How do I cite a dissertation in MLA style?
Note: This post relates to content in the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook . For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
A dissertation is a unique type of source. It is a finished, stand-alone work written under the auspices of an institution. In a change from the previous edition of the MLA Handbook , we do not distinguish between published and unpublished dissertations. To cite a dissertation, include in the entry the author, title, and date of publication as core elements. As an optional element, list the institution granting the degree and a description of the work.
Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting . 2010. Northwestern U, PhD dissertation.
If you accessed the dissertation through an online repository, include this fact as the title of the second container:
Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting . 2010. Northwestern U, PhD dissertation. ProQuest , search.proquest.com/docview/305212264?accountid=7432.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in MLA

How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in MLA
Citing a thesis or dissertation.
Thesis – A document submitted to earn a degree at a university.
Dissertation – A document submitted to earn an advanced degree, such as a doctorate, at a university.
The formatting for thesis and dissertation citations is largely the same. However, you should be sure to include the type of degree after the publication year as supplemental information. For instance, state if the source you are citing is an undergraduate thesis or a PhD dissertation.
MLA Thesis and Dissertation Citation Structure (print)
Last, First M. Title of the Thesis/Dissertation. Year Published. Name of University, type of degree.
MLA Thesis and Dissertation Citation Structure (online)
Last, First M. Title of the Thesis/Dissertation. Year Published. Name of University, type of degree. Website Name , URL.
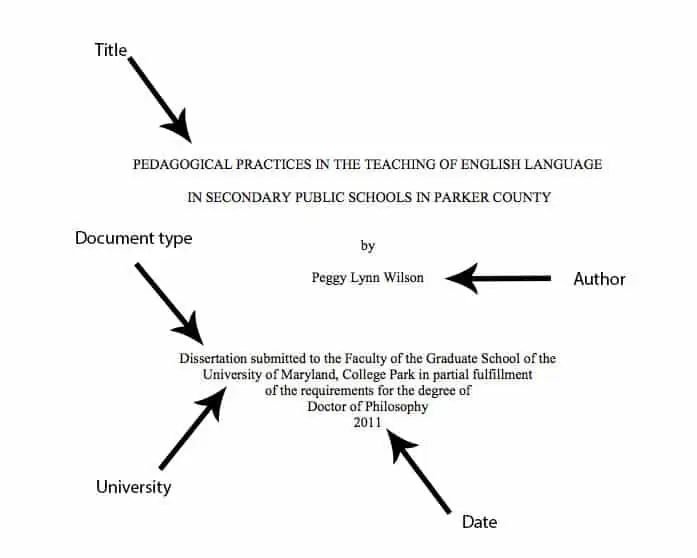
Wilson, Peggy Lynn. Pedagogical Practices in the Teaching of English Language in Secondary Public Schools in Parker County . 2011. University of Maryland, PhD dissertation.
In-text Citation Structure
(Author Last Name page #)
In-text Citation Example
(Wilson 14)
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Recinto Universitario de Mayagüez, Call Box 9000 Mayagüez, PR 00681 (787) 832-4040 ext. 3810, 2151, 2155 [email protected]
MLA 9th Edition Style Guide: Dissertation/Thesis
- Generic Section Labels
- Inclusive Language
- Publisher Abbreviations
- Formatting your Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Social Media
- Audiovisual
- Personal Communication
Dissertation/Thesis
- News Publication
- Classroom Material
- Conference Proceedings and Papers
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Tables and Figures
- Useful Links
Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting . 2010. Northwestern U,
MA thesis. ProQuest , search.proquest.com/docview/305212264?accountid=7432.
Dissertation
PhD dissertation. ProQuest , search.proquest.com/docview/305212264?accountid=7432.
- << Previous: Personal Communication
- Next: News Publication >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 3:20 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uprm.edu/MLA9/en
Biblioteca General © 2024 - Universidad de Puerto Rico. Todos los derechos reservados.
ZSR Library
Mla 8th ed. style guide: dissertations, theses.
- Art, Photography, Music
- Business Resources
- Dissertations, Theses
- Emails, Social Media
- Film, Television, Video
- Journal, Newspaper, & Magazine Articles
- Legal Sources
- Parenthetical (in-text) Citations
- Web Sites, Blogs
- Need more help?
