- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion

How Does Social Media Affect Your Mental Health?
Facebook has delayed the development of an Instagram app for children amid questions about its harmful effects on young people’s mental health. Does social media have an impact on your well-being?

By Nicole Daniels
What is your relationship with social media like? Which platforms do you spend the most time on? Which do you stay away from? How often do you log on?
What do you notice about your mental health and well-being when spending time on social networks?
In “ Facebook Delays Instagram App for Users 13 and Younger ,” Adam Satariano and Ryan Mac write about the findings of an internal study conducted by Facebook and what they mean for the Instagram Kids app that the company was developing:
Facebook said on Monday that it had paused development of an Instagram Kids service that would be tailored for children 13 years old or younger, as the social network increasingly faces questions about the app’s effect on young people’s mental health. The pullback preceded a congressional hearing this week about internal research conducted by Facebook , and reported in The Wall Street Journal , that showed the company knew of the harmful mental health effects that Instagram was having on teenage girls. The revelations have set off a public relations crisis for the Silicon Valley company and led to a fresh round of calls for new regulation. Facebook said it still wanted to build an Instagram product intended for children that would have a more “age appropriate experience,” but was postponing the plans in the face of criticism.
The article continues:
With Instagram Kids, Facebook had argued that young people were using the photo-sharing app anyway, despite age-requirement rules, so it would be better to develop a version more suitable for them. Facebook said the “kids” app was intended for ages 10 to 12 and would require parental permission to join, forgo ads and carry more age-appropriate content and features. Parents would be able to control what accounts their child followed. YouTube, which Google owns, has released a children’s version of its app. But since BuzzFeed broke the news this year that Facebook was working on the app, the company has faced scrutiny. Policymakers, regulators, child safety groups and consumer rights groups have argued that it hooks children on the app at a younger age rather than protecting them from problems with the service, including child predatory grooming, bullying and body shaming.
The article goes on to quote Adam Mosseri, the head of Instagram:
Mr. Mosseri said on Monday that the “the project leaked way before we knew what it would be” and that the company had “few answers” for the public at the time. Opposition to Facebook’s plans gained momentum this month when The Journal published articles based on leaked internal documents that showed Facebook knew about many of the harms it was causing. Facebook’s internal research showed that Instagram, in particular, had caused teen girls to feel worse about their bodies and led to increased rates of anxiety and depression, even while company executives publicly tried to minimize the app’s downsides.
But concerns about the effect of social media on young people go beyond Instagram Kids, the article notes:
A children’s version of Instagram would not fix more systemic problems, said Al Mik, a spokesman for 5Rights Foundation, a London group focused on digital rights issues for children. The group published a report in July showing that children as young as 13 were targeted within 24 hours of creating an account with harmful content, including material related to eating disorders, extreme diets, sexualized imagery, body shaming, self-harm and suicide. “Big Tobacco understood that the younger you got to someone, the easier you could get them addicted to become a lifelong user,” Doug Peterson, Nebraska’s attorney general, said in an interview. “I see some comparisons to social media platforms.” In May, attorneys general from 44 states and jurisdictions had signed a letter to Facebook’s chief executive, Mark Zuckerberg, asking him to end plans for building an Instagram app for children. American policymakers should pass tougher laws to restrict how tech platforms target children, said Josh Golin, executive director of Fairplay, a Boston-based group that was part of an international coalition of children’s and consumer groups opposed to the new app. Last year, Britain adopted an Age Appropriate Design Code , which requires added privacy protections for digital services used by people under the age of 18.
Students, read the entire article , then tell us:
Do you think Facebook made the right decision in halting the development of the Instagram Kids app? Do you think there should be social media apps for children 13 and younger? Why or why not?
What is your reaction to the research that found that Instagram can have harmful mental health effects on teenagers, particularly teenage girls? Have you experienced body image issues, anxiety or depression tied to your use of the app? How do you think social media affects your mental health?
What has your experience been on different social media apps? Are there apps that have a more positive or negative effect on your well-being? What do you think could explain these differences?
Have you ever been targeted with inappropriate or harmful content on Instagram or other social media apps? What responsibility do you think social media companies have to address these issues? Do you think there should be more protections in place for users under 18? Why or why not?
What does healthy social media engagement look like for you? What habits do you have around social media that you feel proud of? What behaviors would you like to change? How involved are your parents in your social media use? How involved do you think they should be?
If you were in charge of making Instagram, or another social media app, safer for teenagers, what changes would you make?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Nicole Daniels joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2019 after working in museum education, curriculum writing and bilingual education. More about Nicole Daniels
Is social media use bad for young people’s mental health? It’s complicated.

July 17, 2023 – On May 23, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory warning about the potential dangers of social media for the mental health of children and teens . Laura Marciano , postdoctoral research fellow at the Lee Kum Sheung Center for Health and Happiness and in the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, says that social media use might be detrimental for young people’s well-being but can also have positive effects.
Q: What are your thoughts on the Surgeon General’s advisory?
A: The advisory highlighted compelling evidence published during the last decade on the potential harmful impact of social media on children and adolescents. Some of what young people experience online—including cyberbullying, online harassment and abuse, predatory behaviors, and exposure to violent, sexual, and hate-based content—can undoubtedly be negative. But social media experiences are not limited to these types of content.
Much of the scientific literature on the effects of social media use has focused on negative outcomes. But the link between social media use and young people’s mental health is complicated. Literature reviews show that study results are mixed: Associations between social media use and well-being can be positive, negative, and even largely null when advanced data analyses are carried out, and the size of the effects is small. And positive and negative effects can co-exist in the same individual. We are still discovering how to compare the effect size of social media use with the effects of other behavioral habits—such as physical activity, sleep, food consumption, life events, and time spent in offline social connections—and psychological processes happening offline. We are also still studying how social media use may be linked positively with well-being.
It’s important to note that many of the existing studies relied on data from people living in so-called WEIRD countries (Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich and Democratic), thus leaving out the majority of the worldwide population living in the Global South. In addition, we know that populations like minorities, people experiencing health disparities and chronic health conditions , and international students can find social media extremely helpful for creating and maintaining social communities to which they feel they belong.
A number of large cohort studies have measured social media use according to time spent on various platforms. But it’s important to consider not just time spent, but whether that time is displacing time for other activities promoting well-being, like physical activity and sleep. Finally, the effects of social media use are idiosyncratic, meaning that each child and adolescent might be affected differently, which makes it difficult to generalize about the effects.
Literature reviews on interventions limiting social media use present a more balanced picture. For example, one comprehensive review on the effects of digital detox—refraining from using devices such as smartphones—wasn’t able to draw any clear conclusions about whether such detox could be effective at promoting a healthy way of life in the digital era, because the findings were mixed and contradictory.
Q: What has your research found regarding the potential risks and benefits of social media use among young people?
A: In my work with Prof. Vish Viswanath , we have summarized all the papers on how social media use is related to positive well-being measures, to balance the ongoing bias of the literature on negative outcomes such as depression and anxiety. We found both positive and negative correlations between different social media activities and well-being. The most consistent results show a link between social media activities and hedonic well-being (positive emotions) and social well-being. We also found that social comparison—such as comparing how many likes you have with how many someone else has, or comparing yourself to digitally enhanced images online—drives the negative correlation with well-being.
Meanwhile, I am working on the “ HappyB ” project, a longitudinal project based in Switzerland, through which I have collected data from more than 1,500 adolescents on their smartphone and social media use and well-being. In a recent study using that cohort, we looked at how social media use affects flourishing , a construct that encompasses happiness, meaning and purpose, physical and mental health, character, close social relationships, and financial stability. We found that certain positive social media experiences are associated with flourishing. In particular, having someone to talk to online when feeling lonely was the item most related to well-being. That is not surprising, considering that happiness is related to the quality of social connections.
Our data suggest that homing in on the psychological processes triggered during social media use is key to determining links with well-being. For example, we should consider if a young person feels appreciated and part of a group in a particular online conversation. Such information can help us shed light on the dynamics that shape young people’s well-being through digital activities.
In our research, we work to account for the fact that social media time is a sedentary behavior. We need to consider that any behavior that risks diminishing the time spent on physical activity and sleep—crucial components of brain development and well-being—might be detrimental. Interestingly, some studies suggest that spending a short amount of time using social media, around 1-2 hours, is beneficial, but—as with any extreme behavior—it can cause harm if the time spent online dominates a child’s or adolescent’s day.
It’s also important to consider how long the effects of social media last. Social media use may have small ephemeral effects that can accumulate over time. A step for future research is to disentangle short- versus long-term effects and how long each last. In addition, we should better understand how digital media usage affects the adolescent brain. Colleagues and I have summarized existing neuroscientific studies on the topic, but more multidisciplinary research is needed.
Q: What are some steps you’d recommend to make social media use safer for kids?
A: I’ll use a metaphor to answer this question. Is a car safe for someone that is not able to drive? To drive safely, we need to learn how to accelerate, recognize road signs, make safe decisions according to certain rules, and wear safety belts. Similarly, to use social media safely, I think we as a society—including schools, educators, and health providers—should provide children and families with clear, science-based information on both its positive and negative potential impacts.
We can also ask social media companies to pay more attention to how some features—such as the number of “likes”—can modulate adolescent brain activity, and to think about ways to limit negative effects. We might even ask adolescents to advise designers on how to create social media platforms specifically for them. It would be extremely valuable to ask them which features would be best for them and which ones they would like to avoid. I think that co-designing apps and conducting research with the young people who use the platforms is a crucial step.
For parents, my suggestion is to communicate with your children and promote a climate of safety and empathy when it comes to social media use. Try to use these platforms along with them, for example by explaining how a platform works and commenting on the content. Also, I would encourage schools and parents to collaborate on sharing information with young people about social media and well-being.
Also, to offset children’s sedentary time spent on social media, parents could offer them alternative extracurricular activities to provide some balance. But it’s important to remember that social well-being depends on the quality of social connections, and that social media can help to promote this kind of well-being. So I’d recommend trying to keep what is good—according to my research that would include instant messaging, the chance to talk to people when someone is feeling lonely, and funny or inspirational content—and minimizing what’s negative, such as too much sedentary time or too much time spent on social comparison.
– Karen Feldscher
Find anything you save across the site in your account
All products are independently selected by our editors. If you buy something, we may earn an affiliate commission.
How Harmful Is Social Media?
By Gideon Lewis-Kraus

