- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff


News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Earthquakes are moving northeast in Midland Basin of Texas, scientists find
7 hours ago

New black hole visualization takes viewers beyond the brink
8 hours ago

Research team develops fast-track process for genetic improvement of plant traits

Boeing's first Starliner mission with humans set for historic Space Coast launch tonight
Researchers develop a nanoparticle that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier
Geologists, biologists unearth the atomic fingerprints of cancer

Listening to giants: The search for the elusive Antarctic blue whale
10 hours ago

Bee body mass, pathogens and local climate influence heat tolerance

Astronomers observe elusive stellar light surrounding ancient quasars
11 hours ago

Engineers solve 'catalysis vs corrosion' mystery in electrochemical ozone production
Relevant physicsforums posts, physics instructor minimum education to teach community college.
15 hours ago
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
Apr 28, 2024
Digital oscilloscope for high school use
Apr 25, 2024
Motivating high school Physics students with Popcorn Physics
Apr 3, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

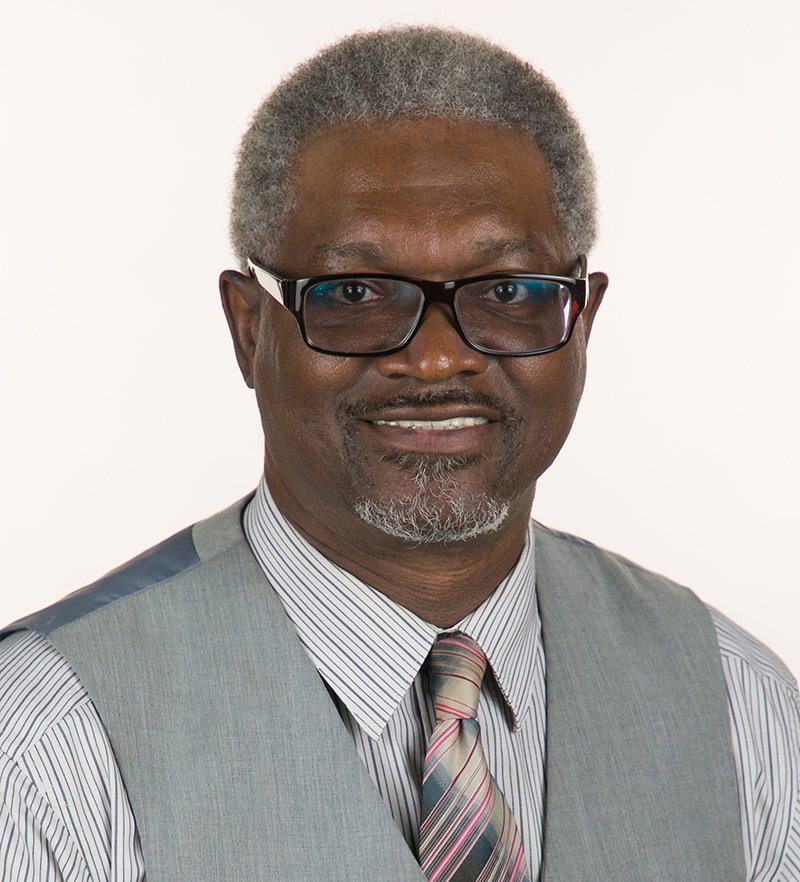
“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
American academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league.
Request More Info
Fill out the form below and a member of our team will reach out right away!
" * " indicates required fields
Is Homework Necessary? Education Inequity and Its Impact on Students

The Problem with Homework: It Highlights Inequalities
How much homework is too much homework, when does homework actually help, negative effects of homework for students, how teachers can help.
Schools are getting rid of homework from Essex, Mass., to Los Angeles, Calif. Although the no-homework trend may sound alarming, especially to parents dreaming of their child’s acceptance to Harvard, Stanford or Yale, there is mounting evidence that eliminating homework in grade school may actually have great benefits , especially with regard to educational equity.
In fact, while the push to eliminate homework may come as a surprise to many adults, the debate is not new . Parents and educators have been talking about this subject for the last century, so that the educational pendulum continues to swing back and forth between the need for homework and the need to eliminate homework.
One of the most pressing talking points around homework is how it disproportionately affects students from less affluent families. The American Psychological Association (APA) explained:
“Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs.”
[RELATED] How to Advance Your Career: A Guide for Educators >>
While students growing up in more affluent areas are likely playing sports, participating in other recreational activities after school, or receiving additional tutoring, children in disadvantaged areas are more likely headed to work after school, taking care of siblings while their parents work or dealing with an unstable home life. Adding homework into the mix is one more thing to deal with — and if the student is struggling, the task of completing homework can be too much to consider at the end of an already long school day.
While all students may groan at the mention of homework, it may be more than just a nuisance for poor and disadvantaged children, instead becoming another burden to carry and contend with.
Beyond the logistical issues, homework can negatively impact physical health and stress — and once again this may be a more significant problem among economically disadvantaged youth who typically already have a higher stress level than peers from more financially stable families .
Yet, today, it is not just the disadvantaged who suffer from the stressors that homework inflicts. A 2014 CNN article, “Is Homework Making Your Child Sick?” , covered the issue of extreme pressure placed on children of the affluent. The article looked at the results of a study surveying more than 4,300 students from 10 high-performing public and private high schools in upper-middle-class California communities.
“Their findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children’s lives; 56% of the students in the study cited homework as a primary stressor in their lives,” according to the CNN story. “That children growing up in poverty are at-risk for a number of ailments is both intuitive and well-supported by research. More difficult to believe is the growing consensus that children on the other end of the spectrum, children raised in affluence, may also be at risk.”
When it comes to health and stress it is clear that excessive homework, for children at both ends of the spectrum, can be damaging. Which begs the question, how much homework is too much?
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association recommend that students spend 10 minutes per grade level per night on homework . That means that first graders should spend 10 minutes on homework, second graders 20 minutes and so on. But a study published by The American Journal of Family Therapy found that students are getting much more than that.
While 10 minutes per day doesn’t sound like much, that quickly adds up to an hour per night by sixth grade. The National Center for Education Statistics found that high school students get an average of 6.8 hours of homework per week, a figure that is much too high according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). It is also to be noted that this figure does not take into consideration the needs of underprivileged student populations.
In a study conducted by the OECD it was found that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance .” That means that by asking our children to put in an hour or more per day of dedicated homework time, we are not only not helping them, but — according to the aforementioned studies — we are hurting them, both physically and emotionally.
What’s more is that homework is, as the name implies, to be completed at home, after a full day of learning that is typically six to seven hours long with breaks and lunch included. However, a study by the APA on how people develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work for about only four hours per day. Similarly, companies like Tower Paddle Boards are experimenting with a five-hour workday, under the assumption that people are not able to be truly productive for much longer than that. CEO Stephan Aarstol told CNBC that he believes most Americans only get about two to three hours of work done in an eight-hour day.
In the scope of world history, homework is a fairly new construct in the U.S. Students of all ages have been receiving work to complete at home for centuries, but it was educational reformer Horace Mann who first brought the concept to America from Prussia.
Since then, homework’s popularity has ebbed and flowed in the court of public opinion. In the 1930s, it was considered child labor (as, ironically, it compromised children’s ability to do chores at home). Then, in the 1950s, implementing mandatory homework was hailed as a way to ensure America’s youth were always one step ahead of Soviet children during the Cold War. Homework was formally mandated as a tool for boosting educational quality in 1986 by the U.S. Department of Education, and has remained in common practice ever since.
School work assigned and completed outside of school hours is not without its benefits. Numerous studies have shown that regular homework has a hand in improving student performance and connecting students to their learning. When reviewing these studies, take them with a grain of salt; there are strong arguments for both sides, and only you will know which solution is best for your students or school.
Homework improves student achievement.
- Source: The High School Journal, “ When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math ,” 2012.
- Source: IZA.org, “ Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement? ,” 2014. **Note: Study sample comprised only high school boys.
Homework helps reinforce classroom learning.
- Source: “ Debunk This: People Remember 10 Percent of What They Read ,” 2015.
Homework helps students develop good study habits and life skills.
- Sources: The Repository @ St. Cloud State, “ Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement ,” 2017; Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
- Source: Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
Homework allows parents to be involved with their children’s learning.
- Parents can see what their children are learning and working on in school every day.
- Parents can participate in their children’s learning by guiding them through homework assignments and reinforcing positive study and research habits.
- Homework observation and participation can help parents understand their children’s academic strengths and weaknesses, and even identify possible learning difficulties.
- Source: Phys.org, “ Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework ,” 2018.
While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects.
Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels.
- Source: USA Today, “ Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In ,” 2021.
- Source: Stanford University, “ Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ,” 2014.
Students with too much homework may be tempted to cheat.
- Source: The Chronicle of Higher Education, “ High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame ,” 2010.
- Source: The American Journal of Family Therapy, “ Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background ,” 2015.
Homework highlights digital inequity.
- Sources: NEAToday.org, “ The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’ ,” 2016; CNET.com, “ The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind ,” 2021.
- Source: Investopedia, “ Digital Divide ,” 2022; International Journal of Education and Social Science, “ Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework ,” 2015.
- Source: World Economic Forum, “ COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it ,” 2021.
Homework does not help younger students.
- Source: Review of Educational Research, “ Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003 ,” 2006.
To help students find the right balance and succeed, teachers and educators must start the homework conversation, both internally at their school and with parents. But in order to successfully advocate on behalf of students, teachers must be well educated on the subject, fully understanding the research and the outcomes that can be achieved by eliminating or reducing the homework burden. There is a plethora of research and writing on the subject for those interested in self-study.
For teachers looking for a more in-depth approach or for educators with a keen interest in educational equity, formal education may be the best route. If this latter option sounds appealing, there are now many reputable schools offering online master of education degree programs to help educators balance the demands of work and family life while furthering their education in the quest to help others.
YOU’RE INVITED! Watch Free Webinar on USD’s Online MEd Program >>
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Top 11 Reasons to get Your Master of Education Degree
Free 22-page Book

- Master of Education
Related Posts


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 5 best homework help websites (free and paid).
Other High School , General Education

Listen: we know homework isn’t fun, but it is a good way to reinforce the ideas and concepts you’ve learned in class. But what if you’re really struggling with your homework assignments?
If you’ve looked online for a little extra help with your take-home assignments, you’ve probably stumbled across websites claiming to provide the homework help and answers students need to succeed . But can homework help sites really make a difference? And if so, which are the best homework help websites you can use?
Below, we answer these questions and more about homework help websites–free and paid. We’ll go over:
- The basics of homework help websites
- The cost of homework help websites
- The five best homework websites out there
- The pros and cons of using these websites for homework help
- The line between “learning” and “cheating” when using online homework help
- Tips for getting the most out of a homework help website
So let’s get started!

