
- Ask a Librarian

Locating and Using Images for Presentations and Coursework
- Free & Open Source Images
- How to Cite Images
- Alt Text Image Descriptions
Copyright Resources
- Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States from Cornell University Library
- Copyright Overview from Purdue University
- U.S. Copyright Office
- Fair Use Evaluator
- Visual Resources Association's Statement of Fair Use of Images for Teaching, Research, and Study
- Creative Commons Licenses
Attribution
Again, the majority of images you find are under copyright and cannot be used without permission from the creator. There are exceptions with Fair Use, but this Libguide is intended to help you locate images you can use with attribution (and in some case, the images are free to use without attribution when stated, such as with stock images from pixabay). ***Please read about public domain . These images aren't under copyright, but it's still good practice to include attribution if the information is available. Attribution : the act of attributing something, especially the ascribing of a work (as of literature or art) to a particular author or artist. When you have given proper attribution, it means you have given the information necessary for people to know who the creator of the work is.
Citation General Guidelines
Include as much of the information below when citing images in a paper and formal presentations. Apply the appropriate citation style (see below for APA, MLA examples).
- Image creator's name (artist, photographer, etc.)
- Title of the image
- Date the image (or work represented by the image) was created
- Date the image was posted online
- Date of access (the date you accessed the online image)
- Institution (gallery, museum) where the image is located/owned (if applicable)
- Website and/or Database name
Citing Images in MLA, APA, Chicago, and IEEE
- Directions for citing in MLA, APA, and Chicago MLA: Citing images in-text, incorporating images into the text of your paper, works cited APA 6th ed.: Citing images in-text and reference list Chicago 17th ed.: Citing images footnotes and endnotes and bibliography from Simon Fraser University
- How to Cite Images Using IEEE from the SAIT Reg Erhardt Library
- Image, Photograph, or Related Artwork (IEEE) from the Rochester Institute of Technology Library
Citing Images in Your PPT
Currently, citing images in PPT is a bit of the Wild West. If details aren't provided by an instructor, there are a number of ways to cite. What's most important is that if the image is not a free stock image, you give credit to the author for the work. Here are some options:
1. Some sites, such as Creative Commons and Wikimedia, include the citation information with the image. Use that citation when available. Copy the citation and add under the image. For example, an image of a lake from Creative Commons has this citation next to it: "lake" by barnyz is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 .
2. Include a marker, such as Image 1. or Figure 1., and in the reference section, include full citation information with the corresponding number
3. Include a complete citation (whatever the required format, such as APA) below the image
4. Below the image, include the link to the online image location
5. Hyperlink the title of the image with the online image location
- << Previous: Free & Open Source Images
- Next: Alt Text Image Descriptions >>
- Last Edited: Jun 8, 2023 3:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/images
Your browser does not support javascript. Some site functionality may not work as expected.
- Images from UW Libraries
- Open Images
- Image Analysis
- Citing Images
- University of Washington Libraries
- Library Guides
- Images Research Guide
Images Research Guide: Citing Images
How to cite images.
There are many ways to cite images. Most important is to include all relevant information so others can locate, understand and evaluate any images you use.
Academic Styles of Citing Images:
APA Style (7th Edition)
MLA Style (9th Edition)
Non-Academic Style:
Image Credits
Reference List
General Format:
Creator, C. (Year of Production or publication). Title of work [Description, Medium, or other relevant information]. Source. Retrieval information or location of work.
Image Found on the Web Euloth, G. (2012). Sleepy Kitty, Purr, Purr, Purr [Photograph]. Flickr. https://flic.kr/p/bD838X
Image from a Database Sharkstar, A.J. (2014). Two Cats Bound Together By A Snake [Sticker]. A rtstor . https://library.artstor.org/public/SS7730635_7730635_12095826
Image from a Book O’Keeffe, G. (1923). Alligator Pears in a Basket [Charcoal drawing]. In Sayre, H.M., Writing about art (6 th ed., pp. 39). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2009.
Image from a Museum or Archive Website Lawrence, J. (1977). The Studio [Painting]. Seattle Art Museum, Seattle, WA, United States. https://art.seattleartmuseum.org/objects/10605/the-studio
Image in a Museum Mirra, H. (2016). Standard Incomparable [Textile]. Pasadena, CA: Armory Center for the Arts.
In-text Citations
(Creator Last Name, Year)
If there is no creator, use (Title, Year)
(Amero, 1951)
Figure Captions
Figure 1. Author, A. A. (Year). Title of material . [Description of material]. Retrieved from http://www.xxxx
Figure 1. Amero, E. (1951). Fiesta. [Print]. Retrieved from Artstor.
Image Credits (Non-Academic Style)
A credit statement can be an alternative to a full academic citation, and especially useful when writing for the Web. Provide a link to the image if you can.
Title by Creator, date (if available), via source (Creative Common License Type, if applicable).
Sleep Kitty, Purr, Purr, Purr by Glenn Euloth, 2012, via Flickr (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0).
Open Attribution Builder:
If you are using an openly licensed image, try generating an image credit with the Open Attribution Builder .

Why Cite Images?
There are many important reasons to cite images you use:
- Give credit to the creator of the image.
- Provide information so others can find and reuse the image
- Participate in ongoing scholarly conversations about images
MLA Style (Ninth Edition, 2021)
Works Cited List
Previously, researchers made citations by following the MLA’s instructions for the source’s publication format (book, DVD, Web page, etc.). Now, there is one standard, universal format that researchers can use to create their citations:
Author. Title of source. Title of container, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location.
Note: Containers are the elements that “hold” the source. For example, if a photo is posted on Flickr, Flickr is the container. Sometimes a source is nested inside of two separate containers, like an image found in a book read on an ebook platform like Ebook Library (EBL). Both the title of the source and its container (or multiple containers) are included in a citation.
Image Found on the Web Euloth, Glenn. Sleepy Kitty, Purr, Purr, Purr. 2012. Flickr , flic.kr/p/bD838X .
Image from a Database Amero, Emilio. Fiesta . 1951. National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C. Artstor , https://library.artstor.org/#/asset/external/8D5Jcj0oMloyLyw%2Ffzx%2FRHsp
Image from a Book O’Keeffe, Georgia. Alligator Pears in a Basket . 1923. Writing about Art by Henry M. Sayre, 6 th ed., Pearson Prentice Hall, 2009, pp. 39.
Image from a Museum or Archive Website Lawrence, Jacob. The Studio . 1977. Seattle Art Museum, Seattle. Seattle Art Museum, www1.seattleartmuseum.org/eMuseum/code/emuseum.asp?style=browse¤trecord=1&page=search&profile=objects&searchdesc=90.27&quicksearch=90.27&newvalues=1&newstyle=single&newcurrentrecord=1.
Image in a Museum Mirra, Helen. Standard Incomparable . 2016, Armory Center for the Arts, Pasadena, CA.
In-text citations
(Creator Last Name, Page Number)
If there is no creator, use (“Title", Page Number)
For images found online, do not list a page number.
Fig 1. Ann Author, Title of Work , Museum and/or Publication information.
Fig 1. Emilio Amero, Fiesta , National Gallery of Art, 1951, Washington, D.C.
- << Previous: Image Analysis
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2023 12:45 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uw.edu/newimages

Quick Links:
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to cite images and graphs in your research paper

Table of Contents
If you are confused about whether you should include pictures, images, charts, and other non-textual elements in your research paper or not, I would suggest you must insert such elements in your research paper. Including non-textual elements like images and charts in the research paper helps extract a higher acceptance of your proposed theories.
An image or chart will make your research paper more attractive, interesting, explanatory, and understandable for the audience. In addition, when you cite an image or chart, it helps you describe your research and its parts with far more precision than simple, long paragraphs.
There are plenty of reasons why you should cite images in your research paper. However, most scholars and academicians avoid it altogether, losing the opportunity to make their research papers more interesting and garner higher readership.
Additionally, it has been observed that there are many misconceptions around the use or citation of images in research papers. For example, it is widely believed and practiced that using pictures or any graphics in the research papers will render it unprofessional or non-academic. However, in reality, no such legit rules or regulations prohibit citing images or any graphic elements in the research papers.
You will find it much easier once you know the appropriate way to cite images or non-textual elements in your research paper. But, it’s important to keep in mind some rules and regulations for using different non-textual elements in your research paper. You can easily upgrade your academic/ research writing skills by leveraging various guides in our repository.
In this guide, you will find clear explanations and guidelines that will teach you how to identify appropriate images and other non-textual elements and cite them in your research paper. So, cut the clutter; let’s start.
Importance of citing images in a research paper
Although it’s not mandatory to cite images in a research paper, however, if you choose to include them, it will help showcase your deep understanding of the research topic. It can even represent the clarity you carry for your research topic and help the audience navigate your paper easily.

There are several reasons why you must cite images in your research paper like:
(i) A better explanation for the various phenomenon
While writing your research paper, certain topics will be comparatively more complex than others. In such a scenario where you find out that words are not providing the necessary explanation, you can always switch to illustrating the process using images. For example, you can write paragraphs describing climate change and its associated factors and/or cite a single illustration to describe the complete process with its embedded factors.
(ii) To simplify examples
To create an impeccable research paper, you need to include evidence and examples supporting your argument for the research topic. Rather than always explaining the supporting evidence and examples through words, it will be better to depict them through images. For example, to demonstrate climate change's effects on a region, you can always showcase and cite the “before and after” images.
(iii) Easy Classification
If your research topic requires segregation into various sub-topics and further, you can easily group and classify them in the form of a classification tree or a chart. Providing such massive information in the format of a classification tree will save you a lot of words and present the information in a more straightforward and understandable form to your audience.
(iv) Acquire greater attention from the audience
Including images in your research paper, theses, and dissertations will help you garner the audience's greater attention. If you add or cite images in the paper, it will provide a better understanding and clarification of the topics covered in your research. Additionally, it will make your research paper visually attractive.
Types of Images that you can use or cite in your research paper
Using and citing images in a research paper as already explained can make your research paper more understanding and structured in appearance. For this, you can use photos, drawings, charts, graphs, infographics, etc. However, there are no mandatory regulations to use or cite images in a research paper, but there are some recommendations as per the journal style.
Before including any images in your research paper, you need to ensure that it fits the research topic and syncs with your writing style. As already mentioned, there are no strict regulations around the usage of images. However, you should make sure that it satisfies certain parameters like:
- Try using HD quality images for better picture clarity in both print and electronic formats
- It should not be copyrighted, and if it is, you must obtain the license to use it. In short cite the image properly by providing necessary credits to its owner
- The image should satisfy the context of the research topic
You can cite images in your research paper either at the end, in between the topics, or in a separate section for all the non-textual elements used in the paper. You can choose to insert images in between texts, but you need to provide the in-text citations for every image that has been used.
Additionally, you need to attach the name, description and image number so that your research paper stays structured. Moreover, you must cite or add the copyright details of the image if you borrow images from other platforms to avoid any copyright infringement.
Graphs and Charts
You can earn an advantage by providing better and simple explanations through graphs and charts rather than wordy descriptions. There are several reasons why you must cite or include graphs and charts in your research paper:
- To draw a comparison between two events, phenomena, or any two random parameters
- Illustration of statistics through charts and graphs are most significant in drawing audience attention towards your research topic
- Classification tree or pie charts goes best to show off the degree of influence of a specific event, or phenomenon in your research paper
With the usage of graphs and charts, you can answer several questions of your readers without them even questioning. With charts and graphs, you can provide an immense amount of information in a brief yet attractive manner to your readers, as these elements keep them interested in your research topic.
Providing these non-textual elements in your research paper increases its readability. Moreover, the graphs and charts will drive the reader’s attention compared to text-heavy paragraphs.
You can easily use the graphs or charts of some previously done research in your chosen domain, provided that you cite them appropriately, or else you can create your graphs through different tools like Canva, Excel, or MS PowerPoint. Additionally, you must provide supporting statements for the graphs and charts so that readers can understand the meaning of these illustrations easily.
Similarly, like pictures or images, you can choose one of the three possible methods of placement in your research paper, i.e., either after the text or on a different page right after the corresponding paragraph or inside the paragraph itself.
How to Cite Images and Graphs in a Research Paper?
Once you have decided the type of images you will be using in your paper, understand the rules of various journals for the fair usage of these elements. Using pictures or graphs as per these rules will help your reader navigate and understand your research paper easily. If you borrow or cite previously used pictures or images, you need to follow the correct procedure for that citation.
Usage or citation of pictures or graphs is not prohibited in any academic writing style, and it just differs from each other due to their respective formats.
Cite an Image/Graphs in APA (American Psychological Association) style
Most of the scientific works, society, and media-based research topics are presented in the APA style. It is usually followed by museums, exhibitions, galleries, libraries, etc. If you create your research paper in APA style and cite already used images or graphics, you need to provide complete information about the source.
In APA style, the list of the information that you must provide while citing an element is as follows:
- Owner of the image (artist, designer, photographer, etc.)
- Complete Date of the Image: Follow the simple DD/MM/YYYY to provide the details about the date of the image. If you have chosen a certain historical image, you can choose to provide the year only, as the exact date or month may be unknown
- Country or City where the Image was first published
- A Name or Title of the Image (Optional: Means If it is not available, you can skip it)
- Publisher Name: Organization, association, or the person to whom the image was first submitted
If you want to cite some images from the internet, try providing its source link rather than the name or webpage.
Format/Example of Image Citation:
Johanson, M. (Photographer). (2017, September, Vienna, Austria. Rescued bird. National gallery.
Cite an Image/Graphs in MLA (Modern Language Association) style
MLA style is again one of the most preferred styles worldwide for research paper publication. You can easily use or cite images in this style provided no rights of the image owner get violated. Additionally, the format or the information required for citation or usage is very brief yet precise.
In the MLA style, the following are the details that a used image or graph must carry:
- Name of the creator of the owner
- Title, Name, or the Description of the Image
- Website Or the Source were first published
- Contributors Name (if any)
- Version or Serial Number (if any)
- Publisher’s Details; at least Name must be provided
- Full Date (DD:MM: YYYY) of the first published Image
- Link to the original image
Auteur, Henry. “Abandoned gardens, Potawatomi, Ontario.” Historical Museum, Reproduction no. QW-YUJ78-1503141, 1989, www.flickr.com/pictures/item/609168336/
Final Words
It is easy to cite images in your research paper, and you should add different forms of non-textual elements in the paper. There are different rules for using or citing images in research papers depending on writing styles to ensure that your paper doesn’t fall for copyright infringement or the owner's rights get violated.
No matter which writing style you choose to write your paper, make sure that you provide all the details in the appropriate format. Once you have all the details and understanding of the format of usage or citation, feel free to use as many images that make your research paper intriguing and interesting enough.
If you still have doubts about how to use or cite images, join our SciSpace (Formerly Typeset) Community and post your questions there. Our experts will address your queries at the earliest. Explore the community to know what's buzzing and be a part of hot discussion topics in the academic domain.
Learn more about SciSpace's dedicated research solutions by heading to our product page. Our suite of products can simplify your research workflows so that you can focus more on what you do best: advance science.
With a best-in-class solution, you can handle everything from literature search and discovery to profile management, research writing, and formatting.
But Before You Go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

