
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students

Dissertation vs Thesis: The Differences that Matter
Updated: January 24, 2023
Published: April 26, 2020

As a graduate student, you will have many different types of challenging coursework and assignments. However, the biggest project that you’ll work on when earning your master’s or doctoral degree will be your thesis or dissertation . The differences between a dissertation vs thesis are plenty. That’s because each of these pieces of writing happen at different times in one’s educational journey.
Let’s break down what a dissertation and thesis are so that you have a strong handle on what’s expected. For both a thesis and a dissertation, there is an obvious fluency and understanding of the subject one studies.
Let’s take a look at their similarities and differences.
Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
What is a dissertation.
When you enter a doctoral program to earn a PhD, you will learn a lot about how to conduct your own research. At the culmination of your degree program, you’ll produce a dissertation.
A dissertation is a lengthy piece of written work that includes original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic. As the doctoral student, you get to choose what you want to explore and write about within your field of study.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis is also a scholarly piece of writing, but it is for those who are graduating from a master’s program. A thesis allows students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying.
Main Differences Between a Thesis vs. Dissertation
The biggest difference between a thesis and a dissertation is that a thesis is based on existing research.
On the other hand, a dissertation will more than likely require the doctoral student to conduct their own research and then perform analysis. The other big difference is that a thesis is for master’s students and the dissertation is for PhD students.
Structural Differences Between a Thesis and a Dissertation
Structurally, the two pieces of written analysis have many differences.
- A thesis is at least 100 pages in length
- A dissertation is 2-3x that in length
- A thesis expands upon and analyzes existing research
- A dissertation’s content is mostly attributed to the student as the author
Research Content and Oral Presentation
Once completed, some programs require students to orally present their thesis and dissertation to a panel of faculty members.
Typically, a dissertation oral presentation can take several hours. On the other hand, a thesis only takes about an hour to present and answer questions.
Let’s look at how the two scholarly works are similar and different:
Similarities:
- Each is considered a final project and required to graduate
- Both require immense understanding of the material
- Written skills are key to complete both
- Neither can be plagiarized
- Both are used to defend an argument
- Both require analytical skills
- You will have to draft, rewrite, and edit both pieces of writing
- For both, it is useful to have another person look over before submission
- Both papers are given deadlines
Differences:
- A dissertation is longer than a thesis
- A dissertation requires new research
- A dissertation requires a hypothesis that is then proven
- A thesis chooses a stance on an existing idea and defends it with analysis
- A dissertation has a longer oral presentation component
The Differences in Context: Location Matters
The united states.
In the US, everything that was previously listed is how schools differentiate between a thesis and a dissertation. A thesis is performed by master’s students, and a dissertation is written by PhD candidates.
In Europe, the distinction between a thesis and dissertation becomes a little more cloudy. That’s because PhD programs may require a doctoral thesis to graduate. Then, as a part of a broader post-graduate research project, students may complete a dissertation.
Photo by Russ Ward on Unsplash
The purpose behind written research.
Each piece of writing is an opportunity for a student to demonstrate his or her ability to think critically, express their opinions in writing, and present their findings in front of their department.
Graduate degrees take a lot of time, energy, and hard work to complete. When it comes to writing such lengthy and informative pieces, there is a lot of time management that is involved. The purpose of both a thesis and a dissertation are written proof that you understand and have mastered the subject matter of your degree.
Degree Types
A doctoral degree, or PhD, is the highest degree that one can earn. In most cases, students follow the following path to achieve this level of education: Earn a bachelor’s degree, then a master’s, and then a PhD. While not every job title requires this deep educational knowledge, the salaries that come along with each level of higher education increase accordingly.
Earning Your Degree
Whether you are currently a prospective student considering earning your higher education degree or a student enrolled in a master’s or doctoral program, you know the benefits of education.
However, for some, earning a traditional degree on-campus doesn’t make sense. This could be because of the financial challenges, familial obligations, accessibility, or any other number of reasons.
For students who are seeking their higher education degrees but need a flexible, affordable, and quality alternative to traditional college, take a look at the programs that the University of the People has to offer.
University of the People is an entirely online, US accredited and tuition-free institution dedicated to higher education. You can earn your Master’s in Business Administration or your Master’s in Education . Not to mention, there are a handful of associate’s and bachelor’s degree programs to choose from as well.
If you want to learn more, get in touch with us !
The Bottom Line
Regardless of where and when you earn your master’s or doctoral degree, you will likely have to complete a thesis or dissertation. The main difference between a thesis and dissertation is the level at which you complete them. A thesis is for a master’s degree, and a dissertation is for a doctoral degree.
Don’t be overwhelmed by the prospect of having to research and write so much. Your educational journey has prepared you with the right time management skills and writing skills to make this feat achievable!
Related Articles
- Home »
- Advice »
What is the Difference Between a Dissertation and a Thesis?
Find your perfect postgrad program search our database of 30,000 courses.
And to make it even more confusing, some institutions or departments will even use the terms differently!
But what are we all really talking about when we refer to a dissertation or a thesis? And does the term you use actually impact on what you actually end up writing?
This article covers the main differences between a dissertation and thesis, and how the terms may differ depending on the course, university and location.
What is a dissertation?
A dissertation is a piece of academic writing centred around original research. In their dissertations, students review existing research but also build on this with unique hypotheses and approaches.
A dissertation can be used to disprove a previous theory or take existing theories and research in a new direction. It is a large research project that is usually completed at the end of the academic year.
Usually, a dissertation starts with a dissertation proposal , which is approved by a study supervisor. The student then completes the research and writes up the methodology , findings, evaluations and conclusions from the research.
Dissertations can be undertaken by both undergraduate and postgraduate students. At undergraduate level the word count is around 5,000 to 8,000 and at postgraduate level it is usually 10,000 to 15,000.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an academic paper covering an in-depth review of existing research in a particular discipline. It will involve an academic argument, although it doesn’t usually require original research from the student. The existing research is used to support and evaluate the proposed argument.
A thesis is not usually required at undergraduate level and is more common at postgraduate level.
This large piece of written-up research is usually completed at the end of a masters degree. Some masters courses require a thesis to graduate.
Differences between a dissertation vs thesis
The main purpose of a writing a dissertation is to add new findings to the existing literature in that field with original research. Whereas theses tend to evaluate existing findings, as their purpose is to demonstrate knowledge and skills within the course’s subject matter.
In terms of how long it takes to complete a thesis or dissertation project, a thesis is typically shorter than a dissertation since there are fewer original research aspects involved. This means that it will probably take less time. However, this can differ depending on the university and the course.
Dissertations sometimes require an oral presentation, known as a viva , where findings are showcased to academics who ask questions about the research. Theses usually do not require this.
The root of the words
The word ‘dissertation’ originates from the Latin word ‘dissertare’, meaning to continue to discuss and the Latin word ‘disserere’ which means to examine and discuss .
The word ‘thesis’ originally comes from the Greek word ‘tithenai’, which means to place or position. This later evolved into the Latin ‘thesis’, which had two meanings: an abstract question and to put something forward .
Similarities between a dissertation vs thesis
Although there are some key differences between a dissertation and a thesis, there are also similarities.
- Both are generally long pieces of academic writing, much longer than a typical essay.
- Both explore a topic in depth, whether you are conducting totally unique research or structuring an argument based on existing research.
- Both are considered a final project and usually required to graduate from a degree, masters or PhD. Students can graduate without a thesis or dissertation if they choose to complete a postgraduate diploma or postgraduate certificate instead.
- Excellent academic writing skills are highly important for both types of research project.
Is a dissertation harder than a thesis?
Though, the difficulty of a thesis or dissertation depends on your personal skill set. For instance, students that learn better by developing their own research ideas may find a dissertation easier than a thesis.
Difficulty can also depend on the level of the course. For instance, a thesis completed at doctorate level is likely to require more advanced knowledge than a thesis at undergraduate level.
The difficulty of either type of research project can also vary depending on the subject matter and the resources available to you.
Both dissertations and theses can be challenging, but don’t be put off by the thought of having to produce a larger body of work. Your supervisor will be there to support you.
Definitions depend on where you are
The terms ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ are sometimes used interchangeably, and the meanings can differ depending on the country and university.
There are plenty of differences between the variant forms of English, such as British English and American English. Around the world, different English-speaking countries use the words ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ differently.
Generally, nations with British-based academic systems of university education use dissertation to refer to the body of work at the end of an undergraduate or masters level degree . British-based institutions generally use thesis to refer to the body of work produced at the end of a PhD .
In countries and institutions that are based on the American system of education, the words tend to be used in reverse. However, institutions and even different departments in the same university can use the words differently.
If you're in doubt, then stick with the way the university and department you're currently attending use the terms.
Definitions can depend on the subject
In the UK, the terms ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ are generally applied equally across institutions and subjects.
However, in the US the meanings can differ between different subject areas. The term ‘thesis’ can be used to describe a piece of original research in US academia, whereas original research is usually referred to as a dissertation in the UK.
If you’re studying in the US , you may complete a thesis at masters level in another subject area that involves wide-ranging reading and understanding rather than original research and still call it a thesis.
With so much interchangeability between the two terms, it’s understandable that there is often confusion in the debate between a dissertation vs thesis, as there is no clear answer.
Always read specific course details to understand exactly what’s involved in the research project that you are required to produce.
Examples from US and UK universities
Georgetown University in the US refers to a dissertation and a thesis as both adding to your 'field of knowledge' . The University of Edinburgh recommends that you refer to your individual course handbook for guides to dissertations, so each department will have their own guidelines to using the word dissertation and thesis. At University College London they refer to a thesis as the piece of work at the end of an EngD, MPhil, MD(Res) or PhD, which are all research degrees.
In conclusion
Ultimately, it doesn't really matter which word you use as both refer to a serious and lengthy piece of work where you can show what you have researched and understood as part of your postgraduate studies.
As long as you are referring to the piece of work that you are compiling in the same way as those in your department then you will avoid confusion.
It is important to check whether the research piece involves original research or expects you to build upon existing research.
Writing a dissertation or a thesis requires a substantial amount of planning and work and you don't want to let yourself down at the last hurdle with poor presentation of your work, so always keep an eye on your course or department guidelines.
Related articles
Top Tips On Writing Your Postgraduate Dissertation Or Thesis
How To Write A Thesis
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Top Thesis Writing Tools
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Sign up now!

