Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business

Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions

Online only.

How to Write a Sales Plan

Table of Contents
Every business needs a business plan as well as more detailed road maps that offer guidance to each department working toward that common goal. As the revenue-generating engine of your company, the sales department should be a top priority for this type of document, aptly named the “sales plan.” This guide introduces the concept of a sales plan and gives you all the guidance you need to create a sales plan that works for your business.
What is a sales plan?
A sales plan details the overall sales strategy of a business, including the revenue objectives of the company and how the sales department will meet those goals. This may also include revenue goals, the target audience and tools the team will use in their day-to-day. In addition, the sales plan should include examples of the hurdles and pain points the team might encounter, as well as contingency plans to overcome them.
“[A sales plan] is essential to support the growth of an organization,” said Bill Santos, vice president of the ITsavvy Advanced Solutions Group. “A sales plan helps individual reps understand the priorities of the business as well as the measurements by which they will be evaluated.”
Business plans vs. sales plans
Business plans and sales plans are closely linked. A sales plan, though, should outline the actions that the sales department will take to achieve the company’s broader goals. A sales plan differs from a business plan, though both work toward the same end.
“A business plan is a ‘what’ [and] a sales plan is a ‘how,'” said James R. Bailey , professor of management and Hochberg Professional Fellow of Leadership Development at the George Washington University School of Business. “Business plans are where a firm wants to go. A sales plan is a part of how they can achieve that. A business plan is direction; a sales plan is execution.”
For example, a software company that developed a new mobile application might state in its business plan that the app will be installed by 1 million users within a year of launch, while the sales plan describes how that will actually be achieved.
How to write a sales plan
Every sales plan should suit the individual needs of a different company, so they come in all shapes and sizes. There is no one-size-fits-all sales plan; the one you create will be unique to your business. With careful planning, you’ll have a much clearer vision of what you need to accomplish and a road map for how to get there.
Chris Gibbs, vice president of global sales at Centripetal Networks, named some additional items that every sales plan should include.
- Targeted accounts: Assign each salesperson a few key accounts to focus on, and grow from that base.
- Targeted verticals: Sales teams might focus on specific market segments or verticals, such as a particular industry.
- SKUs: Salespeople should emphasize certain SKUs or inventory items rather than get lost in a broad catalog of merchandise to sell.
- Sales and marketing coordination: Sales and marketing teams should work together to create promotions to help generate sales.
- Product road maps: Every company has a road map, and each product should have a road map that shows the plan and direction for a product offering over time to chart out when a product will launch and when it might sunset or be replaced by a newer model.
- Forecasts: Sales forecasting is projecting sales volumes and expectations by comparing them historically to sales of previous years, and then conducting market comparison to determine where sales will fall against the competition.
“Sales plans are extremely important to ensure there is cohesiveness between product teams, sales and marketing,” Gibbs said. “In addition, they’re important for ensuring that timing of new products and/or new version releases coincide with sales objectives and forecasts.”
What are the steps to create a sales plan?
A sales plan is necessary for businesses of every size, from an individual entrepreneur to a Fortune 500 company. When you’re ready to actually write your sales plan, follow these steps:
1. Define the objectives.
Clearly outlining your goals and stating your objectives should always be the first step in creating a sales plan or any other business venture. You should include the expected sales volume and any markets or territories you expect to reach.
For example, let’s say you own a retail store selling household goods and electronics. If your purpose is to establish yourself as a trusted local retailer, ask yourself the following questions:
- If so, are they purchasing anything or just browsing?
- Was it word of mouth?
- Was it through marketing efforts, such as email marketing, direct mail or social media?
- How many are new customers?
- How many are repeat customers?
- Where do you want your sales to come from?
- What are some external and internal factors that could impact your sales? These include industry trends and economic conditions.
When you can precisely state your key objectives, you are setting yourself up to plan later steps around achieving your goals.
2. Assess the current situation.
The next step is to create an honest overview of your business situation in relation to the goal you set in the first step.
Review your strengths and assets. Take a look at your resources and how you can apply them to your goal. This can include personal relationships and competitive advantages like new products or services.
For example, if your goal is to enhance your relationship with your customers, you’d need to ask yourself some questions to examine your current situation:
- What is your current relationship with your customers?
- Where did most of your sales come from?
- Where would you like to expand your sales?
When examining your strengths and opportunities, conduct a SWOT analysis to get a clearer picture of where your business stands.
3. Determine and outline the sales strategies.
Sales strategies are the actual tactics your team will use to reach customers. They can include marketing channels as well as procedures for lead generation and client outreach employed by your salespeople.
Here are two examples of potential sales strategies:
- Use your POS system to retain customer information so you can track current and new customers.
- Employ email marketing, text message marketing , social media, outbound call center services and direct mail marketing campaigns.
4. Define roles for the sales team.
Each member of the sales team should be assigned clear roles, whether they vary from person to person or everyone performs the same functions.
Defining the sales direction of the team is crucial, as it shows the focus of the company and helps the team target and execute sales most effectively.
The plan of attack for the sales team should be communicated clearly by leadership, whether it is from team leaders or the CEO.
5. Inform other departments of sales objectives.
A sales plan shouldn’t just update a company president or C-suite; it should inform the whole organization of the sales team’s objectives.
Clearly outline your plan for the rest of the company to help them understand the goals and procedures of the sales team. Other departments become more efficient when interacting with the sales team and clients. This also conveys a certain level of quality and professionalism to the clients about the company.
6. Provide tools for the sales team.
Provide the tools each member of the sales team needs to achieve the stated goals, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software. The best CRM software is customizable to meet a company’s needs, making it much easier for your team to use the software and work efficiently.
7. Detail how the department will track progress.
Offer strategic direction and insight on how progress will be monitored. Having a quarterly review to assess whether the company is on target is just as important as the plan itself.
Markets change, and so should your sales plan. Keeping it up to date will help you capitalize on the market and achieve your goals. Tracking progress is made easier by the tools you use to collect data. That data will then have to be analyzed and presented in a way which all departments can understand and use for future growth.
Key elements of a sales plan
Every sales plan should also include the following elements.
Realistic goals
You need to set achievable goals . Challenge your sales team, but don’t push too hard. Bailey said that these “deliverables” are among the key points to include in a sales business plan.
“Deliverables need to be as specific as possible and moderately difficult to achieve – specific inasmuch as being measurable in a manner that is uncontested [and] moderately difficult inasmuch as making sales goals too difficult can lead to failure and discouragement.”
Midpoint goals also help build morale and keep the team working toward a larger goal. Instead of having one giant goal, creating smaller goals to achieve along the way will keep your team focused.
Set milestones that give you the opportunity to regularly determine whether you are on track to achieve your sales goals or need to make adjustments.
Sales tools
Tracking sales throughout the term is helpful, and you can employ tools to keep track of each team member as well as the department overall. It also helps establish a culture of accountability among salespeople.
“Tools can help, especially project management and CRM software,” Santos said. “Having a weekly cadence of update and review is also important, as it sends a message that ownership and updates are important.”
Clear expectations and a defined commission structure
Assign goals and responsibilities to each team member to make expectations clear. This is true whether or not each team member has the same goals.
“We meet with each individual to come up with a plan that works for them so that they can reach their goals,” said Leah Adams, director of client success at Point3 Security. “We measure results based on numbers. Each team member has his own plan and how they’re going to get there.”
It’s also necessary to spell out the commission structure in full detail.
“The only real difference is how sales count,” Bailey said. “In petroleum-based products … a few big clients are necessary. Compensation needs to be structured not just in contract value, but in graduated terms: Above $1 million, commissions move from 5% to 9%, and so forth. In smaller-volume enterprises, commissions might be front-loaded with higher percentages early, then graduated down. You have to reward what you want.”
Training programs
Along the way, some training might be necessary to maintain the momentum.
“What’s important to us is that we’re teaching these individuals to be the best salesperson they can be,” Adams said. “We help them do that by constantly training them and giving them knowledge of what’s going on in our industry. Everything stays on track because each member of the team knows their individual goal; though each person has a number, they also know the ultimate goal is for the entire team to hit.”
Adams said that an effective CRM keeps things organized and helps delegate tasks and responsibilities on a schedule that uses the company’s lead information.
Key steps to follow when devising a sales plan
Here are some best practices for creating a sales plan:
- Refer to the business plan. The sales plan should directly address the objectives of the business plan and how those objectives can be achieved.
- Advance clear objectives. The clearer the objectives are, the easier it will be to reach your goals.
- Reference prior sales data. Chart sales over the previous few terms, and project the trend for the current term. New businesses can create sales projections based on expectations.
- Outline the commission structure. This will help motivate your team and help you calculate anticipated costs.
- Be clear about how progress is measured. There should be no dispute about this. If larger clients carry more weight than lower-volume buyers, that should be stated upfront.
The benefits of a sales plan
A sales plan keeps the sales department on track, considering the details of how they must operate to hit their targets and achieve company objectives. Because the sales team is the primary driver of revenue, it is an incredibly important document. [Related article: Adopting a CRM? How to Get Buy-in From Your Sales Department ]
“It’s extremely important to have a sales plan in place, almost a must,” Adams said. “Without this plan, it’s almost impossible to get through the year and hit the company’s sales goals.”
It’s not uncommon to encounter obstacles along the way, however. A good sales plan accounts for that.
“Almost always, you’ll run into the speed bumps along the way, but with a plan in place, it makes it a whole lot easier to navigate through it all,” Adams said. “The sales plan allows you to adjust when necessary so the goal can still be hit. I strongly believe a plan allows you to stay in control and reduce the risk while being able to measure the team’s results along the way to that finish line.”
A solid sales plan helps you deal with unexpected events and acts as a benchmark for where your company is and where you want it to go.
Sales plan templates
Sales templates are helpful in that many of them are based on tried-and-true formats that have been used by businesses across several industries. They can also provide structure so that it is clear to each employee what their role and responsibilities are.
Create your own sales plan by downloading our free template .
“A template helps plan each individual’s daily activities in a structured way,” Adams said. “If you know what each person is doing daily, it’s easier to help correct what’s going wrong. It helps with things like conversion rates, etc. Yes, these templates can be customized in any way a team’s manager sees fit, based on how he believes the team will perform better.”
Sales plans should be unique to the company; however, there are key components they should always include. Because there is somewhat of a formula, you can use a template.
Templates are extremely helpful, Gibbs said. “It creates uniformity for the team, as well as a yearly or quarterly sales plan to present to senior management.”
Gibbs added that templates can easily be customized to meet the needs of a particular business or sales team.
Keeping your team on track with a sales plan
Planning is vital for any business, especially when dealing with sales targets. Before selling your product or service, you must outline your goals and ways to execute them. Essentially, a sales plan enables you to mitigate problems and risks. When there is a clear plan of action, you will know how to proceed in order to attain your goals.
Enid Burns contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
Sales | How To
How to Create a Sales Plan in 10 Steps (+ Free Template)
Published March 9, 2023
Published Mar 9, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Jess Pingrey
WRITTEN BY: Jillian Ilao
This article is part of a larger series on Sales Management .
- 1 Establish Your Mission Statement
- 2 Set Sales Goals & Objectives
- 3 Determine Your Ideal Customer
- 4 Set Your Sales Budget
- 5 Develop Sales Strategies & Tactics
- 6 Implement Sales Tools
- 7 Develop Your Sales Funnel
- 8 Create Your Sales Pipeline
- 9 Assign Roles & Responsibilities
- 10 Monitor Progress & Adjust Accordingly
- 11 Examples of Other Free Small Business Sales Plan Templates
- 12 Sales Planning Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13 Bottom Line
Sales plans enable businesses to set measurable goals, identify resources, budget for sales activities, forecast sales, and monitor business progress. These all contribute to guiding the sales team toward the company’s overall strategy and goals. In this article, we explore how to create a sales plan, including details on creating an action plan for sales, understanding the purpose of your business, and identifying your ideal customers.
What Is a Sales Plan? A sales plan outlines the strategies, objectives, tools, processes, and metrics to hit your business’ sales goals. It entails establishing your mission statement, setting goals and objectives, determining your ideal customer, and developing your sales strategy and sales funnel. To effectively execute your sales plan, assign roles and responsibilities within your sales team and have metrics to measure your outcomes versus your goals and objectives.
Ten steps to creating an effective sales plan
Download and customize our free sales planning template and follow our steps to learn how to create a sales plan to reach your company’s revenue goals.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
Free Sales Plan Template

