
- Case Studies
- Free Coaching Session

Production Plan in Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide to Success
Last Updated:
February 26, 2024

In any business venture, a solid production plan is crucial for success. A production plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the steps, resources, and strategies required to manufacture products or deliver services efficiently. By carefully crafting a production plan within a business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure optimal utilisation of resources, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of creating an effective production plan in a business plan , exploring its key components, strategies, and the importance of aligning it with overall business objectives .
Key Takeaways on Production Plans in Business Planning
- A production plan : a detailed outline that guides efficient product manufacturing or service delivery.
- Importance of a production plan : provides a roadmap for operations, optimises resource utilisation, and aligns with customer demand.
- Key components : demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance.
- Strategies : lean manufacturing, JIT inventory, automation and technology integration, supplier relationship management, and continuous improvement.
- Benefits of a well-executed production plan : improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced product quality, and increased profitability.

What is a Production Plan?
A production Seamless Searches plan is a detailed outline that specifies the processes, resources, timelines, and strategies required to convert raw materials into finished goods or deliver services. It serves as a blueprint for the entire production cycle, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. The production plan considers factors such as demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, and quality assurance to ensure efficient operations and optimal customer satisfaction.
Why is a Production Plan Important in a Business Plan?
The inclusion of a production plan in a business plan is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, it provides a clear roadmap for business operations, helping entrepreneurs and managers make informed decisions related to production processes. A well-developed production plan ensures that resources are utilised efficiently, minimising wastage and optimising productivity.
Additionally, a production plan allows businesses to align their production capabilities with customer demand. By forecasting market trends and analysing customer needs, businesses can develop a production plan that caters to current and future demands, thus avoiding overstocking or understocking situations.
Furthermore, a production plan helps businesses enhance their competitive advantage. By implementing strategies such as lean manufacturing and automation, companies can streamline their production processes, reduce costs, improve product quality, and ultimately outperform competitors.
Key Components of a Production Plan
To create an effective production plan, it is crucial to consider several key components. These components work together to ensure efficient operations and successful fulfilment of customer demands. Let's explore each component in detail.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of production planning. By analysing historical data, market trends, and customer behaviour, businesses can predict future demand for their products or services. Accurate demand forecasting allows companies to optimise inventory levels, plan production capacity, and ensure timely delivery to customers.
One approach to demand forecasting is quantitative analysis, which involves analysing historical sales data to identify patterns and make predictions. Another approach is qualitative analysis, which incorporates market research, customer surveys, and expert opinions to gauge demand fluctuations. By combining both methods, businesses can develop a robust demand forecast, minimising the risk of underproduction or overproduction. Utilising a free notion template for demand forecasting can further streamline this process, allowing businesses to organise and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data efficiently in one centralised location.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning involves determining the optimal production capacity required to meet projected demand. This includes assessing the production capabilities of existing resources, such as machinery, equipment, and labour, and identifying any gaps that need to be addressed. By conducting a thorough capacity analysis, businesses can ensure that their production capacity aligns with customer demand, avoiding bottlenecks or excess capacity.
An effective capacity plan takes into account factors such as production cycle times, labour availability, equipment maintenance, and production lead times. It helps businesses allocate resources efficiently, minimise production delays, and maintain a consistent level of output to meet customer expectations.
Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is crucial for a successful production plan. It involves balancing the cost of holding inventory with the risk of stockouts. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, businesses can reduce carrying costs while ensuring that sufficient stock is available to fulfil customer orders.
Inventory management techniques, such as the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model and Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory system, help businesses strike the right balance between inventory investment and customer demand. These methods consider factors such as order frequency, lead time, and carrying costs to optimise inventory levels and minimise the risk of excess or insufficient stock.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation plays a pivotal role in a production plan. It involves assigning available resources, such as labour, materials, and equipment, to specific production tasks or projects. Effective resource allocation ensures that resources are utilised optimally, avoiding underutilisation or overutilisation.
To allocate resources efficiently, businesses must consider factors such as skill requirements, resource availability, project timelines, and cost constraints. By conducting a thorough resource analysis and implementing resource allocation strategies, businesses can streamline production processes, minimise bottlenecks, and maximise productivity.
Quality Assurance
Maintaining high-quality standards is essential for any production plan. Quality assurance involves implementing measures to monitor and control the quality of products or services throughout the production process. By adhering to quality standards and conducting regular inspections, businesses can minimise defects, ensure customer satisfaction, and build a positive brand reputation.
Quality assurance techniques, such as Total Quality Management (TQM) and Six Sigma , help businesses identify and rectify any quality-related issues. These methodologies involve continuous monitoring, process improvement, and employee training to enhance product quality and overall operational efficiency.
In addition to the core components of a production plan, it's also important for businesses to consider the broader aspects of their business strategy, including marketing and advertising. Understanding the costs and returns of different marketing approaches is crucial for comprehensive business planning. For instance, direct response advertising costs can vary significantly, but they offer the advantage of measurable responses from potential customers. This type of advertising can be a valuable strategy for businesses looking to directly engage with their target audience and track the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Strategies for Developing an Effective Production Plan
Developing an effective production plan requires implementing various strategies and best practices. By incorporating these strategies into the production planning process, businesses can optimise operations and drive success. Let's explore some key strategies in detail.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a systematic Seamless Searches approach aimed at eliminating waste and improving efficiency in production processes. It emphasises the concept of continuous improvement and focuses on creating value for the customer while minimising non-value-added activities.
By adopting lean manufacturing principles, such as just-in-time production, standardised work processes, and visual management, businesses can streamline operations, reduce lead times, and eliminate unnecessary costs. Lean manufacturing not only improves productivity but also enhances product quality and customer satisfaction.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory is a strategy that aims to minimise inventory levels by receiving goods or materials just when they are needed for production. This strategy eliminates the need for excess inventory storage, reducing carrying costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
By implementing a JIT inventory system, businesses can optimise cash flow, reduce storage space requirements, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. However, it requires robust coordination with suppliers, accurate demand forecasting, and efficient logistics management to ensure timely delivery of materials.
Automation and Technology Integration
Automation and technology integration play a crucial role in modern production planning. By leveraging technology, businesses can streamline processes, enhance productivity, and reduce human error. Automation can be implemented in various aspects of production, including material handling, assembly, testing, and quality control.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of effective production planning. It involves regularly evaluating production processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance efficiency and quality.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can drive innovation, optimise resource utilisation, and stay ahead of competitors. Techniques such as Kaizen, Six Sigma, and value stream mapping can help businesses identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and streamline production workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the role of a production plan in business planning.
A1: A production plan plays a crucial role in business planning by providing a roadmap for efficient production processes. It helps align production capabilities with customer demand, optimise resource utilisation, and ensure timely delivery of products or services.
How does a production plan affect overall business profitability?
A2: A well-developed production plan can significantly impact business profitability. By optimising production processes, reducing costs, and enhancing product quality, businesses can improve their profit margins and gain a competitive edge in the market.
What are the common challenges faced in production planning?
A3: Production planning can present various challenges, such as inaccurate demand forecasting, capacity constraints, supply chain disruptions, and quality control issues. Overcoming these challenges requires robust planning, effective communication, and the implementation of appropriate strategies and technologies.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term production planning?
A4: Short-term production planning focuses on immediate production requirements, such as daily or weekly schedules. Long-term production planning, on the other hand, involves strategic decisions related to capacity expansion, technology investments, and market expansion, spanning months or even years.
How can a production plan be adjusted to accommodate changes in demand?
A5: To accommodate changes in demand, businesses can adopt flexible production strategies such as agile manufacturing or dynamic scheduling. These approaches allow for quick adjustments to production levels, resource allocation, and inventory management based on fluctuating customer demand.
In conclusion, a well-crafted production plan is essential for business success. By incorporating a production plan into a comprehensive business plan, entrepreneurs can optimise resource utilisation, meet customer demands, enhance product quality, and drive profitability. Through effective demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance, businesses can streamline production processes and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Related Articles:
Client Success!! Watch THIS >>>
Client Success - Case Study

© 2016 - 2024 Robin Waite. All rights reserved.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Stage of Development Section
Production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Keeping focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and disposed.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.
The Physical Plant
Describe the type, site, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory .
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystalize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.
Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance's newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!
Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a manufacturing company can be an exciting but challenging endeavor. To ensure success, you need a solid business plan that covers all the essential aspects of your operations. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Companies comes in!
Our template provides a comprehensive framework for outlining your company's goals, conducting market analysis, projecting finances, and strategizing your operations. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be able to:
- Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and objectives
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand your target audience and competitors
- Develop financial projections and budgets to secure funding and attract investors
- Create operational strategies to optimize production, logistics, and quality control
Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting out, our Business Plan Template will guide you through the process of building a successful manufacturing company. Don't miss out on the opportunity to turn your vision into reality—get started with ClickUp today!
Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company Benefits
Creating a solid business plan is crucial for success in the manufacturing industry. By using the Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company, you can:
- Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and goals
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to identify target customers and competitors
- Develop a comprehensive financial plan, including revenue projections and cost analysis
- Outline your manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and quality control measures
- Present a professional and well-structured document to potential investors and lenders
- Guide strategic decision-making and ensure alignment with your long-term objectives
- Monitor and track progress towards your business milestones and objectives
Main Elements of Manufacturing Company Business Plan Template
When it comes to creating a comprehensive business plan for your manufacturing company, ClickUp has you covered with its Business Plan Template. Here are the main elements you'll find in this template:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of different sections of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add important details to your business plan using custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section, allowing you to easily organize and categorize information.
- Custom Views: Access different perspectives of your business plan using views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, making it easy to navigate and present your plan effectively.
- Document Collaboration: Collaborate with your team in real-time using ClickUp's Docs feature to work together on your business plan.
- Task Management: Break down your business plan into actionable tasks, assign them to team members, set due dates, and track progress using ClickUp's powerful task management features.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
If you're looking to create a business plan for your manufacturing company, follow these 6 steps using ClickUp's Business Plan Template:
1. Define your company's mission and vision
Start by clearly defining the mission and vision of your manufacturing company. What do you aim to achieve and how do you plan to do it? This will serve as the guiding principles for your business plan.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to outline your company's mission and vision statements.
2. Conduct market research
Thorough market research is essential to understand your target audience, competitors, and industry trends. Identify your niche, analyze customer needs, and assess the competitive landscape. This will help you position your manufacturing company effectively.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to compile and analyze market data, including customer demographics, competitor analysis, and industry trends.
3. Develop your product offerings
Outline the products and services your manufacturing company will offer. Determine the unique selling points of your offerings and how they address customer needs. Consider factors such as pricing, quality, and delivery timelines.
Use tasks in ClickUp to create a product development plan and assign tasks to team members responsible for designing, manufacturing, and testing the products.
4. Create a marketing and sales strategy
Define your marketing and sales strategies to promote your manufacturing company. Identify the channels and tactics you will use to reach your target audience. This may include digital marketing, trade shows, partnerships, or direct sales.
Use Goals in ClickUp to set specific marketing and sales objectives, such as lead generation targets or revenue goals.
5. Establish operational processes
Develop a plan for your manufacturing processes, including procurement, production, quality control, and logistics. Define the roles and responsibilities of your team members and ensure smooth coordination across departments.
Use Automations in ClickUp to streamline your operational processes by automating repetitive tasks and setting up notifications for key milestones.
6. Create financial projections
Project your financials, including revenue, expenses, and cash flow projections for the next few years. Consider factors such as production costs, pricing, sales volume, and market demand. This will help you assess the viability and profitability of your manufacturing company.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to track and visualize your financial projections, allowing you to monitor your company's performance and make informed decisions.
By following these steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be well-equipped to create a comprehensive and effective business plan for your manufacturing company.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
Entrepreneurs and business owners in the manufacturing industry can use the Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company to create a comprehensive plan for their business.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a solid business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize the different sections of your business plan, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Financial Projections, and Operational Strategies.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and visualize the timeline for completing each section of your business plan.
- Use the Business Plan View to have a comprehensive overview of your entire plan, with all the sections and details in one place.
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide you with step-by-step instructions and tips on how to effectively use the template and create a successful business plan.
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional information and track important details.
- Update statuses and custom fields as you make progress and receive feedback from stakeholders.
- Monitor and analyze your business plan to ensure it aligns with your goals and attracts investors.
- Business Plan Template for Distance Learning
- Business Plan Template for Medication Errors
- Business Plan Template for Little Caesars
- Business Plan Template for Technology
- Business Plan Template for Gym Owners
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors
How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers If your company makes things, you'll want to detail the manufacturing production process.
By Eric Butow • Oct 27, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 8 / 11 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 5: Organizing Operations and Finances series.
Companies that make things have certain characteristics that set them apart from others, including retailers and service firms. They take raw materials and labor and transform them into sellable products. Although they may also distribute the products and sell directly to customers (thus involving the retail and service aspects of operations), most manufacturers concentrate on the production end and farm out the retail and service to other firms.
Process Points
The lead actor in manufacturing is the process of production. Product development, marketing, and distribution play essential roles, but the production process sets manufacturers apart from all other enterprises. And the better your production process, the better a manufacturer you will be. It's the star that leads to your company's success.
Related: How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
A manufacturing production process consists of several components. One step is usually fabrication, or the making of products from raw materials. There is also assembly of components, testing, and inspection of finished goods.
Manufacturing processes can become highly detailed, as is the case with the many parts found in mobile technology. If you're an operations-minded entrepreneur, you may revel in these details. But control your enthusiasm for such details when writing a business plan. Stick to the critical processes that are essential to your production or give you a unique competitive advantage.
These include:
- Personel and materials
- Equipment and Facilities
The following manufacturing company checklist might help organize your company's operation details.
- Marketing plan completed
- Staffing completed (or staffing plan completed)
- Organization chart completed
- Product plan completed
- Basic manufacturing operations listed in sequence
- Raw materials purchased
- Equipment obtained
- Labor skills available and assigned
- Timelines and deadlines assigned
- Potential roadblocks identified
- Managerial controls in place
- Sales policies reviewed
- Customer relations policies outlined
- Service delivery policies developed
- Administering monitoring and control policies
- Follow-up procedures checked
Your checklist will most likely differ depending on your business. A small contractor, for example, makes things but is less complex, so might have a checklist like this:
- Develop work schedule
- Set up equipment
- Acquire necessary materials
- Monitor work schedule
Be sure to tailor your checklist to your business's requirements.
Related: What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
manufacturing business plan example
The U.S. manufacturing industry has been a linchpin of the nation’s economic development, tracing its roots back to the Industrial Revolution. From humble artisan workshops, the U.S. manufacturing sector has evolved into sophisticated, technology-driven enterprises, marked by continual growth propelled by innovation, automation, and a steadfast commitment to producing top-quality goods.
Noteworthy among the leaders in this sector are manufacturing giants such as General Electric (GE), boasting diverse manufacturing interests spanning aviation, healthcare, power, and renewable energy. Boeing , a major player in aerospace and defense, is complemented by General Motors and Ford Motor Company, two automotive behemoths. Procter & Gamble (P&G) extends its influence in the consumer goods realm, while Johnson & Johnson takes center stage in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer goods. Caterpillar , IBM , 3M , and Honeywell International further enrich the manufacturing landscape with expertise in construction, technology, and diverse product offerings.
In business planning for manufacturing enterprises, meticulous strategies are imperative. Developing a robust manufacturing business plan involves careful consideration of factors such as production processes, supply chain management, and market positioning. Such plans serve as blueprints for success, encompassing key elements like quality control and financial projections . Recognizing the significance of a comprehensive business plan for manufacturing, companies employ various manufacturing business model and manufacturing plan examples tailored to their specific industry needs.
Business Plan for Manufacturing
A well-crafted manufacture business plan serves as the cornerstone for any manufacturing enterprise, offering a strategic roadmap for navigating the dynamic and competitive terrain of the production and industry landscape. While recognizing that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, using manufacturing business plan example becomes crucial for navigating the process effectively..
Manufacturing business plans take many forms including advanced manufacturing . The manufacturer business model is shifting as new production processes introduce updated deadlines and expectations.
How Technology is Transforming Production Business Plans
Crafting a quality business plan for a manufacturing company requires a strategic approach that integrates technology and business goals. Here are the key components:
Digital Twin Technology
By integrating digital twin technology into a business plan for production company, simulation and prototyping become integral components. This approach enables virtual testing before physical production, accelerating development timelines while ensuring cost-effective and high-quality outcomes.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Real-time monitoring powered by IoT sensors forms a cornerstone in manufacturing plans. This facilitates data-driven decision-making, optimizing performance, predicting maintenance needs, and upholding stringent quality control standards.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML )
The integration of AI and ML algorithms is paramount for predictive analytics and quality control. These technologies analyze production data, predict equipment failures, and guarantee the production of high-quality goods.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation elevate production line efficiency, reducing labor costs and enhancing precision. Making business plan revolves around embracing these technologies to streamline processes.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Through 3D printing, you can achieve intricate designs with precision. Leveraging nanotechnology enhances material properties at a molecular level, allowing your manufacturing business to surpass expectations in strength, weight, and durability.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies play a crucial role in training and maintenance. This can enhance employee skills and troubleshoot issues efficiently, contributing to the overall success of manufacturing operations.
By incorporating these technological advancements into your ultimate business plan for manufacturing business, you are positioned for sustained success in the digital age.

