How to write a PhD in a hundred steps (or more)
A workingmumscholar's journey through her phd and beyond, annotated bibliography to literature review: a way in.
This post reflects on the affordances and challenges of creating an annotated bibliography as a way in to scoping your field, and drafting your literature review, whether for a paper or a postgraduate thesis.
I am working on a project with 3 colleagues at the moment, the first part of which is writing a literature review scoping the relevant parts of the field addressed in this study. It’s a significant amount of reading, and this literature is new to me, so the work was daunting at first. I felt a bit overwhelmed at the scale of the reading, note-making and writing I would have to do to actually create a relatively short, concise literature review. One of the co-investigators helpfully suggested that one of the outputs be an annotated bibliography , out of which we could craft the literature review. I must add here that I then had to google what this was, because I have never written one before, although the term is not new.

In essence, to create an annotated bibliography, you compile a list of relevant readings on the topic you are writing about, read these, and then create concise, focused summaries that evaluate the quality and accuracy of the source, and its relevance to the research you are doing (a useful example here ). Some guides say you should keep these to 150 words, others indicate that you can go up to about 300 or so words. The main point seems to be to go beyond a simple, descriptive summary of the article, to be critical of the source, and its relevance to your proposed research. It’s useful here to remember that critique is not criticism ; it is rather about inserting your researcher voice and position in relation to the text, and commenting from that position.
This all sounds rather simple, in theory. I am finding it a little harder in practice. This is partly because the summaries I tend to write in my reading journals tend towards the descriptive, and only become critical when I evaluate their relevance and connection to my research. I don’t actually think all that critically about the quality or accuracy of the source, or the authority of the authors, unless this is obviously suspect (for example, a low-impact study that tries to be more, or data that is not clearly described or is atheoretically analysed). These papers, unless that really say something helpful, are usually left out of my eventual literature review.
In the annotated bibliography, you are creating sharp, focused annotations or commentaries (rather than summaries) that point to the type of study (qualitative/quantitative; larger/smaller scale; single/multi-context and so on); the theory or methodology perhaps (as this influences relevance and also accuracy or quality); how (and how clearly or effectively) the argument is made; and how/why the article is relevant to the research you are doing. As you start to grow your bibliography, you can add a comment about how the study connects with, extends or contradicts other studies you have included thus far.

My research is at play here, of course, as it is guiding the selection of sources, and what I am looking for in the reading I am doing. However, I am finding that my argument is rather fuzzier than it could be at this stage; the reading is guided by a general sense of what I am trying to find out about, but my actual argument is not yet formed. I am finding this tricky, as I am working with literature that is new to me. I don’t necessarily know who the ‘names’ are , or what the influential studies are. I’m starting to work this out as the same studies and names are cited over and over in the papers I am reading, but I’m still getting the ‘lie of the land’. But, while I may not yet have my firm argument, I am able to see it emerging from the mists because I know the basic problem or question I am trying to answer.
Holding onto a basic, albeit fuzzy, sense of why I am doing all of this and what I am looking for enables me to manage the annotation process more effectively. I can trim out readings that are irrelevant, too old, or otherwise unfit for this purpose, and add in new readings that are useful and on point. I can keep the annotations clear, concise and focused on the research problem. I can start to make connections between studies, seeing how the authors are talking to one another, and creating a conversation in which there are both agreements and disagreements. This all takes me closer to my literature review, which is where I will make and defend an argument of sorts in response to my research question.
In the literature review I will be doing far more than copying and pasting from my summaries: I will be drawing out key themes in relation to my research problem/question, and elaborating on these using the annotations I have created, but rewriting and connecting these into a framework that illuminates: what the research problem is; why this problem needs to be addressed in our context; how it has been addressed in other contexts; and where the gap is that this project seeks to fill, i.e. the contribution or argument advanced in this research. This will then set us up for creating a suitable methodological plan for going about evidencing or supporting our argument.

I have, as I said, never done an exercise like this before. But, I am really enjoying the intellectual challenge of creating the annotations – it has taken me a while to work this out and the word limit is tough! I am excited at how ‘organically’ the debates, conversations and connections between the different contexts and studies within the readings are emerging, like a puzzle slowly forming out of a mess of pieces. Putting it all into one document – one long bibliography – may seem unwieldy, but this enables me to search for key terms, and to pull threads together in the literature review that is not starting to take shape. It’s making my literature review work less overwhelming, because the annotations are written in my own words, contain my research position, and are critical rather than descriptive, so I am well on my way to creating a literature review that comments on , rather than summarises, the relevant body of literature, and does so in relation to my research problem.
Given how stressful literature reviews are for so many postgraduate writers, and how many are critiqued for being too descriptive and not critical enough, this ‘tool’ could be a useful, practical and manageable way in to your field, and to finding your researcher voice and position.

Share this:
[…] reality is that you have to spend about a year reading, writing reading journal or annotated bibliography entries, making connections, taking a few wrong turns and doubling back, and talking a lot with […]
[…] have written here and here and here about literature reviews, and Pat Thomson and Inger Mewburn have some useful posts that you […]
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Search Website
- Office Directory
- Employee Directory
- Learning Commons
- Topic Sentences
Annotated Bibliography vs. Literature Review
What's the big deal.
There are fundamental differences between an annotated bibliography and a literature review that are crucial to completing the assignment correctly. The chart below is provides an overview of the biggest differences between the two types of assignments in a side-by-side comparison. However, if you need more specific information about either assignment, visit our Annotated Bibliography and/or Literature Review pages for more detailed information on how to complete them.
Differences between an annotated bibliography and literature review
Research Methods at SCS
- Basic Strategies
Literature Reviews
Annotated bibliographies, writing the literature review, matrix for organizing sources for literature reviews / annotated bibliographies, sample literature reviews.
- Qualitative & Quantitative Methods
- Case Studies, Interviews & Focus Groups
- White Papers
A literature review is a synthesis of published information on a particular research topics. The purpose is to map out what is already known about a certain subject, outline methods previously used, prevent duplication of research, and, along these lines, reveal gaps in existing literature to justify the research project.
Unlike an annotated bibliography, a literature review is thus organized around ideas/concepts, not the individual sources themselves. Each of its paragraphs stakes out a position identifying related themes/issues, research design, and conclusions in existing literature.
An annotated bibliography is a bibliography that gives a summary of each article or book. The purpose of annotations is to provide the reader with a summary and an evaluation of the source. Each summary should be a concise exposition of the source's central idea(s) and give the reader a general idea of the source's content.
The purpose of an annotated bibliography is to:
- review the literature of a particular subject;
- demonstrate the quality and depth of reading that you have done;
- exemplify the scope of sources available—such as journals, books, websites and magazine articles;
- highlight sources that may be of interest to other readers and researchers;
- explore and organize sources for further research.
Further Reading:
- Annotated Bibliographies (Purdue OWL)
- How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography (Cornell University)
" Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students " 2009. NC State University Libraries
Review the following websites for tips on writing a literature review:
Literature Reviews. The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Write a Literature Review: Virginia Commonwealth University.
- Matrix for Organizing Sources
Levac, J., Toal-Sullivan, D., & O`Sullivan, T. (2012). Household Emergency Preparedness: A Literature Review. Journal Of Community Health , 37 (3), 725-733. doi:10.1007/s10900-011-9488-x
Geale, S. K. (2012). The ethics of disaster management. Disaster Prevention and Management, 21 (4), 445-462. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/09653561211256152
- << Previous: Basic Strategies
- Next: Qualitative & Quantitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Jan 26, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.georgetown.edu/research

Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Organizing and Managing your Resources
- Define Your Research Question
- Search The Literature
What is an Annotated Bibliography
What is a Literature Review - video
Michelle Early

Difference Between a Literature Review and an Annotated Bibliography
Literature review.
A literature review should not be confused with an annotated bibliography. A literature review is not simply a summary of information you have found on a topic. Literature reviews are more in depth and provides analysis of multiple works relating to a research question. An annotated bibliography is a list of the resources, that you consulted when working on a research project. Each citation is accompanied by a brief written analysis of its usefulness to your research.

