and responsive touchscreen. However, the company faced a critical drawback—its Symbian software, serving as an operating system, proved to be inadequate and significantly lagged behind the more advanced iOS and Android platforms available at the time.
In contrast, the iPhone experienced a surge in popularity, with Apple witnessing a steady growth in revenue.
2010: Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo was replaced by Stephen Elop

During the period from 2008 to 2010, Nokia encountered a series of product launches that failed to resonate with consumers and achieve commercial success. Concurrently, manufacturers of Android smartphones like Samsung and Huawei experienced substantial growth, further intensifying the competitive landscape. Faced with these challenges, Nokia came to the realization that significant changes were necessary to avoid stagnation and potential decline. Consequently, the company made the decision to replace Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo with Stephen Elop, who was recruited from Microsoft.
2011: Nokia partnered with Microsoft
In 2011, Nokia unveiled the N9 smartphone, which operated on its self-developed operating system called MeeGo. Regrettably, due to a rushed development process and a lack of expertise in operating systems, MeeGo encountered widespread issues, including security concerns and a limited selection of applications, which made it less appealing to developers. Consequently, the N9 faced an untimely demise, despite Nokia’s investment in a marketing campaign to promote the new product.
Following the disappointing outcome of MeeGo and the N9, Nokia sought a partnership with Microsoft to produce smartphones running on the Windows Phone operating system. Little did Nokia anticipate that this decision would become yet another misstep for the company’s management.

Following a collaborative effort, Nokia ventured into the Android market with its Nokia Lumia product line . This strategic move aimed to counter the decline in market share, leveraging the user-friendly interface design offered by the Windows Phone operating system. However, the Windows Phone platform still lagged significantly behind iOS and Android in terms of application stores. In an attempt to address this weakness, Microsoft made various efforts to attract developers, but these initiatives failed to yield substantial results, as Google and Apple had already established a stronger foothold in this aspect. Consequently, despite initial hopes, Nokia continued to experience a decline in market position approximately six months later.
2014: Nokia was on the verge of bankruptcy
In 2014, Nokia was on the verge of bankruptcy. With no other choice, Nokia had to sell its mobile phone business to Microsoft for just $7 billion.
After a period of time, Microsoft introduced the Nokia X and Nokia XL models, which ran on the Android operating system. However, these Nokia devices were criticized for their limited development time, resulting in a noticeable lag compared to other phone manufacturers, such as Samsung and Huawei, who had extensively optimized their devices for the Android ecosystem.
In subsequent years, Microsoft shifted its focus away from phone production, allocating fewer resources to the manufacturing of mobile devices. Instead, the company redirected its investments towards other product lines, including Windows, Office, Xbox, and Surface.
Now: Nokia is only a memory
Also Read: Case Study | How Nokia Built A Powerful Technology Brand
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts

A Deep Dive into the Marketing Strategies of Broadcom
Who are the top competitors and alternatives of tesla, who are the top competitors and alternatives of aramco.
Terms and Conditions
Brought to you by:

Nokia: The Inside Story of the Rise and Fall of a Technology Giant
By: Quy Huy, Timo O. Vuori, Lisa Duke
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top…
- Length: 15 page(s)
- Publication Date: Sep 26, 2016
- Discipline: General Management
- Product #: IN1289-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of longer-term more beneficial activities. Nokia's once-stellar performance was undermined by misaligned collective fear: top managers were afraid of competition from rival products, while middle managers were afraid of their bosses and even their peers. It was their reluctance to share negative information with top managers - who thus remained overly optimistic about the organisation's capabilities - that generated inaccurate feedback and poorly adapted organizational responses that led to the company's downfall. The case covers the period from the early 2000s to 2010, with a focus on 2007 (the introduction of the iPhone) to 2010, when the CEO left.
Learning Objectives
After reading and analysing the case, students will understand (i) how emotional dynamics influence hard technological and strategic decisions in organizations as they translate into challenges for innovation, (ii) how emotional dynamics can undermine innovation and performance.
Sep 26, 2016 (Revised: Dec 12, 2022)
Discipline:
General Management
IN1289-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

The Rise and Fall of Nokia review – fascinating insight into the Finnish, and now finished, tech firm
With a flawless idea, the mobile phone pioneer cornered the market. But by ignoring the touchscreen, things quickly went south
F amous and Finnish? Jean Sibelius, Tove Jansson, Kimi Räikkönen and – almost certainly most famous of all – Nokia . Dada da da, dada da da, dada da da, daaaa. (That’s the ringtone tune, if you can’t read music – composed by a Spaniard, as it happens). If you write it out as actual music, it is a gently tumbling phrase of quavers and crotchets. That in no way reflects the fortunes of the company over time, which are more of a steady upwards incline, followed by a precipice.
Nokia didn’t always do telecommunications and electronics. It started off, in 1865, as a pulp mill before getting into rubber. It made flexible cables, and the company was good at adapting to change, too (well, until later, the precipice). In the latter part of the 20th century, Nokia expanded into phones and became the global market leader. It invented something that cost a little over £100, that everyone in the whole world wanted or needed and, every few years, could be convinced to buy a new version of. As a business idea, it was pretty much the best one ever. Take that one on Dragons’ Den and even Deborah Meaden might show some interest.
Not that it was immediately obvious to everyone. Jorma Nieminen, the “father” of the Finnish mobile phone industry as you know it, remembers his sales manager, Ilpo Rossi, packing the parts of an SRP202 – carphone, receiver, antenna, battery – into a case. Nieminen asked Rossi what he was doing. Rossi said that some people wanted to have a phone at the cottage, on the boat, in a hotel and so on. But they didn’t have a portable one, so he was putting one together. “That started the development of a mobile phone,” says Nieminen.
“Everyone laughed,” remembers Matti Makkonen, another Finnish telecommunications pioneer. “Who’d carry a phone with them?”
Who’s laughing now? (Well, apart from my mum, who is yet to be converted. She does have one, but she doesn’t know where it is and she can’t ring it as she doesn’t know the number.)
There are several moments like that in this documentary. Who would imagine that X (something now everyday and normal) would become a thing? Having a phone that wasn’t the same size as your cottage or your boat; text messaging; offering different ringtones (just in case you got bored of the original); games such as Snake . But the guys at Nokia knew. And they continued to adapt and develop and expand until they were biggest and the best.
Now, you might think that a film, in Finnish with subtitles, in which a bunch of suits and techies, blokes (almost exclusively) called Matti, Ilpo, Jorma, Mika and Ove talk about SRP202s and NMT900s and reminisce in a rather self-congratulatory manner about how they came to rule the world, would have limited appeal, unless you were looking for some kind of motivational business experience. But you would be wrong.
First, because Nokia is – was – more than just a telecommunications company in Finland. Its annual budget was larger than the government’s. It was a part of the country, certainly a source of national pride. Until the pride was replaced by shame.
Second, because it all went wrong (there is a clue in the title to be fair). While this might have been bad news for Ove, Mika, Jorma et al – as well as bad news for the economy of their country – it makes it a much more interesting documentary. Not just grey techy men, but The Fallen. Not just a business story, but a morality tale for late-era capitalism.
Some people made a lot of money, went off and bought cottages and boats that were even bigger than that first SRP202. But, with global domination, quality lost out to quantity. The pioneering spirit lost, Nokia took its eye off the ball and Apple and Samsung usurped it when the smartphone came of age.
So, when in the past it had been them coming up with ideas that people laughed at before fully adopting, this time it was someone else. Steve Jobs. No buttons on his phone, just a screen that you touch and swipe, and not just a phone but everything; your life, the love of your life ... hahaha... Oh.“
Nokia had dismissed touchscreens as a gimmick that used too much battery. After which they were playing catchup and they didn’t ever manage it. Their market share eroded and Nokia’s mobile phone business was bought by Microsoft in 2014. At its peak Nokia was valued at $300bn, but in 2016 Microsoft sold it in two parts for a paltry £350m. Phones are no longer produced in Finland, and the Nokia tune – no longer just annoying – took on a note of melancholy.
The Rise and Fall of Nokia was shown on BBC Four
- Television & radio
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
- Success stories
Business Insights
Artículos, noticias, casos de estudio y documentación sobre negocios. Únete a la comunidad de +50.000 suscriptores de todo el mundo.
Áreas y funciones
Casos de estudio, tags destacados, key concepts.
Personas . Procesos . Tecnología .
Creemos que los procesos claros, con el apoyo de la tecnología adecuada, generan un entorno donde las personas trabajan más felices, y en consecuencia vuelve a tu empresa más productiva.
World class technology. Soluciones de primer nivel para tu empresa.