In April, the social psychologist Jonathan Haidt published an essay in The Atlantic in which he sought to explain, as the piece’s title had it, “Why the Past 10 Years of American Life Have Been Uniquely Stupid.” Anyone familiar with Haidt’s work in the past half decade could have anticipated his answer: social media. Although Haidt concedes that political polarization and factional enmity long predate the rise of the platforms, and that there are plenty of other factors involved, he believes that the tools of virality—Facebook’s Like and Share buttons, Twitter’s Retweet function—have algorithmically and irrevocably corroded public life. He has determined that a great historical discontinuity can be dated with some precision to the period between 2010 and 2014, when these features became widely available on phones.
“What changed in the 2010s?” Haidt asks, reminding his audience that a former Twitter developer had once compared the Retweet button to the provision of a four-year-old with a loaded weapon. “A mean tweet doesn’t kill anyone; it is an attempt to shame or punish someone publicly while broadcasting one’s own virtue, brilliance, or tribal loyalties. It’s more a dart than a bullet, causing pain but no fatalities. Even so, from 2009 to 2012, Facebook and Twitter passed out roughly a billion dart guns globally. We’ve been shooting one another ever since.” While the right has thrived on conspiracy-mongering and misinformation, the left has turned punitive: “When everyone was issued a dart gun in the early 2010s, many left-leaning institutions began shooting themselves in the brain. And, unfortunately, those were the brains that inform, instruct, and entertain most of the country.” Haidt’s prevailing metaphor of thoroughgoing fragmentation is the story of the Tower of Babel: the rise of social media has “unwittingly dissolved the mortar of trust, belief in institutions, and shared stories that had held a large and diverse secular democracy together.”
These are, needless to say, common concerns. Chief among Haidt’s worries is that use of social media has left us particularly vulnerable to confirmation bias, or the propensity to fix upon evidence that shores up our prior beliefs. Haidt acknowledges that the extant literature on social media’s effects is large and complex, and that there is something in it for everyone. On January 6, 2021, he was on the phone with Chris Bail, a sociologist at Duke and the author of the recent book “ Breaking the Social Media Prism ,” when Bail urged him to turn on the television. Two weeks later, Haidt wrote to Bail, expressing his frustration at the way Facebook officials consistently cited the same handful of studies in their defense. He suggested that the two of them collaborate on a comprehensive literature review that they could share, as a Google Doc, with other researchers. (Haidt had experimented with such a model before.) Bail was cautious. He told me, “What I said to him was, ‘Well, you know, I’m not sure the research is going to bear out your version of the story,’ and he said, ‘Why don’t we see?’ ”
Bail emphasized that he is not a “platform-basher.” He added, “In my book, my main take is, Yes, the platforms play a role, but we are greatly exaggerating what it’s possible for them to do—how much they could change things no matter who’s at the helm at these companies—and we’re profoundly underestimating the human element, the motivation of users.” He found Haidt’s idea of a Google Doc appealing, in the way that it would produce a kind of living document that existed “somewhere between scholarship and public writing.” Haidt was eager for a forum to test his ideas. “I decided that if I was going to be writing about this—what changed in the universe, around 2014, when things got weird on campus and elsewhere—once again, I’d better be confident I’m right,” he said. “I can’t just go off my feelings and my readings of the biased literature. We all suffer from confirmation bias, and the only cure is other people who don’t share your own.”
Haidt and Bail, along with a research assistant, populated the document over the course of several weeks last year, and in November they invited about two dozen scholars to contribute. Haidt told me, of the difficulties of social-scientific methodology, “When you first approach a question, you don’t even know what it is. ‘Is social media destroying democracy, yes or no?’ That’s not a good question. You can’t answer that question. So what can you ask and answer?” As the document took on a life of its own, tractable rubrics emerged—Does social media make people angrier or more affectively polarized? Does it create political echo chambers? Does it increase the probability of violence? Does it enable foreign governments to increase political dysfunction in the United States and other democracies? Haidt continued, “It’s only after you break it up into lots of answerable questions that you see where the complexity lies.”
Haidt came away with the sense, on balance, that social media was in fact pretty bad. He was disappointed, but not surprised, that Facebook’s response to his article relied on the same three studies they’ve been reciting for years. “This is something you see with breakfast cereals,” he said, noting that a cereal company “might say, ‘Did you know we have twenty-five per cent more riboflavin than the leading brand?’ They’ll point to features where the evidence is in their favor, which distracts you from the over-all fact that your cereal tastes worse and is less healthy.”
After Haidt’s piece was published, the Google Doc—“Social Media and Political Dysfunction: A Collaborative Review”—was made available to the public . Comments piled up, and a new section was added, at the end, to include a miscellany of Twitter threads and Substack essays that appeared in response to Haidt’s interpretation of the evidence. Some colleagues and kibbitzers agreed with Haidt. But others, though they might have shared his basic intuition that something in our experience of social media was amiss, drew upon the same data set to reach less definitive conclusions, or even mildly contradictory ones. Even after the initial flurry of responses to Haidt’s article disappeared into social-media memory, the document, insofar as it captured the state of the social-media debate, remained a lively artifact.
Near the end of the collaborative project’s introduction, the authors warn, “We caution readers not to simply add up the number of studies on each side and declare one side the winner.” The document runs to more than a hundred and fifty pages, and for each question there are affirmative and dissenting studies, as well as some that indicate mixed results. According to one paper, “Political expressions on social media and the online forum were found to (a) reinforce the expressers’ partisan thought process and (b) harden their pre-existing political preferences,” but, according to another, which used data collected during the 2016 election, “Over the course of the campaign, we found media use and attitudes remained relatively stable. Our results also showed that Facebook news use was related to modest over-time spiral of depolarization. Furthermore, we found that people who use Facebook for news were more likely to view both pro- and counter-attitudinal news in each wave. Our results indicated that counter-attitudinal exposure increased over time, which resulted in depolarization.” If results like these seem incompatible, a perplexed reader is given recourse to a study that says, “Our findings indicate that political polarization on social media cannot be conceptualized as a unified phenomenon, as there are significant cross-platform differences.”
Interested in echo chambers? “Our results show that the aggregation of users in homophilic clusters dominate online interactions on Facebook and Twitter,” which seems convincing—except that, as another team has it, “We do not find evidence supporting a strong characterization of ‘echo chambers’ in which the majority of people’s sources of news are mutually exclusive and from opposite poles.” By the end of the file, the vaguely patronizing top-line recommendation against simple summation begins to make more sense. A document that originated as a bulwark against confirmation bias could, as it turned out, just as easily function as a kind of generative device to support anybody’s pet conviction. The only sane response, it seemed, was simply to throw one’s hands in the air.
When I spoke to some of the researchers whose work had been included, I found a combination of broad, visceral unease with the current situation—with the banefulness of harassment and trolling; with the opacity of the platforms; with, well, the widespread presentiment that of course social media is in many ways bad—and a contrastive sense that it might not be catastrophically bad in some of the specific ways that many of us have come to take for granted as true. This was not mere contrarianism, and there was no trace of gleeful mythbusting; the issue was important enough to get right. When I told Bail that the upshot seemed to me to be that exactly nothing was unambiguously clear, he suggested that there was at least some firm ground. He sounded a bit less apocalyptic than Haidt.
“A lot of the stories out there are just wrong,” he told me. “The political echo chamber has been massively overstated. Maybe it’s three to five per cent of people who are properly in an echo chamber.” Echo chambers, as hotboxes of confirmation bias, are counterproductive for democracy. But research indicates that most of us are actually exposed to a wider range of views on social media than we are in real life, where our social networks—in the original use of the term—are rarely heterogeneous. (Haidt told me that this was an issue on which the Google Doc changed his mind; he became convinced that echo chambers probably aren’t as widespread a problem as he’d once imagined.) And too much of a focus on our intuitions about social media’s echo-chamber effect could obscure the relevant counterfactual: a conservative might abandon Twitter only to watch more Fox News. “Stepping outside your echo chamber is supposed to make you moderate, but maybe it makes you more extreme,” Bail said. The research is inchoate and ongoing, and it’s difficult to say anything on the topic with absolute certainty. But this was, in part, Bail’s point: we ought to be less sure about the particular impacts of social media.
Bail went on, “The second story is foreign misinformation.” It’s not that misinformation doesn’t exist, or that it hasn’t had indirect effects, especially when it creates perverse incentives for the mainstream media to cover stories circulating online. Haidt also draws convincingly upon the work of Renée DiResta, the research manager at the Stanford Internet Observatory, to sketch out a potential future in which the work of shitposting has been outsourced to artificial intelligence, further polluting the informational environment. But, at least so far, very few Americans seem to suffer from consistent exposure to fake news—“probably less than two per cent of Twitter users, maybe fewer now, and for those who were it didn’t change their opinions,” Bail said. This was probably because the people likeliest to consume such spectacles were the sort of people primed to believe them in the first place. “In fact,” he said, “echo chambers might have done something to quarantine that misinformation.”
The final story that Bail wanted to discuss was the “proverbial rabbit hole, the path to algorithmic radicalization,” by which YouTube might serve a viewer increasingly extreme videos. There is some anecdotal evidence to suggest that this does happen, at least on occasion, and such anecdotes are alarming to hear. But a new working paper led by Brendan Nyhan, a political scientist at Dartmouth, found that almost all extremist content is either consumed by subscribers to the relevant channels—a sign of actual demand rather than manipulation or preference falsification—or encountered via links from external sites. It’s easy to see why we might prefer if this were not the case: algorithmic radicalization is presumably a simpler problem to solve than the fact that there are people who deliberately seek out vile content. “These are the three stories—echo chambers, foreign influence campaigns, and radicalizing recommendation algorithms—but, when you look at the literature, they’ve all been overstated.” He thought that these findings were crucial for us to assimilate, if only to help us understand that our problems may lie beyond technocratic tinkering. He explained, “Part of my interest in getting this research out there is to demonstrate that everybody is waiting for an Elon Musk to ride in and save us with an algorithm”—or, presumably, the reverse—“and it’s just not going to happen.”
When I spoke with Nyhan, he told me much the same thing: “The most credible research is way out of line with the takes.” He noted, of extremist content and misinformation, that reliable research that “measures exposure to these things finds that the people consuming this content are small minorities who have extreme views already.” The problem with the bulk of the earlier research, Nyhan told me, is that it’s almost all correlational. “Many of these studies will find polarization on social media,” he said. “But that might just be the society we live in reflected on social media!” He hastened to add, “Not that this is untroubling, and none of this is to let these companies, which are exercising a lot of power with very little scrutiny, off the hook. But a lot of the criticisms of them are very poorly founded. . . . The expansion of Internet access coincides with fifteen other trends over time, and separating them is very difficult. The lack of good data is a huge problem insofar as it lets people project their own fears into this area.” He told me, “It’s hard to weigh in on the side of ‘We don’t know, the evidence is weak,’ because those points are always going to be drowned out in our discourse. But these arguments are systematically underprovided in the public domain.”
In his Atlantic article, Haidt leans on a working paper by two social scientists, Philipp Lorenz-Spreen and Lisa Oswald, who took on a comprehensive meta-analysis of about five hundred papers and concluded that “the large majority of reported associations between digital media use and trust appear to be detrimental for democracy.” Haidt writes, “The literature is complex—some studies show benefits, particularly in less developed democracies—but the review found that, on balance, social media amplifies political polarization; foments populism, especially right-wing populism; and is associated with the spread of misinformation.” Nyhan was less convinced that the meta-analysis supported such categorical verdicts, especially once you bracketed the kinds of correlational findings that might simply mirror social and political dynamics. He told me, “If you look at their summary of studies that allow for causal inferences—it’s very mixed.”
As for the studies Nyhan considered most methodologically sound, he pointed to a 2020 article called “The Welfare Effects of Social Media,” by Hunt Allcott, Luca Braghieri, Sarah Eichmeyer, and Matthew Gentzkow. For four weeks prior to the 2018 midterm elections, the authors randomly divided a group of volunteers into two cohorts—one that continued to use Facebook as usual, and another that was paid to deactivate their accounts for that period. They found that deactivation “(i) reduced online activity, while increasing offline activities such as watching TV alone and socializing with family and friends; (ii) reduced both factual news knowledge and political polarization; (iii) increased subjective well-being; and (iv) caused a large persistent reduction in post-experiment Facebook use.” But Gentzkow reminded me that his conclusions, including that Facebook may slightly increase polarization, had to be heavily qualified: “From other kinds of evidence, I think there’s reason to think social media is not the main driver of increasing polarization over the long haul in the United States.”
In the book “ Why We’re Polarized ,” for example, Ezra Klein invokes the work of such scholars as Lilliana Mason to argue that the roots of polarization might be found in, among other factors, the political realignment and nationalization that began in the sixties, and were then sacralized, on the right, by the rise of talk radio and cable news. These dynamics have served to flatten our political identities, weakening our ability or inclination to find compromise. Insofar as some forms of social media encourage the hardening of connections between our identities and a narrow set of opinions, we might increasingly self-select into mutually incomprehensible and hostile groups; Haidt plausibly suggests that these processes are accelerated by the coalescence of social-media tribes around figures of fearful online charisma. “Social media might be more of an amplifier of other things going on rather than a major driver independently,” Gentzkow argued. “I think it takes some gymnastics to tell a story where it’s all primarily driven by social media, especially when you’re looking at different countries, and across different groups.”
Another study, led by Nejla Asimovic and Joshua Tucker, replicated Gentzkow’s approach in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and they found almost precisely the opposite results: the people who stayed on Facebook were, by the end of the study, more positively disposed to their historic out-groups. The authors’ interpretation was that ethnic groups have so little contact in Bosnia that, for some people, social media is essentially the only place where they can form positive images of one another. “To have a replication and have the signs flip like that, it’s pretty stunning,” Bail told me. “It’s a different conversation in every part of the world.”
Nyhan argued that, at least in wealthy Western countries, we might be too heavily discounting the degree to which platforms have responded to criticism: “Everyone is still operating under the view that algorithms simply maximize engagement in a short-term way” with minimal attention to potential externalities. “That might’ve been true when Zuckerberg had seven people working for him, but there are a lot of considerations that go into these rankings now.” He added, “There’s some evidence that, with reverse-chronological feeds”—streams of unwashed content, which some critics argue are less manipulative than algorithmic curation—“people get exposed to more low-quality content, so it’s another case where a very simple notion of ‘algorithms are bad’ doesn’t stand up to scrutiny. It doesn’t mean they’re good, it’s just that we don’t know.”
Bail told me that, over all, he was less confident than Haidt that the available evidence lines up clearly against the platforms. “Maybe there’s a slight majority of studies that say that social media is a net negative, at least in the West, and maybe it’s doing some good in the rest of the world.” But, he noted, “Jon will say that science has this expectation of rigor that can’t keep up with the need in the real world—that even if we don’t have the definitive study that creates the historical counterfactual that Facebook is largely responsible for polarization in the U.S., there’s still a lot pointing in that direction, and I think that’s a fair point.” He paused. “It can’t all be randomized control trials.”
Haidt comes across in conversation as searching and sincere, and, during our exchange, he paused several times to suggest that I include a quote from John Stuart Mill on the importance of good-faith debate to moral progress. In that spirit, I asked him what he thought of the argument, elaborated by some of Haidt’s critics, that the problems he described are fundamentally political, social, and economic, and that to blame social media is to search for lost keys under the streetlamp, where the light is better. He agreed that this was the steelman opponent: there were predecessors for cancel culture in de Tocqueville, and anxiety about new media that went back to the time of the printing press. “This is a perfectly reasonable hypothesis, and it’s absolutely up to the prosecution—people like me—to argue that, no, this time it’s different. But it’s a civil case! The evidential standard is not ‘beyond a reasonable doubt,’ as in a criminal case. It’s just a preponderance of the evidence.”
The way scholars weigh the testimony is subject to their disciplinary orientations. Economists and political scientists tend to believe that you can’t even begin to talk about causal dynamics without a randomized controlled trial, whereas sociologists and psychologists are more comfortable drawing inferences on a correlational basis. Haidt believes that conditions are too dire to take the hardheaded, no-reasonable-doubt view. “The preponderance of the evidence is what we use in public health. If there’s an epidemic—when COVID started, suppose all the scientists had said, ‘No, we gotta be so certain before you do anything’? We have to think about what’s actually happening, what’s likeliest to pay off.” He continued, “We have the largest epidemic ever of teen mental health, and there is no other explanation,” he said. “It is a raging public-health epidemic, and the kids themselves say Instagram did it, and we have some evidence, so is it appropriate to say, ‘Nah, you haven’t proven it’?”
This was his attitude across the board. He argued that social media seemed to aggrandize inflammatory posts and to be correlated with a rise in violence; even if only small groups were exposed to fake news, such beliefs might still proliferate in ways that were hard to measure. “In the post-Babel era, what matters is not the average but the dynamics, the contagion, the exponential amplification,” he said. “Small things can grow very quickly, so arguments that Russian disinformation didn’t matter are like COVID arguments that people coming in from China didn’t have contact with a lot of people.” Given the transformative effects of social media, Haidt insisted, it was important to act now, even in the absence of dispositive evidence. “Academic debates play out over decades and are often never resolved, whereas the social-media environment changes year by year,” he said. “We don’t have the luxury of waiting around five or ten years for literature reviews.”
Haidt could be accused of question-begging—of assuming the existence of a crisis that the research might or might not ultimately underwrite. Still, the gap between the two sides in this case might not be quite as wide as Haidt thinks. Skeptics of his strongest claims are not saying that there’s no there there. Just because the average YouTube user is unlikely to be led to Stormfront videos, Nyhan told me, doesn’t mean we shouldn’t worry that some people are watching Stormfront videos; just because echo chambers and foreign misinformation seem to have had effects only at the margins, Gentzkow said, doesn’t mean they’re entirely irrelevant. “There are many questions here where the thing we as researchers are interested in is how social media affects the average person,” Gentzkow told me. “There’s a different set of questions where all you need is a small number of people to change—questions about ethnic violence in Bangladesh or Sri Lanka, people on YouTube mobilized to do mass shootings. Much of the evidence broadly makes me skeptical that the average effects are as big as the public discussion thinks they are, but I also think there are cases where a small number of people with very extreme views are able to find each other and connect and act.” He added, “That’s where many of the things I’d be most concerned about lie.”
The same might be said about any phenomenon where the base rate is very low but the stakes are very high, such as teen suicide. “It’s another case where those rare edge cases in terms of total social harm may be enormous. You don’t need many teen-age kids to decide to kill themselves or have serious mental-health outcomes in order for the social harm to be really big.” He added, “Almost none of this work is able to get at those edge-case effects, and we have to be careful that if we do establish that the average effect of something is zero, or small, that it doesn’t mean we shouldn’t be worried about it—because we might be missing those extremes.” Jaime Settle, a scholar of political behavior at the College of William & Mary and the author of the book “ Frenemies: How Social Media Polarizes America ,” noted that Haidt is “farther along the spectrum of what most academics who study this stuff are going to say we have strong evidence for.” But she understood his impulse: “We do have serious problems, and I’m glad Jon wrote the piece, and down the road I wouldn’t be surprised if we got a fuller handle on the role of social media in all of this—there are definitely ways in which social media has changed our politics for the worse.”
It’s tempting to sidestep the question of diagnosis entirely, and to evaluate Haidt’s essay not on the basis of predictive accuracy—whether social media will lead to the destruction of American democracy—but as a set of proposals for what we might do better. If he is wrong, how much damage are his prescriptions likely to do? Haidt, to his great credit, does not indulge in any wishful thinking, and if his diagnosis is largely technological his prescriptions are sociopolitical. Two of his three major suggestions seem useful and have nothing to do with social media: he thinks that we should end closed primaries and that children should be given wide latitude for unsupervised play. His recommendations for social-media reform are, for the most part, uncontroversial: he believes that preteens shouldn’t be on Instagram and that platforms should share their data with outside researchers—proposals that are both likely to be beneficial and not very costly.
It remains possible, however, that the true costs of social-media anxieties are harder to tabulate. Gentzkow told me that, for the period between 2016 and 2020, the direct effects of misinformation were difficult to discern. “But it might have had a much larger effect because we got so worried about it—a broader impact on trust,” he said. “Even if not that many people were exposed, the narrative that the world is full of fake news, and you can’t trust anything, and other people are being misled about it—well, that might have had a bigger impact than the content itself.” Nyhan had a similar reaction. “There are genuine questions that are really important, but there’s a kind of opportunity cost that is missed here. There’s so much focus on sweeping claims that aren’t actionable, or unfounded claims we can contradict with data, that are crowding out the harms we can demonstrate, and the things we can test, that could make social media better.” He added, “We’re years into this, and we’re still having an uninformed conversation about social media. It’s totally wild.”
New Yorker Favorites
The day the dinosaurs died .
What if you started itching— and couldn’t stop ?
How a notorious gangster was exposed by his own sister .
Woodstock was overrated .
Diana Nyad’s hundred-and-eleven-mile swim .
Photo Booth: Deana Lawson’s hyper-staged portraits of Black love .
Fiction by Roald Dahl: “The Landlady”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .

By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Isaac Chotiner

By Richard Brody

By Sinéad O’Sullivan

By Christopher Weyant
- Open access
- Published: 06 July 2023
Pros & cons: impacts of social media on mental health
- Ágnes Zsila 1 , 2 &
- Marc Eric S. Reyes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5280-1315 3
BMC Psychology volume 11 , Article number: 201 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
435k Accesses
15 Citations
107 Altmetric
Metrics details
The use of social media significantly impacts mental health. It can enhance connection, increase self-esteem, and improve a sense of belonging. But it can also lead to tremendous stress, pressure to compare oneself to others, and increased sadness and isolation. Mindful use is essential to social media consumption.
Social media has become integral to our daily routines: we interact with family members and friends, accept invitations to public events, and join online communities to meet people who share similar preferences using these platforms. Social media has opened a new avenue for social experiences since the early 2000s, extending the possibilities for communication. According to recent research [ 1 ], people spend 2.3 h daily on social media. YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat have become increasingly popular among youth in 2022, and one-third think they spend too much time on these platforms [ 2 ]. The considerable time people spend on social media worldwide has directed researchers’ attention toward the potential benefits and risks. Research shows excessive use is mainly associated with lower psychological well-being [ 3 ]. However, findings also suggest that the quality rather than the quantity of social media use can determine whether the experience will enhance or deteriorate the user’s mental health [ 4 ]. In this collection, we will explore the impact of social media use on mental health by providing comprehensive research perspectives on positive and negative effects.
Social media can provide opportunities to enhance the mental health of users by facilitating social connections and peer support [ 5 ]. Indeed, online communities can provide a space for discussions regarding health conditions, adverse life events, or everyday challenges, which may decrease the sense of stigmatization and increase belongingness and perceived emotional support. Mutual friendships, rewarding social interactions, and humor on social media also reduced stress during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 4 ].
On the other hand, several studies have pointed out the potentially detrimental effects of social media use on mental health. Concerns have been raised that social media may lead to body image dissatisfaction [ 6 ], increase the risk of addiction and cyberbullying involvement [ 5 ], contribute to phubbing behaviors [ 7 ], and negatively affects mood [ 8 ]. Excessive use has increased loneliness, fear of missing out, and decreased subjective well-being and life satisfaction [ 8 ]. Users at risk of social media addiction often report depressive symptoms and lower self-esteem [ 9 ].
Overall, findings regarding the impact of social media on mental health pointed out some essential resources for psychological well-being through rewarding online social interactions. However, there is a need to raise awareness about the possible risks associated with excessive use, which can negatively affect mental health and everyday functioning [ 9 ]. There is neither a negative nor positive consensus regarding the effects of social media on people. However, by teaching people social media literacy, we can maximize their chances of having balanced, safe, and meaningful experiences on these platforms [ 10 ].
We encourage researchers to submit their research articles and contribute to a more differentiated overview of the impact of social media on mental health. BMC Psychology welcomes submissions to its new collection, which promises to present the latest findings in the emerging field of social media research. We seek research papers using qualitative and quantitative methods, focusing on social media users’ positive and negative aspects. We believe this collection will provide a more comprehensive picture of social media’s positive and negative effects on users’ mental health.
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Statista. (2022). Time spent on social media [Chart]. Accessed June 14, 2023, from https://www.statista.com/chart/18983/time-spent-on-social-media/ .
Pew Research Center. (2023). Teens and social media: Key findings from Pew Research Center surveys. Retrieved June 14, 2023, from https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/04/24/teens-and-social-media-key-findings-from-pew-research-center-surveys/ .
Boer, M., Van Den Eijnden, R. J., Boniel-Nissim, M., Wong, S. L., Inchley, J. C.,Badura, P.,… Stevens, G. W. (2020). Adolescents’ intense and problematic social media use and their well-being in 29 countries. Journal of Adolescent Health , 66(6), S89-S99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.02.011.
Marciano L, Ostroumova M, Schulz PJ, Camerini AL. Digital media use and adolescents’ mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2022;9:2208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.641831 .
Article Google Scholar
Naslund JA, Bondre A, Torous J, Aschbrenner KA. Social media and mental health: benefits, risks, and opportunities for research and practice. J Technol Behav Sci. 2020;5:245–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00094-8 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Harriger JA, Thompson JK, Tiggemann M. TikTok, TikTok, the time is now: future directions in social media and body image. Body Image. 2023;44:222–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.12.005 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chi LC, Tang TC, Tang E. The phubbing phenomenon: a cross-sectional study on the relationships among social media addiction, fear of missing out, personality traits, and phubbing behavior. Curr Psychol. 2022;41(2):1112–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-0135-4 .
Valkenburg PM. Social media use and well-being: what we know and what we need to know. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022;45:101294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.101294 .
Bányai F, Zsila Á, Király O, Maraz A, Elekes Z, Griffiths MD, Urbán R, Farkas J, Rigó P Jr, Demetrovics Z. Problematic social media use: results from a large-scale nationally representative adolescent sample. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(1):e0169839. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169839 .
American Psychological Association. (2023). APA panel issues recommendations for adolescent social media use. Retrieved from https://apa-panel-issues-recommendations-for-adolescent-social-media-use-774560.html .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Ágnes Zsila was supported by the ÚNKP-22-4 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Psychology, Pázmány Péter Catholic University, Budapest, Hungary
Ágnes Zsila
Institute of Psychology, ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary
Department of Psychology, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, 1008, Philippines
Marc Eric S. Reyes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AZ conceived and drafted the Editorial. MESR wrote the abstract and revised the Editorial. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Marc Eric S. Reyes .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zsila, Á., Reyes, M.E.S. Pros & cons: impacts of social media on mental health. BMC Psychol 11 , 201 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01243-x
Download citation
Received : 15 June 2023
Accepted : 03 July 2023
Published : 06 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01243-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Social media
- Mental health
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Skip to content
Read the latest news stories about Mailman faculty, research, and events.
Departments
We integrate an innovative skills-based curriculum, research collaborations, and hands-on field experience to prepare students.
Learn more about our research centers, which focus on critical issues in public health.
Our Faculty
Meet the faculty of the Mailman School of Public Health.
Become a Student
Life and community, how to apply.
Learn how to apply to the Mailman School of Public Health.
Just How Harmful Is Social Media? Our Experts Weigh-In.
A recent investigation by the Wall Street Journal revealed that Facebook was aware of mental health risks linked to the use of its Instagram app but kept those findings secret. Internal research by the social media giant found that Instagram worsened body image issues for one in three teenage girls, and all teenage users of the app linked it to experiences of anxiety and depression. It isn’t the first evidence of social media’s harms. Watchdog groups have identified Facebook and Instagram as avenues for cyberbullying , and reports have linked TikTok to dangerous and antisocial behavior, including a recent spate of school vandalism .
As social media has proliferated worldwide—Facebook has 2.85 billion users—so too have concerns over how the platforms are affecting individual and collective wellbeing. Social media is criticized for being addictive by design and for its role in the spread of misinformation on critical issues from vaccine safety to election integrity, as well as the rise of right-wing extremism. Social media companies, and many users, defend the platforms as avenues for promoting creativity and community-building. And some research has pushed back against the idea that social media raises the risk for depression in teens . So just how healthy or unhealthy is social media?
Two experts from Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia Psychiatry share their insights into one crucial aspect of social media’s influence—its effect on the mental health of young people and adults. Deborah Glasofer , associate professor of psychology in psychiatry, conducts psychotherapy development research for adults with eating disorders and teaches about cognitive behavioral therapy. She is the co-author of the book Eating Disorders: What Everyone Needs to Know. Claude Mellins , Professor of medical psychology in the Departments of Psychiatry and Sociomedical Sciences, studies wellbeing among college and graduate students, among other topics, and serves as program director of CopeColumbia, a peer support program for Columbia faculty and staff whose mental health has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. She co-led the SHIFT research study to reduce sexual violence among undergraduates. Both use social media.
What do we know about the mental health risks of social media use?
Mellins : Facebook and Instagram and other social media platforms are important sources of socialization and relationship-building for many young people. Although there are important benefits, social media can also provide platforms for bullying and exclusion, unrealistic expectations about body image and sources of popularity, normalization of risk-taking behaviors, and can be detrimental to mental health. Girls and young people who identify as sexual and gender minorities can be especially vulnerable as targets. Young people’s brains are still developing, and as individuals, young people are developing their own identities. What they see on social media can define what is expected in ways that is not accurate and that can be destructive to identity development and self-image. Adolescence is a time of risk-taking, which is both a strength and a vulnerability. Social media can exacerbate risks, as we have seen played out in the news.
Although there are important benefits, social media can also provide platforms for bullying and exclusion, unrealistic expectations about body image and sources of popularity, normalization of risk-taking behaviors, and can be detrimental to mental health. – Claude Mellins
Glasofer : For those vulnerable to developing an eating disorder, social media may be especially unhelpful because it allows people to easily compare their appearance to their friends, to celebrities, even older images of themselves. Research tells us that how much someone engages with photo-related activities like posting and sharing photos on Facebook or Instagram is associated with less body acceptance and more obsessing about appearance. For adolescent girls in particular, the more time they spend on social media directly relates to how much they absorb the idea that being thin is ideal, are driven to try to become thin, and/or overly scrutinize their own bodies. Also, if someone is vulnerable to an eating disorder, they may be especially attracted to seeking out unhelpful information—which is all too easy to find on social media.
Are there any upsides to social media?
Mellins : For young people, social media provides a platform to help them figure out who they are. For very shy or introverted young people, it can be a way to meet others with similar interests. During the pandemic, social media made it possible for people to connect in ways when in-person socialization was not possible. Social support and socializing are critical influences on coping and resilience. Friends we couldn’t see in person were available online and allowed us important points of connection. On the other hand, fewer opportunities for in-person interactions with friends and family meant less of a real-world check on some of the negative influences of social media.
Whether it’s social media or in person, a good peer group makes the difference. A group of friends that connects over shared interests like art or music, and is balanced in their outlook on eating and appearance, is a positive. – Deborah Glasofer
Glasofer : Whether it’s social media or in person, a good peer group makes the difference. A group of friends that connects over shared interests like art or music, and is balanced in their outlook on eating and appearance, is a positive. In fact, a good peer group online may be protective against negative in-person influences. For those with a history of eating disorders, there are body-positive and recovery groups on social media. Some people find these groups to be supportive; for others, it’s more beneficial to move on and pursue other interests.
Is there a healthy way to be on social media?
Mellins : If you feel social media is a negative experience, you might need a break. Disengaging with social media permanently is more difficult—especially for young people. These platforms are powerful tools for connecting and staying up-to-date with friends and family. Social events, too. If you’re not on social media then you’re reliant on your friends to reach out to you personally, which doesn’t always happen. It’s complicated.
Glasofer : When you find yourself feeling badly about yourself in relation to what other people are posting about themselves, then social media is not doing you any favors. If there is anything on social media that is negatively affecting your actions or your choices—for example, if you’re starting to eat restrictively or exercise excessively—then it’s time to reassess. Parents should check-in with their kids about their lives on social media. In general, I recommend limiting social media— creating boundaries that are reasonable and work for you—so you can be present with people in your life. I also recommend social media vacations. It’s good to take the time to notice the difference between the virtual world and the real world.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
64% of Americans say social media have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in the U.S. today
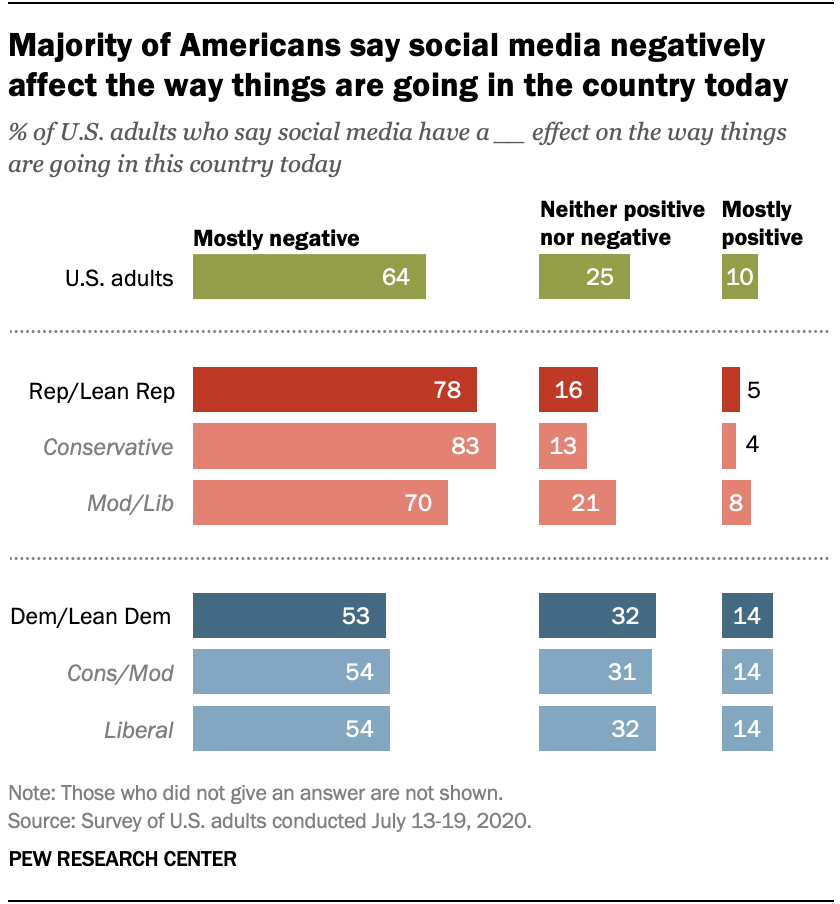
About two-thirds of Americans (64%) say social media have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in the country today, according to a Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted July 13-19, 2020. Just one-in-ten Americans say social media sites have a mostly positive effect on the way things are going, and one-quarter say these platforms have a neither positive nor negative effect.
Those who have a negative view of the impact of social media mention, in particular, misinformation and the hate and harassment they see on social media. They also have concerns about users believing everything they see or read – or not being sure about what to believe. Additionally, they bemoan social media’s role in fomenting partisanship and polarization, the creation of echo chambers, and the perception that these platforms oppose President Donald Trump and conservatives.
This is part of a series of posts on Americans’ experiences with and attitudes about the role of social media in politics today. Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand how Americans think about the impact of social media on the way things are currently going in the country. To explore this, we surveyed 10,211 U.S. adults from July 13 to 19, 2020. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.
The public’s views on the positive and negative effect of social media vary widely by political affiliation and ideology. Across parties, larger shares describe social media’s impact as mostly negative rather than mostly positive, but this belief is particularly widespread among Republicans.
Roughly half of Democrats and independents who lean toward the Democratic Party (53%) say social media have a largely negative effect on the way things are going in the country today, compared with 78% of Republicans and leaners who say the same. Democrats are about three times as likely as Republicans to say these sites have a mostly positive impact (14% vs. 5%) and twice as likely to say social media have neither a positive nor negative effect (32% vs. 16%).
Among Democrats, there are no differences in these views along ideological lines. Republicans, however, are slightly more divided by ideology. Conservative Republicans are more likely than moderate to liberal Republicans to say social media have a mostly negative effect (83% vs. 70%). Conversely, moderate to liberal Republicans are more likely than their conservative counterparts to say social media have a mostly positive (8% vs. 4%) or neutral impact (21% vs. 13%).
Younger adults are more likely to say social media have a positive impact on the way things are going in the country and are less likely to believe social media sites have a negative impact compared with older Americans. For instance, 15% of those ages 18 to 29 say social media have a mostly positive effect on the way things are going in the country today, while just 8% of those over age 30 say the same. Americans 18 to 29 are also less likely than those 30 and older to say social media have a mostly negative impact (54% vs. 67%).
