APA 7th referencing style
- About APA 7th
- Printing this guide
- In-text references
- Direct quotations
- Reference list
- Author information
- Additional referencing information
- Using headings
- Book chapter
- Brochure and pamphlets
- ChatGPT and other generative AI tools
- Conferences
- Dictionary or encyclopaedia
- Government legislation
- Journal article
- Lecture notes and slides
- Legal sources
- Newspaper or magazine article
- Other web sources
- Patents and standards
- Personal communication
- Press (media) release
- Secondary source (indirect citation)
- Social media
- Software and mobile apps
- Specialised health information
- Television program

Thesis - from website
Thesis - from database.
- Works in non-English languages
- Works in non-English scripts, such as Arabic or Chinese
- << Previous: Television program
- Next: Video >>
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 1:31 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uq.edu.au/referencing/apa7
- Library Guides

APA 7th Referencing
Apa 7th referencing: theses.

- In-text referencing
- Compiling a Reference list
- Citing tables and figures
- DOIs and Live hyperlinks
- Secondary sources
- Journal Articles
- Reports & Grey Literature
- Conference Materials
- Datasets, Software & Tests
- Social Media
- Images, tables & figures
- Sound & video
- Legislation & Cases
- Personal Communications
- Standards & Patents
- Course Notes or Course Presentations
- Generative AI
- Sample Reference List
On this page
Basic format to reference a thesis or dissertation.
- Referencing theses: Examples
The basics of a reference list entry for a thesis or dissertation:
- Author. The surname is followed by first initials.
- Year (in round brackets).
- Title (in italics ).
- Level of Thesis or Dissertation [in square brackets].
- University, also in [square brackets] following directly after the Level of Thesis, for e.g. [Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University]
- Database or Archive Name
- The first line of each citation is left adjusted. Every subsequent line is indented 5-7 spaces.
Mosek, E. (2017). Team flow: The missing piece in performance [Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University]. Victoria University Research Repository. http://vuir.vu.edu.au/35038/

- << Previous: Standards & Patents
- Next: Course Notes or Course Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Apr 10, 2024 11:36 AM
- URL: https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing
APA Style 6th Edition: Citing Your Sources
- Basics of APA Formatting
- In Text Quick View
- Block Quotes
- Books & eBooks
- Thesis/Dissertation
Standard Format
Various examples.
- Conference Presentations
- Course Documents
- Social Media
- Government Documents
- Academic Integrity and Plagiarism
- Additional Resources
- Sample Reference Page
Dissertation or thesis available from a database service:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of publication). Title of dissertation or thesis (Doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis). Retrieved from Name of database. (Accession or Order No.)
For an unpublished dissertation or thesis:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of creation). Title of dissertation or thesis (Unpublished doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis). Name of Institution, Location.
See Ch 7 pp. 207-208 APA Manual for more examples and formatting rules
Formatting:
- Italicize the title
- Identify whether source is doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis in parentheses after the title
- << Previous: Articles
- Next: Websites >>
- Last Updated: Sep 22, 2022 11:20 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/APA-citation-style
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Cite a Thesis in APA
Last Updated: January 31, 2023
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Jennifer Mueller is a wikiHow Content Creator. She specializes in reviewing, fact-checking, and evaluating wikiHow's content to ensure thoroughness and accuracy. Jennifer holds a JD from Indiana University Maurer School of Law in 2006. This article has been viewed 10,655 times.
When you're using a thesis as a reference for a research paper, your citation format will vary depending on where you found the thesis. With the American Psychological Association (APA) citation method, if the thesis was published, you would use the same format you would normally use for a book or journal article. However, your in-text citation and reference list entry will vary if you're referencing an unpublished thesis. [1] X Research source
Crafting an In-Text Citation

- For example, you might write: "However, people's cupcake flavor preference is not correlated to their favorite color (Baker 2018)."

- For example, you might write: "According to Baker (2018), people whose favorite color was purple were not necessarily fond of grape-flavored cupcakes."

- For example, you might write: "As late as 2017, scholars suspected that people's favorite foods corresponded with their favorite colors. However, in 2018, Baker's research showed that there was no correlation between people's favorite colors and their favorite cupcake flavors, indicating the correlation between foods and colors may be overstated."

- The citation goes outside the closing quotation marks but inside the closing punctuation for short quotes. For block quotes, place the citation outside the closing punctuation for the quote.
- If you included the author's name in your text, place the year immediately after the author's name. Then place a parenthetical after the quote with only the page number or range.
Parenthetical In-Text Citation Format for a Direct Quote:
(Author Year, p. #).
Including a Reference List Entry

- Example: Baker, C. F.

- Example: Baker, C. F. (2018).

- Example: Baker, C. F. (2018). Constant craving: Assessing the correlation between color and flavor based on self-professed preferences (Unpublished master's thesis).

- Do not abbreviate place names. Omit the name of the city if it is included in the name of the university.
- Example: Baker, C. F. (2018). Constant craving: Assessing the correlation between color and flavor based on self-professed preferences (Unpublished master's thesis). Candyland University, Narnia.
APA Reference List Entry — Unpublished Thesis
Author, A. A. (Year). Title in sentence case: Subtitle in sentence case (Unpublished [level] thesis). University Name, University Location.
Expert Q&A
- This article provides guidance on how to cite an unpublished thesis in APA format. If the thesis is published, use the format that corresponds to the medium in which you found the thesis. [10] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing/theses
- ↑ https://aut.ac.nz.libguides.com/APA6th/theses
- ↑ http://aut.ac.nz.libguides.com/APA6th/intextcitation
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_other_print_sources.html
About this article

Did this article help you?

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Citation guides
All you need to know about citations
How to cite an undergraduate thesis in APA
- Google Docs
To cite an undergraduate thesis in a reference entry in APA style 6th edition include the following elements:
- Author(s) of the thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to seven authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For eight or more authors include the first six names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name.
- Year of publication: Give the year in brackets followed by a full stop.
- Title of the undergraduate thesis: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized.
- URL: Give the full URL where the document can be retrieved from.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of an undergraduate thesis in APA style 6th edition:
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the undergraduate thesis (Bachelor's thesis). Retrieved from URL
If the thesis is available from a database, archive or any online platform use the following template:
- Author(s) of the thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to 20 authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For 21 or more authors include the first 19 names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name.
- Publication number: Give the identification number of the thesis, if available.
- Name of the degree awarding institution: Give the name of the institution.
- Name of Platform: Give the name of the database, archive or any platform that holds the thesis.
- URL: If the thesis was found on a database, omit this element.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of an undergraduate thesis in APA style 7th edition:
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the undergraduate thesis ( Publication number ) [Bachelor's thesis, Name of the degree awarding institution ]. Name of Platform . URL
If the thesis has not been published or is available from a database use the following template:
- Location: Give the location of the institution. If outside the United States also include the country name.
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the undergraduate thesis (Unpublished bachelor's thesis). Name of the degree awarding institution , Location .
If the thesis is not published, use the following template:
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the undergraduate thesis [Unpublished bachelor's thesis]. Name of the degree awarding institution .
APA reference list examples
Take a look at our reference list examples that demonstrate the APA style guidelines for an undergraduate thesis citation in action:
A bachelor's thesis from an online platform
Parekh, P., & Pishchenko, V . ( 2013 ). Factors influencing the choice of bank – An international student perspective ( Bachelor's thesis ). Retrieved from https://www.divaportal.org/smash/get/diva2:653388/FULLTEXT02.pdf
Parekh, P., & Pishchenko, V . ( 2013 ). Factors influencing the choice of bank – An international student perspective [ Bachelor's thesis , Dalarna University ]. Diva Portal . https://www.divaportal.org/smash/get/diva2:653388/FULLTEXT02.pdf
An unpublished undergraduate thesis
Baslow, W . ( 2015 ). The applicability of the qualitative system analysis as decision-making tool in public administration by the example of the municipality Ludwigsburg ( Unpublished undergraduate thesis ). Leuphana University of Lüneburg , Lüneburg, Germany .
Baslow, W . ( 2015 ). The applicability of the qualitative system analysis as decision-making tool in public administration by the example of the municipality Ludwigsburg [ Unpublished undergraduate thesis ]. Leuphana University of Lüneburg .

