

Chapter 1. Introduction
“Science is in danger, and for that reason it is becoming dangerous” -Pierre Bourdieu, Science of Science and Reflexivity
Why an Open Access Textbook on Qualitative Research Methods?
I have been teaching qualitative research methods to both undergraduates and graduate students for many years. Although there are some excellent textbooks out there, they are often costly, and none of them, to my mind, properly introduces qualitative research methods to the beginning student (whether undergraduate or graduate student). In contrast, this open-access textbook is designed as a (free) true introduction to the subject, with helpful, practical pointers on how to conduct research and how to access more advanced instruction.
Textbooks are typically arranged in one of two ways: (1) by technique (each chapter covers one method used in qualitative research); or (2) by process (chapters advance from research design through publication). But both of these approaches are necessary for the beginner student. This textbook will have sections dedicated to the process as well as the techniques of qualitative research. This is a true “comprehensive” book for the beginning student. In addition to covering techniques of data collection and data analysis, it provides a road map of how to get started and how to keep going and where to go for advanced instruction. It covers aspects of research design and research communication as well as methods employed. Along the way, it includes examples from many different disciplines in the social sciences.
The primary goal has been to create a useful, accessible, engaging textbook for use across many disciplines. And, let’s face it. Textbooks can be boring. I hope readers find this to be a little different. I have tried to write in a practical and forthright manner, with many lively examples and references to good and intellectually creative qualitative research. Woven throughout the text are short textual asides (in colored textboxes) by professional (academic) qualitative researchers in various disciplines. These short accounts by practitioners should help inspire students. So, let’s begin!
What is Research?
When we use the word research , what exactly do we mean by that? This is one of those words that everyone thinks they understand, but it is worth beginning this textbook with a short explanation. We use the term to refer to “empirical research,” which is actually a historically specific approach to understanding the world around us. Think about how you know things about the world. [1] You might know your mother loves you because she’s told you she does. Or because that is what “mothers” do by tradition. Or you might know because you’ve looked for evidence that she does, like taking care of you when you are sick or reading to you in bed or working two jobs so you can have the things you need to do OK in life. Maybe it seems churlish to look for evidence; you just take it “on faith” that you are loved.
Only one of the above comes close to what we mean by research. Empirical research is research (investigation) based on evidence. Conclusions can then be drawn from observable data. This observable data can also be “tested” or checked. If the data cannot be tested, that is a good indication that we are not doing research. Note that we can never “prove” conclusively, through observable data, that our mothers love us. We might have some “disconfirming evidence” (that time she didn’t show up to your graduation, for example) that could push you to question an original hypothesis , but no amount of “confirming evidence” will ever allow us to say with 100% certainty, “my mother loves me.” Faith and tradition and authority work differently. Our knowledge can be 100% certain using each of those alternative methods of knowledge, but our certainty in those cases will not be based on facts or evidence.
For many periods of history, those in power have been nervous about “science” because it uses evidence and facts as the primary source of understanding the world, and facts can be at odds with what power or authority or tradition want you to believe. That is why I say that scientific empirical research is a historically specific approach to understand the world. You are in college or university now partly to learn how to engage in this historically specific approach.
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries in Europe, there was a newfound respect for empirical research, some of which was seriously challenging to the established church. Using observations and testing them, scientists found that the earth was not at the center of the universe, for example, but rather that it was but one planet of many which circled the sun. [2] For the next two centuries, the science of astronomy, physics, biology, and chemistry emerged and became disciplines taught in universities. All used the scientific method of observation and testing to advance knowledge. Knowledge about people , however, and social institutions, however, was still left to faith, tradition, and authority. Historians and philosophers and poets wrote about the human condition, but none of them used research to do so. [3]
It was not until the nineteenth century that “social science” really emerged, using the scientific method (empirical observation) to understand people and social institutions. New fields of sociology, economics, political science, and anthropology emerged. The first sociologists, people like Auguste Comte and Karl Marx, sought specifically to apply the scientific method of research to understand society, Engels famously claiming that Marx had done for the social world what Darwin did for the natural world, tracings its laws of development. Today we tend to take for granted the naturalness of science here, but it is actually a pretty recent and radical development.
To return to the question, “does your mother love you?” Well, this is actually not really how a researcher would frame the question, as it is too specific to your case. It doesn’t tell us much about the world at large, even if it does tell us something about you and your relationship with your mother. A social science researcher might ask, “do mothers love their children?” Or maybe they would be more interested in how this loving relationship might change over time (e.g., “do mothers love their children more now than they did in the 18th century when so many children died before reaching adulthood?”) or perhaps they might be interested in measuring quality of love across cultures or time periods, or even establishing “what love looks like” using the mother/child relationship as a site of exploration. All of these make good research questions because we can use observable data to answer them.
What is Qualitative Research?
“All we know is how to learn. How to study, how to listen, how to talk, how to tell. If we don’t tell the world, we don’t know the world. We’re lost in it, we die.” -Ursula LeGuin, The Telling
At its simplest, qualitative research is research about the social world that does not use numbers in its analyses. All those who fear statistics can breathe a sigh of relief – there are no mathematical formulae or regression models in this book! But this definition is less about what qualitative research can be and more about what it is not. To be honest, any simple statement will fail to capture the power and depth of qualitative research. One way of contrasting qualitative research to quantitative research is to note that the focus of qualitative research is less about explaining and predicting relationships between variables and more about understanding the social world. To use our mother love example, the question about “what love looks like” is a good question for the qualitative researcher while all questions measuring love or comparing incidences of love (both of which require measurement) are good questions for quantitative researchers. Patton writes,
Qualitative data describe. They take us, as readers, into the time and place of the observation so that we know what it was like to have been there. They capture and communicate someone else’s experience of the world in his or her own words. Qualitative data tell a story. ( Patton 2002:47 )
Qualitative researchers are asking different questions about the world than their quantitative colleagues. Even when researchers are employed in “mixed methods” research ( both quantitative and qualitative), they are using different methods to address different questions of the study. I do a lot of research about first-generation and working-college college students. Where a quantitative researcher might ask, how many first-generation college students graduate from college within four years? Or does first-generation college status predict high student debt loads? A qualitative researcher might ask, how does the college experience differ for first-generation college students? What is it like to carry a lot of debt, and how does this impact the ability to complete college on time? Both sets of questions are important, but they can only be answered using specific tools tailored to those questions. For the former, you need large numbers to make adequate comparisons. For the latter, you need to talk to people, find out what they are thinking and feeling, and try to inhabit their shoes for a little while so you can make sense of their experiences and beliefs.
Examples of Qualitative Research
You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research “in the field.” A good qualitative researcher will present the product of their hours of work in such a way that it seems natural, even obvious, to the reader. Because we are trying to convey what it is like answers, qualitative research is often presented as stories – stories about how people live their lives, go to work, raise their children, interact with one another. In some ways, this can seem like reading particularly insightful novels. But, unlike novels, there are very specific rules and guidelines that qualitative researchers follow to ensure that the “story” they are telling is accurate , a truthful rendition of what life is like for the people being studied. Most of this textbook will be spent conveying those rules and guidelines. Let’s take a look, first, however, at three examples of what the end product looks like. I have chosen these three examples to showcase very different approaches to qualitative research, and I will return to these five examples throughout the book. They were all published as whole books (not chapters or articles), and they are worth the long read, if you have the time. I will also provide some information on how these books came to be and the length of time it takes to get them into book version. It is important you know about this process, and the rest of this textbook will help explain why it takes so long to conduct good qualitative research!
Example 1 : The End Game (ethnography + interviews)
Corey Abramson is a sociologist who teaches at the University of Arizona. In 2015 he published The End Game: How Inequality Shapes our Final Years ( 2015 ). This book was based on the research he did for his dissertation at the University of California-Berkeley in 2012. Actually, the dissertation was completed in 2012 but the work that was produced that took several years. The dissertation was entitled, “This is How We Live, This is How We Die: Social Stratification, Aging, and Health in Urban America” ( 2012 ). You can see how the book version, which was written for a more general audience, has a more engaging sound to it, but that the dissertation version, which is what academic faculty read and evaluate, has a more descriptive title. You can read the title and know that this is a study about aging and health and that the focus is going to be inequality and that the context (place) is going to be “urban America.” It’s a study about “how” people do something – in this case, how they deal with aging and death. This is the very first sentence of the dissertation, “From our first breath in the hospital to the day we die, we live in a society characterized by unequal opportunities for maintaining health and taking care of ourselves when ill. These disparities reflect persistent racial, socio-economic, and gender-based inequalities and contribute to their persistence over time” ( 1 ). What follows is a truthful account of how that is so.
Cory Abramson spent three years conducting his research in four different urban neighborhoods. We call the type of research he conducted “comparative ethnographic” because he designed his study to compare groups of seniors as they went about their everyday business. It’s comparative because he is comparing different groups (based on race, class, gender) and ethnographic because he is studying the culture/way of life of a group. [4] He had an educated guess, rooted in what previous research had shown and what social theory would suggest, that people’s experiences of aging differ by race, class, and gender. So, he set up a research design that would allow him to observe differences. He chose two primarily middle-class (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly White) and two primarily poor neighborhoods (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly African American). He hung out in senior centers and other places seniors congregated, watched them as they took the bus to get prescriptions filled, sat in doctor’s offices with them, and listened to their conversations with each other. He also conducted more formal conversations, what we call in-depth interviews, with sixty seniors from each of the four neighborhoods. As with a lot of fieldwork , as he got closer to the people involved, he both expanded and deepened his reach –
By the end of the project, I expanded my pool of general observations to include various settings frequented by seniors: apartment building common rooms, doctors’ offices, emergency rooms, pharmacies, senior centers, bars, parks, corner stores, shopping centers, pool halls, hair salons, coffee shops, and discount stores. Over the course of the three years of fieldwork, I observed hundreds of elders, and developed close relationships with a number of them. ( 2012:10 )
When Abramson rewrote the dissertation for a general audience and published his book in 2015, it got a lot of attention. It is a beautifully written book and it provided insight into a common human experience that we surprisingly know very little about. It won the Outstanding Publication Award by the American Sociological Association Section on Aging and the Life Course and was featured in the New York Times . The book was about aging, and specifically how inequality shapes the aging process, but it was also about much more than that. It helped show how inequality affects people’s everyday lives. For example, by observing the difficulties the poor had in setting up appointments and getting to them using public transportation and then being made to wait to see a doctor, sometimes in standing-room-only situations, when they are unwell, and then being treated dismissively by hospital staff, Abramson allowed readers to feel the material reality of being poor in the US. Comparing these examples with seniors with adequate supplemental insurance who have the resources to hire car services or have others assist them in arranging care when they need it, jolts the reader to understand and appreciate the difference money makes in the lives and circumstances of us all, and in a way that is different than simply reading a statistic (“80% of the poor do not keep regular doctor’s appointments”) does. Qualitative research can reach into spaces and places that often go unexamined and then reports back to the rest of us what it is like in those spaces and places.
Example 2: Racing for Innocence (Interviews + Content Analysis + Fictional Stories)
Jennifer Pierce is a Professor of American Studies at the University of Minnesota. Trained as a sociologist, she has written a number of books about gender, race, and power. Her very first book, Gender Trials: Emotional Lives in Contemporary Law Firms, published in 1995, is a brilliant look at gender dynamics within two law firms. Pierce was a participant observer, working as a paralegal, and she observed how female lawyers and female paralegals struggled to obtain parity with their male colleagues.
Fifteen years later, she reexamined the context of the law firm to include an examination of racial dynamics, particularly how elite white men working in these spaces created and maintained a culture that made it difficult for both female attorneys and attorneys of color to thrive. Her book, Racing for Innocence: Whiteness, Gender, and the Backlash Against Affirmative Action , published in 2012, is an interesting and creative blending of interviews with attorneys, content analyses of popular films during this period, and fictional accounts of racial discrimination and sexual harassment. The law firm she chose to study had come under an affirmative action order and was in the process of implementing equitable policies and programs. She wanted to understand how recipients of white privilege (the elite white male attorneys) come to deny the role they play in reproducing inequality. Through interviews with attorneys who were present both before and during the affirmative action order, she creates a historical record of the “bad behavior” that necessitated new policies and procedures, but also, and more importantly , probed the participants ’ understanding of this behavior. It should come as no surprise that most (but not all) of the white male attorneys saw little need for change, and that almost everyone else had accounts that were different if not sometimes downright harrowing.
I’ve used Pierce’s book in my qualitative research methods courses as an example of an interesting blend of techniques and presentation styles. My students often have a very difficult time with the fictional accounts she includes. But they serve an important communicative purpose here. They are her attempts at presenting “both sides” to an objective reality – something happens (Pierce writes this something so it is very clear what it is), and the two participants to the thing that happened have very different understandings of what this means. By including these stories, Pierce presents one of her key findings – people remember things differently and these different memories tend to support their own ideological positions. I wonder what Pierce would have written had she studied the murder of George Floyd or the storming of the US Capitol on January 6 or any number of other historic events whose observers and participants record very different happenings.
This is not to say that qualitative researchers write fictional accounts. In fact, the use of fiction in our work remains controversial. When used, it must be clearly identified as a presentation device, as Pierce did. I include Racing for Innocence here as an example of the multiple uses of methods and techniques and the way that these work together to produce better understandings by us, the readers, of what Pierce studied. We readers come away with a better grasp of how and why advantaged people understate their own involvement in situations and structures that advantage them. This is normal human behavior , in other words. This case may have been about elite white men in law firms, but the general insights here can be transposed to other settings. Indeed, Pierce argues that more research needs to be done about the role elites play in the reproduction of inequality in the workplace in general.
