

The Ultimate Guide to Nursing Assignments: 7 Tips and Strategies
Nursing assignments are a critical component of every nursing student’s academic journey. They serve as opportunities to test your knowledge, apply theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios, and develop essential skills necessary for your future nursing career. However, tackling nursing assignments can often be overwhelming, particularly when you’re juggling multiple responsibilities. In this comprehensive guide, we provide valuable tips, strategies, and expert assignment help services to help you excel in your nursing assignments. Whether you’re struggling with research, structuring your assignment, or proofreading, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding the Nursing Assignments
To excel in nursing assignments , it’s crucial to start by thoroughly understanding the requirements. Take the time to carefully read the assignment prompt, paying close attention to the topic, word count, formatting guidelines, and any specific instructions provided by your instructor. Understanding these key components will ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria.

Conducting Thorough Research
Once you have a clear understanding of the assignment, it’s time to conduct thorough research. Solid research forms the foundation of any successful nursing assignment. Begin by gathering relevant and credible sources, such as nursing textbooks, scholarly articles, reputable websites , and academic databases specific to nursing. These resources will provide you with evidence-based information to support your arguments and demonstrate your understanding of the topic.
Creating a Well-Structured Outline
A well-structured outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and ensuring a logical flow in your nursing assignment. An effective outline acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the writing process and ensuring that you cover all the necessary points.
At [Your Service Name], our expert writers can assist you in creating a comprehensive outline tailored to your specific assignment. By collaborating with us, you can receive personalized guidance in organizing your ideas effectively and structuring your assignment in a logical manner. Our writers understand the nuances of nursing assignments and can help you identify the most important concepts and supporting evidence to include.
Using a Professional Tone
Maintaining a professional tone throughout your nursing assignment is crucial. As aspiring healthcare professionals, it’s essential to communicate your ideas with clarity, conciseness, and professionalism. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or slang that may hinder the reader’s understanding. Present your arguments and supporting evidence in a logical and coherent manner, demonstrating your ability to think critically and apply nursing principles.
Our expert writers have extensive experience in academic writing within the field of nursing. They possess a deep understanding of the professional tone required for nursing assignments and can ensure that your assignment is written to the highest standards. By collaborating with us, you can receive guidance in maintaining a professional tone and effectively conveying your ideas.

Incorporating Practical Examples
In addition to a professional tone, incorporating practical examples into your nursing assignment can greatly enhance its quality. Practical examples bring theoretical concepts to life, illustrating their application in real-life scenarios. They demonstrate your understanding of nursing principles and showcase your ability to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Our team consists of experienced nursing professionals who can assist you in incorporating relevant practical examples into your assignment. Drawing from their extensive knowledge and expertise, they can provide you with real-life scenarios or case studies that strengthen the impact and credibility of your work. By collaborating with us, you can elevate the quality of your assignment by demonstrating your ability to apply nursing concepts in practical settings.
Proofreading and Editing
Proofreading and editing are essential steps in the assignment writing process. They ensure that your nursing assignment is polished, error-free, and effectively communicates your ideas. After completing the initial draft, it’s crucial to take a break and return to your work with fresh eyes. During the proofreading stage, carefully review your assignment for grammar, spelling, punctuation, and sentence structure. Correct any errors and inconsistencies that may affect the clarity and professionalism of your writing.
At nursingresearchhelp.com , we have a dedicated team of proofreaders and editors who specialize in nursing assignments. They meticulously review your work, ensuring that it adheres to formatting guidelines and meets the highest standards of academic writing. Our proofreaders and editors will help you refine your assignment, ensuring that it is polished and error-free. By collaborating with us, you can rest assured that your assignment will be thoroughly reviewed and refined before submission.
Seeking Help When Needed
In addition to proofreading and editing, it’s important to seek help when needed. Nursing assignments can be challenging, and it’s perfectly normal to require assistance. Whether you’re facing difficulties in understanding the assignment prompt, need guidance in specific areas, or simply want a fresh perspective on your work, don’t hesitate to reach out for support.
Our friendly and knowledgeable support team is always available to address any questions or concerns you may have. We understand the unique challenges faced by nursing students and can provide you with the guidance and clarification you need. By seeking help when needed, you can overcome obstacles and ensure the successful completion of your nursing assignments.
Mastering nursing assignments is within your reach with the right tips, strategies, and expert assignment help services. At nursingresearchhelp.com we are committed to supporting nursing students in excelling in their academic pursuits. Our experienced writers, proofreaders, and editors can provide personalized assistance throughout the assignment writing process, ensuring that your assignments meet the highest standards of quality and professionalism.
With our help, you can confidently tackle your nursing assignments and overcome any challenges you may face. Visit our website nursingresearchhelp.com to learn more about our services and how we can support you in achieving academic excellence. Whether you need guidance in understanding the assignment, conducting thorough research, creating a well-structured outline, using a professional tone, incorporating practical examples, or ensuring a polished final product, we are here to assist you. Trust us for reliable and professional assignment help tailored to your needs.
Don’t let the challenges of nursing assignments hold you back—reach out to us for reliable and professional assignment help tailored to your needs.
You might also like

Nursingresearchhelp.com is the fastest, easiest and most reliable way to have content written for your website. You’ll be able to post a project and 1000s of freelance writers from across the globe will have instant access to write your content quickly, professionally, and affordably.
QUICK LINKS
- HOW IT WORKS
- OUR SERVICES
- TERMS OF USE

Call/Text: +1 608 912 3884


- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Writing in Nursing
Although there may be some differences in writing expectations between disciplines, all writers of scholarly work are required to follow basic writing standards such as writing clear, concise, and grammatically correct sentences; using proper punctuation; demonstrating critical thought; and, in all Walden programs, using APA style. When writing in nursing, however, students must also be familiar with the goals of the discipline and discipline-specific writing expectations.
Nurses are primarily concerned about providing quality care to patients and their families, and this demands both technical knowledge and the appropriate expression of ideas (“Writing in nursing,” n.d). As a result, nursing students are expected to learn how to present information succinctly, and even though they may often use technical medical terminology (“Writing in nursing,” n.d.), their work should be accessible to anyone who may read it. Among many goals, writers within this discipline are required to:
- Document knowledge/research
- Demonstrate critical thinking
- Express creative ideas
- Explore nursing literature
- Demonstrate understanding of learning activities. (Wagner, n.d., para. 2)
Given this broad set of objectives, nursing students would benefit from learning how to write diverse literature, including scholarly reports, reviews, articles, and so on. They should aim to write work that can be used in both the research and clinical aspects of the discipline. Walden instructors often ask nursing students to write position and reflective papers, critique articles, gather and analyze data, respond to case studies, and work collaboratively on a project. Although there may be differences between the writing expectations within the classroom and those in the workplace, the standards noted below, though more common in scholarly writing, require skills that are transferrable to the work setting.
Because one cannot say everything there is to say about a particular subject, writers present their work from a particular perspective. For instance, one might choose to examine the shortage of nurses from a public policy perspective. One’s particular contribution, position, argument, or viewpoint is commonly referred to as the thesis and, according to Gerring et al. (2004), a good thesis is one that is “new, true, and significant” (p. 2). To strengthen a thesis, one might consider presenting an argument that goes against what is currently accepted within the field while carefully addressing counterarguments and adequately explaining why the issue under consideration matters (Gerring et al., 2004). The thesis is particularly important because readers want to know whether the writer has something new or worthwhile to say about the topic. Thus, as you review the literature, before writing, it is important to find gaps and creative linkages between viewpoints with the goal of contributing innovative ideas to an ongoing discussion. For a contribution to be worthwhile you must read the literature carefully and without bias; doing this will enable you to identify some of the subtle differences in the viewpoints presented by different authors and help you to better identify the gaps in the literature. Because the thesis is essentially the heart of your discussion, it is important that it is argued objectively and persuasively.
With the goal of providing high quality care, the healthcare industry places a premium on rigorous research as the foundation for evidence-based practices. Thus, students are expected to keep up with the most current research in their field and support the assertions they make in their work with evidence from the literature. Nursing students also must learn how to evaluate evidence in nursing literature and identify the studies that answer specific clinical questions (Oermann & Hays, 2011). Writers are also expected to critically analyze and evaluate studies and assess whether findings can be used in clinical practice (Beyea & Slattery, 2006). (Some useful and credible sources include journal articles, other peer-reviewed sources, and authoritative sources that might be found on the web. If you need help finding credible sources contact a librarian.)
Like other APA style papers, research papers in nursing should follow the following format: title, abstract, introduction, literature review, method, results, discussion, references, and appendices (see APA 7, Sections 2.16-2.25). Note that the presentation follows a certain logic: In the introduction one presents the issue under consideration; in the literature review, one presents what is already known about the topic (thus providing a context for the discussion), identifies gaps, and presents one’s approach; in the methods section, one would then identify the method used to gather data; and in the results and discussion sections, one then presents and explains the results in an objective manner, noting the limitations of the study (Dartmouth Writing Program, 2005). Note that not all papers need to be written in this manner; for guidance on the formatting of a basic course paper, see the appropriate template on our website.
In their research, nursing researchers use quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods. In quantitative studies, researchers rely primarily on quantifiable data; in qualitative studies, they use data from interviews or other types of narrative analyses; and in mixed methods studies, they use both qualitative and quantitative approaches. A researcher should be able to pose a researchable question and identify an appropriate research method. Whatever method the researcher chooses, the research must be carried out in an objective and scientific manner, free from bias. Keep in mind that your method will have an impact on the credibility of your work, so it is important that your methods are rigorous. Walden offers a series of research methods courses to help students become familiar with the various research methods.
Instructors expect students to master the content of the discipline and use discipline- appropriate language in their writing. In practice, nurses may be required to become familiar with standardized nursing language as it has been found to lead to the following:
- better communication among nurses and other health care providers,
- increased visibility of nursing interventions,
- improved patient care,
- enhanced data collection to evaluate nursing care outcomes,
- greater adherence to standards of care, and
- facilitated assessment of nursing competency. (Rutherford, 2008)
Like successful writers in other disciplines and in preparation for diverse roles within their fields, in their writing nursing students should demonstrate that they (a) have cultivated the thinking skills that are useful in their discipline, (b) are able to communicate professionally, and (c) can incorporate the language of the field in their work appropriately (Colorado State University, 2011).
If you have content-specific questions, be sure to ask your instructor. The Writing Center is available to help you present your ideas as effectively as possible.
Beyea, S. C., & Slattery, M. J. (2006). Evidence-based practice in nursing: A guide to successful implementation . http://www.hcmarketplace.com/supplemental/3737_browse.pdf
Colorado State University. (2011). Why assign WID tasks? http://wac.colostate.edu/intro/com6a1.cfm
Dartmouth Writing Program. (2005). Writing in the social sciences . http://www.dartmouth.edu/~writing/materials/student/soc_sciences/write.shtml
Rutherford, M. (2008). Standardized nursing language: What does it mean for nursing practice? [Abstract]. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing , 13 (1). http://ojin.nursingworld.org/MainMenuCategories/ThePracticeofProfessionalNursing/Health-IT/StandardizedNursingLanguage.html
Wagner, D. (n.d.). Why writing matters in nursing . https://www.svsu.edu/nursing/programs/bsn/programrequirements/whywritingmatters/
Writing in nursing: Examples. (n.d.). http://www.technorhetoric.net/7.2/sectionone/inman/examples.html
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Collaborative Writing in Business & Management
- Next Page: Learning Agreements (LAs)
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Writing Tips for Nursing School Students

- Nursing School Writing Types
- Writing a Nursing Essay
- Citations Guide
- Common Writing Mistakes
- Writing Resources
Are you ready to earn your online nursing degree?

Writing is an essential skill nurses should achieve proficiency in early in their career. It is a crucial part of the profession, as nurses need to be able to effectively communicate with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals.
While verbal communication also plays a vital role in nursing, being able to write well builds the nurse’s ability to provide better care.
Being able to accurately detail a patient’s personal history, symptoms, and diagnosis allows for the execution of a precise treatment plan that is clearly communicated to all parties involved, both professional and personal.
From registered nurses to clinical nurses and beyond, being able to communicate effectively and efficiently is a critical soft skill that will help nurses in any role increase their ability to treat their patients.
This guide provides an overview of the types of writing nurses will experience throughout their educational training. Utilize the following tips and tricks to help strengthen your writing skills, which will ultimately help in the development of transferable career skills .
Types of Writing Nurses Will Do in School
Personal statements for nursing school.
Nursing schools want candidates who meet academic and professional requirements. They also want a candidate who demonstrates a sincere passion for patient care and individual connections. You should always craft a personal statement, even when the application doesn’t explicitly require one. Personal statements allow you to describe your goals, characteristics, credentials, volunteer work, and meaningful life experiences. A well-crafted essay can help you stand out among other qualified applicants. And, as with any piece of writing, you must take the time to revise.
In your personal statement, you should portray yourself as determined and empathetic, with characteristics, goals, work ethic, and healthcare philosophy that align with a program’s values. Some nursing schools ask for a general personal statement, while others require a specific prompt. Colleges commonly ask students to describe a hardship they overcame, a difficult task they accomplished, or a professional goal they hope to achieve through the program. Many schools also ask students to detail previous experiences in healthcare. You may decide to write about how you connect with patients or how you provide practical and emotional support to loved ones.
You will also encounter writing prompts during examinations, including standardized tests like the GRE or MCAT, nursing school entrance exams , and course-specific evaluations. You may also take exams to get state licensure or professional certification. In most of these instances, you will need to write one or several long-form essays. Proper planning is key. Though you won’t know what specific prompt the test will require, you can expect certain common topics. You can search online or use study guides to determine which prompts usually appear on each test.
On test day, you should begin by creating an outline that lists three main points in response to the prompt. Using these points, work backwards to write a central thesis to guide the essay’s structure. Review what you’ve written to ensure that the essay actually responds to the prompt at hand. Be sure to leave time to correct spelling, grammar, and stylistic errors.
Research Papers
Like essays, research papers follow a long-form structure. Unlike an essay, which heavily relies on the writer’s point of view, a research paper presents an in-depth investigation of a topic using data, expert opinions, and insights. While an essay evaluates general critical thinking and writing skills, a research paper tests your knowledge, research skills, and original contributions. Research papers also allow you to prove you understand what has been argued and discovered about a topic. Research papers, especially at the graduate and doctoral levels, require independent research and analyses. These papers sometimes take months or years to complete.
To write a successful research paper, you should pick a topic relevant to your interests and the nursing field. Possibilities include elderly care challenges, patient safety and ethics, mental health treatment and regulations in the U.S., and nursing shortages and possible solutions. Whatever your choice, you must plan accordingly. Advanced papers such as dissertations may require funding or help from professors. Research papers often consist of the following sections: abstract, introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, conclusion, and references. You should keep this general structure in mind as you prepare notes and outlines.
How Do You Write a Nursing Essay?
In nursing school, essay writing includes academic papers, personal narratives, and professional compositions. You should become familiar with each of the five major forms below. There are many similarities between these essay types, such as an overarching thesis and a supportive, logical structure. You should support claims with factual, statistical, anecdotal, and rhetorical evidence. However, each form requires distinct skills to achieve specific results.
Comparative
Cause and effect, citations guide for nursing students.
Citations allow readers to know where information came from. By citing sources, you avoid plagiarizing or stealing another person’s ideas, research, language, and analyses. Whether intentional or unintentional, plagiarism is one of the most egregious errors one can make. Consequences for plagiarism include automatic course failure, disciplinary actions from the university, and even legal repercussions. You should take special care to ensure you properly cite sources.
American Psychological Association (APA) Style
APA is the most commonly used style among natural scientists, social scientists, educators, and nurses. Like other citation styles, APA emphasizes clarity of font style, font size, spacing, and paragraph structure. APA citations focus on publication date, and in most cases, the date comes right after the author’s name. This order makes the style particularly useful for scientists, who value new research and updates on current findings. For more information on APA style, visit this official website .
(Author and year of publication, page number) “Punishment, then, will tend to become the most hidden part of the penal process” (Foucault, 1977, p. 9).
Chicago Manual of Style (CMS)
CMS (also known as CMOS or, simply, Chicago) features two citation systems, the notes and bibliography, and the author and date. This style is used primarily by historians, who place high importance on a text’s origin. The notes and bibliography include a superscript number with a corresponding footnote or endnote. Scientific professionals use the author and date citation, a generic parenthetical system with similarities to other citation styles. The CMS official website provides additional information, including changes to citation systems in the current edition.
“Punishment, then, will tend to become the most hidden part of the penal process”. 1 1. Michel Foucault, trans. Alan Sheridan, Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison (New York: Pantheon Books, 1977), 9.
(Author and year of publication, page number) “Punishment, then, will tend to become the most hidden part of the penal process” (Foucault 1977, 9).
Modern Language Association (MLA) Format
MLA format traces its history to 1951 when it was first published as a thin booklet. Today, MLA is the primary format used by academics and professionals in humanities, English, literature, media studies, and cultural studies. To adapt to the rapid growth of new mediums over the past few decades, MLA updates its citation system. Visit the MLA Style Center for in-depth information on new guidelines and ongoing changes. In general, in text citations consist of author and page number, or just page number if the author’s name appears in the text.
(Author and page number) “Punishment, then, will tend to become the most hidden part of the penal process” (Foucault 9).
Associated Press (AP) Style
Published in 1952, the original AP Stylebook was marketed to journalists and other professionals related to the Associated Press. AP now stands as the go-to style for professionals in business, public relations, media, mass communications, and journalism. AP style prioritizes brevity and accuracy. The style includes specific guidelines regarding technological terms, titles, locations, and abbreviations and acronyms. Unlike the previous styles, AP does not use parenthetical or in-text citations. Rather, writers cite sources directly in the prose. For more information, including style-checking tools and quizzes, visit the Associated Press Stylebook .
In the book, “Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison,” first published in English in 1977, philosopher Michel Foucault argues that “Punishment, then, will tend to become the most hidden part of the penal process”.
Which Style Should Nursing Students Use?
Because nurses rely on scientific terms and information, professionals in the field usually use APA style. Regardless of the purpose and specific genre of your text, you should always strive for concise, objective, and evidenced-based writing. You can expect to learn APA style as soon as you enroll in a major course. However, you should also prepare to learn other styles as part of your academic training. For example, freshman composition classes tend to focus on MLA guidelines.
Common Writing Mistakes Students Make
Active vs. passive voice.
Active and passive voice represent two different ways to present the same piece of information. Active voice focuses on the subject performing an action. For example, the dog bites the boy. This format creates clear, concise, and engaging writing. Using active voice, nurses might write, I administered patient care at 11:00. Passive voice, on the other hand, focuses on the object of the sentence or the action being performed. For example, the boy was bitten by the dog. A passive sentence is usually one that contains the verb “to be.” Using passive voice, you might write, patient care was administered at 11:00.
Professionals in the sciences often use passive voice in their writing to create an objective tone and authorial distance. Passive voice can prioritize specific terms, actions, evidence, or research over the writer’s presence. Additionally, nurses use passive voice because it is usually clear that the reported thoughts, actions, and opinions come from them. However, you must also learn how to use active voice.
Punctuation
There are 14 punctuation marks in the English language, each with multiple and sometimes overlapping uses. Additionally, certain punctuation marks only make sense in highly specific and nuanced grammatical instances. To master punctuation, you must learn through practice, particularly by revising your own writing.
For example, colons and semicolons are often used interchangeably, when they actually serve distinct purposes. Generally used before itemized lists, colons stand in for the phrases “here is what I mean” or “that is to say.” For example, I am bringing three things to the picnic: applesauce, napkins, and lemonade. Semicolons separate two independent clauses connected through topic or meaning. For example, It was below zero; Ricardo wondered if he would freeze to death. Comma splices, which create run on sentences, are another common mistake. You can identify a comma splice by learning the differences between an independent and dependent clause.
Grammar refers to the rules of a particular language system. Grammar determines how users can structure words and form sentences with coherent meaning. Aspects include syntax (the arrangement of words to convey their mutual relations in a sentence) and semantics (how individual words and word groups are understood). Unless you major in writing, literature, etymology, or another related field, you generally won’t examine English grammar deeply. Through years of cognitive development and practice, native users implicitly understand how to effectively employ the language.
Distinct grammatical systems exist for each language and, sometimes, even within a single language. For example, African American Vernacular English uses different syntactic rules than General American English. You should learn grammatical terms and definitions. Common errors include subject/verb agreement, sentence fragments, dangling modifiers, and vague or incorrect pronoun usage. Hasty writers can also misuse phonetically similar words (your/you’re, its/it’s, and there/their/they’re).
Writing Resources for Nursing Students
Apa style central, reviewed by:.