This citation style guide is based on the official Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association ( 6 th edition).
More useful guides
- APA Referencing: Theses
- APA 6th referencing style: Theses
- APA 6th Edition Citation Style-Dissertation/Thesis
More great BibGuru guides
- MLA: how to cite a translated book
- MLA: how to cite a master's thesis
- Harvard: how to cite a report
Automatic citations in seconds
Citation generators
Alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
How Do I Reference?
Referencing and Avoiding Plagiarism
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
301 Accesses
References are an important part of your dissertation, and you may need anywhere between 20 and 200 references, possibly more depending on the length of your thesis. But it is important that you reference appropriately and correctly, whether this is in the in-text citations or the list of references at the end of your thesis. This chapter explains the differences between a reference list and a bibliography. You will also want to avoid the risk of plagiarism, and this is explained, to help you ensure that you write your dissertation entirely in your own words.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Cottrell S (2008) The study skills handbook. Palgrave Macmillan, London
Google Scholar
Lindahl JF, Grace D (2018) Students' and supervisors' knowledge and attitudes regarding plagiarism and referencing. Research Integrity and Peer Review 3:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-018-0054-2
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Neville C (2010) The complete guide to referencing and avoiding plagiarism. Open University Press, London
Perry B (2010) Exploring academic misconduct: some insights into student behaviour. Act Learn High Educ 11:97–108
Article Google Scholar
Rumsey S (2008) How to find information, a guide for researchers. Open University Press, London
Reeves S, Jeanes Y (2022) The study skills handbook for nutritionists and dietitians. Open University Press, London
Further Reading
Neville C (2010) The Complete Guide to Referencing and Avoiding Plagiarism. Open University Press, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Reference?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_11
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

APA 7th Edition Referencing Guide1
- What is APA?
In-text citations
- Reference list
- Chapter in an edited book
- Journal articles & Databases
- Works with multiple authors
- Webpages/online & software
- General images faqs
- Audiovisual media
- Personal communication
- Study material
- New Zealand legislation
- Other resources
- Tricky health resources
- Health books
- Health journals
- Health web resources
- Systematic reviews
- Point-of-care resources
- Visual health resources
- Tricky health FAQs
- APA for publication

Quick links
Referencing a thesis or dissertation (from an institution's online archive/repository)
When referencing a thesis or dissertation, include the type and the awarding institution in brackets after the title—e.g., (Master's thesis, The University of Waikato). Give the name of the institution's repository and link directly to the thesis document. For example:
Author, A. (Date). Title of thesis or dissertation: Subtitle in italic sentence case [Type and awarding institution]. Name of Institution's Repository. URL
Stewart, A. S. (2017). C ritical thinking in nursing: A critical discourse analysis of a perpetual paradox [Doctoral thesis, Auckland University of Technology]. Auckland University of Technology Open Theses & Dissertations. https://openrepository.aut.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/10292/10838/StewartA.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
Reference list entry
Stewart, A. S. (2017). Critical thinking in nursing: A critical discourse analysis of a perpetual paradox [Doctoral thesis, Auckland University of Technology]. Auckland University of Technology Open Theses & Dissertations. https://openrepository.aut.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/10292/10838/StewartA.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
Page/paragraph numbers are optional for paraphrased information.
Narrative Stewart (2017) suggests ... (p. 143). Parenthetical ... (Stewart, 2017, p. 143).
Referencing a previous assignment
If you are required to reference work you have submitted for a previous assignment, it is considered unpublished work.
Author, A. (Date). Title of assignment: Subtitle in italic sentence case [Unpublished assignment submitted for Paper code]. Name of Department, Name of Institution.
Mahana, J. (2021). Outside the box thinking in business practice: A creative approach [Unpublished assignment submitted for BIZM540]. Centre for Business and Enterprise, Waikato Institute of Technology.
Mahana, J. (2017). Outside the box thinking in business practice: A creative approach [Unpublished assignment submitted for BIZ540]. Centre for Business and Enterprise, Waikato Institute of Technology.
Narrative Mahana (2021) suggests ... (p. 143). Parenthetical ... (Mahana, 2021, p. 143).
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 11:26 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wintec.ac.nz/APA7
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in MLA
How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in MLA
Citing a thesis or dissertation.
Thesis – A document submitted to earn a degree at a university.
Dissertation – A document submitted to earn an advanced degree, such as a doctorate, at a university.
The formatting for thesis and dissertation citations is largely the same. However, you should be sure to include the type of degree after the publication year as supplemental information. For instance, state if the source you are citing is an undergraduate thesis or a PhD dissertation.
MLA Thesis and Dissertation Citation Structure (print)
Last, First M. Title of the Thesis/Dissertation. Year Published. Name of University, type of degree.
MLA Thesis and Dissertation Citation Structure (online)
Last, First M. Title of the Thesis/Dissertation. Year Published. Name of University, type of degree. Website Name , URL.
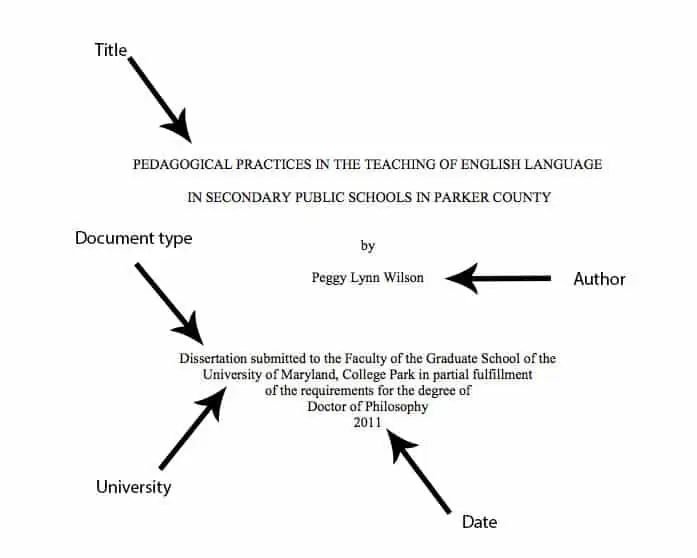
Wilson, Peggy Lynn. Pedagogical Practices in the Teaching of English Language in Secondary Public Schools in Parker County . 2011. University of Maryland, PhD dissertation.
In-text Citation Structure
(Author Last Name page #)
In-text Citation Example
(Wilson 14)
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- Privacy Policy

Home » References in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
References in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

