History Cooperative

French Revolution: History, Timeline, Causes, and Outcomes
The French Revolution, a seismic event that reshaped the contours of political power and societal norms, began in 1789, not merely as a chapter in history but as a dramatic upheaval that would influence the course of human events far beyond its own time and borders.
It was more than a clash of ideologies; it was a profound transformation that questioned the very foundations of monarchical rule and aristocratic privilege, leading to the rise of republicanism and the concept of citizenship.
The causes of this revolution were as complex as its outcomes were far-reaching, stemming from a confluence of economic strife, social inequalities, and a hunger for political reform.
The outcomes of the French Revolution, embedded in the realms of political thought, civil rights, and societal structures, continue to resonate, offering invaluable insights into the power and potential of collective action for change.
Table of Contents
Time and Location
The French Revolution, a cornerstone event in the annals of history, ignited in 1789, a time when Europe was dominated by monarchical rule and the vestiges of feudalism. This epochal period, which spanned a decade until the late 1790s, witnessed profound social, political, and economic transformations that not only reshaped France but also sent shockwaves across the continent and beyond.
Paris, the heart of France, served as the epicenter of revolutionary activity , where iconic events such as the storming of the Bastille became symbols of the struggle for freedom. Yet, the revolution was not confined to the city’s limits; its influence permeated through every corner of France, from bustling urban centers to serene rural areas, each witnessing the unfolding drama of revolution in unique ways.
The revolution consisted of many complex factions, each representing a distinct set of interests and ideologies. Initially, the conflict arose between the Third Estate, which included a diverse group from peasants and urban laborers to the bourgeoisie, and the First and Second Estates, made up of the clergy and the nobility, respectively.
The Third Estate sought to dismantle the archaic social structure that relegated them to the burden of taxation while denying them political representation and rights. Their demands for reform and equality found resonance across a society strained by economic distress and the autocratic rule of the monarchy.
As the revolution evolved, so too did the nature of the conflict. The initial unity within the Third Estate fractured, giving rise to factions such as the Jacobins and Girondins, who, despite sharing a common revolutionary zeal, diverged sharply in their visions for France’s future.
The Jacobins , with figures like Maximilien Robespierre at the helm, advocated for radical measures, including the abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of a republic, while the Girondins favored a more moderate approach.
The sans-culottes , representing the militant working-class Parisians, further complicated the revolutionary landscape with their demands for immediate economic relief and political reforms.
The revolution’s adversaries were not limited to internal factions; monarchies throughout Europe viewed the republic with suspicion and hostility. Fearing the spread of revolutionary fervor within their own borders, European powers such as Austria, Prussia, and Britain engaged in military confrontations with France, aiming to restore the French monarchy and stem the tide of revolution.
These external threats intensified the internal strife, fueling the revolution’s radical phase and propelling it towards its eventual conclusion with the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, who capitalized on the chaos to establish his own rule.
READ MORE: How Did Napoleon Die: Stomach Cancer, Poison, or Something Else?
Causes of the French Revolution
The French Revolution’s roots are deeply embedded in a confluence of political, social, economic, and intellectual factors that, over time, eroded the foundations of the Ancien Régime and set the stage for revolutionary change.
At the heart of the revolution were grievances that transcended class boundaries, uniting much of the nation in a quest for profound transformation.
Economic Hardship and Social Inequality
A critical catalyst for the revolution was France’s dire economic condition. Fiscal mismanagement, costly involvement in foreign wars (notably the American Revolutionary War), and an antiquated tax system placed an unbearable strain on the populace, particularly the Third Estate, which bore the brunt of taxation while being denied equitable representation.
Simultaneously, extravagant spending by Louis XVI and his predecessors further drained the national treasury, exacerbating the financial crisis.
The social structure of France, rigidly divided into three estates, underscored profound inequalities. The First (clergy) and Second (nobility) Estates enjoyed significant privileges, including exemption from many taxes, which contrasted starkly with the hardships faced by the Third Estate, comprising peasants , urban workers, and a rising bourgeoisie.
This disparity fueled resentment and a growing demand for social and economic justice.
Enlightenment Ideals
The Enlightenment , a powerful intellectual movement sweeping through Europe, profoundly influenced the revolutionary spirit. Philosophers such as Voltaire, Rousseau, and Montesquieu criticized traditional structures of power and authority, advocating for principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Their writings inspired a new way of thinking about governance, society, and the rights of individuals, sowing the seeds of revolution among a populace eager for change.
Political Crisis and the Estates-General
The immediate catalyst for the French Revolution was deeply rooted in a political crisis, underscored by the French monarchy’s chronic financial woes. King Louis XVI, facing dire fiscal insolvency, sought to break the deadlock through the convocation of the Estates-General in 1789, marking the first assembly of its kind since 1614.
This critical move, intended to garner support for financial reforms, unwittingly set the stage for widespread political upheaval. It provided the Third Estate, representing the common people of France, with an unprecedented opportunity to voice their longstanding grievances and demand a more significant share of political authority.
The Third Estate, comprising a vast majority of the population but long marginalized in the political framework of the Ancien Régime, seized this moment to assert its power. Their transformation into the National Assembly was a monumental shift, symbolizing a rejection of the existing social and political order.
The catalyst for this transformation was their exclusion from the Estates-General meeting, leading them to gather in a nearby tennis court. There, they took the historic Tennis Court Oath, vowing not to disperse until France had a new constitution.
This act of defiance was not just a political statement but a clear indication of the revolutionaries’ resolve to overhaul French society.
Amidst this burgeoning crisis, the personal life of Marie Antoinette , Louis XVI’s queen, became a focal point of public scrutiny and scandal.
Married to Louis at the tender age of fourteen, Marie Antoinette, the youngest daughter of Holy Roman Emperor Francis I, was known for her lavish lifestyle and the preferential treatment she accorded her friends and relatives.
READ MORE: Roman Emperors in Order: The Complete List from Caesar to the Fall of Rome
Her disregard for traditional court fashion and etiquette, along with her perceived extravagance, made her an easy target for public criticism and ridicule. Popular songs in Parisian cafés and a flourishing genre of pornographic literature vilified the queen, accusing her of infidelity, corruption, and disloyalty.
Such depictions, whether grounded in truth or fabricated, fueled the growing discontent among the populace, further complicating the already tense political atmosphere.
The intertwining of personal scandals with the broader political crisis highlighted the deep-seated issues within the French monarchy and aristocracy, contributing to the revolutionary fervor.
As the political crisis deepened, the actions of the Third Estate and the controversies surrounding Marie Antoinette exemplified the widespread desire for change and the rejection of the Ancient Régime’s corruption and excesses.
Key Concepts, Events, and People of the French Revolution
As the Estates General convened in 1789, little did the world know that this gathering would mark the beginning of a revolution that would forever alter the course of history.
Through the rise and fall of factions, the clash of ideologies, and the leadership of remarkable individuals, this era reshaped not only France but also set a precedent for future generations.
From the storming of the Bastille to the establishment of the Directory, each event and figure played a crucial role in crafting a new vision of governance and social equality.
Estates General
When the Estates General was summoned in May 1789, it marked the beginning of a series of events that would catalyze the French Revolution. Initially intended as a means for King Louis XVI to address the financial crisis by securing support for tax reforms, the assembly instead became a flashpoint for broader grievances.
Representing the three estates of French society—the clergy, the nobility, and the commoners—the Estates General highlighted the profound disparities and simmering tensions between these groups.
The Third Estate, comprising 98% of the population but traditionally having the least power, seized the moment to push for more significant reforms, challenging the very foundations of the Ancient Régime.
The deadlock over voting procedures—where the Third Estate demanded votes be counted by head rather than by estate—led to its members declaring themselves the National Assembly, an act of defiance that effectively inaugurated the revolution.
This bold step, coupled with the subsequent Tennis Court Oath where they vowed not to disperse until a new constitution was created, underscored a fundamental shift in authority from the monarchy to the people, setting a precedent for popular sovereignty that would resonate throughout the revolution.
Rise of the Third Estate
The Rise of the Third Estate underscores the growing power and assertiveness of the common people of France. Fueled by economic hardship, social inequality, and inspired by Enlightenment ideals, this diverse group—encompassing peasants, urban workers, and the bourgeoisie—began to challenge the existing social and political order.
Their transformation from a marginalized majority into the National Assembly marked a radical departure from traditional power structures, asserting their role as legitimate representatives of the French people. This period was characterized by significant political mobilization and the formation of popular societies and clubs, which played a crucial role in spreading revolutionary ideas and organizing action.
This newfound empowerment of the Third Estate culminated in key revolutionary acts, such as the storming of the Bastille in July 1789, a symbol of royal tyranny. This event not only demonstrated the power of popular action but also signaled the irreversible nature of the revolutionary movement.
The rise of the Third Estate paved the way for the abolition of feudal privileges and the drafting of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen , foundational texts that sought to establish a new social and political order based on equality, liberty, and fraternity.
A People’s Monarchy
The concept of a People’s Monarchy emerged as a compromise in the early stages of the French Revolution, reflecting the initial desire among many revolutionaries to retain the monarchy within a constitutional framework.
This period was marked by King Louis XVI’s grudging acceptance of the National Assembly’s authority and the enactment of significant reforms, including the Civil Constitution of the Clergy and the Constitution of 1791, which established a limited monarchy and sought to redistribute power more equitably.
However, this attempt to balance revolutionary demands with monarchical tradition was fraught with difficulties, as mutual distrust between the king and the revolutionaries continued to escalate.
The failure of the People’s Monarchy was precipitated by the Flight to Varennes in June 1791, when Louis XVI attempted to escape France and rally foreign support for the restoration of his absolute power.
This act of betrayal eroded any remaining support for the monarchy among the populace and the Assembly, leading to increased calls for the establishment of a republic.
The people’s experiment with a constitutional monarchy thus served to highlight the irreconcilable differences between the revolutionary ideals of liberty and equality and the traditional monarchical order, setting the stage for the republic’s proclamation.
Birth of a Republic
The proclamation of the First French Republic in September 1792 represented a radical departure from centuries of monarchical rule, embodying the revolutionary ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
This transition was catalyzed by escalating political tensions, military challenges, and the radicalization of the revolution, particularly after the king’s failed flight and perceived betrayal.
The Republic’s birth was a moment of immense optimism and aspiration, as it promised to reshape French society on the principles of democratic governance and civic equality. It also marked the beginning of a new calendar, symbolic of the revolutionaries’ desire to break completely with the past and start anew.
However, the early years of the Republic were marked by significant challenges, including internal divisions, economic struggles, and threats from monarchist powers in Europe.
These pressures necessitated the establishment of the Committee of Public Safety and the Reign of Terror, measures aimed at defending the revolution but which also led to extreme political repression.
Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror, from September 1793 to July 1794, remains one of the most controversial and bloodiest periods of the French Revolution. Under the auspices of the Committee of Public Safety, led by figures such as Maximilien Robespierre, the French government adopted radical measures to purge the nation of perceived enemies of the revolution.
This period saw the widespread use of the guillotine , with thousands executed on charges of counter-revolutionary activities or mere suspicion of disloyalty. The Terror aimed to consolidate revolutionary gains and protect the nascent Republic from internal and external threats, but its legacy is marred by the extremity of its actions and the climate of fear it engendered.
The end of the Terror came with the Thermidorian Reaction on 27th July 1794 (9th Thermidor Year II, according to the revolutionary calendar), which resulted in the arrest and execution of Robespierre and his closest allies.
This marked a significant turning point, leading to the dismantling of the Committee of Public Safety and the gradual relaxation of emergency measures. The aftermath of the Terror reflected a society grappling with the consequences of its radical actions, seeking stability after years of upheaval but still committed to the revolutionary ideals of liberty and equality .
Thermidorians and the Directory
Following the Thermidorian Reaction , the political landscape of France underwent significant changes, leading to the establishment of the Directory in November 1795.
This new government, a five-member executive body, was intended to provide stability and moderate the excesses of the previous radical phase. The Directory period was characterized by a mix of conservative and revolutionary policies, aimed at consolidating the Republic and addressing the economic and social issues that had fueled the revolution.
Despite its efforts to navigate the challenges of governance, the Directory faced significant opposition from royalists on the right and Jacobins on the left, leading to a period of political instability and corruption.
The Directory’s inability to resolve these tensions and its growing unpopularity set the stage for its downfall. The coup of 18 Brumaire in November 1799, led by Napoleon Bonaparte, ended the Directory and established the Consulate, marking the end of the revolutionary government and the beginning of Napoleonic rule.
While the Directory failed to achieve lasting stability, it played a crucial role in the transition from radical revolution to the establishment of a more authoritarian regime, highlighting the complexities of revolutionary governance and the challenges of fulfilling the ideals of 1789.
French Revolution End and Outcome: Napoleon’s Rise
The revolution’s end is often marked by Napoleon’s coup d’état on 18 Brumaire , which not only concluded a decade of political instability and social unrest but also ushered in a new era of governance under his rule.
This period, while stabilizing France and bringing much-needed order, seemed to contradict the revolution’s initial aims of establishing a democratic republic grounded in the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Napoleon’s rise to power, culminating in his coronation as Emperor, symbolizes a complex conclusion to the revolutionary narrative, intertwining the fulfillment and betrayal of its foundational ideals.
Evaluating the revolution’s success requires a nuanced perspective. On one hand, it dismantled the Ancien Régime, abolished feudalism, and set forth the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, laying the cornerstone for modern democracy and human rights.
These achievements signify profound societal and legal transformations that resonated well beyond France’s borders, influencing subsequent movements for freedom and equality globally.
On the other hand, the revolution’s trajectory through the Reign of Terror and the subsequent rise of a military dictatorship under Napoleon raises questions about the cost of these advances and the ultimate realization of the revolution’s goals.
The French Revolution’s conclusion with Napoleon Bonaparte’s ascension to power is emblematic of its complex legacy. This period not only marked the cessation of years of turmoil but also initiated a new chapter in French governance, characterized by stability and reform yet marked by a departure from the revolution’s original democratic aspirations.
The Significance of the French Revolution
The French Revolution holds a place of prominence in the annals of history, celebrated for its profound impact on the course of modern civilization. Its fame stems not only from the dramatic events and transformative ideas it unleashed but also from its enduring influence on political thought, social reform, and the global struggle for justice and equality.
This period of intense upheaval and radical change challenged the very foundations of society, dismantling centuries-old institutions and laying the groundwork for a new era defined by the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
At its core, the French Revolution was a manifestation of human aspiration towards freedom and self-determination, a vivid illustration of the power of collective action to reshape the world. It introduced revolutionary concepts of citizenship and rights that have since become the bedrock of democratic societies.
Moreover, the revolution’s ripple effects were felt worldwide, inspiring a wave of independence movements and revolutions across Europe, Latin America, and beyond. Its legacy is a testament to the idea that people have the power to overthrow oppressive systems and construct a more equitable society.
The revolution’s significance also lies in its contributions to political and social thought. It was a living laboratory for ideas that were radical at the time, such as the separation of church and state, the abolition of feudal privileges, and the establishment of a constitution to govern the rights and duties of the French citizens.
These concepts, debated and implemented with varying degrees of success during the revolution, have become fundamental to modern governance.
Furthermore, the French Revolution is famous for its dramatic and symbolic events, from the storming of the Bastille to the Reign of Terror, which have etched themselves into the collective memory of humanity.
These events highlight the complexities and contradictions of the revolutionary process, underscoring the challenges inherent in profound societal transformation.
Key Figures of the French Revolution
The French Revolutions were painted by the actions and ideologies of several key figures whose contributions defined the era. These individuals, with their diverse roles and perspectives, were central in navigating the revolution’s trajectory, capturing the complexities and contradictions of this tumultuous period.
Maximilien Robespierre , often synonymous with the Reign of Terror, was a figure of paradoxes. A lawyer and politician, his early advocacy for the rights of the common people and opposition to absolute monarchy marked him as a champion of liberty.
However, as a leader of the Committee of Public Safety, his name became associated with the radical phase of the revolution, characterized by extreme measures in the name of safeguarding the republic. His eventual downfall and execution reflect the revolution’s capacity for self-consumption.
Georges Danton , another prominent revolutionary leader, played a crucial role in the early stages of the revolution. Known for his oratory skills and charismatic leadership, Danton was instrumental in the overthrow of the monarchy and the establishment of the First French Republic.
Unlike Robespierre, Danton is often remembered for his pragmatism and efforts to moderate the revolution’s excesses, which ultimately led to his execution during the Reign of Terror, highlighting the volatile nature of revolutionary politics.
Louis XVI, the king at the revolution’s outbreak, represents the Ancient Régime’s complexities and the challenges of monarchical rule in a time of profound societal change.
His inability to effectively manage France’s financial crisis and his hesitancy to embrace substantial reforms contributed to the revolutionary fervor. His execution in 1793 symbolized the revolution’s radical break from monarchical tradition and the birth of the republic.
Marie Antoinette, the queen consort of Louis XVI, became a symbol of the monarchy’s extravagance and disconnect from the common people. Her fate, like that of her husband, underscores the revolution’s rejection of the old order and the desire for a new societal structure based on equality and merit rather than birthright.
Jean-Paul Marat , a journalist and politician, used his publication, L’Ami du Peuple, to advocate for the rights of the lower classes and to call for radical measures against the revolution’s enemies.
His assassination by Charlotte Corday, a Girondin sympathizer, in 1793 became one of the revolution’s most famous episodes, illustrating the deep divisions within revolutionary France.
Finally, Napoleon Bonaparte, though not a leader during the revolution’s peak, emerged from its aftermath to shape France’s future. A military genius, Napoleon used the opportunities presented by the revolution’s chaos to rise to power, eventually declaring himself Emperor of the French.
His reign would consolidate many of the revolution’s reforms while curtailing its democratic aspirations, embodying the complexities of the revolution’s legacy.
These key figures, among others, played significant roles in the unfolding of the French Revolution. Their contributions, whether for the cause of liberty, the maintenance of order, or the pursuit of personal power, highlight the multifaceted nature of the revolution and its enduring impact on history.
References:
(1) Schama, Simon. Citizens: a Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York, Random House, 1990, pp. 119-221.
(2) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 11-12
(3) Hobsbawm, Eric. The Age of Revolution. Vintage Books, 1996, pp. 56-57.
(4) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 24-25
(5) Lewis, Gwynne. The French Revolution: Rethinking the Debate. Routledge, 2016, pp. 12-14.
(6) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 14-25
(7) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 63-65.
(8) Schama, Simon. Citizens: a Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York, Random House, 1990, pp. 242-244.
(9) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 74.
(10) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 82 – 84.
(11) Lewis, Gwynne. The French Revolution: Rethinking the Debate. Routledge, 2016, p. 20.
(12) Hampson, Norman. A Social History of the French Revolution. University of Toronto Press, 1968, pp. 60-61.
(13) https://pages.uoregon.edu/dluebke/301ModernEurope/Sieyes3dEstate.pdf (14) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 104-105.
(15) French Revolution. “A Citizen Recalls the Taking of the Bastille (1789),” January 11, 2013. https://alphahistory.com/frenchrevolution/humbert-taking-of-the-bastille-1789/.
(16) Hampson, Norman. A Social History of the French Revolution. University of Toronto Press, 1968, pp. 74-75.
(17) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 36-37.
(18) Lefebvre, Georges. The French Revolution: From its origins to 1793. Routledge, 1957, pp. 121-122.
(19) Schama, Simon. Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. Random House, 1989, pp. 428-430.
(20) Hampson, Norman. A Social History of the French Revolution. University of Toronto Press, 1968, p. 80.
(21) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 116-117.
(22) Fitzsimmons, Michael “The Principles of 1789” in McPhee, Peter, editor. A Companion to the French Revolution. Blackwell, 2013, pp. 75-88.
(23) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 68-81.
(24) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 45-46.
(25) Schama, Simon. Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. Random House, 1989,.pp. 460-466.
(26) Schama, Simon. Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. Random House, 1989, pp. 524-525.
(27) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 47-48.
(28) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 51.
(29) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 128.
(30) Lewis, Gwynne. The French Revolution: Rethinking the Debate. Routledge, 2016, pp. 30 -31.
(31) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp.. 53 -62.
(32) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 129-130.
(33) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 62-63.
(34) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 156-157, 171-173.
(35) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 65-66.
(36) Schama, Simon. Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. Random House, 1989, pp. 543-544.
(37) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 179-180.
(38) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 184-185.
(39) Hampson, Norman. Social History of the French Revolution. Routledge, 1963, pp. 148-149.
(40) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 191-192.
(41) Lefebvre, Georges. The French Revolution: From Its Origins to 1793. Routledge, 1962, pp. 252-254.
(42) Hazan, Eric. A People’s History of the French Revolution, Verso, 2014, pp. 88-89.
(43) Schama, Simon. Citizens: a Chronicle of the French Revolution. Random House, 1990, pp. 576-79.
(44) Schama, Simon. Citizens: a Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York, Random House, 1990, pp. 649-51
(45) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 242-243.
(46) Connor, Clifford. Marat: The Tribune of the French Revolution. Pluto Press, 2012.
(47) Schama, Simon. Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. Random House, 1989, pp. 722-724.
(48) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 246-47.
(49) Hampson, Norman. A Social History of the French Revolution. University of Toronto Press, 1968, pp. 209-210.
(50) Hobsbawm, Eric. The Age of Revolution. Vintage Books, 1996, pp 68-70.
(51) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 205-206
(52) Schama, Simon. Citizens: a Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York, Random House, 1990, 784-86.
(53) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 262.
(54) Schama, Simon. Citizens: a Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York, Random House, 1990, pp. 619-22.
(55) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 269-70.
(56) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1989, p. 276.
(57) Robespierre on Virtue and Terror (1794). https://alphahistory.com/frenchrevolution/robespierre-virtue-terror-1794/. Accessed 19 May 2020.
(58) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 290-91.
(59) Doyle, William. Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 293-95.
(60) Lewis, Gwynne. The French Revolution: Rethinking the Debate. Routledge, 2016, pp. 49-51.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/the-french-revolution/ ">French Revolution: History, Timeline, Causes, and Outcomes</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
French Revolution
By: History.com Editors
Updated: October 12, 2023 | Original: November 9, 2009