Essential Elements
Citations for dissertations/master's theses should include the following:
1. Name of Author
2. Title of dissertation/thesis (italicized)
3. Date of Publication
5. Institution granting the degree (optional)
6. Description of the work (optional)
7. Database and URL if accessed through a database or repository
Sample Citation - Dissertations
Dissertations
The institution granting the degree and description of the work are optional. If you accessed the work online, include that information.

- << Previous: Business Resources
- Next: Emails, Social Media >>
- Last Updated: Sep 1, 2021 12:15 PM
- URL: https://guides.zsr.wfu.edu/mla8

- Collections
- Research Help
- Teaching & Learning
- Library Home
MLA Citation Style Guide: 7th Edition
- Web Sources
- Journal Articles
- Magazine & News Articles
- Encyclopedias, Dictionaries, & Reference Materials
- Audiovisual Media
- Legal & Government Documents
Dissertation and Theses: Unpublished
Dissertation and theses: published, contact kelly.
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited Page
General, Electronic:
Last-name, First-name. “Title of Dissertation.” Diss. Place of Study, Year. Title of Database . Web. Date Month Year of Access.
Forrester, Pearl. “Psychological Distress and Repeated Television Viewing.” Diss. Miskatonic University, 1990. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses . Web. 13 May 2010.
General, Print:
Last-name, First-name. “Title of Dissertation.” Diss. Place of Study, Year. Print.
Forrester, Pearl. “Psychological Distress and Repeated Television Viewing.” Diss. Miskatonic University, 1990. Print.
General Rule:
Author's Last-name, First-name. Title of Disstertaion . Diss. Place of Study, Year. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication. Format.
Diamond, Oscar. How to Care for Your Diabetic Cat . Diss. West Virginia University, 1999. New York: Knopf, 2000. Print.

- << Previous: Legal & Government Documents
- Next: In-Text Citations >>
- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2023 9:04 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wvu.edu/mlaguide7th
MLA Citation Style Guide: Home
In-text citations.
- MLA Examples - Print
- MLA Examples - Online and Electronic
- MLA Examples - Images, Video, and Audio
- Citation Resources and Guidelines
- 7th Edition MLA Citation Style Guide
MLA 9th Edition notes
The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook continues the method for creating bibliographic entries set out in the eighth edition, which focused on the principles of documenting sources, rather than on strict adherence to a particular format for each source. Below are two examples of popular bibliographic entries.
Citing a print book with one author :
Jacobs, Alan. The Pleasures of Reading in an Age of Distraction . Oxford UP, 2011.
In this version, only the most essential information is included (author’s name, book title, publisher, and date).
Citing an article from a scholarly journal :
Kincaid, Jamaica. “In History.” Callaloo , vol. 24, no. 2, Spring 2001, pp. 620-26.
This version identifies the volume (24), the number (2), and the page numbers (620-26) of the scholarly journal, rather than leaving those numbers without clear explanation. This helps readers best make sense of your citation and allows them to locate your source without getting bogged down with extra information or references that can be difficult to decipher. Also note that punctuation is simple; only commas separate the journal title, volume, number, date, and page numbers.
Citing sources within your paper
Works Cited Examples
Example Citations
- MLA Style Center
- Columbia College MLA Citation Guide
- MLA Works Cited Guide
- Excelsior OWL MLA Citation Guide
- Tutorial: MLA 9th Edition Citation Style
- Video: MLA 9th Edition Citation Style
Your Librarian

MLA Handbook 9th Edition
New Citation Notes: Chat GPT and other AI Tools
From the MLA Style Center :
You should:
- cite a generative AI tool whenever you paraphrase, quote, or incorporate into your own work any content (whether text, image, data, or other) that was created by it
- acknowledge all functional uses of the tool (like editing your prose or translating words) in a note, your text, or another suitable location
- take care to vet the secondary sources it cites
Description of what was generated by the AI tool. Name of AI Tool , version, Publisher, Date generated, URL of the tool.
While the green light in The Great Gatsby might be said to chiefly symbolize four main things: optimism, the unattainability of the American dream, greed, and covetousness (“Describe the symbolism”), arguably the most important—the one that ties all four themes together—is greed.
Works Cited:
“Describe the symbolism of the green light in the book The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald” prompt. ChatGPT, 13 Feb. version, OpenAI, 8 Mar. 2023, chat.openai.com/chat.