References in Research
Definition:
References in research are a list of sources that a researcher has consulted or cited while conducting their study. They are an essential component of any academic work, including research papers, theses, dissertations, and other scholarly publications.
Types of References
There are several types of references used in research, and the type of reference depends on the source of information being cited. The most common types of references include:
References to books typically include the author’s name, title of the book, publisher, publication date, and place of publication.
Example: Smith, J. (2018). The Art of Writing. Penguin Books.
Journal Articles
References to journal articles usually include the author’s name, title of the article, name of the journal, volume and issue number, page numbers, and publication date.
Example: Johnson, T. (2021). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology, 32(4), 87-94.
Web sources
References to web sources should include the author or organization responsible for the content, the title of the page, the URL, and the date accessed.
Example: World Health Organization. (2020). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public
Conference Proceedings
References to conference proceedings should include the author’s name, title of the paper, name of the conference, location of the conference, date of the conference, and page numbers.
Example: Chen, S., & Li, J. (2019). The Future of AI in Education. Proceedings of the International Conference on Educational Technology, Beijing, China, July 15-17, pp. 67-78.
References to reports typically include the author or organization responsible for the report, title of the report, publication date, and publisher.
Example: United Nations. (2020). The Sustainable Development Goals Report. United Nations.
Formats of References
Some common Formates of References with their examples are as follows:
APA (American Psychological Association) Style
The APA (American Psychological Association) Style has specific guidelines for formatting references used in academic papers, articles, and books. Here are the different reference formats in APA style with examples:
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example : Smith, J. K. (2005). The psychology of social interaction. Wiley-Blackwell.
Journal Article
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page numbers.
Example : Brown, L. M., Keating, J. G., & Jones, S. M. (2012). The role of social support in coping with stress among African American adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 22(1), 218-233.
Author, A. A. (Year of publication or last update). Title of page. Website name. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, December 11). COVID-19: How to protect yourself and others. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html
Magazine article
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of Magazine, volume number(issue number), page numbers.
Example : Smith, M. (2019, March 11). The power of positive thinking. Psychology Today, 52(3), 60-65.
Newspaper article:
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of Newspaper, page numbers.
Example: Johnson, B. (2021, February 15). New study shows benefits of exercise on mental health. The New York Times, A8.
Edited book
Editor, E. E. (Ed.). (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example : Thompson, J. P. (Ed.). (2014). Social work in the 21st century. Sage Publications.
Chapter in an edited book:
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of chapter. In E. E. Editor (Ed.), Title of book (pp. page numbers). Publisher.
Example : Johnson, K. S. (2018). The future of social work: Challenges and opportunities. In J. P. Thompson (Ed.), Social work in the 21st century (pp. 105-118). Sage Publications.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Style
The MLA (Modern Language Association) Style is a widely used style for writing academic papers and essays in the humanities. Here are the different reference formats in MLA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Smith, John. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Journal article
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, Publication year, page numbers.
Example : Brown, Laura M., et al. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence, vol. 22, no. 1, 2012, pp. 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name, Publication date, URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC, 11 Dec. 2020, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Publication date, page numbers.
Example : Smith, Mary. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, Mar. 2019, pp. 60-65.
Newspaper article
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Publication date, page numbers.
Example : Johnson, Bob. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, 15 Feb. 2021, p. A8.
Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Thompson, John P., editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. Sage Publications, 2014.
Chapter in an edited book
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last name, Publisher, Publication year, page numbers.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, Sage Publications, 2014, pp. 105-118.
Chicago Manual of Style
The Chicago Manual of Style is a widely used style for writing academic papers, dissertations, and books in the humanities and social sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Chicago style:
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Publication year): page numbers.
Example : Brown, Laura M., John G. Keating, and Sarah M. Jones. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 22, no. 1 (2012): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. Publication date. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. December 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Publication date.
Example : Smith, Mary. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 2019.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Publication date.
Example : Johnson, Bob. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Example : Thompson, John P., ed. Social Work in the 21st Century. Sage Publications, 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, page numbers. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, 105-118. Sage Publications, 2014.
Harvard Style
The Harvard Style, also known as the Author-Date System, is a widely used style for writing academic papers and essays in the social sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Harvard Style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Smith, John. 2005. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number (issue number): page numbers.
Example: Brown, Laura M., John G. Keating, and Sarah M. Jones. 2012. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 22 (1): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. URL. Accessed date.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. Accessed April 1, 2023.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, month and date of publication.
Example : Smith, Mary. 2019. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 2019.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, month and date of publication.
Example : Johnson, Bob. 2021. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Year of publication. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Thompson, John P., ed. 2014. Social Work in the 21st Century. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, page numbers. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. 2014. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, 105-118. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Vancouver Style
The Vancouver Style, also known as the Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals, is a widely used style for writing academic papers in the biomedical sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Vancouver Style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Abbreviated Journal Title. Year of publication; volume number(issue number):page numbers.
Example : Brown LM, Keating JG, Jones SM. The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents. J Res Adolesc. 2012;22(1):218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Webpage. Website Name [Internet]. Publication date. [cited date]. Available from: URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others [Internet]. 2020 Dec 11. [cited 2023 Apr 1]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Title of Magazine. Year of publication; month and day of publication:page numbers.
Example : Smith M. The Power of Positive Thinking. Psychology Today. 2019 Mar 1:32-35.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Title of Newspaper. Year of publication; month and day of publication:page numbers.
Example : Johnson B. New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health. The New York Times. 2021 Feb 15:A4.
Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example: Thompson JP, editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Chapter. In: Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication. page numbers.
Example : Johnson KS. The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities. In: Thompson JP, editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2014. p. 105-118.
Turabian Style
Turabian style is a variation of the Chicago style used in academic writing, particularly in the fields of history and humanities. Here are the different reference formats in Turabian style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Year of publication): page numbers.
Example : Brown, LM, Keating, JG, Jones, SM. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” J Res Adolesc 22, no. 1 (2012): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Name of Website. Publication date. Accessed date. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. December 11, 2020. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Month Day, Year of publication, page numbers.
Example : Smith, M. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 1, 2019, 32-35.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Month Day, Year of publication.
Example : Johnson, B. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Thompson, JP, ed. Social Work in the 21st Century. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s Last name, First name, page numbers. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Johnson, KS. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by Thompson, JP, 105-118. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Style
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) style is commonly used in engineering, computer science, and other technical fields. Here are the different reference formats in IEEE style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Oppenheim, A. V., & Schafer, R. W. Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Abbreviated Journal Title, vol. number, no. issue number, pp. page numbers, Month year of publication.
Example: Shannon, C. E. “A Mathematical Theory of Communication.” Bell System Technical Journal, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 379-423, July 1948.
Conference paper
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Paper.” In Title of Conference Proceedings, Place of Conference, Date of Conference, pp. page numbers, Year of publication.
Example: Gupta, S., & Kumar, P. “An Improved System of Linear Discriminant Analysis for Face Recognition.” In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Harbin, China, Dec. 2011, pp. 144-147.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Name of Website. Date of publication or last update. Accessed date. URL.
Example : National Aeronautics and Space Administration. “Apollo 11.” NASA. July 20, 1969. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/apollo/apollo11.html.
Technical report
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Report.” Name of Institution or Organization, Report number, Year of publication.
Example : Smith, J. R. “Development of a New Solar Panel Technology.” National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL/TP-6A20-51645, 2011.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Patent.” Patent number, Issue date.
Example : Suzuki, H. “Method of Producing Carbon Nanotubes.” US Patent 7,151,019, December 19, 2006.
Standard Title. Standard number, Publication date.
Example : IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic. IEEE Std 754-2008, August 29, 2008
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) style is commonly used in chemistry and related fields. Here are the different reference formats in ACS style:
Author’s Last name, First name; Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Abbreviated Journal Title Year, Volume, Page Numbers.
Example : Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y. Facile Preparation of Fe3O4/graphene Composites Using a Hydrothermal Method for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2715-2721.
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title; Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication.
Example : Carey, F. A. Organic Chemistry; McGraw-Hill: New York, 2008.
Author’s Last name, First name. Chapter Title. In Book Title; Editor’s Last name, First name, Ed.; Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication; Volume number, Chapter number, Page Numbers.
Example : Grossman, R. B. Analytical Chemistry of Aerosols. In Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications; Baron, P. A.; Willeke, K., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, 2001; Chapter 10, pp 395-424.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Webpage. Website Name, URL (accessed date).
Example : National Institute of Standards and Technology. Atomic Spectra Database. https://www.nist.gov/pml/atomic-spectra-database (accessed April 1, 2023).
Author’s Last name, First name. Patent Number. Patent Date.
Example : Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W. US Patent 9,999,999, December 31, 2022.
Author’s Last name, First name; Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. In Title of Conference Proceedings, Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication; Volume Number, Page Numbers.
Example : Jia, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X. Fast Adsorption of Organic Pollutants by Graphene Oxide. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, 2017; Volume 1, pp 223-228.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) style is commonly used in medical and scientific fields. Here are the different reference formats in AMA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Article Title. Journal Abbreviation. Year; Volume(Issue):Page Numbers.
Example : Jones, R. A.; Smith, B. C. The Role of Vitamin D in Maintaining Bone Health. JAMA. 2019;321(17):1765-1773.
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : Guyton, A. C.; Hall, J. E. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2015.
Author’s Last name, First name. Chapter Title. In: Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: Page Numbers.
Example: Rajakumar, K. Vitamin D and Bone Health. In: Holick, M. F., ed. Vitamin D: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2010:211-222.
Author’s Last name, First name. Webpage Title. Website Name. URL. Published date. Updated date. Accessed date.
Example : National Cancer Institute. Breast Cancer Prevention (PDQ®)–Patient Version. National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/breast-prevention-pdq. Published October 11, 2022. Accessed April 1, 2023.
Author’s Last name, First name. Conference presentation title. In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Place of Conference.
Example : Smith, J. R. Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Meta-Analysis. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research; September 20-23, 2022; San Diego, CA.
Thesis or dissertation
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Thesis or Dissertation. Degree level [Doctoral dissertation or Master’s thesis]. University Name; Year.
Example : Wilson, S. A. The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Bone Health in Postmenopausal Women [Doctoral dissertation]. University of California, Los Angeles; 2018.
ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) Style
The ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) style is commonly used in civil engineering fields. Here are the different reference formats in ASCE style:
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Title, volume number, issue number (year): page numbers. DOI or URL (if available).
Example : Smith, J. R. “Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems in Urban Areas.” Journal of Environmental Engineering, vol. 146, no. 3 (2020): 04020010. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001668.
Example : McCuen, R. H. Hydrologic Analysis and Design. 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2013.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In: Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: page numbers.
Example : Maidment, D. R. “Floodplain Management in the United States.” In: Shroder, J. F., ed. Treatise on Geomorphology. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2013: 447-460.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Paper Title.” In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Location. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: page numbers.
Example: Smith, J. R. “Sustainable Drainage Systems for Urban Areas.” In: Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure; November 6-9, 2019; Los Angeles, CA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers; 2019: 156-163.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Report Title.” Report number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. “Hurricane Sandy Coastal Risk Reduction Program, New York and New Jersey.” Report No. P-15-001. Washington, DC: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers; 2015.
CSE (Council of Science Editors) Style
The CSE (Council of Science Editors) style is commonly used in the scientific and medical fields. Here are the different reference formats in CSE style:
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Article Title.” Journal Title. Year;Volume(Issue):Page numbers.
Example : Smith, J.R. “Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems in Urban Areas.” Journal of Environmental Engineering. 2020;146(3):04020010.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Chapter Title.” In: Editor’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial., ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year:Page numbers.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Paper Title.” In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Location. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : Smith, J.R. “Sustainable Drainage Systems for Urban Areas.” In: Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure; November 6-9, 2019; Los Angeles, CA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers; 2019.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Report Title.” Report number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Bluebook Style
The Bluebook style is commonly used in the legal field for citing legal documents and sources. Here are the different reference formats in Bluebook style:
Case citation
Case name, volume source page (Court year).
Example : Brown v. Board of Education, 347 U.S. 483 (1954).
Statute citation
Name of Act, volume source § section number (year).
Example : Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7401 (1963).
Regulation citation
Name of regulation, volume source § section number (year).
Example: Clean Air Act, 40 C.F.R. § 52.01 (2019).
Book citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. Book Title. Edition number (if applicable). Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example: Smith, J.R. Legal Writing and Analysis. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Aspen Publishers; 2015.
Journal article citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Article Title.” Journal Title. Volume number (year): first page-last page.
Example: Garcia, C. “The Right to Counsel: An International Comparison.” International Journal of Legal Information. 43 (2015): 63-94.
Website citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed month day, year).
Example : United Nations. “Universal Declaration of Human Rights.” United Nations. https://www.un.org/en/universal-declaration-human-rights/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Oxford Style
The Oxford style, also known as the Oxford referencing system or the documentary-note citation system, is commonly used in the humanities, including literature, history, and philosophy. Here are the different reference formats in Oxford style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Smith, John. The Art of Writing. New York: Penguin, 2020.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Title volume, no. issue (year): page range.
Example: Garcia, Carlos. “The Role of Ethics in Philosophy.” Philosophy Today 67, no. 3 (2019): 53-68.
Chapter in an edited book citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In Book Title, edited by Editor’s Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Lee, Mary. “Feminism in the 21st Century.” In The Oxford Handbook of Feminism, edited by Jane Smith, 51-69. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed day month year).
Example : Jones, David. “The Importance of Learning Languages.” Oxford Language Center. https://www.oxfordlanguagecenter.com/importance-of-learning-languages/ (accessed 3 January 2023).
Dissertation or thesis citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Dissertation/Thesis.” PhD diss., University Name, Year of Publication.
Example : Brown, Susan. “The Art of Storytelling in American Literature.” PhD diss., University of Oxford, 2020.
Newspaper article citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Month Day, Year.
Example : Robinson, Andrew. “New Developments in Climate Change Research.” The Guardian, September 15, 2022.