Take 2 minutes to sign up to PGS student services and reap the benefits…
- The chance to apply for one of our 5 PGS Bursaries worth £2,000 each
- Fantastic scholarship updates
- Latest PG news sent directly to you.
Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings? In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.
Thesis vs. Dissertation: What’s the difference?
Thesis and dissertation are extensive research papers that differ in terms of their requirements, length, and purpose, with the former being associated with a master's degree and the latter with a doctoral degree, but are often used interchangeably.
Updated on September 15, 2023

A thesis and a dissertation are both extensive research papers, and both require literature searches and novel findings, but the two differ in various ways. Their definitions also differ across regions. Typically, in North America, a thesis is required for the completion of a master’s degree, while a dissertation is required for the completion of a doctoral degree. The former is long, while the latter is longer and more intensive.
Despite these differences, the two terms are often used interchangeably, especially among those who haven’t completed one or the other. Here, we’ll compare the components, length, and purpose of these two academic documents to clearly understand the differences between these important papers in the life of a graduate student.
What’s a thesis?
The term “thesis” explained here is generally consistent with how the word is used in North America to describe this substantive research paper.
A thesis is an extended argument (PDF). It is a research-based document that displays the student’s/author’s knowledge and understanding of a specific subject within their field of study. It generally presents findings on a particular topic.
See this and this (PDFs) for examples. These superb master’s theses from Canada will give you an idea of the size and format of these papers.
Who would write a thesis?
You generally write a thesis if you’re undertaking a research-oriented master's degree program (as opposed to a practical program, which may require a capstone, internship, exam, etc.).
The thesis is the essential part of a program’s research component, demonstrating the student's ability to critically analyze the literature and complete independent research. The process of writing a thesis involves exploring a specific research question, conducting a comprehensive literature review, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings in a structured and cohesive way.
A thesis' specific requirements and expectations differ depending on the academic institution, department, and program.
Components of a thesis
A thesis is typically presented in chapters. How many chapters will vary, but a common structure is:
- Introduction: Presents the research topic, purpose, and objectives, setting the context for the work.
- Literature review: Comprehensive survey of existing scholarly material related to the research topic, highlighting key theories and findings.
- Methodology: Describes the methods, procedures, and tools used in doing the research.
- Research: The actual performing of the study, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to the research question.
- Findings and conclusions: Gives the results obtained and explains their significance in relation to the research question.
- Limitations and future research: Outlines the study’s shortcomings and suggests potential areas for future investigation.
Within that structure, and in addition to those parts, a thesis may also include:
- Cover page: Contains the thesis title, author's name, institution, department, date, and other relevant information
- Abstract : A brief summary of the thesis, highlighting the research objectives, methods, key findings, and conclusions.
- Certificates of own work
- Certificate of readiness to be included in the library
- Certificate that the research has not been presented to another university
- Acknowledgments
- Table of contents: List of the main sections, subsections, and corresponding page numbers.
- Index of figures and tables
- References: A comprehensive list of all the sources cited in the thesis, following a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Appendices (optional): Additional materials include:
- Abbreviations and/or acronyms used
- Questionnaire or interview schedule/s (if used)
- Data acquired in the form of transcripts or numeric tables
- Research protocol
- Ethics protocol
What’s a dissertation?
This is also viewed from a North American perspective, where a dissertation is usually the main research work toward completing a research-based doctoral program.
A dissertation is a comprehensive and in-depth research project completed as part of the requirements for a doctoral degree. It’s a substantial piece of original work that contributes new knowledge to a specific field of study. Naturally, when it’s completed as the major requirement for earning a PhD, it’s longer, more detailed, and the expectations are higher.
Dissertations themselves can add to the literature in the field. For this reason, some students choose to publish them and have them indexed. The research and the data acquired while working on a dissertation can potentially lead to more publications and help define the researcher’s growing area of expertise.
See this and this (PDFs) top-ranking dissertation on ProQuest for good examples.
Who would write a dissertation?
Completion and defense of a dissertation is a standard requirement for doctoral students to earn a PhD or another doctorate such as an EdD or DM. But some specialized degrees, such as a PsyD (Doctor of Psychology), JD (Juris Doctor) or DPT (Doctor of Physical Therapy) may have practice-based requirements in place of a research project, as these courses of study are geared more toward practical application.
Components of a dissertation
A dissertation’s components are generally the same as those of a thesis. You can look at the list above for a thesis to see what typically goes into a dissertation. But, if compared with a master’s thesis, most aspects are longer and more rigorous.
The word count requirements for theses can vary significantly, but doctoral dissertations often range 40,000–80,000 words or, per Harvard , 100–300 pages.
Differences between a thesis and a dissertation
As already touched on, the key differences are in where the two documents are used, length, and rigor. There are also regional differences.
A thesis typically demonstrates a master’s degree program student's grasp and presentation of a specific subject in their field of study. It normally involves a literature review, data analysis, and original research, but it is usually shorter and less comprehensive than a dissertation. The standards for rigor and novelty may also be lower.
A dissertation requires more extensive research, original contributions to the field, and a deeper exploration of the research topic. A dissertation is typically the output associated with a doctoral degree program.
The main differences in structure between a thesis and a dissertation are in the scope and complexity.
The word count requirement for theses and dissertations can vary depending on the institution and program.
A thesis is usually 20,000–40,000 words. However, there have been cases of mathematics dissertations that were only a few pages long!
Doctoral dissertations may range 60,000 to upward of 100,000 words, and exceed 100 pages. Many universities, however, seek around 80,000 words.
Oversight and process
A thesis may simply be submitted to the student's instructor, though rigorous thesis programs require a committee and defense. A dissertation will nearly always require the student to choose a chair, a committee, and then go through a more rigorous defense and revision (if necessary).
- Committee: Master's thesis committees usually have fewer members (typically 2–3) than doctoral dissertation committees (often 4–5, or even more).
- Guidance: Master's students often receive more detailed direction from advisers than doctoral students, who are expected to work more independently.
- Review: Dissertation reviews are typically more rigorous, often involving external reviewers, while thesis reviews are usually internal.
- Defense: A dissertation defense is generally more intense and formal, as it often involves a presentation to the wider academic community, while a thesis defense might be more confined and informal.
- Revision: The revision process for a doctoral dissertation is typically more extensive, given the larger scope of the project and higher stakes involved, compared with those for a master's thesis.
Regional differences
The terms' use varies among (and even within) countries. Here are some general regional differences:
In the United Kingdom, a thesis is commonly associated with both master's and doctoral degree programs. For example, the University College London refers to a thesis for EngD, MPhil, MD(Res), and PhD degrees. At the University of Nottingham , a dissertation is written for a research master’s degree.
In Australia and New Zealand , “thesis” is generally used to refer to a substantial research project completed for a higher degree, though not limited to a master’s (you’ll find ample references to a “PhD thesis”).
In Latin American countries, the thesis is commonly used to refer to both master's and doctoral research projects.
Closing thoughts
Both theses and dissertations are necessary documents for students in graduate programs. Despite the differences in expectations, and even in definitions of these papers, the student-author must do a diligent and rigorous job to earn their degree.
Here are a few helpful resources if you want to get into greater detail:
- Writing the Winning Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-By-Step Guide
- 100 PhD rules of the game to successfully complete a doctoral dissertation (PDF)
- Theses and Dissertations: A Guide to Writing in Social and Physical Sciences
Perfect the English on your thesis or dissertation
Whether you’re submitting a thesis or a dissertation, if it’s in English, it should:
- Have no grammatical or spelling mistakes
- Use field-appropriate language
- Concisely and clearly communicate your research.
That’s what AJE expert editors will do for you. Within days, you can receive an expert English edit of your work. The editor will be familiar with your field of study and will comprehensively improve both the language quality and the delivery of your message. Look into AJE English Editing .

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
AJE will edit your thesis or dissertation
Choose between our expert academic editing services to prepare your thesis or dissertation.

- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life
Dissertation vs Thesis: Your 2024 Guide

If you’ve been thinking about going to graduate school, you may be familiar with the application requirements, rigorous academic schedule, and thesis or dissertation you’ll be expected to complete. So, what exactly is the difference between a thesis and a dissertation? While there are similarities, there’s a clear difference between the two. In our guide, we compare dissertation vs thesis. Discover more about both – and what you can expect during your graduate program. Let’s get started!
- Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is an academic paper or project that’s completed towards the end of a master’s degree program . It is typically completed as the capstone project , meaning it’s the final project required for a student to graduate.
Students need to select a narrow, specific topic within – or relating to – their field of study. Once they’ve selected a topic, students must conduct an in-depth review of existing research on their chosen subjects. The next step is to formulate an academic argument, an assertion they’ll need to support or prove with said research.
Therefore, a thesis is akin to an in-depth research paper. It’s comprised of research that essentially proves what a student has learned during their program.
What Is a Typical Thesis Structure?
A thesis generally follows a rigid structure that’s decided by the program, department, or university. Here is an example of a thesis structure:
- The Title Page
- Summary of Thesis Abstract
- Table of Maps and Figures
- The Thesis Body (Sometimes divided into chapters)
- The Results or Conclusion
Who Needs to Complete a Thesis?
Most master’s degree programs require students to complete a thesis. While some undergraduate programs may also require a thesis, these are generally shorter and narrower in scope.
Some programs will also require a master’s student to defend their thesis in front of a panel or committee.
What Is a Dissertation?
What is “the PhD paper” called? Some people refer to it as a PhD thesis, but it’s most commonly known as a dissertation in the US. Dissertations are the capstone project required at the tail end of a PhD program . It is almost always required, except for a select few one-year PhD programs .
Much like a thesis, dissertations are also academic papers that aim to prove a student’s expertise – while adding to the current body of knowledge – in their field. Thus, a student must look at existing research and conduct their own research .