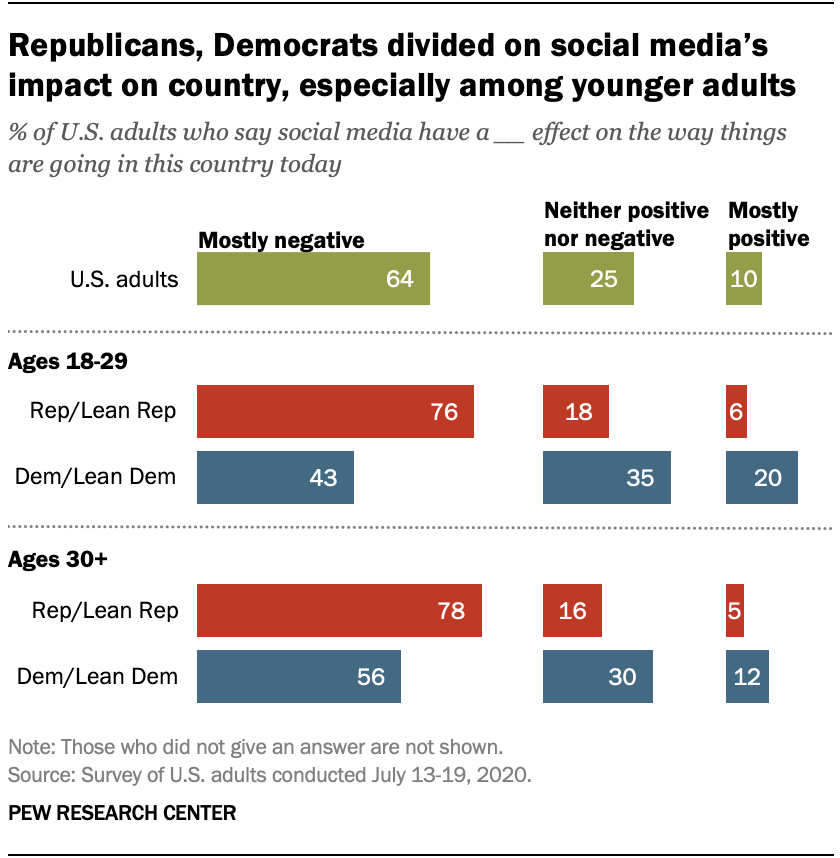
However, views among younger adults vary widely by partisanship. For example, 43% of Democrats ages 18 to 29 say social media have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going, compared with about three-quarters (76%) of Republicans in the same age group. In addition, these youngest Democrats are more likely than their Republican counterparts to say social media platforms have a mostly positive (20% vs. 6%) or neither a positive nor negative effect (35% vs. 18%) on the way things are going in the country today. This partisan division persists among those 30 and older, but most of the gaps are smaller than those seen within the younger cohort.
Views on the negative impact of social media vary only slightly between social media users (63%) and non-users (69%), with non-users being slightly more likely to say these sites have a negative impact. However, among social media users, those who say some or a lot of what they see on social media is related to politics are more likely than those who say a little or none of what they see on these sites is related to politics to think social media platforms have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in the country today (65% vs. 50%).
Past Pew Research Center studies have drawn attention to the complicated relationships Americans have with social media. In 2019, a Center survey found that 72% of U.S. adults reported using at least one social media site. And while these platforms have been used for political and social activism and engagement , they also raise concerns among portions of the population. Some think political ads on these sites are unacceptable, and many object to the way social media platforms have been weaponized to spread made-up news and engender online harassment . At the same time, a share of users credit something they saw on social media with changing their views about a political or social issue. And growing shares of Americans who use these sites also report feeling worn out by political posts and discussions on social media.
Those who say social media have negative impact cite concerns about misinformation, hate, censorship; those who see positive impact cite being informed
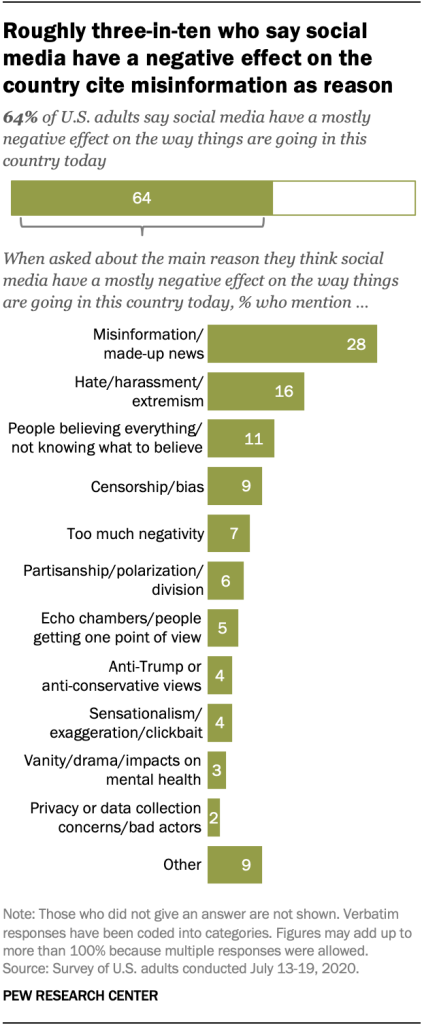
When asked to elaborate on the main reason why they think social media have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in this country today, roughly three-in-ten (28%) respondents who hold that view mention the spreading of misinformation and made-up news. Smaller shares reference examples of hate, harassment, conflict and extremism (16%) as a main reason, and 11% mention a perceived lack of critical thinking skills among many users – voicing concern about people who use these sites believing everything they see or read or being unsure about what to believe.
In written responses that mention misinformation or made-up news, a portion of adults often include references to the spread, speed and amount of false information available on these platforms. (Responses are lightly edited for spelling, style and readability.) For example:
“They allow for the rampant spread of misinformation.” –Man, 36
“False information is spread at lightning speed – and false information never seems to go away.” –Woman, 71
“Social media is rampant with misinformation both about the coronavirus and political and social issues, and the social media organizations do not do enough to combat this.” –Woman, 26
“Too much misinformation and lies are promoted from unsubstantiated sources that lead people to disregard vetted and expert information.” –Woman, 64
People’s responses that centered around hate, harassment, conflict or extremism in some way often mention concerns that social media contributes to incivility online tied to anonymity, the spreading of hate-filled ideas or conspiracies, or the incitement of violence.
“People say incendiary, stupid and thoughtless things online with the perception of anonymity that they would never say to someone else in person.” –Man, 53
“Promotes hate and extreme views and in some cases violence.” –Man, 69
“People don’t respect others’ opinions. They take it personally and try to fight with the other group. You can’t share your own thoughts on controversial topics without fearing someone will try to hurt you or your family.” –Woman, 65
“Social media is where people go to say some of the most hateful things they can imagine.” –Man, 46
About one-in-ten responses talk about how people on social media can be easily confused and believe everything they see or read or are not sure about what to believe.
“People believe everything they see and don’t verify its accuracy.” –Man, 75
“Many people can’t distinguish between real and fake news and information and share it without doing proper research …” –Man, 32
“You don’t know what’s fake or real.” –Man, 49
“It is hard to discern truth.” –Woman, 80
“People cannot distinguish fact from opinion, nor can they critically evaluate sources. They tend to believe everything they read, and when they see contradictory information (particularly propaganda), they shut down and don’t appear to trust any information.” –Man, 42
Smaller shares complain that the platforms censor content or allow material that is biased (9%), too negative (7%) or too steeped in partisanship and division (6%).
“Social media is censoring views that are different than theirs. There is no longer freedom of speech.” –Woman, 42
“It creates more divide between people with different viewpoints.” –Man, 37
“Focus is on negativity and encouraging angry behavior rather than doing something to help people and make the world better.” –Woman, 66
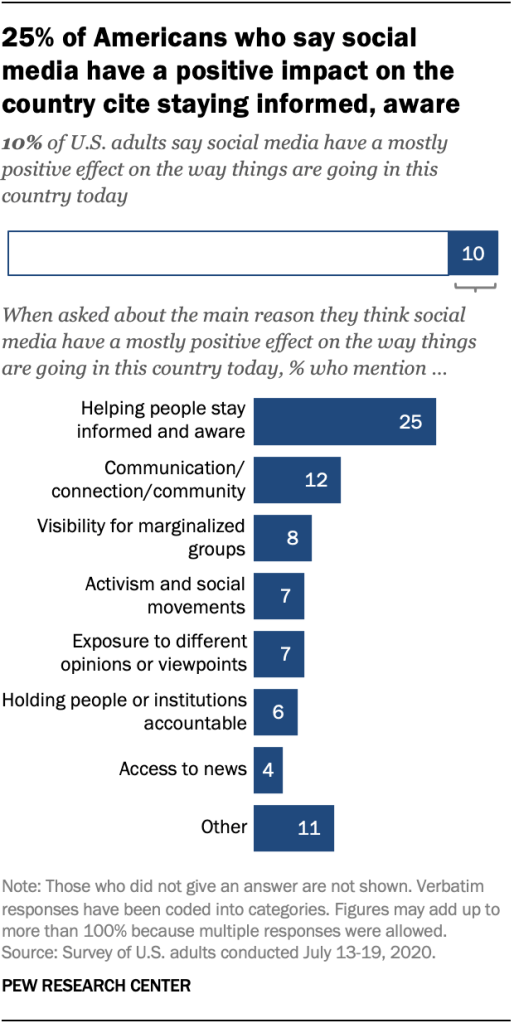
Far fewer Americans – 10% – say they believe social media has a mostly positive effect on the way things are going in the country today. When those who hold these positive views were asked about the main reason why they thought this, one-quarter say these sites help people stay informed and aware (25%) and about one-in-ten say they allow for communication, connection and community-building (12%).
“We are now aware of what’s happening around the world due to the social media outlet.” –Woman, 28
“It brings awareness to important issues that affect all Americans.” –Man, 60
“It brings people together; folks can see that there are others who share the same/similar experience, which is really important, especially when so many of us are isolated.” –Woman, 36
“Helps people stay connected and share experiences. I also get advice and recommendations via social media.” –Man, 32
“It keeps people connected who might feel lonely and alone if there did not have social media …” – Man, 65
Smaller shares tout social media as a place where marginalized people and groups have a voice (8%) and as a venue for activism and social movements (7%).
“Spreading activism and info and inspiring participation in Black Lives Matter.” –Woman, 31
“It gives average people an opportunity to voice and share their opinions.” –Man, 67
“Visibility – it has democratized access and provided platforms for voices who have been and continue to be oppressed.” –Woman, 27
Note: This is part of a series of blog posts leading up to the 2020 presidential election that explores the role of social media in politics today. Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.
Other posts in this series:
- 23% of users in U.S. say social media led them to change views on an issue; some cite Black Lives Matter
- 54% of Americans say social media companies shouldn’t allow any political ads
- 55% of U.S. social media users say they are ‘worn out’ by political posts and discussions
- Americans think social media can help build movements, but can also be a distraction
- Misinformation
- Misinformation Online
- National Conditions
- Political Discourse
- Politics Online
- Social Media
Brooke Auxier is a former research associate focusing on internet and technology at Pew Research Center .
Majorities in most countries surveyed say social media is good for democracy
most americans favor restrictions on false information, violent content online, as ai spreads, experts predict the best and worst changes in digital life by 2035, social media seen as mostly good for democracy across many nations, but u.s. is a major outlier, the role of alternative social media in the news and information environment, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
- Entertainment
Essay Sample about Social Media: Negative Impacts
Social media, the interactive technology that seems to be affecting people like you just by itself. It is becoming increasingly clear that social networks have become a big part of people’s lives. What effect does social media have on you? Just one out of ten Americans say social media has a positive effect on them, that alone says a lot about how negatively social media impacts peoples lives. The latest social media statistics show that there are 3.78 billion social media users worldwide in 2021 and this number is only going to continue growing over the next few years.
Social media is taking away all of the originality and authenticity in us individual human beings. Everything has been generated from social media, we’re all influenced or motivated in a way to change or to do certain things. Influencers on social media present unrealistic body types and they’re labeled as this “perfect body image” . The unrealistic beauty standards and false expectations being pushed onto younger kids can seriously knock down their level of confidence/ self esteem and make people self conscious. with photoshop, images are everywhere and lead to distorted body image among a number of teenagers. People constantly compare themselves to other women or men because they dont look like them, society sets a standard. People start doing more and more fashion trends, making people feel obligated to wear something that they don't feel comfortable in.
Cyberbullying is the use of electronic communication to bully a person, typically by sending messages of an intimidating or threatening nature. Cyberbullying is often done by children, who have early access to these technologies. It causes depression and anxiety which can lead to suicidal thoughts or suicide. About 10% of teens report being bullied on social media and many other users are subjected to offensive comments. Social media platforms can be hotspots for spreading hurtful rumors, lies and abuse that can leave lasting emotional sears.
Human beings need face to face interaction to be mentally healthy. The more you prioritize social media interaction over in person relationships, the more you’re at risk for developing mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
The idea that you’re missing out on certain things can impact your self-esteem, trigger anxiety, and fuel even greater social media use. FOMO - Fear Of Missing Out, can compel you to pick up your phone every few minutes to check for updates, or respond to every alert. A study found that high usage of social media such as facebook, snapchat and instagram have increased rather than decreased feelings of loneliness.This study found that reducing social media usage can make you feel less lonely and isolated and improve your overall wellbeing.
You're scrolling on a little rectangle in your hand, but why? Turning to social media when you’re feeling down, lonely, or bored, you're potentially using it as a way to distract yourself from unpleasant feelings. You’re constantly scrolling through negative news articles or social media posts, seeking out one negative piece of content after another as a coping mechanism. ( meh- kuh-ni-zm)
But is it even working? Social media can become an unhealthy way of coping with uncomfortable emotions. The more we consume social media the worse we feel.
Society today spends most of their time on social media without even realizing the effects. Social skills are important in our everyday lives, sports for instance is a phenomenal way to socialize and stay fit at the same time. We must stop spending so much time staring at a screen in order to bond with family and start interacting face to face. So why don't we all just stop the loop?
Related Samples
- Little Buddha Movie Analysis Essay
- Why People Should Beware of Internet Argumentative Essay Example
- Edward Scissorhands Movie Analysis Essay Example
- Night of the Living Dead Movie Analysis
- Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Social Media (Essay Example)
- Essay Sample about Face-to-Face Communication and Technology
- Impact of Social Media on Relationships Essay Samle
- Unbreakable Movie Analysis
- Good Vs. Evil In The Lion The Witch And The Wardrobe
- Parental Substitute Versus New Best friend: A Look into the Relationships of Alfred, Batman and Robin
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
Social Media: Negative Impacts
Introduction, intrusive advertising, bullying/harassment, privacy threats, works cited.
Social media is a natural phenomenon of modern hi-tech life. The impact of virtual communication is significant as people are often willing to pay more attention to online interaction. Besides, due to the development of technology, social media plays the role of platforms not only for communication but also fir effective advertising and entertainment. Digital content that is published in various groups has a large target audience, which allows influencing people and providing demand for specific goods or services. However, the controversy of the benefits of social media lies in the potentially negative impacts they have. In addition to using specialized web resources for communication, many Internet users utilize them as tools for bullying, intimidation, humiliation, and even violence. An opportunity to remain anonymous opens up significant prospects for cybercriminals, which complicates the task for law enforcement agencies. As a counterargument, today, there are various means of account verification and support services that are ready to ensure the safety of communication on social media and provide users with protection from scammers or blackmailers. Nevertheless, people who are well versed in the digital field can bypass such locks easily. Among the real negative effects that social media have, one can note intrusive advertising, bullying and harassment, privacy threats, fake news, and violence. Social media are gradually losing the function of communication tools and gaining the status of platforms that allow posting any content, including illegal and immoral materials.
Advertising on social media has become so intrusive and widespread that it has ceased to have its promotional function and often causes users more negative emotions than interest. At the same time, it is hard to get rid of advertising completely since many creators of digital content sign contracts with advertisers, and profit depends directly on the activity of the public. However, in case of excess advertising, people feel annoyed and ignore certain offers deliberately. According to Shareef et al., “irritation due to any advertisement can distract consumers from receiving the intended meaning of the statement, and thus can have a negative effect on the value of the advertising” (p. 61). Such a statement is logical because, in their quest for profit, advertisers provoke a natural reaction from the target audience to condemn the excess of promoting content. Customer perception largely depends not only on the essence of specific offers but also on the way marketers deliver them. Therefore, in case of intrusiveness, advertising content on social media causes rejection and is often blocked by users. Shareef et al. confirm this and argue that the context of marketing materials may be more important as a driver to convince the public of the value of specific goods or services (p. 66). The objectivity of such an idea is due to the fact that initially, social media were not intended for advertising, and only the creativity of marketers can be an effective way to attract public attention. Finally, Shareef et al. mention viral marketing as one of the methods of intrusive advertising on social media and note that this form of promotion are relevant only among a narrow target audience. In other words, the more annoying the advertisement is, the lower is the chance to attract a wide range of new consumers. Nevertheless, intrusive advertising is significantly less dangerous than bullying or harassment, which are found in modern social media.
The anonymity factor that may persist when interacting on social media is one of the reasons for bullying that some Internet users are forced to experience. A sense of impunity for aggressive behavior and insults towards another person exacerbate the situation. Moreover, bullying is a trend that is common in children’s communication on social media, which poses a serious threat to the fragile psyche of young users. According to Canty et al., online bullying is a unique phenomenon that has expanded in the virtual space due to the emergence of means to preserve anonymity and, in particular, the ability to go unpunished (p. 52). These factors are most obvious reasons why children, who are often humiliated by their peers on social media, become self-absorbed and cannot figure out the wrongdoers. Harassment is a similar problem, which, however, is characteristic of the adult population and often has a sexual background. Chadha et al. state that modern digital technologies “amplify attacks on gender-based and sexual minorities,” thereby acting as negative consequences of progress (p. 241). This statement assumes that the context of harassment is not limited to one topic. In addition, as findings show, virtual space is a favorable environment for this phenomenon:
Online communities and social media platforms offer many benefits, but they also have become breeding grounds for an assortment of sexist and misogynist behaviors. Importantly, the harassment behaviors evident today differ from off-line and pre-social media-era harassment, given the affordances of these networked spaces, including – but not limited to – the visibility and persistence of content, the anonymity/pseudonymity of users, the spreadability of content, and the multimediality of smartphones (Chadha et al, p. 250).
As a result, the openness of online communication creates a favorable environment for harassment and affects user behavior. Chadha et al. mention requests for personal data and addresses as easy consequences of harassment and note that people who have faced with real threats see this phenomenon as an extremely dangerous and aggressive trend (p. 243). This conclusion is logical because, despite different environments, online and real-life harassment have a common background. In this regard, the issues of privacy and accompanying risks are negative consequences of social media.