TODAY'S HOURS:
Using Images in Research and Presentations
- Finding Images
- Using Images
Why Do I Need to Cite Images?
Creative commons attribution.
Citing all your sources of information and creative work you use is part of academic integrity. You are giving credit where credit is due.
In academic work, images should be followed by and attribution or in text citation whether that be in a note or caption immediately following the image or at the bottom of a presentation slide. A full citation should be found in your Works Cited or Reference List, though you might separate them out into an Image Credit List, depending on the style of citation you are using.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association expended their explanations and examples of how to cite multimedia sources including multimedia materials. Examples of reference are found in Chapter 10 of the Manual and the following sections focus on multimedia sources
- 10.12 Audiovisual works (films, streaming videos, television series, etc.)
- 10.13 Audio works (music, podcast, radio broadcast, etc.)
- 10.14 Visual works (fine art, clip art, infographics, photographs, maps, etc.)
- 10.15 Social media (including Instagram posts).
A related section of the Manual is Chapter 7 which deals with the presentation of tables and figures, so the Manual shows you how images should be incorporated into your work in addition to how they should be cited; see Sample Figure 7.3 for how to include an attribution in the figure note.
Here is an example of how the following photograph (found through Pixabay) should be cited using the APA style.
stokpic. (2015, February 10). Blonde Girl Taking Photo [Photograph]. Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/photos/blonde-girl-taking-photo-629726/

Remember, the library has a copy of the Manual at the Reference Desk if you need to use it.
The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook Appendix 2 has several examples of works-cited-list entries and the examples of citing fine art and still images can be found on pages 331 - 333. The online MLA Style Center also has examples of image citations.
- Citations by Format | MLA Style Center Are you using any other types of information sources in your project? Find more examples of MLA citation styles here.
Here is an example of how the following photograph (found through Pixabay) should be cited using the MLA style.
stokpic. Blonde Girl Taking Photo. 10 February 2015. Pixabay . pixabay.com/photos/blonde-girl-taking-photo-629726/
Remember, the library has a copy of the Handbook at the Reference Desk if you need to use it.
- Use & Remix - Creative Commons The "Use & remix" section of the Creative Commons website details how to properly attribute content licensed under a CC license. Attribution is a condition of all CC licenses. more info... less info... Creative Commons is a nonprofit organization dedicated to building a globally-accessible public commons of knowledge and culture. They provide Creative Commons licenses and public domain tools that give every person and organization in the world a free, simple, and standardized way to grant copyright permissions for creative and academic works; ensure proper attribution; and allow others to copy, distribute, and make use of those works.
- << Previous: Using Images
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 3:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umflint.edu/images
Works-Cited-List Entries
How to cite an image.
To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an image, list the creator of the image, the title of the image, the date of composition, and the location of the image, which would be a physical location if you viewed the image in person. If you viewed the image online, provide the name of the website containing the image and the URL. If you viewed the image in a print work, provide the publication information for the print work, including a page number. Below are sample entries for images along with links to posts containing many other examples.
A Photograph Viewed in Person
Cameron, Julia Margaret. Alfred, Lord Tennyson . 1866, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.
A Painting Viewed Online
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA , www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
An Untitled Image from a Print Magazine
Karasik, Paul. Cartoon. The New Yorker , 14 Apr. 2008, p. 49.
More Examples
Advertisements
Photographs
Slide Presentations
- Previous Example
- Works Cited: A Quick Guide
- The University of Western Australia
- University Library
- Visit our libraries
- Using the Library
- Stay updated
Referencing style - APA 7th: Images, tables and figures
- Introduction
- Books and book chapters
- Journal and newspaper articles
- Reports, theses and grey literature
- Web sources
- Conference papers
- Images, tables and figures
- Music and audiovisual resources
- Data sets and standards
- Secondary Sources
- Personal Communication
- Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Legal sources
- Example text
- Images and Copyright
- Tables and Figures
- More information
APA examples: Images, tables and figures
All images, figures and tables referred to in the text or reproduced in an essay, assignment or presentation, must be cited and included in your reference list.
See this guides images, figures and tables tab to view how the attribution of these examples below are treated within the text.
See APA Style examples, Clip Art Image and Artwork References for general notes and more examples.
- << Previous: Conference papers
- Next: Music and audiovisual resources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 3:59 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uwa.edu.au/apa
CONTENT LICENCE
- logo-uwa-breadcrumb.png
- Library Guides

- Research excellence
- Centres & Institutes
- Alumni and friends
Staff & Students
- Current Students
- 35 Stirling Highway Perth WA 6009 Australia
- (+61 8) 6488 6000
- Campus tour
- Emergency (+61 8) 6488 2222
- Indigenous Commitment
- Privacy at UWA
- Disclaimer and Copyright
- Accessibility
- Group of 8 Australia member
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
Image Research
- Citing Images
- Getting Started
- Finding Images
How to Cite
Examples of image citations.
- Using Images
- Research Tips
- Still Have Questions?
- Information Needed for Citing Images
- Citation Styles
- Citation Tools
- Captions vs. Citations
Once you find an image you would like to use for your project, it is important to properly cite that image just like you would a journal article or book.
Here is some basic information you might need to cite an image:

- Creator name
- Title of the work
- Date work was created
- Source (URL and date of access)
- Image ID number
If you find an image in a book you will need that book's author, title, publisher information, date, and page, figure, or plate number of the reproduction.
Additional information may be needed for works of art. Remember to always refer to specific style manuals for complete information and consult the terms and conditions of image databases used to locate images since database licenses may specify required caption information.
You can also refer to the Image Workstation Help from Reed College and the Finding Images guide from Boston College for more information and examples on citing images.
Consult these style manuals to create your citations. Copies of several of these manuals are available throughout the libraries at UCLA at reference desks or in the stacks.
Most recent print guide to Modern Language Association (MLA) style.
The complete 17th edition of The Chicago Manual of Style.
This is a thorough guide on research and citation published by Purdue University. Guides on APA, Chicago, and MLA can be found through this website.
Need help citing your sources? Try these tools:
Zotero is a free, easy-to-use tool to help you collect, organize, cite, and share your research sources. See the UCLA Library's Zotero Research Guide for additional information.
A basic guide
From the Getting Started: Information Research Tips library research Guide.
Consult your Style guide for information about caption formats.
See Image Resources: Captions, Citations, Examples, for guidance on the distinction between captions and citations, examples with unusual or unknown elements, and links to additional resources.
Also see the Reed College Image Workstation Help , which provides the following guidance (and more:)
MLA Handbook: Captions
- Images should be labeled Figure (usually abbreviated Fig.), assigned an Arabic numeral, and given a caption.
- The caption should appear directly below the image.
- Image captions should always include the image creator's first name, last name (if available), title, work date, and the source of the image.
- For a more descriptive caption, it is acceptable to include a description of materials, measurements, the institution or individual who owns the work, and the location of the institution.
- Note whether the image came from a print, electronic, or other source and cite appropriately.
Print Source Caption Example Fig. 4. Frank Duveneck, Portrait of Maggie Wilson, Oil on board, 38.10 x 30.48 cm, Museum of Fine Arts, Houston, Texas; Unsuspected Genius: the Art and Life of Frank Duveneck, by Robert Neuhaus (San Francisco: Bedford Press, 1987) 227.
Electronic Source Caption Example Fig. 9. Amasis Painter, Lekythos; Women Weaving, 17.15 cm height, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York; Accessed Jan. 12, 2007 from the Reed College CONTENTdm database <http://cdm.reed.edu/u?/vrcwork,38536>.
Other Source Caption Example Fig. 13. Columbia River at Dawn. Personal photograph by author. 13 March 2008.
Bibliography citation:
Gas Power Magazine, Cover. 1904 November. Artstor, library.artstor.org/asset/SS35197_35197_19447297.
This is an MLA style citation generated from Artstor that gives a magazine cover a descriptive title, “Gas Power Magazine, Cover.”

Unknown photographer. Baseball players, Trinity College, Hartford, CT [Athletics], overall. ca. 1900, Image:2019. Artstor, library.artstor.org/asset/24977027.
This is an MLA style citation generated from Artstor that attributes the photograph to “Unknown photographer” as the creator.

Chicago Style
Unidentified Photographer. c. 1870s. Untitled. Photograph. Place: The Cleveland Museum of Art , Cleveland, Ohio, USA, Collection: Photography, Department: Photography, Gift of Mitzie Verne. https://library.artstor.org/asset/24623239.
This is a Chicago style citation generated from Artstor that attributes the photograph to “Unidentified photographer” as the creator and “Untitled” as the title.

[s.n.]. (1980). Derek Jacobi as Hamlet. Retrieved from https://library.artstor.org/asset/SS36790_36790_39613934.
This is an APA style citation generated from Artstor that uses [s.n.] (“sine nomine” meaning “without name”) for a film poster, and gives a descriptive title, “Derek Jacobi as Hamlet.”

Unknown. (1888-1894). View of thatch buildings, probably in Samoa. [lantern slides]. Retrieved from https://library.artstor.org/asset/SS7729540_7729540_13002457.
This is an APA style citation generated from Artstor that attributes the image to “Unknown” as the creator.

Artist: Unidentified. (n.d.). Untitled. [Print]. Retrieved from https://library.artstor.org/asset/24272474
This is an APA citation generated from Artstor that addresses many unknowns, including date.

- << Previous: Finding Images
- Next: Using Images >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 9:35 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/images
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Using Images and Non-Textual Materials in Presentations, Papers, Theses, and Dissertations
- Documenting and Citing Images
- Finding Images - Select Sources
Documenting and Citing Images/Photographs and Their Sources
Please note that this is advice on best practices and considerations in documenting and citing images and non-print materials. It does not represent legal advice on obtaining permissions.
Generally, images copied from other sources should not be used without permissions in publications or for commercial purposes. Many American academic institutions require graduate students to archive their finished and approved theses/dissertations in institutional electronic repositories and/or institutional libraries and repositories, and/or to post them on Proquest's theses database. Unpublished theses and dissertations are a form of scholarly dissemination. Someone else's images, like someone else's ideas, words or music, should be used with critical commentary, and need to be identified and cited. If a thesis/dissertation is revised for publication, waivers or permissions from the copyright holder(s) of the images and non-textual materials must be obtained. Best practices also apply to materials found on the internet and on social media, and, properly speaking, require identification, citation, and clearance of permissions, as relevant.
Use the following elements when identifying and citing an image, depending on the information you have available . It is your responsibility to do due diligence and document as much as possible about the image you are using:
- Artist's/creator's name, if relevant;
- Title of the work/image, if known, or description;
- Ownership information (such as a person, estate, museum, library collection) and source of image;
- Material, if known, particularly for art works;
- Dimensions of the work, if known.
The Chicago Manual of Style online can be searched for norms on appropriate ways to caption illustrations, capitalize titles of visual works, or cite print materials that contain images.
Including images/photographs in a bibliography:
Best practice is to not include images within a bibliography of works cited. It is common, instead, to create a separate list of images (or figures) and their source, such as photographer (even if it's you) or collection. It may be useful to also include location, e.g., museum, geographic reference, address, etc.
Examples of Documenting Images
The image below is scanned from a published book. It can be used in a critical context within a presentation, classroom session, or paper/thesis, as follows:

[ Figure 1. This photograph from 1990 shows the Monument against Fascism designed by Jochen Gerz and Esther Shalev-Gerz, Hamburg, 1986-1993. Image from James Young, ed., Art of Memory: Holocaust Memorials in History (New York: Prestel, 1994), 70]
If you need to use this image in a published work, you will have to seek permission. For example, the book from which this image was scanned should have a section on photo credits which would help you identify the person/archive holding this image.
The image below was found through Google Images and downloaded from the internet. It can be used in a critical context within a presentation, classroom session, or paper/thesis, as follows:

[Figure 2. This image shows the interior of Bibliotheca Alexandrina designed by the Norwegian architecture firm Snøhetta in 2001. Image downloaded from https://mgkhs.com/gallery/alexandria in March 2016.]
If you want to use this image in a published work, you will have to do your best to track down its source to request permission to use. The web site or social media site where you found the image may not be an appropriate source, since it is common for people to repost images without attribution. Just because "everyone does it" does not mean that you should be using such materials without attribution or documentation. In this specific example, you may need to write to the photographer or to the architecture firm. If you have done due diligence and were unable to find the source, or have not received a response, you may be able to use an image found on the internet with appropriate documentation in a publication.
The image below was downloaded from a digitized historic collection of photographs held by an institutional archive. It can be used in a critical context within a presentation, classroom session, or paper/thesis, as follows:

[Figure 3. In the 1920s the urban landscape of Los Angeles started to change, as various developers began building multi-family apartment houses in sections previously zoned for single family dwellings. Seen in this photograph by Dick Whittington is the Warrington apartment building, which was completed in 1928, surrounded by older single family structures. Downloaded from the USC Digital Library in February 2016]
I f you plan to use this photograph in a publication, seek permission from the library/institution from whose digital archive you downloaded the image. Contact information is usually found in the record for the image.
The image below was taken by the author. It can be used in a critical context within a presentation, classroom session , paper/thesis, or a publication* as follows:

[Figure 4. Genex Tower, also known as West City Gate, is a residential tower located in New Belgrade. This example of late 20th century brutalist-style architecture was designed in 1977 by Mihajlo Mitrović. Photographed by the author in 2013.]
*Please note, if you re-photographed someone else's photograph or a work of art, or if you re-photographed a published image, you may not be able to publish your photograph without first seeking permission or credit for its content. If you have done due diligence and were unable to find the source or have not received a response, you may be able to use your image with appropriate documentation.
- << Previous: Fair Use
- Next: Finding Images - Select Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2023 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/fair_use
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite a Picture or Image in MLA
How to Cite a Picture or Image in MLA
Photograph – An image produced by a camera.
Citing a photograph or image displayed in a museum or institution (viewed in-person)
The citations below are based on information from the MLA Style Center .
View Screenshot | Cite your source
Citing a photograph or image from a museum or institution (viewed online)
Many museums have online collections of their work. The citations below are based on information from the MLA Style Center .
Citing a digital image on a web page or online article
Digital Image – A picture that can be viewed electronically by a computer.
Here’s the standard structure for a digital image citation found on a website. It follows guidance found in the MLA Style Center .
View Screenshot | Cite your source
Image search: Do not cite the search engine (example: Google Images) where the image is found, but the website of the image the search engine indexes.
Citing a photograph from a book
Citing a photograph you took.
The photo would be considered as part of a “personal collection.” The example below follows guidance found in the MLA Style Center .
Citing a photograph from a database
View Screenshot | Cite your source
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Updated April 26, 2021.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples

How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite an image with no author in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the title or description, museum or website name, date, and URL if applicable. Templates and examples for in-text citations and works cited list entries for an image with no author (viewed online) are provided below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose and parenthetical citations, use the title of the image.
Citation in prose:
The photograph Robert Frank in Automobile ….
Parenthetical:
….( Robert Frank )
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
Viewed online:
Title of Photograph or Description. Date Published. Name of Gallery/Museum or Website Name, URL.
Robert Frank in Automobile. 1958. National Gallery of Art, https://www.nga.gov/collection/art-object-page.89153.html.
To cite an image with no date in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the artist name, image title, and either the website where the image was viewed online or the museum or gallery name where it was viewed in person. If no date information is provided for an online image, omit the publication date details and instead provide the date you accessed it. Templates and examples for in-text citations and works cited list entries for an image with no date (viewed online and firsthand) are provided below:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the artist on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname. In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the artist.
First mention: Janet Cameron ….
Subsequent occurrences: Cameron ….
….(Cameron).
Viewed firsthand :
Artist Surname, First Name. Title of the Image. Name of the Museum or Gallery, Physical Location (Major City or City, State).
Muybridge, Eadweard. Attitudes of Animals in Motion . Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.
Viewed online :
Artist Surname, First Name. Title of the Image. Name of the Website , URL. Accessed Date.
Cameron, Janet. Who Was Cleopatra? Decoded Past , www.decodedpast.com/philosophy-2/ . Accessed 20 Sept. 2021.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
FLEET LIBRARY | Research Guides
Rhode island school of design, how to cite images.
- Chicago/Art Bulletin Style
MLA Caption Style
- When citing an image, the caption should be labeled as Figure (usually abbreviated Fig.), assigned a number, and given a title or caption
- For images found in a book or journal, include the publication information of the text.
- A caption ordinarily appears directly below the illustration and have the same one-inch margins as the text of the paper.
- Captions should be numbered consecutively.
Fig. 1. Mary Cassatt, Mother and Child , Wichita Art Museum. Illus. in Novelene Ross, Toward an American Identity: Selections from the Wichita Art Museum Collection of American Art (Wichita, Kansas: Wichita Art Museum, 1997) 107. Source: Gibaldi, Joseph. MLA Handbook . 8th ed. New York: Modern Language Association of America, 2016.
Additional Sources
MLA Style Center
Purdue Online Writing Lab: MLA Format
MLA Handbook (8th Ed) in the library
Citing Unidentified Images
When all or part of an image source is unknown or unknowable, use these points to guide your MLA image caption:
Unknown Artist, Author or Creator List that source by title in your works cited list. The title should be followed by the name of the source in the citation, and the remainder of the citation composed as appropriate for the source type. Alphabetize reference list entries beginning with a title using the primary word of the title (excluding a, an, or the).
An Image without a Title If an image is not titled, create a brief, descriptive title for it. Do not italicize this title or place it in quotes, and capitalize only the first word and any proper nouns.
Undated Sources Use "n.d." (for "no date") in the appropriate place in your citation. When this is used after a period in a citation, capitalize the "n" ("N.d.").
Sources consulted: MLA Citation Examples University of Maryland University Colleges Libraries Miscellaneous Photographs Collection , Archives of American Art
- << Previous: Image Captions
- Next: Chicago/Art Bulletin Style >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 6:20 PM
- URL: https://risd.libguides.com/citingimages

Images: Citing Use of Images
- Finding Images
- Citing Use of Images
Citing In a Research Paper
Images should be cited in text and in the references list according to the style of your paper format. Our Citation Styles Guide provides guidance to specific citations.
Images should be cited in-text and on the references page using the proper citation style for whatever format you are working in. For more information on specific formats, check out our Citation Styles Guide .
Example of APA citation for the following image:

Citing in Presentation Slides
Images in Powerpoint presentations should be cited or attributed using the same guidelines as a paper. If you are working within a format (APA, MLA, Chicago), you should include a full citation in that format below the image. Alternatively, you can add a footnote labeling each image (for example, "Image 1") and create a reference slide at the end of your presentation with corresponding image numbers and full citations.
- << Previous: Copyright
- Last Updated: Feb 15, 2024 12:18 PM
- URL: https://libguides.stkate.edu/images
©2024 St. Catherine University Library , St. Paul, Minnesota, USA

- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
How to Cite Images, Tables and Diagrams
The pages outlines examples of how to cite images, tables and diagrams using the Harvard Referencing method .
An image found online
In-text citations
Mention the image in the text and cite the author and date:
The cartoon by Frith (1968) describes ...
If the image has no named author, cite the full name and date of the image:
The map shows the Parish of Maroota during the 1840s (Map of the Parish of Maroota, County of Cumberland, District of Windsor 1840-1849)
List of References
Include information in the following order:
- author (if available)
- year produced (if available)
- title of image (or a description)
- Format and any details (if applicable)
- name and place of the sponsor of the source
- accessed day month year (the date you viewed/ downloaded the image)
- URL or Internet address (between pointed brackets).
Frith J 1968, From the rich man’s table, political cartoon by John Frith, Old Parliament House, Canberra, accessed 11 May 2007, <http: // www . oph.gov.au/frith/theherald-01.html>.
If there is no named author, put the image title first, followed by the date (if available):
Khafre pyramid from Khufu’s quarry 2007, digital photograph, Ancient Egypt Research Associates, accessed 2 August 2007, <http: // www . aeraweb.org/khufu_quarry.asp>.
Map of the Parish of Maroota, County of Cumberland, District of Windsor 1840-1849, digital image of cartographic material, National Library of Australia, accessed 13 April 2007, <http: // nla . gov.au/nla.map-f829>.
Online images/diagrams used as figures
Figures include diagrams, graphs, sketches, photographs and maps. If you are writing a report or an assignment where you include a visual as a figure, unless you have created it yourself, you must include a reference to the original source.
Figures should be numbered and labelled with captions. Captions should be simple and descriptive and be followed by an in-text citation. Figure captions should be directly under the image.
Cite the author and year in the figure caption:

Figure 1: Bloom's Cognitive Domain (Benitez 2012)
If you refer to the Figure in the text, also include a citation:
As can be seen from Figure 1 (Benitez 2012)
Provide full citation information:
Benitez J 2012, Blooms Cognitve Domain, digital image, ALIEM, accessed 2 August 2015, <https: // www . aliem.com/blooms-digital-taxonomy/>.
Online data in a table caption
In-text citation
If you reproduce or adapt table data found online you must include a citation. All tables should be numbered and table captions should be above the table.
Table 2: Agricultural water use, by state 2004-05 (Australian Bureau of Statistics 2006)
If you refer to the table in text, include a citation:
As indicated in Table 2, a total of 11 146 502 ML was used (Australian Bureau of Statistics 2006)
Include the name of the web page where the table data is found.
Australian Bureau of Statistics 2006, Water Use on Australian Farms , 2004-05, Cat. no. 4618.0, Australian Bureau of Statistics, Canberra, accessed 4 July 2007, <https: // www . abs.gov.au>.
FAQ and troubleshooting
Harvard referencing
- How to cite different sources
- How to cite references
- How to cite online/electronic sources
- Broadcast and other sources
- Citing images and tables
- FAQs and troubleshooting
- About this guide
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 7 Feb – 10 Apr 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024

- Spartanburg Community College Library
- SCC Research Guides
Finding & Using Images
- Citing Images in MLA
Citing Images or Graphs
Please see below for MLA guidelines on how to cite images or graphs from the web or from a database.
- From Database
- Using Images in Project
- Using Artwork in a Project
- Help Resources
Citing an Image or Graph from the Web
Format: Author(s). “Title of Image/Graph.” Title of Website in Italics , Website Publisher (if different than title), Date of Publication/Posting, URL.
Example : “Kim Kardashian.” Vanity Fair , Condé Nast, 11 Jan. 2004, www.vanityfair.com.
Example 2: Lange, Dorothea. "Migrant Mother." Prints & Photographs Reading Room Collection , Library of Congress, 11 Jan. 2004, montevideo.usembassy.gov.
Example (No Title) : Penguin sitting on rock. National Geographic , www.natgeo.com/images/149603845. Accessed 9 Feb. 2021.
Example (Artwork): Van Gogh, Vincent. The Starry Night . 1889. MoMALearning , Museum of Modern Art, www.moma.org/learn/moma_learning/vincent-van-gogh-the-starry-night-1889/.
*Note: For images without titles, create a descriptive title in plain text – no italics, no quotes. Capitalize only the first word and any proper nouns. *Note: Italicize titles of formal art work and include the date of creation after the title with a period. The Starry Night . 1889. *Note: Include an accessed date at the end if no date of publication/posting is available. *Note: Image URLs should be from the actual website that hosts the image. Be careful with this. If you use Google or another search engine to find the image, if you copy the URL it may give you Google's search URL rather than the actual URL of the image's website. *Note : You can usually omit the http:// unless needed to hyperlink. *Note: For URLs longer than 3 lines, you can shorten the URL. Always retain the host (main website) of the URL.
Citing an Image or Graph from a Database
Format: Creator(s). "Title of Image/Graph ." Title of Source (if given), Publisher, Date. Database Name, URL.
Example: Johnson, Clinton. "Boston Street Scene." Library of Congress, 1895. Credo Reference, go.openathens.net/redirector/sccsc.edu?url=https%3A%2F%2Fsearch.credoreference.com%2Fcontent%2Fentry%2Fbridgeart%2 Fstate_street_boston_engraved_by_s_lacey_engraving_b_w_photo%2F0%3FinstitutionId%3D2682.
Example: "Daily Time Spent on Social Networking by Internet Users Worldwide from 2012 to 2022 (in Minutes)." Digital 2022: Global Digital Overview , We Are Social / DataReportal / Hootsuite, 26 Jan. 2022. Statista , www.statista.com/statistics/433871/daily-social-media-usage-worldwide/.