AAA (American Anthropological Association) Style
The American Anthropological Association (AAA) style is commonly used in anthropology research papers and journals. Here are the different reference formats in AAA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example : Smith, John. 2019. The Anthropology of Food. New York: Routledge.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Article Title.” Journal Title volume, no. issue: page range.
Example : Garcia, Carlos. 2021. “The Role of Ethics in Anthropology.” American Anthropologist 123, no. 2: 237-251.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Chapter Title.” In Book Title, edited by Editor’s Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example: Lee, Mary. 2018. “Feminism in Anthropology.” In The Oxford Handbook of Feminism, edited by Jane Smith, 51-69. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed day month year).
Example : Jones, David. 2020. “The Importance of Learning Languages.” Oxford Language Center. https://www.oxfordlanguagecenter.com/importance-of-learning-languages/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Title of Dissertation/Thesis.” PhD diss., University Name.
Example : Brown, Susan. 2022. “The Art of Storytelling in Anthropology.” PhD diss., University of California, Berkeley.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Month Day.
Example : Robinson, Andrew. 2021. “New Developments in Anthropology Research.” The Guardian, September 15.
AIP (American Institute of Physics) Style
The American Institute of Physics (AIP) style is commonly used in physics research papers and journals. Here are the different reference formats in AIP style:
Example : Johnson, S. D. 2021. “Quantum Computing and Information.” Journal of Applied Physics 129, no. 4: 043102.
Example : Feynman, Richard. 2018. The Feynman Lectures on Physics. New York: Basic Books.
Example : Jones, David. 2020. “The Future of Quantum Computing.” In The Handbook of Physics, edited by John Smith, 125-136. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Conference proceedings citation
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Title of Paper.” Proceedings of Conference Name, date and location: page range. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example : Chen, Wei. 2019. “The Applications of Nanotechnology in Solar Cells.” Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Nanotechnology, July 15-17, Tokyo, Japan: 224-229. New York: AIP Publishing.
Example : American Institute of Physics. 2022. “About AIP Publishing.” AIP Publishing. https://publishing.aip.org/about-aip-publishing/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Patent citation
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. Patent Number.
Example : Smith, John. 2018. US Patent 9,873,644.
References Writing Guide
Here are some general guidelines for writing references:
- Follow the citation style guidelines: Different disciplines and journals may require different citation styles (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). It is important to follow the specific guidelines for the citation style required.
- Include all necessary information : Each citation should include enough information for readers to locate the source. For example, a journal article citation should include the author(s), title of the article, journal title, volume number, issue number, page numbers, and publication year.
- Use proper formatting: Citation styles typically have specific formatting requirements for different types of sources. Make sure to follow the proper formatting for each citation.
- Order citations alphabetically: If listing multiple sources, they should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name.
- Be consistent: Use the same citation style throughout the entire paper or project.
- Check for accuracy: Double-check all citations to ensure accuracy, including correct spelling of author names and publication information.
- Use reputable sources: When selecting sources to cite, choose reputable and authoritative sources. Avoid sources that are biased or unreliable.
- Include all sources: Make sure to include all sources used in the research, including those that were not directly quoted but still informed the work.
- Use online tools : There are online tools available (e.g., citation generators) that can help with formatting and organizing references.
Purpose of References in Research
References in research serve several purposes:
- To give credit to the original authors or sources of information used in the research. It is important to acknowledge the work of others and avoid plagiarism.
- To provide evidence for the claims made in the research. References can support the arguments, hypotheses, or conclusions presented in the research by citing relevant studies, data, or theories.
- To allow readers to find and verify the sources used in the research. References provide the necessary information for readers to locate and access the sources cited in the research, which allows them to evaluate the quality and reliability of the information presented.
- To situate the research within the broader context of the field. References can show how the research builds on or contributes to the existing body of knowledge, and can help readers to identify gaps in the literature that the research seeks to address.
Importance of References in Research
References play an important role in research for several reasons:
- Credibility : By citing authoritative sources, references lend credibility to the research and its claims. They provide evidence that the research is based on a sound foundation of knowledge and has been carefully researched.
- Avoidance of Plagiarism : References help researchers avoid plagiarism by giving credit to the original authors or sources of information. This is important for ethical reasons and also to avoid legal repercussions.
- Reproducibility : References allow others to reproduce the research by providing detailed information on the sources used. This is important for verification of the research and for others to build on the work.
- Context : References provide context for the research by situating it within the broader body of knowledge in the field. They help researchers to understand where their work fits in and how it builds on or contributes to existing knowledge.
- Evaluation : References provide a means for others to evaluate the research by allowing them to assess the quality and reliability of the sources used.
Advantages of References in Research
There are several advantages of including references in research:
- Acknowledgment of Sources: Including references gives credit to the authors or sources of information used in the research. This is important to acknowledge the original work and avoid plagiarism.
- Evidence and Support : References can provide evidence to support the arguments, hypotheses, or conclusions presented in the research. This can add credibility and strength to the research.
- Reproducibility : References provide the necessary information for others to reproduce the research. This is important for the verification of the research and for others to build on the work.
- Context : References can help to situate the research within the broader body of knowledge in the field. This helps researchers to understand where their work fits in and how it builds on or contributes to existing knowledge.
- Evaluation : Including references allows others to evaluate the research by providing a means to assess the quality and reliability of the sources used.
- Ongoing Conversation: References allow researchers to engage in ongoing conversations and debates within their fields. They can show how the research builds on or contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Fast and free citation generator APA 6th and 7th ed. • MLA 8th ed. • Chicago 16th ed.
- Create Title Page
- Style Guide
- Manage Bibliographies

Mindfullness & COVID-19
- General Format Rules
- In-Text Citations
- General Rules – Reference List
- Encyclopedia & Dictionary
- Government Publication
- Social media
- Dissertation/Thesis
- Online Video
- Audio/Podcast
- Lecture notes
APA 6 Style Guide
Thesis/dissertation – apa reference list, capitalization.
- The document title is in sentence case – Only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. Always capitalize the first word, the first word after a colon or a dash.
- The title of the thesis or dissertation is in title case – Each word in the name is capitalized, except for articles (a, an, the), prepositions (against, between, in, of, to), conjunctions (and, but, for, nor, or, so, yet), and the infinitive 'to'.
Thesis/Dissertation – Unpublished/Print version
For papers written in United States list City and State. For countries outside United States list City and Country.
Author , A . A . ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Unpublished doctoral dissertation [OR] Unpublished master's thesis). Academic Institution , City , State [OR] Country .
- Considine, M. (1986). Australian insurance politics in the 1970s: Two case studies . (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia.
- Kassover,A. (1987). Treatment of abusive males: Voluntary vs. court-mandated referrals (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Nova University, Fort Lauderdale, FL.
Thesis/Dissertation – From a commercial database (e.g., ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database)
Author , A ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from Name of database . ( Accession or Order Number )
Cooley, T. (2009). Design, development, and implementation of a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): The Hartford Job Corps Academy case study (Doctoral dissertation). Available from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database. (UMI No. 3344745)
Thesis/Dissertation – Institutional Database (i.e. University website)
For U.S. thesis do not include university or locations. Include the university and location (City and Country) for a non-U.S. online thesis.
Author , A . A . ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis). Retrieved from http:// url.com
- Adams, R. J. (1973). Building a foundation for evaluation of instruction in higher education and continuing education (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from http://www.ohiolink.edu/etd/
- Barua, S. (2010). Drought assessment and forecasting using a nonlinear aggregated drought index (Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University, Melbourne, Australia). Retrieved from http://vuir.vu.edu.au/1598
Thesis/Dissertation – Web
For U.S. thesis do not include locations. Include the location (City and Country) for a non-U.S. online thesis.
Author , A . A . ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis, Institution issuing degree). Retrieved from http:// www.url.com
- Bruckman, A. (1997). MOOSE Crossing: Construction, community, and learning in a networked virtual world for kids (Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology). Retrieved from http://www-static.cc.gatech.edu/~asb/thesis