Privacy threats are fraught not only with identity theft but also with other problems that may entail anonymous bullying or blackmail. Today, for users of social media, communication options are not limited solely to correspondence. Interlocutors can comment on each other, share links, and perform other actions that go beyond a particular platform. As a result, as Aghasian et al. note, “the distribution of information in real world is almost local, the publically shared information in online social media can be retrieved on the internet anytime, anywhere and by anyone” (p. 13118). The significance of this statement is that virtually no one can be fully protected, and precautions should be taken. Aghasian et al. argue that users should be able to protect their personal data not only from intruders but also from familiar people who can become intermediaries in the leak of information (p. 13118). Those people who face privacy threats may lose their money or valuable digital content through negligence by providing their data to third parties. Due to the widespread use of virtual interaction, various leakage channels are discussed:
For example, a user normally share his/her personal information in Facebook which may pose a privacy risk. This user may share his/her occupation history and background in another site such as LinkedIn. His/her job information has again its own privacy risk, but a combination of the information from two social media accounts can pose the user to higher risk as more information is revealed. Consequently, by considering the overall information from multiple source, a more accurate quantification of the privacy disclosure score can be obtained. (Aghasian et al, p. 13118)
In addition to individual data leakage channels, the forms of privacy risks themselves are numerous. Aghasian et al. mention the threat of government data theft, the disclosure of confidential information about trade transactions, and even religious secrets (13119). Such a variety of risks explains the need for comprehensive protection. Social media, in turn, are a favorable environment for such fraud since the predominant number of Internet users have accounts at least at one specialized site. Wherein, according to Aghasian et al., “one of the challenges in addressing privacy concerns is how to measure the privacy of a user participating in multiple social networks” (p. 13129). The increasing role of social media in people’s lives inevitably leads to threats to personal data, especially if they are stored on different platforms. However, not all negative aspects of virtual communication are aimed at interacting with a particular person, and the example of fake news distributed online is a confirmation.
Social media are becoming the most common sources of news, including both entertaining content and serious political and economic reports, which, however, are not always reliable. One of the main reasons is the desire to attract a large target audience. The greater the news resonance is, the greater is the potential success of a particular media platform. For example, Shu et al. give the following statistics: “62 percent of U.S. adults get news on social media in 2016, while in 2012, only 49 percent reported seeing news on social media” (p. 22). This ratio proves that even the adult population of the country began to use virtual platforms more often. In addition, this growth may be due to the wider use of social media by numerous agencies that have individual accounts. The authors emphasize that fake news as a negative consequence of digital communication is disseminated most actively through social media due to an opportunity to create a public outcry quickly (Shu et al, p. 23). News groups fight for the target audience in any way possible, which entails publications based on unverified or false facts. Spohr explains the reasons and argues that “the producers and curators of fake news content are able to monetize their content through advertising platforms from Facebook and Google” (p. 156). This conclusion is logical since material gain is the most objective explanation for such publications. In addition, the researcher notes that fake news creates a resonance that, regardless of whether it is positive or negative, serves as a means of popularization (Spohr, p. 150). Therefore, the ability to influence the masses opens up prospects for fraudulent actions, although fake news cannot do such harm as violence, which is another negative effect of social media.
Despite the fact that violence in its natural sense cannot be realized online, the manifestations of violent acts through social media are possible. This phenomenon is similar to cyberbullying, but it involves strict measures of intimidation or harassment, while bullying can be superficial. Today, particular attention is paid to youth virtual violence, as children and adolescents are vulnerable groups. As Tripathi notes, “most children and adolescents (65-91%) report little or no involvement in violence over social media platforms” (2). At the same time, the author argues that time spent online is one of the factors on which the risk of violence depends (Tripathi, p. 3). In other words, the longer and more actively a child interacts with other users, the higher is the threat of psychological violence. This statement is reasonable and carries an open message about the need to reduce the access of young users to free online communication. Also, gender-based online violence is another form of bullying, and its consequences can be extremely dangerous from a social perspective:
Gender-based violence online is rampant, ranging from harassment of women who are public figures on social media to stalking intimate partners using purpose-built apps. This is not an issue that can be addressed by individual states alone, nor can it be addressed satisfactorily through legal means. The normalization of misogyny and abuse online both reflects and reinforces systemic inequalities. (Suzor et al, p. 84)
This position on gender-based violence proves the effect that indifference to this problem may cause. According to Suzor et al., most modern social media promote themselves as platforms for expressing individuality and personal opinions, which can be dangerous in conditions of the freedom of speech and anonymity (p. 89). Not only women but also other vulnerable groups can experience the effects of virtual violence, and impunity is one of the most dangerous consequences. The authors are convinced that “deeply entrenched structural features of existing social media platforms often exacerbate the effects of online harassment and abuse” (Suzor et al, p. 94). Thus, social media carry many negative implications, and an opportunity to go unpunished for aggressive or annoying behavior is a severe social omission.
- Aghasian, Erfan, et al. “Scoring Users’ Privacy Disclosure Across Multiple Online Social Networks.” IEEE Access , vol. 5, 2017, pp. 13118-13130.
- Canty, Justin, et al. “The Trouble with Bullying – Deconstructing the Conventional Definition of Bullying for a Child‐Centred Investigation into Children’s Use of Social Media.” Children & Society , vol. 30, no. 1, 2016, pp. 48-58.
- Chadha, Kalyani, et al. “Women’s Responses to Online Harassment.” International Journal of Communication , vol. 14, 2020, pp. 239-257.
- Shareef, Mahmud Akhter, et al. “Social Media Marketing: Comparative Effect of Advertisement Sources.” Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services , vol. 46, 2019, pp. 58-69.
- Shu, Kai, et al. “Fake News Detection on Social Media: A Data Mining Perspective.” ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter , vol. 19, no. 1, 2017, pp. 22-36.
- Spohr, Dominic. “Fake News and Ideological Polarization: Filter Bubbles and Selective Exposure on Social Media.” Business Information Review , vol. 34, no. 3, 2017, pp. 150-160.
- Suzor, Nicolas, et al. “Human Rights by Design: The Responsibilities of Social Media Platforms to Address Gender‐Based Violence Online.” Policy & Internet , vol. 11, no. 1, 2019, pp. 84-103.
- Tripathi, Vivek. “Youth Violence and Social Media.” Journal of Social Sciences , vol. 52, no. 1-3, 2017, pp. 1-7.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, March 10). Social Media: Negative Impacts. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-negative-impacts/
"Social Media: Negative Impacts." StudyCorgi , 10 Mar. 2022, studycorgi.com/social-media-negative-impacts/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Social Media: Negative Impacts'. 10 March.
1. StudyCorgi . "Social Media: Negative Impacts." March 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-negative-impacts/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Social Media: Negative Impacts." March 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-negative-impacts/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Social Media: Negative Impacts." March 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-negative-impacts/.
This paper, “Social Media: Negative Impacts”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: May 25, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Feb 15, 2023
6 Example Essays on Social Media | Advantages, Effects, and Outlines
Got an essay assignment about the effects of social media we got you covered check out our examples and outlines below.
Social media has become one of our society's most prominent ways of communication and information sharing in a very short time. It has changed how we communicate and has given us a platform to express our views and opinions and connect with others. It keeps us informed about the world around us. Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn have brought individuals from all over the world together, breaking down geographical borders and fostering a genuinely global community.
However, social media comes with its difficulties. With the rise of misinformation, cyberbullying, and privacy problems, it's critical to utilize these platforms properly and be aware of the risks. Students in the academic world are frequently assigned essays about the impact of social media on numerous elements of our lives, such as relationships, politics, and culture. These essays necessitate a thorough comprehension of the subject matter, critical thinking, and the ability to synthesize and convey information clearly and succinctly.
But where do you begin? It can be challenging to know where to start with so much information available. Jenni.ai comes in handy here. Jenni.ai is an AI application built exclusively for students to help them write essays more quickly and easily. Jenni.ai provides students with inspiration and assistance on how to approach their essays with its enormous database of sample essays on a variety of themes, including social media. Jenni.ai is the solution you've been looking for if you're experiencing writer's block or need assistance getting started.
So, whether you're a student looking to better your essay writing skills or want to remain up to date on the latest social media advancements, Jenni.ai is here to help. Jenni.ai is the ideal tool for helping you write your finest essay ever, thanks to its simple design, an extensive database of example essays, and cutting-edge AI technology. So, why delay? Sign up for a free trial of Jenni.ai today and begin exploring the worlds of social networking and essay writing!
Want to learn how to write an argumentative essay? Check out these inspiring examples!
We will provide various examples of social media essays so you may get a feel for the genre.
6 Examples of Social Media Essays
Here are 6 examples of Social Media Essays:
The Impact of Social Media on Relationships and Communication
Introduction:.
The way we share information and build relationships has evolved as a direct result of the prevalence of social media in our daily lives. The influence of social media on interpersonal connections and conversation is a hot topic. Although social media has many positive effects, such as bringing people together regardless of physical proximity and making communication quicker and more accessible, it also has a dark side that can affect interpersonal connections and dialogue.
Positive Effects:
Connecting People Across Distances
One of social media's most significant benefits is its ability to connect individuals across long distances. People can use social media platforms to interact and stay in touch with friends and family far away. People can now maintain intimate relationships with those they care about, even when physically separated.
Improved Communication Speed and Efficiency
Additionally, the proliferation of social media sites has accelerated and simplified communication. Thanks to instant messaging, users can have short, timely conversations rather than lengthy ones via email. Furthermore, social media facilitates group communication, such as with classmates or employees, by providing a unified forum for such activities.
Negative Effects:
Decreased Face-to-Face Communication
The decline in in-person interaction is one of social media's most pernicious consequences on interpersonal connections and dialogue. People's reliance on digital communication over in-person contact has increased along with the popularity of social media. Face-to-face interaction has suffered as a result, which has adverse effects on interpersonal relationships and the development of social skills.
Decreased Emotional Intimacy
Another adverse effect of social media on relationships and communication is decreased emotional intimacy. Digital communication lacks the nonverbal cues and facial expressions critical in building emotional connections with others. This can make it more difficult for people to develop close and meaningful relationships, leading to increased loneliness and isolation.
Increased Conflict and Miscommunication
Finally, social media can also lead to increased conflict and miscommunication. The anonymity and distance provided by digital communication can lead to misunderstandings and hurtful comments that might not have been made face-to-face. Additionally, social media can provide a platform for cyberbullying , which can have severe consequences for the victim's mental health and well-being.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the impact of social media on relationships and communication is a complex issue with both positive and negative effects. While social media platforms offer many benefits, such as connecting people across distances and enabling faster and more accessible communication, they also have a dark side that can negatively affect relationships and communication. It is up to individuals to use social media responsibly and to prioritize in-person communication in their relationships and interactions with others.
The Role of Social Media in the Spread of Misinformation and Fake News
Social media has revolutionized the way information is shared and disseminated. However, the ease and speed at which data can be spread on social media also make it a powerful tool for spreading misinformation and fake news. Misinformation and fake news can seriously affect public opinion, influence political decisions, and even cause harm to individuals and communities.
The Pervasiveness of Misinformation and Fake News on Social Media
Misinformation and fake news are prevalent on social media platforms, where they can spread quickly and reach a large audience. This is partly due to the way social media algorithms work, which prioritizes content likely to generate engagement, such as sensational or controversial stories. As a result, false information can spread rapidly and be widely shared before it is fact-checked or debunked.
The Influence of Social Media on Public Opinion
Social media can significantly impact public opinion, as people are likelier to believe the information they see shared by their friends and followers. This can lead to a self-reinforcing cycle, where misinformation and fake news are spread and reinforced, even in the face of evidence to the contrary.
The Challenge of Correcting Misinformation and Fake News
Correcting misinformation and fake news on social media can be a challenging task. This is partly due to the speed at which false information can spread and the difficulty of reaching the same audience exposed to the wrong information in the first place. Additionally, some individuals may be resistant to accepting correction, primarily if the incorrect information supports their beliefs or biases.
In conclusion, the function of social media in disseminating misinformation and fake news is complex and urgent. While social media has revolutionized the sharing of information, it has also made it simpler for false information to propagate and be widely believed. Individuals must be accountable for the information they share and consume, and social media firms must take measures to prevent the spread of disinformation and fake news on their platforms.
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health and Well-Being
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of people around the world using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to stay connected with others and access information. However, while social media has many benefits, it can also negatively affect mental health and well-being.
Comparison and Low Self-Esteem
One of the key ways that social media can affect mental health is by promoting feelings of comparison and low self-esteem. People often present a curated version of their lives on social media, highlighting their successes and hiding their struggles. This can lead others to compare themselves unfavorably, leading to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem.
Cyberbullying and Online Harassment
Another way that social media can negatively impact mental health is through cyberbullying and online harassment. Social media provides a platform for anonymous individuals to harass and abuse others, leading to feelings of anxiety, fear, and depression.
Social Isolation
Despite its name, social media can also contribute to feelings of isolation. At the same time, people may have many online friends but need more meaningful in-person connections and support. This can lead to feelings of loneliness and depression.
Addiction and Overuse
Finally, social media can be addictive, leading to overuse and negatively impacting mental health and well-being. People may spend hours each day scrolling through their feeds, neglecting other important areas of their lives, such as work, family, and self-care.
In sum, social media has positive and negative consequences on one's psychological and emotional well-being. Realizing this, and taking measures like reducing one's social media use, reaching out to loved ones for help, and prioritizing one's well-being, are crucial. In addition, it's vital that social media giants take ownership of their platforms and actively encourage excellent mental health and well-being.

