Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 25 January 2021

Online education in the post-COVID era
- Barbara B. Lockee 1
Nature Electronics volume 4 , pages 5–6 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
139k Accesses
210 Citations
337 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make it work — could permanently change how education is delivered.
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced the world to engage in the ubiquitous use of virtual learning. And while online and distance learning has been used before to maintain continuity in education, such as in the aftermath of earthquakes 1 , the scale of the current crisis is unprecedented. Speculation has now also begun about what the lasting effects of this will be and what education may look like in the post-COVID era. For some, an immediate retreat to the traditions of the physical classroom is required. But for others, the forced shift to online education is a moment of change and a time to reimagine how education could be delivered 2 .

Looking back
Online education has traditionally been viewed as an alternative pathway, one that is particularly well suited to adult learners seeking higher education opportunities. However, the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has required educators and students across all levels of education to adapt quickly to virtual courses. (The term ‘emergency remote teaching’ was coined in the early stages of the pandemic to describe the temporary nature of this transition 3 .) In some cases, instruction shifted online, then returned to the physical classroom, and then shifted back online due to further surges in the rate of infection. In other cases, instruction was offered using a combination of remote delivery and face-to-face: that is, students can attend online or in person (referred to as the HyFlex model 4 ). In either case, instructors just had to figure out how to make it work, considering the affordances and constraints of the specific learning environment to create learning experiences that were feasible and effective.
The use of varied delivery modes does, in fact, have a long history in education. Mechanical (and then later electronic) teaching machines have provided individualized learning programmes since the 1950s and the work of B. F. Skinner 5 , who proposed using technology to walk individual learners through carefully designed sequences of instruction with immediate feedback indicating the accuracy of their response. Skinner’s notions formed the first formalized representations of programmed learning, or ‘designed’ learning experiences. Then, in the 1960s, Fred Keller developed a personalized system of instruction 6 , in which students first read assigned course materials on their own, followed by one-on-one assessment sessions with a tutor, gaining permission to move ahead only after demonstrating mastery of the instructional material. Occasional class meetings were held to discuss concepts, answer questions and provide opportunities for social interaction. A personalized system of instruction was designed on the premise that initial engagement with content could be done independently, then discussed and applied in the social context of a classroom.
These predecessors to contemporary online education leveraged key principles of instructional design — the systematic process of applying psychological principles of human learning to the creation of effective instructional solutions — to consider which methods (and their corresponding learning environments) would effectively engage students to attain the targeted learning outcomes. In other words, they considered what choices about the planning and implementation of the learning experience can lead to student success. Such early educational innovations laid the groundwork for contemporary virtual learning, which itself incorporates a variety of instructional approaches and combinations of delivery modes.
Online learning and the pandemic
Fast forward to 2020, and various further educational innovations have occurred to make the universal adoption of remote learning a possibility. One key challenge is access. Here, extensive problems remain, including the lack of Internet connectivity in some locations, especially rural ones, and the competing needs among family members for the use of home technology. However, creative solutions have emerged to provide students and families with the facilities and resources needed to engage in and successfully complete coursework 7 . For example, school buses have been used to provide mobile hotspots, and class packets have been sent by mail and instructional presentations aired on local public broadcasting stations. The year 2020 has also seen increased availability and adoption of electronic resources and activities that can now be integrated into online learning experiences. Synchronous online conferencing systems, such as Zoom and Google Meet, have allowed experts from anywhere in the world to join online classrooms 8 and have allowed presentations to be recorded for individual learners to watch at a time most convenient for them. Furthermore, the importance of hands-on, experiential learning has led to innovations such as virtual field trips and virtual labs 9 . A capacity to serve learners of all ages has thus now been effectively established, and the next generation of online education can move from an enterprise that largely serves adult learners and higher education to one that increasingly serves younger learners, in primary and secondary education and from ages 5 to 18.
The COVID-19 pandemic is also likely to have a lasting effect on lesson design. The constraints of the pandemic provided an opportunity for educators to consider new strategies to teach targeted concepts. Though rethinking of instructional approaches was forced and hurried, the experience has served as a rare chance to reconsider strategies that best facilitate learning within the affordances and constraints of the online context. In particular, greater variance in teaching and learning activities will continue to question the importance of ‘seat time’ as the standard on which educational credits are based 10 — lengthy Zoom sessions are seldom instructionally necessary and are not aligned with the psychological principles of how humans learn. Interaction is important for learning but forced interactions among students for the sake of interaction is neither motivating nor beneficial.
While the blurring of the lines between traditional and distance education has been noted for several decades 11 , the pandemic has quickly advanced the erasure of these boundaries. Less single mode, more multi-mode (and thus more educator choices) is becoming the norm due to enhanced infrastructure and developed skill sets that allow people to move across different delivery systems 12 . The well-established best practices of hybrid or blended teaching and learning 13 have served as a guide for new combinations of instructional delivery that have developed in response to the shift to virtual learning. The use of multiple delivery modes is likely to remain, and will be a feature employed with learners of all ages 14 , 15 . Future iterations of online education will no longer be bound to the traditions of single teaching modes, as educators can support pedagogical approaches from a menu of instructional delivery options, a mix that has been supported by previous generations of online educators 16 .
Also significant are the changes to how learning outcomes are determined in online settings. Many educators have altered the ways in which student achievement is measured, eliminating assignments and changing assessment strategies altogether 17 . Such alterations include determining learning through strategies that leverage the online delivery mode, such as interactive discussions, student-led teaching and the use of games to increase motivation and attention. Specific changes that are likely to continue include flexible or extended deadlines for assignment completion 18 , more student choice regarding measures of learning, and more authentic experiences that involve the meaningful application of newly learned skills and knowledge 19 , for example, team-based projects that involve multiple creative and social media tools in support of collaborative problem solving.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, technological and administrative systems for implementing online learning, and the infrastructure that supports its access and delivery, had to adapt quickly. While access remains a significant issue for many, extensive resources have been allocated and processes developed to connect learners with course activities and materials, to facilitate communication between instructors and students, and to manage the administration of online learning. Paths for greater access and opportunities to online education have now been forged, and there is a clear route for the next generation of adopters of online education.
Before the pandemic, the primary purpose of distance and online education was providing access to instruction for those otherwise unable to participate in a traditional, place-based academic programme. As its purpose has shifted to supporting continuity of instruction, its audience, as well as the wider learning ecosystem, has changed. It will be interesting to see which aspects of emergency remote teaching remain in the next generation of education, when the threat of COVID-19 is no longer a factor. But online education will undoubtedly find new audiences. And the flexibility and learning possibilities that have emerged from necessity are likely to shift the expectations of students and educators, diminishing further the line between classroom-based instruction and virtual learning.
Mackey, J., Gilmore, F., Dabner, N., Breeze, D. & Buckley, P. J. Online Learn. Teach. 8 , 35–48 (2012).
Google Scholar
Sands, T. & Shushok, F. The COVID-19 higher education shove. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/3o2vHbX (16 October 2020).
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T. & Bond, M. A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/38084Lh (27 March 2020).
Beatty, B. J. (ed.) Hybrid-Flexible Course Design Ch. 1.4 https://go.nature.com/3o6Sjb2 (EdTech Books, 2019).
Skinner, B. F. Science 128 , 969–977 (1958).
Article Google Scholar
Keller, F. S. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 1 , 79–89 (1968).
Darling-Hammond, L. et al. Restarting and Reinventing School: Learning in the Time of COVID and Beyond (Learning Policy Institute, 2020).
Fulton, C. Information Learn. Sci . 121 , 579–585 (2020).
Pennisi, E. Science 369 , 239–240 (2020).
Silva, E. & White, T. Change The Magazine Higher Learn. 47 , 68–72 (2015).
McIsaac, M. S. & Gunawardena, C. N. in Handbook of Research for Educational Communications and Technology (ed. Jonassen, D. H.) Ch. 13 (Simon & Schuster Macmillan, 1996).
Irvine, V. The landscape of merging modalities. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/2MjiBc9 (26 October 2020).
Stein, J. & Graham, C. Essentials for Blended Learning Ch. 1 (Routledge, 2020).
Maloy, R. W., Trust, T. & Edwards, S. A. Variety is the spice of remote learning. Medium https://go.nature.com/34Y1NxI (24 August 2020).
Lockee, B. J. Appl. Instructional Des . https://go.nature.com/3b0ddoC (2020).
Dunlap, J. & Lowenthal, P. Open Praxis 10 , 79–89 (2018).
Johnson, N., Veletsianos, G. & Seaman, J. Online Learn. 24 , 6–21 (2020).
Vaughan, N. D., Cleveland-Innes, M. & Garrison, D. R. Assessment in Teaching in Blended Learning Environments: Creating and Sustaining Communities of Inquiry (Athabasca Univ. Press, 2013).
Conrad, D. & Openo, J. Assessment Strategies for Online Learning: Engagement and Authenticity (Athabasca Univ. Press, 2018).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA
Barbara B. Lockee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Barbara B. Lockee .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lockee, B.B. Online education in the post-COVID era. Nat Electron 4 , 5–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-00534-0
Download citation
Published : 25 January 2021
Issue Date : January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-00534-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
A comparative study on the effectiveness of online and in-class team-based learning on student performance and perceptions in virtual simulation experiments.
BMC Medical Education (2024)
Leveraging privacy profiles to empower users in the digital society
- Davide Di Ruscio
- Paola Inverardi
- Phuong T. Nguyen
Automated Software Engineering (2024)
Growth mindset and social comparison effects in a peer virtual learning environment
- Pamela Sheffler
- Cecilia S. Cheung
Social Psychology of Education (2024)
Nursing students’ learning flow, self-efficacy and satisfaction in virtual clinical simulation and clinical case seminar
- Sunghee H. Tak
BMC Nursing (2023)
Online learning for WHO priority diseases with pandemic potential: evidence from existing courses and preparing for Disease X
- Heini Utunen
- Corentin Piroux
Archives of Public Health (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Online university education is the new normal: but is face-to-face better?
Interactive Technology and Smart Education
ISSN : 1741-5659
Article publication date: 2 August 2021
Issue publication date: 4 October 2021
Following the rapid shift to online learning due to COVID-19, this paper aims to compare the relative efficacy of face-to-face and online university teaching methods.
Design/methodology/approach
A scoping review was conducted to examine the learning outcomes within and between online and face-to-face (F2F) university teaching programmes.
Although previous research has supported a “no significant difference” position, the review of 91 comparative studies during 2000–2020 identified 37 (41%) which found online teaching was associated with better learning outcomes, 17 (18%) which favoured F2F and 37 (41%) reporting no significant difference. Purpose-developed online content which supports “student-led” enquiry and cognitive challenge were cited as factors supporting better learning outcomes.
Research limitations/implications
This study adopts a pre-defined methodology in reviewing literature which ensures rigour in identifying relevant studies. The large sample of studies ( n = 91) supported the comparison of discrete learning modes although high variability in key concepts and outcome variables made it difficult to directly compare some studies. A lack of methodological rigour was observed in some studies.
Originality/value
As a result of COVID-19, online university teaching has become the “new normal” but also re-focussed questions regarding its efficacy. The weight of evidence from this review is that online learning is at least as effective and often better than, F2F modalities in supporting learning outcomes, albeit these differences are often modest. The findings raise questions about the presumed benefits of F2F learning and complicate the case for a return to physical classrooms during the pandemic and beyond.
Digital learning
- Teaching methods
- Universities
- Higher education
Stevens, G.J. , Bienz, T. , Wali, N. , Condie, J. and Schismenos, S. (2021), "Online university education is the new normal: but is face-to-face better?", Interactive Technology and Smart Education , Vol. 18 No. 3, pp. 278-297. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-08-2020-0181
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Garry John Stevens, Tobias Bienz, Nidhi Wali, Jenna Condie and Spyros Schismenos.
Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Rapid technological developments in digital education have seen wide-spread adoption of blended and fully online content across a range of educational institutions, including universities. Advocates of online learning (OL) cite a range of key advantages including greater access, cost-effectiveness and the creation of a democratised “community of learners” able to operate in real-time and asynchronous modes ( Beishuizen, 2008 ; Hass and Joseph, 2018 ). In 2020, the inherent agility of OL came into sharp focus with the international impacts of Covid-19. As a result of the pandemic and almost overnight, online university teaching has become the “new normal”. This rapid shift supported critical business-continuity in the sector, but some argued that it largely completed and was enabled by, the full structural integration of digital education that had been proceeding for decades ( Brown and Duguid, 1996 ; Hiltz and Turoff, 2005 ; Kaplan and Haenlein, 2016 ). While blended modes are quite commonplace in countries such as Australia ( Crawford and Jenkins, 2017 ), the UK ( Adekola et al. , 2017 ), Italy ( Previtali and Scarozza, 2019 ) and Singapore ( Jones and Sharma, 2019 ), many educators and higher education institutions faced both full online delivery, as well as the pedagogical implications of teaching digitally for the first time ( Dhawan, 2020 ). A raft of questions comes to the fore. Are some educators still “resistant” ( Blin and Munro, 2008 ) to digital learning in the contexts of a pandemic? When Covid-19 is still in circulation, why are there calls and initiatives to get students and staff back to campus and physical classrooms? What is the current evidence-base in support of OL? Are its learning outcomes broadly equivalent to face-to-face (F2F) modes and, if so, what is the case for a post-Covid return to F2F teaching?
A long-standing criticism of OL is that it cannot replace F2F modes because it lacks the capacity for the communicative processes that occur with physical presence; processes through which the cognitive, meta-cognitive and social/interactive aspects of learning optimally occur ( Francescato et al. , 2006 ). Learning is situational and materially embedded in the context of the classroom and being physically co-present to learn with fellow students and teaching staff ( Taylor, 2013 ). This is not to say that OL is not situated; it also takes place somewhere and has a physicality and materiality to it. While such presence appears important, it has also been argued that F2F teaching frequently defaults to a “teacher-centred” approach that promotes a passive, disengaged relationship between students and educational content; a factor contributing to poor comprehension and information retention ( Garrison and Cleveland-Innes, 2005 ). There is growing evidence that well-structured online courses which promote “active learning” (characterised by group problem-solving requiring higher-order thinking, task completion and reflection) and have high perceived levels of tutor leadership (or “presence”), achieve learning outcomes that are equivalent to or better than, those achieved via F2F teaching ( Cleveland-Innes and Emes, 2005 ; Garrison and Cleveland-Innes, 2005 ; McLaughlin et al. , 2013 ; Thomas and Thorpe, 2019 ). A comprehensive review of the history of online teaching and learning is beyond the scope of this paper, however, we highlight key aspects of the debate and evidence regarding the relative efficacy of F2F and online modalities, as well as “blended” approaches and their potential to optimise learning outcomes.
The great debate – does mode matter?
Since the early 1990s, much of the consideration regarding the comparative efficacy of digital education has been framed around a wider controversy often referred to as the “Clark/Kozma debate”. Clark’s original meta-analysis on the influence of media on learning ( Clark, 1983 ) led him to conclude that media do not influence learning outcomes under any circumstances. In what came to be known as the “no significant difference” position, Clark proposed that researchers should cease exploring the relationship between media and learning, unless they could also provide substantive theory as to why media-specific differences exist ( Clark , 1983, 1994 ). The debate “proper” commenced in 1991 when Kozma outlined a learner “interaction” theory which proposed a synergistic relationship between media, content and the learner ( Kozma , 1991, 1994 ). He argued that different media have distinct symbolic/relational systems and processing, that may both compliment an individual learner and provide effective learning experiences.
Kozma’s theory has been highly influential in framing the social/interactive theory behind blended learning and active learning approaches, including recent initiatives regarding online “community of inquiry” teacher/student collaborations to achieve educational outcomes ( Rubin et al. , 2013 ). Despite such developments, the evidence has remained largely inconclusive regarding any single media (i.e. primary F2F and OL formats) being capable of producing significantly better learning outcomes. While some studies have reported significantly poorer learning outcomes for online university courses ( Brown and Liedholm, 2002 ), such findings have been in the minority. Meta-analyses after 2000 examining learning outcomes ( Bernard et al. , 2004 ; Shachar and Neumann, 2003 ) typically concluded that modality, per se , was not a significant factor in learning outcomes; findings Clark drew upon to re-iterate his original claims ( Clark and Feldon, 2005 ; Clark, 2007 ). This position statement remains essentially unchanged ( Becker, 2010 ; Clark, 2014 ), despite some recent meta-analyses showing that university learning outcomes are generally better with OL modes ( Jayakumar et al. , 2015 ; Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Nguyen, 2015 ). Critics of this status-quo argued that Clark’s commentary reflected a lack of understanding regarding educational applications of “new media” and their educational applications (e.g. gaming platforms and social media) which may be found to provide qualitatively distinct outcomes ( Becker, 2010 ; Rideout et al. , 2010 ) and, many of the claimed “no difference” findings were drawn from studies with poor methodology (e.g. non-random selection, poor control of teacher/student variables and matching of content and contact hours) or which focus on aggregate-level outcomes (e.g. student course grades, tutor/student satisfaction) which may not identify process elements of specific media that are uniquely beneficial ( Francescato et al. , 2006 ; Garrison and Cleveland-Innes, 2005 ; Mullen, 2019 ).
More recent studies have tended to explore the factors associated with developing and delivering a student-centred curriculum that may be associated with optimal learning outcomes, irrespective of the primary teaching mode used. Educators are using digital technologies and new social media platforms to reconceptualise and reconstitute teacher-student relationships and extend learning conversations beyond the traditional classroom ( Condie et al. , 2018 ; Graham, 2014 ). Positioning higher education students as “colleagues in training” ( Condie et al. , 2018 , p. 14) and “students as producers” ( Hynes, 2018 ) is more possible with the affordances of the “participatory web” ( Costa, 2014 ) and within open digital educational practices ( Cronin, 2017 ). As such, earlier constructivist models of individual computer-assisted learning ( Crook, 1998 ) have been relegated in favour of cooperative learning based on social learning theory. These models posit that highly effective learning occurs through interactive work with others and shared task completion and reflection.
Cleveland-Innes and Emes (2005) found that social and academic interaction were critical factors in achieving quality educational outcomes, irrespective of whether the learning environments were F2F or online. However, related research ( Garrison and Cleveland-Innes, 2005 ) has shown interaction, per se , is not sufficient to achieve the kind of critical discourse (and related critical thinking) needed to achieve “deep learning” ( Biggs, 1998 ). Both student-student and tutor-student interactions are important in the creation of critical discourse. However, research indicates that the perceived structure and cohesion associated with the tutor role (often defined as teacher leadership or “presence”) is a stronger predictor of critical discourse and overall effectiveness of both OL and F2F teaching ( Hay et al. , 2004 ), but possibly a greater predictor in online environments ( Thomas and Thorpe, 2019 ; Wu and Hiltz, 2004 ). Educator presence, rapport and a sense of community and trust amongst learners are essential for effective digital learning experiences ( Lambrinidis, 2014 ; Ragusa and Crampton, 2018 ; Stone, 2017 ).
The aim of this review is to compare university learning modes, such that the substantive comparison is between fully online and F2F delivery. As such, our search is limited to studies involving a reasonably rigorous approach to comparing these modalities, that is, using an experimental or quasi-experimental design. Our research question is whether, based upon aggregate findings during the period 2000-2020, fully online or F2F learning modes are more effective in achieving commonly recognised learning outcomes such as test grades and course marks. In posing this comparison, we are mindful that digitised learning commonly blends these approaches, but our primary question goes to the matter of a possibly unique contribution of F2F modes and how this may inform future use of this format, particularly in a post-Covid environment.
This review adopts a scoping review methodology as outlined by Arksey and O’Malley (2005) . The scoping method follows a structured approach to map and presents a descriptive or summative overview of the literature on a topic. This method has been adopted across disciplines and is being increasingly recognised as an effective method when compared to a literature review ( Pham et al. , 2014 ). The focus of this review was to use existing data sources to address our research question, i.e. secondary data sources and did not include any primary data. The scoping process has four stages: identifying the research question; identifying relevant studies; study selection and charting the data and collating, summarizing and reporting the results. This process allows transparency and clarity of data collection, study selection and the collating of results.
Terminology
There are a plethora of terms used to refer to these respective teaching modalities, as well as those which combine their use. Throughout this paper, we use the following standard terms to delineate teaching modes and roles; traditional, F2F and OL; combined F2F/OL (“blended” but also “flipped” when indicated); and teaching practitioners (“tutors” or “instructors”). We use the term OL in preference to e-learning and digitised learning as the latter is less specific to mode and often applied to blended formats. The terms “learning” and “teaching” are typically used as presented by the authors. Unless otherwise specified, “course” refers to a single unit of study (e.g. one-semester Introduction to Sociology unit).
Identifying the research question
The review examined the outcomes and relative efficacy of online (web-based) and F2F university teaching.
Identifying relevant studies
Google Scholar was used as the primary search engine with advanced search options. Google Scholar is multidisciplinary and has broad coverage across health, social science and education. The education-specific database of the Education Resources Information Centre (ERIC) was then used to identify any education-related studies that could have been missed in the primary search via Google Scholar.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Search items were restricted to articles that were: journal articles, published research dissertations and reports; published in the English language; published between 2000 and 2020; and based on key terms. The stated inclusion criteria allowed us to limit the search output to a manageable number of relevant items. This was particularly important regarding the restriction to “title search” only, as earlier searches of full-text articles produced a large number of articles (in the thousands).
Search terms
Primary search involved keywords combination: “online” x “face to face” x “learning” x “comparison”. Key synonyms were also used in a number of other combinations, notably: “eLearning”, “internet”, “web-based”, “teaching”, “traditional” (i.e. teaching), “experiment”, “outcomes”, “review” (to identify relevant descriptive/systematic reviews and meta-analyses). The selected search terms also reflect the review requirement which involves an experimental design or other direct comparisons of the relative learning outcomes of OL and F2F teaching.
Study selection and charting the data
The scoping review included studies that were within the parameters of our enquiry, with all other articles being excluded. These could be studies that did not directly compare teaching modalities; where the teaching modalities were unclear or did not provide a substantive comparison of the two modalities; or where the study predominantly involved non-tertiary students (e.g. high school students). Only journal articles, published research dissertations and reports were included. All other document types including books, non-empirical book chapters, articles that could not be found/opened and studies in a language other than English were excluded.
Our review was conducted in two stages; a preliminary search followed by a combined analysis. The preliminary search yielded 76 studies which, after review, were reduced to 28 relevant items ( Table 1 ). These 28 studies included 1 scoping review and 6 meta-analyses, which constituted a substantial number of individual studies that warranted more detailed review and the inclusion of those that met our study criteria. This combined analysis found a total of 131 studies for review. A number of studies were then excluded for these reasons; published before the year 2000 (4 studies), insufficient information in the meta-analysis to draw clear determinations or the individual paper was not accessible (10 studies), duplicates (6 studies) and outside the scope of this study such as non-university population (1 study) or not directly comparing primary OL and F2F conditions (e.g. using blended learning as a primary condition (19 studies). For the purposes of this analysis, a meta-analysis or scoping review was counted as a separate study/finding (i.e. 7 studies) in addition to the studies it contained and which met out criteria. The combined analysis yielded a final sample of 91 individual studies for review ( Table 2 ).
Collating, summarising and reporting the results
This review narrates the findings from the included studies using an approach consistent with Snilstveit et al. (2012) . The following method was used for collating and reporting the results. For individual studies, the results of statistical analyses and/or author direct statements were used to determine whether learning outcomes favoured OL or F2F or no significant difference was observed. To determine if an individual study within a meta-analysis favoured one mode, the effect sizes (g) were used (i.e. positive effect sizes were counted in favour of OL and negative in favour of F2F). Direct statements by the meta-analysis authors were also used. With regard to the outcome measures used to assess university student learning, the most recognised performance metrics used in meta-analyses are the scores of standardised tests, grade point average (GPA) or overall course grade ( Jayakumar et al. , 2015 ; Jurewitsch, 2012 ). Other measures assess specific learning processes such as cognitive/metacognitive processes ( Kurt and Gürcan, 2010 ) and stress adaptation ( San Jose and Kelleher, 2009 ). A range of other student self-report measures are also used such as satisfaction, confidence, knowledge and performance. Some authors of meta-analyses state that finding and qualifying performance measures between studies can be an issue ( Jayakumar et al. , 2015 ; Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Nguyen, 2015 ). Table 2 details the range of learning outcomes identified in these studies. While the meta-analyses include studies published in 2000–2015 there are several individual studies published between 2015 and 2020 that are included in this study, therefore expanding the time-horizon of previous research.
The combined analysis reviewed individual study reports, as well as the constituent individual studies within relevant meta-analyses and the scoping review. This identified an initial pool of 131 studies. This was reduced to a final sample of 91 studies, which met our inclusion criteria. From these, a total of 37 studies (41%) found online teaching was associated with better student learning outcomes, 17 studies (18%) reported better outcomes with F2F and 37studies (41%) found no significant differences ( Table 2 ). Summary findings from these respective categories are detailed below, including the breakdown of results within the composite studies.
Face-to-face
Addis (2009) and Callister and Love (2016) found that F2F Elementary Education students performed better. The Addis (2009) study found gains in student learning were pronounced in each condition, but the F2F group significantly outperformed the online group on post-test scores due to easier collaboration in the F2F setting and OL students taking longer to get accustomed to the new mode. Callister and Love (2016) compared four master’s level Negotiation classes at two universities but taught by the same professor. Test scores indicated that F2F learners achieved higher negotiation outcomes than online learners. The researchers attributed this to increased instructor interaction and reduced hostility in the F2F settings, even when using the same technology (Google Chat).
Bond and Peterson (2004) found that F2F learners displayed better mastery of subject matter. The study assessed the quality of the problem-based learning (PBL) unit (for teaching delivery) based on several indices. The subjects of the study were university students in an Instructional Planning class. The study authors concluded that the on-campus group selected a wider variety of instructional materials, planned more detailed instruction, used more pedagogical terminology and placed a higher value on planning. They argued that observing the teacher and emulating the teacher’s preparation methods led to these differences in performance. Both groups were similar in problem selection, length of unit, number of materials, organisation of student groups and integration of technology. McKenzie (2013) found that medical students in F2F classes gave significantly higher ratings to teaching staff and reported greater knowledge attainment, which was supported by higher test scores. The researchers suggested these differences may have been due to both technical limitations with the online version of the course (which constrained the complexity of online activity) and the greater complexity and feedback opportunities that were permitted within the F2F course. Despite this both groups reported similar levels of confidence.
San Jose and Kelleher (2009) set up an experimental comparison based on the ecoshock index, a 12-item measure of stress adaptation to new learning environments, developed and tested to measure differences in university students’ responses toF2F and OL learning ecologies. They found that online students reported greater adaptive stress (ecoshock). The index yielded promising internal reliability scores in pilot testing and experimental conditions. Construct validity was supported with evidence from within-subjects experimental comparisons (N = 49) showing that ecoshock was significantly higher online compared to F2F conditions, as the authors had predicted. Also as predicted, ecoshock correlated negatively with an 8-item index of affective learning, which was found to be greater in F2F conditions than OL conditions. While such factors could potentially undermine learning outcomes(the authors, citing Fontaine, 2000 ), this report does not provide information as to whether higher reported adaptive stressor lower affective learning was associated with poorer performance.
In addition to these individual studies, the dis-aggregation of the meta-analyses produced 12 additional findings that met our inclusion criteria and reported results favouring F2F delivery; Lack (2013 : 1 study), Means et al. (2009 : 7 studies), Nguyen (2015 : 2 studies) and Voutilainen et al. (2017 : 2 studies).In total, 17/91 studies (18%)found that OL was the more effective delivery mode.
Heckman and Annabi (2005) found that asynchronous learning networks (ALN) executed through a web-based application generate high levels of cognitive activity equal to and in some cases superior to, the cognitive processes in the F2F classroom. The study also found that student-to-student interactions contain a greater proportion of high-level cognitive indicators than do student-to-teacher interactions. These cognitive indicators are grouped on different hierarchical levels corresponding to the respective level of cognitive activity. These commence with exploration and analysis and culminate with integration as the highest level of activity. Similarly, Williams and Castro (2010) investigated teams of organisational behaviour students about their perceived team performance and concluded that relationships in online teams were better. The authors found that “the flexibility provided by the online environment might allow for more ongoing learning and more frequent exchanges” (p. 141) than in F2F contexts. Team setting moderated the relationship that member teamwork orientation and member social interaction had on individual team-source learning; the relationships were stronger in online teams.
Raynauld (2006) investigated an Economic Policy and a Finance course where the author found that online students perform better (in terms of final grade) in Economic Policy, but there are no significant differences in Finance. While the online version of the Economic Policy course was well-tailored towards the needs of online students, it was the first time that the Finance course was conducted through an online format. This led the authors to propose that the type of course, the setup of the learning environment and the assessment decisions influence the success of online courses.
The scoping review of Nguyen (2015) found online delivery to be at least as effective as F2F delivery. From the 22 constituent studies, 5 met the inclusion criteria for this scoping review, of which 2 favoured OL, 2 favoured F2F and 1 found no significant differences. As the overall finding of the meta-analysis was also in favour of OL, it is categorised as an OL finding within our combined analysis. The report author offered this assessment, “Taken as a whole, there is robust evidence to suggest online learning is generally at least as effective as the traditional format” (p. 309).
The meta-analysis of Jayakumar et al. (2015) found that online students performed better. From the 38 constituent studies, only 3 met the inclusion criteria for this scoping review and all were in favour of OL. Jurewitsch (2012) drew a similar conclusion in his meta-analysis and found that online students performed better in problem-based learning. From the 5 constituent studies, only 3 could be located and accessed and all of them favoured OL. Overall effect size was found to be slightly in favour of online problem-based learning in terms of student performance outcomes (test scores).
The dis-aggregation of the other meta-analyses produced 24 findings that met inclusion criteria and supported OL delivery; Lack (2013 : 3 studies), Means et al. (2009 : 16 studies), McCutcheon et al. (2014 : 2 studies) and Voutilainen et al. (2017 : 2 studies).In total, 37/91 studies (41%)found that OL was more effective than F2F delivery.
No difference
In total, 11 studies, which used standard student performance metrics(e.g. test mark, final grade) found that there were no significant differences between F2F and OL modes ( Cavanaugh and Jacquemin, 2015 ; Driscoll et al. , 2012 ; Ghonsooly and Seyyedrezaie, 2014 ; Herman and Banister, 2007 ; Horspool and Yang, 2010 ; Johnson et al. ,2000 ; Pilbeam and Barrus, 2010 ; Rosell-Aguilar, 2006 ; Sussman and Dutter, 2010 ; Woolsey, 2013 ; Yen et al. , 2018 ).
Cavanaugh and Jacquemin (2015) examined a teaching database with information from 140,444 students enrolled across 6,012 university courses and taught by over 100 faculty members between 2010 and 2013. Notable findings were that students with higher GPAs perform even better in online courses or alternatively, struggling students perform worse when taking courses in an online format compared to a F2F format. Driscoll et al. (2012) conducted a quasi-experimental study of introductory Sociology students and found that differences in student performance between the two modes may be due to a selection effect. Herman and Banister (2007) found no difference in learning outcomes, post-graduate Education students. Johnson et al. (2000) found a similar result for students in a Human Resources course and noted that while those in F2F courses held slightly more positive perceptions about their tutors this did not affect course grades. Pilbeam and Barrus (2010) found that while grades in Computer Literacy courses varied little between modes the percentage of “A” grades were higher in F2F.
Nine studies used outcome measures, which assessed learning processes, mode-related adaptation,and a range of subjective appraisals of performance or engagement ( Driscoll et al. , 2012 ; Ghonsooly and Seyyedrezaie, 2014 ; Groves et al. , 2014 ; Horspool et al. , 2010; Johnson et al. , 2000 ; Kurt and Gürcan, 2010 ; Rosell-Aguilar, 2006 ; Woolsey, 2013 ; Yen et al. , 2018 ).
Kurt and Gürcan (2010) and Ghonsooly and Seyyedrezaie (2014) found that there were no significant differences in student learning strategies between F2F and OL. Kurt and Gürcan (2010) investigated the relationship of undergraduate students’ success with learning strategies and computer anxiety. No significant difference regarding cognitive and metacognitive learning strategies (assessed with separate scales developed by Namlu (2005) ) was found. However, the authors did find average scores for learning anxiety were significantly lower in the F2F instruction group. Ghonsooly and Seyyedrezaie (2014) found that there were no significant differences between the two groups of learners regarding preferences for language learning strategies and reading comprehension. The study measured the outcome of 200 language students with a 50-item translated version of the Strategy Inventory for Language Learning and a test of reading comprehension.
Rosell-Aguilar (2006) found that there were few differences between F2F and OL. The subjects were undergraduate students in a language course. The study found that there were not many differences between online andF2F learners but there are differences in course marks; 10% moreF2F learners achieved a distinction than online learners. Online learners expressed less intention to miss tutorials than theirF2F counterparts. However, more online learners never attended at all. There was a higher number of students who wished to switch from online to F2F rather than vice-versa suggesting a quarter of the online students did not have a good enough experience with the online tuition to wish to continue using the medium. In this and several other studies, it was noted that the students voiced a preference for F2F tuition but this statement was often qualified by stating that the quality of the online course was lacking (often because it was the first time the course was offered via an OL format). Groves et al. (2014) found that there were no significant differences in spiritual awareness between F2F and OL. The primary sample was health-care students and the study concluded that such awareness was achieved independently of the mode of course delivery.
The meta-analysis of McCutcheon et al. (2014) found no significant difference in nursing student performance measures examined across 19studies. Five of these met our inclusion criteria, of which 3 found no significant differences and 2 supported OL. The authors mention that the variation of the intervention made comparison difficult and that there is a clear need for well-structured and controlled research. Notably, the combined evidence suggests that online learning for teaching clinical skills is no less effective than traditional means. At the same time, this review highlights a broader lack of available evidence on the implementation of OL to teaching clinical skills in undergraduate nurse education and the need for further research in this area.
Means et al. (2009) is the largest available meta-analyses and determined that there were no significant differences between teaching modes. It includes 27 studies across a range of courses, which directly compared F2F vs OL conditions and found a small but non-significant effect in favour of OL modes (a mean effect of +0.05 and p = 0.46) This led the authors to conclude that “instruction conducted entirely online is as effective as classroom instruction but no better” (p. 18) Amongst these 27 studies 23 met our inclusion criteria of which 16 favoured OL and 7 supported F2F.
The two remaining meta-analyses were unable to draw a clear conclusion from the available data. Lack (2013) concluded that due to the difficulty of drawing on comparable results between the studies, the overall result of the study was unclear. However, of the 30 included studies, 20 met the inclusion criteria of the current review and did draw a clear finding. Amongst this group 16 found no significant differences, 3 favoured OL and 1 supported F2F. Voutilainen (2017) investigated 9 health-care studies of which 4 met the inclusion criteria of this scoping review. The review indicated that 2 studies supported OL and 2 studies supported F2F. The meta-analysis resulted in the weighted mean of 5.24 (0.13-10.3, CI) on a 0–100 scale, indicating that e-learning improved the knowledge/skill scores 5.24 points more than conventional learning, on average. However, as the range of the weighted mean was wide (−11.2 to 21.7), the authors concluded that generalisations could not be drawn. The authors of both meta-analyses indicated that the various studies differed substantially and that the results were too situational to make claims as to generalisability.
The dis-aggregation of the one remaining met-analysis in this category found a single study, which observed no significant difference ( Nguyen, 2015 ; 1 study). The combined analysis found 37/91 studies (41%) in which no significant differences were observed between the two teaching modes.
The primary focus of our review was to determine, based on the weight of evidence over the past two decades, whether F2F or online teaching modalities provide greater efficacy regarding university learning outcomes or whether the “no significant difference” position ( Clark , 2007, 2014 ) continues to reflect their relative status. Our combined analysis provided a clear answer to our research question. From the 91 identified studies which directly compared these two teaching modes, 37 (41%) found online teaching was associated with better learning outcomes, 17 (18%) favoured F2F teaching and 37 studies (41%) found no significant differences. Following the early “debate” of Clark (1983) and Kozma (1991) and more recent findings that modality, per se , is not a significant factor in learning outcomes ( Bernard et al. , 2004 ; Clark, 2007 ; Shachar and Neumann, 2003 ) the current data indicate that, in aggregate terms, online modalities are producing better learning outcomes for university students. Also consistent with the original thesis of Kozma (1991) are recent findings that the better outcomes associated with online learning are possibly due to the qualitatively different relationship that appears to develop between this media, the learning content and the learner ( Cavanaugh and Jacquemin, 2015 ; Heckman and Annabi, 2005 ; Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Nguyen, 2015 ; Williams and Castro, 2010 ).
If online university education appears to provide consistently better learning outcomes than F2F approaches, what factors may contribute to this difference? There is some evidence that OL and the working environments that it creates enable higher levels of cognitive activity which can lead to better performance. Heckman and Annabi (2005) found that student-to-student interactions foster higher cognitive activity and that students assume some parts of the teacher role in OL modes. Small group learning (e.g. “break-out” groups, team tasks) may afford a greater comfort in learning from peers, particularly as they are often distinctly “separate” spaces in the OL environment. This may allow higher functioning students to provide greater input and direction to the process, reinforcing their own learning and content-related leadership, while other students may feel more confident to address questions and uncertainties directly to fellow students ( Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Nguyen, 2015 ). This appears consistent with findings by Cavanaugh and Jacquemin (2015), who observed that well-performing students perform better when taking the online version of a class, although one small study (Kurt et al. , 2010) reported lower aggregate levels of learning anxiety in a F2F course. Another argument as to why OL results in better student performance is that geographical distance does not play a role in student enrolment, and therefore the range of potential students is increased ( Jurewitsch, 2012 ). Similarly, the flexibility of synchronous and asynchronous OL has been found to be associated with increased student performance ( Nguyen, 2015 ). This is consistent with the finding from Williams and Castro (2010) that OL allows “for more ongoing learning and more frequent exchanges” (p. 141).
Nguyen (2015) and Jurewitsch (2012) state that OL plays a specific role in enabling better performance by providing an accessible and safe learning environment. Both studies found OL can cater to more learning styles, enables learning through a variety of formats and materials and can more readily cater to individual learning needs, all of which contribute to increased performance. As such, it is critical that the course setup is well-tailored to the specific needs and strengths of OL environments, rather than simply transferring F2F-developed content to online platforms. Several of the included studies reported good and poor translations of such content to online platforms and their effects on student performance ( Jayakumar et al. , 2015 ; Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Raynauld, 2006 ). Raynauld (2006) concluded that the setup of the learning environment is a key determinant for student performance in online courses, as measured by final grade. He found that well-established F2F and OL Economics courses favoured OL, but an established F2F Finance course compared with an OL version delivered for the first time showed no difference, possibly indicating the advantage of online consolidation was lost(albeit the cross-compared courses were different). Jayakumar et al. (2015) found that the web offers significantly more tools for teaching and learning and that the combination of teaching methods is what creates superior performance outcomes for OL courses. Jurewitsch (2012) reported that optimal group size to support problem-based learning and the right mix of synchronous/asynchronous interactions with tutors are amongst key factors which result in superior performance with OL. Moreover, while digital technologies have developed rapidly, student cohorts are increasingly highly adapted to them and able to draw out the best of what these evolving platforms have to offer ( Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Yen et al. , 2018 ).
Challenges and opportunities with Covid-19
In a review of the pedagogical responses of 20 countries within the “intra-period Covid-19 response”, Crawford et al. (2020) found a range of approaches have been taken by universities, which are highly dependent upon their respective country’s political decisions on Higher Education policy, infection rates and pandemic control measures. In countries such as Jordan, the pandemic is enabling an arguably overdue digitalisation of Higher Education. In places such as Australia, there is a desire to keep campuses open and get back to F2F teaching with physical distancing protocols as soon as possible. The reasons for returning to or maintaining F2F teaching are complex. These range from (often unfounded) presumptions of teaching quality and student preference, to concerns about wider social and economic implications of moving away from physical campuses. This disruption is mirrored in the corporate sector where some companies, based on their pandemic experiences, now see a future with “much less real estate” ( Schatzker, 2020 ).
It is notable that while several studies in our review found the physical presence of a tutor conferred distinct learning advantages ( Addis, 2009 ; Bond and Peterson, 2004 ; Callister and Love, 2016 ) this was only observed in a small proportion of the total sample. More direct time with instructors and the ability to observe and emulate their practice (e.g. elementary school educators) were cited advantages, although some of these same studies noted adjustments to new online formats and technical constraints may have affected their relative outcomes. While newer digital platforms have likely reduced such gaps( Williamson, 2019 ), online delivery has the potential to compromise academic quality and curriculum standards, particularly where academics are overworked, inexperienced and/or unsupported by their institutions to make the digital transition. The rapid move of some teaching to fully online formats during the pandemic presents substantial risks in this regard and the heightened need for sharing good practice. Crawford et al. (2020) advise that universities “need to be conscious of their ability to continuously monitor the quality of the learning design” (p. 20) in such times of rapid change and uncertainty.
By grounding our review in the empirical comparisons between online and F2F delivery, we travel some way beyond Burns (2020) critique of the utopian discourse that digital technologies can and will save us and can and have saved higher education “the first time from austerity funding models, the second time from a pandemic” (p. 247) to find that many aspects of digital education are beneficial for student learning. However, there is also a warning here; that when digital technologies meet neoliberal policy reforms, academia and academics may not be able to respond to the kind of political-economic restructuring that follows ( Kornbluh, 2020 ). Beyond the surface issue of learning modalities, there is much at stake for higher education when it is reworked by the application of digital technologies for neoliberal purposes in a pandemic.
Limitations and future research
A broad limitation of the review findings relates to the substantial variability that exists regarding research-related terminology, examined learning processes and outcomes and the associated measures used to determine learning efficacy. This high variability made it difficult, within the scope of the current analysis, to be able to meaningfully compare outcomes between some studies. This issue has been highlighted by several researchers examining this topic ( Jayakumar et al. , 2015 ; Jurewitsch, 2012 ; Nguyen, 2015 ). The comparability limitations risk a lack of “critical mass” regarding well-aligned and controlled studies and an ability to address key issues at a level of detail. Many of, which did not randomly allocate subjects or otherwise control for variables, which could potentially confound outcomes (e.g. mode self-selection). For example, there is evidence of student preferences towards online courses, due to their convenience and other factors ( Jurewitsch, 2012 ) and that better students may adjust more readily and perform better in digital education ( Cavanaugh and Jacquemin, 2015 ). Similarly, better educators may adapt more readily to the online environment and are better capitalise on the learning advantages it offers. Such factors indicate that wider determinations regarding relative efficacy must be drawn with caution and with recognition of these existing limitations with study methods. As noted, future research could resolve some of this uncertainty using well-controlled studies. Such research could also move beyond the coarser indicators of learning effectiveness (e.g. final grade) to examine process elements associated with optimal learning such as group interactive processes ( Shea and Bidjerano, 2012 ) and cognitive analysis and integration in these contexts ( Heckman and Annabi, 2005 ; Kurt and Gürcan, 2010 ). Research is also needed to determine optimal mode combinations within synchronous hybrid OL/F2Fmethods such as Hyflex ( Beatty, 2014 ), including clarification of the “best use” of F2F delivery, particularly as classroom delivery will increasingly be embedded within such formats ( Brown et al. , 2020 ). Another limitation is that our analysis rests on a binary distinction between F2F and online teaching modes. While reflecting on a current reality for some educators, it is an increasingly difficult boundary to maintain given how integrated and enmeshed we are in digital infrastructures, systems and devices within our everyday lives. Costa et al. (2019) call for more advanced theoretical work around technology in education that goes beyond modes, individual tools and binary distinctions and conceptualise technology and its pedagogical impacts “in more nuanced and critical ways” (p. 396) to make new possibilities for higher education in the present and foreseeable future.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate that there is little consistent evidence after the year 2000 that F2F university teaching supports better student learning outcomes. Conversely, there is evidence at an aggregate level that OL is at least as effective and often confers a modest advantage compared with F2F modalities across a range of study disciplines. These results can inform university educators and administrators as to the broad-based efficacy of this teaching mode, particularly as the pandemic has brought its use and value into sharp focus. While it is possible that the current findings reflect forms of systematic bias, mitigating against this conclusion is the aggregate nature of these results; mode-specific findings favouring OL outcomes at a 2:1 ratio when compared to F2F delivery. Key factors within this appear to be the role and “presence” of online tutors and their capacity to create “well-scaffolded”, engaging learning activities, particularly those conducted through small-group interactive tasks which develop independent learning skills. Peer facilitation developed this way may be one of the best strategies to encourage participation, while also freeing the teacher’s role to focus on developing consensus or specific learning outcomes. Importantly, such student-to-student interactions appear to generate higher levels of cognitive challenge and activity, with the reviewed evidence indicating these specific relationships were often stronger in online team environments.
While the current findings highlight the mounting evidence-based regarding online learning, further research is needed to support its conclusions but also to better understanding the constituent elements contributing to effective learning outcomes across modalities and within hybrid approaches. This requires a greater body of well-designed studies with large, cross-institutional samples that can support statistically significant findings. These should also provide a detailed examination of interactive-process elements, including peer facilitation and teacher leadership/presence, their relationship with learning outcomes and whether mode-specific factors enable such processes. A final question of interest to our research group is whether the learning of instrumental (“hands-on”) skills is better achieved through F2F modes. The current review included studies, which found skills-based learning outcomes (e.g. musical performance and medical procedures) were similar in online and F2F modes, but the evidence-base remains limited. As university learning increasingly shifts to digitised formats, this is a key issue affecting higher education and industry sectors alike and is the focus of further research within our team.
Primary search combinations and relevant studies identified
Summary of primary university learning outcomes by teaching mode
In composite studies/meta-analyses – indicated outcome variable is that most used
Composite/meta-analyses report overall efficacy finding; results of included individual studies were:
Means et al. (2009) F2F(7); OL(16); ND(0)
Jurewitsch (2012) F2F(0); OL(3); ND(0)
Lack (2013) F2F(1); OL(3); ND(16) [no clear determination from assessed data]