Citing Images in a Presentation
MLA gives two different ways to cite an images in a presentation or paper depending on how you are using the image in your presentation. The difference depends on whether the image is just for illustration or decoration (a stand along image), or if you're going to refer to this image in your presentation (the image itself is part of the content of your presentation.
Option 1: Image is for Illustration or Decoration (not going to talk directly about the image during your presentation).
In this case, list the entire citation information in the caption of the image. Do not list it on your Works Cited page at the end.
Option 2: Image is Part of the Presentation (going to talk about the image specifically during your presentation)
In this case, you'll still include a caption for the image, but the caption will only include an in-text citation, and the entire citation information will go on the Works Cited page like you with a regular source.
See the two different ways you could use the image below in a presentation, and how the citing would differ.
Option 1: If the image below is on a slide about massage therapists, but you don't directly talk about the image, then you'd include the full citation information in the caption for the image. See below.

Fig. 1: Cuttingham, Alyssa. Massage Chair. Massage & Bodywork , vol. 28, no. 3, Dec. 2016, p. 14. Vocational and Career Collection , search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,sso&db=imh&AN=imh984947&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=s9007306.
Option 2: If you're displaying this image of the massage chair in order to talk about the correct positioning and demonstrate how someone should sit in the chair, meaning that you'll talk about this image and what it shows, then you would include the citation information in your Works Cited, and the caption would just include an in-text citation.

Fig. 1: Correct Positioning in a Massage Chair (Cuttingham 14).
Works Cited
Cuttingham, Alyssa. Massage Chair. Massage & Bodywork , vol. 28, no. 3, Dec. 2016, p. 14. Vocational and Career Collection, search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,sso&db=imh&AN=imh984947&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=s9007306.
Citing Artwork in a Project
There are several ways to cite Artwork in a project in MLA format.
When you include artwork directly into your paper or presentation, it should be labeled as "Fig." with a number, followed by a period. (Example: Fig. 1.).
Under the image, place a caption that will start with the Figure label and number. Then you have options for how to finish the caption.
Give the full MLA citation for your source. Do not invert the creator's name (if you have one listed).
If you include the full MLA citation in your caption and you do not cite the source again in your project, you do not need to include the source in your Works Cited.

Fig 1. Vincent Van Gogh. Self Portrait . 1889. National Gallery of Art , www.nga.gov/collection/art-object-page.106382.html.
Give basic information about your source such as the creator of the image, title, year, and any other important information. If you do not include the full MLA citation, your source must be added to your Works Cited page.
Fig. 1. Vincent Van Gogh, Self Portrait, oil on canvas, 1889.
Van Gogh, Vincent. Self Portrait . 1889. National Gallery of Art , www.nga.gov/collection/art-object-page.106382.html.
- << Previous: Citing Images in a Project in MLA
- Next: Citing Images in a Project in APA >>
- Finding Images
- Citing Images in a Project in MLA
- Citing Images in a Project in APA
- Citing Images in APA
Questions? Ask a Librarian

- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sccsc.edu/images-copyright
Giles Campus | 864.592.4764 | Toll Free 866.542.2779 | Contact Us
Copyright © 2024 Spartanburg Community College. All rights reserved.
Info for Library Staff | Guide Search
Return to SCC Website

Finding and referencing images: Referencing images
- Referencing images
- Finding images and videos
Introduction
In this guide, ' IMAGE ' is used to refer to any visual resource such as a diagram, graph, illustration, design, photograph, or video. They may be found in books, journals, reports, web pages, online video, DVDs and other kinds of media. This guide also refers to ‘ CREATOR ’. This could be an illustrator, photographer, author or organisation.
The examples are presented in Harvard (Bath) style and offer general guidelines on good practice. For essays, project reports, dissertations and theses, ask your School or Department which style they want you to use. Different referencing styles require the use of similar information but will be formatted differently. For more information on other referencing styles, visit our referencing guide .
Using images to illustrate or make clear the description and discussion in your text is useful, but it is important that you give due recognition to the work of other people that you present with your own. This will help to show the value of their work to your assignment and how your ideas fit with a wider body of academic knowledge.
It is just as important to properly cite and reference images as it is the journal articles, books and other information sources that you draw upon. If you do not, you could find yourself accused of plagiarism and/or copyright infringement.
Using images and copyright
For educational assignments it is sufficient to cite and reference any image used. If you publish your work in any way , including posting online, then you will need to follow copyright rules. It is your responsibility to find out whether, and in what ways, you are permitted to use an image in your coursework or publications. Please refer to our copyright guidance and ask for further assistance if you are unsure.
Some images are given limited rights for reuse by their creators. This is likely to be accompanied with a requirement to give recognition to their work and may limit the extent to which it can be modified. The ‘Creative Commons’ copyright licensing scheme offers creators a set of tools for telling people how they wish their work to be used. You can find out more about the different kinds of licence, and what they mean, on the organisation’s web pages .
What is a caption?
Any image that you use should be given a figure number and a brief description of what it is. Permission for use of an image in a published work should be acknowledged in the figure caption. Some organisations will require the permission statement to be given exactly as they specify. If they are required, permissions need to be stated in addition to the citing and referencing guidance given below.
Referencing images in PowerPoint slides
For a presentation you should include a brief citation under the image. Keep a reference list to hand (e.g. hidden slide) for questions. Making a public presentation or posting it online is publishing your work. You must include your references and observe permission and copyright rules.
Example of a caption

Figure 1. Library book. Reproduced with permission from: Rogers, T., 2015, University of Bath Library
Citing and referencing images
Citing images from a book or journal article.
If you wish to refer to images used in a book or journal, they are cited in the same way as text information , for example:
The functions and flow of genetic information within a plant cell can be visualised as a complex system (Campbell et al., 2015, pp. 282-283).
Campbell et al. (2015, pp. 282-283) have clearly illustrated how a plant cell functions.
If you were to include this example in an essay the caption and citation below the image would look similar to this:
Figure 7. The functions and flow of genetic information within a plant cell (Campbell et al., 2015, pp. 282-283).
The reference at the end of the work would be as recommended for a book reference in our general referencing guide .
For a large piece of work such as a dissertation, thesis or report, a list of figures may be required at the front of the work after the contents page. Check with your department for information on specific requirements of your work.
Google images
When referencing an image found via Google you need to make sure that the information included in your reference relates to the original website that your search has found. Click on the image within the results to get to the original website and take your reference information from there. Take care to use credible sources with good quality information.
Citing and referencing images from a web page
If you use an image from a web page, blog or an online photograph gallery you should reference the individual image . Cite the image creator in the caption and year of publication. The creator may be different from the author of the web page or blog. They may be individual people or an organisation. Figure 2 below gives an example of an image with a corporate author:

List the image reference within your references list at the end of your work, using the format:
NASA, 2015. NASA astronaut Tim Kopra on Dec. 21 spacewalk [Online]. Washington: NASA. Available from: https://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/nasa-astronaut-tim-kopra-on-dec-21-spacewalk [Accessed 7 January 2015].
Wikipedia images
If you want to reference an image included in a Wikipedia article, double-click on the image to see all the information needed for your reference. This will open a new page containing information such as creator, image title, date and specific URL. The format should be:
Iliff, D., 2006. Royal Crescent in Bath, England - July 2006 [Online] . San Francisco: Wikimedia Foundation. Available from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Royal_Crescent_in_Bath,_England_-_July_2006.jpg [Accessed 7 January 2016].
Images and designs from exhibitions, museums or archives
If you want to reference an image or design that you have found in an exhibition, museum or archive, then you also need to observe copyright rules and reference the image correctly. The format is:
For example, if you want to reference an old black and white photograph from 1965 that is held in an archive at the University of Bath:
Bristol Region Building Record, 1965. Green Park House (since demolished), viewed from southwest [Photograph]. BRBR, D/877/1. Archives & Research Collections, University of Bath Library.
NB if you were to reproduce this archive image in your work, or any part of it (rather than just cite it), you would also need to note ‘© University of Bath Library’. This copyright note should be added to the image caption along with the citation.
Referencing your own images
If you take a photograph, you do not have to reference it. For sake of clarity you may want to add “Image by author” to the caption. If you create an original illustration or a diagram that you have produced from your own idea then you do not have to cite or reference them. If you generate an image from a graphics package, for example a molecular structure from chemistry drawing software, you do not need to cite the source of the image.
Referencing images that you adapt from elsewhere
If you use someone else’s work for an image then you must give them due credit. If you reproduce it by hand or using graphics software it is the same as if you printed, scanned or photocopied it. You must cite and reference the work as described in this guide. If the image is something that you have created in an earlier assignment or publication you need to reference earlier piece of work to avoid self-plagiarism. If you want to annotate information to improve upon, extend or change an existing image you must cite the original work. However, you would use the phrase ‘adapted from’ in your citation and reference the original work in your reference list.
AI generated images
If you have used an AI tool to generate an image you must acknowledge that tool as a source (see point 7 of the academic integrity statement ).
This content is not recoverable; it cannot be linked or retrieved. There is no published source that you can reference directly. Instead you would give an in-text, ‘personal communications’ citation , as described in part 15 of our 'Write a citation' guidance (from the Harvard Bath guide). This type of citation includes the author details followed by (pers. comm.) and the date of the communication.
For example, an image of a shark in a library generated with Craiyon with a ‘personal communications’ citation included in the image caption:

Figure 3. Shark in a library image generated using an AI tool (Craiyon, AI Image Generator (pers. comm.) 14 July 2022).
Online images and resources for your work
The library has compiled a list of useful audio-visual resources, including images, that can be used for essays or assignments. Visit the ' finding images and videos ' tab of this guide to find out more.
- Next: Finding images and videos >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 2:32 PM
- URL: https://library.bath.ac.uk/images

Citation Styles
- Citing and referencing figures / images (APA 7th)
- How to cite Gen AI content in APA style
- Citing and Referencing in ASA 7th
- How to cite Gen AI content in Chicago Style
- Citing and referencing figures / images (IEEE)
In-text citation and references
- How to cite Gen AI content in IEEE Style
- How to cite Gen AI content in MLA Style
- Legal Citations
- ACS Citation Style
Citations of figures / images in the paper must be in numerical order. Place it below the figure / image.
Citations to figures in text always carry the abbreviation “Fig.” followed by the figure number. The figure number must have a period after it. Then comes the caption followed by Adapted from [the number in the reference list in which you provide the details of the source]. The first word of the caption should be capitalized. Do not use A, An, or The at the beginning of a figure or table caption.
![how to cite images from research paper Fig. 1. Footwear collected from the shorelines of Midway Atoll. Adapted from [x]](https://libapps-au.s3-ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/accounts/168285/images/sustainabilty_picture.png)
Fig. 1. Footwear collected from the shorelines of Midway Atoll. Adapted from [2]
a) In the reference list give the details of the source, the webpage from which the image is taken in IEEE citation style (IEEE Reference Guide 2018).
[2] NOAA Photo Library. “fis01484." Flickr.com. https://www.flickr.com/photos/noaaphotolib/27889266330/in/album-72157670783471385/ (accessed Oct. 3, 2021).
or b) Cite the image as Artwork in IEEE citation style.
[2] NOAA Photo Library, fis01484. 2013. Accessed: Aug. 22, 2023. [Photo]. Available: https://www.flickr.com/photos/noaaphotolib/27889266330/
Acknowledgement for the use of the photograph used in the example:
We acknowledge the use of the photograph fis01484 by Kristen Kelly, taken from https://www.flickr.com/photos/noaaphotolib/27889266330/in/album-72157670783471385/ under CC BY 2.0
- << Previous: IEEE
- Next: How to cite Gen AI content in IEEE Style >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 12:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ntu.edu.sg/citationstyles
You are expected to comply with University policies and guidelines namely, Appropriate Use of Information Resources Policy , IT Usage Policy and Social Media Policy . Users will be personally liable for any infringement of Copyright and Licensing laws. Unless otherwise stated, all guide content is licensed by CC BY-NC 4.0 .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 15 April 2024
Revealed: the ten research papers that policy documents cite most
- Dalmeet Singh Chawla 0
Dalmeet Singh Chawla is a freelance science journalist based in London.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
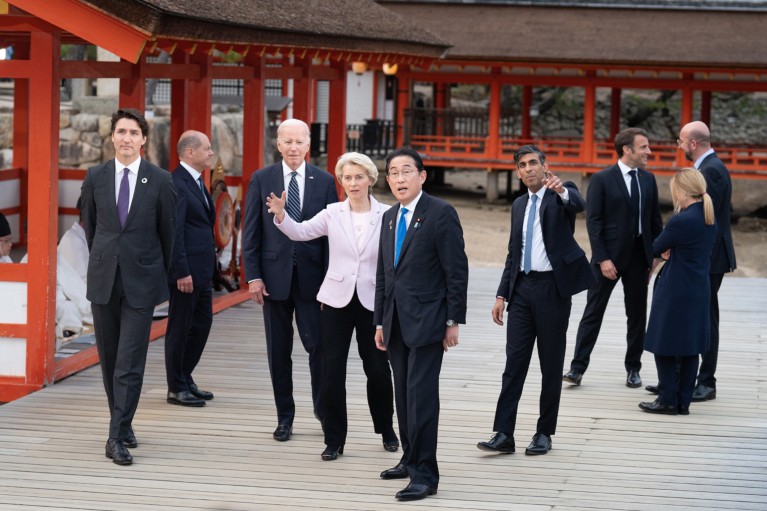