Courtesy of Washington University Library
“Library Guides: Annotated Bibliographies: Overview.” Overview - Annotated Bibliographies - Library Guides at University of Washington Libraries , guides.lib.uw.edu/tacoma/annotated.
Purdue Owl Annotated Bibliographies
Purdue owl annotated bibliography information, annotated bibliography breakdown, stem cell research: an annotated bibliography.
Holland, Suzanne. The Human Embryonic Stem Cell Debate: Science, Ethics, and Public Policy . Boston: MIT P, 2001.
This is the annotation of the above source, which is formatted according to MLA 2016 (8 th ed.) guidelines for the bibliographic information listed above. If one were really writing an annotation for this source, one would offer a brief summary of what this book says about stem cell research.
After a brief summary, it would be appropriate to assess this source and offer some criticisms of it. Does it seem like a reliable and current source? Why? Is the research biased or objective? Are the facts well documented? Who is the author? Is she qualified in this subject? Is this source scholarly, popular, some of both?
The length of your annotation will depend on the assignment or on the purpose of your annotated bibliography. After summarizing and assessing, you can now reflect on this source. How does it fit into your research? Is this a helpful resource? Too scholarly? Not scholarly enough? Too general/specific? Since "stem cell research" is a very broad topic, has this source helped you to narrow your topic?
Senior, K. "Extending the Ethical Boundaries of Stem Cell Research." Trends in Molecular Medicine , vol. 7, 2001, pp. 5-6.
Not all annotations have to be the same length. For example, this source is a very short scholarly article. It may only take a sentence or two to summarize. Even if you are using a book, you should only focus on the sections that relate to your topic.
Not all annotated bibliographies assess and reflect; some merely summarize. That may not be the most helpful for you, but, if this is an assignment, you should always ask your instructor for specific guidelines.
Wallace, Kelly. "Bush Stands Pat on Stem Cell Policy." CNN . 13 Aug. 2001.
Using a variety of sources can help give you a broader picture of what is being said about your topic. You may want to investigate how scholarly sources are treating this topic differently than more popular sources. But again, if your assignment is to only use scholarly sources, then you will probably want to avoid magazines and popular web sites.
- Next: Organizing and Managing your Resources >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 2:20 PM
- URL: https://libguides.xavier.edu/Bib_lit
- How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography
- East Tennessee State University
- Literature Reviews
- What is an Annotated Bibliography?
- Examples of Annotated Bibliographies
Difference between Annotated Bibliography and Literature Review
Although both types of writing involve examining sources, a literature review attempts to correlate the information and draw connections between the sources.
Examples of Literature Reviews
- Student Example
- Journal Example
Citation Help
- MLA Center The Modern Language Association website can help you cite sources in MLA style.
- APA Style Blog The American Psychology Association can help you cite sources in APA style.
- Chicago Manual of Style Use this site to help you site sources in Chicago Manual of Style.
- Purdue's Online Writing Lab (OWL) Purdue's Online Language Writing Lab contains up-to-date information on MLA and APA styles.
What is a Literature Review?
Literature Review - from The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. It usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates.
Organizing a Literature Review
There is not one "standard" for literature reviews but they should include the following:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing your literature review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you write about your materials according to when they were published. The oldest date is first and the most recent publication date is last.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend.
- By trend: A better way to organize sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as "evil" in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the "methods" of the researcher or writer. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
- << Previous: Examples of Annotated Bibliographies
Call Local Call Toll-Free Text Email Research Help
Call Toll-Free
Things to remember.

Be Selective
Summarize and Synthesize
Keep Your Own Voice
Use Caution When Paraphrasing
Revise, Revise, Revise
Source: Literature Reviews - The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill
Things to Clarify
Items to clarify if not in assignment:
- How many sources should be included?
- What types of sources should be included? (scholarly articles, books, websites, etc.)
- Should information be reviewed by a common theme or issue?
- Should subheadings and background information be provided? (i.e. definitions and/or a history?)
- Should the review be in chronological or publication order?
- Last Updated: Aug 14, 2023 10:48 AM
- URL: https://libraries.etsu.edu/guides/howto/lib101annotatedbibliographies
USF Libraries Hours by campus
Libraries locations.
- Libraries Hours
- Outages & Maintenance Alerts
RESEARCH TOOLS
- Subject & Course Guides
- USF Libraries Catalog
- Quicksearch All-in-one-search
- Citing Sources
- Find my Librarian
GUIDES / HOW-TO
- Tutorials & Workshops
- Finding Books and Articles
- Finding Reserves
- Checking Out & Renewing
- Reserve a Study Room
- Additional Help Topics
- star Other Services
- For Faculty
- For Graduate Students
- For Undergrads
- Requesting Books & Articles (ILL)
- Textbook Affordability (TAP)
- Library Instruction
- Laptop Checkout
- Schedule Research Help
- Geographic Information Systems
- Data Management Planning
- Copyright & Intellectual Property
- Scholarly Publishing
- Other Services
COLLECTIONS
- What are Collections?
- Special Collections
- Digital Collections
- Digital Heritage & Humanities
- Digital Commons @ USF
- Oral Histories
- Online Exhibitions
- Printing in the Library
- IT Help Desk
- Digital Media Commons (DMC)
- Writing Studio
- Office of Development
- Office for Undergraduate Research
- Directions to the Library
- Library Info & Floor Maps
- Connect From Off Campus
- Renew Materials Online
- Check UBorrow Status
- Printing Help
- Report a Problem
- About the USF Libraries
- University of South Florida Libraries
- General Guides
Conducting a Literature Review
- Creating an Annotated Bibliography
- The Research Process
- Finding Books
- Finding Journal Articles
- Finding Theses and Dissertations This link opens in a new window
- Writing a Literature Review
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, documents and other resources. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
- Annotated Bibliographies Guide from the OWL Offers information about bibliographies, annotations, and how they are useful for your research.
- << Previous: Finding Theses and Dissertations
- Next: Writing a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2023 2:34 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.usf.edu/LitReview

- WESTCHESTER CAMPUS
- Social Media Center
- Directories
ENG 201: Research Introduction, Annotated Bibliography & Literature Review (PLV)
- Research Introduction
Annotated Bibliographies & Literature Reviews
Writing an annotated bibliography, why do we write literature reviews, what are scholarly journals & peer review.
- Strategic Searching
- Locating Sources Online & At Pace
- Citing Your Sources

How are annotated bibliographies and literature reviews related?
Annotated bibliographies collect sources and present citations along with a summary and analysis that connects the information to your research question. In a literature review , the author synthesizes multiple sources together to present the major themes, arguments and theories around a topic.
Therefore, an annotated bibliography can provide an opportunity to review and analyze individual sources before o rganizing them around common denominators found across sources.

Creating an annotated bibliography:
- Review your assignment to determine how your professor would like your annotated bibliography to look.
- Search ! The "Strategic Searching" and "Locating Sources Online & At Pace" pages on this guide for assistance in locating potential sources.
- Create the citations for your sources.
- Write a paragraph for each citation summarizing, analyzing and determining the relevance of that source to your paper. Icon by freepik
Examples:
- University of Wisconsin: Annotated Bibliographies Research Guide This Research Guide page walks through the step by step process of creating an annotated bibliography.
- Rasmussen College: Annotated Bibliography Research Guide Watch the video and see an example of an annotated bibliography.

Literature reviews serve a purpose in research by:
- Showing the writer's understanding of their topic area including key concepts, terminology, theories and definitions
- Identifying what research has been done in that area
- Finding gaps in the research or current areas of interest to help the writer tweak their own research question, if needed
- Identifying main areas of agreement, disagreement or controversy within the topic area
- Convincing the reader that your research question is significant, important and interesting
You are writing a MAP to the scholarly conversation on your topic.
- Planning and Creating a Literature Review Video Tips for searching, analyzing, and organizing sources for your literature review.
For your Literature Review you will summarize, evaluate, and synthesize, existing scholarship related to your research question. This "scholarship" is found in academic, scholarly, peer-reviewed journals. These differ from magazines and articles written for the general public because scholarly journals are written for researchers and experts in the discipline area.