The Use of Social Media in Political Activism and Social Movements
Social media has recently become increasingly crucial in political action and social movements. Platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram have given people new ways to express themselves, organize protests, and raise awareness about social and political issues.
Raising Awareness and Mobilizing Action
One of the most important uses of social media in political activity and social movements has been to raise awareness about important issues and mobilize action. Hashtags such as #MeToo and #BlackLivesMatter, for example, have brought attention to sexual harassment and racial injustice, respectively. Similarly, social media has been used to organize protests and other political actions, allowing people to band together and express themselves on a bigger scale.
Connecting with like-minded individuals
A second method in that social media has been utilized in political activity and social movements is to unite like-minded individuals. Through social media, individuals can join online groups, share knowledge and resources, and work with others to accomplish shared objectives. This has been especially significant for geographically scattered individuals or those without access to traditional means of political organizing.
Challenges and Limitations
As a vehicle for political action and social movements, social media has faced many obstacles and restrictions despite its many advantages. For instance, the propagation of misinformation and fake news on social media can impede attempts to disseminate accurate and reliable information. In addition, social media corporations have been condemned for censorship and insufficient protection of user rights.
In conclusion, social media has emerged as a potent instrument for political activism and social movements, giving voice to previously unheard communities and galvanizing support for change. Social media presents many opportunities for communication and collaboration. Still, users and institutions must be conscious of the risks and limitations of these tools to promote their responsible and productive usage.
The Potential Privacy Concerns Raised by Social Media Use and Data Collection Practices
With billions of users each day on sites like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, social media has ingrained itself into every aspect of our lives. While these platforms offer a straightforward method to communicate with others and exchange information, they also raise significant concerns over data collecting and privacy. This article will examine the possible privacy issues posed by social media use and data-gathering techniques.
Data Collection and Sharing
The gathering and sharing of personal data are significant privacy issues brought up by social media use. Social networking sites gather user data, including details about their relationships, hobbies, and routines. This information is made available to third-party businesses for various uses, such as marketing and advertising. This can lead to serious concerns about who has access to and uses our personal information.
Lack of Control Over Personal Information
The absence of user control over personal information is a significant privacy issue brought up by social media usage. Social media makes it challenging to limit who has access to and how data is utilized once it has been posted. Sensitive information may end up being extensively disseminated and may be used maliciously as a result.
Personalized Marketing
Social media companies utilize the information they gather about users to target them with adverts relevant to their interests and usage patterns. Although this could be useful, it might also cause consumers to worry about their privacy since they might feel that their personal information is being used without their permission. Furthermore, there are issues with the integrity of the data being used to target users and the possibility of prejudice based on individual traits.
Government Surveillance
Using social media might spark worries about government surveillance. There are significant concerns regarding privacy and free expression when governments in some nations utilize social media platforms to follow and monitor residents.
In conclusion, social media use raises significant concerns regarding data collecting and privacy. While these platforms make it easy to interact with people and exchange information, they also gather a lot of personal information, which raises questions about who may access it and how it will be used. Users should be aware of these privacy issues and take precautions to safeguard their personal information, such as exercising caution when choosing what details to disclose on social media and keeping their information sharing with other firms to a minimum.
The Ethical and Privacy Concerns Surrounding Social Media Use And Data Collection
Our use of social media to communicate with loved ones, acquire information, and even conduct business has become a crucial part of our everyday lives. The extensive use of social media does, however, raise some ethical and privacy issues that must be resolved. The influence of social media use and data collecting on user rights, the accountability of social media businesses, and the need for improved regulation are all topics that will be covered in this article.
Effect on Individual Privacy:
Social networking sites gather tons of personal data from their users, including delicate information like search history, location data, and even health data. Each user's detailed profile may be created with this data and sold to advertising or used for other reasons. Concerns regarding the privacy of personal information might arise because social media businesses can use this data to target users with customized adverts.
Additionally, individuals might need to know how much their personal information is being gathered and exploited. Data breaches or the unauthorized sharing of personal information with other parties may result in instances where sensitive information is exposed. Users should be aware of the privacy rules of social media firms and take precautions to secure their data.
Responsibility of Social Media Companies:
Social media firms should ensure that they responsibly and ethically gather and use user information. This entails establishing strong security measures to safeguard sensitive information and ensuring users are informed of what information is being collected and how it is used.
Many social media businesses, nevertheless, have come under fire for not upholding these obligations. For instance, the Cambridge Analytica incident highlighted how Facebook users' personal information was exploited for political objectives without their knowledge. This demonstrates the necessity of social media corporations being held responsible for their deeds and ensuring that they are safeguarding the security and privacy of their users.
Better Regulation Is Needed
There is a need for tighter regulation in this field, given the effect, social media has on individual privacy as well as the obligations of social media firms. The creation of laws and regulations that ensure social media companies are gathering and using user information ethically and responsibly, as well as making sure users are aware of their rights and have the ability to control the information that is being collected about them, are all part of this.
Additionally, legislation should ensure that social media businesses are held responsible for their behavior, for example, by levying fines for data breaches or the unauthorized use of personal data. This will provide social media businesses with a significant incentive to prioritize their users' privacy and security and ensure they are upholding their obligations.
In conclusion, social media has fundamentally changed how we engage and communicate with one another, but this increased convenience also raises several ethical and privacy issues. Essential concerns that need to be addressed include the effect of social media on individual privacy, the accountability of social media businesses, and the requirement for greater regulation to safeguard user rights. We can make everyone's online experience safer and more secure by looking more closely at these issues.
In conclusion, social media is a complex and multifaceted topic that has recently captured the world's attention. With its ever-growing influence on our lives, it's no surprise that it has become a popular subject for students to explore in their writing. Whether you are writing an argumentative essay on the impact of social media on privacy, a persuasive essay on the role of social media in politics, or a descriptive essay on the changes social media has brought to the way we communicate, there are countless angles to approach this subject.
However, writing a comprehensive and well-researched essay on social media can be daunting. It requires a thorough understanding of the topic and the ability to articulate your ideas clearly and concisely. This is where Jenni.ai comes in. Our AI-powered tool is designed to help students like you save time and energy and focus on what truly matters - your education. With Jenni.ai , you'll have access to a wealth of examples and receive personalized writing suggestions and feedback.
Whether you're a student who's just starting your writing journey or looking to perfect your craft, Jenni.ai has everything you need to succeed. Our tool provides you with the necessary resources to write with confidence and clarity, no matter your experience level. You'll be able to experiment with different styles, explore new ideas , and refine your writing skills.
So why waste your time and energy struggling to write an essay on your own when you can have Jenni.ai by your side? Sign up for our free trial today and experience the difference for yourself! With Jenni.ai, you'll have the resources you need to write confidently, clearly, and creatively. Get started today and see just how easy and efficient writing can be!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Sociology of Media and Communication — Social Media
Argumentative Essays About Social Media
This is a comprehensive resource to help you find the perfect social media essay topic. Whether you're navigating the complexities of digital communication, exploring the impact of social media on society, or examining its effects on personal identity, the right topic can transform your essay into a captivating and insightful exploration. Remember, selecting a topic that resonates with your personal interests and academic goals not only makes the writing process more enjoyable but also enriches your learning experience. Let's dive into a world of creativity and critical thinking!
Essay Types and Topics
Below, you'll find a curated list of essay topics organized by type. Each section includes diverse topics that touch on technology, society, personal growth, and academic interests, along with introduction and conclusion paragraph examples to get you started.
Argumentative Essays
Introduction Example: "In the digital age, social media platforms have become central to our daily interactions and self-perception, particularly among teenagers. This essay explores the impact of social media on teen self-esteem, arguing that while it offers a space for expression and connection, it also presents significant challenges to self-image. "
Conclusion Example: "Having delved into the complex relationship between social media and teen self-esteem, it is clear that the digital landscape holds profound effects on individual self-perception. This essay reaffirms the thesis that social media can both uplift and undermine teen self-esteem, calling for a balanced approach to digital engagement."
Introduction Example: "As political landscapes evolve, social media has emerged as a powerful tool for political mobilization and engagement. This essay investigates the role of social media in shaping political movements, positing that it significantly enhances communication and organizational capabilities, yet raises questions about information authenticity. "
Conclusion Example: "Through examining the dual facets of social media in political mobilization, the essay concludes that while social media is a pivotal tool for engagement, it necessitates critical scrutiny of information to ensure a well-informed public discourse."
Compare and Contrast Essays
Introduction Example: "In the competitive realm of digital marketing, Instagram and Twitter stand out as leading platforms for brand promotion. This essay compares and contrasts their effectiveness, revealing that each platform caters to unique marketing strengths due to its specific user engagement and content dissemination strategies. "
Conclusion Example: "The comparative analysis of Instagram and Twitter highlights distinct advantages for brands, with Instagram excelling in visual storytelling and Twitter in real-time engagement, underscoring the importance of strategic platform selection in digital marketing."
Descriptive Essays
Introduction Example: "Today's social media landscape is a vibrant tapestry of platforms, each contributing to the digital era's social fabric. This essay describes the characteristics and cultural significance of current social media trends, illustrating that they reflect and shape our societal values and interactions. "
Conclusion Example: "In portraying the dynamic and diverse nature of today's social media landscape, this essay underscores its role in molding contemporary cultural and social paradigms, inviting readers to reflect on their digital footprints."
Persuasive Essays
Introduction Example: "In an era where digital presence is ubiquitous, fostering positive social media habits is essential for mental and emotional well-being. This essay advocates for mindful social media use, arguing that intentional engagement can enhance our life experiences rather than detract from them. "
Conclusion Example: "This essay has championed the cause for positive social media habits, reinforcing the thesis that through mindful engagement, individuals can navigate the digital world in a way that promotes personal growth and well-being."
Narrative Essays
Introduction Example: "Embarking on a personal journey with social media has been both enlightening and challenging. This narrative essay delves into my experiences, highlighting how social media has influenced my perception of self and community. "
Conclusion Example: "Reflecting on my social media journey, this essay concludes that while it has significantly shaped my interactions and self-view, it has also offered invaluable lessons on connectivity and self-awareness, affirming the nuanced role of digital platforms in our lives."
Engagement and Creativity
As you explore these topics, remember to approach your essay with an open mind and creative spirit. The purpose of academic writing is not just to inform but to engage and provoke thought. Use this opportunity to delve deep into your topic, analyze different perspectives, and articulate your own insights.
Educational Value
Each essay type offers unique learning outcomes. Argumentative essays enhance your analytical thinking and ability to construct well-founded arguments. Compare and contrast essays develop your skills in identifying similarities and differences. Descriptive essays improve your ability to paint vivid pictures through words, while persuasive essays refine your ability to influence and convince. Finally, narrative essays offer a platform for personal expression and storytelling. Embrace these opportunities to grow academically and personally.
Some Easy Argumentative Essay Topics on Social Media
- The Impact of Social Media: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Is Social Media Enhancing or Eroding Our Real-Life Social Skills?
- Should There Be Stricter Regulations on Social Media Content to Protect Youth?
- Social Media's Role in Relationships: Communication Enhancer or Barrier
- Does Social Media Contribute to Political Polarization?
- The Role of Social Media in Shaping Perceptions of Divorce
- The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Benefit or Harm?
- Can Social Media Be Considered a Reliable Source of News and Information?
- Is Social Media Responsible for the Rise in Cyberbullying?
- Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Does Social Media Promote Narcissism and Self-Centered Behaviors?
- The Role of Social Media in Business Marketing: Is It Indispensable?
The Impact of Social Media: Causes and Effects
Facebook sonnet by sherman alexie: summary, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Social Media Engagement on Brand Loyalty in Millennials
Social media is beneficial to the mankind, the detrimental effects of social media on the young generation, the effect of social media challenges on current generation, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Pros and Cons of Social Media: Social Networking
Positive and negative effects of social media, sleeping habits and social media usage, negative effect of social media on young people, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Social Media Cons and Prons: Evaluating Its Advantages and Disadvantage
The importance of staying safe on social media, impact of social media on our lives, social media: negative effects and addiction, discussion on whether is social media beneficial or harmful for society, negative effects of social media: relationships and communication, social media pros and cons, social media - good and bad sides, a study of the role of social media concerning confidentiality of personal data, how social media causes stereotyping, social media addiction: consequences and strategies for recovery, the role of social media in making us more narcissistic, the effect social media is having on today's society and political atmosphere, digital/social media, censorship in social media, why teenagers are addicted to social media and how it affects them, advantages and disadvantages of social media for society, enormous impact of mass media on children, the role of social media in the current business world, social media is the reason for many of the world’s problems and solutions.
Social media refers to dynamic online platforms that enable individuals to actively engage in the generation and dissemination of various forms of content, including information, ideas, and personal interests. These interactive digital channels foster virtual communities and networks, allowing users to connect, communicate, and express themselves. By harnessing the power of technology, social media platforms provide a space for individuals to share and exchange content, fostering connections and facilitating the flow of information in an increasingly digital world.
In a peculiar manner, the inception of social media can be traced back to May 24, 1844, when a sequence of electronic dots and dashes was manually tapped on a telegraph machine. Although the origins of digital communication have deep historical roots, most contemporary narratives regarding the modern beginnings of the internet and social media often point to the emergence of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) in 1969. The year 1987 witnessed the establishment of the direct precursor to today's internet, as the National Science Foundation introduced the more robust and expansive NSFNET, a nationwide digital network. A significant milestone occurred in 1997 when Six Degrees, the first genuine social media platform, was launched.
Mark Zuckerberg is a notable figure in the realm of social media as the co-founder and CEO of Facebook. Zuckerberg played a pivotal role in transforming Facebook from a small networking platform for college students into a global social media giant with billions of users. His innovative ideas and strategic decisions have reshaped the way people connect and share information online, making him one of the most influential individuals in the digital age. Jack Dorsey is recognized as one of the key pioneers of social media, notably for co-founding Twitter. Dorsey's creation revolutionized online communication by introducing the concept of microblogging, allowing users to share short messages in real-time. Twitter quickly gained popularity, becoming a powerful platform for news dissemination, public conversations, and social movements. Dorsey's entrepreneurial spirit and vision have contributed significantly to the evolution of social media and its impact on society. Sheryl Sandberg is a prominent figure in the social media landscape, known for her influential role as the Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Facebook.Sandberg played a crucial part in scaling and monetizing Facebook's operations, transforming it into a global advertising powerhouse. She is also recognized for her advocacy of women's empowerment and leadership in the tech industry, inspiring countless individuals and promoting diversity and inclusion within the social media sphere. Sandberg's contributions have left an indelible mark on the growth and development of social media platforms worldwide.
Social Networking Sites: Facebook, LinkedIn, and MySpace. Microblogging Platforms: Twitter. Media Sharing Networks: Instagram, YouTube, and Snapchat. Discussion Forums and Community-Based Platforms: Reddit and Quora. Blogging Platforms: WordPress and Blogger. Social Bookmarking and Content Curation Platforms: Pinterest and Flipboard. Messaging Apps: WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and WeChat.
Facebook (2004), Reddit (2005), Twitter (2006), Instagram (2010), Pinterest (2010), Snapchat (2011), TikTok (2016)
1. Increased Connectivity 2. Information Sharing and Awareness 3. Networking and Professional Opportunities 4. Creativity and Self-Expression 5. Supportive Communities and Causes
1. Privacy Concerns 2. Cyberbullying and Online Harassment 3. Information Overload and Misinformation 4. Time and Productivity Drain 5. Comparison and Self-Esteem Issues
The topic of social media holds significant importance for students as it plays a prominent role in their lives, both academically and socially. Social media platforms provide students with opportunities to connect, collaborate, and share knowledge with peers, expanding their learning networks beyond the confines of the classroom. It facilitates communication and access to educational resources, allowing students to stay updated on academic trends and research. Additionally, social media enhances digital literacy and prepares students for the realities of the digital age. However, it is crucial for students to develop critical thinking skills to navigate the potential pitfalls of social media, such as misinformation and online safety, ensuring a responsible and balanced use of these platforms.
The topic of social media is worthy of being explored in an essay due to its profound impact on various aspects of society. Writing an essay on social media allows for an in-depth examination of its influence on communication, relationships, information sharing, and societal dynamics. It offers an opportunity to analyze the advantages and disadvantages, exploring topics such as privacy, online identities, social activism, and the role of social media in shaping cultural norms. Additionally, studying social media enables a critical evaluation of its effects on mental health, politics, and business. By delving into this subject, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex and ever-evolving digital landscape we inhabit.
1. Social media users spend an average of 2 hours and 25 minutes per day on social networking platforms. This amounts to over 7 years of an individual's lifetime spent on social media, highlighting its significant presence in our daily lives. 2. Instagram has over 1 billion monthly active users, with more than 500 million of them using the platform on a daily basis. 3. YouTube has over 2 billion logged-in monthly active users. On average, users spend over 1 billion hours watching YouTube videos every day, emphasizing the platform's extensive reach and the power of video content. 4. Social media has become a major news source, with 48% of people getting their news from social media platforms. This shift in news consumption highlights the role of social media in shaping public opinion and disseminating information in real-time. 5. Influencer marketing has grown exponentially, with 63% of marketers planning to increase their influencer marketing budget in the coming year. This showcases the effectiveness of influencers in reaching and engaging with target audiences, and the value brands place on leveraging social media personalities to promote their products or services.
1. Schober, M. F., Pasek, J., Guggenheim, L., Lampe, C., & Conrad, F. G. (2016). Social media analyses for social measurement. Public opinion quarterly, 80(1), 180-211. (https://academic.oup.com/poq/article-abstract/80/1/180/2593846) 2. Appel, G., Grewal, L., Hadi, R., & Stephen, A. T. (2020). The future of social media in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing science, 48(1), 79-95. (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11747-019-00695-1?error=cookies_not_support) 3. Aichner, T., Grünfelder, M., Maurer, O., & Jegeni, D. (2021). Twenty-five years of social media: a review of social media applications and definitions from 1994 to 2019. Cyberpsychology, behavior, and social networking, 24(4), 215-222. (https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/cyber.2020.0134) 4. Ruths, D., & Pfeffer, J. (2014). Social media for large studies of behavior. Science, 346(6213), 1063-1064. (https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.346.6213.1063) 5. Hou, Y., Xiong, D., Jiang, T., Song, L., & Wang, Q. (2019). Social media addiction: Its impact, mediation, and intervention. Cyberpsychology: Journal of psychosocial research on cyberspace, 13(1). (https://cyberpsychology.eu/article/view/11562) 6. Auxier, B., & Anderson, M. (2021). Social media use in 2021. Pew Research Center, 1, 1-4. (https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/wp-content/uploads/sites/9/2021/04/PI_2021.04.07_Social-Media-Use_FINAL.pdf) 7. Al-Samarraie, H., Bello, K. A., Alzahrani, A. I., Smith, A. P., & Emele, C. (2021). Young users' social media addiction: causes, consequences and preventions. Information Technology & People, 35(7), 2314-2343. (https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/ITP-11-2020-0753/full/html) 8. Bhargava, V. R., & Velasquez, M. (2021). Ethics of the attention economy: The problem of social media addiction. Business Ethics Quarterly, 31(3), 321-359. (https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/business-ethics-quarterly/article/ethics-of-the-attention-economy-the-problem-of-social-mediaaddiction/1CC67609A12E9A912BB8A291FDFFE799)
Relevant topics
- Effects of Social Media
- Media Analysis
- Discourse Community
- Sex, Gender and Sexuality
- Cultural Appropriation
- Social Justice
- Sociological Imagination
- American Identity
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts
It is evident that social media has negative and positive impacts on the lives of many people. MySpace, Facebook, Twitter and other social media networks have brought changes to the communication industry. This can be attributed to advanced technology and innovation. Equally, many people are conducting research with an aim of contributing to social media. In my opinion, social media is part of the human life in the 21st century.
In fact, it has reached a point where people cannot do without social media. However, social media has two contradicting perspectives. One of the perspectives views social media as an aspect that has made life easy as compared to the last century. On the other hand, some people view social media as an aspect that has made more harm than good to society. Thus, this paper seeks to bring out the two aspects in a clear manner.
Social media has enabled people to get connected regardless of the distance between them. For instance, social media has facilitated communication between people in different continents. It has been determined to be the best and cheapest way of communication.
Unlike the use of cellphones, there is an opportunity for video conferencing. Research shows that the only cost incurred encompasses internet services. Once a person is connected to a reliable internet service provider, they can communicate with their friends, peers, family members and other people in any part of the world.
Social media has enabled many people to get connected in many parts of the world. Equally, remarkable business operations have been accomplished through social media. In the same way, social media has enabled people that had lost contact to reunite.
Besides, people need not travel because they can use video conferencing to communicate via social media. Thus, travel costs and the burden associated with traveling have been eliminated by the use of social media.
Equally, social media is used in marketing and advertising activities. This presents customers and consumers an opportunity to make a choice of products that they need. Additionally, social media has seen to it that there is proper dissemination of information of consumer products. Thus, it has seen the proliferation of business activities across the globe.
On the other hand, some people view social media as a bad thing. In fact, some people have associated social media with negative aspects. For instance, they claim that social media makes people lazy. Before social media was invented, people travelled so that they would meet with other people. In most cases, people would walk to the place where they agreed to meet.
Equally, after meeting, some people would decide to take a walk. This made them active and made their bodies healthy. However, the introduction of social media brought about many changes. People became lazy because they would communicate at the comfort of their beds and couches.
Further, this made them have poor health. In fact, most users of social media do not travel or even go for walks. Hence, the body does not burn the extra calories resulting in excess weight gain and the associated medical conditions.
Also, some schools of thoughts say that social media has isolated people rather than connecting them. In my opinion, this is true. For instance, people do not physically meet with their relatives, neighbors, friends, and even peers.
Social media networks such as Facebook, Twitter and Skype detach people instead of connecting them. People spend most of their time chatting over the social media at the expense of physical meeting. This underpins isolation and personal contact is lost.
There are other times that people misunderstand each other. Research shows that some of them find solace in the use of social media. People whose relationships are not working tend to run to the social media for help. Social media has become a channel of airing their views and sentiments. They are consoled and encouraged on the social media by other social media users.
Equally, some seek fame on the social media. Likewise, some people upload photos of magnificent places and even outfits that they love with the main aim of seeking attention. True to that, they get attention from friends and other users of social media.
However, this does not solve their problems. In fact, the situation worsens. After going offline, they find themselves in the same situation. Thus, they are not even ready to reconcile with their loved ones. Besides, social media has facilitated infidelity and other social evils encompassing marriages. It has facilitated cheating that has led to sour relationships among lovers and couples.
Others social evils that have been associated with social media include sharing of illegal or unethical content. For instance, some users of social media share pornographic material on the internet. Similarly, drug and child trafficking have been associated with social media. Communication relating to the above unethical practices has been achieved through the use of social media networks owing to their security aspects.
In summary, social media is an invention that has made communication and dissemination of information easy. However, it has been associated with negative aspect and social evils. Therefore, people have the responsibility of doing the right thing or ethical things when using the social media.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, June 3). Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-4/
"Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts." IvyPanda , 3 June 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-4/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts'. 3 June.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts." June 3, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-4/.
1. IvyPanda . "Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts." June 3, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-4/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Social Media: Negative and Positive Impacts." June 3, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-4/.
- Business Proposal Project and Macroeconomics Policy
- Analysing and Presenting Complex Communication
- Facebook and Twitter: Privacy Policy
- The Effect of Social Media on Today’s Youth
- Media Ethics: Beavis and Butthead
- Intimacy and Sexuality Behaviors in Social Media
- Social media effect on the purchase decision of the young generation in Saudi Arabia
- Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay
Essay on Social Media for School Students and Children
500+ words essay on social media.
Social media is a tool that is becoming quite popular these days because of its user-friendly features. Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and more are giving people a chance to connect with each other across distances. In other words, the whole world is at our fingertips all thanks to social media. The youth is especially one of the most dominant users of social media. All this makes you wonder that something so powerful and with such a massive reach cannot be all good. Like how there are always two sides to a coin, the same goes for social media. Subsequently, different people have different opinions on this debatable topic. So, in this essay on Social Media, we will see the advantages and disadvantages of social media.