Manufacturing Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Manufacturing Business Plan Template
If you want to start a Manufacturing business or expand your current Manufacturing company, you need a business plan.
The following Manufacturing business plan template gives you the key elements to include in a winning Manufacturing business plan.
You can download our business plan template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Below are links to each of the key sections of a sample manufacturing business plan. Once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors.
I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan
Comments are closed.
Manufacturing Business Plan Home I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan

- See all articles
- Business tips
- Inventory management
- Manufacturing
- Product updates
Strategies for manufacturing: How to plan for the future
James humphreys.
Senior Content Manager
The reality is that very few manufacturing businesses will be successful without a solid strategy in place. But why are strategies for manufacturing important? How have they evolved, and what manufacturing strategies are easy for companies to implement?
In this article, we’ll answer all these questions and more.
What is a manufacturing strategy?
A manufacturing strategy has been previously defined as “a long-range plan to use the resources of the manufacturing system to support the business strategy and, in turn, meet the business objectives. (Cimorelli and Chandler, 1996).
The connection that binds all the eras together is manufacturing strategy. Whether it’s a humble artisan in a side-street pottery shop or a technological wiz-kid wanting to build a smart factory, they both need a manufacturing strategy.
As already identified, strategies for manufacturing have been around for many years.
The definition of a what is a manufacturing strategy has also been around for a long time. According to Hayes and Wheelwright, 1984 , it is “a sequence of decisions that, over time, enables a business unit to achieve the desired manufacturing structure, infrastructure, and set of specific capabilities.”
Nowadays, manufacturing strategy is often intertwined with a company’s digital strategy, with the tactical management of production and technology at the heart of everything a company achieves.
As was noted by Gündüz Ulusoy back in 2003, formulating a marketing strategy requires making three strategic choices in three key areas: Competitive priorities, manufacturing objectives, and action plans.
Competitive priorities include choices on:
- Quality levels
- Reliability
- Design change
- Deliveries
- New products
Manufacturing objectives involve decision-making on:
- Unit costs
- Market share
- Profitability
- Product development time
And action plans include making decisions about:
- Production
- Energy saving
- Employee empowerment
- Staff training
Once these decisions have been made and a company’s priorities have been identified, an overarching marketing strategy can be formulated.
The history of manufacturing strategy
Whether you are a B2B (business-to-business) or a D2C (direct-to-consumer) manufacturing company , the chances are high that you have a structured manufacturing process in place. Hopefully, this relates back to your manufacturing strategy. This relationship between process and strategy has existed for hundreds of years.
The art of manufacturing has humble beginnings. Way before industrialization was conceptualized, skilled artisans worked to produce commodities. They relied on their craftmanship and secrecy to ensure that their products were in demand and couldn’t be copied.
The first example of a manufacturing strategy was probably when forward-thinking artisans realized they could sub-contract their work to others, thus producing more products and increasing their profits.
Manufacturing was transformed dramatically and definitively in the 18th century during the Industrial Revolution. The invention of machines that could do the work on a mass scale meant that industries such as glassmaking, mining, textiles , and agriculture could produce much more on a much cheaper scale. The mass production concept followed, bringing us to where we are today.
Interestingly, we are on the brink of another transformation in the industrial sector, with the birth of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, 4IR, or Industry 4.0. This is the notion that interconnectivity, smart automation, and digital process management will considerably strengthen production flow, improve quality, and reduce costs. In short, the various parts of a supply chain will interact without human interference.
This may seem almost like a sci-fi fantasy to some, but we are speeding quickly toward this new norm. Who knows what the future of manufacturing looks like? But, the reality is that strategies for manufacturing will always be a priority in the transformation of this fast-paced industry.
Why is a manufacturing strategy important?
A manufacturing strategy is the backbone of how a business operates when you break it down. To ensure your manufacturing strategy is aligned with the overall business strategy, it must be focused on:
- maximizing quality
- minimizing costs
- avoiding wastage
- improving flexibility
All the while being motivated by more lofty goals such as increasing market share and profitability.
Strategies for marketing ensure that a company avoids inefficiencies, optimizes production, and ultimately reaches the goals it is aiming for.
As Steve Lam, Senior Vice President of Patheon’s Biologics Business, states, whether you are processing medicines , clothing , beauty products , or the latest tech-gadgets , “considering your manufacturing strategy early on in development pays dividends down the line.”
So why is a manufacturing strategy important? The answer to this is another question:
Would your business survive without it?
Easy strategies for manufacturing that companies can implement
When choosing a new manufacturing strategy, it’s important to remember it’s not a case of a one-size-fits-all approach but rather finding one that is relevant for your business.
Just because a manufacturing strategy is world-class for some doesn’t mean it will be for others. Be sure to strategize with intent and ensure that your manufacturing strategy gives your company the competitive edge it needs in an increasingly competitive environment. Start by articulating your competitive advantage and then build your strategy around it.
Every decision, from the machinery you use to the automation system you choose, needs to take you one step closer to maximizing that competitive advantage.
So, what are some manufacturing strategy examples that you could implement?
1. Adopt technology
It is crucial to have an agile IT function that can respond flexibly to your business’s demands. Identifying which technologies are applicable and useful to your manufacturing processes is often the first building block in a sturdy manufacturing strategy. Is there a service or app out there that you have not yet considered?
2. Shrink your costs and production waste
This is a no-brainer. If your business has holes in its manufacturing processes that let money flow out of them, then this part of your manufacturing strategy must be robust. Production times, processes, and product quality are things that cannot be compromised on.
3. Stock inventory
Adopting the principles of lean inventory saves you a fortune and gives you a serious competitive edge. Having a better understanding of your stock levels and responding to your customer’s needs more intuitively could result in huge improvements for your business.
4. Automate your processes
The automation of day-to-day tasks can make your business leaner and more efficient. Services like Katana cloud inventory platform can be the bridge that finally connects your procurement, order processing, supply chain, customer service, production, and operations together. Automatically monitoring the movement of your inventory will minimize waste like never before. Furthermore, Katana’s software easily integrates with e-commerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce to reduce the risk of stock-outs and to keep your products moving to the customers who want them.
5. Look to the future
Industry 4.0 is just the latest in many changes in the industrial and manufacturing world. Do your research and ensure your manufacturing strategies are robust yet flexible enough so you can pivot if you need to.
Designing manufacturing strategies for success
Strategies for manufacturing are essential to keep a business moving. The most successful businesses over time have been the ones that have chosen strategies that support their long-term ambitions.
Innovative software, visibility, and control are often the backbones of any successful manufacturing strategy, but how you implement these must be unique to your business.
For example, adopting a manufacturing ERP software would be the perfect manufacturing strategy for businesses struggling to keep track of the movement of their inventory.
The key is to be smart about it — Be sure to identify the manufacturing strategies that fit your business model right now and will help you to stay ahead of the competition in the future. Evaluating and measuring your success every step of the way will ensure that you can provide your customers with the products they need before they even know they need them!
James Humphreys has produced content on manufacturing and inventory management practices for 5+ years. He began his journey into writing via the creative industry, writing and producing plays, some of which toured the UK and Europe.
Related Articles
23 small manufacturing business ideas you can use, digital manufacturing: a new way to work, manufacturing control: creating a plan to optimize output, what is ppe manufacturing, and why is it important, operations in manufacturing: how to stay in control, manufacturing analytics: the metrics you need, going lean with cellular manufacturing, packaging and contract manufacturing: thinking outside the box, trending articles, electronic components inventory: how to do it right, sustainable manufacturing: the why, the how, and the who, how to know when it’s time for better clothing warehouse organization, untangle the complex web of pharma supply chain and logistics, 11 warehouse mistakes and how to fix them, erp vs. wms: which one is right for your business, inventory liquidation: why, when, and how to do it, woocommerce inventory sync solutions for your business.
Updated on September 27, 2023
Manufacturing Business Plan: How to Draft One

A business plan serves as your roadmap to success. Starting a manufacturing business without a business plan is like driving off on a road trip without a destination in mind. It’s critical to put time and effort into building a worthwhile business plan. We will explore how to build a manufacturing business plan. Plus, explore why you need one in the first place.
Key Points: A business plan is a document you create as a roadmap to your business goals. You can use your business plan to brainstorm solutions for potential problems on paper. While you will likely make adjustments along the way, a business plan puts you on the path to success.
Understanding Manufacturing Business Plans
Businesses of all shapes and sizes create business plans. Without a business plan, you are essentially flying blind as you build out your business. A carefully thought-out business plan can help you avoid potential pitfalls.
What’s the Purpose of a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A manufacturing business plan is a document that will help you chart a course to success.
- Chart a course to success : You can use this document to define success and make a clear path to achieving those goals.
- Consider potential challenges : You can use the document to find solutions for problems before they throw a wrench in your business.
- Showcase your idea : While potential investors and lenders might ask to see this document, it’s also a useful tool for business owners to outline their vision of success.
Who Needs a Manufacturing Business Plan?
Everyone who wants to build a manufacturing business should create a manufacturing business plan. Here’s a look at the process:
- Getting started : If you are just diving into your business idea, a business plan serves as a useful way to organize your thoughts.
- Along the way : If you jumped into your business without creating a plan, it’s never too late. Consider building a business plan from where you currently are.
Important Factors to Consider When Writing a Business Plan for a Manufacturing Company
As you write your business plan , keep these factors in mind.
- Patience : It can take time to build out a comprehensive business plan. That’s okay. Be patient with yourself throughout the process.
- Stay flexible : Your business will not operate in a vacuum. When things change, stay flexible and make any necessary adjustments along the way.
Essential Elements of a Manufacturing Business Plan
Every manufacturing business plan should include some basic elements. Below is a breakdown of what should be included.
Executive Summary
An executive summary involves a short description of your manufacturing business.
- Why it matters : You can use the executive summary to make a good impression on readers.
- What to include : Get the ball rolling by providing your mission statement, a summary of your business financial situation, and the products you plan to manufacture.
Chase the vision, not the money, the money will end up following you. – Tony Hsieh, Zappos CEO
Business Description
A description of your business goes beyond your goals, it gets into a detailed description of the products you plan to offer.
- Why it matters : Even if you don’t have a physical product in hand, this section should illuminate exactly what you plan to sell. Anyone who reads this document should know exactly what you are selling.
- What to include : Share what makes your product special, from a customer’s point of view. While this idea might be your baby, you need to create a product that customers want to buy.
The only thing worse than starting something and failing… is not starting something. – Seth Godin, Squidoo founder, author and blogger
Market Analysis
An overview of the competition can help you understand where your business can stand out.
- Why it matters : Scope out the competition to determine where you can outshine your competitors. For example, if your competitors are missing a key product feature, try to include that in your product.
- What to include : Find statistics about the industry, potential customer demographics, and current industry trends.
Marketing and Sales Strategies
You don’t have a business until you make sales to your customers.
- Why it matters : Outline exactly how you plan to get your product into the hands of eager customers.
- What to include : Build out a strategy on how you plan to reach customers and make sales. Maybe you already have a list of people who have asked about this type of product, or you know exactly where your target customer hangs out online.
Operational Plan
The operational plan includes how you plan to go from idea to delivered product.
- Why it matters : Manufacturing businesses rely on efficient operations to create worthwhile profits.
- What to include : Map out how you will get your hands on a physical product that meets all of your requirements. Don’t forget to write down the final steps of getting that physical product in your customer’s hands.
Management and Organization
The right team can make all the difference to your business.
- Why it matters : Any potential investors or lenders will want to confirm your team has the necessary experience to succeed.
- What to include : Start by highlighting any management team members. From there, include an organizational hierarchy that highlights any decision-makers and a complete staffing plan.
Financial Projections
Finally, your business plan should include some basic financial projections.
- Why it matters : Anyone with a stake in the company, including yourself, wants to know what the potential rewards are.
- What to include : Share your financial projections in great detail. At the very least, you should include any manufacturing loans , equipment financing plans , start-up costs, revenue projections, a sample profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a break-even analysis. Be realistic when tallying up any of these numbers.

Benefits of Having a Manufacturing Business Plan
- Providing a roadmap : A business plan gives you some direction to aim for as you build your business.
- Attracting investors and securing funding : Investors and lenders will want to see a carefully developed business plan before committing to any funding.
- Guiding day-to-day operations and decision-making : As you build the business, you can refer to this document as a guide when it’s time to make decisions.
- Mitigating risks : You can potentially spot problems before hitting the obstacle in real life. This gives you a chance to think of effective solutions.
- Identifying opportunities : When you evaluate the market, you should look for any opportunity to stand apart from the crowd.
- Monitoring progress and setting measurable goals : It’s easy to get lost in the process of building your business. A written plan gives you a way to measure your progress.
Anything that is measured and watched, improves. – Bob Parsons, GoDaddy founder
How to Write a Manufacturing Business Plan
As you build out your business plan, here are some steps to follow:
- Start with a template : A free online template can give you a starting point if you aren’t sure where to get started.
- Visualize success : As you write out each section, you should keep your vision of success in your mind’s eye. Consider building a vision board to keep on hand during the process.
- Make the time : It will take time and energy to build a worthwhile business plan. Give this task the time it deserves.
Tips for Crafting a Compelling Manufacturing Business Plan
- Do your homework : Back up all of the claims you make in your business plan with facts. A business plan isn’t the place to dream, it’s the place to set realistic goals.
- Focus on your competition : A close look at your competition is a useful way to see where you can make your own mark on the industry. Look for gaps in their strategy that you could fill for customers.
- Be conservative with your numbers : It’s better to exceed expectations than to miss the mark.
- Ask for help : If you run into questions, reach out to a mentor for help.
Mistakes to Avoid When Creating Your Manufacturing Business Plan
- Don’t skip legal advice : The legal structure of your business might require a professional opinion. It’s a good idea to reach out to professionals with any questions you have.
- Don’t skimp on the numbers : The financial projections are a key component of your business plan. Always be realistic and honest with yourself as you build out these projections.
- Avoid industry jargon : Anyone should be able to understand your vision when they read your business plan clearly.
Bottom Line
A manufacturing business plan offers a roadmap that points to your ultimate business success. It’s tempting to do a sloppy job on this document that only you might read. But it’s critical to do your research and organize your thoughts in a business plan. If you are starting a manufacturing business , don’t skip this step.
This app literally changed my like. It provides a great experience. I absolutely love it!
About the Author

Sarah Sharkey
Sarah Sharkey is a personal finance writer who enjoys helping people make better financial decisions.
Related Articles

What Does Manufacturing Mean in Business?