Shrilekha Deshaies, MSN, RN
Shri Deshaies is a nurse educator with over 20 years of experience teaching in hospital, nursing school, and community settings. Deshaies’ clinical area of expertise is critical care nursing and she is a certified critical care nurse. She has worked in various surgical ICUs throughout her career, including cardiovascular, trauma, and neurosurgery.
Shri Deshaies is a paid member of our Healthcare Review Partner Network. Learn more about our review partners here .
Page last reviewed November 30, 2021
Whether you’re looking to get your pre-licensure degree or taking the next step in your career, the education you need could be more affordable than you think. Find the right nursing program for you.
You might be interested in

HESI vs. TEAS Exam: The Differences Explained
Nursing schools use entrance exams to make admissions decisions. Learn about the differences between the HESI vs. TEAS exams.

10 Nursing Schools That Don’t Require TEAS or HESI Exam

For Chiefs’ RB Clyde Edwards-Helaire, Nursing Runs in the Family
Your web browser is outdated and may be insecure
The RCN recommends using an updated browser such as Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome

Academic writing: what you need to know
10 top tips to help with your studies

Don’t worry, it's a new skill
Start reading, take your time, consider tone.
Nursing is an evidence-based discipline
Think about specialised language
Ask a librarian for help, critical thinking isn’t about criticising.
Use the skills you’ve already developed in other areas
Learn from feedback
Ditch the imposter syndrome, remember your end goal, useful information .
- Find out about literature searching and training .
- Find out more about RCN libraries.
- Podcast series from RCN Magazine: Placements: A Student Survival Guide .

Students: conquer placement nerves
Nervous about an upcoming placement? You're not alone

Student placements: surprising skills in a residential home

RAAC: what you need to know
Crumbling concrete, found in some hospitals, is a safety risk. Here's what to do if you're worried

5 ways to support staff observing Ramadan
Hamira shares her tips for how to support colleagues taking part

How were staffing levels on your last shift?
Complete our survey to help us continue the fight for better staffing levels and patient care.

Student finances: practical tips
Struggling to make your finances add up?
{{ article.Title }}
{{ article.Summary }}
A Complete Guide To Writing Nursing Paper For Medical Students

Medical students have to endure countless hardships during their tenure in the college. Among them, the difficult one is writing a nursing paper on a topic related to their field. It’s not just about composing words after going through the research. It relates to their future learning and demonstrating professionalism in their nursing career.
Don’t worry if this explanation seems daunting or a deal-breaker! Today, we will embark on a journey to understand this topic deeply from within. We will learn why these nursing topics are so complicated and how we can write them without any trouble. Furthermore, we will discuss the importance of evidence-based practice for nursing students. The bonus will be the medical topics that are sure to broaden the extent of your knowledge. Without further ado, let’s get ready!
Table of Contents
What Is a Nursing Paper? (What’s All The Fuss About)
A nursing paper is an assignment given to medical students to develop their understanding of clinical practices. They go through the topic under the strict guidelines from the American School of Nursing & Allied Health. By doing this, they collect vital information related to this field and equip themselves with practical knowledge prior to starting a professional career.
Since it’s a critical care profession that revolves around saving human lives, therefore it requires mistake-free decision-making. Every nursing professional must be equipped with nerves of steel because they cannot perform their job without it. Nursing assignments tend to challenge the student’s comfort zone and take them out of it. That’s why these learners require nursing paper writing service to complete their assignments appropriately.
Different Types of Nursing Papers
There are different types of nursing papers for medical students depending on the discipline they choose. Like medical science that has various branches, similarly, nursing has many types that are explained below.
- Pediatric Nursing
- Geriatric Nursing
- Medical Nursing
- Nephrology Nursing
- Hepatology Nursing
- Ophthalmology Nursing
- Endocrinology Nursing
- Neurology Nursing
- Psychiatric Nursing
- Orthopedic Nursing
- Pulmonology Nursing
- Oncology Nursing
- Radiology Nursing
- Dental Nursing
- Emergency Nursing
- Dermatology Nursing
How to Write a Nursing Research Paper?
It’s not easy to write a nursing paper without appropriate professional tips . Each word of nursing students is critically examined with a critical eye. They need to understand the subject and patient care that will be provided later in their profession.
Let’s start learning the basics of writing a nursing assignment from scratch. It will be the best guide you’ll ever get in your career.
Understand the Prompt and Requirements
The first step that every student overlooks is not understanding the assignment prompt. A half-hearted look at the essay prompt is bad for your grades. If a student doesn’t understand or read what the assignment or their professor wants from them, it’s impossible to make it as required from them.
Secondly, every assignment has some requirements, such as making it on a specific disease or patient type. Similarly, your professor might want to assess your knowledge on the latest nursing guidelines or new major breakthroughs in patient care, etc. Here’s how you can improve your practices by following these steps:
- Don’t just read your prompt but chew on it. Read at least three times to have knowledge from all perspectives.
- Ask your professor promptly before you start your assignment blindly
- Evaluate your skills in comparison with the demands of the topic
- In case where you feel it will overwhelm you, ask your professor to change the subject.
- Many students who have pre-existing phobias such as hemophobia should avoid such topics that discuss blood or anything related to its types.
- If you’re more interested in patient education than direct patient care, then you should discuss this with your professor to assign you topics related to that discipline.
Understanding the requirements also helps your professor to make an accurate judgment about your work. Since your task is about how you’ll cope with real-world pressure when helping or caring for patients, you must demonstrate your best skills at your subject.
Choose a Nursing Research Paper Topic
The second step is choosing a topic that helps you present your stance on a subject. Whether it’s a topic you’ve been given or choose, it has to justify your skills and capabilities as a certified nurse or medical practitioner. Your subject should be broad and can accommodate new research or findings to modify guidelines or challenge the existing ones.
In picking a topic, students must remember to do this process by targeting a niche that helps them navigate in one direction rather than all over the place. Subject selection is difficult if you’re doing it on your own, especially for new students. It’s a time-consuming one. To overcome your shortcomings in this part, you should brainstorm for the topics that excite not only you but also your audience.
Secondly, for subject selection, you can explore new books, medical journals or articles related to nursing and patient care. Since patient care is a discipline that’s evolving continuously, therefore choosing a topic that talks about best nursing practices may take the crown. Here we will present an example of a topic related to nursing that may help you in this process:
Nursing care in Type-1 Diabetics
Having a topic that has plenty of research available will help you broaden your investigation into a multi-faceted one. If you choose a topic that can only accommodate narrow or single-sided research, it’s better to choose a new one. Your subject is your hallmark so you must choose one that helps you expand your knowledge base and skill set. After the selection of the topic, you should move on to the research section.
Start Your Investigation
Research in nursing paper is pivotal to your success. To start your investigation into your topic, you must take a deep dive into reading books to gather credible sources. A research can be divided into two or three sections depending on the nature of the investigation and requirements. Here we will discuss the research methods that students will employ in making their nursing papers .
Research Methods For Nursing Papers
The first step for students is to gather primary sources of research methods. This part includes reading books, journals, and articles directly related to your topic and its outcomes. Since it’s the most valuable part of your investigation, you should give it ample time for appropriate evidence collection. Primary research sources are the ones that are written by doctors or physicians, medical experts etc. Adding these pieces of evidence makes your assignment paper strong and authentic.
In cases where it’s impossible to acquire primary data, you may gather secondary research sources. Secondary sources or evidence is the one that is based on primary evidence, reviews, interviews and expert’s opinion are its examples.
Sometimes your topic requires you to add secondary evidence to support primary research or evidence. This is known as consolidating your arguments in academic practices. So it’s essential to add both research sources in your nursing paper.
For higher education in nursing subjects where they are working alongside medical professionals, adding tertiary sources of research is a plus. Your three-way research supports your arguments and covers all the logic to strengthen your stance on the subject.
After you collect primary, secondary and tertiary sources of research, organize them according to their category. This way you’ll know where to use these evidences and understand their effective usage.
Develop Your Thesis Statement
Researching provides you with ground for developing your thesis statement . Your thesis sentence is your short research-based answer on your research question. Without doing a good research, you won’t be able to compose it. After having sufficient information, you may narrow down the answer into a few lines. Your entire paper will be based on it. In making a thesis statement, do remember the following points:
- It should be between one or a maximum two lines
- Make it using persuasive words so your readers can grab the core idea without going through the entire content
- Place your thesis statement in the introduction paragraph
- Your entire paper must be based on your premise statement. Every argument and evidence should point to it.
After developing a thesis statement, you may start working on your paper’s content. A thesis sentence example may look like this if you’re working on your nursing paper.
“IDF (International Diabetes Federation) and ADA (American Diabetes Association) both agree that Type-2 Diabetics have three-fold risk of developing “Nephropathy” within five years of diagnosis”.
By following the above example, you can easily make a premise statement for your paper.
Write the Introduction Paragraph
The introduction part is where you need to make a difference. It’s the first writing part of your paper that will be seen and read by your professors and peers. Therefore, it must be good and thought-provoking. A nursing essay’s introduction contains three parts, a hook sentence, background information and a thesis statement. These parts of the intro’s outline are essential and help you present your opinion on the topic.
A hook sentence is the first sentence at the start of the paper and captures your reader’s attention quickly. It can be a quote, fact, historical information or thought-provoking statement. Its primary job is to make your readers stay on the page so they feel excited about the information you added in the paper.
Background information is where you provide information related to your topic’s history. Here you must inform your audience about the existence of the problem and the need for a solution. With historical context, it’s easy for your readers to understand the issue and show interest in finding its solution.
The last part is a thesis statement that we already talked about and it will be placed after providing a background to your readers. Let’s have a look at a nursing paper introduction example on “Diabetes”.
“According to the IDF (International Diabetes Federation) 90% of diabetics are suffering from CKD (Chronic Kidney Disease). From 1812 diabetes was classified as a disease but there was no information available related to its treatment and onset. In 1979 the classification and its mechanism was understood by physicians in America and the UK. Now diabetes is the leading cause of ESRD (End Stage Renal Disease) around the world with more than 10 million deaths every year”.
Add Your Arguments in Body Paragraph(s)
The body part is where you must add your arguments and its supporting evidence. Your academic challenges start here and end here. An immaculate body paragraph guarantees your dominance over the subject under discussion. Medical students need to structure their papers in a specific, organized form that helps them convey their opinions.
Academic learners may start the body paragraph of their nursing assignment with a topic sentence that summarizes the entire content in one line. By reading this sentence, your audience knows what’s inside the paragraph and its content.
Key Points to Remember while composing body section
- Topic sentence should start your paragraph and must be relatable to your thesis statement.
- After writing this sentence, break it down and explain each point with evidence.
- Evidence that you’ve collected from books, journals, articles or online videos must be mentioned here. You must back your argument with this evidence collected from the sources mentioned above.
- Presenting evidence is not as important as analyzing it and proving your point. You might want to challenge the findings. Hence you must present your analysis on it.
- If you have plenty of evidence, add them one by one and comment on them similarly.
- Use transitions to connect two different ideas or continuation of your narrative.
Have a look at a mock example of a nursing research paper for a better understanding:
“Since the 1960s diabetes has caused a rapid increase in mortality and comorbidity in patients. On average, diabetics live 15 to 20 years less than non-diabetics. ADA (American Diabetes Association) conducted a study in 2001 that provides mean results that prove Diabetics live 8 years less than non-diabetics. Diabetes is the biggest reason for MI (Myocardial Infarction) and ACD (Acute Coronary Disease).
Moreover, Diabetes costs American insurance companies more than 25$ Billion every year in treatments. With continuous evolution in diagnostics and biotechnology in detecting early onset, diabetes is spreading rapidly. IDF (International Diabetes Federation) has predicted that by 2030, there will be a 12% increase in patients suffering from diabetes.
While many healthcare governing bodies like WHO, IDF, EASD and ADA are doing their best, it’s still not enough. UKPDS and ADVANCE-ON studies have shown quantitative results in which the majority of diabetics have no or less information regarding their disease. These results highlight the importance and value a “Diabetes Educator” can play in spreading valuable information to patients.
The benefits of a medical check-up with your physician are important, but a home visit by a diabetes educator can help in overcoming this pandemic. In France, it’s mandatory for patients to have a weekly home appointment with an educator. That’s a primary reason France has seen a 13% decline in hospitalization of diabetics in 2013.
Based on the above discussion, we can safely conclude that Diabetes is a global pandemic. Healthcare bodies are doing their best to curb its damages by issuing new guidelines and approval of new medicines such as “Semaglutide” , “DPP4” inhibitors and “Sulfonylureas”. Along with physicians, diabetes educators can prevent the severity and further complications of this disease.
Add a Conclusion
A conclusion summarizes the paper’s discussion in one paragraph by a few techniques that we will mention here. To start a nursing assignment’s conclusion, you must restate your thesis statement and provide a connection between the intro, body and its ending.
Secondly, a summary of the main discussion provides your audience with an overview of the entire story. Even if they missed an important point of the topic, they can read it in the summary of the main points. A conclusion provides you an opportunity for a last chance to persuade your readers and convince them of your stance.
Common mistakes that might make your concluding paragraph powerless are mentioned below:
- Using repetitive words, same as used in the above paragraphs.
- Don’t force your audience but persuade them through evidence and their significance.
- Use new words but don’t change your narrative because changing the narrative will also change the context.
- A closing statement should not be your thesis statement but your personal opinion based on your research. Avoid repetition in making this part redundant.
An example of a mock conclusion
“In this paper we have seen multiple results that point to premature deaths in diabetics regardless of the medication used. Diabetes does result in complications like nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, macro and micro vascular complications. Role of primary care physicians, endocrinologists and diabetes educators is more important than anyone else. By making mandatory home visits, diabetes educators can help in managing diabetes and informing patients on the consequences of this disease.”
Student attendants can follow this example and effortlessly write amazing research in nursing paper.
Choosing Appropriate Citation Style
The last part of writing a nursing research paper is choosing the appropriate citation style. This format style guides you on how to cite sources you’ve collected in APA or MLA. The most commonly used citation format is APA (American Psychological Association) and then MLA (Modern Language Association).
Nursing Papers Unveiled: Impact and Significance
Students need to understand the academic importance of nursing papers. These assignments played a significant role in their medical understanding and development of professionalism. Let’s discuss this topic thoroughly:
Importance of Nursing Papers in Student’s Life
Medical assignments are the most important factor in a student’s life. They help develop thoughts and provide opportunities to research and understand disease and its treatment. An assignment for medical nursing students plays the following role in their lives.
- Providing hands-on experience in understanding the subject matter from a practitioner’s point of view.
- It provides them with in-depth information on a particular topic and lets them brainstorm.
- Promotes medical knowledge that will be pivotal in their clinical practices and patient care.
- Enhancing problem solutions without wasting time.
- Understanding the critical needs of patients and managing them appropriately.
- Preparing students beforehand so they perform better in real-world or healthcare practice.
- Finding better treatment prophylaxis and helping in the continual improvement of medical care.
- Working with Medical Specialists and learning from their experiences
These are some of the important roles these medical assignments play in students’ lives.
Exploring Trending Nursing Paper Topics
If you’re searching for the best subjects for your nursing assignment, end your search here. Thoroughly check this list and choose any one of your likings that fulfills the criteria.
20+ Interesting Nursing Paper Topics
- Managing patients in an oncology ward
- Treatment for ACS (Acute Coronary Syndrome)
- How to care for a first-degree burn patient?
- Metabolic acidosis in CKD (Chronic Kidney Disease) patients
- Five basic rules of blood transfusion
- Treatment prophylaxis for skin lesions
- Protocols for Covid-19 patients
- Use of PPE (Personal Protection Equipment) in medical facility
- Fundamentals of Dialysis Center
- DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) and its protocols of treatment
- Snake bites and use of anti-venom in standing urgent care and medical emergency
- Food poisoning and its treatment
- Supervision of cannabis usage in patients suffering from cancer
- Managing patient care in remote areas
- AIDS and patient care
- Orthopedic patient care and mobility issues
- Misuse of drugs by medical staff
- Responsibilities of nursing staff
- Sexual relationships between nurses
- Clinical malpractices and how to avoid it
- Inaccurate physician’s assessment and tackling it
- Rapid plasma glucose checkup
- Treating patients of STD (Sexual Transmitted Disease)
- Needs of rape victims in a healthcare facility
- Psychological support to patients
Check this out, we have written 200 Nursing topics to help you better understand.
These carefully curated topics will help you find your niche in medical nursing assignments. Help yourself by choosing anyone and make a powerful impact on your class.
Integrating Evidence-Based Practice in Your Paper
It’s vital for students to establish evidence-based practice in nursing papers and create an effective plan to implement them in their work. There are many ways you can achieve the best results by following them:
- Take guidelines from CMDT (Current Medical Treatment & Diagnosis).
- Regularly visit the website of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) for new practice guidelines.
- Apply for membership in the Nursing and Allied Health Resources Section. You can get authentic resources of practice and take notes of them for using them in your assignment.
- Read CDC (Center for Disease Control) and FDA (Food and Drug Administration) guidelines on different disease treatment protocols and latest trials.
You can easily apply evidence-based practice in nursing papers by visiting these sources.
Nurturing Ideas: Crafting Pediatric Nursing Papers
Pediatrics is a field of medical science that deals with treating diseases that affect children up to the age of 16 years. It’s the same as treating general patients who are adults but treatment protocols here change due to the less potent immune systems of children and neonates. Similarly, pediatric nursing papers are the backbone of innovation and new drug introduction. Nursing students who like to practice in the pediatric department need to work twice as hard as in the general medicine department.
Additionally, pediatric nursing papers present new challenges, and students must be able to withstand them. A small mistake can have catastrophic outcomes. Hence students are required to do 6 months of supervision work with trained nurses before they are allowed to practice alone.
Guide to Geriatric Nursing Papers
Similar to pediatrics, geriatrics nursing papers are equally challenging. In medical science, geriatrics deals with patients older than 60 or 65 years. These patients require special care because of their age and vulnerability to getting sick quickly due to weaker immune systems.
To make geriatric nursing papers with absolutely no mistakes, students must spend a few hours in this speciality. Students may take notes from their ward visits, review each case and brainstorm for the best treatment and care solutions. Students are more likely to adopt best practices by doing this every day.