Click the link below titled, "Anatomy of a Scholarly Journal Article" to view an interactive journal article and review what each section means.
You may need a few peer reviewed sources for your literature review. But what does that mean?
Peer-reviewed and refereed publications include articles that are read and approved by an editor and one or more experts in that field to confirm accuracy of information and the contribution of that information to the scholarly conversation.
- Anatomy of a Scholarly Journal Article Click to explore what makes up a "scholarly journal article." From the North Carolina State University Library.
- How to Read a Scholarly Article A visual demonstration, from Western Libraries.
- Example of a Scholarly Article
- Example #2 of a Scholarly Journal
- << Previous: Research Introduction
- Next: Strategic Searching >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 3:45 PM
- URL: https://libguides.pace.edu/eng201
- © Pace University
- Work at Pace
- Privacy Policy

EDL 7108 Action Research I: Literature Reviews and Annotated Bibliographies
- Discovery System
- Search Tips and Tutorials
- Research Methods
- Distinguishing Article Type
- Literature Reviews and Annotated Bibliographies
- Interlibrary Loan - ILLiad This link opens in a new window
- APA Citation Help
Literature Reviews: An Overview
Annotated Bibliography and Literature Review Information
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It Created by Written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto.
- Conducting Literature Reviews - University of North Carolina
- Creating Annotated Bibliographies - OWL at Purdue University
- Annotated Bibliographies - University of Illinois at Urbana- Champaign
- Lit review check list
- Annotated Bibliography Review Chapter 7 - Section 2>> Annotated Bibliographies.
The Literature Review
According to Hart (1998), “A literature review is an objective, thorough summary and critical analysis of the relevant available research and non-research literature on the topic being studied” (as cited in Cronin, Ryan & Coughlan 2008).
The Literature Review Process
- Selecting a review topic
- Searching the literature
- Gathering, reading and analyzing the literature
- Writing the review
Lit Review Process

Types of Literature Reviews
- Systematic literature review
Implemented in response to specific questions about clinical practice; designation of criteria for including/excluding literature is important part of this type of review.
Purpose : aims at producing an inclusive list of the entire literature on a topic; set apart the literature on a topic based on predefined criteria; assess and synthesize these sources
- Traditional or narrative review
Summarizes, synthesizes and discusses literature on chosen topic; selective with regard to sources included.
Purpose : to give a comprehensive overview of the literature in a chosen area; to identify gaps in existing research; to develop conceptual framework; to refine research topic/question
(Cronin et al. 2008, 38)
Questions your lit review should answer
- Why is this subject important?
- Who else thinks it is important?
- Who has worked on this subject before?
- Who has done something similar to what I am doing?
- What can be adapted to my own study?
- What are the gaps in the research?
- Who is going to use my material?
- What use will my project be?
- What will my contribution be?
- What specific question will I answer?
- What specific questions will my research not be able to address?
(Murray 2006:115)
- << Previous: Distinguishing Article Type
- Next: Interlibrary Loan - ILLiad >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:07 AM
- Guide URL: https://libguides.wilmu.edu/EDL7108

Module 10: The Research Process—Finding and Evaluating Sources
Annotated bibliographies and literature reviews, learning objectives.
- Describe the structure and value of an annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliographies

Figure 1 . Annotated bibliographies are helpful when finding sources and determining how that source might be helpful for your paper.
An annotated bibliography is a list of all your sources, including full citation information and notes on how you will use the sources. Writers often create annotated bibliographies as a part of a research project, as a means of recording their thoughts and deciding which sources to actually use to support the purpose of their research. Some writers include annotated bibliographies at the end of a research paper as a way of offering their insights about the sources’ usability to their readers.
College instructors often assign annotated bibliographies as a way to help students think through their sources’ quality and appropriateness to their research question or topic. Although it may take a while to complete the annotated bibliography, the annotations themselves are relatively brief.
Link to Learning
You can see a sample annotated bibliography from a student if you have not completed an annotated bibliography in the past.
Why Annotated Bibliographies?
Annotated bibliographies are useful for several reasons. If you keep one while you research, the annotated bibliography will function as a useful guide. It will be easier for you to revisit sources later because you will already have notes explaining how you want to use each source. If you find an annotated bibliography attached to one of the sources you are using, you can look at it to find other possible resources.
Constructing Your Citations
The first part of each entry in an annotated bibliography is the source’s full citation. We examine citations in another section of this course, and detailed instructions for creating the citation can be found in the style manual for whatever format (APA, MLA, etc.) your professor wants you to use.
What to Include in Each Annotation
A good annotation has three parts, in addition to the complete bibliographic information for the source:
- a brief summary of the source ,
- a critique and evaluation of credibility, and
- an explanation of how you will use the source in your essay .
Start by stating the main idea of the source. If you have space, note the specific information that you want to use from the source, such as quotations, chapters, or page numbers. Then explain if the source is credible, and note any potential bias you observe. Finally, explain how that information is useful to your own work.
You may also consider including the following information:
- an explanation about the authority and/or qualifications of the author
- the main purpose of the work
- any detectable bias or interpretive stance
- the intended audience and level of reading
Writing the Annotated bibliography
Keep these suggestions in mind as you construct an annotated bibliography:
- a relatively narrow focus: a relatively narrow research question or a working thesis sentence with a clear angle
- select the sources most related: skim the sources first; then more carefully read those that seem useful to your research focus.
- summarize the source: reproduce the author’s main ideas in your own words. Be careful to change the wording and the structure as you put the information from the source into your own words.
- analyze the source: ask yourself questions. Is there enough relevant information to address my narrow focus? Does the author delve deeply into the subject as opposed to offering a general overview? What type of evidence does the author use? Does the author use statistical information accurately, to the best of my knowledge?
- evaluate the source’s usefulness to the narrow focus of your research. Make connections between the source and your focus for your project.
- use the assigned bibliographic style (usually MLA or APA style) to create the bibliography entry that begins each annotated source on your list.
In most annotated bibliographies, the summary, analysis, and evaluation for each source becomes the body of the annotation for that source. Some annotated bibliographies may not require all three of these elements, but most will. Be sure to consult your instructor, and ask questions if you’re unsure about the required elements within each entry of your annotated bibliography.
Example Annotation
Source: Farley, John. “The Spontaneous-Generation Controversy (1700–1860): The Origin of Parasitic Worms.” Journal of the History of Biology , 5 (Spring 1972), 95–125.
- Notes: This essay discusses the conversation about spontaneous generation that was taking place around the time that Frankenstein was written. In addition, it introduces a distinction between abiogenesis and heterogenesis. The author argues that the accounts of spontaneous generation from this time period were often based on incorrect assumptions: that the discussion was focused primarily on micro-organisms, and that spontaneous-generation theories were disproved by experiments. The author takes a scientific approach to evaluating theories of spontaneous generation, and the presentation of his argument is supported with sources. It is a reliable and credible source. The essay will be helpful in forming a picture of the early 19th-century conversation about how life is formed, as well as explaining the critical perception of spontaneous-generation theories during the 19th century.
Literature Review
The literature of a literature review is not made up of novels and short stories and poetry—but is the collection of writing and research that has been produced on a particular topic.
The purpose of the literature review is to give you an overview of a particular topic. Your job is to discover the research that has already been done, the major perspectives, and the significant thinkers and writers (experts) who have published on the topic you’re interested in. In other words, it’s a survey of what has been written and argued about your topic.
By the time you complete your literature review you should have written an essay that demonstrates that you:
- Understand the history of what’s been written and researched on your topic.
- Know the significance of the current academic thinking on your topic, including what the controversies are.
- Have a perspective about what work remains to be done on your topic.
Thus, a literature review synthesizes your research into an explanation of what is known and what is not known on your topic. If the topic is one from which you want to embark on a major research project, doing a literature review will save you time and help you figure out where you might focus your attention so you don’t duplicate research that has already been done.
Just to be clear: a literature review differs from a research paper in that a literature review is a summary and synthesis of the major arguments and thinking of experts on the topic you’re investigating, whereas a research paper supports a position or an opinion you have developed yourself as a result of your own analysis of a topic.
Another advantage of doing a literature review is that it summarizes the intellectual discussion that has been going on over the decades—or centuries—on a specific topic and allows you to join in that conversation (what academics call academic discourse) from a knowledgeable position.
The following presentation will provide you with the basic steps to follow as you work to complete a literature review.
Literature Reviews
annotated bibliography: a list of your sources for your research, including full citation information and notes on how you will use the sources
literature review: a summary and synthesis of the major arguments and thinking of experts on the topic you’re investigating
- Literature Reviews. Provided by : Excelsior College Online Writing Lab. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/literature-reviews/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Annotated Bibliographies. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/annotated-bibliographies/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Using Your Sources. Provided by : Boundless. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-writing/chapter/using-your-sources/ . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