The Nokia Case: fall and rise
Multinationals are not always a guarantee of permanent success, even though they are considered indestructible over time and avant-garde in terms of technological innovations.
<<< Good strategies: What do winning brands have in common? >>>
This is the case of what happened a few years ago with the Finnish telecommunications company Nokia, which by not adapting to the most ambitious change in mobile telephony (the smartphone) lost its followers and their phones resoundingly, which could do nothing against the competition and were forgotten.
Although over time, Nokia managed to recover from that fall by finally adapting to the demand of the market and of demanding users by incorporating the Android operating system, it took several years behind the shadows to be able to achieve it, until just two or three years ago its incipient rise was noted with the launch of the first smartphones that still retain the distinctive mark of strength and durability that catapulted the brand.
In this article, we tell you all the details of the fall and rise of Nokia , the company that was once the market leader and today retains a discreet place alongside leading companies such as Apple, Samsung, Xiaomi, and Huawei.
Story of a fall and rise.
It all started when in 2007, even when Nokia was still leading the world cell phone market, the first iPhone smartphone was launched, led by the prestigious Apple, which was here not only to stay but to unseat the Finnish giant that was beginning to sense its decline.
Faced with the stark prospect of an increasingly demanding market that fed unattainable competitors, the company decided to join forces with Microsoft to be able to deal with the operating systems that were already prevalent at that time.
But unfortunately, it became aware of this reality late because, like many companies with a long history, it resisted change. However, it attempted.
In 2011, Nokia launched the Nokia N9, running the MeeGo operating system. Then it also presented the first terminals of the Asha series, but clearly, the Finnish giant was looking to bet stronger as soon as it realized that they were losing to other competitors who had already launched more advanced phones than the N and the Asha.
Examples of this unequal competition were the Android devices that Samsung and Sony Ericsson were already launching to capture the desire of users with a growing market share.
It was then, in that same year, Nokia established a strategic alliance with Microsoft so that all the company's smartphones would incorporate the Windows Phone operating system, leaving aside MeeGo and Symbian, except in the most basic models. Two years later, in 2013, Microsoft announced the purchase of mobile devices and the licensing of Nokia patents in a global agreement.
From this strategic alliance, the Nokia Lumia series of smartphones was born, which had the Windows Phone operating system. But despite all the efforts between the two multinationals, the Nokia Lumia failed to charm consumers because the competition led by IOS and Android left them no room for maneuver.
So, finally, in 2014, Microsoft decided to stop the production of Windows Phones Lumia, once it understood that there was no point in fighting against operating systems that were easier to use, faster, and more efficient for users. Consequently, he announced the latest public version of Windows Phone 8.1.
The bet on Android.
Due to Nokia's extensive history in the mobile phone market, it was not easy to overcome old preconceptions concerning preserving a certain distinctive brand of producing resistant phones made of hard materials and with classic keys.
That is why they fell behind and did not see the flood of Android and IOS coming, which was installed among people to erase from their memory any remnants of experience with that obsolete technology for the new digital age.
10 years have passed since the checkmate that iPhone and Android did to the proud Nokia. Ten years of bad decisions, of which the alliance with Microsoft was the worst of all. However, there was still a glimmer of hope in this path of darkness into which the Finnish giant had plunged. There was still the part that Microsoft had not bought, and that was its salvation.
Satya Nadella, the new CEO of Nokia at that time (2015), did something very practical to give the Finnish company back the prestige it once had: he demolished everything that Microsoft had built since it bought it, leaving almost not a single vestige of that failed alliance. He had understood that if he wanted to re-emerge as a brand and recover lost market share, he had to do something different, not dig through the rubble.
In this way, he made the best decision he could to win back the public that had abandoned him: surrender to Android. And far from seeming like a risky act, it was the best decision because he played it safe. Android then became the answer that the company needed to resurface and be competitive again, and in 2017 the firm, together with HMD, launched the Nokia 6, the first mid-range smartphone that incorporates Android as an operating system.
Although at first it was only launched in the Chinese market, it meant the company's most anticipated return to the cell phone market. And it was not bad at all because the terminal was renewed in increasingly advanced devices.
Nokia forever.
This story teaches us that no multinational company is guaranteed success if the right decisions are not made to stay updated, which was precisely what Anssi Vanjoki, the company's CEO during the early days of Android, did not do, expecting to be successful without betting on change.
Then the desperation not to go bankrupt drives the company to ally with Microsoft - the worst of decisions - and launch very interesting phones but not what consumers wanted after flirting with Android and Apple, which shows that they made a failed market study for uselessly believing that their buyer persona would continue to buy small phones with keys or poor imitations of smartphones without WhatsApp or an application store to download for free and unlimitedly.
But as failures teach us to reinvent ourselves and improve, fortunately, Nokia reinvented itself when it decided to maintain its design and resistant materials to take advantage of Android to create very powerful phones that are gradually climbing positions in the market. And it's still Nokia, its quality phone essence was not diluted by Microsoft's handling.
<<< How digital strategies are redefining brands >>>
In final words, this was the story of the fall and rise of Nokia, a multinational that had everything to be the best indefinitely, but bad decisions precipitated its failure just when the competition adopted Android to sink it further. But thinking about customers was what saved it because customers wanted Nokia with Android, and now they finally have it.