Advantages of Social Media
When we look at the positive aspect of social media, we find numerous advantages. The most important being a great device for education . All the information one requires is just a click away. Students can educate themselves on various topics using social media.
Moreover, live lectures are now possible because of social media. You can attend a lecture happening in America while sitting in India.
Furthermore, as more and more people are distancing themselves from newspapers, they are depending on social media for news. You are always updated on the latest happenings of the world through it. A person becomes more socially aware of the issues of the world.
In addition, it strengthens bonds with your loved ones. Distance is not a barrier anymore because of social media. For instance, you can easily communicate with your friends and relatives overseas.
Most importantly, it also provides a great platform for young budding artists to showcase their talent for free. You can get great opportunities for employment through social media too.
Another advantage definitely benefits companies who wish to promote their brands. Social media has become a hub for advertising and offers you great opportunities for connecting with the customer.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Disadvantages of Social Media
Despite having such unique advantages, social media is considered to be one of the most harmful elements of society. If the use of social media is not monitored, it can lead to grave consequences.

Thus, the sharing on social media especially by children must be monitored at all times. Next up is the addition of social media which is quite common amongst the youth.
This addiction hampers with the academic performance of a student as they waste their time on social media instead of studying. Social media also creates communal rifts. Fake news is spread with the use of it, which poisons the mind of peace-loving citizens.
In short, surely social media has both advantages and disadvantages. But, it all depends on the user at the end. The youth must particularly create a balance between their academic performances, physical activities, and social media. Excess use of anything is harmful and the same thing applies to social media. Therefore, we must strive to live a satisfying life with the right balance.

FAQs on Social Media
Q.1 Is social media beneficial? If yes, then how?
A.1 Social media is quite beneficial. Social Media offers information, news, educational material, a platform for talented youth and brands.
Q.2 What is a disadvantage of Social Media?
A.2 Social media invades your privacy. It makes you addicted and causes health problems. It also results in cyberbullying and scams as well as communal hatred.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


- ENCYCLOPEDIA
- IN THE CLASSROOM
Home » Perspective » Why removing protections on social media – in the name of free speech – is bad for peacebuilding
Why removing protections on social media – in the name of free speech – is bad for peacebuilding
By Paul Reilly, the Conversation, published on May 13, 2024

On May 16 the world will mark the U.N. International Day of Living Together in Peace. It is a rallying call for people to listen respectfully to others and promote tolerance and understanding.
Perhaps someone should tell tech entrepreneurs Mark Zuckerberg and Elon Musk. The online platforms they head up – Facebook, Instagram, Twitter/X – have become synonymous with fake news, hate speech, misinformation and other online harms.
Social media has been widely blamed for destabilizing democracies and fomenting civil unrest in Europe and North America. In July 2023, the French president, Emmanuel Macron, proposed restricting access to online platforms in order to quell rioting.
This is a far cry from 2009, when Facebook proudly claimed it had created “friendships” between seemingly irredeemably rival groups: Sunni and Shia Muslims, Muslims and Jews, Pakistanis and Indians, Greeks and Turks, conservatives and liberals.
“Peace on Facebook” was a classic example of what social scientist Nicholas John refers to as “social media bulls–t.” Such PR blurbs are designed to convince the public these tech companies are a force for good. They purposefully describe themselves as “platforms” – rather than commercial entities – to emphasize how benign they are.
In reality, these companies financially benefit from every click, like, share and comment users on their platforms make. The more inflammatory the content, the more profitable it is. My research shows that such online incivility only makes it harder to promote peaceful coexistence.
Divisive content
There appears little chance of social media platforms taking stronger action to remove divisive content. Since tech entrepreneur Elon Musk’s acquisition of the X (formerly Twitter) microblogging platform in October 2022, the guardrails designed to protect minorities have, in fact, been dismantled.
Twitter’s Trust and Safety Council was dissolved in December 2022. This move, among many other policy changes, prompted an insider to go public with fears that the site could no longer protect users from trolling, disinformation and sexual exploitation.
Musk has reportedly described himself as a “free-speech absolutist.” This is particularly problematic for those whose real job it is to promote peace in deeply divided societies.
There is already extensive evidence that online platforms such as Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) have been used to spread hate speech. They have been used to incite sectarian violence, too, in countries including India and Myanmar .
In Sri Lanka, following anti-Muslim rioting in 2018, Facebook issued an apology for its role in the unrest. The company hired Article One, the human-rights consultancy, to investigate what had happened. It concluded that the hate speech and misinformation that was amplified by Facebook users online “may have led” to violence offline.
Amplified rumors
My research shows that rumors, misinformation and disinformation have frequently been amplified by social media during contentious parades and protests in Northern Ireland. There is little evidence that such online activity inevitably leads to sectarian rioting. The indirect effects of online incivility, however, is that it makes it harder to promote reconciliation between former antagonists.
In effect, online platforms at present focus more attention on what divides rather than unites different communities.
Research shows that unsupervised intergroup contact , both on and offline, is unlikely to foster positive peace in societies that are transitioning out of conflict. Reducing prejudices against outgroups is much easier when there are rules in place to respond to content that inflames tensions between different communities. In other words, rival groups are unlikely to find common ground in unregulated online spaces where hate speech flourishes.
Clearly, frequent exposure to the online hate speech amplified by social media platforms is unlikely to aid peacebuilding. Communities who do not typically share the same physical space are unlikely to think differently about each other when they see such negative stereotypes being perpetuated online.
Social media such as Facebook and X might not be the best place to promote peace. These platforms are designed to generate profit, not improve community relations.
For intergroup dialogue in contemporary societies to be effective, minorities and vulnerable communities need stronger protections, not less. A public service internet , guardrails included, might be a better way to promote reconciliation in divided societies. Paul Reilly is senior lecturer in communications, media and democracy at the University of Glasgow. The Conversation is an independent and nonprofit source of news, analysis and commentary from academic experts.
The Free Speech Center newsletter offers a digest of First Amendment- and news media-related news every other week. Subscribe for free here: https://bit.ly/3kG9uiJ
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
Joint streaming venture involving ESPN, Fox, Warner Bros. Discovery will be called Venu Sports
May 17, 2024
2 Ill. bills would bolster local newspapers
May 16, 2024
Perspective
New book explores John Stuart Mill’s influence on U.S. free speech protections
May 7, 2024
Nashville Scene reporter describes arrest at Vanderbilt University
April 10, 2024
Explore The First Amendment Encyclopedia
More than 1,700 articles on First Amendment topics, court cases and history

The Often Overlooked Positive Side of Social Media
What healthy tech use actually looks like..
Updated May 16, 2024 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader
- Young Americans flourish digitally, feeling connected and benefiting from positive social comparison.
- Social comparison online can inspire well-being, especially with similar peers and inspiring content.
- Social media can strengthen teen friendships and support, enhanced by parental involvement and digital skills.