McCutcheon et al. (2014) F2F(0); OL(2); ND(3)
Jayakumar et al. (2015) F2F(0); OL(3); ND(0)
Nguyen (2015) F2F(2); OL(2); ND(1) [categorised OL based on main study finding]
Voutilainen et al. (2017) F2F(2); OL(2); ND(0) [no clear determination from assessed data]
Addis , A.J. ( 2009 ), “ A comparison of face-to-face and online learning environments to prepare teachers to use technology ”, unpublished doctoral dissertation, UNLV Theses, Dissertations, Professional Papers, and Capstones, 33, University of Nevada , Las Vegas. NV , available at: https://digitalscholarship.unlv.edu/thesesdissertations/33
Adekola , J. , Dale , V.H. and Gardiner , K. ( 2017 ), “ Development of an institutional framework to guide transitions into enhanced blended learning in higher education ”, Research in Learning Technology , Vol. 25 , doi: 10.25304/rlt.v25.1973 .
Arksey , H. and O’Malley , L. ( 2005 ), “ Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework ”, International Journal of Social Research Methodology , Vol. 8 No. 1 , pp. 19 - 32 , doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616 .
Beatty , B. ( 2014 ), “ Hybrid courses with flexible participation: the HyFlex course design ”, in Kyei-Blankson , L. and Ntuli , E. (Eds), Practical Applications and Experiences in K-20 Blended Learning Environments , IGI Global , Hershey, PA , pp. 153 - 177 , doi: 10.4018/978-1-4666-4912-5.ch011 .
Becker , K. ( 2010 ), “ The Clark-Kozma debate in the 21st century ”, Canadian Network for Innovation in Education Conference 2010: Heritage Matters: Inspiring Tomorrow , Saint John, New Brunswick .
Beishuizen , J. ( 2008 ), “ Does a community of learners foster self‐regulated learning? ”, Technology, Pedagogy and Education , Vol. 17 No. 3 , pp. 183 - 193 , doi: 10.1080/14759390802383769 .
Bernard , R.M. , Abrami , P.C. , Lou , Y. , Borokhovski , E. , Wade , A. , Wozney , L. , Wallet , P.A. , Fiset , M. and Huang , B. ( 2004 ), “ How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A Meta-analysis of the empirical literature ”, Review of Educational Research , Vol. 74 No. 3 , pp. 379 - 439 , doi: 10.3102%2F00346543074003379 .
Biggs , J. ( 1998 ), “ Learning from the Confucian heritage: so size doesn’t matter? ”, International Journal of Educational Research , Vol. 29 No. 8 , pp. 723 - 738 , doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(98)00060-3 .
Blin , F. and Munro , M. ( 2008 ), “ Why hasn’t technology disrupted academics’ teaching practices? Understanding resistance to change through the lens of activity theory ”, Computers and Education , Vol. 50 No. 2 , pp. 475 - 490 , doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2007.09.017 .
Bond , N. and Peterson , C.L. ( 2004 ), “ Preparing preservice teachers to plan problem based learning: a qualitative case study of online and face-to-face learning ”, Action in Teacher Education , Vol. 26 No. 3 , pp. 82 - 95 , doi: 10.1080/01626620.2004.10463335 .
Brown , B.W. and Liedholm , C.E. ( 2002 ), “ Can web courses replace the classroom in principles of microeconomics? ”, American Economic Review , Vol. 92 No. 2 , pp. 444 - 448 , available at: https://pubs.aeaweb.org/doi/pdf/10.1257/000282802320191778
Brown , J.S. and Duguid , P. ( 1996 ), “ Universities in the digital age ”, Change: The Magazine of Higher Learning , Vol. 28 No. 4 , pp. 11 - 19 , doi: 10.1080/00091383.1996.9937757 .
Brown , M. , McCormack , M. , Reeves , J. , Brook , D.C. , Grajek , S. , Alexander , B. , Bali , M. , Bulger , S. , Dark , S. , Engelbert , N. , Gannon , K. , Gauthier , A. , Gibson , D. , Gibson , R. , Lundin , B. , Veletsianos , G. and Weber , N. ( 2020 ), 2020 Educause Horizon Report Teaching and Learning Edition , EDUCAUSE , Louisville, CO , available at: www.learntechlib.org/p/215670/
Burns , R. ( 2020 ), “ A COVID-19 panacea in digital technologies? Challenges for democracy and higher education ”, Dialogues in Human Geography , Vol. 10 No. 2 , pp. 246 - 249 , doi: 10.1177%2F2043820620930832 .
Callister , R.R. and Love , M.S. ( 2016 ), “ A comparison of learning outcomes in skills‐based courses: online versus face‐to‐face formats ”, Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education , Vol. 14 No. 2 , pp. 243 - 256 , doi: 10.1111/dsji.12093 .
Cavanaugh , J.K. and Jacquemin , S.J. ( 2015 ), “ A large sample comparison of grade based student learning outcomes in online vs. face-to-face courses ”, Online Learning , Vol. 19 No. 2 , ISSN 1939-5256.
Clark , R.E. ( 1983 ), “ Reconsidering research on learning from media ”, Review of Educational Research , Vol. 53 No. 4 , pp. 445 - 459 , doi: 10.3102%2F00346543053004445 .
Clark , R.E. ( 1994 ), “ Media will never influence learning ”, Educational Technology Research and Development , Vol. 42 No. 2 , pp. 21 - 29 , doi: 10.1007/BF02299088 .
Clark , R.E. ( 2007 ), “ Learning from serious games? Arguments, evidence, and research suggestions ”, Educational Technology , Vol. 47 No. 3 , pp. 56 - 59 , available at: www.jstor.com/stable/44429512
Clark , R. ( 2014 ), “ Cognitive task analysis for expert-based instruction in healthcare ”, in Spector , J. , Merrill , M. , Elen , J. and Bishop , M. (Eds), Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology , Springer , New York, NY , doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-3185-5_42 .
Clark , R.E. and Feldon , D.F. ( 2005 ), “ Five common but questionable principles of multimedia learning ”, in Mayer , R. (Ed.) Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning , Cambridge University Press , Cambridge , pp. 97 - 116 .
Cleveland-Innes , M.F. and Emes , C. ( 2005 ), “ Social and academic interaction in higher education contexts and the effect on deep learning ”, Journal of Student Affairs Research and Practice , Vol. 42 No. 2 , pp. 387 - 408 , doi: 10.2202/1949-6605.1475 .
Condie , J.M. , Ayodele , I. , Chowdhury , S. , Powe , S. and Cooper , A.M. ( 2018 ), “ Personalizing twitter communication: an evaluation of ‘rotation-curation’ for enhancing social media engagement within higher education ”, Journal of Marketing for Higher Education , Vol. 28 No. 2 , pp. 192 - 209 , doi: 10.1080/08841241.2018.1453910 .
Costa , C. ( 2014 ), “ Double gamers: academics between fields ”, British Journal of Sociology of Education , Vol. 37 No. 7 , pp. 993 - 1013 , doi: 10.1080/01425692.2014.982861 .
Costa , C. , Hammond , M. and Younie , S. ( 2019 ), “ Theorising technology in education: an introduction ”, Technology, Pedagogy and Education , Vol. 28 No. 4 , pp. 395 - 399 , doi: 10.1080/1475939X.2019.1660089 .
Crawford , J. , Butler-Henderson , K. , Rudolph , J. , Malkawi , B. , Glowatz , M. , Burton , R. , Magni , P. and Lam , S. ( 2020 ), “ COVID-19: 20 countries' higher education intra-period digital pedagogy responses ”, Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching , Vol. 3 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 20 , doi: https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2020.3.1.7.
Crawford , R. and Jenkins , L. ( 2017 ), “ Blended learning and team teaching: adapting pedagogy in response to the changing digital tertiary environment ”, Australasian Journal of Educational Technology , Vol. 33 No. 2 , doi: 10.14742/ajet.2924 .
Cronin , C. ( 2017 ), “ Openness and praxis: exploring the use of open educational practices in higher education ”, The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , Vol. 18 No. 5 , pp. 15 - 34 , doi: 10.19173/irrodl.v18i5.3096 .
Crook , C. ( 1998 ), “ Children as computer users: the case of collaborative learning ”, Computers and Education , Vol. 30 Nos 3/4 , pp. 237 - 247 , doi: 10.1016/S0360-1315(97)00067-5 .
Dhawan , S. ( 2020 ), “ Online learning: a panacea in the time of COVID-19 crisis ”, Journal of Educational Technology Systems , Vol. 49 No. 1 , pp. 5 - 22 , doi: 10.1177/0047239520934018 .
Driscoll , A. , Jicha , K. , Hunt , A.N. , Tichavsky , L. and Thompson , G. ( 2012 ), “ Can online courses deliver in-class results?: a comparison of student performance and satisfaction in an online versus a face-to-face introductory sociology course ”, Teaching Sociology , Vol. 40 No. 4 , pp. 312 - 331 , doi: 10.1177%2F0092055X12446624 .
Fontaine , G. ( 2000 ), “ Skills for successful international assignments to, from, and within Asia and the pacific: Implications for preparation, support, and training ”, Management Decision , Vol. 35 No. 8 , pp. 631 - 643 , doi: 10.1108/00251749710176190 .
Francescato , D. , Porcelli , R. , Mebane , M. , Cuddetta , M. , Klobas , J. and Renzi , P. ( 2006 ), “ Evaluation of the efficacy of collaborative learning in face-to-face and computer-supported university contexts ”, Computers in Human Behavior , Vol. 22 No. 2 , pp. 163 - 176 , doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2005.03.001 .
Garrison , D.R. and Cleveland-Innes , M. ( 2005 ), “ Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough ”, American Journal of Distance Education , Vol. 19 No. 3 , pp. 133 - 148 , doi: 10.1207/s15389286ajde1903_2 .
Ghonsooly , B. and Seyyedrezaie , Z.S. ( 2014 ), “ The comparison of language learning strategies and reading comprehension of Iranian EFL students taking web-based and face-to-face instruction ”, Theory and Practice in Language Studies , Vol. 4 No. 6 , pp. 1296 - 1302 , doi: 10.4304/tpls.4.6.1296-1302 .
Graham , M. ( 2014 ), “ Social media as a tool for increased student participation and engagementoutside the classroom in higher education ”, Journal of Perspectives in Applied Academic Practice , Vol. 2 No. 3 , doi: 10.14297/jpaap.v2i3.113 .
Groves , K. , Baldry , C. and Sherrat , C. ( 2014 ), “ What’s the “e” in e-learning for spirituality: a comparison of online and face to face course versions for healthcare workers ”, BMJ Supportive and Palliative Care , Vol. 4 No No. Suppl 1 , doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2014-000654.86 .
Hass , A. and Joseph , M. ( 2018 ), “ Investigating different options in course delivery – traditional vs online: is there another option? ”, The International Journal of Information and Learning Technology , Vol. 35 No. 4 , pp. 230 - 239 , doi: 10.1108/ijilt-09-2017-0096 .
Hay , A. , Hodgkinson , M. , Peltier , J.W. and Drago , W.A. ( 2004 ), “ Interaction and virtual learning ”, Strategic Change , Vol. 13 No. 4 , pp. 193 - 204 , doi: 10.1002/jsc.679 .
Heckman , R. and Annabi , H. ( 2005 ), “ A content analytic comparison of learning processes in online and face-to-face case study discussions ”, Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , Vol. 10 No. 2 , doi: 10.1111/j.1083-6101.2005.tb00244.x .
Herman , T. and Banister , S. ( 2007 ), “ Face-to-face versus online coursework: a comparison of learning outcomes and costs ”, Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education , Vol. 7 No. 4 , pp. 318 - 326 . ISSN 1528-5804.
Hiltz , S.R. and Turoff , M. ( 2005 ), “ Education goes digital: the evolution of online learning and the revolution in higher education ”, Communications of the ACM , Vol. 48 No. 10 , pp. 59 - 64 , doi: 10.1145/1089107.1089139 .
Horspool , A. and Yang , S.S. ( 2010 ), “ A comparison of university student perceptions and success learning music online and face-to-face ”, MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching , Vol. 6 No. 1 , pp. 15 - 29 , available at: https://jolt.merlot.org/vol6no1/horspool_0310.pdf .
Hynes , M. ( 2018 ), “ Students-as-producers: developing valuable student-centered research and learning opportunities ”, International Journal of Research Studies in Education , Vol. 7 No. 4 , pp. 1 - 13 , doi: 10.5861/ijrse.2017.1858 .
Jayakumar , N. , Brunckhorst , O. , Dasgupta , P. , Khan , M.S. and Ahmed , K. ( 2015 ), “ E-learning in surgical education: a systematic review ”, Journal of Surgical Education , Vol. 72 No. 6 , pp. 1145 - 1157 , doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2015.05.008 .
Johnson , S.D. , Aragon , S.R. and Shaik , N. ( 2000 ), “ Comparative analysis of learner satisfaction and learning outcomes in online and face-to-face learning environments ”, Journal of Interactive Learning Research , Vol. 11 No. 1 , pp. 29 - 49 . ISSN 1093-023X.
Jones , K.A. and Sharma , R.S. ( 2019 ), “ An experiment in blended learning: higher education without lectures ”, International Journal of Digital Enterprise Technology , Vol. 1 No. 3 , pp. 241 - 275 , doi: 10.1504/IJDET.2019.097846 .
Jurewitsch , B. ( 2012 ), “ A Meta-analytic and qualitative review of online versus face-to-face problem-based learning ”, Journal of Distance Education , Vol. 26 No. 2 , available at: www.ijede.ca/index.php/jde/article/download/787/1399?inline=1
Kaplan , A.M. and Haenlein , M. ( 2016 ), “ Higher education and the digital revolution: about MOOCs, SPOCs, social media, and the cookie monster ”, Business Horizons , Vol. 59 No. 4 , pp. 441 - 450 , doi: 10.1016/j.bushor.2016.03.008 .
Kornbluh , A. ( 2020 ), “ Academe’s coronavirus shock doctrine ”, The Chronicle of Higher Education, 12 March , available at: www.chronicle.com/article/academes-coronavirus-shock-doctrine/ ( accessed 20 June 2020 ).
Kozma , R.B. ( 1991 ), “ Learning with media ”, Review of Educational Research , Vol. 61 No. 2 , pp. 179 - 211 , doi: 10.3102%2F00346543061002179 .
Kozma , R.B. ( 1994 ), “ The influence of media on learning: the debate continues ”, School Library Media Research SLMQ , Vol. 22 No. 4 , available at: www.ala.org/aasl/sites/ala.org.aasl/files/content/aaslpubsandjournals/slr/edchoice/SLMQ_InfluenceofMediaonLearning_InfoPower.pdf
Kurt , A.A. and Gürcan , A. ( 2010 ), “ The comparison of learning strategies, computer anxiety and success states of students taking web-based and face-to-face instruction in higher education ”, Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 9 , pp. 1153 - 1157 , doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.12.299 .
Lack , K.A. ( 2013 ), “ Current status of research on online learning in postsecondary education ”, Ithaka S+R , available at: https://sr.ithaka.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/ithaka-sr-online-learning-postsecondary-education-may2012.pdf ( accessed 15 June 2020 ).
Lambrinidis , G. ( 2014 ), “ Supporting online, non-traditional students through the introduction of effective e-learning tools in a pre-university tertiary enabling programme ”, Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management , Vol. 36 No. 3 , pp. 257 - 267 , doi: 10.1080/01587919.2014.899053 .
McCutcheon , K. , Lohan , M. , Traynor , M. and Martin , D. ( 2014 ), “ A systematic review evaluating the impact of online or blended learning vs. face‐to‐face learning of clinical skills in undergraduate nurse education ”, Journal of Advanced Nursing , Vol. 71 No. 2 , pp. 255 - 270 , doi: 10.1111/jan.12509 .
McKenzie , K. ( 2013 ), “ A comparison of the effectiveness of a game informed online learning activity and face to face teaching in increasing knowledge about managing aggression in health settings ”, Advances in Health Sciences Education , Vol. 18 No. 5 , pp. 917 - 927 , doi: 10.1007/s10459-012-9430-8 .
McLaughlin , J.E. , Roth , M.T. , Glatt , D.M. , Gharkholonarehe , N. , Davidson , C.A. , Griffin , L.M. , Esserman , D.A. and Mumper , R.J. ( 2013 ), “ The flipped classroom: a course redesign to foster learning and engagement in a health professions school ”, Academic Medicine , Vol. 89 No. 2 , pp. 236 - 243 , doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000000086 .
Means , B. , Toyama , Y. , Murphy , R. , Bakia , M. and Jones , K. ( 2009 ), “ Evaluation of evidence-based practices in online learning: a meta-analysis and review of online learning studies”, US department of education ”, available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED505824.pdf ( accessed 1 June 2020 ).
Mullen , C. ( 2019 ), “ Does modality matter? A comparison of aspiring leaders’ learning online and face-to-face ”, Journal of Further and Higher Education , Vol. 44 No. 5 , pp. 670 - 688 , doi: 10.1080/0309877x.2019.1576859 .
Namlu , A.G. ( 2005 ), “ BSartilgisayarözyeterliliğialgisiilebilişselöğrenmestratejileriarasindakiilişki ”, EğitimAraştirmalariDergisi , p. 19 .
Nguyen , T. ( 2015 ), “ The effectiveness of online learning: beyond no significant difference and future horizons ”, MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching , Vol. 11 No. 2 , pp. 309 - 319 , available at: https://jolt.merlot.org/Vol11no2/Nguyen_0615.pdf
Pham , M.T. , Rajić , A. , Greig , J.D. , Sargeant , J.M. , Papadopoulos , A. and McEwen , S.A. ( 2014 ), “ A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency ”, Research Synthesis Methods , Vol. 5 No. 4 , pp. 371 - 385 , doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1123. .
Pilbeam , R. and Barrus , A. ( 2010 ), “ Transitioning from face-to-face to online learning: a case study ”, in Simonson , M. (Ed.), On the Practice of Educational Communications and Technology Presented at the Annual Convention of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology , Nova Southeastern University , Anaheim, CA , available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED514647.pdf ( accessed 15 June 2020 ).
Previtali , P. and Scarozza , D. ( 2019 ), “ Blended learning adoption: a case study of one of the oldest universities in Europe ”, International Journal of Educational Management , Vol. 33 No. 5 , pp. 990 - 998 , doi: 10.1108/IJEM-07-2018-0197 .
Ragusa , A.T. and Crampton , A. ( 2018 ), “ Sense of connection, identity and academic success in distance education: sociologically exploring online learning environments ”, Rural Society , Vol. 27 No. 2 , pp. 125 - 142 , doi: 10.1080/10371656.2018.1472914 .
Raynauld , J. ( 2006 ), “ A comparison of online and face-to-face learning in undergraduate finance and economic policy courses ”, Preliminary , HEC Montréal , QC .
Rideout , V.J. , Foehr , U.G. and Roberts , D.F. ( 2010 ), Generation M2: Media in the Lives of 8-18 Year-Olds , The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation , Menlo Park, CA , available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED527859.pdf
Rosell-Aguilar , F. ( 2006 ), “ The face-to-face and the online learner: a comparative study of tutorial support for open and distance language learning and the learner experience with audio-graphic SCMC ”, Reading Matrix: An International Online Journal , Vol. 6 No. 3 , pp. 248 - 268 .
Rubin , B. , Fernandes , R. and Avgerinou , M.D. ( 2013 ), “ The effects of technology on the community of inquiry and satisfaction with online courses ”, The Internet and Higher Education , Vol. 17 , pp. 48 - 57 , doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2012.09.006 .
San Jose , D.L. and Kelleher , T. ( 2009 ), “ Measuring ecoshock and affective learning: a comparison of student responses to online and face-to-face learning ecologies ”, MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching , Vol. 5 No. 3 , pp. 469 - 476 .
Shachar , M. and Neumann , Y. ( 2003 ), “ Differences between traditional and distance education academic performances: a meta-analytic approach ”, The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , Vol. 4 No. 2 , doi: 10.19173/irrodl.v4i2.153 .
Schatzker , E. ( 2020 ), “ Morgan stanley CEO sees a future for the bank with ‘much less real estate ”, Bloomberg, 17 April , available at: www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-04-16/gorman-sees-morgan-stanley-future-with-much-less-real-estate ( accessed 30 June 2020 ).
Shea , P. and Bidjerano , T. ( 2012 ), “ Learning presence as a moderator in the community of inquiry model ”, Computers and Education , Vol. 59 No. 2 , pp. 316 - 326 , doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.01.011 .
Snilstveit , B. , Oliver , S. and Vojtkova , M. ( 2012 ), “ Narrative approaches to systematic review and synthesis of evidence for international development policy and practice ”, Journal of Development Effectiveness , Vol. 4 No. 3 , pp. 409 - 429 , doi: 10.1080/19439342.2012.710641 .
Stone , C. ( 2017 ), “ Opportunity through online learning: improving student access, participation and success in higher education ”, National Centre for Student Equity in Higher Education , Perth, WA , available at: www.ncsehe.edu.au/publications/opportunity-online-learning-improving-student-access-participation-success-higher-education/ ( accessed 28 June 2020 ).
Sussman , S. and Dutter , L. ( 2010 ), “ Comparing student learning outcomes in face-to-face and online course delivery ”, Online Journal of Distance Learning Administration , Vol. 8 No. 4 .
Taylor , C.A. ( 2013 ), “ Objects, bodies and space: gender and embodied practices of mattering in the classroom ”, Gender and Education , Vol. 25 No. 6 , pp. 688 - 703 , doi: 10.1080/09540253.2013.834864 .
Thomas , G. and Thorpe , S. ( 2019 ), “ Enhancing the facilitation of onlinegroups in higher education: a review of the literature on face-to-face and online group-facilitation ”, Interactive Learning Environments , Vol. 27 No. 1 , pp. 62 - 71 , doi: 10.1080/10494820.2018.1451897 .
Voutilainen , A. , Saaranen , T. and Sormunen , M. ( 2017 ), “ Conventional vs. e-learning in nursing education: a systematic review and meta-analysis ”, Nurse Education Today , Vol. 50 , pp. 97 - 103 , doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.12.020 .
Williams , E.A. and Castro , S.L. ( 2010 ), “ The effects of teamwork on individual learning and perceptions of team performance: a comparison of face‐to‐face and online project settings ”, Team Performance Management: An International Journal , Vol. 16 Nos 3/4 , pp. 124 - 147 , doi: 10.1108/13527591011053232 .
Williamson , B. ( 2019 ), “ Policy networks, performance metrics and platform markets: charting the expanding data infrastructure of higher education ”, British Journal of Educational Technology , Vol. 50 No. 6 , pp. 2794 - 2809 , doi: 10.1111/bjet.12849. .
Woolsey , S. ( 2013 ), Learning and Experiential Outcomes of Face-to-Face versus Online Communications Courses , Brock University (distributor) , St. Catharines, ON , available at: https://dr.library.brocku.ca/bitstream/handle/10464/4302/Brock_Woolsey_Shantal_2013.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y ( accessed 1 July 2020 ).
Wu , D. and Hiltz , S.R. ( 2004 ), “ Predicting learning from asynchronous online discussions ”, Online Learning , Vol. 8 No. 2 , pp. 139 - 152 , doi: 10.24059/olj.v8i2.1832 .
Yen , S.C. , Lo , Y. , Lee , A. and Enriquez , J. ( 2018 ), “ Learning online, offline, and in-between: comparing student academic outcomes and course satisfaction in face-to-face, online, and blended teaching modalities ”, Education and Information Technologies , Vol. 23 No. 5 , pp. 2141 - 2153 , doi: 10.1007/s10639-018-9707-5 .
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the School of Social Sciences, Humanitarian and Development Research Initiative (HADRI) and the Young and Resilient Research Centre at Western Sydney University, Australia.
Corresponding author
About the authors.
Garry John Stevens is a Senior Lecturer in the Humanitarian and Development Studies Programme at Western Sydney University. As part of the Humanitarian and Development Research Initiative (HADRI), he is involved in projects examining population preparedness for disasters and critical incidents, including occupational risk and resilience factors amongst emergency service workers, Disaster Medical Assistance Teams and humanitarian aid workers and trainees. His recent work with Aid practitioners focusses on worker self-care and well-being in the context of work-related stress. He is also involved in population mental health and epidemiology, including technology-assisted mental health-care in hospital and community settings.
Tobias Bienz holds a master’s degree in International Affairs from the University of St. Gallen. In the process of completing his degree, he consulted for the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation. He also taught a class on “Innovative Projects for a Sustainable Future”. Furthermore, he was selected as a Leader of Tomorrow at the 2018 St. Gallen Symposium, having successfully submitted an essay on the future of work, which was later presented in the adapted form at the Asia Pacific Humanitarian Leadership Conference in Melbourne. Tobias is also a social impact entrepreneur engaged in starting, growing and scaling social impact start-ups.
Nidhi Wali is a Senior Research Officer at the HADRI at Western Sydney University. She holds a master’s degree in Development Studies from the University of Sussex, UK and is pursuing her Doctor of Philosophy research at Western Sydney University focussing on “Child undernutrition in South Asia”. In India, she has worked with the national government, as well as with international organisations such as CARE, Public Health Resource Network and UNICEF on maternal and child health and nutrition programmes. Her present research focusses on international development, public health and migrant issues of settlement and access to services and has published across these issues.
Jenna Condie is a Senior Lecturer in Digital Society in the Social of Social Sciences and a School-based Research Fellow with the Young and Resilient Research Centre at Western Sydney University. Her interdisciplinary research traverses critical psychology, geography and technology studies. Jenna’s research is concerned with what people and places are becoming with digital technologies. Current projects focus on women’s safety, digital geographies of fear and equitable mobilities. She co-leads Travel in the Digital Age (TinDA) and Social Technologies (SoTech) research teams.
Spyros Schismenos is currently a PhD Fellow and Member of HADRI at the School of Social Sciences, Western Sydney University, Australia. Since 2016, he has been working closely with the UNESCO Chair on Conservation and Ecotourism of Riparian and Deltaic Ecosystems as the Focal Point for the Wider Region of Asia-Pacific. He is a Member of the Youth International Soil Governance Commission (YISGC) of the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) of the United Nations. His research disciplines focus on Humanitarian Engineering, Disaster Management, Renewable Energy, Distance Learning, Disaster Education and Community Development.
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Teaching and Learning in the New Normal: Responding to Students’ and Academics’ Multifaceted Needs
- Conference paper
- First Online: 09 July 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Andriani Piki ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0376-1713 9 &
- Magdalena Brzezinska ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4213-8636 10
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNCS,volume 14026))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction
594 Accesses
1 Citations
Alongside the prolonged social and economic instability and the escalating demands for upskilling, Covid-19 pandemic had a detrimental impact on students’ and academics’ mental health and wellbeing. Social isolation and the emergency transition to remote education caused high levels of psychological distress, hindering students’ self-efficacy and academic performance. The pandemic also induced sudden changes affecting academics’ personal and professional lives, leading to mental disorders and risk of burnout. While recent research focuses on addressing the effects of the pandemic on either students or academics, this paper presents a collective analysis. The key themes that emerged by examining the experiences of both students and academics in higher education are framed in a multi-layered support system embracing qualities such as: self-efficacy, wellbeing, equality, diversity, and inclusion, social interactions, human-centred technologies, and authentic pedagogical methods. The findings are discussed with the aim to extract informed recommendations for enhancing teaching and learning experiences in the post-pandemic era.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abu Elnasr, E.S., Hasanein, A.M., Abu Elnasr, A.E.: Responses to COVID-19 in higher education: Social media usage for sustaining formal academic communication in developing countries. Sustainability 12 (16), 6520 (2020)
Google Scholar
Al Miskry, A.S.A., Hamid, A.A.M., Darweesh, A.H.M.: The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on University Faculty, Staff, and Students and Coping Strategies Used During the Lockdown in the United Arab Emirates. Frontiers in Psychology 12 (2021)
Al-Taweel, D., et al.: Multidisciplinary academic perspectives during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Int. J. Health Planning Manag. 35 (6), 1295–1301 (2020)
Aucejo, E.M., French, J., Araya, M.P.U., Zafar, B.: The impact of Covid-19 on student experiences and expectations: Evidence from a survey. Journal of public economics, 191 (2020)
Bates, A.W.: Teaching in a Digital Age, 2nd edn. Tony Bates Associates Ltd., Vancouver, B.C. (2019)
Berger, T.: How to Maslow Before Bloom, All Day Long. Edutopia (2020). https://www.edutopia.org/article/how-maslow-bloom-all-day-long/
Bożykowski, M., Izdebski, A., Jasiński, M., Konieczna-Sałamatin, J.: Nauczanie w dobie pandemii i perspektywa powrotu do normalności, Pracownia Ewaluacji Jakości Kształcenia Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego (University of Warsaw) (2021)
Brzezinska, M., Cromarty, E.: Emergency Remote Teaching in the University Context: Responding to Social and Emotional Needs During a Sudden Transition Online. In: Meiselwitz, G. (eds) Social Computing and Social Media: Applications in Education and Commerce. HCII 2022. LNCS, vol. 13316. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05064-0_3
Brzezinska, M.: Global skills in the global pandemic: how to create an effective bichronous learning experience during an emergency shift to remote instruction. In: Auer, M.E., Pester, A., May, D. (eds.) Learning with Technologies and Technologies in Learning. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 456. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04286-7_32
Cassibba, R., Ferrarello, D., Mammana, M.F., Musso, P., Pennisi, M., Taranto, E.: Teaching mathematics at distance: a challenge for universities. Educ. Sci. 11 (1), 1 (2020)
Czaja, K., et al.: Zdalne kształcenie na Wydziale Humanistycznym Uniwersytetu Śląskiego w Katowicach. Report (March-April 2020). (A Report. Remote Education at the Department of Humanities of the University of Silesia in Katowice), Uniwersytet Śląski w Katowicach 2020, https://us.edu.pl/wydzial/wh/wp-content/uploads/sites/15/Nieprzypisane/ZDALNE-KSZTAŁCENIE-NA-WYDZIALE-HUMANISTYCZNYM-RAPORT.pdf
Darby, F., Lang, J.M.: Small Teaching Online: Applying Learning Science in Online Classes (1st ed.). Jossey-Bass (2019)
Dewey, J.: How we think: A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process. DC Heath (1933)
Dinu, L.M., et al.: A case study investigating mental wellbeing of university academics during the COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Sci. 11 (11), 702 (2021)
Article Google Scholar
Engelbrecht, J., Borba, M. C., Llinares, S., Kaiser, G.: Will 2020 be remembered as the year in which education was changed? ZDM – Math. Educ. 52 (5), 821–824 (2020)
Flaherty, C.: Faculty pandemic stress is now chronic. Inside Higher Ed, 19 (2020)
France, P.E.: Reclaiming Personalized Learning: A Pedagogy for Restoring Equity and Humanity in Our Classrooms (First). Corwin (2020)
France, P.E.: Humanizing Distance Learning: Centering Equity and Humanity in Times of Crisis (First). Corwin (2021)
Gewin, V.: Pandemic Burnout Is Rampant in Academia. Nature Publishing Group (2021). https://media.nature.com/original/magazine-assets/d41586-021-00663-2/d41586-021-00663-2.pdf
Gierdowski, D.C.: ECAR Study of Undergraduate Students and Information Technology (Research report). Louisville, CO: EDUCAUSE Center for Applied Research, October 2019 (2019). http://www.educause.edu/ecar
Halabieh, H., et al.: The future of higher education: identifying current educational problems and proposed solutions. Educ. Sci. 12 (12), 888 (2022)
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T., Bond, A.: The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. EDUCAUSE Rev. 2020 , 3 (2020)
Hughes, G.J., Byrom, N.C.: Managing student mental health: the challenges faced by academics on professional healthcare courses. J. Adv. Nurs. 75 (7), 1539–1548 (2019)
Joosten, T., Weber, N., Baker, M., Schletzbaum, A.: Planning for a Blended Future: A Research-Driven Guide for Educators (2021). Available online: https://eduq.info/xmlui/handle/11515/38291
Kara, M.: Revisiting online learner engagement: exploring the role of learner characteristics in an emergency period. J. Res. Technol. Educ., 1–17 (2021)
Killen, C., Langer-Crame, M., Penrice, S.: Teaching Staff Digital Experience Insights Survey 2020: UK Higher Education Findings (2021). https://www.jisc.ac.uk/reports/teaching-staff-digital-experience-insights-survey-2020-uk-higher-education
Kita, Y., Yasuda, S., Gherghel, C.: Online education and the mental health of faculty during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 1–9 (2022)
Kukulska-Hulme, A., et al.: Innovating Pedagogy 2022: Open University Innovation Report 10. Milton Keynes: The Open University (2022)
Kumar, S., Martin, F., Budhrani, K., Ritzhaupt, A.: Award-winning faculty online teaching practices: Elements of award-winning courses. Online Learning 23(4) (2019)
Leone, V., Brzezinska, M.: Transatlantic Educators Dialogue (TED) Program for Global Citizenship. Idee in Form@Zione, 99–115 (2021)
Leong, K., Sung, A., Au, D., Blanchard, C.: A review of the trend of microlearning. J. Work-Appl. Manage. 13 (1), 88–102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/JWAM-10-2020-004
Ma, X., Liu, J., Liang, J., Fan, C.: An empirical study on the effect of group awareness in CSCL environments. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1758730
Marinoni, G., van’t Land, H.: The Impact of COVID-19 on Global Higher Education. International Higher Education. Special Issue 102, pp. 7–9 (2020)
McGaughey, F., et al.: This can’t be the new norm’: academics’ perspectives on the COVID-19 crisis for the Australian university sector. Higher education research & development, 1–16 (2021)
McKee, C., Ntokos, K.: Online microlearning and student engagement in computer games higher education. Res. Learn. Technol. 30 (2022). https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v30.2680
McKenzie, L.: Bridging the Digital Divide: Lessons From Covid-19. Inside Higher Ed (2021). https://www.insidehighered.com/content/bridging-digital-divide-lessons-covid-19
Meletiou-Mavrotheris, M., Eteokleous, N., Stylianou-Georgiou, A.: Emergency remote learning in higher education in Cyprus during COVID-19 lockdown: a zoom-out view of challenges and opportunities for quality online learning. Educ. Sci. 12 (7), 477 (2022)
Muñoz-Carril, P.C., Hernández-Sellés, N., Fuentes-Abeledo, E.J., González-Sanmamed, M.: Factors influencing students’ perceived impact of learning and satisfaction in Computer Supported Collaborative Learning. Comput. Educ. 174 , 104310 (2021)
Peters, D., Calvo, R.A., Ryan, R.M.: Designing for motivation, engagement and wellbeing in digital experience. Front. Psychol. 9 , 797 (2018)
Piki, A.: An exploration of student experiences with social media and mobile technologies during emergency transition to remote education. In: The Proceedings of the 19th World Conference on Mobile, Blended and Seamless Learning (mLearn 2020), November 2–4, 2020, Cairo, Egypt (2020)
Piki, A.: Re-imagining the distributed nature of learner engagement in computer-supported collaborative learning contexts in the post-pandemic era. In: Meiselwitz, G. (eds.) Social Computing and Social Media: Applications in Education and Commerce. HCII 2022 (June 26-July 1, 2022). LNCS, vol. 13316. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05064-0_13
Piki, A., Andreou, L., Markou, M.: Students’ perspectives on the emergency transition to online education – a case study in mathematics education. In: 16th Annual International Technology, Education and Development Conference (INTED2022), March 7–2, 2022 (2022)
Raygoza, M., Leon, R. Norris, A.: Humanizing Online Teaching (2020). https://digitalcommons.stmarys-ca.edu/school-education-faculty-works/1805
Rifkin, J.: The Empathetic Civilization: The Race to Global Consciousness in a World of Crisis. Penguin, New York, NY (2009)
Shaw, A.: Authentic Assessment in the Online Classroom. Center for Teaching and Learning. Wiley Education Services (2020)
Stefan, I.A., Gheorghe, A.F., Stefan, A., Piki, A., Tsalapata, H., Heidmann, O.: Constructing seamless learning through game-based learning experiences. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. (IJMBL) 14 (4), 1–12 (2022)
UUK (Universities UK) (2021). Stepchange Mentally Healthy Universities. https://www.universitiesuk.ac.uk/what-we-do/policyand-research/publications/stepchange-mentally-healthy-universities
Urbina-Garcia, A.: What do we know about university academics’ mental health? a systematic literature review. Stress. Health 36 (5), 563–585 (2020)
Veluvali, P., Surisetti, J.: Learning management system for greater learner engagement in higher education—a review. High. Educ. Future 9 (1), 107–121 (2022)
Vijayan, R.: Teaching and learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: a topic modeling study. Educ. Sci. 11 , 347 (2021)
Vlachopoulos, D.: COVID-19: threat or opportunity for online education? High. Learn. Res. Commun. 10 (1), 16–19 (2020)
Wang, Y., Cao, Y., Gong, S., Wang, Z., Li, N., Ai, L.: Interaction and learning engagement in online learning: the mediating roles of online learning self-efficacy and academic emotions. Learn. Individ. Differ. 94 , 102128 (2022)
Watchorn, D., Heckendorf, E., Smith, C.: Locked down, burned out: Publishing in a pandemic: The impact of Covid on academic authors. De Gruyter, Germany (2020)
Watermeyer, R., Crick, T., Knight, C., Goodall, J.: COVID-19 and digital disruption in UK universities: afflictions and affordances of emergency online migration. High. Educ. 81 (3), 623–641 (2021)
Whitman, G., Kelleher, I.: Your Checklist for Virtual Project-Based Learning. Edutopia (2020). https://www.edutopia.org/article/your-checklist-virtual-project-based-learning
WHO/UNESCO (2021). Making every school a health-promoting school: implementation guidance. Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (2021). https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240025073
Wray, S., Kinman, G.: Supporting Staff Wellbeing in Higher Education (ISBN 978-1-7399860-1-8). Education Support, London (2021)
Yiapanas, G., Constantinou, M., Marcoulli, E.: The readiness of higher education academic staff in cyprus for shifting the instructional delivery mode from face-to-face to emergency remote teaching. In: Handbook of Research on Digital Innovation and Networking in Post-COVID-19 Organizations, pp. 301–323. IGI Global (2022)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Central Lancashire – Cyprus, Larnaca, Cyprus
Andriani Piki
WSB University, Poznan, Poland
Magdalena Brzezinska
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Magdalena Brzezinska .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania
Adela Coman
University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
Simona Vasilache
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Piki, A., Brzezinska, M. (2023). Teaching and Learning in the New Normal: Responding to Students’ and Academics’ Multifaceted Needs. In: Coman, A., Vasilache, S. (eds) Social Computing and Social Media. HCII 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14026. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35927-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35927-9_9
Published : 09 July 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-35926-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-35927-9
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 21 December 2020
Transitioning to the “new normal” of learning in unpredictable times: pedagogical practices and learning performance in fully online flipped classrooms
- Khe Foon Hew ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4149-533X 1 ,
- Chengyuan Jia 1 ,
- Donn Emmanuel Gonda 1 &
- Shurui Bai 1
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 17 , Article number: 57 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
467k Accesses
85 Citations
12 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 outbreak has compelled many universities to immediately switch to the online delivery of lessons. Many instructors, however, have found developing effective online lessons in a very short period of time very stressful and difficult. This study describes how we successfully addressed this crisis by transforming two conventional flipped classes into fully online flipped classes with the help of a cloud-based video conferencing app. As in a conventional flipped course, in a fully online flipped course students are encouraged to complete online pre-class work. But unlike in the conventional flipped approach, students do not subsequently meet face-to-face in physical classrooms, but rather online. This study examines the effect of fully online flipped classrooms on student learning performance in two stages. In Stage One, we explain how we drew on the 5E framework to design two conventional flipped classes. The 5E framework consists of five phases—Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. In Stage Two, we describe how we transformed the two conventional flipped classes into fully online flipped classes. Quantitative analyses of students’ final course marks reveal that the participants in the fully online flipped classes performed as effectively as participants in the conventional flipped learning classes. Our qualitative analyses of student and staff reflection data identify seven good practices for videoconferencing - assisted online flipped classrooms.
Introduction
“It’s now painfully clear that schools ought to have had more robust disaster-preparedness plans in place in the event of interruptions in their campus operations. But because many schools did not have such plans in place…online learning is about to get a bad reputation at many campuses, I suspect.” Michael Horn, cited in Lederman ( 2020 ), ‘Inside Higher Ed’.
In early January 2020, scientists identified a new infectious disease caused by a novel coronavirus. Since then, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused widespread disruptions to schools and universities. According to UNESCO, as of April 10, 2020, more than 188 countries had implemented nationwide school and university closures, impacting over 91% of the world’s student population (UNESCO n.d.).
During these school closures, all face-to-face lessons were cancelled, compelling many institutions, including our own university, to immediately transition from face-to-face in-person learning to completely online lessons. The abrupt switch to fully online learning has been particularly stressful for many instructors and students who prefer in-person instruction. Online learning is often stigmatized as a weaker option that provides a lower quality education than in-person face-to-face learning (Hodges et al. 2020 ). Indeed, such negative attitudes to fully online learning were revealed by a large EDUCAUSE survey (Pomerantz and Brooks 2017 ). The survey of 11,141 faculty members from 131 U.S. institutions found that only 9% of faculty prefer to teach a fully online course. In other words, a whopping 91% of faculty do not wish to teach in a completely online environment. Students’ opinions of fully online courses are not much better; a recent student survey by EDUCAUSE of more than 40,000 students across 118 American universities revealed that as many as 70% of the respondents mostly or completely prefer face-to-face learning environments (Gierdowski 2019 ).
Clearly, many faculty members and students do not see the value of fully online learning, despite the fact that online learning has been around for many decades. During the current health crisis, many instructors have had to improvise quick online learning solutions (Hodges et al. 2020 ). For example, in our own university, there are anecdotal reports of a myriad of emergency online methods. Some instructors, for example, merely uploaded their PowerPoint slides or papers onto a learning management system such as Moodle and asked students to read them on their own. Any questions were asked asynchronously on the Moodle forum. Other instructors recorded their own lectures (usually at least one hour long) and asked students to asynchronously watch the video lectures and then ask individual questions later. Still others talked for more than two hours via synchronous video platforms watched by students in their own homes. Although these online methods may be an efficient method of delivering content, they are not particularly effective in promoting active learning and interest (Bates and Galloway 2012 ). As one student remarked, “Sitting in front of my computer to watch a 2-h live lecture without any active learning activities such as group work is pretty boring!” Indeed, without any active learning activities such as peer interaction, a fully online course will feel more like an interactive book than a classroom (Sutterlin 2018 ).
Well-planned active online learning lessons are markedly different from the emergency online teaching offered in response to a crisis (Hodges et al. 2020 ). One promising strategy for promoting online active learning is the fully online flipped classroom pedagogical approach, hereafter referred to as the online flipped classroom approach. An online flipped classroom is a variant of the conventional flipped model. A conventional flipped classroom model consists of online learning of basic concepts before class, followed by face-to-face learning activities (Bishop and Verleger 2013 ). The conventional flipped model has become very popular in recent years due to its association with active learning, which emphasizes students’ active learning (Xiu and Thompson 2020 ). Active learning activities such as peer discussions can help students construct better understandings of the subject material (Deslauriers et al. 2019 ). Recent meta-analyses have provided consistent overall support for the superiority of the conventional flipped classroom approach over traditional learning for enhancing student learning (e.g., Låg and Sæle 2019 ; Lo and Hew 2019 ; Shi et al. 2019 ; van Alten et al. 2019 ).
The online flipped classroom is similar to the conventional flipped classroom model in that students are encouraged to prepare for class by completing some pre-class activities (e.g., watching video lectures, completing quizzes). However, unlike the conventional flipped classroom approach, students in online flipped classrooms do not meet face-to-face, but online (Stohr et al. 2020 ). Although the online flipped classroom appears to be gathering momentum in higher education, very few studies have examined its effectiveness (for an exception, see Stohr et al. 2020 , who compared the online flipped classroom format with a conventional non-flipped teaching format). So far, we are not cognizant of any research that evaluated the efficacy of the fully online flipped classroom relative to the conventional flipped classroom. Establishing the effectiveness of online flipped classrooms is important, as practitioners need to know whether this active learning approach can be used during prolonged school closures.
Against this backdrop, this study compares the effects of online flipped classrooms versus conventional flipped classrooms on student learning outcomes. To this end, two conventional flipped classes in the Faculty of Education are transformed into online flipped classrooms. Students in both the online and flipped classes participated in the online pre-class activity asynchronously using a learning management system. However, students in the online flipped classes joined the online in-class learning synchronously using a video conferencing app whereas their counterparts in the conventional flipped classes attended face-to-face classes. The online flipped courses were designed using the 5E conceptual framework and used a cloud-based video conferencing app. We used the Zoom application after careful consideration of many different videoconferencing platforms. Our reasons for doing so are given in the Section of “Stage Two: Transforming conventional flipped classes into online flipped classes”.
The 5E framework consists of five phases—Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate (Bybee et al. 2006 ).
Engage—The first phase aims to engage students in the learning process. Methods to engage students usually include using a real-world scenario, or problem, asking students questions that allow them to brainstorm or think critically, and helping them to create connections to their past experiences.
Explore—In the exploration phase, the teacher, who works as a facilitator or coach, gives the students time and opportunity to explore the content and construct their own understanding of the topic at hand.
Explain—This phase starts with students attempting to explain specific aspects of the engagement and exploration experiences. Based on these explanations, the teacher introduces terminology in a direct and explicit manner to facilitate concept building.
Elaborate—In this phase, the teacher provided more detailed information about the subject content through the use of mini lectures and/or whole class discussions. Students are also given the opportunity to apply what they have learned and receive feedback from the teacher and their peers.
Evaluate—Formative assessments (e.g., quizzes) can be used to evaluate students’ mastery of the subject material at the beginning and throughout the 5E phases, and teachers can complete a summative assessment after the elaboration phase (e.g., final exams).
We adopted the 5E framework for the following reasons. First, the 5E framework, which is based on various educational theories and models (e.g., Herbart’s instructional model, Dewey’s instructional model, Atkin-Karplus Learning Cycle) (Bybee et al. 2006 ), provides a sound instructional sequence for designing a course and planning activities. The 5E framework can help instructors organize and integrate both the in-class and out-of-class learning activities (Lo 2017 ).
Second, previous research has shown the positive effect of the 5E framework on student achievement. These positive effects were initially established in science education (e.g., Akar 2005 ; Boddy et al. 2003 ). Recently, the 5E model has yielded positive results when applied to various subject areas and when used to design inquiry- and interaction-based learning activities. Mullins ( 2017 ), for example, found that undergraduate students in a 5E-supported class outperformed their peers in a traditional lecture setting. Hew et al. ( 2018 ) designed two postgraduate courses based on the 5E model in order to foster students’ active learning. Ninety-two percent of the participants agreed that the 5E supported courses were more engaging than traditional classroom instruction.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. First, we describe our study design and methodology. This is followed by a description of our two stages of research. In Stage One, we explain how we use the 5E framework to design our two conventional flipped classes; In Stage Two, we describe how we transformed the two conventional flipped classes into fully online flipped classes, using a cloud-based video conferencing app. We describe the various pedagogical practices that Zoom videoconferencing can facilitate before and during online flipped classes. In this paper, we use the term “pedagogical practices” to refer to specific activities that are used to structure teaching and learning. This study is guided by the following two questions.
What effect does the change from a conventional flipped classroom format to an online flipped format have on student learning performance?
What are the good practices for videoconferencing - assisted online flipped classrooms, as perceived by students and/or teaching staff?
This study was conducted in a large public Asian university. Four classes were involved: (a) conventional flipped Course 1, (b) conventional flipped Course 2, (c) online flipped Course 1, and (d) online flipped Course 2. Conventional flipped Courses 1 and 2 were the control group. Online flipped Courses 1 and 2 were the experimental group. To avoid any potential instructor confounding bias, the same professor and teaching assistants (TAs) taught the conventional and online flipped formats of each class. Ethical approval to conduct the study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board at the University of Hong Kong and consent forms from all participants in the study were collected.
Data collection and analysis
To reiterate, this study had two purposes: (a) to determine the effect of an online flipped classroom on student learning performance as determined by student final course marks, and (b) to determine good practices for videoconferencing - assisted online flipped classrooms, as perceived by the participants (students and teaching staff). We adopted a mixed methods involving quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a deeper understanding of the research problem (Ivankova et al. 2006 ).
The data collection spanned across two semesters, which corresponded to the aforementioned two stages of the research. The conventional flipped classes were implemented in conventional flipped Courses 1 and 2 during the semester of 2019 Fall before the pandemic (Stage One). Due to the outbreak of Covid-19, all courses were required to be delivered online in our university in the 2020 Spring semester. Therefore, the online flipped classes were conducted in online flipped Courses 1 and 2 during the pandemic in 2020 Spring (Stage Two). Students’ knowledge and skills of the course content were checked at the beginning of the each course. Students final course marks in each course were collected and used as measure of the student learning outcomes at the end of the semester (See Fig. 1 for the research timeline).
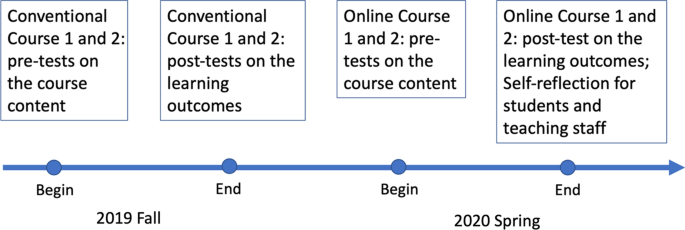
Timeline of data collection: 2019 Fall (before the pandemic), 2020 Spring (during the pandemic)
To address the first purpose, we compared the students’ final course marks in the online flipped classrooms and conventional flipped classrooms. Quantitative data from 99 students were collected (see Table 1 ). We used the students’ final course marks to measure performance.
To identify the perceived good practices for videoconferencing - assisted online flipped classrooms, we invited students and the teaching staff to complete a self-reflection exercise based on the following question: “What do you perceive as good practices in a videoconferencing-supported online flipped classroom?” The qualitative data collected from students and instructors were analyzed as follows. The first step was an initial reading of all of the response data to obtain an overall impression. The first author then applied the grounded approach (Strauss and Corbin 1990 ) to the qualitative data to generate relevant codes. Similar codes were organized into themes. In order to increase the consistency of coding, several exemplary quotes that clearly illustrated each constructed theme were identified. We also allowed new themes (if any) to emerge inductively during the coding process. The second author coded the data. There was perfect agreement with the coding. Table 2 summarizes how the data for each research question were collected and analyzed.
Stage one: designing conventional flipped classes using the 5E framework
In this section, we first describe how we use the 5E framework to design our two conventional flipped classes (Course 1: E-Learning Strategies , and Course 2: Engaging Adult Learners ). In the next section, we describe how we transform these two conventional flipped classes into fully online flipped classes. Figure 2 shows the 5E framework that guided our design of the conventional flipped classes. Table 3 shows some of the teaching and learning activities used in each of the 5E phases.
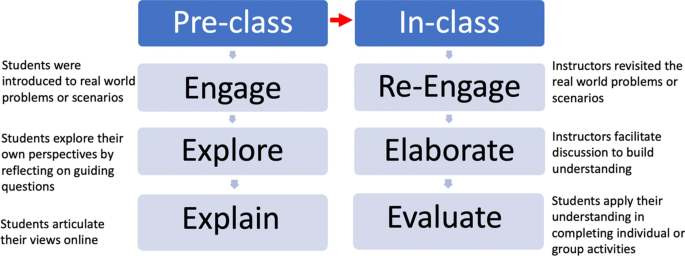
5E framework used to design the two conventional flipped classes
Conventional flipped course 1: E-learning strategies
This course discussed the various e-learning strategies that can be employed to foster six types of learning, including problem-solving, attitude learning, factual learning, concept learning, procedural learning, and principle learning. There were eight sessions in the course. The first seven sessions were flipped—each consisting of an online pre-class learning component and a 3-h face-to-face in-class component. The last session was devoted to students’ presentations. Figure 3 shows an example of how the 5E framework was used in Course 1.
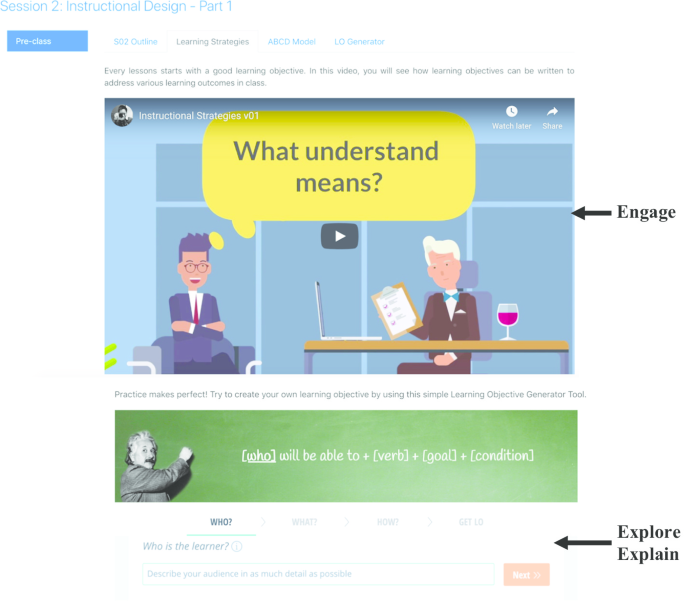
Example of a pre-class activity in Course 1
For instance, in the pre-class phase of Session 2: Instructional Design—Part 1 , we posted a video that posed the question “What do we mean by ‘understand’”. This video engaged students’ curiosity about the importance of writing clear and measurable learning objectives. The instructor in the video highlighted the pitfalls of using vague words such as “know” and “understand” when writing learning objectives. Students then explored and explained their own individual learning objectives using the ABCD model (audience, behavior, condition, degree). Students were able to use a mobile instant messaging (MIM) app such as WeChat to ask questions of their peers or instructor. When a message arrived, a notification appeared on the receiver’s phone screen, encouraging timely feedback and frequent interaction (Rosenfeld et al. 2018 ).
During the face-to-face in-class session, the instructor re-engaged students’ attention by discussing basic instructional design issues such as “How do we write good lesson objectives?” The instructor conducted short debriefing sessions to discuss the strengths and weaknesses of students’ pre-class work. The instructor also facilitated class or small group discussions to build students’ understanding of how to write measurable lesson objectives that help students to achieve specific learning outcomes (e.g., factual learning). These discussions allowed students to elaborate on good lesson objectives practices. To evaluate the students’ understanding, the instructor asked them to work in groups of four on an instructional design scenario (e.g., teaching participants how to deal with angry customers), and then write a learning objective for the lesson in an online forum; their peers then commented on the posted learning objectives (Fig. 4 ).
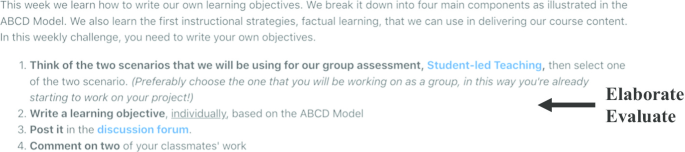
Example of an in-class activity in Course 1
Conventional flipped course 2: engaging adult learners
This course discussed the key principles of adult learning, as well as strategies used in adult education (e.g., transformational learning theory). There were eight sessions in the course, each session lasted three hours. An example of how the 5E instructional model was used is shown in Fig. 5 .
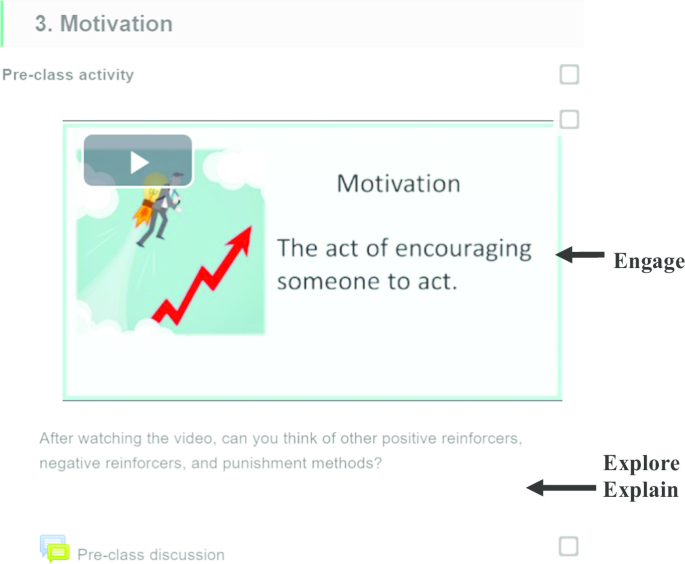
Example of a pre-class activity in Course 2
For example, in the pre-class session for Session 3: Motivation, we uploaded a four-minute video that briefly described the concepts of reinforcement and punishment. The aim of the video was to engage students’ attention on the focal topic. To help students explore the topic in further, they were asked to respond to the following question: “After watching the video, can you think of other positive reinforcers, negative reinforcers, and punishment methods?” Students posted their opinions ( explained ) on a discussion forum. Students also used the WeChat app to ask questions of their peers or instructor.
During the subsequent face-to-face lesson (Fig. 6 ), the instructor facilitated whole class discussions using relevant questions to elaborate on the topics covered in the pre-class video. An example of a question used was ‘When should we employ positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, or punishment?’ Based on the students’ responses, the instructor was able to provide more in-depth explanation of the subject matter, or correct any student misunderstanding. This will help enhance students’ comprehension of the subject content. The instructor also discussed the notion of intrinsic motivation (e.g., the self-determination theory). In addition to elaborating on the content, the instructor also evaluated the students’ understanding by asking students to complete small group discussion activities. An example of a small group discussion activity was ‘Did you have any experience where you did not like learning a subject or doing an activity? How would you motivate yourself in that situation? Please try to use a mixture of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation factors.’ Upon completion of the small group activity, students from each group presented their views to the whole class. The instructor, as well as the rest of the classmates provided feedback.