The Basics About Homework Help Websites–Free and Paid
Homework help websites are designed to help you complete your homework assignments, plain and simple.
What Makes a Homework Help Site Worth Using
Most of the best sites allow users to ask questions and then provide an answer (or multiple possible answers) and explanation in seconds. In some instances, you can even send a photo of a particular assignment or problem instead of typing the whole thing out!
Homework help sites also offer more than just help answering homework questions. Common services provided are Q&A with experts, educational videos, lectures, practice tests and quizzes, learning modules, math solving tools, and proofreading help. Homework help sites can also provide textbook solutions (i.e. answers to problems in tons of different textbooks your school might be using), one-on-one tutoring, and peer-to-peer platforms that allow you to discuss subjects you’re learning about with your fellow students.
And best of all, nearly all of them offer their services 24/7, including tutoring!
What You Should Should Look Out For
When it comes to homework help, there are lots–and we mean lots –of scam sites out there willing to prey on desperate students. Before you sign up for any service, make sure you read reviews to ensure you’re working with a legitimate company.
A word to the wise: the more a company advertises help that veers into the territory of cheating, the more likely it is to be a scam. The best homework help websites are going to help you learn the concepts you’ll need to successfully complete your homework on your own. (We’ll go over the difference between “homework help” and “cheating” a little later!)

You don't need a golden piggy bank to use homework help websites. Some provide low or no cost help for students like you!
How Expensive Are the Best Homework Help Websites?
First of all, just because a homework help site costs money doesn’t mean it’s a good service. Likewise, just because a homework help website is free doesn’t mean the help isn’t high quality. To find the best websites, you have to take a close look at the quality and types of information they provide!
When it comes to paid homework help services, the prices vary pretty widely depending on the amount of services you want to subscribe to. Subscriptions can cost anywhere from $2 to $150 dollars per month, with the most expensive services offering several hours of one-on-one tutoring with a subject expert per month.
The 5 Best Homework Help Websites
So, what is the best homework help website you can use? The answer is that it depends on what you need help with.
The best homework help websites are the ones that are reliable and help you learn the material. They don’t just provide answers to homework questions–they actually help you learn the material.
That’s why we’ve broken down our favorite websites into categories based on who they’re best for . For instance, the best website for people struggling with math might not work for someone who needs a little extra help with science, and vice versa.
Keep reading to find the best homework help website for you!
Best Free Homework Help Site: Khan Academy
- Price: Free!
- Best for: Practicing tough material
Not only is Khan Academy free, but it’s full of information and can be personalized to suit your needs. When you set up your account , you choose which courses you need to study, and Khan Academy sets up a personal dashboard of instructional videos, practice exercises, and quizzes –with both correct and incorrect answer explanations–so you can learn at your own pace.
As an added bonus, it covers more course topics than many other homework help sites, including several AP classes.
Runner Up: Brainly.com offers a free service that allows you to type in questions and get answers and explanations from experts. The downside is that you’re limited to two answers per question and have to watch ads.
Best Paid Homework Help Site: Chegg
- Price: $14.95 to $19.95 per month
- Best for: 24/7 homework assistance
This service has three main parts . The first is Chegg Study, which includes textbook solutions, Q&A with subject experts, flashcards, video explanations, a math solver, and writing help. The resources are thorough, and reviewers state that Chegg answers homework questions quickly and accurately no matter when you submit them.
Chegg also offers textbook rentals for students who need access to textbooks outside of their classroom. Finally, Chegg offers Internship and Career Advice for students who are preparing to graduate and may need a little extra help with the transition out of high school.
Another great feature Chegg provides is a selection of free articles geared towards helping with general life skills, like coping with stress and saving money. Chegg’s learning modules are comprehensive, and they feature solutions to the problems in tons of different textbooks in a wide variety of subjects.
Runner Up: Bartleby offers basically the same services as Chegg for $14.99 per month. The reason it didn’t rank as the best is based on customer reviews that say user questions aren’t answered quite as quickly on this site as on Chegg. Otherwise, this is also a solid choice!

Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath
- Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services)
- Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems
This site allows you to t ake a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept. Photomath also includes animated videos that break down mathematical concepts to help you better understand and remember them.
The basic service is free, but for an additional fee you can get extra study tools and learn additional strategies for solving common math problems.
Runner Up: KhanAcademy offers in-depth tutorials that cover complex math topics for free, but you won’t get the same tailored help (and answers!) that Photomath offers.
Best Site for English Homework Help: Princeton Review Academic Tutoring
- Price: $40 to $153 per month, depending on how many hours of tutoring you want
- Best for: Comprehensive and personalized reading and writing help
While sites like Grammarly and Sparknotes help you by either proofreading what you write via an algorithm or providing book summaries, Princeton Review’s tutors provide in-depth help with vocabulary, literature, essay writing and development, proofreading, and reading comprehension. And unlike other services, you’ll have the chance to work with a real person to get help.
The best part is that you can get on-demand English (and ESL) tutoring from experts 24/7. That means you can get help whenever you need it, even if you’re pulling an all-nighter!
This is by far the most expensive homework site on this list, so you’ll need to really think about what you need out of a homework help website before you commit. One added benefit is that the subscription covers over 80 other subjects, including AP classes, which can make it a good value if you need lots of help!

Best Site for STEM Homework Help: Studypool
- Best for: Science homework help
- Price: Varies; you’ll pay for each question you submit
When it comes to science homework help, there aren’t a ton of great resources out there. The best of the bunch is Studypool, and while it has great reviews, there are some downsides as well.
Let’s start with the good stuff. Studypool offers an interesting twist on the homework help formula. After you create a free account, you can submit your homework help questions, and tutors will submit bids to answer your questions. You’ll be able to select the tutor–and price point–that works for you, then you’ll pay to have your homework question answered. You can also pay a small fee to access notes, lectures, and other documents that top tutors have uploaded.
The downside to Studypool is that the pricing is not transparent . There’s no way to plan for how much your homework help will cost, especially if you have lots of questions! Additionally, it’s not clear how tutors are selected, so you’ll need to be cautious when you choose who you’d like to answer your homework questions.

What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Homework Help Sites?
Homework help websites can be a great resource if you’re struggling in a subject, or even if you just want to make sure that you’re really learning and understanding topics and ideas that you’re interested in. But, there are some possible drawbacks if you don’t use these sites responsibly.
We’ll go over the good–and the not-so-good–aspects of getting online homework help below.
3 Pros of Using Homework Help Websites
First, let’s take a look at the benefits.
#1: Better Grades Beyond Homework
This is a big one! Getting outside help with your studies can improve your understanding of concepts that you’re learning, which translates into better grades when you take tests or write essays.
Remember: homework is designed to help reinforce the concepts you learned in class. If you just get easy answers without learning the material behind the problems, you may not have the tools you need to be successful on your class exams…or even standardized tests you’ll need to take for college.
#2: Convenience
One of the main reasons that online homework help is appealing is because it’s flexible and convenient. You don’t have to go to a specific tutoring center while they’re open or stay after school to speak with your teacher. Instead, you can access helpful resources wherever you can access the internet, whenever you need them.
This is especially true if you tend to study at off hours because of your extracurriculars, work schedule, or family obligations. Sites that offer 24/7 tutoring can give you the extra help you need if you can’t access the free resources that are available at your school.
#3: Variety
Not everyone learns the same way. Maybe you’re more of a visual learner, but your teacher mostly does lectures. Or maybe you learn best by listening and taking notes, but you’re expected to learn something just from reading the textbook .
One of the best things about online homework help is that it comes in a variety of forms. The best homework help sites offer resources for all types of learners, including videos, practice activities, and even one-on-one discussions with real-life experts.
This variety can also be a good thing if you just don’t really resonate with the way a concept is being explained (looking at you, math textbooks!).

Not so fast. There are cons to homework help websites, too. Get to know them below!
3 Cons of Using Homework Help Websites
Now, let’s take a look at the drawbacks of online homework help.
#1: Unreliable Info
This can be a real problem. In addition to all the really good homework help sites, there are a whole lot of disreputable or unreliable sites out there. The fact of the matter is that some homework help sites don’t necessarily hire people who are experts in the subjects they’re talking about. In those cases, you may not be getting the accurate, up-to-date, and thorough information you need.
Additionally, even the great sites may not be able to answer all of your homework questions. This is especially true if the site uses an algorithm or chatbot to help students…or if you’re enrolled in an advanced or college-level course. In these cases, working with your teacher or school-provided tutors are probably your best option.
#2: No Clarification
This depends on the service you use, of course. But the majority of them provide free or low-cost help through pre-recorded videos. Watching videos or reading info online can definitely help you with your homework… but you can’t ask questions or get immediate feedback if you need it .
#3: Potential For Scamming
Like we mentioned earlier, there are a lot of homework help websites out there, and lots of them are scams. The review comments we read covered everything from outdated or wrong information, to misleading claims about the help provided, to not allowing people to cancel their service after signing up.
No matter which site you choose to use, make sure you research and read reviews before you sign up–especially if it’s a paid service!

When Does “Help” Become “Cheating”?
Admittedly, whether using homework help websites constitutes cheating is a bit of a grey area. For instance, is it “help” when a friend reads your essay for history class and corrects your grammar, or is it “cheating”? The truth is, not everyone agrees on when “help” crosses the line into “cheating .” When in doubt, it can be a good idea to check with your teacher to see what they think about a particular type of help you want to get.
That said, a general rule of thumb to keep in mind is to make sure that the assignment you turn in for credit is authentically yours . It needs to demonstrate your own thoughts and your own current abilities. Remember: the point of every homework assignment is to 1) help you learn something, and 2) show what you’ve learned.
So if a service answers questions or writes essays for you, there’s a good chance using it constitutes cheating.
Here’s an example that might help clarify the difference for you. Brainstorming essay ideas with others or looking online for inspiration is “help” as long as you write the essay yourself. Having someone read it and give you feedback about what you need to change is also help, provided you’re the one that makes the changes later.
But copying all or part of an essay you find online or having someone write (or rewrite) the whole thing for you would be “cheating.” The same is true for other subjects. Ultimately, if you’re not generating your own work or your own answers, it’s probably cheating.

5 Tips for Finding the Best Homework Help Websites for You
Now that you know some of our favorite homework help websites, free and paid, you can start doing some additional research on your own to decide which services might work best for you! Here are some top tips for choosing a homework help website.
Tip 1: Decide How You Learn Best
Before you decide which site or sites you’re going to use for homework help, y ou should figure out what kind of learning style works for you the most. Are you a visual learner? Then choose a site that uses lots of videos to help explain concepts. If you know you learn best by actually doing tasks, choose a site that provides lots of practice exercises.
Tip 2: Determine Which Subjects You Need Help With
Just because a homework help site is good overall doesn’t mean that it’s equally good for every subject. If you only need help in math, choose a site that specializes in that area. But if history is where you’re struggling, a site that specializes in math won’t be much help. So make sure to choose a site that you know provides high-quality help in the areas you need it most.
Tip 3: Decide How Much One-On-One Help You Need
This is really about cost-effectiveness. If you learn well on your own by reading and watching videos, a free site like Khan Academy is a good choice. But if you need actual tutoring, or to be able to ask questions and get personalized answers from experts, a paid site that provides that kind of service may be a better option.
Tip 4: Set a Budget
If you decide you want to go with a paid homework help website, set a budget first . The prices for sites vary wildly, and the cost to use them can add up quick.
Tip 5: Read the Reviews
Finally, it’s always a good idea to read actual reviews written by the people using these homework sites. You’ll learn the good, the bad, and the ugly of what the users’ experiences have been. This is especially true if you intend to subscribe to a paid service. You’ll want to make sure that users think it’s worth the price overall!