Basically, it’s the magnum opus of a doctoral journey in the United States. A dissertation isn’t just a long research paper; it’s a beast of a project. It demands extensive research, originality, and the ability to make a meaningful contribution to your chosen field. Think of it as a research odyssey guided by a seasoned mentor. Once you’ve conquered this scholarly quest and defended your findings, you’ll proudly emerge with your hard-earned doctoral degree, a testament to your dedication and scholarly prowess.
A dissertation typically comes after a PhD student completes their required courses and passes their qualifying exams. In some programs, the dissertation process is embedded into the coursework. In such cases, students receive a jump start on their work, allowing them to potentially finish their program earlier.
What Does a Dissertation Do?
PhD candidates must present a new theory or hypothesis. Alternatively, they must present their research to question (or disprove) the existing accepted theory on their chosen subject. Students may choose to tackle their topic from a new angle or take their research in a different direction.
Most programs will require students to defend their dissertations. During the defense, candidates must be able to justify the methodology of their research and the results and interpretation of their findings. Defenses are typically oral presentations in front of a dissertation committee , where the students are asked questions or presented with challenges.
Although the defense may seem daunting, PhD students work closely with their advisors to prepare for their dissertations. Students receive feedback and advice to guide their dissertations in their chosen direction.
What Is the Typical Dissertation Structure?
Dissertations follow a rigid structure typically set by the program, department, or university. Here is an example format:
- The Acknowledgments Page
- The Abstract
- Introduction
- The Literature Review & Theoretical Framework
- The Methodology
- Findings/Results
- Discussions of the Findings, including analysis, interpretation, and applications
- The Conclusion
- List of References
- Any Appendices
What Is a Doctoral Thesis?
A doctoral thesis is a substantial piece of scholarly work that marks the pinnacle of a doctoral degree program, such as a PhD. Think of it as the academic grand finale. Its primary mission? To showcase the candidate’s mastery in their chosen field and their knack for delving deep into research.

In a nutshell, a doctoral thesis is a mammoth project that calls for originality. You’ve got to dig, investigate, gather data, crunch numbers, and present real data-supported findings. All this hard work usually happens under the watchful eye of a knowledgeable mentor. Once you’ve conquered this scholarly mountain and defended your thesis successfully, you’ll be proudly awarded your well-deserved doctoral degree. It’s the hallmark of your expertise and contribution to your field.
And how does a doctoral thesis differ from a dissertation? That’s mainly a geographic explanation. While they’re largely similar in scope and purpose, when comparing a doctoral thesis vs. a dissertation:
- A dissertation is the PhD capstone requirement in the US .
- A doctoral thesis is the PhD capstone requirement in Europe .
Related Reading: The Easiest PhDs
Dissertation vs. Thesis: The Similarities
In the master’s thesis vs dissertation discussion, there are plenty of similarities. Both are lengthy academic papers that require intense research and original writing. They’re also capstone projects which are completed at the tail end of their respective programs.
Students must work closely with their respective committees (e.g., faculty members, advisors, professionals) who provide feedback and guidance on their research, writing, and academic arguments. Both thesis and dissertation committees have a committee chair with whom the students work closely.
In some ways, the requirements for theses and dissertations are quite similar. They require a skillful defense of a student’s academic arguments. What’s more, both papers require critical thinking and good analytical reasoning, as well as in-depth expertise in the chosen field of study.
Students must also invest a significant amount of time into both projects while also being able to accept and action feedback on their work.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: The Differences
What are the differences between a PhD dissertation vs. thesis? The first and most distinct difference is the degree program requiring a PhD dissertation or thesis. A dissertation is typically the capstone project for a doctorate, while a thesis is the capstone project for a master’s degree program (or undergraduate program).
Candidates will have to defend their dissertation during an oral presentation in front of their committee. Only some master’s theses require this.
During a thesis, students typically conduct research by reviewing existing literature and knowledge on their chosen subject. During a dissertation, students must do their own research and prove their theory, concept, or hypothesis. They should also expect to develop a unique concept and defend it based on the practical and theoretical results achieved from their rigorous research.
Theses are also typically shorter (around 40 to 80 pages). Dissertations, however, are much longer (between 100 and 300 pages). Of course, the actual length of the paper may depend on the topic, program, department, or university.
Related Reading : PhD Candidate vs Student: What’s the Difference?
Dissertations and Theses: US vs. Europe
Whether you’re in the US or Europe, dissertations and theses are similar. However, European requirements and conventions differ slightly:
Doctoral Thesis
To ensure your PhD graduation, a dissertation is generally required. Doctoral theses in Europe are much like a PhD dissertation in the US : You must complete your own research and add to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
Master’s Dissertation
It may seem odd to require a dissertation for master’s degree programs, but in Europe, this is exactly what you’ll need. A master’s dissertation is a broader post-graduate program research project , though it’s most typically required for master’s programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are a few of the most common questions we hear about the meaning of thesis vs. dissertation.
Is a Thesis and a Dissertation the Same?
Yes and no. In some ways, a dissertation and a thesis are the same. For example, both require original writing, critical skills, analytical thinking, plenty of research, and lots of academic effort. However, a thesis is more commonly reserved for master’s – and some undergraduate – programs. Dissertations are generally required by PhD programs in the United States.
Additionally, a thesis typically calls for heavy research and compilation of existing knowledge and literature on a subject. A dissertation requires candidates to conduct their own research to prove their own theory, concept, or hypothesis – adding to the existing body of knowledge in their chosen field of study.
How Long Is a Thesis vs. a Dissertation?
One of the primary differences between thesis and dissertation papers is their length. While a thesis might be anywhere from 40 to 80 pages long, a dissertation can easily run from 100 to 300. It’s important to note that these numbers depend on the specific program and university.
Does a PhD Require a Thesis or a Dissertation?
It all depends on where you are! While a US-based PhD requires you to complete a dissertation, a thesis (or “doctoral thesis”) is more commonly required for PhD candidates in Europe. In the US, a thesis is more commonly reserved for master’s degree programs and occasionally undergraduate programs. In Europe, a “master’s dissertation” is typically required for the completion of a master’s degree.
So, there you have it: an in-depth comparison of the dissertation vs. thesis academic requirements. Now that you know the primary similarities and differences between the two, it might become easier to decide your academic path. Just remember, you may be able to find a master’s program without a thesis or a doctorate without a dissertation requirement if you prefer. Good luck!
Are you ready to jump into your doctorate? Find out if you need a master’s degree to get a PhD .

Chriselle Sy
Chriselle has been a passionate professional content writer for over 10 years. She writes educational content for The Grad Cafe, Productivity Spot, The College Monk, and other digital publications. When she isn't busy writing, she spends her time streaming video games and learning new skills.
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ Graduate Certificate vs Degree: What’s the Difference? [2024 Guide]
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ The 18 Best Scholarships for Black Students in 2024-2025
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ The 25 Best Gifts for Nursing Students in 2024
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ 7 Best Laptops for Engineering Students in 2024
This Week’s Top 5 Graduate Opportunities
These are the best states to start your tech career, related posts.

- 12 Best Laptops for Computer Science Students

- Is a Master’s Degree Worth It? [2024 Guide]

BA vs BS: What You Need to Know [2024 Guide]

How To Apply to Grad School: Ultimate 2024 Guide


7 Best Laptops for Engineering Students in 2024

Grad School Resume 2024: Tips, FAQs, and Templates

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Breaking Records: Yale Sees Most Selective Grad Admissions Season Yet
- Applying to Big Tech This Year? Here’s How to Ace It.
- 73% of job seekers believe a degree is needed for a well-paying role–but is it?

© 2023 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us

Thesis Vs. Dissertation — Know the difference and similarities!
The academic world is filled with many different types of writing assignments, each with its own unique set of requirements and expectations. One common source of confusion for students is the distinction between a thesis and a dissertation. Both are long-form academic works, but there are several key differences between the two that are important to understand.
In Shakespeare’s day, a candidate for a master’s degree would write a thesis, an original paper in which he maintained a certain proposition. Whereas, completion of a doctoral program required submission and defense of a dissertation. He would read his thesis to his committee, after which he sat in silence while two faculty members gave point-by-point refutations of everything the candidate said.
The focus here was on the student’s ideas and his ability to arrange and express them clearly. If a student wished to advance further in academia he could pursue a dissertation. This was more of a literature review . He would read widely in a particular area and write up his findings, discussing the various authorities and their opinions. The point was to demonstrate that he was well-versed in the literature of the field. While the confusion between the two terms is understandable, we shall tackle the dissertation vs. thesis topic in this article and provide unambiguous insights on it.
Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is a critically written scholarly piece of research work. Typically, it is submitted by students graduating from a master’s program. The purpose of a thesis is to allow students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying as part of the program.
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a comparatively lengthier piece of scholarly writing that accounts for your research work throughout the doctoral program. A researcher earns the Ph.D. after submitting and defending his/her dissertation. It includes all information about the original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic conducted by the Ph.D. candidate.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Differences
- The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master’s program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D.
- A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is well-informed and has knowledge about the research topic learned in the study program. On the other hand, a dissertation provides an opportunity for the researcher to contribute new theories and information to the existing literature in the research field.
- A thesis is a presentation of learned and existing information, while the purpose of a dissertation is to develop a unique concept and defend it based on theoretical and practical results.
- A master’s thesis is approximately 100 pages in length. However, a Ph.D. dissertation should be much longer than a thesis and must include background and research information. A dissertation must include your research proposal, grant proposal, literature review , ideation of research topic, and every other minute detail about your research. Ideally, a dissertation inclusive of all details mentioned above should be three times the length of a master’s thesis.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Similarities
- Both a thesis and a dissertation are considered final projects and are required to graduate from respective programs.
- The thesis and dissertation both require a deep and accurate understanding of the research problem.
- Both forms of scholarly written pieces must address specific research questions.
- Academic writing skills are imperative for a thesis as well as a dissertation.
- Ethical practices must be followed while collating and documenting research data.
- Plagiarism is not accepted in either.
- Both require analytical skills to support the findings.
- It is essential that both undergo intense dissertation/ thesis editing and critical proofreading before final submission.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Europe
In Europe, the original distinction between a thesis and a dissertation has been largely retained. A doctoral thesis is a focused piece of original research that is performed to obtain a Ph.D. A dissertation is part of a broader post-graduate research project.