Example 3: Amplified Advantage (Mixed Methods: Survey Interviews + Focus Groups + Archives)
The final example comes from my own work with college students, particularly the ways in which class background affects the experience of college and outcomes for graduates. I include it here as an example of mixed methods, and for the use of supplementary archival research. I’ve done a lot of research over the years on first-generation, low-income, and working-class college students. I am curious (and skeptical) about the possibility of social mobility today, particularly with the rising cost of college and growing inequality in general. As one of the few people in my family to go to college, I didn’t grow up with a lot of examples of what college was like or how to make the most of it. And when I entered graduate school, I realized with dismay that there were very few people like me there. I worried about becoming too different from my family and friends back home. And I wasn’t at all sure that I would ever be able to pay back the huge load of debt I was taking on. And so I wrote my dissertation and first two books about working-class college students. These books focused on experiences in college and the difficulties of navigating between family and school ( Hurst 2010a, 2012 ). But even after all that research, I kept coming back to wondering if working-class students who made it through college had an equal chance at finding good jobs and happy lives,
What happens to students after college? Do working-class students fare as well as their peers? I knew from my own experience that barriers continued through graduate school and beyond, and that my debtload was higher than that of my peers, constraining some of the choices I made when I graduated. To answer these questions, I designed a study of students attending small liberal arts colleges, the type of college that tried to equalize the experience of students by requiring all students to live on campus and offering small classes with lots of interaction with faculty. These private colleges tend to have more money and resources so they can provide financial aid to low-income students. They also attract some very wealthy students. Because they enroll students across the class spectrum, I would be able to draw comparisons. I ended up spending about four years collecting data, both a survey of more than 2000 students (which formed the basis for quantitative analyses) and qualitative data collection (interviews, focus groups, archival research, and participant observation). This is what we call a “mixed methods” approach because we use both quantitative and qualitative data. The survey gave me a large enough number of students that I could make comparisons of the how many kind, and to be able to say with some authority that there were in fact significant differences in experience and outcome by class (e.g., wealthier students earned more money and had little debt; working-class students often found jobs that were not in their chosen careers and were very affected by debt, upper-middle-class students were more likely to go to graduate school). But the survey analyses could not explain why these differences existed. For that, I needed to talk to people and ask them about their motivations and aspirations. I needed to understand their perceptions of the world, and it is very hard to do this through a survey.
By interviewing students and recent graduates, I was able to discern particular patterns and pathways through college and beyond. Specifically, I identified three versions of gameplay. Upper-middle-class students, whose parents were themselves professionals (academics, lawyers, managers of non-profits), saw college as the first stage of their education and took classes and declared majors that would prepare them for graduate school. They also spent a lot of time building their resumes, taking advantage of opportunities to help professors with their research, or study abroad. This helped them gain admission to highly-ranked graduate schools and interesting jobs in the public sector. In contrast, upper-class students, whose parents were wealthy and more likely to be engaged in business (as CEOs or other high-level directors), prioritized building social capital. They did this by joining fraternities and sororities and playing club sports. This helped them when they graduated as they called on friends and parents of friends to find them well-paying jobs. Finally, low-income, first-generation, and working-class students were often adrift. They took the classes that were recommended to them but without the knowledge of how to connect them to life beyond college. They spent time working and studying rather than partying or building their resumes. All three sets of students thought they were “doing college” the right way, the way that one was supposed to do college. But these three versions of gameplay led to distinct outcomes that advantaged some students over others. I titled my work “Amplified Advantage” to highlight this process.
These three examples, Cory Abramson’s The End Game , Jennifer Peirce’s Racing for Innocence, and my own Amplified Advantage, demonstrate the range of approaches and tools available to the qualitative researcher. They also help explain why qualitative research is so important. Numbers can tell us some things about the world, but they cannot get at the hearts and minds, motivations and beliefs of the people who make up the social worlds we inhabit. For that, we need tools that allow us to listen and make sense of what people tell us and show us. That is what good qualitative research offers us.
How Is This Book Organized?
This textbook is organized as a comprehensive introduction to the use of qualitative research methods. The first half covers general topics (e.g., approaches to qualitative research, ethics) and research design (necessary steps for building a successful qualitative research study). The second half reviews various data collection and data analysis techniques. Of course, building a successful qualitative research study requires some knowledge of data collection and data analysis so the chapters in the first half and the chapters in the second half should be read in conversation with each other. That said, each chapter can be read on its own for assistance with a particular narrow topic. In addition to the chapters, a helpful glossary can be found in the back of the book. Rummage around in the text as needed.
Chapter Descriptions
Chapter 2 provides an overview of the Research Design Process. How does one begin a study? What is an appropriate research question? How is the study to be done – with what methods ? Involving what people and sites? Although qualitative research studies can and often do change and develop over the course of data collection, it is important to have a good idea of what the aims and goals of your study are at the outset and a good plan of how to achieve those aims and goals. Chapter 2 provides a road map of the process.
Chapter 3 describes and explains various ways of knowing the (social) world. What is it possible for us to know about how other people think or why they behave the way they do? What does it mean to say something is a “fact” or that it is “well-known” and understood? Qualitative researchers are particularly interested in these questions because of the types of research questions we are interested in answering (the how questions rather than the how many questions of quantitative research). Qualitative researchers have adopted various epistemological approaches. Chapter 3 will explore these approaches, highlighting interpretivist approaches that acknowledge the subjective aspect of reality – in other words, reality and knowledge are not objective but rather influenced by (interpreted through) people.
Chapter 4 focuses on the practical matter of developing a research question and finding the right approach to data collection. In any given study (think of Cory Abramson’s study of aging, for example), there may be years of collected data, thousands of observations , hundreds of pages of notes to read and review and make sense of. If all you had was a general interest area (“aging”), it would be very difficult, nearly impossible, to make sense of all of that data. The research question provides a helpful lens to refine and clarify (and simplify) everything you find and collect. For that reason, it is important to pull out that lens (articulate the research question) before you get started. In the case of the aging study, Cory Abramson was interested in how inequalities affected understandings and responses to aging. It is for this reason he designed a study that would allow him to compare different groups of seniors (some middle-class, some poor). Inevitably, he saw much more in the three years in the field than what made it into his book (or dissertation), but he was able to narrow down the complexity of the social world to provide us with this rich account linked to the original research question. Developing a good research question is thus crucial to effective design and a successful outcome. Chapter 4 will provide pointers on how to do this. Chapter 4 also provides an overview of general approaches taken to doing qualitative research and various “traditions of inquiry.”
Chapter 5 explores sampling . After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (Observations? Interviews?), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview , the sample should follow the research question and research design. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. Chapter 5 explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Chapter 6 addresses the importance of reflexivity in qualitative research. Related to epistemological issues of how we know anything about the social world, qualitative researchers understand that we the researchers can never be truly neutral or outside the study we are conducting. As observers, we see things that make sense to us and may entirely miss what is either too obvious to note or too different to comprehend. As interviewers, as much as we would like to ask questions neutrally and remain in the background, interviews are a form of conversation, and the persons we interview are responding to us . Therefore, it is important to reflect upon our social positions and the knowledges and expectations we bring to our work and to work through any blind spots that we may have. Chapter 6 provides some examples of reflexivity in practice and exercises for thinking through one’s own biases.
Chapter 7 is a very important chapter and should not be overlooked. As a practical matter, it should also be read closely with chapters 6 and 8. Because qualitative researchers deal with people and the social world, it is imperative they develop and adhere to a strong ethical code for conducting research in a way that does not harm. There are legal requirements and guidelines for doing so (see chapter 8), but these requirements should not be considered synonymous with the ethical code required of us. Each researcher must constantly interrogate every aspect of their research, from research question to design to sample through analysis and presentation, to ensure that a minimum of harm (ideally, zero harm) is caused. Because each research project is unique, the standards of care for each study are unique. Part of being a professional researcher is carrying this code in one’s heart, being constantly attentive to what is required under particular circumstances. Chapter 7 provides various research scenarios and asks readers to weigh in on the suitability and appropriateness of the research. If done in a class setting, it will become obvious fairly quickly that there are often no absolutely correct answers, as different people find different aspects of the scenarios of greatest importance. Minimizing the harm in one area may require possible harm in another. Being attentive to all the ethical aspects of one’s research and making the best judgments one can, clearly and consciously, is an integral part of being a good researcher.
Chapter 8 , best to be read in conjunction with chapter 7, explains the role and importance of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) . Under federal guidelines, an IRB is an appropriately constituted group that has been formally designated to review and monitor research involving human subjects . Every institution that receives funding from the federal government has an IRB. IRBs have the authority to approve, require modifications to (to secure approval), or disapprove research. This group review serves an important role in the protection of the rights and welfare of human research subjects. Chapter 8 reviews the history of IRBs and the work they do but also argues that IRBs’ review of qualitative research is often both over-inclusive and under-inclusive. Some aspects of qualitative research are not well understood by IRBs, given that they were developed to prevent abuses in biomedical research. Thus, it is important not to rely on IRBs to identify all the potential ethical issues that emerge in our research (see chapter 7).
Chapter 9 provides help for getting started on formulating a research question based on gaps in the pre-existing literature. Research is conducted as part of a community, even if particular studies are done by single individuals (or small teams). What any of us finds and reports back becomes part of a much larger body of knowledge. Thus, it is important that we look at the larger body of knowledge before we actually start our bit to see how we can best contribute. When I first began interviewing working-class college students, there was only one other similar study I could find, and it hadn’t been published (it was a dissertation of students from poor backgrounds). But there had been a lot published by professors who had grown up working class and made it through college despite the odds. These accounts by “working-class academics” became an important inspiration for my study and helped me frame the questions I asked the students I interviewed. Chapter 9 will provide some pointers on how to search for relevant literature and how to use this to refine your research question.
Chapter 10 serves as a bridge between the two parts of the textbook, by introducing techniques of data collection. Qualitative research is often characterized by the form of data collection – for example, an ethnographic study is one that employs primarily observational data collection for the purpose of documenting and presenting a particular culture or ethnos. Techniques can be effectively combined, depending on the research question and the aims and goals of the study. Chapter 10 provides a general overview of all the various techniques and how they can be combined.
The second part of the textbook moves into the doing part of qualitative research once the research question has been articulated and the study designed. Chapters 11 through 17 cover various data collection techniques and approaches. Chapters 18 and 19 provide a very simple overview of basic data analysis. Chapter 20 covers communication of the data to various audiences, and in various formats.
Chapter 11 begins our overview of data collection techniques with a focus on interviewing , the true heart of qualitative research. This technique can serve as the primary and exclusive form of data collection, or it can be used to supplement other forms (observation, archival). An interview is distinct from a survey, where questions are asked in a specific order and often with a range of predetermined responses available. Interviews can be conversational and unstructured or, more conventionally, semistructured , where a general set of interview questions “guides” the conversation. Chapter 11 covers the basics of interviews: how to create interview guides, how many people to interview, where to conduct the interview, what to watch out for (how to prepare against things going wrong), and how to get the most out of your interviews.
Chapter 12 covers an important variant of interviewing, the focus group. Focus groups are semistructured interviews with a group of people moderated by a facilitator (the researcher or researcher’s assistant). Focus groups explicitly use group interaction to assist in the data collection. They are best used to collect data on a specific topic that is non-personal and shared among the group. For example, asking a group of college students about a common experience such as taking classes by remote delivery during the pandemic year of 2020. Chapter 12 covers the basics of focus groups: when to use them, how to create interview guides for them, and how to run them effectively.
Chapter 13 moves away from interviewing to the second major form of data collection unique to qualitative researchers – observation . Qualitative research that employs observation can best be understood as falling on a continuum of “fly on the wall” observation (e.g., observing how strangers interact in a doctor’s waiting room) to “participant” observation, where the researcher is also an active participant of the activity being observed. For example, an activist in the Black Lives Matter movement might want to study the movement, using her inside position to gain access to observe key meetings and interactions. Chapter 13 covers the basics of participant observation studies: advantages and disadvantages, gaining access, ethical concerns related to insider/outsider status and entanglement, and recording techniques.
Chapter 14 takes a closer look at “deep ethnography” – immersion in the field of a particularly long duration for the purpose of gaining a deeper understanding and appreciation of a particular culture or social world. Clifford Geertz called this “deep hanging out.” Whereas participant observation is often combined with semistructured interview techniques, deep ethnography’s commitment to “living the life” or experiencing the situation as it really is demands more conversational and natural interactions with people. These interactions and conversations may take place over months or even years. As can be expected, there are some costs to this technique, as well as some very large rewards when done competently. Chapter 14 provides some examples of deep ethnographies that will inspire some beginning researchers and intimidate others.
Chapter 15 moves in the opposite direction of deep ethnography, a technique that is the least positivist of all those discussed here, to mixed methods , a set of techniques that is arguably the most positivist . A mixed methods approach combines both qualitative data collection and quantitative data collection, commonly by combining a survey that is analyzed statistically (e.g., cross-tabs or regression analyses of large number probability samples) with semi-structured interviews. Although it is somewhat unconventional to discuss mixed methods in textbooks on qualitative research, I think it is important to recognize this often-employed approach here. There are several advantages and some disadvantages to taking this route. Chapter 16 will describe those advantages and disadvantages and provide some particular guidance on how to design a mixed methods study for maximum effectiveness.
Chapter 16 covers data collection that does not involve live human subjects at all – archival and historical research (chapter 17 will also cover data that does not involve interacting with human subjects). Sometimes people are unavailable to us, either because they do not wish to be interviewed or observed (as is the case with many “elites”) or because they are too far away, in both place and time. Fortunately, humans leave many traces and we can often answer questions we have by examining those traces. Special collections and archives can be goldmines for social science research. This chapter will explain how to access these places, for what purposes, and how to begin to make sense of what you find.
Chapter 17 covers another data collection area that does not involve face-to-face interaction with humans: content analysis . Although content analysis may be understood more properly as a data analysis technique, the term is often used for the entire approach, which will be the case here. Content analysis involves interpreting meaning from a body of text. This body of text might be something found in historical records (see chapter 16) or something collected by the researcher, as in the case of comment posts on a popular blog post. I once used the stories told by student loan debtors on the website studentloanjustice.org as the content I analyzed. Content analysis is particularly useful when attempting to define and understand prevalent stories or communication about a topic of interest. In other words, when we are less interested in what particular people (our defined sample) are doing or believing and more interested in what general narratives exist about a particular topic or issue. This chapter will explore different approaches to content analysis and provide helpful tips on how to collect data, how to turn that data into codes for analysis, and how to go about presenting what is found through analysis.