Thank you for downloading!
💡 Quick Tip:
Once you’ve created a sales plan, give your sales team the tools to execute it effectively with robust customer relationship management (CRM) software.
Use a CRM like HubSpot CRM to help your sales team collaborate on deals, develop sales reports, track deals, and create custom sales dashboards
1. Establish Your Mission Statement
A mission statement summarizing why you’re in business should be part of your action plan for sales. It should include a broad overview of your business’ products or services and your brand’s unique selling proposition. For example, you wouldn’t say, “We provide customers with insurance policies.” Instead, you might frame it as “We provide customers with cost-effective financial risk management solutions.”
It’s essential to fully understand your unique selling proposition before creating a mission statement. This allows you to learn why you’re different from competitors in your industry. It also helps you determine how your unique proposition suits a niche market better.
Steps on how to create a unique selling proposition
For instance, using the same insurance example above, you may realize specific markets are easier to sell based on that selling proposition. Therefore, it’s a good idea to narrow in on your mission statement by saying, “We provide startup businesses with cost-effective risk management solutions.”
2. Set Sales Goals & Objectives
Once you have summarized why you’re in business in a mission statement, begin setting sales goals . Typically, business goals will include one year, but may also include three- or five-year projections.
Steps on how to set sales goals
Here are a few options for how to set sales revenue goals for your business:
- Set sales amount: You may have a specific amount in mind for a sales goal. For instance, you may determine that $200,000 is a reasonable sales goal based on prior sales and your company’s ability to generate new business.
- Desired profitability: First, calculate the total anticipated expenses for the set time period to find the break-even point. From there, you can calculate how much revenue your team needs to bring in to make a certain profit margin. For example, if annual operating costs are expected to be $100,000, and you want to make a 30% profit, your sales goal is $130,000.
- Projected sales forecast: Based on an industry-standard or estimates you attained by running a sales forecast, you may find it’s better to use a projected sales forecast as your sales goal.
Pro tip: Projecting sales can be challenging without a suitable sales forecasting model. Our free sales forecast templates help you create simple, long-term, budget-based, multi-product, subscription-based, and month-to-month business sales forecasts. Some customer relationship managers (CRMs) like Freshsales have sales goal-tracking functionalities that allow you to set and assign sales goals for your team.
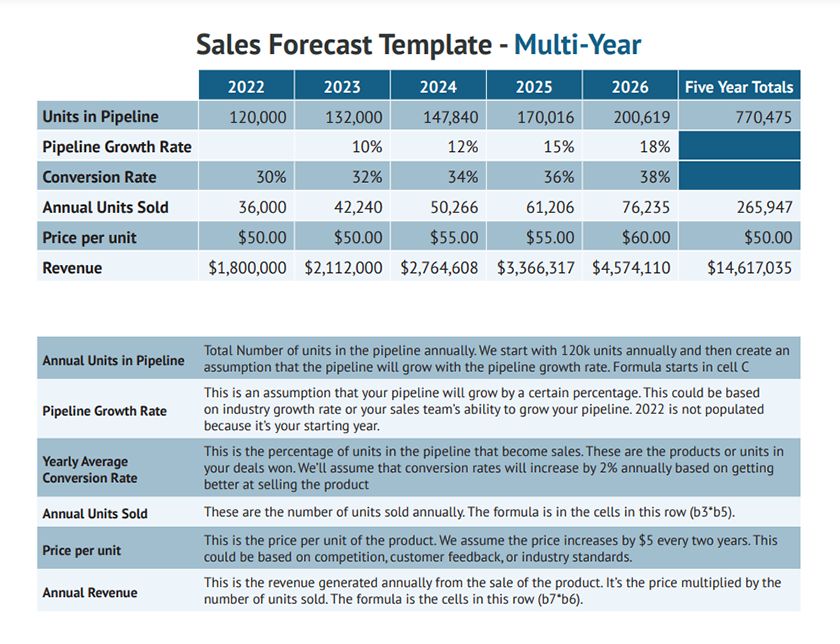
Five-year sales forecast template example (Source: Fit Small Business )
Sales goal tracking in Freshsales (Source: Freshsales )
Sales goals must reflect new business revenue and sales from existing or recurring customers. Then, you must add specific sales objectives that identify and prioritize the sales activities your team needs to complete to meet sales goals. This creates an objective way to measure success in hitting goals at all levels: organizational, sales department, team, and individual sales rep, which is an essential part of sales management .
For example, imagine your total revenue goal is $200,000 in year two and $300,000 in year three. You then add an objective, such as stating you want your business’ revenue from existing customers to grow 15% in year three. This can be measured by evaluating your percentage of revenue from existing customers in year three compared to year two.
3. Determine Your Ideal Customer
Determining the ideal customer or target market is the next step of your business plan for sales reps. It may have been accomplished when you developed your mission statement, but also when you set your sales goals and discovered how broad your market needs to be to reach them. Describing your ideal customer helps dictate who you’re selling to and your selling approach.
One way to establish your ideal customer is by creating a series of unique customer profiles . Each profile specifies key demographics, behaviors, interests, job positions, and geographic information about one of your ideal buyer types. Based on your customer profiles, you can then develop more targeted marketing strategies for lead generation and nurturing to move leads through the sales process more efficiently and close more deals.
Pro tip: Making a customer persona can be challenging, especially if it is based on the wrong data or if you just focus on the demographics. Check out our article on creating a customer persona to help you define your company’s ideal buyer types and guide your lead generation and marketing activities.
4. Set Your Sales Budget
After establishing your objectives and identifying your ideal customer personas—and before developing your actual strategies and tactics—you must identify a sales budget to work with. It should include estimated expenses for salaries, travel expenses, and the cost of any software tools or service providers used to help with sales and marketing. While these are meant to be estimates, research and due diligence should be done to avoid financial errors.
One way to set your sales budget, particularly for software tools and services you may be interested in, is to create and issue a request for proposal (RFP). Issuing an RFP allows you to post a summary of your needs to solicit proposals on potential solutions. In addition to providing accurate budget estimates from various qualified vendors and contractors, it may also help you discover cost-effective or high-performing options you were previously unaware of.
5. Develop Sales Strategies & Tactics
A sales strategy explains how you plan to outsell your competitors and accomplish your sales goals. It defines specific, detailed tactics your team will use to pursue your sales goals. These may involve using Google Ads, cold calling, and drip email marketing campaigns as part of a lead generation strategy. Available strategies differ depending on your company’s resources, skill sets, sales operation, and product or service offerings.
Strategies and tactics should be personalized for your ideal customers based on their unique interests, behaviors, and the best ways to connect with them. For example, some customer profiles show your ideal buyer generally only makes purchases based on trusted referrals. In this case, you could implement a referral strategy that provides incentives to generate more customer referrals .
Plus, different sales strategies will be needed to acquire new business vs keeping existing customers. When selling to existing customers, for example, your strategy could include cross-selling tactics where additional products are recommended based on prior purchases. The short-term cross-selling tactics could require customer service reps to send 30 emails per week recommending a complementary product to existing customers.
For a new business strategy, sales reps might rely on emotional selling methods when using cold calling as a tactic. Instead of product features, cold calling scripts would be geared to evoke feelings that lead to buying decisions. Tactics could reflect the objective of having reps make 15 cold calls each week. They could use a script that opens with a story about how a purchase made a customer feel or how someone felt because they didn’t purchase the product.
Pro tip: Ensuring your strategies are properly executed requires excellent sales leadership and a healthy environment for sales reps to operate in. Our how-to guide for building a positive sales culture shows you how to create an environment that promotes high job satisfaction, low employee turnover, and profitability.
6. Implement Sales Tools
Your sales strategy template should reference the software, hardware, and materials you use to manage the sales operation and make each team member more efficient. One of the most notable tools to include is the customer relationship management (CRM) system . It allows your team to organize contact information, streamline sales tasks, and facilitate communication with customers and leads.
HubSpot CRM , for instance, makes it easy to organize information about leads, contacts, and deal opportunities. Additionally, from a HubSpot CRM lead profile, you can initiate a conversation with that contact by calling, emailing, or scheduling an appointment.
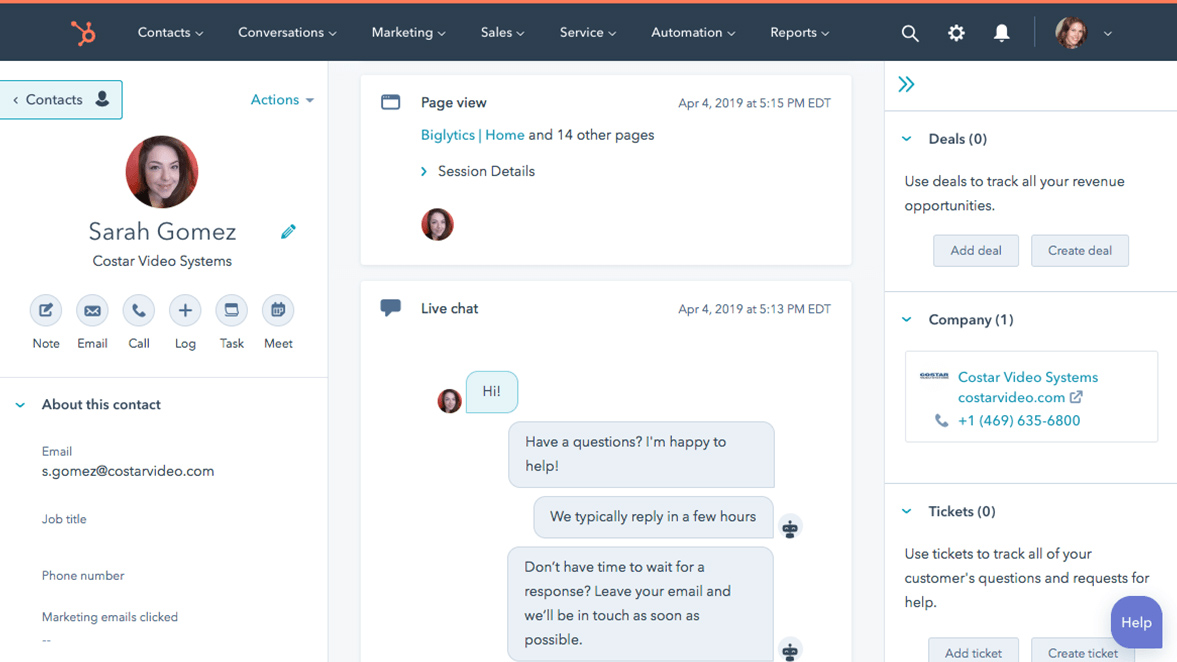
HubSpot CRM contact profile (Source: HubSpot )
CRMs are also used to monitor and report sales progress. For example, many have dashboards and functionality, such as alerts, which make it easy to identify where your team may be underperforming. These could also tell you which leads are most likely to convert and should be focused on. Sales information such as deals closed, revenue generated, and leads created can be presented in a detailed report .
These types of insights can also be shown on the CRM’s system dashboard . Pipedrive is an example of a CRM that has a customizable dashboard that displays both activity information and performance-based data. Activity data include emails sent, received, and outstanding tasks to be completed. Performance-based data, on the other hand, have deals lost or the average value of won deals.
Pipedrive’s customizable dashboard (Source: Pipedrive )
Other sales enablement tools can make your sales team more effective. These include voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone systems , lead generation platforms, email campaign tools, content creation platforms, and task automation software. These tools can be found within CRM software or through CRM integrations and standalone applications.
In addition to technology tools, sales and marketing templates should be used to streamline outreach initiatives. Scenario-based, premade sales email templates , for instance, allow salespeople to have an email already crafted for their specific situation.
Creating and storing business proposal templates in your CRM also streamlines the contact procurement and business proposal generation process . This way, whenever a prospect says they’d like to receive a quote or you’re responding to a request for a proposal, you already have a customizable template ready to go.
Pro tip: Effective cold calling scripts sales reps can use as a guide when placing calls to new leads is a tremendous sales tool to include in your action plan for sales. Get started using our guide for writing a cold calling script , which includes examples and free templates.
7. Develop Your Sales Funnel
Setting up a sales funnel within your sales strategy template lets you visualize the stages of the customer journey, from becoming aware of your business to buying from it. By creating and understanding the different statuses of your leads, you can track progress and determine how effective you are at converting leads to the next stages in the funnel.
Using a sales funnel with conversion rates also makes it easier for you to adjust your sales strategies and tactics based on how effectively you’re getting leads through the funnel. For instance, let’s say you have 100 leads in the awareness stage of the funnel. You decide to cold call 50 of them and write a sales email to the other 50 to qualify leads by setting up a product demonstration.
After each campaign, you find you were able to qualify seven of the leads that were cold-called and only two of the leads you had emailed. Based on these funnel conversion rates of 14% (7/50) from cold calling and 4% (2/50) from emailing, you would likely adjust your tactics to focus more on calling instead of emailing.
Do you need help creating a sales funnel for your business? Our guide to creating a sales funnel explains the step-by-step sales funnel creation process and provides free templates and specific examples.
8. Create Your Sales Pipeline
Once your sales process’ sales funnel stages are identified, develop the sales pipeline stages . These stages include your team’s sales activities to move leads through the funnel. For example, you need to get a lead from the sales funnel stage of brand awareness to show interest in learning more about one of your services. To do this, you could add a sales pipeline activity like setting up a demo or presentation appointment through a cold call.
Adding your sales pipeline to your sales strategy is essential because it describes all the activities your sales reps need to do to close a sales deal. CRM systems like Freshsales allow you to create and track the pipeline stages for each lead or deal within the lead record.
Funnel view of Freshsales’ deal pipeline (Source: Freshsales )
Listing each pipeline stage also helps you identify tools and resources needed to perform the activities for each stage. For example, if you use phone calls to initiate contact with or introduce a product to a lead, you could develop outbound sales call scripts for your team.
After the initial contact by phone, you may use email to follow up after a call and then nurture leads throughout the sales process. As part of your follow-up, create and automate a sales follow-up email template to get them to the next pipeline stage.
The sales funnel shows where a lead is in the sales process. The sales pipeline, on the other hand, lists activities needed to drive leads to the next stage in the sales funnel. Both should be used in your sales strategy when defining the repeatable steps required to generate leads and close deals. Check out our article to learn how to create a winning sales process with insights on both creating a sales process and measuring its success.
9. Assign Roles & Responsibilities
Regardless of the size of your business or sales operation, your business plan for sales reps should include the role and responsibility of each person in the sales team. Each role should have a name, such as someone being a sales development representative (SDR). There should also be a summary of their responsibilities, such as “the SDR is responsible for setting up sales appointments using the activities listed in the sales pipeline.”
Measuring the performance of any sales position is simple through key performance indicators (KPIs). Specific KPIs should be used to measure performance for each role and should be included in your plan. Below are some examples of KPIs that can be used by the members of the sales team and their respective responsibility:
- Sales development representative: Responsible for introducing products and services, qualifying leads, and setting up appointments for the account executive. Performance is measured by calls placed, emails sent, and appointments generated.
- Account executive: Responsible for nurturing qualified leads, delivering the sales pitch , sending quotes, and closing deals. Performance is measured by business proposals sent, the average time in the proposal consideration stage, deals closed, and deal closing rate.
- Customer service representative: Responsible for managing customer needs, handling billing, and managing service tickets by assisting customers. Performance is measured by customer satisfaction, retention rates, and total tickets resolved.
- Sales manager: Responsible for the entire sales operation or team for a specific region or product/service line. Performance is measured by job satisfaction rates of sales reps, pipeline and funnel conversion rates, team sales deals closed, and team revenue growth.
While assigning roles in your plan, a sales rep’s territory could be based on geography, industry, potential deal size, or product/service line, creating more specialization for better results. Our six-step process on proper sales territory management is an excellent resource for segmenting, creating, and assigning sales territories.
This section of the business plan is also a prime spot for individually setting sales quotas for each rep or team needed to hit your organizational sales goals. Sales quotas should be a specific KPI for that sales role and be set based on the experience, skill level, and resources of that individual or team. These quotas should also be based on your organizational, department, and team goals and objectives.
10. Monitor Progress & Adjust Accordingly
Once the strategic business plan is in motion, monitor its progress to make any required adjustments. For instance, while your sales operation is running, you may find certain sales tactics are working better than expected, and vice versa. Your sales goal template should account for using that tactic more, as well as any new sales tools, budgetary changes, new roles, and possibly even a new sales goal.
As in the earlier example, if you found that cold calling was significantly more effective than emailing, reduce or abandon the email method in favor of cold calling. You could also invest in sales tools especially useful for cold calling, such as power dialing using a voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone system, or hire additional staff to place calls. All of these will be part of your updated business plan.
Pro tip: Focusing on the big picture by creating, executing, and adjusting a strategic business plan is one of the most critical traits of an effective sales leader. For more insights on what it means to be a sales leader and how to become one, check out our ultimate guide to sales leadership .
Examples of Other Free Small Business Sales Plan Templates
Apart from our free downloadable sales strategy template, other providers have shared their version of a free strategic sales plan examples. Click on our picks below to see if these templates fit your business process better:
HubSpot’s free sales planning template helps users outline their company’s sales strategy. It contains sections found in most sales plans, as well as prompts for you to fill out your company’s tactics and information. These include company history and mission, team structure, target market, tools and software used, positioning, market strategy, action plan, goals, and budget.

HubSpot sales strategy template (Source: HubSpot )

HubSpot’s sales goals template with the mission, vision, and story of the company (Source: HubSpot )
Visit HubSpot
Asana’s free sales plan template helps organizations analyze their current sales process, establish their sales objectives, identify success metrics, and plan actionable steps. The sales business plan template is embedded within Asana’s platform, automatically integrating aspects such as goals and measuring them against results or sales performance.
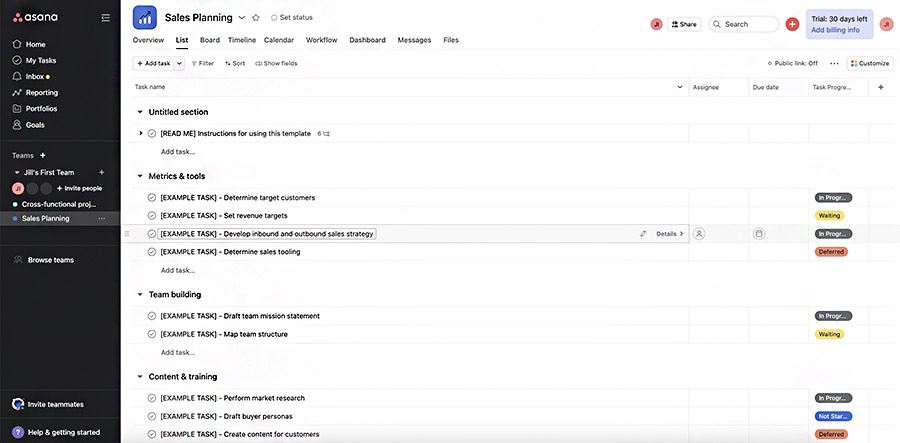
Asana sales plan example (Source: Asana )
Visit Asana
Sales Planning Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is sales planning.
Sales planning is creating a document that outlines your sales strategy, objectives, target audience, potential obstacles, and tools to achieve goals within a specified period. This may include your daily, monthly, quarterly, yearly, and long-term revenue objectives.
What is included in a sales plan?
A sales strategy plan template typically includes the following key elements:
- Target customers, accounts, or verticals
- Stock-keeping units (SKUs)
- Revenue targets or forecasts
- Strategies and tactics
- Pricing and promotions
- Deadlines and directly responsible individuals (DRIs)
- Team structure and coordination
- Market conditions
What are the different types of strategic sales planning?
The type of strategic planning for sales that you choose for your team ultimately depends on different factors. These include your revenue goals, available resources, the ability and bandwidth of your sales team, and your personal commitment to your plans. Once you have determined the details of these factors, you can choose from these types of strategic sales planning:
- Revenue-based sales action plan template: This is ideal for teams aiming for a specific revenue goal. It focuses on in-depth sales forecasting, improvement of conversion rates, and closing more deals.
- Sales business plan based on the target market: This plan is best for businesses that cater to several markets that are different from each other. In this situation, you must create separate sales goal templates for enterprise companies and small businesses.
- Sales goals plan: This focuses on other goals such as hiring, onboarding, sales training plans, or sales activity implementation.
- New product sales business plan: This plan is developed for the launch and continued promotion of a new product.
Bottom Line
While any business can set bold sales goals, creating a sales plan outlines how your team will achieve them. By following the best practices and 10-step process laid out above, your sales goal template defines what your sales process will look like. It will help establish baselines for accountability and identify optimal strategies, tactics, and the tools needed to make your team as efficient as possible.
About the Author

Jillian Ilao
Jill is a sales and customer service expert at Fit Small Business. Prior to joining the company, she has worked and produced marketing content for various small businesses and entrepreneurs from different markets, including Australia, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Singapore. She has extensive writing experience and has covered topics on business, lifestyle, finance, education, and technology.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design
How To Write a Sales Plan That Converts (+ Templates)
By Letícia Fonseca , Nov 17, 2021

Sales plans are often considered the foundation of any successful business plan.
A sales plan outlines an organization’s goals for its future operations and steers the sales team in the right direction.
Every successful business relies on a sales plan to reach its sales goals and pivot its strategy when necessary.
Learn what you need to succeed in writing an impactful sales plan that boosts your conversions and increases customer loyalty.
Don’t know where to start? Create a sales business plan with Venngage’s templates and improve your growth strategy.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a sales strategy plan, what is included in a sales plan, what are the objectives of sales and operations planning.
- How do you write an excellent sales plan?
A sales strategy plan is a document that lists what a company is going to sell, how much the company intends to earn, and how the company plans to go about it.
The sales strategy helps the company determine how to maximize profit margins and stay competitive in the industry.
Here’s an example of a sales strategy plan that includes every action that the sales team is expected to perform.

This ensures that sales managers know what they are responsible for and how the desired output or deliverables for the sales process tie into the business plan.
Return to Table of Contents
A good sales strategy includes a sales plan for your product or service, as well as a plan to market it. Goals to reach your target customers make a sales campaign easy to create and follow.

Here are the most important points to include in a sales strategy plan:
- Product research
- Target audience
- Customer service and customer retention
- Product and service pricing
- Marketing and advertising plan
- Estimated budget for the entire campaign
This sales plan highlights measurable milestones for sales reps to aim for.
We’ve already touched on reasons why companies should use a sales plan, like this example, for their upcoming campaigns.

Below are the four main objectives of creating a sales plan and how they help with sales forecasting.
Align company departments and sales department goals
Different departments can have different perspectives on priorities and progress.
By aligning the company’s other departments with your sales team’s goals, you can ensure that all teams have a shared understanding of the sales plan’s objectives and their holistic contribution towards the business goal.

Create strategic direction for sales teams
A strategic direction plan establishes the company’s goals and objectives for the sales team.
You can formulate strategic direction plans by identifying the following:
- Target audience demographics
- Brand and product niche
- Actions that you want your customers to take
- The best channels to reach customers, such as social media and search engines

Once you’ve identified these, you can create an in-depth plan that can generate conversions in no time. Effective plans, like the one below, keep every customer detail in check.
Better customer-relationship management
A sales plan identifies the individuals and teams responsible for producing results that qualify as milestones for an upcoming business campaign.
With clear assignments, sales managers will easily know which individual or sales team member to approach for additional data.
Mark sales team milestones
Measuring plan milestones are important because they help assess a plan’s performance in a given period or by the end of its execution.