The French Revolution was a watershed event in world history that began in 1789 and ended in the late 1790s with the ascent of Napoleon Bonaparte. During this period, French citizens radically altered their political landscape, uprooting centuries-old institutions such as the monarchy and the feudal system. The upheaval was caused by disgust with the French aristocracy and the economic policies of King Louis XVI, who met his death by guillotine, as did his wife Marie Antoinette. Though it degenerated into a bloodbath during the Reign of Terror, the French Revolution helped to shape modern democracies by showing the power inherent in the will of the people.
Causes of the French Revolution
As the 18th century drew to a close, France’s costly involvement in the American Revolution , combined with extravagant spending by King Louis XVI , had left France on the brink of bankruptcy.
Not only were the royal coffers depleted, but several years of poor harvests, drought, cattle disease and skyrocketing bread prices had kindled unrest among peasants and the urban poor. Many expressed their desperation and resentment toward a regime that imposed heavy taxes—yet failed to provide any relief—by rioting, looting and striking.
In the fall of 1786, Louis XVI’s controller general, Charles Alexandre de Calonne, proposed a financial reform package that included a universal land tax from which the aristocratic classes would no longer be exempt.
Estates General
To garner support for these measures and forestall a growing aristocratic revolt, the king summoned the Estates General ( les états généraux ) – an assembly representing France’s clergy, nobility and middle class – for the first time since 1614.
The meeting was scheduled for May 5, 1789; in the meantime, delegates of the three estates from each locality would compile lists of grievances ( cahiers de doléances ) to present to the king.
Rise of the Third Estate
France’s population, of course, had changed considerably since 1614. The non-aristocratic, middle-class members of the Third Estate now represented 98 percent of the people but could still be outvoted by the other two bodies.
In the lead-up to the May 5 meeting, the Third Estate began to mobilize support for equal representation and the abolishment of the noble veto—in other words, they wanted voting by head and not by status.
While all of the orders shared a common desire for fiscal and judicial reform as well as a more representative form of government, the nobles in particular were loath to give up the privileges they had long enjoyed under the traditional system.
Tennis Court Oath
By the time the Estates General convened at Versailles , the highly public debate over its voting process had erupted into open hostility between the three orders, eclipsing the original purpose of the meeting and the authority of the man who had convened it — the king himself.
On June 17, with talks over procedure stalled, the Third Estate met alone and formally adopted the title of National Assembly; three days later, they met in a nearby indoor tennis court and took the so-called Tennis Court Oath (serment du jeu de paume), vowing not to disperse until constitutional reform had been achieved.
Within a week, most of the clerical deputies and 47 liberal nobles had joined them, and on June 27 Louis XVI grudgingly absorbed all three orders into the new National Assembly.
The Bastille
On June 12, as the National Assembly (known as the National Constituent Assembly during its work on a constitution) continued to meet at Versailles, fear and violence consumed the capital.
Though enthusiastic about the recent breakdown of royal power, Parisians grew panicked as rumors of an impending military coup began to circulate. A popular insurgency culminated on July 14 when rioters stormed the Bastille fortress in an attempt to secure gunpowder and weapons; many consider this event, now commemorated in France as a national holiday, as the start of the French Revolution.
The wave of revolutionary fervor and widespread hysteria quickly swept the entire country. Revolting against years of exploitation, peasants looted and burned the homes of tax collectors, landlords and the aristocratic elite.
Known as the Great Fear ( la Grande peur ), the agrarian insurrection hastened the growing exodus of nobles from France and inspired the National Constituent Assembly to abolish feudalism on August 4, 1789, signing what historian Georges Lefebvre later called the “death certificate of the old order.”
Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen
IIn late August, the Assembly adopted the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen ( Déclaration des droits de l ’homme et du citoyen ), a statement of democratic principles grounded in the philosophical and political ideas of Enlightenment thinkers like Jean-Jacques Rousseau .
The document proclaimed the Assembly’s commitment to replace the ancien régime with a system based on equal opportunity, freedom of speech, popular sovereignty and representative government.
Drafting a formal constitution proved much more of a challenge for the National Constituent Assembly, which had the added burden of functioning as a legislature during harsh economic times.
For months, its members wrestled with fundamental questions about the shape and expanse of France’s new political landscape. For instance, who would be responsible for electing delegates? Would the clergy owe allegiance to the Roman Catholic Church or the French government? Perhaps most importantly, how much authority would the king, his public image further weakened after a failed attempt to flee the country in June 1791, retain?
Adopted on September 3, 1791, France’s first written constitution echoed the more moderate voices in the Assembly, establishing a constitutional monarchy in which the king enjoyed royal veto power and the ability to appoint ministers. This compromise did not sit well with influential radicals like Maximilien de Robespierre , Camille Desmoulins and Georges Danton, who began drumming up popular support for a more republican form of government and for the trial of Louis XVI.
French Revolution Turns Radical
In April 1792, the newly elected Legislative Assembly declared war on Austria and Prussia, where it believed that French émigrés were building counterrevolutionary alliances; it also hoped to spread its revolutionary ideals across Europe through warfare.
On the domestic front, meanwhile, the political crisis took a radical turn when a group of insurgents led by the extremist Jacobins attacked the royal residence in Paris and arrested the king on August 10, 1792.
The following month, amid a wave of violence in which Parisian insurrectionists massacred hundreds of accused counterrevolutionaries, the Legislative Assembly was replaced by the National Convention, which proclaimed the abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of the French republic.
On January 21, 1793, it sent King Louis XVI, condemned to death for high treason and crimes against the state, to the guillotine ; his wife Marie-Antoinette suffered the same fate nine months later.
Reign of Terror
Following the king’s execution, war with various European powers and intense divisions within the National Convention brought the French Revolution to its most violent and turbulent phase.
In June 1793, the Jacobins seized control of the National Convention from the more moderate Girondins and instituted a series of radical measures, including the establishment of a new calendar and the eradication of Christianity .
They also unleashed the bloody Reign of Terror (la Terreur), a 10-month period in which suspected enemies of the revolution were guillotined by the thousands. Many of the killings were carried out under orders from Robespierre, who dominated the draconian Committee of Public Safety until his own execution on July 28, 1794.
Did you know? Over 17,000 people were officially tried and executed during the Reign of Terror, and an unknown number of others died in prison or without trial.
Thermidorian Reaction
The death of Robespierre marked the beginning of the Thermidorian Reaction, a moderate phase in which the French people revolted against the Reign of Terror’s excesses.
On August 22, 1795, the National Convention, composed largely of Girondins who had survived the Reign of Terror, approved a new constitution that created France’s first bicameral legislature.
Executive power would lie in the hands of a five-member Directory ( Directoire ) appointed by parliament. Royalists and Jacobins protested the new regime but were swiftly silenced by the army, now led by a young and successful general named Napoleon Bonaparte .
French Revolution Ends: Napoleon’s Rise
The Directory’s four years in power were riddled with financial crises, popular discontent, inefficiency and, above all, political corruption. By the late 1790s, the directors relied almost entirely on the military to maintain their authority and had ceded much of their power to the generals in the field.
On November 9, 1799, as frustration with their leadership reached a fever pitch, Napoleon Bonaparte staged a coup d’état, abolishing the Directory and appointing himself France’s “ first consul .” The event marked the end of the French Revolution and the beginning of the Napoleonic era, during which France would come to dominate much of continental Europe.
Photo Gallery

French Revolution. The National Archives (U.K.) The United States and the French Revolution, 1789–1799. Office of the Historian. U.S. Department of State . Versailles, from the French Revolution to the Interwar Period. Chateau de Versailles . French Revolution. Monticello.org . Individuals, institutions, and innovation in the debates of the French Revolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences .

HISTORY Vault
Stream thousands of hours of acclaimed series, probing documentaries and captivating specials commercial-free in HISTORY Vault

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Search on OralHistory.ws Blog
The French Revolution: Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity

From 1789 to 1799, the French Revolution stands as one of the most pivotal episodes in world history. This tumultuous decade witnessed the dramatic overthrow of the Bourbon monarchy, the rise of radical political factions, and the eventual ascent of Napoleon Bonaparte. Rooted deeply in the Enlightenment ideals, the revolution was more than just a change in political leadership. It signified a profound metamorphosis of societal values, marked prominently by the revolutionary triad: Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity. These guiding principles did not merely serve as ideological rallying cries but were the bedrock upon which the new republic was built. Through a nuanced exploration of these core tenets, this essay will elucidate the essence of the French Revolution and its enduring imprint on the annals of democratic thought.
Table of content
Liberty – Breaking the Chains
Liberty, the very lifeblood of the French Revolution, embodied the deep-seated yearning of a populace stifled under absolute monarchy. This was not a fleeting desire but a fervent aspiration that echoed through the streets of Paris and the countryside of France alike.
Pre-revolutionary France was characterized by an entrenched system of royal absolutism, where the Bourbon kings wielded unchallenged power. Their unchecked authority, rampant corruption, and regressive taxation cultivated an environment of suffocation. The Enlightenment thinkers, such as Voltaire and Rousseau, sowed the seeds of liberty in the minds of the French. They championed the idea that individuals had inalienable rights, free from the whims and fancies of monarchs.
The storming of the Bastille, while a physical act, bore symbolic weight. It was not just dismantling a fortress prison but a resounding message against oppression. Liberty evolved from an abstract concept to concrete legislative reforms as the Revolution progressed. The suppression of censorship, the proclamation of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen, and the gradual diminishing of the king’s power were tangible manifestations of this pursuit.
However, it is crucial to note that this road to liberty was fraught with challenges. While the revolution sought to free the citizenry from the shackles of the old regime, new chains of radical factions and the Reign of Terror emerged. Nevertheless, once ignited, the spirit of liberty refused to be extinguished. Even amidst the revolution’s darkest hours, the flame of liberty continued to burn, guiding the nation toward a more democratic future.
Equality – Leveling the Field
The clarion call for Equality during the French Revolution was more than just a repudiation of the aristocratic privileges; it was a radical reimagining of societal structures. The ancien régime had perpetuated a stratified society where birthright and lineage overshadowed merit and individual capability. This systemic inequality was entrenched in the legal and political fabric and deeply woven into France’s cultural and social tapestry.
With its archaic representation, the Estates-General was a glaring example of this inequity. The First and Second Estates, representing the clergy and nobility, respectively, enjoyed disproportionate influence despite being a minuscule fraction of the population. In contrast, the Third Estate, representing most of the populace, was marginalized. The growing resentment of this imbalance paved the way for the revolutionaries to demand a more equitable society.
Revolutionary reforms sought to dismantle these outdated hierarchies. The abolition of feudalism in 1789 marked a seismic shift, toppling centuries-old structures of serfdom and manorial rights. Likewise, the Civil Constitution of the Clergy sought to break the ecclesiastical stronghold, making the Church subordinate to the state. This transformative period also witnessed the rise of the bourgeoisie, as wealth and education began to rival, if not surpass, nobility as markers of societal status.
However, the quest for equality was a double-edged sword. As much as the revolution aimed to flatten societal disparities, it also grappled with internal contradictions. The Reign of Terror, while championing the cause of the common man, often veered into a despotic purge of perceived counter-revolutionaries. This underscores the complexity of the revolution’s pursuit of equality: an aspiration both noble in its intent and intricate in its execution.
Fraternity – A Unified Nation
Fraternity, often overshadowed by the more tangible tenets of Liberty and Equality, played an integral role in shaping the ethos of the French Revolution. At its core, Fraternity evoked a sense of communal belonging, a shared destiny, and a collective purpose. It was not just about fostering bonds among citizens but was a call to stitch together a nation fragmented by centuries of divisions.
Before the Revolution, France was not the homogenous entity we envision today. It was a patchwork of regions, dialects, customs, and allegiances. While unifying to an extent, the Bourbon monarchy often played one faction against another, exacerbating regional and class distinctions for political gains.
The Revolution sought to mend these fractures. Fraternity became the rallying cry for creating a cohesive national identity. This was not just a sentiment but actualized through policies and symbols. The adoption of “La Marseillaise” as the national anthem, the establishment of a unified legal code in the form of the Napoleonic Code, and the promotion of the French language at the expense of regional dialects were all geared towards forging a united France.
However, the road to fraternity was not without its paradoxes. The desire for a unified nation sometimes clashed with recognizing individual and regional identities. The de-Christianization campaigns, while aimed at reducing the Church’s influence, alienated many devout citizens. Similarly, the aggressive promotion of French as the lingua franca often came at the expense of regional identities and cultures.
Nevertheless, despite these challenges, the spirit of Fraternity endured. The French Revolution may have been tumultuous and, at times, contradictory, but its emphasis on a united national identity laid the groundwork for the modern French nation-state. It served as a testament to the enduring human desire to belong, connect, and forge a shared destiny.
The French Revolution, with its whirlwind of events, ideologies, and personalities, remains a seminal chapter in the annals of history. Through its embrace of Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity, it not only redefined the contours of French society but also set a precedent for global movements advocating democratic principles.
In dissecting these tenets, we are offered a lens through which the revolution’s multifaceted nature becomes evident. Liberty, with its call for personal freedoms, was both an aspiration and a challenge constantly sought after and fought for in the face of evolving threats. Equality, a demand for societal leveling, was an endeavor to bridge the yawning chasm between the elite and the commoner, reimagining the societal structures that had held sway for centuries. Fraternity, perhaps the most nuanced of the three, sought to weave a tapestry of shared identity from the disparate threads of regional, class, and religious affiliations.
Nevertheless, beyond the theoretical lies the pragmatic. The French Revolution was not a linear progression of ideals but a crucible where these principles were tested, redefined, and, at times, compromised. It was a testament to the complexities of nation-building and the intricacies of balancing individual rights with collective responsibility.
As we reflect upon the legacy of the revolution, its resonances are palpable even today. From the Arab Spring to civil rights movements, the echoes of Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity reverberate, reminding us of the universality of these aspirations. The French Revolution, thus, is not just a historical event confined to textbooks but a living testament to humanity’s relentless quest for a more just, equitable, and united world.
119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples
French Revolution essay is a popular task in colleges and universities. As such, you should know what you are expected to write when given this topic. For example, discuss the worldwide context in which the Revolution took place.
🏆 Best French Revolution Topics
📑 good research topics about french revolution, 🎓 simple french revolution essay topics, 📌 interesting french revolution research topics, ❓ french revolution essay questions.
Before the French Revolution, Europe was a land where monarchy was a dominant mode of government. It was supported by religious figures, with their propositions such as the divine mandate and the general illiteracy of the population. However, the Enlightenment changed the situation as more and more people became educated and interested in state affairs.
The consequences of the Revolution, locally and internationally, are a significant matter for discussion. By covering these ideas and following The French Revolution essay requirements, you will create powerful work. You can discuss the dynamics of power in its execution and how pragmatic leaders eventually replaced idealistic ones.
Napoleon Bonaparte is an important figure, as he emerged as the ultimate victor of the Revolution. France began as a monarchy and ended as an empire under dictatorial rule, showing the issues inherent in revolutions.
Try to concentrate on a specific topic instead of discussing everything you can think of. Use side topics as arguments in support of your thesis. If you find yourself struggling, visit IvyPanda to find a variety of useful, professionally written samples!
- Napoleon Bonaparte’s Role in the French Revolution Despite the outstanding development, Napoleon stayed in the position of the second lieutenant for six years; it was not until the beginning of the French Revolution that he was able to advance his career in […]
- Music and the French Revolution They also wanted to do away with the Christianity as well as the old method of days of the week and naming the years from the birth of Christ.
- History of French Revolution The whole French terrorism was a means of dealing with the rivals of the bourgeoisie that is feudalism and absolutism. In the estates general, there was the clergy, nobility and the rest of the people.
- French Revolution: Role of Propaganda and Music The history of propaganda is based on three interweaving fundamentals: first, the mounting need, with the growth of civilization and the rise of nation-state, to win the battle for people’s minds; second, the increasing sophistication […]
- Comparison of American and French Revolution Both the revolutions were for a cause, the American Revolution took place because the Americans wanted to free themselves from the enslavement of the British and similarly the French revolution took place because the rich […]
- The French Revolution: Romanticism Period Romanticism was anchored in the work of the poets which was evident in the daily lives of the society. Besides, the role of women in romantic literature was significant, thus; they were greatest poets and […]
- A Tale of Two Cities: A Balanced Portrayal of the French Revolution The novel paints a vivid picture of the French Revolution, the fervor and radicalism of the revolutionaries and the terror and bloodshed spread by the revolutionaries.
- Industrialization, Enlightenment, French Revolution Human history has been shaped greatly by three periods: The industrial revolution, the period of enlightenment, the French revolution, and finally the period of protest and revolution 1815-1850.
- “The Old Regime and the French Revolution” by Alexis De Tocqueville Consequently, in chapter 2, Tocqueville explains that the Church was targeted by the anti-elitist and semi-anarchist aims of the Revolution due to being a part of the feudal system.
- Food Scarcity Factor in French Revolution Many writings and works devoted to the investigation of European history in the 18th century have captured the chronicles of a long-term hunger that was spread across France on the eve of the Revolution.
- French Revolution and War Periods The themes of the songs before the French Revolution of 1848 and shortly before and during the time of the Paris Commune in 1871 were mostly political and revolutionary.
- Restoring Justice Through the French Revolution However, the role of breakthroughs, which spurred the rise of capitalism and the bourgeoisie with its intentions to change order within the country, led to the French Revolution, which restored justice.
- The French Revolution in Its Historical Context The French Revolution was a series of events that marked the downfall of the Bourbon monarchy and the rise of a democratic republic in France.
- Society and Cultural Changes in the West During the French Revolution The main influence on the development of the political life of Western countries in the second period of New History was the French Revolution, which put forward the ideas of freedom, equality, and fraternity.
- The French Revolution and National Regeneration The ideas presented by the interpretations of the effects and consequences of the revolution are important in offering knowledge of new political ideologies.
- The Nationalism Role During the French Revolution One of the most developed variants of this concept is the nationalism of the era of the French Revolution. In 1789, with the outbreak of the French Revolution, the idea of nationalism spread throughout France, […]
- Why the French Revolution Led to War Between France and Prussia & Austria To understand why the French Revolution led to war between France on the one side and Prussia and Austria on the other in 1792, one should briefly recall the essence of this revolution.
- Origins of the French Revolution Tired of the current situation and raring for change, the French people had to find a reason to revolt. She was convicted and executed of the same.
- The Role of Napoleon Bonaparte in the French Revolution The aftermath of the revolutionary actions was disastrous and the society would have faced the need to readjust to more alternations in political orders.
- French Revolution: Women Studies French revolution was first witnessed in the year 1789.in the year 1792 June a number of women demonstrated towards the legislative chambers of the king1. The government was against this and women were banned from […]
- Print Making During the French Revolution Print making entails the use of originality in the creation of prints as opposed to the reproduction of a painting using photographic means.
- French Revolution Main Events The year 1789 was marked by celebrations of the centenary of the glorious revolution in Britain. There was much travel between Britain and France and the individuals who supported events in France started to dress […]
- Enlightenment Ideas During the French Revolution Period This happened due to the adoption of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen which was approved on the 26th of August 1789 and which promised legal equality and liberty to every […]
- French Revolution in World History The French revolution, in this part of the world at least, was the inspiration for all subsequent uprisings and revolts throughout Europe in the nineteenth century and its ideals, in part, are visible in many […]
- Women During the French Revolution: Olympe de Gouges As a move to fight for the women rights, I wrote the Declaration of the Rights of Women and the citizens in 1791.
- Western Civilization: The French Revolution 1789-99 One of the most popular theories includes the idea that the fall of the monarchy was simply a result of the fall of the social class with which it was most closely associated, that of […]
- French Revolution and the European Music For instance many of the ideas of democracy taken for granted in many parts of the world today like the freedom and impartiality of individuals, the importance of written establishments in supervision of a country, […]
- How Revolutionary Was the French Revolution? The French Revolution was the most revolutionary era in the history of France as the country underwent radical reforms. One of the greatest landmark revolutions was the spread of the Napoleonic culture and some of […]
- French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars: Idea of Nation While studying the French Revolution of 1789 and the Napoleonic Wars of 1803-1815, I was challenged by the question of their impact on the ideas of nations.
- The French Revolution and Its Factors The French revolution is seen as a period of both social and political upheavals in the History of Europe and France. It was the French revolution that was seen to overthrow this old regime to […]
- French Revolution, Its Social Causes and Legacies The French revolution owes its occurrence, foremost, to the significant increase of the French population throughout the eighteenth century. The implication of this stratification was the lumping of a majority of the population into the […]
- Robespierre’s Influence During the French Revolution Besides, the title of the article does not directly capture the interest of the reader since it approaches the focus of the reader from a broad perspective; The Economic Terror of the French Revolution.
- French Revolution and Societal Transformation The French Revolution was a period of political and social instabilities in France, which lasted between 1789 and 1799, and was partially planned and carried out by Napoleon in the course of the French Empire […]
- The French Revolution Role in the History The French Revolution was a major event not only in the history of the French Empire but also in the history of the world.
- Neoclassicism in French Revolution As a matter of fact, the roles played by art in the social realms could not be ignored during the revolution years. The cruel nature of the French regime was depicted in the Marat’s figure […]
- French Revolution and Napoleonic Era Subsequently, rebellion and a spirit of revolution began to ferment among the commoners, the nobility and the clergy as well as the wider French society.
- Edmund Burke: Reflection on Liberty and the French Revolution One of the things that Burke seems not to appreciate is the fact that freedom and liberty are not a one-time achievement.
- Industrial and French Revolutions In addition, people from the middle classes were the greatest beneficiaries while peasants and the poor were the losers in the revolutions.
- French revolution and the Napoleon era The enlightenment era consisted of quite a number of ideas that changed the French society in addition to growing wave of civilization in the West.
- The French Revolution and Napoleon’s Governance Like any substantial change in the political life of any country, the French Revolution consisted of several stages of the dramatic transformation of the state system, political and social life in France. During the decade […]
- The effect of the French Revolution on Lazare Carnot The period of the French revolution was celebrated with a lot of enthusiasm and it can be perceived to have laid the groundwork and the birth of the new world socio-political order.
- How Did the French Revolution Impacted the Issue of Slavery and the History of Santo Domingo? The French Revolution led to the spread of revolutionary ideas. After the French Revolution, the law prohibited slavery and abolished in Santo Domingo.
- Origins and trajectory of the French Revolution The Second Estate consisted of the nobility, another privileged group which held the highest positions in the government, the Church and the army.
- The French Revolution Movie The movie by the name Marie Antoinette tells the story of the Austrian-born queen and the events leading to the collapse of the monarchy in France.
- Liberty and Nation: The French Revolution This paper will discuss the role of the French Revolution in shaping the concept of nation, freedom, and citizenship. This author argued that people of the Third Estate constituted the bulk of the French nation […]
- Major social groups in France prior to the French revolution The First Estate consisted of the clergy; the second one was nobility while the third estate was known as the commoners. The major goal of the commoners was to attain more power and independence from […]
- French Revolution: Liberal and Radical Portions Of course, a hope that the presence of revolution promoted certain changes and made the government to think about the improvement of citizens’ lives and wellbeing was inherent to the French.
- The American vs. French Revolution: Ideals Matter The development of the first Heliocentric theory of the universe and the Pythagorean system had profound revolutionary implications on man’s conception of the universe and natural law.
- What Caused the French Revolution? The American Revolution: In 1775-1783, America experienced a revolution and the government of France sent its troops and navy to help the rebelling colonists. This consequently led to the rise of hunger and high prices […]
- Absolutism in French Revolution It means that the contemporaries of Louis XIV did not use this term, but preferred to use the word-combination “absolute power of the crown”, which they understood as the “concentration of sovereign authority in the […]
- An Analysis of a Document Written by an Anonymous French Sugar Planter Who Escaped the French Revolution by Going to Saint Domingue
- An Analysis of French Revolution Differ in American Revolution
- An Analysis of Political Upheavals of the French Revolution
- A History of the French Revolution and the Origin of Totalitarianism
- An Analysis of the Significance of the Reign of Terror in the French Revolution
- An Analysis of the Significance of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars to Modernity
- An Analysis of the Causes and Impact of the French Revolution in the 16th Century
- Age of Enlightenment and French Revolution
- An Overview of the Preliminary Stage in Politics and the Causes of the French Revolution
- A Biography of Maximilien Robespierre, a Famous Leader of the French Revolution
- An Analysis of the Goals of the French Revolution Produced by the Enlightenment
- An Analysis of the Specific Themes in Charles Dickens’ Novel A Tale of Two Cities Regarding the French Revolution
- An Overview of A True Revolution in French Revolution and the Brutality
- An Analysis of the Primary Causes of Social and Political Upheaval in the French Revolution
- A Description of the French Revolution as a Significant Milestone in European History
- A Look at France and England During The French Revolution in A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens
- An Analysis of the Beginning of Time on the Concept of Revolution and the Principles Behind the French Revolution in Europe
- An Analysis of the Investigation on Napoleon’s Betrayal in the French Revolution
- A Better Understanding of the Causes of the French Revolution in the 1700’s
- A Description of Both Conservatism and Liberalism Which Were Both Born in the French Revolution
- A Look at the French Revolution and the Killings During the Devolution
- An Analysis of the Ideological Connection between the Enlightenment and the French Revolution
- An Analysis of the Great Changes in the Society and Government of France Brought By The French Revolution
- Anne Robert Jacques Turgot and His Relevance to the French Revolution
- An Examination of the Estates General: The First Step to the French Revolution
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of The French Revolution
- An Overview of the French Revolution as a Major Theme of Change in the 18th Century
- An Examination of the Influence of French Revolution on the Society of Europe
- An Analysis of the Causes of the French Revolution: the Financial Debt of the Government and the Long-Standing Political Differences in the Government
- An Analysis of Queen Marie Antoinette’s Involvement in the French Revolution
- A History of the Fall of Bastille and the French Revolution
- Assess the View That the Enlightenment Had Been the Main Cause of the French Revolution
- An Analysis and an Introduction to Revolutionary Leaders and the Effects of the French Revolution
- A Comparison between the American Revolution and the French Revolution
- An Evaluation of the French Revolution, Social Injustice, Love and Compassion in Les Miserables, a Play by Victor Hugo
- A Discussion of the Creation of Conservatism and Liberalism During the French Revolution
- A Look at the Major Revolutions and the Differences in the French Revolution
- An Analysis of the Essential Cause for the French Revolution in the End of 18th Century
- An Analysis of the Three Main Views Interpreted in the French Revolution
- How Far Was Christianity Seriously Threatened by the French Revolution Between 1789 and 1815?
- Was Napoleon the Son or the Enemy of the French Revolution?
- How and Why Did the French Revolution Affect Ireland?
- How Much Does Napoleon Owe to the French Revolution?
- Did Marie Antoinette Play a Decisive Role in the French Revolution?
- How Did American Revolution Serve as the Inspiration for the French Revolution?
- Did Napoleon Abuse the Ideas of the French Revolution?
- How Did the Enlightenment Influence the French Revolution?
- Did the American Revolution Help Spur the French Revolution?
- How Did the French Revolution Impact Western Civilization?
- How Did the French Revolution Become More Radical in 1789-1793?
- Did the French Revolution Have Occurred Without the Enlightenment?
- How Did the French Revolution Both Support and Violate the Motto – “Equality, Liberty and Fraternity”?
- Was Napoleon Bonaparte the Saviour or the Destroyer of the Ideals of the French Revolution?
- How Did the French Revolution Enter a New Phase After the Storming of the Bastille?
- Was the French Revolution a Class War?
- How Did the French Revolution Lead to the Unification of Germany and Italy?
- Was the French Revolution Successful?
- How Did the French Revolution Undermine Democracy?
- Was the French Revolution Necessary?
- How Did the Social Upheaval of the French Revolution Influence the Beliefs of the Romantic Poets?
- Was the French Revolution Preventable?
- How Effectively Did Pitt Deal With the External Threats of the French Revolution?
- Was the French Revolution the Birth of Modernity?
- How Far Did Napoleon Maintain the Aims of the French Revolution Till 1815?
- What Are the Four Main Causes of the French Revolution?
- How Far Was Louis XVI to Blame for the French Revolution in 1789?
- What Caused and Sustained the Second French Revolution?
- How Important Was the Part Played by the Third Estate in the French Revolution up to 1793?
- How Important Were Economic Causes of the French Revolution?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 24). 119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/french-revolution-essay-examples/
"119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples." IvyPanda , 24 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/french-revolution-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples'. 24 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/french-revolution-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/french-revolution-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/french-revolution-essay-examples/.
- Equality Topics
- American Revolution Topics
- Libertarianism Research Topics
- Revolutionary War Essay Ideas
- Revolution Essay Topics
- Industrialization Topics
- Cuban Revolution Ideas
- World History Topics
- Arab Spring Research Topics
- Russian Revolution Paper Topics
- Oppression Research Topics
- Industrial Revolution Research Ideas
- Determinism Research Topics
- Social Democracy Essay Titles
- Globalization Essay Topics
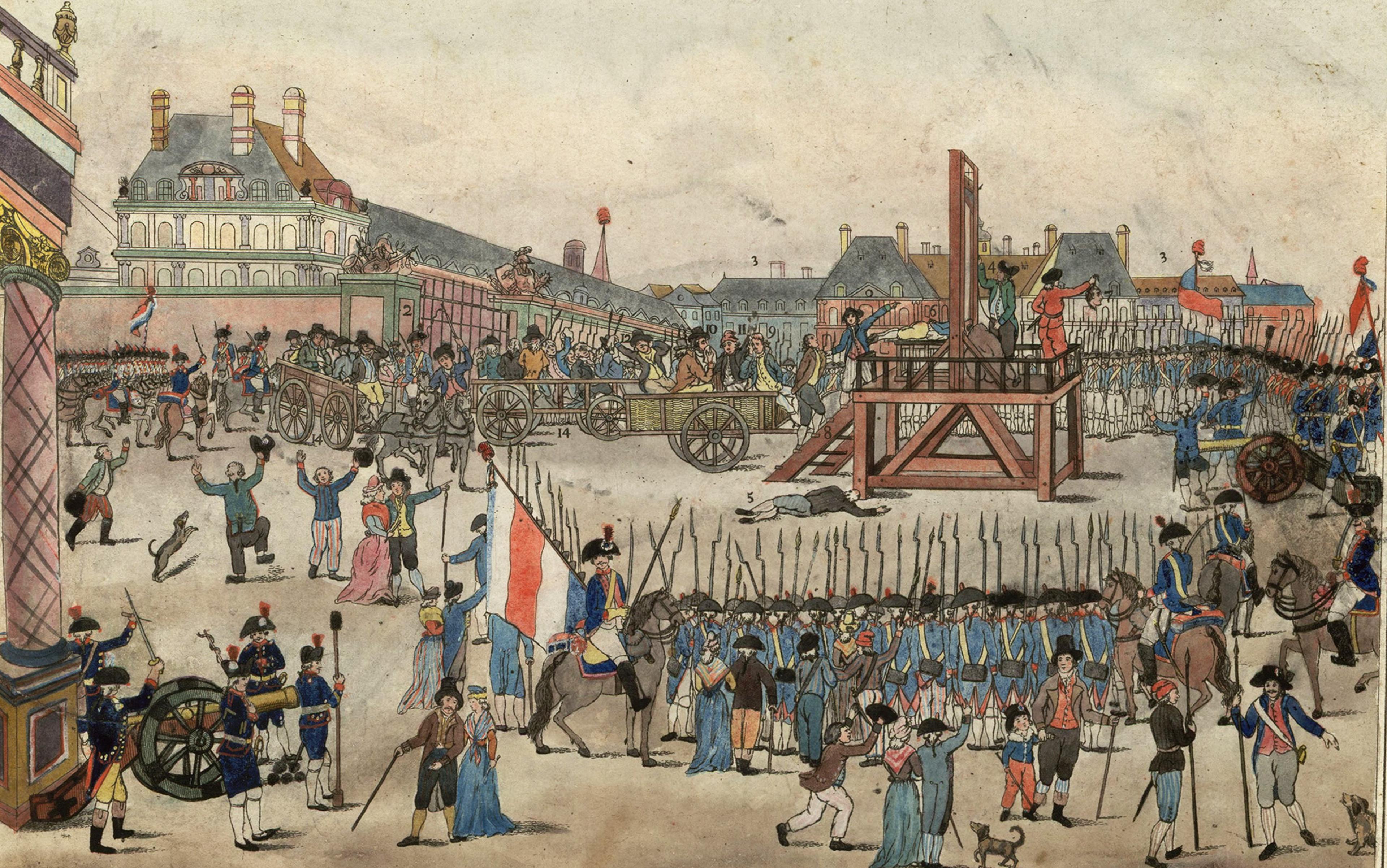
The execution of Robespierre and his accomplices, 17 July 1794 (10 Thermidor Year II). Robespierre is depicted holding a handkerchief and dressed in a brown jacket in the cart immediately to the left of the scaffold. Photo courtesy the Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris
Vive la révolution!
Must radical political change generate uncontainable violence the french revolution is both a cautionary and inspiring tale.
by Jeremy Popkin + BIO
If the French Revolution of 1789 was such an important event, visitors to France’s capital city of Paris often wonder, why can’t they find any trace of the Bastille, the medieval fortress whose storming on 14 July 1789 was the revolution’s most dramatic moment? Determined to destroy what they saw as a symbol of tyranny, the ‘victors of the Bastille’ immediately began demolishing the structure. Even the column in the middle of the busy Place de la Bastille isn’t connected to 1789: it commemorates those who died in another uprising a generation later, the ‘July Revolution’ of 1830.
The legacy of the French Revolution is not found in physical monuments, but in the ideals of liberty, equality and justice that still inspire modern democracies. More ambitious than the American revolutionaries of 1776, the French in 1789 were not just fighting for their own national independence: they wanted to establish principles that would lay the basis for freedom for human beings everywhere. The United States Declaration of Independence briefly mentioned rights to ‘liberty, equality, and the pursuit of happiness’, without explaining what they meant or how they were to be realised. The French ‘Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen’ spelled out the rights that comprised liberty and equality and outlined a system of participatory government that would empower citizens to protect their own rights.
Much more openly than the Americans, the French revolutionaries recognised that the principles of liberty and equality they had articulated posed fundamental questions about such issues as the status of women and the justification of slavery. In France, unlike the US, these questions were debated heatedly and openly. Initially, the revolutionaries decided that ‘nature’ denied women political rights and that ‘imperious necessity’ dictated the maintenance of slavery in France’s overseas colonies, whose 800,000 enslaved labourers outnumbered the 670,000 in the 13 American states in 1789.
As the revolution proceeded, however, its legislators took more radical steps. A law redefining marriage and legalising divorce in 1792 granted women equal rights to sue for separation and child custody; by that time, women had formed their own political clubs, some were openly serving in the French army, and Olympe de Gouges’s eloquent ‘Declaration of the Rights of Woman’ had insisted that they should be allowed to vote and hold office. Women achieved so much influence in the streets of revolutionary Paris that they drove male legislators to try to outlaw their activities. At almost the same time, in 1794, faced with a massive uprising among the enslaved blacks in France’s most valuable Caribbean colony, Saint-Domingue, the French National Convention abolished slavery and made its former victims full citizens. Black men were seated as deputies to the French legislature and, by 1796, the black general Toussaint Louverture was the official commander-in-chief of French forces in Saint-Domingue, which would become the independent nation of Haiti in 1804.
The French Revolution’s initiatives concerning women’s rights and slavery are just two examples of how the French revolutionaries experimented with radical new ideas about the meaning of liberty and equality that are still relevant. But the French Revolution is not just important today because it took such radical steps to broaden the definitions of liberty and equality. The movement that began in 1789 also showed the dangers inherent in trying to remake an entire society overnight. The French revolutionaries were the first to grant the right to vote to all adult men, but they were also the first to grapple with democracy’s shadow side, demagogic populism, and with the effects of an explosion of ‘new media’ that transformed political communication. The revolution saw the first full-scale attempt to impose secular ideas in the face of vocal opposition from citizens who proclaimed themselves defenders of religion. In 1792, revolutionary France became the first democracy to launch a war to spread its values. A major consequence of that war was the creation of the first modern totalitarian dictatorship, the rule of the Committee of Public Safety during the Reign of Terror. Five years after the end of the Terror, Napoleon Bonaparte, who had gained fame as a result of the war, led the first modern coup d’état , justifying it, like so many strongmen since, by claiming that only an authoritarian regime could guarantee social order.
The fact that Napoleon reversed the revolutionaries’ expansion of women’s rights and reintroduced slavery in the French colonies reminds us that he, like so many of his imitators in the past two centuries, defined ‘social order’ as a rejection of any expansive definition of liberty and equality. Napoleon also abolished meaningful elections, ended freedom of the press, and restored the public status of the Catholic Church. Determined to keep and even expand the revolutionaries’ foreign conquests, he continued the war that they had begun, but French armies now fought to create an empire, dropping any pretence of bringing freedom to other peoples.
T he relevance of the French Revolution to present-day debates is the reason why I decided to write A New World Begins: The History of the French Revolution (2020), the first comprehensive English-language account of that event for general readers in more than 30 years. Having spent my career researching and teaching the history of the French Revolution, however, I know very well that it was more than an idealistic crusade for human rights. If the fall of the Bastille remains an indelible symbol of aspirations for freedom, the other universally recognised symbol of the French Revolution, the guillotine, reminds us that the movement was also marked by violence. The American Founding Fathers whose refusal to consider granting rights to women or ending slavery we now rightly question did have the good sense not to let their differences turn into murderous feuds; none of them had to reflect, as the French legislator Pierre Vergniaud did on the eve of his execution, that their movement, ‘like Saturn, is devouring its own children’.
It is hard to avoid concluding that there was a relationship between the radicalism of the ideas that surfaced during the French Revolution and the violence that marked the movement. In my book, I introduce readers to a character, the ‘Père Duchêne’, who came to represent the populist impulses of the revolution. Nowadays, we would call the Père Duchêne a meme. He was not a real person: instead, he was a character familiar to audiences in Paris’s popular theatres, where he functioned as a representative of the country’s ordinary people. Once the revolution began, a number of journalists began publishing pamphlets supposedly written by the Père Duchêne, in which they demanded that the National Assembly do more to benefit the poor. The small newspapers that used his name carried a crude woodcut on their front page showing the Père Duchêne in rough workers’ clothing. Holding a hatchet over his head, with two pistols stuck in his belt and a musket at his side, the Père Duchêne was a visual symbol of the association between the revolution and popular violence.
The elites had enriched themselves at the expense of the people, and needed to be forced to share their power
Although his crude language and his constant threat to resort to violence alienated the more moderate revolutionaries, the Père Duchêne was the living embodiment of one of the basic principles incorporated in the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen. The sixth article of that document affirmed that ‘the law is the expression of the general will’ and promised that ‘all citizens have the right to participate personally, or through their representatives, in its establishment’. The fictitious Père Duchêne’s message to readers, no matter how poor and uneducated they might be, was that an ordinary person could claim a voice in politics.