What’s Next?
If you want to get good grades on your homework, it’s a good idea to learn how to tackle it strategically. Our expert tips will help you get the most out of each assignment…and boost your grades in the process.
Doing well on homework assignments is just one part of getting good grades. We’ll teach you everything you need to know about getting great grades in high school in this article.
Of course, test grades can make or break your GPA, too. Here are 17 expert tips that’ll help you get the most out of your study prep before you take an exam.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science

Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
9 Best Homework Help Websites
July 22, 2023

When I was in high school, resources for extra homework help weren’t exactly abundant. If you were struggling with a Shakespeare sonnet, you could always run to the bookstore and pick up a CliffNotes guide. SparkNotes was also gaining in popularity. But these early homework help resources had limited catalogs and were focused primarily on literature. Today, I imagine students suffer from the opposite problem—having too many choices when it comes to homework help websites. When the options are seemingly endless, knowing what to look out for takes on an added importance. Below, I’ll go through a list of 9 stand-out homework help websites and briefly discuss what makes them worth a visit.
Homework Help Websites – The Basics
The best homework help websites do more than just spit out an answer to that tricky math problem. They actually help students learn the material. Common features of homework help websites are educational videos and lectures, practice tests and quizzes, study tools like flashcards, and Q&As with experts. Many sites offer features that allow students to ask specific questions and get real-time feedback. There are also a number of services that offer one-on-one tutoring. Some homework help sites are free, while others require a paid subscription.
1) Khan Academy
Khan Academy is an amazing resource for students of all ages. It’s free, and it really is an academy—it offers full courses in a wide array of subjects, from pre-K math to high school physics. The courses consist of readings, video lectures, practice exercises, and quizzes. The breadth of material is impressive. In math alone, I see course listings for Algebra 1 and 2, Geometry, Trigonometry, Precalculus, Statistics, Multivariable calculus—you get the idea. Khan Academy also offers a wide variety of AP courses, state-specific curricula, test-prep programs, and life skill courses, like personal finance.
It’s important to note that Khan Academy isn’t a one-on-one tutoring platform. But because of their extensive library of material, the search function is especially powerful. Try it out. I did a search for argumentative essay help, and found a comprehensive guide to writing argumentative essays that was a part of a larger writing course.
Chegg is a paid homework help service. Unlike Khan Academy, Chegg isn’t built around specific courses. Rather, it offers a variety of homework-support resources. Among those resources are plagiarism and grammar checkers, a proofreading service, and a “math solver”, which allows students to enter a problem and get back both a solution and a detailed step-by-step explanation of how the problem was solved. Perhaps the most powerful tool Chegg offers is its “Expert Q&A” feature. This service allows students to take a picture of their homework problem, upload it to the site, and get a detailed response in return. Chegg’s emphasis on process and explanation make it a valuable educational resource for students—not just a way to get a quick answer.
Best Homework Help Websites (Continued)
Quizlet is a well-known and worthwhile study resource. It offers a variety of courses, and it also has an expert-response feature. But Quizlet’s best feature, in my option, is the flashcards tool. Students can create their own digital decks of cards and practice them on Quizlet—just like an old fashion set of index cards. I had a ton of success using Quizlet’s flash card feature to help me memorize words for my foreign language requirement in college. It’s a simple but powerful tool. Although often maligned as a learning method, rote rehearsal and spaced repetition are effective ways to encode information . Quizlet’s flashcard feature is a great way to put those techniques into practice.
4) Socratic
is an AI-powered homework support app that allows students to type or take pictures of questions and receive solutions right away. Since it works with AI, it relies on the web’s vast stores of accumulated knowledge—you’re not interacting with a human tutor. Nonetheless, I found it to be an extremely helpful tool. I tried it out first using a specific math problem. In just a few seconds I was provided with the solution and an explainer with relevant formulas, plus a graphic to help visualize the underlying logic. There were also suggested links to additional resources. For example, when I asked Socratic to explain how the German genitive case works, it suggested a YouTube video and a number of articles from blogs and other language-learning sites.
Since Socratic doesn’t feature courses or one-on-one tutoring support, I wouldn’t lean on it if I were really struggling in a particular class. But as a tool to check your work, make sure you’re on the right track, and become aware of additional resources, it’s worth a download.
5) Photomath
Photomath is, as you might have guessed, a site for math homework help. Like other homework help websites, Photomath allows students to take a picture of a problem and receive an instant, step-by-step solution. Included along with the solution is an explanation of relevant concepts and formulas, plus videos covering mathematical concepts. Photomath does offer a few basic courses, too. So if in addition to homework-specific help you want to brush up on the basics, they’ve got you covered in arithmetic, algebra, and calculus crash courses.
6) Studypool
Studypool is a paid homework support service that provides solutions to specific questions. Studypool offers support in all the major subjects, with a particular emphasis on science. Students can ask questions on everything from anatomy to physics. Like other services, students upload their exact questions or problems directly to the site. But Studypool’s payment model is a bit different: instead of paying for tutoring time or a monthly subscription, students pay for solutions to each question they submit. When a student submits a question, tutors submit bids to answer them. The student then can select which tutor/price option works best. After students select the price and tutor they want, they’re connected with the tutor and given the solution and explanation via messenger.
The draw of Studypool is that it gives students access to real (i.e., human) tutors who are experts in their field. The downside is that pricing isn’t transparent, and students pay per question.
7) College Info Geek
College Info Geek is the study-support website that I wish I knew about when I was in high school and college (they didn’t pay me to write that, I swear). The site focuses not on specific courses or questions, but on how to become a more effective learner. Here it’s all about “learning how to learn”—study tips, memorization and note-taking techniques, and much more. The articles are well-researched, clearly-communicated, practical, and comprehensive. For example, the article on how to improve your memory includes a breakdown of the different types of memory processes, memorization techniques, and even a discussion of how nutrition affects memory. College Info Geek is a great resource for everyone, not just high school and college students.
8) SparkNotes
Yes, Sparknotes made the list! The site offers lessons in a whole bunch of subjects—biology, chemistry, computer science, history, philosophy, math—but its specialty is literature. SparkNotes provides summaries and analyses of novels, short stories, poetry, and non-fiction, from The Canterbury Tales to Toni Morrison, Saul Bellow, and Junot Diaz. SparkNotes breaks down books into sub-sections and provides synopses and analyses for each section. There are also separate pages for character breakdowns, discussions of themes and motifs, and explanations of important quotes. I’d caution against using SparkNotes if you’re trying to “hack” a novel or poem and get simple answers about what it “means.” But as a way to supplement your own understanding and interpretation, it’s a great resource. Shmoop is also worth checking out for extra support in literature, poetry, mythology, and the history of literary movements.
9) Grammarly
I’m not sure if Grammarly is an obvious or unexpected choice to round out the list. Either way, it deserves a mention here. Grammarly is a writing tool. It checks and suggests corrections for incorrectly spelled words and misused punctuation. But Grammarly also scans and corrects for things like clarity and vocab usage. It flags sentences that are vague, or overly wordy, and alerts you if you’re using that flashy vocab word incorrectly. It even gives suggestions if it thinks your writing is a bit bland. I don’t see Grammarly as a crutch, but rather as a tool. It can help you master those pesky recurring grammar and usage issues. Always mix up effect and affect? Grammarly will continue to course correct until you’ve got it down yourself.
Homework Help Websites – Final Thoughts
None of the above homework help websites should be seen as a panacea. Each has benefits and drawbacks, strengths and weak points. The list is far from exhaustive. And the sites don’t have to be used in isolation. Try a few out, mix and match. College Info Geek is an excellent supplement to any study regimen. Socratic can be used as a tool to check answers for math homework, and at the same time you can use Grammarly to describe your problem to a tutor on Chegg. At their best, these sites are more than quick fixes to stubborn homework problems—they’re aids to genuine learning.
Additional Resources
You should also check out College Transitions’ “ High School Success ” blogs for help with a number of common high school assignments, including:
- Lord of the Flies Summary & Analysis
- The Great Gatsby and The American Dream
- Analysis of Hamlet’s “To be or not to be” Speech
- Robert Frost’s Road Not Taken Analysis
- High School Success

Dane Gebauer
Dane Gebauer is a writer and teacher living in Miami, FL. He received his MFA in fiction from Columbia University, and his writing has appeared in Complex Magazine and Sinking City Review .
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
- Our Mission
Assigning More Meaningful Math Homework
A small set of problems or even one substantial problem can be enough to supplement classroom instruction.