Ethics in Nursing Papers: Navigating Moral Dilemmas
Composing medical assignments challenges your skills and knowledge and offers a view for moral perspectives. There are many ethical considerations in nursing papers that students must adhere to. These reservations include the following points:
- Always use scientific data from reputable sources.
- Never claim anything without properly identifying the nature and results of the research.
- Only use sources after getting prior authorization to use them in your nursing paper.
- Patient care always comes first, regardless of the nature or conflicts in medical treatment.
- Always acquiring and using patient data with signed and attested papers for research purposes and informing them of all the intricacies.
- Never copy data or details of other students’ work to use in your research paper unless your professor allows it.
Nursing learners must adhere to these ethical considerations in nursing papers. Following these principles and moralities serve their profession well and make them honest in their work.
Avoid These Mistakes While Writing Your Research Paper on Nursing
Students make many mistakes when they start a research paper on nursing. Some of the common ones are mentioned below:
- Using irrelevant data
- Not doing thorough research
- Not having enough understanding of the disease
- Making assumptions on disease prognosis without evidence
- Using proprietary research without authorization
- Selecting a topic out of discipline or nature of scope
- Using plagiarized content
- Adding disputed research with dubious record
- Non-adherence to academic rules and guidelines provided by your professor
Abstract Writing for Nursing Papers
An abstract is your summary of the entire research, it’s a concise 300 to 600 words section. Nursing paper abstracts are sometimes lengthier than typical research papers. Here is an example of this section:
“Diabetes causes various types of disease that range from macro and micro vascular ones to metabolic. This research paper has acquired data from IDF and EASD and came to a conclusion that more than 80% of patients suffer premature deaths and renal failures. The data acquisition method is quantitative with retrospective diagnosis and diagnostic tests such as eGFR, Random Blood Serum and Fasting Blood Serum Testing kits in use. Majority of the patients have elevated serum glucose level 240 mg/dl or above. eGFR of 92% patients was between 60ml/min that puts them on stage 3 CKD. It’s evident that diabetes causes mortality and renal failure.”
It’s hard for students to compose nursing paper abstracts from scratch. This mock example will help them in the long term.
Perfecting Your Nursing Paper: Editing and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading is the last thing you must consider when making last-minute changes to your content. Polishing your nursing paper helps you present your opinion clearly and concisely without vague statements.
Writing a nursing paper is only possible when students know all the medical details of this profession. Our guide provides you with sufficient medical details related to this subject. Read it carefully, and you’ll be able to create amazing assignments for medical class. This expert’s guide helps to overcome the gaps in this field by allowing students to jump-start the learning process.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Academic essays part 3: how to pass an assignment.
John Fowler
Educational Consultant, explores how to survive your nursing career
View articles
John Fowler , Educational Consultant, explores academic writing

Writing an academic essay is a skill, and like any other skill it can be learnt and improved upon. This is easier if the skill is broken down into steps that can be identified, followed and practised. Whereas nurse educators recognise the need to teach practical skills by identifying the various steps involved in the process—such as nursing assessments or applying sterile dressings—they are not so good at helping students identify the essential components of a successful academic essay. If the student can appreciate why these components are essential, they can be honed and practised to improve academic performance. These principles can also be used to give structure for lecturers introducing an assignment or formulating individual feedback.
Essential components of a successful essay
I've been setting and marking essays for over 30 years, supporting a range of staff from first-year students to specialist nurses undertaking Masters and PhDs. From this, I've identified eight components that make up the skill of successful academic essay writing:
- Clear thinking and factually correct The essay is a clear and logical exploration of the question set, based on the best available evidence. This demonstrates that the student has understood the subject and researched the question, going beyond their own opinions.
- Use of evidence-based literature and correct referencing technique The subject is explored using published evidence from journals and appropriate sources such as www.nice.org.uk and Cochrane databases. This demonstrates that the student can extract up-to-date information from reliable sources and reference the sources correctly as per the specific university guidelines.
- Evaluation of the evidence Rather than just repeating that an author said ‘A+B = C’ the student asks questions of the reliability of the evidence in terms of research style and sample size. Do the findings from one clinical setting transfer to another setting? This demonstrates that although the student understands the importance of evidence-based practice, they are not just accepting that anything in print can be directly applied without question.
- Comparative analysis The essay is not just a list of what different authors have said. It demonstrates that the student has read different papers and has attempted to make sense of how the opinions and findings agree or disagree. For example: Brown and Smith (2015) identified ‘patient-controlled analgesia’ as an important factor in a patient's perception of postoperative pain on a surgical ward. This was supported by Raby (2019) with patients on a orthopaedic ward, but not identified by Raine (2018), whose work centred on palliative care wards .
- Use of own experience to comment on the literature The student uses their own experience to comment on the literature, either agreeing, disagreeing or offering an explanation. This is very different from the student stating an opinion and then saying Smith (2010) agrees with me . Thus in the example above of factors affecting a patient's pain perception, the student might add an opinion as to why the results from a palliative care setting did not identify patient-controlled analgesia as an important factor. It is important that the nurse's experience is offered as a possible explanation rather than as a solid fact.
- Identification of gaps in the literature Once the evidence from the literature has been collected the student can use their clinical experience to comment on possible gaps in the literature. This is a valuable way to use clinical experience. It demonstrates understanding of the principles regarding the topic set in the question and acknowledges that there are many aspect of nursing not fully explored in the literature. It can also demonstrate originality of thought and ideas.
- Development of an argument The essay is not just a collection of ‘stand alone’ paragraphs. There should be a structure to the essay in which the main theme of the question set is explored, with each paragraph exploring a different sub theme. These sub themes should build together, linking and complementing each other. As the essay progresses it develops the interaction of the themes and the deepening of the argument based on the assignment question.
- Clear conclusion The conclusion should be about 8-10% of the essay. It should draw out the findings from the body of the essay and present them clearly and concisely. The argument that has been developed in the essay should be summarised and the implications for nursing discussed. The student should be succinctly answering any points in the original question.
Essay writing is a skill. Too often students of all professions are left to develop this skill by trial and error, never really understanding why one essay achieved a high mark and the next one didn't. Once you begin to understand the various components of this skill then you can begin to incorporate and build them into your work. Understanding why they are important and then practising them will help you develop and improve this important skill.
Nursing Care Plans (NCP): Ultimate Guide and List