Like present-day populists, the Père Duchêne had a simple political programme. The elites who ruled France before 1789 had enriched themselves at the expense of the people. They needed to be forced to share their power and wealth. When the revolution did not immediately improve the lives of the masses, the Père Duchêne blamed the movement’s more moderate leaders, accusing them of exploiting it for their own benefit. The journalists who wrote under the name of the Père Duchêne used colourful language laced with obscenities; they insisted that their vulgarity showed that they were ‘telling it like it is’. Their tone was vindictive and vengeful; they wanted to see their targets humiliated and, in many cases, sent to the guillotine. The most successful Père Duchêne journalist, Jacques-René Hébert, built a political career through his success in using the media. At the height of the Reign of Terror, he pushed through the creation of a ‘revolutionary army’ controlled by his friends to intimidate enemies of the revolution, and seemed on the verge of taking over the government.
Maximilien Robespierre and his more middle-class colleagues on the Committee of Public Safety feared that Hébert’s populist movement might drive them from power. They decided that they had no choice but to confront Hébert and his followers, even if it meant alienating the ‘base’ of ordinary Paris residents, the famous sans-culottes . Using the same smear tactics that the Père Duchêne had perfected, they accused Hébert of dubious intrigues with foreigners and other questionable activities. Like many bullies, Hébert quickly collapsed when he found himself up against serious opponents determined to fight back; the crowd that cheered his dispatch to the guillotine in March 1794 was larger than for many of the executions that he had incited. But he and the other Père Duchênes, as well as their female counterparts, the Mère Duchênes who flourished at some points in the revolution, had done much to turn the movement from a high-minded crusade for human rights into a free-for-all in which only the loudest voices could make themselves heard.
T he ambivalent legacy of the French Revolution’s democratic impulse, so vividly brought to life in the figure of the Père Duchêne, underlines the way in which the movement begun in 1789 remains both an inspiration and a warning for us today. In the more than 200 years since the storming of the Bastille, no one has formulated the human yearning for freedom and justice more eloquently than the French revolutionaries, and no one has shown more clearly the dangers that a one-sided pursuit of those goals can create. The career of the most famous of the radical French revolutionaries, Robespierre, is the most striking demonstration of that fact.
Robespierre is remembered because he was the most eloquent defender of the dictatorship created during the revolution’s most radical period, the months known as the Reign of Terror. Robespierre’s speech on the principles of revolutionary government, delivered on 25 December 1793, made an uncompromising case for the legitimacy of extreme measures to defeat those he called ‘the enemies of liberty’. Paradoxically, he insisted, the only way to create a society in which citizens could exercise the individual freedoms promised in the Declaration of Rights was to suspend those rights until the revolution’s opponents were conclusively defeated.
Robespierre’s colleagues on the all-powerful Committee of Public Safety chose him to defend their policies because he was more than just a spokesman for harsh measures against their opponents. From the time he first appeared on the scene as one of the 1,200 deputies to the Estates General summoned by Louis XVI in May 1789, his fellow legislators recognised the young provincial lawyer’s intelligence and his unswerving commitment to the ideals of democracy. The renegade aristocrat the comte de Mirabeau, the most prominent spokesman of the revolutionary ‘patriots’ in 1789 but an often cynical pragmatist, quickly sized up his colleague: ‘That man will go far, because he believes everything he says.’ Unlike the Père Duchêne, Robespierre always dressed carefully and spoke in pure, educated French. Other revolutionary leaders, like the rabblerousing orator Georges Danton, were happy to join insurrectionary crowds in the streets; Robespierre never personally took part in any of the French Revolution’s explosions of violence. Yet no one remains more associated with the violence of the Reign of Terror than Robespierre.
To reduce Robespierre’s legacy to his association with the Terror is to overlook the importance of his role as a one of history’s most articulate proponents of political democracy. When the majority of the deputies in France’s revolutionary National Assembly tried to restrict full political rights to the wealthier male members of the population, Robespierre reminded them of the Declaration of Rights’ assertion that freedom meant the right to have a voice in making the laws that citizens had to obey. ‘Is the law the expression of the general will, when the greater number of those for whom it is made cannot contribute to its formation?’ he asked. Long before our present-day debates about income inequality, he denounced a system that put real political power in the hands of the wealthy: ‘And what an aristocracy! The most unbearable of all, that of the rich.’ In the early years of the revolution, Robespierre firmly defended freedom of the press and called for the abolition of the death penalty. When white colonists insisted that France could not survive economically without slavery, Robespierre cried out: ‘Perish the colonies rather than abandon a principle!’
The majority of the population was not ready to embrace a radical secularist movement
Explaining how Robespierre, the principled defender of liberty and equality, became in just a few short years the leading advocate of a system of revolutionary government that foreshadowed the 20th century’s totalitarian dictatorships is perhaps the greatest challenge in defending the legacy of the French Revolution. Robespierre was no innocent, and in the last months of his short political career – he was only 36 when he died – his clumsy confrontations with his colleagues made him a dangerous number of enemies. Unlike the Père Duchêne, however, Robespierre never embraced violence as an end in itself, and a close examination of his career shows that he was often trying to find ways to limit the damage caused by policies he had not originally endorsed. In 1792, when most of his fellow Jacobin radicals embraced the call for a revolutionary war to ensure France’s security by toppling the hostile monarchies surrounding it, Robespierre warned against the illusion that other peoples would turn against their own governments to support the French. ‘No one loves armed missionaries,’ he insisted, a warning that recent US leaders might have done well to heed.
When radicals such as Hébert started a campaign to ‘de-Christianise’ France, in order to silence opposition to the movement’s effort to reform the Catholic Church and sell off its property for the benefit of the revolution, Robespierre reined them in. He recognised that the majority of the population was not ready to embrace a radical secularist movement bent on turning churches into ‘temples of reason’ and putting up signs in cemeteries calling death ‘an eternal sleep’. Robespierre proposed instead the introduction of a purified and simplified ‘cult of the Supreme Being’, which he thought believers could embrace without abandoning their faith in a higher power and their belief in the immortality of the soul.

Robespierre knew that many of the revolution’s bitterest opponents were motivated by loyalty to the Catholic Church. The revolution had not begun as an anti-religious movement. Under the rules used in the elections to what became the French National Assembly in 1789, a fourth of all the deputies were clergy from the Catholic Church, an institution so woven into the fabric of the population’s life that hardly anyone could imagine its disappearance. Criticism that the Church had grown too wealthy and that many of its beliefs failed to measure up to the standards of reason promoted by the Enlightenment was widespread, even among priests, but most hoped to see religion, like every other aspect of French life, ‘regenerated’ by the impulses of the revolution, not destroyed.
The revolutionaries’ confrontation with the Church began, not with an argument about beliefs, but because of the urgent need to meet the crisis in government revenues that had forced king Louis XVI to summon a national assembly in the first place. Determined to avoid a chaotic public bankruptcy, and reluctant to raise taxes on the population, the legislators decided, four months after the storming of the Bastille, to put the vast property of the Catholic Church ‘at the disposition of the nation’. Many Catholic clergy, especially underpaid parish priests who resented the luxury in which their aristocratic bishops lived, supported the expropriation of Church property and the idea that the government, which now took over the responsibility for funding the institution, had the right to reform it. Others, however, saw the reform of the Church as a cover for an Enlightenment-inspired campaign against their faith, and much of the lay population supported them. In one region of France, peasants formed a ‘Catholic and Royal Army’ and revolted against the revolution that had supposedly been carried out for their benefit. Women, who found in the cult of Mary and female saints a source of psychological support, were often in the forefront of this religiously inspired resistance to the revolution.
To supporters of the revolution, this religious opposition to their movement looked like a nationwide conspiracy preventing progress. The increasingly harsh measures taken to quell resistance to Church reform prefigured the policies of the Reign of Terror. The plunge into war in the spring of 1792, justified in part to show domestic opponents of the revolution that they could not hope for any support from abroad, allowed the revolutionaries to define the disruptions caused by diehard Catholics as forms of treason. Suspicions that Louis XVI, who had accepted the demand for a declaration of war, and his wife Marie-Antoinette were secretly hoping for a quick French defeat that would allow foreign armies to restore their powers led to their imprisonment and execution.
A ccusations of foreign meddling in revolutionary politics, a so-called foreign plot that supposedly involved the payment of large sums of money to leading deputies to promote special interests and undermine French democracy, were another source of the fears that fuelled the Reign of Terror. Awash in a sea of ‘fake news’, political leaders and ordinary citizens lost any sense of perspective, and became increasingly ready to believe even the most far-fetched accusations. Robespierre, whose personal honesty had earned him the nickname ‘The Incorruptible’, was particularly quick to suspect any of his colleagues who seemed ready to tolerate those who enriched themselves from the revolution or had contacts with foreigners. Rather than any lust for power, it was Robespierre’s weakness for seeing any disagreement with him as a sign of corruption that led him to support the elimination of numerous other revolutionary leaders, including figures, such as Danton, who had once been his close allies. Other, more cynical politicians joined Robespierre in expanding the Reign of Terror, calculating that their own best chance of survival was to strike down their rivals before they themselves could be targeted.
Although the toxic politics of its most radical phase did much to discredit the revolution, the ‘Reign of Terror’, which lasted little more than one year out of 10 between the storming of the Bastille and Napoleon’s coup d’état , was also a time of important experiments in democracy. While thousands of ordinary French men and women found themselves unjustly imprisoned during the Terror, thousands of others – admittedly, only men – held public office for the first time. The same revolutionary legislature that backed Robespierre and the Committee of Public Safety took the first steps toward creating a modern national welfare system and passed plans for a comprehensive system of public education. Revolutionary France became the first country to create a system of universal military conscription and to promise ordinary soldiers that, if they proved themselves on the battlefield, there was no rank to which they could not aspire. The idea that society needed a privileged leadership class in order to function was challenged as never before.
Among the men from modest backgrounds who rose to positions they could never have attained before 1789 was a young artillery officer whose strong Corsican accent marked him as a provincial: Napoleon. A mere lieutenant when the Bastille was stormed, he was promoted to general just four years later, after impressing Robespierre’s brother Augustin with his skill in defeating a British invasion force on France’s southern coast. Five years after the overthrow of Robespierre on 27 July 1794 – or 9 Thermidor Year II, according to the new calendar that the revolutionaries had adopted to underline their total break with the past – Napoleon joined with a number of revolutionary politicians to overthrow the republican regime that had come out of the revolution and replace it with what soon became a system of one-man rule. Napoleon’s seizure of power has been cited ever since as evidence that the French Revolution, unlike the American, was essentially a failure. The French revolutionaries, it is often said, had tried to make too many changes too quickly, and the movement’s violence had alienated too much of the population to allow it to succeed.
To accept this verdict on the French Revolution is to ignore a crucial but little-known aspect of its legacy: the way in which the movement’s own leaders, determined to escape from the destructive politics of the Reign of Terror after Robespierre’s death, worked to ‘exit from the Terror’, as one historian has put it, and create a stable form of constitutional government. The years that history books call the period of the ‘Thermidorian reaction’ and the period of the Directory, from July 1794 to November 1799, comprise half of the decade of the French Revolution. They provide an instructive lesson in how a society can try to put itself back on an even keel after an experience during which all the ordinary rules of politics have been broken.
The post-Robespierre republic was brought down by the disloyalty of its own political elite
One simple lesson from the post-Terror years of the revolution that many subsequent politicians have learned is to blame all mistakes on one person. In death, Robespierre was built up into a ‘tiger thirsty for blood’ who had supposedly wanted to make himself a dictator or even king. All too aware that, in reality, thousands of others had helped to make the revolutionary government function, however, Robespierre’s successors found themselves under pressure to bring at least some of the Terror’s other leaders to justice. At times, the process escaped from control, as when angry crowds massacred political prisoners in cities in the south during a ‘white terror’ in 1795. On the whole, however, the republican leaders after 1794 succeeded in convincing the population that the excesses of the Terror would not be repeated, even if some of the men in power had been as deeply implicated in those excesses as Robespierre.
For five years after Robespierre’s execution, France lived under a quasi-constitutional system, in which laws were debated by a bicameral legislature and discussed in a relatively free press. On several occasions, it is true, the Directory, the five-man governing council, ‘corrected’ the election results to ensure its own hold on power, undermining the authority of the constitution, but the mass arrests and arbitrary trials that had marked the Reign of Terror were not repeated. The Directory’s policies enabled the country’s economy to recover after the disorder of the revolutionary years. Harsh toward the poor who had identified themselves with the Père Duchêne, it consolidated the educational reforms started during the Terror. Napoleon would build on the Directory’s success in establishing a modern, centralised system of administration. He himself was one of the many military leaders who enabled France to defeat its continental enemies and force them to recognise its territorial gains.
Although legislative debates in this period reflected a swing against the expanded rights granted to women earlier in the revolution, the laws passed earlier were not repealed. Despite a heated campaign waged by displaced plantation-owners, the thermidorians and the Directory maintained the rights granted to the freed blacks in the French colonies. Black men from Saint-Domingue and Guadeloupe were elected as deputies and took part in parliamentary debates. In Saint-Domingue, the black general Louverture commanded French forces that defeated a British invasion; by 1798, he had been named the governor of the colony. His power was so great that the American government, by this time locked in a ‘quasi-war’ with France, negotiated directly with him, hoping to bring pressure on Paris to end the harassment of American merchant ships in the Caribbean.
The post-Robespierre French republic was brought down, more than anything else, by the disloyalty of its own political elite. Even before Napoleon unexpectedly returned from the expedition to Egypt on which he had been dispatched in mid-1798, many of the regime’s key figures had decided that the constitution they themselves had helped to draft after Robespierre’s fall provided too many opportunities for rivals to challenge them. What Napoleon found in the fall of 1799 was not a country on the verge of chaos but a crowd of politicians competing with each other to plan coups to make their positions permanent. He was able to choose the allies who struck him as most likely to serve his purposes, knowing that none of them had the popularity or the charisma to hold their own against him once the Directory had been overthrown.
One cannot simply conclude, then, that the history of the French Revolution proves that radical attempts to change society are doomed to failure, or that Napoleon’s dictatorship was the inevitable destination at which the revolution was doomed to arrive. But neither can one simply hail the French movement as a forerunner of modern ideas about liberty and equality. In their pursuit of those goals, the French revolutionaries discovered how vehemently some people – not just privileged elites but also many ordinary men and women – could resist those ideas, and how dangerous the impatience of their own supporters could become. Robespierre’s justification of dictatorial methods to overcome the resistance to the revolution had a certain logic behind it, but it opened the door to many abuses.
Despite all its violence and contradictions, however, the French Revolution remains meaningful for us today. To ignore or reject the legacy of its calls for liberty and equality amounts to legitimising authoritarian ideologies or arguments for the inherent inequality of certain groups of people. If we want to live in a world characterised by respect for fundamental individual rights, we need to learn the lessons, both positive and negative, of the great effort to promote those ideals that tore down the Bastille in 1789.