I Help to Study
Useful information for students
Home » Thesis » Method of writing references in thesis writing
- Academic Writing
- Assignments
- Business Plans
- Buy Services
- Custom Writing
- Dissertations
- For Professionals
- Help & Assistance
- Useful Services
- Various Papers

Method of writing references in thesis writing

At the end of all pieces of academic writing, you need a list of materials that you have used or referred to. This usually has a heading: references but may be bibliography or works cited depending on the conventions of the system you use.
The object of your writing is for you to say something for yourself using the ideas of the subject, for you to present ideas you have learned in your own way. The emphasis should be on working with other people’s ideas, rather than reproducing their words. The ideas and people that you refer to need to be made explicit by a system of referencing. This consists of a list of materials that you have used at the end of the piece of writing and references to this list at various points throughout the essay. The purpose of this is to supply the information needed to allow a user to find a source.
Therefore, at the end of your assignment you need a list of the materials you have used – a bibliography or a reference list.
There are many ways of writing a list of references – check with your department for specific information.
- The most common system is called the Harvard system. There is no definitive version of the Harvard system and most universities have their own. But the one used here – the American Psychological Association style – is well known and often used (American Psychological Association, 1983, 1994, 1999, 2001, 2010).
- Click here or see Gibaldi (2003) and Modern Languages Association (1998, 2009) for another way.
- Many scientists use a numerical system, often called the Vancouver style or BS 1629. Click here or see International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (1991) for more information.

Abercrombie, D. (1968). Paralanguage. British Journal of Disorders of Communication, 3, 55-59. Barr, P. Clegg, J. Wallace, C. (1981). Advanced reading skills . London: Longman. Chomsky, N. (1973). Linguistic theory. In J. W. Oller J. C. Richards (Eds.), Focus on the learner (pp. 29-35). Rowley, Massachusetts: Newbury House. Fromkin, V. Rodman, R. (1983). An introduction to language. London: Holt-Saunders. Guiora, A. Z. Paluszny, M. Beit-Hallahmi, B. Catford, J. C. Cooley, R. E. Dull, C. Y. (1975). Language and person: Studies in language behaviour. Language Learning, 25 . 43-61. GVU’s 8th WWW user survey. (n.d.). Retrieved from cc.gatech.edu/gvu/usersurveys/survey1997-10/ Kinsella, V. (Ed.). (1978). Language teaching and linguistics: Surveys. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Lipinsky, E. Bender, R. (1980). Critical voices on the economy. Survey, 25, 38-42. Oller, J. W. Richards, J. C. (Eds.). (1973). Focus on the learner. Rowley, Massachusetts: Newbury House. Longman dictionary of contemporary English. (1978). London: Longman. Smith, F. (1978). Reading. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Stern, H. H. Weinrib, A. (1978). Foreign languages for younger children: Trends and assessment. In V. Kinsella (Ed.), Language teaching and linguistics: Surveys (pp. 152-172). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Use heading: References.

Use italics (or underlining in handwriting) for titles of books, periodicals, newspapers etc.
Use alphabetical order. Alphabetise works with no author by the first significant word in the title.
All co-authors should be listed.
Indent second etc. lines
Use (n.d.) if no date is given.
If the author of a document is not given, begin the reference with the title of the document.
Smith, F. (1978). Reading . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Fromkin, V. Rodman, R. (1983). An introduction to language. London: Holt-Saunders.
Barr, P. Clegg, J. Wallace, C. (1981). Advanced reading skills . London: Longman.
Kinsella, V. (Ed.). (1978). Language teaching and linguistics: Surveys . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Oller, J. W. Richards, J. C. (Eds.). (1973). Focus on the learner . Rowley, Massachusetts: Newbury House.
British Council Teaching Information Centre. (1978). Pre-sessional courses for overseas students. London: British Council.
Longman dictionary of contemporary English. (1978). London: Longman. The Times atlas of the world (5th ed.). (1975). New York: New York Times.
Fromkin, V. Rodman, R. (1983). An introduction to language (3rd ed.). London: Holt-Saunders.
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences (rev. ed.). New York: Plenum Press.
Piaget, J. Inhelder, B. (1951). La genése de l’idée de hasard chez l’enfant [The origin of the idea of danger in the child]. Paris: Presses Universitaires de France.
Luria, A. R. (1969). The mind of a mnemonist (L. Solotaroff, Trans.). New York: Avon Books. (Original work published 1965)
Lyons, J. (1981a). Language and linguistics . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Lyons, J. (1981b). Language, meaning and context . London: Fontana.
3. Periodical articles
Abercrombie, D. (1968). Paralanguage. British Journal of Disorders of Communication, 3, 55-59.
Lipinsky, E. Bender, R. (1980). Critical voices on the economy. Survey, 25, 38-42.
Guiora, A. Z. Paluszny, M. Beit-Hallahmi, B. Catford, J. C. Cooley, R. E. Dull, C. Y. (1975). Language and person: Studies in language behaviour. Language Learning, 25 . 43-61.
Carmody, T. P. (1982). A new look at medicine from a social perspective [Review of the book Social contexts of health, illness and patient care . by E. G. Mishler, L. R. Amarasingham, S. D. Osherson, S. T. Hauser, N. E. Waxler R. Liem]. Contemporary Psychology, 27 . 208-209.
Maley, A. (1994). [Review of the book Critical language awareness . by N. Fairclough]. Applied Linguistics, 15 . 348-350.
Gardner, H. (1981, December). Do babies sing a universal song? Psychology Today . 70-76.
James, R. (1991, December 15). Obesity affects economic social status. The Guardian, p. 18
Acid attack ‘;scarred girl for life’. (1986, October 21). The Guardian . p. 4. (In the essay use a short form of the title for citation: (“Acid Attack.” 1986))
Hain, P. (1986, October 21). The police protection that women want [Letter to the editor]. The Guardian, p. 4.
Johns, A. M. (in press) Written argumentation for real audiences. TESOL Quarterly.
4. Selections from edited collections
Chomsky, N. (1973). Linguistic theory. In J. W. Oller J. C. Richards (Eds.), Focus on the learner (pp. 29-35). Rowley, Massachusetts: Newbury House.
Stern, H. H. Weinrib, A. (1978). Foreign languages for younger children: Trends and assessment. In V. Kinsella (Ed.), Language teaching and linguistics: Surveys (pp. 152-172). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wadeson, H. (2001). An eclectic approach to art therapy. In J. A. Rubin (Ed.), Approaches to art therapy: Theory and technique (2nd ed. pp. 306-318). New York, NY: Brunner-Routledge.
5. CD ROMs etc
Gardner, H. (1981, December). Do babies sing a universal song? Psychology Today [CD-ROM], pp. 70-76.
Meyer, A. S. Bock, K. (1992). The tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon: Blocking or partial activation? [CD-ROM]. Memory Cognition, 20, 715-726. Abstract from: SilverPlatter File: PsycLIT Item: 80-16351
Crime. (1996). In Microsoft Encarta 1996 Encyclopedia [CD-ROM]. Redmond, WA: Microsoft Corporation.
Oxford English dictionary computer file: On compact disc (2nd ed.) [CD-ROM]. (1992). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
6. Documents obtained from the Internet
All references begin with the same information that would be provided for a printed source (or as much of that information as possible). The WWW information is then placed at the end of the reference in the same way as publishing information is given for books. It is not necessary to give the date of retrieval unless the document on the Web may change in content – e.g. a wiki – move, or be removed from a site altogether.
The object of this is the same as all referencing – to supply the information needed to allow a user to find a source. If you do not know the author or the date and it does not have a clear title, think carefully before using it. See Evaluating Sources .
Jacobson, J. W. Mulick, J. A. Schwartz, A. A. (1995). A history of facilitated communication: Science, pseudoscience, and antiscience: Science working group on facilitated communication. American Psychologist, 50, 750-765. Retrieved from apa.org/journals/jacobson.html
Sleek, S. (1996, January). Psychologists build a culture of peace. The New York Times, pp. 1, 33 Retrieved from nytimes.com
Li, X. Crane, N. (1996, May 20). Bibliographic formats for citing electronic information . Retrieved from uvm.edu/
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). (1995, May 15). About the World Wide Web . Retrieved from w3.org/hypertext/WWW/
American Psychological Association (1996). How to cite information from the world wide web . Retrieved from apa.org/journals/webref.html
A field guide to sources on, about and on the Internet: Citation formats . (1995, Dec 18). Retrieved from cc.emory.edu/WHSCL/citation.formats.html
WWW user survey. (n.d.). Retrieved from wast.ac.uk/usersurveys/survey2000-10/
Rosenthal, R. (1995). State of New Jersey v. Margaret Kelly Michaels: An overview [Abstract]. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 1, 247271. Retrieved from apa.org/journals/ab1.html
Psychology. (n.d.). In Wikipedia. Retrieved October 14, 2009, from en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychology
Heuristic (n.d.) In Merriam-Webster’s online dictionary (11th ed.). Retrieved from m-w.com/dictionary/heuristic
National Institute of Mental Health. (1982). Television and behaviour: Ten years of scientific progress and implications for the eighties (DHHS Publication No. ADM82-1195). Washington DC: US Government Printing Office.
Malachi, Z. (Ed.). (n.d.) Proceedings of the International Conference on Literary and Linguistic Copmputing. Tel Aviv: Faculty of Humanities, Tel Aviv University.
Devins, G. M. (1981). Helplessness, depression, and mood in end-stage renal disease . Unpublished doctoral dissertation, McGill University, Montreal.
Howarth, P. (1995, March). Phraseological standards in EAP. Paper presented at the meeting of the British Association of Lecturers in English for Academic Purposes, Nottingham.
Maas, J. B. (Producer), and Gluck, D. H. (Director). (1979). Deeper into hypnosis [Film]. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Related Articles:

Latest Posts

- Privacy Policy
© 2016 | IHelptoStudy.Com
Please Wait!


- Engaging With Sources Effectively
by acburton | Apr 30, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
We’ve talked about the three ways to integrate sources effectively that allow writers to provide evidence and support for their argument, enter the scholarly conversation, and give credit to the original authors of the work that has helped and informed them. Sources also encourage writers to share their own knowledge and authority with others, help readers find additional sources related to the topic they are interested in, and protect you by giving credit where credit is due (thus avoiding plagiarism). In other words, sources are much more than just something we add on at the end of our writing!
When writing about a source or simply referencing it, we are positioning ourselves in response to, or in conversation with that source, with the goal of focusing our writing on our own argument/thesis. Sources do not stand on their own within a piece of writing and that is why, alongside finding strong and reputable sources worth responding to and making sure that we fully understand sources (even before writing about them), it is critical to engage with our sources in meaningful ways. But how exactly do we effectively engage with our sources in our writing?
Joseph Harris, in How To Do Things with Texts , presents four different ways of “rewriting the work of others”, three of which provide insight into the how of engaging sources. When a writer forwards the work of another writer, they are applying the concepts, topics, or terms from one reading, text, or situation to a different reading, text or situation. By countering the ideas found in source material, a writer argues “against the grain of a text” by underlining and countering ideas that a writer may be in disagreement with. Taking an approach is the adaptation of a theory or method from one writer to a new set of issues or texts. Harris’ book provides a thorough classification of methods to engage with a source. For something a little simpler, here are three basic ways you can get started effectively engaging with sources (Harris 5-7).
3 Basic Ways to Engage with Sources Effectively
- Disagree and Explain Why. Persuade your reader that the argument or information in a source should be questioned or challenged.
- Agree, But With Your Own Take. Add something new to the conversation. Expand a source’s insights or argument to a new situation or your own example. Provide new evidence and discuss new implications.
- Agree and Disagree Simultaneously. This is a nuanced approach to complex sources or complex topics. You can, for example, agree with a source’s overall thesis, but disagree with some of its reasoning or evidence.
Remember that this is not an exhaustive list. When engaging with others’ sources as a way to support our own ideas and argument, it is crucial that we engage with critical thinking, nuance, and objectivity to ensure that we are constructing unbiased, thoughtful, and compelling arguments.
Some of the different areas throughout your essay that will benefit from effective engagement with source material include: your thesis statement, analysis, and conclusion.
- Thesis Statement. The argument that you make in your thesis statement can challenge, weaken, support, or strengthen what is being argued by your source or sources.
Analysis. Thorough analysis in your body paragraphs emphasize the role of your argument in comparison to that found in your source material. Bring your analysis back to your thesis statement to reinforce the connection between the two.
- Conclusion. Consider the “big picture” or “takeaways” to leave your reader with.
There are many other, sometimes optional, essay sections or writing styles that benefit from critical engagement with a source. These can include literature reviews, reflections, critiques, and so on.
Strategies for Engaging Critically From Start to Finish
- Aim to dig deeper than surface level. Ask the ‘how’ and ‘why’ of a source, as well as ‘how’ and ‘why’ it is relevant to the topic at hand and the argument you are making.
- Ask yourself if you’ve addressed every possible question, concern, critique, or “what if” that comes to mind; put yourself in the place of your readers.
- Use TEAL body paragraph development as a template and guide for developing thorough analysis in your body paragraphs. Effectively engaging with your sources is essential to the analysis portion of the TEAL formula and to creating meaningful engagement with your sources.
- Visit the Writing Center for additional support on crafting engaging analyses and for other ways to engage with your source material from thesis to conclusion.
Our Newest Resources!
- Revision vs. Proofreading
- The Dos and Don’ts of Using Tables and Figures in Your Writing
- Synthesis and Making Connections for Strong Analysis
- Writing Strong Titles
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Navigating HR Challenges? Find Solutions in Our HR Hub.
How to Write a Reference Letter (Template & Examples)
By Ammar Ahmed
Published: January 29, 2024
A reference letter serves as a formal endorsement of an individual’s skills, character, and achievements, typically penned by a former employer, colleague, or academic mentor.
This guide aims to empower professionals with the tools and knowledge to craft effective reference letters, combining best practices with practical templates to streamline this essential task.
Types of Reference Letters
Understanding the different types of reference letters is crucial for professionals, as each type caters to specific contexts and highlights various aspects of an individual’s profile. Below, we explore three key types: Professional, Academic, and Character Reference Letters.
Professional Reference Letters
Professional reference letters are written by a previous employer, supervisor, or professional colleague. They focus on the applicant’s work experience, skills, and professional achievements. These letters are often required during job applications or for career advancement opportunities.
These letters should detail the individual’s role, responsibilities, key accomplishments, and work ethic. It’s essential to mention specific instances where the individual demonstrated their skills and contributed to the organization’s success.
Related Article: Who to Use for Professional References
Academic Reference Letters
Academic reference letters are typically requested for educational pursuits, such as college admissions, scholarships, or academic awards. Written by teachers, professors, or academic advisors, these letters highlight the individual’s academic achievements, intellectual capabilities, and potential for future success in their field of study.
They should reflect on the individual’s academic performance, participation in class, and any notable projects or research work. This type of letter often emphasizes the individual’s dedication, curiosity, and ability to overcome academic challenges.
Character Reference Letters
Character reference letters focus primarily on the personal attributes of an individual. They are usually written by someone who knows the person well but is not a family member, such as a mentor, family friend, or community leader.
These letters are particularly important when assessing an individual’s suitability for a role that requires a high degree of trust and integrity. They should provide insights into the individual’s character, values, and behaviors, illustrating how these traits have been beneficial in various situations.
Related Article : How Many References Should You Have?
Letter of Recommendation Examples
In crafting a letter of recommendation, it’s essential to tailor the content to the specific needs and strengths of the individual. Whether it’s for a professional role, character assessment, or a remote work position, each letter should effectively highlight the candidate’s unique qualities and contributions.
These examples are designed to provide a clear understanding of how to articulate a candidate’s abilities and achievements in a manner that resonates with the recipient, ensuring the letter is both compelling and relevant to the candidate’s desired opportunity.
Professional Employment Reference Letter
Taylor Robinson Hiring Committee Chair Innovatech Solutions 321 Future St. Techville, TV 32167 April 5, 2024
Dear Mr./Ms. Robinson,
It is with great enthusiasm that I recommend Laura Smith for the position of Project Manager at Innovatech Solutions. As the Senior Director of Project Management at TechGenius, I had the privilege of observing Laura’s professional growth and remarkable contributions over her four-year tenure as an Assistant Project Manager.
Laura’s standout achievement was her leadership in the “GreenTech Initiative” project in 2020. Under her guidance, the project not only met but exceeded its objectives, achieving a 30% increase in energy efficiency for our client’s products. Her strategic planning, combined with her ability to seamlessly integrate new technology into existing systems, was critical to the project’s success. Laura’s innovative approach and meticulous attention to detail were instrumental in securing a 15% grant for future sustainability projects for TechGenius.
Beyond her technical skills, Laura’s interpersonal abilities truly set her apart. Her team leadership and conflict resolution skills were pivotal during challenging project phases, ensuring team cohesion and maintaining client satisfaction. Her mentorship of junior staff members has left a lasting positive impact on our department.
I am confident that Laura will bring the same level of exceptional performance, dedication, and innovation to the Project Manager role at Innovatech Solutions. Her blend of strategic foresight, technical expertise, and leadership ability makes her an excellent fit for your team. I strongly recommend her for this position and believe she will be a valuable asset to your organization.
Please feel free to contact me for any further information or clarification.
John Doe Senior Director of Project Management, TechGenius [email protected] +1 555 123 4567
Character Reference Letter for a Coworker
Jane Doe Human Resources Manager Green Earth Initiatives 123 Business Rd. Business City, BC 12345 January 1, 2024
Dear Ms. Doe,
I am writing to express my wholehearted support for Emily Johnson’s application for the Community Outreach Coordinator position at Green Earth Initiatives. As Emily’s coworker at Design & Innovate Corp for over five years, I have had the privilege of witnessing her exceptional character and dedication to community service.
Emily has always been more than just a proficient graphic designer ; she is a driving force for positive change within our community. One of her most notable contributions was her volunteer work with the local “Food for All” campaign, where she not only designed impactful promotional materials but also played a crucial role in organizing community food drives. Her efforts helped raise awareness and significant donations for the cause, demonstrating her compassion and commitment to helping those in need.
What truly sets Emily apart is her genuine empathy and integrity. She often takes the initiative to support new team members and creates an inclusive and welcoming work environment. Her ability to connect with people from diverse backgrounds, combined with her strong ethical values, makes her an outstanding role model and team player.
Emily’s passion for community engagement, along with her innate ability to inspire and mobilize people toward a common goal, makes her an ideal candidate for the Community Outreach Coordinator role. I am confident that her exceptional interpersonal skills and dedication to social causes will enable her to excel in this position and make a meaningful impact at Green Earth Initiatives.
Please do not hesitate to contact me if you require any further information or insights regarding Emily’s character and abilities.
Warm regards,
David Thompson Senior Graphic Designer, Design & Innovate Corp [email protected] +1 555 678 9101
Remote Work Employment Reference Letter
Alex Martinez Hiring Manager VirtualTech Inc 456 Justice Ave. Law City, LC 45678 March 10, 2024
Dear Attorney Martinez,
I am delighted to recommend Mark Benson for the position of Lead Software Engineer at VirtualTech Inc. As the CTO of NetSolutions, where Mark has been working remotely for the past three years, I have had ample opportunity to observe his exceptional technical abilities and adaptability to the remote working model.
During his tenure with us, Mark was instrumental in developing our flagship product, CloudSync, a complex cloud storage solution. His technical expertise, particularly in cloud computing and cybersecurity, was vital in overcoming the project’s significant challenges. Despite the remote setting, Mark’s consistent communication and collaboration were standout qualities. He regularly led virtual team meetings and coding sessions, ensuring that all team members, regardless of their location, were aligned and engaged.