Policymakers often work behind closed doors — but the documents they produce offer clues about the research that influences them. Credit: Stefan Rousseau/Getty
When David Autor co-wrote a paper on how computerization affects job skill demands more than 20 years ago, a journal took 18 months to consider it — only to reject it after review. He went on to submit it to The Quarterly Journal of Economics , which eventually published the work 1 in November 2003.
Autor’s paper is now the third most cited in policy documents worldwide, according to an analysis of data provided exclusively to Nature . It has accumulated around 1,100 citations in policy documents, show figures from the London-based firm Overton (see ‘The most-cited papers in policy’), which maintains a database of more than 12 million policy documents, think-tank papers, white papers and guidelines.
“I thought it was destined to be quite an obscure paper,” recalls Autor, a public-policy scholar and economist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. “I’m excited that a lot of people are citing it.”
The most-cited papers in policy
Economics papers dominate the top ten papers that policy documents reference most.
Data from Sage Policy Profiles as of 15 April 2024
The top ten most cited papers in policy documents are dominated by economics research. When economics studies are excluded, a 1997 Nature paper 2 about Earth’s ecosystem services and natural capital is second on the list, with more than 900 policy citations. The paper has also garnered more than 32,000 references from other studies, according to Google Scholar. Other highly cited non-economics studies include works on planetary boundaries, sustainable foods and the future of employment (see ‘Most-cited papers — excluding economics research’).
These lists provide insight into the types of research that politicians pay attention to, but policy citations don’t necessarily imply impact or influence, and Overton’s database has a bias towards documents published in English.
Interdisciplinary impact
Overton usually charges a licence fee to access its citation data. But last year, the firm worked with the London-based publisher Sage to release a free web-based tool that allows any researcher to find out how many times policy documents have cited their papers or mention their names. Overton and Sage said they created the tool, called Sage Policy Profiles, to help researchers to demonstrate the impact or influence their work might be having on policy. This can be useful for researchers during promotion or tenure interviews and in grant applications.
Autor thinks his study stands out because his paper was different from what other economists were writing at the time. It suggested that ‘middle-skill’ work, typically done in offices or factories by people who haven’t attended university, was going to be largely automated, leaving workers with either highly skilled jobs or manual work. “It has stood the test of time,” he says, “and it got people to focus on what I think is the right problem.” That topic is just as relevant today, Autor says, especially with the rise of artificial intelligence.
Most-cited papers — excluding economics research
When economics studies are excluded, the research papers that policy documents most commonly reference cover topics including climate change and nutrition.
Walter Willett, an epidemiologist and food scientist at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts, thinks that interdisciplinary teams are most likely to gain a lot of policy citations. He co-authored a paper on the list of most cited non-economics studies: a 2019 work 3 that was part of a Lancet commission to investigate how to feed the global population a healthy and environmentally sustainable diet by 2050 and has accumulated more than 600 policy citations.
“I think it had an impact because it was clearly a multidisciplinary effort,” says Willett. The work was co-authored by 37 scientists from 17 countries. The team included researchers from disciplines including food science, health metrics, climate change, ecology and evolution and bioethics. “None of us could have done this on our own. It really did require working with people outside our fields.”
Sverker Sörlin, an environmental historian at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, agrees that papers with a diverse set of authors often attract more policy citations. “It’s the combined effect that is often the key to getting more influence,” he says.

Has your research influenced policy? Use this free tool to check
Sörlin co-authored two papers in the list of top ten non-economics papers. One of those is a 2015 Science paper 4 on planetary boundaries — a concept defining the environmental limits in which humanity can develop and thrive — which has attracted more than 750 policy citations. Sörlin thinks one reason it has been popular is that it’s a sequel to a 2009 Nature paper 5 he co-authored on the same topic, which has been cited by policy documents 575 times.
Although policy citations don’t necessarily imply influence, Willett has seen evidence that his paper is prompting changes in policy. He points to Denmark as an example, noting that the nation is reformatting its dietary guidelines in line with the study’s recommendations. “I certainly can’t say that this document is the only thing that’s changing their guidelines,” he says. But “this gave it the support and credibility that allowed them to go forward”.
Broad brush
Peter Gluckman, who was the chief science adviser to the prime minister of New Zealand between 2009 and 2018, is not surprised by the lists. He expects policymakers to refer to broad-brush papers rather than those reporting on incremental advances in a field.
Gluckman, a paediatrician and biomedical scientist at the University of Auckland in New Zealand, notes that it’s important to consider the context in which papers are being cited, because studies reporting controversial findings sometimes attract many citations. He also warns that the list is probably not comprehensive: many policy papers are not easily accessible to tools such as Overton, which uses text mining to compile data, and so will not be included in the database.

The top 100 papers
“The thing that worries me most is the age of the papers that are involved,” Gluckman says. “Does that tell us something about just the way the analysis is done or that relatively few papers get heavily used in policymaking?”
Gluckman says it’s strange that some recent work on climate change, food security, social cohesion and similar areas hasn’t made it to the non-economics list. “Maybe it’s just because they’re not being referred to,” he says, or perhaps that work is cited, in turn, in the broad-scope papers that are most heavily referenced in policy documents.
As for Sage Policy Profiles, Gluckman says it’s always useful to get an idea of which studies are attracting attention from policymakers, but he notes that studies often take years to influence policy. “Yet the average academic is trying to make a claim here and now that their current work is having an impact,” he adds. “So there’s a disconnect there.”
Willett thinks policy citations are probably more important than scholarly citations in other papers. “In the end, we don’t want this to just sit on an academic shelf.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00660-1
Autor, D. H., Levy, F. & Murnane, R. J. Q. J. Econ. 118 , 1279–1333 (2003).
Article Google Scholar
Costanza, R. et al. Nature 387 , 253–260 (1997).
Willett, W. et al. Lancet 393 , 447–492 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Steffen, W. et al. Science 347 , 1259855 (2015).
Rockström, J. et al. Nature 461 , 472–475 (2009).
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

Citizenship privilege harms science
Comment 15 APR 24

What the India election means for science
News 10 APR 24
How to break big tech’s stranglehold on AI in academia
Correspondence 09 APR 24

Last-mile delivery increases vaccine uptake in Sierra Leone
Article 13 MAR 24

Global supply chains amplify economic costs of future extreme heat risk

How science is helping farmers to find a balance between agriculture and solar farms
Spotlight 19 FEB 24
Assistant Professor - Cell Physiology & Molecular Biophysics
Opportunity in the Department of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics (CPMB) at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC)
Lubbock, Texas
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, School of Medicine
Postdoctoral Associate- Curing Brain Tumors
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Energy AI / Grid Modernization / Hydrogen Energy / Power Semiconductor Concentration / KENTECH College
21, Kentech-gil, Naju-si, Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea(KR)
Korea Institute of Energy Technology
Professor in Macromolecular Chemistry
The Department of Chemistry - Ångström conducts research and education in Chemistry. The department has 260 employees and has a turnover of 290 mil...
Uppsala (Stad) (SE)
Uppsala University
Postdoctoral research fellow focused on generative modelling of synthetic cohorts in brain research
Lunds universitet, Institutionen för kliniska vetenskaper Malmö Lund University was founded in 1666 and is repeatedly ranked among the world’s top ...
Lund (Stad), Skåne (SE)
Lund University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via this form .
The best AI image generators to try right now