Manufacturing Grants: Fueling Industry Growth

Manufacturing Startups: What Are They & How to Start One
Manufacturing Equipment Financing: Know Your Options
How to Start a Manufacturing Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Production Planning in Manufacturing: Best Practices for Production Plans

As the creation of products and services has become more extensive and varied, the manufacturing industry has become more competitive. There are many things to keep an eye on such as material requirements planning, supply chain management and inventory control. Operations continue to become more complex, and this means manufacturing companies require more thorough production planning.
A production plan is the best way to guarantee you deliver high-quality products/services as efficiently as possible.
What Is Production Planning?
Production planning is the process of deciding how a product or service will be manufactured before the manufacturing process begins. In other words, it is how you plan to manage your supply chain, raw materials, employees and the physical space where the manufacturing process takes place.
Production planning is very important for manufacturers as it affects other important aspects of their business such as:
- Supply chain management
- Production scheduling
- Material requirements planning
- Production lead time
- Capacity planning
ProjectManager is a project management software that helps manufacturers cover every aspect of production planning. Plan with Gantt charts, execute with kanban boards and manage your resources along the way. No other software offers sophisticated project and resource management features in one intuitive package. Get started today for free.
Why Is Production Planning Important?
If a manufacturing operation wishes to expand, that evolution demands careful production planning and production scheduling. Someone must take on the responsibility of managing resources and deciding how they will be allocated. This process is a big part of capacity planning —how much can be made in a certain period of time, with the available resources?
Without production planning, it is easy to use too much of a resource for one product and not leave enough for another, or fail to schedule your resources properly, which results in delays that affect your overall production management process. It’s just as easy to let resources go to waste. These issues indicate a lack of efficiency in your production planning process.
Production planning is the best way to ensure resources are used appropriately, products and services are high-quality and nothing goes over budget .
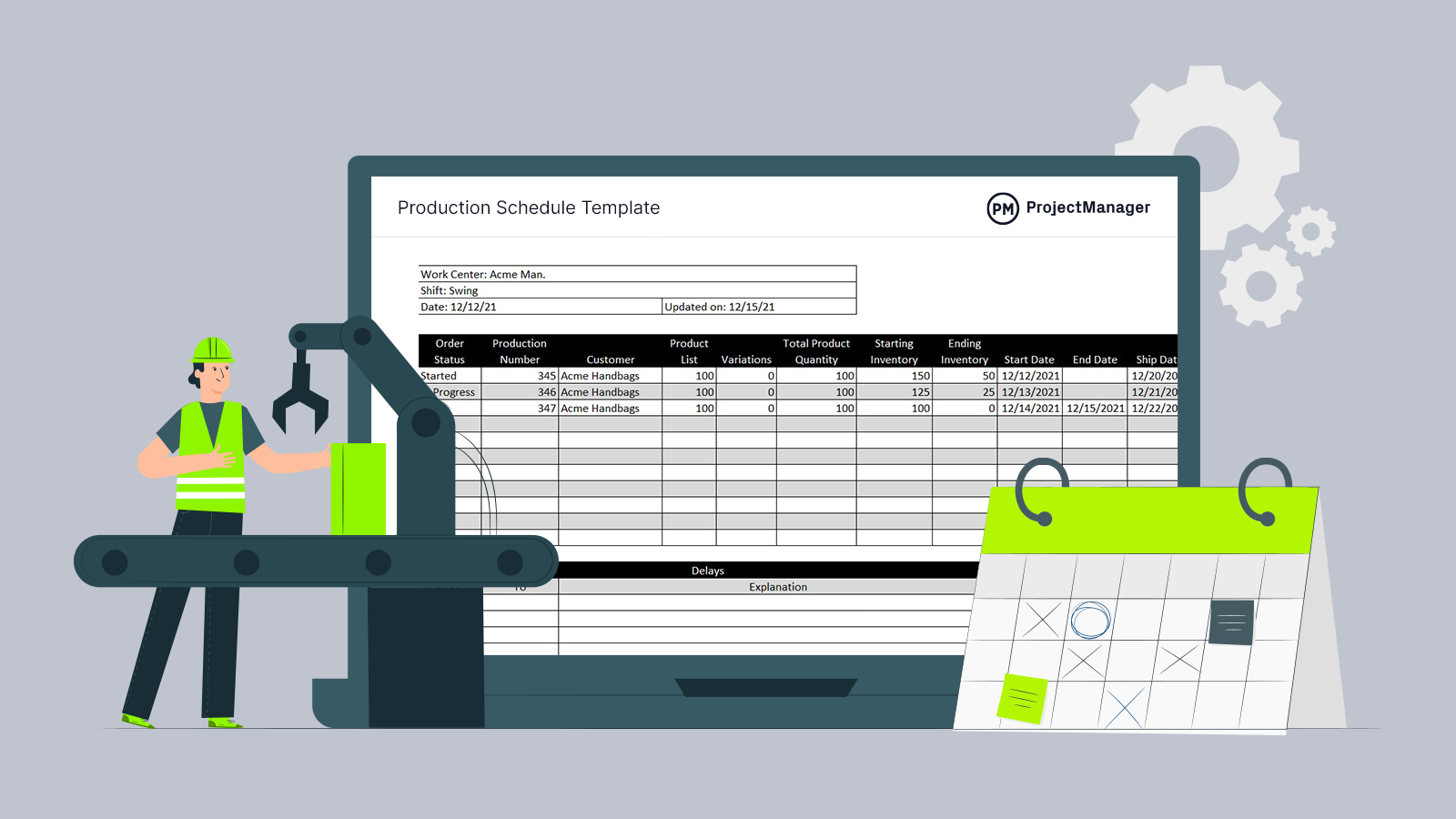
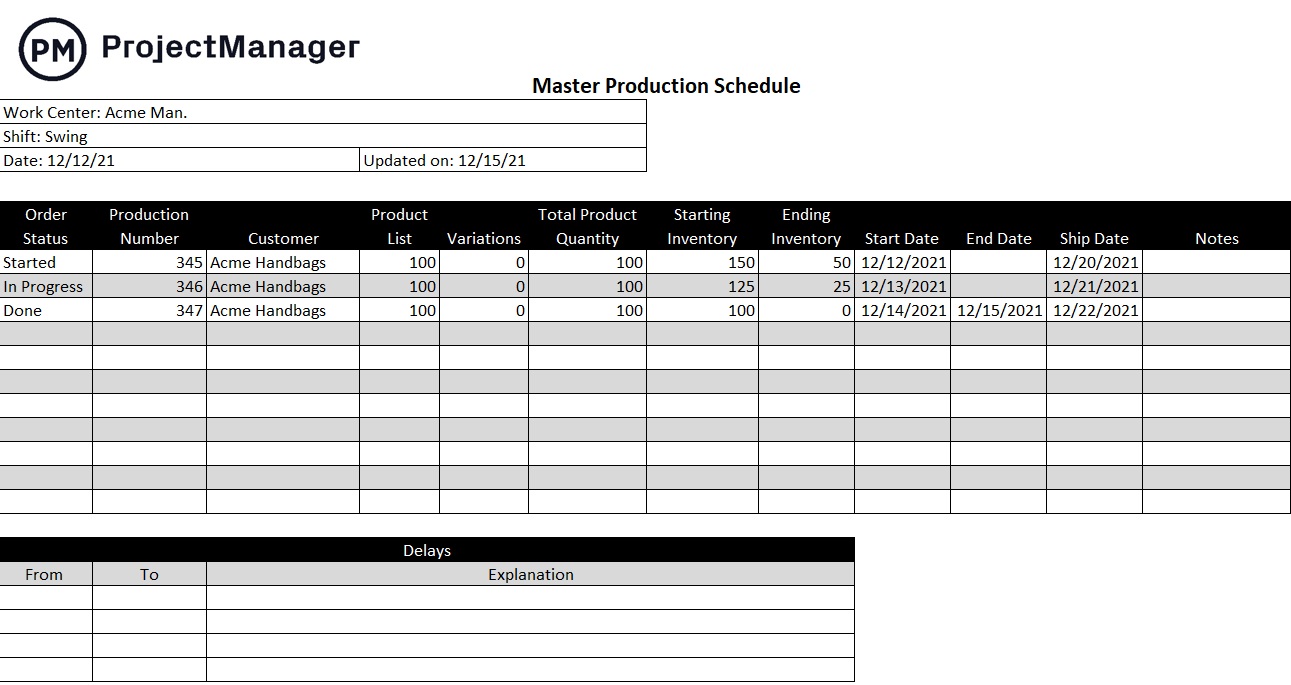
Get your free
- Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Types of Production Planning
Every operation is unique, and the same production plan isn’t right for everyone. In order to get the most from project planning, you need to decide which method is best for your manufacturing process. Here’s a quick intro to the different types of production planning.
The job method is often used when manufacturing a single product, for which a unique production plan is created. This production planning method is generally used in smaller-scale productions, but it can also be applied to larger manufacturing facilities. The job method is especially advantageous when a production order requires specific customizations.
Batch Production Method
Batch production consists in manufacturing goods in groups, instead of being produced individually or through continuous production . This method is useful when manufacturing products on a large scale.
Flow Method
The flow method is a demand-based manufacturing model that minimizes the production lead time by speeding up the production line. The manufacturing process starts based on work orders, and once it starts, it doesn’t stop until all finished goods are produced. This is called continuous production and it’s achieved by using machinery and little intervention to minimize waiting time.
Process Method
The process method is more or less what most people picture when they think about production—an assembly line. With the process method, there will generally be different types of machinery completing separate tasks to put together the finished goods.
Related: 10 Free Manufacturing Templates for Excel
Mass Production Method
The mass production method is primarily focused on creating a continuous flow of identical products. It’s similar to the flow method, but at a much bigger scale, which cuts production costs. When uniformity is just as critical as efficiency, you need to use “standardized processes” to guarantee all products look exactly the same.
What Is a Production Plan?
A production plan is a document that describes how production processes will be executed, and it’s the final outcome of the production planning process. It describes the human resources, raw materials and equipment that will be needed and the production schedule that will be followed.
The person responsible for production planning must also be very familiar with the operation’s inner workings, project resources and the products/services they produce. This usually entails collaborating with people on the floor, in the field or in different departments to create products and deliver services.
This free production schedule template helps you keep track of the status of your production orders, starting and ending production inventories, due dates and more.
How to Make a Production Plan
When you set out to create a production plan, make sure to follow these steps to make it as robust as possible.
1. Estimate/Forecast Product Demand
Understanding product demand planning is the best way to decide which product planning method is the best choice for your operation. You’ll need to use diverse sales forecasting techniques to better understand what will be the future demand for your product. From here, you’ll be able to estimate which resources are required and how they’ll be used in the manufacturing process.
2. Access Inventory
Accessing inventory is about more than simply taking stock: you should make an inventory management plan so that you don’t experience shortages or let things go to waste. For this step, focus on the inventory control and inventory management techniques you can use to handle inventory in the most efficient way possible.
3. Create a Production Budget
A production budget is a document that’s used to calculate the number of units that should be produced by a company to meet the customer demand for a period of time such as a month, quarter or even a year.
Creating a production budget involves doing an assessment of the current product inventory, the production capacity, sales forecasts and the ending inventory that should remain at the end of the time period. Once you analyze these variables and use the production budgeting formula, you’ll know what’s the required level of production for a given time period.
4. Resource Planning
A successful production plan requires you to be familiar with the resource planning details of the manufacturing process. Note the minimum number of people and raw material requirements necessary to create a product or execute a service. You need to also consider what machines and systems are essential for executing your production plan.
Related: Free Resource Plan Template for Excel
5. Estimate Production Costs
Once you’ve determined what the required level of production is and the resources that will be needed, you’ll need to estimate the cost of production . It’s important to make sure the production process will be profitable before creating a production schedule.
6. Create a Production Schedule
Now it’s time to create a production schedule based on the sales forecasts, production capacity and production budget that you’ve outlined. Making a production schedule is key to making sure your manufacturing team delivers products on time, but also guides efforts in other areas such as supply chain management and logistics management.
7. Production control
As production takes place, monitor how the results compare to the production schedule and resource management projections. This is something that should continually take place and be documented during the production process. Production control is especially important for the fifth step in the production planning process.
8. Adjust the Plan to Make Production More Efficient in the Future
The final step of production planning is to reflect on the information you gained in step four and strategize what can be done to make the production plan run more smoothly in the future. Production planning is about manufacturing a product or service, yes, but it should also be a learning experience for creating even better production plans for next time.
Common Production Planning Mistakes
You must stay vigilant of common missteps, as you go through the production planning process. Here are three mistakes often made during production planning. Luckily, they can be prevented.
Not Expecting the Unexpected
This means having risk management strategies in place if things go awry. The goal is to never have to employ them, of course, but it’s better to have them and not need them. Production planning is not complete if it doesn’t anticipate risks, issues and changes. When you plan for them, you’re ready to problem-solve if and when they happen.
Getting Stuck Behind the Desk
You should work with intelligent production planning tools, but that doesn’t mean you should only rely on enterprise resource planning software for production planning and not oversee resources and manufacturing operations in person. When production planning is only done from behind a screen, the end result will not be as informed as it could be. The best production planning is active and collaborative.
Neglecting Equipment
In order to get the most from your equipment, you need to take care of it. This means tracking usage and keeping up with regular maintenance. This looks different depending on the industry and product or service, but the principle is the same: continually take care of your equipment before it becomes a problem that will slow down production.