Where chapter 17 has pushed us towards data analysis, chapters 18 and 19 are all about what to do with the data collected, whether that data be in the form of interview transcripts or fieldnotes from observations. Chapter 18 introduces the basics of coding , the iterative process of assigning meaning to the data in order to both simplify and identify patterns. What is a code and how does it work? What are the different ways of coding data, and when should you use them? What is a codebook, and why do you need one? What does the process of data analysis look like?
Chapter 19 goes further into detail on codes and how to use them, particularly the later stages of coding in which our codes are refined, simplified, combined, and organized. These later rounds of coding are essential to getting the most out of the data we’ve collected. As students are often overwhelmed with the amount of data (a corpus of interview transcripts typically runs into the hundreds of pages; fieldnotes can easily top that), this chapter will also address time management and provide suggestions for dealing with chaos and reminders that feeling overwhelmed at the analysis stage is part of the process. By the end of the chapter, you should understand how “findings” are actually found.
The book concludes with a chapter dedicated to the effective presentation of data results. Chapter 20 covers the many ways that researchers communicate their studies to various audiences (academic, personal, political), what elements must be included in these various publications, and the hallmarks of excellent qualitative research that various audiences will be expecting. Because qualitative researchers are motivated by understanding and conveying meaning , effective communication is not only an essential skill but a fundamental facet of the entire research project. Ethnographers must be able to convey a certain sense of verisimilitude , the appearance of true reality. Those employing interviews must faithfully depict the key meanings of the people they interviewed in a way that rings true to those people, even if the end result surprises them. And all researchers must strive for clarity in their publications so that various audiences can understand what was found and why it is important.
The book concludes with a short chapter ( chapter 21 ) discussing the value of qualitative research. At the very end of this book, you will find a glossary of terms. I recommend you make frequent use of the glossary and add to each entry as you find examples. Although the entries are meant to be simple and clear, you may also want to paraphrase the definition—make it “make sense” to you, in other words. In addition to the standard reference list (all works cited here), you will find various recommendations for further reading at the end of many chapters. Some of these recommendations will be examples of excellent qualitative research, indicated with an asterisk (*) at the end of the entry. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. A good example of qualitative research can teach you more about conducting research than any textbook can (this one included). I highly recommend you select one to three examples from these lists and read them along with the textbook.
A final note on the choice of examples – you will note that many of the examples used in the text come from research on college students. This is for two reasons. First, as most of my research falls in this area, I am most familiar with this literature and have contacts with those who do research here and can call upon them to share their stories with you. Second, and more importantly, my hope is that this textbook reaches a wide audience of beginning researchers who study widely and deeply across the range of what can be known about the social world (from marine resources management to public policy to nursing to political science to sexuality studies and beyond). It is sometimes difficult to find examples that speak to all those research interests, however. A focus on college students is something that all readers can understand and, hopefully, appreciate, as we are all now or have been at some point a college student.
Recommended Reading: Other Qualitative Research Textbooks
I’ve included a brief list of some of my favorite qualitative research textbooks and guidebooks if you need more than what you will find in this introductory text. For each, I’ve also indicated if these are for “beginning” or “advanced” (graduate-level) readers. Many of these books have several editions that do not significantly vary; the edition recommended is merely the edition I have used in teaching and to whose page numbers any specific references made in the text agree.
Barbour, Rosaline. 2014. Introducing Qualitative Research: A Student’s Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A good introduction to qualitative research, with abundant examples (often from the discipline of health care) and clear definitions. Includes quick summaries at the ends of each chapter. However, some US students might find the British context distracting and can be a bit advanced in some places. Beginning .
Bloomberg, Linda Dale, and Marie F. Volpe. 2012. Completing Your Qualitative Dissertation . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Specifically designed to guide graduate students through the research process. Advanced .
Creswell, John W., and Cheryl Poth. 2018 Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Traditions . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a classic and one of the go-to books I used myself as a graduate student. One of the best things about this text is its clear presentation of five distinct traditions in qualitative research. Despite the title, this reasonably sized book is about more than research design, including both data analysis and how to write about qualitative research. Advanced .
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. A readable and personal account of conducting qualitative research by an eminent sociologist, with a heavy emphasis on the kinds of participant-observation research conducted by the author. Despite its reader-friendliness, this is really a book targeted to graduate students learning the craft. Advanced .
Lune, Howard, and Bruce L. Berg. 2018. 9th edition. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences. Pearson . Although a good introduction to qualitative methods, the authors favor symbolic interactionist and dramaturgical approaches, which limits the appeal primarily to sociologists. Beginning .
Marshall, Catherine, and Gretchen B. Rossman. 2016. 6th edition. Designing Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Very readable and accessible guide to research design by two educational scholars. Although the presentation is sometimes fairly dry, personal vignettes and illustrations enliven the text. Beginning .
Maxwell, Joseph A. 2013. Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced .
Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a comprehensive text that served as my “go-to” reference when I was a graduate student. It is particularly helpful for those involved in program evaluation and other forms of evaluation studies and uses examples from a wide range of disciplines. Advanced .
Rubin, Ashley T. 2021. Rocking Qualitative Social Science: An Irreverent Guide to Rigorous Research. Stanford : Stanford University Press. A delightful and personal read. Rubin uses rock climbing as an extended metaphor for learning how to conduct qualitative research. A bit slanted toward ethnographic and archival methods of data collection, with frequent examples from her own studies in criminology. Beginning .
Weis, Lois, and Michelle Fine. 2000. Speed Bumps: A Student-Friendly Guide to Qualitative Research . New York: Teachers College Press. Readable and accessibly written in a quasi-conversational style. Particularly strong in its discussion of ethical issues throughout the qualitative research process. Not comprehensive, however, and very much tied to ethnographic research. Although designed for graduate students, this is a recommended read for students of all levels. Beginning .
Patton’s Ten Suggestions for Doing Qualitative Research
The following ten suggestions were made by Michael Quinn Patton in his massive textbooks Qualitative Research and Evaluations Methods . This book is highly recommended for those of you who want more than an introduction to qualitative methods. It is the book I relied on heavily when I was a graduate student, although it is much easier to “dip into” when necessary than to read through as a whole. Patton is asked for “just one bit of advice” for a graduate student considering using qualitative research methods for their dissertation. Here are his top ten responses, in short form, heavily paraphrased, and with additional comments and emphases from me:
- Make sure that a qualitative approach fits the research question. The following are the kinds of questions that call out for qualitative methods or where qualitative methods are particularly appropriate: questions about people’s experiences or how they make sense of those experiences; studying a person in their natural environment; researching a phenomenon so unknown that it would be impossible to study it with standardized instruments or other forms of quantitative data collection.
- Study qualitative research by going to the original sources for the design and analysis appropriate to the particular approach you want to take (e.g., read Glaser and Straus if you are using grounded theory )
- Find a dissertation adviser who understands or at least who will support your use of qualitative research methods. You are asking for trouble if your entire committee is populated by quantitative researchers, even if they are all very knowledgeable about the subject or focus of your study (maybe even more so if they are!)
- Really work on design. Doing qualitative research effectively takes a lot of planning. Even if things are more flexible than in quantitative research, a good design is absolutely essential when starting out.
- Practice data collection techniques, particularly interviewing and observing. There is definitely a set of learned skills here! Do not expect your first interview to be perfect. You will continue to grow as a researcher the more interviews you conduct, and you will probably come to understand yourself a bit more in the process, too. This is not easy, despite what others who don’t work with qualitative methods may assume (and tell you!)
- Have a plan for analysis before you begin data collection. This is often a requirement in IRB protocols , although you can get away with writing something fairly simple. And even if you are taking an approach, such as grounded theory, that pushes you to remain fairly open-minded during the data collection process, you still want to know what you will be doing with all the data collected – creating a codebook? Writing analytical memos? Comparing cases? Having a plan in hand will also help prevent you from collecting too much extraneous data.
- Be prepared to confront controversies both within the qualitative research community and between qualitative research and quantitative research. Don’t be naïve about this – qualitative research, particularly some approaches, will be derided by many more “positivist” researchers and audiences. For example, is an “n” of 1 really sufficient? Yes! But not everyone will agree.
- Do not make the mistake of using qualitative research methods because someone told you it was easier, or because you are intimidated by the math required of statistical analyses. Qualitative research is difficult in its own way (and many would claim much more time-consuming than quantitative research). Do it because you are convinced it is right for your goals, aims, and research questions.
- Find a good support network. This could be a research mentor, or it could be a group of friends or colleagues who are also using qualitative research, or it could be just someone who will listen to you work through all of the issues you will confront out in the field and during the writing process. Even though qualitative research often involves human subjects, it can be pretty lonely. A lot of times you will feel like you are working without a net. You have to create one for yourself. Take care of yourself.
- And, finally, in the words of Patton, “Prepare to be changed. Looking deeply at other people’s lives will force you to look deeply at yourself.”
- We will actually spend an entire chapter ( chapter 3 ) looking at this question in much more detail! ↵
- Note that this might have been news to Europeans at the time, but many other societies around the world had also come to this conclusion through observation. There is often a tendency to equate “the scientific revolution” with the European world in which it took place, but this is somewhat misleading. ↵
- Historians are a special case here. Historians have scrupulously and rigorously investigated the social world, but not for the purpose of understanding general laws about how things work, which is the point of scientific empirical research. History is often referred to as an idiographic field of study, meaning that it studies things that happened or are happening in themselves and not for general observations or conclusions. ↵
- Don’t worry, we’ll spend more time later in this book unpacking the meaning of ethnography and other terms that are important here. Note the available glossary ↵
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
In contrast to methodology, methods are more simply the practices and tools used to collect and analyze data. Examples of common methods in qualitative research are interviews , observations , and documentary analysis . One’s methodology should connect to one’s choice of methods, of course, but they are distinguishable terms. See also methodology .
A proposed explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation. The positing of a hypothesis is often the first step in quantitative research but not in qualitative research. Even when qualitative researchers offer possible explanations in advance of conducting research, they will tend to not use the word “hypothesis” as it conjures up the kind of positivist research they are not conducting.
The foundational question to be addressed by the research study. This will form the anchor of the research design, collection, and analysis. Note that in qualitative research, the research question may, and probably will, alter or develop during the course of the research.
An approach to research that collects and analyzes numerical data for the purpose of finding patterns and averages, making predictions, testing causal relationships, and generalizing results to wider populations. Contrast with qualitative research .
Data collection that takes place in real-world settings, referred to as “the field;” a key component of much Grounded Theory and ethnographic research. Patton ( 2002 ) calls fieldwork “the central activity of qualitative inquiry” where “‘going into the field’ means having direct and personal contact with people under study in their own environments – getting close to people and situations being studied to personally understand the realities of minutiae of daily life” (48).
The people who are the subjects of a qualitative study. In interview-based studies, they may be the respondents to the interviewer; for purposes of IRBs, they are often referred to as the human subjects of the research.
The branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. For researchers, it is important to recognize and adopt one of the many distinguishing epistemological perspectives as part of our understanding of what questions research can address or fully answer. See, e.g., constructivism , subjectivism, and objectivism .
An approach that refutes the possibility of neutrality in social science research. All research is “guided by a set of beliefs and feelings about the world and how it should be understood and studied” (Denzin and Lincoln 2005: 13). In contrast to positivism , interpretivism recognizes the social constructedness of reality, and researchers adopting this approach focus on capturing interpretations and understandings people have about the world rather than “the world” as it is (which is a chimera).
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Research based on data collected and analyzed by the research (in contrast to secondary “library” research).
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The practice of being conscious of and reflective upon one’s own social location and presence when conducting research. Because qualitative research often requires interaction with live humans, failing to take into account how one’s presence and prior expectations and social location affect the data collected and how analyzed may limit the reliability of the findings. This remains true even when dealing with historical archives and other content. Who we are matters when asking questions about how people experience the world because we, too, are a part of that world.
The science and practice of right conduct; in research, it is also the delineation of moral obligations towards research participants, communities to which we belong, and communities in which we conduct our research.
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Research, according to US federal guidelines, that involves “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research: (1) Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens; or (2) Obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens.”
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
A method of observational data collection taking place in a natural setting; a form of fieldwork . The term encompasses a continuum of relative participation by the researcher (from full participant to “fly-on-the-wall” observer). This is also sometimes referred to as ethnography , although the latter is characterized by a greater focus on the culture under observation.
A research design that employs both quantitative and qualitative methods, as in the case of a survey supplemented by interviews.
An epistemological perspective that posits the existence of reality through sensory experience similar to empiricism but goes further in denying any non-sensory basis of thought or consciousness. In the social sciences, the term has roots in the proto-sociologist August Comte, who believed he could discern “laws” of society similar to the laws of natural science (e.g., gravity). The term has come to mean the kinds of measurable and verifiable science conducted by quantitative researchers and is thus used pejoratively by some qualitative researchers interested in interpretation, consciousness, and human understanding. Calling someone a “positivist” is often intended as an insult. See also empiricism and objectivism.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A method of both data collection and data analysis in which a given content (textual, visual, graphic) is examined systematically and rigorously to identify meanings, themes, patterns and assumptions. Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is concerned with gathering and interpreting an existing body of material.
A word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data (Saldaña 2021:5).
Usually a verbatim written record of an interview or focus group discussion.