If you've ever searched Google high and low to find an image you needed to no avail, artificial intelligence (AI) may be able to help.
With AI image generators, you can type in a prompt as detailed or vague as you'd like to fit an array of purposes and have the image you were thinking of instantly pop up on your screen. These tools can help with branding, social media content creation, and making invitations, flyers, business cards, and more.
Also: ChatGPT no longer requires a login, but you might want one anyway. Here's why
Even if you have no professional use for AI, don't worry -- the process is so fun that anyone can (and should) try it out.
OpenAI's DALL-E 2 made a huge splash because of its advanced capabilities as the first mainstream AI image generator. However, since its initial launch, there have been many developments. Other companies have released models that rival DALL-E 2, and OpenAI even released a more advanced model known as DALL-E 3 , discontinuing its predecessor.
To help you discover which models are the best for different tasks, I put the image generators to the test by giving each tool the same prompt: "Two Yorkies sitting on a beach that is covered in snow". I also included screenshots to help you decide which is best.
Also: DALL-E adds new ways to edit and create AI-generated images. Learn how to use it
While I found the best overall AI image generator is Image Creator from Microsoft Designer , due to its free-of-charge, high-quality results, other AI image generators perform better for specific needs. For the full roundup of the best AI image generators, keep reading.
The best AI image generators of 2024
Image creator from microsoft designer (formerly bing image creator), best ai image generator overall.
- Powered by DALL-E 3
- Convenient to access
- Need a Microsoft account
- In preview stage
Image Creator from Microsoft Designer is powered by DALL-E 3, OpenAI's most advanced image-generating model. As a result, it produces the same quality results as DALL-E while remaining free to use as opposed to the $20 per month fee to use DALL-E.
All you need to do to access the image generator is visit the Image Creator website and sign in with a Microsoft account.
Another major perk about this AI generator is that you can also access it in the same place where you can access Microsoft's AI chatbot, Copilot (formerly Bing Chat) .
This capability means that in addition to visiting Image Creator on its standalone site, you can ask it to generate images for you in Copilot. To render an image, all you have to do is conversationally ask Copilot to draw you any image you'd like.
Also: How to use Image Creator from Microsoft Designer (formerly Bing Image Creator)
This feature is so convenient because you can satisfy all your image-generating and AI-chatting needs in the same place for free. This combination facilitates tasks that could benefit from image and text generation, such as party planning, as you can ask the chatbot to generate themes for your party and then ask it to create images that follow the theme.
Image Creator from Microsoft Designer f eatures: Powered by: DALL-E 3 | Access via: Copilot, browser, mobile | Output: 4 images per prompt | P rice: Free
DALL-E 3 by OpenAI
Best ai image generator if you want to experience the inspiration.
- Not copyrighted
- Accurate depictions
- Confusing credits
OpenAI, the AI research company behind ChatGPT, launched DALL-E 2 in November 2022. The tool quickly became the most popular AI image generator on the market. However, after launching its most advanced image generator, DALL-E 3, OpenAI discontinued DALL-E 2.
DALL-E 3 is even more capable than the original model, but this ability comes at a cost. To access DALL-E 3 you must be a ChatGPT Plus subscriber, and the membership costs $20 per month per user. You can access DALL-E 3 via ChatGPT or the ChatGPT app.
Using DALL-E 3 is very intuitive. Type in whatever prompt you'd like, specifying as much detail as necessary to bring your vision to life, and then DALL-E 3 will generate four images from your prompt. As you can see in the image at the top of the article, the renditions are high quality and very realistic.
OpenAI even recently added new ways to edit an image generated by the chatbot, including easy conversational text prompts and the ability to click on parts of the image you want to edit.
Like with Copilot, you can chat and render your images on the same platform, making it convenient to work on projects that depend on image and text generation. If you don't want to shell out the money, Image Creator by Designer is a great alternative since it's free, uses DALL-E 3, and can be accessed via Copilot.
DALL-E 3 features: Powered by: DALL-E 3 by OpenAI | Access via: ChatGPT website and app | Output: 4 images per credit | Price: ChatGPT Plus subscription, $20 per month
ImageFX by Google
The best ai image generator for beginners.
- Easy-to-use
- High-quality results
- Expressive chips
- Need a Google account
- Strict guardrails can be limiting
Google's ImageFX was a dark horse, entering the AI image generator space much later than its competition, over a year after DALL-E 2 launched. However, the generator's performance seems to have been worth the wait. The image generator can produce high-quality, realistic outputs, even objects that are difficult to render, such as hands.
Also: I just tried Google's ImageFX AI image generator, and I'm shocked at how good it is
The tool boasts a unique feature, expressive chips, that make it easier to refine your prompts or generate new ones via dropdowns, which highlight parts of your prompt and suggest different word changes to modify your output.
ImageFX also includes suggestions for the style you'd like your image rendered in, such as photorealistic, 35mm film, minimal, sketch, handmade, and more. This combination of features makes ImageFX the perfect for beginners who want to experiment.
ImageFX from Google: Powered by: Imagen 2 | Access via: Website | Output: 4 images | Price: free
DreamStudio by Stability AI
Best ai image generator for customization.
- Accepts specific instruction
- Open source
- More entries for customization
- Paid credits
- Need to create an account
Stability AI created the massively popular, open-sourced, text-to-image generator, Stable Diffusion. Users can download the tool and use it at no cost. However, using this tool typically requires technical skill.
Also : How to use Stable Diffusion AI to create amazing images
To make the technology readily accessible to everyone (regardless of skill level), Stability AI created DreamStudio, which incorporates Stable Diffusion in a UI that is easy to understand and use.
One of the standouts of the platform is that it includes many different entries for customization, including a "negative prompt" where you can delineate the specifics of what you'd like to avoid in the final image. You can also easily change the image ratio -- that's a key feature, as most AI image generators automatically deliver 1:1.
DreamStudio features: Powered by: SDXL 1.0 by Stability AI | Access via: Website | Output: 1 image per 2 credits | Price: $1 per 100 credits | Credits: 25 free credits when you open an account; buy purchase once you run out
Dream by WOMBO
Best ai image generator for your phone.
- Remix your own images
- Multiple templates
- One image per prompt
- Subscription cost for full access
This app took the first-place spot for the best overall app in Google Play's 2022 awards , and it has five stars on Apple's App Store with 141.6K ratings. With the app, you can create art and images with the simple input of a quick prompt.
An added plus is this AI image generator allows you to pick different design styles such as realistic, expressionist, comic, abstract, fanatical, ink, and more.
Also : How to use Dream by WOMBO to generate artwork in any style
In addition to the app, the tool has a free desktop mobile version that is simple to use. If you want to take your use of the app to the next level, you can pay $90 per year or $10 per month.
Dream by WOMBO f eatures: Powered by: WOMBO AI's machine-learning algorithm | Access via: Mobile and desktop versions | Output: 1 image with a free version, 4 with a paid plan | Price: Free limited access
Best no-frills AI image generator
- Unlimited access
- Simple to use
- Longer wait
- Inconsistent images
Despite originally being named DALL-E mini, this AI image generator is NOT affiliated with OpenAI or DALL-E 2. Rather, it is an open-source alternative. However, the name DALL-E 2 mini is somewhat fitting as the tool does everything DALL-E 2 does, just with less precise renditions.
Also : How to use Craiyon AI (formerly known as DALL-E mini)
Unlike DALL-E 2, the outputs from Craiyon lack quality and take longer to render (approximately a minute). However, because you have unlimited prompts, you can continue to tweak the prompt until you get your exact vision. The site is also simple to use, making it perfect for someone wanting to experiment with AI image generators. It also generates six images, more than any other chatbot listed.
Craiyon f eatures: Powered by: Their model | Access via : Craiyon website | Output: 6 images per prompt | Price: Free, unlimited prompts
Best AI image generator for highest quality photos
- Very high-quality outputs
- Discord community
- Monthly cost
- Confusing to set up
I often play around with AI image generators because they make it fun and easy to create digital artwork. Despite all my experiences with different AI generators, nothing could have prepared me for Midjourney -- in the best way.
The output of the image was so crystal clear that I had a hard time believing it wasn't an actual picture that someone took of my prompt. This software is so good that it has produced award-winning art .
However, I think Midjourney isn't user-friendly and it confuses me. If you also need extra direction, check out our step-by-step how-to here: How to use Midjourney to generate amazing images and art .
Another problem with the tool is that you may not access it for free. When I tried to render images, I got this error message: "Due to extreme demand, we can't provide a free trial right now. Please subscribe to create images with Midjourney."
To show you the quality of renditions, I've included a close-up below from a previous time I tested the generator. The prompt was: "A baby Yorkie sitting on a comfy couch in front of the NYC skyline."
Midjourney f eatures: Powered by: Midjourney; utilizes Discord | Access via: Discord | Output: 4 images per prompt | Price: Starts at $10/month
Adobe Firefly
Best ai image generator if you have a reference photo.
- Structure and Style Reference
- Commercial-safe
- Longer lag than other generators
- More specific prompts required
Adobe has been a leader in developing creative tools for creative and working professionals for decades. As a result, it's no surprise that its image generator is impressive. Accessing the generator is easy. Just visit the website and type the prompt of the image you'd like generated.
Also: This new AI tool from Adobe makes generating the images you need even simpler
As you can see above, the images rendered of the Yorkies are high-quality, realistic, and detailed. Additionally, the biggest standout features of this chatbot are its Structure Reference and Style Reference features.
Structure Reference lets users input an image they want the AI model to use as a template. The model then uses this structure to create a new image with the same layout and composition. Style Reference uses an image as a reference to generate a new image in the same style.
These features are useful if you have an image you'd like the new, generated image to resemble, for example, a quick sketch you drew or even a business logo or style you'd like to keep consistent.
Another perk is that Adobe Firefly was trained on Adobe Stock images, openly licensed content, and public domain content, making all the images generated safe for commercial use and addressing the ethics issue of image generators.
Adobe Firefly f eatures: Powered by: Firefly Image 2 | Access via: Website | Output: 4 images per prompt | P rice: Free
Generative AI by Getty Images
Best ai image generator for businesses.
- Commercially safe
- Contributor compensation program
- Personalized stock photos
- Not clear about pricing
- Not individual-friendly
One of the biggest issues with AI image generators is that they typically train their generators on content from the entirety of the internet, which means the generators use aspects of creators' art without compensation. This approach also puts businesses that use generators at risk of copyright infringement.
Generative AI by Getty Images tackles that issue by generating images with content solely from Getty Images' vast creative library with full indemnification for commercial use. The generated images will have Getty Images' standard royalty-free license, assuring customers that their content is fair to use without fearing legal repercussions.
Another pro is that contributors whose content was used to train the models will be compensated for their inclusion in the training set. This is a great solution for businesses that want stock photos that match their creative vision but do not want to deal with copyright-related issues.
ZDNET's Tiernan Ray went hands-on with the AI image generator. Although the tool did not generate the most vivid images, especially compared to DALL-E, it did create accurate, reliable, and useable stock images.
Generative AI by Getty Images f eatures: Powered by: NVIDIA Picasso | Access via: Website | Output: 4 images per prompt | P rice: Paid (price undisclosed, have to contact the team)
What is the best AI image generator?
Image Creator from Microsoft Designer is the best overall AI image generator. Like DALL-E 3, Image Creator from Microsoft Designer combines accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness, and can generate high-quality images in seconds. However, unlike DALL-E 3, this Microsoft version is entirely free.
Whether you want to generate images of animals, objects, or even abstract concepts, Image Creator from Microsoft Designer can produce accurate depictions that meet your expectations. It is highly efficient, user-friendly, and cost-effective.
Note: Prices and features are subject to change.
Which is the right AI image generator for you?
Although I crowned Image Creator from Microsoft Designer the best AI image generator overall, other AI image generators perform better for specific needs. For example, suppose you are a professional using AI image generation for your business. In that case, you may need a tool like Generative AI by Getty Images which renders images safe for commercial use.
On the other hand, if you want to play with AI art generating for entertainment purposes, Craiyon might be the best option because it's free, unlimited, and easy to use.
How did I choose these AI image generators?
To find the best AI image generators, I tested each generator listed and compared their performance. The factors that went into testing performance included UI/UX, image results, cost, speed, and availability. Each AI image generator had different strengths and weaknesses, making each one the ideal fit for individuals as listed next to my picks.
What is an AI image generator?
An AI image generator is software that uses AI to create images from user text inputs, usually within seconds. The images vary in style depending on the capabilities of the software, but can typically render an image in any style you want, including 3D, 2D, cinematic, modern, Renaissance, and more.
How do AI image generators work?
Like any other AI model, AI image generators work on learned data they are trained with. Typically, these models are trained on billions of images, which they analyze for characteristics. These insights are then used by the models to create new images.
Are there ethical implications with AI image generators?
AI image generators are trained on billions of images found throughout the internet. These images are often artworks that belong to specific artists, which are then reimagined and repurposed by AI to generate your image. Although the output is not the same image, the new image has elements of the artist's original work not credited to them.
Are there DALL-E 3 alternatives worth considering?
Contrary to what you might think, there are many AI image generators other than DALL-E 3. Some tools produce even better results than OpenAI's software. If you want to try something different, check out one of our alternatives above or the three additional options below.
Nightcafe is a multi-purpose AI image generator. The tool is worth trying because it allows users to create unique and original artwork using different inputs and styles, including abstract, impressionism, expressionism, and more.
Canva is a versatile and powerful AI image generator that offers a wide range of options within its design platform. It allows users to create professional-looking designs for different marketing channels, including social media posts, ads, flyers, brochures, and more.
Artificial Intelligence
The best ai chatbots: chatgpt isn't the only one worth trying, google and mit launch a free generative ai course for teachers, dall-e adds new ways to edit and create ai-generated images. learn how to use it.
Generate accurate Chicago citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- Chicago Style
- How to Cite an Image in Chicago Style | Format & Examples
How to Cite an Image in Chicago Style | Format & Examples
Published on May 25, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 9, 2024.
Chicago Citation Generator
In Chicago notes and bibliography style , it’s recommended to just cite images in notes, omitting them from the bibliography. List an image in your bibliography only if you cite it frequently, if it’s essential to your argument, or if your university requires you to.
Follow the format shown below to create a note and—if necessary—a bibliography entry for an image viewed online. Make sure to cite the page where the image is hosted, not, for example, the Google search results where you found it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing an artwork from a museum, citing an image from a book, image citations in chicago author-date style, frequently asked questions about chicago style citations.
When you viewed an artwork in person at a museum, gallery, or other location, provide information about the institution housing it. Include a URL if the museum website has a page dedicated to the artwork.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
An image you encountered in a book , journal article , or other print source should be cited by first listing information about the image itself, then listing information about the source it was contained in, including the page number where the image can be found.
Use italics for the title an image originally created outside the context of the book or article (e.g., an artwork) and quotation marks for the title of an image original to the book or article (e.g., an infographic). Use plain text to describe an untitled image.
An example citation of an artwork from a book is shown below.
In Chicago author-date style , an in-text citation for an image consists of the author’s last name and the year the image was created.
These citations correspond to entries in your reference list. Reference list entries are similar to bibliography entries, except that the year comes immediately after the author’s name.
- Online image
- Museum artwork
- Image from a book
In Chicago style , when you don’t just refer to an image but actually include it in your (research) paper , the image should be formatted as a figure. Place the figure before or after the first paragraph where it is mentioned. Refer to figures by their numbers in the text (e.g., “see fig. 1”).
Below the figure, place a caption providing the figure number followed by a period (e.g., “Figure 1.”), a reference to the source (if you didn’t create the image yourself), and any relevant information to help the reader understand the image (if needed).
The caption is single-spaced and left-aligned, and followed by a blank line before the continuation of the main text.
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
In a Chicago footnote citation , when the author of a source is unknown (as is often the case with websites ), start the citation with the title in a full note. In short notes and bibliography entries, list the organization that published it as the author.
In Chicago author-date style , treat the organization as author in your in-text citations and reference list.
When an online source does not list a publication date, replace it with an access date in your Chicago footnotes and your bibliography :
If you are using author-date in-text citations , or if the source was not accessed online, replace the date with “n.d.”
In Chicago notes and bibliography style , the usual standard is to use a full note for the first citation of each source, and short notes for any subsequent citations of the same source.
However, your institution’s guidelines may differ from the standard rule. In some fields, you’re required to use a full note every time, whereas in some other fields you can use short notes every time, as long as all sources are listed in your bibliography . If you’re not sure, check with your instructor.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, April 09). How to Cite an Image in Chicago Style | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/chicago-style/image-citations/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite a website in chicago style | formats & examples, how to cite a book in chicago style | format & examples, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: openbias: open-set bias detection in text-to-image generative models.
Abstract: Text-to-image generative models are becoming increasingly popular and accessible to the general public. As these models see large-scale deployments, it is necessary to deeply investigate their safety and fairness to not disseminate and perpetuate any kind of biases. However, existing works focus on detecting closed sets of biases defined a priori, limiting the studies to well-known concepts. In this paper, we tackle the challenge of open-set bias detection in text-to-image generative models presenting OpenBias, a new pipeline that identifies and quantifies the severity of biases agnostically, without access to any precompiled set. OpenBias has three stages. In the first phase, we leverage a Large Language Model (LLM) to propose biases given a set of captions. Secondly, the target generative model produces images using the same set of captions. Lastly, a Vision Question Answering model recognizes the presence and extent of the previously proposed biases. We study the behavior of Stable Diffusion 1.5, 2, and XL emphasizing new biases, never investigated before. Via quantitative experiments, we demonstrate that OpenBias agrees with current closed-set bias detection methods and human judgement.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Amanda Hoover
Students Are Likely Writing Millions of Papers With AI
Students have submitted more than 22 million papers that may have used generative AI in the past year, new data released by plagiarism detection company Turnitin shows.
A year ago, Turnitin rolled out an AI writing detection tool that was trained on its trove of papers written by students as well as other AI-generated texts. Since then, more than 200 million papers have been reviewed by the detector, predominantly written by high school and college students. Turnitin found that 11 percent may contain AI-written language in 20 percent of its content, with 3 percent of the total papers reviewed getting flagged for having 80 percent or more AI writing. (Turnitin is owned by Advance, which also owns Condé Nast, publisher of WIRED.) Turnitin says its detector has a false positive rate of less than 1 percent when analyzing full documents.
ChatGPT’s launch was met with knee-jerk fears that the English class essay would die . The chatbot can synthesize information and distill it near-instantly—but that doesn’t mean it always gets it right. Generative AI has been known to hallucinate , creating its own facts and citing academic references that don’t actually exist. Generative AI chatbots have also been caught spitting out biased text on gender and race . Despite those flaws, students have used chatbots for research, organizing ideas, and as a ghostwriter . Traces of chatbots have even been found in peer-reviewed, published academic writing .
Teachers understandably want to hold students accountable for using generative AI without permission or disclosure. But that requires a reliable way to prove AI was used in a given assignment. Instructors have tried at times to find their own solutions to detecting AI in writing, using messy, untested methods to enforce rules , and distressing students. Further complicating the issue, some teachers are even using generative AI in their grading processes.
Detecting the use of gen AI is tricky. It’s not as easy as flagging plagiarism, because generated text is still original text. Plus, there’s nuance to how students use gen AI; some may ask chatbots to write their papers for them in large chunks or in full, while others may use the tools as an aid or a brainstorm partner.
Students also aren't tempted by only ChatGPT and similar large language models. So-called word spinners are another type of AI software that rewrites text, and may make it less obvious to a teacher that work was plagiarized or generated by AI. Turnitin’s AI detector has also been updated to detect word spinners, says Annie Chechitelli, the company’s chief product officer. It can also flag work that was rewritten by services like spell checker Grammarly, which now has its own generative AI tool . As familiar software increasingly adds generative AI components, what students can and can’t use becomes more muddled.
Detection tools themselves have a risk of bias. English language learners may be more likely to set them off; a 2023 study found a 61.3 percent false positive rate when evaluating Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) exams with seven different AI detectors. The study did not examine Turnitin’s version. The company says it has trained its detector on writing from English language learners as well as native English speakers. A study published in October found that Turnitin was among the most accurate of 16 AI language detectors in a test that had the tool examine undergraduate papers and AI-generated papers.