Writing the best nursing care plan requires a step-by-step approach to complete the parts needed for a care plan correctly. This tutorial will walk you through developing a care plan. This guide has the ultimate database and list of nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnosis samples for our student nurses and professional nurses to use—all for free! Care plan components, examples, objectives, and purposes are included with a detailed guide on writing an excellent nursing care plan or a template for your unit.
Table of Contents
Standardized care plans, individualized care plans, purposes of a nursing care plan, three-column format, four-column format, student care plans, step 1: data collection or assessment, step 2: data analysis and organization, step 3: formulating your nursing diagnoses, step 4: setting priorities, short-term and long-term goals, components of goals and desired outcomes, types of nursing interventions, step 7: providing rationale, step 8: evaluation, step 9: putting it on paper, basic nursing and general care plans, surgery and perioperative care plans, cardiac care plans, endocrine and metabolic care plans, gastrointestinal, hematologic and lymphatic, infectious diseases, integumentary, maternal and newborn care plans, mental health and psychiatric, musculoskeletal, neurological, pediatric nursing care plans, reproductive, respiratory, recommended resources, references and sources, what is a nursing care plan.
A nursing care plan (NCP) is a formal process that correctly identifies existing needs and recognizes a client’s potential needs or risks. Care plans provide a way of communication among nurses, their patients, and other healthcare providers to achieve healthcare outcomes. Without the nursing care planning process, the quality and consistency of patient care would be lost.
Nursing care planning begins when the client is admitted to the agency and is continuously updated throughout in response to the client’s changes in condition and evaluation of goal achievement. Planning and delivering individualized or patient-centered care is the basis for excellence in nursing practice.
Types of Nursing Care Plans
Care plans can be informal or formal: An informal nursing care plan is a strategy of action that exists in the nurse ‘s mind. A formal nursing care plan is a written or computerized guide that organizes the client’s care information.
Formal care plans are further subdivided into standardized care plans and individualized care plans: Standardized care plans specify the nursing care for groups of clients with everyday needs. Individualized care plans are tailored to meet a specific client’s unique needs or needs that are not addressed by the standardized care plan.
Standardized care plans are pre-developed guides by the nursing staff and health care agencies to ensure that patients with a particular condition receive consistent care. These care plans are used to ensure that minimally acceptable criteria are met and to promote the efficient use of the nurse’s time by removing the need to develop common activities that are done repeatedly for many of the clients on a nursing unit.
Standardized care plans are not tailored to a patient’s specific needs and goals and can provide a starting point for developing an individualized care plan .
Care plans listed in this guide are standard care plans which can serve as a framework or direction to develop an individualized care plan.
An individualized care plan care plan involves tailoring a standardized care plan to meet the specific needs and goals of the individual client and use approaches shown to be effective for a particular client. This approach allows more personalized and holistic care better suited to the client’s unique needs, strengths, and goals.
Additionally, individualized care plans can improve patient satisfaction . When patients feel that their care is tailored to their specific needs, they are more likely to feel heard and valued, leading to increased satisfaction with their care. This is particularly important in today’s healthcare environment, where patient satisfaction is increasingly used as a quality measure.
Tips on how to individualize a nursing care plan:
- Perform a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s health, history, health status, and desired goals.
- Involve the patient in the care planning process by asking them about their health goals and preferences. By involving the client, nurses can ensure that the care plan is aligned with the patient’s goals and preferences which can improve patient engagement and compliance with the care plan.
- Perform an ongoing assessment and evaluation as the patient’s health and goals can change. Adjust the care plan accordingly.
The following are the goals and objectives of writing a nursing care plan:
- Promote evidence-based nursing care and render pleasant and familiar conditions in hospitals or health centers.
- Support holistic care, which involves the whole person, including physical, psychological, social, and spiritual, with the management and prevention of the disease.
- Establish programs such as care pathways and care bundles. Care pathways involve a team effort to reach a consensus regarding standards of care and expected outcomes. In contrast, care bundles are related to best practices concerning care for a specific disease.
- Identify and distinguish goals and expected outcomes.
- Review communication and documentation of the care plan.
- Measure nursing care.
The following are the purposes and importance of writing a nursing care plan:
- Defines nurse’s role. Care plans help identify nurses’ unique and independent role in attending to clients’ overall health and well-being without relying entirely on a physician’s orders or interventions.
- Provides direction for individualized care of the client. It serves as a roadmap for the care that will be provided to the patient and allows the nurse to think critically in developing interventions directly tailored to the individual.
- Continuity of care. Nurses from different shifts or departments can use the data to render the same quality and type of interventions to care for clients, therefore allowing clients to receive the most benefit from treatment.
- Coordinate care. Ensures that all members of the healthcare team are aware of the patient’s care needs and the actions that need to be taken to meet those needs preventing gaps in care.
- Documentation. It should accurately outline which observations to make, what nursing actions to carry out, and what instructions the client or family members require. If nursing care is not documented correctly in the care plan, there is no evidence the care was provided.
- Serves as a guide for assigning a specific staff to a specific client. There are instances when a client’s care needs to be assigned to staff with particular and precise skills.
- Monitor progress. To help track the patient’s progress and make necessary adjustments to the care plan as the patient’s health status and goals change.
- Serves as a guide for reimbursement. The insurance companies use the medical record to determine what they will pay concerning the hospital care received by the client.
- Defines client’s goals. It benefits nurses and clients by involving them in their treatment and care.
A nursing care plan (NCP) usually includes nursing diagnoses, client problems, expected outcomes, nursing interventions, and rationales. These components are elaborated on below:
- Client health assessment , medical results, and diagnostic reports are the first steps to developing a care plan. In particular, client assessment relates to the following areas and abilities: physical, emotional, sexual, psychosocial, cultural, spiritual/transpersonal, cognitive, functional, age-related, economic, and environmental. Information in this area can be subjective and objective.
- Nursing diagnosis . A nursing diagnosis is a statement that describes the patient’s health issue or concern. It is based on the information gathered about the patient’s health status during the assessment.
- Expected client outcomes. These are specific goals that will be achieved through nursing interventions. These may be long and short-term.
- Nursing interventions . These are specific actions that will be taken to address the nursing diagnosis and achieve expected outcomes . They should be based on best practices and evidence-based guidelines.
- Rationales. These are evidence-based explanations for the nursing interventions specified.
- Evaluation . These includes plans for monitoring and evaluating a patient’s progress and making necessary adjustments to the care plan as the patient’s health status and goals change.
Care Plan Formats
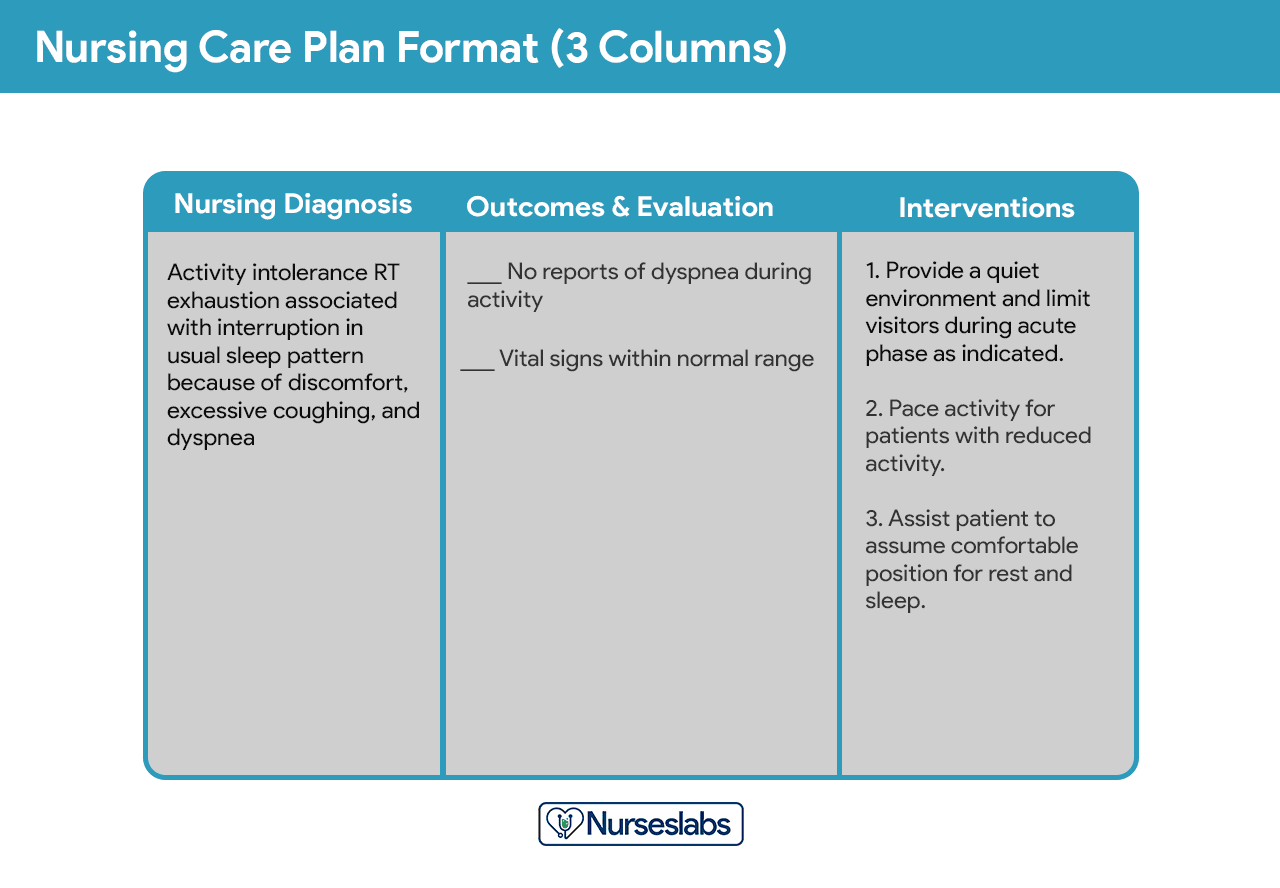
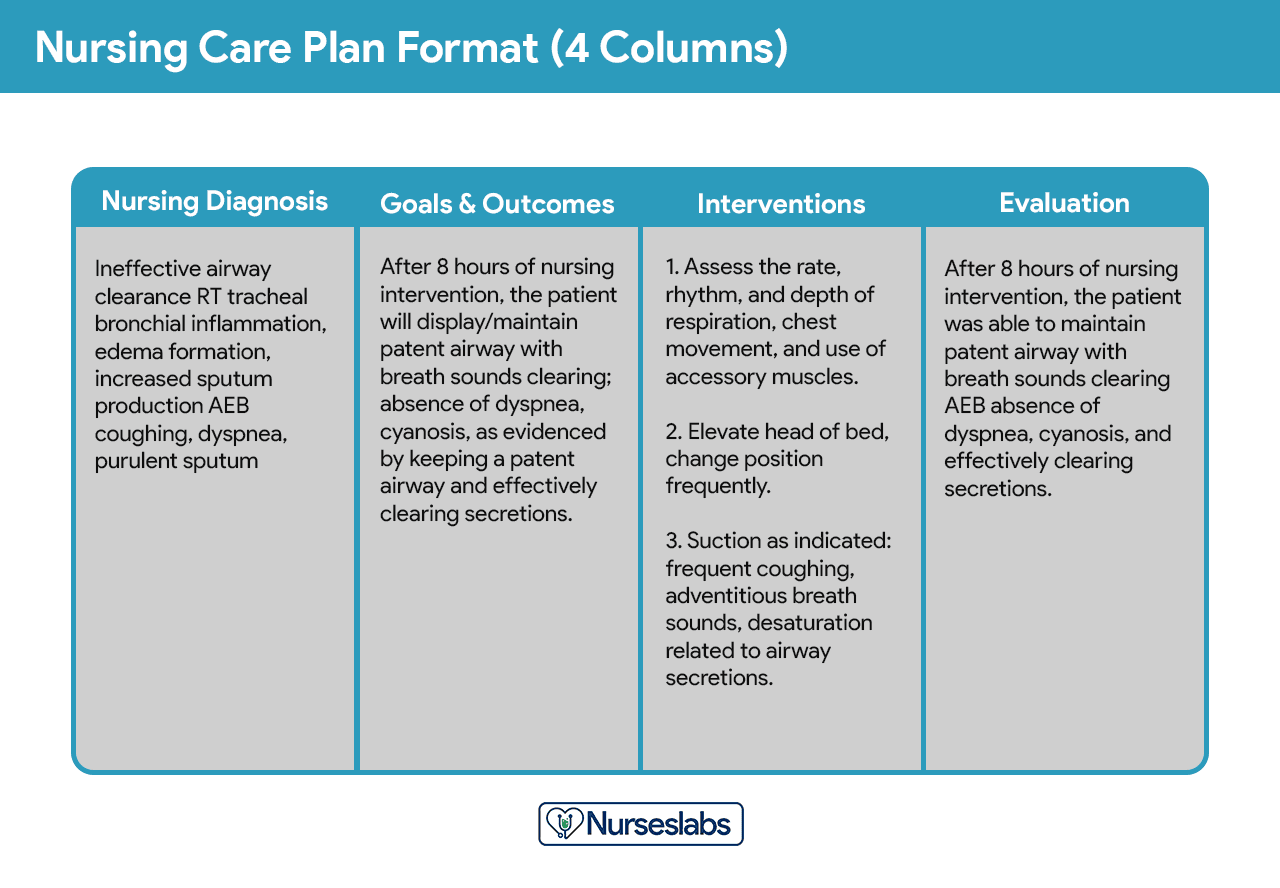
Nursing care plan formats are usually categorized or organized into four columns: (1) nursing diagnoses, (2) desired outcomes and goals, (3) nursing interventions, and (4) evaluation. Some agencies use a three-column plan where goals and evaluation are in the same column. Other agencies have a five-column plan that includes a column for assessment cues.
The three-column plan has a column for nursing diagnosis, outcomes and evaluation, and interventions.
This format includes columns for nursing diagnosis, goals and outcomes, interventions, and evaluation.
Below is a document containing sample templates for the different nursing care plan formats. Please feel free to edit, modify, and share the template.
Download: Printable Nursing Care Plan Templates and Formats
Student care plans are more lengthy and detailed than care plans used by working nurses because they serve as a learning activity for the student nurse.
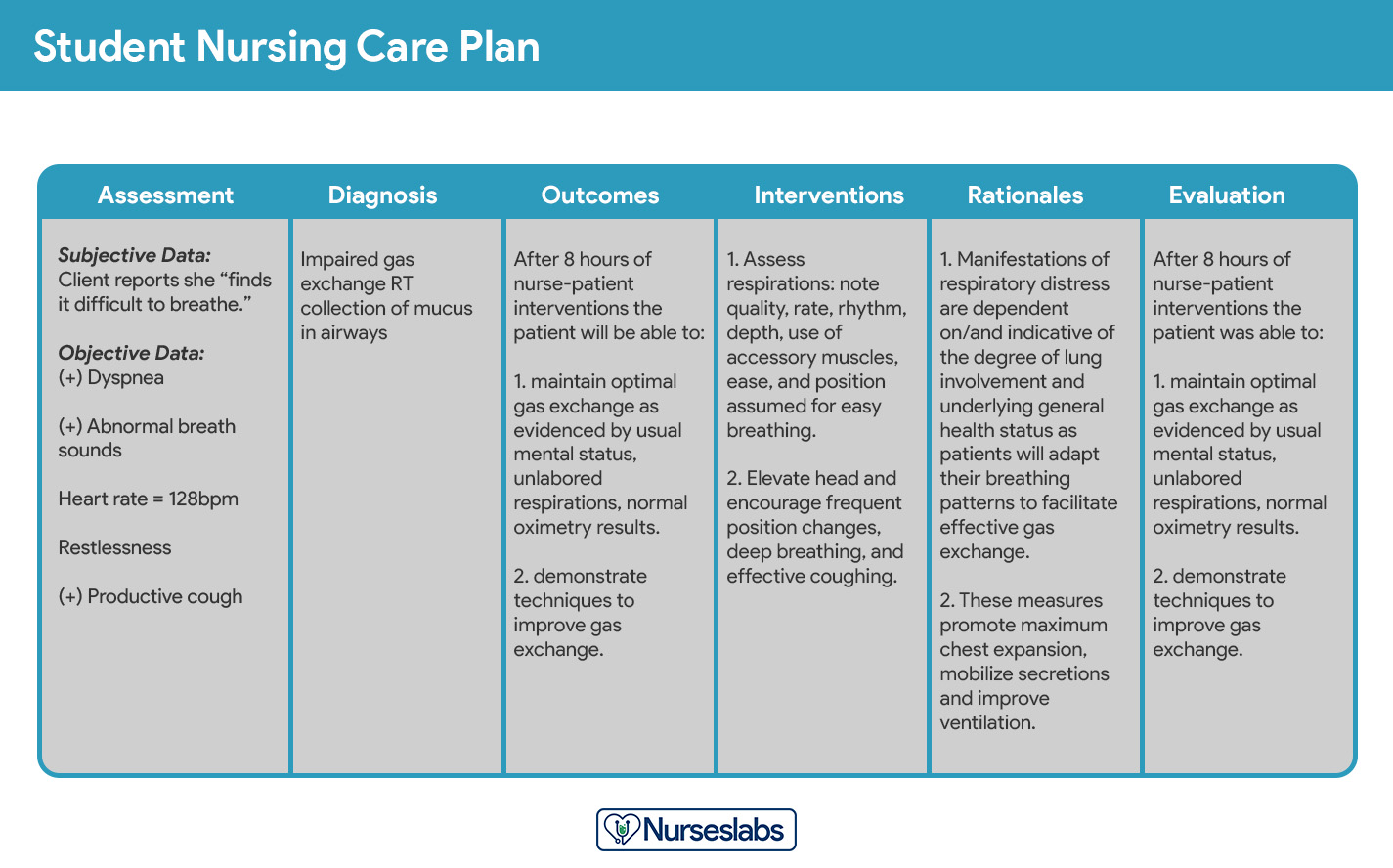
Care plans by student nurses are usually required to be handwritten and have an additional column for “Rationale” or “Scientific Explanation” after the nursing interventions column. Rationales are scientific principles that explain the reasons for selecting a particular nursing intervention.
Writing a Nursing Care Plan
How do you write a nursing care plan (NCP)? Just follow the steps below to develop a care plan for your client.
The first step in writing a nursing care plan is to create a client database using assessment techniques and data collection methods (physical assessment, health history, interview, medical records review, and diagnostic studies). A client database includes all the health information gathered . In this step, the nurse can identify the related or risk factors and defining characteristics that can be used to formulate a nursing diagnosis. Some agencies or nursing schools have specific assessment formats you can use.
Critical thinking is key in patient assessment, integrating knowledge across sciences and professional guidelines to inform evaluations. This process, crucial for complex clinical decision-making, aims to identify patients’ healthcare needs effectively, leveraging a supportive environment and reliable information
Now that you have information about the client’s health, analyze, cluster, and organize the data to formulate your nursing diagnosis, priorities, and desired outcomes.
Nursing diagnoses are a uniform way of identifying, focusing on and dealing with specific client needs and responses to actual and high-risk problems. Actual or potential health problems that can be prevented or resolved by independent nursing intervention are termed nursing diagnoses.
We’ve detailed the steps on how to formulate your nursing diagnoses in this guide: Nursing Diagnosis (NDx): Complete Guide and List .
Setting priorities involves establishing a preferential sequence for addressing nursing diagnoses and interventions. In this step, the nurse and the client begin planning which of the identified problems requires attention first. Diagnoses can be ranked and grouped as having a high, medium, or low priority. Life-threatening problems should be given high priority.