The primary form of data for fieldwork , participant observation , and ethnography . These notes, taken by the researcher either during the course of fieldwork or at day’s end, should include as many details as possible on what was observed and what was said. They should include clear identifiers of date, time, setting, and names (or identifying characteristics) of participants.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
A detailed description of any proposed research that involves human subjects for review by IRB. The protocol serves as the recipe for the conduct of the research activity. It includes the scientific rationale to justify the conduct of the study, the information necessary to conduct the study, the plan for managing and analyzing the data, and a discussion of the research ethical issues relevant to the research. Protocols for qualitative research often include interview guides, all documents related to recruitment, informed consent forms, very clear guidelines on the safekeeping of materials collected, and plans for de-identifying transcripts or other data that include personal identifying information.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Qualitative Research: Model and Hypotheses Refinement
- First Online: 18 November 2021
Cite this chapter

- Kerstin Kurzhals 2
Part of the book series: Gabler Theses ((GT))
373 Accesses
Despite the active discussion of firms policies to foster innovation generation, few researchers have engaged in analysing RRs, their characteristics and key drivers, be it from a management or a research perspective. On the other hand, conceptual elaborations have been made within the DC literature, and “the dynamic capability framework is drawing support and increased validity by researchers, empirical studies of dynamic capabilities remain relatively rare”. Scattered research has emerged in recent years stating the increased relevance of DCs in firms and conceptually investigating the notion of DCs, hitherto “we have little theoretical or empirical evidence on which to base any suggestions as to how dynamic capabilities can be deliberately built”.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
noventum consulting GmbH is an international IT management consulting group, founded 1996 in Germany. The group is represented in Turkey, Luxembourg and Southafrica. The consulting approach combines strategic and procedural issues with technical solutions. The focus of noventum’s service offering lies in the definition, optimisation and implementation of commercial and IT processes, beside this noventum is active in the field of innovation and future management, where service offerings cover the development of future concepts, future management workshops, innovation and ideas management (source: www.noventum.de )
All interviewees were categorised based on their self-rated level of experience in RR activities, leading to an equal number of interviewees with a high and moderate level of experience in RR activities.
Note from the author: The quotes from the interviews display the original and transcribed outcome of the interviews, which is that often interviewees interrupted sentences, switched their thoughts within the same sentence, and used a rough wording. Nonetheless, to avoid any change of meaning, the quotes were included in its original wording without any grammatical or language corrections.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Strategic and Applied Management, Coventry University Business School, Coventry, UK
Kerstin Kurzhals
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kerstin Kurzhals .
4.1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (PDF 1802 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Kurzhals, K. (2021). Qualitative Research: Model and Hypotheses Refinement. In: Resource Recombination in Firms from a Dynamic Capability Perspective. Gabler Theses. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-35666-8_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-35666-8_4
Published : 18 November 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-35665-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-35666-8
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7.4 Qualitative Research
Learning objectives.
- List several ways in which qualitative research differs from quantitative research in psychology.
- Describe the strengths and weaknesses of qualitative research in psychology compared with quantitative research.
- Give examples of qualitative research in psychology.
What Is Qualitative Research?
This book is primarily about quantitative research . Quantitative researchers typically start with a focused research question or hypothesis, collect a small amount of data from each of a large number of individuals, describe the resulting data using statistical techniques, and draw general conclusions about some large population. Although this is by far the most common approach to conducting empirical research in psychology, there is an important alternative called qualitative research. Qualitative research originated in the disciplines of anthropology and sociology but is now used to study many psychological topics as well. Qualitative researchers generally begin with a less focused research question, collect large amounts of relatively “unfiltered” data from a relatively small number of individuals, and describe their data using nonstatistical techniques. They are usually less concerned with drawing general conclusions about human behavior than with understanding in detail the experience of their research participants.
Consider, for example, a study by researcher Per Lindqvist and his colleagues, who wanted to learn how the families of teenage suicide victims cope with their loss (Lindqvist, Johansson, & Karlsson, 2008). They did not have a specific research question or hypothesis, such as, What percentage of family members join suicide support groups? Instead, they wanted to understand the variety of reactions that families had, with a focus on what it is like from their perspectives. To do this, they interviewed the families of 10 teenage suicide victims in their homes in rural Sweden. The interviews were relatively unstructured, beginning with a general request for the families to talk about the victim and ending with an invitation to talk about anything else that they wanted to tell the interviewer. One of the most important themes that emerged from these interviews was that even as life returned to “normal,” the families continued to struggle with the question of why their loved one committed suicide. This struggle appeared to be especially difficult for families in which the suicide was most unexpected.
The Purpose of Qualitative Research
Again, this book is primarily about quantitative research in psychology. The strength of quantitative research is its ability to provide precise answers to specific research questions and to draw general conclusions about human behavior. This is how we know that people have a strong tendency to obey authority figures, for example, or that female college students are not substantially more talkative than male college students. But while quantitative research is good at providing precise answers to specific research questions, it is not nearly as good at generating novel and interesting research questions. Likewise, while quantitative research is good at drawing general conclusions about human behavior, it is not nearly as good at providing detailed descriptions of the behavior of particular groups in particular situations. And it is not very good at all at communicating what it is actually like to be a member of a particular group in a particular situation.
But the relative weaknesses of quantitative research are the relative strengths of qualitative research. Qualitative research can help researchers to generate new and interesting research questions and hypotheses. The research of Lindqvist and colleagues, for example, suggests that there may be a general relationship between how unexpected a suicide is and how consumed the family is with trying to understand why the teen committed suicide. This relationship can now be explored using quantitative research. But it is unclear whether this question would have arisen at all without the researchers sitting down with the families and listening to what they themselves wanted to say about their experience. Qualitative research can also provide rich and detailed descriptions of human behavior in the real-world contexts in which it occurs. Among qualitative researchers, this is often referred to as “thick description” (Geertz, 1973). Similarly, qualitative research can convey a sense of what it is actually like to be a member of a particular group or in a particular situation—what qualitative researchers often refer to as the “lived experience” of the research participants. Lindqvist and colleagues, for example, describe how all the families spontaneously offered to show the interviewer the victim’s bedroom or the place where the suicide occurred—revealing the importance of these physical locations to the families. It seems unlikely that a quantitative study would have discovered this.
Data Collection and Analysis in Qualitative Research
As with correlational research, data collection approaches in qualitative research are quite varied and can involve naturalistic observation, archival data, artwork, and many other things. But one of the most common approaches, especially for psychological research, is to conduct interviews . Interviews in qualitative research tend to be unstructured—consisting of a small number of general questions or prompts that allow participants to talk about what is of interest to them. The researcher can follow up by asking more detailed questions about the topics that do come up. Such interviews can be lengthy and detailed, but they are usually conducted with a relatively small sample. This was essentially the approach used by Lindqvist and colleagues in their research on the families of suicide survivors. Small groups of people who participate together in interviews focused on a particular topic or issue are often referred to as focus groups . The interaction among participants in a focus group can sometimes bring out more information than can be learned in a one-on-one interview. The use of focus groups has become a standard technique in business and industry among those who want to understand consumer tastes and preferences. The content of all focus group interviews is usually recorded and transcribed to facilitate later analyses.
Another approach to data collection in qualitative research is participant observation. In participant observation , researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying. The data they collect can include interviews (usually unstructured), their own notes based on their observations and interactions, documents, photographs, and other artifacts. The basic rationale for participant observation is that there may be important information that is only accessible to, or can be interpreted only by, someone who is an active participant in the group or situation. An example of participant observation comes from a study by sociologist Amy Wilkins (published in Social Psychology Quarterly ) on a college-based religious organization that emphasized how happy its members were (Wilkins, 2008). Wilkins spent 12 months attending and participating in the group’s meetings and social events, and she interviewed several group members. In her study, Wilkins identified several ways in which the group “enforced” happiness—for example, by continually talking about happiness, discouraging the expression of negative emotions, and using happiness as a way to distinguish themselves from other groups.
Data Analysis in Quantitative Research
Although quantitative and qualitative research generally differ along several important dimensions (e.g., the specificity of the research question, the type of data collected), it is the method of data analysis that distinguishes them more clearly than anything else. To illustrate this idea, imagine a team of researchers that conducts a series of unstructured interviews with recovering alcoholics to learn about the role of their religious faith in their recovery. Although this sounds like qualitative research, imagine further that once they collect the data, they code the data in terms of how often each participant mentions God (or a “higher power”), and they then use descriptive and inferential statistics to find out whether those who mention God more often are more successful in abstaining from alcohol. Now it sounds like quantitative research. In other words, the quantitative-qualitative distinction depends more on what researchers do with the data they have collected than with why or how they collected the data.
But what does qualitative data analysis look like? Just as there are many ways to collect data in qualitative research, there are many ways to analyze data. Here we focus on one general approach called grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967). This approach was developed within the field of sociology in the 1960s and has gradually gained popularity in psychology. Remember that in quantitative research, it is typical for the researcher to start with a theory, derive a hypothesis from that theory, and then collect data to test that specific hypothesis. In qualitative research using grounded theory, researchers start with the data and develop a theory or an interpretation that is “grounded in” those data. They do this in stages. First, they identify ideas that are repeated throughout the data. Then they organize these ideas into a smaller number of broader themes. Finally, they write a theoretical narrative —an interpretation—of the data in terms of the themes that they have identified. This theoretical narrative focuses on the subjective experience of the participants and is usually supported by many direct quotations from the participants themselves.
As an example, consider a study by researchers Laura Abrams and Laura Curran, who used the grounded theory approach to study the experience of postpartum depression symptoms among low-income mothers (Abrams & Curran, 2009). Their data were the result of unstructured interviews with 19 participants. Table 7.1 “Themes and Repeating Ideas in a Study of Postpartum Depression Among Low-Income Mothers” shows the five broad themes the researchers identified and the more specific repeating ideas that made up each of those themes. In their research report, they provide numerous quotations from their participants, such as this one from “Destiny:”
Well, just recently my apartment was broken into and the fact that his Medicaid for some reason was cancelled so a lot of things was happening within the last two weeks all at one time. So that in itself I don’t want to say almost drove me mad but it put me in a funk.…Like I really was depressed. (p. 357)
Their theoretical narrative focused on the participants’ experience of their symptoms not as an abstract “affective disorder” but as closely tied to the daily struggle of raising children alone under often difficult circumstances.
Table 7.1 Themes and Repeating Ideas in a Study of Postpartum Depression Among Low-Income Mothers
The Quantitative-Qualitative “Debate”
Given their differences, it may come as no surprise that quantitative and qualitative research in psychology and related fields do not coexist in complete harmony. Some quantitative researchers criticize qualitative methods on the grounds that they lack objectivity, are difficult to evaluate in terms of reliability and validity, and do not allow generalization to people or situations other than those actually studied. At the same time, some qualitative researchers criticize quantitative methods on the grounds that they overlook the richness of human behavior and experience and instead answer simple questions about easily quantifiable variables.
In general, however, qualitative researchers are well aware of the issues of objectivity, reliability, validity, and generalizability. In fact, they have developed a number of frameworks for addressing these issues (which are beyond the scope of our discussion). And in general, quantitative researchers are well aware of the issue of oversimplification. They do not believe that all human behavior and experience can be adequately described in terms of a small number of variables and the statistical relationships among them. Instead, they use simplification as a strategy for uncovering general principles of human behavior.
Many researchers from both the quantitative and qualitative camps now agree that the two approaches can and should be combined into what has come to be called mixed-methods research (Todd, Nerlich, McKeown, & Clarke, 2004). (In fact, the studies by Lindqvist and colleagues and by Abrams and Curran both combined quantitative and qualitative approaches.) One approach to combining quantitative and qualitative research is to use qualitative research for hypothesis generation and quantitative research for hypothesis testing. Again, while a qualitative study might suggest that families who experience an unexpected suicide have more difficulty resolving the question of why, a well-designed quantitative study could test a hypothesis by measuring these specific variables for a large sample. A second approach to combining quantitative and qualitative research is referred to as triangulation . The idea is to use both quantitative and qualitative methods simultaneously to study the same general questions and to compare the results. If the results of the quantitative and qualitative methods converge on the same general conclusion, they reinforce and enrich each other. If the results diverge, then they suggest an interesting new question: Why do the results diverge and how can they be reconciled?
Key Takeaways
- Qualitative research is an important alternative to quantitative research in psychology. It generally involves asking broader research questions, collecting more detailed data (e.g., interviews), and using nonstatistical analyses.
- Many researchers conceptualize quantitative and qualitative research as complementary and advocate combining them. For example, qualitative research can be used to generate hypotheses and quantitative research to test them.
- Discussion: What are some ways in which a qualitative study of girls who play youth baseball would be likely to differ from a quantitative study on the same topic?
Abrams, L. S., & Curran, L. (2009). “And you’re telling me not to stress?” A grounded theory study of postpartum depression symptoms among low-income mothers. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 33 , 351–362.
Geertz, C. (1973). The interpretation of cultures . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Chicago, IL: Aldine.
Lindqvist, P., Johansson, L., & Karlsson, U. (2008). In the aftermath of teenage suicide: A qualitative study of the psychosocial consequences for the surviving family members. BMC Psychiatry, 8 , 26. Retrieved from http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-244X/8/26 .
Todd, Z., Nerlich, B., McKeown, S., & Clarke, D. D. (2004) Mixing methods in psychology: The integration of qualitative and quantitative methods in theory and practice . London, UK: Psychology Press.
Wilkins, A. (2008). “Happier than Non-Christians”: Collective emotions and symbolic boundaries among evangelical Christians. Social Psychology Quarterly, 71 , 281–301.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Open access
- Published: 09 May 2024
Exploring factors affecting the unsafe behavior of health care workers’ in using respiratory masks during COVID-19 pandemic in Iran: a qualitative study
- Azadeh Tahernejad 1 ,
- Sanaz Sohrabizadeh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9170-178X 1 &
- Somayeh Tahernejad 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 608 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
88 Accesses
Metrics details
The use of respiratory masks has been one of the most important measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 among health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, correct and safe use of breathing masks is vital. The purpose of this study was to exploring factors affecting the unsafe behavior of health care workers’ in using respiratory masks during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran.
This study was carried out using the conventional qualitative content analysis. Participants were the number of 26 health care workers selected by purposive sampling method. Data collection was conducted through in-depth semi-structured interviews. Data analysis was done using the content analysis approach of Graneheim and Lundman. This study aligns with the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) checklist and was conducted between December 2021 and April 2022.
The factors affecting the unsafe behavior of health care workers while using respiratory masks were divided into 3 main categories and 8 sub-categories. Categories included discomfort and pain (four sub-categories of headache and dizziness, skin discomfort, respiratory discomfort, feeling hot and thirsty), negative effect on performance (four sub-categories of effect on physical function, effect on cognitive function, system function vision, and hearing), and a negative effect on the mental state (two subcategories of anxiety and depression).