Example of an in-class activity in Course 2
Stage two: transforming conventional flipped classes into online flipped classes
The outbreak of COVID-19 inspired us to transform the two conventional flipped classes discussed above into fully online flipped classes. After careful consideration, the Zoom videoconferencing app was used for the synchronized online meetings (see Table 4 ). The whole transformation process took about one week with the bulk of the time was spent on exploring and testing the features of Zoom.
Zoom is a Web videoconferencing service that allows users to communicate online with individuals in real time via computer, tablet, or mobile device. We chose Zoom because of its ease of use (Kim 2017 ; Sutterlin 2018 ), its lower bandwidth requirements (Sutterlin 2018 ), and its ability to record and store sessions without recourse to third-party software (Archibald et al. 2019 ). More importantly, Zoom was chosen because its functions could easily support the implementation of our online flipped classroom. For instance, it allows instructors to easily create breakout rooms for group discussions. It also makes team-teaching possible by allowing more than one host and giving all of the hosts administrative capabilities such as sharing screens and remote control over shared screens (Johnston 2020 ).
To keep our online meetings secure, we activated the “ only authenticated users can join ” option. Specifically, we only allowed participants using our own university’s email domain to join the online meetings. In addition, we enabled the “ waiting room ” feature so that we could screen all of participants in the “ waiting room ” and admit only students officially enrolled in our classes into the online meeting. After all of the participants had entered, we then locked the meeting using the “ Lock the meeting ” feature. Once we had locked a meeting, no new participants could join.
The same learning materials used in the conventional flipped classes were used in the online flipped classes. Table 4 shows some of the teaching and learning activities. Students in the online flipped classes completed pre-class activities that were similar to those used in the conventional flipped classes, but these were not followed by face-to-face meetings, but by online meetings conducted on the Zoom videoconferencing app.
Online flipped course 1: E-learning strategies
Like the conventional flipped course, the online flipped Course 1 consisted of eight sessions. The first seven sessions were flipped—students were encouraged to complete a set of pre-class sessions asynchronously (similar to Fig. 3 ). Students also used the WeChat MIM app to ask questions of their peers or instructors. However, unlike the conventional flipped approach, the “in-class” session for the online flipped students was conducted completely online through Zoom videoconferencing. In the final session (Session 8), the online flipped students also presented their work on Zoom. Each online “in-class” session lasted three hours—similar in duration to the in-class component of the conventional flipped format.
In the online synchronous “in-class” sessions, the instructor started by reminding students to switch on their webcams and to mute their microphones when not speaking. Next, the instructor lead a short class debriefing session to elaborate on the materials covered in the pre-class session. This was similar to the structure of the conventional flipped class format. For example, the instructor might discuss the students’ completed pre-class work and highlight the overall strengths and weaknesses. The main purpose of these short debriefing sessions was to clarify students’ initial doubts or misconceptions. Following the debriefing sessions, the instructor facilitated class discussions that delved deeper into the subject content. To evaluate students’ understanding of the materials, students were asked to work individually or participate in small group discussions on specific questions similar to those used in the conventional flipped classes. Students then presented their work online to the whole class, and received peer and instructor feedback.
To engage the participants, the instructor used a number of features of the Zoom videoconferencing system. For example, the instructor posed questions during the whole class discussion and used the polling feature to rapidly collect and analyze student responses. The polling feature provided a function similar to a clicker or student response system. Based on the poll results, the instructor then addressed students’ misunderstandings. To enable small group discussions, the instructor used the breakout rooms feature of Zoom . Each student was assigned to one of several groups. Each group consisted of four to five students. Other students could not “drop” into other groups, but the instructor could drop into any group and participate in the discussions. When it was time for the small groups to return to the whole class, students would receive a time indicator reminding them that they were rejoining the whole class. Table 5 shows how the specific features of Zoom helped support the online “in-class” teaching and learning activities. Figure 7 illustrates some of the Zoom features used in the course.
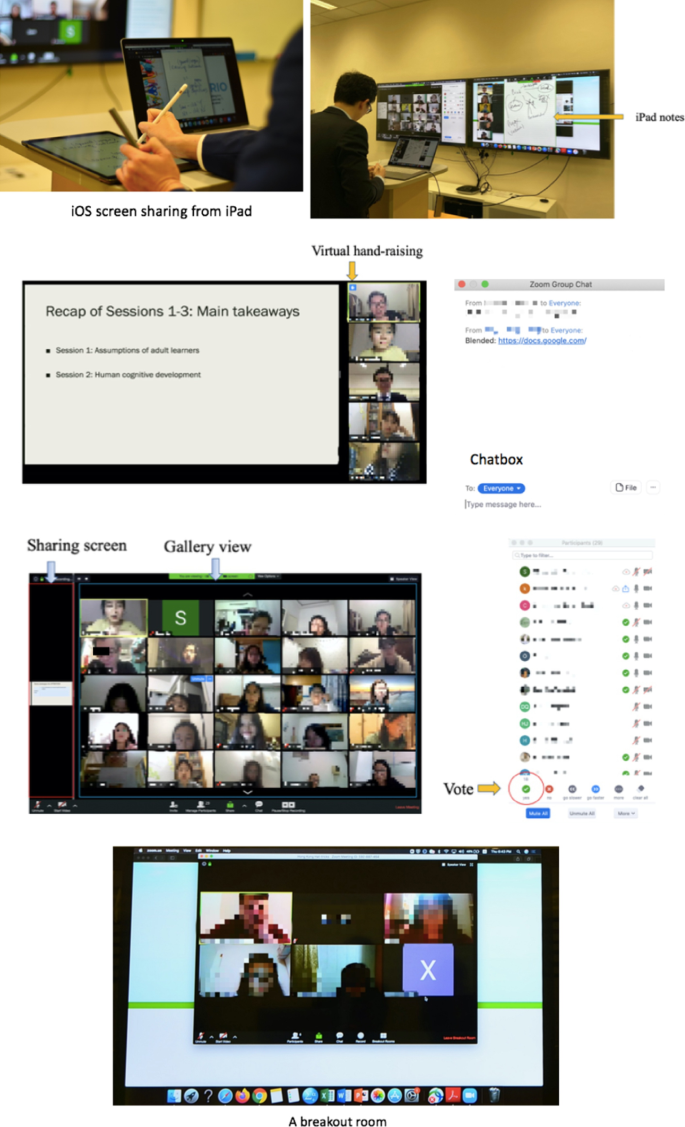
Examples of Zoom features used in Course 1
Online flipped course 2: engaging adult learners
Similar to the conventional flipped course, the online flipped course had eight sessions. The pre-class and in-class activities used in the conventional flipped course were also used in the online flipped course (see Fig. 5 for an example of a pre-class activity). Students also used the WeChat MIM app to ask questions of their peers or instructors. The last three sessions were used for students’ online presentations via videoconferencing. Each online “in-class” session lasted three hours—similar in duration to the in-class component of the conventional flipped class. In the online synchronous “in-class” sessions, the instructor reminded students to switch on their webcams and to mute their microphones when not speaking. The instructor used the features of the Zoom videoconferencing system shown in Table 5 and Fig. 7 .
Results and discussion
Conventional flipped versus online flipped course 1: e-learning strategies.
To address Research Question 1, the learning outcomes of students in the conventional flipped Course 1 and the online flipped Course 1 were measured and compared. The main purpose of both courses was to teach students the skills needed to create an e-learning storyboard and to develop a fully online course based on the 5E framework on Moodle. At the beginning of both the conventional flipped and online flipped classes, students were surveyed if they had any experience creating storyboards or fully online courses. None of the students had any such prior experience. Therefore, we assumed that both groups of students had similar levels of prior knowledge/skill. Next, we used both groups of students’ final course marks as a measure of the student learning outcomes. The maximum final marks in the final assessment was 100.
We first checked the normality of the final course marks data. If there were a significant deviation from normality, the Mann–Whitney U would be the most appropriate test for comparing the groups; otherwise, an independent samples t -test would be appropriate. The results showed that the course marks for both the conventional flipped ( W (23) = 0.920, p = 0.068) and online flipped classes ( W (26) = 0.964, p = 0.479) were normally distributed, as assessed by the Shapiro–Wilk’s test. There was also homogeneity in the variances for the course marks, as assessed by Levene’s test for equality of variances ( p = 0.652). In addition, there were no outliers in the data, as assessed by an inspection of the boxplots (Fig. 8 ).
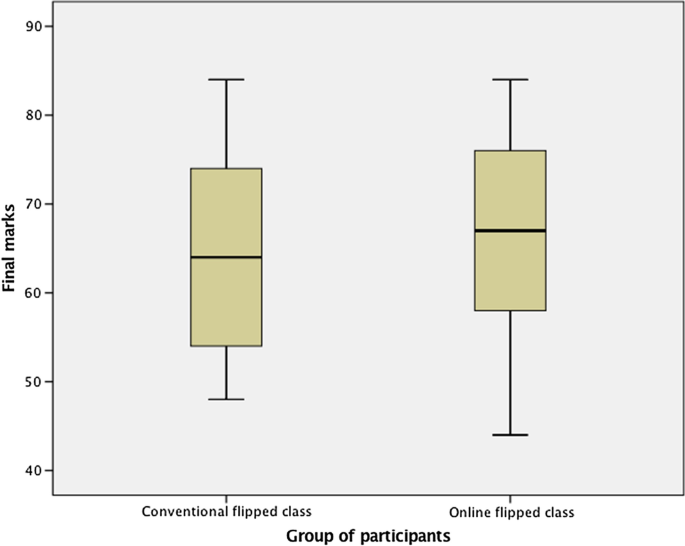
The boxplots of final marks in Course 1 for conventional flipped class and online flipped class
An independent-samples t -test was therefore conducted to determine if there were differences in the final marks of the conventional flipped and online flipped classes. The results suggested that online flipped participants ( M = 66.00, SD = 11.63) performed as effectively as participants in the conventional flipped learning format ( M = 65.04, SD = 11.80), t (47) = 0.285, p = 0.777.
Conventional flipped versus online flipped course 2: engaging adult learners
The main purpose of both the conventional flipped and online flipped Engaging Adult Learners courses was to introduce students to the key characteristics of adult learners, the key principles of adult learning, and strategies for adult education. First, to test if there were any initial differences in students’ prior knowledge of the course content, a short quiz was administered to both groups at the start of the semester. The Mann–Whitney U test found no significant initial differences between the conventional flipped group ( Mdn = 0) and the online flipped group ( Mdn = 0.5), U = 218.5, p = 0.06.
Next, we used the students’ final course marks as a measure of the student learning outcomes. The final assessment included individual written reflections on course topics and relevant articles, and a group demonstration of an adult-teaching strategy. The maximum final marks for the final assessment was 100. As in the above analysis, we first checked the normality of the final course mark data. The course marks for both the conventional flipped and online flipped classes were normally distributed, as assessed by Shapiro–Wilk’s test: W (25) = 0.963, p = 0.470 for the conventional flipped course and W (24) = 0.930, p = 0.096 for the online flipped course. There was also a homogeneity of variances, as assessed by Levene’s test for equality of variances ( p = 0.304). In addition, there were no outliers in the data, as assessed by an inspection of the boxplots (Fig. 9 ).
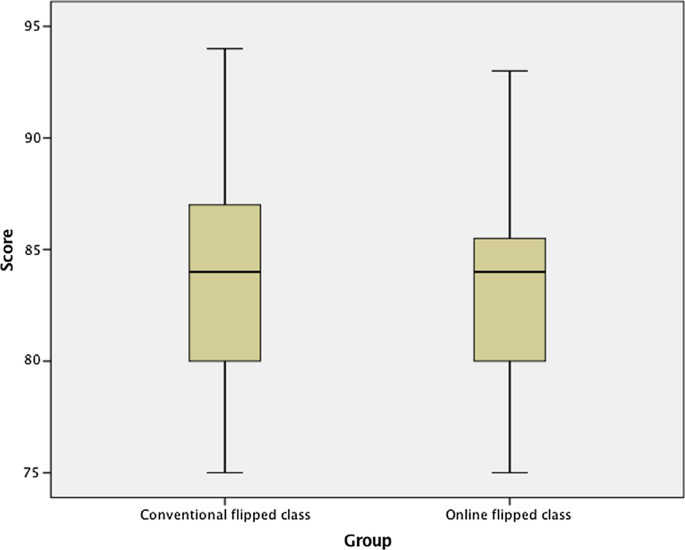
The boxplots of final marks in Course 2 for conventional flipped class and online flipped class
We subsequently carried out an independent-samples t-test to examine if there was any significant difference in the final course marks of the conventional flipped and online flipped classes. The results suggested that online flipped learning participants ( M = 83.25, SD = 4.56) performed as effectively as participants in the conventional flipped learning classes ( M = 83.40, SD = 5.51), t (47) = 0.104, p = 0.918.
What are the good practices for videoconferencing-assisted online flipped classrooms, as perceived by students and/or teaching staff?
The analyses of the participants’ comments identified the following seven good practices for videoconferencing-assisted online flipped classrooms.
Remind participants to mute their microphones when not speaking to eliminate undesirable background noise . According to Gazzillo ( 2018 ), muting participants’ microphones allows the speaker to have center stage while eliminating the distraction of audio feedback. As one teaching staff member said, .
It’s a good practice at the beginning to mute all of the participants by selecting the “Mute All” button at the bottom of the participants panel. This will eliminate all background noise (e.g., television sounds, audio feedback). I will then ask the participants to turn their audio back on if they wish to talk
In terms of Zoom functionality, by pressing and holding the “space bar” allows the participants to temporarily switch on their microphone. We also ask the participants to install an AI-enabled application called “Krisp” to minimize the background noise of the participants.
Remind participants before the online “in-class” session begins to switch on their webcams . Webcams show a person’s face to other people on the video call, which can help to increase online social presence among classmates (Conrad and Donaldson 2011 ). Online social presence is positively correlated with student satisfaction and student perceived learning (Richardson et al. 2017 ). The participants also strongly prefer to see a face during instruction as it is perceived as more educational (Kizilcec et al. 2014 ). Students’ facial expressions are also a valuable source of feedback for the instructor to know whether the students could understand the subject matter (Sathik and Jonathan 2013 ). An instructor can use students’ facial expressions to determine whether to speed up, or slow down, or provide further elaborations. Feedback from the teaching staff included the following comments.
It is important to ask students to turn on their cameras. Students will be more focused and interactive and teaching will be better when teachers can see students’ responses.
As an instructor, I do not feel as if I’m talking to a wall when I can see some actual faces. Students also feel they are talking to someone rather than to an empty black screen. But it’s important to inform the students in advance to switch on their webcams so that they can do their hair properly or put on makeup beforehand—this was what some students actually told me!
During teaching, seeing your students' faces will give you another form of feedback. For example, when they look confused or nod their heads, it allows me to fine-tune the delivery of the content. These reactions give me visual feedback on whether I need further explanations or examples to elaborate on the topic.
Feedback from the students included the following comments.
Showing our faces is really helpful as we can see our classmates’ faces and remember them. Also, it makes the class more alive because we can see their expressions. Showing our faces is very helpful! It can make me feel like I’m in a real class! I enjoy the feeling of having a class with my classmates.
Turning on the camera helps us be more attentive in the online class.
To avoid showing any undesirable background objects (e.g., a messy bedroom) during the video meeting, participants can choose to replace their actual background with a virtual background. The participants can easily do this using the Zoom virtual background feature.
Manage the transition to the online flipped classroom approach for students . Not every student will be familiar with the videoconferencing app or the flipped classroom approach. Therefore, to promote student buy-in of this new pedagogical approach, it is important for the staff to directly address two main issues: (a) the structure and activities of the online flipped course, and (b) the functions of the video conferencing app. Feedback from the students included the following comments.
If teachers would like to use some functions in Zoom, they need to first help students get familiar with it. A brief introduction to Zoom at the beginning of the class is helpful.
First, I informed the students that these two courses would have two components: a pre-class session and an online “in-class” session. This helped students understand the flipped approach better. Next, my teaching assistant and I conducted a short introduction to using Zoom online before the class began. This helped students get familiar with the features we would be using in Zoom.
Constant fine-tuning is also a key element in managing the transition to the online flipped classroom. Asking the students what works and what doesn’t have become our practice every after the lesson. These comments allow us to rethink and re-plan for the next online synchronous session.
Feedback from the teaching staff included the following comments.
Having a technical-related orientation session before the actual class starts helps a lot for students who are not familiar with the videoconferencing tool.
Instructors should use dual monitors to simulate, as close as possible, the look and feel of a face-to-face class—one monitor to view all the participants in “gallery view,” and the other to view the presentation material . It is very useful for instructors and teaching assistants to use the dual-monitor display function, which allows the video layout and screen share content to be presented on two separate monitors. One monitor can be used to view the participants (up to 49) in “gallery view,” and the other to display the presentation materials. In the “gallery view,” the instructor can see thumbnail displays of all of the participants in a grid pattern that expands and contracts automatically as participants join and leave the meeting (Zoom Video Communications 2019 ). The use of a dual monitor feature is also useful for PowerPoint presentations and hiding notes from the participants. Feedback from the teaching staff included:
During the preparation for this course, we would like to simulate, as close as possible, the look and feel of a face-to-face class. This thinking brought us to the dual monitor layout for our Zoom sessions. The first monitor is for the teaching assistant; in this case, it acts as a co-host for the Zoom session. The teaching assistant extends the computer screen to a monitor to show the participants’ faces or the “gallery view.” This monitor acts as a “classroom” in the traditional face-to-face class. During the session, this first monitor also serves as a tool for classroom management. This view is where the “chat” and “raise hand” functions can be seen. The second monitor is where the instructor places the presentation materials. This view acts as the projector in the traditional face-to-face class. Occasionally, we added a third screen, which is an iPad to do real-time annotation. This iPad can is a replacement of the conventional “whiteboard” in a face-to-face class.
Activate and evaluate students’ pre-class learning with a short review. At the beginning of the online “in-class” sessions, instructors should use short formative assessment methods (e.g., a quiz) to activate and evaluate students’ understanding of the pre-class activities. The activation of prior learning enhances student learning because it is the foundation for the new material presented in the classroom (Merrill 2002 ). Indeed, recent meta-analyses have suggested that flipped learning is more effective when formative assessments (e.g., quizzes or reviews) are used before and/or during class time (e.g., Hew and Lo 2018 ; Låg and Sæle 2019 ; Lo et al. 2017 ; van Alten et al. 2019 ). Students in this study reported positive benefits of using short formative assessments such as reviews or quizzes. Examples of student feedback include the following comments.
I find the reviews at the beginning of the “in-class” sessions very helpful! It’s good to start from something we are familiar with, and then go to the new materials. The reviewing of pre-class work is great because we can know what points we do not understand well and how we can improve.
The reviews helped me understand the issue more deeply. I could find out what my misunderstandings of the content are.
I find the teachers’ explanation and review of the pre-class work helpful.
Use an MIM app on mobile phones to foster quicker online response times and to communicate with students during their online breakout sessions . Although students can ask questions via discussion forums or email, the asynchronicity of these apps creates a time lag between postings and replies which can discourage students from communicating with each other (Hew et al. 2018 ). In contrast, MIM apps such as WhatsApp and WeChat allow users to engage in quasi synchronous communications on their mobile phones. When communication needs are urgent, many students may only have their phones available. As soon as an MIM message is sent, a notification automatically shows up on the user’s phone screen, which encourages timely response (Hew et al. 2018 ; Rosenfeld et al. 2018 ). In addition, MIM is more popular than voice calls, emails, and even face-to-face communication among young people (Lenhart et al. 2010 ). As of March 2019, more than 41 million mobile instant messages are sent every minute (Clement 2019 ). Student feedback on using MIM in classrooms included the following comments.
I like using MIM such as WeChat because it allows us to communicate with other people immediately.
I enjoy using WeChat to ask questions and get immediate feedback from my classmates and teaching staff.
Use a variety of presentation media as well as a variety of activities to sustain student interest . No matter how interested a learner is in the topic of a presentation or discussion, that interest will wane in the face of monotony (Driscoll 2000 ). Therefore, it is recommended that instructors sustain student interest by varying the use of presentation media. Instructors, for example, can alternate the use of PowerPoint slides with digital handwriting on an iPad. The instructor in this study made the following comments.
I find continual use of PowerPoint slides to be boring. It’s always the same style: a bullet list of information with some animations or pictures. I find it useful to sustain my students’ attention by writing on an iPad.
Comments from the students were also positive.
I find the instructor writing on an iPad helps to focus my attention better than PowerPoint slides.
Writing on the iPad is like writing on a whiteboard in real face-to-face classrooms. It helps me develop a better understanding of the topic.
Digital writing on an iPad can help learners see the progressive development of the subject content (Hulls 2005 ), and follow the instructor’s cognitive process better than pre-prepared PowerPoint presentations (Lee and Lim 2013 ). Writing on an iPad can also enable an instructor to immediately adjust his or her instruction in response to the students’ needs. Using digital writing can significantly improve students’ understanding of conceptual knowledge when compared to PowerPoint-based presentation lectures (Lee and Lim 2013 ).
In addition to varying the presentation media, an instructor should also use different activities, including guest speakers, during the online class session. Feedback from the students included the following comments.
The use of different functions in Zoom, such as breakout rooms for group activities, voting, and raising hands, is useful because they help us to be involved. It helps increase the learner-learner and learner-instructor interaction, which may be lacking in a fully online class.
During the three-hour online class, we had not only the teacher’s explanations, but also had a guest speaker and online group discussions via breakout rooms, which made the class engaging.
In this study, the instructor invited a United Kingdom-based practicing instructional designer as a guest speaker in the two online flipped courses to talk about her experience in developing e-learning courses and engaging adult learners. Guest speakers enhance students’ educational experience by giving them real-world knowledge (Metrejean and Zarzeski 2001 ). Guest speakers can offer students a different point of view, one that students may better understand. Guest speakers can also alleviate the monotony of listening to a single instructor.
Amidst the burgeoning use of online learning during the unpredictable present, this study evaluates the efficacy of a videoconferencing - supported fully online flipped classroom. It compares student outcomes in four higher education classes: conventional flipped Course 1 versus online flipped Course 1, and conventional flipped Course 2 versus online flipped Course 2. Overall, this study makes three contributions to the literature on flipped classrooms. First, it provides a thick description of the development of the conventional flipped classroom approach based on the 5E framework, and the transformation of the conventional flipped classroom into a fully online flipped classroom. A thick description of the development of the flipped classrooms is provided to encourage replication by other researchers and practitioners. Second, our findings reveal that the online flipped classroom approach can be as effective as the conventional flipped classroom. Third, we identify seven good practices for using videoconferencing to support online flipped classrooms. This set of good practices can provide useful guidelines for other instructors who might be interested in implementing an online flipped approach.
One potential limitation of our study is that it was relatively short in duration (8 weeks). However, according to Fraenkel et al. ( 2014 ), some researchers do collect data within a fairly short time. A short-term data collection period enables researchers to collect and analyze data to see if an intervention is workable before committing to a longer study (Creswell 2015 ). We therefore urge future researchers to examine the use of videoconferencing - supported online flipped classrooms over a longer period of time, such as one year or more, to verify the results of this study.
Another interesting area for future work will be examining how instructors can support learners’ self-regulation during online flipped classroom (Cheng et al. 2019 ), as well as what strategies can best motivate students to complete the pre-class work.
Availability of data and materials
The anonymized datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Akar, E. (2005). Effectiveness of 5e learning cycle model on students’ understanding of acid-base concepts . MS Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara.
Archibald, M. M., Ambagtsheer, R. C., Casey, M. G., & Lawless, M. (2019). Using Zoom videoconferencing for qualitative data collection: perceptions and experiences of researchers and participants. Int J Qual Methods, 18, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406919874596 .
Article Google Scholar
Bates S, Galloway R. The inverted classroom in a large enrolment introductory physics course: A case study. https://www.heacademy.ac.uk/assets/documents/stem-conference/PhysicalSciences/Simon_Bates_Ross_Galloway.pdf (2012)
Bishop, J. L., & Verleger, M. A. (2013). The flipped classroom: A survey of the research. 120 Am Soc Eng Educ Annu Conf Expo, 30, 1–18.
Google Scholar
Boddy, N., Watson, K., & Aubusson, P. (2003). A trial of the five e’s: a referent model for constructivist teaching and learning. Research in Science Education , 33 , 27–42. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023606425452 .
Bond, M. (2020). Facilitating student engagement through the flipped learning approach in K-12: A systematic review. Computers & Education . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103819
Bybee, R. W., et al. (2006). The BSCS 5E instructional model: origins and effectiveness. Off Sci Educ Natl Inst Health, 2006, 1–80.
Cheng, L., Ritzhaupt, A. D., & Antonenko, P. (2019). Effects of the flipped classroom instructional strategy on students’ learning outcomes: a meta-analysis. Etr&D, 67 (4), 793–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9633-7
Clement J. Global number of mobile messaging users 2018–2022. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/483255/number-of-mobile-messaging-usersworldwide/ (2019)
Conrad, R. M., & Donaldson, J. A. (2011). Engaging the online learner: activities and resources for creative instruction . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Creswell, J. W. (2015). Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research . Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Deslauriers, L., et al. (2019). Measuring actual learning versus feeling of learning in response to being actively engaged in the classroom. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116 (39), 19251–19257. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821936116
Driscoll, M. P. (2000). Psychology of learning for instruction (2nd ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E., & Hyun, H. H. (2014). How to design and evaluate research in education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Gazzillo L. Tech tip: muting participants in Zoom. Yale Library IT News . https://campuspress.yale.edu/libraryitnews/2018/01/23/tech-tip-muting-participants-in-zoom/ (2018)
Gierdowski DC. 2019 study of undergraduate students and information technology. EDUCAUSE Center for Analysis and Research. https://library.educause.edu/resources/2019/10/2019-study-of-undergraduate-students-and-information-technology (2019)
Hew, K. F., & Lo, C. K. (2018). Flipped classroom improves student learning in health professions education: a meta-analysis. BMC Medical Education . https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-018-1144-z
Hew, K., et al. (2018). Examining a WeChat-supported 5E-flipped classroom pedagogical approach. Int J Serv Stand, 12, 224–242.
Hodges C, Moore S, Lockee B, Trust T, Bond, A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educause Review. https://er.educause.edu/articles/2020/3/the-difference-between-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning (2020)
Hulls CCW. Using a tablet PC for classroom instruction. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference of Frontiers in Education, Indianapolis, Indiana, 19–22 October
Ivankova, N. V., Creswell, J. W., & Stick, S. L. (2006). Using mixed-methods sequential explanatory design: From theory to practice. Field Methods, 18 (1), 3–20.
Johnston N. Google Hangouts Meet vs. Zoom: Which conferencing tool is better for you? https://www.androidcentral.com/google-hangouts-meet-vs-zoom (2020)
Kim J. Zoom is hot in higher ed. Inside Higher Ed . Retrieved from https://www.insidehighered.com/blogs/technology-and-learning/zoom-hot-higher-ed (2017)
Kizilcec RF, Papadopoulos K, Sritanyaratana L. Showing face in video instruction: Effects on information retention, visual attention, and affect. In Proceedings of SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 2095–2102). New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery (2014)
Låg, T., & Sæle, R. G. (2019). Does the flipped classroom improve student learning and satisfaction? A systematic review and meta-analysis. AERA Open, 5 (3), 1–17.
Lederman D. Will shift to remote teaching be boon or bane for online learning? Inside Higher Ed . Retrieved from https://www.insidehighered.com/digital-learning/article/2020/03/18/most-teaching-going-remote-will-help-or-hurt-online-learning (2014)
Lee, H. W., & Lim, K. Y. (2013). Does digital handwriting of instructors using the iPad enhance student learning? Asia-Pacific Educ Res, 22 (3), 241–245.
Lenhart A, et al. Social media & mobile internet use among teens and young adults. Pew Internet and American Life Project, 2010 (2010).
Lo, C. K. (2017). Toward a flipped classroom instructional model for history education: a call for research. Int J Cult Hist, 3 (1), 36–43.
Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2019). The impact of flipped classrooms on student achievement in engineering education: a meta-analysis of 10 years of research. Journal of Engineering Education, 108 (4), 523–546.
Lo, C. K., Hew, K. F., & Chen, G. (2017). Toward a set of design principles for mathematics flipped classrooms: a synthesis of research in mathematics education. Educ Res Rev, 22, 50–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2017.08.002
Merrill, M. D. (2002). First principles of instruction. Educ Technol Res Dev, 50 (3), 43–59.
Metrejean, C., & Zarzeski, M. (2001). Bring the world to the classroom. J Account, 19 (3), 73–76.
Mullins, M. H. (2017). Actively teaching research methods with a process oriented guided inquiry learning approach. J Teach Soc Work, 37 (4), 309–332.
Pomerantz J, Brooks DC. ECAR study of faculty and information technology. Research report . Louisville, CO: ECAR. https://library.educause.edu/-/media/files/library/2017/10/facultyitstudy2017.pdf (2017)
Richardson, J. C., Maeda, Y., Lv, J., & Caskurlu, S. (2017). Social presence in relation to students’ satisfaction and learning in the online environment: a meta-analysis. Computers in Human Behavior, 71, 402–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.02.001
Rosenfeld, A., Sina, S., Sarne, D., Avidov, O., & Kraus, S. (2018). WhatsApp usage patterns and prediction of demographic characteristics without access to message content. Demographic Research , 39 (22), 647–670. https://doi.org/10.4054/DemRes.2018.39.22 .
Sathik, M., & Jonathan, S. G. (2013). Effect of facial expressions on student’s comprehension recognition in virtual educational environments. SpringerPlus, 2, 455. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-455
Shi, Y., Ma, Y., MacLeod, J., & Yang, H. H. (2019). College students’ cognitive learning outcomes in flipped classroom instruction: a meta-analysis of the empirical literature. J Comput Educ . https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-019-00142-8
Stohr, C., Demaziere, C., & Adawi, T. (2020). The polarizing effect of the online flipped classroom. Computers & Education . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103789
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: grounded theory procedures and techniques . Newbury Park: Sage Publications.
Sutterlin J. Learning is social with Zoom videoconferencing in your classroom. eLearn magazine . https://elearnmag.acm.org/featured.cfm?aid=3236697 (2018)
UNESCO. (n.d.). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/coronavirus-school-closures
van Alten, D. C. D., Phielix, C., Janssen, J., & Kester, L. (2019). Effects of flipping the classroom on learning outcomes and satisfaction: a meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev, 28, 100281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2019.05.003
Xiu, Y., & Thompson, P. (2020). Flipped university class: a study of motivation and learning. J Inform Technol Educ, 19, 41–63.
Zoom Video Communications Inc. Displaying participants in gallery view. https://support.zoom.us/hc/en-us/articles/360000005883-Displaying-participants-in-gallery-view (2019)
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.

Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, The University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong SAR
Khe Foon Hew, Chengyuan Jia, Donn Emmanuel Gonda & Shurui Bai
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KFH conceptualized the study, analysed the data, and wrote the initial draft. CJ analysed the data, and revised the draft. DEG provided critical feedback and edited the manuscript. SB provided Zoom support and critical feedback. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Khe Foon Hew .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hew, K.F., Jia, C., Gonda, D.E. et al. Transitioning to the “new normal” of learning in unpredictable times: pedagogical practices and learning performance in fully online flipped classrooms. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 17 , 57 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00234-x
Download citation
Received : 24 June 2020
Accepted : 28 September 2020
Published : 21 December 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00234-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online flipped classroom
- Flipped learning
- Good practices
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Supplements
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About Journal of Public Health
- About the Faculty of Public Health of the Royal Colleges of Physicians of the United Kingdom
- Editorial Board
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
- < Previous
Adapting to the culture of ‘new normal’: an emerging response to COVID-19
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Jeff Clyde G Corpuz, Adapting to the culture of ‘new normal’: an emerging response to COVID-19, Journal of Public Health , Volume 43, Issue 2, June 2021, Pages e344–e345, https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdab057
- Permissions Icon Permissions
A year after COVID-19 pandemic has emerged, we have suddenly been forced to adapt to the ‘new normal’: work-from-home setting, parents home-schooling their children in a new blended learning setting, lockdown and quarantine, and the mandatory wearing of face mask and face shields in public. For many, 2020 has already been earmarked as ‘the worst’ year in the 21st century. Ripples from the current situation have spread into the personal, social, economic and spiritual spheres. Is this new normal really new or is it a reiteration of the old? A recent correspondence published in this journal rightly pointed out the involvement of a ‘supportive’ government, ‘creative’ church and an ‘adaptive’ public in the so-called culture. However, I argue that adapting to the ‘new normal’ can greatly affect the future. I would carefully suggest that we examine the context and the location of culture in which adaptations are needed.
To live in the world is to adapt constantly. A year after COVID-19 pandemic has emerged, we have suddenly been forced to adapt to the ‘new normal’: work-from-home setting, parents home-schooling their children in a new blended learning setting, lockdown and quarantine, and the mandatory wearing of face mask and face shields in public. For many, 2020 has already been earmarked as ‘the worst’ year in the 21st century. 1 Ripples from the current situation have spread into the personal, social, economic and spiritual spheres. Is this new normal really new or is it a reiteration of the old? A recent correspondence published in this journal rightly pointed out the involvement of a ‘supportive’ government, ‘creative’ church and an ‘adaptive’ public in the so-called culture. 2 However, I argue that adapting to the ‘new normal’ can greatly affect the future. I would carefully suggest that we examine the context and the location of culture in which adaptations are needed.
The term ‘new normal’ first appeared during the 2008 financial crisis to refer to the dramatic economic, cultural and social transformations that caused precariousness and social unrest, impacting collective perceptions and individual lifestyles. 3 This term has been used again during the COVID-19 pandemic to point out how it has transformed essential aspects of human life. Cultural theorists argue that there is an interplay between culture and both personal feelings (powerlessness) and information consumption (conspiracy theories) during times of crisis. 4 Nonetheless, it is up to us to adapt to the challenges of current pandemic and similar crises, and whether we respond positively or negatively can greatly affect our personal and social lives. Indeed, there are many lessons we can learn from this crisis that can be used in building a better society. How we open to change will depend our capacity to adapt, to manage resilience in the face of adversity, flexibility and creativity without forcing us to make changes. As long as the world has not found a safe and effective vaccine, we may have to adjust to a new normal as people get back to work, school and a more normal life. As such, ‘we have reached the end of the beginning. New conventions, rituals, images and narratives will no doubt emerge, so there will be more work for cultural sociology before we get to the beginning of the end’. 5
Now, a year after COVID-19, we are starting to see a way to restore health, economies and societies together despite the new coronavirus strain. In the face of global crisis, we need to improvise, adapt and overcome. The new normal is still emerging, so I think that our immediate focus should be to tackle the complex problems that have emerged from the pandemic by highlighting resilience, recovery and restructuring (the new three Rs). The World Health Organization states that ‘recognizing that the virus will be with us for a long time, governments should also use this opportunity to invest in health systems, which can benefit all populations beyond COVID-19, as well as prepare for future public health emergencies’. 6 There may be little to gain from the COVID-19 pandemic, but it is important that the public should keep in mind that no one is being left behind. When the COVID-19 pandemic is over, the best of our new normal will survive to enrich our lives and our work in the future.
No funding was received for this paper.
UNESCO . A year after coronavirus: an inclusive ‘new normal’. https://en.unesco.org/news/year-after-coronavirus-inclusive-new-normal . (12 February 2021, date last accessed) .
Cordero DA . To stop or not to stop ‘culture’: determining the essential behavior of the government, church and public in fighting against COVID-19 . J Public Health (Oxf) 2021 . doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdab026 .
Google Scholar
El-Erian MA . Navigating the New Normal in Industrial Countries . Washington, D.C. : International Monetary Fund , 2010 .
Google Preview
Alexander JC , Smith P . COVID-19 and symbolic action: global pandemic as code, narrative, and cultural performance . Am J Cult Sociol 2020 ; 8 : 263 – 9 .
Biddlestone M , Green R , Douglas KM . Cultural orientation, power, belief in conspiracy theories, and intentions to reduce the spread of COVID-19 . Br J Soc Psychol 2020 ; 59 ( 3 ): 663 – 73 .
World Health Organization . From the “new normal” to a “new future”: A sustainable response to COVID-19. 13 October 2020 . https: // www.who.int/westernpacific/news/commentaries/detail-hq/from-the-new-normal-to-a-new-future-a-sustainable-response-to-covid-19 . (12 February 2021, date last accessed) .
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1741-3850
- Print ISSN 1741-3842
- Copyright © 2024 Faculty of Public Health
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
A Year After Coronavirus: An Inclusive ‘New Normal’