Production Planning Best Practices
No matter what product or service is being manufactured, there are many tried-and-true best practices to increase your operational efficiency . When creating a production plan, keep these two in mind.
Make Accurate Forecasts
When you don’t properly estimate the demand for your product or service, it is impossible to create a detailed production plan. Demand planning is never static. You need to consider buying trends from previous years, changes in demographics, changes in resource availability and many other factors. These demand planning forecasts are the foundation of skillful production planning.
Know Your Capacity
Capacity planning means knowing the maximum capacity your operation can manage—the absolute most of a product or service it can offer during a period of time. This is the only way to anticipate how much of each resource you will need in order to create X amount of products.
When you don’t know the production capacity , your production planning is like taking a shot in the dark.
Use ProjectManager for Production Planning and Scheduling
As the nature of manufacturing goods and services changes, you need modern tools to plan production and make schedules. ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software that offers all the tools you need for excellent production planning and scheduling. With it, you can plan projects, create schedules, manage resources and track changes with one tool.
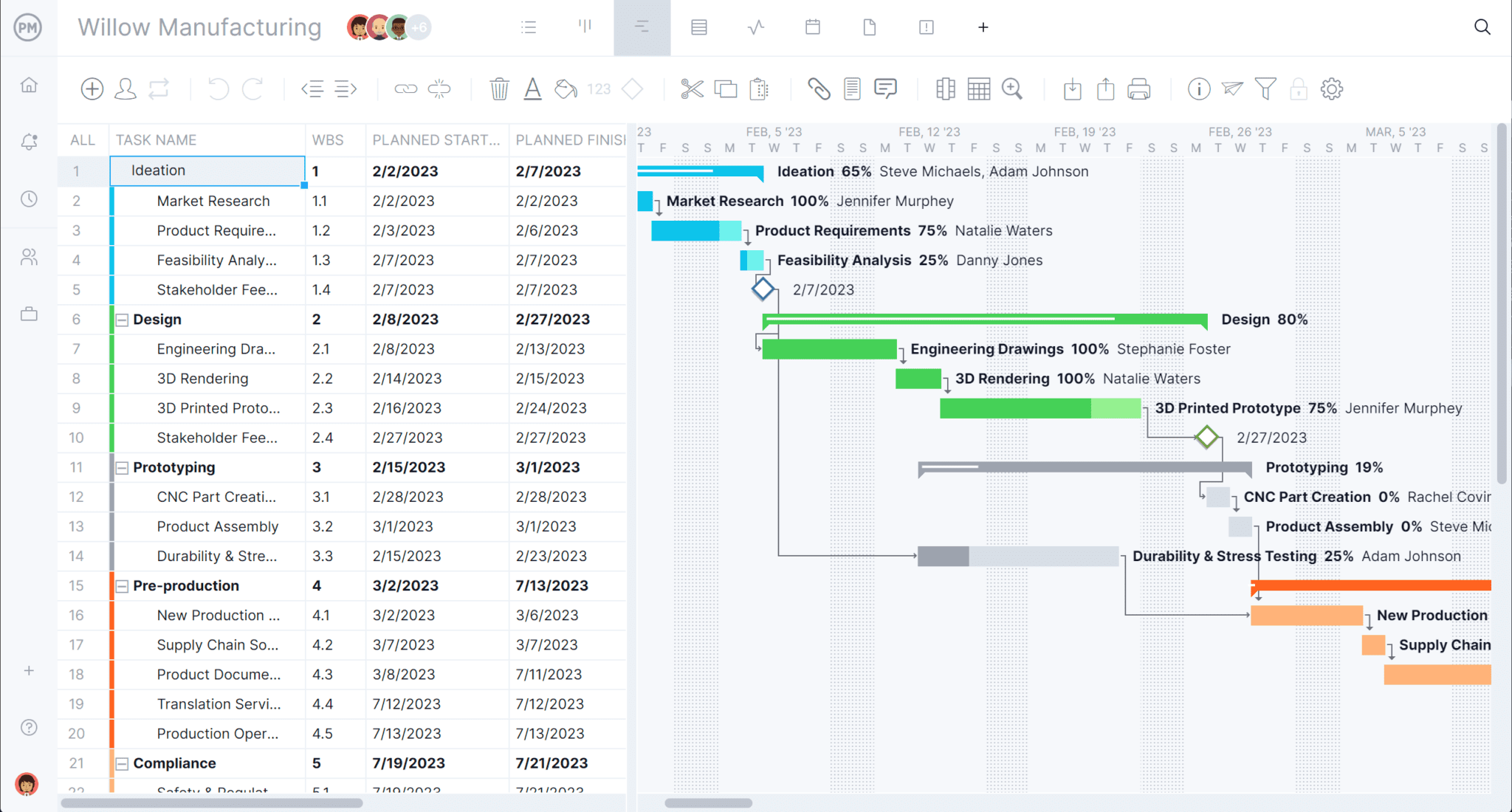
Plan with Gantt Charts
Manage your product manufacturing across a timeline with our Gantt chart view. With it, you can view your resources to help you track your cost of production to make sure you’re never overspending. You can then link any dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks in your manufacturing.
Get a Birds-Eye-View
To keep your production plan on track, you need to have a high-level view so that you can pinpoint setbacks before or as they occur. Our real-time dashboard collects your data and converts it into colorful graphs and charts that give you at-a-glance analytics.
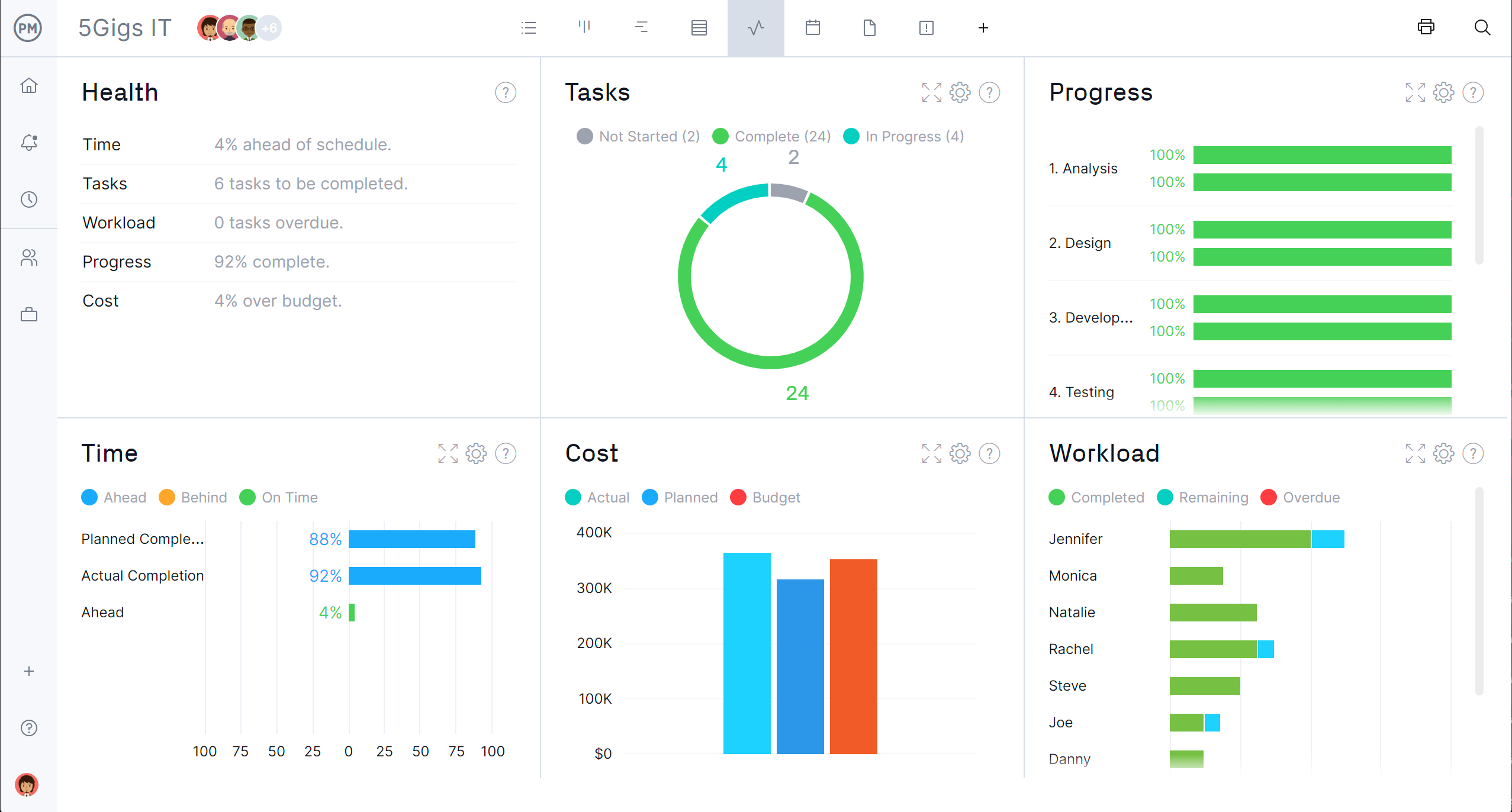
Easily Measure and Report Your Progress
Any operation will have stakeholders, and they want to be kept in the loop. ProjectManager’s project status reports make it easy to share key data points. They can be generated in a single click, making it simple to generate them before important meetings.
Related Production Planning Content
The production planning process involves many different activities such as estimating the quantity of goods to be produced, the resources that will be needed, the production schedule and much more. That’s why we’ve created dozens of blogs, guides and templates on production-related topics. Here are some of them.
- Production vs. Manufacturing
- How to Make a Production Flow Chart for Manufacturing
- Best Production Scheduling Software Rankings
- How to Create a Master Production Schedule (MPS)
Manage every detail of your operation with ProjectManager’s powerful cloud-based project management tools. Our suite of tools is trusted by tens of thousands of teams, from NASA to Volvo, to aid them in the planning, scheduling, tracking and reporting on the progress and performance of their production plans. Our software makes lets you get out from behind your desk and make adjustments on the go. Try it for yourself for free for 30 days!

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
All Formats
Plan Templates
15+ manufacturing business plan templates.
If you’re striking out on your own to start a business, whatever sort it might be, you will benefit from having a business plan template to work from. Such a tool will aid you in your crucial planning and takeoff stages. But there’s more to a business than getting started, and how you proceed from there will largely grow out of the conditions you’ve set for yourself in your business plan. This becomes especially important when you are getting into commodity production. Nowhere else is your command of production lines, personnel, and funding going to be so hard-pressed as in a simple manufacturing business.

Plan Template Bundle

- Google Docs
Construction Business Plan Template Bundle

Construction Business Continuity Plan Bundle

Construction Marketing Business Plan Template Bundle

Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Factory Business Plan Template

Business Plan Outline in Word

Printable Business Plan Template in Word

Simple Business Plan Template

Business Continuity Plan Template

Editable Marketing Business Plan Template

Retail Business Plan Template

Food Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Clothing Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Brick Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Manufacturing Business Continuity Plan Template


What Goes into a Manufacturing Business Plan?
- Executive summary . Here is where you condense your business’s intended purposes and goals. What is your mission-vision statement?
- Company description. Define the nature of your intended business, the commodities you are producing, where you will be located, etc.
- Market analysis . Where do you fit in the larger economy and what your relationship will be to existing businesses and competition? Define your target market and your role in fulfilling a real economic need.
- Strategy and implementation. Here you propose your methodology to achieve your goals.
- Management and organization. Assign your founding team and determine its structure and member responsibilities.
- Financial plan and projections. Estimate a budget and forecast your earnings.
- See also Manufacturing Business Marketing Plan to go from production to marketing.
- Also, see Manufacturing Business Continuity Plan above to establish a sustainable company.
Garment Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Furniture Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Manufacturing Business Marketing Plan Template

Manufacturing and Operation Plan Template

How to Use These Plan Templates
- They will give you the outline of an effective, comprehensive, and adequately detailed business plan.
- They will provide key insights into the real considerations you have to take into account per business type.
General FAQs
1. what is the manufacturing business plan, 2. what are the components of a manufacturing business plan.
- Executive Summary
- Business Description
- Products and Services
- Market Research
- Sales & Marketing
- Operations Financials.
3. What is the Purpose of a Manufacturing Business Plan?
4. who should your manufacturing business plan convince, 5 what are the different types of manufacturing businesses.
- Food, Beverage, and Tobacco
- Textiles, Leather, and Apparel
- Wood, Paper, and Printing
- Petroleum and Coal
- Chemicals, Plastics, and Rubber
- Metals and Machinery
- Computer and Electronics.
More in Plan Templates
Manufacturing overhead budget template, manufacturing company budget template, manufacturing company roadmap template, manufacturing production budget template, manufacturing non-conformance report template, manufacturing budget template, manufacturing equipment inventory template, manufacturing statement of work template, manufacturing operation template, manufacturing profit and loss template.
- 7+ Financial Plan Templates
- 10+ Operational Plan Templates
- 9+ Training Plan Templates
- 5+ Shooting Schedule Template
- 11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
- 9+ Interdisciplinary Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Continuity Plan Templates in Google Docs | Ms Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Compensation Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Executive Bonus Plan Templates in PDF
- 8+ Facility Management Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Diversity Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Corrective Action Plan Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
- 9+ Recruitment Agency Marketing Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Recruitment Marketing Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Student Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
How to write a business plan for a steel manufacturer?

Creating a business plan for a steel manufacturer is an essential process for any entrepreneur. It serves as a roadmap that outlines the necessary steps to be taken to start or grow the business, the resources required, and the anticipated financial outcomes. It should be crafted with method and confidence.
This guide is designed to provide you with the tools and knowledge necessary for creating a steel manufacturer business plan, covering why it is so important both when starting up and running an established business, what should be included in your plan, how it should be structured, what tools should be used to save time and avoid errors, and other helpful tips.
We have a lot to cover, so let's get to it!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a steel manufacturer?
What information is needed to create a business plan for a steel manufacturer.
- What goes in the financial forecast for a steel manufacturer?
- What goes in the written part of a steel manufacturer business plan?
- What tool can I use to write my steel manufacturer business plan?
Having a clear understanding of why you want to write a business plan for your steel manufacturer will make it simpler for you to grasp the rationale behind its structure and content. So before delving into the plan's actual details, let's take a moment to remind ourselves of the primary reasons why you'd want to create a steel manufacturer business plan.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
Small businesses rarely experience a constant and predictable environment. Economic cycles go up and down, while the business landscape is mutating constantly with new regulations, technologies, competitors, and consumer behaviours emerging when we least expect it.
In this dynamic context, it's essential to have a clear roadmap for your steel manufacturer. Otherwise, you are navigating in the dark which is dangerous given that - as a business owner - your capital is at risk.
That's why crafting a well-thought-out business plan is crucial to ensure the long-term success and sustainability of your venture.
To create an effective business plan, you'll need to take a step-by-step approach. First, you'll have to assess your current position (if you're already in business), and then identify where you'd like your steel manufacturer to be in the next three to five years.
Once you have a clear destination for your steel manufacturer, you'll focus on three key areas:
- Resources: you'll determine the human, equipment, and capital resources needed to reach your goals successfully.
- Speed: you'll establish the optimal pace at which your business needs to grow if it is to meet its objectives within the desired timeframe.
- Risks: you'll identify and address potential risks you might encounter along the way.
By going through this process regularly, you'll be able to make informed decisions about resource allocation, paving the way for the long-term success of your business.
To get visibility on future cash flows
If your small steel manufacturer runs out of cash: it's game over. That's why we often say "cash is king", and it's crucial to have a clear view of your steel manufacturer's future cash flows.
So, how can you achieve this? It's simple - you need to have an up-to-date financial forecast.
The good news is that your steel manufacturer business plan already includes a financial forecast (which we'll discuss further in this guide). Your task is to ensure it stays current.
To accomplish this, it's essential to regularly compare your actual financial performance with what was planned in your financial forecast. Based on your business's current trajectory, you can make adjustments to the forecast.
By diligently monitoring your steel manufacturer's financial health, you'll be able to spot potential financial issues, like unexpected cash shortfalls, early on and take corrective actions. Moreover, this practice will enable you to recognize and capitalize on growth opportunities, such as excess cash flow enabling you to expand to new locations.
To secure financing
Whether you are a startup or an existing business, writing a detailed steel manufacturer business plan is essential when seeking financing from banks or investors.
This makes sense given what we've just seen: financiers want to ensure you have a clear roadmap and visibility on your future cash flows.
Banks will use the information included in the plan to assess your borrowing capacity (how much debt your business can support) and your ability to repay the loan before deciding whether they will extend credit to your business and on what terms.
Similarly, investors will review your plan carefully to assess if their investment can generate an attractive return on investment.
To do so, they will be looking for evidence that your steel manufacturer has the potential for healthy growth, profitability, and cash flow generation over time.
Now that you understand why it is important to create a business plan for a steel manufacturer, let's take a look at what information is needed to create one.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Writing a steel manufacturer business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast.
In this section, we cover three key pieces of information you should gather before drafting your business plan!
Carrying out market research for a steel manufacturer
As you consider writing your business plan for a steel manufacturer, conducting market research becomes a vital step to ensure accurate and realistic financial projections.
Market research provides valuable insights into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies, and other key factors that can significantly impact the commercial success of your business.
Through this research, you may uncover trends that could influence your steel manufacturer.
Your market research could reveal that customers may be looking for steel products with improved durability or that may offer greater value for money. Additionally, your market research might reveal that customers could be increasingly seeking out steel products that are more eco-friendly or that are designed to meet certain sustainability goals.
Such market trends play a significant role in forecasting revenue, as they offer valuable data about potential customers' spending habits and preferences.
By incorporating these findings into your financial projections, you can present investors with more accurate information, helping them make informed decisions about investing in your steel manufacturer.
Developing the sales and marketing plan for a steel manufacturer
Budgeting sales and marketing expenses is essential before creating a steel manufacturer business plan.
A comprehensive sales and marketing plan should provide an accurate projection of what actions need to be implemented to acquire and retain customers, how many people are needed to carry out these initiatives, and how much needs to be spent on promotions, advertising, and other aspects.
This helps ensure that the right amount of resources is allocated to these activities in order to hit the sales and growth objectives forecasted in your business plan.
The staffing and equipment needs of a steel manufacturer
As you embark on starting or expanding your steel manufacturer, having a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) is essential for ensuring your business's success.
Both the recruitment and investment plans must align with the timing and level of growth projected in your forecast, and they require appropriate funding.
A steel manufacturer might incur staffing costs such as employee wages, benefits, and payroll taxes. They might also incur equipment costs such as purchasing and maintaining machinery, tools, and other equipment needed to produce steel. They may even need to pay for regular inspections and maintenance of the equipment to ensure it is functioning properly and safely.
To create a realistic financial forecast, you also need to consider other operating expenses associated with the day-to-day running of your business, such as insurance and bookkeeping.
With all the necessary information at hand, you are ready to begin crafting your business plan and developing your financial forecast.
What goes into your steel manufacturer's financial forecast?
The financial forecast of your steel manufacturer will enable you to assess the profitability potential of your business in the coming years and how much capital is required to fund the actions planned in the business plan.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for a steel manufacturer are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement ,
- The projected balance sheet ,
- The cash flow forecast ,
- And the sources and uses table .
Let's take a closer look at each of these.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement for a steel manufacturer shows how much revenue and profit your business is expected to make in the future.
A healthy steel manufacturer's P&L statement should show:
- Sales growing at (minimum) or above (better) inflation
- Stable (minimum) or expanding (better) profit margins
- A healthy level of net profitability
This will of course depend on the stage of your business: numbers for a startup will look different than for an established steel manufacturer.
The forecasted balance sheet of your steel manufacturer
The projected balance sheet of your steel manufacturer will enable the reader of your business plan to assess the overall financial health of your business.
It shows three elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: are productive resources owned by the business, such as equipment, cash, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: are debts owed to creditors, lenders, and other entities, such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers).
- Equity: includes the sums invested by the shareholders or business owners and the profits and losses accumulated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). It is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
Analysing your steel manufacturer projected balance sheet provides an understanding of your steel manufacturer's working capital structure, investment and financing policies.
In particular, the readers of your plan can compare the level of financial debt on the balance sheet to the equity value to measure the level of financial risk (equity doesn't need to be reimbursed, while financial debt must be repaid, making it riskier).
They can also use your balance sheet to assess your steel manufacturer's liquidity and solvency:
- A liquidity analysis: focuses on whether or not your business has sufficient cash and short-term assets to cover its liabilities due in the next 12 months.
- A solvency analysis: takes and longer view to assess whether or not your business has the capacity to repay its debts over the medium-term.
The cash flow forecast
As we've seen earlier in this guide, monitoring future cash flows is the key to success and the only way of ensuring that your steel manufacturer has enough cash to operate.
As you can expect showing future cash flows is the main role of the cash flow forecast in your steel manufacturer business plan.
It is best practice to organise the cash flow statement by nature in order to show the cash impact of the following areas:
- Cash flow generated from operations: the operating cash flow shows how much cash is generated or consumed by the business's commercial activities
- Cash flow from investing activities: the investing cash flow shows how much cash is being invested in capital expenditure (equipment, real estate, etc.) either to maintain the business's equipment or to expand its capabilities
- Cash flow from financing activities: the financing cash flow shows how much cash is raised or distributed to financiers
Looking at the cash flow forecast helps you to make sure that your business has enough cash to keep running, and can help you anticipate potential cash shortfalls.
Your steel manufacturer business plan will normally include both yearly and monthly cash flow forecasts so that the readers can view the impact of seasonality on your business cash position and generation.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan - also called a sources and uses table - is an important tool when starting a steel manufacturer.
It shows where the money needed to set up the business will come from (sources) and how it will be allocated (uses).
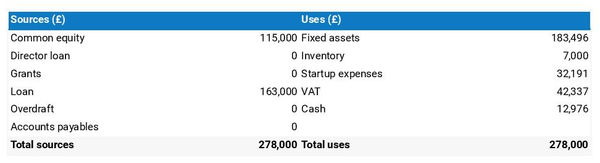
Having this table helps understand what costs are involved in setting up the steel manufacturer, how the risks are distributed between the shareholders and the lenders, and what will be the starting cash position (which needs to be sufficient to sustain operations until the business breaks even).
Now that the financial forecast of a steel manufacturer business plan is understood, let's focus on what goes into the written part of the plan.
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