The findings can help identify and analyze possible scenarios to reduce unsafe behaviors at the time of using breathing masks. The necessary therapeutic and preventive interventions regarding the complications of using masks, as well as planning to train personnel for the correct use of masks with minimal health effects are suggested.
Peer Review reports
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought unprecedented challenges to healthcare systems worldwide, requiring Health Care Workers (HCWs) to adopt strict infection control measures to protect themselves [ 1 ]. Among these measures, the proper use of respiratory masks plays a crucial role in preventing the transmission of the virus [ 2 ]. Iran was among the initial countries impacted by COVID-19. In Iran, as in many other countries, HCWs have been at the forefront of the battle against COVID-19, facing various challenges in utilizing respiratory masks effectively [ 3 ]. Over 7.6 million Iranians have been infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, with more than 146,480 reported deaths as of August 2023 [ 4 ]. Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, Iran’s healthcare system experienced significant impacts as well [ 5 ].
Despite the passage of several years since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, new variant of the virus continues to emerge worldwide. It is crucial to be prepared for future pandemics and similar biological disasters.
Due to the SARS-CoV-2 virus transmission via respiratory droplets, the use of masks and personal protective equipment is essential [ 6 ]. The World Health Organization recommended the use of medical masks, such as surgical masks, for HCWs during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 7 ]. These masks are designed to provide a barrier to respiratory droplets and help reduce the transmission of the virus [ 8 ].
Few studies have been devoted to negative aspects of using respiratory masks in human being. The physiological and adverse effects of using PPE have been investigated in a systematic review study [ 9 ]. In another review study, of skin problems related to the use of respiratory masks were studied [ 10 ]. Also, in some studies, a significant relationship has been found between the time of using masks and the severity of the adverse effects of using masks [ 11 ]. In all the above studies, questionnaires have been used to check the prevalence of these adverse effects among HCWs.
Incorrect use of masks is considered as the unsafe behaviors of HCWs. In some studies, unsafe behaviors are defined as disobeying an accepted safe method while working with the capability of causing an accident [ 12 ]. Since the reasons for unsafe behavior are complex and multifaceted, their prevention requires a clear understanding of important and influential factors. In various studies about the prevalence of unsafe behaviors in work environments, several factors such as individual characteristics, psychological aspects, safety conditions, perceived risk, and stress have been introduced as effective factors in demonstrating the unsafe behaviors [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. However, the findings are still unable to provide a deep understanding of the underlying causes and motivations contributing to unsafe behaviors.
In the present study, unsafe behaviors while using respiratory masks is defined as the behaviors that are seen by some HCWs, which reduce the effectiveness of respiratory masks due to improper placement on the face or hand contact with the mask [ 15 ]. Some researchers in their studies indicated that other unknown factors are also effective in the unsafe behaviors [ 14 ]. However, the findings are still unable to provide a deep understanding of the underlying causes and motivations contributing to unsafe behaviors. Qualitative studies are needed to answer these questions and determine its causes. Hence, the present study is aimed to explore the factors affecting the unsafe behavior of HCWs while using respiratory masks during the COVID-19 pandemic through a qualitative study.
Study design
This study was carried out using conventional qualitative content analysis (item 9 in COREQ checklist). The interviews explored HCWs’ experiences regarding factors affecting the unsafe behavior in using respiratory masks during covid-19 pandemic in Iran. This research adheres to the guidelines outlined in the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ).
This study was conducted in government and non-government hospitals in Tehran, Mashhad and Rafsanjan that admitted patients with COVID-19 disease. The authors’ place of work and access to participants were important causes of choosing the settings. Moreover, these hospitals experienced a large amount of patients seeking healthcare during the Covid-19 pandemic. This study was performed between December 2021 and April 2022.
Participants
In this study, interviews were performed with healthcare workers (HCWs) including nurses, physicians and hospital workers who had direct contact with patients that used masks for more than 4 h in each work shift. Also, participants frequently utilized surgical masks. Among them, few employed filter masks or a combination of both types. The inclusion criteria were people with experience of using respiratory masks for more than one year and the ability to express their experiences and point of views. The sole exclusion criterion of the current study was a lack of interest in further participation. The participants were selected using purposive sampling method (item 10 in COREQ checklist) in which the researcher selected the most informed people who could explain their experiences regarding the research topic [ 16 ]. The number of participants was determined based on the data saturation principle in which no new concepts were obtained. Data saturation was achieved after 24 interviews, and to ensure saturation, two more interviews were also performed. Finally, the total number of participants was 26 people (items 12–13 in COREQ checklist).
Data gathering
Data collection was performed through in-depth face to face (item 11 in COREQ checklist) semi-structured interviews. The first author, who received training in qualitative research methods, conducted all the interviews (items 1–5 in COREQ checklist). The participants were presented with information about the research topic, objectives, and the researchers’ identities. The researcher thoroughly described the study procedure to those who consented to participate, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants (items 6–8 in COREQ checklist). The data was gathered in the workplace of the participants. Additionally, demographic data of the participants was documented (items 14–16 in COREQ checklist). At first, 5 unstructured interviews were done to extract the primary concept, and then, 21 semi-structured interviews were conducted using the interview guide. The interviews were done in a quiet and comfortable place. The interviews started with simple and general topics and were gradually directed to specific questions based on the answers. Some of the questions were: Based on your experience, what factors are effective in not using your mask safely?
New concepts were extracted from each interview, and this process continued until data saturation was reached. After obtaining permission from the participants to record the interviews, the implementation of the interviews was done immediately after the completion of each interview to increase the accuracy of the obtained data. The duration of the interviews was between 15 and 40 min (30 min on average). Field notes were made during or after the interview and transcripts were returned to participants for the comments and corrections (items 17–23 in COREQ checklist).
Data analysis
Data analysis was done using the five-step content analysis approach of Graneheim and Lundman [ 17 ]. Immediately after conducting each interview, the recorded file of the interview was transcribed in Word software. The interview text was read several times and based on the research question, all the content related to the participants’ experiences were extracted in the form of meaning units. In addition, notes were written in the margins of the text and then, the abstracted meaning units were designated as the code. Subsequently, the compiled codes were categorized into subcategories according to similarities. This process was repeated for all transcribed interviews until the main categories were established. The whole data analysis process was carried out by the researchers. Direct quotes from the interviews included in the results section to elucidate the codes, categories, and themes. (items 24–32 in COREQ checklist).
Trustworthiness
The strategies of transferability, dependability, credibility outlined by Lincoln and Guba were employed to achieve data trustworthiness [ 18 ]. Credibility and dependability were established through data triangulation approach, which involved interviews and field notes. Furthermore, peer check and member check were applied for ensuring credibility. To obtain member check, the transcribed interviews and codes were shared with some participants to receive their feedbacks. In the case of peer check, the research team and independent experts were verified the extracted codes and sub-categories. Data transferability and Confirmability were met through the detailed explanation of the research stages and process.
Women were 50% of all participants and the highest frequency of education was bachelor’s degree ( n = 17). Furthermore, the highest amount of work experience was 22 years (Table 1 ).
In the present study, 689 initial codes were identified in the initial writing, and after removing duplicate codes and cleaning, the number of final codes included 132 codes. After reviewing and analyzing the data, the factors affecting the unsafe behavior of HCWs while using respiratory masks were divided into 3 main categories and 8 sub-categories (Table 2 ). Categories included discomfort and pain (four sub-categories of headache and dizziness, skin discomfort, respiratory discomfort, feeling hot and thirsty), negative effect on performance (four sub-categories of effect on physical function, effect on cognitive function, system function vision and hearing), and a negative effect on the mental state (two subcategories of anxiety and depression).
Pain and discomfort
Some of the participants reported that the reason for improper and unsafe use of the mask is feeling pain and discomfort, and the reasons include the four subcategories of headache and dizziness, skin discomfort, respiratory discomfort, discomfort caused by heat and thirst.
Skin disorders
The side effects of the mask on the skin are of the important factors in this category. Thus, some participants, due effects of the mask to their skin, limited the use of the mask or did not use it correctly. Among the skin problems experienced by the participants were acne and skin sensitivities, which in some cases required drug treatments. The subcategory of skin sensitivities such as itching and burning was mentioned by more than 70% of the samples as the most important cause of discomfort.
“…I can’t help touching my mask. After half an hour when I put on the new mask, my face, especially my nose, starts to itch badly and I often have to blow my nose from under the mask or over the mask with my fingers, palm or the back of my hand…” (P1)
Respiratory disorders
Most of the participants in the study noted to problems such as difficulty in breathing, heart palpitations, carbon dioxide and unpleasant smell inside the mask as the most important respiratory problems. Therefore, it can be one of the important reasons for removing the mask and unsafe behavior in using the mask.
“… at any opportunity, I remove my mask to take a breath…” (P15)
Feeling hot and thirsty
Temperature discomfort, especially in long-term use and when people had to use two masks, was mentioned as an annoying factor.
“… the heat inside the mask bothers me a lot, I sweat and the mask gets wet… no matter how much water I drink, I still feel thirsty…” (P6)
Unfitness of mask with the individual’s face
Another important point extracted from the interviews was the importance of when to use the mask. In this way, as the time of using the mask increased, the person’s feeling of discomfort due to the mismatch between the belt and the mask increased, because the feeling of pressure and pain on the nose, behind the ears, and the face usually occurs several hours after wearing the mask. Several participants reported experiencing discomfort and headaches after wearing the mask. Although These headaches were often short-term and didn’t have long-term complications according to the participants’ reports, they could affect the work performance of HCWs and their behavior in the correct use of respiratory masks.
“…. After a while, the mask puts pressure on my nose and parts of my head and face. Sometimes I touch and move it unintentionally…” (P3) “… if I don’t move the mask on my face, I get a headache because the mask strap puts pressure on my head and nose…” (P21)
Effects on performance
The participants reported that wearing a mask for a long time is one of their important problems in performing their duties, and one of the main categories extracted from this study is the effects on performance, which includes the physical, cognitive, vision and hearing performance.

Effects on physical performance
The effect on the physical performance of HCWs had less effect on their unsafe behavior in using masks than other cases. But when masks were used for a long time and people were more physically tired, sometimes people removed the mask to increase their ability to perform physical work.
“…when I wear a mask, it becomes difficult for me to walk and do physical work, as if I am short of breath…” (P17)
Effects on cognitive function
It was the most frequent subcategory. Because when people feel uncomfortable, their attention decreases and part of the working memory is involved in feeling uncomfortable. Of course, it should be noted that many of the participants in the present study reported the decrease in alertness to be an effective factor in reducing their cognitive performance.
“…When I take off the mask, I can focus better on my work. Especially when I wear it in longer times, I get tired. Many times, I move the mask to finish my job faster…” (P8)
Based on the participants’ point of views, data perception (understanding information through the visual and auditory systems) decreases while using the mask. However, the negative effect of mask on the visual performance affects the unsafe behavior of the HCWs in the incorrect use of the mask and moving it on the face more than other cases. Most of the people who used glasses reported the steam condensation under the glasses as an important cause of discomfort and interference of the mask with their work duties.
“…Using glasses with a mask is really annoying. I have eye pain and burning, and there is always a fog in front of my eyes…” (P2)
Effects on mental status
Among the other main categories extracted in this study is the effects on mental status, which includes the subcategories of depression and anxiety. The negative effect of the mask on the mental state unconsciously affects the person’s behavior in using the respiratory mask.
Some of the participants in this study reported feeling anxious while wearing the mask for various reasons. Therefore, they refuse to wear masks, although they have no justification for doing so. In many cases, the participants in this study expressed that during higher psychological stress, they suffer more from wearing masks and tend to wear them improperly.
“… Sometimes I distractedly take off my mask so that the other person hears my voice better. However, there are many patients, So I am afraid of getting infected. Sometimes I have to speak loudly and this makes me furious … I worry about making a mistake or misunderstanding the conversation, and …” (P4)
One of the most important factors mentioned as a cause of depression was harder communication with colleagues and patients while wearing a mask. This occurs by increasing the physical and mental workload and placing people in social isolation. In this situation, HCWs sometimes consciously take off their masks, so that they can communicate with each other more conveniently.
“…When I wear a mask, I get tired when talking to others. I prefer not to talk to my colleague. Sometimes I don’t pay attention, I take the mask down so they can understand me …” (P5)
To the best of our knowledge, this research is one of the first qualitative studies to extract the experiences of HCWs for explaining the factors affecting the unsafe behavior of HCWs in using respiratory masks during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran. Although many reasons can cause the unsafe behavior of HCWs in the correct use of respiratory masks in the hospital, according to the present results, three main categories include discomfort and pain, effects on performance, effects on mental status. Skin and respiratory discomforts and the negative effect of the mask on cognitive functions are among the most important factors affecting the unsafe behavior of HCWs in the field of correct use of respiratory masks.
Based on the present study, the participants experienced discomfort and pain while using the mask, and this was one of the important factors of unsafe use of respiratory masks. Discomfort while wearing masks has been confirmed in several studies [ 19 ]. Additionally, in a similar study, researchers found that wearing face masks during the COVID-19 era heightens the discomfort experienced by HCWs [ 20 ]. Some studies have delved into these discomforts in greater detail. For example, the prevalence of skin disorders among HCWs using PPE during the COVID-19 pandemic was reported to be significant [ 21 ]. Some researchers also reported significant prevalence of respiratory disorders and headaches when using PPE [ 22 ]. The findings of a study suggested that a novel form of headache has emerged among HCWs when using a mask during the COVID-19 pandemic. Both exacerbation of existing headaches and the onset of new headaches have been observed to rise with mask usage, irrespective of the use duration [ 23 ]. In some studies, a significant percentage of people reported feeling thirsty and dehydrated after long-term use of respiratory masks [ 24 ]. Several studies reported disturbing rates of perspiration from prolonged use of respiratory masks [ 25 , 26 , 27 ]. A similar study reported that prolonged exposure to masks and protective gear, especially among HCWs, can lead to various issues such as acne, skin irritation, cognitive impairment, and headaches [ 28 ]. According to the results of the present study, discomfort often causes HCWs to move the mask and disturb the correct fitness of the mask on their face.