What impresses me most about Mark is his self-motivation and time management skills, crucial in a remote work environment. He has an innate ability to prioritize tasks effectively and meet deadlines without compromising on the quality of work. His initiative to conduct weekly virtual training sessions for the team not only enhanced our collective skill set but also fostered a sense of community and teamwork among remote employees.
Mark’s blend of technical acumen, excellent communication, and leadership skills, along with his proven ability to thrive in a remote work environment, makes him an ideal candidate for VirtualTech Inc. I am confident that he will be a valuable asset to your team and contribute significantly to your company’s success in the digital realm.
Please feel free to contact me if you would like further information or specific examples of Mark’s work and achievements.
Susan Lee Chief Technology Officer , NetSolutions [email protected] +1 555 234 5678
What to Include in a Reference Letter
When composing a reference letter, it’s essential to include certain key elements to ensure the letter is effective and provides a comprehensive overview of the candidate’s qualifications.
These elements include:
1. Sender’s Information
The sender’s information is a critical component of any reference letter, as it establishes the credibility and authority of the person writing the letter.
This section should be clearly outlined at the top of the letter and include the following details:
- Name: The full name of the individual writing the reference letter.
- Title or Position: The professional title or position of the sender, which adds weight to the reference. This should be the current title or the one held while working with the individual being recommended.
- Company or Organization: The name of the company or organization where the sender is employed or affiliated.
- Contact Information: Including an address, phone number, and email address is crucial. It not only offers a means for the recipient to verify the information or seek further clarification but also demonstrates transparency and openness.
2. Recipient’s Information
- Name: The full name of the recipient. If the recipient’s name is not known, a general title or department can be used, such as “Hiring Manager” or “Admissions Committee.”
- Title or Position: Including the recipient’s professional title or position helps in directing the letter to the appropriate person, especially in large organizations where multiple individuals may be involved in the decision-making process.
- Company or Organization: The name of the company or organization where the recipient works. This acknowledges the professional setting into which the candidate is seeking entry or advancement.
- Address: The full postal address of the company or organization.
3. Salutation
The salutation in a reference letter is more than just a formality; it sets the tone for the communication and shows respect for the recipient.
Here are key elements to consider:
- A Formal Greeting: Begin with a formal greeting such as “Dear,” which is universally recognized as professional and respectful.
- Addressing the Recipient: If you know the recipient’s name, use it directly after the greeting, e.g., “Dear Mr. Smith,” or “Dear Dr. Jones.”
- Inclusive and Respectful Language: If the recipient’s name or gender is unknown, use a neutral and inclusive salutation like “Dear Hiring Manager,” “Dear Selection Committee,” or “To Whom It May Concern”.
4. Opening Paragraph
The opening paragraph of a reference letter is pivotal in establishing the context of your relationship with the candidate and setting the stage for the endorsement to follow.
Here are some elements to include in this initial section:
- Introduce Yourself: Start by introducing yourself to give the recipient an understanding of who you are. Mention your name and your professional position or title, as this adds credibility to your recommendation.
- Your Relationship with the Candidate: Clearly state your professional or academic relationship with the person you are recommending. This could be as their supervisor, colleague, professor, or mentor.
- Duration of Relationship: Include how long you have known the individual. This time frame helps the recipient gauge the depth and extent of your experience with the candidate.
- Purpose of the Letter: Briefly mention the purpose of your letter – to recommend the individual for a specific position, program, or opportunity. This sets a clear context for the rest of your letter.
5. Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are the core of the reference letter, where you provide detailed insights into the candidate’s qualifications, skills, achievements, and character.
Here’s how to structure this section effectively:
- Specific Examples and Details: Use concrete examples to illustrate the person’s skills and qualifications. For instance, if you are highlighting their leadership skills, mention a specific project they led and the positive outcomes that resulted from it.
- Highlight Relevant Experiences and Accomplishments: Discuss experiences that directly relate to the position or opportunity the individual is pursuing. For example, if they’re applying for a managerial role focus on instances where they demonstrated effective management skills.
- Unique Qualities or Strengths: Point out any unique strengths or qualities that make the individual stand out. This could include exceptional problem-solving skills, innovative thinking, or a strong commitment to teamwork.
- Personal Anecdotes or Stories: Including a brief story or anecdote can make your letter more engaging and memorable. This could be an instance where the individual overcame a significant challenge or went above and beyond in their role.
- Balanced Perspective: While it’s important to focus on positive attributes, offering a balanced perspective can add authenticity to your letter. If appropriate, you can mention areas where the candidate has shown growth during your relationship.
Remember, the goal of these paragraphs is to provide a vivid picture of the candidate’s abilities and character. Well-chosen examples and stories make your endorsement more convincing and help the recipient understand why the individual is an excellent fit for the opportunity.
6. Closing Paragraph
The closing paragraph of a reference letter is where you encapsulate your overall recommendation and express your support for the individual.
Here are some elements to include:
- Summarize Key Points: Briefly restate the most important qualities, achievements, or skills of the candidate that you have highlighted in the letter. This reinforces your endorsement and reminds the reader of the candidate’s suitability for the position or opportunity.
- Express Your Strong Recommendation: Clearly state your confidence in the candidate and your belief in their suitability for the role or opportunity. Use affirmative language like, “I highly recommend,” or “I am confident that,” to leave no doubt about your support.
- Offer to Provide Further Information: Indicate your willingness to provide additional information or clarification if needed. This shows your genuine support and readiness to assist further in the candidate’s application process.
- Contact Information Reminder: Although your contact information is already at the top, a brief reminder here ensures that it is easily accessible for the reader, should they wish to follow up with you.
7. Closing Salutation
Here’s how to conclude your letter appropriately:
- Use a Professional Closing: Opt for a formal and universally accepted closing phrase. Common examples include “Sincerely,” “Best regards,” or “Yours truly.”
- Consistency with the Tone: Ensure that the closing salutation matches the overall tone of your letter. If your letter is highly formal, a closing like “Sincerely” is appropriate. For a slightly less formal tone, “Best regards” can be a good choice.
- Space for Signature: If you are sending a hard copy or a scanned version of the letter, leave space for your handwritten signature above your typed name. This personal touch adds authenticity to the document.
- Typed Name and Title: Below the signature space, type your full name and title again.
Related Article: When Do Employers Check References?
Reference Letter Template
This reference letter template is designed for professionals to easily adapt and customize according to the specific needs of the individual being recommended. Simply fill in the blanks and modify the text as necessary to suit your context.
[Your Name] [Your Title or Position] [Your Company or Organization] [Your Contact Information (Address, Phone Number, Email)] [Date]
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Title or Position] [Recipient’s Company or Organization] [Recipient’s Address]
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to recommend [Candidate’s Full Name] for [Position/Opportunity/Program] at [Recipient’s Company/Organization/School]. As [Your Position] at [Your Company/Organization], I have had the pleasure of working with [Candidate’s Name] for [Duration of Relationship] and have witnessed [his/her/their] significant contributions first-hand.
[In this paragraph, provide specific examples of the candidate’s skills, achievements, and qualities. Mention a particular project or responsibility and the impact of their work. Highlight any unique attributes that set the candidate apart.]
[This paragraph should continue to build on the candidate’s qualifications. Include personal anecdotes or stories that illustrate their capabilities and character. Focus on how their contributions positively affected your team or organization.]
I am confident that [Candidate’s Name] will bring [his/her/their] remarkable [skills/qualities, such as leadership, creativity, dedication] to [Recipient’s Company/Organization/School]. [His/Her/Their] ability to [specific skill or contribution] makes [him/her/them] well-suited for [Position/Opportunity/Program]. I strongly endorse [his/her/their] candidacy and believe [he/she/they] will be a valuable addition to your [team/program/organization].
Please feel free to contact me at [Your Contact Information] if you require any further information or specific examples of [Candidate’s Name]’s work and achievements.
[Your Handwritten Signature (if applicable)]
[Your Typed Name] [Your Position]
Related Article: How to Provide References for a Job
Tips for Writing Letters of Recommendation
Crafting effective letters of recommendation requires a delicate balance of showcasing the candidate’s strengths, providing specific examples, and employing persuasive language. Here are some valuable tips to help you navigate the intricacies of this crucial task.
Quantify Achievements
When writing a letter of recommendation, it’s powerful to quantify the candidate’s achievements. Use specific figures and statistics to illustrate their accomplishments. For example, instead of saying “significantly increased sales,” specify “increased sales by 30% over six months.” This provides concrete evidence of their capabilities and makes their achievements more tangible and credible. Quantifying contributions also helps the recipient gauge the scale and impact of these accomplishments, offering a clearer picture of the candidate’s potential.
Connect to the Position or Opportunity
Tailor the letter to the specific position or opportunity the candidate is applying for. Highlight skills and experiences that are directly relevant to the job requirements or academic program. For instance, if the candidate is applying for a leadership role, emphasize their successful team management experiences. This shows that you understand what the role entails and have thoughtfully considered how the candidate’s skills and experiences make them a good fit, making your recommendation more relevant and persuasive.
Include Keywords
Identify important terms in the job listing or academic program description, such as “project management,” “analytical thinking,” or “creative problem-solving,” and weave them into your letter. This not only tailors the letter to the specific role but also ensures it passes through any automated screenings, increasing the chance that your recommendation will be read by decision-makers.
Leverage Technology for Reference Letter Management
Utilize technology platforms for efficient reference letter management. For example, online reference request platforms simplify the process of requesting, writing, storing, and submitting letters of recommendation. These tools often offer templates, reminders, and the ability to submit letters directly to institutions or employers.
Leveraging such technology can streamline the process, ensuring timely submission and organization of your reference letters, while also offering a secure way to manage sensitive personal information contained within these documents.
Related Article: Reference Check Questions