Yes, social media poses many challenges. They are designed to keep us hooked and release the neurotransmitter dopamine that makes us spend way more time on it then we intended to. And yes, specifically for young female adolescents, image-based platforms can significantly impact body image and self-esteem . But , social media can also lead to digital flourishing, inspiration, feelings of loving connection and social support.
Do these positive effects make up for all the negative ones? Probably not. But, thinking about the problems from a solution-oriented, positive framework can broaden the ways in which we can think about solving such issues. That is, in addition to pushing for phone-free schools and norms to push the age limit for social media use to 16 years, as proposed in Jonathan Haidt’s new book The Anxious Generation, we can think about what healthy and nourishing technology looks like that fosters well-being, resilience , and character strengths in young adults. We need to know what “healthy” tech use actually looks like to foster it.
My research is based on the framework of positive psychology, which explores ways in which we can live our best lives, rather than lives in the absence of illness. Over the past 10 years, I have explored ways in which media in general, as well as new media such as social media and computer-mediated communication, can lead to happiness and fulfillment for ourselves as well as prosociality and greater connectedness to others.
Here are three key insights from positive media psychology:
1. Young Americans do digitally flourish. With a sample representative of the American population, my recent research revealed that younger individuals (18-34) perceive themselves to flourish digitally more than older individuals, even when controlling for the amount of time spent communicating online in general. Young adults specifically indicated feeling more connected when communicating digitally and engaged in positive social comparison more so than older adults. The latter finding specifically speaks against a lot of earlier research, and press releases for that matter, that showcase the detriments of online social comparison for well-being. But, if we look closely, more recent evidence accumulates that indicates positive well-being effects from social comparison processes online.
2. Social comparison online can lead to inspiration and positive well-being effects. A recent review on the role of social comparison on social media from one of my colleagues from the University of Nuremberg shows that social comparison can lead to well-being for specific people under specific conditions. For example, one of my own studies showed that when college students share inspiring content on Facebook with others, over time, they feel more love and compassion toward others. In another study , we found that inspiring social media and online video use, but not overall time spent on social media, was positively related to everyday experiences of gratitude , awe , vitality and prosocial motivations and behaviors. Similarly, research from Sheffield Institute in the U.K. further shows that social comparison on Instagram is more likely to lead to inspiration when adolescents compare themselves to similar others instead of unachievable influencers. Thus, one of the conditions for whether social comparison may lead to positive or negative effects also stems from the content we consume and the people we follow. So, let’s keep in mind: social comparison is not always bad and young adults do experience inspiration online that is oftentimes overlooked.

3. Social media strengthens teens' friendships more so than it harms them. We are living in a digitized world. And while us old millennials picked up the home phone to talk to our friends for hours in our room, today teens do this on their mobile device. In a Pew Research study from 2022 that surveyed U.S. teens 13-17 years of age, 80% of teens say that social media makes them more connected to what’s going on in their friend’s life, 71% say they have a place where they can show their creative side, and 67% say they like that they have people on social media who can support them through tough times. Moreover, a teenager's mindset matters . The Pew study also revealed that those who believe social media has a general positive effect on their peers also experience more positive personal experiences than those that believe social media has an overall negative effect on their peers. Such a positive outlook on technology can be influenced by a multitude of factors, but specifically for young teenagers , parents play an active role in their kids' digital lives. In fact, parental involvement can be the deciding factor whether a teen digitally flourishes or not. In a study I co-authored that was just published last month, in April 2024, in the Journal of Child Development , we tracked adolescents’ (11-21 years of age, average age 15) digital flourishing for a year and found that for half of the sample their digital flourishing score was high to begin with and remained mostly stable over time (with slight increases in positive social comparison). For the other half of the sample, digital flourishing was lower to begin with and specifically self-control decreased over time. What differentiated the two groups was that the first, highly flourishing group, had parents with high digital skills and a keen investment into their teenager’s tech live.
Don’t get me wrong. I am no denier of the problems that social media brings and I'm all for new COPPA2.0 regulations and other initiatives put forth by admirable institutions such as The Center for Humane Technology and the Digital Wellness Institute. But when we approach these problems from a positive psychology perspective, we might discover resources and strength in the consumer and tech platforms themselves that we can leverage to avoid or lessen the harm and promote thriving.

Sophie H. Janicke-Bowles, Ph.D., is a positive media psychologist working as an Associate Professor at Chapman University in California.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
The Dark Side of Social Media: Negative Effects on Society
Exploring the harmful impacts of social media on individuals.

In today's digital age, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. While it has brought many benefits, such as connecting people from different parts of the world and providing a platform for sharing ideas and information, there are also negative effects associated with its use. In this article, we will delve into some of the harmful consequences of social media on society.
One of the most concerning negative effects of social media is the loss of privacy that many people experience. With the constant sharing of personal information and the tracking of online activities, individuals are at risk of having their privacy compromised. This can lead to identity theft, cyberstalking, and other forms of online harassment.
In addition to privacy concerns, social media has also been linked to a decrease in social relationships for some individuals. While it may seem like social media allows us to stay connected with friends and family, studies have shown that excessive use of these platforms can actually lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Moreover, social media has become a breeding ground for terrorists and extremists to recruit new members. The ease of communication and dissemination of information on the internet has made it easier for these groups to spread their ideologies and radicalize vulnerable individuals.
Another negative effect of social media is the overwhelming amount of information that is readily available on demand. While this can be beneficial in some ways, it can also lead to information overload and a lack of critical thinking skills. People may find it difficult to discern between credible sources and misinformation, leading to the spread of fake news and conspiracy theories.
Furthermore, the ways in which people connect with one another have greatly changed due to social media. While it has made communication more convenient, it has also eroded the quality of face-to-face interactions and interpersonal relationships. Many people now prefer to communicate through screens rather than in person.
Cyberbullying is another harmful consequence of social media, with many individuals falling victim to online harassment and abuse. The anonymity that social media provides can embolden bullies to target their victims without fear of consequences, leading to psychological distress and even suicide in extreme cases.
The next two sections of this report include additional comments from experts, organized under the most common themes found in their research. America traditionally had few immigration restrictions, but since the 1920s, the law has banned most aspiring immigrants. Today, fewer than...
In conclusion, while social media has revolutionized the way we communicate and share information, it also has negative effects on society. It is important for individuals to be mindful of the risks associated with these platforms and to use them responsibly. By being aware of the potential harm that social media can cause, we can work towards creating a safer and more positive online environment for everyone.

Study finds avoiding social media before an election has little to no effect on people's political views
I n the weeks before and after the 2020 presidential election, researchers ran a number of tests to try to understand how much Facebook and its corporate cousin, Instagram, may be contributing to the nation's political divide.
One of those experiments—led by Matthew Gentzkow and Hunt Allcott, economics professors at Stanford University—centered on more than 35,000 Facebook and Instagram users who were paid to stay off the platforms in the run-up to Election Day. There's a lot that researchers could glean from the social media hiatus, including whether people's political attitudes shifted and in what ways. If views changed dramatically, that would support the argument that Facebook and Instagram, and social media generally, are helping to drive Americans apart.
The results of that deactivation exercise—the largest ever involving social media users and the first to include Instagram—are in: Staying off Facebook and Instagram in the final stretch of the November vote had little or no effect on people's political views, their negative opinions of opposing parties, or beliefs around claims of election fraud.
But when it comes to Facebook's impact on what people believed about current events, the researchers reached two conclusions. Those who were off Facebook were worse at answering news quiz questions, but they were also less likely to fall for widely circulated misinformation, suggesting that the platform can be an important conduit for both real and false news.
These findings, published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , are in line with the main takeaways of the other experiments into Facebook and Instagram's potential influence around the 2020 election, in which changing news feeds and limiting re-sharing of posts didn't reduce polarization or change beliefs about whether the voting process was tainted.
Those tests were detailed in four papers published in July 2023 in Science and Nature .
Taken together, the papers suggest that, when it comes to U.S. politics, Facebook and Instagram may not have as much ability to shape political attitudes during an election season as the popular narrative suggests.
And like the previous studies, the Gentzkow and Allcott-led study doesn't absolve Meta Platforms, which owns Facebook and Instagram, from the messy state of U.S. politics. For one thing, the results support the view that Facebook may create harm by distributing misinformation. Gentzkow says it's also possible that the platforms contributed to polarization in the past, even if people's use of them in the run-up to the election had limited impact.
"We are not ruling out the possibility that Facebook and Instagram contribute to polarization in other ways over time," says Gentzkow, who—along with Alcott—is a senior fellow at the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research (SIEPR).
He also notes another finding suggesting that using Facebook in the weeks before the 2020 presidential election may have made people somewhat more likely to vote for Donald Trump and somewhat less likely to vote for Joe Biden. This could suggest that, for Facebook users who still were on the site, Trump's campaign was savvier at building support than Biden's team was.
"This effect was not quite statistically significant, so we need to take it with a grain of salt," Gentzkow says. "But if it's real, it's big enough that it could impact the outcome of a close election."
The study led by Gentzkow and Allcott—and the four that preceded it—are part of a massive research project that has been billed as the most comprehensive, evidence-based investigation yet into the role of social media in American democracy.
The project came together following critiques of Meta's role in the spread of fake news, Russian influence, and the Cambridge Analytica data breach. The collaboration between academics and Meta researchers involved a series of steps to protect the integrity of the research ; Meta, for example, agreed not to prohibit any findings from being published. In all, nearly 20 external social scientists from universities across the country are part of the project, with the external academic team being co-led by Professors Talia Stroud (University of Texas-Austin) and Joshua Tucker (New York University).
"Access to Meta's proprietary data has allowed us to jump over big barriers to research on extremely important issues involving social media and politics," says Gentzkow, who is also the Landau Professor of Technology and the Economy in the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences.
Gentzkow and Allcott's study involved roughly 19,900 Facebook users and 15,600 Instagram users who agreed to stop using the platforms ahead of the 2020 election. About a quarter of them agreed to deactivate their accounts for six weeks before the November vote. The rest comprised a control group that logged off for just one week.
The study's analysis relies on a number of measures, among them participant surveys, state voting records, campaign donations, and Meta platform data. Some participants also allowed the researchers to track how they used other news and social media services when they were off Facebook or Instagram.
On top of the findings on polarization, knowledge, and Republican support, the authors conclude that Facebook and Instagram help people engage in the political process—mostly through posting about politics and signing petitions online (voter turnout didn't change).
Takeaways for 2024 and beyond
Gentzkow says that the study's finding that Facebook and Instagram didn't change people's political attitudes or beliefs in claims of electoral fraud in 2020 is especially interesting in light of his previous research with Allcott. In an earlier smaller-scale study of Facebook users who stayed off the platform for a month ahead of the 2018 midterms, the authors did find evidence that it contributes to polarization.
The distinction, Gentzkow says, could be that people are aware enough of political issues during a presidential election, so Facebook and Instagram have little or no effect on their beliefs or attitudes. But during other elections, when information about candidates or issues are not so front and center, social media may have more influence over what people think.
"Even though Facebook and Instagram did not contribute to polarization in the runup to the 2020 election, it's possible that they are helping to widen political divides in other contexts where people's views are less entrenched," Gentzkow says.
And though the study was limited to the six weeks leading up to the presidential vote, it's still a critical time in U.S. politics—hence the phenomenon known as the " October surprise ."
"Things happen in the home stretch of a presidential election that can change poll numbers," he says. "We've learned from this study that altering how much time people spend on Facebook and Instagram during that period isn't likely to make a huge difference."
More information: Gentzkow, Matthew, The effects of Facebook and Instagram on the 2020 election: A deactivation experiment, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2321584121 . doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2321584121
Provided by Stanford University


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Facebook said on Monday that it had paused development of an Instagram Kids service that would be tailored for children 13 years old or younger, as the social network increasingly faces questions ...
A: In my work with Prof. Vish Viswanath, we have summarized all the papers on how social media use is related to positive well-being measures, to balance the ongoing bias of the literature on negative outcomes such as depression and anxiety. We found both positive and negative correlations between different social media activities and well-being.
Given the popularity of social media among students, the relationship between SNS use and academic success has become a major topic of debate. Social media use is reported to be a risk factor for academic underperformance (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010). Several processes may account for a negative link between social media use and academic ...
Phoon (2017) in his essay explains why social media is bad for people's communication as it "has robbed people's ability to find trust and comfort in one another, replacing our need for warm, supportive interaction and fellowship with a virtual, hollow connection". ... In relation to social media, negative effects include false sense of ...
In April, the social psychologist Jonathan Haidt published an essay in The Atlantic in which he sought to explain, as the piece's title had it, "Why the Past 10 Years of American Life Have ...
So far, most research investigating the effects of social media on mental health has focused on the potential negative aspects. For instance, a 2019 study involving 6,595 teenagers from the United ...
Benefits. The use of social media significantly impacts mental health. It can enhance connection, increase self-esteem, and improve a sense of belonging. But it can also lead to tremendous stress, pressure to compare oneself to others, and increased sadness and isolation. Mindful use is essential to social media consumption.
Social media really impacts my life a lot, from morning to night. (Hanna, aged 17) Social media is intertwined with daily life—for school-aged teens in developed countries, interacting with and through social media platforms (SMPs) is "just part of [the] routine." Among US-based 13- to 17-year-olds, 94% use one or more SMPs (AP-NORC, 2017b).
Too much time on social media apps can lead to an increase in body dissatisfaction, eating disorders and low self-esteem. While this is particularly concerning for teen girls, reports show that 46 ...
A recent investigation by the Wall Street Journal revealed that Facebook was aware of mental health risks linked to the use of its Instagram app but kept those findings secret. Internal research by the social media giant found that Instagram worsened body image issues for one in three teenage girls, and all teenage users of the app linked it to experiences of anxiety and depression.
their heavy use of social media, which has a double negative effect on their physical and. psychological health (depression, anxiety, jealousy, comparison). Consequentially, mass. media culture ...
About two-thirds of Americans (64%) say social media have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in the country today, according to a Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted July 13-19, 2020. Just one-in-ten Americans say social media sites have a mostly positive effect on the way things are going, and one-quarter say ...
Turning to social media when you're feeling down, lonely, or bored, you're potentially using it as a way to distract yourself from unpleasant feelings. You're constantly scrolling through negative news articles or social media posts, seeking out one negative piece of content after another as a coping mechanism. ( meh- kuh-ni-zm)
Among the real negative effects that social media have, one can note intrusive advertising, bullying and harassment, privacy threats, fake news, and violence. Social media are gradually losing the function of communication tools and gaining the status of platforms that allow posting any content, including illegal and immoral materials.
People's reliance on digital communication over in-person contact has increased along with the popularity of social media. Face-to-face interaction has suffered as a result, which has adverse effects on interpersonal relationships and the development of social skills. Decreased Emotional Intimacy.
1 page / 621 words. In the poem "Facebook Sonnet" by Sherman Alexie, the poet explores the complexities of modern technology and social media, particularly Facebook, and its impact on human relationships and communication. Through a series of witty and poignant observations, Alexie delves into the paradoxical nature of social...
Exclusively available on IvyPanda. Updated: Nov 23rd, 2023. It is evident that social media has negative and positive impacts on the lives of many people. MySpace, Facebook, Twitter and other social media networks have brought changes to the communication industry. This can be attributed to advanced technology and innovation.
500+ Words Essay on Social Media. Social media is a tool that is becoming quite popular these days because of its user-friendly features. Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and more are giving people a chance to connect with each other across distances. In other words, the whole world is at our fingertips all thanks to ...
BACKGROUND Social media (SM) has received considerable attention as a potential risk factor for adolescent suicide. Few empirical studies, however, have examined adolescents' daily negative and positive experiences on SM and its proximal impacts on suicidal ideation (SI), particularly using intensive monitoring designs. METHOD Adolescents (N = 60; 14-17 years; 49% girls; 62% LGBTQ+) recruited ...
The lack of social skills, perception of an idealized reality and increase in isolation are the adverse effects of social media. In an era where technology is all around, it is no surprise that there is a noticeable difference in the social skills of many generations. The delay in response time on social media allows people to be reactive ...
Communities who do not typically share the same physical space are unlikely to think differently about each other when they see such negative stereotypes being perpetuated online. Social media such as Facebook and X might not be the best place to promote peace. These platforms are designed to generate profit, not improve community relations.
2. Social comparison online can lead to inspiration and positive well-being effects. A recent review on the role of social comparison on social media from one of my colleagues from the University ...
Another negative effect of social media is the overwhelming amount of information that is readily available on demand. While this can be beneficial in some ways, it can also lead to information overload and a lack of critical thinking skills. People may find it difficult to discern between credible sources and misinformation, leading to the ...
There's a lot that researchers could glean from the social media hiatus, including whether people's political attitudes shifted and in what ways. ... their negative opinions of opposing parties ...