Six months into a new decade, 2020 has already been earmarked as ‘the worst’ year in the 21st century. The novel coronavirus has given rise to a global pandemic that has destabilized most institutional settings. While we live in times when humankind possesses the most advanced science and technology, a virus invisible to the naked eye has massively disrupted economies, healthcare, and education systems worldwide. This should serve as a reminder that as we keep making progress in science and research, humanity will continue to face challenges in the future, and it is upon us to prioritize those issues that are most relevant in the 21st century.
Even amidst the pandemic, Space X, an American aerospace manufacturer, managed to become the first private company to send humans to space. While this is a tremendous achievement and prepares humanity for a sustainable future, I feel there is a need to introspect the challenges that we are already facing. On the one hand, we seem to be preparing beyond the 21st century. On the other hand, heightened nationalism, increasing violence against marginalized communities and multidimensional inequalities across all sectors continue to act as barriers to growth for most individuals across the globe. COVID-19 has reinforced these multifaceted economic, social and cultural inequalities wherein those in situations of vulnerability have found it increasingly difficult to get quality medical attention, access to quality education, and have witnessed increased domestic violence while being confined to their homes.
Given the coronavirus’s current situation, some households have also had time to introspect on gender roles and stereotypes. For instance, women are expected to carry out unpaid care work like cooking, cleaning, and looking after the family. There is no valid reason to believe that women ought to carry out these activities, and men have no role in contributing to household chores. With men having shared household chores during the lockdown period, it gives hope that they will realize the burden that women have been bearing for past decades and will continue sharing responsibilities. However, it would be naïve to believe that gender discrimination could be tackled so easily, and men would give up on their decades' old habits within a couple of months. Thus, during and after the pandemic, there is an urgent need to sensitize households on the importance of gender equality and social cohesion.
Moving forward, developing quality healthcare systems that are affordable and accessible to all should be the primary objective for all governments. This can be done by increasing expenditure towards health and education and simultaneously reducing expenditure on defence equipment where the latter mainly gives rise to an idea that countries need to be prepared for violence. There is substantial evidence that increased investment in health and education is beneficial in the long-term and can potentially build the basic foundation of a country.
If it can be established that usage of nuclear weapons, violence and war are not solutions to any problem, governments (like, for example, Costa Rica) could move towards disarmament of weapons and do their part in building a more peaceful planet that is sustainable for the future. This would further promote global citizenship wherein nationality, race, gender, caste, and other categories, are just mere variables and they do not become identities of individuals that restrict their thought process. The aim should be to build responsible citizens who play an active role in their society and work collectively in helping develop a planet that is well-governed, inclusive, and environmentally sustainable.
‘A year after Coronavirus’ is still an unknown, so I think that our immediate focus should be to tackle the complex problems that have emerged from the pandemic so that we make the year after coronavirus one which highlights recovery and acts as a pathway to fresh beginnings. While there is little to gain from such a fatal cause, it is vital that we also use it to make the ‘new normal’ in favour of the environment and ensure that no one is left behind.
Related items
- Country page: India
- UNESCO Office in New Delhi
- SDG: SDG 3 - Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
This article is related to the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals .

Other recent articles

The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how

With schools shut across the world, millions of children have had to adapt to new types of learning. Image: REUTERS/Gonzalo Fuentes
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Cathy Li
Farah lalani.
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Education, Gender and Work is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, education, gender and work.
- The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom.
- As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms.
- Research suggests that online learning has been shown to increase retention of information, and take less time, meaning the changes coronavirus have caused might be here to stay.
While countries are at different points in their COVID-19 infection rates, worldwide there are currently more than 1.2 billion children in 186 countries affected by school closures due to the pandemic. In Denmark, children up to the age of 11 are returning to nurseries and schools after initially closing on 12 March , but in South Korea students are responding to roll calls from their teachers online .
With this sudden shift away from the classroom in many parts of the globe, some are wondering whether the adoption of online learning will continue to persist post-pandemic, and how such a shift would impact the worldwide education market.

Even before COVID-19, there was already high growth and adoption in education technology, with global edtech investments reaching US$18.66 billion in 2019 and the overall market for online education projected to reach $350 Billion by 2025 . Whether it is language apps , virtual tutoring , video conferencing tools, or online learning software , there has been a significant surge in usage since COVID-19.
How is the education sector responding to COVID-19?
In response to significant demand, many online learning platforms are offering free access to their services, including platforms like BYJU’S , a Bangalore-based educational technology and online tutoring firm founded in 2011, which is now the world’s most highly valued edtech company . Since announcing free live classes on its Think and Learn app, BYJU’s has seen a 200% increase in the number of new students using its product, according to Mrinal Mohit, the company's Chief Operating Officer.
Tencent classroom, meanwhile, has been used extensively since mid-February after the Chinese government instructed a quarter of a billion full-time students to resume their studies through online platforms. This resulted in the largest “online movement” in the history of education with approximately 730,000 , or 81% of K-12 students, attending classes via the Tencent K-12 Online School in Wuhan.
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023.
Other companies are bolstering capabilities to provide a one-stop shop for teachers and students. For example, Lark, a Singapore-based collaboration suite initially developed by ByteDance as an internal tool to meet its own exponential growth, began offering teachers and students unlimited video conferencing time, auto-translation capabilities, real-time co-editing of project work, and smart calendar scheduling, amongst other features. To do so quickly and in a time of crisis, Lark ramped up its global server infrastructure and engineering capabilities to ensure reliable connectivity.
Alibaba’s distance learning solution, DingTalk, had to prepare for a similar influx: “To support large-scale remote work, the platform tapped Alibaba Cloud to deploy more than 100,000 new cloud servers in just two hours last month – setting a new record for rapid capacity expansion,” according to DingTalk CEO, Chen Hang.
Some school districts are forming unique partnerships, like the one between The Los Angeles Unified School District and PBS SoCal/KCET to offer local educational broadcasts, with separate channels focused on different ages, and a range of digital options. Media organizations such as the BBC are also powering virtual learning; Bitesize Daily , launched on 20 April, is offering 14 weeks of curriculum-based learning for kids across the UK with celebrities like Manchester City footballer Sergio Aguero teaching some of the content.
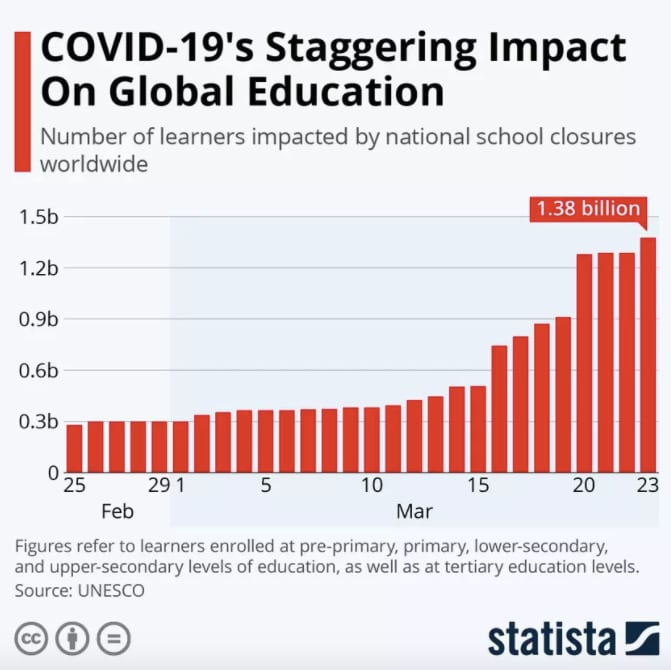
What does this mean for the future of learning?
While some believe that the unplanned and rapid move to online learning – with no training, insufficient bandwidth, and little preparation – will result in a poor user experience that is unconducive to sustained growth, others believe that a new hybrid model of education will emerge, with significant benefits. “I believe that the integration of information technology in education will be further accelerated and that online education will eventually become an integral component of school education,“ says Wang Tao, Vice President of Tencent Cloud and Vice President of Tencent Education.
There have already been successful transitions amongst many universities. For example, Zhejiang University managed to get more than 5,000 courses online just two weeks into the transition using “DingTalk ZJU”. The Imperial College London started offering a course on the science of coronavirus, which is now the most enrolled class launched in 2020 on Coursera .
Many are already touting the benefits: Dr Amjad, a Professor at The University of Jordan who has been using Lark to teach his students says, “It has changed the way of teaching. It enables me to reach out to my students more efficiently and effectively through chat groups, video meetings, voting and also document sharing, especially during this pandemic. My students also find it is easier to communicate on Lark. I will stick to Lark even after coronavirus, I believe traditional offline learning and e-learning can go hand by hand."
These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning
The challenges of online learning.
There are, however, challenges to overcome. Some students without reliable internet access and/or technology struggle to participate in digital learning; this gap is seen across countries and between income brackets within countries. For example, whilst 95% of students in Switzerland, Norway, and Austria have a computer to use for their schoolwork, only 34% in Indonesia do, according to OECD data .
In the US, there is a significant gap between those from privileged and disadvantaged backgrounds: whilst virtually all 15-year-olds from a privileged background said they had a computer to work on, nearly 25% of those from disadvantaged backgrounds did not. While some schools and governments have been providing digital equipment to students in need, such as in New South Wales , Australia, many are still concerned that the pandemic will widenthe digital divide .
Is learning online as effective?
For those who do have access to the right technology, there is evidence that learning online can be more effective in a number of ways. Some research shows that on average, students retain 25-60% more material when learning online compared to only 8-10% in a classroom. This is mostly due to the students being able to learn faster online; e-learning requires 40-60% less time to learn than in a traditional classroom setting because students can learn at their own pace, going back and re-reading, skipping, or accelerating through concepts as they choose.
Nevertheless, the effectiveness of online learning varies amongst age groups. The general consensus on children, especially younger ones, is that a structured environment is required , because kids are more easily distracted. To get the full benefit of online learning, there needs to be a concerted effort to provide this structure and go beyond replicating a physical class/lecture through video capabilities, instead, using a range of collaboration tools and engagement methods that promote “inclusion, personalization and intelligence”, according to Dowson Tong, Senior Executive Vice President of Tencent and President of its Cloud and Smart Industries Group.
Since studies have shown that children extensively use their senses to learn, making learning fun and effective through use of technology is crucial, according to BYJU's Mrinal Mohit. “Over a period, we have observed that clever integration of games has demonstrated higher engagement and increased motivation towards learning especially among younger students, making them truly fall in love with learning”, he says.
A changing education imperative
It is clear that this pandemic has utterly disrupted an education system that many assert was already losing its relevance . In his book, 21 Lessons for the 21st Century , scholar Yuval Noah Harari outlines how schools continue to focus on traditional academic skills and rote learning , rather than on skills such as critical thinking and adaptability, which will be more important for success in the future. Could the move to online learning be the catalyst to create a new, more effective method of educating students? While some worry that the hasty nature of the transition online may have hindered this goal, others plan to make e-learning part of their ‘new normal’ after experiencing the benefits first-hand.
The importance of disseminating knowledge is highlighted through COVID-19
Major world events are often an inflection point for rapid innovation – a clear example is the rise of e-commerce post-SARS . While we have yet to see whether this will apply to e-learning post-COVID-19, it is one of the few sectors where investment has not dried up . What has been made clear through this pandemic is the importance of disseminating knowledge across borders, companies, and all parts of society. If online learning technology can play a role here, it is incumbent upon all of us to explore its full potential.
Our education system is losing relevance. Here's how to unleash its potential
3 ways the coronavirus pandemic could reshape education, celebrities are helping the uk's schoolchildren learn during lockdown, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Socio-economic inequalities drive antimicrobial resistance risks. Here's how – and how to curb it
Michael Anderson, Gunnar Ljungqvist and Victoria Saint
May 15, 2024

From our brains to our bowels – 5 ways the climate crisis is affecting our health
Charlotte Edmond
May 14, 2024

Health funders unite to support climate and disease research, plus other top health stories
Shyam Bishen
May 13, 2024

How midwife mentors are making it safer for women to give birth in remote, fragile areas
Anna Cecilia Frellsen
May 9, 2024

From Athens to Dhaka: how chief heat officers are battling the heat
Angeli Mehta
May 8, 2024

How a pair of reading glasses could increase your income
Emma Charlton
For the best Oliver Wyman website experience, please upgrade your browser to IE9 or later

- Global (English)
- India (English)
- Middle East (English)
- South Africa (English)
- Brazil (Português)
- China (中文版)
- Japan (日本語)
- Southeast Asia (English)
- Belgium (English)
- France (Français)
- Germany (Deutsch)
- Italy (Italiano)
- Netherlands (English)
- Nordics (English)
- Portugal (Português)
- Spain (Español)
- Switzerland (Deutsch)
- UK And Ireland (English)

Education In The New Normal
This was first published on June 3, 2020
Covid-19 has created numerous and significant challenges to the education system, and education leadership must implement a holistic strategy to mitigate the impact of the pandemic and adapt to the new reality.
In April 2020 we published our first insights on Education Continuity During Covid-19 , which provided an overview of country responses to ensure education continuity and outlined a set of recommendations, targeted at education policymakers and delivery institutions, to build resilience into their education systems and ensure continuity during times of public crisis.
In this, the second installment, we dive deeper into the recommendations and look at core initiatives taken by education leadership in response to the pandemic and provide practical guidance and examples.
Education Leadership Detailed Response Framework
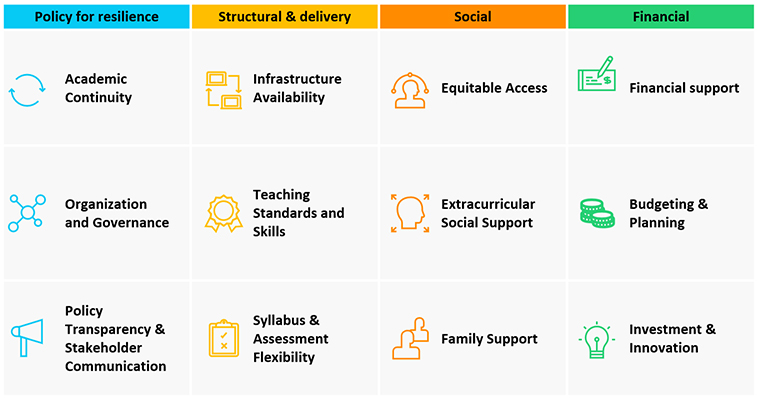
OUR EXPERTISE
Industries .
- Communications, Media, And Technology
- Energy And Natural Resources
- Financial Services
- Government And Public Institutions
- Health And Life Sciences
- Industrial Products
- Private Equity And Principal Investors
- Retail And Consumer Goods
- Transportation And Services
- Velocity Podcast
capabilities
- Climate And Sustainability
- Oliver Wyman Engineers
- People And Organizational Performance
- Performance Transformation
- Pricing, Sales, And Marketing
- Risk Management
- Turnaround And Restructuring
- Oliver Wyman Quotient
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Letter of Recommendation
What I’ve Learned From My Students’ College Essays
The genre is often maligned for being formulaic and melodramatic, but it’s more important than you think.