The written part of a steel manufacturer business plan
The written part of a steel manufacturer business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Throughout these sections, you will seek to provide the reader with the details and context needed for them to form a view on whether or not your business plan is achievable and your forecast a realistic possibility.
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
The first section of your steel manufacturer's business plan is the executive summary which provides, as its name suggests, an enticing summary of your plan which should hook the reader and make them want to know more about your business.
When writing the executive summary, it is important to provide an overview of the business, the market, the key financials, and what you are asking from the reader.
Start with a brief introduction of the business, its name, concept, location, how long it has been in operation, and what makes it unique. Mention any services or products you plan to offer and who you sell to.
Then you should follow with an overview of the addressable market for your steel manufacturer, current trends, and potential growth opportunities.
You should then include a summary of your key financial figures such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Finally, you should detail any funding requirements in the ask section.
2. The presentation of the company
As you build your steel manufacturer business plan, the second section deserves attention as it delves into the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
In the structure and ownership part, you'll provide valuable insights into the legal structure of the business, the identities of the owners, and their respective investments and ownership stakes. This level of transparency is vital, particularly if you're seeking financing, as it clarifies which legal entity will receive the funds and who holds the reins of the business.
Moving to the location part, you'll offer a comprehensive view of the company's premises and articulate why this specific location is strategic for the business, emphasizing factors like catchment area, accessibility, and nearby amenities.
When describing the location of your steel manufacturer, you could emphasize the potential for growth and development, as the area is well-connected to major transportation networks and has access to a large pool of skilled labor. Additionally, its proximity to potential customers and suppliers may create a competitive advantage. The area may also boast a business-friendly tax structure, which could make it an attractive investment opportunity.
Lastly, you should introduce your esteemed management team. Provide a thorough explanation of each member's role, background, and extensive experience.
It's equally important to highlight any past successes the management team has achieved and underscore the duration they've been working together. This information will instil trust in potential lenders or investors, showcasing the strength and expertise of your leadership team and their ability to deliver the business plan.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your business plan should include a detailed description of what your company offers, who are the target customers, and what distribution channels are part of your go-to-market.
For example, your steel manufacturer might offer custom steel fabrication services, such as cutting and welding, to its customers to help them create the exact product they need. It might also offer a variety of steel products, such as sheets, bars, beams, and plates, so that customers can purchase the exact amount of steel they need for their projects. Finally, the manufacturer might offer value-added services, such as surface treatments, to ensure that the steel products meet the customer's exact specifications.
4. The market analysis
When outlining your market analysis in the steel manufacturer business plan, it's essential to include comprehensive details about customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and relevant regulations.
The primary aim of this section is to give the reader an understanding of the market size and appeal while demonstrating your expertise in the industry.
To begin, delve into the demographics and segmentation subsection, providing an overview of the addressable market for your steel manufacturer, key marketplace trends, and introducing various customer segments and their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
Next, shift your focus to the target market subsection, where you can zoom in on the specific customer segments your steel manufacturer targets. Explain how your products and services are tailored to meet the unique needs of these customers.
For example, your target market might include small independent building contractors. These contractors often require a range of steel products, from structural beams to pipes for plumbing. As well as needing a reliable supplier of steel, they are likely to appreciate good customer service from a manufacturer.
In the competition subsection, introduce your main competitors and explain what sets your steel manufacturer apart from them.
Finally, round off your market analysis by providing an overview of the main regulations that apply to your steel manufacturer.
5. The strategy section
When you write the strategy section of your steel manufacturer business plan, remember to cover key elements such as your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
In the competitive edge subsection, elaborate on what makes your company stand out from competitors. This becomes especially important if you're a startup, aiming to carve a place for yourself amidst established players in the marketplace.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you plan to maintain profitability while offering competitive prices to attract customers.
Outline your sales & marketing plan, detailing how you'll reach out to new customers and retain existing ones through loyalty programs or special offers.
For the milestones subsection, outline your company's achievements to date and your main objectives for the future, complete with specific dates to set clear expectations for progress.
Lastly, the risks and mitigants subsection should address the main risks that could affect your plan's execution. Explain the measures you've put in place to minimize these risks, assuring potential investors or lenders.
Your steel manufacturer faces a range of risks. For example, they may experience a disruption in raw material supply, which could adversely affect production. In addition, they could be exposed to volatile market conditions, which could result in decreased demand for their products and lower revenues.
6. The operations section
The operations of your steel manufacturer must be presented in detail in your business plan.
Begin by addressing your staff, specifying the main roles and your recruitment plan to support the anticipated growth. Outline the qualifications and experience needed for each role and discuss your recruitment strategies, which may involve using job boards, referrals, or headhunters.
Next, clearly state your steel manufacturer's operating hours, allowing the reader to gauge the adequacy of your staffing levels. Additionally, mention any considerations for varying opening times during peak seasons and your approach to handling customer queries outside regular operating hours.
The key assets and intellectual property (IP) required to run your business should also be highlighted. If you rely on licenses, trademarks, physical structures like equipment or property, or lease agreements, ensure they are well-documented in this section.
You may have key assets such as steel production equipment and technology that could be used to create a competitive advantage. Additionally, the steel manufacturer might also have intellectual property such as patents or trade secrets related to the production process or the steel product itself. This IP could be a valuable asset that could help the manufacturer maintain its competitive edge.
Finally, provide a comprehensive list of suppliers you intend to collaborate with, along with a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms, such as price, payment terms, break clauses and contract duration. Investors often seek insight into the reasons behind your supplier choices, which may include a preference for higher-quality products or established relationships from past ventures.
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will include the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of the content of a steel manufacturer business plan, let's look at some of the tools you can use to create yours.
What tool should I use to write my steel manufacturer's business plan?
There are two main ways of creating your steel manufacturer business plan:
- Using specialized business planning software,
- Hiring a business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your steel manufacturer's business plan
Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to create a steel manufacturer business plan.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here .
Need a solid financial forecast?
The Business Plan Shop does the maths for you. Simply enter your revenues, costs and investments. Click save and our online tool builds a three-way forecast for you instantly.
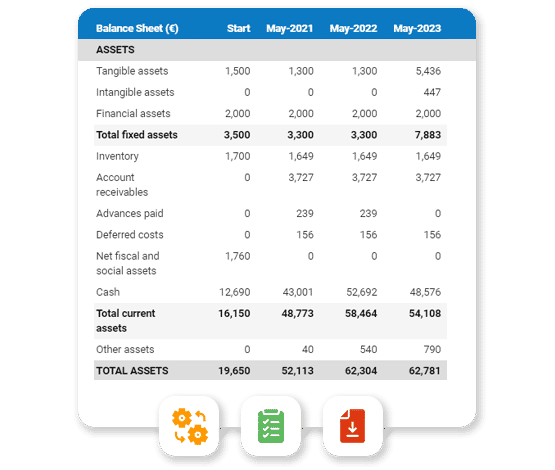
Hiring a business plan writer to write your steel manufacturer's business plan
Outsourcing your steel manufacturer business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
Business plan writers are experienced in writing business plans and adept at creating financial forecasts without errors. Furthermore, hiring a consultant can save you time and allow you to focus on the day-to-day operations of your business.
However, hiring business plan writers is expensive as you are paying for the software used by the consultant, plus their time, and their profit margin of course.
From experience, you need to budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax for a complete business plan, more if you need to make changes after the initial version (which happens frequently after the initial meetings with lenders or investors).
You also need to be careful when seeking investment. Investors want their money to be used to grow the business, not spent on consulting fees. Therefore, the amount you spend on business plan writing services (and other consulting services such as legal services) needs to be negligible relative to the amount raised.
The other drawback is that you usually don't own the business plan itself: you just get the output, while the actual document is saved in the consultant's business plan software - which makes it difficult to maintain the document up to date without hiring the consultant on a retainer.
For these reasons, outsourcing the steel manufacturer business plan to a business plan writer should be considered carefully, weighing both the advantages and disadvantages of hiring outside help.
Ultimately, it may be the right decision for some businesses, while others may find it beneficial to write their business plan using online software.
Why not create your steel manufacturer's business plan using Word or Excel?
Using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write a steel manufacturer business plan is a terrible idea.
For starters, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel (or any spreadsheet) is very technical and requires both a strong grasp of accounting principles and solid skills in financial modelling.
As a result, it is unlikely anyone will trust your numbers unless - like us at The Business Plan Shop - you hold a degree in finance and accounting and have significant financial modelling experience in your past.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the 1990s and early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Also, using software makes it easy to compare actuals vs. forecasts and maintain our forecasts up to date to maintain visibility on future cash flows - as we discussed earlier in this guide - whereas this is a pain to do with a spreadsheet.
That's for the forecast, but what about the written part of my steel manufacturer business plan?
This part is less error-prone, but here also software brings tremendous gains in productivity:
- Word processors don't include instructions and examples for each part of your business plan
- Word processors don't update your numbers automatically when they change in your forecast
- Word processors don't handle the formatting for you
Overall, while Word or Excel may be viable options for creating a steel manufacturer business plan for some entrepreneurs, it is by far not the best or most efficient solution.
- A business plan has 2 complementary parts: a financial forecast showcasing the expected growth, profits and cash flows of the business; and a written part which provides the context needed to judge if the forecast is realistic and relevant.
- Having an up-to-date business plan is the only way to keep visibility on your steel manufacturer's future cash flows.
- Using business plan software is the modern way of writing and maintaining business plans.
We hope that this practical guide gave you insights on how to write the business plan for your steel manufacturer. Do not hesitate to get in touch with our team if you still have questions.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- In-depth business plan structure
- Key steps to write a business plan?
- Free business plan template
Know someone who owns or wants to start a steel manufacturer? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here

Develop A Manufacturing Strategy That Works: Examples, Tips & Free Template

Manufacturing companies need a rock-solid strategic plan to thrive in today's ultra-competitive business environment. But, let's face it, executing that plan with precision and consistency is where the real hustle begins.
According to Deloitte , “In 2024, manufacturers are expected to face economic uncertainty, the ongoing shortage of skilled labor, lingering and targeted supply chain disruptions, and new challenges spurred by the need for product innovation.”
But hey, with a solid plan in place and the ability to pivot on a dime, you can overcome these challenges and come out on top!
In this article, we'll explore the ins and outs of manufacturing strategy, from its key elements and benefits to best practices and success stories. And to make your life easier, we'll also hook you up with Cascade's manufacturing strategy templates —a powerful tool for crushing your goals!

What Is A Manufacturing Strategy?
A manufacturing strategy outlines how a company will use its resources to produce goods and services that meet the needs of its customers while achieving its financial goals. It involves a range of considerations, including the allocation of resources , the use of technology and equipment, the management of inventory and supply chains, and the optimization of production processes to achieve the company's overall business goals.
A well-designed manufacturing strategy can help a company optimize its operations, increase efficiency, reduce costs, improve quality, and ultimately increase profitability.
What Are The Key Elements Of A Manufacturing Strategy?
To develop an effective manufacturing strategy, a company must consider several key elements. While the specific goals, initiatives, and objectives may vary, some essential components are common to all successful strategies.
Product development and design
This involves creating products that meet customer needs while being produced efficiently. Key considerations include product features, specifications, functionality, and cost.
For instance, a company designing a new smartphone would need to decide on the size, weight, screen resolution, processing power, camera quality, and other features that meet the target market's needs.
Technology and equipment
Selecting and deploying appropriate manufacturing technology and equipment is crucial to manufacturing products efficiently and effectively. This includes deciding on equipment types, maintenance, and updates.
For example, an organization may invest in robotic equipment to automate its assembly line, resulting in faster and more accurate production and reduced labor costs.
Sourcing and management of materials
Identifying and sourcing raw materials and supplies are crucial components to ensure the efficient manufacturing of products. Key considerations include the quality, availability, and cost of the materials.
As an example, a company may source high-quality leather from a reliable supplier to produce premium leather bags.
Production processes and operations
Managing production processes and manufacturing operations is essential to ensure the efficient and effective manufacturing of products. Key considerations include resource use, labor management, and quality control.
A company may adopt lean manufacturing principles, for example, to optimize its production processes and eliminate waste, leading to reduced costs and increased efficiency.
Quality control and assurance
Implementing quality control and assurance measures ensures that products meet customer specifications and quality standards. Key considerations include testing, inspection, and continuous improvement.
A company may use statistical process control to monitor and improve product quality, resulting in fewer defects and higher customer satisfaction.
Inventory management and logistics
Managing inventory levels and logistics is essential to ensure products are available when and where needed. Key considerations include inventory control, order fulfillment, and supply chain management.
For instance, a company may use just-in-time inventory management to minimize inventory holding costs while ensuring on-time delivery to customers.
Continuous improvement and innovation
Continually improving and innovating manufacturing processes enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves product quality. Key considerations include the adoption of new technologies, process improvements, and customer feedback.
For instance, a company may use customer feedback to design and launch new products that meet evolving market needs, such as a smartphone with a longer battery life or a car with advanced safety features.
What Are The Benefits Of A Manufacturing Strategy?
A well-designed manufacturing strategy can offer numerous benefits to a company, including:
- Improved efficiency : Optimizing production processes can reduce costs and increase profitability by allowing a company to produce goods more efficiently.
- Increased flexibility : Responding to changes in demand or the market becomes easier with a strong manufacturing strategy in place, enabling a company to adjust production levels, product mix, or other factors as needed.
- Better quality control : Implementing quality control measures improves product quality, reducing inefficiencies, the likelihood of defects or product recalls, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced competitiveness : Manufacturing strategies can help companies produce goods more efficiently, offer better quality products, or deliver products more quickly than competitors, giving them a competitive edge in the marketplace.
- Improved supply chain management : Better supply chain management, achieved through a manufacturing strategy, can lead to cost savings and better customer service by reducing lead times and improving reliability.
- Greater innovation : Manufacturing strategies that focus on continuous improvement and innovation can help companies develop new products, processes, or technologies, which gives them a competitive advantage.
- Increased profitability : By improving efficiency, quality, flexibility, and innovation, a manufacturing strategy can help a company increase its profitability and growth potential.
6 Examples Of Manufacturing Strategies To Adopt
Companies can adopt several manufacturing strategies, depending on their specific goals, market conditions, and production processes. Let’s take a look at some examples!
Lean Manufacturing
This strategy aims to reduce waste, increase efficiency, and improve quality by streamlining production processes and eliminating non-value-added activities. Companies that use this approach focus on continuous improvement, employee empowerment, and the use of visual management techniques.
Toyota is a well-known example of a company that has successfully implemented lean manufacturing practices. The Toyota Production System (TPS) empowers employees to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities in the production process to reduce waste, increase efficiency, and improve quality.