- Next: In-text Citations >>
- Last Updated: Dec 8, 2023 9:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.miamioh.edu/MLA_citation_guide

- Otis College of Art and Design
- Otis College LibGuides
- Millard Sheets Library
Citation Guide (MLA 9th Edition) UNDER CONSTRUCTION
- Theses and Dissertations
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributor
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
Citation Templates
Print versions, electronic versions.
- Videos & DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- In-Text Citations
- Sample Works Cited List
- Sample Annotations This link opens in a new window
- Plagiarism This link opens in a new window
Dissertations and theses
Dissertations and theses are written to fulfil an academic degree requirement, usually at the Masters or PhD level. They usually have only 1 author.
For the most part, treat them like books with supplemenal elements.
- Since dissertations and theses are often re-worked into articles and books, it is important to note when your source was written to fulfill an academic degree requirement
- The publisher is the degree-granting instution
- Do not include the program, department, school, division, or similar information
- Usually placed before the container of the online repository which houses the publication
- Automatic citation generators often treat online theses and dissertations as websites or journal articles, so will be missing the key information
Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book: Subtitle. Publication Date. University name, Degree conferred .
Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book: Subtitle. Publication Date. University name, Degree conferred . Online Repository , URL.
In-Text Citation
(Author's Last Name ##)
Replace ## with page number(s) for quotes or where the idea is discussed.
Smith, Kate Elizabeth. The Influence of Audrey Hepburn and Hubert de Givenchy on American Fashion, 1952-1965 . 2001. Michigan State University, MA Thesis.
Austin, Katherine. Rasquache Baroque in the Chicana/o Borderlands . 2012. McGill U, PhD thesis. eScholarship , https://escholarship.mcgill.ca/concern/theses/8p58ph61j. Accessed 6 Jan. 2023.
- eScholarship is McGill University's online repository of dissertations and theses
- Followed McGill's lead and used "thesis" instead of "dissertation"
Grullon, Jaymi Leah. Campy Musical Black Queer Forms: Finding Utopia in Lil Nas X's World of "Montero ". St. John's University, MA Thesis. St. John's Scholar , https://scholar.stjohns.edu/theses_dissertations/477
- St. John's Scholar is the university's online repository of dissertations and theses
Hutchinson, Jennifer. Emotional Response to Climate Change Learning: An Existential Inquiry . 2021. Antioch University, Antioch University, Doctoral dissertation. EBSCOhost , search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,sso&db=ddu&AN=29DBEAFBF585BC45&site=eds-live&scope=site.
- Found record in OwlCat, so used EBSCOhost as the repository
- Could be more specific and replace the EBSCOhost info with: OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center , http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=antioch1602019356792951.
- << Previous: Social Media
- Next: Videos & DVDs >>
- Last Updated: Feb 23, 2024 4:22 PM
- URL: https://otis.libguides.com/mla_citations
Otis College of Art and Design | 9045 Lincoln Blvd. Los Angeles, CA 90045 | MyOtis
Millard Sheets Library | MyOtis | 310-665-6930 | Ask a Librarian
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- A complete guide to MLA in-text citations
MLA In-text Citations | A Complete Guide (9th Edition)
Published on July 9, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024.
An MLA in-text citation provides the author’s last name and a page number in parentheses.
If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by “ et al. ”
If the part you’re citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range. If you want to cite multiple non-consecutive pages at the same time, separate the page numbers with commas.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Where to include an mla in-text citation, citing sources with no author, citing sources with no page numbers, citing different sources with the same author name, citing sources indirectly, frequently asked questions about mla in-text citations.
Place the parenthetical citation directly after the relevant quote or paraphrase , and before the period or other punctuation mark (except with block quotes , where the citation comes after the period).
If you have already named the author in the sentence, add only the page number in parentheses. When mentioning a source with three or more authors outside of parentheses, use “and others” or “and colleagues” in place of “et al.”
- MLA is the second most popular citation style (Smith and Morrison 17–19) .
- According to Smith and Morrison , MLA is the second most popular citation style (17–19) .
- APA is by far “the most used citation style in the US” (Moore et al. 74) , but it is less dominant in the UK (Smith 16) .
- Moore and colleagues state that APA is more popular in the US than elsewhere (74) .