How to Write an Annotated Bibliography - APA Style (7th Edition)
What is an annotation, how is an annotation different from an abstract, what is an annotated bibliography, types of annotated bibliographies, descriptive or informative, analytical or critical, to get started.
An annotation is more than just a brief summary of an article, book, website, or other type of publication. An annotation should give enough information to make a reader decide whether to read the complete work. In other words, if the reader were exploring the same topic as you, is this material useful and if so, why?
While an abstract also summarizes an article, book, website, or other type of publication, it is purely descriptive. Although annotations can be descriptive, they also include distinctive features about an item. Annotations can be evaluative and critical as we will see when we look at the two major types of annotations.
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100–200 words in length.
Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes:
- Provide a literature review on a particular subject
- Help to formulate a thesis on a subject
- Demonstrate the research you have performed on a particular subject
- Provide examples of major sources of information available on a topic
- Describe items that other researchers may find of interest on a topic
There are two major types of annotated bibliographies:
A descriptive or informative annotated bibliography describes or summarizes a source as does an abstract; it describes why the source is useful for researching a particular topic or question and its distinctive features. In addition, it describes the author's main arguments and conclusions without evaluating what the author says or concludes.
For example:
McKinnon, A. (2019). Lessons learned in year one of business. Journal of Legal Nurse Consulting , 30 (4), 26–28. This article describes some of the difficulties many nurses experience when transitioning from nursing to a legal nurse consulting business. Pointing out issues of work-life balance, as well as the differences of working for someone else versus working for yourself, the author offers their personal experience as a learning tool. The process of becoming an entrepreneur is not often discussed in relation to nursing, and rarely delves into only the first year of starting a new business. Time management, maintaining an existing job, decision-making, and knowing yourself in order to market yourself are discussed with some detail. The author goes on to describe how important both the nursing professional community will be to a new business, and the importance of mentorship as both the mentee and mentor in individual success that can be found through professional connections. The article’s focus on practical advice for nurses seeking to start their own business does not detract from the advice about universal struggles of entrepreneurship makes this an article of interest to a wide-ranging audience.
An analytical or critical annotation not only summarizes the material, it analyzes what is being said. It examines the strengths and weaknesses of what is presented as well as describing the applicability of the author's conclusions to the research being conducted.
Analytical or critical annotations will most likely be required when writing for a college-level course.
McKinnon, A. (2019). Lessons learned in year one of business. Journal of Legal Nurse Consulting , 30 (4), 26–28. This article describes some of the difficulty many nurses experience when transitioning from nursing to a nurse consulting business. While the article focuses on issues of work-life balance, the differences of working for someone else versus working for yourself, marketing, and other business issues the author’s offer of only their personal experience is brief with few or no alternative solutions provided. There is no mention throughout the article of making use of other research about starting a new business and being successful. While relying on the anecdotal advice for their list of issues, the author does reference other business resources such as the Small Business Administration to help with business planning and professional organizations that can help with mentorships. The article is a good resource for those wanting to start their own legal nurse consulting business, a good first advice article even. However, entrepreneurs should also use more business research studies focused on starting a new business, with strategies against known or expected pitfalls and issues new businesses face, and for help on topics the author did not touch in this abbreviated list of lessons learned.
Now you are ready to begin writing your own annotated bibliography.
- Choose your sources - Before writing your annotated bibliography, you must choose your sources. This involves doing research much like for any other project. Locate records to materials that may apply to your topic.
- Review the items - Then review the actual items and choose those that provide a wide variety of perspectives on your topic. Article abstracts are helpful in this process.
- The purpose of the work
- A summary of its content
- Information about the author(s)
- For what type of audience the work is written
- Its relevance to the topic
- Any special or unique features about the material
- Research methodology
- The strengths, weaknesses or biases in the material
Annotated bibliographies may be arranged alphabetically or chronologically, check with your instructor to see what he or she prefers.
Please see the APA Examples page for more information on citing in APA style.
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2023 11:27 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/annotated-bibliography-apa
- Licensing Information
- Contributing Authors
- 1. Let's Get Writing
- 1.1. The 5 C Guidelines
- 1.2. How to Write Articles Quickly and Expertly
- 2. Critical Thinking
- 2.1. Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- 2.2. Necessary and Sufficient Conditions
- 2.3. Good Logic
- 3. APA for Novices
- 3.1. Hoops and Barriers
- 3.2. Crafts and Puzzles
- 3.3. The Papers Trail
- 3.4. The Fine Art of Sentencing
- 3.5. Hurdles
- 3.6. Small Stressors
- 4. Literature Reviews
- 4.1. Introduction to Literature Reviews
- 4.2. What is a Literature Review?
- 4.3. How to Get Started
- 4.4. Where to Find the Literature
- 4.5. Evaluating Sources
- 4.6. Documenting Sources
- 4.7. Synthesizing Sources
- 4.8. Writing the Literature Review
- 4.9. Concluding Thoughts on Literature Reviews
- Technical Tutorials
Constructing an Annotated Bibliography with Zotero
- Extracting Resource Metadata from a Citation List with AnyStyle.io
- Exporting Zotero to a Spreadsheet
- APA 7 Job Aid
- Index of Topics
- Translations
Choose a Sign-in Option
Tools and Settings
Questions and Tasks
Citation and Embed Code


Learning Objectives
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Generate an annotated bibliography from resources collected in Zotero.
An annotated bibliography can be a useful precursor to a literature review. When engaging in any scholarly writing, it is helpful to begin with an outline that is gradually fleshed out with details and explanations. An annotated bibliography is a structured outline of a literature review topic that includes citations to each resource, summaries of those resources, and syntheses of how the resources fit together within the larger narrative. Thus, an annotated bibliography is both a worthwhile outcome on its own and a good in-between stage for moving from a barebones outline to a fully-fledged literature review.
Because the literature review process requires the management, analysis, and synthesis of many complex resources, such as various research articles that each have their own unique questions, contexts, methods, results, and limitations, staying organized is essential. This means that you need to collect resources and organize them in a way that allows for easy retrieval and that any notes, summaries, and important quotes that you find while reading a resource are attached to that resource in a way that you can make sense of them as you proceed.
As stated in a previous chapter, there are many tools available to support you in the collection, organization, and citation of resources, such as Mendeley, EndNote, and Zotero. Many of these tools are compatible with one another, and a library in one (such as Mendeley) can be exported and then imported into another (such as Zotero). Each of these tools has its own strengths and weaknesses, but for the purposes of this chapter, we will use Zotero, because it (1) allows for folder-level organization of resources, (2) allows for modification of output styles, and (3) can automatically generate a bibliography document that includes unique fields (such as the Abstract and Extra field).
1. Install Zotero and the Appropriate Browser Connector