Andy Greenberg
Charlie Wood

Brian Barrett

Schools that use Turnitin had access to the AI detection software for a free pilot period, which ended at the start of this year. Chechitelli says a majority of the service’s clients have opted to purchase the AI detection. But the risks of false positives and bias against English learners have led some universities to ditch the tools for now. Montclair State University in New Jersey announced in November that it would pause use of Turnitin’s AI detector. Vanderbilt University and Northwestern University did the same last summer.
“This is hard. I understand why people want a tool,” says Emily Isaacs, executive director of the Office of Faculty Excellence at Montclair State. But Isaacs says the university is concerned about potentially biased results from AI detectors, as well as the fact that the tools can’t provide confirmation the way they can with plagiarism. Plus, Montclair State doesn’t want to put a blanket ban on AI, which will have some place in academia. With time and more trust in the tools, the policies could change. “It’s not a forever decision, it’s a now decision,” Isaacs says.
Chechitelli says the Turnitin tool shouldn’t be the only consideration in passing or failing a student. Instead, it’s a chance for teachers to start conversations with students that touch on all of the nuance in using generative AI. “People don’t really know where that line should be,” she says.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: The best and weirdest stories from WIRED’s archive
Jeffrey Epstein’s island visitors exposed by data broker
8 Google employees invented modern AI. Here’s the inside story
The crypto fraud kingpin who almost got away
It's shadow time! How to view the solar eclipse, online and in person

Steven Levy

Reece Rogers

Estelle Erasmus

Will Knight
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
3 Abu Ghraib prison detainees finally get their day in a U.S. court
Twenty years after images of American soldiers abusing detainees at Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq were published, three men are getting their day in a U.S. court.
LEILA FADEL, HOST:
More than 20 years after they were tortured at a U.S. military prison in Iraq, three survivors of Abu Ghraib get their day in court today. They are suing a U.S.-based military contractor, CACI, accusing it of enabling and participating in their abuse. That torture was made public in disturbing images released two decades ago this month. They include male prisoners stacked in naked pyramids and U.S. soldiers smiling as prisoners were being abused. Matthew Barakat is a reporter with the Associated Press who is covering the lawsuit, and he joins us now. Good morning.
MATTHEW BARAKAT: Good morning.
FADEL: So who are the three men who filed these lawsuits?
BARAKAT: Well, they were all detainees at Abu Ghraib, at what they called the hard site. One of them was a farmer. One of them was a former Al-Jazeera reporter. And they were all at that prison from anywhere from two months to a year. And they say that they endured some of that sort of shocking treatment that we saw in the photos that you were just describing.
FADEL: So what exactly do they say happened to them at Abu Ghraib? And how do they say CACI was involved?
BARAKAT: What they - it's sort of a list of horribles. They're talking about sexual assaults, beatings, being dragged around on a rope naked, stress positions, being forced to wear women's underwear, threatened with dogs, all those sorts of things. And then the second part of your question.
FADEL: How do they say CACI was involved?
BARAKAT: You know, they say that CACI was a contractor that supplied interrogators that questioned the detainees at this prison, and they don't allege that the CACI interrogators were directly inflicting this abuse. But they say that they set up the conditions, that some of those interrogators asked the military police to soften up detainees for interrogations. And so they say that CACI filled that role.
FADEL: Now, this was abuse by U.S. soldiers. So why are they suing a military contractor rather than the U.S. government?
BARAKAT: Well, there's questions about whether or not the U.S. government would have immunity from a lawsuit. And that may have been an assumption. And as this has been bouncing around for 16 years, CACI had claimed that it would also have what it called derivative immunity. And so in one of the times this was bouncing around through the case, the judge in this case was Leonie Brinkema, and she wrote a long sort of first of its kind ruling about immunity in this case. And what she said is that the U.S. government actually doesn't have immunity when you're talking about these kind of violations of international norms like torture. She said the government doesn't have immunity, therefore CACI doesn't have immunity. But, initially, one of the assumptions would be that the government enjoys immunity from these kind of lawsuits.
FADEL: Now, this torture came to light 20 years ago, and this case was filed in 2008. So why has it taken so long to get to court?
BARAKAT: A lot of appeals - CACI has filed, I think, more than 20 motions to have the case dismissed. In the early years, the judge that was hearing the case did have it dismissed, said that it couldn't be dealt with. It should be - if there was a suit, it should be filed in Iraq. He later ruled that it was what they call a political question and that, you know, courts can't decide that.
FADEL: Matthew Barakat is a reporter with the Associated Press. Thank you so much for your time.
BARAKAT: Sure.
FADEL: We reached out to CACI for comment and have not received a response.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Engineering 190w - spring 2024 - tateri sections.
- Assignments
- Conducting Research
- Using Databases
- Specialized Resources
- Media Resources Center
- All about AI & Writing
Connecting from Off-Campus
Researching from home? Use the VPN Links below to access our databases. Instructions on connecting from off-campus should be followed - for additional information, consult with OIT at 949-824-2222
Software VPN - strongly urge you to rely upon this method if you use the same computer all the time - less hiccups and complications
More Information Regarding the VPN
Ask a Librarian
For Chat, Text, eMail and to schedule a Research Consultation with a Librarian, use:
Ask A Librarian
- Mobile Access Optimized @ UCI
Course Introduction
This class focuses on your career as an Engineering major and allows you to focus on communicating the major issues that you have focused on and and how to jump-start your career in practice as an Engineer or if you continue your graduate education. It introduces you to:
- the work style of engineers in different settings - promoting empathy and compassion with a better understanding of diversity
- how engineering information is released using specialized content such as patents, standards, papers, proceedings, journal literature, book content and related materials
- how written and verbal communication, both technical and casual conducted individually and within groups can determine the outcomes you want for success
- engineering ethics
- the value of sourcing & correctly citing your information, evaluating it carefully, and being informed about misinformation
- thinking about presentation, using images, prompts, and addressing different audiences
- how engineering is supported by diversity, equity, inclusion and social justice
There is an accompanying PowerPoint presentation below that reviews technical communication issues with examples of resources highlighting the forms and formats of engineering literature.
- Powerpoint presentation for this course
Evaluating Information
When using Online or Internet Resources , consider Search Engines vs. metasites - evaluate resource - be attentive to domain -may include .com, .edu, .org, .gov, .net
Evaluation of evaluating strategies - there are many different strategies and this guide highlights two, CRAAP and S.I.F.T. and at the end I will also note some other methods - but consider the following criteria:
Applying the CRAAP Test - for Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, Purpose
https://www.csuchico.edu/lins/handouts/eval_websites.pdf
Goal is to establish relevancy. The evaluation criteria includes these issues:
Scope of coverage
Currency – be able to distinguish currency from timeliness
Relevance – meaningful to what audience; at what level; will you cite it as authoritative?
Authority – stem is author – establishes the source of the information – author/publisher/source/sponsor; organizational affiliations & credentials; contact information
Accuracy – reliability, correctness of content; supported by evidence; is it verifiable; is tone unbiased, objective, impartial & free of emotion; free of errors?
Purpose – are hypotheses and authors’ intentions clear? Why is content important – to inform, teach, sell, entertain or persuade? Any political, ideological, cultural, religious, institutional or personal biases?
Ease of use – Capturing, copying, citing; design & presentation
Another method to evaluate is S.I.F.T - so:
- CCOW - for Credentials, Claims, Objectives
- RADAR Test - Relevancy, Authority, Date, Appearance, Reason for Writing
Remember when we cite or quote, we are CHOOSING to bring other voices into our paper or scholarly work.
Let's ask, Why we cite?
- to give credit to authors
- to show your work
- to be a responsible researcher
- to avoid plagiarism
Often called Citation Chasing we have the standard two parts:
- Backward chasing - refers to the set of references or bibliography of a work that has influenced current citation
- Forward chasing - refers to the method of future citations that referenced the specific work - may be more nuanced or specific but also provides new applications
Think of 5 criteria you use to evaluate information and what questions to you ask yourself to determine relevancy or whether your information need is met?
- consider that we are on information overload - how to distinguish between accurate information & misinformation
- stop - open up a browser tab & enter a search term
- investigate the source(s) - who wrote or said this? who is the author? what process or methodology was used to produce this information and what systems are in place with this source to catch mistakes and correct them?
- find better coverage - consult other sources, demonstrating the historical context, disciplinary approaches, are there patterns of perspectives or dominant ideas that emerge, and what voices are missing?
- trace things back to the original context - is the evidence misquoted or misrepresented; where is the data from & how was it collected and can we make legitimate conclusions from it?
- watch this video on lateral reading strategies (3.47) from the Civic Online Reasoning curriculum, co-sponsored by the Stanford History Education Group
Citing Sources
In order to avoid plagiarism and to honor intellectual integrity, make sure that you cite the authority in a bibliographic reference to anything that is not your original writing or creation - that means when you quote a passage, insert a graphic image, figures, or illustration, that you cite the original source. The style manual you choose to follow should document how you cite electronic resources. Examples of resources that support multiple style manuals is noted in the Quick Reference Guide for Writing . Standard formats include the following reference elements:
Standard formats include the following reference elements:
For a Journal article or conference proceeding:
Author(s) - last name, first name, MI, - [include multiple authors if noted] (date), Title of article. Source of Article/Title of Journal. volume #, (issue #): pages. If it is only an electronic publication with no reference to print pages, then you cite the DOI - Digital Object Identifier and the date last visited.
If it is a conference paper, then you cite the Source of the Publication, Title of conference, date and location of meeting.
For books, the format is:
Author, editor of volume or chapter, (imprint date). Title of chapter in Title of Book, edited by editor if different. City of Publication: Publisher, page references. Note if it is an eBook.
For full volume:
Author, (date). Title of Book. City of Publisher, Publisher: pages
IEEE Citation Style - The IEEE Editorial Style Manual (2019) notes the specific ways that references and footnotes are to be handled in submissions to IEEE publications. The IEEE Referencing Guide notes practices and they are different than other styles, so follow this and perhaps these guides from the following university libraries will give more examples: Murdoch University o r Purdue University's Owl series for IEEE.
MLA Style Format is documented in the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 2009 at any of the UCI Library Reference Desks at REF LIB 2369 G53 2009
APA Style Format - The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 7th ed., 2020 is at every Reference Desk - REF BF 76.7 P83 2020. It is NOT currently available online. A cheatsheet with many examples of how to cite different types of sources in many formats can be consulted. Additional recommended resources are noted at this site.
Chicago Style Manual - an online version of the Chicago Style Manual is now available
Other hints:
- very important now
- when interviewing for job
Bibliographic Management Software
BIBLIOGRAPHIC MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE - allows you to discover, find, manage, recall and apply the citations you retrieve from all formats of work - journal articles, book chapters, edited volumes, standards, specifications, patents, conference papers & proceedings, lectures, etc. Neither Zotero nor EndNote support BibTeX or LaTeX, only the usual wordprocessing languages or Legal Style Manual. For additional information, please visit the Bibliographic Management Software page.
- EndNote EndNote is a robust product for Bibliographic Management Software, but it needs to be purchased and is dependent upon access on one computer. EndNote Web is a modified web-based product available via the Web of Science platform. more... less... There is an abbreviated free web version available via the Web of Science Databases. However, there is no UCI campus license to the full coverage of EndNote and if one chooses to use EndNote, it is recommended that one go to the UCI Bookstore and purchase it with an academic discount, and load it on a personal computer or laptop. Currently the Libraries provide access to EndNote version 6 in the Multimedia Resources Center (MRC), Langson Library Technology Enhanced Classroom (TEC), Interactive Learning Center (ILC), and in the Grunigen Medical Library at the UCI Medical Center. It is recommended that you take the trial on the Registration Page first before you invest in this product to see how it supports your workstyle.
- Mendeley Mendeley is a free reference manager and academic social network that can help you organize your research, collaborate with others online, and discover the latest research. Software can be downloaded on a specific computer.
- Zotero Zotero is a free extension for Firefox 2.0, which enables browsers to capture citation information from Web pages quickly and easily. Must be downloaded to personal computer. Supports nonconventional scripts & images well. more... less... Researchers can add searchable notecards to their citations, organize them with tags, attach files to them, arrange them into folders, or export them as formatted citations. Zotero can capture a single citation or an entire results list of sources, which researchers can work with either online or offline.
- Complore Complore encourages scholars and students to save their lectures, articles, and papers in the bibliographic bookmarking service. Researchers can join groups, subscribe to a site-wide RSS feed, and generate BibTeX records.
- Bibsonomy Bibsonomy is a scholarly bookmarking service that offers its users related tags, the ability to create groups, and the ability to export records to BibTeX. more... less... Bibsonomy members can construct friends networks, import their del.icio.us links, generate private entries, and import their BibTeX libraries.
- Mathematica Provides quick links to support documents for Mathematica software.
Organizing and Managing Images
- Digital Image Collections Wikispaces This Wiki is a resource of Free- and Fair Use digital image collections that are available for anyone to use for educational or personal purposes.
- Google Images If you like to search Google for information, then you are likely to find Google Images a good source for images.
- Flickr - The Commons World's public photography collection / archive. Library of Congress, various museums, and libraries have also posted photographs for you to view
- UCI Subject Guide for Images Lists and describes many sources for a variety of images.
Liaison Librarian