The environment
Emergency action
Could civil disobedience be morally obligatory in a society on a collision course with climate catastrophe?
Rupert Read

Return of the descendants
I migrated to my ancestral homeland in a search for identity. It proved to be a humbling experience in (un)belonging
Jessica Buchleitner

Economic history
Credit card nation
Americans have always borrowed, but how exactly did their lives become so entangled with the power of plastic cards?
Sean H Vanatta

Human rights and justice
My elusive pain
The lives of North Africans in France are shaped by a harrowing struggle to belong, marked by postcolonial trauma
Farah Abdessamad

Conscientious unbelievers
How, a century ago, radical freethinkers quietly and persistently subverted Scotland’s Christian establishment
Felicity Loughlin

History of technology
Why America fell for guns
The US today has extraordinary levels of gun ownership. But to see this as a venerable tradition is to misread history
French Revolution - List of Free Essay Examples And Topic Ideas
The French Revolution (1789-1799) was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France, leading to significant changes in French and global history. Essays on the French Revolution could explore its causes, significant events like the Storming of the Bastille or the Reign of Terror, and its lasting impact on French society and the wider world. Moreover, discussions on the ideologies and key figures of the Revolution would provide a deeper insight. We have collected a large number of free essay examples about French Revolution you can find at Papersowl. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Womens Rights in the French Revolution
Prior to the French revolution, events such as the Enlightenment also known as the “Age of Reason” sparked a new outlook on traditional french society. From this movement arose the spirit of question in which the people began to question just about everything including the manner in which they treat women. Throughout the 18th century concepts and principles established by both Catholic Church and Protestant authorities were highly valued. Therefore the “ideal” woman was perceived to be poise and subordinate […]
The American and the French Revolutions
The right of revolution was an idea proposed by Enlightenment Philosopher John Locke, which inspired and challenged the colonies in America and the people of France to revolt. Displeased with their current positions with their governments, they mustered up the courage and strength to challenge authority. Through their battles and hardships, both revolutions sought a government that mirrored the Enlightenment beliefs of natural rights, power of the people, and equality. With those goals in mind, they demonstrated the idea that […]
Differences between French, Russian and American Revolutions
A revolution is a successful attempt made by a large group of people to change / challenge the political system of their country. People who are willing to engage and take action in a revolution are trying to fix the struggles in justice, reminding people not to forget the future against the past. People who want to change the political system are looking out for the future of their country. Revolution was the only way average people or citizens felt […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Enlightenment and the French Revolution
The main ideas of Enlightenment thinking led to the French Revolution in many ways. The Enlightenment was a movement that took place in Europe in the 1800s. There were many different views and concepts that were introduced during the period. France was made of three estates or social classes, which were the Clergy, the nobility, and then the commoners or bourgeoisie. There were constant struggles between members of each class. French people like the bourgeoisie loved the ideas of the […]
Was the French Revolution Successful
King Louis XVI once said “The interests of the state must come first.” But it's funny because that's actually the complete opposite of how he did things while he was king. I think the French Revolution was very successful because multiple things got accomplished from it. For example, the social classes went away and everybody was equal, the taxes went down, and France got a new and better ruler that benefited the people a lot more. But how did they […]
American, French and Mexican Revolutions
When it comes to the American Revolution, there was one individual that gave American people an idea of what they should be fighting for. John Locke’s idea of “life, liberty, and estate” heavily inspired Thomas Jefferson’s “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness” when fighting against the British. So why did the Americans revolt? What beliefs did they have? One thing the American, French, and Mexican revolutions have in common is that their governments were corrupt. The Colonists called for […]
The Effects of the French Revolution in the Caribbean
The French Revolution had a major impact on the French colonies of the Caribbean. Eric Martone the author of the article “Gens de Couleur in Saint Domingue and France during the French Revolution” explained that prior to the French Revolution the Caribbean colonies that were owned by France were the top producers of the “Western society’s sugar and coffee.” The majority of this sugar and coffee was produced in San Domingue. As a result of the French Revolution, San Domingue, […]
Causes of the French Revolution
The French Revolution was a huge event in European history, one that shaped the way the French government worked forever. However, there was not just one cause that led to this war. There were many causes in the 1780s that led to the French Revolution, the most important being political unrest, failure to reform, and economic crisis. The first major cause of the French Revolution was political unrest throughout the country. The people of the Third Estate wanted the government […]
Napoleon Bonaparte’s Rise to Power
Napoleon’s Youth Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea, closer to Italy then France. It was governed by Genoa, which was a port in Italy, then local revolutionaries to over. I was later taken by France on 1768 with the Treaty of Versailles. Napoleon was born to a noble family, however, after he was born, the family lost their money. Napoleon was good at math, so he had a special in artillery in the army. Napoleon during the revolution […]
The French Revolution: Great Changes in France
The French Revolution brought about great changes in the society and government of France. The revolution, which lasted from 1789 to 1799, also had far-reaching effects on the rest of Europe. The revolution toppled the government, set up a republic, accelerated political strife under Napoleon who conveyed many of his standards to territories he defeated in Western Europe. Inspired by liberal and radical thoughts, the Revolution significantly changed the course of current history, setting off the worldwide decrease of total […]
The French Revolution Within Frankenstein
Almost twenty years after the end of the French Revolution, Mary Shelley published her gothic horror novel, Frankenstein, in 1818. Shelley grew up with parents who were intellectual radicals (Sterrenburg 143). Yet, she was detached from radicalism and opted for a more conservative perspective (Sterrenburg 143). She did a vast amount of readings on the French Revolution (Sterrenburg 143). By extensively studying the ideas around the revolution, it is not a surprise that they appear embedded through her work, more […]
How the Age of Enlightenment Changed France and the United States
The Enlightenment Age in Europe, which include both the late 17th and 18th centuries, was a period of numerous achievements in various areas of reason such as science, politics, as well as philosophy. During this era, individuals drastically changed their views of the world by questioning and challenging authority and coming up with novel ways of improving humanity and the general society. The changing aspects of philosophy were particularly substantial in this period since philosophers established a structure of ideas […]
The French Revolution: Social and Political Crisis in France
The French Revolution was a watershed period of social and political crisis in France and its colonies that began in 1789 and lasted until the late 1790s. This period consisted of the French citizens that were razed and wanted to redesign their country’s political landscape by uprooting absolute monarchy and the feudal system. The French Revolution played a critical role in overthrowing their own monarchy, establishing a republic, and shaping modern nations by showing the rest of the world the […]
Economic Crisis Druing the French Revolution
The economic issues made by the French kings additionally added to the Revolution. Amid the eighteenth century, the French government spent more cash than it gathered in expenses. By 1788, the nation was bankrupt. Arthur Young, an Englishmen, and spectator, who ventured out to France from 1787 to 1789 furiously portray the living conditions of the workers in his book Travels in France (Campbell, 18). The measure of expense every individual must pay is out of line. Landholders found in […]
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts. They lasted from 1792 until 1802. They happened because of the French Revolution. They fought against Great Britain, Austria and several other monarchies that were extremely popular at the time. How it all Started On Apr. 20, 1792, France started a war with Austria. They lacked discipline, and many noble officers had emigrated. The Austrian and Prussian forces under Charles William Ferdinand, duke of Brunswick, quickly crossed the frontier […]
The Great Changes during French Revolution
The time of the revolutions brought great changes to their focus. The French Revolution, which took place in late 18th century France, was aimed at overthrowing the King or Absolute Monarch who had control over France. The people of France took action upon themselves to dethrone the King and execute him for the crimes he had committed, leading to a war being waged with other countries. These actions led to the Reign of Terror, a bloody and gruesome phase for […]
Was the Reign of Terror Justified Essay
According to an history editor in 1789 the French revolution started as a watershed modern European history when the French revolution ended in the 1790s the Napoleon Bonaparte. The citizen of the country destroy their own country's political landscape, removing long age institutions like absolute monarchy and feudal system. This disaster was ignited by an extensive act of discontent with the French monarchy and also with the bad and poor policies made by Louis XVI in his economy sector, though […]
The Sugar Act and the French Revolution
In addition to the Sugar Act, the government decided to place the Stamp Act in 1765, placing taxes on items like documents, newspapers, and even playing cards. The colonists began to revolt this and petitioned against the Parliament. With this, the colonists began to feel that they were being treated unfairly because of how they were being targeted even though they did not have a say in the government and they did not have certain rights (www.ups.org). The British government […]
The Start of the French Revolution
The start of The French Revolution began due to the disconnect between the people of France and the monarchy, resulting in one of the bloodiest revolts in history. Economic, social and political conditions in France added to the discontent that was felt by many French citizens particularly those from the third estate. One of the main factors that lead to the contribution of the revolution was the crisis in the monarchy. The thoughts of the scholarly people of the Enlightenment […]
The French Revolution and Louis XVI
Louis XVI was one of the rulers during the French Revolution. He was not an impactful leader for the people. He wanted to run from issues instead of facing them head on and he made some promises that could not be kept and had poor decisions. In time of crisis he could not take charge. The rebellion of the Third Estate showed that they felt unrepresented and did not have equal rights as the other estates did, and Louis XVI […]

Social and Political Upheaval in France during French Revolution
During 1789 The French Revolution was a period of a far-reaching social and political upheaval in France and its colonies. The French Revolution started May 5, 1789 and ended around November 9, 1799. There was many causes that cause the French Revolution to break apart and rebuild.The upheaval was caused by the widespread with the French monarchy and the poor economic policies. One of the causes that made the revolution the way it is now was the land that was […]
An Analysis of Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte is broadly viewed as probably the best winner to ever live. Conceived the child of a respectable off the banks of Italy, it just took him years and years to ascend to unmistakable quality during the French Revolution, which started in July 1789 . For the duration of his life he was consistently a student, acquired constantly information; he was an enthusiastic peruser of history, science and reasoning . Beside his goal-oriented character, his diligent qualities likewise helped […]
The French Revolutions Impact on Romantics
The French Revolution is undoubtedly one of the most influential events in Europe during the late 18th century, with lasting concepts in politics, culture, and literature. During this period, Romantic poetry arose and introduced a generation of authors that each uniquely portrayed their own perspectives on the revolution through their works. Some poets referenced a more concrete political standpoint, while others went towards a more intangible concept of freedom and equality. The works written by authors: William Wordsworth and Mary […]
How the American Revolution Led to the French Revolution
In the American Revolution, the thirteen colonies were able to gain independence from Great Britain and an important cause of the victory was the help of the French who made a major impact on the war and were allies of the colonists. They fought together closely and exchanged several ideas, which included thinking that led to the start of the American Revolution. After the war of almost eight years, there were many parts of French culture that had been affected […]
The Tumultuous Tides: Unraveling the Causes of the French Revolution
The French Revolution, which spanned from 1789 to 1799, stands as a pivotal moment in world history. The events that transpired during these turbulent ten years fundamentally altered the trajectory of France and had lasting impacts on the world at large. But what were the catalysts that sparked this massive upheaval? As with most monumental shifts, the French Revolution was a product of an intricate interplay of various factors, which together forged a tempest of change. First and foremost, the […]
An Introduction to the Age of Enlightenment and the French Revolution
On 9th November 1799, the future emperor, Napoleon Bonaparte, took power. The intervening period may be divided into several stages: first the Regency, followed by the reigns of Louis XV and Louis XVI, and finally the French Revolution. France, the most populated country in Europe, was to experience almost eighty years of domestic peace and economic prosperity. The emergence of the philosophical spirit in salons, cafes, and clubs led to the gradual erosion of monarchical authority. Strengthened by their newfound […]
Success and Justice of American Revolution
For thousands of years, people have defended their countries to make sure injustice would never arise, they would even fight against their countries and governments if injustice and corruption ever arose. This longing for freedom, justice and independency evolved into revolutions that attempted and sometimes succeeded in destroying the very building blocks of society over the past 400 years. Out of all the revolutions that tore apart towns, cities and countries, the American, French, Industrial and Mexican revolutions are seen […]
The Scientific Revolution in Western Europe
The Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment were revolutionary for Western Europe and the world. This is because they opened up new ideas through philosophy and science. Their characteristics were scientific ideas that contradicted prior religious beliefs. Additionally, the Enlightenment had characteristics that were full of ideas and innovation to improve people and society. A new form of religion called Deism became popular. Deists believe that God created the Earth, but then left it and is not an “active power.” Tolerance […]
Napoleon Bonaparte Influence on Art
In the 19th century the Europeans were enamored by the exotic culture that they believed was taking place in the Middle Eastern cultures. The Europeans believed that this eastern world was a very eccentric, foreign, feminized and sexualized culture in this far away land. European artists began to depict this Middle Eastern culture in their art whether or not they visited the land. These works were thought to be a clear glimpse into the Middle Eastern land and its people. […]
Napoleon Bonaparte Style to Honour Soldiers
The initial discussion will describe in detail the historical narratives and art periods of both monuments.Next, there will be some exploration of some comparisons, as well as some contrasts between the two pieces. Finally, comparing the two monuments contextually, with a more contemporary piece of art there will be a discussion on how all three monuments historically, symbolically, and politically prove that even in honor, there are moral compasses and hidden political agendas that exist. Arc de Triomphe de l'Étoile […]
Additional Example Essays
- Was the American Revolution really Revolutionary?
- Why Was The American Revolution a Conservative Movement?
- Compare And Contrast In WW1 And WW2
- A Raisin in the Sun Theme
- Logical Fallacies in Letter From Birmingham Jail
- How the Roles of Women and Men Were Portrayed in "A Doll's House"
- Positive Effects of Social Media
- Importance Of Accountability
- The History of the United States of America
- Women in Ancient Greece Theatre Practices
- The Harlem Renaissance Essay
- Two Adjectives to Describe Poe's Literary Works: Dark and Haunting
How To Write an Essay About French Revolution
Understanding the french revolution.
Before starting an essay about the French Revolution, it's crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of this pivotal historical event. The French Revolution, which took place from 1789 to 1799, was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France that had a lasting impact on French history and the wider world. Begin your essay by outlining the key causes of the Revolution, including the financial crisis, social inequalities, and the influence of Enlightenment ideas. Discuss the major events of the Revolution such as the fall of the Bastille, the Reign of Terror, and the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte. Understanding the complexities of these events and their interrelations is essential for writing a well-informed essay.
Developing a Thesis Statement
A strong essay on the French Revolution should be centered around a clear, concise thesis statement. This statement should present a specific viewpoint or argument about the Revolution. For instance, you might analyze the role of the Third Estate in propelling the Revolution, the impact of the Revolution on the establishment of democratic principles, or the reasons for the transition from revolution to the Napoleonic era. Your thesis will guide the direction of your essay and provide a structured and coherent analysis.
Gathering Historical Evidence
To support your thesis, gather historical evidence from credible sources. This may include primary sources like contemporary letters, speeches, and political documents, as well as secondary sources like scholarly articles and history books. Analyze this evidence critically, considering the context, perspective, and purpose of each source. Use this evidence to build your argument and provide depth to your analysis of the French Revolution.
Analyzing Key Events and Figures
Dedicate a section of your essay to analyzing key events and figures of the French Revolution. Discuss how these events were pivotal in the progress of the Revolution and examine the roles and contributions of significant figures such as Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette, Maximilien Robespierre, and Napoleon Bonaparte. This analysis will help readers understand the complexities and dynamics of the Revolution.
Concluding the Essay
Conclude your essay by summarizing the main points of your discussion and restating your thesis in light of the evidence presented. Your conclusion should tie together your analysis and emphasize the significance of the French Revolution in shaping modern political and social thought. You might also want to reflect on the broader implications of the Revolution, such as its impact on the concept of citizenship and the spread of democratic ideals.
Reviewing and Refining Your Essay
After completing your essay, review and refine it for clarity and coherence. Ensure that your arguments are well-structured and supported by historical evidence. Check for grammatical accuracy and ensure that your essay flows logically from one point to the next. Consider seeking feedback from peers, teachers, or historians to further refine your essay. A well-written essay on the French Revolution will not only demonstrate your understanding of this crucial period in history but also your ability to engage critically with historical narratives.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Home — Essay Samples — History — French Revolution — The French Revolution: Causes and Effects of Nation’s Uprising
The French Revolution: Causes and Effects of Nation's Uprising
- Categories: French Revolution Revolution
About this sample

Words: 1593 |
Published: Apr 17, 2023
Words: 1593 | Pages: 4 | 8 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, causes of the french revolution, rise of the third estate, tennis court oath, the bastille and the great fear, declaration of the rights of man and of the citizen, french revolution turns radical, reign of terror, french revolution ends: napoleon's rise.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: History