In doing so, team leaders can determine whether the project efficiently used every team member’s efforts and company resources to achieve the plan’s objectives.
The following are excellent examples of milestones for a sales plan:
- Completion of the research phase
- Development of the plan
- Approval of the plan
- Implementation of the plan
How do you write a sales plan?
Take a look at this sales plan. It’s fully detailed, sets deadlines, and keeps everyone updated with the most relevant and newest information so the team is aware of their responsibilities.

Here’s an overview of making an excellent and greatly convincing sales plan:
Compile data from the previous sales year
Create sales targets that meet your sales plan objectives, create a swot analysis, identify demand trends using sales data, look for existing market gaps.
- Appoint key roles for each of your objectives
So, let’s get to it!
Evaluating data from previous marketing campaigns could reveal helpful trends that can improve your upcoming sales plans.
Previous sales data can indicate accurate demographic data, such as lifestyle, age, income, and high sales activities in a given area.
With this data, your team can develop a detailed sales plan that includes your products while keeping in mind your demographic’s language, lifestyle, sensibilities, and more.
Here’s a great way to present this to your superiors and team members.
Related: 10 Demographic Infographic Templates to Share Population Data and More
Simple food sales action plan template
Take your reports from dull to comprehensively lively with this Venngage template. This is a great sales plan template when you have a significant amount of data to show.

You want to get to the point with your sales plan presentations. This fully customizable template makes it easy to share your sales plan data quickly and easily.
With Venngage, you can share your sales plan online with anyone. And when you upgrade to a business account, you can download your plan in a variety of formats, including PNG, PNG HD, PDF, Interactive PDF, and PowerPoint.
All sales targets must be clear, measurable goals that are specific and realistic with a defined deadline.
For example, ‘increase customer retention by 20 percent by the fourth quarter of this year’ is a specific, measurable, attainable, and timely goal.
Aligning your sales targets with the company’s general objectives is the best way to create sales plan objectives that incentivize customers to take action and make a purchase.
These sales KPIs or key performance indicators will keep the sales team aligned and on track with sales goals.
Light strategic sales action plan template
Organize your KPIs for measuring with this simple template. It’s easy to add to a project management interface. Alternately, it can be shared via email.
This helps to have everyone synchronized with the sales plan objectives.

All the colors in this template are neutral, and you can switch them out with your branding assets using Venngage’s convenient drag-and-drop editor.
A SWOT analysis is a tool utilized in the business world to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that a company’s business model may face.
Conducting a SWOT analysis is important for business owners to ensure that their company is as prepared as possible for the future. It can help businesses identify what strategies should be utilized for sales plans.
There are numerous reasons why businesses should use a SWOT analysis:
- A SWOT analysis makes forecasting easier when it is difficult to accurately predict the direction of an industry
- The SWOT analysis is a simplified view of the company’s situation and helps in reaching revenue targets
- It helps companies compare themselves to competitors and create a sales plan that is impactful
It’s undeniable that the data a SWOT analysis produces is essential for any brand.
Blue competitor SWOT analysis template
Easily organize your thoughts with this simple but effective SWOT analysis template.

The grid format helps your team organize their thoughts and build an efficient sales pipeline.
Change the color scheme to suit your brand, or add a background or header image to make the text stand out.
Related: 15+ Business Plan Examples to Win Your Next Round of Funding
Demand trends are changes in the type and quantity of goods that consumers want to buy.
This is crucial data for sales plans because demand helps sales managers gauge if people identify the brand’s products as essentials or luxuries.
One way to identify demand trends is to use a scatter plot. This is what a scatter plot graph looks like:

This graph is an excellent way to find trends and correlations in your data. Here’s how:
- Plot two sets of data on the same graph
- Pick a line that divides the graph into two equal halves
- Compare the height of each data point on the left side of the line to the height of data points on the right side of the line
- Consider how many data points are on one side of the line than the other
If there are more data points on one side, there is likely a correlation between the two sides and possible causation.
Once you’ve identified these trends, you can include graphs and charts on a sales plan template during your presentation.
Visuals and well-made infographic designs are excellent ways to present your data without cluttering your documents or slides.
Revenue scatter plot chart
A great way to present prospective trends is by customizing this simple scatter plot graph.

This template fits perfectly into a presentation slide deck. There aren’t heavy visuals in this template. The layout is clean and simple, leaving nothing to the reader’s imagination.
You can make the chart more relevant by adding brand-related or relevant images. Or use an image from the 3 million+ stock photos available in the Venngage library.
Upload your own images, change the colors and fonts, and more with this template.
Related: How to Choose the Best Types of Charts For Your Data
A market gap is a space between supply and demand. It’s important because if there is a large market gap, it can indicate an economic opportunity for a company to capitalize on.
Market gaps can be as simple as solving a problem identified by an emerging group of customers.
For example, not every business has food delivery services because it’s expensive to make a fleet, and this gap helped create food delivery services.
A market team can find gaps based on three inputs:
- Forecasting models that help analyze data from the company’s previous-year data
- Qualitative research on lacking areas and industry expert reports identifying the target audience’s pain points
- Finding micro to small emerging trends that are already existing in the market
Market research mind map template
Display your research data with an easy-to-understand template, like the example below. You can present every single detail of your research without making it look like a cluttered report.

Using visuals and an easy-to-understand table, your readers can easily follow the strategic sales plan process from start to finish.
Appoint key roles for each of your sales objectives
With a strategic sales plan, you’ll need to appoint team members or departments to specific tasks. This is crucial for achieving the sales plan’s goals.
A good sales manager will assign roles according to each member’s specialty. For example, front-facing sales reps are better positioned to handle the CRM components of sales plans.
Appointing key roles can be as simple as using a table to align a team member’s position with their responsibilities.
However, you will need much more complex diagrams if you’re assigning tasks to projects with dozens of members.
Food Customer Sales Action Plan Template
Highlight every important detail with this free sales plan template that you can send to team members and other departments.

This sales plan template includes a dedicated section for your target market, customer profile, action plan, and task assignments. It’s a great briefing document for both internal and external use.
Fully customize this sales plan template for your brand with Venngage’s My Brand Kit feature.
Related: 9 Sales Infographics to Guide Strategy and Increase Sales
Now you can execute your sales plan with confidence and grow your customer base
Sales plans should be visually attractive as well as impactful. It isn’t always easy to create a sales plan without design experience.
Use the free sales plan template examples in this post to write a sales plan that is powerful and effective.
With these examples as inspiration, you can help team members and your business convince your target market about the dependability and quality of your products.
The Venngage sales plan templates will help you reach your sales goals faster and grow your business in the process.
The Best Free Business Plan Template For Individual Sales Reps
Published: August 14, 2023
Working in sales is challenging at times, and after a while, you may begin to feel fatigued or experience low motivation. Drafting a strategy using a sales business plan template can be just the thing to help refocus your goals.

As a sales rep or account executive , a business plan requires you to think about your efforts from a high level. Who are you targeting? What are your performance goals? How do you plan to achieve them? Not only will a high-level view of your audience and goals help you meet and exceed them, but it might even help you climb the sales career ladder .

Next, I'll share the key elements of a sales business plan as well as provide templates to help get you started.
Sales Business Plan Layout
Free business plan template, the sales plan.
- Individual Business Plan Examples
- High-Level Review
- Tactics and Actions
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Sales and Marketing Alignment
- Obstacles to Success
- Personal and Professional Development
Fill out this form to access your template.
Before writing your plan, doing a bit of work prior to getting started with a template will help you better organize the information you'll need to include. Here's a roadmap to help you brainstorm:
.webp)
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
I’ve found it easiest to start with the end in mind and work backward from there. Naturally, your goals will include your company’s expectations (i.e., quota), but why not go even further?
Be more specific. What do you want to achieve?
A promotion? A certain level of income? A certain number of conversions per month? X number of new clients acquired over the year? How about increasing your average deal size? Whatever it is, put it down in writing and build a plan to get yourself there.
It’s powerful to write down our goals. One year, I decided to write five goals on the whiteboard in my office. At year-end, I had hit four of them, including finally buying the classic car I have had my eye on for 30 years.
2. High-Level Review
Got your goals on hand? Great. Now take a few minutes to ponder the strategies you pursued previously. Which ones worked well and made sense to incorporate again this year? And which didn’t work at all and either need to be adjusted or scrapped altogether?
This review will be your guidepost as you create a strategy and action plan. Be honest with yourself during this reflection. Consider asking for feedback from managers, peers, and clients. You might even seek feedback from prospects who didn’t end up buying from you. What can you do better? Was there anything about your sales tactics that put them off ? Why did they choose a competitor over you?
If this all sounds vague, take a numbers approach to this review. Instead of reviewing your sales strategies , review how your numbers fared throughout the year — revenue generated, number of meetings, number of proposals, number of demos, close rate, and so on. (Your review will be even more telling and powerful if you combine that qualitative review with a quantitative one.)
3. A Strategy
Once you have articulated what you want to achieve, here are the next logical questions to ask:
- How will you do better to reach your goals?
- What new markets will you approach?
- Which customers and prospects will you target?
- How will you frame the sales conversation or sharpen your sales story?
- What new things will you try on the phone, online, or face-to-face?
See that review that we did in that last step? This is where it’ll come in handy. Having a clear idea of what worked and what didn’t will tell you what you should keep or remove from your new strategy. For example, if last year you sent follow-up emails three days after a demo, you could try sending follow-up emails two days this time. This is one of the tactics you could use.
That brings me to my next point. After creating a strategy, it’s time to come up with some tactics and take action.
4. Tactics and Actions
This section is critical because sales is a verb (it may not be in the dictionary, but in my book, it is).
The most well-intentioned goals and the soundest strategies mean nothing if you don’t know what steps to take to achieve them. So for this section of your plan, ask yourself, "What activities am I going to commit to?"
For example, you’ll have X number of face-to-face conversations per month or make Y prospecting calls per week. Whatever the activities are, they should drive what ends up on your calendar on a daily or weekly basis.
Let's say your goal is to make more sales in a shorter time. Include the resources and tools you'll use to achieve that goal in your business plan. In this case, one option would be to use a CRM database to help you keep track of your prospects and eliminate manual data entry (e.g., logging emails and calls), ultimately increasing your efficiency.
5. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Action is action, but if there’s no way to measure its success, you won’t know what worked and what didn’t. You’ll therefore want to put metrics in place to monitor your progress. I recommend setting target numbers for the following KPIs:
- Raw number of deals closed
- Close ratio
- Revenue per account
- Customer retention rate
- Calls and emails
- Quotes or proposals
Remember, set a target number for each of these metrics. That way, you have something to reach toward. You can manually keep track of this information or use dedicated sales software . Or you can ask your manager to give you the performance data.
6. Sales and Marketing Alignment
You know what you want to do, how you’re going to do it, and which metrics you want to track. As you carry out your strategy, be sure to align your efforts with the efforts of your company’s marketing team.
Aligning your sales plan with a whole other department may sound over-the-top, but hear me out: sales teams depend on marketing teams to deliver leads. Even when you’re prospecting, marketing has likely identified the types of companies — and the best job titles — you should use for outreach.
When those leads get to your desk, it’s time to sell to them in a way that continues the nurturing process that marketing started. Say the lead was acquired when they downloaded an ebook on how to improve their productivity. When that lead gets assigned to you, propose your company’s product as a solution. Don’t try to sell it as if you don’t know the person and why they’re there.
It’s helpful to have a CRM that keeps track of your leads’ marketing-related activity. That way, you know which pages they’ve visited, what they’ve downloaded, and whether they’ve reached out to your company before. When carrying out your sales strategy, do so in a way that can fulfill the promises extended by marketing. Take a look at the content on your website, your company’s slogan, and your buyer personas . Use this information to create the perfect pitch.
After, connect with the marketing team to let them know whether that was a good lead or whether the buyer personas and the content on the website need adjustment. If your team does not meet regularly with marketing, bring the issue to your manager. Marketing and sales alignment is critical for your plan’s success.
But there are other obstacles to look out for, too — and you must have them.
7. Obstacles to Success
This is a unique addition I haven’t seen in many plans, but I think it’s an important component. This is where you lay out what could prevent you from reaching your goals and highlight areas where you might need some help. The truth is that you likely know what will get in the way of your success. So instead of using these obstacles as excuses later, point them out at the beginning.
Think carefully: What obstacles will keep you from succeeding?
Do you need new tools or different technology? More flexibility? Better internal support? Put it down in writing now. That way, when you present your plan to your manager (and I strongly encourage you to present your plan to your manager and maybe even a few peers), you give them a chance to support you.
They can either remove the obstacle or tell you it can't be removed in the short term. Either way, it’s in your best interest to declare these potential pitfalls now so that they’re not excuses down the road.
8. Personal and Professional Development
This is another important aspect of the business plan that's often overlooked. I regularly see salespeople fail because they’ve stopped learning and growing.
Many have become stale. Others are bored and ineffective from deploying the same techniques year after year. You wouldn’t go to a doctor that didn’t read medical journals and was treating patients with the same protocol he used twenty years ago, would you?
So commit to growing as a sales professional this year. What are you going to do to grow in your career?
What conferences are you going to attend? Which books are you going to read? Which sales blogs will you follow?
Now, once you have the layout for your sales business plan solidified, you must do two things:
- Get it down on paper - You’re more likely to achieve goals if you write them down. Just trust me on that.
- Get more specific - Using an actual business plan template can prompt you to think deeper about your motivation and action plan.
Below is a free business plan template you can use to get started.
Start building your business plan with this free template.
Featured Resource: Free Business Plan Template