Combining citations
If a sentence is supported by more than one source, you can combine the citations in a single set of parentheses. Separate the two sources with a semicolon .
Livestock farming is one of the biggest global contributors to climate change (Garcia 64; Davies 14) .
Consecutive citations of the same source
If you cite the same source repeatedly within a paragraph, you can include the full citation the first time you cite it, then just the page number for subsequent citations.
MLA is the second most popular citation style (Smith and Morrison 17–19) . It is more popular than Chicago style, but less popular than APA (21) .
You can do this as long as it remains clear what source you’re citing. If you cite something else in between or start a new paragraph, reintroduce the full citation again to avoid ambiguity.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

For sources with no named author , the in-text citation must match the first element of the Works Cited entry. This may be the name of an organization, or the title of the source.
If the source title or organization name is longer than four words, shorten it to the first word or phrase in the in-text citation, excluding any articles ( a, an, and the ). The shortened title or organization name should begin with the word the source is alphabetized by in the Works Cited.
Follow the general MLA rules for formatting titles : If the source is a self-contained work (e.g. a whole website or an entire book ), put the title in italics; if the source is contained within a larger whole (e.g. a page on a website or a chapter of a book), put the title in quotation marks.
If a source does not have page numbers but is divided into numbered parts (e.g. chapters, sections, scenes, Bible books and verses, Articles of the Constitution , or timestamps), use these numbers to locate the relevant passage.
If the source does not use any numbering system, include only the author’s name in the in-text citation. Don’t include paragraph numbers unless they are explicitly numbered in the source.
Note that if there are no numbered divisions and you have already named the author in your sentence, then no parenthetical citation is necessary.
If your Works Cited page includes more than one entry under the same last name, you need to distinguish between these sources in your in-text citations.
Multiple sources by the same author
If you cite more than one work by the same author, add a shortened title to signal which source you are referring to.
In this example, the first source is a whole book, so the title appears in italics; the second is an article published in a journal, so the title appears in quotation marks.
Different authors with the same last name
To distinguish between different authors with the same last name, use the authors’ initials (or, if the initials are the same, full first names) in your in-text citations:
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Sometimes you might want to cite something that you found quoted in a secondary source . If possible, always seek out the original source and cite it directly.
If you can’t access the original source, make sure to name both the original author and the author of the source that you accessed . Use the abbreviation “qtd. in” (short for “quoted in”) to indicate where you found the quotation.
In these cases, only the source you accessed directly is included in the Works Cited list.
You must include an MLA in-text citation every time you quote or paraphrase from a source (e.g. a book , movie , website , or article ).
Some source types, such as books and journal articles , may contain footnotes (or endnotes) with additional information. The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation :
- To cite information from a single numbered note, write “n” after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2)
- To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write “nn” and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1–2)
- To cite information from an unnumbered note, write “un” after the page number, with a space in between, e.g. (Jones 250 un)
If a source has two authors, name both authors in your MLA in-text citation and Works Cited entry. If there are three or more authors, name only the first author, followed by et al.
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title . Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation .
If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only the author’s name (or the title).
If you already named the author or title in your sentence, and there is no locator available, you don’t need a parenthetical citation:
- Rajaram argues that representations of migration are shaped by “cultural, political, and ideological interests.”
- The homepage of The Correspondent describes it as “a movement for radically different news.”
Yes. MLA style uses title case, which means that all principal words (nouns, pronouns , verbs, adjectives , adverbs , and some conjunctions ) are capitalized.
This applies to titles of sources as well as the title of, and subheadings in, your paper. Use MLA capitalization style even when the original source title uses different capitalization .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). MLA In-text Citations | A Complete Guide (9th Edition). Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/in-text-citations/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to format your mla works cited page, block quoting in mla style, how to cite a book in mla, what is your plagiarism score.
Citation guides
All you need to know about citations
How to cite “The Graduate” (movie)
Apa citation.
Formatted according to the APA Publication Manual 7 th edition. Simply copy it to the References page as is.
If you need more information on APA citations check out our APA citation guide or start citing with the BibguruAPA citation generator .
Nichols, M. (1967). The Graduate . Embassy Pictures.
Chicago style citation
Formatted according to the Chicago Manual of Style 17 th edition. Simply copy it to the References page as is.
If you need more information on Chicago style citations check out our Chicago style citation guide or start citing with the BibGuru Chicago style citation generator .