However, the thesis has evolved since original research nowadays requires plenty of background research . So, a thesis will contain extensive citations and references to earlier work, although the focus remains on the original work that comes out of it.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: USA
In the United States, the definition of a thesis is almost the opposite of that in Europe. Because a thesis is shorter than a dissertation it gradually came to mean a preliminary degree on the way to a doctorate. A thesis is now performed to earn a Master’s degree. In scientific fields, a master’s candidate takes advanced coursework and gains hands-on experience in a research project but does not direct the project to the same extent that he would in a doctoral program. In a master’s project, the student’s ideas are welcomed and expected but the focus is on obtaining technical expertise, not doing original research. Engineering students commonly obtain Master’s degrees and seldom go on to get PhDs. In other fields such as Chemistry, the opposite is true, with a Master’s degree no longer being required as the first step for a doctorate. Almost everyone I know who received a Master’s degree in Chemistry got one because they dropped out of graduate school and wrote their truncated research as a Master’s project.
In a Nutshell
Needless to say, the dissertation vs. thesis facts are real. Therefore, using one term instead of another is not acceptable as an academic. One must remember the purpose of each and use them accordingly. However, one is not undermined by the other. Whether you are writing a thesis or a dissertation, both must be done with the same seriousness. Both require critical technical and soft skills. Improving your time management and academic writing skills plays a major role in acing both forms of scholarly writing.
How do you decipher dissertation vs. thesis? Should the interchanged usage of these terms be acceptable? How is your approach to writing a thesis different from that of a dissertation? What are the other differences associated with the thesis and dissertation? Let us know in the comments section below!
Frequently Asked Questions
"Dissertation" and "thesis" are used interchangeably but differ in: Academic Level: Thesis for master's, dissertation for doctoral degrees (US). Scope and Depth: Thesis shorter, demonstrates mastery; dissertation extensive, original research. Originality: Thesis may involve original analysis; dissertation presents significant new insights. Time and Effort: Dissertations require more resources and time than theses.
The length of a dissertation varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, dissertations are longer than theses, ranging from 10,000 to over 100,000 words. However, word count alone does not reflect the quality or depth of the research. Guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for specific requirements.
The length of a thesis varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, the word count ranges from around 10,000 to 50,000 words. Specific guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for precise requirements.
Has helped develop my writing skills through science-based study.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Masters Thesis vs. PhD Dissertation: Key Differences
Whether you are a graduate student just starting out in academia or a professor advising a student, making the distinction between a dissertation and a thesis is critically important to writing a strong dissertation and becoming a stronger writer. Unfortunately, the difference remains unclear since the terms are used interchangeably by graduate students, doctoral researchers, academic publishers & universities.
If you’re not sure whether you’re writing a thesis or a dissertation, this article will help you understand the differences between the two whether you’re a PhD or master’s degree student.
Main Differences Between a Dissertation and a Thesis
While theses and dissertations share many similarities (they are both advanced graduate research papers), they actually refer to two different types of academic writing, and their differences include important concepts such as scope, purpose, length, and research requirements.
Most importantly, the difference between a thesis and a dissertation depends on the level of education. Far beyond being a simple essay, a thesis is for graduate students pursuing a master’s degree while a dissertation is written by doctoral students, also referred to as PhD candidates.
There are a few key differences between a thesis versus a dissertation.
The biggest difference between a thesis and a dissertation is that a thesis makes arguments based on existing research. Meanwhile, a dissertation often requires the PhD candidate to conduct research and then perform an analysis.
More specifically, a thesis often takes the form of a literature review , which is a compilation of research knowledge in a particular field of study that proves one is competent in that subject. On the other hand, a dissertation is a more specific type of research paper written by those working toward a specific doctorate degree that contributes knowledge, theory, or methods to a field of study.
What is a master’s thesis?
A master’s thesis is an academic research paper that requires a greater degree of research than an undergraduate thesis or term paper. It is marked by a higher standard of writing, and students are expected to demonstrate competence, literacy, and mastery of a subject. It usually takes two or three years to complete. Finally, a master’s degree thesis is usually written in order to obtain a research degree and is not intended to be published separately.
What is a PhD dissertation?
A PhD dissertation is a substantial piece of independent research that is required of all students who are pursuing a doctorate degree. It is a piece of original work that has not been published elsewhere and, most importantly, makes a new contribution to the field. This contribution may be a new way of thinking about an existing topic or even a novel theory. The research performed for a dissertation is usually conducted over a period of several years to half a decade.
Features of a Master’s Thesis vs PhD Dissertation
Content and structural differences.
So how is dissertation writing different from thesis writing?
Now that you know the definitions of a dissertation and thesis, let’s dive into some clear ways in which they differ in structure and other main characteristics.
How long is a thesis vs dissertation?
Length is the most obvious factor in differentiating between writing a thesis or dissertation.
Generally, a doctoral dissertation has greater breadth, depth, and intention than a master’s thesis since it is based on original research. While the standard length of a master’s thesis is around 100 pages , a doctoral dissertation can be upwards of 400-500 pages.
While most students can finish their PhD dissertation or thesis in as little as 1-2 years, it can take as long as 7 years depending on the school, program, and dissertation topic. As doctoral programs have their own formatting requirements, check with your school or university to find out what you need for your own dissertation or thesis. Most dissertations are organized into chapters, but the number of chapters varies as well.
Differences in research methods
A thesis and dissertation are both graduate-level research reports. This means they require students to investigate and report on a specific topic. But what is the difference in the scale of research between a master’s versus doctoral degree? The answer comes down to how much and what type of data you collect .
Data sources for a thesis vs dissertation
A master’s thesis is limited to secondary or reported knowledge . This knowledge has already been published, analyzed, and scrutinized in the literature. A thesis does not typically offer anything new in that regard. Your purpose is usually to write a comprehensive literature review on a novel or underreported topic using already-reported data.
On the other hand, a doctoral dissertation reports on novel data and is published so it can be scrutinized by others. It culminates in your dissertation defense.
The above lists clearly show that a PhD researcher and dissertation writer must have specific hands-on experience about not only the result of others’ research but also how the researchers obtained the data. A dissertation must venture into criticism of how other studies performed their experiments, whereas a master’s student will only report on and evaluate the results.
Differences in research scope
As mentioned above, a thesis is more of a literature review written to demonstrate competence and mastery of a field of study. In short, you are a reliable “reporter” of information related to that subject. A thesis shows that you know the technical jargon, understand the subject, are familiar with industry tools, and can translate that information to a general audience. This is why a master’s degree is sufficient and often preferred for industry jobs.
In contrast, a doctoral dissertation goes beyond simply using the building blocks of your subject and actually creates new tools, knowledge, and theories to advance the subject as a whole. If a master’s degree holder is like a seasoned Rolling Stone journalist, then a doctorate is the band/musician who actually makes the music.

So should you pursue a thesis or a dissertation?
The benefits of earning a graduate degree are huge. According to the US Census Bureau , those with an advanced degree earn 3.7 times as much as a high school dropout, and 13.1% hold a master’s, professional, or doctorate degree. If you’re a curious undergraduate student thinking of applying to graduate school, which is the right choice?
In short, a dissertation is more focused and in-depth than a thesis. While a doctoral dissertation is based on original research, a thesis is often an extension or review of others’ research in order to demonstrate literacy. Further, a dissertation can be used as the basis or subject of a thesis, but not vice versa.
Editing a Dissertation vs Thesis
So far, we’ve focused a lot on differences such as research and purpose, but in the end, a thesis or dissertation is a written document that requires skill, focus, discipline, subject knowledge, organization, and scheduling.
For non-native English speakers, the challenge is especially difficult since English is the lingua franca of academia and research.
How does an editing service improve your dissertation or thesis ?
From body spacing and pagination, to font size and citation formatting, the dissertation guidelines are exhaustive. Even worse, they vary by school. So besides the actual English writing and grammar, graduate students must worry about consistency, formatting, nomenclature, and terminology. That’s quite the burden!
This is why it’s very common for graduate students, especially ESL and foreign ones, to seek out dissertation editing services that specifically cater to the academic needs of researchers and students.
Here are just a few reasons why dissertation proofreading is so helpful and what these editors do:
- Correct grammar, punctuation, syntax, and structural errors
- Offer suggestions to rewrite, remove, and revise writing
- Ensure formatting and nomenclature are consistent
- Knowledgeable academic editors with master’s and PhD degrees
- Free up your time to focus on research, revisions, and content instead of looking for mistakes
- Provide a language editing certificate , which may be necessary for non-native English-speaking students
Lastly, most PhD advisors recommend that students seek out professional editing services , specifically thesis editing or dissertation editing , since professors prefer to assess the actual research content of a dissertation, not mundane writing errors. Any graduate student reading this knows professors don’t like their time to be wasted!
Be sure to check out other academic resources on how to improve your academic manuscript and the benefits of proofreading and editing.
And try the Wordvice FREE Citation Generator, which provides citations for four academic formatting styles: APA Citation Generator , MLA Citation Generator , Chicago Citation Generator , and Vancouver Citation Generator .
Difference between a research paper, dissertation & thesis
When it comes to writing academic papers, students should have the right skills if they must succeed. Whether it is doing a weekly essay assignment, crafting a term paper, or doing research, the best learners are those who have mastered the art of literary composition. You should also note that understanding how each school paper differs from the other puts you ahead of the pack. Most of the schools, universities and institutions require you to undertake research at some point or another in form of coursework .
Often, students mistake research for term papers or thesis for dissertations. The worst-case scenario is when instead of writing a thesis; you end up with a dissertation paper. Such is an occurrence that often denies students marks. And so, the big question we want to answer in this post is what the differences between research, dissertation, and thesis are? Keep reading to learn more.