A nursing diagnosis encompasses Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and helps to prioritize and plan care based on patient-centered outcomes. In 1943, Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchy based on basic fundamental needs innate to all individuals. Basic physiological needs/goals must be met before higher needs/goals can be achieved, such as self-esteem and self-actualization. Physiological and safety needs are the basis for implementing nursing care and interventions. Thus, they are at the base of Maslow’s pyramid, laying the foundation for physical and emotional health.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Basic Physiological Needs: Nutrition (water and food), elimination (Toileting), airway (suction)-breathing (oxygen)-circulation (pulse, cardiac monitor, blood pressure) (ABCs), sleep , sex, shelter, and exercise.
- Safety and Security: Injury prevention ( side rails , call lights, hand hygiene , isolation , suicide precautions, fall precautions, car seats, helmets, seat belts), fostering a climate of trust and safety ( therapeutic relationship ), patient education (modifiable risk factors for stroke , heart disease).
- Love and Belonging: Foster supportive relationships, methods to avoid social isolation ( bullying ), employ active listening techniques, therapeutic communication , and sexual intimacy.
- Self-Esteem: Acceptance in the community, workforce, personal achievement, sense of control or empowerment, accepting one’s physical appearance or body habitus.
- Self-Actualization: Empowering environment, spiritual growth, ability to recognize the point of view of others, reaching one’s maximum potential.
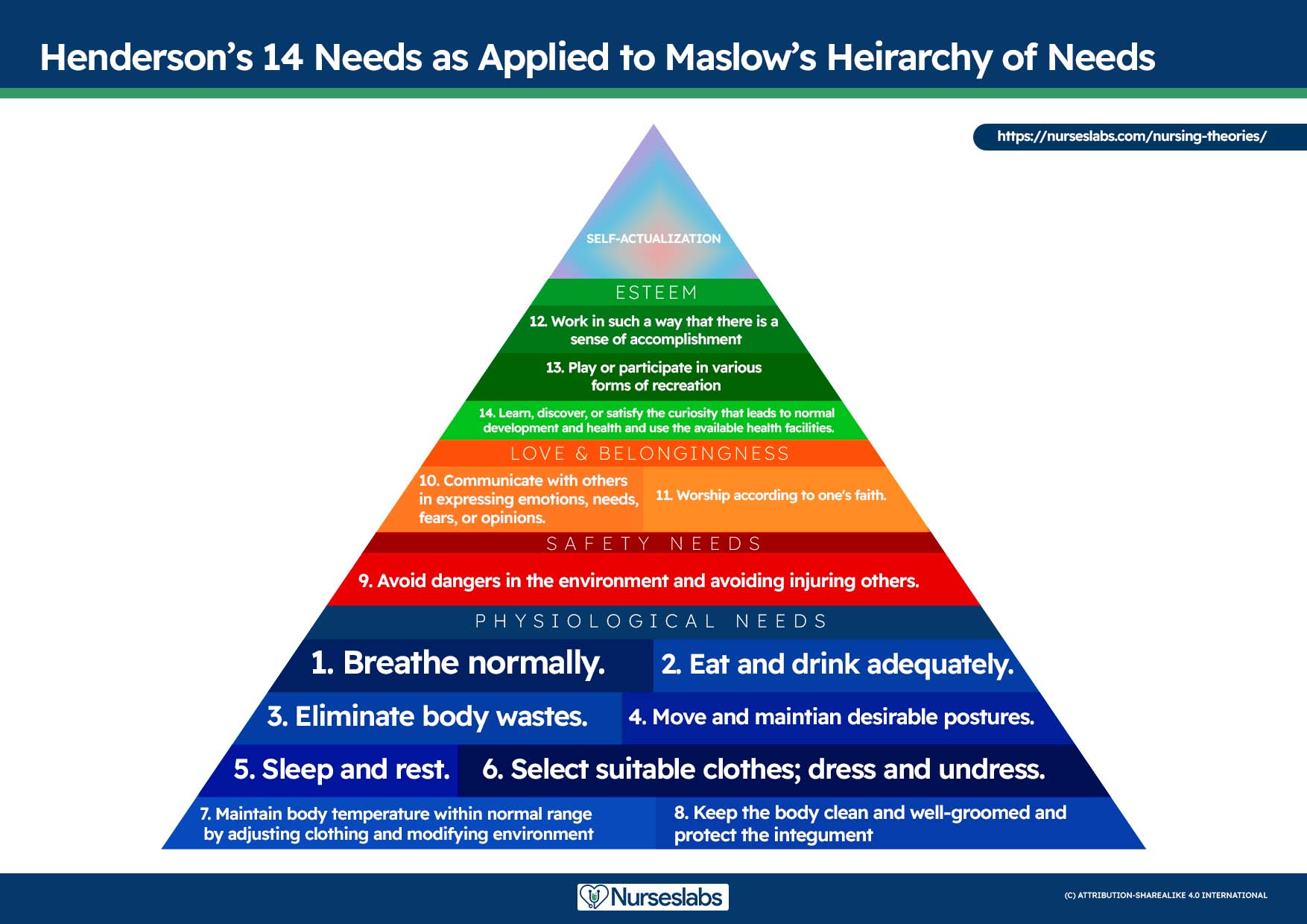
The client’s health values and beliefs, priorities, resources available, and urgency are factors the nurse must consider when assigning priorities. Involve the client in the process to enhance cooperation.
Step 5: Establishing Client Goals and Desired Outcomes
After assigning priorities for your nursing diagnosis, the nurse and the client set goals for each determined priority. Goals or desired outcomes describe what the nurse hopes to achieve by implementing the nursing interventions derived from the client’s nursing diagnoses. Goals provide direction for planning interventions, serve as criteria for evaluating client progress, enable the client and nurse to determine which problems have been resolved, and help motivate the client and nurse by providing a sense of achievement.
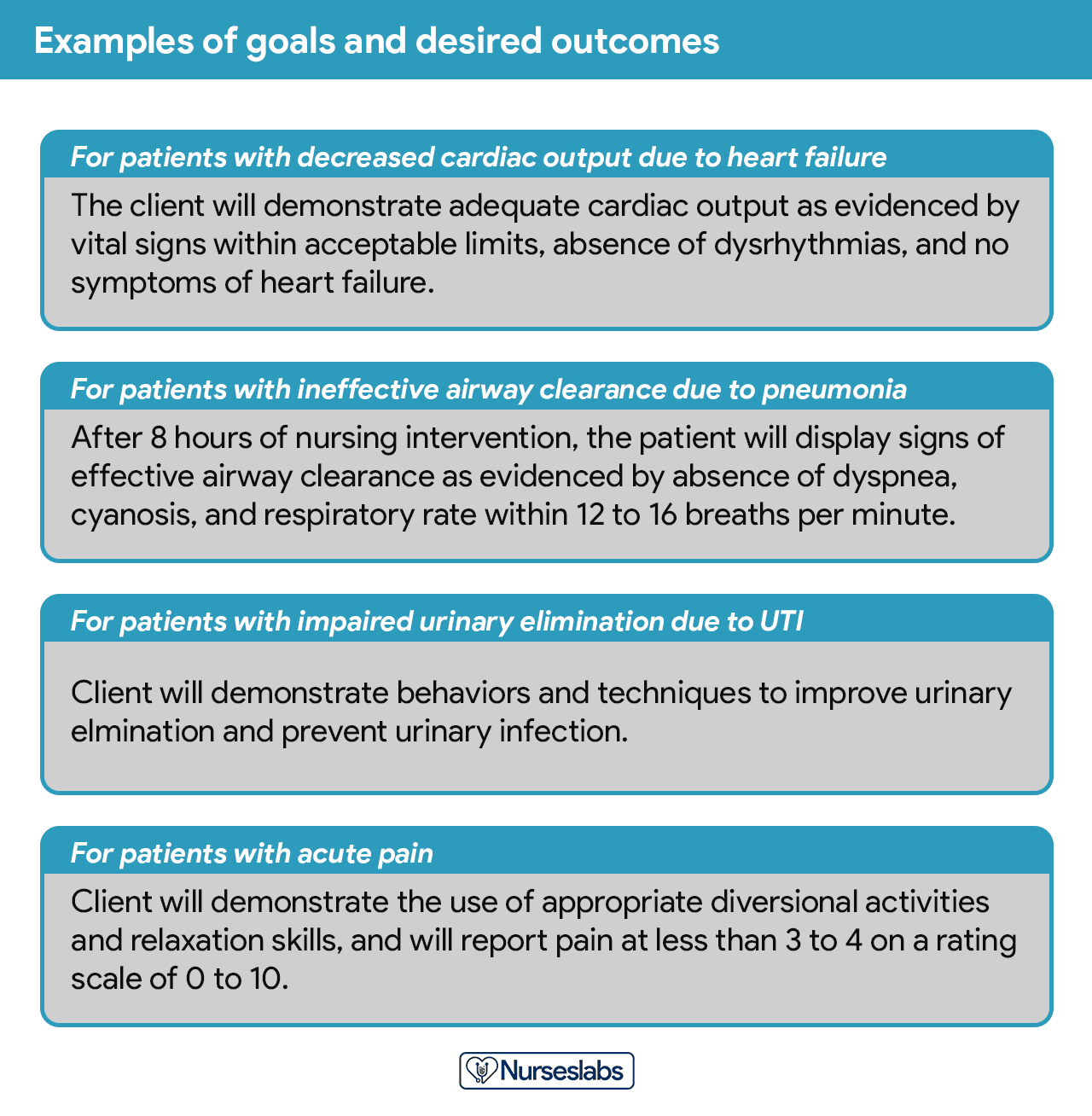
One overall goal is determined for each nursing diagnosis. The terms “ goal outcomes “ and “expected outcome s” are often used interchangeably.
According to Hamilton and Price (2013), goals should be SMART . SMART stands for specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-oriented goals.
- Specific. It should be clear, significant, and sensible for a goal to be effective.
- Measurable or Meaningful. Making sure a goal is measurable makes it easier to monitor progress and know when it reaches the desired result.
- Attainable or Action-Oriented. Goals should be flexible but remain possible.
- Realistic or Results-Oriented. This is important to look forward to effective and successful outcomes by keeping in mind the available resources at hand.
- Timely or Time-Oriented. Every goal needs a designated time parameter, a deadline to focus on, and something to work toward.
Hogston (2011) suggests using the REEPIG standards to ensure that care is of the highest standards. By this means, nursing care plans should be:
- Realistic. Given available resources.
- Explicitly stated. Be clear about precisely what must be done, so there is no room for misinterpretation of instructions.
- Evidence-based. That there is research that supports what is being proposed.
- Prioritized. The most urgent problems are being dealt with first.
- Involve. Involve both the patient and other members of the multidisciplinary team who are going to be involved in implementing the care.
- Goal-centered. That the care planned will meet and achieve the goal set.
Goals and expected outcomes must be measurable and client-centered. Goals are constructed by focusing on problem prevention, resolution, and rehabilitation. Goals can be short-term or long-term . Most goals are short-term in an acute care setting since much of the nurse’s time is spent on the client’s immediate needs. Long-term goals are often used for clients who have chronic health problems or live at home, in nursing homes, or in extended-care facilities.
- Short-term goal . A statement distinguishing a shift in behavior that can be completed immediately, usually within a few hours or days.
- Long-term goal . Indicates an objective to be completed over a longer period, usually weeks or months.
- Discharge planning . Involves naming long-term goals, therefore promoting continued restorative care and problem resolution through home health, physical therapy, or various other referral sources.
Goals or desired outcome statements usually have four components: a subject, a verb, conditions or modifiers, and a criterion of desired performance.
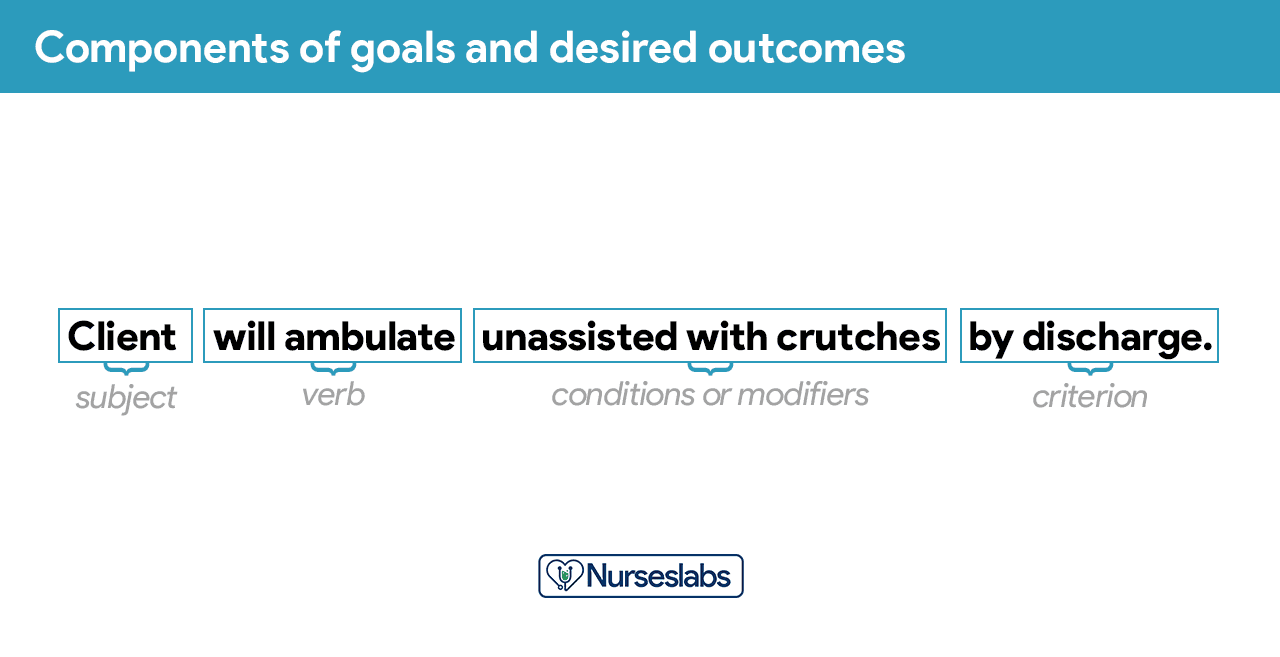
- Subject. The subject is the client, any part of the client, or some attribute of the client (i.e., pulse, temperature, urinary output). That subject is often omitted in writing goals because it is assumed that the subject is the client unless indicated otherwise (family, significant other ).
- Verb. The verb specifies an action the client is to perform, for example, what the client is to do, learn, or experience.
- Conditions or modifiers. These are the “what, when, where, or how” that are added to the verb to explain the circumstances under which the behavior is to be performed.
- Criterion of desired performance. The criterion indicates the standard by which a performance is evaluated or the level at which the client will perform the specified behavior. These are optional.
When writing goals and desired outcomes, the nurse should follow these tips:
- Write goals and outcomes in terms of client responses and not as activities of the nurse. Begin each goal with “Client will […]” help focus the goal on client behavior and responses.
- Avoid writing goals on what the nurse hopes to accomplish, and focus on what the client will do.
- Use observable, measurable terms for outcomes. Avoid using vague words that require interpretation or judgment of the observer.
- Desired outcomes should be realistic for the client’s resources, capabilities, limitations, and on the designated time span of care.
- Ensure that goals are compatible with the therapies of other professionals.
- Ensure that each goal is derived from only one nursing diagnosis. Keeping it this way facilitates evaluation of care by ensuring that planned nursing interventions are clearly related to the diagnosis set.
- Lastly, make sure that the client considers the goals important and values them to ensure cooperation.
Step 6: Selecting Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions are activities or actions that a nurse performs to achieve client goals. Interventions chosen should focus on eliminating or reducing the etiology of the priority nursing problem or diagnosis. As for risk nursing problems, interventions should focus on reducing the client’s risk factors. In this step, nursing interventions are identified and written during the planning step of the nursing process ; however, they are actually performed during the implementation step.
Nursing interventions can be independent, dependent, or collaborative:
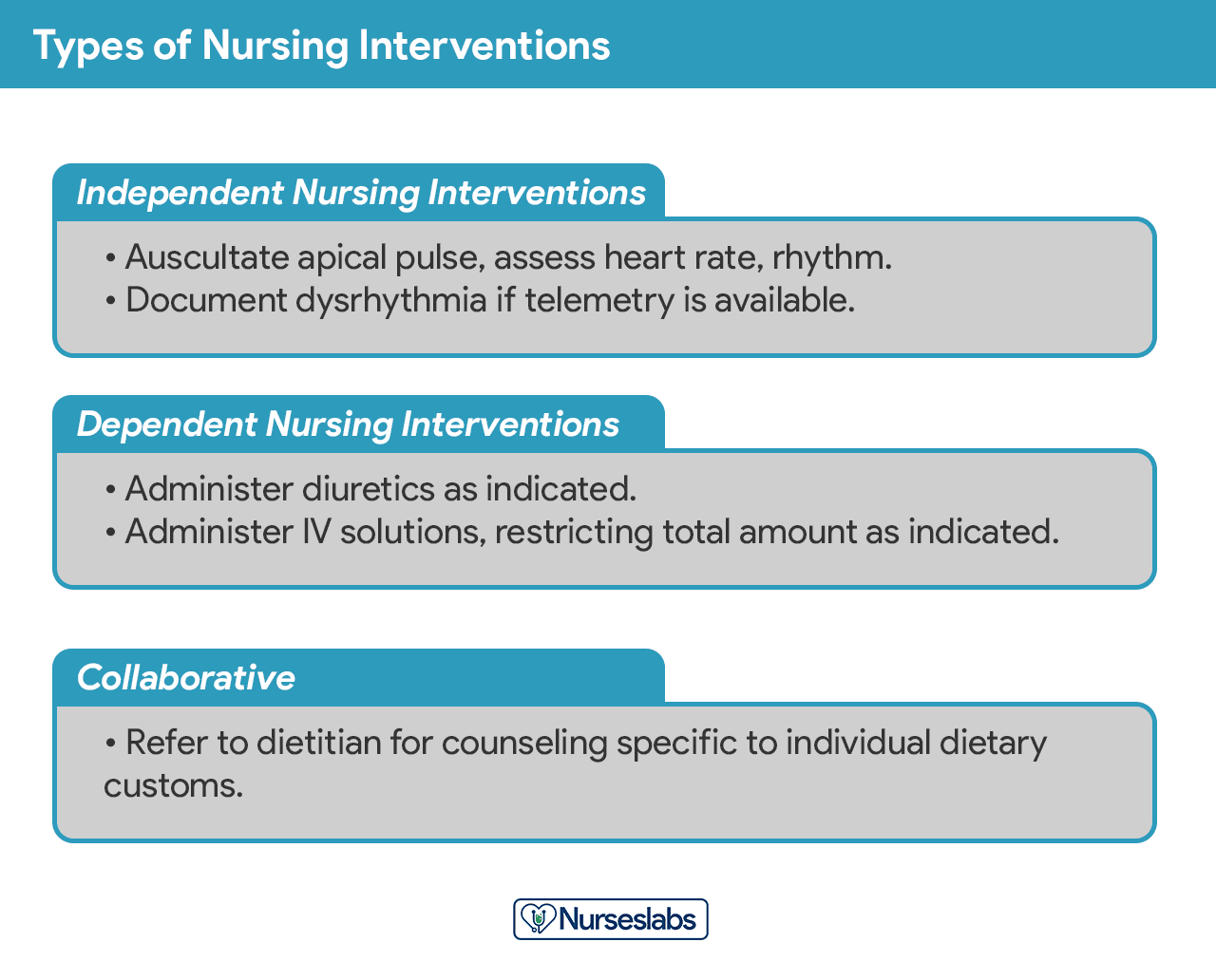
- Independent nursing interventions are activities that nurses are licensed to initiate based on their sound judgement and skills. Includes: ongoing assessment, emotional support, providing comfort, teaching, physical care, and making referrals to other health care professionals.
- Dependent nursing interventions are activities carried out under the physician’s orders or supervision. Includes orders to direct the nurse to provide medications, intravenous therapy , diagnostic tests, treatments, diet, and activity or rest. Assessment and providing explanation while administering medical orders are also part of the dependent nursing interventions.
- Collaborative interventions are actions that the nurse carries out in collaboration with other health team members, such as physicians, social workers, dietitians, and therapists. These actions are developed in consultation with other health care professionals to gain their professional viewpoint.
Nursing interventions should be:
- Safe and appropriate for the client’s age, health, and condition.
- Achievable with the resources and time available.
- Inline with the client’s values, culture, and beliefs.
- Inline with other therapies.
- Based on nursing knowledge and experience or knowledge from relevant sciences.
When writing nursing interventions, follow these tips:
- Write the date and sign the plan. The date the plan is written is essential for evaluation, review, and future planning. The nurse’s signature demonstrates accountability.
- Nursing interventions should be specific and clearly stated, beginning with an action verb indicating what the nurse is expected to do. Action verb starts the intervention and must be precise. Qualifiers of how, when, where, time, frequency, and amount provide the content of the planned activity. For example: “ Educate parents on how to take temperature and notify of any changes,” or “ Assess urine for color, amount, odor, and turbidity.”
- Use only abbreviations accepted by the institution.
Rationales, also known as scientific explanations, explain why the nursing intervention was chosen for the NCP.
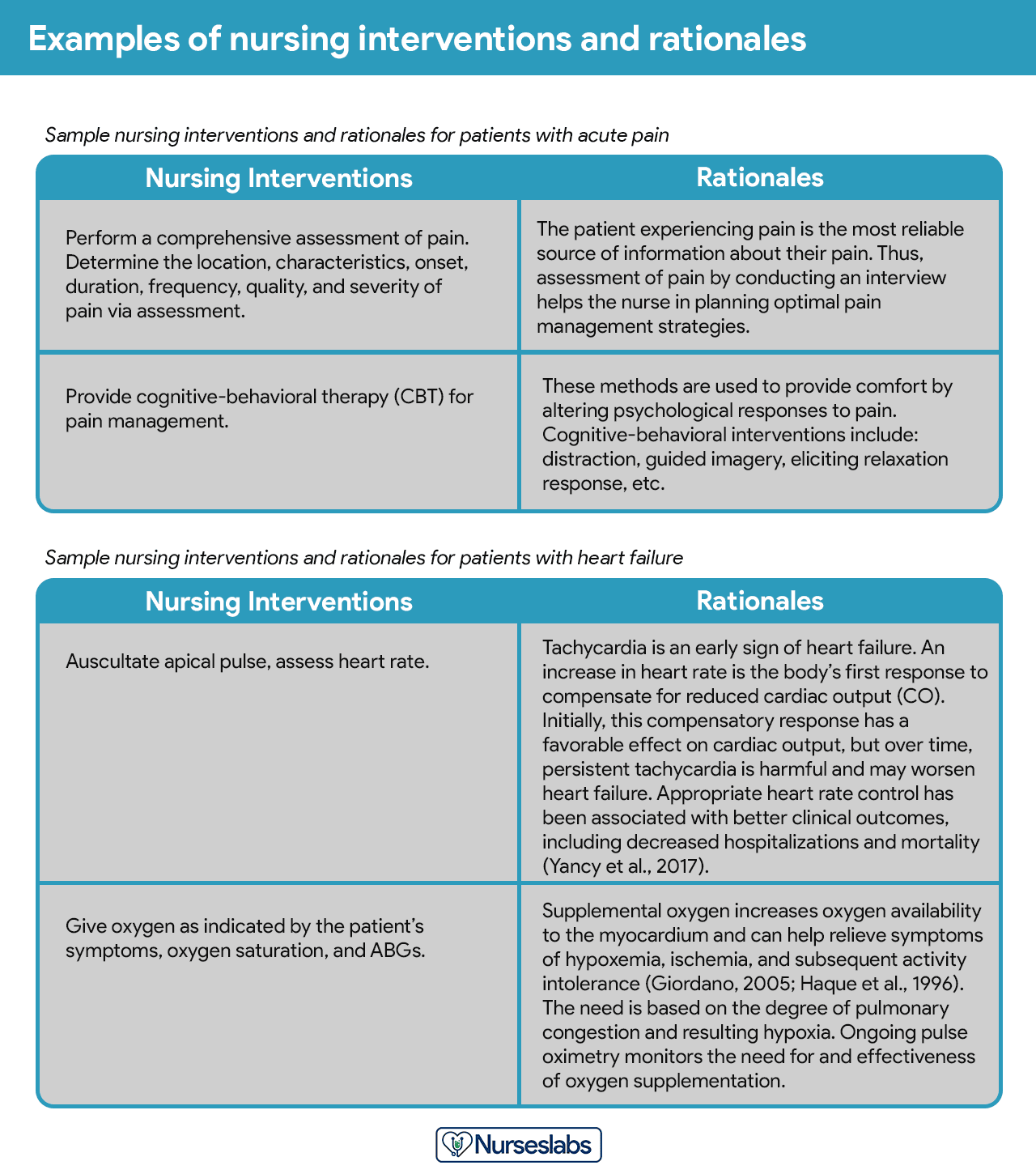
Rationales do not appear in regular care plans. They are included to assist nursing students in associating the pathophysiological and psychological principles with the selected nursing intervention.
Evaluation is a planned, ongoing, purposeful activity in which the client’s progress towards achieving goals or desired outcomes is assessed, and the effectiveness of the nursing care plan (NCP). Evaluation is an essential aspect of the nursing process because the conclusions drawn from this step determine whether the nursing intervention should be terminated, continued, or changed.
The client’s care plan is documented according to hospital policy and becomes part of the client’s permanent medical record, which may be reviewed by the oncoming nurse. Different nursing programs have different care plan formats. Most are designed so that the student systematically proceeds through the interrelated steps of the nursing process , and many use a five-column format.
Nursing Care Plan List
This section lists the sample nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnoses for various diseases and health conditions. They are segmented into categories:
Miscellaneous nursing care plans examples that don’t fit other categories:
Care plans that involve surgical intervention.
Nursing care plans about the different diseases of the cardiovascular system :
Nursing care plans (NCP) related to the endocrine system and metabolism:
Care plans (NCP) covering the disorders of the gastrointestinal and digestive system :
Care plans related to the hematologic and lymphatic system :
NCPs for communicable and infectious diseases:
All about disorders and conditions affecting the integumentary system :
Nursing care plans about the care of the pregnant mother and her infant. See care plans for maternity and obstetric nursing:
Care plans for mental health and psychiatric nursing:
Care plans related to the musculoskeletal system:
Nursing care plans (NCP) for related to nervous system disorders:
Care plans relating to eye disorders:
Nursing care plans (NCP) for pediatric conditions and diseases:
Care plans related to the reproductive and sexual function disorders:
Care plans for respiratory system disorders:
Care plans related to the kidney and urinary system disorders:
Recommended nursing diagnosis and nursing care plan books and resources.
Disclosure: Included below are affiliate links from Amazon at no additional cost from you. We may earn a small commission from your purchase. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
Ackley and Ladwig’s Nursing Diagnosis Handbook: An Evidence-Based Guide to Planning Care We love this book because of its evidence-based approach to nursing interventions. This care plan handbook uses an easy, three-step system to guide you through client assessment, nursing diagnosis, and care planning. Includes step-by-step instructions showing how to implement care and evaluate outcomes, and help you build skills in diagnostic reasoning and critical thinking.