- Next: Assignments >>
- Last Updated: Apr 13, 2024 5:34 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/ENGR190W_Tateri_Spring2024
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
Prestigious cancer research institute has retracted 7 studies amid controversy over errors

Seven studies from researchers at the prestigious Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have been retracted over the last two months after a scientist blogger alleged that images used in them had been manipulated or duplicated.
The retractions are the latest development in a monthslong controversy around research at the Boston-based institute, which is a teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School.
The issue came to light after Sholto David, a microbiologist and volunteer science sleuth based in Wales, published a scathing post on his blog in January, alleging errors and manipulations of images across dozens of papers produced primarily by Dana-Farber researchers . The institute acknowledged errors and subsequently announced that it had requested six studies to be retracted and asked for corrections in 31 more papers. Dana-Farber also said, however, that a review process for errors had been underway before David’s post.
Now, at least one more study has been retracted than Dana-Farber initially indicated, and David said he has discovered an additional 30 studies from authors affiliated with the institute that he believes contain errors or image manipulations and therefore deserve scrutiny.
The episode has imperiled the reputation of a major cancer research institute and raised questions about one high-profile researcher there, Kenneth Anderson, who is a senior author on six of the seven retracted studies.
Anderson is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and the director of the Jerome Lipper Multiple Myeloma Center at Dana-Farber. He did not respond to multiple emails or voicemails requesting comment.
The retractions and new allegations add to a larger, ongoing debate in science about how to protect scientific integrity and reduce the incentives that could lead to misconduct or unintentional mistakes in research.
The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute has moved relatively swiftly to seek retractions and corrections.
“Dana-Farber is deeply committed to a culture of accountability and integrity, and as an academic research and clinical care organization we also prioritize transparency,” Dr. Barrett Rollins, the institute’s integrity research officer, said in a statement. “However, we are bound by federal regulations that apply to all academic medical centers funded by the National Institutes of Health among other federal agencies. Therefore, we cannot share details of internal review processes and will not comment on personnel issues.”
The retracted studies were originally published in two journals: One in the Journal of Immunology and six in Cancer Research. Six of the seven focused on multiple myeloma, a form of cancer that develops in plasma cells. Retraction notices indicate that Anderson agreed to the retractions of the papers he authored.
Elisabeth Bik, a microbiologist and longtime image sleuth, reviewed several of the papers’ retraction statements and scientific images for NBC News and said the errors were serious.
“The ones I’m looking at all have duplicated elements in the photos, where the photo itself has been manipulated,” she said, adding that these elements were “signs of misconduct.”
Dr. John Chute, who directs the division of hematology and cellular therapy at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and has contributed to studies about multiple myeloma, said the papers were produced by pioneers in the field, including Anderson.
“These are people I admire and respect,” he said. “Those were all high-impact papers, meaning they’re highly read and highly cited. By definition, they have had a broad impact on the field.”
Chute said he did not know the authors personally but had followed their work for a long time.
“Those investigators are some of the leading people in the field of myeloma research and they have paved the way in terms of understanding our biology of the disease,” he said. “The papers they publish lead to all kinds of additional work in that direction. People follow those leads and industry pays attention to that stuff and drug development follows.”
The retractions offer additional evidence for what some science sleuths have been saying for years: The more you look for errors or image manipulation, the more you might find, even at the top levels of science.
Scientific images in papers are typically used to present evidence of an experiment’s results. Commonly, they show cells or mice; other types of images show key findings like western blots — a laboratory method that identifies proteins — or bands of separated DNA molecules in gels.
Science sleuths sometimes examine these images for irregular patterns that could indicate errors, duplications or manipulations. Some artificial intelligence companies are training computers to spot these kinds of problems, as well.
Duplicated images could be a sign of sloppy lab work or data practices. Manipulated images — in which a researcher has modified an image heavily with photo editing tools — could indicate that images have been exaggerated, enhanced or altered in an unethical way that could change how other scientists interpret a study’s findings or scientific meaning.
Top scientists at big research institutions often run sprawling laboratories with lots of junior scientists. Critics of science research and publishing systems allege that a lack of opportunities for young scientists, limited oversight and pressure to publish splashy papers that can advance careers could incentivize misconduct.
These critics, along with many science sleuths, allege that errors or sloppiness are too common , that research organizations and authors often ignore concerns when they’re identified, and that the path from complaint to correction is sluggish.
“When you look at the amount of retractions and poor peer review in research today, the question is, what has happened to the quality standards we used to think existed in research?” said Nick Steneck, an emeritus professor at the University of Michigan and an expert on science integrity.
David told NBC News that he had shared some, but not all, of his concerns about additional image issues with Dana-Farber. He added that he had not identified any problems in four of the seven studies that have been retracted.
“It’s good they’ve picked up stuff that wasn’t in the list,” he said.
NBC News requested an updated tally of retractions and corrections, but Ellen Berlin, a spokeswoman for Dana-Farber, declined to provide a new list. She said that the numbers could shift and that the institute did not have control over the form, format or timing of corrections.
“Any tally we give you today might be different tomorrow and will likely be different a week from now or a month from now,” Berlin said. “The point of sharing numbers with the public weeks ago was to make clear to the public that Dana-Farber had taken swift and decisive action with regard to the articles for which a Dana-Farber faculty member was primary author.”
She added that Dana-Farber was encouraging journals to correct the scientific record as promptly as possible.
Bik said it was unusual to see a highly regarded U.S. institution have multiple papers retracted.
“I don’t think I’ve seen many of those,” she said. “In this case, there was a lot of public attention to it and it seems like they’re responding very quickly. It’s unusual, but how it should be.”
Evan Bush is a science reporter for NBC News. He can be reached at [email protected].

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Citing an image in APA Style. In an APA Style reference entry for an image found on a website, write the image title in italics, followed by a description of its format in square brackets. Include the name of the site and the URL. The APA in-text citation just includes the photographer's name and the year. APA format. Author last name, Initials.
An APA image citation includes the creator's name, the year, the image title and format (e.g. painting, photograph, map), and the location where you accessed or viewed the image. Last name, Initials. ( Year ). Image title [ Format ]. Site Name. or Museum, Location. URL.
Copy the citation and add under the image. For example, an image of a lake from Creative Commons has this citation next to it: "lake" by barnyz is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0. 2. Include a marker, such as Image 1. or Figure 1., and in the reference section, include full citation information with the corresponding number. 3.
Citing vs. 'reproducing' This guide provides information on how to cite images and photographs. However, reproducing the image inside of your essay or research paper might require additional permissions and/or attributions. Section 12.15 of the Publication Manual provides more information on reproducing images and graphics.
Image Credits (Non-Academic Style) A credit statement can be an alternative to a full academic citation, and especially useful when writing for the Web. Provide a link to the image if you can. General Format: Title by Creator, date (if available), via source (Creative Common License Type, if applicable). Example:
You can cite images in your research paper either at the end, in between the topics, or in a separate section for all the non-textual elements used in the paper. You can choose to insert images in between texts, but you need to provide the in-text citations for every image that has been used. Additionally, you need to attach the name ...
The only official, authorized book on MLA style. The new, ninth edition builds on the MLA's unique approach to documenting sources using a template of core elements facts, common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date that allows writers to cite any type of work, from books, e-books, and journal articles in databases to song lyrics, online images, social media posts ...
Knowing how to cite an image in APA format, whether it's classic art or an infographic, is an essential part of writing a research paper.The seventh edition of APA Style requires that, for photos and images, you list the creator's name, image title, year of origin, type of media, and location from which you accessed the image (such as a website URL or museum name).
How to Cite an Image. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an image, list the creator of the image, the title of the image, the date of composition, and the location of the image, which would be a physical location if you viewed the image in person. If you viewed the image online, provide the name of the website containing the image and ...
Today, finding and citing a digital or online image is simple. You'll need the following information: Photographer's name. (Year published) Title of the photograph, italizised. Available at: URL (Accessed: the date you sourced the image) In-text citation structure and example: (Photographer's name, Year published) OR.
In-Text Citation. Reference List & Notes. Copied Image (reproduced within the document) For Figure 2 Pilotus Flowers (Family Amaranthaceae) Example: Species such as the Pilotus flower (Figure 2) are ideal for weed control due to their spreading habit. Note: No need to cite the author of an image when you refer to an image figure within your text.
Here is some basic information you might need to cite an image: Creator name. Title of the work. Date work was created. Source (URL and date of access) Format. Image ID number. If you find an image in a book you will need that book's author, title, publisher information, date, and page, figure, or plate number of the reproduction.
Reasonable use of images and media in teaching, course papers, and graduate theses/dissertations is generally covered by fair use. Fair Use; Documenting and Citing Images; ... Please note that this is advice on best practices and considerations in documenting and citing images and non-print materials. It does not represent legal advice on ...
Image: The image portion of the figure would be the chart, graph, photograph, drawing, or other illustration itself. Legend: A figure legend, or key, if present should be positioned with the border of the figure and explain any symbols in the figure. Note: Add Note. if needed under the image. There are three types of notes: general, specific ...
Citing a photograph you took. The photo would be considered as part of a "personal collection.". The example below follows guidance found in the MLA Style Center. Works Cited. Structure. Your Last Name, First Name. Image description or Image Title. Day Month Year taken. Author's personal collection.
MLA Style. MLA Caption Style. When citing an image, the caption should be labeled as Figure (usually abbreviated Fig.), assigned a number, and given a title or caption. For images found in a book or journal, include the publication information of the text. A caption ordinarily appears directly below the illustration and have the same one-inch ...
Citing In a Research Paper. ... Chicago), you should include a full citation in that format below the image. Alternatively, you can add a footnote labeling each image (for example, "Image 1") and create a reference slide at the end of your presentation with corresponding image numbers and full citations.
The pages outlines examples of how to cite images, tables and diagrams using the Harvard Referencing method. An image found online. In-text citations. Mention the image in the text and cite the author and date: The cartoon by Frith (1968) describes ... If the image has no named author, cite the full name and date of the image:
Citing Images in a Presentation. MLA gives two different ways to cite an images in a presentation or paper depending on how you are using the image in your presentation. The difference depends on whether the image is just for illustration or decoration (a stand along image), or if you're going to refer to this image in your presentation (the ...
Cite the image creator in the caption and year of publication. The creator may be different from the author of the web page or blog. They may be individual people or an organisation. Figure 2 below gives an example of an image with a corporate author: Figure 2. NASA astronaut Tim Kopra on Dec. 21 spacewalk (NASA, 2015)
Citations of figures / images in the paper must be in numerical order. Place it below the figure / image. Citations to figures in text always carry the abbreviation "Fig." followed by the figure number.
The top ten most cited papers in policy documents are dominated by economics research. When economics studies are excluded, a 1997 Nature paper 2 about Earth's ecosystem services and natural ...
Discover the latest AI image generators that can create stunning visuals from text prompts. Compare DALL-E with other fun and creative alternatives.
Use plain text to describe an untitled image. An example citation of an artwork from a book is shown below. Chicago bibliography. Author last name, First name. Image Title. Year. In Author first name Last name, Book Title, Page number. City: Publisher, Year. Bruegel, Pieter, the Elder.
Text-to-image generative models are becoming increasingly popular and accessible to the general public. As these models see large-scale deployments, it is necessary to deeply investigate their safety and fairness to not disseminate and perpetuate any kind of biases. However, existing works focus on detecting closed sets of biases defined a priori, limiting the studies to well-known concepts ...
Students have submitted more than 22 million papers that may have used generative AI in the past year, new data released by plagiarism detection company Turnitin shows. A year ago, Turnitin rolled ...
That torture was made public in disturbing images released two decades ago this month. They include male prisoners stacked in naked pyramids and U.S. soldiers smiling as prisoners were being abused.
the value of sourcing & correctly citing your information, evaluating it carefully, and being informed about misinformation; thinking about presentation, using images, prompts, and addressing different audiences; ... MLA Style Format is documented in the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 2009 at any of the UCI Library Reference Desks ...
Scientific images in papers are typically used to present evidence of an experiment's results. Commonly, they show cells or mice; other types of images show key findings like western blots — a ...