The results of the present study indicated that respiratory masks have the ability to hinder the work performance of their users. Various studies have confirmed the adverse effect of respiratory masks on HCWs performance. A similar research indicated that respiratory masks reduce physical performance [ 29 ]. Several studies have highlighted the issue of mask users’ ability to see and read being hindered by fogging of glasses [ 22 , 27 , 30 ]. The feel of weakness to perform cognitive tasks has also been reported in various studies [ 31 , 32 ]. An increase in physical fatigue has been mentioned in some studies as an adverse effect of respiratory masks [ 27 , 31 ]. A research showed the effect of respiratory mask on hearing and visual performance [ 33 ]. Another study reported that high-protection respiratory masks reduced physiological and psychological ability, especially if the workers perform physical work [ 34 ].
The third category is related to the negative impact on the psychological state of HCWs. Some studies noted the use of some PPE, including respiratory masks, as one of the possible reasons for the increase of mental health problems among HCWs [ 35 , 36 ]. Before the prevalence of the COVID-19 virus, the hypothesis of the negative effect of respiratory masks on the mental state of people was investigated and confirmed by some studies [ 37 ]. Furthermore, one study reported that wearing respiratory masks leads to an increase in anxiety [ 38 ].
The non-ergonomic nature of respiratory masks (the lack of suitability of masks for people for long-term use) can affect the effectiveness of respiratory masks by encouraging people to perform unsafe behaviors in using respiratory masks [ 39 ]. An important point was that the attitude and knowledge of health care works regarding the use of respiratory masks were not identified as the cause of unsafe behavior of HCWs. However, this factor has been reported in some previous studies as a reason for people not using PPE properly [ 40 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic situation and the extensive information collected about this pandemic may improve the level of awareness and the attitude of the HCWs.
The escalation in infection rates among HCWs, despite receiving training and utilizing personal protective equipment, served as a catalyst for this research endeavor. So far, there has been a deficiency in the context-specific research that could offer a more profound understanding of this issue. Therefore, the outcomes of this qualitative study may prove beneficial in enhancing the design and execution of respiratory protection programs for HCWs in infectious hospital departments or during similar pandemics.
Implications for nursing practice
It is expected that the findings of this study can provide a better understanding of the factors influencing the unsafe behavior of HCWs while using masks. Furthermore, it can be used as a preliminary study to evaluate the effectiveness of safety and infection control programs in hospitals in the COVID-19 pandemic and similar disasters in the future.
Discomfort and pain, effects on performance, and effects on mental status are important factors for unsafe behavior of HCWs’ in using respiratory masks. Our results could contribute to the identification and analysis of possible scenarios to reduce unsafe behaviors in the use of respiratory masks. Accordingly, it is recommended to provide the necessary therapeutic and preventive interventions regarding the complications of using masks. Planning to reduce the side effects of masks and training personnel on the correct use of masks with minimal health effects are recommended as well.
Limitations
The physical and cognitive workload of HCWs which increased during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 41 ], had possible impacts on the work ability of the staff [ 42 ]. Therefore, their explanation about the negative effects of wearing masks may be affected by their specific working conditions.
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Al-Tawfiq JA, Temsah M-H. Perspective on the challenges of COVID-19 facing healthcare workers. Infection. 2023;51(2):541–4.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
SeyedAlinaghi S, Karimi A, Afsahi AM, Mirzapour P, Varshochi S, Mojdeganlou H et al. The effectiveness of face masks in preventing covid-19 transmission: a systematic review. Infectious disorders-drug targets (formerly current drug targets-infectious disorders). 2023;23(8):19–29.
Carvalho T, Krammer F, Iwasaki A. The first 12 months of COVID-19: a timeline of immunological insights. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(4):245–56.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Razimoghadam M, Yaseri M, Rezaee M, Fazaeli A, Daroudi R. Non-COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran: a longitudinal assessment of 41 million people in 2019–2022. BMC Public Health. 2024;24(1):380.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Takian A, Aarabi SS, Semnani F, Rayati Damavandi A. Preparedness for future pandemics: lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran. Int J Public Health. 2022;67:1605094.
Toksoy CK, Demirbaş H, Bozkurt E, Acar H, Börü ÜT. Headache related to mask use of healthcare workers in COVID-19 pandemic. Korean J pain. 2021;34(2):241–5.
Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar
Matusiak Ł, Szepietowska M, Krajewski P, Białynicki-Birula R, Szepietowski JC. Inconveniences due to the use of face masks during the COVID‐19 pandemic: a survey study of 876 young people. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(4).
Seresirikachorn K, Phoophiboon V, Chobarporn T, Tiankanon K, Aeumjaturapat S, Chusakul S, et al. Decontamination and reuse of surgical masks and N95 filtering facepiece respirators during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021;42(1):25–30.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ha JF. The COVID-19 pandemic, personal protective equipment and respirator: a narrative review. Int J Clin Pract. 2020;74(10):e13578.
Johnson AT. Respirator masks protect health but impact performance: a review. J Biol Eng. 2016;10(1):1–12.
Article Google Scholar
Shubhanshu K, Singh A. Prolonged use of N95 mask a boon or bane to healthcare workers during covid–19 pandemic. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021:1–4.
Arghami S, Pouya Kian M, Mohammadfam I. Effects of safety signs on the modification of unsafe behaviours. J Adv Med Biomedical Res. 2009;17(68):93–8.
Google Scholar
Hashemi Nejad N, Mohammad Fam I, Jafari Nodoshan R, Dortaj Rabori E, Kakaei H. Assessment of unsafe behavior types by safety behavior sampling method in oil refinery workers in 2009 and suggestions for control. Occup Med Q J. 2012;4(1):25–33.
Asadi Z, Akbari H, Ghiyasi S, Dehdashti A, Motalebi Kashani M. Survey of unsafe acts and its influencing factors in metal smelting industry workers in Kashan, 2016. Iran Occup Health. 2018;15(1):55–64.
Khandan M, Koohpaei A, Mobinizadeh V. The relationship between emotional intelligence with general health and safety behavior among workers of a manufacturing industry in 2014-15. J Sabzevar Univ Med Sci. 2017;24(1):63–70.
Rahmanian E, Nekoei-Moghadam M, Mardani M. Factors affecting futures studies in hospitals: a qualitative study. J Qualitative Res Health Sci. 2020;7(4):361–71.
Graneheim UH, Lundman B. Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ Today. 2004;24(2):105–12.
Korstjens I, Moser A, Series. Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 4: trustworthiness and publishing. Eur J Gen Pract. 2018;24(1):120–4.
Shenal BV, Radonovich LJ Jr, Cheng J, Hodgson M, Bender BS. Discomfort and exertion associated with prolonged wear of respiratory protection in a health care setting. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2012;9(1):59–64.
Nwosu ADG, Ossai EN, Onwuasoigwe O, Ahaotu F. Oxygen saturation and perceived discomfort with face mask types, in the era of COVID-19: a hospital-based cross-sectional study. Pan Afr Med J. 2021;39(1).
Montero-Vilchez T, Cuenca‐Barrales C, Martinez‐Lopez A, Molina‐Leyva A, Arias‐Santiago S. Skin adverse events related to personal protective equipment: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35(10):1994–2006.
Jose S, Cyriac MC, Dhandapani M. Health problems and skin damages caused by personal protective equipment: experience of frontline nurses caring for critical COVID-19 patients in intensive care units. Indian J Crit care Medicine: peer-reviewed Official Publication Indian Soc Crit Care Med. 2021;25(2):134.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Dargahi A, Jeddi F, Ghobadi H, Vosoughi M, Karami C, Sarailoo M, et al. Evaluation of masks’ internal and external surfaces used by health care workers and patients in coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) wards. Environ Res. 2021;196:110948.
Tabah A, Ramanan M, Laupland KB, Buetti N, Cortegiani A, Mellinghoff J, et al. Personal protective equipment and intensive care unit healthcare worker safety in the COVID-19 era (PPE-SAFE): an international survey. J Crit Care. 2020;59:70–5.
Davey SL, Lee BJ, Robbins T, Randeva H, Thake CD. Heat stress and PPE during COVID-19: impact on healthcare workers’ performance, safety and well-being in NHS settings. J Hosp Infect. 2021;108:185–8.
Bansal K, Saji S, Mathur VP, Rahul M, Tewari N. A survey of self-perceived physical discomforts and health behaviors related to personal protective equipment of Indian dental professionals during COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Clin Pediatr Dentistry. 2021;14(6):784.
Agarwal A, Agarwal S, Motiani P. Difficulties encountered while using PPE kits and how to overcome them: an Indian perspective. Cureus. 2020;12(11).
Rosner E. Adverse effects of prolonged mask use among healthcare professionals during COVID-19. J Infect Dis Epidemiol. 2020;6(3):130.
Engeroff T, Groneberg DA, Niederer D. The impact of ubiquitous face masks and filtering face piece application during rest, work and exercise on gas exchange, pulmonary function and physical performance: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Sports medicine-open. 2021;7:1–20.
Arif A, Bhatti AM, Iram M, Masud M, Hadi O, Inam S. Compliance and difficulties faced by health care providers with variants of face masks, eye protection and face shield. Pakistan J Med Health Sci. 2021;15:94–7.
Garra GM, Parmentier D, Garra G. Physiologic effects and symptoms associated with extended-use medical mask and N95 respirators. Annals Work Exposures Health. 2021;65(7):862–7.
Sahebi A, Hasheminejad N, Shohani M, Yousefi A, Tahernejad S, Tahernejad A. Personal protective equipment-associated headaches in health care workers during COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2022;10.
Unoki T, Sakuramoto H, Sato R, Ouchi A, Kuribara T, Furumaya T, et al. Adverse effects of personal protective equipment among intensive care unit healthcare professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review. SAGE Open Nurs. 2021;7:23779608211026164.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
AlGhamri AA. The effects of personal protective respirators on human motor, visual, and cognitive skills. 2012.
Chew NW, Lee GK, Tan BY, Jing M, Goh Y, Ngiam NJ, et al. A multinational, multicentre study on the psychological outcomes and associated physical symptoms amongst healthcare workers during COVID-19 outbreak. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;88:559–65.
Sharif S, Amin F, Hafiz M, Benzel E, Peev N, Dahlan RH, et al. COVID 19–depression and neurosurgeons. World Neurosurg. 2020;140:e401–10.
Maison N, Herbrüggen H, Schaub B, Schauberger C, Foth S, Grychtol R, et al. Impact of imposed social isolation and use of face masks on asthma course and mental health in pediatric and adult patients with recurrent wheeze and asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021;17(1):93.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Johnson AT, Dooly CR, Blanchard CA, Brown EY. Influence of anxiety level on work performance with and without a respirator mask. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1995;56(9):858–65.
Jazani RK, Seyedmehdi SM, Kavousi A, Javazm ST. A novel questionnaire to ergonomically assess respirators among health care staff: development and validation. Tanaffos. 2018;17(4):257.
Winter S, Thomas JH, Stephens DP, Davis JS. Particulate face masks for protection against airborne pathogens-one size does not fit all: an observational study. Crit Care Resusc. 2010;12(1):24–7.
PubMed Google Scholar
de Oliveira Souza D. Health of nursing professionals: workload during the COVID-19 pandemic. Revista Brasileira De Med Do Trabalho. 2020;18(4):464.
Amirmahani M, Hasheminejad N, Tahernejad S, Nik HRT. Evaluation of work ability index and its association with job stress and musculoskeletal disorders among midwives during the Covid-19 pandemic. La Medicina Del Lavoro. 2022;113(4).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to appreciate all participants who accepted our invitations for interviews and shared their valuable experiences with us.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health in Disasters and Emergencies, School of Public Health and Safety, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, 1983535511, Iran
Azadeh Tahernejad & Sanaz Sohrabizadeh
Department of Occupational Health Engineering and Safety at Work, School of Public Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran
Somayeh Tahernejad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the manuscript. AT, SS, ST are responsible for the overall conceptualization and oversight of the study, including study design, data interpretation, and manuscript write-up. AT is responsible for the first draft. All authors reviewed and provided feedback on the manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sanaz Sohrabizadeh .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (ethical code: IR.SBMU.PHNS.REC.1401.108). All the participants signed the written informed consent. Accordingly, all participants were informed about the research objectives, confidentiality of their personal information, and the possibility of their leaving or declining the interview sessions at any time. In addition, all methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tahernejad, A., Sohrabizadeh, S. & Tahernejad, S. Exploring factors affecting the unsafe behavior of health care workers’ in using respiratory masks during COVID-19 pandemic in Iran: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 608 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11000-4
Download citation
Received : 03 September 2023
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11000-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Respiratory mask
- Health care workers
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

New Content From Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science
- Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Meta-Analysis
- Methodology
- Preregistration
- Reproducibility

A Practical Guide to Conversation Research: How to Study What People Say to Each Other Michael Yeomans, F. Katelynn Boland, Hanne Collins, Nicole Abi-Esber, and Alison Wood Brooks
Conversation—a verbal interaction between two or more people—is a complex, pervasive, and consequential human behavior. Conversations have been studied across many academic disciplines. However, advances in recording and analysis techniques over the last decade have allowed researchers to more directly and precisely examine conversations in natural contexts and at a larger scale than ever before, and these advances open new paths to understand humanity and the social world. Existing reviews of text analysis and conversation research have focused on text generated by a single author (e.g., product reviews, news articles, and public speeches) and thus leave open questions about the unique challenges presented by interactive conversation data (i.e., dialogue). In this article, we suggest approaches to overcome common challenges in the workflow of conversation science, including recording and transcribing conversations, structuring data (to merge turn-level and speaker-level data sets), extracting and aggregating linguistic features, estimating effects, and sharing data. This practical guide is meant to shed light on current best practices and empower more researchers to study conversations more directly—to expand the community of conversation scholars and contribute to a greater cumulative scientific understanding of the social world.