About the Author
Read more articles by Ammar Ahmed
Continue Reading
How to Write an Employee Write-Up Form (With Template)
How to write a job rejection email (template & examples), how to write a job offer letter (template & examples), how to create an employee schedule (with templates), what is holiday pay everything you need to know, how to conduct a reference check (with questions), what is staff augmentation everything you need to know.

COMMENTS
Citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database. If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It's similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences: Structure: Author's last name, F. M. (Year published).
To cite an unpublished dissertation (one you got directly from the author or university in print form), add "Unpublished" to the bracketed description, and list the university at the end of the reference, outside the square brackets. APA format. Author last name, Initials. ( Year ).
The same format can be adapted for other published theses, including undergraduate theses, by changing the wording of the bracketed description as appropriate (e.g., "Undergraduate honors thesis"). Include a URL for the dissertation or thesis if the URL will resolve for readers (as shown in the Miranda and Zambrano-Vazquez examples).
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
Thesis, from a commercial database. Lope, M. D. (2014). Perceptions of global mindedness in the international baccalaureate middle years programme: The relationship to student academic performance and teacher characteristics (Order No. 3682837) [Doctoral dissertation, University of Maryland].ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
EndNote reference type: Thesis. Add Archive Name to Name of Database field. Thesis - from database. Elements of the reference: Author - last name, initials. (Year). Title of thesis - italicised (Publication No. - if available) [Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis, Institution]. Database Name. In-text reference
Basic format to reference a thesis or dissertation. The basics of a reference list entry for a thesis or dissertation: Author. The surname is followed by first initials. Year (in round brackets). Title (in italics ). Level of Thesis or Dissertation [in square brackets]. University, also in [square brackets] following directly after the Level of ...
How to Cite a Dissertation or Thesis in APA 7th Edition. The APA dissertation or thesis citation isn't a one size fits all type of citation. The reason behind this is because APA offers a different format for a published and unpublished thesis or dissertation. However, you'll need to include information like: Author, A. A. (Year).
Title of dissertation or thesis (Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis). Retrieved from Name of database. (Accession or Order No.) For an unpublished dissertation or thesis: Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of creation). Title of dissertation or thesis (Unpublished doctoral dissertation or master's thesis). Name of ...
Thesis Paper AI Proofreader Essay Checker PhD dissertation APA editing Academic editing College ... Improve your in-text citations and references for errors and inconsistencies using Scribbr's AI technology or human experts. Run a free check. Grammar Checker. Eliminate grammar errors and improve your writing with our free AI-powered grammar ...
Title of the Master's thesis: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized. Publication number: Give the identification number of the thesis, if available. Name of the degree awarding institution: Give the name of the institution. Name of Platform: Give the name of the database, archive or any platform that holds the ...
1. Use the author's name and year for a parenthetical citation. For a standard in-text citation, place the author's name and the year the thesis was submitted in parentheses at the end of any sentence in which you paraphrase information from it. Your citation should fall inside the closing punctuation for the sentence.
Year of publication: Give the year in brackets followed by a full stop. Title of the undergraduate thesis: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized. Publication number: Give the identification number of the thesis, if available. Name of the degree awarding institution: Give the name of the institution.
To reference a book, you will need to know the author (s) name (s), the year when the book was published, the title of the book, as well as the place the book was published, and the name of publisher, for example: Reeves, S. & Jeanes, Y. (2022) The Study Skills Handbook for Nutritionists and Dietitians.
Referencing a thesis or dissertation (from an institution's online archive/repository) When referencing a thesis or dissertation, include the type and the awarding institution in brackets after the title—e.g., (Master's thesis, The University of Waikato). Give the name of the institution's repository and link directly to the thesis document.
Include all relevant information: For each source used in the thesis, include the author's name, publication date, title of the work, and the name of the publisher/journal. For online sources, include the URL or DOI. Order the references alphabetically: Arrange the references in alphabetical order according to the author's last name.
Dissertation - A document submitted to earn an advanced degree, such as a doctorate, at a university. The formatting for thesis and dissertation citations is largely the same. However, you should be sure to include the type of degree after the publication year as supplemental information. For instance, state if the source you are citing is an ...
Journal Articles. References to journal articles usually include the author's name, title of the article, name of the journal, volume and issue number, page numbers, and publication date. Example: Johnson, T. (2021). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology, 32 (4), 87-94.
Thesis/Dissertation - APA Reference List Capitalization. The document title is in sentence case - Only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. Always capitalize the first word, the first word after a colon or a dash. The title of the thesis or dissertation is in title case - Each word in the name is capitalized, except for articles (a, an, the), prepositions ...
A Guide to Writing a Thesis in History and Literature | page 11 Writing the Proposal Okay, you've spent some time gathering together the basic building blocks of a research project in the form of articulated interests, primary sources, and a whole slew of questions. Now your job is to start sifting through those raw materials and evaluating them.
Use alphabetical order. Alphabetise works with no author by the first significant word in the title. All co-authors should be listed. Indent second etc. lines. Use (n.d.) if no date is given. If the author of a document is not given, begin the reference with the title of the document.
Some of the different areas throughout your essay that will benefit from effective engagement with source material include: your thesis statement, analysis, and conclusion. Thesis Statement. The argument that you make in your thesis statement can challenge, weaken, support, or strengthen what is being argued by your source or sources. Analysis.
Step 1: Start with a question. You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis, early in the writing process. As soon as you've decided on your essay topic, you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services. A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind.
The sender's information is a critical component of any reference letter, as it establishes the credibility and authority of the person writing the letter. This section should be clearly outlined at the top of the letter and include the following details: Name: The full name of the individual writing the reference letter.