First things first note that variations between different types of academic papers could be in the form of writing style , definition, presentation of arguments, not to mention the purpose of writing and level of academia. You should not expect high school students, for example, to partake in thesis writing. But when it comes to writing research papers, it can happen at any level of academia right from high school through college and university.
Note: There are differences in how these terminologies are used. In few countries they are used interchangeably, while in other countries thesis is related to bachelor’s or master’s degree course and dissertation is used in the context of a doctorate degree, whereas in some countries the reverse is true. For example, in Indian context, PhD students are required to submit a “thesis” whereas M. Phil students are required to submit a dissertation. Thesis is considered to be much longer form of research which is opposite in case of USA.
Differences based on the definition
Definitive differences between academic papers simplify things for a college newbie yet to write his or her academic paper. Now, on defining the thesis, research and dissertation, the following are worth noting:
- A research paper refers to a piece of literary composition, often a class requirement. The most notable aspect of research papers is that before you craft them, you must gather knowledge independently. After collecting data and information, students then put together findings in a descriptive format. Learners must also present their arguments based on their evaluation of a subject under study. A good research paper opens the gates to advanced academic writing which will involve the implementation of findings.
- A dissertation is a paper that students write as a requirement for the conferment of a diploma or degree. In some countries, Ph.D. students also write dissertations.
- A thesis is a paper students craft as a requirement for a degree at college or university level. You do realize that all the three types of academic papers lead to something, often an academic qualification that would see one earn a degree or get admitted to the next level of academia.
Length of paper and methodology
While the methodology of writing these papers is similar, often constituting sections such as introduction, abstract, literature review, research method, presentation/finings, discussions, conclusion and recommendations, the length of each paper does vary. Research papers and dissertations are generally long. However, thesis papers tend to be short hence requiring less time to write. Dissertations and research require a comprehensive study of a study and gathering information/data. You, therefore, spend more time on them before and during writing. You may even use an editing service to help you research, write, and proofread your dissertation properly.
Differences based on knowledge inference and hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess. Before you conduct a study, assumptions have to be made that something will turn out in some way. Most importantly, how the outcome will impact a population informs the construction of a hypothesis/thesis statement. In research and dissertation writing, students must exhibit a rigorous understanding of a subject based on a study. It is on this premise that they must come up with/infer a meaningful conclusion. However, when writing thesis papers, the formulation of a hypothesis comes after researching and writing on a subject.
Differences based on the approach
How students go about crafting research, dissertation and thesis is another way of differentiating the three papers. In writing research and dissertation papers, students must use existing pieces of literature to back their findings. However, thesis papers more often rely on existing research work to prove a point. You can, for example, sample different research papers on climate change to prove your study on the same. Ostensibly, you are using existing and published academic papers to ascertain that phenomena or a problem exist.
Mode of publication and utilization
You should also note that academic papers exhibit differences based on the reason for which they get published and also how people use them. Dissertation papers are like complete and newly published books given their voluminous nature. You could refer to yours as an academic book. It makes you a published author. However, thesis and research work are like articles that shed light on a subject but not as comprehensively as dissertations.
Differences based on the level of academia
While students can write research papers at any level, they are most common at the undergraduate level. Completion of a research paper often leads to the conferment of an undergraduate degree. And when it comes to writing dissertation papers, the bargain is qualifying for a master’s degree, thusly; postgraduate, Mphil or MBA. It means if you are not writing a dissertation to obtain a postgraduate degree, you do so as a means of enrolling in a postgraduate program. Thesis papers lead to the conferment of a Ph.D. degree or a doctorate as some scholars call it. Students who write thesis papers do so within the last two years of their academic life.
Final Thoughts
Many factors distinguish academic papers. But regardless of the methodology or purpose of these papers, the most important thing is that students showcase their literary skills. Moreover, academic paper tests the knowledge of students on different issues and subjects. Whether it is writing about how past events led to present-day situations or how human activities will lead to something happening in the future, knowledge dispensation helps societies grow.
In the interest of time, research work involved in crafting academic papers is meant to unearth critical findings on a subject and provide solutions to an existing problem. As a rule of the thumb, students who write research, dissertation or thesis papers must demonstrate their understanding of the society and problems that bedevil it. It is through doing so that recommendations for solving a problem become trustworthy, dependable, acceptable and applicable. Most importantly, learners must meet a set academic threshold before writing the above papers.
About The Author
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
College of Media & Communication
- CoMC News and Information
- All Stories
Master's Report vs. Thesis Project: What’s the Difference?
Alana Krafsur
January 10, 2020

In the College of Media & Communication Graduate Program , master's students must complete a final research project in the form of a master's report or thesis project . Find out which of the two options is the best fit for your aspirations.
Master's Report
The master's report, MCOM 6050 , is the final course which all master's students on the professional track or sports media track must complete before attaining their degree. Completing an applied research project provides portfolio material and proves that students are masters of their crafts. Similar to an independent study, this course is completed with the help of a professor who serves as an adviser and helps oversee the research project. A “6050 project” takes one semester to complete.
There are three different forms of 6050 projects:
- A project completed for an organization as an employee, intern or volunteer.
- A project completed for an organization not as an employee, intern or volunteer.
- A project in an area of student interest.
Required elements:
- Secure an idea.
- Choose a CoMC faculty adviser.
- Complete an approved project proposal.
- Collect original data.
- Write a report.
- Present work in an oral presentation.
Previous master's report projects have included:
- Politics, Social Media & the 2020 Democratic Primary – Logan McDonald
- An Analysis of Best Practices in Industry Application of Neuromarketing Research – Linh Nguyen
- Reestablishing Trust in News Media – David Olshansky
- Crisis Management in International Non-Profit Governmental Organizations – Simranjit Singh
Student Testimonials
Casey Montalvo, Sports Media Focus:
"My 6050 project focuses on comparing male and female sports fans based on how the media frames them, specifically Texas Tech fans. As a woman who wants to work in the sports communications industry after I graduate, this topic intrigued me. I am a communications intern for Texas Tech Athletics, and since my research is tailored to TTU specifically, I can give them my results."
Alana Krafsur, Professional Track:
"With a passion for the women's rights industry, I am focusing my 6050 project on a large-scale event I coordinated, “Female Genital Mutilation: A Survivor's Story.” My research seeks to find ways to market human rights issues to increase emotional engagement and generate action. What I like most about the CoMC graduate program is there are many directions you can take for a 6050 project. You can tailor your interests to align with your professional aspirations."
Thesis Project
Master's students on the thesis track must complete original research that increases our understanding of media and communication phenomena and theory. Completing a thesis prepares master's students for in-depth studies in theory and research, and provides the foundation for the pursuit of a Ph.D. degree . A thesis project takes at least two semesters to complete.
- Choose an adviser and faculty committee.
- Complete an approved thesis proposal.
Previous thesis projects have included:
- Why do People Use Memes to Talk About Politics? Application of Uses & Gratifications Theory to Political Memes – Bingbing Zhang
- Transporting, Identifying and Expanding: Superheroes in Series Television – Jeanette Moya
- Creativity and Healing: How Creative Media Help Us Cope with Mental Illness – Bethany Pitchford
Bethany Pitchford, Thesis Track:
"While I started out on the 6050 track, I realized early on that I was probably going to want to pursue a Ph.D., so I switched to the thesis track. The overarching question of my thesis relates to how creativity helps people cope with, and communicate about, their mental illness to others. Ultimately, I enjoyed writing a thesis because it provided me the space to explore questions I was, and still am, highly curious about."
Camden Smith, Thesis Track:
"I believe a thesis is absolutely preparing me to go into academia and enroll in a doctoral program. I think if I was more eager to get back to the industry, I would be on the 6050 track; however, this track is really helping keep my eyes on the prize – which is a doctoral dissertation."
To learn more about the graduate program, email [email protected]
Read more college news !
tags: CoMC News , CoMC News and Information , M.A. , Ph.D. , Students
- Like College of Media & Communication on Facebook Like College of Media & Communication on Facebook
- Follow College of Media & Communication on X (twitter) Follow College of Media & Communication on X (twitter)
- Subscribe to College of Media & Communication on YouTube Subscribe to College of Media & Communication on YouTube
- Follow College of Media & Communication on Instagram Follow College of Media & Communication on Instagram
- Connect with College of Media & Communication on LinkedIn Connect with College of Media & Communication on LinkedIn
Understanding the Differences Between Dissertation, Thesis, and Capstone Projects
This article explains the key differences between dissertation, thesis, and capstone projects, and offers insights into how to approach each project to ensure academic success.
If you're pursuing an advanced degree, you may be required to complete a dissertation, thesis, or capstone project as part of your program. While these projects share some similarities, there are also important differences to understand.
A dissertation is typically required for a doctoral degree, while a thesis is required for a master's degree. Both involve extensive research, data collection and analysis, and a written report that contributes to the body of knowledge in the field of study. A capstone project, on the other hand, is typically a culminating project required for a variety of undergraduate and graduate degree programs. It may involve original research, but can also take the form of a creative project or a community service project.
Dissertation: A dissertation is a research project required to complete a doctoral degree program. It is a comprehensive study that contributes to the existing body of knowledge in the field of study. A dissertation typically involves original research, data collection and analysis, and a written report that is expected to make a significant contribution to the field of study.
Thesis: A thesis is a research project required to complete a master's degree program. It is usually a shorter and less complex study compared to a dissertation. A thesis may involve original research, but it can also be a literature review, a case study, or a critical analysis of existing research in the field of study.
Capstone: A capstone is a culminating project required to complete a degree program. It is typically undertaken in the final year of study and integrates the knowledge and skills gained throughout the program. A capstone can take various forms, such as a research project, a creative work, or a community service project. It is designed to demonstrate the student's ability to apply what they have learned to real-world problems.
To successfully complete a dissertation, thesis, or capstone project, it's important to have a clear understanding of the project's purpose and requirements. For example, a dissertation will require a more extensive literature review, data collection, and data analysis than a thesis or capstone project. A thesis may require more original research than a capstone project, but less than a dissertation.
In addition, it's important to work closely with your advisor or instructor throughout the project to ensure that you are meeting the requirements and expectations. You may also want to consider seeking out additional resources, such as writing support or statistical analysis services, to help you complete the project successfully.
By understanding the differences between dissertation, thesis, and capstone projects, and approaching each project with a clear plan and support, you can successfully complete your degree program and contribute to the body of knowledge in your field. In summary, a dissertation is a research project required to complete a doctoral degree program, a thesis is a research project required to complete a master's degree program, and a capstone is a culminating project required to complete a degree program.