Click Here to Download the Template
Your goal is to think like a business. I’ll teach you how to adapt each section of this general business plan to fit your role as a sales representative.
Business Plan Sections Explained
1. the business opportunity.
The business opportunity is an overview of why you’re doing what you’re doing, who you’re doing it for, and what you hope to achieve. Include your mission statement as a sales representative and why you’re working with the leads and accounts you chose.
In a typical business plan, this section is called an executive summary and highlights the most crucial information for readers. This means you can get creative and inspirational with it, summarizing the information that will motivate you most.
2. Company Description
The company description can refer to the organization(s) you sell for, or you can consider yourself the business being described. Because this is a personal document, choose the format that will most benefit you.
Keep in mind that there are a few elements to include in this section:
3. Company Purpose
This is a short description of the business, providing a high-level overview of who they are, what they offer, and who they offer it to. You might consider creating multiple purposes if you sell on behalf of more than one organization or outlining your purpose as a salesperson.
4. Mission Statement
A mission statement is a formal summary of the aims and values of an organization. If you’re making multiple company descriptions, include one for each organization. You can also include a personal mission statement for why you’ve chosen this organization and how you plan to support their success.
For example, say I’m a sales rep for an editorial company. My mission statement might be “to reach out to writers suffering from imposter syndrome and encourage them to consider editorial help so they can publish with confidence … and inspire future writers who dream of doing the same.”
5. Core Values
Use the core values for the organization(s) you work for, why you chose them, and how they will manifest in your interactions with prospects. For example, HubSpot’s values are humility, empathy, adaptability, remarkableness, and transparency.
If your organization doesn’t have clear core values defined, feel free to come up with your own that will serve as your modus operandi. Three to five values are what you want to have.
6. Product & Service Lines
This section will include:
- Product or service offerings - What are the lines you’re trying to sell, and what functionality does each have?
- Pricing model - How much does each product or service cost prospects, how much commission do you make for each sale, and what parameters do you have for discounts or special deals?
Outline this information in an easy-to-scan table.
In a typical business plan, this would manifest as an overview of the company and all the key leadership roles. However, the most relevant information could be key contacts at your company or companies you sell to, including your sales and marketing contacts (if applicable). If you’re filling out the template to create your sales plan, you’d simply include yourself.
8. Industry Analysis
In this section, you’ll take a look at the state of the industry, including your company’s competitors and your prospect’s competitors. You’ll ask:
- Is the market in growth or decline?
- Who are your competitors?
- What edge do they have over your product?
- How can you get your prospects to buy into the product you’re selling instead?
Your sales manager might already have answers for you or relay new information as it becomes available.
If you’re filling out a business plan to understand your prospects, you’ll want to answer similar questions:
- Who are their competitors?
- What challenges are they looking to solve?
- Is their industry in decline, and if so, can your product help them grow during this decline?
9. Target Market
This will manifest in your business plan as an overview or outline of whom you’re targeting, including general demographics and psychographics. You might want to include:
- Business title
- Location and language
- Pains or problems they're looking to solve
Consider consolidating this information and creating dedicated buyer personas .
10. Buyer Personas
Buyer personas are fictional representations of individuals within your target market. The best practice is to create a buyer persona for each “type” of customer you serve. You can do so using HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool and exporting the information into your business plan.
If you’re filling out the template for a prospect, come up with a buyer persona for the target audience they serve.
11. Location Analysis
Where is the geographic location of your target market? Explain why you’ve chosen the location and the benefits of it. Do the same for your prospects and customers if you’re using the template for them.
Here’s a template you can use:
[Organization name] serves [Location] because [reason]. We found that one of the key drivers of a successful acquisition is [key element], which means our target buyers tend to be in [more specific location descriptor]. We plan to tap into this market by [method].
This might manifest as something like:
“Editorial Company serves authors throughout the United States because editorial work can be done online with virtual meetings and file sharing. We found that one of the key drivers of a successful acquisition is participation in online writing groups, which means our target buyers tend to be active in social media circles. We plan to tap into this market with inbound marketing.”
12. Implementation Timeline
In this section, a business typically specifies how long it will take for its operation to be up and running. They take logistics, partnerships, and other operational elements into account. For your sales plan, you might specify an implementation timeline for various checkpoints, including software adoption, sales-marketing meetings, and more.
Say you told your sales manager you need sales software to keep track of the KPIs you identified earlier. You should take into account the time it will take for that CRM to be purchased and distributed to your team.
If you’re filling out the template to understand a prospect, consider laying out a timeline that specifies when they’ll buy the product, when you’re to follow up with them, and so on.
13. Marketing Plan
If your organization is an inbound sales organization with a marketing department, you might include your marketing and sales service-level agreement (SLA) in this section.
On the other hand, if you’re responsible for cold outreach and prospecting, this section might be helpful to complete on your own. The elements you’ll need to consider are:
Positioning Strategy
- How is this product or service unique and unbeatable compared to its competitors?
- Why are potential buyers going to be interested in the product or service?
- How will you address the buyer persona’s biggest challenges and goals?
Acquisition Channels
- What are your main lead acquisition channels (e.g., search engine marketing, event marketing, blogging, paid advertising, etc.)?
- What do you plan to prioritize this year for lead acquisition?
Tools and Technology
- What tools or systems are you equipped with (e.g., CMS , marketing automation software , etc.)?
14. Financial Considerations and Funding Required
This section is likely more suited for sales reps who are commission-only. You’ll want to consider how much financial collateral will be your responsibility as you sell for the organization. You’ll want to outline:
- Startup costs
- Sales forecasts
- When you'll break even
- Profit and loss projections
These things can be estimated and calculated in Excel and then imported into the template. There’s also a section on the funding required, but you won’t need to fill it out as an individual sales representative. And since your prospects have already secured funding or are established firms, you won’t need to fill this out to understand their business.
Now, finally, we’ve reached the sales plan. This will be done in a separate worksheet — a Google Doc or Word document that you can continue to edit as you evolve in your sales role. You will likely be able to draw on your experience to outline the following:
Sales Methodology
- How will you reach and engage with new leads?
- Are you pursuing an inbound or outbound sales strategy?
- Why does your prospecting strategy make sense for your business?
Sales Organization Structure
- Who do you report to within the organization?
- Is there a marketing department and existing SLA between the departments?
- How are leads qualified?
Sales Channels
- What are your main customer acquisition channels (e.g., online purchasing, through a rep, on location, via email, etc.)?
- What tools or systems are you equipped with (e.g., CMS, live chat , etc.)?
We've covered the different parts of a sales reps' business plan, but what does one of these plans actually look like? Here are five amazing examples of individual business plans for sales reps.
Individual Business Plan Examples for Sales Reps
1. individual development plan.
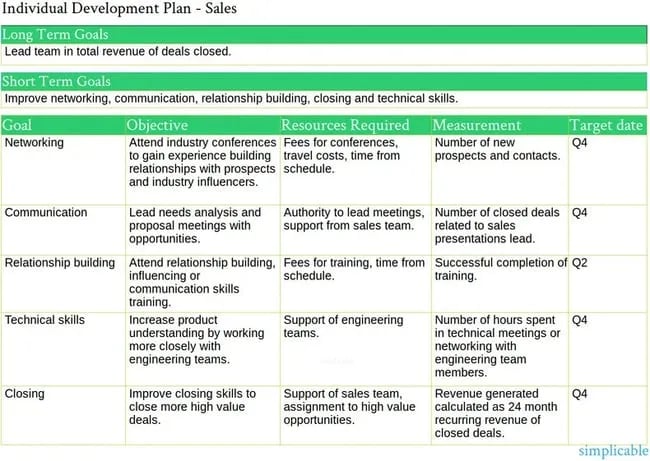
Image Source
An individual development plan (IDP) is a document that you would make to identify your goals and objectives to your employer. After identifying your goals, ensure that your objectives follow the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goal framework. Lastly, for each action, assign a target date. While it does not need to be a specific day of the year, set your timeline by quarters of the year — as seen in the above example.
In addition to the long-term and short-term goals that the above example from Simplicable demonstrates, the resources required section is another useful component of the individual development plan. It directly informs your employer that you require support to achieve the goals and objectives that will ultimately benefit the entire company.
2. Medical Sales Business Plan
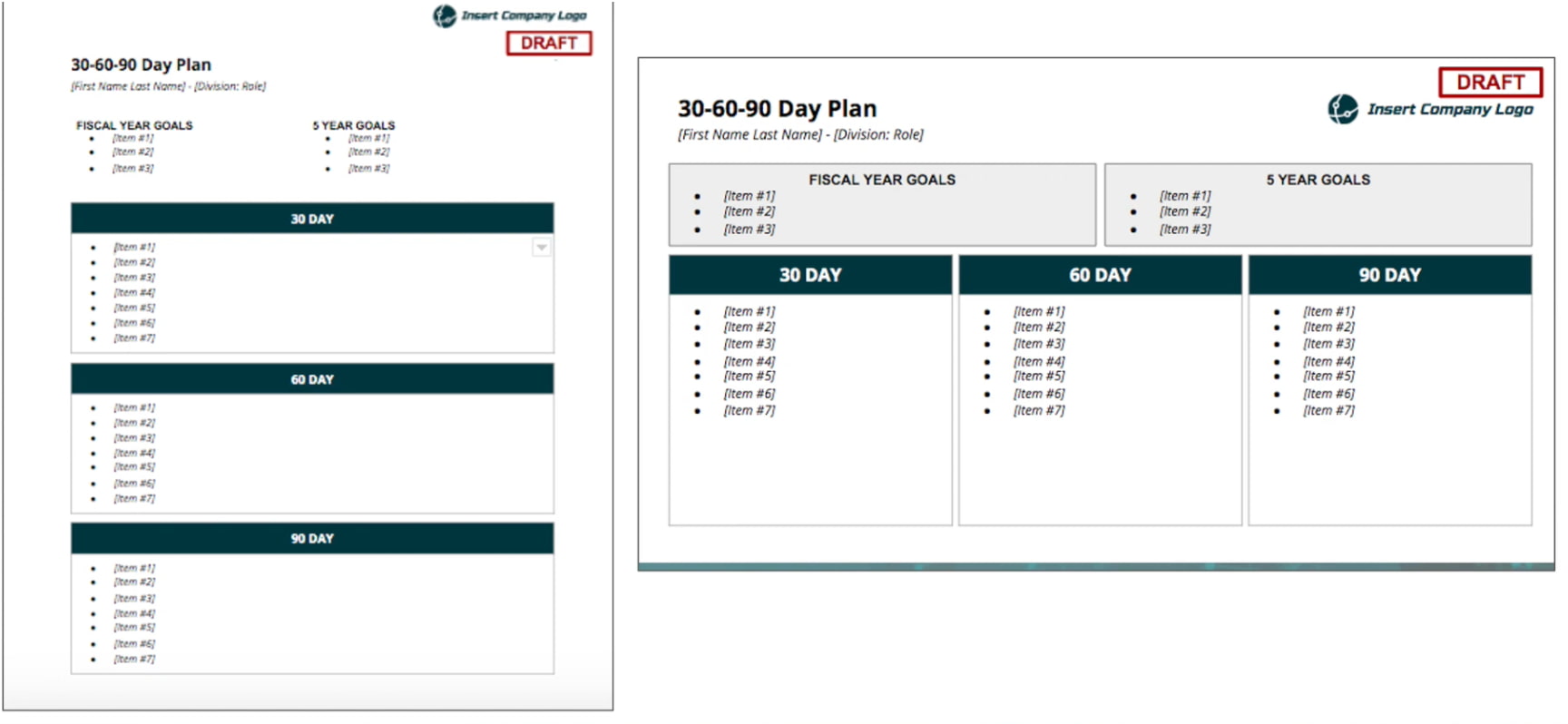
Automotive sales business plans are slightly more challenging than other business plans because there are a lot of factors to consider. When building your plan, you need to start with an analysis. It includes an analysis of your company, industry, customers, and competitors.
Once you have included in-depth analysis, focus on demonstrating your ideas with the four Ps of marketing . The four Ps of marketing are product, price, place, and promotion.
First, outline your focus products. Second, discuss price. You can include current pricing and any proposed changes. Further analysis would include how these prices stack up against competitors and how they affect your customers.
Third, concentrate on your location. This information should detail how your location either adds or decreases traffic and propose solutions for the latter. Lastly, recommend promotions. In the automotive industry, customers are always looking for the best deal.
You also have to be very visible with your marketing. Possibly one of the most important sections of your automotive sales business template, include a detailed course of action for promotional ideas and plans.
4. Territory Business Plan
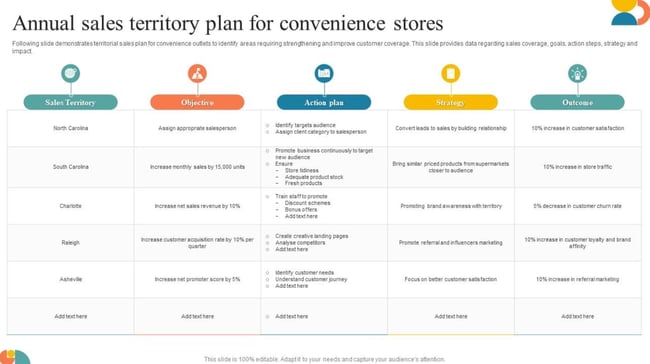
A territory business plan should cover your sales territory. Historically, sales territory is the division of geographical regions for assignments to sales representatives. These representatives are responsible for all customers or clients within that area. This template from Slide Team is for convenience stores, but it can be adapted to suit your business type.
Now, industry, sales potential, and customer type affect territory business planning. An example of customer type is focusing your territory planning on individuals with the same median income. Instead of using geography, this alternative can lead to more strategic success.
When creating a territory business plan, you want to start by analyzing your business goals and objectives. As you build your plan, include an analysis of your prospects and a SWOT analysis . It’s a planning technique that identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information will allow you to propose strategies for sales territories and devise an action plan.
5. Quarterly Business Plan
Creating a business plan for an entire year can be too complex. By separating the year into quarters, you can make your business strategy more actionable. Quarterly business planning is when you set goals and objectives and measure performance after each quarter. Typically, the year segments into Quarter 1 (January 1 to March 31), Quarter 2 (April 1 to June 30), Quarter 3 (July 1 to September 30), and Quarter 4 (October 1 to December 31).
Quarterly business planning focuses on short-term goals that ultimately help fulfill any long-term goals. Your quarterly business plan should include your focus areas, metrics for determining success, and your action plan.
Crush Your Sales Goals with a Business and Sales Plan
With the plan I’ve shared, you'll be prepared to take on any goal or challenge in your career. Consider it a gift to yourself that keeps on giving. Use your plan like a living document, review it weekly, and make tweaks as necessary along the way. Let it dictate what makes it onto your calendar. At year-end, you will be amazed at what you accomplished and thankful you invested the time to do this now.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in May 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

5 Tactics for Becoming the Ultimate Dealmaker, According to BetterYou's CEO

CEO vs COO: Job Roles, Skills, and Salary

The Complete Guide to Business Acumen Training

Business Acumen Interview Questions: What They Are & How to Answer Them

Why Business Acumen is Key to Sales Success (And How to Get It)

The 5 Biggest Ways Technology Has Transformed Sales

7 Ways Salespeople Can Improve Their Business Acumen

17 Columnists Worth Reading on Fast Company, Inc., HBR, Entrepreneur, and More

The Ultimate Sales Glossary: 61 Terms Explained
![writing a sales business plan A Visual Introduction to Customer Lifetime Value [Infographic]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hs-fs/hub/53/file-2225659318-jpg/price_tags-1.jpg)
A Visual Introduction to Customer Lifetime Value [Infographic]
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
How to Write a Sales and Marketing Plan

2 min. read
Updated January 3, 2024
You’ve addressed what you’re selling and why in the products and services section. You now have an understanding of the market and an ideal customer in mind thanks to your market analysis. Now, you need to explain how you will actually reach and sell to them.
The marketing and sales section of your business plan dives into how you’re going to accomplish your goals. You’ll be answering questions like:
- Based on your audience, how will you position your product or service in the current market?
- What marketing channels, messaging, and sales tactics will you implement?
- What’s your business model and how will your business operate day-to-day?
By the end of this section, you should have an outline of what growth looks like, what milestones you intend to hit, and how you’ll measure success. Basically, you’re backing up the opportunity you’ve identified with a solid go-to-market plan.
What to include in the sales and marketing section
The sections you should include act as a useful framework for exploring and defining your marketing and sales tactics.
Create a positioning statement
How does your business differ? What do you do that others don’t? If you’re unsure, work through a handful of strategic exercises to create a simple but convincing positioning statement.
Outline your marketing strategy
A marketing plan brings together strategic goals with tangible marketing activities designed to reach and engage your target market—ultimately convincing them to purchase your product.
Craft your sales plan
A good sales strategy provides actionable steps to reach your goals. Estimate how much you intend to sell and outline a process that anyone else in your business can execute.
Optional sales and marketing information to include
The basics of a marketing and sales plan are fairly straightforward. However, it’s also the perfect place to flesh out any details that you think will make your outreach efforts successful.
Create a unique value proposition
What makes your business unique? How does the solution you provide stand out? This is your chance to point to what you believe potential customers will find more valuable about your business over the competition.
Don't forget digital marketing
While we don’t recommend creating separate traditional and digital marketing plans, it may be wise to explore and address them separately within your plan.
Build your promotional plan
How will you convince your customers to buy your products or services? While actual ads and promotions may be months away, it’s best to think through and even mock up designs now.
Conduct a SWOT analysis
With this simple analysis, you’ll better understand your strengths and weaknesses, along with the opportunities and threats you should account for.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- What to include
- Optional information
Related Articles