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 963 words
2 pages / 696 words
2 pages / 701 words
1 pages / 1849 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on French Revolution
The historical relationship between Toussaint L'Ouverture and Napoleon Bonaparte is a complex and multi-faceted one that has been the subject of much scholarly debate and analysis. Both figures played pivotal roles in the [...]
The American and French Revolutions are two pivotal events in world history that have shaped the modern political landscape. Both revolutions were fueled by a desire for freedom, equality, and democracy, but they unfolded in [...]
The French Revolution, an epochal event that reshaped not only the course of French history but also the global political landscape, was ignited by a multifaceted interplay of political, social, and economic factors. To grasp [...]
Revolutions are pivotal events in history that have shaped the political, social, and economic landscape of the world. Two of the most influential revolutions are the French and American Revolutions, which occurred in the 18th [...]
h3>1. How do you think Louis XVI’s qualities as a leader led to the French Revolution?Louis did not know how to lead the general population effectively, and the general population discussed knew this. Louis had never needed to [...]
The Reign of Terror, a period of extreme violence and chaos during the French Revolution, has been a subject of much debate among historians and scholars. Some argue that the Reign of Terror was a necessary response to the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Publish with JSH?
- About Journal of Social History
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
- < Previous
Intellectual History and the Causes of the French Revolution
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Jack R Censer, Intellectual History and the Causes of the French Revolution, Journal of Social History , Volume 52, Issue 3, Spring 2019, Pages 545–554, https://doi.org/10.1093/jsh/shy082
- Permissions Icon Permissions
From the outbreak of the French Revolution in 1789, historians, politicians, and even the interested public believed radical ideas to be at the bottom of this upheaval. Upstaged by social explanations, particularly in the first two-thirds of the twentieth century, intellectual accounts have regained prominence, as recent scholarship has reiterated that ideas mattered. But what ideas? This essay focuses on those ideas that became evident at and around the outbreak of the revolution in 1788–89. For this period, a new wave of scholarship emphasizes not the idea of equality but rather historic rights and patriotism. In these accounts, Enlightenment notions of natural law provided the central justification for radicalizing the revolution as the decade proceeded. Beyond patriotism and rights, this essay also examines other competing discourses, especially those that challenged the church.
Many histories of the French Revolution, beginning with those written in the era itself, assumed, almost axiomatically, that the ideas of the philosophes had caused the “coming” of the event. 1 As social and other historians undermined that theory, intellectual historians moved in new directions, particularly toward the social history of ideas. Most visibly, in the 1960s, Robert Darnton and François Furet showed how subversive (even if not actually revolutionary) ideas had seeped into political culture through pornography and porous state borders. 2 Jürgen Habermas enlarged this vision by arguing that a “public sphere” had emerged in France that allowed subversive ideas and practices in various milieus, such as Freemasonry, the growing periodical press, and learned societies. 3 Still, few scholars claimed a direct link between these ideas and revolution.
Nonetheless, scholarly interest in ideas radically sharpened after the publication of François Furet’s Penser la revolution française in 1978, which opened up a new approach to intellectual history. 4 The first half of the book lambasted the Marxist explanation for the Revolution, which Furet labeled a “catechism” with class struggle at its absolute, immutable center. The twentieth-century Marxists who advocated this view saw themselves as the obvious heirs to the founding of the French republic, but Furet dismissed the Marxist interpretation as sheer fabrication.
Having pushed aside class conflict as the Revolution’s central dynamic, Furet succinctly posited his own theory that even before 1789 the monarchy was toothless. Into that power vacuum, sailed Rousseau’s Social Contract , a tract so powerful that its message eclipsed other ideologies and installed a potent logic—the absolute dominance of popular sovereignty. Yet, activating popular sovereignty required an advocate, an individual who could claim to embody the people’s will. Robespierre filled this role admirably, but he also created the potential for individual tyranny far more potent than that of a king whose authority was inherent in his body but surely did not represent the France of millions of people. From this fatal flaw eventually followed the Committee of Public Safety and the Terror. Furet’s theory was novel: by reducing the Revolution to the Terror, and blaming all of it on the logic of popular sovereignty derived from Rousseau, he tied the philosophe directly to the Revolution. Furet’s approach, drawn sharply to make a criticism of the Revolution as well as a scholarly point, was more specific than those that more generally connected the Enlightenment to the Revolution.
Although Furet’s interpretation did much to supplant Marxist and more traditional intellectual interpretations, it was criticized by scholars who contended that Rousseau’s fame had sprung far more from his sentimental writings than from the Social Contract . More recently, however, some scholars have resuscitated Rousseau’s influence. 5 Nonetheless, Furet provided no explanation for the revolutionaries’ acceptance of Rousseauian ideas other than the political vacuum and the rigorous logic springing from Rousseau’s belief that equality had no limits. How could these specific ideas hijack the mindset of a population?
Keith Baker articulated a parallel but different explanation for the acceptance of revolutionary ideology. 6 He put forth the abstract concept that every individual lives in an environment with discourses—ideational resources—that compete for attention. Facing these choices, people rather unconsciously pick and assemble notions that provide concrete solutions to material problems. In 1789, as governmental problems abounded, the elite—particularly dissatisfied elites—adopted three somewhat disparate discourses to frame their response. Baker labeled these three languages justice (opposition to despotism), reason (opposition to political views accepted because of their antiquity), and will (the right to implement enlightened concepts). The discourse of will approximated Furet’s notion of the role of equality and popular sovereignty. Yet Baker departed from Furet’s understanding of the way that ideology worked, adopting a more complex explanation for the creation of revolutionary ideology that included both chance and an alignment with material conditions. Nonetheless, Furet and Baker generally agreed on the important role of ideas or, more precisely, cultural change as a logic for revolution. 7
Continued work by Keith Baker, now collaborating with Dan Edelstein, remains highly visible, thanks in part to the impressive development of Stanford’s Digital Archive. 8 The architecture of the website springs from Edelstein’s and Baker’s priorities, which reflect their own understanding of the Revolution’s origins. Now, with a twenty-first century digital toolbox, Baker, Edelstein, and others at Stanford oversee technologists who are able to create algorithms that help scholars discover word associations, the building blocks for political discourse, on a far grander scale than what was possible even a few years ago. Still more important in extending their view of the power of ideas has been their new book Scripting Revolution , whose introduction confidently asserts that a revolution only assumes that form after being named a revolution. In practice, this theory implies that the French Revolution did not actually begin after the elections and the seizure of the Bastille in 1789 but instead only commenced later that year when Louis-Marie Prudhomme’s periodical Révolutions de Paris published a contemporary history of the events that labeled them revolutionary. Although Baker’s essay on the eighteenth-century use of the term “revolution” indicated the necessity of naming or “scripting,” he asserted this stronger point after Pierre Rétat pointed out Prudhomme’s essay. But what Rétat had begun in a fairly obscure article (that Baker carefully acknowledged and credited), Baker emphatically embraced and applied to all subsequent revolutions. In short, events called for the label; then, the label “revolution” defined subsequent actions. 9
Despite the significant achievements of Furet and Baker in reconceptualizing the intellectual origins of the Revolution, a new paradigm—classical republicanism—has exerted significant influence since 2000, at least in the English-speaking wing of the field. Baker would hardly contest this, it seems to me, since the convergence between the newer notion and his own arguments is considerable. In fact, he and his former student Johnson Kent Wright have done much to introduce this perspective to explain the French Revolution. 10 What neither they nor anyone else has provided is a standard definition of classical republicanism. For the purposes of this essay, one might assert that the essence of the term lies in the Greek and Roman defense of virtue and personal liberty against an empire. In the eighteenth century, according to this view, resistance fell to the nobility, which, motivated by honor, defended a populace that was itself only motivated by interest and largely incapable of taking up this necessary battle.
The ascendance of classical republicanism in accounts of the events of 1788–89 has tended to relegate the emphasis on natural rights (that Baker links to the language of “will”) to the subsequent radicalization of the Revolution. But this relationship was never quite settled, as Rousseau’s Social Contract advocated both republicanism and natural rights. Furthermore, advocates of classical republicanism also had their eye on equality, although they conceived of it more as the ennobling of all rather than leveling. In short, the equality born of natural law was minimized in 1788–89. Equality had proved difficult to accommodate consistently, much less realize, in the early part of revolutionary struggle driven by classical republicanism. 11
Worth noting as an aside is the prescience of two of the canonical works from a previous generation of scholars. Peter Gay clearly recognized the philosophes’ interest in the ancients but focused on their views that castigated religion, while Robert R. Palmer’s “intermediate bodies” are congruent with the resistance of elites, though clearly he imagined a social elite wider than the nobility of classical republicanism. 12
Evidence for how broad has been the reach of classical republicanism as an explanation for revolution are two distinguished studies in the related fields of fiscal policy and the economy. John Shovlin’s book, The Political Economy of Virtue details the debates beginning in the 1740 s between those who favored “virtuous” small producers over the wealthier, parasitic echelons of society. 13 His study depicts a battle between producers on one side and financiers and the comfortable on the other. Contemporaries believed that luxury and profit were derived from the exploitation of honest workers. Shovlin follows this division through the decades of the eighteenth century; though positions evolved, the rich and the oppressed remained opposed. To be sure, the author sometimes resorts to fancy footwork, as some entrepreneurial activities dropped by the rich and adopted by the poor apparently change from despicable to honored simply by virtue of who performed the work. He praises profit well earned by the hands of the poor and attacks that when the rich become the recipients.
During the revolutionary crisis, Shovlin argues, the advocates for the peasantry and the workers seized the upper hand. Dealing with the deficit, their representatives came to believe that piecemeal reforms would not do and the problem at bottom was an excess of luxury. At the center of this attack was Mirabeau, who argued that “speculation creates a false wealth which undermines real sources of riches in agriculture and in commerce.” 14 Further, Shovlin states that patriotism had influenced and shaped how ordinary citizens understood political economy. Although the author seldom acknowledges the link between patriotism and classical republicanism, the rhetoric he uncovers fits neatly with the broader theory of classical republicanism. 15
In his valuable work Privilege and the Politics of Taxation in Eighteenth Century France , Michael Kwass analyzes the resistance to royal taxation that boiled over in the Old Regime and into the Revolution and directly points out the immediate relevance of classical republicanism to the debate. Kwass notes that the contemporary meaning of classical republicanism included a king and “representative bodies” that coexisted in a milieu where a “vigilant” mistrust of authority and hostility to finance were augmented by the embrace of an authentic rustic existence in which virtue reigned. Watchfulness was necessary, even though somewhat powerless against the encroachment of the sovereign. But Kwass believes that Mireabeau, in the long term struggle of this scenario, articulated in 1750–51 the possibility of coexistence. Morally, the king was obliged toward restraint. Royal taxation had produced crises; only an end to arbitrary rule and its replacement could be successful. 16
Decades later, according to Kwass, Jacques Necker mobilized a similar rhetoric. Brought into government to address the deficit, Necker appealed to patriotism rather than duty to the king, whom he advised to encourage public involvement. As Kwass notes: “By publicizing the working of the state . . . both patriotism and public opinion would emerge to guide the nation to reform, stability, and fiscal strength.” 17 Such remarks were more than just a rhetorical similarity to classical republicanism, as shown by a popular engraving, which linked the minister and his fiscal plan to antiquity. Hallmarks of this classical allusion are the cupids who crowned Necker and his policies with garlands. Central to the piece is a monument labeled as a pyramid, whose lettering indicated that taxes linked to the king were to be eliminated, replaced by charity, equity, and abundance. 18
Although classical republican ideals were thus supposed to inhabit the economy and fiscal policy, they were, compared to the rhetoric of the political sphere, limited at best. Jay M. Smith’s provocative Nobility Reimagined asserts that the revolutionaries desired but failed to construct a republic based on the antique values of honor and virtue. The study describes the nobles’ hostility to Louis XIV’s absolutism and their desire to base society on patriotism and political virtue. As Smith notes, the French were familiar with ancient authors such as Livy, Tacitus, and Plutarch and “the ‘civic humanism’ idiom that served as an important vehicle for transmitting the values of the ancient republics to the early modern Atlantic world.” 19 The embrace of antiquity fueled the pride of nobles but also reminded them of family heritage and their disproportionate political and economic power. This cauldron yielded a compensatory embrace of virtue.
According to Smith, an increased interest in adding equality to the mix of values emerged at mid-century. In particular, commerce, premised on equality in moral and physical goods, was widely considered valuable. The publication in 1756 of Gabriel-François Coyer’s La Noblesse commerçante , which elevated the dignity of the merchant’s profession, furthered change. The contemporary Pierre Jaubert claimed even more as he asserted that “virtue, valor, zeal for the patrie , probity, ability, talent, experience, scorn for dangers, the honor of becoming a martyr for one’s patrie . . . in short, personal merit, are always hereditary in families.” 20 Smith claimed that such attributes were intended to incorporate commoners into the elite. Antique republicanism was socially expansive. In fact, by the 1760 s, the French had turned to ennobling the nation.
Despite all of these signs of inclusivity, Smith also indicates that many nobles were uneasy with this change. With the Revolution opening the door to unimaginable equality, the nobles asserted their difference, particularly by refusing to double the number of commoner representatives to the Third Estate. This action gave rise to a bitter struggle that animated the Revolution. Despite the ultimate demolition of the ideal of classical republicanism in revolutionary France, the passions ignited in 1788–89 reveal its importance to contemporaries and its relevance to history.
The monarch’s multiple foreign policy failures, the subsistence crises of 1788–89, the credit crunch of the 1780s, and the institutional paralysis that undermined all royal efforts at reform would also need to be integrated into any comprehensive analysis of the causes of the Old Regime’s collapse in 1789. 21
Agreeing with Kwass, Smith argues that in the end, these events and discourses cannot be “easily separated.” 22 Thus, politics and circumstances led to a radical division in which the nobility and the king ended up as the opponents of republican morality. To judge by the work of Shovlin, Kwass, and Smith, the central role of ideas in the complex crises of the late 1780 s seems well established. These scholars have begun to connect classical republicanism to the actions taken during this key historical conjuncture.
Ushered by classical republicanism into a smaller space in the intellectual ferment, the role of natural law requires reevaluation. Scholars who focus on classical republicanism in the origins of the Revolution sometimes imply through offhand remarks that natural law exerted a major impact as the Revolution continued. More work needs to be done to chart natural law and connect it to revolutionary events. Historians’ use of these two separate logics undermines the fundamental coherence of revolutionary thinking and perhaps that of the Enlightenment itself. Whereas classical republicanism is premised on the historic resistance to central control, natural law focuses on human equality, yielding a contradiction—perhaps even a useful one—that still resonates throughout modern politics.
Largely outside the political maelstrom, other ideas flourished. Particularly impressive is the study by Darrin McMahon on the “counter enlightenment,” a group that absorbed some progressive notions. 23 Even more astonishing—as it certainly would have been to Voltaire—has been the work on the Catholic enlightenment. Important new books by Jeffrey Burson and Ulrich Lehner have revivified an effort whose roots lie in R. R. Palmer’s Catholics and Unbelievers , which illuminated the balance of tradition and change. 24 Also relevant in this vein are Alan Kors’s studies of the Catholic Church. In his earliest work on Baron d’Holbach, Kors focused on the loneliness of atheists. More recently, he produced two important books that unequivocally revealed that notions of atheism circulated far more widely than even he earlier imagined. In seeking to reject atheism, the Church amplified the reach of what it sought to repress. 25 A new book by Anton Matysin on scepticism and doubt takes a similar tack. 26 Nonetheless, John Robertson’s persuasive The Case for the Enlightenment concludes that the Enlightenment, linked as it was to critiquing religion, was fundamentally reformist. 27 Nevertheless, none of these books on religious doubt attempt to relate their subjects directly to the upheaval in 1789.
None of these recent approaches seems to have raised the importance of intellectuals to quite the level achieved in France’s sister rebellion in North America. Sophia Rosenfeld has chronicled how Tom Paine’s pamphlet Common Sense , highlighting the acuity and value of the thinking of the common man, galvanized public opinion and incited the North American Revolution. Scholars, including Rosenfeld herself, have found no similar impact on the French Revolution. In fact, counterrevolutionaries actually marshaled the notion of common sense to sway the people against the uprising. The complexity and abstractness of many revolutionary plans created an opportunity for reactionaries to argue that common sense did not embrace, or in fact even respect, revolutionary goals. 28
Nonetheless, scholars, including Jay Smith, have noted the pamphlet war preceding 1788–89, in which Sieyès’s What Is the Third Estate? was most visible. 29 William Sewell’s work on Sieyès and Kenneth Margerison’s on pamphlets more generally provide additional evidence for the importance of these texts. 30 Doubtless, these publications could prove to be the most promising place to link the various prerevolutionary languages to the revolutionary plans enacted in Versailles, Paris, and throughout the country, though little evidence exists that the rural population knew much of this exchange among propagandists. Nonetheless, this explosion of print may provide fertile ground to examine the role of ideas.
Entering the crowded arena regarding the intellectual origins of the French Revolution has been Jonathan Israel, who approaches the role of ideas by postulating a direct connection between individual Enlightenment thinkers and specific views that would compete in the Revolution. In this way, Israel is rehabilitating the older approach that focuses not on languages or presuppositions but on on individuals and the power of ideas. Although his work (five books totaling four thousand pages published from 2001 to 2014) could be useful, its combativeness, the overemphases of its argument, and its length all undercut that potential contribution. In fact, his corpus has inspired the most acrimonious debate on the intellectual history of the Revolution in recent years. Largely because of the prominence of this debate, Israel’s work has somewhat obscured the previous decades of more sober, though still contentious scholarship. For this reason, both its arguments and the reactions it has provoked thus require a brief review. 31
To pursue the connection between ideas and the Revolution, Israel sorted the philosophes into two camps. Beginning in the seventeenth century with Spinoza, whose theory denied the spiritual and insisted on atheism, Israel focuses on Spinoza’s belief in “monism,” which held that only one substance (material not spiritual) made up the universe. The philosopher opposed “deists” and others—very prominently Rousseau—who posited a creator who fashioned the universe. From this sharp division, Israel finds two separate logics. The deists, believing in God, held that little could be done to improve on his perfection; monists, holding all matter to be equal, averred that everyone could participate in making life better. In this analysis, the atheists become the source of the moderate, incremental revolution, while the religious appear as political fanatics and authors of the Terror.
Israel presents his thesis forcibly, and the rebuttals have shown similar intensity. Although Furet attacked the Marxists and offended others by insisting that the Jacobin dictatorship was the logical end of the Revolution, even that of 1789, Israel undertakes a far larger, even compulsive effort to organize the Revolution around his Manichaean notion and refute other interpretations.
A storm of criticism greeted Israel’s work. 32 Kent Wright, Carolina Armenteros, Keith Baker, and Harvey Chisick found much to criticize and little to praise in the book. Israel seemingly found it impossible to acknowledge any of their critiques, which he completely rejected. For an example, consider the interchange between Baker and Israel. As author of the iconic biography of Condorcet, Baker had noted that that philosophe did not even include Spinoza in his narrative of human progress. Such a challenge to Israel’s linkages led the latter to remark condescendingly that this could “conceivably” be right, but nonetheless, the two philosophes still strongly shared goals. 33
Possibly, Israel’s resistance to criticism accounts for even more critical reviews that followed, by highly distinguished scholars Lynn Hunt, Jeremy Popkin, and David Bell. 34 In his review, Bell remarked that “Israel, in some remarkably cavalier pages, treats . . . popular actions almost with annoyance. . . . He takes no interest in the common people’s culture.” Israel’s unwillingness to engage with the work of other scholars piqued Lynn Hunt who derided his one-sided accounts: “Israel’s palette is too black and white for . . . subtleties. He is always right, and so are his heroes.” 35
Despite all its faults, Israel’s work does suggest the value in plumbing the ideas of individual intellectual predecessors of the French Revolution. Though few will follow his precise path, a focus on the use of ideas, from the Greeks to the physiocrats, could help illuminate the intellectual history of the revolutionary maelstrom. With this narrower focus, scholars just might be able to supplement the interplay of discourses and embedded presuppositions by seeing ideas at work among intellectuals.
The author wishes to thank Jane Turner Censer and Gary Kates for their advice and assistance.
See, for example, Edmund Burke’s early assertions in his Reflections on the Revolution in France (1790; rept. ed., Garden City, NY, 1961), first published in 1790.
Over the last several decades, Robert Darnton and François Furet have published numerous works in this area. See especially, Robert Darnton, The Forbidden Best-Sellers of Pre-revolutionary France (New York, 1995); and François Furet et al., Livre et société dans la France du XVIIIe siècle (Paris, 1965–70), 2 vols.
Jürgen Habermas, The Structural Transformation of the Public Sphere: An Inquiry into a Category of Bourgeois Society , trans. Thomas Burger (Boston, MA, 1993). See also Ran Halévi, Les Loges maçonniques dans la France d’Ancien Régime: Aux origins de la sociabilité démocratique (Paris, 1984).
François Furet, Interpreting the French Revolution , trans. Elborg Forster (New York, 1981).
See for example, Carol Blum, Rousseau and the Republic of Virtue: The Language of Politics in the French Revolution (Ithaca, NY, 1986); and more recently, Dan Edelstein, The Terror of Natural Right: Republicanism, the Cult of Nature, & the French Revolution (Chicago, 2010). See below for a discussion of Jonathan Israel’s work.
Keith Michael Baker, Inventing the French Revolution: Essays on French Political Culture in the Eighteenth Century (Cambridge, 1990).
For an even more poignant criticism of the role of ideas, consult Roger Chartier, The Cultural Origins of the French Revolution , trans Lydia G. Cochrane (Princeton, NJ, 1991), 67–91. Chartier argues that “books” do not make revolutions; rather it is the cultural act of reading that possesses power.
The website can be found at: https://frda.stanford.edu .
Keith Michael Baker and Dan Edelstein, eds., Scripting Revolution: A Historical Approach to the Comparative Study of Revolution (Stanford, CA, 2015). See Rétat’s article, “Forme et discours d’un journal Révolutionnaire: Les Révolutions de Paris en 1789,” in Claude Labrosse, Pierre Rétat, and Henri Duranton, L’Instrument périodique: La function de la presse au XVIIIe siècle (Lyon, France, 1985), 139–66. One can see Baker’s use of the article in Scripting Revolution , 96–97. Baker was even more emphatic on this point in a discussion at a conference at Haifa University in 1989.
Keith Michael Baker, “A Script for a French Revolution: The Political Consciousness of the Abbé Mably,” in Inventing the French Revolution (Cambridge, 1990); and Johnson Kent Wright, A Classical Republican in Eighteenth-Century France: The Political Thought of Mably (Stanford, CA, 1997). See also Rachel Hammersley, The English Republican Tradition and Eighteenth-Century France: Between the Ancients and the Moderns (Manchester, England, 2010). For more on the mixture of natural law and the right to resist overweening monarchs in the Atlantic world, consult Jack R. Censer, Debating Modern Revolution: The Evolution of Revolutionary Ideas (London, 2016), 7–52.
Edelstein, The Terror of Natural Right .
Peter Gay, The Enlightenment: An Interpretation , 2 vols. (New York, 1967, 1969); and R. R. Palmer, The Age of Democratic Revolution: A Political History of Europe and America, 1760–1800 , 2 vols. (Princeton, NJ, 1959, 1964).
John Shovlin, The Political Economy of Virtue: Luxury, Patriotism, and the Origins of the French Revolution (Ithaca, NY, 2006). Marisa Linton, The Politics of Virtue in Enlightenment France (New York, 2001); Andrew Jainchill, Reimagining Politics after the Terror: The Republican Origins of French Liberalism (Ithaca, NY, 2008).
Shovlin, The Political Economy , 171.
Henry C. Clark, Compass of Society: Commerce and Absolutism in Old Regime France (Lanham, MD, 2007) shows how resistance and accommodation limited at first the liberty of both producers and polity. However, it must be said that such values triumphed as the nineteenth century rolled along. In fact, James Livesey, Making Democracy in the French Revolution (Cambridge, MA, 2001) argues persuasively that already in the Directory (1795–99), both liberal economy and politics had revived, if only briefly before dominating in a later period.
Michael Kwass, Privilege and the Politics of Taxation in Eighteenth Century France: Liberté, Égalité, Fiscalité (Cambridge, 2000), 234–38.
Kwass, Privilege and the Politics of Taxation , 251.
Kwass, Privilege and the Politics of Taxation , 245.
Jay M. Smith, Nobility Reimagined: The Patriotic Nation in Eighteenth-Century France (Ithaca, NY, 2005), 32.
Smith, Nobility Reimagined , 133.
Smith, Nobility Reimagined , 265.
Smith, Nobility Reimagined , 266.
Darrin M. McMahon, Enemies of the Enlightenment: The French Counter-Enlightenment and the Making of Modernity (New York, 2001).
Jeffrey D. Burson, The Rise and Fall of Theological Enlightenment: Jean-Martin de Prades and Ideological Polarization in Eighteenth-Century France (South Bend, IN, 2010); Ulrich L. Lehner, The Catholic Enlightenment: The Forgotten History of a Global Movement (New York, 2016); and R. R. Palmer, Catholics and Unbelievers in 18th Century France (Princeton, NJ, 1939).
Alan Charles Kors, D’Holbach’s Coterie: An Enlightenment in Paris (Princeton, 1976); Epicureans and Atheists in France, 1650–1729 (Cambridge, 2016); and Naturalism and Unbelief in France, 1650–1729 (Cambridge, 2016).
Anton M. Matysin, The Specter of Skepticism in the Age of Enlightenment (Baltimore, MD, 2016).
John Robertson, The Case for the Enlightenment: Scotland and Naples, 1680–1760 (Cambridge, 2005). In fact, in his The Enlightenment: A Very Short Introduction (Oxford, 2015), 116, Robertson goes farther to note that “the Revolution was the antithesis of Enlightenment.”
Sophia Rosenfeld, Common Sense: A Political History (Cambridge, MA, 2011).
Smith, Nobility Reimagined , 255–57. Of course, Peter Gay found group solidarity in the eighteenth-century philosophes in his The Party of Humanity: Essays in the French Enlightenment (New York, 1964).
William H. Sewell, Jr., A Rhetoric of Bourgeois Revolution: The Abbé Sieyes and What Is the Third Estate? (Durham, NC, 1994); and Kenneth Margerison, Pamphlets & Public Opinion: The Campaign for a Union of Orders in the Early French Revolution (West Lafayette, IN, 1998).
Jonathan I. Israel, Radical Enlightenment: Philosophy and the Making of Modernity 1650–1750 (Oxford, 2001); Enlightenment Contested: Philosophy, Modernity, and the Emancipation of Man, 1670–1752 (Oxford, 2006); A Revolution of the Mind: Radical Enlightenment and the Intellectual Origins of Modern Democracy (Princeton, 2010); Democratic Enlightenment: Philosophy, Revolution, and Human Rights 1750–1790 (Oxford, 2011); and Revolutionary Ideas: An Intellectual History of the French Revolution from The Rights of Man to Robespierre (Princeton, 2014).
H-France Forum 9, no. 1 (Winter 2014).
H-France Forum 9, no. 1, 80.
This paragraph is based on the following reviews and responses: David A. Bell, “A Very Different French Revolution,” New York Review of Books (July 10, 2014); Jonathan Israel, “The French Revolution: An Exchange,” New York Review of Books , October 10, 2014; Lynn Hunt, “Louis XVI Wasn’t Killed by Ideas,” New Republic , June 27, 2014; Jonathan Israel and Lynn Hunt, “Was Louis XVI Overthrown by Ideas?” New Republic , July 31, 2014; Jeremy D. Popkin, “Review of Jonathan Israel, Revolutionary Ideas,” H-France Review 15, no. 66 (May 2015); Jonathan Israel, “Response to Jeremy Popkin’s Review, H-France Review 15, no. 67 (May 2015).
Bell, “A Very Different French Revolution,” 2; Hunt, “Louis XVI,” 8.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1527-1897
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Essay on French Revolution
Students are often asked to write an essay on French Revolution in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on French Revolution
What was the french revolution.
The French Revolution was a big change in France’s history, starting in 1789 and ending in 1799. It was a time when people in France fought against their king and rich nobles. They wanted fairness, less poverty, and more say in government. This fight led to the end of the French king’s rule, a new way of making laws, and it even affected other countries.
Causes of the Revolution
France’s government was out of money, and the people were very poor while the king and nobles lived well. High taxes and costly bread made life hard. Angry and hungry, people wanted change.
Major Events
Key events included the Storming of the Bastille, a prison, on July 14, 1789. This showed the king that the people wanted change. Later, the king was removed, and France became a place without a king, called a republic.
Impact of the Revolution
The revolution changed laws in France and gave rights to people who had none. It spread ideas about freedom and equality. These ideas inspired other countries to fight for change, shaping the modern world.
250 Words Essay on French Revolution
Introduction to the french revolution.
The French Revolution was a big change in France’s history. It started in 1789 and lasted for 10 years. People in France were unhappy because the rich had a good life while the poor did not. This led to a big fight for equality and fairness.
Before the revolution, France’s king, Louis XVI, spent a lot of money, and the country was in debt. Poor harvests made food prices go up, making life hard for the common people. The rich, called the nobles, did not pay taxes, so the burden was on the poor. This unfairness made the people angry and ready to change things.
The Revolution Begins
On July 14, 1789, angry people stormed a prison called the Bastille. This event showed that the people wanted to fight against the king’s power. It marked the start of the revolution. After this, the revolutionaries made a new government that said everyone should be treated the same.
Changes and Outcomes
The revolution brought many changes. The king and queen were removed from power and later executed. A new system without a king was tried, but it led to more violence. Eventually, a man named Napoleon took over and became the ruler of France.
The French Revolution was important because it changed how France was governed. It tried to make life fairer for everyone, although it was a very hard and messy time. Today, we remember it as a time when people stood up for their rights and changed their country.
500 Words Essay on French Revolution
The French Revolution was a big change in France’s history. It started in 1789 and lasted for 10 years. During this time, the people of France fought against their rulers because they wanted more fairness and better lives. They were tired of the rich having everything while the poor had very little.
Before the revolution, France was divided into three parts called estates. The first estate was the church, the second was the nobles, and the third was everyone else, including farmers, merchants, and workers. The third estate was not happy because they had to pay most of the taxes while the first and second estates paid very little. The country was also in debt, and there was not enough food for everyone.
The Start of the Revolution
The revolution began when the third estate decided they wanted to make their own group called the National Assembly. They wanted to make laws that were fair for everyone. On July 14, 1789, people stormed a prison called the Bastille, looking for weapons. This event is now celebrated in France every year as Bastille Day.
Changes During the Revolution
Many things changed because of the revolution. The National Assembly made new laws that gave more people rights. They took land from the church and the nobles and gave it to the poor. The king and queen, Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette, were caught trying to leave France and later were killed.
The Reign of Terror
A time called the Reign of Terror happened during the revolution. A man named Maximilien Robespierre was in charge, and many people were killed if they were thought to be against the revolution. This scared a lot of people and showed that even a revolution for good things can sometimes go wrong.
The End of the Revolution and Its Impact
The revolution ended when a man named Napoleon Bonaparte took control of France. He became a very powerful leader and changed many things in France and Europe. Even though the revolution had many sad and scary moments, it is important because it showed that people could fight for their rights and change their country.
The French Revolution is a big part of history because it helped to start the idea that all people should have freedom and be treated equally. It inspired other countries to think about their own governments and how they could make them better for everyone. The French Revolution teaches us that when people work together, they can make big changes in the world.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Mental Health Of Students
- Essay on Mental Health In The Black Community
- Essay on Mental Health Importance
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