Open-Science Guidance for Qualitative Research: An Empirically Validated Approach for De-Identifying Sensitive Narrative Data Rebecca Campbell, McKenzie Javorka, Jasmine Engleton, Kathryn Fishwick, Katie Gregory, and Rachael Goodman-Williams
The open-science movement seeks to make research more transparent and accessible. To that end, researchers are increasingly expected to share de-identified data with other scholars for review, reanalysis, and reuse. In psychology, open-science practices have been explored primarily within the context of quantitative data, but demands to share qualitative data are becoming more prevalent. Narrative data are far more challenging to de-identify fully, and because qualitative methods are often used in studies with marginalized, minoritized, and/or traumatized populations, data sharing may pose substantial risks for participants if their information can be later reidentified. To date, there has been little guidance in the literature on how to de-identify qualitative data. To address this gap, we developed a methodological framework for remediating sensitive narrative data. This multiphase process is modeled on common qualitative-coding strategies. The first phase includes consultations with diverse stakeholders and sources to understand reidentifiability risks and data-sharing concerns. The second phase outlines an iterative process for recognizing potentially identifiable information and constructing individualized remediation strategies through group review and consensus. The third phase includes multiple strategies for assessing the validity of the de-identification analyses (i.e., whether the remediated transcripts adequately protect participants’ privacy). We applied this framework to a set of 32 qualitative interviews with sexual-assault survivors. We provide case examples of how blurring and redaction techniques can be used to protect names, dates, locations, trauma histories, help-seeking experiences, and other information about dyadic interactions.
Impossible Hypotheses and Effect-Size Limits Wijnand van Tilburg and Lennert van Tilburg
Psychological science is moving toward further specification of effect sizes when formulating hypotheses, performing power analyses, and considering the relevance of findings. This development has sparked an appreciation for the wider context in which such effect sizes are found because the importance assigned to specific sizes may vary from situation to situation. We add to this development a crucial but in psychology hitherto underappreciated contingency: There are mathematical limits to the magnitudes that population effect sizes can take within the common multivariate context in which psychology is situated, and these limits can be far more restrictive than typically assumed. The implication is that some hypothesized or preregistered effect sizes may be impossible. At the same time, these restrictions offer a way of statistically triangulating the plausible range of unknown effect sizes. We explain the reason for the existence of these limits, illustrate how to identify them, and offer recommendations and tools for improving hypothesized effect sizes by exploiting the broader multivariate context in which they occur.
It’s All About Timing: Exploring Different Temporal Resolutions for Analyzing Digital-Phenotyping Data Anna Langener, Gert Stulp, Nicholas Jacobson, Andrea Costanzo, Raj Jagesar, Martien Kas, and Laura Bringmann
The use of smartphones and wearable sensors to passively collect data on behavior has great potential for better understanding psychological well-being and mental disorders with minimal burden. However, there are important methodological challenges that may hinder the widespread adoption of these passive measures. A crucial one is the issue of timescale: The chosen temporal resolution for summarizing and analyzing the data may affect how results are interpreted. Despite its importance, the choice of temporal resolution is rarely justified. In this study, we aim to improve current standards for analyzing digital-phenotyping data by addressing the time-related decisions faced by researchers. For illustrative purposes, we use data from 10 students whose behavior (e.g., GPS, app usage) was recorded for 28 days through the Behapp application on their mobile phones. In parallel, the participants actively answered questionnaires on their phones about their mood several times a day. We provide a walk-through on how to study different timescales by doing individualized correlation analyses and random-forest prediction models. By doing so, we demonstrate how choosing different resolutions can lead to different conclusions. Therefore, we propose conducting a multiverse analysis to investigate the consequences of choosing different temporal resolutions. This will improve current standards for analyzing digital-phenotyping data and may help combat the replications crisis caused in part by researchers making implicit decisions.
Calculating Repeated-Measures Meta-Analytic Effects for Continuous Outcomes: A Tutorial on Pretest–Posttest-Controlled Designs David R. Skvarc, Matthew Fuller-Tyszkiewicz
Meta-analysis is a statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to arrive at a more robust and reliable estimate of an overall effect or estimate of the true effect. Within the context of experimental study designs, standard meta-analyses generally use between-groups differences at a single time point. This approach fails to adequately account for preexisting differences that are likely to threaten causal inference. Meta-analyses that take into account the repeated-measures nature of these data are uncommon, and so this article serves as an instructive methodology for increasing the precision of meta-analyses by attempting to estimate the repeated-measures effect sizes, with particular focus on contexts with two time points and two groups (a between-groups pretest–posttest design)—a common scenario for clinical trials and experiments. In this article, we summarize the concept of a between-groups pretest–posttest meta-analysis and its applications. We then explain the basic steps involved in conducting this meta-analysis, including the extraction of data and several alternative approaches for the calculation of effect sizes. We also highlight the importance of considering the presence of within-subjects correlations when conducting this form of meta-analysis.
Reliability and Feasibility of Linear Mixed Models in Fully Crossed Experimental Designs Michele Scandola, Emmanuele Tidoni
The use of linear mixed models (LMMs) is increasing in psychology and neuroscience research In this article, we focus on the implementation of LMMs in fully crossed experimental designs. A key aspect of LMMs is choosing a random-effects structure according to the experimental needs. To date, opposite suggestions are present in the literature, spanning from keeping all random effects (maximal models), which produces several singularity and convergence issues, to removing random effects until the best fit is found, with the risk of inflating Type I error (reduced models). However, defining the random structure to fit a nonsingular and convergent model is not straightforward. Moreover, the lack of a standard approach may lead the researcher to make decisions that potentially inflate Type I errors. After reviewing LMMs, we introduce a step-by-step approach to avoid convergence and singularity issues and control for Type I error inflation during model reduction of fully crossed experimental designs. Specifically, we propose the use of complex random intercepts (CRIs) when maximal models are overparametrized. CRIs are multiple random intercepts that represent the residual variance of categorical fixed effects within a given grouping factor. We validated CRIs and the proposed procedure by extensive simulations and a real-case application. We demonstrate that CRIs can produce reliable results and require less computational resources. Moreover, we outline a few criteria and recommendations on how and when scholars should reduce overparametrized models. Overall, the proposed procedure provides clear solutions to avoid overinflated results using LMMs in psychology and neuroscience.
Understanding Meta-Analysis Through Data Simulation With Applications to Power Analysis Filippo Gambarota, Gianmarco Altoè
Meta-analysis is a powerful tool to combine evidence from existing literature. Despite several introductory and advanced materials about organizing, conducting, and reporting a meta-analysis, to our knowledge, there are no introductive materials about simulating the most common meta-analysis models. Data simulation is essential for developing and validating new statistical models and procedures. Furthermore, data simulation is a powerful educational tool for understanding a statistical method. In this tutorial, we show how to simulate equal-effects, random-effects, and metaregression models and illustrate how to estimate statistical power. Simulations for multilevel and multivariate models are available in the Supplemental Material available online. All materials associated with this article can be accessed on OSF ( https://osf.io/54djn/ ).
Feedback on this article? Email [email protected] or login to comment.
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
Privacy Overview
- Open access
- Published: 06 May 2024
Perceptions of Chinese women with a history of gestational diabetes regarding health behaviors and related factors: a directed qualitative content analysis
- Xiaoxia Ma 1 , 2 ,
- Yun Yang 1 ,
- Shuhua Qian 1 ,
- Yan Ding 1 ,
- Qiping Lin 1 &
- Na Wang 1
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 1237 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
297 Accesses
Metrics details
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is one of the most common metabolic disorders during pregnancy and is associated with adverse outcomes in both mothers and their children. After delivery, women who experience GDM are also at higher risk of both subsequent GDM and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) than those who do not. Therefore, healthcare providers and public health practitioners need to develop targeted and effective interventions for GDM. In this study, we aimed to explore the perceptions regarding health behaviors and related factors during the inter-pregnancy period among Chinese women with a history of GDM through the lens of the theory of planned behavior (TPB).
Between December 2021 and September 2022, 16 pregnant Chinese women with a history of GDM were purposively recruited from a tertiary maternity hospital in Shanghai for face-to-face semi-structured interviews. They were asked questions regarding their health behaviors and related factors. The transcribed data were analyzed using a directed qualitative content analysis method based on the theory of TPB.
The health-related behaviors of the women varied substantially. We identified five domains that influenced women’s behaviors according to TPB constructs and based on the data collected: behavioral attitude (perceived benefits of healthy behaviors and the relationship between experience and attitude towards the oral glucose tolerance testing); subjective norms (influences of significant others and traditional cultural beliefs); perceived behavior control (knowledge of the disease, multiple-role conflict, the impact of COVID-19, an unfriendly external environment and difficulty adhering to healthy diets), incentive mechanisms (self-reward and external incentives); preferences of professional and institutional support (making full use of social media platform and providing continuous health management).
Conclusions
The health-related behaviors of women with a history of GDM were found to be affected by multiple factors. Healthcare professionals are recommended to provide women with sufficient information regarding the disease and to take advantage of the power of the family and other social support networks to improve women’s subjective norms and to promote the adoption of a healthy lifestyle.
Peer Review reports
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) refers to impaired glucose tolerance that is first identified during pregnancy [ 1 ], and is increasingly prevalent worldwide. It is estimated that 21.1 million (16.7%) of live births to women in 2021 were associated with some form of hyperglycemia during pregnancy [ 2 ]. Of these, 80.3% cases were the result of GDM [ 2 ], which is associated with adverse outcomes in both perinatal women and the fetus, including preeclampsia, emergency caesarean section, macrosomia, and premature birth [ 3 ]. After delivery, mothers who experience GDM are at a tenfold higher risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and the recurrence of GDM in a subsequent pregnancy than those who do not [ 4 , 5 ]. Besides, the exposure of high glucose environment within the uterus leads to increased risk of long-term metabolic diseases such as obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease in offspring [ 6 , 7 ].
Postpartum health behaviors, and especially diet and physical activity levels, are strongly associated with the risk of diabetes. The Da Qing Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Diabetes Study [ 8 ], which was performed in China, showed that diet and/or exercise interventions led to significant reductions in the incidence of diabetes over the following 6-year period in women with impaired glucose tolerance. A similar study performed in the United States, the National Diabetes Prevention Program [ 9 ], which had the goals of a ≥ 7% weight loss and 150 min of physical activity per week, reduced the incidence of diabetes in patients at high risk by 58%. According to the statement position of the American Heart Association [ 10 ] and the American Diabetes Association [ 11 ] on postpartum and interpregnancy management of GDM, women should undergo oral glucose tolerance testing (OGTT) 4–12 weeks postpartum, weight loss and exercise for diabetes prevention, etc. However, following childbirth, most women do not make the appropriate lifestyle adjustments or undergo OGTT as recommended. Studies performed in China and other countries have shown that attendance at a clinic for glucose screening is undesirable in women who have recently experienced GDM [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. In fact, only 58% of women were found to take up the offer of glucose screening during the first year following delivery and the percentage attending declined substantially in the second and third years [ 15 ]. Furthermore, women who experience GDM tend to return to their unhealthy lifestyle, have irregular meal patterns, exercise at lower intensity, and gain more body weight than women who remain normoglycemic during pregnancy [ 16 , 17 ].
In real-world settings, changes in health behavior are difficult to maintain. Studies have suggested that women who have previously experienced GDM face multiple barriers to the maintenance of healthy behaviors following delivery, including a lack of knowledge regarding diabetes risk, insufficient social support, negative emotions, and prioritization of the needs of their family [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. Therefore, effective interventions that take into account these barriers and involve tailored solutions should be developed. In China, the government has gradually relaxed fertility restrictions from the one-child policy to universal two- and three-child policies. With these changes in family planning policy, an increasing number of women have become pregnant at a more advanced age, along with a high body mass index and a history of GDM, which have led to increases in the incidences of pregnancy complications and comorbidities [ 21 , 22 ]. However, to date, evidence regarding the prevention of recurrence of GDM through comprehensive lifestyle interventions is scarce. And few studies have applied implementation science and behavioral change theories to develop and implement interventions that enable sustained behavioral changes in the target population; for example, women with a history of GDM in China, which has unique culture and healthcare systems.
The aim of the present study was to explore the perception regarding health behaviors and related factors during the inter-pregnancy period among Chinese women with a history of GDM through the lens of the theory of planned behavior (TPB). TPB suggests that behavioral intention determines individual behavior, which in turn is influenced by behavioral attitudes (the positive or negative evaluation of a particular behavior), subjective norms (the influence of important others or groups on individual decisions) and perceptual behavior control (perception of the ease or difficulty of a particular behavior) [ 23 ]. It has been well developed and proven to have strong explanatory power and predictive ability for health behaviors, widely used in areas such as physical activity and diet behaviors [ 24 , 25 ].
Design and setting
We performed a qualitative study that used in-depth interviews to explore the perceptions and influences on inter-pregnancy health-related behaviors, of women who had experienced GDM and who attended a tertiary maternity hospital in Shanghai, China, between December 2021 and September 2022. Shanghai is the largest city in China and the study hospital is a university-affiliated hospital at which there were ~ 12,000 births annually over the preceding 5 years.
Participants
Pregnant women with a history of GDM were selected at the hospital to obtain a wide range of maternal ages and numbers of gestational weeks. The participants were recruited according to the following eligibility criteria: a diagnosis of GDM during the previous pregnancy, based on the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups criteria published in 2010 [ 26 ]; age ≥ 18 years, and fluency in Mandarin Chinese. Women with mental or cognitive impairment were excluded from the study. Briefly, women who attended their first routine antenatal care session at the hospital were approached by a trained nurse, who considered their eligibility, and they were then referred to two interviewers (Na Wang and Xiaoxia Ma).