Differences Finder
What is the Difference Between Thesis and Report
Thesis and Report are two commonly confused terms, each with its own unique features, purposes, and formats. While both are written in an academic setting, there are several distinct differences between the two that should …
Published on: Education
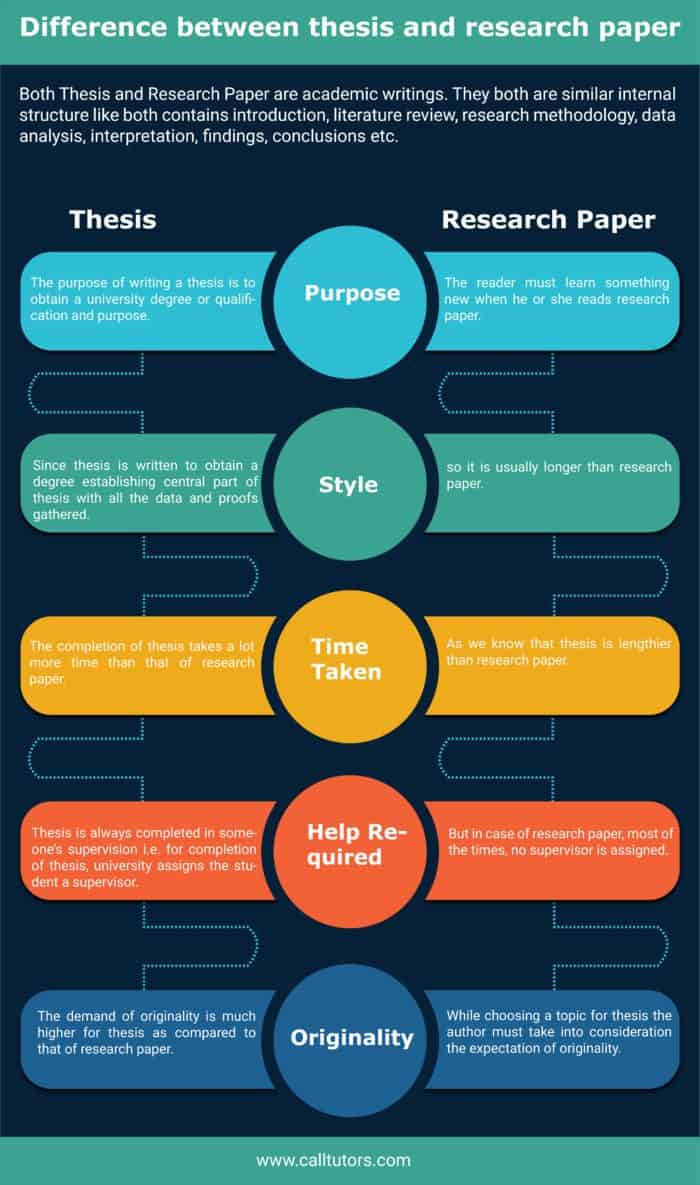
Thesis and Report are two commonly confused terms, each with its own unique features, purposes, and formats. While both are written in an academic setting, there are several distinct differences between the two that should be taken into consideration.
A thesis is typically a long, research-based essay that is written as part of a student’s degree program. It is an in-depth exploration of a specific topic and involves the student’s own research and analysis. The primary purpose of a thesis is to demonstrate that the student has a comprehensive understanding of the topic, and is capable of applying the knowledge they have acquired during their degree program to a specific problem or issue. A thesis is usually written in the form of a book, which includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and conclusion.
On the other hand, a report is a shorter document that is typically written in response to a specific problem or issue. It may be based on research, but its primary purpose is to provide an accurate description of a current situation or past event. Reports are generally written in a more concise and descriptive format, as opposed to the more analytical style of a thesis. Reports also usually include recommendations for further action based on the findings.
In conclusion, while both a thesis and a report are written in an academic setting, there are several differences between the two that should be taken into consideration. A thesis is an in-depth exploration of a specific topic and is typically written in the form of a book, while a report is a shorter document that is usually written in response to a specific problem or issue. Additionally, the primary purpose of a thesis is to demonstrate that the student has a comprehensive understanding of the topic, while a report is primarily designed to provide an accurate description of a current situation or past event.
Thesis vs Report: An Overview
Thesis and report writing are two distinct processes that are used in academic writing to convey different types of information. To understand the differences between the two, we must first define them. A thesis is an extensive paper that is written as a requirement for a degree or diploma at a university or college. It is typically a long-term project that involves a considerable amount of research and analysis. A report, on the other hand, is a shorter written work, usually composed of facts and figures, that is used to present information in a concise manner.
Thesis vs Report: Content and Structure
The content and structure of a thesis and a report are very different. A thesis is typically an in-depth exploration of a specific topic, and it may include a series of chapters that discuss related concepts, theories, and research. The structure of the thesis typically follows the standard academic format, with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction of a thesis typically explains the topic that will be explored and provides an overview of the structure of the document. The body paragraphs of the thesis will then discuss the research, theories, and evidence that relate to the topic. Finally, the conclusion will summarize the research and offer a conclusion or opinion on the topic.
A report, on the other hand, is typically shorter than a thesis and is generally used to present specific information in a concise manner. Reports often contain a title page, an executive summary, a table of contents, and sections that present the data and discuss the implications of the findings. Reports are typically used to present data related to a particular field or topic, such as a market analysis or a financial statement. Reports may also include charts and graphs to help illustrate the data.
Thesis vs Report: Purpose and Style
The purpose and style of a thesis and a report also differ significantly. The purpose of a thesis is typically to explore a particular topic in depth, and the document should be written in an academic style with formal language. The thesis should also include citations to sources that are used to support the arguments that are presented.
The purpose of a report, on the other hand, is typically to present facts and figures in a concise manner. Reports are typically written in a more formal style than a thesis and should include citations to sources when necessary. Reports may also include visuals such as charts and graphs to help illustrate the data. Additionally, reports should be written in a clear and concise manner to ensure that the information is easily understood by the reader.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
About Diffinder
Difference Between Anova and Ancova
Difference between left and right handed scissors.
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Essay and Report

On the other hand, an essay can be understood as a piece of writing, on a specific topic or subject, which expresses the author’s own ideas and knowledge about the subject.
The basic difference between essay and report is that while an essay is argumentative and idea-based, reports are informative and fact-based. Now, let us move further to understand some more points of differences.
Content: Essay Vs Report
Comparison chart, definition of essay.
An essay can be understood as a comprehensive literary composition, written in a narrative style and presents a particular topic, supports an argument and highlights the writer’s view or ideology. An essay is used to check a person’s outlook and understanding on specific matters and also his/her ability to describe and argue in a way which convinces the reader or informs him/her about a specific topic.
One can make use of learned materials, along with his/her own research, to write an essay effectively. It includes both narrative and subjective thoughts. Further, an essay supports a single idea at a time, for which several components need to be covered in it so as to appear logical and chronological.
It can be a learned argument, observation of day to day life, literary criticism, political manifestos, recollections, and reflections of the writer. It starts with a question and attempts to answer or give suggestions to the problem, on the basis of the existing theories or the writer’s personal opinion and assessment.
While writing an essay, it must be kept in mind that the approach used by the writer should be positive, even if the topic of argument is negative.
Definition of Report
The report implies a well structured factual document which is created and presented after conducting an independent enquiry, research or investigation on a specific subject. It serves as a basis for problem-solving and decision making.
Reports are prepared for a definite purpose and contain relevant information in a proper format, for a particular audience. It is used to identify, observe and analyse the issues, events, findings, that occurred practically, i.e. in real life.
A report is designed with the aim of informing the reader about the event, situation or issue, in a very simple and objective manner, while enabling them to get the desired information quickly and easily. It provides recommendations for future actions. Information collected from research, or from carrying out a project work is presented in a clear and concise manner, under a set of headings and subheadings, that helps the reader to get the desired information quickly and easily.
Characteristics of an Ideal Report
- It must be clear and concise.
- It is written in easy language which the readers can understand easily.
- It has to be appropriate and accurate.
- It should be well drafted and organised, with specific sections, headings and sub-headings.
A report summary can be provided orally, however detailed reports are usually in the form of written documents. It contains – Title Page, Acknowledgement, Authorization Letter, Table of Contents, Executive Summary, Introduction, Discussion, Results, Conclusion, Recommendations and References.
Moreover, Cover letter, Copyright notice, Bibliography, Glossary and Appendices may also form part of a report.
Key Differences Between Essay and Report
The difference Between report and essay is discussed here in detail:
- An essay is a brief literary composition, which is used to describe, present, argue, and analyse the idea or topic. Conversely, a report is a formal and concise document consisting of findings from the practical research. It aims at investigating and exploring the problem under study.
- An essay is written on the basis of subjective analysis of theories and past research, by other people and own ideas, on the concerned subject. As against, a report is objective and factual, which is based on past research, as well as present data and findings.
- An essay talks about general facts and events along with the writer’s personal ideas and views, on the topic in a non-fictional manner. On the contrary, a report contains information which the reader can use to identify the facts or support in decision making or solving issues if any.
- When it comes to sections, a report usually contains different sections, with catchy headings which may attract the attention of the audience. As against, an essay does not have any section, its flow is continuous. However, it is divided into cohesive paragraphs.
- A report uses tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, statistics and many more for a clear and better presentation of the information. But, in the case of essays, they are not used.
- The conclusion in an essay is based on the writer’s personal opinion and views on the topic itself which must be optimistic, and it does not provide any recommendations for future actions. On the other hand, a report gives an independent conclusion, but it may contain the opinion of the experts or previous researchers and recommendations are included, about how the research can be improved and extended.
In a nutshell, Essays are descriptive, subjective and evaluative, whereas, a report is descriptive, objective and analytical. Essays are mainly used in an academic context, whereas reports are preferred in the field of research.
The report is used to present the researched information in a written format, to the audience. Conversely, essays are used to identify what the writer knows about the topic and how well the writer understand the question.
You Might Also Like:

Anna H. Smith says
November 26, 2020 at 3:22 pm
Thank you for explaining this so eloquently. Excellent post, I will keep this handy and refer to it often from now on, the information is so clear and so insightful, thanks for giving a clear difference. It’s a very educative article.!
Presley Dube says
November 20, 2021 at 3:43 pm
very useful to me thank you.
Leonard says
August 8, 2022 at 2:52 pm
Thanks for sharing such nice information about this topic.
Ignatius Phiri says
March 20, 2023 at 10:39 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What is the difference between dissertation and report?
A dissertation is an extended piece of writing based on extended reading and some independent research at Undergraduate or Masters level.
It is a research finding presented as part of conclusion of a programme of learning.
Whereas, a report is a specific form of writing that is organised around concisely identifying and examining issues, events, or findings that have happened in a physical sense, such as events that have occurred within an organisation, or findings from a research investigation.
These events can also pertain to events or issues that have been presented within a body of literature. The key to report writing is informing the reader simply and objectively about all relevant issues. There are three features that, together, characterise report writing at a very basic level: a pre-defined structure, independent sections, and reaching unbiased conclusions.
(Sourced from the web)
A dissertation is a formal academic document that presents original research as part of a doctoral program, while a report is a document that conveys information, analysis, or findings on a specific topic, often for a professional or non-academic audience. Dissertations require more extensive research and analysis, and are typically longer and more detailed than reports.
Add your answer:
Couid I get Free Dissertation Report on job satisfaction download?
a format of dissertation on job satisfaction
What is dissertation report?
Dissertation Help is a valuable service that supports students in their academic journey by providing essential guidance and assistance in crafting a dissertation report. A dissertation report, in the context of academia, refers to a comprehensive document that presents the findings, analysis, and conclusions of an individual's research study or investigation. With the aid of Dissertation Help, students can receive expert support throughout the research process, methodology development, data analysis, and effective communication of their scholarly work. These services play a crucial role in helping students navigate the challenges of writing a dissertation, showcasing their ability to conduct independent research, demonstrate critical thinking skills, and make a valuable contribution to the existing body of knowledge in their specific field of study.
What is the difference between a header and a title on a report?
what is the difference between titles and headings in general.
What is the difference between a factual and a persuasive report?
A factual report presents information objectively without attempting to sway the reader's opinion, focusing on presenting data and findings accurately. On the other hand, a persuasive report aims to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint or course of action by including arguments, opinions, and recommendations to influence their beliefs or decisions.
What are the major Difference between informational and analytical report?
An informational report focuses on presenting facts, data, and information without providing interpretations or analysis, while an analytical report involves an in-depth examination, evaluation, and interpretation of the data to draw conclusions and make recommendations. In an informational report, the focus is on presenting information objectively, whereas in an analytical report, the emphasis is on providing insights and recommendations based on the analysis.
Characteristic of a good feasibility report?
difference between feasibility report and project proposal
What is the difference between a query and a report?
A query (inquiry) is seeking information. A report provides information.
Where can you download free dissertation report?
Do you mean you want to download a dissertation? A dissertation is not a report. It is a research study to complete a PhD and off hand I don't think you can download one because it has a copyright on it. College and university libraries usually have a section of completed dissertations and you can purchase a dissertation. The writer does get a small ( very small)royalty on the sold dissertation. Four years ago I completed mine and have yet had anyone buy it. I expect it is on a dusty shelf in my college library, but I know that I wouldn't want anyone downloading my 4 years of work and using it for their own.
What is difference between solicited and unsolicited report?
A solicited report is requested by a person. They give permission for the report. An unsolicited report is not expressly requested by a person and is produced for them without their permission.
What is the difference between a budget and a financial report?
The main difference is, budget is a planned activity to meet the targets whereas financial report is the one which shows the health/wealth of the organization.
Difference between Crystal Reports and data report in visual basic?
Data report it reports data .. Crystal report it reports crystal thanks GENIUS
What is the difference between an unbound report and a left bound report?
An unbound report does not have any pre-defined margins, headers, or footers, allowing for more flexibility in layout and design. On the other hand, a left-bound report typically has a fixed left margin, which helps in maintaining a consistent format throughout the report. It can be easier to align content in a left-bound report compared to an unbound report.
Top Categories

- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Commercial Law
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
- Difference between Research Paper and Review Paper
- Difference between Data Science and Operations Research
- Difference between Printer and Scanner
- Difference between proto and prototype
- Difference Between Hypothesis And Theory
- Difference between Procedures and Methods
- Difference Between VTP and DTP
- Difference between SRS and FRS
- Difference between Project Report and Research Report
- Difference between Projects and Operations
- Difference between Socket and Port?
- Difference between Project and Product
- Difference between Product and Process
- Difference Between FTP and SSH
- Difference between Program and Project
- Difference between TELNET and FTP
- Difference between Software and Framework
- Difference between Paragrah and Essay
- Difference between Vertical search and Horizontal search
- Difference between E-paper and LCD
- Difference Between PERT and CPM
- Difference between Server and Mainframe
- Difference between ShareFile and pCloud
- Difference between Case Study and Action research
- Difference between Word Processor and Text Editor
- Difference between Survey and Experiment
- Difference between Project Report and Synopsis Report
- Difference between BRD and SRS
- Difference between Descriptive Research and Experimental Research
Difference between Thesis and Research Paper
A thesis is a comprehensive academic document that presents original research and contributes new knowledge to the field, whereas a research paper explores and discusses a topic based on existing literature. Both forms of academic writing serve different purposes and audiences, requiring distinct approaches in terms of depth of analysis, format, and completion timeline.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis is a comprehensive document written by a student pursuing a higher academic degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D. It is the culmination of original research conducted by the student under the guidance of a supervisor or advisor. The primary purpose of a thesis is to present a scholarly argument or hypothesis on a specific topic or research question. It involves conducting in-depth research, analyzing data, and synthesizing findings to contribute new knowledge to the field of study. A thesis typically consists of several chapters, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Key Features of a Thesis:
- Original Research: A thesis involves original research conducted by the student, contributing new knowledge or insights to the academic field.
- Comprehensive Analysis: This typically includes a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, methodologies, data, and findings related to the research topic.
- Formal Defense: A thesis is defended orally before a committee of faculty members or experts, who evaluate the student’s research methods, findings, and conclusions.
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is a shorter, more focused document that presents the findings of a specific research study or investigation. It is commonly written by students at the undergraduate or graduate level as part of a course assignment or academic project. The primary purpose of a research paper is to communicate the results of research, analysis, or experimentation on a particular topic or research question. It aims to contribute to the existing body of knowledge in a given field or area of study. A research paper typically follows a standardized format, including sections such as an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Key Features of a Research Paper:
- Focused Study: A research paper focuses on presenting the findings of a specific research study or investigation, often within a narrower scope than a thesis.
- Standardized Format: It follows a standardized format, including sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Evaluation Criteria: Research papers are evaluated based on factors such as the clarity of writing, the rigor of research methods, the relevance of findings, and the contribution to the field, often as part of a course assignment or academic project.
Thesis and Research Paper – FAQs
Is a thesis longer than a research paper.
Yes, typically a thesis is more extensive and detailed compared to a research paper due to its original research component and comprehensive structure.
Do research papers require original research?
Research papers primarily rely on existing literature and sources, providing critical analysis or interpretation without necessarily presenting new findings.
Can a research paper be published in academic journals?
Yes, research papers can be submitted for publication in academic journals, providing they meet the journal’s criteria for quality and relevance.
What is the role of a thesis advisor or committee?
Thesis advisors and committee members provide guidance, feedback, and evaluation throughout the thesis process, ensuring academic rigor and quality.
Can a thesis be revised after completion?
Yes, a thesis may undergo revisions based on feedback from advisors or committee members before final submission and defense.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Commerce - Difference Between

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Timothy Alabi (Customer) asked a question.
What are the differences between report from professional feed and Security center
My report professional feed does not include some of the column . what can i de?
- Tenable Nessus
Related Questions
Trending articles.
- Troubleshooting credentialed scanning on Windows
- Nessus Essentials
- What ports are required for Tenable products?
- How to check the SSL/TLS Cipher Suites in Linux and Windows
- How to view and change the Windows Registry Settings for the SSL/TLS Protocols on a Windows Host
Unanswered Questions: Do you have the answer?
- Number of Views 2.61K
- Number of Views 2.42K
- Number of Views 1.58K
- Number of Views 1.43K
- Number of Views 1.26K
- © Tenable™, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- Participation Guidelines
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- 508 Compliance
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
New Study Bolsters Idea of Athletic Differences Between Men and Trans Women
Research financed by the International Olympic Committee introduced new data to the unsettled and fractious debate about bans on transgender athletes.