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan

How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
How To Build a Strategic Sales Plan + 10 Examples
- March 28, 2024
Every sales team has some sort of plan, even if it’s just “sell more of the product/service that you’re employed to sell.”
A sales plan is a portfolio that includes a layout of your processes, target audience, objectives and tactics. It’s used to guide your sales strategy and predict cost and returns.
Yet without a codified sales plan, it can be difficult to give a sales team the motivation and purpose they need to successfully engage customers and continue to generate revenue.
Not having a sales plan that’s written down and signed off on by stakeholders can lead to confusion around what sales reps should and shouldn’t be doing , which can be demotivating.
It might seem daunting or time-consuming to put together an entire sales plan, but it doesn’t need to be. Here’s how to create a thorough sales plan in 10 simple steps.
What Is a Sales Plan?
A successful sales plan defines your target customers, business objectives, tactics, obstacles and processes. An effective plan will also include resources and strategies that are used to achieve target goals. It works similarly to a business plan in the way it’s presented, but only focuses on your sales strategy.
A sales plan should include the following three components:
- Ideas: If you use specific business methodologies, you may choose to outline key principles and examples of them in action within your sales plan. An example could be conversation tactics when pitching your product to your target customer.
- Processes: In order to streamline productivity and business strategy, you’ll want to make sure your processes are defined within your sales plan. Your sales team should be able to refer to the sales plan when they’re in need of direction.
- Tools and tactics: The most effective sales plans include not only high-level business strategies, but also step-by-step approaches for your sales team to utilize. These tools can include key conversation pieces for your sales reps to use when pitching a product or content to close out a deal.
Solidifying a sales plan is crucial for a strong business model. Taking the time to narrow in on the components above will set you and your business up for success down the road.
Sales Planning Process
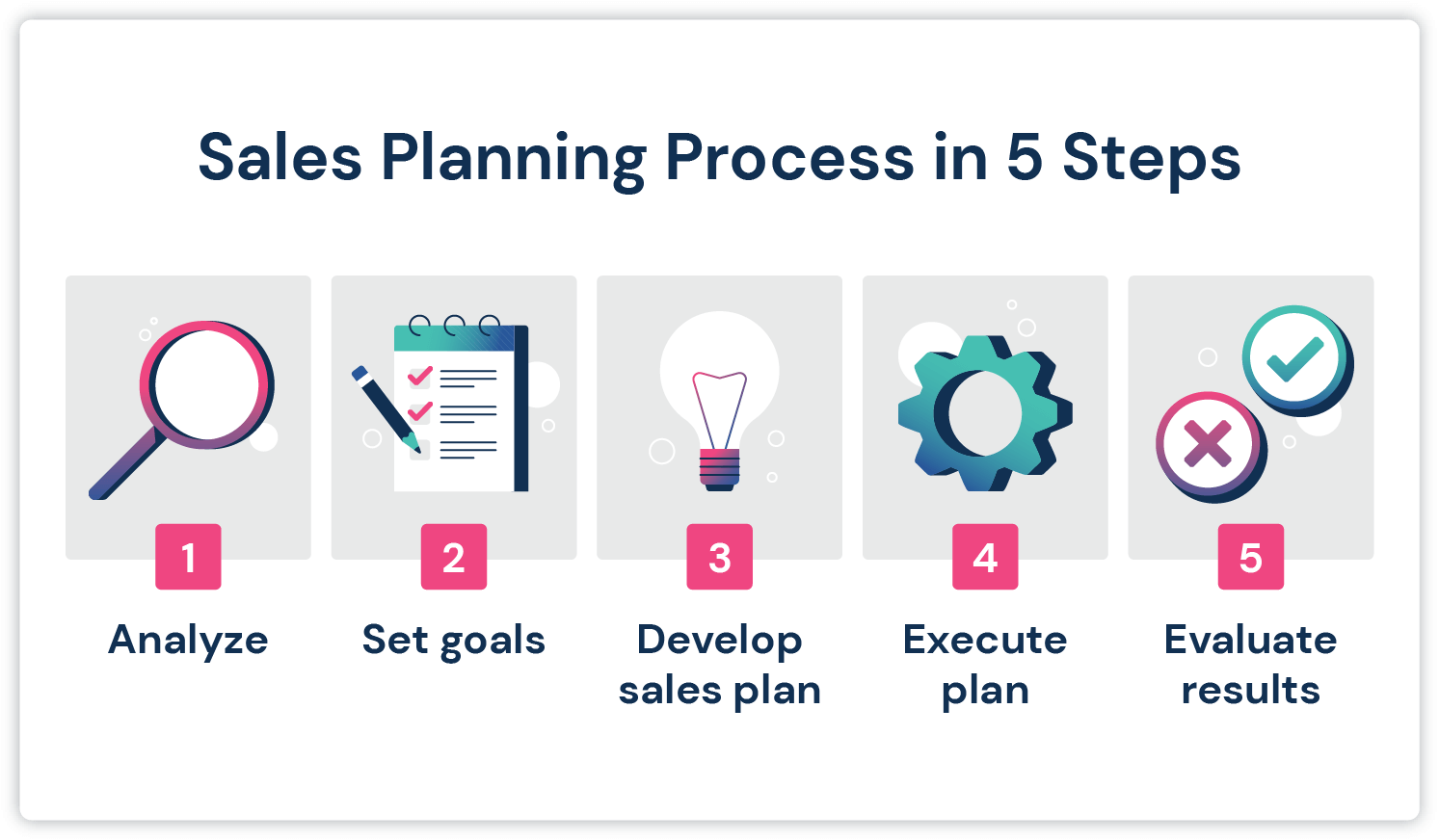
It’s important to keep in mind that sales planning isn’t just about creating a sales plan document. A sales plan should be a go-to item that’s used every day by your team, rather than sitting on your desk collecting dust. Creating an effective sales plan requires high-level strategy.
You should:
- Decide on a timeline for your goals and tactics
- Outline the context
- Write out the company mission and values
- Describe the target audience and product service positioning
- Include sales resources
- Draw out an overview of concurrent activities
- Write an overview of your business road map
- Outline your goals and KPIs
- Outline an action plan
- Create a budget
Below we dive into each of these steps to create your ideal sales plan.
1. Decide on Your Timeline
Setting goals and outlining tactics is not going to be productive if you’re not working toward a date by which you’ll measure your efforts.
Determining the timeline of your sales plan should therefore be your number one consideration. When will you be ready to kick-start your plan, and when is a reasonable time to measure the outcomes of your plan against your SMART goals?
Remember that you need to give the plan a chance to make an impact, so this timeline shouldn’t be too restrictive. However, you also want to make sure that you’re flexible enough to adjust your plan if it’s not producing the desired results.
Most sales plan timelines cover about a year, which may be segmented into four quarters and/or two halves to make it a little more manageable.
2. Outline the Context
Use the first page of your sales plan to outline the context in which the plan was created.
What is the current state of the organization? What are your challenges and pain points? What recent wins have you experienced?
Do you have tighter restrictions on cash flow, or does revenue appear to be growing exponentially? How is your sales team currently performing?
While you’ll discuss your business plan and road map later in the document, you can also outline the long-term vision for your business in this section. For example, where do you want to see the business in five years?
Tip: Comparing the current situation with your vision will emphasize the gap between where you are now and where you need to be.
3. Company Mission and Values
It’s essential that you put your mission and values at the heart of your business. You need to incorporate them into every function – and this includes your sales plan.
Outlining your mission and values in your sales plan ensures that you remember what the company is striving for, and in turn helps ensure that your approach and tactics will support these objectives.
Remember: A strong brand mission and authentic values will help boost customer loyalty, brand reputation and, ultimately, sales.
4. Target Market and Product/Service Positioning
Next, you’ll need to describe the market or markets that you’re operating in.
What is your target market or industry? What research led you to conclude that this was the optimal market for you?
Who within this industry is your ideal customer? What are their characteristics? This could be a job title, geographical location or company size, for example. This information makes up your ideal customer profile .
If you’ve delved further into audience research and developed personas around your target market, then include them in here, too.
5. Sales Team and Resources
This step is simple: Make a list of your sales resources, beginning with a short description of each member of your sales team.
Include their name, job title, length of time at the company and, where appropriate, their salary. What are their strengths? How can they be utilized to help you hit your goals?
You should also include notes around the gaps in your sales team and whether you intend to recruit any new team members into these (or other) roles.
Tip: Communicate the time zones your team members work in to be mindful of designated work hours for scheduling meetings and deadlines.
Then, list your other resources. These could be tools, software or access to other departments such as the marketing team – anything that you intend to use in the execution of your sales plan. This is a quick way to eliminate any tools or resources that you don’t need.
6. Concurrent Activities
The next step in creating your sales plan involves providing an overview of non-sales activities that will be taking place during the implementation of your sales plan.
Any public marketing plans, upcoming product launches, or deals or discounts should be included, as should any relevant events. This will help you plan sales tactics around these activities and ensure that you’re getting the most out of them.
7. Business Road Map
For this step, write up an overview of your business’s overall road map, as well as the areas where sales activities can assist with or accelerate this plan. You’ll need to collaborate with the CEO, managing director or board of directors in order to do this.
In most cases, the business will already have a road map that has been signed off on by stakeholders. It’s the sales manager’s job to develop a sales plan that not only complements this road map, but facilitates its goals.
Tip: Highlight areas of the road map that should be touchpoints for the sales team.
Ask yourself what your department will need to do at each point in the road map to hit these overarching company goals.
8. Sales Goals and KPIs
Another important part of the sales plan involves your sales goals and KPIs.
Outline each goal alongside the KPIs you’ll use to measure it. Include a list of metrics you’ll use to track these KPIs, as well as a deadline for when you project the goal will be achieved.
It’s vital to make these goals tangible and measurable.
A bad example of a goal is as follows:
Goal 1: Increase sales across company’s range of products and services.
A better goal would look something like:
Goal 1: Generate $500,000+ in revenue from new clients through purchases of X product by X date.
9. Action Plan
Now that you’ve laid out your goals, you need to explain how you will hit them.
Your action plan can be set out week by week, month by month, or quarter by quarter. Within each segment, you must list out all of the sales activities and tactics that you will deploy – and the deadlines and touchpoints along the way.
Tip: Organize your action plan by department – sales, business development and finance.
While this is arguably the most complex part of the sales plan, this is where sales leaders are strongest. They know which approach will work best for their team, their company and their market.
Budgets vary from team to team and company to company, but whatever your situation, it’s important to include your budget in your sales plan.
How are you going to account for the money spent on new hires, salaries, tech, tools and travel? Where the budget is tight, what are your priorities going to be, and what needs to be axed?
The budget section should make references back to your action plan and the sales team and resources page in order to explain the expenditures.
6 Strategic Sales Plan Examples
You can create different types of strategic sales plans for your company, depending on how you want to structure your sales plan. Here are a few examples.
Customer Profile
A customer profile outlines your ideal customer for your service or product. It will usually include industry, background, attributes and decision-making factors.
Creating a customer profile helps narrow in on the target customer your sales team should focus on while eliminating unproductive leads.
Buyer’s Guide
A buyer’s guide is an informational sheet that describes your company’s services or products, including benefits and features. This document is useful both for your sales team but also for a potential customer who requires more information on the product before purchasing.
30-60-90-Day Plan
This plan is organized based on time periods. It includes outlines of goals, strategy and actionable steps in 30-day periods. This is a useful sales plan model for a new sales representative tracking progress during their first 90 days in the position or meeting quotas in a 90-day period.
This type of sales plan is also ideal for businesses in periods of expansion or growth. It’s helpful to minimize extra effort in onboarding processes.
Market Expansion Plan
A market expansion plan clarifies target metrics and list of actions when moving into a new territory or market. This sales plan model is typically used with a target market that resides in a new geographical region.
You’ll want to include a profile of target customers, account distribution costs and even time zone differences between your sales representatives.
Marketing-alignment Plan
Creating a marketing-alignment sales plan is useful if your organization has yet to align both your sales and marketing departments. The goal of the sales plan is finalizing your target customer personas and aligning them with your sales pitches and marketing messages.
New Product/Service Plan
If your organization is launching a new service or product, it’s best to create a sales plan to track revenue and other growth metrics from the launch. You’ll want to include sales strategy, competitive analyses and service or product sales positioning.
Sales Plan Template
4 additional sales plan templates.
Here are some additional templates you can use to create your own unique sales plan.
- Template Lab
- ProjectManager
5 Tips for Creating a Sales Plan
Now that you’ve seen and read through a few examples and a sales plan template, we’ll cover some easy but useful tips to create a foolproof sales plan.
- Create a competitive analysis: Research what sales strategies and tactics your close competitors are using. What are they doing well? What are they not doing well? Knowing what they are doing well will help you create a plan that will lead to eventual success.
- Vary your sales plans: First create a base sales plan that includes high-level goals, strategies and tactics. Then go more in depth on KPIs and metrics for each department, whether it’s outbound sales or business development .
- Analyze industry trends: Industry trends and data can easily help strengthen your sales approach. For example, if you’re pitching your sales plan to a stakeholder, use current market trends and statistics to support why you believe your sales strategies will be effective in use.
- Utilize your marketing team: When creating your sales plan, you’ll want to get the marketing department’s input to align your efforts and goals. You should weave marketing messages throughout both your sales plan and pitches.
- Discuss with your sales team: Remember to check in with your sales representatives to understand challenges they may be dealing with and what’s working and not working. You should update the sales plan quarterly based on feedback received from your sales team.
When Should You Implement a Strategic Sales Plan?
Does your organization currently not have a sales plan in place that is used regularly? Are you noticing your organization is in need of structure and lacking productivity across departments? These are definite signs you should create and implement a sales plan.
According to a LinkedIn sales statistic , the top sales tech sellers are using customer relationship management (CRM) tools (50%), sales intelligence (45%) and sales planning (42%) .
Below are a few more indicators that you need an effective sales plan.
To Launch a New Product or Campaign
If you’re planning to launch a new service or product in six months, you should have a concrete marketing and sales strategy plan to guarantee you’ll see both short- and long-term success.
The sales plan process shouldn’t be hasty and rushed. Take the time to go over data and competitor analysis. Work with your team to create objectives and goals that everyone believes in. Your sales plan should be updated formally on a quarterly basis to be in line with industry trends and business efforts.
To Increase Sales
If your team is looking to increase revenue and the number of closed sales, you may need to widen and define your target audience. A sales plan will help outline this target audience, along with planning out both sales and marketing strategies to reach more qualified prospects and increase your sales conversion rate.
Now that you’ve seen sales plan examples and tips and tricks, the next step after creating your sales plan is to reach those ideal sales targets with Mailshake . Connect with leads and generate more sales with our simple but effective sales engagement platform.

- Content Marketing
- Practical Prospecting Podcast
- Success Stories
Continue reading

5 Types of Sales Quotas to Help Your Team Exceed Your Revenue Targets

Accelerate: Reimagining the Sales Game

12 Sales Training Ideas for Your Next Sales Meeting
Grow your revenue faster, automate all your sales outreach with mailshake..

- Mailshake Blog
- Cold Email Masterclass
- Cold Email Academy
- Prospecting Podcast
- Accelerate Newsletter
- Follow-Up Strategy
- Email Analyzer
- Live Training
- Data Finder
- LinkedIn Automation
- AI Email Writer
- Email Deliverability
- Lead Catcher
- Chrome Extension
- Integrations

- Leadership Development
- Sales Coaching
- Sales Hiring and Retention
- Sales Performance
- Prospecting
- Sales Strategy
- Negotiation
- Sales Training
- Sales Culture
- See All Blogs
- Why The Brooks Group
- Meet Our Team
- Meet Our Sales Training Facilitators
- Awards & Press
- White Papers & Guides
- Success Stories
- Sales Performance Research
- See All Resources
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Distribution
- Energy & Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Professional Services
- Software & Technology
- Transportation
- See All Industries
- Coaching to IMPACT
- Sales Leadership Accelerator
- Train the Trainer
- Sales Training Reinforcement
- Sales Consulting Services
- Sales Team Insights
- Sales Culture Insights
- See All Sales Leadership Programs
- IMPACT Selling®
- IMPACT for Customer Service
- IMPACT Refresher
- Sales Negotiations
- Strategic Account Management
- Sales Territory Planning
- Conversations with Confidence
- Sales Skills Workshops
- Customer Service Training
- Open Enrollment Training Programs
- See All Sales Training Programs
- Sales Training Programs
- Sales Leadership Training
- Sales Assessment Solutions
- Training Delivery Methods
- Keynotes & Workshops
- See All Solutions
6 Steps to Create a Successful Sales Business Plan
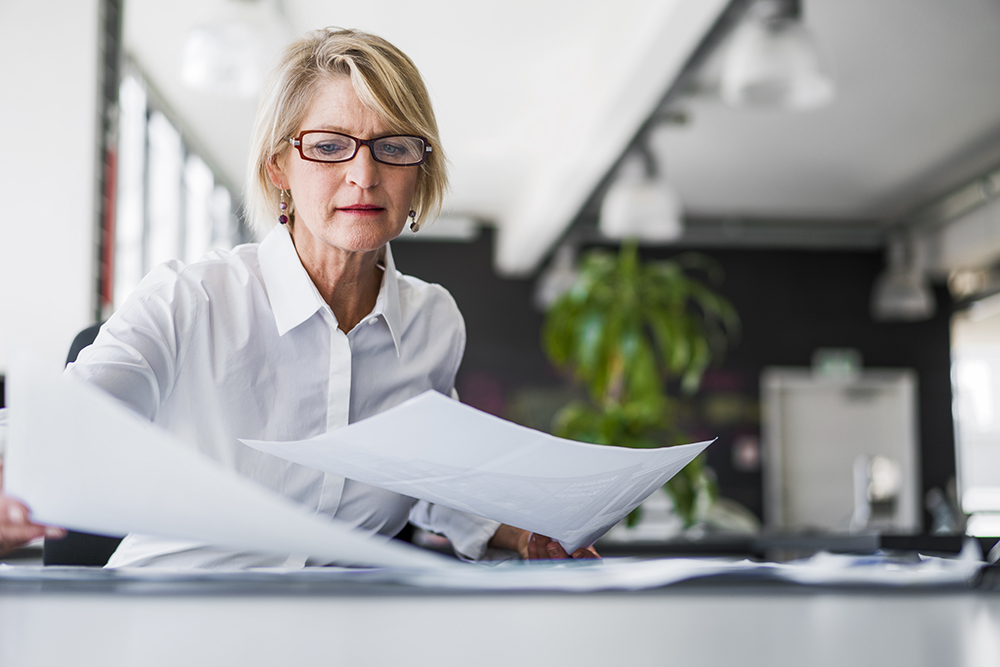


Step 5: Collaborate with Marketing
Sales and marketing alignment is key, and can really give your organization a competitive advantage.
Suggest that each of your salespeople meet with the marketing team to discuss their one-page business plan.
When the marketing department understands your team’s sales strategy, they can create a marketing plan to support the sales team and drive quality leads.
Step 6: Execute the Sales Business Plan
The final and most important step of the business plan is execution. Urge your salespeople to keep their sales action plan where they can see it each day, and have them schedule the activities they committed to on their personal calendars.
By prioritizing and carving out the necessary time, your sales team will have no excuses when it comes to execution –and they’ll be well on their way to success.
The exercise of creating a business plan helps your sales team manage their daily activities in a way that moves them towards achieving their long-term goals.
Alan Lakein, says “ Planning is bringing the future into the present so that you can do something about it now.”
The summer season is a great time to give your sales reps the skills needed to build their own sales plans, and overcome any other challenges they’re up against.
The Brooks Group can help your team stay efficient and upgrade their sales performance this summer with targeted skills training customized to your unique needs.
In a world where time is a precious commodity, you can’t afford to let these summer months go to waste. Learn more here .
Have a question? Submit it to The Brooks Group Help Desk and an expert will get back to you within 24 hours. [email protected]
Watch the video below to learn more about the Sales Territory Planning Workshop
Written By Michelle Richardson
Michelle Richardson
Join over 17,000 sales leaders getting the best content right in their inbox.
- Presentation Skills
- Prospecting Skills
- Sales Assessments
- Sales Compensation
- Sales Goals
- Sales Leader Blog
- Sales Meetings
- Sales Performance Improvement
- Sales Performance Research Center
- Sales Pitches
- Sales Prospects
- Sales Team Motivation
- Time Management
- Virtual Sales
You may also like

51 Examples of Powerful Open-Ended Sales Questions
Apr 16, 2024
As a sales leader, meeting your organization’s revenue goal is job #1. That means helping your sales professionals be...

Highly Effective Prospecting Techniques for Your Sales Team
Apr 10, 2024
In baseball, “keep your eye on the ball” means watch where the ball is at all times. In sales, it means staying...