Nichols, Mike. 1967. The Graduate . United States: Embassy Pictures.
MLA citation
Formatted according to the MLA handbook 9 th edition. Simply copy it to the Works Cited page as is.
If you need more information on MLA citations check out our MLA citation guide or start citing with the BibGuru MLA citation generator .
Nichols, Mike. The Graduate . Embassy Pictures, 1967.
Other citation styles (Harvard, Turabian, Vancouver, ...)
BibGuru offers more than 8,000 citation styles including popular styles such as AMA, ASA, APSA, CSE, IEEE, Harvard, Turabian, and Vancouver, as well as journal and university specific styles. Give it a try now: Cite The Graduate now!
Movie details

MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): Unpublished Manuscript or Paper
- Advertisements
- Audio Materials
- Books, Ebooks, & Book Chapters
- ChatGPT or Other Generative AI
- Class Materials (Notes, Slides, & Recordings)
- Creative Commons Works
- Encyclopedias, & Dictionaries
- Images, Charts, Graphs, & Tables
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communications (Interviews, Emails, etc.)
- Religious Works
- Social Media
- Unpublished Manuscript or Paper
- Websites (includes documents/PDFs posted online)
- When Information Is Missing
- When a Work Is Quoted in Another Source
- Works in Another Language / Translations
- Permalinks, URLs, & DOIs!
- Quoting vs. Paraphrasing
- Works Cited & Paper Format
- Citation Tools
Unpublished Manuscripts or Papers
- Student Paper (including your own!)
Unpublished Manuscript
Student paper (including if you are citing your own previous work).
- << Previous: Statistics
- Next: Videos >>
- Last Updated: Mar 19, 2024 10:41 AM
- URL: https://owhlguides.andover.edu/mla
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Books

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
When you are gathering book sources, be sure to make note of the following bibliographic items: the author name(s), other contributors such as translators or editors, the book’s title, editions of the book, the publication date, the publisher, and the pagination.
The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
Please note these changes in the new edition:
- Commas are used instead of periods between Publisher, Publication Date, and Pagination.
- Medium is no longer necessary.
- Containers are now a part of the MLA process. Commas should be used after container titles.
- DOIs should be used instead of URLS when available.
- Use the term “Accessed” instead of listing the date or the abbreviation, “n.d."
Below is the general format for any citation:
Author. Title. Title of container (do not list container for standalone books, e.g. novels), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs URL or DOI). 2 nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Basic Book Format
The author’s name or a book with a single author's name appears in last name, first name format. The basic form for a book citation is:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Date.
* Note: the City of Publication should only be used if the book was published before 1900, if the publisher has offices in more than one country, or if the publisher is unknown in North America.
Book with One Author
Gleick, James. Chaos: Making a New Science . Penguin, 1987.
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
Book with More Than One Author
When a book has two authors, order the authors in the same way they are presented in the book. Start by listing the first name that appears on the book in last name, first name format; subsequent author names appear in normal order (first name last name format).
Gillespie, Paula, and Neal Lerner. The Allyn and Bacon Guide to Peer Tutoring . Allyn and Bacon, 2000.
If there are three or more authors, list only the first author followed by the phrase et al. (Latin for "and others") in place of the subsequent authors' names. (Note that there is a period after “al” in “et al.” Also note that there is never a period after the “et” in “et al.”).
Wysocki, Anne Frances, et al. Writing New Media: Theory and Applications for Expanding the Teaching of Composition . Utah State UP, 2004.
Two or More Books by the Same Author
List works alphabetically by title. (Remember to ignore articles like A, An, and The.) Provide the author’s name in last name, first name format for the first entry only. For each subsequent entry by the same author, use three hyphens and a period.
Palmer, William J. Dickens and New Historicism . St. Martin's, 1997.
---. The Films of the Eighties: A Social History . Southern Illinois UP, 1993.
Book by a Corporate Author or Organization
A corporate author may include a commission, a committee, a government agency, or a group that does not identify individual members on the title page.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry.
American Allergy Association. Allergies in Children . Random House, 1998.
When the author and publisher are the same, skip the author, and list the title first. Then, list the corporate author only as the publisher.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.
Book with No Author
List by title of the book. Incorporate these entries alphabetically just as you would with works that include an author name. For example, the following entry might appear between entries of works written by Dean, Shaun and Forsythe, Jonathan.