Zotero can be freely downloaded and installed for various operating systems by going to the Zotero download page [https://edtechbooks.org/-WXs] . Once you have installed Zotero, you can open the program as a window on your desktop.
After doing this, you will also want to install the appropriate browser connector for Zotero from the download page [https://edtechbooks.org/-WXs] . This allows you to collect resources directly in your browser that are then piped to Zotero for saving and annotation.
2. Collect a Resource
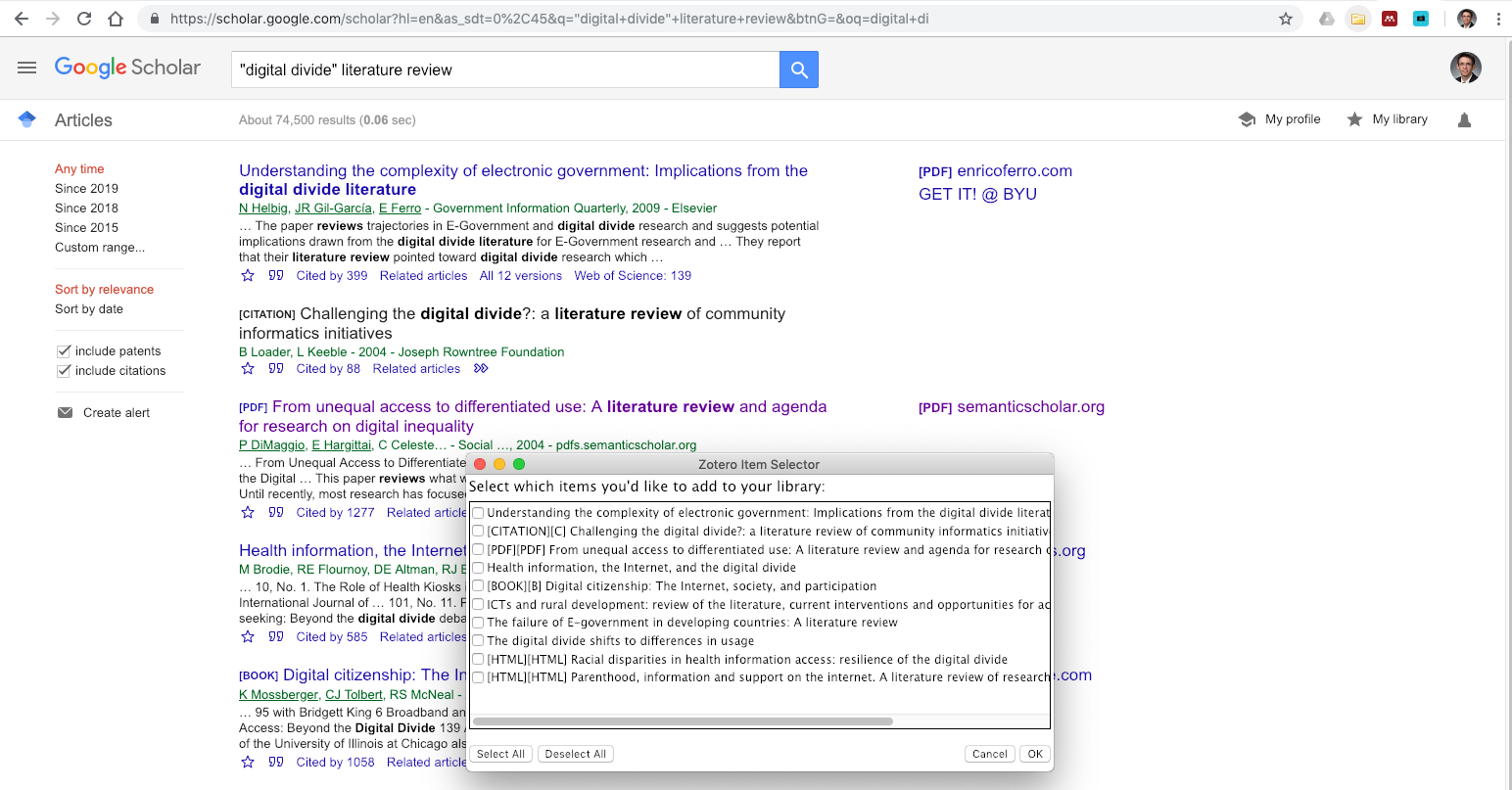
The first step in this process is to begin collecting your resources. Following the guidelines in previous chapters, as you find an appropriate resource, simply click on the Zotero icon at the top-right of your browser window and select the folder you would like to place it in. (The Zotero app must be open on your desktop for this to work.)
Depending on the metadata available on a site, you might be able to do this with either a single resource (such as an open article) or a list of resources (such as from a database search result). Once the resource is saved to Zotero, you can switch to the app to verify that it was saved.
Additionally, if you have access to the PDF for the resource, you can right-click on it in Zotero and choose "Find availalable PDFs" to allow Zotero to attempt to fetch it for you. If successful, a triangle will appear to the left of the item, which means that the PDF was saved in Zotero. Alternatively, if you have the PDF saved on your computer, you can drag it onto the entry to have Zotero save it for you. To view the PDF, double-click the entry.
Additionally, if you already have a collection of resources in another tool (such as Mendeley), you can export and import them into Zotero (either individually or en masse) by using the RDF format or another standard format (e.g., BibTex, RIS).
3. Update or Verify Information
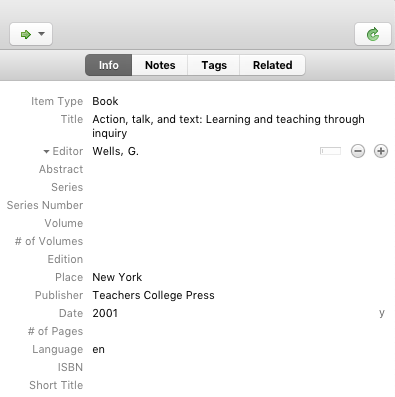
Zotero tries to populate the metadata for each resource as best it can, but it sometimes makes mistakes. For each item, be sure read through the entries for each field and make sure (1) that the information is placed in the correct field and (2) typos and spelling errors are removed.
4. Organize the Resource into a Collection and Subcollection
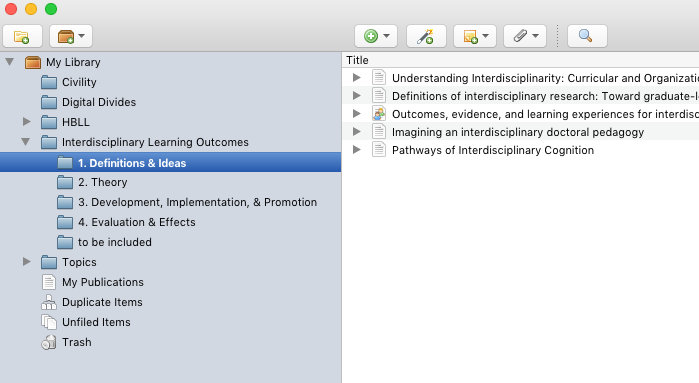
To keep things organized, you should create a Collection for your topic, and since the overall topic of a bibliography might be huge, you should also create thematic subcollections (much like an outline when you are writing). Example subcollections that are commonly used might be "Definitions," "Theoretical Foundations," or "Empirical Studies." Drag your resource into the appropriate subcollection.
5. Summarize the Resource in its Abstract Field
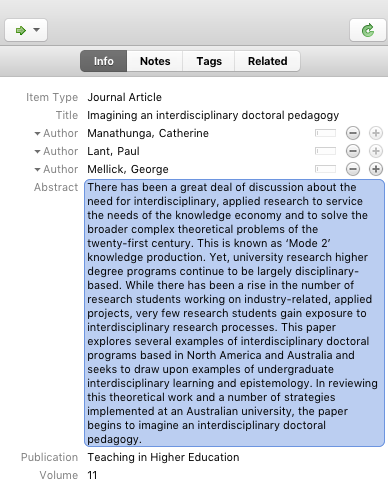
Your bibliography should reflect your own understanding of the resources and to avoid plagiarism should 100% reflect your own words. As you read each resource, you should replace any content in the Abstract field with your own summary of the resource, explaining what it is about, how it relates to your overall topic, what limits might be placed on the study, and so forth. This should generally be about 100 to 200 words in length and should not include any direct quotes.
6. Include Direct Quotes from the Resource in its Extra Field
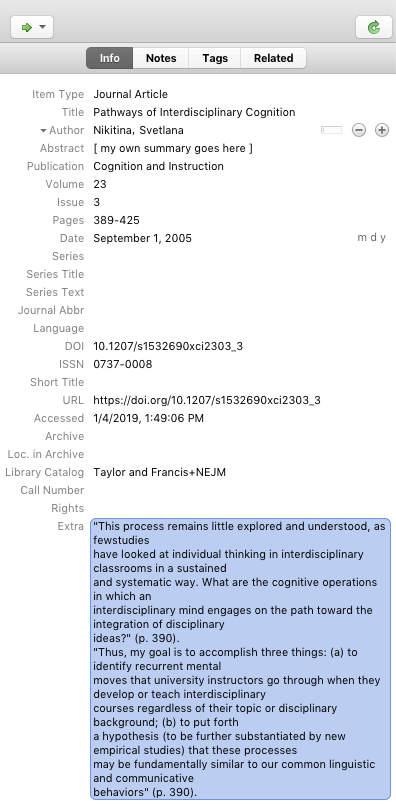
Especially if you plan to turn your annotated bibliography into a literature review later on, you should also find direct quotations from each resource that are valuable for your topic. Copy and paste this into the Extra field. Be sure to encapsulate any direct quote in parentheses (to avoid potential plagiarism down the road) and include an in-text citation with the page number, such as (Kimmons, 2017).
7. Repeat Steps 2 Through 6
Bibliographies may include anywhere from 10 to 1,000 resources. So, repeat Steps 2 through 6 for each resource, and consult other chapters in this book to help you determine what to include, how to manage your scope, and so forth.
8. Install the Custom Style
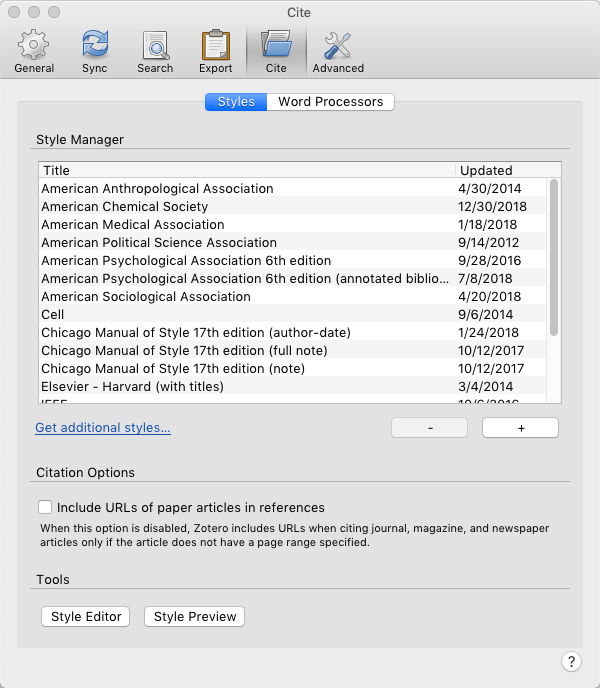
Zotero does not have a default way to export your bibliography with your annotations. To do this, you must install a custom style. Choose the appropriate format from the list below (depending on whether or not you want direct quotes in your bibliography):
- Annotated bibliography style with the Abstract field [https://edtechbooks.org/-whhY]
- Annotated bibliography style with the Abstract and Extra field [https://edtechbooks.org/-VrPc]
If the file opens in your browser rather than downloading, you will need to go to File > Save As or right-click on the link and choose Save link as... to save the file to your machine.
Once downloaded, open your Preferences tab in Zotero, and click on Cite > Styles > +. You can then add your downloaded style to the list of available styles.
9. Export Subcollections Separately
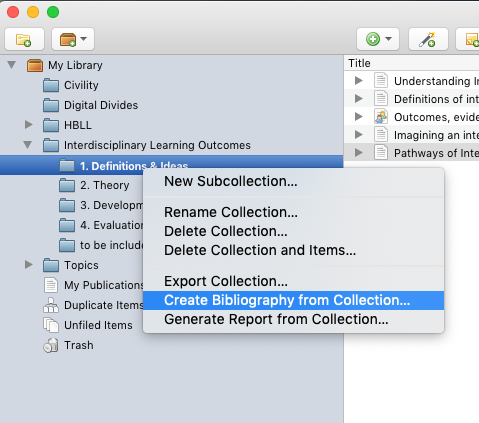
For each subcollection, right-click on the subcollection title, and select Create Bibliography from Collection... .
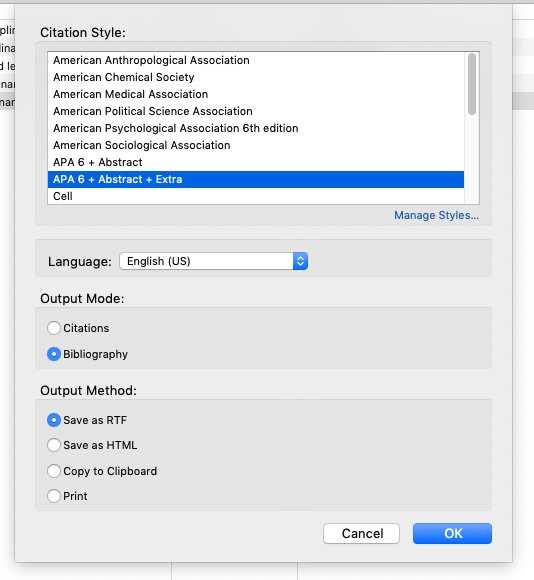
Then select the appropriate style from the available menu (either APA 6 + Abstract or APA 6 + Abstract & Extra ). Be sure that Output Mode is set to Bibliography and that Output Method is set to RTF . Click OK to save. Give the file an appropriate name, and save it in a place where you can find it.
10. Copy/Paste Subcollection Bibliographies Together in Your Word Processing Application
Once each subcollection is exported, open each one separately and copy/paste the files contens into a master annotated bibliography document. Be sure to create separate headings for each subcollection that you are pasting in so that you are able to keep thematic groups separated.
11. Correct Formatting
Go through this merged document and correct formatting. You may need to add hanging indents to citations and add additional line breaks to provide separation for separate bibliography items.
12. Add Section Summaries
And finally, go through the document and add synthesizing summaries to each subcollection section. These should generally be 100 to 400 words in length and should summarize what the resources in the subcollection as a whole have to say about the topic.
And that's it!
Good luck bibliography-ing!
This content is provided to you freely by EdTech Books.
Access it online or download it at https://edtechbooks.org/rapidwriting/annotated_bibliography .