As a math teacher of more than 23 years, I have had the habit, almost like a muscle memory repetition, of assigning daily math homework for my middle school students. It wasn’t until recently that I paused to reflect, “Why am I assigning this?” The easy answer is, “My students need to practice to develop their skills.”
If I dig a bit deeper into the “why,” I wonder, “Are all of my students benefiting from this assignment? Did I assign an appropriate amount and level of problems? What resources do my students have or not have to be successful with this assignment? Is the assignment meaningful or busywork?”
Consider the following suggestions for making math homework more meaningful.
3 Ways to Create More Meaningful Math Homework
1. Think quality over quantity. The National Council for Teachers of Mathematics Homework page of tips for teachers suggests, “Only assign what’s necessary to augment instruction. If you can get sufficient information by assigning only five problems, then don’t assign fifty.”
Worksheets and problem sets from textbook publishers might contain dozens of problems that repeat the same concepts. It is OK to assign part of a page, such as “p. 34 #s 3, 5, and 17.” I tell my middle school students, “I handpicked these particular problems because they capture the objective of today’s lesson.” When students know that their teacher carefully “handpicked” a problem set, they might pay more attention to the condensed assignment because it was tailored for them.
Even one problem can be sufficient. Robert Kaplinsky, cofounder of Open Middle , routinely shares on X (formerly Twitter) single problems that are really engaging and give students a good chance to practice skills.
The depth and exploration that can come from one single problem can be richer than 20 routine problems. You might be surprised by how much depth can be inspired by a single problem.
2. Consider choice and variety. It’s unrealistic to create a personalized daily homework assignment for each student in your class. Student voice and choice can be applied to your preexisting assignments without your having to re-create the homework wheel.
Traditional assignments can be modified by offering students choice. This might look like “ Choose any five of these problems ,” or take this tip from educator Peter Liljedahl and designate problems as “mild, medium, or spicy” and let students pick their level for that assignment.
Offering homework level choice also promotes a culture of growth mindset through messaging like “You might choose mild problems for this lesson; however, tomorrow you might feel you’re ready for a medium level.” Level choice can vary day to day—your math level is not fixed.
Daily homework can also be spiced up by offering a variety of types of assignments. Consider assigning problems that go beyond providing a single number answer. Here are a few examples to get students thinking beyond just getting a particular problem right:
- When simplifying (4 + 5) x 5 - 3, what is the first step?
- When simplifying (4 + 5) x 5 - 3, Ali got the answer 18. What advice do you have for her?
- Write your own order of operations problem with a solution of 42.
Check out these websites for even more creative ways to vary homework:
- Three-Acts Math Tasks
- Open Middle
- Would You Rather Math
3. Remember, accountability doesn’t have to result in a grade. There is a major difference between assigning homework for a grade and assigning homework purely for practice. When a grade is the result of an assignment, the stakes get higher for the student.
In the February 2023 Washington Post article “ A deep dive into whether—and how—homework should be graded ,“ former teacher Rick Wormeli wrote, “When early attempts at mastery are not used against them, and accountability comes in the form of actually learning content, adolescents flourish.” If homework is truly for practice, this is an opportunity for students to make mistakes and take risks without the fear of a penalty.
Even if homework is graded as a completion grade, there are considerations of equity and meaningfulness of the practice.
Consider the following questions when deciding to give a completion grade for a homework assignment: Do all students have a home environment that is supportive of homework? Do some students have additional support, such as tutors or parents, to help them get the homework completed? Would students copy homework assignments from each other just to earn the completion grade?
If not grades, then how do we hold students accountable for practicing outside of class?
Student presentations and discussions are a way to check for understanding of an assignment and to let students know you expect them to attempt the problems. This might look like a debate in which students take sides on how to approach a problem . Alternatively, students could post their work on the board to share their strategies with the class or discuss their solutions in small groups. Communicating their mathematical thinking deepens their understanding .
Education consultants Ashley Marlow and Katie Novak write in their Edutopia article “ Making Math Accessible for All Students ” (July 2022), “When students have opportunities to think, reason, explain, and model their thinking, they are more readily able to develop a deep understanding of mathematics beyond rote memorization. The goal is for all students to experience success in higher learning of mathematics—requiring those reasoning and sense-making skills and increasing engagement.”
The next time you’re planning your lessons and assignments, pause and reflect on the meaningfulness of the homework assignment. Could it be shorter but more in-depth? Can students have a choice in their work? Will students find value in doing the work even if it is not for a grade? You might find that students take more ownership and care in their homework if it’s more meaningful to them.

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Students’ Study Time and Their “Homework Problem”
- Published: 18 December 2008
- Volume 93 , pages 111–115, ( 2009 )
Cite this article

- Jiri Zuzanek 1
2072 Accesses
4 Citations
Explore all metrics
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Bennett, S., & Kalish, N. (2006). The case against homework . Bethel: Crown Publishers.
Google Scholar
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 , 1–62.
Article Google Scholar
Kohn, A. (2006). The homework myth. Why our kids are getting too much of a bad thing . Cambridge, MA: De Capo Press.
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2000). The end of homework. How homework overburdens children, and limits learning . Boston: Beacon Press.
Zuzanek, J. (2005). Adolescent time use and well-being from a comparative perspective. Loisir & Societe/Society and Leisure, 28 , 5–42.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada
Jiri Zuzanek
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jiri Zuzanek .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zuzanek, J. Students’ Study Time and Their “Homework Problem”. Soc Indic Res 93 , 111–115 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-008-9411-8
Download citation
Accepted : 01 August 2008
Published : 18 December 2008
Issue Date : August 2009
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-008-9411-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Experience Sampling Method
- Homework Problem
- Homework Time
- Adolescent Stress
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Learn Smarter, Not Harder with AI
Introducing StudyMonkey, your AI-powered tutor .
StudyMonkey AI can tutor complex homework questions, enhance your essay writing and assess your work—all in seconds.
No more long all-nighters
24/7 solutions to questions you're stumped on and essays you procrastinated on.
No more stress and anxiety
Get all your assignments done with helpful answers in 10 seconds or less.
No more asking friends for help
StudyMonkey is your new smart bestie that will never ghost you.
No more staying after school
AI tutoring is available 24/7, on-demand when you need it most.
AI Tutor for any subject
American college testing (act), anthropology, advanced placement exams (ap exams), arabic language, archaeology, biochemistry, chartered financial analyst (cfa) exam, communications, computer science, certified public accountant (cpa) exam, cultural studies, cyber security, dental admission test (dat), discrete mathematics, earth science, elementary school, entrepreneurship, environmental science, farsi (persian) language, fundamentals of engineering (fe) exam, gender studies, graduate management admission test (gmat), graduate record examination (gre), greek language, hebrew language, high school entrance exam, high school, human geography, human resources, international english language testing system (ielts), information technology, international relations, independent school entrance exam (isee), linear algebra, linguistics, law school admission test (lsat), machine learning, master's degree, medical college admission test (mcat), meteorology, microbiology, middle school, national council licensure examination (nclex), national merit scholarship qualifying test (nmsqt), number theory, organic chemistry, project management professional (pmp), political science, portuguese language, probability, project management, preliminary sat (psat), public policy, public relations, russian language, scholastic assessment test (sat), social sciences, secondary school admission test (ssat), sustainability, swahili language, test of english as a foreign language (toefl), trigonometry, turkish language, united states medical licensing examination (usmle), web development, step-by-step guidance 24/7.
Receive step-by-step guidance & homework help for any homework problem & any subject 24/7
Ask any question
StudyMonkey supports every subject and every level of education from 1st grade to masters level.
Get an answer
StudyMonkey will give you an answer in seconds—multiple choice questions, short answers, and even an essays are supported!
Review your history
See your past questions and answers so you can review for tests and improve your grades.
It's not cheating...
You're just learning smarter than everyone else
How Can StudyMonkey Help You?
Hear from our happy students.
"The AI tutor is available 24/7, making it a convenient and accessible resource for students who need help with their homework at any time."
"Overall, StudyMonkey is an excellent tool for students looking to improve their understanding of homework topics and boost their academic success."
Upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium!
Why not upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium and get access to all features?
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access Only $1 for 4 weeks
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition
America’s Colleges Are Reaping What They Sowed
Universities spent years saying that activism is not just welcome but encouraged on their campuses. Students took them at their word.