Encyclopedia of Indiana . Somerset, 1993.
Remember that for an in-text (parenthetical) citation of a book with no author, you should provide the name of the work in the signal phrase and the page number in parentheses. You may also use a shortened version of the title of the book accompanied by the page number. For more information see the In-text Citations for Print Sources with No Known Author section of In-text Citations: The Basics .
A Translated Book
If you want to emphasize the work rather than the translator, cite as you would any other book. Add “translated by” and follow with the name(s) of the translator(s).
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . Translated by Richard Howard, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
If you want to focus on the translation, list the translator as the author. In place of the author’s name, the translator’s name appears. His or her name is followed by the label, “translator.” If the author of the book does not appear in the title of the book, include the name, with a “By” after the title of the book and before the publisher. Note that this type of citation is less common and should only be used for papers or writing in which translation plays a central role.
Howard, Richard, translator. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . By Michel Foucault, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Republished Book
Books may be republished due to popularity without becoming a new edition. New editions are typically revisions of the original work. For books that originally appeared at an earlier date and that have been republished at a later one, insert the original publication date before the publication information.
For books that are new editions (i.e. different from the first or other editions of the book), see An Edition of a Book below.
Butler, Judith. Gender Trouble . 1990. Routledge, 1999.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine . 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
An Edition of a Book
There are two types of editions in book publishing: a book that has been published more than once in different editions and a book that is prepared by someone other than the author (typically an editor).
A Subsequent Edition
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the number of the edition after the title.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students . 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
A Work Prepared by an Editor
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the editor after the title with the label "edited by."
Bronte, Charlotte. Jane Eyre, edited by Margaret Smith, Oxford UP, 1998.
Note that the format for citing sources with important contributors with editor-like roles follows the same basic template:
...adapted by John Doe...
Finally, in the event that the source features a contributor that cannot be described with a past-tense verb and the word "by" (e.g., "edited by"), you may instead use a noun followed by a comma, like so:
...guest editor, Jane Smith...
Anthology or Collection (e.g. Collection of Essays)
To cite the entire anthology or collection, list by editor(s) followed by a comma and "editor" or, for multiple editors, "editors." This sort of entry is somewhat rare. If you are citing a particular piece within an anthology or collection (more common), see A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection below.
Hill, Charles A., and Marguerite Helmers, editors. Defining Visual Rhetorics . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2004.
Peterson, Nancy J., editor. Toni Morrison: Critical and Theoretical Approaches . Johns Hopkins UP, 1997.
A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection
Works may include an essay in an edited collection or anthology, or a chapter of a book. The basic form is for this sort of citation is as follows:
Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , edited by Editor's Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry.
Some examples:
Harris, Muriel. "Talk to Me: Engaging Reluctant Writers." A Tutor's Guide: Helping Writers One to One , edited by Ben Rafoth, Heinemann, 2000, pp. 24-34.
Swanson, Gunnar. "Graphic Design Education as a Liberal Art: Design and Knowledge in the University and The 'Real World.'" The Education of a Graphic Designer , edited by Steven Heller, Allworth Press, 1998, pp. 13-24.
Note on Cross-referencing Several Items from One Anthology: If you cite more than one essay from the same edited collection, MLA indicates you may cross-reference within your works cited list in order to avoid writing out the publishing information for each separate essay. You should consider this option if you have several references from a single text. To do so, include a separate entry for the entire collection listed by the editor's name as below:
Rose, Shirley K, and Irwin Weiser, editors. The Writing Program Administrator as Researcher . Heinemann, 1999.
Then, for each individual essay from the collection, list the author's name in last name, first name format, the title of the essay, the editor's last name, and the page range:
L'Eplattenier, Barbara. "Finding Ourselves in the Past: An Argument for Historical Work on WPAs." Rose and Weiser, pp. 131-40.
Peeples, Tim. "'Seeing' the WPA With/Through Postmodern Mapping." Rose and Weiser, pp. 153-67.
Please note: When cross-referencing items in the works cited list, alphabetical order should be maintained for the entire list.
Poem or Short Story Examples :
Burns, Robert. "Red, Red Rose." 100 Best-Loved Poems, edited by Philip Smith, Dover, 1995, p. 26.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories , edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
If the specific literary work is part of the author's own collection (all of the works have the same author), then there will be no editor to reference:
Whitman, Walt. "I Sing the Body Electric." Selected Poems, Dover, 1991, pp. 12-19.