Nursing Care Plans – Nursing Diagnosis & Intervention (10th Edition) Includes over two hundred care plans that reflect the most recent evidence-based guidelines. New to this edition are ICNP diagnoses, care plans on LGBTQ health issues, and on electrolytes and acid-base balance.

Nurse’s Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions, and Rationales Quick-reference tool includes all you need to identify the correct diagnoses for efficient patient care planning. The sixteenth edition includes the most recent nursing diagnoses and interventions and an alphabetized listing of nursing diagnoses covering more than 400 disorders.

Nursing Diagnosis Manual: Planning, Individualizing, and Documenting Client Care Identify interventions to plan, individualize, and document care for more than 800 diseases and disorders. Only in the Nursing Diagnosis Manual will you find for each diagnosis subjectively and objectively – sample clinical applications, prioritized action/interventions with rationales – a documentation section, and much more!

All-in-One Nursing Care Planning Resource – E-Book: Medical-Surgical, Pediatric, Maternity, and Psychiatric-Mental Health Includes over 100 care plans for medical-surgical, maternity/OB, pediatrics, and psychiatric and mental health. Interprofessional “patient problems” focus familiarizes you with how to speak to patients.

Recommended reading materials and sources for this NCP guide:
- Björvell, C., Thorell-Ekstrand, I., & Wredling, R. (2000). Development of an audit instrument for nursing care plans in the patient record. BMJ Quality & Safety , 9 (1), 6-13. [ Link ]
- DeLaune, S. C., & Ladner, P. K. (2011). Fundamentals of nursing: Standards and practice . Cengage learning.
- Freitas, F. A., & Leonard, L. J. (2011). Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and student academic success . Teaching and learning in Nursing , 6 (1), 9-13.
- Hamilton, P., & Price, T. (2007). The nursing process, holistic. Foundations of Nursing Practice E-Book: Fundamentals of Holistic Care , 349.
- Lee, T. T. (2004). Evaluation of computerized nursing care plan: instrument development . Journal of Professional Nursing , 20 (4), 230-238.
- Lee, T. T. (2006). Nurses’ perceptions of their documentation experiences in a computerized nursing care planning system . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 15 (11), 1376-1382.
- Rn, B. O. C., Rn, H. M., Rn, D. T., & Rn, F. E. (2000). Documenting and communicating patient care: Are nursing care plans redundant?. International Journal of Nursing Practice , 6 (5), 276-280.
- Stonehouse, D. (2017). Understanding the nursing process . British Journal of Healthcare Assistants , 11 (8), 388-391.
- Yildirim, B., & Ozkahraman, S. (2011). Critical thinking in nursing process and education . International journal of humanities and social science , 1 (13), 257-262.
63 thoughts on “Nursing Care Plans (NCP): Ultimate Guide and List”
This page is helpful!
Thank you! Hope we’ve helped you write better nursing care plans!
Will definitely use this site to help write care plans. How should I cite this link when using APA format. Thank You
HI Can some one help me to do assignment on Impaired renal perfusion. 1.Goal 2.Related Action 3.Rational 4.Evaluate outcome
Wow God bless plenty Nurseslabs really relieve my burdens 😊😊
Thank you for all this useful info! I have been looking for something like this online.
You’re welcome! :)
Quite educative thank you
The notes were indeed useful
I hope to learn more and improve my skills towards nursing
Thank you so so much! This website is of great assistance to me. God bless you.
It’s so great for nursing student
Very beautiful ,Good work keep it up
Nice work. Well done
Very helpful
Great job,thank you
Thanks so much , it’s of much support for students .
Risk for ineffective thermoregulation would be a good one for you to do next for newborn.
Hi, i have learnt a lot THANK YOU. i would kindly like to learn more on paper 1 since am yet to sit for my nursing council exams and feel challenged on the paper.please do assist me thank you.
This site is a total lifesaver!
What is a nursing care plan a mother in second stage of labour?
Please see: 36 Labor Stages, Induced and Augmented Labor Nursing Care Plans
What is the nursing care plan for pulmonary oedema?
I m interest in receiving a blank nursing care plan template for my students to type on. I was wondering if it was available and if so can you please direct me on where to find it?
Hi! You can download it here: Nursing Care Plan Template
I love this website!!! Is there a textbook version of the Nurseslabs that I can purchase??
Thank you Nurseslabs. This is a wonderful note you’ve prepared for all nurses. I would like a pdf of this. Thanks.
I wish I had had this resource when i was in nursing school 2008!!
Yeah! It’s nice
Thanks for this information!
God bless you sis…Thank you for all this useful info!
This is the kind of step-by-step guidance that I needed. Thank you!
Thank you. I have learned a lot!
Wow! This is a hidden treasure!
Thanks a lot for this, it is really helpful!
Hi Matt! I would like to purchase a textbook of your nursing care plan. Where I can purchase pls help!
Hi Criselda,
Sorry, we don’t have a textbook. All of our resources are here on the website and free to use.
Good day, I would like to know how can I use your website to help students with care plans.
Sincerely, Oscar A. Acosta DNP, RN
Oh I love your works. Your explanations
I’m glad I’ve met your website. It helps me a lot. Thank you
I love this, so helpful.
These care plans are great for using as a template. I don’t have to reinvent the wheel, and the information you provided will ensure that I include the important data without leaving things out. Thanks a million!
Hi, I have learnt a lot, this is a wonderful note you’ve prepared for all nurses thank you.
Matt, this page is very informative and I especially appreciate seeing care plans for patients with neurological disorders. I notice, though, that traumatic brain injury is not on your list. Might you add a care plan page for this?
Thanks alot I had gained much since these are detailed notes 🙏🙏
OMG, this is amazing!
Wow very helpful.thank you very much🙏🙏
Hi, is there a downloadable version of this, pdf or other files maybe this is awesome!
Hi Paul, on your browser go to File > Print > Save as PDF. Hope that helps and thanks for visiting Nurseslabs!
Matt, I’m a nursing instructor looking for tools to teach this. I am interested in where we can find “rules” for establishing “related to” sections…for example –not able to utilize medical diagnosis as a “related to” etc. Also, resources for nursing rationale.
Hello, please check out our guide on how to write nursing diagnoses here: https://nurseslabs.com/nursing-diagnosis/
Nursing care plan is very amazing
Thanks for your time. Nursing Care Plan looks great and helpful!
complete knowledge i get from here
great resource. puts it all together. Thank for making it free for all
Hello Ujunwa, Thanks a lot for the positive vibes! 🌟 It’s super important to us that everyone has access to quality resources. Just wondering, is there any specific topic or area you’d love to see more about? We’re always looking to improve and add value!
Great work.
Hi Abbas, Thank you so much! Really glad to hear you found the nursing care plans guide useful. If there’s a specific area or topic you’re keen on exploring more, or if you have any suggestions for improvement, feel free to share. Always aiming to make our resources as helpful as possible!
It has been good time me to use these nursing guides.
What is ncp for acute pain
For everything you need to know about managing acute pain, including a detailed nursing care plan (NCP), definitely check out our acute pain nursing care plan guide . It’s packed with insights on assessment, interventions, and patient education to effectively manage and alleviate acute pain.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
How to Write a Nursing Case Study [Examples, Format, & Tips]
✒️ case study topics for nursing students.
- 🩺️ The Basics
- 💉 Nursing Case Study: Writing Rules
📑 Nursing Case Study Format
📝 nursing case study examples.
- ⏱️ Tips on Quick Writing
🔗 References
A nursing case study is an in-depth analysis of the health situation of an individual patient.

The analysis is based on:
- medical history,
- other relevant criteria.
In most cases, you will be asked to diagnose to suggest the first aid measures. Alternatively, nurses can be asked to describe a patient in their practice and analyze the correctness of their actions. The purpose is to recreate a realistic hospital setting in the classroom and make students reflect on the treatment process from diagnosis to treatment.
- Anaphylactic shock in a teenager with peanut allergy.
- Non-compliant patient with diabetes: ways to improve adherence.
- Telehealth intervention for managing chronic disease.
- Communication strategies to address vaccine hesitancy in a rural community.
- Postpartum hemorrhage in a new mother: risk factors and interventions.
- Ways to improve recognition of dehydration in aging adults.
- The effective ways of maintaining work-life balance for nurses.
- Cultural competency in providing care to migrants and refugees.
- Why should every patient’s medical history remain confidential?
- The use of massage therapy in relieving pain.
- The challenges facing medicine in 2024.
- How does modern technology impact nursing?
- The significance of regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider.
- What are the primary treatments for postpartum depression?
- The use of steroids in cancer treatment.
🩺️ Nursing Case Study: What Is It About?
As a nursing student, you should understand that no two patients are the same. Each has a unique clinical record and condition. And although most nursing case study tasks will ask you to suggest a diagnosis or treatment, your focus should rest on the patient.
Busy nurses can sometimes see their patients in the framework of an illness to be treated or a procedure to be fulfilled. But you should do your best to remember that each patient is a living person with a complex set of needs, emotions, and preferences. A ready-made textbook answer is rarely the best solution for them. Moreover, it rarely helps to analyze a condition in isolation from the patient.
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don’t do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types.
Once again:
A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient’s condition. Meanwhile, a nursing essay will explore the disease, prevention methods, treatment, or possible consequences of the disease.
Even if the case is hypothetical, it should focus on the suggested reality. On the other hand, essays are usually literature-based. You are expected to do some reading for a case study too, but you should research and present the information within the context of the patient. In simple terms, a case study uses information in the actual application, and an essay uses it for the sake of generalized suggestions.
💉 How to Write a Nursing Case Study: 3 Key Rules
- Do the fieldwork. Before setting your hands to writing, you should collect all of the available materials: clinical notes, results of medical tests, x-rays, sickness records, etc. Use this information to draw a clear picture of the story. It is always helpful to ask yourself, “What is interesting or unusual about this patient’s condition?” In the course of writing, recall your answer from time to time not to get lost in words. It will help you to convey a definite and appropriate message.
- Stick to the facts. A nursing case study should be an accurate description of the actual situation. Restrain from speculating about the inherent mechanisms of the illness or the general treatment methodology. In fact, students are rarely prepared enough to discuss pathology and physiology. Leave this to reputable experts. The best result you can provide in a case study is an honest account of clinical events.
- Concentrate on the patients and their progress. Remember that a nursing case study is a story of a patient’s progress and not a narrative about their nurse. No matter how efficiently the medical specialist acted, it would be incorrect to add any praiseful remarks. The optimal way is to tell the story in its logical and time order and outline the result of treatment. In this case, the outcome will speak for itself.
Introduction
It is where you should tell the reader why this case is interesting . Place your study in a social or historical context. If, during your preliminary research, you found some similar cases, describe them briefly. If you had a hard time diagnosing the patient or your proposed treatment is complicated, mention it here. Don’t forget to cite the references to each of them!
The introduction should not exceed several paragraphs. The purpose is to explain why the reader will benefit from reading about the case.

Case Presentation
- Why did the patient seek medical help? (Describe the symptoms.)
- What is known about the patient? (Mention only the information that influenced your diagnosis. Otherwise, explain why some information is irrelevant to the diagnosis.)
- Stick to the narrative form. (Make it a story!)
- What are the variants for diagnosis? (Make a shortlist of possible disorders that fall under the patient’s symptoms. But make it specific: not just “pneumonia” but “bilateral pneumonia,” for example. Besides, this point is optional.)
- What were the results of your clinical examination? (If you saw the patient in person.)
- Explain the results of lab tests. (The words “positive” or “negative” are not always clear.)
Actions and Their Results
This section describes the care that has been provided and/or is planned. You can answer the following questions in narrative form . If some information is missing, skip the point:
- What preliminary actions have been taken? (Be specific: not just “wound care,” but “wound cleaning and dressing.”)
- How long has the patient been under care?
- Has the previous treatment given any visible result?
- Why was it suspended or finished?
- Why did the patient withdraw from treatment (if applicable)?
- How could you improve the patient’s condition if the result was negative?
- If the disease is incurable (like in the case of diabetes), which activities would stabilize the patient’s condition?
- If possible, include the patient’s reports of their own physical and mental health.
In this section, you should identify your questions about the case. It is impossible to answer all of them in one case study. Likewise, it is unreal to suggest all the relevant hypotheses explaining the patient’s condition. Your purpose is to show your critical thinking and observation skills. Finalize your conclusion by summarizing the lessons you learned from the nursing case study.
Whenever you directly or indirectly cite other sources or use data from them, add these books and documents to the references list. Follow the citation style assigned by your professor. Besides, 15 items are already too much. Try to make a list of up to 10. Using textbooks as references can be viewed as bad manners.
Include all the tables, photographs, x-rays, figures, and the journal of medication usage in this section. Unless required otherwise in the assignment, start each item from a new page, naming them “Appendix A,” “Appendix B…”.
Below you will find case study samples for various topics. Using them as a reference will improve your writing. If you need more ideas, you are welcome to use our free title-generating tool .
- Case study: healing and autonomy.
- Sara’s case study: maternal and child nursing.
- COPD medical diagnostics: case study.
- Care standards in healthcare institutions: case study.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis: case study analysis.
- Alzheimer disease: the patient case study.
- The treatment of foot ulcers in diabetic patients: case study.
- Hypertension: C.D’s case study.
- Myocardial infarction: cardiovascular case study.
- Major depressive disorder case.
- Case study of the patient with metabolic syndrome .
- Pulmonary analysis case study .
- Older adults isolation: Case study .
- The holistic care: Case study .
- Medical ethics: Case study .
- Patient diagnoses and treatment: Case study .
- Obesity case study: Mr. C .
- Nurse Joserine: Case study problems .
- Chronic stable angina: Case study .
- Fetal abnormality: Case study .
- Researching SOAP: Case study .
- Case study for a patient with hormonal disorders .
- Obesity in the elderly: The case study .
- “Walking the Tightrope”: A case study analysis .
- ARNP approach: Case study analysis .
- Case study on biomedical ethics in the Christian narrative .
- Thermal injury: Case study .
- Ethical dilemma in nursing: Case study .
- Asthma: A case study of the patient .
- Asthma discharge plan: Mini case study .
- Case study: An ethics of euthanasia .
- Case study: Head-to-toe assessment steps .
- Pain management strategies: Case study .
- Case study: Inflammatory bowel disease .
- Sleep deprivation and insomnia: The case study .
- The case study of a heart failure .
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: Disease case study .
- Case study: Hardy Hospital case summary .
- Obesity and its complications: Case study .
- Angina disease case study .
- Nursing ethics case study .
- Case study of a patient: Assessment and treatment plan .
- Cecile case study: Mrs. J .
- Nursing power in the emergency department: Case study .
- Heart failure case study: Mrs. J .
- Application of ethics in nursing: Case study .
- Sudden visual impairment: Case study .
- Epidemiology case study: Outbreak at Watersedge — Public health discovery game .
- Wellness of senior citizens: Case study .
- Healthcare organization evaluation: Case study of Banner Health .
⏱️ Bonus: Tips on Writing a Case Study in Record Time
Need to prepare a case study on nursing or in another field? Below you’ll find a collection fo tips that will help you do it as quickly as possible!
3 Shortcuts for a Quick Start
If you’re about to start writing a case study, you should check yourself if you’re not doing any of the following:
- spending too much time on selecting a topic;
- reading too much before selecting a topic;
- making conclusions too early – creating bias.
Instead of killing time doing the three useless things discussed above, consider these:
- Choose approach. Note that there are 2 major approaches to case studies: the analytical approach (investigating possible reasons without making any conclusions) and problem-oriented approach (focusing on a particular problem and investigating it).
- Skim some sources (DON’T READ THEM). Select several sources. Simply skim abstracts and conclusions.
- Start making notes early. Simply reading is ineffective unless you’re lucky to have a phenomenal memory. Always make notes of any useful arguments.
4 Shortcuts Not to Get Stuck in the Middle
Even if you kick started your case study, it’s too early to celebrate it. Consider the following traps in the middle of the project:
- Watch the structure. The classic logical structure is your formula of success. It will help you move from one point to another without the unnecessary procrastination:
- Respect the logic. Make your case study flow – make logical transitions between the different parts and make it consistent. Avoid changing your position throughout the paper.
- Be detail-oriented. Any trifle deserves attention when you write a case study.
- Avoid bias. Be sure that all your opinions are based on the specific arguments form the case study. Avoid pouring your biased views into the project.
3 Shortcuts for a Happy Ending
- Offer a realistic solution. College case study is a rehearsal of real-life situations. Take the responsibility for your suggestions.
- Keep your conclusion short. Avoid repeating the details and don’t include any new information.
- Consider creating a Power Point. If your task is not only writing a case study, but also presenting it – why not create PowerPoint slides to help you?
As the last step on your way to a perfect nursing case study, prepare the title page. Its format usually depends on the professor’s requirements. But if you know the citation style, our Title Page Maker is a perfect tool to apply the right formatting and accelerate the process. And if you have any know-how on how to write a medical case study, you are very welcome to share it with other students in the comments below.
❓ Nursing Case Study: FAQ
What is a case study in nursing.
A nursing case study explores the condition of a patient. It is based on previous clinical records, lab reports, and other medical and personal information. A case study focuses on the patient and describes the treatment that was (or should be) applied and its (expected) outcome.
How to Write a Nursing Case Study?
- Collect the bulk of data available about the patient.
- Read literature about the diagnosed condition.
- Focus on the individual patient and their symptoms.
- Describe the situation and outline its development in time.
- Analyze the actions of the medical personnel that have been done.
- Plan further treatment of the patient.
Why Are Case Studies Good for Nursing Students?
Nursing case studies offer you a priceless opportunity to gain experience of different patient conditions and cure methods without visiting the clinic. You can think about whether the proposed treatment was appropriate or wrong and suggest a better solution. And the best thing, your teacher will indicate your mistakes (and no patient will be hurt in the process).
Why Are Case Studies Important in Nursing?
- You learn to distinguish the relevant data and analyze it.
- You learn to ask the right questions.
- You learn to evaluate the severity of symptoms.
- You learn to make better diagnoses.
- You train your critical thinking in terms of treatment methods
- Case studies are in-class simulators of authentic atmosphere in a clinical ward.
- What is a case study? | Evidence-Based Nursing
- Case Studies – Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Case Study Research Design in Nursing
- Case study report for Nursing | Learning Lab – RMIT University
- Case Study or Nursing Care Study? – jstor
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.