Top Tactics for Selling to a Buying Committee
Apr 9, 2024
Finance, operations, and management, oh my! The B2B buying journey is getting longer and more complex. The average B2B...
Ready to maximize the performance of your sales team? A representative from The Brooks Group can help get you started.
How to Write a Sales Business Plan
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Write a Business Plan
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
How to Create an Annual Report for Sales & Marketing
The difference between sales plans & sales projections, preparing for a sales strategy meeting.
- How to Find Market Share by Sales Revenue
- How to Calculate Sales Tax on Gross Income
Having a solid business plan is essential for the success of any company. It outlines your goals for the future and the tactics you'll use to achieve those goals. A sales business plan is much the same as a regular business plan except its focus is on sales and marketing — specifically, what your target market is and how you'll market and sell your product or service.
Describe your target market, and be specific. Include information such as gender, age and location — whether you intend to market your product or service to local residents, residents throughout the state or nation, or through the Internet, for example. Describe why your product or service is important to your target market and how they will benefit from it. If you work for a large company, break down your target market by territory and include information about prospective customers in each territory.
Discuss your marketing strategy. Include details about what your marketing budget will be, exactly how you plan to market your product or service and the sequence of the steps in your plan. This section should include information related to the promotion of the product or service — advertising and direct mail, for example. If your company is large and covers many territories, break down the marketing strategy section by territory.
Explain your sales strategy and tactics. The strategy is your overall plan, and the tactics are the specific actions you'll take in order to achieve your strategy. For example, a strategy might be to increase new customers in a certain territory by 20 percent during the first quarter of the fiscal year, and one of the tactics to accomplish that might be to add an additional salesperson to that territory in order to more effectively identify prospective customers.
Define your timeline in which you plan to implement your sales strategy and tactics. Break it down in whatever way makes most sense for your company and your plan. List, for example, what goals you plan to accomplish in the first 30 days, 60 days, 90 days and 180 days of the new fiscal year. Remember that these goals comprise your sales strategy.
Provide an analysis of your competition. Explain the advantages of your product or service above theirs. If the competition offers benefits to the target market that you do not, it's important to identify those benefits and plan how to either change your product or service accordingly or devise a marketing and sales strategy that will rise above those challenges.
Develop a sales forecast. Include sales projections month by month for at least one year, and preferably for two or three. Use historical data as a basis to project sales of an existing product or service. If you're trying to project sales for a new product or service, look at sales of a similar existing product or service sold by another company to give you some idea of the potential.
- Businessballs: Business Plans and Marketing Strategy
- Bplans: Forecasting Your Sales
- Don't combine marketing and sales in your sales business plan. They are different functions. Marketing includes promotion, advertising, product branding and pricing. Selling refers to the actual sale of the product or service to a customer.
In addition to a successful career as a professional writer, Cindy White spent several years in mid-management positions for a Fortune 500 company. Prior to that, she enjoyed her tenure as a technical writer and technical documentation supervisor in the manufacturing industry. She holds a bachelor's degree in English from the University of Nevada-Reno.
Related Articles
New year business marketing plan & annual strategy goal update, sales plan vs. marketing plan, how to identify the appropriate price strategy, how to make a yearly sales target plan, how to calculate weekly sales commission, new territory sales strategy, how to set short-term and long-term goals for a business, how to write sales goals & objectives for a new year, how to plan & grow a business venture, most popular.
- 1 New Year Business Marketing Plan & Annual Strategy Goal Update
- 2 Sales Plan Vs. Marketing Plan
- 3 How to Identify the Appropriate Price Strategy
- 4 How to Make a Yearly Sales Target Plan
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Write a Sales Plan
Last Updated: May 20, 2020 Approved
This article was co-authored by Michael R. Lewis and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Michael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article has 17 testimonials from our readers, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 463,735 times.
When your business is sales, many of the factors that determine success are out of your control. Whether you are trying to develop an overarching guide to your sales business strategy, or are a salesperson seeking to define your goals and tactics for meeting (and exceeding) your targets, writing a sales plan can help you take a bit more control in the unpredictable world of sales.
Writing a Sales Business Plan

- The executive summary is the introduction to your business. It defines the problem or need in the market, and explains how you are uniquely capable of solving / providing for it. It tells people unfamiliar with your business what you do and why you will succeed.
- It should also touch on your marketing, financial, and management strategies, and projections for your business going forward. Essentially, it should provide a “taste” of the information included in the business plan as a whole.
- Take, the “summary” part seriously, though. It should be brief, at most a couple of paragraphs. It is also acceptable to use bullet points, graphics, or other means to making the key points clear and accessible. You want those outside the field to clearly understand it.

- Provide brief details on when and how your business was formed, where it is located, and its legal structure (sole proprietorship, LLC, etc.).
- Define the value of your product or service. Identify the unique and specific benefits your product or service provides for your target population. Your product may save people money, improve their health or advance their knowledge. Clarify the exact need that you are meeting.

- Establish your position in the market. Determine the exact niche for your product or service. Your product may be an innovative tool for solving a common problem in a particular demographic. Or it may be similar to other products, yet more affordable for a specific demographic.
- If you provide small-business IT services, for instance, you want to provide an overview of the larger industry and any ongoing or likely changes within it.
- Consider the trends in your industry and market in order to project your future growth or success (hopefully) moving forward.
- Consider the geographic limits of the market area. Service companies in particular are often disadvantaged by higher costs of travel to extended areas versus local competitors.

- If you sell relaxing bath products, for example, you target population may be working mothers between ages 25 and 49. Provide brief demographic and geographic information, along with projections moving ahead.

- If, say, you are a regional snack-food producer, you should outline the strengths and weaknesses of your main competitors, and delineate why you have (or will have) the upper hand. It could be an innovative product line, marketing strategy, distribution technique, pricing model, and so on.
- Be realistic in your analysis, but don’t be shy to state why you will “win.” Now is not the time for modesty.

- Examine your pricing structure. Writing a sales plan is an opportunity to establish a pricing strategy. Research similar products and services in the industry and set prices accordingly. Prices should allow you to remain competitive and still generate profits. Include plans for incremental price increases in line with manufacturing costs.
- Outline your long-term and short-term revenue goals. Be as realistic as possible in your forecast. Use your recent revenue history as a guide, accounting for significant changes in the market that may decrease your revenue or create new opportunities in the future.
- Identify ideal locations for your products and services. Opening a new store location and making your products available to resellers are possible options. Your sales plan should include where all of your sales activity will take place and the costs associated with each location.
- Define your advertising approach. Websites, print publications, television advertising and banners are a few advertising options. Evaluate the performance of each marketing strategy throughout the history of your business and include the successful options in your marketing plan.
- Outline the activities of your sales and marketing team. Include the sales strategies that have proven effective in the past. Cold calling, attending trade shows and partnering with organizations are examples of sales and marketing activities. Describe the approach that your sales team will use both in the short-term and long-term to generate leads and close deals.

- This is not an essay, so, as mentioned, bullet points, graphics, tables, and the like can be used to provide key information succinctly and explicitly. Try to keep a consistent style for readability.
- Some may extol the virtues of the one-page sales business plan, [6] X Research source but if you find that this is too restrictive, don’t fret. There is no real standard for length either, although brevity is indeed valued.
- I. Executive Summary; II. The Business and Its Products / Services; III. Industry Analysis; IV Customer / Market Analysis; V. Competitive Analysis
- I. Executive Summary; II. Company Overview; III. Industry Analysis; IV. Customer Analysis; V. Competitive Analysis; VI. Marketing / Sales Plan
Writing an Individual Sales Plan

- Start your plan by establishing your sales target — weekly, monthly, yearly, or otherwise — and then outline several overarching strategies that you will use to achieve it.
- Strategies for enhancing sales might include increasing awareness in the community, obtaining more referrals from existing customers, or adding to your number of weekly “cold calls” to potential customers.

- For instance, if one of your strategies is to increase community awareness, your tactics may include attending a set minimum of community events and volunteering at least so many times per month / quarter / year in the community.
- If one of your tactics is to enhance your social media presence, you should provide specific details. For instance, how many social media posts do you intend to average per day? [10] X Research source

- One strategy, for example, may be to increase your opportunities for at least monthly interaction with each of your existing clients.
- If so, your tactics could include calling once per month with a relevant idea or tip, setting up an interactive newsletter, or taking a minimum number of existing clients to lunch per month.

- Your strategies here could in fact be listed as “increase sales within my existing client base” and “identify new clients through my existing client base.”
- Your tactics could include meeting with the key decision-maker for every account you hold, scanning client social media outlets daily for useful news, or including promotional materials with every delivery of goods or services.

- Simple and direct is key. You want something you, your boss, or anyone else who wants to look can scan quickly and understand. Think of it as something you can (and may actually want to) post on a bulletin board.
- Simple and direct plans are also easier to revise as times and circumstances change. You should indeed revisit and revise your individual sales plan regularly.
- I. New Business Acquisition Strategies
- II. New Business Acquisition Tactics
- III. Existing Business Growth Strategies
- IV. Existing Business Growth Tactics
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ http://www.wahm.com/articles/how-to-write-a-one-page-sales-business-plan.html
- ↑ http://www.businessbee.com/resources/sales/analytics-reporting/creating-a-successful-sales-plan-4-important-questions-to-ask-yourself/
- ↑ http://www.entrepreneur.com/article/69864
About this article

Start a business sales plan with a summary of the problem your business is solving. Add details about when your business was formed and what its legal structure is. Establish your position in the market relative to other, similar businesses, and then define your target demographic and potential customers. Include information about why your business in particular will succeed. Finally, include a section about your sales and pricing strategies. For advice from our Financial reviewer about how to write an individual sales plan, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Reuben Polk
Jul 10, 2016
Did this article help you?
Kiaran Green
Oct 2, 2016
Russ Piatos
Mar 6, 2017
Don Penolio
Jan 23, 2018
Francis Isaac
Apr 12, 2017