By Jeré Longman
A new study financed by the International Olympic Committee found that transgender female athletes showed greater handgrip strength — an indicator of overall muscle strength — but lower jumping ability, lung function and relative cardiovascular fitness compared with women whose gender was assigned female at birth.
That data, which also compared trans women with men, contradicted a broad claim often made by proponents of rules that bar transgender women from competing in women’s sports. It also led the study’s authors to caution against a rush to expand such policies, which already bar transgender athletes from a handful of Olympic sports.
The study’s most important finding, according to one of its authors, Yannis Pitsiladis, a member of the I.O.C.’s medical and scientific commission, was that, given physiological differences, “Trans women are not biological men.”
Alternately praised and criticized, the study added an intriguing data set to an unsettled and often politicized debate that may only grow louder with the Paris Olympics and a U.S. presidential election approaching.
The authors cautioned against the presumption of immutable and disproportionate advantages for transgender female athletes who compete in women’s sports, and they advised against “precautionary bans and sport eligibility exclusions” that were not based on sport-specific research.
Outright bans, though, continue to proliferate. Twenty-five U.S. states now have laws or regulations barring transgender athletes from competing in girls and women’s sports, according to the Movement Advancement Project , a nonprofit that focuses on gay, lesbian, bisexual and transgender parity. And the National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics , the governing body for smaller colleges, this month barred transgender athletes from competing in women’s sports unless their sex was assigned female at birth and they had not undergone hormone therapy.
Two of the most visible sports at this summer’s Paris Games — swimming and track and field — along with cycling have effectively barred transgender female athletes who went through puberty as males. Rugby has instituted a total ban on trans female athletes, citing safety concerns, and those permitted to participate in other sports often face stricter requirements in suppressing their levels of testosterone.
The International Olympic Committee has left eligibility rules for transgender female athletes up to the global federations that govern individual sports. And while the Olympic committee provided financing for the study — as it does on a variety of topics through a research fund — Olympic officials had no input or influence on the results, Dr. Pitsiladis said.
In general, the argument for the bans has been that profound advantages gained from testosterone-fueled male puberty — broader shoulders, bigger hands, longer torsos, and greater muscle mass, strength, bone density and heart and lung capacity — give transgender female athletes an inequitable and largely irreversible competitive edge.
The new laboratory-based, peer-reviewed and I.O.C.-funded study at the University of Brighton, published this month in the British Journal of Sports Medicine , tested 19 cisgender men (those whose gender identity matches the sex they were assigned at birth) and 12 trans men, along with 23 trans women and 21 cisgender women.
All of the participants played competitive sports or underwent physical training at least three times a week. And all of the trans female athletes had undergone at least a year of treatment suppressing their testosterone levels and taking estrogen supplementation, the researchers said. None of the participants were athletes competing at the national or international level.
The study found that transgender female participants showed greater handgrip strength than cisgender female participants but lower lung function and relative VO2 max, the amount of oxygen used when exercising. Transgender female athletes also scored below cisgender women and men on a jumping test that measured lower-body power.
The study acknowledged some limitations, including its small sample size and the fact that the athletes were not followed over the long term as they transitioned. And, as previous research has indicated, it found that transgender female athletes did retain at least one advantage over cisgender female athletes — a measurement of handgrip strength .
But it is a combination of factors, not a single parameter, that determines athletic performance, said Dr. Pitsiladis, a professor of sport and exercise science.
Athletes who grow taller and heavier after going through puberty as males must “carry this big skeleton with a smaller engine” after transitioning, he said. He cited volleyball as an example, saying that, for transgender female athletes, “the jumping and blocking will not be to the same height as they were doing before. And they may find that, overall, their performance is less good.”
But Michael J. Joyner, a doctor at the Mayo Clinic who studies the physiology of male and female athletes, said that, based on his research and the research of others, science supports the bans in elite sports, where events can be decided by the smallest of margins.
“We know testosterone is performance enhancing,” Dr. Joyner said. “And we know testosterone has residual effects.” Additionally, he added, declines in performance by trans women after taking drugs to suppress their testosterone levels do not fully reduce the typical differences in athletic performance between men and women.
Supporters of transgender athletes, and some scientists who disagree with bans, have accused governing bodies and lawmakers of enacting solutions for a problem that doesn’t exist. There are few elite trans female athletes, they have noted. And there has been limited scientific study of presumed unalterable advantages in strength, power and aerobic capacity gained by experiencing puberty as a male.
For those who have competed in the Olympics, results have varied widely. At the 2021 Tokyo Games, Quinn , a soccer player who is trans nonbinary and was assigned female at birth, helped Canada’s team win a gold medal. But Laurel Hubbard , a transgender weight lifter from New Zealand, failed to complete a lift in her event.
“The idea that trans women are going to take over women’s sports is ludicrous,” said Joanna Harper, a leading researcher of trans athletes and a postdoctoral scholar at Oregon Health & Science University.
Dr. Harper, who is transgender, said it was important for sports to consider physiological differences between transgender women and cisgender women and that she supported certain restrictions, such as requiring the suppression of testosterone levels. But she called blanket bans “unnecessary and unjustified” and said she welcomed the I.O.C.-funded study.
“This fear that trans women aren’t really women, that they’re men who are invading women’s sports, and that trans women will carry all of their male athleticism, their athletic capabilities, into women’s sports — neither of those things are true,” Dr. Harper said.
Sebastian Coe, the president of World Athletics, which governs global track and field, acknowledged that the science remains unresolved. But the organization decided to bar transgender female athletes from international track and field, he said, because “I’m not going to take a risk on this.”
“We think this is in the best interest of preserving the female category,” Mr. Coe said.
In at least two prominent cases, the fight over transgender bans has moved to the courts. The former University of Pennsylvania swimmer Lia Thomas is challenging a ban imposed by World Aquatics, swimming’s global governing body, after she won the 500-yard freestyle race at the 2022 N.C.A.A. championships. That victory made Thomas, who had been among the best men’s swimmers in the Ivy League, the first known trans athlete to win a women’s championship event in college sports’ top division.
Thomas did not dominate all of her races, though, finishing tied for fifth in a second race and eighth in a third. Her winning time in the 500 was more than nine seconds slower than the N.C.A.A. record. Her case, filed at the Swiss-based Court of Arbitration for Sport, is not expected to be resolved before the Paris Olympics begin in July.
Meanwhile, more than a dozen current and former U.S. college athletes, including at least one who competed against Thomas, sued the N.C.A.A. last month . They claimed that, by letting Thomas participate in the national championships, the organization had violated their rights under Title IX, the law that prohibits sex discrimination at institutions that receive federal funding. (Title IX has also been relied upon to argue in favor of transgender female athletes.)
Outsports , a website that reports on L.G.B.T.Q. issues, hailed the I.O.C.-funded study as a “landmark” that concluded that “blanket sports bans are a mistake.” But some scientists and athletes called the study deeply flawed in an article in The Telegraph , which labeled the suggestion that transgender women are at a disadvantage in sports a “new low” for the I.O.C.
So heated is the debate that Dr. Pitsiladis said he and his research team have received threats. That, he warned, could lead other scientists to shy away from pursuing research on the topic.
“Why would any scientist do this if you’re going to get totally slammed and character-assassinated?” he said. “This is no longer a science matter. Unfortunately, it’s become a political matter.”
Jeré Longman covers international sports, focusing on competitive, social, cultural and political issues around the world. More about Jeré Longman

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The other big difference is that a thesis is for master's students and the dissertation is for PhD students. Structural Differences Between a Thesis and a Dissertation. Structurally, the two pieces of written analysis have many differences. A thesis is at least 100 pages in length; A dissertation is 2-3x that in length; A thesis expands upon ...
The words ' dissertation ' and 'thesis' both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country: In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor's or master's degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
The main difference between a dissertation and thesis is the scope of the research. A dissertation develops unique and original concepts in a particular field of research, whereas a thesis is usually a culmination of existing research. The main purpose of a writing a dissertation is to add new findings to the existing literature in that field ...
Abstract or executive summary. The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report - in other words, it should be able to ...
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
A dissertation requires more extensive research, original contributions to the field, and a deeper exploration of the research topic. A dissertation is typically the output associated with a doctoral degree program. Structure. The main differences in structure between a thesis and a dissertation are in the scope and complexity. Length
How Long Is a Thesis vs. a Dissertation? One of the primary differences between thesis and dissertation papers is their length. While a thesis might be anywhere from 40 to 80 pages long, a dissertation can easily run from 100 to 300. It's important to note that these numbers depend on the specific program and university.
The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master's program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D. A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is well-informed and has knowledge about ...
Key Differences Between Dissertation and Thesis Purpose and Structure. The primary difference between a dissertation and a thesis lies in their purpose and structure. A dissertation aims to contribute new knowledge to a specific field of study and is typically a more extensive and comprehensive project. It involves an in-depth exploration of a ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Generally, a doctoral dissertation has greater breadth, depth, and intention than a master's thesis since it is based on original research. While the standard length of a master's thesis is around 100 pages, a doctoral dissertation can be upwards of 400-500 pages. While most students can finish their PhD dissertation or thesis in as little ...
The difference between thesis and dissertation are discussed hereunder: Thesis refers to an extraordinary piece of writing prepared after a deep research on a topic as a part of university or degree program, wherein a particular idea or concept is put forward as a statement for further discussion.
A good research paper opens the gates to advanced academic writing which will involve the implementation of findings. A dissertation is a paper that students write as a requirement for the conferment of a diploma or degree. In some countries, Ph.D. students also write dissertations. A thesis is a paper students craft as a requirement for a ...
There are some obvious differences: an essay is relatively short - usually 1500 to 2500 words - and you are told clearly what to do by someone else. For example: Describe and evaluate major theories of globalisation. A dissertation is a subject you chose for yourself. The first usage of the word in the English language in 1651 also gives a ...
A thesis project takes at least two semesters to complete. Required elements: Secure an idea. Choose an adviser and faculty committee. Complete an approved thesis proposal. Collect original data. Write a report. Present work in an oral presentation. Previous thesis projects have included: Why do People Use Memes to Talk About Politics?
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN RESEARCH REPORTS, MINI-DISSERTATIONS, DISSERTATIONS AND THESES ... Research Component Research Report (Afr - Navorsingsverslag) Mini-dissertation (Afr - Miniverhandeling) Mini-dissertation (Afr - Miniverhandeling) Dissertation (Afr - Verhandeling) Thesis (Afr - Proefskrif) Credits (as per HEQF) 30 of 120 60 of 180 ...
As nouns the difference between dissertation and report is that dissertation is dissertation (for a doctoral degree) while report is report (all senses). dissertation . English. Noun A formal exposition of a subject, especially a research paper that students write in order to complete the requirements for a doctoral degree; a thesis.
A dissertation typically involves original research, data collection and analysis, and a written report that is expected to make a significant contribution to the field of study. Thesis: A thesis is a research project required to complete a master's degree program. It is usually a shorter and less complex study compared to a dissertation.
Thesis vs Report: An Overview. Thesis and report writing are two distinct processes that are used in academic writing to convey different types of information. To understand the differences between the two, we must first define them. A thesis is an extensive paper that is written as a requirement for a degree or diploma at a university or college.
While both thesis and research papers are academic writings, there is a difference between the two. A thesis refers to a scholarly research report that a scholar writes and submits for fulfilling academic requirements and obtaining a higher degree. It opens up various lines of enquiry into a range of possibilities like an antithesis.
The difference Between report and essay is discussed here in detail: An essay is a brief literary composition, which is used to describe, present, argue, and analyse the idea or topic. Conversely, a report is a formal and concise document consisting of findings from the practical research.
Dissertation Help is a valuable service that supports students in their academic journey by providing essential guidance and assistance in crafting a dissertation report. A dissertation report, in ...
A thesis is a comprehensive academic document that presents original research and contributes new knowledge to the field, whereas a research paper explores and discusses a topic based on existing literature. Both forms of academic writing serve different purposes and audiences, requiring distinct approaches in terms of depth of analysis, format ...
My report professional feed does not include some of the column . what can i de? Expand Post Translate with Google Show Original Show Original Choose a language
The study's most important finding, according to one of its authors, Yannis Pitsiladis, a member of the I.O.C.'s medical and scientific commission, was that, given physiological differences ...
Now let's take a look at this month's updates: Expanded capabilities. Copilot with Graph-grounded chat now available in Outlook. Use local files to ground Copilot prompts. Create and consume Word documents more efficiently with Copilot. Generate multiple formula columns with Copilot in Excel.