Carter, Angela. "The Tiger's Bride." Burning Your Boats: The Collected Stories, Penguin, 1995, pp. 154-69.
Article in a Reference Book (e.g. Encyclopedias, Dictionaries)
For entries in encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference works, cite the entry name as you would any other work in a collection but do not include the publisher information. Also, if the reference book is organized alphabetically, as most are, do not list the volume or the page number of the article or item.
"Ideology." The American Heritage Dictionary. 3rd ed. 1997.
A Multivolume Work
When citing only one volume of a multivolume work, include the volume number after the work's title, or after the work's editor or translator.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
When citing more than one volume of a multivolume work, cite the total number of volumes in the work. Also, be sure in your in-text citation to provide both the volume number and page number(s) ( see "Citing Multivolume Works" on our in-text citations resource .)
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980. 4 vols.
If the volume you are using has its own title, cite the book without referring to the other volumes as if it were an independent publication.
Churchill, Winston S. The Age of Revolution . Dodd, 1957.
An Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword
When citing an introduction, a preface, a foreword, or an afterword, write the name of the author(s) of the piece you are citing. Then give the name of the part being cited, which should not be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks; in italics, provide the name of the work and the name of the author of the introduction/preface/foreword/afterword. Finish the citation with the details of publication and page range.
Farrell, Thomas B. Introduction. Norms of Rhetorical Culture , by Farrell, Yale UP, 1993, pp. 1-13.
If the writer of the piece is different from the author of the complete work , then write the full name of the principal work's author after the word "By." For example, if you were to cite Hugh Dalziel Duncan’s introduction of Kenneth Burke’s book Permanence and Change, you would write the entry as follows:
Duncan, Hugh Dalziel. Introduction. Permanence and Change: An Anatomy of Purpose, by Kenneth Burke, 1935, 3rd ed., U of California P, 1984, pp. xiii-xliv.
Book Published Before 1900
Original copies of books published before 1900 are usually defined by their place of publication rather than the publisher. Unless you are using a newer edition, cite the city of publication where you would normally cite the publisher.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Italicize “The Bible” and follow it with the version you are using. Remember that your in-text (parenthetical citation) should include the name of the specific edition of the Bible, followed by an abbreviation of the book, the chapter and verse(s). (See Citing the Bible at In-Text Citations: The Basics .)
The Bible. Authorized King James Version , Oxford UP, 1998.
The Bible. The New Oxford Annotated Version , 3rd ed., Oxford UP, 2001.
The New Jerusalem Bible. Edited by Susan Jones, Doubleday, 1985.
A Government Publication
Cite the author of the publication if the author is identified. Otherwise, start with the name of the national government, followed by the agency (including any subdivisions or agencies) that serves as the organizational author. For congressional documents, be sure to include the number of the Congress and the session when the hearing was held or resolution passed as well as the report number. US government documents are typically published by the Government Printing Office.
United States, Congress, Senate, Committee on Energy and Natural Resources. Hearing on the Geopolitics of Oil . Government Printing Office, 2007. 110th Congress, 1st session, Senate Report 111-8.
United States, Government Accountability Office. Climate Change: EPA and DOE Should Do More to Encourage Progress Under Two Voluntary Programs . Government Printing Office, 2006.
Cite the title and publication information for the pamphlet just as you would a book without an author. Pamphlets and promotional materials commonly feature corporate authors (commissions, committees, or other groups that does not provide individual group member names). If the pamphlet you are citing has no author, cite as directed below. If your pamphlet has an author or a corporate author, put the name of the author (last name, first name format) or corporate author in the place where the author name typically appears at the beginning of the entry. (See also Books by a Corporate Author or Organization above.)
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Your Rights Under California Welfare Programs . California Department of Social Services, 2007.
Dissertations and Master's Theses
Dissertations and master's theses may be used as sources whether published or not. Unlike previous editions, MLA 8 specifies no difference in style for published/unpublished works.
The main elements of a dissertation citation are the same as those for a book: author name(s), title (italicized) , and publication date. Conclude with an indication of the document type (e.g., "PhD dissertation"). The degree-granting institution may be included before the document type (though this is not required). If the dissertation was accessed through an online repository, include it as the second container after all the other elements.