Drew's editorial team
¿nos dejas un comentario.

Nokia | The Rise And Fall [Part 1]
Posted: May 2, 2024 | Last updated: May 2, 2024
This is part 1 of a 3 part Nokia documentary series taking the look at the history of Nokia, how they rose to prominence and how they ultimately failed as a company.PART 2: <a href="http://youtu.be/RQEn19symz0Soundtrack:Burn">http://youtu.be/RQEn19symz0Soundtrack:Burn</a> Water (Dagogo Altraide) - Hidehttps://soundcloud.com/burnwater/hideMontgomery - Piñata (Japanese Wallpaper Remix)Catching Flies - Quiet NightsFavela - GongKOA - All My Love SirensCeol - Lost In Time» Google + | <a href="http://www.google.com/+coldfustion»">http://www.google.com/+coldfustion»</a> Facebook | <a href="http://www.facebook.com/ColdFusionTV»">http://www.facebook.com/ColdFusionTV»</a> Patreon | <a href="https://www.patreon.com/ColdFusion_TV»">https://www.patreon.com/ColdFusion_TV»</a> My music | <a href="http://burnwater.bandcamp.com">http://burnwater.bandcamp.com</a> or » <a href="http://www.soundcloud.com/burnwater»">http://www.soundcloud.com/burnwater»</a> Collection of music used in videos: <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YOrJJKW31OAEditing">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YOrJJKW31OAEditing</a> website: <a href="http://www.cfnstudios.comColdfusTion">www.cfnstudios.comColdfusTion</a> Android Launcher: <a href="https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=nqr.coldfustion.com&hl=en»">https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=nqr.coldfustion.com&hl=en»</a> Twitter | @Coldfustion
More for You
US congressman and wife charged with taking bribes
31 '90s Icons You've Forgotten (But Shouldn't Have)
The worst-behaved dog breed, according to data—plus, see if your dog is one of the least obedient breeds
The IRS is overhauling how it audits. Here’s who is a target
Apron Belly: How to Reduce Stomach Sagging
I’m 62 with no debt and a part-time job. My advisers say keep saving, but my kids say spend — do I go for a Roth 401(k)?
10 Movies That Flopped at the Box Office But Are Truly Worth Watching
The Coolest Car From the Year You Were Born (1945-1995)
The 5 states in America people never leave—and why
10% of travelers have had their medicines confiscated. Here's how you can avoid it.
17 Animals You Can’t Keep as Pets in the US
The Best 27 Red Carpet Moments of the '70s
Famous Roles That 16 Actors Never Want to Play Again
25 of the Most Ahead-Of-Their-Time Cars Ever Built
Second Boeing whistleblower dies ‘suddenly’ in Oklahoma
Scientists change the number of steps needed to stay healthy
A 64-year-old 'peak boomer' worries his savings and Social Security won't be enough to retire: 'My biggest fear is finding myself at 75 standing at the door at Walmart.'
Lost Planet Theia Is Hidden Inside the Earth, New Study Says
15 of the biggest comebacks in Hollywood history
WNBA preseason power rankings: Reigning champion Aces on top, but several teams made gains
Nokia joins Ericsson in forecasting stronger second half
- Medium Text

- Nokia Q1 profit misses forecasts
- Sales slump on fall in demand for 5G technology
- CEO sees improvement in second half
- Nokia reiterates full-year guidance
Sign up here.
Reporting by Olivier Sorgho in Gdansk; Editing by Anna Ringstrom, Gerry Doyle and Sharon Singleton
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Technology Chevron
Google trial wraps up as judge weighs landmark us antitrust claims.
Google and the U.S. Justice Department wrapped up closing arguments on Friday over claims that the Alphabet unit has unlawfully dominated web search and related advertising, in a case the government contends could shape the “future of the internet.”

Luminar Technologies , a maker of lidar sensors for self-driving cars, said on Friday that it would cut its workforce by about 20%, as part of a restructuring plan for the current year.
The ghosts of ‘Wintel’: What leaders can learn from the diverging paths that made Microsoft a $3 trillion powerhouse and flatlined Intel

Steve Jobs wasn’t accustomed to hearing “no.” But that was the answer from Paul Otellini, CEO of Intel .
It was 2006, and Intel, the global king of computer chips, was bringing in record revenue and profits by dominating the kinds of chips in hottest demand—for personal computers and data centers. Now Jobs wanted Intel to make a different type of chip for a product that didn’t even exist, which would be called the iPhone.
Otellini knew chips for phones and tablets were the next big thing, but Intel had to devote substantial capital and its best minds to the fabulously profitable business it already possessed. Besides, “no one knew what the iPhone would do,” he told The Atlantic seven years later, just before he stepped down as CEO. “There was a chip that they were interested in, that they wanted to pay a certain price for and not a nickel more, and that price was below our forecasted cost. I couldn’t see it.”
Otellini, who died in 2017, was a highly successful CEO by many measures. But if that decision had gone the other way, Intel might have become a chip titan of the post-PC era. Instead, it gave up on phone chips in 2016 after losing billions trying to become a significant player. As he left the company, Otellini seemed to grasp the magnitude of his decision: “The world would have been a lot different if we’d done it.”

Meantime, some 800 miles north, in Seattle, Microsoft was struggling to find its role in a tech world dominated by the internet, mobile devices, social media, and search. Investors were not impressed by its efforts. No one could have foreseen that years later, a few key decisions would set the company up as an AI powerhouse and send its stock soaring. There was a time not so long ago that Microsoft and Intel were both atop the tech world. They were neither competitors nor significant customers of each other, but what New York University’s Adam Brandenburger and Yale’s Barry Nalebuff deemed “complementors.” Microsoft built its hugely profitable Windows operating system over the years to work on computers that used Intel’s chips, and Intel designed new chips to run Windows (hence “Wintel”). The system fueled the leading tech product of the 1990s, the personal computer. Microsoft’s Bill Gates became a celebrity wonk billionaire, and Intel CEO Andy Grove was Time ’s 1997 Man of the Year.
Since then their paths have diverged sharply. Microsoft in 2000 was the world’s most valuable company, and after losing that distinction for many years, it’s No. 1 again. Intel was the world’s sixth most valuable company in 2000 and the largest maker of semiconductors; today it’s No. 69 by value and No. 2 in semiconductors by revenue, far behind No. 1 TSMC (and in some years also behind Samsung ).