How to Write an Annotated Bibliography for Research

Introduction
What is an annotated bibliography, writing an annotated bibliography, analyzing an annotated bibliography.
A literature review is more than just a collection of articles that inform your research project. For a literature review to benefit your research, you need to structure it in a way that organizes scientific knowledge and synthesizes this knowledge to justify your research project.
An annotated bibliography is one tool that provides that organization. In this article, we will explore why it's important to craft an annotated bibliography for your research and what to put into one so it can serve as a foundation for your future research inquiries.

Annotated bibliographies are a tool to organize existing research in a way that helps you to demonstrate your familiarity with a particular research topic. Each annotated bibliography entry outlines each study in your literature review and includes your analysis of the study.
A bibliography refers to the full list of references included in your literature review. An annotation refers to notes, summaries, and reflections about each reference. Thus, an annotated bibliography consists of the references in your literature review and your notes on each reference.
How is it different from a literature review?
A literature review is a collection of articles on the latest research and the subsequent synthesis of the theoretical developments arising from that research. An annotated bibliography can help you achieve that synthesis by organizing the information in a systematic way and providing space for your analysis (and critiques, where appropriate).
How long is an annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography includes all the relevant contemporary research conducted on the topics covered by the research questions you want to address. Ultimately, the current state of the research area you are addressing will dictate the length of your literature review and annotated bibliography.
Research topics that have greater theoretical coherence will have more relevant studies, while less-explored research questions will have fewer studies. In the end, it is the up to the researcher's judgment to determine whether they have collected sufficient research for their annotated bibliography.
Organization of knowledge
We've all likely made the mistake of simply downloading journal articles and other scholarly publications relevant to our research and throwing them in a folder on our computer, seldom to be read until it comes time to write our paper. At this point, these articles are just a jumble of information that is difficult to sift through. Of course, it is possible to synthesize knowledge without using annotated bibliographies, but the process will be time-consuming and tedious.
Think of information that you collect for an annotated bibliography as unstructured data that needs to be organized in a way that facilitates the identification of useful insights. Having all the existing research distilled into a succinct form is important, but providing a structure that organizes that knowledge will make it much easier to synthesize theory and present theory in your resulting research manuscripts or presentations.
From start to finish, ATLAS.ti is there for every stage of research
Find out how your research question becomes rich analysis with a free trial of ATLAS.ti.
An annotated bibliography is more of a visual organizer for your thoughts about the existing research than it is a required element in your paper or presentation. That said, there should be an intentional process applied to the writing of annotated bibliographies that is important to outline in this section.
Conducting a literature review
The literature review informs the annotated bibliography and the subsequent research inquiries that it provokes. Ultimately, you will want to search for the most recent scholarly articles containing the most relevant information that pertains to the concept or theory you want to research.
When putting together a literature review, remember to search for the most recent research articles outlining important theoretical developments relevant to your research question. Be sure to consult various web sites, scholarly databases, and bibliographies of key articles for research that aligns with your research interests.
How do you format an annotated bibliography?
While there is no particular standard used to write annotations, there are a few common criteria used to analyze existing research sources:
- Bibliographic citation . Citing research papers is an important part of the research publication process. By providing a reference in the proper citation format now, you can make it easier to copy and paste this reference entry into your paper later.
- Keywords . Articles often come with a list of keywords that make it easy for you to search for when conducting your literature review. They are also useful for determining what aspects of your research inquiry are and aren't being explored by the collected research.
- Study description . A brief summary (typically one paragraph) of each research paper can help you conduct your literature review. Complete sentences may not be necessary, but writing your own understanding of each paper now can make writing your background section easier later on.
- Research context . Context is important because cultural influences, historical factors, and other sociocultural resources inform the data collection and analysis. Be sure to outline the relevant details of the place in which the study was conducted.
- Methods . The various methods employed in qualitative research look at phenomena in profoundly different ways. Make sure to list the methods for each study to identify any methodological gaps when analyzing your annotated bibliography.
- Potential critiques . Use this space in your annotated bibliography to note what each study has overlooked in terms of theory or methods. These critiques will contribute to the problem statement that defines your research question and the resulting study.
Other items to include in your reference list might include DOI numbers, theoretical frameworks , study limitations, and any other information that would be worth sorting or filtering when you conduct your analysis .
Ultimately, the annotated bibliography format is either determined by your assignment guidelines (if it is a requirement of your coursework) or your own judgment (when you are distilling research for designing a study ). Some annotated bibliographies are written in paragraph form like a series of little essays, each describing a particular bibliographic citation. Others can also take the form of a table that visually organizes the information in a form where it is easy to spot patterns and limitations.
Whatever you decide, the format should be consistent across each annotated bibliography entry. The effort it takes to consistently format your bibliography will save time later on as your collected research will be easier to read and synthesize.
If you do use your annotated bibliography in your research paper for publication, ensure that your citations conform to Modern Language Association (MLA) format, American Psychological Association (APA) format, or the reference format used in the journal to which you are submitting your research. You can refer to a publication manual like the MLA Handbook, but it's probably more helpful to look for annotated bibliography examples online that can serve as models for your own bibliography.
Doing a quick search for journal articles that synthesize existing research in a literature review might give you some useful annotated bibliography examples.
Once you have organized your literature review in an annotated bibliography, the next step is identifying useful pathways for your own research to explore. Locating the gaps in the current scholarship is a necessary task for formulating a research question , defining your theoretical framework , and designing your overall study .
The Code-Document Analysis tool in ATLAS.ti can serve as a good annotated bibliography generator. Code your collected studies and analyze those codes in the Code-Document Analysis tool to gain a sense of what theories and developments are discussed in each study. By generating a visual understanding of the current state of research, you can make it easier to define subsequent lines of research inquiry that justify the study you want to conduct.
From start to finish, ATLAS.ti makes your research work
Download a free trial of our data analysis platform to see how you can turn your literature into insights.