- Log in ▼
- Our Guarantees
- Our Services
- How it Works
How to write a Nursing Assignment: Beginners Guide
Are you in search of internet guidance on how to write a nursing assignment? Are you frustrated with the overwhelming quantity of incorrect or untrustworthy responses to your questions? Don’t worry; we know your issue and its resolution.
The information in this article will assist you in comprehending the challenges you will face when writing your nursing assignments. Additionally, you will know how simple it is to overcome obstacles with the help of nursing assignment writers or professional assistance.
Nursing assignment definition
Are you perplexed by the question, “What is a nursing assignment?” Don’t be concerned. Nursing focuses on providing health care services to society and its citizens. Medical school nursing tasks need students to care for patients, improve human well-being, and treat health-related disorders and problems.
How to write a successful nursing assignment for beginners
Writing assignments is difficult for many nursing students. Do you believe it’s difficult to write one? If you don’t know how to write effectively, completing the assignment can be tough. Furthermore, the law is a subject that contains a great deal of detail.
You must supply appropriate information when speaking and writing. Many students struggle to complete their assignments on time and with complete accuracy. However, reputable nursing assignment help firms can assist you in overcoming assignment difficulties.
Here is a guide that will walk you through the phases of producing an excellent nursing assignment to assist you with the writing process. When you are working on an academic nursing activity and you want to understand how to write a nursing assignment, follow these steps:
- Choose a topic
To move on to the next step, you must first choose a topic for your essay. If you have a choice, choose a subject that suits you and one you are competent at. It ought to inspire you to write.
- Follow the format suggested
The following step is to adhere to the format set by the lecturer. The professor will provide the format for writing at the start. He’ll also give you some further directions for the body region and so on.
Follow the instructions. Keep in mind that you are writing for the lecturer. As a result, you must write in the manner specified by your lecturer. Pay close attention to the directions.
- Do your research
Many students use Google to research topics; however, scholarly sources should be used when writing nursing papers . Use your class notes, textbooks, research resources, newspaper articles, workshops, seminars, and other sources to conduct research. Also, seek out expert assistance if necessary.
- Plan ahead of time
Decide what you want to include in the various areas of the assignment, such as essential points, examples, answers to questions, and so on. It may take some time to organize, but it will make your paper look more professional and remarkable.
- Respond to the assignment questions
Students frequently forget to respond to the assignment’s question. To comprehend the question, read it again and again. Avoid making a mistake by forgetting something crucial. Never fail to respond to a question. You’ll get good scores for it.
- Avoid concerns with plagiarism
Unknowingly or mistakenly, you may incorporate plagiarized text. Make certain that the plagiarized text in the paper is replaced. To detect plagiarized content, employ trustworthy plagiarism checkers. If you cannot detect any problems, get professional help for your nursing care plan assignment.
- Review, then submit
Proofreading is the last step before turning in the assignment. Look over the paper for errors and fix them. Please don’t submit the paper until it has been proofread.
Get assistance with your nursing reflective assignment
Through online nursing assignment help services offered by web pages, nursing students can obtain help for reflective assignments in nursing. These services allow students to receive essay-related advice or full expert assistance.
If you’re stuck on how to write a nursing assignment, internet specialists can offer the greatest nursing assignment help.
Nursing essay writing services
You may be asked to write about many nursing assignment topics, so you must think critically and swiftly. You can get help for writing essays in nursing assignments from an expert writer.
Your professor may assign nursing discussion postings that entail analyzing patient data and history. You can get help writing effective discussion posts on what information to obtain and how to complete the case study project.
What nursing assignment services are offered?
You might contact a professional writer to guide you on a travel nursing assignment you need to submit or consult. Similarly, you can use a professional writer as a guide to learn about questions concerning risky nursing assignments, etc., or other nursing-related issue.
But what if you come across the most difficult nursing assignment and still don’t understand the processes despite spending so much time on it? Will you still want to devote additional time to seeking advice? You don’t have to waste any more time because you can pay someone to perform my nursing assignment.
You have to send the task information to the writer and request that he do your nursing project. The rest of the work will be done by our authors, who are always willing to assist. They will do your work according to the specifications.
Tips for writing the best nursing assignments
Understanding academic discourse is essential for writing a successful nursing assignment because it is a field with its jargon. To successfully persuade the assignment markers and audience that you understand the subject, you must utilize specific language.
You must learn how to write a nursing assignment. Use the following tips to write the winning nursing assignments you desire.
- Go over the topic with care
Every time you write on nursing assignment topics, it is crucial to understand them thoroughly. When it comes to nursing assignments, this truth is also true. To create an engaging assignment, you must investigate the subject.
Students frequently jump right into writing the paper without attempting to comprehend the topic, which is a tremendous error! Instead, spend the time learning the topic’s deeper meaning.
- Conduct research
Another critical component strongly recommended by nursing assignment help specialists. Carry out the necessary study to obtain a thorough understanding of the issue. You must acquire information to meet all of the topic-related requirements.
Because of medical terminology, research is especially important in nursing areas. A thoroughly researched assignment task is of high quality and guarantees A+ grades in your class.
- Adhere to the rules
Due to blatant disregard for the requirements set forth by the professors, students frequently lose marks on their assignments. Always adhere to the formatting guidelines provided by the assignment’s assigner. It demonstrates your commitment to your academics and the in-class discussions.
- Create an outline
We cannot emphasize the importance of creating an outline before putting your ideas on paper. Following the completion of the study, the outline aids in the organization of thoughts into a logical order.
Do you know why nursing assignment professionals consistently write flawless papers? They stick to their game plan. The outline is necessary for organizing and systematically presenting the obtained information. This is a surefire way to impress your professors.
- Keep the academic style
A poor writing style will render your expertise useless even if you are well-versed in the subject. Always use formal language, which is acceptable in academic settings. It would be best if you refrained from using slang and jargon that appear informal.
- Maintain proper structure
You must ensure that the entire assignment is organized into different sections pertinent to the subject. Keeping your paper well-structured improves its appearance and readability. An introductory paragraph, main body paragraphs, and a conclusion should all be included in your nursing assignment.
Experienced nursing assignment service providers use this method often. Each body paragraph should focus on and explain a certain theme and be connected to the next paragraph with a meaningful transition.
- Keep away from distractions
Students often don’t think about the place they choose to study. The environment greatly affects how well you do in school and at work. If you want to work without distractions, find a quiet spot.
Set up a study table in a quiet place instead of sitting on the bed. Turn off your phone and other digital devices so you can focus on the work.
- Improve your first draft
It’s time to start working on the draft now that you have gathered useful information on the subject and created an outline. It would be best if you started with a clear strategy to find your path to move things forward. Keep the data list and an effective outline close to hand.
You can then break up the entire assignment into several headings and subheadings. The experts that provide nursing assignment help strongly advise it. You have the opportunity to be imaginative while giving all the details required for successful outcomes.
- Never plagiarize
Plagiarism in any form is dishonesty at its core. It’s blatant plagiarism as soon as the words and ideas have been taken. You’re free to put your spin on the information by rephrasing it. But that doesn’t imply you should change anything else about it.
If you want to make it sounds more like you, follow your writing style and keep all the facts the same. Nursing assignment help providers that use plagiarism detection software may guarantee that their clients always receive authentic work. You can use one of the many free plagiarism checkers to make sure your papers are completely original.
- Verify your draft
To ensure the accuracy and clarity of your assignment’s structure, proofread the draft copy. It should make sense and follow a logical progression. The likelihood of errors in grammar, spelling, structure, etc., is reduced thanks to proofreading. Additionally, you can remove any extraneous or useless information from the copy.
Top nursing assignment suggestions
Nursing assignments are crucial since they provide a complete understanding and affect your marks. Nursing assignment writing can be of several types, depending on the topic’s requirements, and the instructor can vary the criteria as the subject demands.
Nursing assignment writing primarily concerns technicalities and in-depth research for various criteria. Students can train themselves to write good nursing assignments. You must devote some time to the job and examine the following criteria on how to write a nursing assignment.
- Knowledge of the Subject
It is easy if your instructor gives you a nursing assignment and asks you to prepare an assignment based on the material provided. To consider the given work’s technicality level, you need a fundamental understanding of the subject.
- Prepare to write
Before you begin writing, plan out your complete task. Check the assignment’s importance about semester marks to determine how much time to spend on it. Then, completely review the assignment’s requirements and note them.
Write down exactly what you need to do to do your task, such as research, reading, or conducting experiments. Planning the entire process can assist you in avoiding important missing aspects of the assignment.
- Textual organization
In nursing assignment writing, the arrangement of the text is extremely important. It makes no difference how well you apply your knowledge or how wonderful your reading is if the material supplied is not properly organized.
The text layout is extremely responsive to the assignment paper’s quality. Begin and end properly, and ensure you begin and conclude well while giving relevant and credible information.
In conclusion
One of the most important things you can do is create an amazing nursing assignment. For that reason, we made the decision to discuss the topic of how to write a nursing assignment. Using the writing guidelines and examples in this piece, you can create a superior, knowledgeable nursing assignment.
Remember that it is always better to document too much than too enough. Contact onlinenursingpapers.com for academic and professional nursing writing services to help you with your questions and problems about the topic.
Why We Are the Best
- 100% non-plagiarized Papers
- Dedicated nursing and healthcare writers
- 24/7 /365 Service Available
- Affordable Prices
- Money-back and Privacy guarantees
- Unlimited Amendments upon request
- Satisfaction guarantee

- Online Nursing Assignment Help
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Nursing Dissertation Writing Services
- Nursing Capstone Project Writing Services
- Best Nursing Essay Writing Company
- Best Online Nursing Assignment Help
- Nursing Term Paper Writing Services
- Nursing Report Writing Services
- Nursing Annotated Bibliography by Professional
- Nursing Essay Assignments
- Nursing Assignment Writing
- Nursing Case Study Writing Services
- Nursing Coursework Writing
- Online Nursing Research Paper writing service
- PICO Question Examples
- Nursing Thesis Writing Services
- Nursing Research Paper Writing Services
- Nursing Presentation Writing
- Terms and Conditions
- Epidemiology assignment help
- Write my nursing dissertation for Me
- Nursing Essay Writing Service

Nursing: How to Write a Literature Review
- Traditional or Narrative Literature Review
Getting started
1. start with your research question, 2. search the literature, 3. read & evaluate, 4. finalize results, 5. write & revise, brainfuse online tutoring and writing review.
- RESEARCH HELP
The best way to approach your literature review is to break it down into steps. Remember, research is an iterative process, not a linear one. You will revisit steps and revise along the way. Get started with the handout, information, and tips from various university Writing Centers below that provides an excellent overview. Then move on to the specific steps recommended on this page.
- UNC- Chapel Hill Writing Center Literature Review Handout, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- University of Wisconsin-Madison Writing Center Learn how to write a review of literature, from the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
- University of Toronto-- Writing Advice The Literature Review: A few tips on conducting it, from the University of Toronto.
- Begin with a topic.
- Understand the topic.
- Familiarize yourself with the terminology. Note what words are being used and keep track of these for use as database search keywords.
- See what research has been done on this topic before you commit to the topic. Review articles can be helpful to understand what research has been done .
- Develop your research question. (see handout below)
- How comprehensive should it be?
- Is it for a course assignment or a dissertation?
- How many years should it cover?
- Developing a good nursing research question Handout. Reviews PICO method and provides search tips.
Your next step is to construct a search strategy and then locate & retrieve articles.
- There are often 2-4 key concepts in a research question.
- Search for primary sources (original research articles.)
- These are based on the key concepts in your research question.
- Remember to consider synonyms and related terms.
- Which databases to search?
- What limiters should be applied (peer-reviewed, publication date, geographic location, etc.)?
Review articles (secondary sources)
Use to identify literature on your topic, the way you would use a bibliography. Then locate and retrieve the original studies discussed in the review article. Review articles are considered secondary sources.
- Once you have some relevant articles, review reference lists to see if there are any useful articles.
- Which articles were written later and have cited some of your useful articles? Are these, in turn, articles that will be useful to you?
- Keep track of what terms you used and what databases you searched.
- Use database tools such as save search history in EBSCO to help.
- Keep track of the citations for the articles you will be using in your literature review.
- Use RefWorks or another method of tracking this information.
- Database Search Strategy Worksheet Handout. How to construct a search.
- TUTORIAL: How to do a search based on your research question This is a self-paced, interactive tutorial that reviews how to construct and perform a database search in CINAHL.
The next step is to read, review, and understand the articles.
- Start by reviewing abstracts.
- Make sure you are selecting primary sources (original research articles).
- Note any keywords authors report using when searching for prior studies.
- You will need to evaluate and critique them and write a synthesis related to your research question.
- Consider using a matrix to organize and compare and contrast the articles .
- Which authors are conducting research in this area? Search by author.
- Are there certain authors’ whose work is cited in many of your articles? Did they write an early, seminal article that is often cited?
- Searching is a cyclical process where you will run searches, review results, modify searches, run again, review again, etc.
- Critique articles. Keep or exclude based on whether they are relevant to your research question.
- When you have done a thorough search using several databases plus Google Scholar, using appropriate keywords or subject terms, plus author’s names, and you begin to find the same articles over and over.
- Remember to consider the scope of your project and the length of your paper. A dissertation will have a more exhaustive literature review than an 8 page paper, for example.
- What are common findings among each group or where do they disagree?
- Identify common themes. Identify controversial or problematic areas in the research.
- Use your matrix to organize this.
- Once you have read and re-read your articles and organized your findings, you are ready to begin the process of writing the literature review.
2. Synthesize. (see handout below)
- Include a synthesis of the articles you have chosen for your literature review.
- A literature review is NOT a list or a summary of what has been written on a particular topic.
- It analyzes the articles in terms of how they relate to your research question.
- While reading, look for similarities and differences (compare and contrast) among the articles. You will create your synthesis from this.
- Synthesis Examples Handout. Sample excerpts that illustrate synthesis.
Regis Online students have access to Brainfuse. Brainfuse is an online tutoring service available through a link in Moodle. Meet with a tutor in a live session or submit your paper for review.
- Brainfuse Tutoring and Writing Assistance for Regis Online Students by Tricia Reinhart Last Updated Oct 26, 2023 81 views this year
- << Previous: Traditional or Narrative Literature Review
- Next: eBooks >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 12:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.regiscollege.edu/nursing_litreview