Listen to this article
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
N ick Wilson, a sophomore at Cornell University, came to Ithaca, New York, to refine his skills as an activist. Attracted by both Cornell’s labor-relations school and the university’s history of campus radicalism, he wrote his application essay about his involvement with a Democratic Socialists of America campaign to pass the Protecting the Right to Organize Act . When he arrived on campus, he witnessed any number of signs that Cornell shared his commitment to not just activism but also militant protest, taking note of a plaque commemorating the armed occupation of Willard Straight Hall in 1969.
Cornell positively romanticizes that event: The university library has published a “ Willard Straight Hall Occupation Study Guide ,” and the office of the dean of students once co-sponsored a panel on the protest. The school has repeatedly screened a documentary about the occupation, Agents of Change . The school’s official newspaper, published by the university media-relations office, ran a series of articles honoring the 40th anniversary, in 2009, and in 2019, Cornell held a yearlong celebration for the 50th, complete with a commemorative walk, a dedication ceremony, and a public conversation with some of the occupiers. “ Occupation Anniversary Inspires Continued Progress ,” the Cornell Chronicle headline read.
As Wilson has discovered firsthand, however, the school’s hagiographical odes to prior protests have not prevented it from cracking down on pro-Palestine protests in the present. Now that he has been suspended for the very thing he told Cornell he came there to learn how to do—radical political organizing—he is left reflecting on the school’s hypocrisies. That the theme of this school year at Cornell is “Freedom of Expression” adds a layer of grim humor to the affair.
Evan Mandery: University of hypocrisy
University leaders are in a bind. “These protests are really dynamic situations that can change from minute to minute,” Stephen Solomon, who teaches First Amendment law and is the director of NYU’s First Amendment Watch—an organization devoted to free speech—told me. “But the obligation of universities is to make the distinction between speech protected by the First Amendment and speech that is not.” Some of the speech and tactics protesters are employing may not be protected under the First Amendment, while much of it plainly is. The challenge universities are confronting is not just the law but also their own rhetoric. Many universities at the center of the ongoing police crackdowns have long sought to portray themselves as bastions of activism and free thought. Cornell is one of many universities that champion their legacy of student activism when convenient, only to bring the hammer down on present-day activists when it’s not. The same colleges that appeal to students such as Wilson by promoting opportunities for engagement and activism are now suspending them. And they’re calling the cops.
The police activity we are seeing universities level against their own students does not just scuff the carefully cultivated progressive reputations of elite private universities such as Columbia, Emory University, and NYU, or the equally manicured free-speech bona fides of red-state public schools such as Indiana University and the University of Texas at Austin. It also exposes what these universities have become in the 21st century. Administrators have spent much of the recent past recruiting social-justice-minded students and faculty to their campuses under the implicit, and often explicit, promise that activism is not just welcome but encouraged. Now the leaders of those universities are shocked to find that their charges and employees believed them. And rather than try to understand their role in cultivating this morass, the Ivory Tower’s bigwigs have decided to apply their boot heels to the throats of those under their care.
I spoke with 30 students, professors, and administrators from eight schools—a mix of public and private institutions across the United States—to get a sense of the disconnect between these institutions’ marketing of activism and their treatment of protesters. A number of people asked to remain anonymous. Some were untenured faculty or administrators concerned about repercussions from, or for, their institutions. Others were directly involved in organizing protests and were wary of being harassed. Several incoming students I spoke with were worried about being punished by their school before they even arrived. Despite a variety of ideological commitments and often conflicting views on the protests, many of those I interviewed were “shocked but not surprised”—a phrase that came up time and again—by the hypocrisy exhibited by the universities with which they were affiliated. (I reached out to Columbia, NYU, Cornell, and Emory for comment on the disconnect between their championing of past protests and their crackdowns on the current protesters. Representatives from Columbia, Cornell, and Emory pointed me to previous public statements. NYU did not respond.)
The sense that Columbia trades on the legacy of the Vietnam protests that rocked campus in 1968 was widespread among the students I spoke with. Indeed, the university honors its activist past both directly and indirectly, through library archives , an online exhibit , an official “Columbia 1968” X account , no shortage of anniversary articles in Columbia Magazine , and a current course titled simply “Columbia 1968.” The university is sometimes referred to by alumni and aspirants as the “Protest Ivy.” One incoming student told me that he applied to the school in part because of an admissions page that prominently listed community organizers and activists among its “distinguished alumni.”
Joseph Slaughter, an English professor and the executive director of Columbia’s Institute for the Study of Human Rights, talked with his class about the 1968 protests after the recent arrests at the school. He said his students felt that the university had actively marketed its history to them. “Many, many, many of them said they were sold the story of 1968 as part of coming to Columbia,” he told me. “They talked about it as what the university presents to them as the long history and tradition of student activism. They described it as part of the brand.”
This message reaches students before they take their first college class. As pro-Palestine demonstrations began to raise tensions on campus last month, administrators were keen to cast these protests as part of Columbia’s proud culture of student activism. The aforementioned high-school senior who had been impressed by Columbia’s activist alumni attended the university’s admitted-students weekend just days before the April 18 NYPD roundup. During the event, the student said, an admissions official warned attendees that they may experience “disruptions” during their visit, but boasted that these were simply part of the school’s “long and robust history of student protest.”
Remarkably, after more than 100 students were arrested on the order of Columbia President Minouche Shafik—in which she overruled a unanimous vote by the university senate’s executive committee not to bring the NYPD to campus —university administrators were still pushing this message to new students and parents. An email sent on April 19 informed incoming students that “demonstration, political activism, and deep respect for freedom of expression have long been part of the fabric of our campus.” Another email sent on April 20 again promoted Columbia’s tradition of activism, protest, and support of free speech. “This can sometimes create moments of tension,” the email read, “but the rich dialogue and debate that accompany this tradition is central to our educational experience.”
Evelyn Douek and Genevieve Lakier: The hypocrisy underlying the campus-speech controversy
Another student who attended a different event for admitted students, this one on April 21, said that every administrator she heard speak paid lip service to the school’s long history of protest. Her own feelings about the pro-Palestine protests were mixed—she said she believes that a genocide is happening in Gaza and also that some elements of the protest are plainly anti-Semitic—but her feelings about Columbia’s decision to involve the police were unambiguous. “It’s reprehensible but exactly what an Ivy League institution would do in this situation. I don’t know why everyone is shocked,” she said, adding: “It makes me terrified to go there.”
Beth Massey, a veteran activist who participated in the 1968 protests, told me with a laugh, “They might want to tell us they’re progressive, but they’re doing the business of the ruling class.” She was not surprised by the harsh response to the current student encampment or by the fact that it lit the fuse on a nationwide protest movement. Massey had been drawn to the radical reputation of Columbia’s sister school, Barnard College, as an open-minded teenager from the segregated South: “I actually wanted to go to Barnard because they had a history of progressive struggle that had happened going all the way back into the ’40s.” And the barn-burning history that appealed to Massey in the late 1960s has continued to attract contemporary students, albeit with one key difference: Today, that radical history has become part of the way that Barnard and Columbia sell their $60,000-plus annual tuition.
Of course, Columbia is not alone. The same trends have also prevailed at NYU, which likes to crow about its own radical history and promises contemporary students “ a world of activism opportunities .” An article published on the university’s website in March—titled “Make a Difference Through Activism at NYU”—promises students “myriad chances to put your activism into action.” The article points to campus institutions that “provide students with resources and opportunities to spark activism and change both on campus and beyond.” The six years I spent as a graduate student at NYU gave me plenty of reasons to be cynical about the university and taught me to view all of this empty activism prattle as white noise. But even I was astounded to see a video of students and faculty set upon by the NYPD, arrested at the behest of President Linda Mills.
“Across the board, there is a heightened awareness of hypocrisy,” Mohamad Bazzi, a journalism professor at NYU, told me, noting that faculty were acutely conscious of the gap between the institution’s intensive commitment to DEI and the police crackdown. The university has recently made several “cluster hires”—centered on activism-oriented themes such as anti-racism, social justice, and indigeneity—that helped diversify the faculty. Some of those recent hires were among the people who spent a night zip-tied in a jail cell, arrested for the exact kind of activism that had made them attractive to NYU in the first place. And it wasn’t just faculty. The law students I spoke with were especially acerbic. After honing her activism skills at her undergraduate institution—another university that recently saw a violent police response to pro-Palestine protests—one law student said she came to NYU because she was drawn to its progressive reputation and its high percentage of prison-abolitionist faculty. This irony was not lost on her as the police descended on the encampment.
After Columbia students were arrested on April 18, students at NYU’s Gallatin School of Individualized Study decided to cancel a planned art festival and instead use the time to make sandwiches as jail support for their detained uptown peers. The school took photos of the students layering cold cuts on bread and posted it to Gallatin’s official Instagram. These posts not only failed to mention that the students were working in support of the pro-Palestine protesters; the caption—“making sandwiches for those in need”—implied that the undergrads might be preparing meals for, say, the homeless.
The contradictions on display at Cornell, Columbia, and NYU are not limited to the state of New York. The police response at Emory, another university that brags about its tradition of student protest, was among the most disturbing I have seen. Faculty members I spoke with at the Atlanta school, including two who had been arrested—the philosophy professor Noëlle McAfee and the English and Indigenous-studies professor Emil’ Keme—recounted harrowing scenes: a student being knocked down, an elderly woman struggling to breathe after tear-gas exposure, a colleague with welts from rubber bullets. These images sharply contrast with the university’s progressive mythmaking, a process that was in place even before 2020’s “summer of racial reckoning” sent universities scrambling to shore up their activist credentials.
In 2018, Emory’s Campus Life office partnered with students and a design studio to begin work on an exhibit celebrating the university’s history of identity-based activism. Then, not long after George Floyd’s murder, the university’s library released a series of blog posts focusing on topics including “Black Student Activism at Emory,” “Protests and Movements,” “Voting Rights and Public Policy,” and “Authors and Artists as Activists.” That same year, the university announced its new Arts and Social Justice Fellows initiative, a program that “brings Atlanta artists into Emory classrooms to help students translate their learning into creative activism in the name of social justice.” In 2021, the university put on an exhibit celebrating its 1969 protests , in which “Black students marched, demonstrated, picketed, and ‘rapped’ on those institutions affecting the lives of workers and students at Emory.” Like Cornell’s and Columbia’s, Emory’s protests seem to age like fine wine: It takes half a century before the institution begins enjoying them.
N early every person I talked with believed that their universities’ responses were driven by donors, alumni, politicians, or some combination thereof. They did not believe that they were grounded in serious or reasonable concerns about the physical safety of students; in fact, most felt strongly that introducing police into the equation had made things far more dangerous for both pro-Palestine protesters and pro-Israel counterprotesters. Jeremi Suri, a historian at UT Austin—who told me he is not politically aligned with the protesters—recalls pleading with both the dean of students and the mounted state troopers to call off the charge. “It was like the Russian army had come onto campus,” Suri mused. “I was out there for 45 minutes to an hour. I’m very sensitive to anti-Semitism. Nothing anti-Semitic was said.” He added: “There was no reason not to let them shout until their voices went out.”
From the May 1930 issue: Hypocrisy–a defense
As one experienced senior administrator at a major research university told me, the conflagration we are witnessing shows how little many university presidents understand either their campus communities or the young people who populate them. “When I saw what Columbia was doing, my immediate thought was: They have not thought about day two ,” he said, laughing. “If you confront an 18-year-old activist, they don’t back down. They double down.” That’s what happened in 1968, and it’s happening again now. Early Tuesday morning, Columbia students occupied Hamilton Hall—the site of the 1968 occupation, which they rechristened Hind’s Hall in honor of a 6-year-old Palestinian girl killed in Gaza—in response to the university’s draconian handling of the protests. They explicitly tied these events to the university’s past, calling out its hypocrisy on Instagram: “This escalation is in line with the historical student movements of 1968 … which Columbia repressed then and celebrates today.” The university, for its part, responded now as it did then: Late on Tuesday, the NYPD swarmed the campus in an overnight raid that led to the arrest of dozens of students.
The students, professors, and administrators I’ve spoken with in recent days have made clear that this hypocrisy has not gone unnoticed and that the crackdown isn’t working, but making things worse. The campus resistance has expanded to include faculty and students who were originally more ambivalent about the protests and, in a number of cases, who support Israel. They are disturbed by what they rightly see as violations of free expression, the erosion of faculty governance, and the overreach of administrators. Above all, they’re fed up with the incandescent hypocrisy of institutions, hoisted with their own progressive petards, as the unstoppable force of years’ worth of self-righteous rhetoric and pseudo-radical posturing meets the immovable object of students who took them at their word.
In another video published by The Cornell Daily Sun , recorded only hours after he was suspended, Nick Wilson explained to a crowd of student protesters what had brought him to the school. “In high school, I discovered my passion, which was community organizing for a better world. I told Cornell University that’s why I wanted to be here,” he said, referencing his college essay. Then he paused for emphasis, looking around as his peers began to cheer. “And those fuckers admitted me.”
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Experts fear ‘catastrophic’ college declines thanks to botched FAFSA rollout
Ashnaelle Bijoux poses on campus, Saturday, April 27, 2024, at Norwich Free Academy in Norwich, Conn. Bijoux, a senior at NFA, has been unable to complete the FAFSA form due to a glitch with the form. Without the form and the financial aid it brings, Bijoux won’t be able to pursue her goal of going to Southern Connecticut State University to become a therapist. (AP Photo/Jessica Hill)
- Copy Link copied