Literature Review: Annotated bibliography
- Traditional or narrative literature reviews
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic literature reviews
Annotated bibliography
- Keeping up to date with literature
- Finding a thesis
- Evaluating sources and critical appraisal of literature
- Managing and analysing your literature
- Further reading and resources
Creating an annotated bibliography part 1
Creating an annotated bibliography part 2
An annotated bibliography is a bibliography where references are given annotations or notes. There are generally four types of annotations -
- Descriptive annotations that describe the work
- Summary annotations that provide a summary of the key points of a particular work
- Critical annotations which evaluate where the work fits or doesn't fit within your research topic
- Combined annotations which use all or some of the above styles.
Depending on your assignment you may be asked to reflect, summarise, critique, evaluate or analyse the source. You may be asked to find a specific number of items to include in the annotated bibliography. These items are most commonly refereed or peer reviewed journal articles but can include book chapters, books, conference papers and other information sources. You may be asked to write an annotated bibliography as a stand alone assignment or as a component of a larger project.
Questions to consider
You need to consider carefully the texts that you select for your annotated bibliography. Keep the following questions in mind to help clarify your choices.
- What topic/ problem am I investigating?
- What question(s) am I exploring? Identify the aim of your literature research.
- What kind of material am I looking at and why? Am I looking for journal articles, reports, policies or primary historical data?
- Am I being judicious in my selection of texts? Does each text relate to my research topic and assignment requirements?
What are the essential or key texts on my topic? Am I finding them? Are the sources valuable or often referred to in other texts?
Which writing style should I use in the annotations?
- Each annotation should be concise. Do not write too much—remember, you are writing a summary, not an essay. Annotations should not extend beyond one paragraph unless otherwise stipulated in your assignment guidelines. As this is not an extended piece of writing, only mention significant and relevant details.
- Any information apparent in the title of the text or journal can be omitted from the annotation.
- Background materials and references to previous work by the same author usually are not included. As you are addressing one text at a time, there is no need to cross reference or use in-text citations to support your annotation.
- Unless otherwise stipulated, you should write in full sentences using academic vocabulary.
Further Reading : University Of New South Wales Annotated Bibliography
EndNote for Annotated Bibliographies
Using endnote to create an annotated list..
Step 1. Create an EndNote group for your annotated bibliography references.
Step 2. Creating your Annotated list in a Word document.
- Select the references that you want to use, by either selecting the whole group or select multiple references using the Ctrl key for Windows, or Command key if using a Mac.
- Use the Copy formatted shortcut, Ctrl k to copy these to your clipboard.
Step 3. Paste the results to your Word document.
- You can insert your annotations below each reference to create your annotated Bibliography.
Note: The references below do not show the required indent for APA 7th, due to this guide's settings.
Bay, U. (2013). Transition town initiatives promoting transformational community change in tackling peak oil and climate change challenges. Australian Social Work, 66 (2), 171-186. https://doi.org/10.1080/0312407X.2013.78120
This paper focuses on quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur?
Beaumont, E., Chester, P., & Rideout, H. (2017). Navigating ethical challenges in social media: Social work student and practitioner perspectives. Australian Social Work, 70 (2), 221-228. https://doi.org/10.1080/0312407X.2016.1274416
This gives and interesting perspective of ut enim ad minima veniam, quis nostrum exercitationem ullam corporis suscipit laboriosam, nisi ut aliquid ex ea commodi consequatur? Quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur?
Beddoe, L. (2010). Social work and power. Australian Social Work, 63 (3), 361-362. https://doi.org/10.1080/0312407X.2010.500650
The author presents a case where quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur?
- << Previous: Systematic literature reviews
- Next: Developing a search strategy >>
- Last Updated: Apr 10, 2024 5:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csu.edu.au/review

Charles Sturt University is an Australian University, TEQSA Provider Identification: PRV12018. CRICOS Provider: 00005F.
How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography: The Annotated Bibliography
- The Annotated Bibliography
- Fair Use of this Guide
Explanation, Process, Directions, and Examples
What is an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
Annotations vs. Abstracts
Abstracts are the purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes. Annotations are descriptive and critical; they may describe the author's point of view, authority, or clarity and appropriateness of expression.
The Process
Creating an annotated bibliography calls for the application of a variety of intellectual skills: concise exposition, succinct analysis, and informed library research.
First, locate and record citations to books, periodicals, and documents that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic. Briefly examine and review the actual items. Then choose those works that provide a variety of perspectives on your topic.
Cite the book, article, or document using the appropriate style.
Write a concise annotation that summarizes the central theme and scope of the book or article. Include one or more sentences that (a) evaluate the authority or background of the author, (b) comment on the intended audience, (c) compare or contrast this work with another you have cited, or (d) explain how this work illuminates your bibliography topic.
Critically Appraising the Book, Article, or Document
For guidance in critically appraising and analyzing the sources for your bibliography, see How to Critically Analyze Information Sources . For information on the author's background and views, ask at the reference desk for help finding appropriate biographical reference materials and book review sources.
Choosing the Correct Citation Style
Check with your instructor to find out which style is preferred for your class. Online citation guides for both the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA) styles are linked from the Library's Citation Management page .
Sample Annotated Bibliography Entries
The following example uses APA style ( Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th edition, 2019) for the journal citation:
Waite, L., Goldschneider, F., & Witsberger, C. (1986). Nonfamily living and the erosion of traditional family orientations among young adults. American Sociological Review, 51 (4), 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
This example uses MLA style ( MLA Handbook , 9th edition, 2021) for the journal citation. For additional annotation guidance from MLA, see 5.132: Annotated Bibliographies .
Waite, Linda J., et al. "Nonfamily Living and the Erosion of Traditional Family Orientations Among Young Adults." American Sociological Review, vol. 51, no. 4, 1986, pp. 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
Versión española
Tambíen disponible en español: Cómo Preparar una Bibliografía Anotada
Content Permissions
If you wish to use any or all of the content of this Guide please visit our Research Guides Use Conditions page for details on our Terms of Use and our Creative Commons license.
Reference Help

- Next: Fair Use of this Guide >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2022 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/annotatedbibliography