By Nell Freudenberger
Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn’t supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they’re afraid that packaging the genuine trauma they’ve experienced is the only way to secure their future. The college counselor at the Brooklyn high school where I’m a writing tutor advises against trauma porn. “Keep it brief , ” she says, “and show how you rose above it.”
I started volunteering in New York City schools in my 20s, before I had kids of my own. At the time, I liked hanging out with teenagers, whom I sometimes had more interesting conversations with than I did my peers. Often I worked with students who spoke English as a second language or who used slang in their writing, and at first I was hung up on grammar. Should I correct any deviation from “standard English” to appeal to some Wizard of Oz behind the curtains of a college admissions office? Or should I encourage students to write the way they speak, in pursuit of an authentic voice, that most elusive of literary qualities?
In fact, I was missing the point. One of many lessons the students have taught me is to let the story dictate the voice of the essay. A few years ago, I worked with a boy who claimed to have nothing to write about. His life had been ordinary, he said; nothing had happened to him. I asked if he wanted to try writing about a family member, his favorite school subject, a summer job? He glanced at his phone, his posture and expression suggesting that he’d rather be anywhere but in front of a computer with me. “Hobbies?” I suggested, without much hope. He gave me a shy glance. “I like to box,” he said.
I’ve had this experience with reluctant writers again and again — when a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously. Of course the primary goal of a college essay is to help its author get an education that leads to a career. Changes in testing policies and financial aid have made applying to college more confusing than ever, but essays have remained basically the same. I would argue that they’re much more than an onerous task or rote exercise, and that unlike standardized tests they are infinitely variable and sometimes beautiful. College essays also provide an opportunity to learn precision, clarity and the process of working toward the truth through multiple revisions.
When a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously.
Even if writing doesn’t end up being fundamental to their future professions, students learn to choose language carefully and to be suspicious of the first words that come to mind. Especially now, as college students shoulder so much of the country’s ethical responsibility for war with their protest movement, essay writing teaches prospective students an increasingly urgent lesson: that choosing their own words over ready-made phrases is the only reliable way to ensure they’re thinking for themselves.
Teenagers are ideal writers for several reasons. They’re usually free of preconceptions about writing, and they tend not to use self-consciously ‘‘literary’’ language. They’re allergic to hypocrisy and are generally unfiltered: They overshare, ask personal questions and call you out for microaggressions as well as less egregious (but still mortifying) verbal errors, such as referring to weed as ‘‘pot.’’ Most important, they have yet to put down their best stories in a finished form.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around “small moments” that lead to a concluding lesson or aspiration for the future. I never get tired of working with students on these essays because each one is different, and the short, rigid form sometimes makes an emotional story even more powerful. Before I read Javier Zamora’s wrenching “Solito,” I worked with a student who had been transported by a coyote into the U.S. and was reunited with his mother in the parking lot of a big-box store. I don’t remember whether this essay focused on specific skills or coping mechanisms that he gained from his ordeal. I remember only the bliss of the parent-and-child reunion in that uninspiring setting. If I were making a case to an admissions officer, I would suggest that simply being able to convey that experience demonstrates the kind of resilience that any college should admire.
The essays that have stayed with me over the years don’t follow a pattern. There are some narratives on very predictable topics — living up to the expectations of immigrant parents, or suffering from depression in 2020 — that are moving because of the attention with which the student describes the experience. One girl determined to become an engineer while watching her father build furniture from scraps after work; a boy, grieving for his mother during lockdown, began taking pictures of the sky.
If, as Lorrie Moore said, “a short story is a love affair; a novel is a marriage,” what is a college essay? Every once in a while I sit down next to a student and start reading, and I have to suppress my excitement, because there on the Google Doc in front of me is a real writer’s voice. One of the first students I ever worked with wrote about falling in love with another girl in dance class, the absolute magic of watching her move and the terror in the conflict between her feelings and the instruction of her religious middle school. She made me think that college essays are less like love than limerence: one-sided, obsessive, idiosyncratic but profound, the first draft of the most personal story their writers will ever tell.
Nell Freudenberger’s novel “The Limits” was published by Knopf last month. She volunteers through the PEN America Writers in the Schools program.
- Open access
- Published: 08 May 2024
The digital transformation in pharmacy: embracing online platforms and the cosmeceutical paradigm shift
- Ahmad Almeman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6521-9463 1
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition volume 43 , Article number: 60 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
437 Accesses
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
In the face of rapid technological advancement, the pharmacy sector is undergoing a significant digital transformation. This review explores the transformative impact of digitalization in the global pharmacy sector. We illustrated how advancements in technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and online platforms are reshaping pharmacy services and education. The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the growth of online pharmacy platforms and the pivotal role of telepharmacy and telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, it discusses the burgeoning cosmeceutical market within online pharmacies, the regulatory challenges faced globally, and the private sector’s influence on healthcare technology. Conclusively, the paper highlights future trends and technological innovations, underscoring the dynamic evolution of the pharmacy landscape in response to digital transformation.
Introduction
Digital technology is driving a massive shift in the worldwide pharmacy industry with the goal of improving productivity, efficiency, and flexibility in healthcare delivery. In the pharmacy industry, implementing digital technologies like automation, computerization, and robotics is essential to cutting expenses and enhancing service delivery [ 1 ]. With a predicted 14.42% annual growth rate, the digital pharmacy market is expanding significantly and is expected to reach a market volume of about $35.33 billion by 2026. This expansion reflects the pharmacy industry’s growing reliance on and promise for digital technologies [ 2 ].
Pharmacy services have always been focused on face-to-face communication and paper-based procedures. However, the drive for more effective, transparent, and patient-centered healthcare is clear evidence of the growing need for digital transformation. Breakthroughs like mobile communications, cloud computing, advanced analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping the healthcare sector. These breakthroughs have the potential to greatly improve patient care and service delivery, as demonstrated in other industries including banking, retail, and media [ 3 ].
In the pharmacy industry, a number of significant factors are hastening this digital transition. Important concerns include the desire for cost-effectiveness, enhanced patient care, and more transparency and efficiency in medication development and manufacture. This change has been made even more rapid by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has highlighted the necessity for digital solutions to address the difficulties associated with providing healthcare in emergency situations [ 4 ].
In terms of specific technologies being adopted, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing a pivotal role. The McKinsey Global Institute estimates that AI in the pharmaceutical industry could generate nearly $100 billion annually across the U.S. healthcare system. The use of AI and machine learning enhances decision-making, optimizes innovation, and improves the efficiency of research and clinical trials. This results in more effective patient care and a more streamlined drug development process [ 5 ].
The digital transformation in the pharmacy sector represents a pivotal shift in the delivery and experience of healthcare services. This evolution is more than a transient trend; it’s a fundamental alteration in the healthcare landscape [ 6 ]. The adoption of digital technologies is reshaping aspects of healthcare, including patient engagement and medication adherence, leading to enhanced healthcare outcomes. Research indicates that digital tools in pharmacy practices have resulted in more individualized and efficient patient care. Telehealth platforms, exemplified by companies like HealthTap, are being increasingly incorporated by pharmacies to augment patient care via technological solutions. The contribution of digital health technology to medication adherence is notable, employing a variety of tools such as SMS, mobile applications, and innovative devices like virtual pillboxes and intelligent pill bottles. These advancements are pivotal in addressing the critical issue of medication nonadherence in healthcare. Furthermore, digital health tools are empowering pharmacists with expanded clinical responsibilities, particularly in the management of chronic diseases like diabetes, where apps and smart devices provide essential features such as blood glucose tracking and medication reminders. This comprehensive integration of digital health into pharmacy practice signifies a transformative era in healthcare delivery and patient management [ 7 ].
Online platforms are being used increasingly by the pharmaceutical sector and educational institutions to improve efficiency, flexibility, and accessibility. The telepharmacy program at CVS Pharmacy is an example of how telepharmacy services, which provide remote counseling and prescription verification, bring pharmaceutical care to underprivileged communities [ 8 ]. Prescription accuracy and drug management are enhanced by e-prescribing software like Epic’s MyChart and digital health apps like Medisafe [ 9 ; 10 ]. Blockchain technology is also being investigated for transparent and safe supply chain management. Continuous learning and professional networking are made possible in education by Virtual Learning Environments (VLEs) like Moodle [ 11 ], simulation software like SimMan 3G Plus [ 12 ], Continuing Professional Development (CPD) platforms like the American Pharmacists Association [ 13 ], and online conference platforms, as shown in Fig. 1 . While these platforms offer significant benefits like enhanced access and cost-effectiveness, they also present challenges, including addressing the digital divide and ensuring the quality and credibility of online services to maintain professional standards and patient safety.
In this review, we summarized the digital transformation in the pharmacy sector, emphasizing the integration of online platforms and the emerging significance of cosmeceuticals. We discussed the global shift towards digital healthcare, including telehealth and online pharmacy services, and how these changes have been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The paper also examined the impact of digital technologies on pharmacy practice and education, with a focus on telepharmacy services, e-prescribing software, and digital health apps. Additionally, it addresses the challenges and opportunities presented by this transformation, including regulatory and safety concerns, and the need for continuous professional development in the digital era.
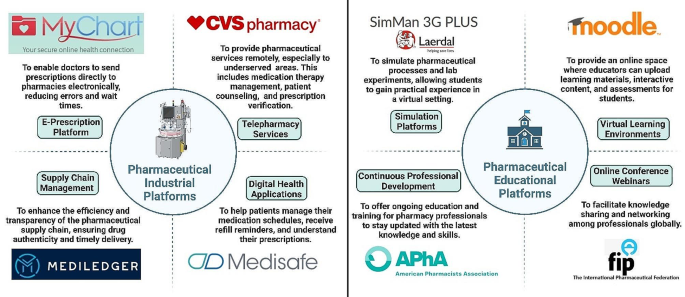
Comprehensive overview of different platforms in the pharmaceutical industry and education illustrating purposes and exemplary cases
The global impact of online pharmacy platforms
In recent years, the landscape of pharmacy practice and education has undergone a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and catalyzed by the global COVID-19 pandemic. A study highlighting the increasing consumer trust in online medication purchases pre, during, and post-pandemic reveals a shift in consumer behavior towards online pharmacies [ 14 ]. This trend underscores a greater reliance on these platforms, where the perceived benefits significantly outweigh the perceived risks, indicating a positive reception and growing trust in digital healthcare solutions.
The adoption of telehealth, including telepharmacy, exemplifies this shift. In the United States, patient adoption of telehealth services surged from 11% in 2019 to 46%, with healthcare providers expanding their telehealth visits [ 15 ]. This shift is a reflection of how adaptable the healthcare sector is to digital platforms and how customer acceptance is increasing. The epidemic has also served as a catalyst, hastening the creation and uptake of online telepharmacy services throughout the world. The “new normal” has forced the addition of new platforms to support established sources of health information. The creation and evaluation of an online telepharmacy service in the Philippines during the pandemic serves as an example of this, demonstrating how quickly the global pharmacy industry adopted digital solutions. These services are essential for providing and elucidating pharmaceutical information within the context of primary healthcare delivery; they are not merely supplementary [ 16 ].
Simultaneously, pharmacist-led companies such as MedEssist and MedMehave, innovated digital platforms to facilitate services like flu shots or COVID-19 tests, reflecting a move towards customer-centric, digital-first services [ 17 ]. This transition enhances convenience and access to care but also introduces significant regulatory challenges. As the growth of online medicine sales disrupts traditional pharmacy markets, navigating these challenges becomes crucial for maintaining patient safety, quality standards, and fostering a trustworthy online healthcare environment [ 18 ].
Parallel to the practice changes, educational platforms for pharmacy have also evolved, especially under the impetus of the pandemic. These platforms have integrated a mix of traditional and student-centered teaching methodologies, including remote didactic lectures and on-site experiential training. The implementation of blended learning approaches, which combine remote lectures with on-site laboratory classes, reflects a broader educational trend towards hybrid models. This approach aims to leverage the advantages of both online and traditional methods, offering a more flexible and potentially more effective educational experience [ 19 ].
It takes more than just implementing new tools to integrate educational technology into pharmacy education, it also requires understanding how these technologies affect instruction and student learning. To effectively improve the educational experience, their utilization must have a purpose. There is an increasing amount of scholarly interest in this field, as evidenced by systematic reviews of the effects of new technologies on undergraduate pharmacy teaching and learning [ 20 ]. These digital platforms will probably become more significant in the future of pharmacy education, helping to mold the profession and guaranteeing that pharmacists are equipped to fulfill the ever-changing demands of the healthcare system. This development is indicative of a larger trend in the healthcare industry toward a more flexible, patient-focused, and technologically advanced environment [ 21 ].
Digital transformation in global healthcare
The recent advancements in digital transformation within global healthcare are significantly reshaping the landscape of healthcare and pharmacy services. These transformations are largely driven by the integration of digital technologies, which are redefining the tools and methods used in health, medicine, and biomedical science, ultimately aiming to create a healthier future for people worldwide [ 22 ]. In a 2018 report [ 23 ], Amazon’s potential entry into the $500 billion U.S. pharmacy market, the second-largest retail category, through mail-order and online pharmacies was highlighted as a significant industry disruptor. With licenses in at least 12 states in the US and a strategy focused on bypassing middlemen, Amazon’s historical success positions it to transform the pharmacy landscape, promising enhanced efficiency and cost savings for consumers.
One of the critical areas identified in recent research is the establishment of five priorities of e-health policy making: strategy, consensus-building, decision-making, implementation, and evaluation. These priorities emerged from stakeholders’ perceptions and are crucial for the effective integration and adoption of digital health technologies [ 24 ]. This holistic approach is increasingly relevant for scholars and practitioners, suggesting a focus on how multiple stakeholders implement digital technologies for management and business purposes in the healthcare sector [ 25 ]. The deployment of technological modalities, encompassed within five distinct clusters, can facilitate the development of a digital transformation model. This model ensures operational efficiency through several dimensions: enhanced operational efficacy by healthcare providers, the adoption of patient-centered methodologies, the integration of organizational factors and managerial implications, the refinement of workforce practices, and the consideration of socio-economic factors [ 25 ].
Studies focusing on value creation through digital means suggest healthcare as a consumer-centric realm ripe for center-edge transformations, characterized by self-service and feedback cycles. These transformations are vital in addressing inherent tensions between patients and physicians, steering the focus towards value co-creation and service-dominant logic [ 26 ]. Participatory design and decision-making approaches are emphasized for enhancing health information technology’s performance and institutional healthcare innovation. Such approaches are particularly crucial in developing national electronic medical record systems and improving chronic disease treatment through electronic health records. Additionally, telehealth research integrates patients’ perceptions, contributing to the understanding of technology, bureaucracy, and professionalism within healthcare [ 27 ].
The impact of health information technology (HIT) on operational efficiencies is profound. Empirical studies, such as those by Hong and Lee [ 28 ], Laurenza et al. [ 29 ], and Mazor et al. [ 30 ], demonstrate positive correlations between HIT and patient satisfaction, quality of care, and operational efficiency. However, challenges remain, as Rubbio et al. [ 31 ] highlight deficiencies in resilience-oriented practices for patient safety. Organizational and managerial factors in digital healthcare transformation also receive significant attention. Hikmet et al. [ 32 ] and Agarwal et al. [ 33 ] investigate the role of organizational variables and barriers in HIT adoption, whereas Cucciniello et al. [ 34 ] delve into the interdependence between implementing electronic medical records (EMR) systems and organizational conditions. Further, Eden et al. [ 35 ] and Huber and Gärtner [ 36 ] explore workforce adaptations and the implications of health information systems in hospitals that can increases transparency of work processes and accountability. Lastly, examining healthcare financialization and digital division provides an international perspective, contrasting the regulated environment in the EU with the US’s use of online medical crowdfunding as a potential solution to reduce bankruptcy [ 37 ; 38 ]. Collectively, these studies suggest a comprehensive model where stakeholders leverage digital transformation for management, enhancing operational efficiency in healthcare service providers.
Marques and Ferreira [ 39 ] performed a systematic literature review of digital transformation in healthcare, spanning the period from 1973 to 2018. Utilizing the SMARTER (Simple Multi-attribute Rating Technique Exploiting Ranks) method, 749 potential articles were analyzed, culminating in the prioritization and selection of 53 articles for detailed examination. The literature was organized into seven thematic areas: (1) Integrated management of IT in healthcare, (2) Medical images, (3) Electronic medical records, (4) IT and portable devices in healthcare, (5) Access to e-health, (6) Telemedicine, and (7) Privacy of medical data. It was observed that the predominant focus of research resides in the domains of integrated management, electronic medical records, and medical images. Concurrently, emerging trends were identified, notably the utilization of portable devices, the proliferation of virtual services, and the escalating concerns surrounding privacy. See Fig. 2 for visual representation of multifaceted digital transformation in healthcare.
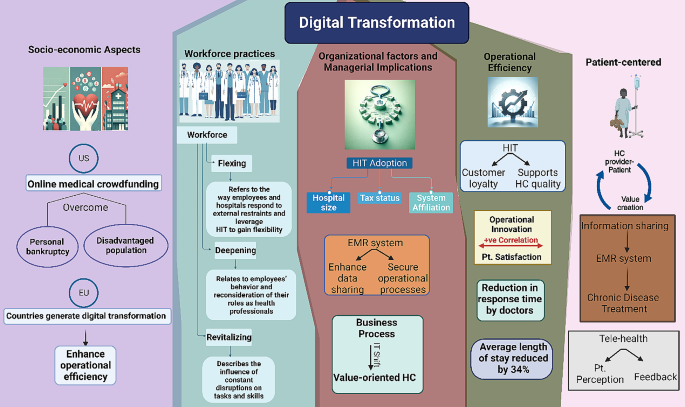
Visual representation of multifaceted digital transformation in healthcare: a synthesis of provider-patient dynamics, HIT impact, and strategic management. HIT; health information technology, HC; healthcare, EMR; electronic medical records. IT; information technology, Pt.; patient
Telehealth and online pharmacy advancements in pandemic management
In the realm of online pharmacies and telehealth, digital health technologies have been instrumental in managing the COVID-19 pandemic through surveillance, contact tracing, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. These technologies ensure that healthcare, including pharmacy services, is delivered more effectively, addressing the challenges of accessibility and timely care. The role of telemedicine and e-pharmacies, in particular, has been emphasized in improving access to care worldwide. By enabling remote consultations and drug delivery, these platforms are making healthcare more accessible, especially in regions where traditional healthcare infrastructure is limited or overstretched [ 40 ].
The Canadian Virtual Care Policy Framework advocates for the swift adoption and integration of virtual care, propelled by the COVID-19 pandemic. It emphasizes enhancing access and quality, ensuring equity and privacy, and devising appropriate remuneration models, employing a collaborative, patient-centered approach while addressing digital disparities. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Canadian provinces and territories rapidly adopted virtual health care, leading to 60% of visits being virtual by April 2020, up from 10 to 20% in 2019. However, these implementations were often temporary and not fully integrated into healthcare systems. By August 2020, virtual visits decreased to 40%, with variations across regions, while provinces and territories used temporary billing codes for these services. The framework’s “Diagnostique” provides a thorough analysis of policy enablers and strategies for virtual care, underscoring the need for comprehensive policy and partnership engagement [ 41 ]. In the context of digital transformation in pharmacy, the Hospital News article outlines the application and infrastructure of telepharmacy services in Canada, highlighting the geographical challenges and the early adoption of telepharmacy in certain regions since 2003. It notes the use of various technologies like Medication Order Management, Videoconferencing, and Remote Camera Verification. Although lacking specific quantitative data, the article underscores the necessity for expanded telepharmacy services to ensure uniform care quality across diverse locations [ 42 ].
Similarly, Telehealth offers extensive resources for patients and providers in the United States, emphasizing programs like the Affordable Connectivity Program and Lifeline to facilitate access. The Health Resources and Services Administration enhances telehealth through support services, research, and technical assistance, reflecting a significant outreach impact [ 43 ]. The Office for the Advancement of Telehealth (OAT) under Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) works to improve access to quality health care through integrated telehealth services in the US. It supports direct services, research, and technical assistance, with over 6,000 telehealth technical assistance requests sent to Telehealth Resource Centers and approximately 22,000 patients served [ 44 ].
Internationally, In the UK, the National Health Service (NHS) spearheads digital health and care, providing significant innovation opportunities through vast data management. Support for digital health spans various stages, from discovery with organizations like Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and Intelligent Data Analysis (IDA) research group, to development with networks such as Catapults and CPRD, and delivery with entities like the Academic Health Science Networks (AHSNs) and DigitalHealth.London. Regulatory bodies like the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) and NICE ensure safety and efficacy. The collaborative ecosystem involves academic, healthcare, and industry stakeholders, aiming to enhance health and care services through technology and innovation [ 45 ].
In Australia, the government’s investment of over $4 billion into COVID-19 telehealth measures has facilitated universal access to quality healthcare. This initiative has provided over 85 million telehealth services to more than 16 million patients, with approximately 89,000 healthcare providers engaging in this service delivery. From 1 January 2022, telehealth services, initially introduced in response to COVID-19, will become an ongoing part of Medicare. This will allow eligible patients across Australia continued access to general practice (GP), nursing, midwifery, and allied health services via telehealth, deemed clinically appropriate by the health professional [ 46 ].
European nations such as the Netherlands, Austria, and Italy are at the forefront of implementing cross-organizational patient records, significantly enhancing telehealth communication and facilitating cross-border healthcare. The role of strong government support in advancing telehealth is pivotal. Ursula von der Leyen, the President of the European Commission, has been a prominent advocate for eHealth. She proposed the establishment of a European Health Data Space to streamline health data exchange across member states. France, a leader in telehealth legislation for nearly a decade, has pioneered a public funding scheme for tele-expertise at a national scale. Despite these advancements, challenges like legislative barriers and the lack of consistent political direction continue to impede progress in the telehealth domain [ 47 ].
The Asia-Pacific region anticipates a surge in telehealth adoption driven by digital demand and pandemic-induced behavioral changes, while South East Asia exhibits widespread telehealth growth across healthcare aspects [ 48 ]. The telehealth adoption across the Asia-Pacific region has shown remarkable growth between 2019 and 2021 and is projected to continue rising by 2024. China’s adoption nearly doubled to 47% and is expected to reach 76%. Indonesia’s usage more than doubled to 51%, with a forecast of 72%. Malaysia and the Philippines both anticipate reaching a 70% adoption rate, increasing from 30% to 29%, respectively. India’s adoption is projected to more than double to 68%, while Singapore, which had a significant increase from 5 to 45%, is expected to achieve a 60% adoption rate. This trend indicates a robust uptake of telehealth services in the region [ 48 ].
Global telemedicine and E-pharmacy policy dynamics
In the context of telemedicine and e-pharmacy regulations within South East Asia, a notable distinction emerges with Singapore, Malaysia, and Indonesia being the only countries to have formalized legal frameworks governing both telemedicine practices and the dissemination of electronic information. In these countries, tele-consultation is restricted to patients already under the care of healthcare practitioners or as part of ongoing treatment, specifically in Singapore and Malaysia. Additionally, for scenarios requiring more intensive medical intervention, such as new referrals, emergency cases, or invasive procedures, both Malaysia and Indonesia mandate physical presence and face-to-face consultations, emphasizing a cautious and regulated approach to remote healthcare. In Malaysia, the regulations further stipulate that online prescriptions, excluding narcotics and psychotropic substances, are permissible solely under the continuation of care model, reflecting a judicious use of digital prescription services [ 49 ].
In Central and Eastern Europe (CEE), telemedicine has experienced substantial growth, primarily catalyzed by the COVID-19 pandemic, which necessitated rapid advancements in technology and alterations in healthcare practices. The region’s robust digital infrastructure, coupled with the innovative drive of local companies and the challenges posed by an aging demographic, has significantly contributed to this expansion. According to the European Commission’s Market Study on Telemedicine, the global telemedicine market was projected to grow annually by 14% by 2021, a rate that was likely surpassed due to the pandemic’s impact. More specifically, the Europe Telehealth Market, valued at US $6,185.4 million in 2019, is anticipated to witness an annual growth rate of 18.9% from 2020 to 2030. This trend underscores the increasing reliance on and potential of telemedicine in addressing healthcare needs in the CEE region [ 50 ].
In the Middle East, telehealth and telepharmacy, have seen varied degrees of adoption and progress. Despite attempts to reform healthcare delivery in the region, the progress of telemedicine has been somewhat slow, with certain expectations yet to be fully realized. However, there has been notable development in the use and adoption of these technologies [ 51 ]. In a survey comparing the utilization of digital-health applications in Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), it was observed that a higher percentage of Saudi participants have utilized online pharmacy services (48%) compared to the UAE (36%). Conversely, awareness of teleconsultation services without prior use was higher in the UAE (43%) than in Saudi Arabia (35%). Retention data indicates that a significant proportion of users in both countries continue to engage with these services, with 80% of Saudi participants and 71% of UAE participants using teleconsultations at varying frequencies. Notably, a substantial majority of users in Saudi Arabia reported regular use of online pharmacies (90%), slightly higher than the UAE (78%), reflecting robust ongoing engagement with these digital health modalities. Notably, consumer adoption of telehealth products is primarily driven by time savings (48%) and convenience (47%), with 24-hour accessibility and efficacy both influencing 34% of users. Affordability and personal recommendations are also notable factors, while a wide range of options and quality are lesser but relevant considerations [ 52 ].
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, a cross-sectional study was conducted among 391 licensed community pharmacists in the United Arab Emirates to assess the adoption and impact of telepharmacy services. The study revealed a predominant use of telepharmacy services, particularly via phone (95.6%) and messaging applications (80.0%). The findings highlighted that pharmacies with more pharmacists and those operating as part of a group or chain were more likely to implement a diverse range of telepharmacy services. The study identified significant barriers to telepharmacy adoption in individual pharmacies, including limited time, inadequate training, and financial constraints. There was a noticeable shift in service provision during the lockdown, with an increased reliance on telepharmacy, especially among pharmacies serving 50–100 patients per day. However, a reduction in services such as managing mild diseases and selling health products was observed during the lockdown period. The study concluded that telepharmacy played a pivotal role in supporting community pharmacies during the pandemic, with its expansion facilitated by the UAE’s advanced internet infrastructure, supportive health policies, and widespread digital connectivity [ 53 ]. Collectively, these insights reflect a global shift towards integrating and enhancing telehealth services as a response to emerging healthcare needs and technological advancements.
Unni et al. [ 54 ] provided an extensive review of telepharmacy initiatives adopted globally during the COVID-19 pandemic. Predominantly, virtual consultations were utilized to enable at-risk patients and others to remotely access pharmacists, thereby monitoring chronic illnesses, optimizing medication usage, and providing educational support [ 55 ]. Home delivery of medicines was widely implemented to decrease the necessity for in-person visits and mitigate exposure risks [ 56 ]. Additionally, patient education was prioritized to ensure effective management of health conditions from a distance [ 57 ]. Notably, a network of hospitals in China developed cloud-pharmacy care, allowing patients to consult pharmacists via text and the internet, while Spain utilized information and communication technologies for remote pharmaceutical care [ 58 ; 59 ]. Zero-contact pharmaceutical care, introduced in China, facilitated online medication consultations, eliminating direct contact [ 60 ]. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and other regions adapted new e-tools and teleprescriptions to enhance service accessibility [ 61 ]. The U.S. focused on credentialing pharmacists for telehealth to ensure competent service provision, and New Zealand implemented hotline numbers for phone consultations to further reduce physical visits [ 62 ; 63 ]. These initiatives reflect a significant shift towards innovative, technology-driven solutions in pharmaceutical care during a global health crisis. Refer to Fig. 3 for a graphical depiction of the worldwide distribution and applications of telepharmacy initiatives.
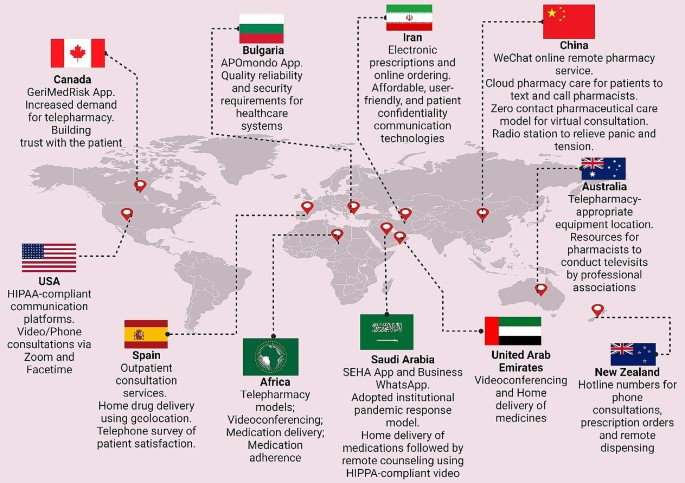
The global distribution of telepharmacy programs with an analysis of geographical distribution, technological applications, and associated benefits
Tracing the Private Sector’s Impact on Healthcare’s Technological Transformation
The role of the private sector in the fourth industrial revolution.
The World Economic Forum underscores the private sector’s leading role in digital inclusion and the acceleration of actions pertinent to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This revolution affects economies, industries, and global issues profoundly, indicating the private sector’s critical role in driving technological advancements and digital platforms that deliver impactful healthcare solutions [ 64 ].
Mapping digital transformation in healthcare
A comprehensive analysis performed by Dal Mas et al. [ 65 ] meticulously maps the intricate terrain of digital transformation in healthcare, spotlighting the private sector’s instrumental role. Initially, the investigation encompassed an extensive array of diverse studies, leading to the identification of five main areas of digital technologies: smart health technologies, data-enabled and data collection technologies, Industry 4.0 tools and technologies, cognitive technologies, and drug & disease technologies. These domains frame the future research pathways, primarily steered by the private sector’s innovative drive. A significant proportion of the literature addresses healthcare broadly, suitable for both private and public sectors, yet a notable segment specifically focuses on the private sector’s endeavors, with a pronounced emphasis on the pharmaceutical domain [ 66 ; 67 ].
Public-private partnerships in healthcare delivery
The highlighted technologies, including digital platforms and telemedicine, exemplify the private sector’s trailblazing contributions to digital healthcare advancements. For instance, public-private partnerships (PPP) in India have emerged as a pivotal model for realizing universal healthcare (UHC), especially against the backdrop of acute healthcare shortages and urban-rural divides. Notably, mega PPP projects have successfully deployed technology-enabled remote healthcare (TeRHC), demonstrating its feasibility and impact in reaching isolated communities. These initiatives, overcoming various challenges, serve as a compelling example for global adoption, underscoring the transformative role of PPP in healthcare delivery [ 68 ].. Furthermore, a considerable majority of the literature in telemedicine underscores the necessity for profound research implications, yet a significant minority suggests policy implications [ 69 ; 70 ], reflecting a complex synergy between the private and public sectors in sculpting the digital healthcare framework [ 71 ]. This synthesis underscores the private sector’s critical influence in propelling the digital transformation in healthcare, charting a course that progressively fuses technological innovation with healthcare provision.
A study highlights Indonesia’s strategic initiatives to capitalize on telehealth business opportunities, driven by the Ministry of Research and Technology’s robust support for Technology-Based Start-up Company schemes [ 72 ]. With a demographic boon of 298 million from 2020 to 2024, escalating non-communicable diseases (71%), and a growing base of 222.4 million JKN participants, the stage is set for transformative growth. Despite a critical shortage of health workers (0.4 doctors per 1000 population), the enthusiasm for telemedicine is evident, with 71% satisfaction in hospital telemedicine and 32 million active telehealth users. The Ministry’s foresight in fostering technology start-ups, exemplified by the TEMENIN platform with its 11 health platforms, is steering Indonesia towards a future where high-quality healthcare is accessible and sustainable.
Lab@AOR: a model for PPPs in healthcare sector
The “Lab@AOR” initiative stands as a paradigmatic example of PPPs effectuating digital transformation within the healthcare sector. This strategic collaboration, between the University Hospital of Marche and Loccioni [ 73 ], a private entity, underscores the capacity of PPPs to navigate intricate challenges, stimulate international cooperation, and contribute to the development of sustainable, patient-centric healthcare solutions. Specifically, Lab@AOR was instituted to confront the nuanced challenges associated with the robotization of healthcare service delivery, highlighting the initiative’s role in fostering technological advancement through public and private sector synergy [ 74 ]. The project illustrates the evolution of Lab@AOR through three main phases: the pioneering stage, where groundwork for collaboration was laid; the nurturing stage, where collaborative exchanges were fostered; and the harvesting stage, wherein the potential of the PPP was fully unleashed. In the pioneering stage, Lab@AOR focused on a critical healthcare service component: the in-hospital preparation of medications for oncological patients. The University Hospital of Marche identified a need for innovation to improve service quality, efficiency, and safety, while Loccioni sought a real-life setting to test and refine its robotized system, APOTECAchemo [ 75 ]. This convergence of needs led to a symbiotic partnership aiming to enhance healthcare delivery through technological advancement.
During the nurturing stage, the partnership expanded the scope of APOTECAchemo to include non-oncological medications and developed additional tools like APOTECAps for manual preparation support. This phase was characterized by intensive collaboration, knowledge sharing, and continuous innovation, demonstrating the dynamic capability of the PPP to adapt and evolve in response to emerging healthcare challenges. The harvesting stage marked the international expansion of Lab@AOR, transforming it from a local initiative to an international community focused on leveraging digitalization and robotization to improve care quality and patient-centeredness. The PPP’s growth was catalyzed by its open perspective and inclusive approach, engaging entities from various cultural and institutional contexts, and fostering a network of 31 nodes across 19 countries and 3 continents.