How to Write a Good Nursing Annotated Bibliography

As part of evidence-based practice, a successful nurse should be able to find and evaluate evidence. You can achieve that by looking for empirical nursing articles from nursing databases.
In many cases, you will be assigned to research peer-reviewed articles from the library and write an annotated bibliography that culminates into a nursing research paper, essay, term paper, concept analysis paper, policy analysis paper , dissertation, or nursing capstone project . And for many nursing students, especially those writing an annotated bibliography for the first time, the entire process can be scary.
In this guide, our online nursing essay experts take you through the process of writing a perfect nursing annotated bibliography so that you get it right on the first attempt.
What is a Nursing Annotated Bibliography?
The purpose of writing a nursing annotated bibliography is to search for relevant research related to your general, EBP, or PICOT topic and present a formal analysis of each source in regard to how it helps you explore the topic in question.
It is a combined list of citations to books, articles, and other scholarly sources followed by a summary (annotations); usually, about 150-200 words, that describes, synthesizes, and evaluates the source.
The annotated bibliography informs the reader about the currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, quality, and purpose of the sources used in writing a paper.
Nursing students at BSN, MSN, and DNP might be required to write an annotated bibliography before writing an essay, term paper, or research paper.
Parts of an Annotated Bibliography
There are two primary components of an annotated bibliography: citation and annotation .
The citation provides information about the source's author, title, date, source, and publisher. The citations are formatted mainly in APA (APA 6 of 7), AMA, ASA, or Harvard format.
The annotation refers to the concise and informative description that summarizes and evaluates the contents of the resource. Let?s assume you are writing an essay about pediatric pain management for kids with cancer, and you find a source like Pediatric pain treatment and prevention for hospitalized children ; you will first cite the source in APA format as demonstrated in the next sections of this guide.
In about 150-200 words, you will explain more information about the source, including its significance and relevance to your essay. We will use the source above to do this practically as an example.
In a nutshell, the annotation should contain the following:
- A description of the content of the resource
- An evaluation of the usefulness of the source in exploring a specific nursing topic
- Explanation of the methodology used by the authors
- The themes addressed by the authors
- The strengths and weaknesses of the source
- A discussion of the reliability of the authors or the source
- A critical evaluation of the accuracy, bias, and authority of the source
Let?s put everything to place as an example to see how a good annotated bibliography should be written in the nursing class context. Many students panic when assigned to write such a paper, but it is easy if you get the facts right.
Example of a Nursing Annotated Bibliography
Taking the example of the source we mentioned before, the annotated bibliography will appear in your paper as below:
Friedrichsdorf, S.J. and Goubert, L. (2020) ?Pediatric pain treatment and prevention for
hospitalized children,? PAIN Reports , 5(1). Available at:
https://doi.org/10.1097/pr9.0000000000000804.
This peer-reviewed journal by Friedrichsdorf Stefan and Goubert Liesbetd looks into how to address the prevention and treatment of acute and chronic pain in children [Authority] . Friedrichsdorf Stefan is a pain management specialist working with various healthcare organizations, including Benioff Children?s Hospital in Oakland and San Francisco, CA. Goubert Liesbetd works at the department of Experimental-clinical and Health Psychology at Ghent University in Belgium [ Information about the authors] . The authors intended to evaluate pain management strategies, including pain caused by needles, through analgesic starting doses [Purpose of the Journal Article] . Having reviewed the best evidence-based practice [Methodology], the authors concluded that it is imperative to implement evidence-based pain prevention and treatment strategies for children in medical facilities [Summary of the Findings] . Specifically, they recommend using multimodal analgesia administered through an interdisciplinary rehabilitative approach. As for needle pain, topical analgesia, sucrose or breastfeeding, age-appropriate distraction, and comfort positioning are highly recommended. The article is timely, descriptive, and evidence-based and informs my topic about pain management for pediatric patients in the hospital for cancer treatment and care [Evaluation] .
Steps for Writing a Good Nursing Annotated Bibliography
Now that you are assigned to write an annotated bibliography for your nursing class, you should follow the process below to arrive at an annotated bib paper that will score highly and facilitate you in writing a good nursing EBP research paper , concept analysis paper or nursing essay . Below are the steps:
1. Read the instructions
Usually, your professor or instructor will give you a document highlighting how to prepare the annotated bibliography assignment. You should read it keenly because it offers guidance on the appropriate style and other essential aspects to consider. If you are a BSN, MSN, or DNP student, you should prepare the paper in APA or Harvard style, depending on your university's requirements or preferred style. It will help if you look into the assignment rubric to write a paper that scores the highest grade possible by putting everything as per your professor's expectations.
2. Choose a Relevant Topic
Having internalized the instructions, you need to develop a good nursing topic. Check out our list of evidence-based nursing topics . We also have an entire article on debate topics in nursing , epidemiology , and informatics topics , and you can also look at your course readings and topic suggestions from the professor. You might be needed to write a PICOT question or statement and get it approved before doing the annotated bibliography. Whatever comes first, choose a manageable topic so that you can find relevant scholarly nursing journal articles from reliable nursing journals such as PubMed, OVID, or BMC.
Related Article: nursing theories to include in a nursing paper.
3. Research Widely and Identify the Best Sources
Conduct a library search for scholarly research and articles related to your topic. If possible, limit your search to identify the empirical nursing articles published within the last five years. Go through the abstracts of the empirical studies to determine if they are credible, current, accurate, authoritative, and relevant to your topic. Does it answer your proposed PICOT question or research question? Is the methodology right? Consider getting the highest level of evidence in nursing , such as Systematic Reviews, RCTs, meta-analyses of RCTs, or experimental nursing studies. Check Cochrane, DARE, Ovid MEDLINE, and PubMed for meta-analyses and systematic reviews.
4. Write the Annotation
Once you have located the appropriate number of empirical research articles that relate to your proposed PICOT question, research question, or nursing topic, write an annotation for each article.
You must generate the full citations in A-Z as they appear in your reference list and then write the relevant annotations. Citations should be in APA or Harvard referencing styles, and the annotation should then follow. Each annotation should concisely summarize the article's central theme and scope. You should also evaluate the background of the author or authority. You should also, in your annotation, include a comment on the intended audience and compare or contrast the work with others in your list. Lastly, indicate the relevance of the source in illuminating your bibliography topic.
5. Polish and Submit
The last step in writing an annotated bibliography is to edit and proofread the essay to correct all the errors and check for omissions. Polish the paper to meet your university or college's writing level requirements and standards. Some universities use LOPES write, SafeAssign or Turnitin to submit nursing assignments, be keen that your annotated bibliography has low similarity or plagiarism. If anything, only the citations should have similarities, but the annotations should have zero plagiarism.
The Bottom Line
Nursing annotated bibliographies like nursing papers are formatted mostly in APA in American nursing colleges and universities. If you are taking nursing courses in Australia or the UK, most of your papers will be formatted in Harvard, and so do your nursing papers (essays, case studies, QI reports , term papers, dissertations, and capstone projects).
Remember, an annotated bibliography contains reference list entries with short annotations, which should be alphabetical and double-spaced. Besides, the sources used should be empirical and related to the research paper or nursing assignment you will write after approval.
If you want help writing your nursing annotated bibliography, do not hesitate to place your order on our website. We have polished annotated bibliography writers that you can pay to write your annotated bibliography. The good thing is that they will provide PDF copies of the journal articles yielded from the search. We are ever online, and as an affordable nursing papers website, you can get it done cheaply but efficiently. Don?t fumble or waste time; let us do it for you!
Struggling with
Related Articles

A Review of the WGU RN to BSN Nursing Program (Expert Insights)

Nursing Student's Ultimate Guide to Writing a Nursing Care Plan

Principlism Essay: Exploring How to Write Ethics Papers in Nursing
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing in Nursing Bibliography

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Provides an introduction to writing across the curriculum and writing in the disciplines, a list of links to Writing Across the Curriculum/Writing in the Disciplines (WAC/WID) programs, and a selected bibliography for further reading.
Writing is integral to nursing for a number of different reasons. Patient care, issues of nursing liability, and the learning of different nursing skills are all reliant upon writing as a tool and source of communication. Writing occurs in the forms of nurses' notes, clinical studies, and scholarly research.
Much has been written about the role the writing plays in the development of student nurses into professionals. This bibliography is intended to be a starting place for persons interested in using writing in their courses or as a resource for those who are already using writing in their courses but are looking for new ways to implement its use. (This resource was originally written by Created by Julia Romberger, 2000.) If you are looking for resources that will help you with writing in nursing, please visit the OWL's Writing in Nursing material.
Writing in the Nursing Classroom: Experiences, Strategies, and Assignments
Bean, John C. Engaging Ideas: The Professor's Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1996.
John Bean"s intent in this work is to present a "nuts and bolts guide" to assist teachers in all the disciplines to design and integrate writing assignments into their classrooms. The book discuss the theoretical foundations for such practices, gives detailed advice on constructing a variety of different assignments, and attempts to provide options for using writing to promote thinking. The book does not presume previous familiarity with either composition or pedagogical theory and is written in a direct and accessible style.
Bean, John. Drenk, Dean, and F.D. Lee. "Microtheme Strategies for Developing Cognitive Skills." Teaching Writing in all the Disciplines . 27 - 38.
In this chapter, the strategy of using micro-themes or short essays within either large or small classroom contexts is explored. The authors give examples of several different genres of micro-themes including: the summary, argumentation and thesis support, inductive reasoning from data,and quandary posing. The chapter concludes with an examination of the pedagogical validity of the use of micro-themes and suggestions for implementing their use.
Boyd, Laurel "Involvement? Write a letter: One Curriculum Strategy" Nurse Educator . 10.6 (Nov/Dec 1985) 26 - 8.
The assignment idea outlined and utilized by Professor Boyd incorporates basic principles of both WAC and Cultural Studies and suggests several real-world forums in which students can participate. This assignment engages them in relevant audience and social issues as well as giving added import to writing assignments.
Brown, Hazel and Jeanne Sorrell. "Use of Clinical Journals to Enhance Critical Thinking" Nurse Educator . 18.5 (Sept/Oct. 1993) 16-19.
Critical thinking skills can be enhanced by giving students structured writing assignments. Suggestions are given for different assignment focuses (objective writing, summary writing, argument writing) that specifically target certain skills. Additionally, pitfalls to be avoided in grading and assignment design are listed.
Cameron, Brenda L. and Agnes M Mitchell. "Reflective Peer Journals: Developing Authentic Nurses" Journal of Advanced Nursing . 18.2 (Feb 1993) 290-97.
Drawing from literature in the composition and nursing fields, Cameron and Mitchell propose a theoretical framework for the use of journals in nursing courses. The problems of the log format are discussed using the peer journal format, which is endorsed by the authors. Guidelines for peer journals are developed based on the theory the article explores.
Fulwiler, Toby, ed. The Journal Book . Portsmouth, NH: Boynton/Cook, 1987.
This book was pivotal in the movement to introduce journal writing to a variety of classroom settings. The introduction of the book provides guidelines for the use of journals in the classroom. The third section of the book focuses on the use of journals in the quantitative and qualitative classrooms. The articles are written by a variety of teachers who successfully used journals in their various disciplinary classrooms from elementary through the collegiate level.
Heinrich, Kathleen T. "Intimate Dialogue: Journal Writing by Students"" Nurse Educator . 17.6 (Nov/Dec 1992) 17-21.
Professor Heinrich gives a critical examination of the uses and potential misuse of journaling within a nursing course. Specific recommendations for journal assignments are given based upon experiences with various course sizes and learning styles. The author draws the theoretical and pedagogical basis for these suggestions from literature in the fields of composition studies, nursing, and education.
Hurtig, Wendy Olive Younge, Danin Bodnar and Marilyn Berg. "Interactive Journal: A Clinical Teaching Tool" Nurse Educator . 14.6 (Nov/Dec 1989) 17, 31, 35.
This article looks at journal writing from another perspective, that of a valuable tool for opening up communication between students and faculty. It discusses the use of journaling within a specific context (psychiatric clinical experience) and how it operated for the participants.
McCarthy, Donna O. and Barbara J. Bowers. "Implementation of Writing to Learn in a Program of Nursing" Nurse Educator . 19.3 (May/June 1994) 32-5.
In this article, the issue of introducing Writing to Learn into a nursing curriculum is addressed. The authors draw upon both composition and nursing pedagogy to suggest strategies and assignments. The article ends with a discussion of faculty experience with implementing these strategies.
Implementation of WID, WAC, and Writing to Learn in Nursing Curricula
Allen, David G., Barbara Bowers and Nancy Diekelmann. "Writing to Learn: A Reconceptualization of Thinking and Writing in the Nursing Curriculum" Journal of Nursing Education . v. 28.1 (Jan 1989) 6-11.
This piece gives a clear demonstration of the differences between learning to write and Writing to Learn. The authors explore the ways that Writing to Learn can be integrated into a nursing curricula and discuss the benefits to instructors and students.
Lashley, Mary and Rosemary Wittstadt. "Writing Across the Curriculum: An Integrated Curricular Approach to Developing Critical Thinking Through Writing." Journal of Nursing Eduction . 32. 9 (Nov 1993) 422-4.
Lashley and Wittstadt explain how one school implemented WAC throughout a nursing curriculum. They describe the steps of reviewing the literature, selecting types of assignments, surveying faculty on existing writing requirements, and making recommendations, which they include, for creating writing requirements in courses that build upon previous course experiences.
Megel, Mary. "Nursing Scholars, Writing Dimensions and Productivity" Research in Higher Education . 27.3 (1987) 226 - 43.
The study builds on initial research in composition studies by specifically examining the difficulties of nursing scholars at the doctoral level. After conducting observations and collecting the data presented in the article, the author comes to a position relevant to proponents of WAC. Scholarly productivity was related directly to the amount of writing engaged in each week. Additionally, the author recommends that faculty develop strategies for fostering better writing skills and positive attitudes toward writing.
Pinkava, Barbara and Carol Haviland. "Teaching Writing and Thinking Skills" Nursing Outlook . 32.5 (Sept/Oct 1984) 270-72.
The authors discuss the successful experience of implementing Writing to Learn pedagogy into a nursing program through coordination between nursing faculty and writing center staff both within and without the classroom.
Poirrier, Gail. Writing to Learn: Curricular Strategies for Nursing and other Disciplines . New York: NLN Press, 1997.
This collection of essays covers a wide range of topics including a basic introduction to the principles of WAC and the theoretical basis for using Writing to Learn in a nursing curriculum, a variety of assignments, projects, and classroom experiences with them, and useful discussions on designing curriculum that incorporates Writing to Learn pedagogy.
Sorrell, Jeanne. "The Composing Process of Nursing Students in Writing Nurses" Notes" Journal of Nursing Education . 30.4 (April 1991) 162-7.
This study of the composition process of 62 nursing students in lab and the hospital is valuable for locating the difficulties students have in making the transition from one environment to the next. The article stresses that these difficulties must be examined carefully and taken into consideration by teachers and strategies developed to ease the transition.
Sorrell, Jeanne M. and James Metcalf. "Nurses as Writers" Nursing Connections . 11.2 (Summer 1998) 24-32.
This article provides a well-grounded practical argument for the use of Writing in the Disciplines within a nursing curriculum. It outlines a course, Nurses as Writers, specifically designed to teach the various types of writing required in the nursing profession, and discusses the experiences of students and their reactions to the class.
Rationale for the WAC, WID, and Writing to Learn: An Annotated Bibliography for Nursing Curricula
Content for this bibliography was chosen for its relevancy to the following:
- the concerns of nursing programs
- application of nursing education pedagogy
- application of composition studies theory.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Proofreading and Editing. Proofreading and editing are essential steps in the assignment writing process. They ensure that your nursing assignment is polished, error-free, and effectively communicates your ideas. After completing the initial draft, it's crucial to take a break and return to your work with fresh eyes.
Walden instructors often ask nursing students to write position and reflective papers, critique articles, gather and analyze data, respond to case studies, and work collaboratively on a project. Although there may be differences between the writing expectations within the classroom and those in the workplace, the standards noted below, though ...
Nursing school writing assignments are an excellent way for students to understand concepts taught in the classroom. You might wonder what kinds of assignments nursing students do. These assignments come in various forms and help students build critical thinking, creativity, research, clinical reasoning, and problem-solving skills that are ...
Regardless of the purpose and specific genre of your text, you should always strive for concise, objective, and evidenced-based writing. You can expect to learn APA style as soon as you enroll in a major course. However, you should also prepare to learn other styles as part of your academic training.
This tutorial discusses expectations for written assignments, how to plan an assignment, and strategies for effective writing.
Decide on the process. Now that you've gathered the information you need, you're ready to develop your plan for assigning nurses. This step usually combines the unit layout with your patient flow. Nurses typically use one of three processes—area, direct, or group—to make assignments. (See Choose your process.)
Are you a nursing student that's new to APA? Today we'll review how to write your nursing assignment in APA format with advice and tips from Professor Jus B ...
Good nursing case study writing forms the basis of the nursing curriculum and healthcare assignment help in the healthcare industry, enabling pupils to grow into capable, responsible, and caring ...
Nursing is an evidence-based discipline. Reflect this in your writing by avoiding opinion and using the third person. This creates a tone of objectivity and provides evidence. For example, instead of saying: "I think that…", you might use: "research has found that…" or "studies show that…". Nursing is an evidence-based discipline
Each word of nursing students is critically examined with a critical eye. They need to understand the subject and patient care that will be provided later in their profession. Let's start learning the basics of writing a nursing assignment from scratch. It will be the best guide you'll ever get in your career.
Abstract. John Fowler, Educational Consultant, explores academic writing. Writing an academic essay is a skill, and like any other skill it can be learnt and improved upon. This is easier if the skill is broken down into steps that can be identified, followed and practised. Whereas nurse educators recognise the need to teach practical skills by ...
Make the different parts of the text flow into each other. This is one of the challenging steps in perfecting your nursing assignment. When you read through the final version of your text, make sure that you haven't failed to do this. Find the last sentence and check that it contains a hint to the next paragraph.
We'll discuss the steps involved, from selecting a patient to presenting the case study, and provide tips to ensure a comprehensive and informative analysis. Step 1: Selecting the Patient. The first step in completing a nursing case study with an actual patient scenario is to select an appropriate patient.
Step 1: Data Collection or Assessment. The first step in writing a nursing care plan is to create a client database using assessment techniques and data collection methods (physical assessment, health history, interview, medical records review, and diagnostic studies). A client database includes all the health information gathered.
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don't do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types. Once again: A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient's condition.
D raught the article. Using the appropriate structure, begin writing the draught within an outline: I ntroduction: A succinct paragraph providing a quick overview of the assignment. To help ...
Nursing assignment writing can be of several types, depending on the topic's requirements, and the instructor can vary the criteria as the subject demands. Nursing assignment writing primarily concerns technicalities and in-depth research for various criteria. Students can train themselves to write good nursing assignments.
1. Write. Once you have read and re-read your articles and organized your findings, you are ready to begin the process of writing the literature review. 2. Synthesize. (see handout below) Include a synthesis of the articles you have chosen for your literature review.
5. Polish and Submit. The last step in writing an annotated bibliography is to edit and proofread the essay to correct all the errors and check for omissions. Polish the paper to meet your university or college's writing level requirements and standards.
If you are looking for resources that will help you with writing in nursing, please visit the OWL's Writing in Nursing material. Writing in the Nursing Classroom: Experiences, Strategies, and Assignments. Bean, John C. Engaging Ideas: The Professor's Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom. San ...
1.1. Decoding the Prompt. Breaking down the assignment prompt is the first step to success. Highlight the keywords and phrases that define the main topic, such as "nursing care," "patient ...
8 Effective Tips to Write an Impressive Nursing Assignment Nursing is one of the most challenging courses that a student does. To do well in this, they must have good knowledge and skills.
0 likes, 0 comments - global_assignment_service444March 6, 2023 on : "How to Write a Nursing Assignment for College compose a university assignment. Strict guidelines ...