WASHINGTON (AP) — The last thing standing between Ashnaelle Bijoux and her college dream is the FAFSA form — a financial aid application that’s supposed to help students go to college, but is blocking her instead. She has tried to submit it over and over. Every time, it fails to go through.
“I feel overwhelmed and stressed out,” said Bijoux, 19. She came close to tears the last time she tried the form. “I feel like I’m being held back.”
Normally a time of celebration for high school seniors, this spring has been marred by the federal government’s botched rollout of the new FAFSA application . By May 1, students usually know where they’re headed to college in the fall. This year, most still haven’t received financial aid offers. Three months before the start of fall classes, many don’t know where they’re going to college, or how they’re going to pay for it.
“We’re asking them to make probably one of the biggest financial decisions — and decisions that will have the biggest implications on their lives going forward — without all of the information,” said Justin Draeger, president and CEO of the National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators.
The FAFSA, or Free Application for Federal Student Aid, went through a massive overhaul that was supposed to make it simpler and shorter. But a series of blunders by the Education Department made it harder than ever, delaying college decisions by months and raising fears that hundreds of thousands of students will forgo college entirely.
Across the United States, the number of students who have successfully submitted the FAFSA is down 29% from this time last year, and it’s even worse at schools with more low-income students, according to the National College Attainment Network.
The group’s CEO, Kim Cook, warned members of Congress this month about a potentially “catastrophic” drop in college enrollments that would make the decreases of the pandemic seem mild.
For Bijoux, of Norwich, Connecticut, the FAFSA problems threaten to undermine the promise of higher education.
To her, college is a chance to seize the opportunities that weren’t available to her mother, who immigrated from Haiti to the U.S. as an adult. Bijoux hopes to become a therapist and set a positive example for her three younger brothers.
If her FAFSA goes through, she should be eligible for enough financial aid to help with the $ 13,000-a-year tuition at Southern Connecticut State University. If not, she might go to a local community college, but even that would require loans if she can’t complete the FAFSA.
“That’s why it hurts, because it’s like you work so hard to go somewhere and do something and make something of yourself,” Bijoux said. “I thought I would start at a four-year (college) and then work hard continuously, like I’ve been doing basically my whole life. But that’s not the case.”
The updated FAFSA form has one section filled out by students and another by their parents. But when Bijoux finishes her part, nothing shows up on her mom’s online account. She keeps trying, but nothing seems to change.
Similar problems have been reported across the country, along with numerous other bugs that the Education Department has scrambled to fix. Families who call for customer service have faced long wait times or say the call center hung up on them.
It “drains all the momentum” from families working to send their children to college, especially those navigating the process for the first time, said Anne Zinn, a counselor at Norwich Free Academy, where Bijoux goes to school.
“I can only say so many times, ‘Just be patient, just be patient,’ before they throw their hands up and they’re like, ‘Why am I doing this? I’m just gonna go get a job ,’” she said.
The rollout has attracted bipartisan criticism in Congress, and it’s being investigated at the request of Republicans. Last week, Richard Cordray, the federal student loan chief who oversaw the FAFSA update, announced he’s stepping down at the end of June.
For colleges, too, the delays pose a major threat.
Enrollment decreases like those being projected now could put many small colleges out of business, or necessitate deep cuts in staff. Some colleges are pushing for emergency relief just to stay afloat, said Angel Pérez, CEO of the National Association for College Admission Counseling.
“If they don’t get checks from the federal government to basically get them through next year, they will not survive,” Pérez said.
The FAFSA has been the linchpin of student financial aid for decades. It’s used to determine eligibility for the federal Pell grant, a scholarship for low-income students, and it’s required to receive federal student loans . Colleges and states also use FAFSA to distribute their own scholarships.
FAFSA had long been maligned for being tedious, difficult and intimidating to families without college experience. Congress passed legislation in 2020 meant to simplify the form. The Education Department was ordered to reduce the number of questions from more than 100 to about 40, and change the formula to expand aid to more students.
Problems started piling up as soon as the new form went online in December, already months overdue.
The first applications were incorrectly processed using an outdated calculation for inflation. Later, a federal contractor miscalculated a different formula on more than 200,000 applications. Each mistake added to delays, leaving students waiting longer to hear anything about financial aid.
Even more worrisome is a misstep that blocked students from finishing the form if they have a parent without a Social Security number. Advocates say the system locked out hundreds of thousands of students who are U.S. citizens or permanent residents but whose parents are not.
The Education Department on Tuesday said it’s giving those parents a new way to enter their tax information manually. But as recently as this week, some students said they were still blocked from submitting the form.
Federal education officials say they’re addressing lingering bugs but making progress. More than 8 million student applications have now been processed and sent to colleges, the agency said, and new applications are being processed within three days.
Still, the wait is far from over. It usually takes weeks for schools to prepare financial aid offers. Some colleges have extended decision deadlines to give students more time to weigh their options. But some stuck to May 1, forcing students to choose a college — and make a nonrefundable payment to hold their spot — without knowing all their scholarship options.
In West Virginia, Gov. Jim Justice on Tuesday declared a state of emergency that allows students to receive state scholarships without having their FAFSA processed by the federal government. West Virginia has the lowest number of college graduates in the nation, and the state’s high school FAFSA completion rates are currently down nearly 40%, said Justice, a Republican.
“Really and truly, a lot of kids are sitting on the sidelines ... wondering, ‘Am I going to be able to go to college?’ ” he said during a news briefing.
In Baltimore, Camryn Carter is waiting to find out if he’ll get a full ride to the University of Maryland or face tens of thousands of dollars in student loans.
A top student and captain of his baseball and wrestling teams, Carter sees college as a step up in life. He thinks back to the times in the grocery store line when he had to put items back on the shelf because his mom couldn’t afford the bill. A college degree would give him the stability he didn’t always have, the 18-year-old said.
But when he looks at tuition, it’s intimidating . Along with Maryland, he’s also considering McDaniel College, a private school in Maryland. If he enrolls there, he expects to borrow almost $30,000 a year.
“I try to make the best decisions now so I can have a good future,” he said. “I’m a little nervous that things won’t work out. But I’m faithful.”
Leah Willingham contributed reporting from Charleston, West Virginia.
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .

Opinion At Columbia, excuse the students, but not the faculty
Paul Berman’s books include “A Tale of Two Utopias: The Political Journey of the Generation of 1968.”
My own experience as a Columbia University student radical under arrest took place in late April 1968 in the course of a massive campus uprising. The uprising was led, or at least initiated, by a radical social-democratic organization called Students for a Democratic Society, or SDS, together with the Student Afro-American Society, or SAS. And, since I was a stalwart of SDS, I spent a week camping out in the university president’s office and elsewhere, too, which I regarded as an exercise in insurrectionary citizenship. The authorities preferred to regard it as “criminal trespass.”
So I passed the night in the dismal Manhattan jail known as the Tombs, in the dankest of cells with a morose group of other criminal trespassers, among the nearly 700 of us who had been rounded up for arrest by the New York Police Department. And in the morning, when I returned to my campus dormitory, I discovered a further residue of the police raid, beyond the mass arrests, which consisted of large dark bloodstains coagulated on the walkway.
Those were large experiences, the bloodstains especially. And today those experiences cause me to observe Columbia’s new student rebellion through a lens of curious and strange emotions — amused at first, almost happy in a paternal spirit, for a deluded half-minute, and then, half a minute later, horrified, first on a simple level, in solidarity with Columbia’s harassed Jewish students, then on a deeper level.
Sympathetic adults used to say to us student radicals in 1968, “I agree with your ends but not with your means.” By this they meant to applaud our lofty ideals and to deplore our raucous and too-raucous riots and mayhem. But these days, I discover that my own views have taken an opposite turn. The raucous aspect of student protests seems to me only a secondary problem even now.
The students want to take over the lawn? It would not be so terrible, if some of them did not insist on persecuting Jews. But I recoil at what are plainly the ends.
In the weeks after my return to the Columbia campus from the Tombs, back in 1968, I raced around the quads helping to foment our mighty student strike. And, as I did so, one professor after another accosted me on the brick walkways to harangue me with lectures about politics and the past. Robert Gorham Davis, the respected literary critic, upbraided me repeatedly, and so did David Sidorsky, my philosophy professor, such that, after a while, I realized that I was in extended debate with those distinguished people. It turned out to be a debate about Germany in the 1930s.
The professors were haunted by Germany and its history, which might seem odd in the context of a student strike in 1968 in New York. But nothing was odd. In 1968, the defeat of the Nazis was only 23 years behind us, and the era of World War II and the catastrophe of the Jews had not yet definitively disappeared into the past — at least, not in the professors’ eyes. They wanted me to understand that Germany’s leftists in the 1930s had failed to understand Nazism’s danger. Foolish left-wing radicalism had helped undermine the German universities, which ought to have been a place of anti-Nazi resistance. They wanted me to understand, all in all, that what people think they are doing might not be what they are actually doing, and, in the name of high ideals, society might be weakened, and the worst of disasters might be brought about.
Today a memory of those walkway debates floods back on me because, in my own eyes, it has become impossible to mistake that, historically speaking, the era of World War II and the catastrophes of those times have still not come to an end. And in my eyes, it is impossible to mistake that, among the student radicals, things have taken a wrong turn.
The students — the students of today, the best of them — will defend themselves by explaining that, if they are occupying Columbia’s South Lawn and chanting and drumming, it is because extremist Israeli settlers are oppressing the West Bank Palestinians , which is a right and worthy point to raise. The students will emphasize that, in launching its riposte in Gaza, Israel’s army has ended up killing immense numbers of civilians , which is also incontestable. And the Israeli effort to crush Hamas has ended up imposing famine-like conditions and one dreadful thing after another, all of which is true and horrific and enraging.
And yet it has to be acknowledged that ultimately the central issue in the war is Hamas and its goal, which has lately seemed more realistic than anyone among Israel’s friends has imagined in recent years. The goal is and has always been the eradication of the Israeli state. And the radical students at Columbia, even if not all of them, have shown that, at some level, if not at every level, they understand and embrace the goal.
I grant that, when students chant “ from the river to the sea ,” some people will claim to hear nothing more than a call for human rights for Palestinians. The students, some of them, might even half-deceive themselves on this matter. But it is insulting to have to debate these points, just as it is insulting to have to debate the meaning of the Confederate flag.
The slogan promises eradication. It is an exciting slogan because it is transgressive, which is why the students love to chant it. And it is doubly shocking to see how many people rush to excuse the students without even pausing to remark on the horror embedded in the chants.
My experience as a student (and, briefly, political prisoner!) back in 1968 qualifies me, I think, to offer a constructive observation to Columbia’s administration. Minouche Shafik, the university president, has clamped down on more than 100 student radicals. In her congressional testimony , she explained that two of the more extreme professors have been rebuked (“spoken to”), and a third “will never teach at Columbia again,” as if dealing with three professors and the unruly students would solve the problem. But I worry about this.
If I were the autocratic overlord of Columbia University, I would be generous, despite everything, to the student radicals, even if they horrify me. How could I be otherwise, considering that, more than a half-century ago, I myself was not without what might be called moments of excess? I would amnesty the whole lot of them, except for anyone who seems genuinely a menace.
But I would turn in wrath on Columbia’s professors — not just the handful who sound crazy, but the professors who sound reasonable. These are the professors who have created a disastrous climate of opinion at Columbia. They are the professors who maintain that Hamas’s Oct. 7 massacre could plausibly be regarded as (I quote a statement by well more than 100 Columbia professors, some of them very brilliant people, a mere three weeks after the massacre) “just one salvo in an ongoing war between an occupying state and the people it occupies.” Or the massacre could be regarded “as an occupied people exercising a right to resist violent and illegal occupation.”
I would turn on those professors out of a belief that, at Columbia, appalling chants and occasional hints of violence from students on a tear are not ultimately the problem. Intellectual degeneration is the problem. Otherwise, the existential attacks on Jews, euphemistically advocated, would not be under discussion. I would turn in anger on the professors out of a belief, in short, that a university ought to be a place of resistance to the worst of ideas, and not a place of acquiescence.
That was my own lesson from 1968, hammered into me by thoughtful professors who remembered the 1930s, which I offer back to the Columbia administrators and the more levelheaded professors in 2024 exactly as I would if I myself were on the faculty right now, and I had run into bright and beloved students on the redbrick walks who had gone out of their minds, as students sometimes do.
- Opinion | Read Vladimir Kara-Murza’s Pulitzer Prize-winning commentary on Russia May 6, 2024 Opinion | Read Vladimir Kara-Murza’s Pulitzer Prize-winning commentary on Russia May 6, 2024
- Opinion | Lifelong lessons in coping with fear and humiliation May 6, 2024 Opinion | Lifelong lessons in coping with fear and humiliation May 6, 2024
- Opinion | The special counsel made a dangerous argument about Trump immunity May 1, 2024 Opinion | The special counsel made a dangerous argument about Trump immunity May 1, 2024

- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Where are the US college campus protests and what is happening?
Protest encampments have been set up on more than 80 campuses across the US over the Israel-Gaza war, with unrest flaring at some after police moved in to clear out protesters
Tensions are boiling over on university campuses across the US as student protests in support of Palestinians continue to grow, and are increasingly met with police violence despite students and faculty insisting the demonstrations have been peaceful.
The White House weighed in on the growing unrest on Thursday. “Dissent is essential for democracy,” Biden said. “But dissent must never lead to disorder.”
His words came after more than 100 protesters were arrested at UCLA on Thursday morning in a tense raid that followed several arrests across US campuses on Wednesday. Tensions are high after a weeks-long protest movement over the Israel-Gaza war that has put student demonstrators at odds with university leadership.
Demonstrators have set up encampments on more than 80 campuses across the US and are demanding that academic institutions sever financial ties with Israel or companies connected to the Israeli military’s war in Gaza.
The exact number of arrests remains unclear but is believed to have exceeded 1,300 since the start of the latest bout of protests two weeks ago, with more students being detained on Wednesday evening. Here’s a summary of the main campuses where arrests have taken place this week:
Columbia University, New York

The protest movement was sparked at New York’s Columbia University on 17 April when students pitched tents in the middle of campus and began rallying in support of Palestinians in Gaza .
Police first tried to clear the encampment a day later, when they arrested more than 100 people. That move motivated Columbia protesters to regroup.
On Tuesday night, hundreds of police entered Columbia’s campus at the request of the university president after protesters occupied an academic building. Less than two hours later, all protesters had been removed from Columbia.
The Manhattan district attorney Alvin Bragg said 282 arrests had been made at the Columbia and City University of New York, or Cuny campuses.
University of California, Los Angeles

Police cleared UCLA’s student encampment in a late-night operation, and arrested at least 132 pro-Palestine demonstrators early on Thursday morning . The school’s student newspaper said “ hundreds ” had been arrested, including students and members of faculty.
The raid came after UCLA was the site of some of the worst violence seen in the protests so far, when counter-protesters “forcefully attacked” a pro-Palestinian encampment on the campus on Tuesday night.
Fifteen people were injured during the UCLA confrontation , including one person who was hospitalised, while multiple news reports said security guards and law enforcement officials at the scene initially retreated or failed to intervene.
California’s governor, Gavin Newsom, called the violence “unacceptable” while the Los Angeles mayor, Karen Bass, called for a “full investigation” into the incident.

Emory University
Emory entered the spotlight last week after students there set up their own encampment; Atlanta police descended on the scene within hours of the tents getting pitched.
Faculty members were even caught on camera being arrested by Atlanta police in riot gear.
Police deployed teargas and beat students with batons to force them to disperse. At least 28 individuals – 20 of whom were Emory University community members – were arrested on 26 April.
In a widely shared video, the philosophy department chair, Noëlle McAfee, was seen being handcuffed by police. She asked the person recording to inform her colleagues that she’d been arrested.
CNN reported the economics professor Caroline Fohlin was also arrested and charged with battery against a police officer.
The university is now under federal investigation for anti-Muslim discrimination, per a recent Guardian report , with students claiming they have been doxxed, and called terrorists and Hamas-sympathizers.
George Washington University
In Washington DC, students pitched their tents on the school’s “University Yard” just over a week ago. The encampment is being overseen by DC Metropolitan police and has yet to be dismantled.
Nearby House republicans have visited the protest in an attempt to agitate the campus.
The far-right representative Lauren Boebert of Colorado told a crowd on Wednesday through a megaphone: “The mayor must step up and do something to clear this. This is not the summer of love and we are not bowing a knee to the terrorists who caused the riots and chaos is in our cities anymore.”
City University of New York
About 170 of the total 282 arrests were blocks away at the Cuny campus, reports said , with the total number of students involved unclear.
In a statement , the university said the calling in of police on Tuesday night was a “public safety approach [that] was a response to repeated acts of violence and vandalism”.
Video footage late on Tuesday showed officers forcing protesters to the ground and shoving others as they cleared the street and sidewalks. The City news site said an unspecified number of staff and faculty stayed home from work on Wednesday in solidarity with the protesters.
Fordham University, New York

Police officers in riot gear began arresting protesters on Wednesday evening, the New York Times reported, adding that demonstrators “did not appear to resist”.
The university’s chapter of Students for Justice in Palestine (SJP) had organized a small encampment in the Lowenstein Lobby building to urge Fordham to divest from Israel on Wednesday morning.
The university paper, the Fordham Ram , reported that all students participating in the encampment had been arrested and suspended by 6.30pm. The university said it had called in the police with the “utmost regret” but added that it had requested a police presence until 22 May.
The city’s pro-Palestine movement reassembled across four different locations on Wednesday evening, including at a joint Columbia and City universities gathering at the Cuny campus in Harlem.
University of Wisconsin, Madison
In Madison on Wednesday, a scrum broke out after police with shields removed all but one tent at the university’s encampment and shoved protesters. Four officers were injured, including a state trooper who was hit in the head with a skateboard, authorities said.
More tents sprang up within hours. More than 30 people were initially detained, but police said only four were charged, with battering law enforcement.
University of Arizona, Tucson

Police at the University of Arizona in Tucson fired “non-lethal” chemical weapons at protesters and arrested four people in the early hours of Wednesday, the Arizona Daily Star reported , to break up a protest camp that had been set up on Tuesday. At least one protester was hit with a rubber bullet.
The university’s president, Robert C Robbins, said police’s “minimal use” of pepper balls and rubber bullets in breaking up the protest was warranted and claimed that officers had been “assaulted with projectiles”.
Student leaders disagreed with the police tactics, saying: “the use of force against peaceful students has never and will never deserve to have a place on our campus”.
University of Texas, Dallas
The University of Texas in Dallas confirmed that 17 protesters had been arrested on its campus as of Wednesday evening, after police moved in at the request of university officials.
According to local media, the police operation involved dozens of state troopers in riot gear. The entire encampment was dismantled within about 20 minutes and additional law enforcement remained on the campus until about 6pm.
About 100 protesters are reportedly continuing demonstrations on another part of the campus.
Another Gaza solidarity encampment protest was set up on Thursday in UT Arlington.
The school’s flagship university, the University of Texas, Austin, has also seen two police crackdowns since a student encampment was set up last week, which has since been dismantled by police and security.
At least 79 people were arrested on Monday and sent to Travis county jail.
Tulane University in New Orleans, Louisiana

Fourteen people including two students were arrested early on Wednesday when police were called in to clear a two-day encampment, the Tulane Hullabaloo news site reported. University officials said they supported “free speech and the freedom to protest” but were opposed to trespassing, hate speech and antisemitism.
- US campus protests
- US universities

Israelis voice sadness and defiance over Gaza protests on US campuses

Manhattan DA investigating after officer fired gun inside Columbia University - as it happened

UCLA Gaza protesters in tense standoff with police – video

Protests continue at university campuses across US – in pictures

Thursday briefing: How Gaza protests have gripped American universities

Campus protests: UCLA students in standoff with police as demonstrations spread across US

Columbia University faculty ‘horrified’ by mass arrests of student protesters

‘I was lying on the ground beside a wall of cops’: student photographers’ best images of the campus protests
Most viewed.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Biden forgives more than $6 billion in loans for 317,000 Art Institutes students

Student loan borrowers and advocates gather for the People's Rally To Cancel Student Debt During The Supreme Court Hearings On Student Debt Relief on February 28, 2023 in Washington, DC. Jemal Countess/Getty Images for People's Rally hide caption
Student loan borrowers and advocates gather for the People's Rally To Cancel Student Debt During The Supreme Court Hearings On Student Debt Relief on February 28, 2023 in Washington, DC.
President Biden announced on Wednesday that the White House would forgive more than $6.1 billion on student loan debt for 317,000 borrowers who attended The Art Institutes, a private art school system in the U.S. that shuttered last year.
The latest on student debt relief — and how young voters are feeling about it
"This institution falsified data, knowingly misled students, and cheated borrowers into taking on mountains of debt without leading to promising career prospects at the end of their studies," said Biden in a statement.
"We will never stop fighting to deliver relief to borrowers, hold bad actors accountable, and bring the promise of college to more Americans," the President added.
The relief will apply to students who were enrolled in the school system between January 1, 2004 and October 16, 2017, during which the U.S. Department of Education found that The Art Institutes made "pervasive and substantial misrepresentations to prospective students about postgraduation employment rates, salaries, and career services during that time," according to a statement from the DOE.

A $95.5 million settlement in a for-profit college case
The DOE will immediately begin notifying borrowers who are eligible for forgiveness, including those who have not formally applied for borrower defense. Previous payments made for student loans will also be refunded. The total available averages out to about $19,000 per borrower.
This latest round of student loan forgiveness brings the total approved by the Biden Administration to almost $160 billion for nearly 4.6 million borrowers, an average of nearly $35,000 per student.
- student loan debt
- student loans
- student loan
- biden administration
Advertisement
Supported by
A Small Campus in the Redwoods Has the Nation’s Most Entrenched Protest
Pro-Palestinian protesters have occupied the administration building at California State Polytechnic University, Humboldt, for the past week and forced a campus closure until May 10.
- Share full article