Mass Customization
Producing customized products on a large scale using flexible production processes and advanced technology is the focus of this strategy. Companies that use this approach aim to meet the individual needs of customers while achieving economies of scale through efficient production processes.
Nike uses mass customization to offer a wide range of personalized products to customers. Nike's iD program allows customers to customize the colors, materials, and other features of their shoes, which are then manufactured and delivered within a few weeks.
Agile Manufacturing
Emphasizing flexibility, responsiveness, and innovation, this strategy enables companies to quickly adapt to changes in demand or new product opportunities. Companies that use this approach typically have highly automated production processes, advanced data analytics capabilities, and a culture of continuous improvement.
Apple is known for its agile manufacturing practices, which enable the company to quickly respond to changes in demand and introduce new products to the market. Apple's advanced supply chain management and manufacturing processes enable rapid scaling of production and response to changes in customer demand.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
To improve product quality and customer satisfaction, this strategy embeds quality control and assurance measures throughout the production process. Companies focus on process improvements, employee involvement, and data-driven decision-making to achieve higher levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
Ford has implemented a TQM strategy to improve product quality and customer satisfaction. Ford's Quality Operating System (QOS) focuses on continuous improvement, employee involvement, and data-driven decision-making to achieve higher levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing
To minimize inventory levels, reduce waste in the production process, and produce goods based on customer demand, this strategy is used. Companies aim to achieve higher levels of efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer responsiveness by producing and delivering products quickly and reliably.
Dell is known for its use of just-in-time manufacturing practices, producing and delivering custom-configured computers quickly and efficiently. Dell's advanced supply chain management and manufacturing processes enable the company to produce and deliver products in a matter of days.
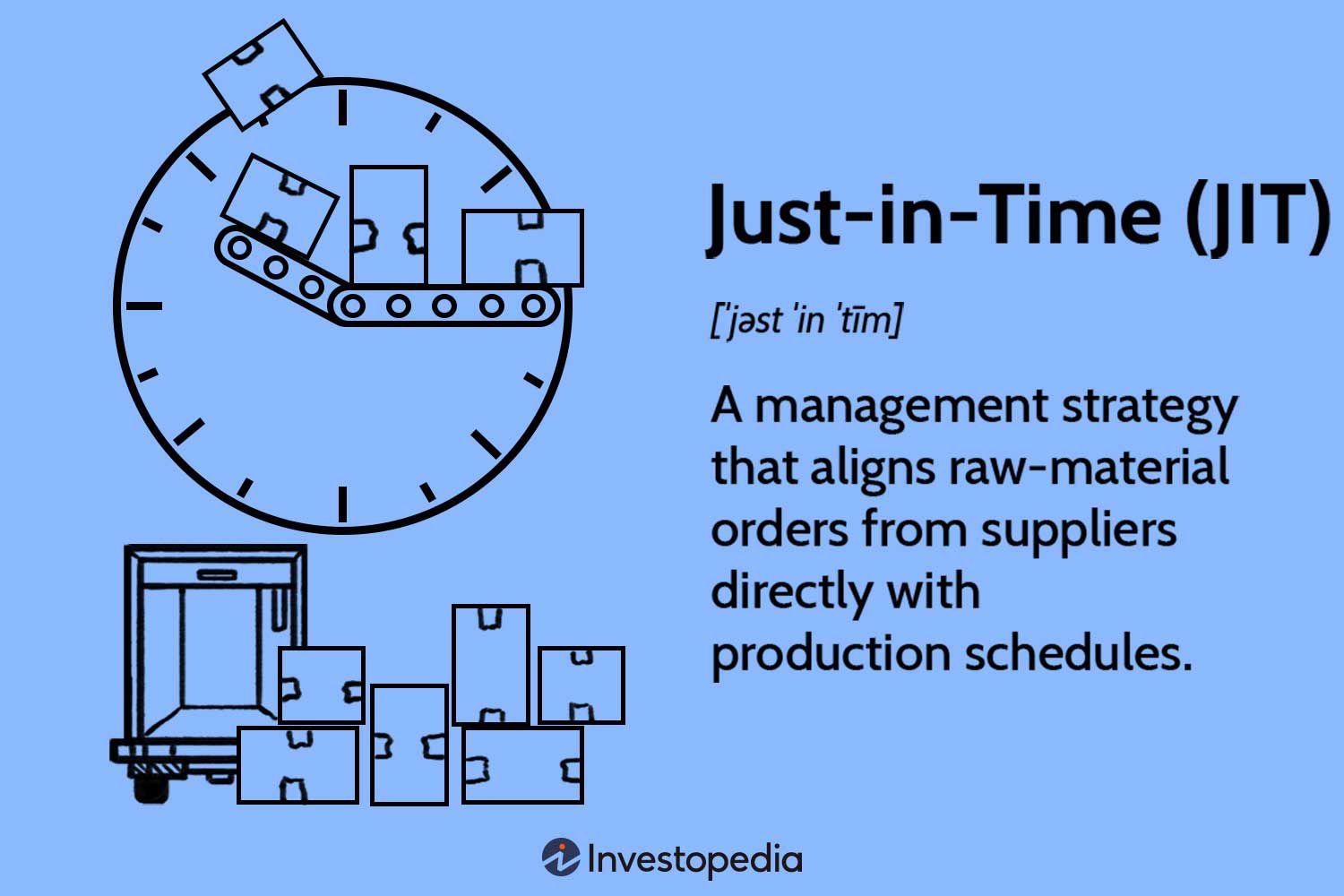
Green Manufacturing
This strategy revolves around bolstering sustainability by mitigating the environmental impact of production processes, minimizing waste, and optimizing resource efficiency. Companies aim to meet the growing demand for sustainable products and production processes while achieving cost savings through reduced energy use, waste reduction, and improved supply chain management.
Patagonia sets the benchmark as an exemplary company that has implemented green manufacturing practices to reduce its environmental impact. Patagonia's Worn Wear program promotes repairing and reusing clothing, reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. The company also uses sustainable materials and production processes to reduce its environmental impact.

Jumpstart Your Manufacturing Strategy With Customizable Templates!
Developing a manufacturing plan from scratch can be a challenging task. To ease this burden, we have designed multiple templates that offer a systematic approach to creating a manufacturing strategy.
These templates are flexible and can be tailored to meet the unique needs of your manufacturing business.
Manufacturing Strategy Template

Develop a clear and effective manufacturing strategy with our Manufacturing Strategy Template , a comprehensive tool that helps organizations develop a clear and effective manufacturing strategy. Customize it to fit your business needs, covering inventory, production, quality, supply chain, and performance measurement.
👉 Click here to start building your own.
Production & Manufacturing Strategy Template
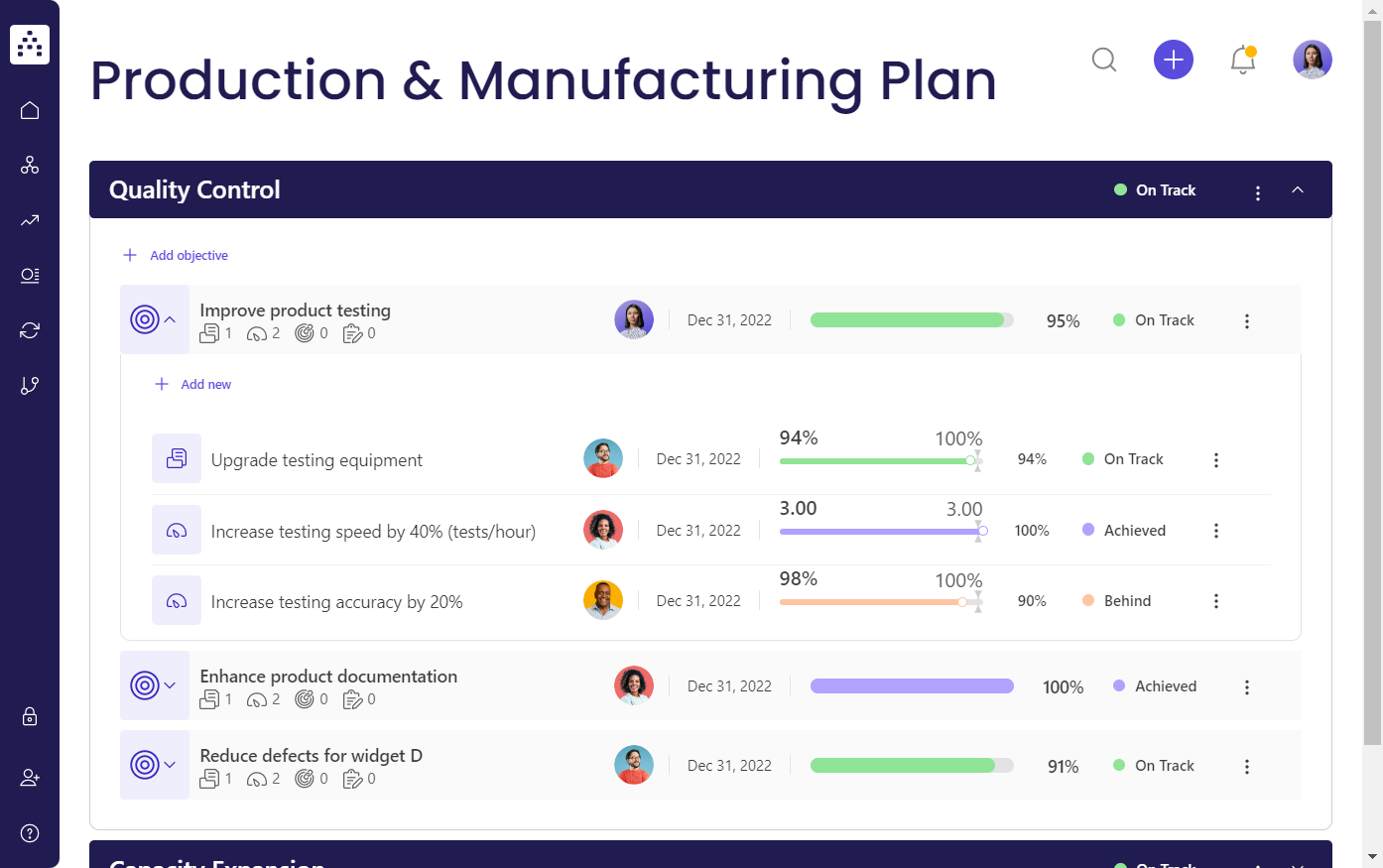
Get a comprehensive plan for your production and manufacturing processes. Improve processes, plan capacity, manage quality, and handle supply chain. It’s easy-to-use and adaptable to different organizations.
Manufacturing Quality Plan Template

Our Manufacturing Quality Plan Template is ideal for companies looking to develop a quality plan for their manufacturing processes. It covers all aspects of quality management, including quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement.
Manufacturing Capacity Plan Template
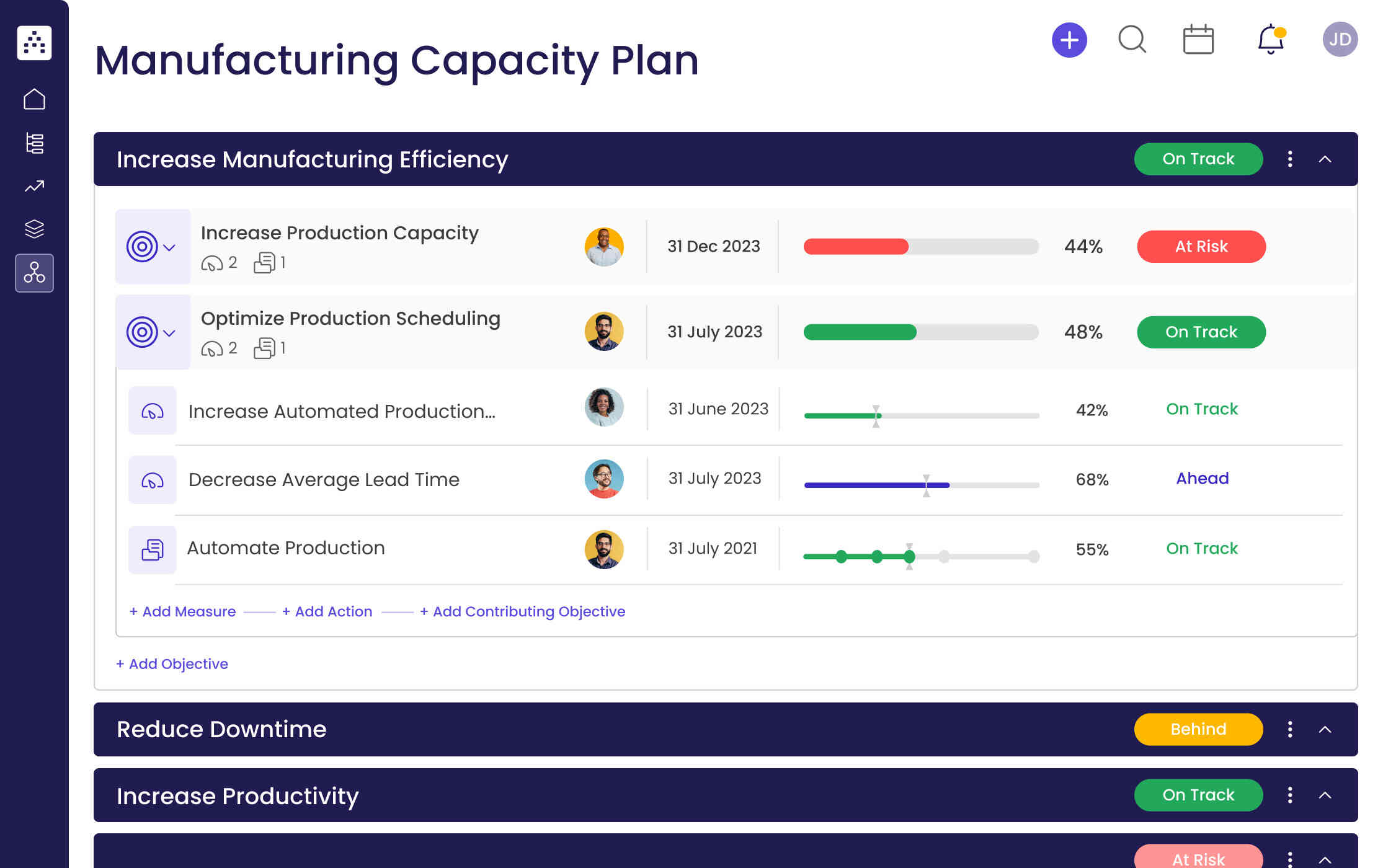
Manage your manufacturing capacity with a detailed plan with this template covering all aspects of capacity planning, including forecasting demand, managing production schedules, and optimizing resource utilization. It’s pre-filled with examples and easily adaptable to your organization.
Manufacturing Contingency Plan Template

Be prepared for contingencies in your manufacturing processes with this Manufacturing Contingency Plan Template. Identify potential risks, develop contingency plans, and implement measures to ensure your manufacturing business not only thrives but succeeds!
Common Manufacturing Sub-Industries (+ Templates)
Manufacturing is a diverse industry with many sub-industries, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Some of the most common manufacturing sub-industries include pharmaceutical, food and beverage, industrial, metal and mineral, and computer and electronic product manufacturing. Depending on the sub-industry, manufacturing strategies can vary significantly.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing requires strict compliance with regulations and quality standards. A manufacturing strategy for this sub-industry would focus on quality control and regulatory compliance. To create a manufacturing plan for pharmaceuticals, use our Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Strategy Template .
Food and beverage manufacturing , on the other hand, requires compliance with food safety regulations. A manufacturing strategy for this sub-industry would focus on supply chain management and inventory control. To create a manufacturing plan for food and beverage products, use our Food and Beverage Manufacturing Strategy Template .
Industrial manufacturing encompasses a wide range of products, including machinery, tools, and equipment. A manufacturing strategy for this sub-industry would focus on efficiency and cost-effectiveness. To create a manufacturing plan for industrial products, use our Industrial Manufacturing Plan Template .
Metal and mineral manufacturing involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, such as iron and aluminum, into finished products. A manufacturing strategy for this sub-industry would focus on reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. To create a manufacturing plan for metal and mineral products, use our Metal and Mineral Manufacturing Strategy Template .
Lastly, computer and electronic product manufacturing requires constant innovation and adaptation to keep up with rapid technological advancements. A manufacturing strategy for this sub-industry would focus on research and development, as well as supply chain management. To create a manufacturing plan for computer and electronic products, use our Computer and Electronic Product Manufacturing Strategy Plan Template .
Execute Your Manufacturing Strategy With Cascade 🚀
Getting started with your Manufacturing Strategy is easy with Cascade . Here’s a step-by-step guide to set it up and use it for your organization’s planning:
1. Get your manufacturing strategy template
Getting started with your manufacturing strategy template is as easy as 1, 2, 3.
- Choose one of the manufacturing templates shared in this article and click on the link.
- Sign up for a free forever account in Cascade .
- Your template will automatically load on your Cascade workspace and be ready to use.
💡 Want to explore other templates? Check out our Strategy Template Library with over +1,000 free, ready-to-use templates.
2. Customize your template
Your template will feature prefilled focus areas, goals, actions, and metrics. But changing them is easy to do. You can tailor your strategy’s:
- Focus Areas
- Project Titles
- Dependencies
Click on the items/title/metric or other variables you want to adjust to tweak them to fit your goals. If some variables align with your planning, keep them in, alter them, or add to them. Remember, this is your manufacturing strategy—make it your own!
3. Invite your team
Send an invite to your team members to collaborate on shared KPIs and ensure everyone is on the same page. With Cascade, you can assign roles and responsibilities, set up notifications, and communicate with your teams in one place.
4. Bring your data into one place
By connecting your existing data and inputs to your template, you can create a single source of truth for your plan and its execution. This provides unprecedented accuracy and control over the performance of your plan.
With Cascade’s +1,000 integrations , you can:
- Add collaboration tools like Teams , Slack , and Outlook .
- Integrate metrics and KPIs from Google Sheets , Excel , Jira , and Salesforce .
- Sync your plan, objectives, and their due-dates with your existing calendar in Google , Outlook , and iCalendar.
💡 Bonus Tip : If you have a custom integration requirement, contact our team, and we’ll help set it up.
5. Start executing the right way
Keep your plan from sitting idle for the rest of the year. You now have a living manufacturing strategy that can be shared and worked on in one place.
From here on out, you can add additional role players, set up teams for different projects, and track progress against projected outcomes.
If plans need to be adjusted, you can quickly make changes on the platform and update the entire team in one go.
💡 Bonus Tip : If you want to improve your manufacturing process, use Cascade’s key features to centralize your strategy execution for better and faster decision-making.
Reports : A simplified yet powerful approach to creating beautiful strategy reports on your progress. Spend less time finding data points and formatting and more time driving execution forward.
.png)
Dashboards : Set up custom dashboards to monitor execution as your teams work towards goals. Choose the metrics that matter to you and get real-time updates on how your teams move forward.
Timeline View (Roadmap) : With the Timeline View feature, you can get a visual Gantt-style chart view of the Manufacturing schedule, complete with deadlines, priorities, and timelines.
Alignment Map : Build multiple plans in Cascade and visualize how they all work together to achieve your goals. You can easily see how your manufacturing strategy connects to your overarching business strategy or even to functional plans like your finance or marketing strategy.