A Fortune 500 CEO makes thousands of decisions in a career, a few of which will turn out to be momentous. What’s easy to explain in hindsight—that Microsoft would be at the forefront of AI, that Google would become a behemoth, that Blockbuster would fade into obscurity—is never preordained. Often the fateful decisions are identifiable only in retrospect. Nothing more vividly illustrates this than the parallel stories of Microsoft and Intel. The case study of what went right and wrong at those two giant corporations offers a master class in business strategy not just for today’s front-runners at the likes of Google, Open AI, Amazon , and elsewhere—but also for any Fortune 500 leader hoping to survive and thrive in the coming decade.
Wintel’s origin story
The two companies were founded a mere seven years apart. Intel’s founders in 1968 included Robert Noyce, coinventor of the computer chip, and Gordon Moore, who had written the seminal article observing that the number of transistors on a chip doubled every year, which he later revised to two years—Moore’s law, as others later called it. Andy Grove was employee No. 3. All three are still regarded as giants of the industry.
Bill Gates famously dropped out of Harvard to cofound Microsoft with Paul Allen, a childhood friend. They were excited by the prospects of creating software for a new concept, the personal computer, also called a microcomputer. They launched Microsoft in 1975.

The two companies’ paths crossed when IBM decided in 1980 to produce a PC and wanted to move fast by using existing chips and an existing operating system developed by others. It chose Intel’s chips and Microsoft’s operating system, profoundly transforming both companies and the people who ran them. IBM’s size and prestige made its design the industry standard, so that virtually all PCs, regardless of manufacturer, used the same Intel chips and Microsoft operating system for decades thereafter. As PCs swept America and the world, Intel and Microsoft became symbols of technology triumphant, glamour, success, and the historic bull market of 1982 to 2000.
Then everything changed.
The reign of Gates and Grove peters out
In October, 2000, Fortune ran an article with an illustration depicting Gates and Grove as monumental Egyptian sphinxes. The headline: “Their Reign Is Over.”
The reasoning: “Gates and Grove attained hegemony by exploiting a couple of key choke points in computer architecture—the operating system and the PC microprocessor,” the article explained. “But in the new, more diverse IT world wired together by universal internet protocols, there are no such obvious choke points to commandeer.”
Thus began a multiyear identity crisis for both companies. Intel’s PC chips and Microsoft’s PC operating system and applications remained bountifully profitable businesses, but both companies and their investors knew those were not the future. So what was? And who would lead this new era?
In January of 2000, Gates stepped down as CEO after 25 years, and Steve Ballmer, Microsoft’s president and a college friend of Gates, took his place; Gates remained chairman. Two days later, Microsoft’s stock rocket ran out of fuel. On that day the company’s market value hit $619 billion, a level it would not reach again for almost 18 years.
Grove was no longer Intel’s CEO in 2000, having handed the job to Craig Barrett, a longtime company executive, in 1998. But as Intel’s visionary and most successful CEO, Grove remained an important presence as chairman of the board. His health was becoming an issue; he had been diagnosed with prostate cancer in 1995, and in 2000 he was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. Intel’s stock roared until August, when the company’s market value peaked at $500 billion. It has never reached that level since.
But most significantly, 2000 was the year that the internet began to seem like it just might make Wintel irrelevant.
At Intel, Barrett responded with acquisitions, many of which were in telecommunications and wireless technology. In concept, that made great sense. Cell phones were going mainstream, and they required new kinds of chips. “Craig tried to very aggressively diversify Intel by acquiring his way into new businesses,” says David Yoffie, a Harvard Business School professor who was on Intel’s board of directors at the time. “I would say that was not his skill set, and 100% of those acquisitions failed. We spent $12 billion, and the return was zero or negative.”
In the lean years after the dotcom balloon popped, Barrett continued to invest billions in new chip factories, known as fabs, and in new production technologies, so Intel would be well positioned when demand rebounded. That is a hint to one of the most important lessons of the Wintel saga and beyond: Protecting the incumbent business, even in a time of transition, is almost impossible to resist. That course usually sounds reasonable, but it holds the danger of starving the company’s future. As the great management writer Peter Drucker said: “If leaders are unable to slough off yesterday, to abandon yesterday, they simply will not be able to create tomorrow.”
‘We screwed it up’
At Microsoft in the 2000s, “it was not at all obvious what would happen with the shape and volume of PCs, with operating system margins, or the future of applications like Word or Excel,” says Ray Ozzie, a top-level Microsoft executive from 2005 to 2010. “There was significant internal debate at Microsoft and in the industry on whether, in the future, the PC was dead, or if it would continue to grow and thrive.” Maybe Word, Excel, and those other applications that resided on your hard drive would move to the internet, like Google Docs, introduced in early 2006. In that case Microsoft would need a new business model. Should it develop one? Some executives thought so. But no one knew for sure.
During this period, Microsoft was hardly a model of corporate innovation, and succumbed to what often happens when successful companies are disrupted. Ozzie explains: “When you are rolling in resources and there are multiple existential threats, the most natural action to protect the business is to create parallel efforts. It’s more difficult to make a hard opinionated choice and go all in. Unfortunately, by creating parallel efforts, you create silos and internal conflict, which can be dysfunctional.”
As competing teams fought for primacy, Microsoft missed the two most supremely profitable businesses since the PC era: search and cell phones. Those misses were not fatal because Microsoft still had two reliable, highly profitable businesses: the Windows operating system and the Office suite of apps. But in Drucker’s terms, those were yesterday businesses. Investors didn’t see substantial tomorrow businesses, which is why the stock price went essentially nowhere for years. Missing search and cell phones didn’t threaten Microsoft’s existence, but it threatened Microsoft’s relevance and importance in a changing world, which could eventually damage the company’s appeal among investors and the world’s best employees. The reasons for those crucial misses are instructive.
In 2000 Google was an insignificant internet search startup with no clear business model, but it had an inkling that selling advertising could be profitable. We know how that turned out: Google’s 2023 ad revenue was $238 billion. The model was entirely foreign to Microsoft, which made tons of money by creating software and selling it at high prices. Charging users nothing? Selling ads? Microsoft had never run a business at all like Google’s. By the time Google’s model had proved itself, Microsoft was hopelessly far behind. Today its Bing search engine has a 3% market share across all platforms worldwide, says the StatCounter web-traffic analysis firm. Google’s share is 92%.