By Jonathan Wolfe
Reporting from Arcata, Calif.
When university administrators across the nation worry about the potential fallout from campus protests, they may have Siemens Hall in mind.
The building at California State Polytechnic University, Humboldt, includes the campus president’s office and has been occupied for a week by pro-Palestinian protesters who barricaded themselves inside and fought off an early attempt by the police to remove them. Protesters have since tagged walls and renamed it “Intifada Hall” by ripping off most of the signage on the brick exterior.
Inside, they painted graffiti messages like “Time 2 Free Gaza,” “Pigs Not Allowed,” and “Land Back,” according to a video posted by the local news site Redheaded Blackbelt . They occupied and defaced the office of the president, Tom Jackson Jr., spraying “Blood On Your Hands” across one framed wall hanging and “I Will Live Free or Die Trying” on his door.
The school, situated more than 275 miles north of San Francisco among the ancient coastal redwoods that drip with fog mist, is the site of the nation’s most entrenched campus protest. It has gone well beyond the encampments seen on many college quads elsewhere; at Cal Poly Humboldt, protesters took over the power center of the campus and have rejected increasingly desperate entreaties from officials for them to vacate the premises.
The university has shut down the entire campus, first for a couple days, then a week and now through May 10, one day before its scheduled commencement. After the Siemens Hall takeover, protesters set up dozens of tents on patches of grass around the hall, and demonstrators took over a second building to use its bathrooms and hold meetings. University officials estimate the damage to be in the millions of dollars.
Nelson Hall
On Tuesday, police officers
arrested protesters and
ended the occupation
of two buildings on campus.
Source: Aerial image from Nearmap
By Leanne Abraham
To those outside Northern California, the show of force at Cal Poly Humboldt, in the college town of Arcata, has been a surprising turn in a region more typically associated with a hippie pacifism and marijuana farms. But beneath the good-vibes image, locals say, a culture of protest and resentment toward authority has percolated at the 6,000-student campus.
“Because of the long history of activism, we recognize that putting a tent out in front of the building may not be as effective of a statement for a student protest,” said Anthony Silvaggio, who is a professor and the chair of the school’s sociology department and was a student at the university in the 1990s.
The majestic redwoods in the region draw tourists from across the world; nearby, visitors can drive through a tree with a 21-foot diameter. The forests also have satisfied the thirst for lumber in the growing West as far back as the early Gold Rush days when San Francisco became a boomtown.
The natural beauty and the timber industry have long been at odds, however. The region was an early battleground in the “timber wars,” in which environmentalists fought against logging companies to prevent the destruction of old growth forests across the Pacific Northwest in the 1980s and 1990s. Perhaps the most famous protest of that era occurred in Humboldt County, where the activist Julia Butterfly Hill lived for 738 days in a California redwood that she named Luna.
Cal Poly Humboldt had modest beginnings, opening in 1914 as the Humboldt State Normal School to educate schoolteachers, starting with a graduating class of 15 women. Its academic mission expanded over the next century to offer a breadth of subjects, including forestry. (The school mascot is the Lumberjacks.)
The campus is isolated from most of California, requiring at least a five-hour drive to reach San Francisco or Sacramento. Only 2 percent of undergraduates are Jewish, according to Hillel International , and the campus does not seem to have an active Jewish organization.
Pro-Palestinian protesters have made several demands since taking over Siemens Hall on April 22, including that the school disclose its holdings with Israel, divest from companies profiting from military action in Gaza, cut ties with Israeli universities and that charges against three students who were arrested the first night be dropped. They also want the university to call for a cease-fire in the Israel-Hamas war. More than 34,000 Palestinians have been killed in the conflict, according to the Gaza health ministry.
Cal Poly Humboldt leaders replied point by point, disclosing the school’s holdings and collaborations with Israel in an attempt “to make a good faith effort to respond.” By Friday, however, administrators had seemingly had enough. They told building occupiers that they had a brief “opportunity to leave with a guarantee of no immediate arrest.” A spokeswoman for the university said several protesters left the building, but protesters disputed that there had been any desertion in their ranks.
On Sunday night, the president’s team again asked them to “leave the campus peacefully now,” but this time with no offer of immunity.
The university said in a statement that the protest had “nothing to do with free speech or freedom of inquiry” and called the protests “lawless behavior” that harmed students, damaged the school’s reputation and “drained resources from the accomplishment of our core educational purpose.”
Demonstrators see it differently.
“The graffiti, the destruction of property, all of that is a poetic symbolism to me, because the ultimate overall point is that people are more valuable than property,” said Cozy Hunter, 32, a graduate student in social psychology academic research.
In 2019, Mr. Jackson became the president at Humboldt after having served the same role at Black Hills State University in South Dakota. Mr. Jackson, a veteran of the U.S. Coast Guard Reserve, was instrumental in transforming the campus into a polytechnic university, one of three in California, that places an added emphasis on STEM disciplines. The revamp came with $458 million from the state, a welcome infusion of cash at a school that was at risk of closure as enrollment declined over the years.
“I’m an engineer, so when he brought in the money and turned this into a Cal Poly, that was really cool because we had done cuts for years,” Jim Graham, a professor of geospatial science, said.
While previous campus presidents engaged with student protesters and generally allowed sit-ins, Mr. Jackson was more distant and took a harder-line approach, Mr. Graham said.
In November, after the university discovered that some students were living in their vehicles on campus because they could not afford housing, the school ordered them to move out or face disciplinary action . In 2022, Mr. Jackson apologized for comments he made during a welcome address that some saw as an attempt to hide reports of sexual assault in the campus community.
“That was sort of the beginning of him totally disappearing,” said Cindy Moyer, the chair of the university’s department of dance, music and theater. “He does not appear to take controversy well.”
Mr. Jackson was unavailable for comment, according to a spokeswoman. But last Friday, he told the local Times-Standard newspaper that the protesters were “criminals” and did not rule out sending in police at some point. “Everything is on the table,” he said.
Bob Ornelas, who is a former mayor of Arcata and a graduate of the university, said that the response to the protest in the community, which is largely liberal, has been “a really mixed bag.” Mr. Ornelas, 70, said many residents are sympathetic but also anxious about the effects on local business and concerned about potential divisiveness in the community.
Since the protests started, the 32-room Hotel Arcata has lost about $1,000 per day to cancellations, whether for special events or rooms for the families of graduates, said Sherrie Potter, 55, the hotel’s general manager. The university has not canceled commencement, though many wonder how it will still take place.
“I understand where they’re coming from, I do,” Ms. Potter said of the protesters. “But I’m torn. I also see how this is hurting the college and the businesses around it, including our own.”
Protesters said they initially wanted to stage a sit-in and bring their concerns directly to administrators. When the local police showed up in riot gear, they feared for their safety, and began barricading themselves inside, they said. Most refused to give their names because they feared retribution from the university and said they did not want to be doxxed.
“The rate of acceleration, and the escalation, was so shockingly high,” said Rouhollah Aghasaleh, an assistant professor in education who has tried to facilitate communication between protesters and the university.
Over the weekend, as the likelihood of a police incursion increased, protesters beefed up the barricades that blocked off their encampment with chain-link fences, rows of chairs and large sheets of glass. In a nod to the past environmental protests in the area, they installed a “tree sit” about 60 feet up in a redwood near the quad, with a wooden platform that had the phrases “Free Gaza” and “End Empire.” The protester manning the perch — who would not give a name, other than “Ripples” — settled in with a mattress pad, sleeping bag and crank radio.
“A tree sitter actually indicates that there’s a desire for a much longer occupation,” Ms. Hunter, the graduate student, said. “Because a tree sitter — especially in this region after Julia Butterfly Hill — is just like, ‘Oh, I’m down to sit for Palestine until there is complete U.S. divestment.’ That’s essentially what that move means.”
Jose Quezada contributed reporting from Arcata, Calif., and Shawn Hubler contributed from Sacramento.
Jonathan Wolfe is a senior staff editor on the newsletters team at The Times. More about Jonathan Wolfe
Our Coverage of the U.S. Campus Protests
News and Analysis
Columbia : After weeks of student protests, Columbia University announced that it would be canceling its main commencement ceremony .
UChicago : The University of Chicago, which says that free speech is sacred, has allowed protest encampments. But they have also disrupted campus life, and the school’s leaders want the tents down .
U.S.C.: The Los Angeles Police Department and campus police removed a pro-Palestinian encampment for the second time at the University of Southern California.
Outside Agitators: Officials in New York City have blamed “external actors” for escalating demonstrations at Columbia, but student protesters reject the claim .
Clashes at U.C.L.A.: A New York Times examination of more than 100 videos from clashes at the University of California, Los Angeles, shows how counterprotesters provoked the violence .
Reactions Abroad: The world is watching what is happening on American campuses with shock, pride, relish and alarm. Here is a selection of views from outside the United States .
A Spotlight on Student Journalists: Columbia’s radio station and other student-led news outlets have provided some of the most detailed coverage of the turmoil engulfing campuses.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight ...
You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you've got SAT studying to do. It's just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you're reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time. 5.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students' learning. I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt.
The challenge: Managing time and staying organized. Some kids struggle with keeping track of time and making a plan for getting all of their work done. That's especially true of kids who have trouble with executive function. Try creating a homework schedule and set a specific time and place for your child to get homework done.
Build Persistence and Determination: By working on problems at home, students develop key skills such as persistence, problem-solving, and determination. Develop Useful Habits: Regular homework practice helps students develop discipline, time management skills, and a strong work ethic essential for academic success and beyond.
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students.
Higher-achieving students — those who may have more homework — are at particular risk for stress-related health issues including sleep deprivation, weight loss, stomach problems and headaches. Source: Stanford University, " Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ," 2014.
Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath. Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services) Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems. This site allows you to take a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept.
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
5) Photomath. Photomath is, as you might have guessed, a site for math homework help. Like other homework help websites, Photomath allows students to take a picture of a problem and receive an instant, step-by-step solution. Included along with the solution is an explanation of relevant concepts and formulas, plus videos covering mathematical ...
3 Ways to Create More Meaningful Math Homework. 1. Think quality over quantity. The National Council for Teachers of Mathematics Homework page of tips for teachers suggests, "Only assign what's necessary to augment instruction. If you can get sufficient information by assigning only five problems, then don't assign fifty.". Worksheets ...
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills, forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking.
Homework is perceived by students as more challenging, more important and, surprisingly, even less boring than time spent in class (excepting tests). Although homework is associated with higher levels of time pressure, it generates less desire to do something else than time spent in class. Thus, the "class time problem" seems to have ...
Homework also helps students develop key skills that they'll use throughout their lives: Accountability. Autonomy. Discipline. Time management. Self-direction. Critical thinking. Independent problem-solving. The skills learned in homework can then be applied to other subjects and practical situations in students' daily lives.
Homework problems prevent students with ADHD from reaching their full academic potential and from displaying their true ability. Unfortunately, homework problems also tend to be a leading cause of conflict and disagreement between parents and their children with ADHD. They often argue about what work teachers assigned, when work is due, and how ...
A 24/7 free homework AI tutor that instantly provides personalized step-by-step guidance, explanations, and examples for any homework problem. Improve your grades with our AI homework helper!
11. This letter is missing something. Software engineers enjoy solving problems and building things with computers. If a typical homework problem seems like a boring drudge, or 'too hard' for you, you're going to hate working as a software engineer. Software engineers need to learn new things all the time.
America is in knots over the foolishness — or worse — of its campus protesters. But it is adults who are making the biggest dunces of themselves. The role of grown-ups facing student unrest is ...
Another student who attended a different event for admitted students, this one on April 21, said that every administrator she heard speak paid lip service to the school's long history of protest ...
The bungled rollout of a new federal student aid form has left millions of students in limbo and some wondering if their college dreams will survive. Menu. Menu. World. U.S. Election 2024 ... Connecticut, the FAFSA problems threaten to undermine the promise of higher education. To her, college is a chance to seize the opportunities that weren ...
At Columbia, excuse the students, but not the faculty. By Paul Berman. April 26, 2024 at 7:58 p.m. EDT. Student protesters at Columbia University in New York on April 24, 1968. (Jacob Harris/AP) 8 ...
The protest movement was sparked at New York's Columbia University when students pitched tents in the middle of campus and began rallying in support of Palestinians in Gaza on 17 April. Police ...
President Joe Biden's support for the Israeli military offensive in Gaza mixed with student anger over police crackdowns on anti-war campus protests are complicating the work of Democratic youth ...
Jemal Countess/Getty Images for People's Rally. President Biden announced on Wednesday that the White House would forgive more than $6.1 billion on student loan debt for 317,000 borrowers who ...
The school, situated more than 275 miles north of San Francisco among the ancient coastal redwoods that drip with fog mist, is the site of the nation's most entrenched campus protest. It has ...