The Key to Manufacturing Success: An Execution-Ready Strategic Plan
In the competitive world of manufacturing, having a solid strategic plan is essential, but it's only the beginning. The key to success is executing that plan flawlessly. That's where Cascade comes in to revolutionize the traditional approach to strategic manufacturing management and planning. With Cascade, you can turn your vision into an actionable and achievable plan that's ready to be executed.
So, if you're looking to take your manufacturing business to the next level, Cascade is the solution you’re looking for. Whether it's optimizing your production processes, streamlining your supply chain, or improving your quality control, Cascade can help you achieve your goals and maximize your performance.
Don't wait any longer to unlock your manufacturing potential. Book a guided 1:1 tour with one of our Cascade in-house strategy execution experts.
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment
How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.

8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
8 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
A business plan template can be an excellent tool to simplify the creation of your business plan.
The pre-set structure helps you organize ideas, covers all critical business information, and saves you time and effort on formatting.
The only issue? There are SO many free business plan templates out there.
So, which ones are actually worth using?
To help remove the guesswork, I’ve rounded up some of the best business plan templates you can access right now.
These are listed in no particular order, and each has its benefits and drawbacks.
What to look for in a business plan template
Not all business plan templates are created equal. As you weigh your options and decide which template(s) you’ll use, be sure to review them with the following criteria in mind:
- Easy to edit: A template should save you time. That won’t be the case if you have to fuss around figuring out how to edit the document, or even worse, it doesn’t allow you to edit at all.
- Contains the right sections: A good template should cover all essential sections of a business plan , including the executive summary, product/service description, market/competitive analysis, marketing and sales plan, operations, milestones, and financial projections.
- Provides guidance: You should be able to trust that the information in a template is accurate. That means the organization or person who created the template is highly credible, known for producing useful resources, and ideally has some entrepreneurial experience.
- Software compatibility: Lastly, you want any template to be compatible with the software platforms you use. More than likely, this means it’s available in Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PDF format at a minimum.
1. Bplans — A plan with expert guidance

Since you’re already on Bplans, I have to first mention the templates that we have available.
Our traditional and one-page templates were created by entrepreneurs and business owners with over 80 years of collective planning experience. We revisit and update them annually to ensure they are approachable, thorough, and aligned with our team’s evolving best practices.
The templates, available in Word, PDF, or Google Doc formats, include in-depth guidance on what to include in each section, expert tips, and links to additional resources.
Plus, we have over 550 real-world sample business plans you can use for guidance when filling out your template.
Download: Traditional lender-ready business plan template or a simple one-page plan template .
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. SBA — Introduction to business plans

The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two different business plan templates along with a short planning guide.
While not incredibly in-depth, it’s enough to help you understand how traditional and lean plans are structured and what information needs to be covered. The templates themselves are more like examples, providing you with a finished product to reference as you write your plan.
The key benefit of using these templates is that they were created by the SBA. While they may provide less guidance, you can be assured that the information and structure meet their expectations.
Explore: The SBA’s planning guide and free templates
3. SCORE — Planning workbook

SCORE’s template is more like a workbook. It includes exercises after each section to help you get your ideas down and turn them into a structured plan.
The market research worksheets are especially useful. They provide a clear framework for identifying your target market and analyzing competitors from multiple angles. Plus, they give you an easy way to document all the information you’re collecting.
You will likely have to remove the exercises in this template to make it investor-ready. But it can be worth it if you’re struggling to get past a blank page and want a more interactive planning method.
Download: SCORE’s business plan template
4. PandaDoc — A template with fillable forms

PandaDoc’s library offers a variety of industry-specific business plan templates that feature a modern design flair and concise instructions.
These templates are designed for sharing. They include fillable fields and sections for non-disclosure agreements, which may be necessary when sending a plan to investors.
But the real benefit is their compatibility with PandaDoc’s platform. Yes, they are free, but if you’re a PandaDoc subscriber, you’ll have far more customization options.
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry.
Explore: PandaDoc’s business plan template library
5. Canva — Pitch with your plan

Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool. It offers a diverse array of templates built by their in-house team and the larger creative community, meaning the number of options constantly grows.
You will need to verify that the information in the template you choose matches the standard structure of a traditional business plan.
You should do this with any template, but it’s especially important with any tool that accepts community submissions. While they are likely reviewed and approved, there may still be errors.
Remember, you can only edit these templates within Canva. Luckily, you only need a free subscription, and you may just miss out on some of the visual assets being used.
To get the most value, it may be best to create a more traditional planning document and transfer that information into Canva.
Explore: Canva’s business plan gallery
6. ClickUp — The collaborative template

Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp’s is the most approachable.
Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
There’s also a completed sample plan (structured like an expanded one-page plan) for you to reference and see how the more traditional document can connect to the product management features. You can set goals, target dates, leave comments, and even assign tasks to someone else on your team.
These features are limited to the ClickUp platform and will not be useful for everyone. They will likely get in the way of writing a plan you can easily share with lenders or investors.
But this is a great option if you’re looking for a template that makes internal collaboration more fluid and keeps all your information in one place.
Sign Up: Get a free trial of ClickUp and explore their template library
7. Smartsheet — A wide variety of templates

I’m including Smartsheet’s library of templates on this list because of the sheer number of options they provide.
They have a simple business plan template, a one-page plan, a fill-in-the-blank template, a plan outline, a plan grading rubric, and even an Excel-built project plan. All are perfectly usable and vary in visual style, depth of instructions, and the available format.
Honestly, the only drawback (which is also the core benefit) is that the amount of templates can be overwhelming. If you’re already uncertain which plan option is right for you, the lengthy list they provide may not provide much clarity.
At the same time, it can be a great resource if you want a one-stop shop to view multiple plan types.
Explore: Smartsheet’s business plan template library
8. ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan

I’m adding ReferralRock’s template to this list due to its specificity.
It’s not your standard business plan template. The plan is tailored with specific sections and guidance around launching an affiliate marketing business.
Most of the template is dedicated to defining how to choose affiliates, set commissions, create legal agreements, and track performance.
So, if you plan on starting an affiliate marketing business or program, this template will provide more specific guidance. Just know that you will likely need to reference additional resources when writing the non-industry sections of your plan.
Download: ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan template
Does it matter what business plan template you use?
The short answer is no. As long as the structure is correct, it saves you time, and it helps you write your business plan , then any template will work.
What it ultimately comes down to, is what sort of value you hope to get from the template.
- Do you need more guidance?
- A simple way to structure your plan?
- An option that works with a specific tool?
- A way to make your plan more visually interesting?
Hopefully, this list has helped you hone in on an option that meets one (or several) of these needs. Still, it may be worth downloading a few of these templates to determine the right fit.
And really, what matters most is that you spend time writing a business plan . It will help you avoid early mistakes, determine if you have a viable business, and fully consider what it will take to get up and running.
If you need additional guidance, check out our library of planning resources . We cover everything from plan formats , to how to write a business plan, and even how to use it as a management tool .
If you don’t want to waste time researching other templates, you can download our one-page or traditional business plan template and jump right into the planning process.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.

Table of Contents
- Qualities of a good template
- ReferralRock
- Does the template matter?
Related Articles

10 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan

3 Min. Read
How Long Should a Business Plan Be?

14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Plastic Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook
Are you interested in starting your own plastic manufacturing company but unsure of where to start? We can assist you with our plastic manufacturing business plan template and how-to manual. You can simply construct a business plan that details every facet of your enterprise, from market analysis and financial predictions to marketing plans and operational tactics, with the help of our comprehensive template and professional advice. Making your concept a reality is simple with our step-by-step process for starting a profitable plastic manufacturing company. With the help of our tried-and-true template and direction, you can confidently start the process of creating a successful plastic manufacturing company. Join the ranks of prosperous plastic manufacturing businesses by getting started right away!

Get worry-free services and support to launch your business starting at $0 plus state fees.
- How to Start a Profitable Plastic Manufacturing Business [11 Steps]
- 25 Catchy Plastic Manufacturing Business Names:
- List of the Best Marketing Ideas For Your Plastic Manufacturing Business:
How to Write a Plastic Manufacturing Business Plan in 7 Steps:
1. describe the purpose of your plastic manufacturing business..
The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your plastic manufacturing business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind thinking about the customers’ problems. It also helps you identify what makes your business different from others in its industry.
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
Here is an example of a purpose mission statement for a plastic manufacturing business:
Our mission is to produce high-quality, cost-effective plastic that meets the needs of our customers. We will accomplish this by providing a safe work environment for our employees and investing in the latest equipment. We will also ensure that all stakeholders are treated with respect and value their input in order to make sure we’re always making the best decisions possible.

2. Products & Services Offered by Your Plastic Manufacturing Business.
The next step is to outline your products and services for your plastic manufacturing business.
When you think about the products and services that you offer, it's helpful to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is my business?
- What are the products and/or services that I offer?
- Why am I offering these particular products and/or services?
- How do I differentiate myself from competitors with similar offerings?
- How will I market my products and services?
You may want to do a comparison of your business plan against those of other competitors in the area, or even with online reviews. This way, you can find out what people like about them and what they don’t like, so that you can either improve upon their offerings or avoid doing so altogether.

3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
If you don't have a marketing plan for your plastic manufacturing business, it's time to write one. Your marketing plan should be part of your business plan and be a roadmap to your goals.
A good marketing plan for your plastic manufacturing business includes the following elements:
Target market
- Who is your target market?
- What do these customers have in common?
- How many of them are there?
- How can you best reach them with your message or product?
Customer base
- Who are your current customers?
- Where did they come from (i.e., referrals)?
- How can their experience with your plastic manufacturing business help make them repeat customers, consumers, visitors, subscribers, or advocates for other people in their network or industry who might also benefit from using this service, product, or brand?
Product or service description
- How does it work, what features does it have, and what are its benefits?
- Can anyone use this product or service regardless of age or gender?
- Can anyone visually see themselves using this product or service?
- How will they feel when they do so? If so, how long will the feeling last after purchasing (or trying) the product/service for the first time?
Competitive analysis
- Which companies are competing with yours today (and why)?
- Which ones may enter into competition with yours tomorrow if they find out about it now through word-of-mouth advertising; social media networks; friends' recommendations; etc.)
- What specific advantages does each competitor offer over yours currently?
Marketing channels
- Which marketing channel do you intend to leverage to attract new customers?
- What is your estimated marketing budget needed?
- What is the projected cost to acquire a new customer?
- How many of your customers do you instead will return?
Form an LLC in your state!

4. Write Your Operational Plan.
Next, you'll need to build your operational plan. This section describes the type of business you'll be running, and includes the steps involved in your operations.
In it, you should list:
- The equipment and facilities needed
- Who will be involved in the business (employees, contractors)
- Financial requirements for each step
- Milestones & KPIs
- Location of your business
- Zoning & permits required for the business
What equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a plastic manufacturing business?
Plastic manufacturing businesses produce a wide range of plastic products, such as containers, packaging materials, and consumer goods. The equipment and supplies needed to run a plastic manufacturing business can vary depending on the specific products produced and the processes used, but may include:
- Raw materials, such as plastic resins and additives, to create the plastic products
- Manufacturing equipment, such as injection molding machines, extruders, and blow molding machines, to shape and form the plastic products
- Quality control equipment, such as gauges and testing devices, to ensure the products meet specifications and standards
- Packaging materials, such as bags, boxes, and pallets, to package and protect the finished products
- Transportation equipment, such as trucks and trailers, to deliver the products to customers
In addition to the equipment and supplies needed to run a plastic manufacturing business, it is important to obtain any necessary permits and licenses that may be required by local regulations. These permits and licenses may vary depending on the location of the business and the specific products produced.
In summary, the equipment, supplies, and permits needed to run a plastic manufacturing business can include raw materials, manufacturing equipment, quality control equipment, packaging materials, and transportation equipment, as well as any necessary licenses and permits.
5. Management & Organization of Your Plastic Manufacturing Business.
The second part of your plastic manufacturing business plan is to develop a management and organization section.
This section will cover all of the following:
- How many employees you need in order to run your plastic manufacturing business. This should include the roles they will play (for example, one person may be responsible for managing administrative duties while another might be in charge of customer service).
- The structure of your management team. The higher-ups like yourself should be able to delegate tasks through lower-level managers who are directly responsible for their given department (inventory and sales, etc.).
- How you’re going to make sure that everyone on board is doing their job well. You’ll want check-ins with employees regularly so they have time to ask questions or voice concerns if needed; this also gives you time to offer support where necessary while staying informed on how things are going within individual departments too!
6. Plastic Manufacturing Business Startup Expenses & Captial Needed.
This section should be broken down by month and year. If you are still in the planning stage of your business, it may be helpful to estimate how much money will be needed each month until you reach profitability.
Typically, expenses for your business can be broken into a few basic categories:
Startup Costs
Startup costs are typically the first expenses you will incur when beginning an enterprise. These include legal fees, accounting expenses, and other costs associated with getting your business off the ground. The amount of money needed to start a plastic manufacturing business varies based on many different variables, but below are a few different types of startup costs for a plastic manufacturing business.
Running & Operating Costs
Running costs refer to ongoing expenses related directly with operating your business over time like electricity bills or salaries paid out each month. These types of expenses will vary greatly depending on multiple variables such as location, team size, utility costs, etc.
Marketing & Sales Expenses
You should include any costs associated with marketing and sales, such as advertising and promotions, website design or maintenance. Also, consider any additional expenses that may be incurred if you decide to launch a new product or service line. For example, if your plastic manufacturing business has an existing website that needs an upgrade in order to sell more products or services, then this should be listed here.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
A financial plan is an important part of any business plan, as it outlines how the business will generate revenue and profit, and how it will use that profit to grow and sustain itself. To devise a financial plan for your plastic manufacturing business, you will need to consider a number of factors, including your start-up costs, operating costs, projected revenue, and expenses.
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your plastic manufacturing business plan:
- Determine your start-up costs: This will include the cost of purchasing or leasing the space where you will operate your business, as well as the cost of buying or leasing any equipment or supplies that you need to start the business.
- Estimate your operating costs: Operating costs will include utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water, as well as labor costs for employees, if any, and the cost of purchasing any materials or supplies that you will need to run your business.
- Project your revenue: To project your revenue, you will need to consider the number of customers you expect to have and the average amount they will spend on each visit. You can use this information to estimate how much money you will make from selling your products or services.
- Estimate your expenses: In addition to your operating costs, you will need to consider other expenses, such as insurance, marketing, and maintenance. You will also need to set aside money for taxes and other fees.
- Create a budget: Once you have estimated your start-up costs, operating costs, revenue, and expenses, you can use this information to create a budget for your business. This will help you to see how much money you will need to start the business, and how much profit you can expect to make.
- Develop a plan for using your profit: Finally, you will need to decide how you will use your profit to grow and sustain your business. This might include investing in new equipment, expanding the business, or saving for a rainy day.
Frequently Asked Questions About Plastic Manufacturing Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a plastic manufacturing business.
A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve those goals. It is important to have a business plan for your plastic manufacturing business because it helps to focus the efforts of the company, communicate the business's goals and objectives to potential investors, and provide a roadmap for the business to follow. Additionally, a business plan can be used to help secure funding from investors or lenders, who will want to see that the business has a solid plan in place before they provide funding.
How to write a business plan for your plastic manufacturing business?)
To build a business plan for your plastic manufacturing business, start by researching your industry, competitors, and target market. Use this information to define your business's goals and objectives, as well as the strategies and tactics that you will use to achieve those goals. Next, create a financial plan that outlines your projected income, expenses, and profit. This should include a projected income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. Once you have all of this information, you can use it to create a comprehensive business plan that outlines the goals and objectives of your business, as well as the strategies and tactics that you will use to achieve those goals. A well-written plastic manufacturing business plan contains the following sections: Purpose, Products & Services, Marketing Plan (including Marketing Strategy), Operations/Management Plan (including Operations/Management Strategy), Financial Plan (including Financial Forecasts), and Appendixes.
Can you write a plastic manufacturing business plan yourself?
Yes, you can write a plastic manufacturing business plan yourself. Writing a business plan is a valuable exercise that can help you clarify your business idea, identify potential challenges and opportunities, and develop a roadmap for success. While there are many resources and templates available to help you write a business plan, the process of creating one is ultimately up to you.
Related Business Plans