Microsoft’s failure in cell phones was, in a large sense, similar—the company didn’t fully grasp the structure of the business until it was too late. The company assumed the cell phone industry would develop much like the PC industry, in which sellers like Dell combined Intel’s chips and Microsoft’s software in a final product. But Apple’s starkly different iPhone business model, in which it designs its own chips and writes its own software, was an enormous hit. The other big winner in the industry, Google’s Android smartphone operating system, likewise ignored the PC model. Instead of selling its operating system, Google gives it away to phone makers like Samsung and Motorola. Google makes money by putting its search engine on every phone and by charging app makers a fee when users buy apps.
Bill Gates acknowledges that Microsoft’s miss in cell phones was life-changing for the company. Looking back on his career in 2020, he said: “It’s the biggest mistake I made in terms of something that was clearly within our skill set.”
Intel also lost the mammoth cell phone opportunity, and in a similar way. It couldn’t adapt. Intel understood the opportunity and was supplying chips for the highly popular BlackBerry phone in the early 2000s. The trouble was, Intel hadn’t designed the chips. They were designed by Arm, a British firm that designs chips but doesn’t manufacture them. Arm had developed a chip architecture that used less power than other chips, a critical feature in a cell phone. Intel was manufacturing the chips and paying a royalty to Arm.

Understandably, Intel preferred to make phone chips with its own architecture, known as x86. Paul Otellini decided to stop making Arm chips and to create an x86 chip for cell phones—in retrospect, “a major strategic error,” says Yoffie. “The plan was that we would have a competitive product within a year, and we ended up not having a competitive product within a decade,” he recalls. “It wasn’t that we missed it. It was that we screwed it up.”
Groping for a megatrend
Just as 2000 was a turning point for Intel and Microsoft, so was 2013. Broadly they were in the same fix: still raking in money from the businesses that made them great; getting into the next big opportunities too late or unsuccessfully; groping for a megatrend they could dominate. Their stock prices had more or less flatlined for at least a decade. Then, in May 2013, Paul Otellini stepped down as Intel’s CEO. In August, Steve Ballmer announced he would step down as Microsoft’s CEO.
Succession is the board of directors’ No. 1 job, more important than all its other jobs combined. The stakes are always high. How the Intel and Microsoft boards handled their successions, nine months apart, largely explains why the two companies’ storylines have diverged so dramatically.
Under Otellini’s successor, Brian Krzanich, Intel kept missing new-chip deadlines—ironically failing to keep up with Moore’s law even as competitors did so—and lost market share. The company gave up on smartphone chips. After five years as CEO, Krzanich resigned abruptly when an investigation found he had had a consensual relationship with an employee. CFO Bob Swan stepped in as CEO, and the production troubles continued until, by 2021, for the first time in Intel’s existence, its chips were two generations behind competitors’. Those competitors were Taiwan’s TSMC and South Korea’s Samsung.
In crisis mode, Intel’s board brought back Pat Gelsinger, an engineer who had spent 30 years at Intel before leaving for 11 years to be a high-level executive at EMC and then CEO of VMware . As Intel’s CEO he has announced an extraordinarily ambitious and expensive plan to reclaim the company’s stature as the world leader in chip technology.
Microsoft’s board spent almost six months finding Ballmer’s successor under worldwide scrutiny. At least 17 candidates were publicly speculated upon. British and Las Vegas bookies offered odds on the eventual winner; Satya Nadella, who recently marked 10 years as CEO, was a 14-to-1 long shot.
Nadella has arguably been the best corporate succession choice, regardless of industry, in years or perhaps decades. Under his leadership the stock finally broke out of its 14-year trading range and shot upward, rising over 1,000%. Microsoft again became the world’s most valuable company, recently worth $3.1 trillion. Gelsinger, with just over three years in the job, can’t be fully evaluated; industry experts wonder if he’ll be Intel’s Nadella. But both CEOs offer useful examples of how to move a company from the past to the future.
Nadella orchestrated Microsoft’s dramatic turnaround by taking an outsider’s look at the company and making big changes with little drama. He began by making Office apps (Word, Excel) compatible with Apple iPhones and iPads—heresy at Microsoft, which regarded Apple as an archenemy. But Nadella realized the two companies competed very little, and why not let millions more people rely on Office apps? The move sent a message to the company and the world: The Microsoft culture’s endemic arrogance would be dialed down considerably. Interoperating with other companies could now be okay.
That was largely a new business model at the company, with many more to follow. For example, Nadella bought LinkedIn , a player in social media, which Microsoft had entirely missed, and later bought GitHub, a repository of open-source code, which Microsoft had previously despised. Both deals and several others have been standout successes.
More broadly, Nadella brought a new leadership style for a new environment. In a company known for vicious infighting that could paralyze action, he settled long-running debates over major projects. For example, in 2016 he sold the Nokia cell phone business that Microsoft had bought a year before he became CEO, acknowledging that the company had lost the battle for phones. “People don’t quite grok why things have blossomed under Satya,” says a former executive. “His superpower is to make a choice, eliminate conflict, and let the business blossom.”
At Intel, Gelsinger also introduced culture-defying changes. The company had risen to dominance by designing leading-edge chips and manufacturing them with industry-leading skill. Amid that intense pride, the idea of creating a separate foundry business—manufacturing chips designed by others—was anathema. Yet under Gelsinger, Intel has created a new foundry business while also relying more on other foundries, including TSMC, the world’s largest chipmaker, for some of its own chips—a double shock to the culture.
Getting a long-established company with a titanium-strength culture to adopt seemingly strange business models as Nadella and Gelsinger did can be painfully hard. Often only a new CEO can bring the openness necessary to make it happen. The same problem arises when a company needs to update its corporate strategy. Microsoft had been seeking and debating the next big thing for years, but Nadella saw that the company didn’t need to find a potentially huge new future-facing business. It already had one: Azure, its cloud computing service. Amazon Web Services was and is the industry leader, but Azure has grown to a strong No. 2 because Nadella has given it abundant capital and some of the company’s brightest workers. He also made an unorthodox investment in OpenAI, creator of ChatGPT, commiting $13 billion to the company starting before it was famous. Now Azure offers its customers OpenAI technology. In Drucker’s terms, it’s a big, thriving tomorrow business.
Gelsinger changed Intel’s strategy even more radically. He bet heavily and successfully on billions of dollars from the U.S. government. Via the CHIPS and Science Act, Intel could receive up to $44 billion in aid for new U.S. chip factories the company is building in coming years. “As I like to joke, no one has spent more shoe leather on the CHIPS Act than yours truly,” he tells Fortune. “I saw an awful lot of senators, House members, caucuses in the different states. It’s a lot to bring it across the line.”
A key insight is that for a major company with a history of success, like Microsoft and Intel, moving beyond an outmoded strategy and fully embracing a new one is traumatically difficult and sometimes impossible. For years both companies tried and failed to do it. A related insight: Doing it is easier for Nadella and Gelsinger because they have the advantage of being “insider outsiders,” leaders with deep knowledge of their organization but without heavy investment in its strategy; Nadella was working on Azure, not the Windows operating system or Office apps, long before he became CEO, and Gelsinger’s 11-year absence from Intel gave him license to rethink everything.
A larger lesson is that, in the stories of these two great companies, succession is the most important factor. Considering that Microsoft on the whole has fared better than Intel over the past 24 years, it’s significant that over that period, Microsoft has had only two CEOs and Intel has had five. Most people study the CEO when explaining a company’s performance, but they should first examine those who choose the CEO, the board of directors.
Looking back at these stories, asking “what if” is irresistible. What if Paul Otellini had said yes to Steve Jobs? What if any of Intel’s or Microsoft’s CEOs had been someone else? What if Intel, under a different CEO, had developed a successful GPU, the kind of chip that powers today’s AI engines (it tried)—would you ever have heard of Nvidia? Bill Gates said in 2019, “We missed being the dominant mobile operating system by a very tiny amount.” What if that tiny amount had shifted slightly? Whose phone would you be using today?
It’s all endlessly tantalizing but of course unknowable. The value of looking back and asking “what if,” is to remind us that every day leaders are creating the future—and neglecting their duty if they don’t learn from the past.
5 lessons from the Wintel case study:
1. Success can be a company’s worst enemy. The great management writer Peter Drucker said every company must “abandon yesterday” before it can “create tomorrow.” But in a successful company, every incentive pushes leaders to protect yesterday. Intel and Microsoft struggled for years to create their tomorrows. 2. Leaders must be open to business models that seem strange. Whether giving away software or manufacturing chips designed by others as a separate business, both Microsoft and Intel faced competitors doing things differently. 3. Get everyone on the same page. Debate is healthy up to a point, but at Microsoft it continued far too long until Nadella became CEO and set clear priorities. At Intel a series of CEOs backed differing solutions to its declining business, which prolonged a muddled strategy. 4. Succession is the board’s No. 1 job, more important than all its other jobs combined. Everyone knows it, but some boards still do their job poorly. If they make a mistake, none of the other lessons matter. Considering that Microsoft has come through the past 24 years better than Intel, it may be significant that Microsoft has had only two CEOs in that period while Intel has had five. 5. Failure isn’t fatal. The Wintel story is a pointed reminder that all companies, including the best, suffer failures and fall into crises. There are no exceptions. The leaders of any company, even the grandest, must always be ready to engage the skills of organizational rescue, and know that even that can be part of greatness.
Latest in Leadership