French Revolution Essay: Writing Topics and Examples

The French Revolution is one of the most significant historical events, undeniably impacting the world. It marked the end of the monarchy, sparked a quest for freedom, and transformed societies forever. Understanding this pivotal moment requires diving into its layers of politics, social change, and passionate beliefs. In this article, we’ll share proven tips on how to write a French Revolution paper and provide vivid examples. If you need urgent and practical help with this assignment, hire an essay writer online right now!
When Was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution occurred between 1789 and 1799, marking France's tumultuous decade of radical social and political change. Here's a brief French Revolution timeline of key events during this period:

- May 5: Estates-General convenes for the first time since 1614, marking the beginning of the revolutionary process.
- June 17: The National Assembly is formed by members of the Third Estate, signaling defiance against the absolute monarchy.
- July 14: The storming of the Bastille, a symbol of royal tyranny, ignites widespread revolt across France.
- July 14: The National Constituent Assembly adopts the Constitution of 1791, establishing a constitutional monarchy.
- April 20: France declares war on Austria, initiating the French Revolutionary Wars.
- August 10: The storming of the Tuileries Palace led to the monarchy's fall and the establishment of the First French Republic.
- September 20: The National Convention abolishes the monarchy and proclaims the First French Republic.
- September 22: French troops achieve victory at the Battle of Valmy, halting the advance of Austrian and Prussian forces.
- January 21: King Louis XVI is executed by guillotine.
- June 2: The Montagnards seize control of the National Convention, leading to the Reign of Terror.
- July 13: Assassination of Jean-Paul Marat, a prominent Jacobin leader.
- September 17: The Law of Suspects is passed, leading to mass arrests and executions.
- October 16: Queen Marie Antoinette is executed.
- July 28: Maximilien Robespierre, a key figure in the Reign of Terror, is executed, marking the end of the most intense phase of the revolution.
- August 22: The National Convention adopts the Constitution of the Year III, establishing the Directory as the new form of government.
- November 9–10: Napoleon Bonaparte stages a coup d'état, overthrowing the Directory and establishing the Consulate, effectively ending the revolution and leading to the rise of Napoleon as the ruler of France.
French Revolution Essay Topics
Here are 10 compelling topics you can use to produce an essay connected to the French Revolution:
- Causes of the French Revolution and its effects.
- The economic factors behind the French Revolution: Struggles of the Third Estate.
- How did the American Revolution influence the French Revolution?
- The role of Enlightenment ideas in sparking the French Revolution.
- When did the French Revolution start, and how?
- Women in the French Revolution: Voices of resistance and reform.
- Who is Napoleon, French Revolution key figure?
- The impact of the French Revolution on European monarchies: A catalyst for change or consolidation of power?
- Reign of Terror: French Revolution.
- How does the French Revolution continue to shape national identity today?
If you need more interesting topics or even a custom-tailored paper, simply say, ‘ write my essays ,’ and our experts will cater to all your wishes.