Advancements in telehealth business models and frameworks
In their investigative study, Velayati et al. [ 76 ] delved into the articulation of emergent business models in telehealth and scrutinized the deployment of established frameworks across a variety of telehealth segments. The research spanned an extensive range of sectors, notably telemonitoring, telemedicine, mobile health, and telerehabilitation, alongside telehealth more broadly. The scope further extended to encompass niche areas such as assisted living technologies, sensor-based systems, and specific fields like mobile teledermoscopy, teleradiology, telecardiology, and teletreatment, presenting a thorough analysis of the telehealth landscape. Within the telemedicine and telehealth services sector, Barker et al. [ 77 ] introduced the Arizona Telemedicine Program (ATP) Model, a quintet-layer approach aimed at efficiently distributing telemedicine services throughout Arizona. Complementing this, Lee and Chang [ 78 ] proposed a four-component model specifically tailored for mobile health (mHealth) services pertaining to chronic kidney disease, focusing on offering a cost-effective platform for disease support and management. In the realm of telemonitoring, Dijkstra et al. [ 79 ] utilized the Freeband Business Blueprint Method (FBBM), which includes service, technological, organizational, and financial domains, to facilitate multiple telemonitoring services. Furthermore, the systemic and economic differences were explored in care coordination through Business to customer (B2C) and business (B2B) models for telemonitoring patients with chronic diseases, with the B2C model’s economic advantages were highlighted [ 80 ].
General telemedicine frameworks also received attention. Lin et al. [ 81 ] constructed a six-component framework analyzing major telemedicine projects in Taiwan, while Peters et al. [ 82 ] developed the CompBizMod Framework in Germany, encompassing value proposition, co-creation, communication and transfer, and value capture, designed to evaluate and enhance competitive advantages in telemedicine. In the specialized field of telecardiology, a comprehensive nine-component sustainable business model was crafted to facilitate mutual benefits for service providers and patients. This model emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach in ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of healthcare delivery within this domain [ 83 ]. Meanwhile, Mun et al. [ 84 ] presented a suite of five teleradiology business models aimed at providing effective, high-quality, and cost-efficient diagnoses.
The teletreatment sector saw innovative models from Kijl et al. [ 85 ], who designed a model for treating patients with chronic pain, focusing on the interrelation of components in the value network and the role of information technology. Complementarily, Fusco and Turchetti [ 86 ] introduced four models for telerehabilitation post-total knee replacement, emphasizing partnerships between care units and equipment suppliers to reduce costs and waiting lists. The mHealth and assisted living technology sector witnessed the introduction of a wearable biofeedback system model by Hidefjäll and Titkova [ 87 ], which employed Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas and focused on a comprehensive commercialization process. Additionally, Oderanti and Li [ 88 ] presented a seven-component sustainable business model for assisted living technologies, aimed at encouraging older individuals to invest in eHealth services while reducing the pressure on health systems. These diverse clusters and models reflect the multifaceted nature of telehealth, each tailoring its approach to meet the unique demands of its domain. They collectively aim to optimize service delivery, stakeholder involvement, cost efficiency, and patient care quality, marking significant strides in the ongoing evolution of digital healthcare.
Challenges and biases in healthcare technology
One key aspect is the emergence of novel medical technologies and their potential biases. These biases are often a result of insufficient consideration of patient diversity in the development and testing phases. For example, disparities in the performance of medical devices like pulse oximeters among different racial groups have been observed, potentially due to a lack of diverse representation in clinical trials. This indicates a tendency for the development of healthcare technologies that may not adequately serve all patient populations [ 89 ]. A study on the profitability and risk-return comparison across health care industries highlights the use of return on equity (ROE) as a measure of profitability from a shareholder’s perspective. This measure combines profit margin, asset utilization, and financial leverage. The study analyzed financial data of publicly traded healthcare companies, providing insights into the financial dynamics of the healthcare sector. It revealed that while companies like Pfizer Inc. and UnitedHealth Group reported similar profitability, they had substantial differences in profit margin and asset utilization, indicating diverse financial strategies within the healthcare sector. This study underscores the complexity of financial performance in healthcare, where profitability measures need to be balanced with risk assessment and the broader impact on healthcare provision [ 90 ].
Additionally, an article discusses the benefits, pitfalls, and potential biases in healthcare AI. It emphasizes that as the healthcare industry adopts AI, machine learning, and other modeling techniques, it is seeing benefits for both patient outcomes and cost reduction. However, the industry must be mindful of managing the risks, including biases that may arise during the implementation of AI. Lessons from other industries can provide a framework for acknowledging and managing data, machine, and human biases in AI. This perspective is crucial in understanding how the integration of advanced technologies in healthcare can be influenced by the drive for profitability and efficiency, possibly at the expense of equitable and patient-centered care [ 91 ; 92 ].
Cosmeceuticals in the online pharmacy market
Cosmeceuticals, a term derived from the combination of cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, refer to a category of products that are formulated to provide both aesthetic improvements and therapeutic benefits. These products, typically applied topically, are designed to enhance the health and beauty of the skin, going beyond the mere cosmetic appearance. The exploration of cosmeceuticals in the online pharmacy market reveals a multifaceted and rapidly expanding industry. Bridging the gap between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, they form a significant portion of the skincare industry. Cosmeceuticals are formulated from various ingredients, with their main categories being constantly discussed and analyzed in the scientific community [ 93 ]. They have taken a considerable share of the personal care industry globally, constituting a significant part of dermatologists’ prescriptions worldwide [ 94 ]. This surge is further fueled by increasing consumer demand for effective and safe products, including anti-aging skincare cosmeceuticals, a need which has been intensified by concerns over pollution, climate change, and the COVID-19 pandemic [ 95 ].
The global cosmeceuticals market is experiencing robust growth. Valued at USD 56.78 billion in 2022, it’s projected to expand to USD 95.75 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.45%. This growth trajectory is propelled by the innovative integration of bioactive ingredients known for their medical benefits [ 96 ]. Another report confirms this upward trend, indicating the market was worth $45.56 billion in 2021 and is on a path of significant growth to USD 114 billion by 2030. The global disease burden is significantly impacted by various skin diseases, with dermatitis, psoriasis, and acne vulgaris among the most prevalent, contributing 0.38%, 0.19%, and 0.29% respectively. The pervasive nature of these conditions drives a substantial demand for effective treatments, propelling the integration of cosmeceuticals into the online pharmacy market. This integration not only offers convenient access to a range of therapeutic skincare products but also caters to the rising consumer inclination towards self-care and preventive healthcare. As a result, the online availability of cosmeceuticals is not just addressing the immediate needs of individuals suffering from skin conditions but is also reshaping the landscape of personal healthcare by making specialized treatments more accessible and customizable [ 97 ]. See Fig. 4 .
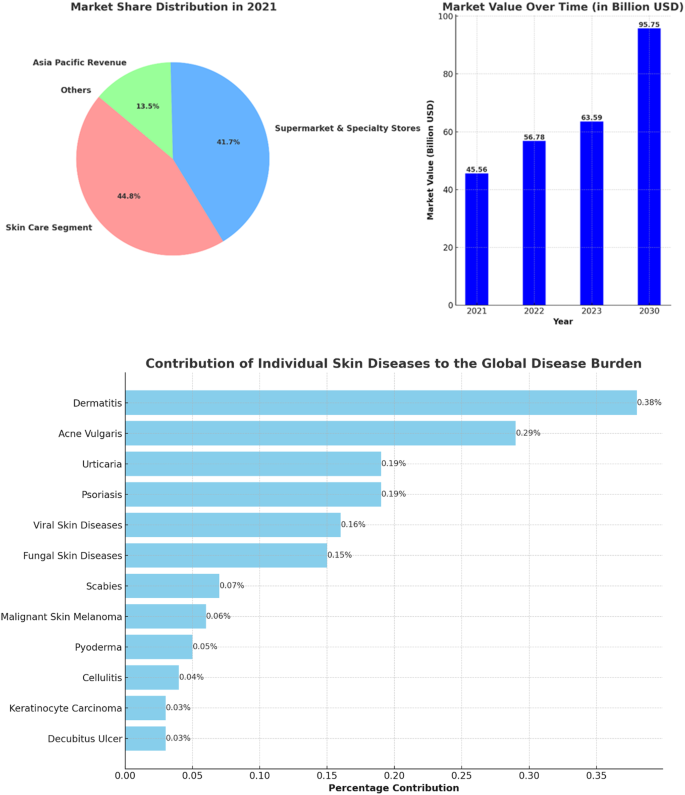
The left panel presents the market share distribution for key segments in the cosmeceuticals industry in 2021, including Skin Care Segment, and Supermarket & Specialty Stores, for Asia Pacific Revenue, with percentages for each category. The right panel displays the market value progression over time from 2021 to the projected value in 2030, with bold numbers indicating the value in billion USD for each year. The lower horizontal bar chart depicts the percentage contribution of various skin diseases to the global disease burden
Several factors are contributing to this expansion of the cosmeceuticals market. The market is driven by innovation in natural ingredients and a significant penetration of internet, smartphone, and social media applications, which attract potential consumer populations and reflect constantly changing consumer behavior [ 98 ]. The cosmeceuticals market’s robust CAGR and revenue share, especially in regions like Asia Pacific, further signify its burgeoning presence and potential within the global market [ 99 ]. Integration into online pharmacies is a key aspect of this market’s evolution, offering easier access to these products for a wider customer base. As the market continues to grow, it’s anticipated that the blend of cosmeceuticals with online pharmaceutical platforms will become increasingly seamless, offering consumers a diverse range of accessible, effective, and beneficial skincare and health products. This integration is likely to be driven by the growing trend of e-commerce and digitalization in healthcare and personal care sectors.
The landscape of online pharmacies, particularly concerning cosmeceuticals, is evolving. While the overall penetration for non-specialty drugs in mail-order and online pharmacies is low, they represent a significant portion of specialty prescription revenues at 37%. Despite this, only 13% of consumers consider these as their primary pharmacy choice, indicating a growing but still emerging market. Strategies are in place to enhance the market appeal of these pharmacies, focusing on speed, convenience, and personalized experiences, such as video telehealth visits, to attract a broader consumer base [ 100 ].
The dissertation “L’Oréal Portugal: A Digital Challenge for the Active Cosmetics Division” authored by Ascenso [ 101 ] provides an in-depth examination of the impact of digital evolution on the Portuguese cosmeceutical sector and its implications for L’Oréal, a significant cosmetics company. It posits that while L’Oréal has foundational digital competencies, the rapidly evolving digital landscape presents a broad spectrum of potential risks and opportunities. The study details the operations of L’Oréal’s Active Cosmetics Division, which manages brands predominantly sold in pharmacies and parapharmacies, and explores the potential repercussions of digitalization on L’Oréal Portugal’s strategic and operational frameworks. Furthermore, the thesis highlights the expanding role of e-pharmacies and the need for legal reforms to facilitate their operation. It discusses the prevalent trends in the cosmetic industry, such as the increasing demand for natural, male-focused, and environmentally friendly products. The dissertation scrutinizes L’Oréal’s strategic pillars, including innovation, acquisition, and regional growth, emphasizing the need for the company to integrate advanced technologies and recalibrate its business methodologies in light of digital progression [ 101 ]. Although L’Oréal has initiated some digital strategies targeting consumers and pharmacies, there’s a recognized need for an intensified focus on digital marketing aimed at clients. An exploratory attempt by L’Oréal to implement an online ordering platform for pharmacies did not meet success, indicating possible industry unreadiness for such advancements. This case study serves as a critical examination of how traditional companies in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics sectors must adapt to the digital age’s challenges and opportunities [ 101 ].
In a collaborative endeavor with L’Oréal, an associated digital agency provided a comprehensive suite of services that encompasses the full management of social media pages, the development of e-commerce websites, the establishment of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms tailored for pharmacies, and the execution of digital campaigns leveraging QR codes, SMS marketing, and newsletters. These digital tools confer a competitive edge, facilitating a deeper comprehension of consumer behavior and the potential to augment value extraction from customer interactions. For the laboratories, particularly those associated with cosmetics, the advantages are twofold: an increase in sell-out figures, thereby enhancing direct sales to end consumers, and a boost in sell-in metrics, reflecting a rise in transactions to pharmacies or wholesalers. The online ordering feature, as noted by João Roma, a manager at La Roche-Posay, could result in a cacophony of processes if laboratories were to individually develop distinct methods. He advocates for the utilization of pre-existing platforms, such as the established e-learning infrastructure, to spearhead ventures into the online marketplace [ 101 ].
A survey conducted specifically for L’Oréal’s e-learning platform, cosmeticaactiva.pt [ 102 ], across the Portuguese landscape garnered responses from 324 participants, comprising 71% general pharmacists, 13% technical assistants, 8% directors, 7% individuals responsible for procurement from laboratories, and 2% beauty/cosmetic advisors. The findings from this survey underscore the pervasive adoption of digital tools within the pharmacy sector: 82% of respondents affirmed the presence of their pharmacies on social media platforms, 80% reported the use of basic management software, 64% indicated the deployment of advanced management systems, 61% were conversant with online ordering systems directed at laboratories, 38% utilized a store locator, 28% had an established website presence, and a smaller segment of 12% offered online shopping facilities.
Another survey conducted within this study to evaluate the significance of dermocosmetic products in pharmacies yielded a mean importance rating of 4.38 out of 5, indicating that a majority of pharmacists consider these products to be highly important to their business operations. Factors critical to the differentiation of a proficient laboratory/supplier were innovation and cost-effectiveness, with mean scores of 1.9 and 2.7 respectively, on a scale from 1 (most important) to 5 (least important). A substantial majority of pharmacists, amounting to 81.8%, perceive their pharmacies as beacons of innovation and modernity. Detailed interviews elucidated that digital tools are indispensable in augmenting sales for cosmeceutical products by catalyzing demand—a dynamic not feasible with medicinal products. These tools are paramount in managing customer loyalty, facilitating enhanced communication with existing clients via online and mobile channels. Despite the challenges posed by digitalization, particularly in the realms of logistics and human resources, the management at L’Oréal is well-equipped to swiftly adapt to the evolving business landscape, as evidenced by the proactive adoption and integration of these digital strategies [ 101 ] as illustrated in Fig. 5 .
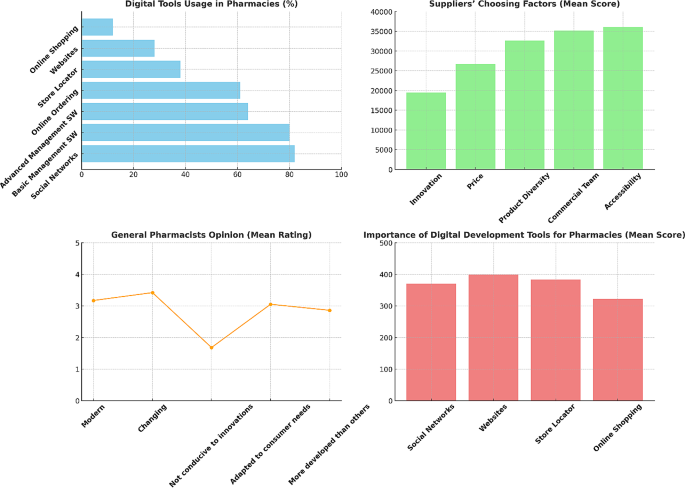
Results from Ascenso [ 101 ] survey assessing digital challenges for L’Oréal in the Portuguese cosmeceutical sector. Digital Tools Usage in Pharmacies (upper left) : the bar chart showing the percentage of respondents using various digital tools in pharmacies. Suppliers’ Choosing Factors (upper right) : the bar chart displaying the mean scores of factors that distinguish a good laboratory/supplier. General Pharmacists Opinion (lower left) : A line chart illustrating the mean ratings of pharmacists’ opinions on whether the pharmaceutical sector is modern, changing, conducive to innovations, adapted to consumer needs, and more developed than other sectors. Importance of Digital Development Tools for Pharmacies (lower right) : A vertical bar chart demonstrating the mean scores for the importance of different digital development tools for pharmacies
The digital transformation strategies, exemplified by companies like L’Oréal, extend beyond the mere targeting of end consumers, encompassing the perspectives of various stakeholders, including retailers. This broadened focus reflects a holistic and integrated approach to digital marketing and customer engagement, indicative of a larger trend within the market. The significance of digital channels in facilitating comprehensive customer interaction and brand development is increasingly recognized. The distinction of organizations such as L’Oréal in their digital initiatives highlights the competitive advantage that can be garnered through innovative digital strategies.
The receptiveness of industry professionals, such as pharmacists, to emerging digital trends, along with the readiness of companies to engage in non-face-to-face sales models, marks a paradigm shift in traditional sales and distribution methods. This shift is reflective of a broader market trend where digital platforms are becoming integral to the customer journey. Furthermore, the potential for online sales in specialized sectors, such as dermocosmetics, and the benefits that organizations derive from the technological advancement of their client base, underscore an escalating acknowledgment of e-commerce and digital tools as crucial elements of a business strategy. This trend, with L’Oréal as a prime example, emphasizes the broader market movement towards digital transformation, not merely as an option but as a necessity for maintaining relevance and competitiveness in an ever-evolving market landscape.
The global regulatory landscape for cosmeceuticals
Sophisticated regulatory legislation and enforcement mechanisms characterize many developed countries such as the USA, EU Member States, Canada, and Japan. These nations, along with influential organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO), significantly shape international market rules and regulations due to their market size and regulatory capacity [ 103 ]. The WHO is particularly noted for its crucial role in setting global standards, with a focus on developing and promoting international standards related to food, biological, pharmaceutical, and similar products [ 104 ]. In contrast to pharmaceuticals, the cosmetic industry necessitates a more advanced international regulatory framework due to consumers’ extensive exposure to these products. The distinction between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals varies significantly across different countries, with the USA employing a voluntary registration system for cosmetics and the EU and Japan requiring mandatory product filings prior to marketing [ 105 ]. Concerns over the safety of pharmaceutical and cosmetic products are highlighted, with an increasing consumer focus on “natural, ecological, and clean” products [ 106 ]. However, the lack of a regulatory framework for these categories underscores the need for more advanced regulations to mitigate health risks.
Intergovernmental cooperation is emphasized, with the US and EU portrayed as dominant players in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries, respectively. Regulatory capacity, which is essential for defining, implementing, and monitoring market rules, varies among countries and markets. This capacity depends on several factors, including staff expertise, statutory sanctioning authority, and the degree of centralization of regulatory authority [ 103 ]. The regulatory systems of the EU and US are explored, focusing on their unique approaches to medicine authorization and regulation. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the EU and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the US serve as pivotal regulatory bodies [ 107 ; 108 ]. The EMA’s centralized procedure and the FDA’s premarket approval process are detailed, along with subsequent postmarket regulatory procedures. For instance, EU and US cosmetic regulations are compared, revealing differences in their approaches and the evolution of the EU’s regulatory landscape through various amendments and directives. In particular, directive 76/768/EC has been superseded by Regulation (EC) N° 1223/2009, serving as the principal regulatory framework for finished cosmetic products in the EU market. This regulation enhances product safety, optimizes the sector’s framework, and eases procedures to promote the internal cosmetic market. Incorporating recent technological advancements, including nanomaterials, it maintains an internationally acknowledged regime focused on product safety without altering existing animal testing prohibitions [ 109 ].
The Eurasian Economic Union’s (EAEU) regulatory framework for medicines and medical devices is detailed, including the legal framework established for regulating the circulation of these products. The conformity assessment methods, such as the EAC Declaration and the State Registration process, are required for manufacturers to demonstrate their products’ compliance with the standards [ 110 ]. Armenia is also part of the EAEU’s legal framework, which aims to unify regulations for the production and registration of pharmaceuticals and medical products by 2025. This unification is expected to reduce administrative costs for manufacturers and improve medicinal products for patients. Despite significant developments in the cosmetics industry, Armenia does not have an extensive regulatory framework for it. Prior to joining the EAEU, the only regulation concerning cosmetic products was the Order of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Armenia on “Hygiene Requirements of the Production and Safety of Perfume-Cosmetic Products.” Since joining the EAEU, Armenia has unified its national legislation with EAEU regulations, but there are challenges and gaps in the direct applicability of the EAEU’s technical regulations in the country [ 111 ].
In the context of the necessity for clear regulatory framework stems from two reasons. Firstly, cosmeceuticals - products straddling cosmetics and drugs - demand intensified regulatory attention. Examples include the 2007 FDA seizure of Jan Marini’s Age Intervention Eyelash, which contained the drug ingredient bimatoprost, and products boasting human stem cell cultured media, which claim rejuvenating effects but may pose safety risks due to minimal oversight [ 112 ]. A noted 1450% increase in FDA warnings (from 4 to 62 letters) between 2007 and 2011 and 2012–2017, with 8 targeting stem cell ingredient promotions, underscores the growing concern [ 113 ]. The FDA’s limited capacity to identify and assess potential drug-adulterated cosmetics raises concerns.
The second aspect focuses on the necessity for a more comprehensive and unbiased scientific and medical perspective in the FDA’s ingredient review process. The Personal Care Products Safety Act proposes a balanced committee formation including industry, consumer, and medical representatives, yet advocates for the inclusion of specialized professionals like chemists, dermatologists, toxicologists, and endocrinologists. Specific ingredients like diazolidinyl urea and quarternium-15, although effective antimicrobials, are flagged for potential skin allergy risks and formaldehyde release. The preservative 4-methylisothiazolinone, banned in Europe for rinse-off products, is noted for increasing allergic contact dermatitis cases in the US [ 114 ]. The lag in US cosmetic regulation compared to the EU is acknowledged, with the Personal Care Products Safety Act considered a significant advancement, albeit in need of further refinement [ 115 ].
The importance of consumer safety in the global regulatory landscape for cosmeceuticals, particularly for products that blur the line between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, is a critical issue due to several key factors. Firstly, the cosmeceutical market is expanding rapidly, driven by new ingredients promising various skincare benefits like anti-aging and photoprotection. This growth necessitates clear regulatory guidelines to ensure that these products are safe and their claims are clinically proven. The FDA, for instance, differentiates between cosmetics and cosmeceuticals based on their intended use, particularly if a product is marketed as a cosmetic but functions in a way that affects the structure of the human body, classifying it as a cosmeceutical [ 116 ].
Secondly, the legal and regulatory distinctions between drugs and cosmetics are significant. Drugs are subject to FDA approval based on their intended use in treating diseases or affecting the body’s structure or function, whereas cosmetics are not. This difference becomes crucial when products are marketed with drug-like claims but are not regulated as drugs, potentially leading to consumer safety issues. For example, botanical cosmeceuticals, which contain natural ingredients like herbal extracts, need thorough evaluation to ensure consistency in therapeutic effects [ 117 ]. Additionally, cosmeceutical manufacturers must be careful with marketing and advertising claims to avoid legal implications. Misleading claims can lead to lawsuits and regulatory actions, as seen in past cases where companies faced consequences for unfounded product claims. Moreover, the FDA advises cosmeceutical manufacturers to follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to reduce the risk of misbranding or mislabeling. These guidelines include production practices and specific warning statement guidelines, emphasizing the importance of substantiating the safety of these products [ 118 ].
The global regulatory landscape for online pharmacy
Online pharmacies pose various risks to consumers, including the potential health hazards from counterfeit or substandard medications and the inappropriate use of prescription drugs. The regulatory landscape for these pharmacies varies significantly across nations, with some countries like the United States implementing specific laws, while others, such as France, have instituted outright bans [ 119 ]. The European Union, for instance, has implemented a mandate effective from 1 July 2015, which requires member states to adhere to legal provisions for a common logo specific to online pharmacies. This is coupled with an obligation for national regulatory authorities to maintain a registry of all registered online medicine retailers, as detailed by the European Medicines Agency [ 120 ]. Furthermore, the sale of certain medications online within the EU is permissible, contingent upon the registration of the pharmacy or retailer with respective national authorities [ 121 ]. Additionally, the Council of Europe’s MEDICRIME Convention introduces an international treaty that criminalizes the online sale of counterfeit medicinal products, enforcing prosecution irrespective of the country in which the crime is perpetrated [ 122 ].
Switzerland presents a unique stance, where Swissmedic strongly advises against the online purchase of medicines due to the high risk of illegal sourcing and poor quality. However, Swiss mail-order pharmacies with a valid cantonal license to operate a mail-order business are exempted from this advisory [ 123 ]. The Swiss Mail-Order Pharmacists Association and its affiliates, such as Zur Rose AG and MediService AG, actively advocate for a modern and equitable regulation of mail-order medicine sales [ 124 ]. The legislative framework is further bolstered by the Federal Act on Medicinal Products and Medical Devices, which regulates therapeutic products to guarantee their quality, safety, and efficacy [ 125 ]. In the Middle East, community pharmacy practice is predominantly governed by national Ministries of Public Health or equivalent governmental entities, with most community pharmacies being privately owned [ 126 ]. The region’s involvement in the Global Cooperation Group, which encompasses various international regulatory bodies like the EMA and USFDA, signifies a collaborative approach towards drug regulatory affairs in the MENA region [ 127 ]. Despite these advances in regulatory collaboration, it is notable that currently no specific regulations have been detected for online purchases from online pharmacies in the Middle East, highlighting a significant area for potential regulatory development. Furthermore, a notable transition is observed in pharmacy education across several Middle Eastern nations, with an inclination towards introducing Pharm.D degrees to replace traditional pharmacy degrees, reflective of evolving educational standards in the pharmaceutical field [ 128 ]. This shift in education parallels the need for updated regulatory frameworks, especially in the context of the burgeoning online pharmacy sector.
Furthermore, Australia permits the sale of both Prescription-Only Medicines (POMs) and Over-the-Counter (OTC) medications online, provided that brick-and-mortar pharmacies comply with all relevant laws and practice standards [ 129 ]. In contrast, South Korea maintains a stringent stance, prohibiting the online sale of both POMs and OTC medicines, with sales confined exclusively to physical stores registered with the Regulatory Authority (RA) [ 130 ]. China, Japan, Russia, Singapore, and Malaysia exhibit a more selective regulatory framework. China and Russia allow the online sale of OTC medicines only, with China imposing additional restrictions on third-party e-commerce platforms and Russia having introduced a draft law in December 2017 to formalize this practice [ 131 ; 132 ]. Japan permits the online sale of certain OTC medicines, explicitly excluding specific substances such as fexofenadine and loratadine [ 133 ]. Similarly, Singapore and Malaysia endorse the online sale of specific OTC medicines only, adopting a “buyers beware” approach to caution consumers about the associated risks [ 134 ; 135 ]. Lastly, the legal landscapes in India and Indonesia remain ambiguous. India’s RA has effectively banned the online sale of medicinal products, yet this prohibition lacks legislative backing. Indonesia, too, grapples with unclear regulations, leaving the legal status of online pharmacies indeterminate [ 136 ].
In response to these risks, several initiatives have been developed to guide and certify online pharmacies. In the United States, LegitScript offers certification to online pharmacies that comply with criteria such as appropriate licensing and registration [ 137 ]. Similarly, the Verified Internet Pharmacy Practice Sites (VIPPS) program, accredited by the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy, ensures pharmacies adhere to licensing requirements in the states where they dispense medications [ 138 ]. Internationally, the Health On the Net Foundation has introduced the HONcode, an ethical standard for health websites globally. This code certifies sites that provide transparent and qualified information. However, due to the absence of international harmonization, the HONcode’s certification is limited to US and Canadian pharmacies verified by VIPPS [ 139 ]. The lack of a harmonized international approach presents significant challenges. Consumers do not have access to a comprehensive, global repository of all certified pharmacies. The diverse certification schemes are not well articulated or interconnected, leading to consumer unawareness about their significance or existence. Moreover, enforcing standards across different legal jurisdictions is complex without a unified agreement. To enhance consumer protection, it is imperative to develop and promote a standardized, minimal international code of conduct for online pharmacies. Such a code would unify requirements and allow all initiatives to clarify their roles under a common framework. Adequate oversight in the borderless online pharmacy market can only be achieved through collaborative efforts. To visualize the infographic of the global regularity landscape for the online pharmacy see Fig. 6 .
Comprehensive representation of the regulatory landscape for global online pharmacies, detailing international and national initiatives, certification programs, and conventions aimed at minimizing risks associated with the purchase of medications via online platforms
Technological innovations and Future trends in global pharmacy
The global pharmacy sector is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the rapid advancement of technological innovations. As the world becomes increasingly digital, the integration of cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain is setting the stage for a new era in pharmaceutical care and management. These advancements promise to revolutionize the industry by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and security, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a more streamlined healthcare experience [ 140 ].
Walgreens, in partnership with Medline, a telehealth firm, has developed a platform for patient interaction with healthcare professionals via video chat. AI’s role extends to inventory management in retail pharmacies, allowing pharmacists to predict patient needs, stock appropriately, and use personalized software for patient reminders. Although not all inventory management software in retail pharmacies utilizes AI, some, like Blue Yonder’s software developed for Otto group, demonstrate the potential of AI in predicting product sales with high accuracy, thus enhancing supply chain efficiency [ 141 ; 142 ]. At the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) Medical Center, robotic technology is employed to improve patient safety in medication preparation and tracking. This technology has prepared medication doses with a notable error-free record and surpasses human capabilities in accuracy and efficiency. It prepares both oral and injectable medicines, including chemotherapy drugs, freeing pharmacists and nurses to focus on direct patient care. The automated system at UCSF receives electronic medication orders, with robotics handling the picking, packaging, and dispensing of individual doses. This system also assembles medications on bar-coded rings for 12-hour patient intervals and prepares sterile preparations for chemotherapy and intravascular syringes [ 143 ].
In the realm of global pharmacy, blockchain technology emerges as a pivotal force, driving advancements across various facets of healthcare and pharmaceuticals. At the forefront of its application is the enhancement of supply chain transparency [ 144 ]. Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures the provenance and legitimacy of medical commodities, offering an unprecedented level of visibility from manufacturing to distribution. This is particularly vital in areas plagued by counterfeit drugs, where systems like MediLedger are instrumental in verifying the legality and essential details of medicines [ 145 ].
The utility of blockchain extends to the implementation of smart contracts — scripts processed on the blockchain that bolster transparency in medical studies and secure patient data management [ 146 ]. These contracts find extensive use in advanced medical settings, as evidenced by a blockchain-based telemonitoring system for remote patients and Dermonet, an online platform for dermatological consultation [ 147 ].
Furthermore, blockchain is revolutionizing patient care through patient-centric Electronic Health Records (EHRs). By decentralizing EHR maintenance, blockchain empowers patients with secure access to their historical and current health records [ 148 ]. Prototypes like MedRec and systems such as MeD Share exemplify how blockchain can provide complete, permanent access to clinical documents and facilitate the sharing of medical data between untrusted parties, respectively, ensuring high information authenticity and minimal privacy risks [ 149 ; 150 ]. In verifying medical staff credentials, blockchain again proves invaluable. Systems like ProCredEx, based on the R3 Corda blockchain protocol, streamline the credentialing process, offering rapid verification while allowing healthcare entities to leverage their existing data for enhanced transparency and assurance about medical staff experience [ 151 ].
The integration of blockchain with Internet of Things devices for remote monitoring marks another leap forward, significantly bolstering data security. By safeguarding the integrity and privacy of patient data collected by these devices, blockchain mitigates the risk of tampering and ensures that only authorized parties can access sensitive information [ 152 ]. Besides, a blockchain-based drug supply chain initiative, PharmaChain, utilizes AI for approaches against drug counterfeit and ensures the drug supply chain is more traceable, visible, and secure. For online pharmacies, this means a more reliable supply chain and assurance of drug authenticity, crucial for maintaining trust and safety [ 153 ].
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the PharmaGo platform has emerged as an innovative solution in Sri Lanka, revolutionizing the delivery of pharmacy services. As traditional pharmacies grapple with the challenges of meeting all customer needs in one location, PharmaGo addresses this by providing a comprehensive online pharmaceutical service. It allows customers to access a wide range of medications through a single platform, reducing the need to visit multiple pharmacies. Utilizing image processing technology, pharmacy owners can accurately identify prescribed medicines, while the system’s predictive analytics forecasts future drug demands, enhancing stock management. Additionally, PharmaGo’s AI-powered medical chatbot offers real-time guidance, ensuring a seamless and efficient customer experience. This platform represents a significant advancement in healthcare accessibility and pharmacy service delivery in the pandemic era [ 154 ]. In the same context, ontology-based medicine information system, enhancing search relevance through a chatbot interface was presented by Amalia et al. [ 155 ]. Addressing conventional search engines’ limitations in interpreting data relationships, it employs semantic technology to represent metadata informatively. The ontology as a knowledge base effectively delineates disease-medicine relationships, with evaluations indicating a 90% response validity from the chatbot, offering a robust reference for medical information retrieval and its semantic associations.
Future trends for the digital transformation of in the pharmaceutical sector
Future trends for the digital transformation of pharmacies globally are heavily influenced by the transformative impact of digital technologies on healthcare delivery. The integration of telemedicine, electronic health records, and mobile health applications is pivotal in enhancing patient care. These technologies are instrumental in improving data sharing and collaboration among healthcare professionals, increasing the efficiency of healthcare services. Additionally, they offer significant potential for personalized medicine through data analytics and play a crucial role in patient engagement and self-management of health. The importance of these technologies in creating a more connected and efficient healthcare system is underscored, marking a significant shift in the global healthcare landscape [ 156 ].
In the pharmaceutical sector, the COVID-19 pandemic has catalyzed a significant shift towards Pharmaceutical Digital Marketing (PDM), particularly for over-the-counter drugs. This shift focuses on utilizing online pharmacies and digital platforms for targeted advertising, directly reaching consumers. The trend towards purchasing OTC drugs online has grown, driven by the convenience and efficiency of digital channels. While PDM faces challenges like regulatory constraints and the need for digital proficiency, it offers substantial opportunities in enhancing customer engagement and precise marketing. The future of PDM is poised to be more consumer-centric, integrating advanced technologies like AI, and emphasizing personalized marketing strategies to strengthen brand engagement and customer interaction [ 157 ].