Lack of supervision at psychiatric facility led to violent assaults and a patient’s escape to a pond: report

New Florida resident Jeff Bezos pumped $60 million into making lab-grown meat taste better. Ron DeSantis just banned it from the state

OpenAI’s Sam Altman doesn’t care how much AGI will cost: Even if he spends $50 billion a year, some breakthroughs for mankind are priceless

CHROs are more powerful than ever—but they’ll have to fight to hold on to their new status

7-to-7 is the new 9-to-5: Research shows that workers’ days in the office are fewer but longer than pre-pandemic

Berkshire board member blesses Buffett’s successor but warns—’he’s not going to be as entertaining as Warren and Charlie’
Most popular.

Another Boeing whistleblower is dead—this time a healthy 45-year-old who battled a sudden, severe infection

Move over, American dream: The goal of many Gen Z and millennial women is now to be a DINK—with dual income and no kids

Elon Musk publicly dumped California for Texas—now Golden State customers are getting revenge, dumping Tesla in droves

Peloton, the fallen fitness unicorn, faces a harsh truth despite its shiny new deal with Hyatt hotels: ‘I don’t think they thought [about] what was going to happen post-pandemic’

U.S. panic over national debt might mark a culture shift—are Americans becoming more ‘European’ about money?

U.S. fishermen poised to harvest billions of baby eels worth $2,000 a pound as authorities battle illegal sales
NIOSH Science Blog: The Problem of Falls from Elevation in Construction and Prevention Resources
The current situation with falls.
In 2022 falls from elevation represented approximately 81% of all fatal and 20% of all nonfatal slips, trips, and falls for all industry workers (BLS 2023a, BLS 2023b). Many of these falls occurred in the construction industry, and significantly impact construction employers, workers, and their families. In fact, construction workers made up nearly half (49%) of all fatal occupational slips, trips, and falls (BLS 2023). Since 2013, construction workers have suffered approximately 300 fatal and 20,000 nonfatal fall-related injuries per year (CPWR 2024). Four out of 10 of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) top citations involved falls, including general fall protection, ladders, scaffolding, and fall protection training.
Roofing contractors, residential building construction, and commercial/institutional building construction had the highest number of fatalities in 2022 compared to previous years and other industries (CPWR 2024). In addition, approximately 70% of all fatal falls in construction occurred to those working for employers with less than 10 employees (CPWR 2024).
Causes of Falls
The causes of construction workers’ falls from elevation are complex and multifaceted. There are many different factors at play. In 2021, CPWR conducted a fall experience survey that found that insufficient or ineffective planning is a key underlying cause of falls.
In addition, lack of planning was associated with reduced likelihood of using fall protection. Using fall protection was 71% lower for workers whose employer did not do any planning. Approximately half (49%) of survey respondents said that no fall protection was being used at the time of the fall. Lack of fall protection is particularly problematic for small residential construction firms with fewer than 10 employees (CPWR 2022).
Ladders and Ladder Safety
Falls from ladders are a common cause of injury for construction workers (CPWR 2024). Employers should be familiar with safety and regulatory requirements before using a ladder, including:
Planning work tasks to eliminate or reduce the need to work at elevation.
Providing the right equipment. This includes alternative equipment for extended work periods at elevation, such as aerial lifts, supported scaffolds, or mast climbing platforms. If a ladder must be used, properly select the ladder for the location and height of the task and the weight of the worker. Ensure it is thoroughly inspected before each use.
Training all workers in a language they understand on the proper use, care, and inspection of each type of ladder being used.
A recent webinar hosted by CPWR – The Center for Construction Research and Training (CPWR) discussed ladder safety and ways to improve ladder design, usage, and training. The webinar included a panel of experts who conduct laboratory research on ways to prevent common ladder fall injuries, such as slipping off a ladder and falling with the ladder. The audio from the webinar is also available in Spanish .
Ladder Safety Resources
Ladder Safety App
National Ladder Safety Month website
ALI Training
ANSI blog on 5 most common causes of ladder incidents based on ALI study
OSHA Stairways and Ladders
OSHA Letter of Interpretation on three points of contact
Rescue Planning
Falls can occur quickly, even when all precautions are taken and using proper fall prevention and protection methods. Personal Fall Arrest Systems are a critical option to keep workers safe when performing tasks at heights, but rescue planning is essential.
If a fall occurs and a worker is suspended in a harness for more than a few minutes, a lack of circulation can cause unconsciousness, suspension trauma, and even death.
Every fall protection plan must include a rescue strategy to help workers after a fall and reduce fall-related injuries including suspension trauma even when using a Personal Fall Arrest System. Another finding from CPWR’s fall experience survey was that the odds of a fall being fatal were 76% lower for those who had self-rescue training compared to those who did not have this training. The rescue plan should be tailored to each jobsite and prioritize methods to preserve blood circulation for the worker. Ensure equipment for self-rescue is available, such as trauma straps and self-rescue harness units. The rescue plan should ensure other equipment is available, ready to be used, and in good condition, such as a ladder, aerial lift, or bucket truck.
Rescue Planning Resources
CPWR General Fall Protection Plan (English)
CPWR General Fall Protection Plan (Spanish)
OSHA Model Fall Protection Plan
OSHA Standard Interpretations – Rescue of a suspended worker following a fall event
CPWR Fall Rescue Planning Tipsheet
CPWR Fall Rescue Planning Tipsheet (Spanish)
The National Safety Stand-Down to Prevent Falls in Construction
The National Campaign to Prevent Falls in Construction (Falls Campaign) began in 2012 and was followed in 2014 by the National Safety Stand-Down to Prevent Falls in Construction (Stand-Down). The Falls Campaign idea originated with the National Occupational Research Agenda (NORA) Construction Sector Council. The Sector Council consists of industry experts on health and safety representing contractors, trade associations, labor, government, and academia. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), OSHA, and CPWR are the Falls Campaign organizing partners. The Falls Campaign and Stand-Down are important events because of the high burden falls place on construction workers and their families.