What Caused the French Revolution?
The French Revolution causes were propelled by a complex interplay of political, social, and economic factors that simmered for decades before erupting into open rebellion. At its core, the revolution was sparked by deep resentment towards the monarchy and the aristocracy, who held disproportionate power and privileges. At the same time, much of the population suffered from poverty and oppression.
The financial crisis exacerbated by the extravagant spending of King Louis XVI and the French participation in the American Revolutionary War further strained the economy, burdening the already impoverished masses with heavy taxation and economic hardship. Meanwhile, the Enlightenment ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity had permeated French society, inspiring a growing sense of political consciousness and a desire for reform among the educated bourgeoisie and the disenfranchised lower classes. As discontent simmered and economic grievances worsened, the stage was set for a revolution that would forever alter the course of French and world history.
Moreover, the rigid social structure of the Ancien Régime, with its entrenched privileges and hierarchical divisions, exacerbated tensions within French society. The feudal system, characterized by feudal dues and obligations imposed on peasants, fueled resentment and discontent among the rural population, who bore the brunt of the economic burden.
Meanwhile, the bourgeoisie, comprising the educated middle class, chafed against their exclusion from political power and sought to assert their influence. The Estates-General, which represented the three estates of French society – the clergy, the nobility, and the commoners – highlighted the stark disparities in representation and exacerbated social divisions. As grievances mounted and calls for reform intensified, the failure of the traditional institutions to address the burgeoning crisis laid the groundwork for a revolutionary uprising that would ultimately sweep away the old order and herald the dawn of a new era in French history. Are you struggling with analyzing historical events in the form of short compositions? We suggest you say, ‘ write my history essay for me ,’ so our authors can help you swiftly.
How to Write an Essay About What Caused the French Revolution?
Here are some useful tips for writing an essay about the causes of the French Revolution:
.png)
- Thematic Organization
Instead of simply listing causes chronologically, consider organizing your essay thematically. Group relevant causes under overarching themes such as social inequality, economic hardship, and political discontent. This approach allows for a more nuanced analysis and clearer presentation of your arguments.
- Primary Source Analysis
Incorporate primary sources, such as letters, diaries, and speeches from the period, into your essay. Analyzing primary sources provides firsthand accounts and perspectives that can enrich your understanding of the causes of the French Revolution and add depth to your analysis.
- Historiographical Debate
Engage with historiographical debates surrounding the causes of the French Revolution. Explore differing interpretations among historians and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of various arguments. This demonstrates a critical approach to the topic and adds complexity to your essay.
- Global Context
Situate the French Revolution within a broader global context. Consider how Enlightenment ideas, revolutionary movements in other countries, and global economic trends influenced events in France. This global perspective adds depth and relevance to your analysis.
- Comparative Analysis
Compare the causes of the French Revolution with other historical revolutions or periods of social upheaval. Drawing parallels and contrasts can shed light on common patterns and unique factors contributing to revolutionary change, enriching your analysis and providing a broader perspective.
- Historical Contingency
Emphasize the contingency of historical events by considering alternative outcomes and turning points. Explore how different decisions or circumstances could have altered the events leading up to the French Revolution. This fosters a deeper understanding of the complex interplay of factors involved.
- Interdisciplinary Insights
Draw on insights from other disciplines, such as sociology, economics, and political science, to enrich your analysis of the causes of the French Revolution. Consider how social structures, economic systems, and political institutions interacted to shape historical outcomes.
- Critical Reflection
Reflect critically on the relevance and implications of studying the causes of the French Revolution today. Consider how historical narratives are constructed and shape our understanding of contemporary issues such as inequality, democracy, and social change.
- Revision and Peer Review
Seek feedback from peers or instructors on your essay drafts. Revision and peer review can help you identify areas for improvement, clarify your arguments, and strengthen your overall essay.
- Ethical Considerations
Reflect on the ethical dimensions of studying historical events such as the French Revolution. Consider whose voices are represented in historical narratives and whose perspectives may be marginalized or overlooked. Aim for a balanced and inclusive approach that acknowledges diverse experiences and viewpoints.
What Impact Did the French Revolution Have on the Rest of Europe?
In an essay on the French Revolution, writing about its historical impact is one of the most popular pathways for students. The French Revolution reverberated across Europe, igniting revolutionary fervor and political upheaval in many countries. Its impact was profound and far-reaching, influencing the course of European history for decades. In the immediate aftermath of the revolution, neighboring monarchies grew increasingly alarmed by the spread of revolutionary ideals and the threat they posed to the established order. This led to military interventions to quell revolutionary movements and restore monarchic authority, such as the Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna. Additionally, the French Revolution inspired nationalist movements and calls for constitutional reform in European countries, fueling demands for greater political participation and individual rights.
Furthermore, the French Revolution challenged the legitimacy of traditional monarchical rule and paved the way for the rise of new political ideologies, such as liberalism and socialism. The revolutionary upheaval prompted rulers to enact reforms to appease restless populations and prevent further unrest. In some cases, these reforms led to the gradual transition towards constitutional monarchy or representative government, as rulers sought to balance the demands of their subjects with the need to maintain stability and control. However, the spread of revolutionary ideas also incited conservative backlash and repression as ruling elites sought to suppress dissent and preserve their grip on power.
Ultimately, the French Revolution reshaped the political landscape of Europe, accelerating the decline of absolute monarchy and feudalism while laying the groundwork for modern democratic principles and institutions. Its legacy is evident in the waves of political reform, social change, and nationalist sentiment that swept across the continent in the 19th and 20th centuries. Although the revolution initially faced resistance and backlash from entrenched conservative forces, its ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity inspired movements for social justice and political reform throughout Europe and beyond. We also have an insightful guide on how to write an essay on the American Revolution , so be sure to consult it, too!
The End of French Revolution
One of the themes for your essay is when did the French Revolution end and what came next. The French Revolution is generally considered to have ended with the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte to power in 1799. This marked the beginning of the Napoleonic era, which saw the consolidation of power under Napoleon's rule and the establishment of the French Consulate. While the revolutionary fervor of the early years subsided, many of the revolutionary ideals and reforms introduced during the Revolution continued to shape French society and politics throughout the Napoleonic period and beyond.
Napoleon's ascent to power marked a significant turning point in French history, ending the tumultuous revolutionary political turmoil and social upheaval. Under Napoleon's leadership, France experienced a period of relative stability and centralization of power as he implemented a series of reforms to modernize the country and consolidate his authority. However, Napoleon's ambitious military campaigns and imperial expansion eventually led to his downfall, culminating in the defeat of the French Empire in 1815 and the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy. While the French Revolution formally ended with Napoleon's rise to power, its legacy endured, shaping subsequent developments in France and influencing movements for social and political change worldwide. If you’re interested in other pivotal historical moments, read more about the Battle of Hastings 1066 .
The French Revolution Aftermath
The aftermath of the French Revolution was characterized by a complex interplay of political, social, and economic repercussions reverberating throughout France and beyond. While the revolution achieved significant political change, including abolishing the monarchy and establishing a republic, it also unleashed a period of internal conflict, violence, and instability known as the Reign of Terror.
The revolution's radicalism and upheaval led to the widespread destruction of traditional institutions and social norms, leaving a legacy of deep division and mistrust within French society. Additionally, the revolutionary wars sparked by France's expansionist ambitions resulted in widespread devastation and loss of life across Europe. Despite these challenges, the French Revolution also laid the groundwork for modern concepts of democracy, human rights, and citizenship, leaving an indelible mark on Western history. Before we get down to the most important facts about the French Revolution, use our political science essay writing service without hesitation if your deadlines are too short.
What Everyone Should Know About the French Revolution?
Here are 10 captivating French Revolution facts you should know:
- On July 14, 1789, angry Parisians stormed the Bastille, a symbol of royal tyranny and oppression, sparking the French Revolution.
- During the Reign of Terror (1793-1794), led by Maximilien Robespierre, thousands of perceived enemies of the revolution were executed, including King Louis XVI and Queen Marie Antoinette.
- The guillotine became synonymous with the French Revolution's brutality, providing a swift and "humane" method of execution for thousands, including high-profile figures like Robespierre himself.
- Robespierre attempted to create a new state religion, the Cult of the Supreme Being, to replace Catholicism but failed to gain widespread acceptance.
- In October 1789, thousands of women from Paris marched to Versailles to demand bread and protest against the high cost of living, forcing King Louis XVI to return to Paris.
- In June 1789, members of the National Assembly took a pivotal oath on a tennis court, vowing not to disband until a new constitution was established, signaling the end of absolute monarchy in France.
- Adopted in August 1789, the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen proclaimed the rights of all citizens, including liberty, equality, and fraternity, influencing future declarations of human rights worldwide.
- Passed in 1790, the Civil Constitution of the Clergy law aimed to subordinate the Catholic Church to the state, sparking conflict with the Pope and dividing French society along religious lines.
- In July 1794, Robespierre was overthrown in a coup known as the Thermidorian Reaction, leading to the end of the Reign of Terror and a period of political moderation in France.
- Despite its turbulent end, the French Revolution had a profound and lasting impact, inspiring subsequent revolutions, shaping modern concepts of democracy and human rights, and influencing political ideologies worldwide.
Examples of a French Revolution Essay
Writing a French Revolution essay may be difficult from a technical perspective due to the abundance of themes related to this event. However, with the French Revolution essay example in front of you, writer’s block will easily vanish, giving way to creativity and genuine interest in the topic.
The Role of Women in the French Revolution: Challenges to Gender Norms and Struggles for Equality
This essay explores the integral yet often overlooked role of women in the French Revolution, focusing on their defiance of traditional gender norms and their relentless pursuit of equality. Despite being confined to the domestic sphere before the revolution, women emerged as active participants in political activism, forming societies, participating in protests, and contributing to revolutionary discourse. While facing resistance from male-dominated institutions, women such as Pauline Léon, Claire Lacombe, and Olympe de Gouges challenged societal expectations, advocated for political rights, and demanded recognition of their inherent equality.
Economic Turmoil and Social Unrest: Exploring the Impact of Financial Crisis on Revolutionary France
This essay examines the profound interconnection between economic turmoil and social unrest in Revolutionary France, elucidating how financial crises, exacerbated by fiscal mismanagement and regressive taxation, ignited widespread discontent among the populace and catalyzed the collapse of the ancien régime. The economic hardships endured by rural peasants and urban workers alike fueled a climate of social upheaval, manifesting in uprisings, pamphleteering, and demands for political and social reform. The French Revolution of 1789, characterized by the storming of the Bastille and the subsequent establishment of the National Assembly, emerged as a response to the injustices of the existing social order, albeit fraught with political strife and violence. Ultimately, the essay underscores the pivotal role of economic instability in precipitating revolutionary change and shaping the trajectory of modern history.
Legacy of Terror: Assessing the Reign of Terror's Influence on Revolutionary Ideals and Political Discourse
This essay analyzes the enduring legacy of the Reign of Terror during the French Revolution, examining its profound impact on revolutionary ideals and political discourse. It explores how the terror, initially conceived to safeguard the revolution, ultimately devolved into a brutal campaign of violence and repression, betraying the very principles it purported to defend. The essay assesses the ramifications of the terror on revolutionary ideals, highlighting the skepticism it engendered towards violent means of achieving social change and the challenges it posed to the balance between liberty and security. Furthermore, it examines the terror's influence on political discourse, shaping responses to subsequent revolutions and revolutions globally, and underscores the importance of confronting its complexities to navigate contemporary challenges and safeguard democratic principles.
In conclusion, contributing to an essay on the French Revolution necessitates a comprehensive understanding of this transformative period's historical context, key events, and ideological underpinnings.
By employing a structured approach that includes thorough research, critical analysis, and clear argumentation, scholars and students can effectively navigate the complexities of this multifaceted topic.
Emphasizing the significance of economic, social, and political factors while acknowledging the diverse perspectives and interpretations surrounding the revolution enables writers to craft nuanced and insightful essays that contribute to our understanding of this pivotal historical moment.
Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks
You Might Also Like

New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch
EAS Miscellany
Eas miscellany: the digital companion to early american studies: an interdisciplinary journal..

Contemporaneous and Contemporary French Perspectives on the American Revolution: Revisiting the French-American Connection? – Carine Lounissi
The American Revolution was a world event. All of Europe and its colonies were interested in what happened in the North American colonies. French authors and journalists published extensively on the conflict. Consequently, there is a huge corpus of printed materials and archives in continental Europe that scholars are currently exploring to better understand the intellectual, political, economic, and diplomatic aspects of American Independence. In addition, the presence in France of major American figures such Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, and Thomas Jefferson, as well as other less well-known American agents such as merchants and sailors makes it necessary to include the French side of the story in the narrative of the American Revolution. The interactions between Americans and French intellectual, diplomatic, and economic figures also contributed to the definition of American identity. Therefore, I believe that French scholars working on the American Revolution complement U.S.-centered understandings of this event by moving the focus away from the Britain-U.S. perspective. Their work also reminds historians that relations with France were not peripheral to the American Revolution and went beyond the folklore that has come to surround the Marquis de Lafayette.
Studying the American Revolution from the vantage point of a country that has a rich revolutionary tradition of its own has both advantages and drawbacks, however. Because of the French Revolution, French scholars may be more sensitive to the universal meanings of the American Revolution, and they also must acknowledge that the first modern anti-monarchical revolution took place in the U.S. rather than in France. They also have to take stock of the fact that the U.S. invented many of the modern political forms that are still favored by Western democracies, including declarations of rights and written constitutions and conventions. To some extent, the comparison between these two revolutions and the motif of the sister republics still hovers over such studies. The post-Atlantic-Revolutions era of scholarship may have arrived, but the question of the potential “influence” or connection between the American and French Revolutions continues, consciously or not, to influence how scholars study the Age of Revolutions, as the historical sequence of these events still bewilders both French and American scholars.

My own work on French reception of printed works (books, newspapers, and visual representations) pertaining to the American Revolution in the 1770s and 1780s fills a historiographical gap and helps to answer some of the questions raised by the still undecided issue of the connection between the French and American revolutions. It also contributes to our understanding of how ideas circulated in France and between France and the U.S. at key moments in the history of both countries (the end of the Ancien Régime in France and the creation of a republic in the U.S.). The American Revolution brought the topic of colonialism to the foreground of French politics just as debates about French institutions were becoming more central. The French then brought these anti-colonial, anti-aristocratic, and anti-monarchical threads together from 1789 onward. So, on the French side, revisiting French understandings of the American Revolution before the French Revolution may help us better situate our own revolution as well.
Carine Lounissi is Associate Professor of American University at the University of Rouen-Normandy. Her research interests are late eighteenth-century intellectual history and more specifically transatlantic intellectual cooperation and debates during the Age of Revolutions. She has published two books on one of the major figures of these transatlantic circulations, Thomas Paine. The most recent one, relying on new sources and archives by and about Paine, is titled Thomas Paine and the French Revolution (Palgrave Macmillan, 2018). Her current project is devoted to the reception of the American Revolution in France from 1776 onward. She is assistant editor of the Thomas Paine Papers to be published by Princeton University Press in 2025 and a member of the steering committee of the AMERICA2026 project coordinated by Bertrand Van Ruymbeke.
Read Lounissi’s freely accessible article “ The Impact of the American Revolution on French Anticolonial and Antislavery Views in the 1780s ” in EAS ’s Winter 2024 issue.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
French Revolution, revolutionary movement that shook France between 1787 and 1799 and reached its first climax there in 1789—hence the conventional term "Revolution of 1789," denoting the end of the ancien régime in France and serving also to distinguish that event from the later French revolutions of 1830 and 1848.. Origins of the Revolution. The French Revolution had general causes ...
The nobles that were allowed to make legislations were corrupt and often enriched themselves leaving the poor or the so-called third estates to lavish in poverty 1. This paper will attempt to compare and contrast the two revolutions, which occurred in 1789 and 1848, focusing on their causes as well as the impacts associated with their occurrences.
The French Revolution (1789-1799) was a period of major societal and political upheaval in France. It witnessed the collapse of the monarchy, the establishment of the First French Republic, and culminated in the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte and the start of the Napoleonic era. The French Revolution is considered one of the defining events of Western history.
The French Revolution, a cornerstone event in the annals of history, ignited in 1789, a time when Europe was dominated by monarchical rule and the vestiges of feudalism. This epochal period, which spanned a decade until the late 1790s, witnessed profound social, political, and economic transformations that not only reshaped France but also sent ...
The French Revolution was a watershed event in world history that began in 1789 and ended in the late 1790s with the ascent of Napoleon Bonaparte. During this period, French citizens radically ...
From 1789 to 1799, the French Revolution stands as one of the most pivotal episodes in world history. This tumultuous decade witnessed the dramatic overthrow of the Bourbon monarchy, the rise of radical political factions, and the eventual ascent of Napoleon Bonaparte. Rooted deeply in the Enlightenment ideals, the revolution was more than just ...
The French Revolution was a period of political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789, and ended with the coup of 18 Brumaire in November 1799 and the formation of the French Consulate.Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while its values and institutions remain central to modern French political discourse.
Suggested Essay Topics. 1 . To what extent was the French nobility responsible for the crisis that destroyed the ancien régime? 2 . What role did women play in the Revolution? Were they simply a reactionary force—as when bread shortages prompted a march on Versailles—or an active part of the revolutionary public? 3 .
The French Revolution was a time of extreme political and social unrest in Europe and France. France went through an ambitious transformation as privileges of church aristocracy and feudal faded under an unrelenting assault from the other political groups those in the streets and peasants (Spielvogel 526). The further site abruptly overthrew ...
Inventing the French Revolution: Essays on French Political Culture in the Eighteenth Century. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1990. This is one of the best studies of the impact of Rousseau's political philosophy on the French Revolution. de Tocqueville, Alexis. The Old Regime and the French Revolution. Translated by Stuart Gilbert.
119 French Revolution Essay Topics & Research Examples. French Revolution essay is a popular task in colleges and universities. As such, you should know what you are expected to write when given this topic. For example, discuss the worldwide context in which the Revolution took place.
The French Revolution, which unfolded from 1789 to 1799, was a watershed moment that reshaped France's political, social, and cultural landscape and reverberated globally. It signaled the triumph of the people's will against autocratic rule, inspiring movements for liberty, equality, and fraternity across continents.
History of France - The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789-1815: Louis XVI's decision to convene the Estates-General in May 1789 became a turning point in French history. When he invited his subjects to express their opinions and grievances in preparation for this event—unprecedented in living memory—hundreds responded with pamphlets in which the liberal ideology of 1789 gradually ...
France before 1789. 1. Evaluate the French royal court at Versailles, why it existed and the contribution it made to French government and society. 2. "The French nobility did little but concern themselves with leisure, finery, decadence, affairs and intrigues.". To what extent is this statement true in the context of late 18th century ...
The French Revolution is both a cautionary and inspiring tale. The execution of Robespierre and his accomplices, 17 July 1794 (10 Thermidor Year II). Robespierre is depicted holding a handkerchief and dressed in a brown jacket in the cart immediately to the left of the scaffold. Photo courtesy the Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris.
Long Essay on French Revolution Essay is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. Revolutions are a major part of history. Some of the revolution started and faded in time, and some revolutions lasted long enough to bring a change in history and the present. The revolutions are a hot topic in political science studies.
French Revolution - List of Free Essay Examples And Topic Ideas. 43 essay samples found. The French Revolution (1789-1799) was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France, leading to significant changes in French and global history. Essays on the French Revolution could explore its causes, significant events like the Storming of ...
One of the well known revolutions is the French Revolution which occurred in the years 1789 to 1799. Before the French Revolution, France was ruled by an absolute monarchy, this meaning that one ruler had the supreme authority and that said authority was not restricted by any written laws, legislature, or customs. 956 Words.
This essay discusses the French Revolution's causes and effects, also will analyze how the discontent with the French monarchy and King Louis XVI's financial policies led to a massive upheaval that uprooted centuries-old organizations and ultimately played a crucial role in shaping modern nations. Although it failed to reap all of its goals and ...
Many histories of the French Revolution, beginning with those written in the era itself, assumed, almost axiomatically, that the ideas of the philosophes had caused the "coming" of the event. 1 As social and other historians undermined that theory, intellectual historians moved in new directions, particularly toward the social history of ideas. . Most visibly, in the 1960s, Robert Darnton ...
250 Words Essay on French Revolution Introduction to the French Revolution. The French Revolution was a big change in France's history. It started in 1789 and lasted for 10 years. People in France were unhappy because the rich had a good life while the poor did not. This led to a big fight for equality and fairness. Causes of the Revolution
In an essay on the French Revolution, writing about its historical impact is one of the most popular pathways for students. The French Revolution reverberated across Europe, igniting revolutionary fervor and political upheaval in many countries. Its impact was profound and far-reaching, influencing the course of European history for decades.
The French Revolution, which began in 1789, was a transformative event that reshaped France's political, social, and cultural landscape. Lasting for over a decade, this revolution marked a significant departure from the monarchy and heralded the rise of a more egalitarian society. This essay will delve into the key aspects of the French ...
Because of the French Revolution, French scholars may be more sensitive to the universal meanings of the American Revolution, and they also must acknowledge that the first modern anti-monarchical revolution took place in the U.S. rather than in France. ... She is assistant editor of the Thomas Paine Papers to be published by Princeton ...