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- 11 July, 2022
10 Steps to Create a Complete Sales and Marketing Business Plan [Templates included]
Jump to the end of the post to get access to our free sales and marketing business plan templates.
Turning an idea into a functional business requires laser-sharp focus. You must take care of development, marketing, sales, customer success, and whatnot.
While most entrepreneurs start with some form of a plan, they often forget about it soon after.
Blame it on changing dynamics, trial and error to find a product-market fit, or blatant ignorance. But overlooking the planning process is a sure shot reason for failure — as the common saying goes, failing to plan is planning to fail.
An essential part of this document is the sales and marketing segment. The sales and marketing plan outlines everything you need to do to promote your products and generate revenue for your business.
Why do you need a sales and marketing plan?
Having a revolutionary product that solves a genuine problem is great. But it won’t mean anything if people don’t know about you.
A sales and marketing plan helps you get discovered, structure your activities, and move forward with your growth goals.
It’s more or less like a roadmap about what you should do to make things work in your favor.
Your sales and marketing plan will help you:
- Identify the bridge between where you are today and where you want to reach your business goals.
- Get much-needed clarity and avoid conflicts and confusion in case of any disruptions.
- Gain and document insights about your target audience, industry, trends, costs, etc.
- Justify your business model in front of investors and lenders in case you need to raise funds.
- Stay focused on a north star metric, improvise growth tactics and achieve harmony between various growth activities.
- Promote sales and marketing alignment.
Your sales and marketing plan would also help you avoid distractions and save time and money lost.
And you know how easy it is to lose direction and get distracted when starting or running a startup. Documenting everything as a plan will help avoid confusion and add clarity to your everyday affairs and long-term mission.
However, different companies need different plans based on the stage of operations and their unique growth goals.
A clear marketing and sales plan promotes alignment between marketing and sales departments at every stage . This reduces resource waste and creates fewer “blame-game ” occasions in your meetups.
What to include in the marketing & sales plan?
Planning is a subjective activity.
You’d receive several different answers if you read, talk to, and consult multiple experts on what to include in your marketing and sales plan.
So, how should you decide which elements to include in your marketing/sales plan?
Let’s take a step back and understand the “why” of planning.
You need a plan so you don’t get confused and can keep walking towards your goal.
Your plan should:
- Serve as a roadmap for everything related to sales and marketing for the first few months if you’re just starting.
- Outline and articulate the core strategies you’ll experiment with, the desired outcome, and the KPIs to measure performance.
- Set realistic KPIs, outcomes, and objectives based on market understanding, competition, funding requirements, and your target audience’s pain points.
Marketing plan for your startup: The what and why
In an ideal world, every penny you spend in marketing should enhance your visibility, take you closer to your audience, and increase your conversion rates.
But in reality, it takes a lot of effort, time, and investment to make it happen.
A marketing plan helps you navigate through the tricky maze called marketing without getting lost in the process.
Basically, you build a marketing plan to gain enlightenment about how you’ll promote and stay relevant to your audience.
You do it beforehand so that when things get tricky, you have a directional beacon to guide you.
Creating any plan should start with an understanding of the purpose. The same applies to marketing, too. Try to find the reason behind marketing your product – why are you working towards your goal.
Knowing your why would help you gain clarity – an essential element for the success of any activity on the planet. Before you begin, you should try to find answers to the following questions:
- Why are you making the marketing plan?
- What do you want to accomplish with the marketing?
- What will be the value proposition?
- What are the goals that we want to achieve?
These answers will allow you to think better and prepare for strategizing your plan with a better perspective.
Also, while at it, remember that your marketing plan is not a rigid document etched in stone. Instead, it’s a result of an iterative process that depends on five fundamental aspects:
1. Product: What are you marketing?
The product section should explain what you are selling exactly.
- What do you sell?
- How is your offering different from your competitors?
- What are the benefits your potential customers would derive from your offerings?
- What is your core USP?
Answering these questions would help you craft a great positioning statement and marketing message for your marketing campaigns.
2. Place: Where are you available?
This section should outline where you will sell or market your products. How will you get customers to reach out to buy your product or service?
Though this will depend on the nature of business — online or offline, manufacturing or services, answers to the following questions would help you gain clarity:
- Where will you be available for your customers?
- Which distribution channels would you use to be more accessible to customers?
- What percentage of sales/conversions do you expect from different distribution/marketing channels?
3. Price: How much will you charge?
This is an essential part of your planning process. Your pricing decisions would decide how you will generate revenue for your startup .
Your pricing decision should be based on market analysis, competition, value offering, buying behavior, etc.
- What will be the pricing model you’ll adopt to generate revenue?
- What is the most favorable price point that your customers are ready to pay for your offering?
- Will you make any profit/loss at this price point?
- How soon can you break even based on your pricing strategy?
4. Promotion: How will you promote your offering?
You can have the best product, but no one would care if you’re not promoting it.
Moreover, one of the primary reasons to create a marketing plan is to help you promote your offering.
- Who is your target audience?
- How will your reach your target audience?
- What strategies will you adopt to convert your audience into customers?
- Which channels of promotions will you use to promote your offerings?
- How much will you spend on promotions and marketing?
- What will be your team structure for the next quarter, year, and long term?
- How will you track the marketing effectiveness?
5. People: Who will do the marketing?
While most marketing plans you see out there would cover the traditional 4Ps of marketing, often the fifth P, people, is ignored.
And you know there’s no growth or promotion without your team – your people.
This aspect should help you understand your current capabilities and the resources needed in your team. Think about how you will find them, their responsibilities, and where they stand in the big picture.
- Who will do the marketing for you?
- What do you look for in a human resource?
- At what point do you start expanding the team?
- Who are you going to hire first?
- How do you plan to hire for marketing?
- What will be the core responsibilities and KPIs for your team?
- How will you set KPIs/OKRs and analyze your team’s performance?
Sales plan for your startup: The what and the why
Your sales plan would help you generate revenues from your marketing efforts by completing the journey from generating leads to turning them into customers.
A sales plan defines your sales goals, the strategies you’d bet on, your desired results, your challenges, the solutions you have for them, and the structure (people, budget, process, and tools) you need.
Your sales plan would cover everything you need to register sales and generate revenue for your business.
A sales plan is created to:
- Provide a strategic direction to your sales team
- Define the core objectives and goals in terms of sales
- Outline roles and responsibilities
- Analyze and measure your wins in terms of sales.
These reasons help you succeed more than experimental businesses that beat around the bush while trying to make things work in a world where everyone’s selling something. To ensure your sales plan is effective, it should include:
1. Sales goals — What do you want to achieve?
Like any other activity in the world, your sales planning process should also revolve around the end goals for sales
Saying that you want more customers is a generic goal that doesn’t have any tangible metrics attached. Moreover, saying that you wish for more sales is too broad a goal that would involve outlining several action steps.
So, it’s always better to have a SMART goal and break it down into tangible, measurable, and KPI-driven objectives. You can say that you want to:
- Nurture 10% more MQLs into SQLs, and ultimately, customers.
- Reduce your churn rates by 5% before the end of Q1.
- Expand your sales team with 3 people to nurture and convert leads faster — reduce time to conversion by 5 days.
- Increase the customer lifetime value through upsells or cross-sells by $200.
- Expand your sales activities into new territories or regions.
- Optimize your pricing strategy to improve your conversion rates by 8% for new accounts.
2. Tactics — The process and activities
This segment will include the specific tactics, processes, and activities you’ll use to generate revenue for your business .
A solid understanding of your target audience, goals, and capabilities would help you discover exciting and profitable tactics for your industry.
Try to pick and choose the tactics in line with your ideal customer profile. You can conduct a survey and get insights from your marketing team to align your sales efforts accordingly.
An aligned sales and marketing team will help you accelerate sales enablement and strike gold with more leads, higher conversions, and better results.
Interested in exploring new sales tactics? Read this blog on popular sales strategies and techniques for your business.
3. Timelines — The time you’ll need to make things happen
A plan without a timeline is just a wish. You must link your goals, tactics, and sales strategies with realistic deadlines. This will ensure that everyone’s motivated to work towards your goals.
Keep all the stakeholders in the loop by developing a realistic growth goal and attaching a practical timeline to it.
While you’re at it, don’t forget to assign one person who’ll be responsible for ensuring compliance.
This tactic is known differently in business circles.
Some call it a key Point of Contact (POC) for an activity; others call this person a Directly Responsible Individual (DRI).
Another popular approach includes assigning OKR (Objective and Key Results) to an individual in a team who owns up the responsibility of making this happen.
Whatever you may do, make sure you are realistic, practical, and sensible in creating achievable deadlines for your sales teams.
Failure to do so would lead to dissatisfaction among sales team members, ultimately harming your bottom line.
4. KPIs — the metrics you’ll track to determine success
KPIs will help you understand if your sales tactics align with your revenue generation goals. These metrics help enhance sales teams’ performance, optimize the sales funnels, and improve conversion rate.
If you want a solid sales plan, you need to tie everyone (and everything) to a tangible sales metric.
You also need to ensure proper sales and marketing alignment so that all your marketing spends get attributed to some kind of improvement in KPIs.
Here are some questions and corresponding KPIs you can think of adding to your sales plan:
If you track these KPIs well, you’ll understand the challenges better, predict future problems, and get better at generating revenues from your sales activities.
Moreover, the answers you gather and the KPIs would help you keep an eye on the overall efficiency of the sales process and build a strong sales team.
Apart from these standard inclusions to your sales plan, you can also add the following information:
- Team structure: How big your sales team should be, and what will be the responsibility (job role and KPIs) of each member of the team?
- Resources/tools required : What tools and resources do you need to execute the sales tactics and strategies you’ve planned?
- Current market trends: How is the present market regarding customer interest in your product, competition landscape, and overall sentiment in your industry?
Rethinking the traditional plan for digital businesses, service companies, and SaaS startups
The traditional ways of creating a sales and marketing plan are geared more toward the product economy.
Today, most businesses don’t even have a physical “product”.
Distribution and conversion cycles are not so simple, too.
The sales and marketing ecosystem has transitioned from a single-sales mindset to a culture of lead nurturing , upsells/cross-sells, and experiences to enhance the customer’s lifetime value.
Even users don’t look at companies, products, and solutions like they used to anymore.
Don’t you think the old ways should be reimagined?
In his book, Subscribed, Tien Tzuo mentions how the world economy is transitioning to a digital era powered by subscription-based startups and digital businesses.
Naturally, with changing consumer mindset, the traditional business planning models (including sales and marketing plans) should change, too.
There has been a hot debate about reimagining marketing and sales operations for the future — digital businesses, SaaS products, and the subscription economy.
PADRE is a promising framework with all the elements of a traditional business plan, reimagined for the modern digital economy.
The PADRE framework keeps the customer at the heart of everything and divides all activities (including sales and marketing) into eight subsets:
- Position: How will you create awareness, turn it into demand for your product and build a pipeline of leads?
- Acquire: What is your ICPs buyer’s journey? How will you address their pain points and turn them into customers?
- Deploy : How will you onboard , service, and delight your customers as efficiently as possible so they can use your product, service, or SaaS quickly?
- Run: How will you ensure that your customers get what they expect (and deserve) from your product or service?
- Expand: How will you grow your company through retention, growth, and customer advocacy?
- Product: How will you evolve your product, service, or offering and manage everything?
- People: How will you recruit, onboard, train, and retain the best talent to serve your customers?
- Money: Where and how will you fund and fulfill your need for running and growing your business most efficiently?
If you look at the PADRE model carefully, it has almost all the elements discussed above for sales and marketing plans, just in a different way. This differentiation makes more sense for a dynamic digital business than the traditional sales and marketing business plan.
You can take ideas from the PADRE model to create your version of a dynamic business plan based on your unique business idea.
10 steps to create a solid sales and marketing plan
Regardless of your approach to creating a business plan, you will have to gather data, make some important decisions, and collate everything together.
Remember, your sales and marketing plan is a living document that should be revisited repeatedly for optimization.
Here are the steps you can take to create an actionable plan based on the insights shared above:
Step 1: Gather data based on company insights and external trends
“Always measure the depth of the pool you’re diving in!”
Before you start planning your sales and marketing observing and documenting macro-level industry trends is a must. It will give you an understanding and insight into what to expect in the future.
You can use industry insight to strengthen your assumptions, understand the market, add clarity to your sales and marketing mix, and refine your plan.
Always look for industry insights around sales and marketing trends — what worked in the past, how things are changing, and what future trends will drive growth. While industry trends are not a full-proof solution, it gives you a direction to provide a concrete shape to your plans.
Use industry trends to add “meat” to your hypothesis, and see if you can get data about:
- Consumer behavior and psychology that drives sales. Use the Facebook Ads manager audience tool to find your audience’s topics of interest and behavior trends.
- Psychographic analysis of your target audience.
- Marketing effectiveness of different channels. You can use platforms like Similarweb to peak into the traffic sources of your competitors and get an estimated idea of the volume.
- Sales trends of lateral and complimenting businesses.
- Competitor analysis, including their past financial performance and effectiveness in generating revenue.
Step 2: Create your ideal customer profile (ICP)
As a business owner, you must know everything about your target audience.
Without a deep understanding of your ICP, you could end up like a door-to-door salesman trying to sell but end up annoying everyone.
This information helps you take the necessary steps to add context and relevance to your marketing and sales plan.
You should break up your ideal customer persona (ICP) into several sections covering all aspects of your persona’s — the demographic profile, what they think, believe, and trust in, their needs, motivations, drives, and psychographic profile.
Sample questions for building an Ideal Customer Profile
Knowing your audience allows you to talk the way they want to be talked to. Also, you get to understand what makes them buy, their problems and pain points, and where they spend most of their time. All this is crucial for creating an effective marketing strategy.
You can even use this knowledge to segment your audience personas and personalize your marketing campaigns — a powerful tactic to market your brand in 2022.
Step 3: Assess your current situation
Once you’ve gathered data and foresight, start the self-introspection process.
Ask yourself where you stand in your startup journey.
✓ How is your business performing right now?
✓ Are you performing according to your revenue estimates and KPIs?
✓ Do your business and revenue generation efforts align with market and industry trends? Do they need to align?
✓ Are you marketing and selling where your customers are looking for options?
✓ What are your strengths and weaknesses?
✓ What challenges are you facing in getting your business to the next level?
✓ Is there any better way of doing things than you do now?
All these questions will give you ideas to start the actual planning process. Moreover, you’d understand if whatever you did was even worth it.
Step 4: Define metric-driven objectives and goals
Have you ever traveled without a destination?
Well, maybe you have. But that’s not how you run a business. You need to have an exact destination in mind — where you’re headed to.
That’s why having an objective and goal is essential for making a sales and marketing plan. Tangible and realistic goal-setting should be the #1 priority of anyone trying to succeed as an entrepreneur.
Your goals will will allow you to track if you’re making a real impact on your business. Plus, having a metric-driven goal gives you an understanding of what you need to do for success.
Your goals and objectives should be tied to your business vision and mission.
Often, we see there’s a misalignment between sales and marketing objectives. That leads to confusion and, thus, poor performance. Hence setting a SMART goal is critical for ensuring clarity.
SMART objectives for your sales and marketing plans should be:
- Specific: The goal is clearly defined, and everyone within your team understands the goal and its importance.
- Measurable: The goal/objective should be tied to key performance indicators (KPIs) and visibly measurable.
- Achievable: Being realistic is an important factor in setting an attainable goal. Look at your team’s ability, budget, and current situation to ensure the goal is within your limits. Setting the bar too high will only lead to disappointment and wasted time and effort.
- Relevant: Your objectives should be aligned with your business vision and mission. If your marketing and sales aren’t aligned to your bigger picture, it will lead to losses (and potential conflicts).
- Time-bound: Any objective you define must have a clear timeline, which means there should be a start and end date. Without that, your goal is just a wish.
Step 5: Determine metrics for success (KPIs)
You know you need to measure your goals and objectives in real-time.
That would ensure everything’s on track and help you red flag any deviations from your desired path.
But setting a measurable KPI for any business is a tricky business in itself. Especially when there’s a lot to plan in sales and marketing, and every business is different.
KPI or key performance indicators should be planned based on industry best practices, prevailing marketing trends, and taking stakeholders in confidence.
You can align standard industry KPIs with your business or marketing/sales goals to create your version of KPIs that will objectify your success figures.
Standard Goals and KPIs you should track
Always ensure that each KPI you track links to the bigger picture — where and how it contributes to your business’s mission and mission. This will add relevance to your sales and marketing plans giving you more accurate insights for the future periods.
Step 6: Build a forecasting model
Forecasting is an activity that predicts what your sales and marketing efforts will lead to on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis.
Creating a sales or marketing forecast involves taking the opinions of industry leaders, financial consultants, CPAs, marketers, sales managers, and your team members. It also will involve studying and analyzing the insights you gathered in step one.
A forecast will help you make better hiring decisions, budget for your expansion in a better way, and linearly predict your revenues. You can also add dynamic variables to the forecasts to analyze how your KPIs would perform under real-life situations.
Creating a forecasting and budgeting model for your sales and marketing team is highly essential to keep things in check. However, it would be best if you didn’t fall into the lure of creating forecasts for more extended periods as things are changing quite rapidly, especially after COVID-19.
Better to create a forecast for a quarter, review it based on actual expenses and performance, and keep iterating. You can also take advantage of popular forecasting tools for more accurate models.
Step 7: Identify gaps within your assumptions
By this step, you’d have a clear idea about your capabilities, the goals you want to achieve, the industry trends and the forecasts for the future.
This will give you an opportunity to get a bird’s eye view of your sales and marketing activities in terms of your revenue growth.
You can use this information to plug in gaps because of your assumptions and biases, analyze what’s required and the challenges you’d face to make things happen.
Identifying gaps between your existing situation and your goals based on forecasts would help you make informed decisions.
You can choose to hire more people in sales and marketing, increase your budget, try new marketing tactics, or even start an entirely different lead generation and nurturing channel to achieve your goals.
Step 8: Create a team structure and involve stakeholders.
The most important part of the planning process is to understand your capabilities. If you’ve assessed your current scenario correctly, you’ll have a clear picture of who’s responsible for growth, marketing, sales, etc.
And if you’re just starting, this is a great time to start planning a structure for your marketing and sales team, starting with:
- How many people will be needed for each team?
- Who will be responsible for specific KPIs?
- What will be the responsibilities of each member of the team?
- How will teams communicate with each other and ensure alignment between efforts?
- How will the performance be measured?
- What are the challenges marketing and sales teams face in your company (or industry)?
- How will expansion needs be identified?
Remember, if you’re just starting to build a team and have existing team members, take them in confidence and involve every stakeholder before creating a structure.
The more aligned and closely knit your sales and marketing, the faster you achieve your growth goals.
- Build a Strong B2B Marketing Organization Structure for Modern Teams
- Sales Operations Responsibilities: Roles, duties, and obstacles
- Revenue Operations Roles: Who do you need to build a RevOp team?
Step 9: Outline action items
By this step, you’re almost done with the planning. You just need to answer two more questions:
- What do you need to do to achieve your goals?
- How will you do what you need to do?
This means outlining action steps, developing marketing and sales tactics, and finalizing the cogs required to run your marketing/sales engine.
You can start by putting together a rough draft of all the insights you’ve gathered, the available resources, the budget, best industry practices, trends, and growth projections. This will give you foresight into what can work in your favour.
Build a list of action steps that you need to take to move in the direction of your goals.
Step 10: Identify and implement tools and systems
Okay! This is the last step of the planning process. After this, you will be left with the exact steps you need to take daily to achieve your KPIs.
But don’t take this step lightly. Think of this as the building blocks of a bridge that would take you from “here” to “there”.
You’ll need to make a list of tools, systems, and solutions you’d need to make things happen.
For example, if you’ve concluded that you need to set up a lead nurture campaign , you need a tool or platform that makes that happen.
You’ll need to evaluate the available options and pick a tool that aligns with your goals and budget.
While picking up any tool, make sure that it should:
- Save time, money, or effort for your marketing and sales team members.
- Have prominent success stories and case studies that closely relate to your goals, tactics, and life stage.
- Is reliable and doesn’t use any under-the-hood tactics to make things happen.
- Has an active developer and customer success team.
- Is supported by a thriving public community of happy users.
Make sure that whatever tech stack you’re finalizing has a solid mechanism to track success and your KPIs.
This will help you ascertain success quicker. Also, communicate with all the stakeholders about the tools and success metrics.
Ready-to-use sales and marketing plan templates
To make things easy for you, we have prepared comprehensive templates for both your sales and marketing plans. To download the template click on the links below and duplicate the document. Then, fill in the blanks.
Download the Marketing Plan Template
Download the Sales Plan Template
Your sales and marketing plan is a living document. Keep revisiting!
If you’ve come this far with your planning, you should have a functional plan for supercharging your marketing and sales operations in the coming weeks and months..
But remember, sales and marketing planning isn’t a one-time activity. Keep optimizing your plans with fresh insights to stay on track with changing dynamics. And don’t forget to track the right metrics and KPIs.
A marketing automation platform like Encharge can help you to execute your marketing and sales plans. Don’t believe us. Check the success stories to see how others businesses are amping up their marketing and sales game now.
Meet your new marketing automation platform
“encharge helped us visually redesign our onboarding flow resulting in a 10% increase in our trial activation rate .", top 7 marketing automation trends in 2022 according to 103 experts.
Marketing rapidly changes. Despite all the alterations, one thing remains ― marketing is tricky. The principles remain the same, but
How to Write a Business Plan Using a Template
Writing a business plan can be overwhelming. Luckily, there are multiple resources available, including this FREE template and Trailhead.
Share article.
You have this great idea for a business. It’s been brewing for a couple of years now, and you’re finally ready to act on it.
Fantastic! What’s your business strategy ?
Many people preparing to start a business — and even some who have already started one — fail to research and write a business plan that tests the feasibility of their idea. Some may think it’s a “waste of time.” They would rather wing it, stick with a pitch deck, or hope for the best.
But hope, unfortunately, isn’t a strategy for success. Writing a solid plan and executing it kick-starts your road to success.
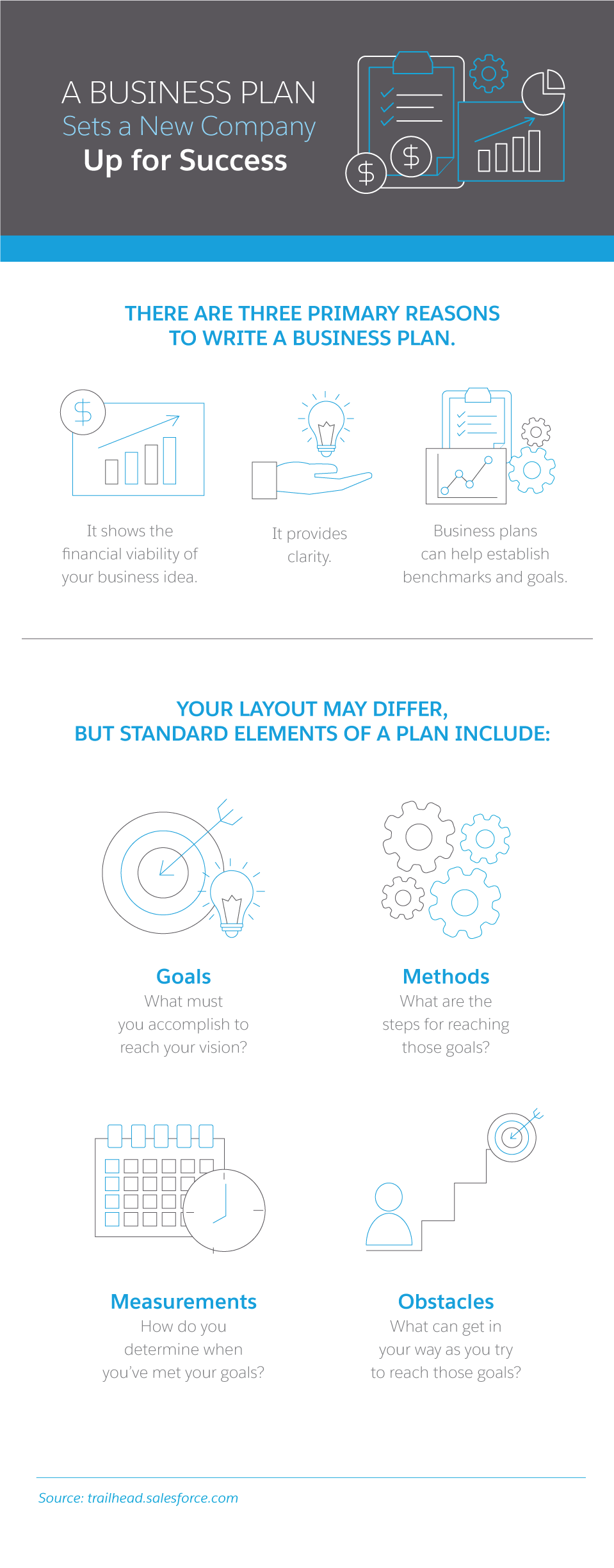
Three Reasons Why You Need to Write a Business Plan
If you haven’t considered writing a business plan until now, here are three key reasons why it’s a crucial tool when starting your business.
1. A Business Plan Provides Clarity
One of the easiest ways to gain clarity on your goals and brand message is to practice how you communicate them. Clearly describe what problem or need your business addresses and why it’s necessary for your target market. This strengthens your case when marketing and selling to your target audience. It’s also useful when you need to apply for or raise funding for your small business. A clear picture of what your goals are will help you chart a course to deliver it as promised.
2. A Business Plan Confirms the Math
A lot of ideas sound great on paper or in casual conversations. But when you dive into the financials, such as how you plan to make money and how much it will cost, those ideas can fall apart. Writing a business plan provides you with the space to create a financial model. It outlines the best- and worst-case scenarios that validate your idea’s worth.
3. A Business Plan Helps Establish Mini Goals
Writing a business plan helps establish benchmark goals — those that are on your path to the main goal — and determine what you need for your success. Setting mini benchmark goals with deadlines for each month, quarter, and year provides you with short-term targets to focus on. Nearly every plan for your business changes as the company grows. These benchmark targets ensure that your company is always moving forward.
Writing a Business Plan Is Not as Difficult as It May Seem
Creating a plan for your business can seem like an overwhelming project. Especially, if it’s your first business or you lack a background in finance or operations. Luckily, there are a number of resources available online, including Trailhead’s “Make a Business Plan” lesson, which helps you write a detailed plan. Your options vary based on your specific industry or product offering. However, all plans share a similar outline that you can follow when writing your own.
Below, we’ve put together a resource template for creating a thorough business action plan . Following a template allows you the opportunity to organise your thoughts and clearly present the plan to prospective partners, investors, or vendors. It can be a lot of trouble to start from scratch. Instead, try using this outline to draft a plan for your business and turn your napkin scribbles into a solid, well-researched plan that’s ready for financial investment.
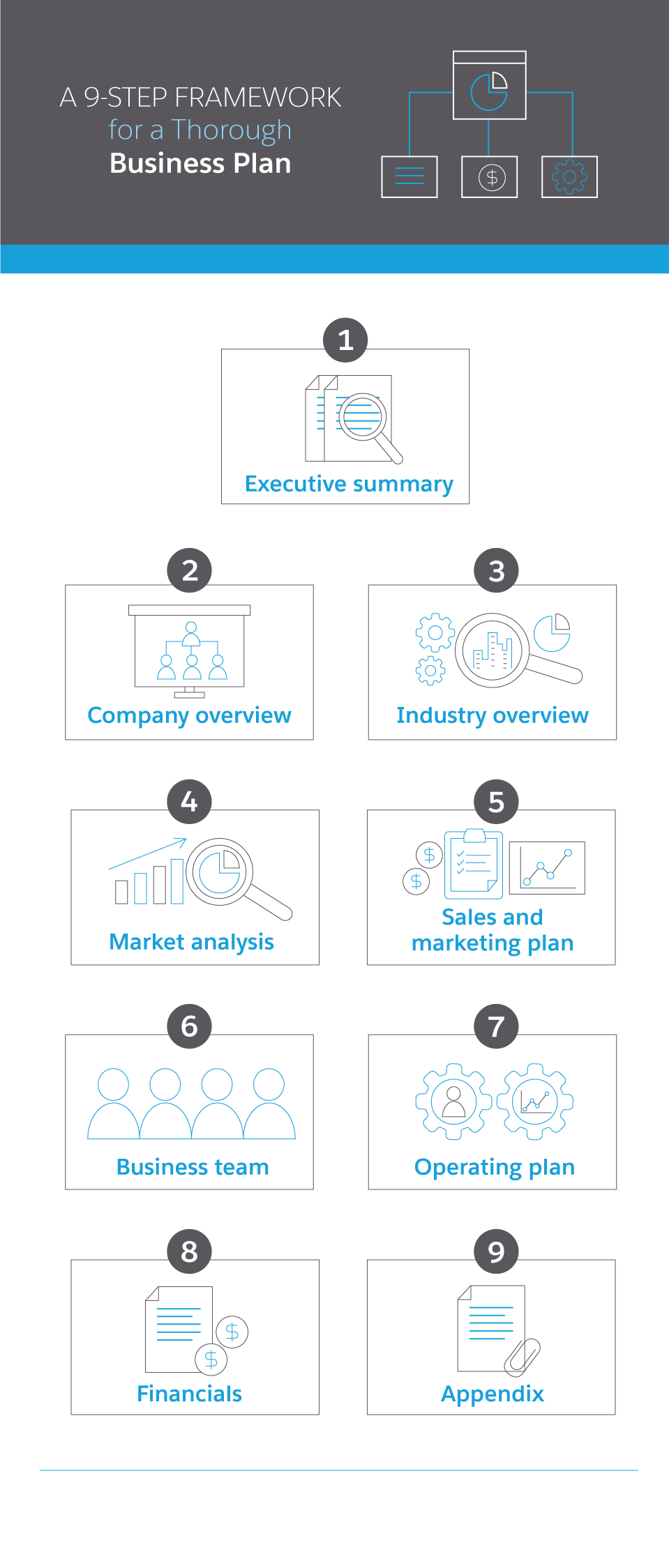
How to Write A Business Plan
Almost every detailed plan for a business follows the same framework. You can expand this however you’d like, but make sure these essential pieces are in place:
- Executive summary
- Company overview
Industry overview
- Market analysis
- Sales and marketing plan
- Business team
Operating plan
Executive Summary
Every thorough plan for a business opens with an executive summary that provides a brief description of the business, a mission statement, the products and services offered, and a summary of plans to succeed in the marketplace. If someone were to ask for a more involved version of your business elevator pitch, you’d recite your executive summary.
Company Overview
This is your napkin drawing on steroids. The company overview section is a snapshot of your business:
- Your business’s history
- A detailed list of products and services
- The physical location (if there is one)
- The problem/need your product or service addresses
Briefly touch on your target audience and how you plan to attract them (you’ll go into more detail later). This is only a snapshot summary for someone to grasp your idea and see the opportunity behind it. You also want to clearly define your company’s strategy for starting or growing in the marketplace.
Industry Overview
Your plan needs to address the industry as a whole, including relevant statistics, current trends, consumer demographics , and any external influences affecting the industry. Use this section to address how your business will fit into a specific industry and what (if any) subsections of the industry you will target.
Market Analysis
Who will you battle for customers? The market analysis section requires you to validate that there is enough demand in the market for your business to both enter and grow. Research competitors in the industry, their market share, and how you plan to compete against them.
This is also a great opportunity to describe any industry barriers upon entry. You can explain how your company will establish itself — including your unique selling proposition — and share how the barriers will help protect your business from other startups or companies that want to go after your market share.
Sales and Marketing Plan
How will you execute your strategies and reach your goals? Your sales and marketing plan should clearly describe how you will grab the attention of busy consumers and persuade them to buy from your company. Use this opportunity to showcase your strengths, account for how your brand will stand out in the marketplace, and detail how you plan to build long-term customer loyalty for repeat business. Don’t forget to describe your pricing strategy and how it compares to the rest of your market, as well as the advertising strategies you will use during your launch and first year.
Business Team
Your business team section should focus on your business’s legal structure. Are you a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or other type of business? Introduce your key team members such as managers, board members, and additional owners. Detail who owns what percentage of the company and each team member’s involvement in the business’s day-to-day operations.
Operating Plan
Your operating plan gives insight into how your business will function on an ongoing basis and what daily operations will look like. The questions you’ll address in your operating plan may include:
- Will you have a physical location?
- What responsibilities will the management team shoulder?
- Do you have a customer invoice prepared?
- What expenses are related to running the business?
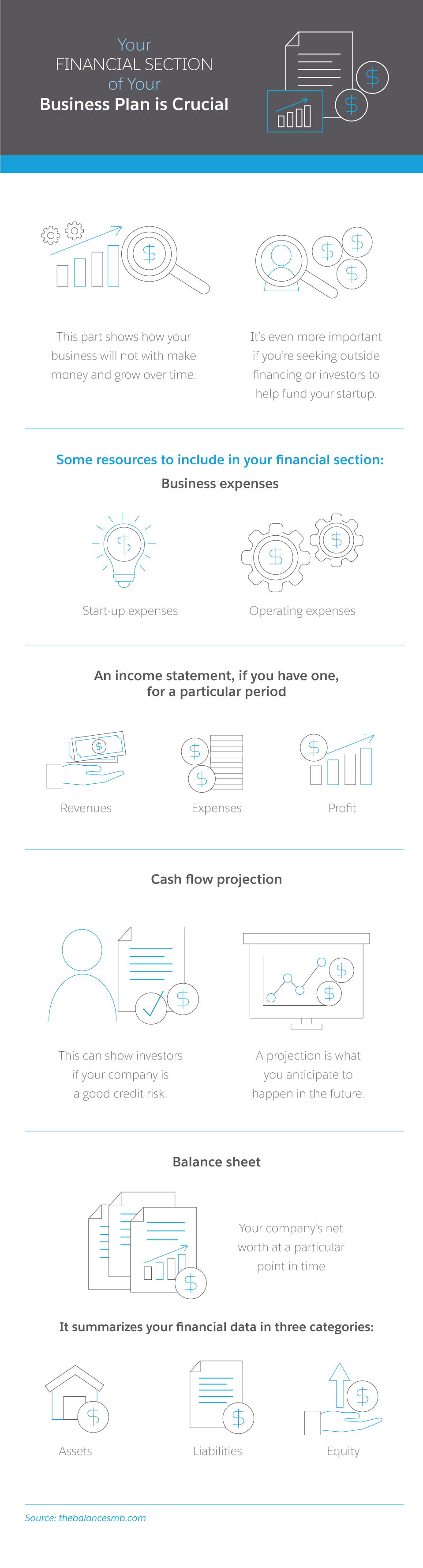
This is the money-making section, which can be an exciting part to investigate and budget. The financials portion of your plan may be the most important because it shows how your business will make money and grow over time. This section is even more crucial if you’re seeking outside financing or investors to help fund your startup. Your financials should outline how your business will generate revenue and profit, and if necessary, how it will repay its loan or investors. Create monthly, annual, and three-to-five-year profit and loss projections and outline anticipated expenses.
Close your business plan with an appendix that provides supporting documentation such as bank statements, employee bios, licenses, agreements, and business credit history. Think of it as your supporting research and reference documents.
What’s Left to Do?
Once you’ve outlined a plan for your business and gathered all the necessary research and documentation, it’s time to write it. By following this template, you should have no problem taking your great idea from a general concept to real life. Your plan doesn’t have to be as long as War and Peace — it simply has to address each key point referenced above and show that your business addresses a need in the market. Then, after you finish writing your business plan, you can follow its guidance and get started on building your business.
Just For You