Home Inventory Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Inspection Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Decor Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Health And Wellness Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hauling Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hardware Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handyman Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hair Extension Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handbag Business Plan Template & Guidebook
I'm Nick, co-founder of newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
Through meticulous research and firsthand experience, I uncover the essential steps, software, tools, and costs associated with launching and maintaining a successful business. By demystifying the complexities of entrepreneurship, I provide the guidance and support needed for others to embark on their journey with confidence.
From assessing market viability and formulating business plans to selecting the right technology and navigating the financial landscape, I am dedicated to helping fellow entrepreneurs overcome challenges and unlock their full potential. As a steadfast advocate for small business success, my mission is to pave the way for a new generation of innovative and driven entrepreneurs who are ready to make their mark on the world.
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
Business Plan: What It Is + How to Write One
Discover what a business plan includes and how writing one can foster your business’s development.
![manufacturing plans in business plan [Featured image] Woman showing a business plan to a man at a desk.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/3GxwyORRIvag1Dj3jnHuiZ/a23bcf202d72e7074fd83a5222a1de79/GettyImages-1127726432__1_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is a business plan?
Think of a business plan as a document that guides the journey to start-up and beyond. Business plans are written documents that define your business goals and the strategies you’ll use to achieve those goals. In addition to exploring the competitive environment in which the business will operate, a business plan also analyses a market and different customer segments, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines financial planning.
How to write a business plan
In the sections below, you’ll build the following components of your business plan:
Executive summary
Business description
Products and services
Competitor analysis
Marketing plan and sales strategies
Brand strategy
Financial planning
Explore each section to bring fresh inspiration and reveal new possibilities for developing your business. Depending on your format, you may adapt the sections, skip over some, or go deeper into others. Consider your first draft a foundation for your efforts and one you can revise, as needed, to account for changes in any area of your business.
1. Executive summary
This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan.
2. Business description
Use this section to provide detailed information about your company and how it will operate in the marketplace.
Mission statement: What drives your desire to start a business? What purpose are you serving? What do you hope to achieve for your business, the team, and your customers?
Revenue streams: From what sources will your business generate revenue? Examples include product sales, service fees, subscriptions, rental fees, licence fees, and more.
Leadership: Describe the leaders in your business, their roles and responsibilities, and your vision for building teams to perform various functions, such as graphic design, product development, or sales.
Legal structure: If you’ve incorporated your business, include the legal structure here and the rationale behind this choice.
3. Competitor analysis
This section will assess potential competitors, their offers, and marketing and sales efforts. For each competitor, explore the following:
Value proposition: What outcome or experience does this brand promise?
Products and services: How does each solve customer pain points and fulfill desires? What are the price points?
Marketing: Which channels do competitors use to promote? What kind of content does this brand publish on these channels? What messaging does this brand use to communicate value to customers?
Sales: What sales process or buyer’s journey does this brand lead customers through?
4. Products and services
Use this section to describe everything your business offers to its target market. For every product and service, list the following:
The value proposition or promise to customers, in terms of how they will experience it
How the product serves customers, addresses their pain points, satisfies their desires, and improves their lives
The features or outcomes that make the product better than those of competitors
Your price points and how these compare to competitors
5. Marketing plan and sales strategies
In this section, you’ll draw from thorough market research to describe your target market and how you will reach it.
Who are your ideal customers?
How can you describe this segment according to their demographics (age, ethnicity, income, location, etc.) and psychographics (beliefs, values, aspirations, lifestyle, etc.)?
What are their daily lives like?
What problems and challenges do they experience?
What words, phrases, ideas, and concepts do consumers in your target market use to describe these problems when posting on social media or engaging with your competitors?
What messaging will present your products as the best on the market? How will you differentiate messaging from competitors?
On what marketing channels will you position your products and services?
How will you design a customer journey that delivers a positive experience at every touchpoint and leads customers to a purchase decision?
6. Brand strategy
In this section, you will describe your business’s design, personality, values, voice, and other details that go into delivering a consistent brand experience.
What are the values that define your brand?
What visual elements give your brand a distinctive look and feel?
How will your marketing messaging reflect a distinctive brand voice, including tone, diction, and sentence-level stylistic choices?
How will your brand look and sound throughout the customer journey?
Define your brand positioning statement. What will inspire your audience to choose your brand over others? What experiences and outcomes will your audience associate with your brand?
7. Financial planning
In this section, you will explore your business’s financial future. Suppose you are writing a traditional business plan to seek funding. In that case, this section is critical for demonstrating to lenders or investors you have a strategy for turning your business ideas into profit. For a lean start-up business plan, this section can provide a useful exercise for planning how to invest resources and generate revenue [ 1 ].
To begin your financial planning, use past financials and other sections of this business plan, such as your price points or sales strategies.
How many individual products or service packages do you plan to sell over a specific period?
List your business expenses, such as subscribing to software or other services, hiring contractors or employees, purchasing physical supplies or equipment, etc.
What is your break-even point or the amount you must sell to cover all expenses?
Create a sales forecast for the next three to five years: (No. of units to sell X price for each unit) – (cost per unit X No. of units) = sales forecast
Quantify how much capital you have on hand.
When writing a traditional business plan to secure funding, you may append supporting documents, such as licences, permits, patents, letters of reference, resumes, product blueprints, brand guidelines, the industry awards you’ve received, and media mentions and appearances.
Business plan key takeaways and best practices
Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even seek funding from lenders and investors.
Keep these best practices in mind:
Your business plan should evolve as your business grows. Return to it periodically, such as quarterly or annually, to update individual sections or explore new directions your business can take.
Make sure everyone on your team has a copy of the business plan, and welcome their input as they perform their roles.
Ask fellow entrepreneurs for feedback on your business plan and look for opportunities to strengthen it, from conducting more market and competitor research to implementing new strategies for success.
Start your business with Coursera
Ready to start your business? Watch this video on the Lean approach from the Entrepreneurship Specialisation on Coursera:
Article sources
Inc. “ How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan , https://www.inc.com/guides/business-plan-financial-section.html.” Accessed April 15, 2024.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

Manufacturing business plans for private nuclear reactor in Butte

A private nuclear power plant could come to Butte. The company behind the plan said it has backing from local government.
Butte-Silver Bow commissioners at a recent meeting were enthusiastic about the nuclear energy proposal from XGen Holdings and the manufacturing jobs it could bring.
Butte-Silver Bow Chief Executive J.P. Gallagher told commissioners he’d been working with the company for several months on the project and said the state was also aware of it.
“This is real. This is an opportunity for Butte-Silver Bow. It’s something I think I can stand behind and I can support,” Gallagher said.
XGen Holdings President Christian Barlow said he intends to purchase 160 acres of land west of Butte to headquarter his company and its manufacturing plants.
He said Westinghouse Electric Corporation agreed to build a small, modular nuclear reactor to power his operation. While discussing the proposal, Barlow told commissioners the following:
“We’ve already talked with the NRC, which is the federal regulation for nuclear power plants. We have talked with them; we have already been greenlit to build here. We do have NRC’s blessing. We’ve gone through a lot of that vetting process already.”
However, after the initial publication of this story, Nuclear Regulatory Commission public affairs officer Scott Burnell told MTPR the agency has not approved the nuclear reactor XGen Holdings described, and that the agency is not reviewing any applications for the reactor from XGen Holdings.
Burnell’s full statement is below:
“There are no applications for XGen before the NRC. There are no approvals from the NRC for the project XGen has described.
The NRC is in early discussions with Westinghouse for the designs that XGen has mentioned. Those are early discussions. There is no application under review for either design. For the micro-reactor that was part of the discussion, the NRC is in “pre-application” discussions with Westinghouse. The company is providing individual pieces of information that, in the future, could be part of an application. But there is nothing in front of the agency that would approve that design for use.”
MTPR reached out to XGen Holdings president Christian Barlow and Butte-Silver Bow Chief Executive J.P. Gallagher and requested clarification on Barlow’s comments.
XGen’s proposed manufacturing plants would build products used in night-vision goggles and air filtration.
Barlow also told commissioners that because the modular nuclear reactors are mobile and air-cooled, the county would not have to “deal with” waste.
Barlow said he intends to have the first reactors online by January 2026. State lawmakers in 2021 repealed a policy that required any proposal for nuclear power to go before voters.

- Using Supply Planning
How to Prevent Creating Planned Orders in a Supply Plan
In some business cases, you might want to prevent the creation of planned orders for particular items. You can use the Create Supply attribute to manage scenarios such as end-of-life items or phasing out of components.
The Create Supply attribute also applies to end items. If set to No for an end item, all remaining demands for the end item are marked as unmet demands after using up all on-hand inventory and on-order inventory.
This topic describes how to prevent the creation of planned orders. If you instead want only to delay the creation of planned orders until after a specified date, see the How to Create New Supplies Only After a Specified Date topic in this guide.
You can use the Create Supply attribute in both constrained and unconstrained supply plans, with a few minor differences, which are noted in this topic.
To prevent creating planned orders in a supply plan:
Set the Create Supply attribute to No for an item-organization.
(Constrained Plans Only) Select your decision rules in the plan options. This step is required only if you defined substitutes or alternates in your plan and want the supply plan to use existing supplies or recommend planned orders on them.
Set the Create Supply Attribute
To prevent the planning process from creating planned orders for a particular item, set the Create Supply attribute to No for an item-organization. To set this attribute, from the Product Information Management work area, navigate to the Items page, Specifications tab. You can also set the Create Supply attribute in the Item simulation set that's available in Supply Chain Planning.
This table describes how the planning process manages supplies when the Create Supply indicator is set to No.
For information on how to configure decision rules for constrained plans, see the Configure Constraints and Decision Rules topic in this guide.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Key Takeaways on Production Plans in Business Planning. A production plan: a detailed outline that guides efficient product manufacturing or service delivery.; Importance of a production plan: provides a roadmap for operations, optimises resource utilisation, and aligns with customer demand.; Key components: demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and ...
In your business plan, the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing ...
Our template provides a comprehensive framework for outlining your company's goals, conducting market analysis, projecting finances, and strategizing your operations. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be able to: Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and objectives. Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand your ...
A manufacturing business plan is a strategic blueprint that outlines the objectives, processes, and resources required to initiate and sustain a manufacturing enterprise. ... quality control plans ...
Tracking Device Maker Business Plan. RQM Technologies (RQM) is a start-up company which will develop and distribute miniaturized Personal Locator Devices. There are plenty of emerging and traditional industries in need of equipment manufacturers. Companies that can do it better, faster, cheaper, or more specifically to suit their needs.
Supply chain management (SCM) is a business process for manufacturing that encompasses all activities, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the finished product to the customer. It includes planning, procurement, manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing.
This library of manufacturing and wholesale business plan examples here can inspire and guide you as you begin to plan your business. So, don't worry; we got you covered on that part. Let's learn more about these manufacturing business plan samples, starting with their benefits. Benefits of using an industry-specific business plan example
Hire labor. Set up equipment. Acquire necessary materials. Monitor work schedule. Be sure to tailor your checklist to your business's requirements. Related: What Equipment and Facilities to ...
A well-crafted manufacture business plan serves as the cornerstone for any manufacturing enterprise, offering a strategic roadmap for navigating the dynamic and competitive terrain of the production and industry landscape. While recognizing that there's no one-size-fits-all approach, using manufacturing business plan example becomes crucial ...
Below are links to each of the key sections of a sample manufacturing business plan. Once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors. I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team
A manufacturing strategy has been previously defined as "a long-range plan to use the resources of the manufacturing system to support the business strategy and, in turn, meet the business objectives. (Cimorelli and Chandler, 1996). The connection that binds all the eras together is manufacturing strategy.
professional business plan with automated financial forecasts. You can also do: 200+ Sample business plans Get access to hundreds of sample business plans covering almost all industries to kick start your business plan writing. This helps you to get an idea how the perfect business plan should look like. View Sample Business Plans Step-By-Step ...
A manufacturing business plan is a document that will help you chart a course to success. Chart a course to success: You can use this document to define success and make a clear path to achieving those goals. Consider potential challenges: You can use the document to find solutions for problems before they throw a wrench in your business.
How to Make a Production Plan. When you set out to create a production plan, make sure to follow these steps to make it as robust as possible. 1. Estimate/Forecast Product Demand. Understanding product demand planning is the best way to decide which product planning method is the best choice for your operation.
A manufacturing business plan is a written document that contains the business goals of a manufacturing company. It lays out plans to achieve these goals within a specified time frame and also includes market analysis , strategy, and much more.
Similarly, the operations plan section of your business plan explains the production and supply of your product. An operations plan is formed to turn plans into actions. It uses the information you gathered from the analysis of the market , customers, and competitors mentioned in the previous parts of your business plan and allows for the ...
Previous successful business plans and experience to draw from. Management's previous business plan helped in closing an SBA package valued at $240,000 for the acquisition of C.N.C manufacturing equipment. ... As the industrial Products and Services Division is a manufacturing setting, this business plan reflects the development of a large ...
The written part of a steel manufacturer business plan. The written part of a steel manufacturer business plan is composed of 7 main sections: The executive summary. The presentation of the company. The products and services. The market analysis. The strategy.
Manufacturing companies need a rock-solid strategic plan to thrive in today's ultra-competitive business environment. But, let's face it, executing that plan with precision and consistency is where the real hustle begins. According to Deloitte, "In 2024, manufacturers are expected to face economic uncertainty, the ongoing shortage of skilled labor, lingering and targeted supply chain ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library. 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan. Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool.
November 30, 2023. Business Plan, Sales & Marketing Strategy. Running a successful manufacturing business demands more than just operational excellence; it requires a strategic approach to sales and marketing. This guide is designed to help you craft a sales and marketing plan tailored to the business plan of your manufacturing business.
We can assist you with our plastic manufacturing business plan template and how-to manual. You can simply construct a business plan that details every facet of your enterprise, from market analysis and financial predictions to marketing plans and operational tactics, with the help of our comprehensive template and professional advice.
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan.
Manufacturing business plans for private nuclear reactor in Butte. A mining headframe in Uptown Butte, Montana with the city in view in the background. A private nuclear power plant could come to Butte. The company behind the plan said it has backing from local government. Butte-Silver Bow commissioners at a recent meeting were enthusiastic ...
This topic describes how you set up replenishment plans for a standard business scenario. In this example, an enterprise has a distribution center that's modeled as an organization. The distribution center has buy from sourcing rules. The two warehouses, which are also set up as organizations, source goods from the distribution center using ...
To prevent creating planned orders in a supply plan: Set the Create Supply attribute to No for an item-organization. (Constrained Plans Only) Select your decision rules in the plan options. This step is required only if you defined substitutes or alternates in your plan and want the supply plan to use existing supplies or recommend planned ...
Asana is an all-in-one productivity and project management software for businesses of any size. It comes with three plans: basic plan is free of cost for individuals to help them get started ...
The Port of Coeymans has been pursuing plans to build facilities for offshore wind component manufacturing related to the canceled projects. Robin K. Cooper By Luke Nathan - Reporter, Albany ...
Administration's plan for a modern manufacturing renaissance is winning over business owners, who give it a better chance of success than future Trump policies.