Artificial intelligence holds immense potential to revolutionize the field of pharmacy, offering numerous benefits that can significantly enhance efficiency and patient care. One of the primary applications of AI in this sector is the automation of routine tasks. By utilizing AI, pharmacies can automate critical processes such as prescription processing, checking for drug interactions, and managing inventory. This automation not only streamlines operations but also minimizes the likelihood of human error, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of pharmacies [ 158 ].
Furthermore, AI can play a pivotal role in personalized medication management. This is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes who require careful management of their insulin dosages, as fluctuations in blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications. AI systems can monitor patients continuously, provide timely reminders for medication intake, and dynamically adjust treatment plans based on individual health data. Such personalized management ensures that patients receive optimal care tailored to their specific needs, potentially improving treatment outcomes. Incorporation of AI into electronic health records presents another significant advancement. By integrating AI with EHRs, healthcare providers can access real-time patient data. This integration empowers healthcare professionals to make more informed care decisions, enhancing the quality of patient care. Moreover, it significantly reduces the likelihood of medication errors, a critical concern in healthcare.
Likewise, AI’s capability to analyze extensive patient data is invaluable. It can identify patterns and trends in medication adherence, detect potential drug interactions, and pinpoint adverse drug reactions. These insights are crucial for healthcare professionals and researchers. By understanding these patterns, they can develop more effective medication adherence strategies and support systems, contributing to better patient outcomes and advancing the overall field of pharmaceutical care.
In the expansive realm of chemical space, the pharmaceutical industry faces the continual challenge of identifying new active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) for diverse diseases [ 159 ]. High throughput screening (HTS), despite its advancements in recent decades, remains resource-intensive and often yields unsuitable hits for drug development. The failure rate of investigational compounds remains high, with a study citing only a 6.2% success rate for orphan drugs progressing from phase I to market approval [ 160 , 161 ].
Machine learning presents a transformative approach to this challenge. It offers an alternative to manual HTS through in silico methodologies. ML-driven drug discovery boasts several advantages: it operates continuously, surpasses the capacity of manual methods, reduces costs by decreasing the number of physical compounds tested, and early identifies negative characteristics of compounds, such as off-target effects and sex-dependent variability [ 162 ].
A substantial advancement in the realm of machine learning has emerged from major pharmaceutical entities, notably AstraZeneca, in conjunction with research institutions. This progress is evidenced by the development of an innovative algorithm that demonstrates both time efficiency and effectiveness in the sphere of drug discovery. The recent introduction of this algorithm significantly enhances the process of determining binding affinities between investigational compounds and therapeutic targets. It surpasses traditional in silico methods in terms of performance. The application of this algorithm underscores the remarkable potential of machine learning in accelerating the identification and development of novel therapeutic agents [ 163 ].
Moreover, the proficiency of machine learning in managing vast and intricate datasets has rendered it indispensable in research focused on cancer targets, utilizing diverse and extensive datasets. This approach is fundamental in numerous drug discovery initiatives, especially those targeting various forms of cancer. A wide array of ML techniques, ranging from supervised to unsupervised learning, are employed to discern chemical attributes that are indicative of potential therapeutic efficacy against a spectrum of cancer targets. This methodology is crucial in identifying novel compounds that could be effective in cancer treatment, leveraging the rich and complex data available in oncological research [ 164 ].
The digital transformation in the pharmacy sector is significantly reshaping healthcare delivery, driven by the integration of cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence and blockchain. This transformation is marked by a substantial growth in the digital pharmacy market, with a projected annual growth rate of 14.42%, leading to a market volume of approximately $35.33 billion by 2026.
One major aspect of this transformation is the growing reliance on online pharmacy platforms, largely influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic. Consumer trust in online medication purchases has significantly increased, indicating a shift towards digital healthcare solutions. The adoption of telehealth services, including telepharmacy, has surged, with patient adoption in the United States increasing from 11% in 2019 to 46%. This shift towards digital-first services enhances convenience and access to care but also introduces regulatory challenges, particularly in maintaining patient safety and quality standards in the rapidly evolving online healthcare environment.
The cosmeceuticals market, a segment within online pharmacies, is experiencing robust growth. Cosmeceuticals, which bridge the gap between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, have become a significant part of the skincare industry. The market, valued at USD 56.78 billion in 2022, is projected to expand to USD 95.75 billion by 2030. This expansion is driven by factors like innovation in natural ingredients and significant penetration of internet, smartphone, and social media applications. Despite the growth, the overall penetration for non-specialty drugs in mail-order and online pharmacies remains low, representing a significant portion of specialty prescription revenues. The evolving landscape of online pharmacies in the cosmeceuticals sector reflects a trend towards more accessible and customizable personal healthcare solutions.
Technological innovations are setting the stage for a new era in pharmaceutical care and management. AI’s role extends to areas like inventory management in retail pharmacies, where it predicts patient needs and enhances supply chain efficiency. Blockchain technology enhances supply chain transparency and legitimizes medical commodities, especially crucial in areas affected by counterfeit drugs. Blockchain also plays a vital role in patient-centric Electronic Health Records and telemonitoring systems. For instance, PharmaGo, an innovative platform developed in response to the pandemic, provides a comprehensive online pharmaceutical service, demonstrating the significant advancements in healthcare accessibility and pharmacy service delivery.
These technological advancements are instrumental in improving data sharing and collaboration among healthcare professionals. They offer significant potential for personalized medicine through data analytics, playing a crucial role in patient engagement and self-management of health. The future trends in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic, indicate a shift towards Pharmaceutical Digital Marketing (PDM) and a more consumer-centric approach. AI’s potential in revolutionizing pharmacy includes automation of routine tasks, personalized medication management, real-time patient data access, and the identification of patterns in medication adherence and potential drug interactions.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Hole G, Hole AS, McFalone-Shaw I. Digitalization in pharmaceutical industry: what to focus on under the digital implementation process? Int J Pharmaceutics: X. 2021;3:100095.
CAS Google Scholar
Shambhavi. Digital Pharmacy on the rise: transforming the Pharma Sector. Brillio.com; Oct. 2022.
Champagne HA, Leclerc D. O., The road to digital success in pharma [Internet]. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/life-sciences/our-insights/the-road-to-digital-success-in-pharma# ~:text=Mobile%20communications%2 C%20the%20cloud%2 C%20advanced,media%2 C%20retail%2 C%20and%20banking%20industries, August 1, 2015.
COVID-19 accelerated. digital transformation of the pharma industry by five years: Poll, Available from: http://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/news/covid-19-accelerated-digital-transformation-of-the-pharma-industry-by-five-years-poll/#:~:text=Digital%20transformation%20in%20the%20pharmaceutical,powerful%20analytics%20than%20ever%20before?cf-view&acf-closed , March 9, 2021.
Raza MA, Aziz S, Noreen M, Saeed A, Anjum I, Ahmed M, Raza SM. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in pharmacy: an overview of innovations. INNOVATIONS Pharm 13 (2022).
Zhang X. Investment analysis based on intrinsic value in the Information Technology and Pharmaceutical sectors for advancements in Digital Healthcare. Finance Econ 1 (2023).
Clark M, Clark T, Bhatti A, Aungst T. The rise of digital health and potential implications for pharmacy practice. J Contemp Pharm Pract. 2017;64:32–40.
Article Google Scholar
Health C, Pharmacy CVS. USA, 2023.
MyChart. Epic’s MyChart software system, USA, 2023.
Medisafe MD, Companion. USA, 2023.
Moodle. Moodle open source learning management system, USA, 2023.
PLUS SG. SimMan 3G PLUS advanced emergency care patient simulators, USA, 2023.
Association AP. American Pharmacists Association, USA, 2023.
Fittler A, Ambrus T, Serefko A, Smejkalová L, Kijewska A, Szopa A, Káplár M. Attitudes and behaviors regarding online pharmacies in the aftermath of COVID-19 pandemic: at the tipping point towards the new normal. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1070473.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hiskey O. The era of telehealth pharmacy practice. J Am Pharmacists Association. 2022;62:10–1.
Plantado ANR, de Guzman HJd, Mariano JEC, Salvan MRAR, Benosa CAC, Robles YR. Development of an online telepharmacy service in the Philippines and analysis of its usage during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Pharm Pract. 2023;36:227–37.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Zhang PC. The future of pharmacy is intertwined with digital health innovation. Can Pharmacists Journal/Revue Des Pharmaciens Du Can. 2022;155:7–8.
Miller R, Wafula F, Onoka CA, Saligram P, Musiega A, Ogira D, Okpani I, Ejughemre U, Murthy S, Garimella S. When technology precedes regulation: the challenges and opportunities of e-pharmacy in low-income and middle-income countries. BMJ Global Health 6 (2021).
Shawaqfeh MS, Al Bekairy AM, Al-Azayzih A, Alkatheri AA, Qandil AM, Obaidat AA, Harbi SA, Muflih SM. Pharmacy students perceptions of their distance online learning experience during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional survey study. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520963039.
Lee CY, Lee SWH. Impact of the educational technology use in undergraduate pharmacy teaching and learning–A systematic review. Pharm Educ. 2021;21:159–68.
Strawbridge J, Hayden JC, Robson T, Flood M, Cullinan S, Lynch M, Morgan AT, O’Brien F, Reynolds R, Kerrigan SW. Educating pharmacy students through a pandemic: reflecting on our COVID-19 experience. Res Social Administrative Pharm. 2022;18:3204–9.
Lin B, Wu S. Digital transformation in personalized medicine with artificial intelligence and the internet of medical things. OMICS. 2022;26:77–81.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Company M. Trends disrupting pharmacy value pools and potential implications for the value chain, 2018.
Stoumpos AI, Kitsios F, Talias MA. Digital Transformation in Healthcare: Technology Acceptance and its applications. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20:3407.
Kraus S, Schiavone F, Pluzhnikova A, Invernizzi AC. Digital transformation in healthcare: analyzing the current state-of-research. J Bus Res. 2021;123:557–67.
Jefferies JG, Bishop S, Hibbert S. Customer boundary work to navigate institutional arrangements around service interactions: exploring the case of telehealth. J Bus Res. 2019;105:420–33.
Patrício L, Teixeira JG, Vink J. A service design approach to healthcare innovation: from decision-making to sense-making and institutional change. AMS Rev. 2019;9:115–20.
Hong KS, Lee D. Impact of operational innovations on customer loyalty in the healthcare sector. Service Bus. 2018;12:575–600.
Laurenza E, Quintano M, Schiavone F, Vrontis D. The effect of digital technologies adoption in healthcare industry: a case based analysis. Bus Process Manage J. 2018;24:1124–44.
Mazor I, Heart T, Even A. Simulating the impact of an online digital dashboard in emergency departments on patients length of stay. J Decis Syst. 2016;25:343–53.
Rubbio I, Bruccoleri M, Pietrosi A, Ragonese B. Digital health technology enhances resilient behaviour: evidence from the ward. Int J Oper Prod Manage. 2020;40:34–67.
Hikmet N, Bhattacherjee A, Menachemi N, Kayhan VO, Brooks RG. The role of organizational factors in the adoption of healthcare information technology in Florida hospitals. Health Care Manag Sci. 2008;11:1–9.
Agarwal R, Gao G, DesRoches C, Jha AK. Research commentary—the digital transformation of healthcare: current status and the road ahead. Inform Syst Res. 2010;21:796–809.
Cucciniello M, Lapsley I, Nasi G. Managing health care in the digital world: a comparative analysis. Health Serv Manage Res. 2016;29:132–42.
Eden R, Burton-Jones A, Casey V, Draheim M. Digital transformation requires workforce transformation. MIS Q Exec. 2019;18:1–17.
Google Scholar
Huber C, Gärtner C. Digital transformations in healthcare professionals’ work: Dynamics of autonomy, control and accountability. Manage Revue. 2018;29:139–61.
Burtch G, Chan J. Investigating the relationship between medical crowdfunding and personal bankruptcy in the United States: evidence of a digital divide. MIS Quarterly (Forthcoming; 2018.
Seddon JJJM, Currie WL. Healthcare financialisation and the digital divide in the European Union: narrative and numbers. Inf Manag. 2017;54:1084–96.
Marques IC, Ferreira JJ. Digital transformation in the area of health: systematic review of 45 years of evolution. Health Technol. 2020;10:575–86.
Naik N, Hameed B, Sooriyaperakasam N, Vinayahalingam S, Patil V, Smriti K, Saxena J, Shah M, Ibrahim S, Singh A. Transforming healthcare through a digital revolution: a review of digital healthcare technologies and solutions. Front Digit Health. 2022;4:919985.
Canada. Virtual care policy framework, Canada, 2023.
Dhaliwall S. Telepharmacy services in Canada. Canada: Hospital News; 2018.
Telehealth HHSgov. Telehealth services in the United States, USA, 2023.
HRSA. Health Resources & Services Administration, USA, 2023.
UK.digital. health, Digital health and care, UK, 2023.
Australia AT, Services. Australia, 2023.
Imenokhoeva M. Telehealth in the European Union: Improving Access to Healthcare, HIMSS, EU, 2020.
Lucy d’Arville, Boulton A, Kapur V. Asia Pacific, Telehealth Adoption is expected to soar through 2024. BIAN and Company; 2022.
Intan Sabrina M, Defi IR. Telemedicine guidelines in South East Asia—a scoping review. Front Neurol. 2021;11:581649.
Wolf.Theiss. Telemedicine– the future of healthcare in Central and Eastern Europe, 2022.
Al-Samarraie H, Ghazal S, Alzahrani AI, Moody L. Telemedicine in Middle Eastern countries: Progress, barriers, and policy recommendations. Int J Med Informatics. 2020;141:104232.
Mahdi AlBasri H, Elwan P, Georgiev, Ustun A. Growth opportunities for digital health in KSA and UAE. McKinsey: McKinsey; 2022.
Ibrahim OM, Ibrahim RM, Al Meslamani AZ, Al Mazrouei N. Role of telepharmacy in pharmacist counselling to coronavirus disease 2019 patients and medication dispensing errors. J Telemed Telecare. 2023;29:18–27.
Unni EJ, Patel K, Beazer IR. Hung, Telepharmacy during COVID-19: a scoping review. Pharmacy. 2021;9:183.
Leila Shafiee Hanjani JS, Bell, Freeman CR. Undertaking medication review by telehealth. Australian J Gen Pract. 2020;49:826–31.
Bejarano AP, Santos PV, Robustillo-Cortés MdlA, Gómez ES, Rubio MDS. Implementation of a novel home delivery service during pandemic. Eur J Hosp Pharm (2020) ejhpharm–2020.
Elson EC, Oermann C, Duehlmeyer S, Bledsoe S. Use of telemedicine to provide clinical pharmacy services during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Am J Health-System Pharm. 2020;77:1005–6.
Li H, Zheng S, Liu F, Liu W, Zhao R. Fighting against COVID-19: innovative strategies for clinical pharmacists. Res Social Administrative Pharm. 2021;17:1813–8.
Margusino-Framiñán L, Illarro-Uranga A, Lorenzo-Lorenzo K, Monte-Boquet E, Márquez-Saavedra E, Fernández-Bargiela N, Gómez-Gómez D, Lago-Rivero N, Poveda-Andrés JL, Díaz-Acedo R, Hurtado-Bouza JL, Sánchez-Gundín J, Casanova-Martínez C. Morillo-Verdugo, Pharmaceutical care to hospital outpatients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telepharmacy Farmacia Hospitalaria. 2020;44:61–5.
PubMed Google Scholar
Hua X, Gu M, Zeng F, Hu H, Zhou T, Zhang Y, Shi C. Pharmacy administration and pharmaceutical care practice in a module hospital during the COVID-19 epidemic. J Am Pharmacists Association. 2020;60:431–e4381.
Asseri AA, Manna MM, Yasin IM, Moustafa MM, Roubie FM, El-Anssasy SM, Baqawie SK. Implementation and evaluation of telepharmacy during COVID-19 pandemic in an academic medical city in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: paving the way for telepharmacy. World J Adv Res Reviews. 2020;7:218–26.
Segal EM, Alwan L, Pitney C, Taketa C, Indorf A, Held L, Lee KS, Son M, Chi M, Diamantides E, Gosser R. Establishing clinical pharmacist telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am J Health-System Pharm. 2020;77:1403–8.
Bukhari N, Rasheed H, Nayyer B, Babar Z-U-D. Pharmacists at the frontline beating the COVID-19 pandemic. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2020;13:8.
Smith RF. The private sector is taking the lead on enabling digital inclusion. Here’s how. in: W.E. Forum, editor, World Economic Forum, 2021.
Dal Mas F, Massaro M, Rippa P, Secundo G. The challenges of digital transformation in healthcare: an interdisciplinary literature review, framework, and future research agenda. Technovation. 2023;123:102716.
Ianculescu M, Alexandru A. Microservices–A Catalyzer for Better Managing Healthcare Data Empowerment. Stud Inf Control. 2020;29:231–42.
López-Martínez F, Núñez-Valdez ER, García-Díaz V, Bursac Z. A case study for a big data and machine learning platform to improve medical decision support in population health management. Algorithms. 2020;13:102.
Ganapathy K, Reddy S. Technology enabled remote healthcare in public private partnership mode: A story from India. Telemedicine, Telehealth and Telepresence: Principles, Strategies, Applications, and New Directions (2021) 197–233.
Gleiss A, Kohlhagen M, Pousttchi K. An apple a day–how the platform economy impacts value creation in the healthcare market. Electron Markets. 2021;31:849–76.
Bonacina S, Koch S, Meneses I, Chronaki C. Can the European EHR exchange format support shared decision making and citizen-driven health science? Public Health and Informatics, IOS; 2021. pp. 1056–60.
Samuel L, TRANSFORMING THE HEALTHCARE SYSTEM: THE PUBLIC-PRIVATE HEALTHCARE DICHOTOMY IN INDIA IN THE ERA OF DIGITAL HEALTH., Proceedings of the International Conference on Public Health, 2020, pp. 18–31.
Antarsih NR, Setyawati SP, Ningsih S, Sulaiman E, Pujiastuti N. Telehealth Business Potential in Indonesia, International Conference on Social, Economics, Business, and Education (ICSEBE 2021), Atlantis Press, 2022, pp. 73–78.
Loccioni LG. Italy, 2023.
Casprini E, Palumbo R. Reaping the benefits of digital transformation through Public-Private Partnership: A service ecosystem view applied to healthcare. Global Public Policy Gov. 2022;2:453–76.
APOTECAchemo. APOTECAchemo Advanced Robotic Chemotherapy Drug Compounding Systems, Italy, 2023.
Velayati F, Ayatollahi H, Hemmat M, Dehghan R. Telehealth business models and their components: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:e33128.
Barker GP, Krupinski EA, McNeely RA, Holcomb MJ, Lopez AM, Weinstein RS. The Arizona telemedicine program business model. J Telemed Telecare. 2005;11:397–402.
Lee Y-L, Chang P. Modeling a mobile health management business model for chronic kidney disease, Nursing Informatics 2016, IOS Press, 2016, pp. 1047–1048.
Dijkstra SJ, Jurriëns JA, van der Mei RD. A business model for telemonitoring services, 14th Annual High Technology Small Firms Conference, HTSF 2006, University of Twente, 2006.
Grustam AS, Vrijhoef HJ, Poulikidis V, Koymans R, Severens JL. Extending the business-to-business (B2B) model towards a business-to-consumer (B2C) model for telemonitoring patients with chronic heart failure. J Bus Models. 2018;6:106–29.
Lin T-C, Chang H-J, Huang C-C. An analysis of telemedicine in Taiwan: a business model perspective. Int J Gerontol. 2011;5:189–92.
Peters C, Blohm I, Leimeister JM. Anatomy of successful business models for complex services: insights from the telemedicine field. J Manage Inform Syst. 2015;32:75–104.
Lin S-H, Liu J-H, Wei J, Yin W-H, Chen H-H, Chiu W-T. A business model analysis of telecardiology service. Telemedicine e-Health. 2010;16:1067–73.
Mun SK, Tohme WG, Platenberg RC, Choi I. Teleradiology and emerging business models. J Telemed Telecare. 2005;11:271.
Kijl B, Nieuwenhuis LJ, Veld RM, Hermens HJ. and M.M. Vollenbroek-Hutten, Deployment of e-health services–a business model engineering strategy. Journal of telemedicine and telecare 16 (2010) 344–353.
Fusco F, Turchetti G, Interactive Business Models for Telerehabilitation after Total Knee Replacement.: Preliminary Results from Tuscany, Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering: Third International Conference, IWBBIO 2015, Granada, Spain, April 15–17, 2015. Proceedings, Part II 3, Springer, 2015, pp. 502–511.
Hidefjäll P, Titkova D. Business model design for a wearable biofeedback system, pHealth, 2015, pp. 213–224.
Oderanti FO, Li F. A holistic review and framework for sustainable business models for assisted living technologies and services. Int J Healthc Technol Manage. 2016;15:273–307.
Valbuena VS, Seelye S, Sjoding MW, Valley TS, Dickson RP, Gay SE, Claar D, Prescott HC, Iwashyna TJ. Racial bias and reproducibility in pulse oximetry among medical and surgical inpatients in general care in the Veterans Health Administration 2013-19: multicenter, retrospective cohort study. BMJ 378 (2022).
Bai G, Rajgopal S, Srivastava A, Zhao R. Profitability and risk-return comparison across health care industries, evidence from publicly traded companies 2010–2019. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0275245.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
McCall CJ, DeCaprio D, Gartner J. The Measurement and Mitigation of Algorithmic Bias and Unfairness in Healthcare AI Models Developed for the CMS AI Health Outcomes Challenge. medRxiv (2022) 2022.09. 29.22280537.
Hsueh P-YS. Ecosystem of patient-centered research and information System Design, Personal Health Informatics: patient participation in Precision Health. Springer; 2022. pp. 329–51.
Martin KI, Glaser DA. Cosmeceuticals: the new medicine of beauty. Mo Med. 2011;108:60.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pandey A, Jatana GK, Sonthalia S, Cosmeceuticals SP. StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC., Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Gurpoonam Jatana declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Sidharth Sonthalia declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies., 2023.
Morganti P, Morganti G, Gagliardini A, Lohani A. From cosmetics to innovative cosmeceuticals—Non-woven tissues as New Biodegradable Carriers. Cosmetics. 2021;8:65.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Market C. Fortune Business Insights., Cosmeceuticals Market, 2023.
LLP SMR. Global Cosmeceuticals Market, A $95.75 Billion Industry Opportunity by 2030., 2022.
R.a. Markets, Global Cosmeceuticals Market - Outlook & Forecast 2023–2028, 2023.
Research SM. Industry Report and Statistics (Facts & Figures) - Number of Users, Price, Demand & Sales Analysis by Product & Distribution Channel, 2021.
Company M. Meeting changing consumer needs: The US retail pharmacy of the future, 2023.
Ascenso FNS. L’Oréal Portugal: a digital challenge for the active cosmetics division, 2016.
cosmeticaactiva. L’Oreal E-Learning Platform in Portugal, 2023.
Bach D, Newman AL. Governing lipitor and lipstick: capacity, sequencing, and power in international pharmaceutical and cosmetics regulation. Rev Int Polit Econ. 2010;17:665–95.
Organization WH. Quality assurance of pharmaceuticals. a compendium of guidelines and related materials: Good manufacturing practices and inspection, 2007.
Rai S, Gupta A, Punetha V. Regulations of Cosmetics across the Globe. Applied Clinical Research. Clin Trials Regul Affairs. 2015;2:137–44.
Natural VLAMBERT. & Organic Living; Say ‘No’ To Chemicals For A Healthy Life. in: Raconteur, editor, 2016.
Agency EM. The European regulatory system for medicines, 2023.
FDA, Food and Drug Adimenstration in the United States of America, 2023.
Cosmetics I, Market. Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs, EU, European Commission 2023.
EEU EEU. TECHNICAL REGULATION ON THE SAFETY OF COSMETICS AND PERFUMERY, 2015.
Danghyan L. Armenian regulatory framework of the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries, and its compliance with international regulations. Whether the existing regulatory framework of cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries complies with international best practice and ensures product safety and consumer protection. American University of Armenia; 2020.
TGA. Australian Public Assessment Report for Bimatoprost, 2017.
Kwa M, Welty LJ, Xu S. Adverse events reported to the US Food and Drug Administration for cosmetics and personal care products. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:1202–4.
DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Belsito DV, Sasseville D, Maibach HI, Taylor JS, Marks JG, Fowler JF, Mathias CT, DeLeo VA. North American contact dermatitis group patch test results 2013–2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:33–46.
Janetos TM, Kwa M, Xu S. Regulation of cosmetics. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1000–1.
Daum C. Self-Regulation in the Cosmetic Industry: A Necessary Reality or a Cosmetic Illusion? 2006.
Schaffer S, Reading Our Lips.: The History of Lipstick Regulation in Western Seats of Power, 2006.
Lincoln JE. Overview of the us fda gmps: good manufacturing practice (gmp)/quality system (qs) regulation (21 CFR part 820). J Validation Technol. 2012;18:17.
van der Heijden I, Pletneva N, Boyer C. How to protect consumers against the risks posed by the online pharmacy market. Swiss Med Inf 29 (2013).
Agency EM. Buying medicines online, 2015.
Union E. Buying medicine online, 2023.
ISPE. Regulating Online Pharmacies & Medicinal Product E-Commerce, 2019.
Swissmedic. Guideline on medicines and the Internet, 2020.
Kulali H. Online Pharmacy in Switzerland: A Full Guide. 2023, Pharmapidya, 2023.
Swissmedic. Current law, 2019.
El Hajj MS, Mekkawi R, Elkaffash R, Saleh R, Awaisi AE, Wilbur K. Public attitudes towards community pharmacy in Arabic speaking Middle Eastern countries: a systematic review. Res Social Administrative Pharm. 2021;17:1373–95.
DelveInsight. The Regulatory process for drug approval in the MENA region, DelveInsight, 2019.
Sallom H, Abdi A, Halboup AM, Başgut B. Evaluation of pharmaceutical care services in the Middle East Countries: a review of studies of 2013–2020. BMC Public Health. 2023;23:1364.
P.B.o. Australia, Guidelines for Dispensing of Medicines., 2019.
Center KLT. Statutes of the Republic of Korea. Pharmaceutical Affairs Act; 2016.
Goryachev I. Russia Federation: Telemedicine Law in Russia, Mondaq, 2018.
Jing M. China FDA stops online med sales, 2016.
L.a.W. o.J. Ministry of Health, List of Sales Sites for over-the-counter Drugs, 2020.
H.S.A.o, Singapore. Dangers of Buying Health Products Online, 2023.
M.o.H.o. Malaysia, Buying Medicines Online: Beware., 2023.
Ganapathy N. India’s pharmacies do battle with online rivals Straitimes, India, 2017.
LegitScript LS. Industry-Leading Certification, 2023.
NABP. The Verified Internet Pharmacy Practice Sites, 2012.
Boyer C, Baujard V, Geissbuhler A. Evolution of health web certification through the HONcode experience. Stud Health Technol Inf. 2011;169:53–7.
Tagde P, Tagde S, Bhattacharya T, Tagde P, Chopra H, Akter R, Kaushik D, Rahman MH. Blockchain and artificial intelligence technology in e-Health. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2021;28:52810–31.
Walgreen. Convenient virtual care., 2023.
Group O. Otto Group, 2023.
U.o.C.S, Francisco, New UCSF. Robotic Pharmacy Aims to Improve Patient Safety, 2011.
Narayanaswami C, Nooyi R, Govindaswamy SR, Viswanathan R. Blockchain anchored supply chain automation. IBM J Res Dev. 2019;63:7: 1–7.
Khezr S, Moniruzzaman M, Yassine A, Benlamri R. Blockchain technology in healthcare: a comprehensive review and directions for future research. Appl Sci. 2019;9:1736.
Xia Q, Sifah EB, Asamoah KO, Gao J, Du X, Guizani M. MeDShare: Trust-less medical data sharing among cloud service providers via blockchain. IEEE access 5 (2017) 14757–14767.
Mannaro K, Pinna A, Marchesi M. Crypto-trading: Blockchain-oriented energy market, 2017 AEIT International Annual Conference, IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–5.
Rallapalli S, Minalkar A. Improving Healthcare-Big Data Analytics for. J Adv Inform Technol 7 (2016).
Wang H, Song Y. Secure cloud-based EHR system using attribute-based cryptosystem and blockchain. J Med Syst. 2018;42:152.
Cyran MA. Blockchain as a foundation for sharing healthcare data. Blockchain Healthc Today (2018).
Funk E, Riddell J, Ankel F, Cabrera D. Blockchain technology: a data framework to improve validity, trust, and accountability of information exchange in health professions education. Acad Med. 2018;93:1791–4.
Khan PW, Byun Y. A blockchain-based secure image encryption scheme for the industrial internet of things. Entropy. 2020;22:175.
Gomasta SS, Dhali A, Tahlil T, Anwar MM, Ali ABMS. PharmaChain: Blockchain-based drug supply chain provenance verification system. Heliyon. 2023;9:e17957.
Gamage RG, Bandara NS, Diyamullage DD, Senadeera KU, Abeywardena KY, Amarasena N. PharmaGo-An Online Pharmaceutical Ordering Platform, 2021 3rd International Conference on Advancements in Computing (ICAC), IEEE, 2021, pp. 365–370.
Amalia A, Sipahutar PYC, Elviwani E, Purnamasari F. Chatbot Implementation with Semantic Technology for Drugs Information Searching System. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 1566 (2020) 012077.
Trenfield SJ, Awad A, McCoubrey LE, Elbadawi M, Goyanes A, Gaisford S, Basit AW. Advancing pharmacy and healthcare with virtual digital technologies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;182:114098.
Anis MS, Hassali MA. Pharmaceutical marketing of over-the-counter drugs in the current digital era: a review. Pharm Sci Asia 49 (2022).
Khan O, Parvez M, Kumari P, Parvez S, Ahmad S. The future of pharmacy: how AI is revolutionizing the industry. Intell Pharm. 2023;1:32–40.
Moshawih S, Hadikhani P, Fatima A, Goh HP, Kifli N, Kotra V, Goh KW, Ming LC. Comparative analysis of an anthraquinone and chalcone derivatives-based virtual combinatorial library. A cheminformatics proof-of-concept study. J Mol Graph Model. 2022;117:108307.
Moshawih S, Goh HP, Kifli N, Idris AC, Yassin H, Kotra V, Goh KW, Liew KB, Ming LC. Synergy between machine learning and Natural products Cheminformatics: application to the lead Discovery of anthraquinone derivatives. Chemical Biology & Drug Design; 2022.
Wong CH, Siah KW, Lo AW. Estimation of clinical trial success rates and related parameters. Biostatistics. 2019;20:273–86.
Moshawih S, Goh HP, Kifli N, Darwesh MAE, Ardianto C, Goh KW, Ming LC. Identification and optimization of TDP1 inhibitors from anthraquinone and chalcone derivatives: consensus scoring virtual screening and molecular simulations. J Biomol Struct Dynamics (2023) 1–25.
Moore JH, Margreitter C, Janet JP, Engkvist O, de Groot BL, Gapsys V. Automated relative binding free energy calculations from SMILES to ∆∆G. Commun Chem. 2023;6:82.
Moshawih S, Lim AF, Ardianto C, Goh KW, Kifli N, Goh HP, Jarrar Q, Ming LC. Target-based small Molecule Drug Discovery for Colorectal Cancer: a review of Molecular pathways and in Silico studies. Biomolecules. 2022;12:878.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The researcher would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research, Qassim University for funding the publication of this project.
Deanship of Scientific Research, Qassim University
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Qassim University, Buraydah, Saudi Arabia
Ahmad Almeman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceived the conceptual framework, Wrote the paper, Designed search strategies, Critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content: A.A.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ahmad Almeman .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Almeman, A. The digital transformation in pharmacy: embracing online platforms and the cosmeceutical paradigm shift. J Health Popul Nutr 43 , 60 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-024-00550-2
Download citation
Received : 14 February 2024
Accepted : 09 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-024-00550-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Digital transformation
- Healthcare technology
- Cosmeceuticals
- Global health
- Patient care
- 2019 novel coronavirus
- Drug safety
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition
ISSN: 2072-1315
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The "new normal" in education is the technological order—a passive technologization—and its expansion continues uncontested and even accelerated by the pandemic. Two Greek concepts, kronos and kairos, allow a discussion of contrasts between the quantitative and the qualitative in education.
DL has become the new normal in education in the country. DepEd (2020), without sacrificing the quality of education, came up with the Learning Continuity Plan (LCP) for the school year 2020-2021. This provides learning interventions that teachers can utilize during the pandemic. This was the jumping board for schools as they offered DL to ...
Keywords: care, inclusion, new normal, open, distance and online education, social justice Highlights What is already known about this topic: • There is a lot of hype about the new normal in education both during the COVID-19 pandemic and in the post-pandemic era characterized by technocentric thinking or an "affordances" account.
This review examines the transformation of educational practices to online and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. It specifically focuses on the challenges, innovative approaches, and successes of this transition, emphasizing the integration of educational technology, student well-being, and teacher development. The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly transformed the educational ...
Metrics. The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make ...
A 2020 review of research identified three dimensions of engagement: 3. Behavioral: the physical behaviors required to complete the learning activity. Emotional: the positive emotional energy associated with the learning activity. Cognitive: the mental energy that a student exerts toward the completion of the learning activity.
The new normal: How virtual learning can benefit K-12 students. Daniell DiFrancesca a Department of Educational Psychology, Penn State Erie, ... It is important to consider how to best facilitate the movement toward true online education as the situations we have experienced during the pandemic are not going to end. Many schools are regularly ...
With the COVID-19 pandemic taking a toll on students, personally and academically, many of them are modeling how to respond to the new normal. So many of us in higher education, and across the world, are exhausted, frustrated, and anxious. Two years ago, everything started to shut down—initially for only two weeks, maybe three—so that we ...
The "New Normal" in Education and the Future of Schooling. Harold John D. Culala. Education. KnE Social Sciences. 2022. This paper explores the catchphrase of the new decade — the 'new normal' in education. The paper offers some analyses of its emergence. Guided by a literature review, mostly about UNICEF, UNESCO, and….
Blended learning and research issues. Blended learning (BL), or the integration of face-to-face and online instruction (Graham 2013), is widely adopted across higher education with some scholars referring to it as the "new traditional model" (Ross and Gage 2006, p. 167) or the "new normal" in course delivery (Norberg et al. 2011, p. 207).). However, tracking the accurate extent of its ...
As a result of COVID-19, online university teaching has become the "new normal" but also re-focussed questions regarding its efficacy. The weight of evidence from this review is that online learning is at least as effective and often better than, F2F modalities in supporting learning outcomes, albeit these differences are often modest.
The unstable social situation and the unpredictable consequences of Covid-19 pandemic have challenged students, academics, and the broader higher education ecosystem (Al Miskry et al. 2021; Halabieh et al. 2022).Recent literature addresses academics' readiness (Yiapanas et al. 2022) and students' preparedness (Meletiou-Mavrotheris et al. 2022; Piki 2022) to respond to the emergency shift ...
The COVID-19 outbreak has compelled many universities to immediately switch to the online delivery of lessons. Many instructors, however, have found developing effective online lessons in a very short period of time very stressful and difficult. This study describes how we successfully addressed this crisis by transforming two conventional flipped classes into fully online flipped classes with ...
Also, distance education encourages student-centred learning and self-learning. It offers a lot of opportunities to tertiary institutions which includes scalability, research innovations, flexible learning, diversity, remote students support, adjustment of assessment methods, innovation opportunity, offer non-academic courses, change of ...
To live in the world is to adapt constantly. A year after COVID-19 pandemic has emerged, we have suddenly been forced to adapt to the 'new normal': work-from-home setting, parents home-schooling their children in a new blended learning setting, lockdown and quarantine, and the mandatory wearing of face mask and face shields in public.
The new normal post-COVID-19 era opens an opportunity for rethinking the goals of education. One of the goals to make the curriculum relevant, appropriate, and responsive is the development of ...
Reading a diverse range of essays from different age groups has given me a more in-depth insight into students' feelings who have been compelled to live and learn in confined spaces in times of COVID-19. It has been encouraging to note that their learnings continued at home during the lockdown. Most writers share a concern for the society while discussing about health, education, the ...
Follow. The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom. As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms. Research suggests that online learning has been shown to ...
Our Expertise Insights Education In The New Normal. This was first published on June 3, 2020. Covid-19 has created numerous and significant challenges to the education system, and education leadership must implement a holistic strategy to mitigate the impact of the pandemic and adapt to the new reality. In April 2020 we published our first ...
This pandemic has drastically changed the education landscape and revealed old and new challenges such as the digital divide (Altbach and De Wit, 2020; HESB, 2020) — a term coined for lack of ...
This article is written by Shikha Pokhriyal, from Delhi Metropolitan Education, GGSIPU. This article talks about the new normal in the education sector that is the popularity of online learning and the challenges faced by people in this new normal. Introduction More than a year has passed since the first lockdown was announced in the […]
Sun.Star Pampanga. My Reflection in the New Normal Education. 2021-01-26 -. Rico Jay C. Mananquil. Much has been written about the new normal in the society as the COVID-19 Pandemic continues to spread in different countries around the world. The new normal will involve higher levels of health precautions.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around ...
The "new normal" has forced the addition of new platforms to support established sources of health information. The creation and evaluation of an online telepharmacy service in the Philippines during the pandemic serves as an example of this, demonstrating how quickly the global pharmacy industry adopted digital solutions.