Data Science Sells: Why Data Scientists Are Key in Sales Today

How Does Data Analytics Help Drive Sales?

Explore related content by topic
- Small Business

Get our bi-weekly newsletter for the latest business insights.

Smart Selling in 2024: 6 Benefits of Using AI for Sales Tools

Everything You Need To Know About AI Copilots for CRM

5 Business Uses for an AI Copilot

Sales Insights: Salesforce at the Catholic University of Portugal

5 Generative AI Terms Every Sales Professional Needs to Know

How Madi International Empowers Sales with Consumer Goods Cloud

Save Time & Close More Deals: Salesforce Sales Cloud Is the Best Tool for Your Sales Process

Mastering Sales Pipeline Management with Salesforce Sales Cloud: How to Boost Efficiency and Drive Revenue

New to Salesforce?
- What is Salesforce?
- What is CRM?
- What is Cloud Computing?
- CRM Solutions
- Customer Success Stories
- Product pricing
About Salesforce
- Security and Performance
- Privacy for Salesforce Products
- Salesforce EU Blog
- Salesforce EU Blog Signup
Popular Links
- Small Business CRM
- Sales Force Automation
- Customer Service Solutions
- Digital Marketing Solutions
- Industry Solutions
- Salesforce Events
- New Release Features
- Manage Subscription
- América Latina (Español)
- Brasil (Português)
- Canada (English)
- Canada (Français)
- United States (English)
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- España (Español)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- France (Français)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Nederland (Nederlands)
- Sverige (Svenska)
- United Kingdom (English)
- All other countries (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- ประเทศไทย (ไทย)
© Copyright 2024 Salesforce, Inc. All rights reserved . Various trademarks held by their respective owners. Salesforce UK Limited, Village 9, Floor 26 Salesforce Tower, 110 Bishopsgate, London, UK, EC2N 4AY. Phone: +353 14403500. Fax: +353 14403501
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
Don't have a Shopify store?
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps
CEO Avada Commerce
Starting a business without a business plan is quite possible. But why would you risk that, especially when you are investing thousands of dollars to set up your startup?
Whether you aim to secure funding, need a roadmap to achieve business objectives, or want to attract the attention of stakeholders—having a well-crafted business plan is like an indispensable asset for your business.
But writing a business plan is not that easy. One needs strategic direction, a bit of writing flair, and a thorough understanding of what each section should include.
A lot for someone who has never written a business plan earlier in their life.
Well, having a useful guide like this blogpost can nudge you in the right direction and teach you how to write for different business plan components.
Ready to get started? Let’s dive right in.
9 Steps to Write Your Business Plan
From creating your executive summary to conducting market research and preparing your financial plan—here is a step-by-step guide to writing your business plan.
- Draft your executive summary
An executive summary is the first and most important section of your business plan.
It is after this section that an investor will decide whether or not to proceed with your business proposal.
Begin this section by introducing your business idea and then summarize the key essentials of a plan in a compelling narrative. Highlight information relating to the market, product, team, competitors, financials, and business goals to help investors get a macro but thorough perspective.
Also, write your executive summary only after you are done writing for the other aspects of a business plan. This will help you distill essential information and present it appropriately.
- Write a brief company overview
A company overview is a detailed summary describing your business and its future objectives. It offers you a chance to tell your business story to the readers, so make sure it is engaging.
Begin this section by detailing your company’s information like its name, location, ownership, and business structure.
Clarify if the business would be registered as a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation. Also, introduce the partners if any, and discuss their profit-sharing ratio.
In this section, you will also highlight the company’s vision statement, its business objectives, and future goals after evaluating your business fundamentals and core values.
Lastly, don’t forget to talk about the milestones you have already achieved and the history of the company, if it has been operating for a long time.
- Define your market research
Market research and analysis is a crucial part of your business plan. It shows that you have a thorough understanding of the market and the industry you are about to enter.
In this section, you should talk about the market size and state of market in the current economy. Elaborate further by defining your Total Addressable Market (TAM), Serviceable Addressable Market (SAM), and Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM) to help lenders get distilled clarity.
Additionally, give an overview of your target market and create a buyer’s persona to show what your ideal customer looks like. Talk about the psychographic and demographic details of your ideal customer, i.e. age, gender, income, interests, pain points, behavioral pattern, etc.
This is essential so that you can create strategies effective for your target market.
Lastly, include details about the emerging trends in your industry and show how your product fits perfectly within that market.

- Conduct competitor’s analysis
Competitor analysis is an aspect of market research that deeply studies the competitive landscape of your business.
In this section of your business plan, you will identify your direct and indirect competition and analyze them on grounds of price, features, and target market.
Such analysis will help you draw your competitive edge in the market. Not only that, it will show the lenders that competition will not come in the way of your business achieving its goals.
- Describe your products and services
This section of your business plan explores your product and service offerings in great detail.
Here, you will list down all the products and services that will bring money to your business. This includes all sorts of primary and secondary products/ services that are available for sale.
For instance, if you are planning to start an online pet store, talk about all sorts of products, brands, and pet needs you will be catering to. Also, include the list of services like pet grooming, vet consultation, puppy training, and others you would be offering on your platform.
When you list down the products also add a brief overview of those products and the prices to give lenders a thorough understanding.
Instead of making this section purely textual, add infographics and HD images to it engaging and informative.
- Explain your operational plan
This section of your business plan shows how you are going to run the business and turn the idea into a reality.
It includes a detailed breakdown of each business procedure, right from the client acquisition, to training protocols, quality control practices, and everything else.
It’s important that you take time and work on your operations plan as it most often works as a guidebook for running a business.
Now if you are wondering what to include in your operations plan, here are a few things it must definitely have:
- Standard operating procedures for running different business activities.
- Logistics and distribution of products through different life cycles.
- Production workflow, if applicable.
- Details of supply chain like vendors and agreements.
- Details about the physical location of your business, its dimensions, agreements, etc.
- Equipment and technologies to perform everyday business activities and their details.
- Staff and hiring plan and an understanding of who will perform what tasks.
Also, include your long-term plans and show how you plan to reach there with streamlined operations.
Again, try to add infographics, charts, and diagrams wherever possible to make this section easily absorbable for the readers.
- Outline your marketing and sales strategies
The marketing and sales section of your business plan offers an in-depth overview of your sales and marketing strategies.
In this section, you will talk about your sales goals, forecasts, and methods to achieve those sales goals. Explain your plans to attract new customers and retain existing clients and discuss your sales strategy in detail.
Further, describe your marketing plan, budget, and methods to track the progress of different marketing activities.
Dive into detail and explain how you will implement different marketing strategies like print media, pay-per-click, email marketing, social media marketing, events/ launch, and others.
Overall, offer an overview of your strategies to achieve the most important objective of your business, sales.
- Introduce your management team
Lenders and investors want to know if you have the right people on the team to pull off your business idea. Well, this is your chance to tell them about solid people on your team.
Introduce the CEO and members of managerial positions in this section. Talk about their experience, expertise, skill sets, achievements, and how they make the right fit for your business.
Don’t you worry about bragging. This is absolutely the right time to brag about your star team.
Further, introduce people at the middle and lower levels and explain the organizational hierarchy in your business through a diagram. Also, add the approximate salaries of the people to give the readers a more nuanced understanding.
- Offer detailed financial forecasts
This is the most critical part of your business plan, especially if you are planning to seek funding from investors.
Now, there are many things you can include in your financial plan. However, if there are 3 quintessential it must include, those are:
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
While making the financial plan, include predictions and forecasts for up to 3-5 years so that investors can gauge the viability and feasibility of your business idea.
Apart from these key statements, you can also include figures for start-up costs, the cost of goods sold (COGS), revenue forecasts, and break-even analysis in this section.
Lastly, ensure that you add visual graphs, charts, and diagrams to make your finances easy to grasp and understand.
Let us now see if there is a way to write your business plan effectively without much effort.

How does AI help in writing your Business Plan?
Writing a business plan from scratch without any assistance, template, or structure can be time-consuming.
However, with AI making the rounds, it is easier than ever to perform creative and repetitive tasks, efficiently. Especially for someone who finds it difficult to transform their ideas into words, AI can make the task of writing a business plan much easier.
Now, generative AI tools like Chat GPT and Bard can help you write the contents of your plan. However, they lack the understanding of specific nuances that a business plan must include.
Using an AI business plan builder instead can be more effective as it structures and plans the contents specifically suited for a business plan.
All you need to do is answer the questions relating to your business and let AI create a unique business ps easy to get a headstart and then make essential changes thereafter using AI assistance.
AI will not only make the process less time-consuming, but it will also help in increasing the effectiveness of your business plan by working strategically on the content and structure.
Business plans are quintessential for any business. Whether you are starting a new venture, expanding the current one, or seeking investment for your startup—having a solid business plan will give you a headstart in the right direction.
Follow this step-by-step guide or get yourself an AI plan builder to write your business plan in no time. Get started now.
Recover lost sales with proven Abandoned Cart Email series

- --> --> --> -->