Bishop, Karen Lynn. Documenting Institutional Identity: Strategic Writing in the IUPUI Comprehensive Campaign . 2002. Purdue University, PhD dissertation.
Bile, Jeffrey. Ecology, Feminism, and a Revised Critical Rhetoric: Toward a Dialectical Partnership . 2005. Ohio University, PhD dissertation.
Mitchell, Mark. The Impact of Product Quality Reducing Events on the Value of Brand-Name Capital: Evidence from Airline Crashes and the 1982 Tylenol Poisonings. 1987. PhD dissertation. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry if the author and publisher are not the same.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To cite a dissertation, include in the entry the author, title, and date of publication as core elements. As an optional element, list the institution granting the degree and a description of the work. Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting. 2010. Northwestern U, PhD dissertation.
To cite a PhD thesis in a reference entry in MLA style 9th edition include the following elements: Author (s) name: Give the last name and name as presented in the source (e. g. Watson, John). For two authors, reverse only the first name, followed by 'and' and the second name in normal order (e. g. Watson, John, and John Watson).
The formatting for thesis and dissertation citations is largely the same. However, you should be sure to include the type of degree after the publication year as supplemental information. For instance, state if the source you are citing is an undergraduate thesis or a PhD dissertation. MLA Thesis and Dissertation Citation Structure (print)
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Times New Roman 12. 1″ page margins. Double line spacing. ½" indent for new paragraphs. Title case capitalization for headings. For accurate citations, you can use our free MLA Citation Generator. Download Word template Open Google Docs template.
To cite a dissertation in a reference entry in MLA style 9th edition include the following elements: Author (s) name: Give the last name and name as presented in the source (e. g. Watson, John). For two authors, reverse only the first name, followed by 'and' and the second name in normal order (e. g. Watson, John, and John Watson).
This guide follows the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook, published by the Modern Language Association in 2021. To cite sources in MLA style, you need. In-text citations that give the author's last name and a page number. A list of Works Cited that gives full details of every source. Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA ...
This guide will assist you in formatting in-text citations and a Works Cited list in the current MLA style. Skip to Main Content Recinto Universitario de Mayagüez, Call Box 9000 Mayagüez, PR 00681 (787) 832-4040 ext. 3810, 2151, 2155 [email protected]
Citations for dissertations/master's theses should include the following: 1. Name of Author . 2. Title of dissertation/thesis (italicized) 3. Date of Publication. 5. Institution granting the degree (optional) 6. Description of the work (optional) 7. Database and URL if accessed through a database or repository
Full Citation Rules. To cite a dissertation in MLA on the Works Cited page, follow this formula: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Dissertation/Thesis. Year. University, Dissertation type. Database.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
General Rule: Author's Last-name, First-name. Title of Disstertaion.Diss. Place of Study, Year. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
The MLA Handbook is published by the Modern Language Association and is the only official, authorized book on MLA style. The new, ninth edition builds on the MLA's unique approach to documenting sources using a template of core elements--facts, common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date--that allows writers to cite any type of work, from books, e-books, and journal ...
How to cite sources according to MLA. Austin, Katherine. Rasquache Baroque in the Chicana/o Borderlands. 2012.McGill U, PhD thesis.
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title.Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation.. If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) is a set of guidelines to properly write, cite, and format papers. This guide contains information on MLA 9th edition citation style including: how to cite sources for the Works Cited page at the end of your paper; how to do in-text citations within the body of your work
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
MLA citation. Formatted according to the MLA handbook 9 th edition. Simply copy it to the Works Cited page as is. If you need more information on MLA citations check out our MLA citation guide or start citing with the BibGuru MLA citation generator. Nichols, Mike. The Graduate. Embassy Pictures, 1967.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Unpublished Manuscripts or Papers. Manuscript. Student Paper (including your own!) Unpublished Manuscript. Works Cited List Citation. Author. "Title of Manuscript/Document.". date of composition (at least year), along with "the name and location of the library, research institution, or personal collection housing the material." Examples:
Unlike previous editions, MLA 8 specifies no difference in style for published/unpublished works. The main elements of a dissertation citation are the same as those for a book: author name(s), title (italicized), and publication date. Conclude with an indication of the document type (e.g., "PhD dissertation").