Safety stand-downs originated in the military and are a time to focus on worker safety by stopping work and reinforcing the importance of fall prevention and fall protection.
This year’s Stand-Down will take place May 6-10, 2024. CPWR, NIOSH, and OSHA are hosting a virtual event on Tuesday May 7 th at 2 pm (Eastern Time) to educate employers and crew leaders on how rescue planning can save lives. Click here to register and submit a question in advance. Attendees will learn more about identifying a competent person to lead fall prevention and rescue planning, incorporating key components of a rescue plan into the pre-job planning process, and using FREE resources and templates to tailor your plans to each unique jobsite. The webinar will be in English with simultaneous translation into Spanish available.
On May 8 th at 2pm (Eastern Time) a second Stand-Down webinar presented entirely in Spanish will be hosted. Click here to register and submit a question in advance.
Hosting a Stand-Down
Thousands of companies have held fall safety stand-downs , reaching millions of workers across all 50 states and internationally. Industry and business leaders, universities, labor organizations, and community groups have all participated. In 2023, there were 3,554 stand-downs reaching more than 463,000 workers.
Construction employers and workers are invited to host a Safety Stand-Down or join one.
Your involvement can be as simple as sharing NIOSH, OSHA, or CPWR resources at your worksite. If you would like to host or join a free event that is open to the public, contact your Regional Stand-Down Coordinator . You can find resources to host a Stand-Down and activities at CPWR’s Promotion and Planning Page .
If you do participate in the Stand-Down, make sure you get a Certificate of Participation from OSHA. The certificates provide recognition for your event(s). After removing all personal information, CPWR used the data to evaluate and improve the Falls Campaign and Stand-Down every year. Previous evaluation reports and factsheets can be found on the Stop Construction Falls Evaluation page .
Stand-down Resources
About the Campaign
CPWR’S Planning and Promotion Page on StopConstructionFalls.com
Suggestions to prepare successful Stand-Downs
Highlights from previous Stand-Downs
OSHA Regional Stand-Down Coordinators
OSHA Certificates of Participation
Additional Tools and Resources
National Falls Campaign & Safety Stand-Down Website
CPWR Data Bulletin
Bilingual Fall Hazards & Prevention YouTube Playlist
Spanish Fall Safety YouTube Playlist (Prevención de caídas)
Christina Socias-Morales, DrPH is a Research Epidemiologist in the NIOSH Office of Construction Safety and Health.
Scott Earnest, PhD, PE, CSP, is the Associate Director for the NIOSH Office of Construction Safety and Health.
Jessica Bunting, MPH, is the Research to Practice Director at the Center for Construction Research and Training (CPWR).
Rosa Greenberg, MPH, is a Research Analyst in Research to Practice at CPWR
Scott Breloff, Ph.D. is a Senior Biomechanical Research Engineer in the Division of Field Studies & Engineering and the Co-Coordinator for the Construction Program in the Office of Construction Safety and Health at NIOSH.
Asha Brogan, MS, is a Heath Communication Fellow in the NIOSH Division of Field Studies & Engineering.
Douglas Trout, MD, MHS, is Deputy Director, Office of Construction Safety and Health at NIOSH.
Bureau of Labor Statistics (2023a). News Release National Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries in 2022. USDL-23-2615. December 19, 2023. Available from: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/cfoi.pdf .
Bureau of Labor Statistics (2023b). Number of nonfatal occupational injuries and illnesses involving days away from work, restricted activity, or job transfer (DART), days away from work (DAFW), and days of restricted work activity, or job transfer (DJTR) by event or exposure leading to injury or illness and industry sector, private industry, 2021-2022 (TABLE R64). November 8, 2023. Available from: https://www.bls.gov/iif/nonfatal-injuries-and-illnesses-tables/case-and-demographic-characteristics-table-r64-2021-2022.xlsx
CPWR (2024). Data Bulletin: Fatal and Nonfatal Falls in the US Construction Industry. The Center for Construction Research and Training. Silver Spring, MD. March 2024. https://www.cpwr.com/wp-content/uploads/DataBulletin-March2024.pdf.
CPWR (2022). Underlying Causes of Falls from Heights (Highlighted Findings from a CPWR Survey). The Center for Construction Research and Training. Silver Spring, MD. March 2022. https://www.cpwr.com/wp-content/uploads/RR-falls_experience_survey.pdf.
Post a Comment
Cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- 50th Anniversary Blog Series
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aging Workers
- Agriculture
- Animal/Livestock hazards
- Artificial Intelligence
- Back Injury
- Bloodborne pathogens
- Cardiovascular Disease
- cold stress
- commercial fishing
- Communication
- Construction
- Cross Cultural Communication
- Dermal Exposure
- Education and Research Centers
- Electrical Safety
- Emergency Response/Public Sector
- Engineering Control
- Environment/Green Jobs
- Epidemiology
- Fire Fighting
- Food Service
- Future of Work and OSH
- Healthy Work Design
- Hearing Loss
- Heat Stress
- Holiday Themes
- Hydraulic Fracturing
- Infectious Disease Resources
- International
- Landscaping
- Law Enforcement
- Manufacturing
- Manufacturing Mondays Series
- Mental Health
- Motor Vehicle Safety
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Nanotechnology
- National Occupational Research Agenda
- Needlestick Prevention
- NIOSH-funded Research
- Nonstandard Work Arrangements
- Observances
- Occupational Health Equity
- Oil and Gas
- Outdoor Work
- Partnership
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Physical activity
- Policy and Programs
- Prevention Through Design
- Prioritizing Research
- Reproductive Health
- Research to practice r2p
- Researcher Spotlights
- Respirators
- Respiratory Health
- Risk Assessment
- Safety and Health Data
- Service Sector
- Small Business
- Social Determinants of Health
- Spanish translations
- Sports and Entertainment
- Strategic Foresight
- Struck-by injuries
- Student Training
- Substance Use Disorder
- Surveillance
- Synthetic Biology
- Systematic review
- Take Home Exposures
- Teachers/School Workers
- Temporary/Contingent Workers
- Total Worker Health
- Translations (other than Spanish)
- Transportation
- Uncategorized
- Veterinarians
- Wearable Technologies
- Wholesale and Retail Trade
- Work Schedules
- Workers' Compensation
- Workplace Medical Mystery
- Workplace Supported Recovery
- World Trade Center Health Program
- Young Workers
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nokia's demise from being the world's best mobile phone company to losing it all by 2013 has become a case study discussed by teachers and students in business management classes.
In this book, the case of Nokia is analysed mainly on the basis of the executive biographies (Alahuhta, 2015 ; Ollila & Saukkomaa, 2013 ; Pa lmu - Joroinen, 2009 ) and interviews (Heikkinen, 2010 ...