- California State University, Northridge
Secondary Education
- Annotated Bibliography & Literature Review
- Getting Started
- Reference & Research Process
- Statistics and Data Sources
- Secondary Ed Journals/Books
- Search Tips: Choosing a Topic
- Search Tips: Choosing Keywords and Building Queries
- Search Tips: Finding & Evaluating Scholarly Articles
- Advanced Search Tips
- Writing Support
- Research Support at CSUN
What is An Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.) with short paragraph about each source. An annotated bibliography is sometimes a useful step before drafting a research paper, or it can stand alone as an overview of the research available on a topic.
Each source in the annotated bibliography has a citation - the information a reader needs to find the original source, in a consistent format to make that easier. These consistent formats are called citation styles. The most common citation styles are MLA (Modern Language Association) for humanities, and APA (American Psychological Association) for social sciences.
Annotations are about 4 to 6 sentences long (roughly 150 words), and address:
- Main focus or purpose of the work
- Usefulness or relevance to your research topic
- Special features of the work that were unique or helpful
- Background and credibility of the author
- Conclusions or observations reached by the author
- Conclusions or observations reached by you
Annotations versus Abstracts
Many scholarly articles start with an abstract, which is the author's summary of the article to help you decide whether you should read the entire article. This abstract is not the same thing as an annotation. The annotation needs to be in your own words, to explain the relevance of the source to your particular assignment or research question.
APA 7th Annotated Bibliography Examples
Journal article.
Alvarez, N. & Mearns, J. (2014). The benefits of writing and performing in the spoken word poetry community. The Arts in Psychotherapy, 41 (3), 263-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aip.2014.03.004 Prior research has shown narrative writing to help with making meaning out of trauma. This article uses grounded theory to analyze semi-structured interviews with ten spoken word poets. Because spoken word poetry is performed live, it creates personal and community connections that enhance the emotional development and resolution offered by the practice of writing. The findings are limited by the small, nonrandom sample (all the participants were from the same community).
- APA 7th Sample Annotated Bibliography
Literature Review Resources
Literature Review How To (Univrsity Library) offers useful tips on how to write a literature review and provides you with information on things you should and should not do.
Literature Reviews (Purdue OWL )
Review of Literature (University of Wisconsin)
Write a Literature Review (UC Santa Cruz)
- << Previous: Citing & Citation Management
- Next: Writing Support >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 11:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.csun.edu/secondary-education
Document Reader
Report ADA Problems with Library Services and Resources

- Finding Sources
- Writing the Annotations
- Formatting the Annotated Bibliography
- Citation This link opens in a new window
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources in proper citation format, each with a descriptive paragraph. The description may critique, analyze or just summarize the content of the item. For this assignment, you will write a critical/evaluative annotation for each source, critically appraising the evidence that addresses your practice problem.
A good annotated bibliography:
- Encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, the importance of the works within the field of study, and the relation of the works to your own research and ideas
- Proves you have read and understand your sources
- Establishes your work as a valid source and you as a competent researcher
- Provides a way for others to decide whether a source will be helpful to their research if they read it
*Excerpted from The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill .
The Annotated Bibliography should be the final result after a thorough review of the literature on your topic. Different databases should be searched to get different perspectives. If 8-10 sources are required, you should be reviewing many more sources (20-25), in detail, before making final selections.
Steps to Writing an Annotated Bibliography
No matter which course or discipline you're researching in, the steps of writing an annotated bibliography should be similar:
- Research, identify, locate and read scholarly and professional articles, books, and documents for your bibliography
- Critically screen, analyze and evaluate the sources
- organize the sources in a logical order
- Create citations in proper APA format (see APA tab)
- Compose annotations
Resources on the Web
For more information on annotated bibliographies, visit these pages:
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto
- Annotated Bibliographies The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Next: Finding Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 6:08 PM
- URL: https://stevenson.libguides.com/annotatedbib
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

COMMENTS
I felt a bit overwhelmed at the scale of the reading, note-making and writing I would have to do to actually create a relatively short, concise literature review. One of the co-investigators helpfully suggested that one of the outputs be an annotated bibliography, out of which we could craft the literature review. I must add here that I then ...
Follow up video on how to convert your annotated bibliography into a literature review. Other Useful Videos: Writing an Annotated Bibliography: https://www.y...
Notice, there a BIG DIFFERENCE between the two. An annotated bibliography is mostly a summary of the reading and a place for you to talk about how and why the literature fits in to your research. A Lit Review provides a summary + critical analysis + synthesis + overview of prior work done on a subject + reveals gaps in research. Structure.
An annotated bibliography is a bibliography that gives a summary of each article or book.The purpose of annotations is to provide the reader with a summary and an evaluation of the source. Each summary should be a concise exposition of the source's central idea(s) and give the reader a general idea of the source's content.
An annotated bibliography must organize sources alphabetically, but a literature review is likely to use problem/solution, cause/effect, comparison/contrast, classification/division, or process to organize sources. The following illustration provides an example of the differences in layout between an annotated bibliography and a literature review.
Progressing Toward a Literature Review . An annotated bibliography can help you understand your information sources and how they relate to each other. A literature review is not just stringing together a series of annotated bibliographies. Usually, you will want to organize your ideas according to main ideas, themes, etc.
A literature review is not simply a summary of information you have found on a topic. Literature reviews are more in depth and provides analysis of multiple works relating to a research question. An annotated bibliography is a list of the resources, that you consulted when working on a research project. Each citation is accompanied by a brief ...
Literature Review - from The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill. A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. It usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, documents and other resources. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
In a literature review, the author synthesizes multiple sources together to present the major themes, arguments and theories around a topic. Therefore, an annotated bibliography can provide an opportunity to review and analyze individual sources before o rganizing them around common denominators found across sources.
Purpose: aims at producing an inclusive list of the entire literature on a topic; set apart the literature on a topic based on predefined criteria; assess and synthesize these sources. Traditional or narrative review; Summarizes, synthesizes and discusses literature on chosen topic; selective with regard to sources included.
Turning an annotated bibliography into a literature review is a seamless endeavor that requires a structured approach. By following specific steps, one can effortlessly transition from a list of sources with brief descriptions to a coherent narrative that synthesizes the knowledge gathered from the sources.
Figure 1. Annotated bibliographies are helpful when finding sources and determining how that source might be helpful for your paper. An annotated bibliography is a list of all your sources, including full citation information and notes on how you will use the sources. Writers often create annotated bibliographies as a part of a research project ...
It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100-200 words in length. Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes: Provide a literature review on a particular subject; Help to formulate a thesis on a subject
Especially if you plan to turn your annotated bibliography into a literature review later on, you should also find direct quotations from each resource that are valuable for your topic. Copy and paste this into the Extra field. Be sure to encapsulate any direct quote in parentheses (to avoid potential plagiarism down the road) and include an in ...
In this episode, we explore how an well-written annotated bibliography can contribute to your literature review - and all in just 3 minutes and 10 seconds.
An annotated bibliography includes all the relevant contemporary research conducted on the topics covered by the research questions you want to address. Ultimately, the current state of the research area you are addressing will dictate the length of your literature review and annotated bibliography. Research topics that have greater theoretical ...
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper, or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic. Scribbr's free Citation Generator allows you to easily create and manage ...
Using EndNote to create an annotated list. Step 1. Create an EndNote group for your annotated bibliography references. Step 2. Creating your Annotated list in a Word document. Select the references that you want to use, by either selecting the whole group or select multiple references using the Ctrl key for Windows, or Command key if using a Mac.
Creating an annotated bibliography calls for the application of a variety of intellectual skills: concise exposition, succinct analysis, and informed library research. First, locate and record citations to books, periodicals, and documents that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic. Briefly examine and review the actual items.
Select the source that matches the title you are looking for. Modify your source as needed and scroll down to the "Annotation" box. Add your annotation into the box and click "Cite.". Once your annotations are done, select "Copy All + Paste" or "Export.". Paste into a Microsoft Word document.
An annotated bibliography is sometimes a useful step before drafting a research paper, or it can stand alone as an overview of the research available on a topic. Each source in the annotated bibliography has a citation - the information a reader needs to find the original source, in a consistent format to make that easier.
an annotated bibliography on e ve ry rea di ng you do (the APA c i t a t i on wi t h a one para gra ph summ a ry of the reading below it). To turn an annotated bibliog ra phy int o a l i t e ra t ure re vi e w: 1) Add a brief second paragra ph under e a c h annota t i on in whi c h you provide a n ori gi na l a na l ysi s (not
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources in proper citation format, each with a descriptive paragraph. The description may critique, analyze or just summarize the content of the item. ... The Annotated Bibliography should be the final result after a thorough review of the literature on your topic. Different databases should be searched to ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
1 International Market Entry Annotated Bibliography Student's Name University Affiliation Course Name Professor's Name Due Date. 2 International Market Entry Annotated Bibliography Article 1 Martín, Ó. M., Chetty, S., & Bai, W. (2022). Foreign market entry knowledge and international performance: The mediating role of international market ...