Someone really should dig into the tale of Nokia Music, that of OD2, a successful independent company bought by Nokia in 2007. In less than four years through marketing bodges, strategic failures, interference from gormless management in the USA, and even more nepotistic and mostly incompetent management in the UK, a profitable company with numerous high profile corporate customers was brought ...
Abstract. In 2013, Nokia sold its Device and Services business to Microsoft for €5.4 billion. For decades Nokia had led the telecommunications (telecom) industry in handsets and networking. By the late 2000s, however, Nokia's position as market leader in mobile devices was threatened by competition from new lower-cost Asian manufacturers.
In single case studies in which the motivation for the study is to explain backwards from the outcome, causal inference becomes very difficult, if not impossible. ... The rise and fall of Nokia. Harvard Business School Case 714-428 (Revised February 2014.) Google Scholar. Alexander, A. (2015). Decision-making authority in British supermarket ...
The case describes Nokia's spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company's handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010.During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia's focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation.
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of ...
Nokia's fall from the top of the smartphone pyramid is typically put down to three factors by executives who attempt to explain it: 1) that Nokia was technically inferior to Apple, 2) that the company was complacent and 3) that its leaders didn't see the disruptive iPhone coming. ... When I taught the case of Nokia to hundreds of senior ...
The case describes Nokia's spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company's handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010. During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia's focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation. It was acknowledged as the first ...
Nokia's loss of dominance in the mobile market after 2007 is one of the most significant failures in modern business history. For Finland, this was an economic catastrophe, when the largest company in the country lost grip on its core business. In 2007, Nokia's mobile division was the leading mobile device manufacturer in the world, with a ...
The Rise And Fall Of A Tech Giant. In the 2000s, everyone had a Nokia phone. Known and desired for its durability and ease of use, it became the preferred device for many worldwide. According to ...
In 2013, Nokia sold its Device and Services business to Microsoft for €5.4 billion. For decades Nokia had led the telecommunications (telecom) industry in handsets and networking. By the late 2000s, however, Nokia's position as market leader in mobile devices was threatened by competition from new lower-cost Asian manufacturers. Apple's 2007 release of its iPhone established an entire new ...
Abstract. In 2013, Nokia sold its Device and Services business to Microsoft for €5.4 billion. For decades Nokia had led the telecommunications (telecom) industry in handsets and networking. By the late 2000s, however, Nokia's position as market leader in mobile devices was threatened by competition from new lower-cost Asian manufacturers.
This case study shows Nokia's failure to keep up with changing technology and its delayed response to industry trends significantly contributed to its downfall. ... The fall of Nokia can be attributed to a combination of factors that hindered its ability to adapt, innovate, and stay competitive in the mobile phone market. ...
The Real Cause of Nokia's Crisis. by. Michael Schrage. February 15, 2011. Nokia's technology isn't a root cause of its current crisis. Don't blame its engineers and designers either. The ...
Nokia is a case study in modern disruption. Let's go back to 2006 to review the essentials of why. Apple was about to launch a phone that nobody in the mobile world thought they had much of a chance.
The rise of Nokia. 1865: Nokia was found. 1984: Nokia's first mobile phone. The Nokia 1011 marked the next major milestone in Nokia's journey of innovation. 1996: Nokia 9000 Communicator & Nokia 8110. 1998: Dominating the global mobile phone market. 2000 - 2006: King of the early digital era. The downfall of Nokia.
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of longer ...
The Rise and Fall of Nokia was shown on BBC Four This article was amended on 11 July 2018. Errors introduced during editing led the review to say Nokia "was bought by Microsoft.
In final words, this was the story of the fall and rise of Nokia, a multinational that had everything to be the best indefinitely, but bad decisions precipitated its failure just when the competition adopted Android to sink it further. But thinking about customers was what saved it because customers wanted Nokia with Android, and now they ...
In this historical case study, we explore the origins of Nokia and their progress toward breaking new ground in telecommunications technology. ... through the rise and fall of Nokia in the mobile ...
In 2013, Nokia sold its Device and Services business to Microsoft for €5.4 billion. For decades Nokia had led the telecommunications (telecom) industry in handsets and networking. By the late 2000s, however, Nokia's position as market leader in mobile devices was threatened by competition from new lower-cost Asian manufacturers. Apple's 2007 release of its iPhone established an entire new ...
This paper presents a comparative case study of the rise and fall of Nokia and Apple technology companies in the mobile device industry, focusing on their different approaches to technology strategy.
Nokia | The Rise And Fall [Part 1] Posted: May 2, 2024 | Last updated: May 2, 2024. This is part 1 of a 3 part Nokia documentary series taking the look at the history of Nokia, how they rose to ...
Finnish telecom gear maker Nokia reported a smaller-than-expected rise in quarterly profit on Thursday as sluggish demand for 5G gear in key markets North America and India continued to weigh on ...
The case study of what went right ... suffer failures and fall into crises. ... Novo Nordisk's market value of $570 billion is now bigger than the entire Danish economy—creating a 'Nokia ...
Using fall protection was 71% lower for workers whose employer did not do any planning. Approximately half (49%) of survey respondents said that no fall protection was being used at the time of the fall. Lack of fall protection is particularly problematic for small residential construction firms with fewer than 10 employees (CPWR 2022).
This study documents the first record of seven-, Quaternary (<27.4 - >1.1 ka) lapilli fall layers at Sumbing volcano, Central Java, Indonesia. These lapilli layers (from lower towards upper stratigraphic height) are named orange-red lapilli, dark brown lapilli, orange lapilli, red-brown lapilli, blackish brown lapilli, pale red lapilli, and red lapilli.