Table 1 shows the sociodemographic characteristics of the participants. In total, 16 pregnant women, ranging in age from 30 to 43 years, who had a history of GDM during their previous pregnancies, were interviewed between December 2021 and September 2022. The gestational intervals of the participants ranged from 2 to 8 years. Half of them had been administered insulin during their previous pregnancies. After giving birth on the previous occasion, only three of the participants (P7, P12 and P16) had undergone OGTT 4–12 weeks postpartum, as recommend by the guidelines, two had been identified as being hyperglycemic when they visited a hospital for another reason 1–2 years postpartum (P5 was diagnosed with diabetes and P14 was diagnosed with insulin resistance), and five participants had their fasting blood glucose or glycosylated hemoglobin levels measured when they attended the routine physical examinations organized by their units, 1 year postpartum, and the remaining six women did not have blood glucose concentrations measured during the inter-pregnancy period at all. Most of the participants (87.5%, 14/16) had experienced recurrence of GDM during their present pregnancy.
The study was approved by the hospital Ethics committee (approval no. 202123), and all the participants provided their written informed consent to be interviewed. The sample size was selected based on the principle of saturation of qualitative research data, and 16 women were finally interviewed.
Data collection
On the basis of the purpose of the present study and a literature review of related studies, semi-structured interview guidelines were developed and used to conduct in-depth interviews. The interview consisted of a standardized set of open-ended questions that focused on the health-related behaviors of women who had previously experienced GDM, which were followed by further probing questions. Two women participated in individual pilot interviews to test the efficacy of the interview procedure before the official interviews. The final list of questions was as follows:
What do you know about this disease?
What do you think about the impact of GDM on your health in the future?
How does it affect your daily life? What changes have you made to your daily life after being diagnosed with GDM?
How about your lifestyle after giving birth? Did someone give you some advice postpartum regarding lifestyle issues, such as diet and exercise, or blood glucose screening, relating to GDM?
What are the challenges you face or the facilitators of the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle following your last birth or during the inter-pregnancy period?
What support, especially from health professionals, do you expect after giving birth? At what time and in what form?
Before starting the interview, the participants were asked to complete a short questionnaire regarding their age, educational background, family history of diabetes, treatments during previous pregnancy, postpartum lifestyle interventions, attendance for postpartum glucose screening, gestational intervals, a diagnosis of GDM during the present pregnancy, and their number of gestational weeks at the time of the interview. After building a rapport, we started the interview with the broad question “What was your experience of GDM in your last pregnancy”? When describing their experiences, participates often talked about the advice given by the medical staff upon diagnosis with GDM along with changes in their lifestyles. Followed by questions further involved their understanding regarding the disease and its impact on their postpartum lifestyles. If they have continued a healthy lifestyle after giving birth, e.g., healthy diet, regular exercise, etc., a follow-up question regarding promoting factors was asked; if not, we further investigated what the barriers were and what support they needed. The interviews were conducted in Mandarin Chinese and field notes regarding the participants’ expressions, emotions, and behaviors during the interview were also taken to facilitate subsequent data analysis.
The interviews were conducted by two well-trained interviewers and audio-recorded. They lasted between 25 and 60 min. We recruited a final sample size of 16 women for data saturation, which means no further information relevant to the research was introduced. Each participant was offered a 20-yuan gift as compensation for their time and cooperation.
Data analysis
Audio recordings were transcribed verbatim, word-by-word, within 24 h, and imported into the qualitative analysis software NVivo 12.0. Adhering to the suggestions provided by Satu Elo [ 27 ], the data analysis process consists of the following steps: (1) selecting the units of analysis and being immersed in the data to gain a holistic understanding of women’ descriptions; (2) developing a categorization matrix deductively derived from TPB (behavioral attitudes, subjective norms, and perceptual behavior control) [ 23 ]; (3) coding the data according the pre-determined categories; (4) besides, through the inductive coding, the new categories that did not fit within the TPB domains emerged. The combination of inductive and deductive approaches used for the data analysis facilitates more synergistic findings to be made regarding the influences on and determinants of women’s behaviors [ 28 ]. The data analysis was conducted concurrently with the data collection, to determine whether new codes and categories emerged during the interviews. To ensure the rigor of the study, two researchers independently reviewed and analyzed the transcripts and field notes. Any discrepancies in the data analysis between the two researchers were resolved through discussion.
The health-related behaviors of the women varied substantially. After careful review of the text, through deductive approach, three categories of related factors were identified that fit the structures of TPB. Additionally, two other categories that did not fit TPB frame (incentive mechanisms and preferences derived from professional and institutional support) were generated using the inductive approach. As presented in Fig. 1 .
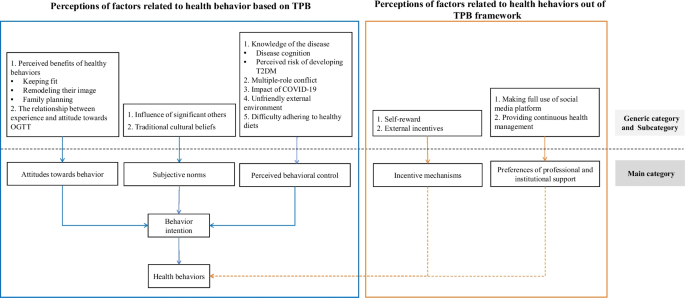
Perceptions of Chinese women with a history of gestational diabetes regarding health behaviors. The orange dotted lines indicate factors related to health behaviors that were beyond the theoretical domain of TPB in this study, which have not been rigorously validated in other populations
Attitudes towards health-related behavior
Perceived benefits of healthy behaviors, keeping fit.
Owing to their irregular eating habits and physical inactivity, 3 women (18.75%) developed cardiovascular diseases following their previous birth, which made them realize that they had to take responsibility for their own health by adopting a healthy lifestyle.
P7: “Six months after the birth, I went for a routine physical examination. The doctor said that I had gained too much weight, almost 25 pounds. Then I was diagnosed with…uh…fat infiltration into my liver, which made me pay more attention to my diet and exercise… I did yoga for about 20 min each evening and I lost a lot of weight.”
P13: “There were a lot of problems at work… and I had to take care of the child after work. It was very stressful (sigh). So, I chose to do yoga, during which I can be alone and relax my mind.”
Remodeling their image
To get slim is a powerful impetus for some women to follow a healthy diet and be physically active.
P10: “In order to lose weight and look beautiful, I insisted on taking a brisk walk for an hour every day, unless it was rainy, and I also went swimming once a week at that time. Besides, I subconsciously balanced my diet, by controlling my sugar intake, eating more vegetables, and reducing the amount of high starchy food I consumed… I lost 20 pounds in 5 months! (loudly).”
P11: “I will return to work after my maternity leave and I must prioritize my body image… which is very important.”
Family planning
Women who plan to have a second child were more likely to have a positive attitude toward glycemic control and to adopt the recommendations regarding the maintenance of a healthy lifestyles before conception.
P13: “After giving birth to my first baby, I planned to have a second one. I thought it was necessary to control my staple food intake and reduce my sugar intake. Therefore, coarse grains, taro, and sweet potatoes were my first choices for every meal.”
In contrast, some participants said that the second pregnancy was accidental, and therefore they did not make any preparations during the early stages, which might have prevented them from maintaining a healthier lifestyle.
P6: “To be honest, I did not plan to have another baby and I haven’t adjusted my lifestyle significantly during the past three or four years… The recurrence (of GDM) was… not surprising.”
The relationship between experience and attitude towards OGTT
The previous experience of the unpleasant taste of the glucose syrup and the repeated venipuncture during OGTT appeared to affect women’s attitude to undergo this procedure again following delivery.
P2: “At that time, he (the doctor) reminded me to do OGTT after delivery, but I remembered that the process was painful. I put it off as long as I could and in the end I did not do the test.”
P5: “The sugary water (consumed during OGTT) was too sweet to drink, so I didn’t want to drink it again.”
Subjective norms
Influence of significant others.
The “significant others” in the lives of the participants were principally family members, colleagues, and health professionals. The influence of their family was identified as a key determinant in the establishment of a healthy lifestyle by women with a history of GDM.
P14: “My husband sets a great example for me because he is a fitness fanatic, which also influences me. In addition, my parents attach great importance to health, and they urge me to make changes every day, such as ‘Why don’t you go running? It’s time to exercise’ (laugh).”
P2: “My husband is very lazy; he always lies on the couch playing with his mobile phone… I must ask someone else if I want to play badminton, which makes me lack motivation to exercise… Uh…in fact, I don’t like exercise myself. None of us like exercise.”
In addition to this, the attitudes and behavior of the women’s friends and colleagues also had an influence on their behavior.
P12: “Experiencing the physical examination organized by the unit in recent years, all of my colleagues feel that one’s health is very important… We have been playing badminton together for the last 2 or 3 years to strengthen our bodies.”
Notably, the health professionals at the maternity hospital were the most authoritative and important influences on the women with GDM regarding the risks of T2DM following GDM and the importance of blood glucose screening and maintaining a healthy lifestyle postpartum. These were in the form of warnings and urging.
P7: “When I was discharged from the hospital, the doctor told me that if I didn’t control my blood sugar after birth, I might develop permanent diabetes. I am worried about it, so I continued to eat a balanced diet after birth. And he also advised me that it was better to test my blood sugar by… drinking sugary water (OGTT) or… something I don’t remember any more, to prevent diabetes. It (diabetes) was likely to continue and affect my later life.”
Despite these responses, most of the women interviewed in the present study reported that no-one had reminded them about maintaining a healthy lifestyle or undergoing blood glucose screening following birth. They had poor awareness of the long-term implications of GDM.
P2: “The doctor didn’t say anything about a relapse of the disease or the probability of diabetes in the future… I was never told before (by the doctor)”.
Traditional cultural beliefs
The observance of the traditional cultural “confinement” custom limits women’s dietary choices and activities during the first month following delivery, and these limitations can continue well into their lactation period.
P10: “When I breastfed my baby after childbirth, my mother-in-law made me drink all kinds of soup every day, such as fish soup, chicken soup and so on, in order to produce more milk; and I was not allowed to go out in the period after giving birth. All I could do every day was to eat, sleep, feed, and eat again.”
P11: “I put on a lot of weight after I gave birth. I breastfed my baby, and the internet and my family and friends said that it is best not to do exercise during the period of breastfeeding… To be honest, I do not understand why, but I started to exercise and lose weight after weaning.”
Perceived behavioral control
Knowledge of the disease, disease cognition.
In the interviews, most women regarded GDM as a temporary abnormality in glucose status. They had poor awareness of the long-term implications of the disease, and rarely realized the importance of either a healthy lifestyle or blood glucose screening following delivery. Knowledge gaps translated into a lower likelihood for them to establish a healthy lifestyle.
P5: “After birth, I quickly resumed my old lifestyle habits, especially with respect to eating fried foods, which I like very much (laugh). This was because I thought that this disease only happened during pregnancy, uh… and my baby was born very healthy; he was not macrosomic. It (GDM) had no effects on him. The doctor just wanted to scare me.”
P14: “Anyway, after giving birth, I didn’t care about it (blood sugar) anymore and did no exercise either… However, about 1 year ago, I felt a little dizzy. Then I was diagnosed with high blood pressure and high blood sugar… It is very strange: no one in our family has diabetes… Is it because I am fat? Now, I am really worried about myself and my baby (sobbing).”
Perceived risk of developing T2DM
Women were more willing to change their sub-optimal lifestyle if they recognized that GDM might increase their risk of metabolic disease, and especially if they were concerned about developing T2DM in the future. 5 women (31.25%) remained a healthy lifestyle for this reason in the postpartum period. This was more evident among women with a family history of T2DM.
P15: “After giving birth, I attached great importance to my lifestyle. You know, I didn’t even dare to eat porridge anymore- I was really strict- because my doctor told me that I was susceptible to T2DM after this (GDM). I must take responsibility for my own health.”
P2: “My grandmother used to have severe diabetes and injected insulin… Unfortunately, she was involved in a car accident a few years ago and her injury did not heal easily… Then she died after that… My uncle also had diabetes, and he experienced retinal bleeding because of diabetes. It scared me! I was worried about whether I would get it in the future.”
Multiple-role conflict
The social roles of women can be categorized as worker, spouse, parent, and daughter. Women need to take care of their newborns and adapt to their new roles as mothers during the early postpartum period. In China, the mothers-in-law of women are the most likely people to help with the care of the children, and sometimes they live with their daughters-in-law. These multiple roles make it difficult for mothers to focus on themselves.
P7: “Uh… It was totally different having and not having a child. Previously, I might have gone to play ball or do some other sports after finishing work, and it didn’t matter if I went home early or late. Now, the first thing I do after work is rush home to look after my baby (laugh). It is completely different!”
P11: “At that time, I was living with my parents-in-law. Uh… There were a lot of conflicts between us, which meant that I was always in a bad mood. I thought it was postpartum depression. And I had to take care of my child and deal with an intense job at the same time… It was too hard (sigh).”
Impact of COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Shanghai underwent a lockdown for approximately 2 months, which limited people’s outdoor activities and their attendance at gyms, as well as the variety of food available.
P3: “I used to go to the gym three times a week. However, owing to the COVID-19 epidemic, I could not go out to exercise and I gained more than ten pounds at that time. It shocked me!”
P5: “We were locked down at home because of the COVID-19 pandemic. We couldn’t buy whole grains, or various vegetables or fruits from the market, and had to accept a limited range of food.”
Unfriendly external environment
Despite growing concerns regarding obesity and diabetes during recent years, provision of healthy meals in public places is still limited, which makes it more difficult for such women to pursue a healthier lifestyle.
P1: “I think the outside environment is not friendly to diabetic people. When eating out, it’s difficult for me to get specific meals.”
P6: “It’s very difficult to bring food every day when I go to work, so I eat in the cafeteria. And in that situation, my sugar, oil, and staple food intake can’t be strictly controlled.”
Difficulty adhering to healthy diets
Owing to the relative lack of flavor of “healthy food”, some women find it difficult to observe a healthy diet.
P4: “After giving birth, I didn’t deliberately maintain the eating habits recommended by the doctors during pregnancy, especially with respect to coarse grains: I couldn’t stand the taste of them. Really, they are terrible; don’t you think so?”
P12: “Compared to low-sugar diets, foods such as bread, cakes, and glutinous rice products are more tempting to me. They are my favorites (laugh).”
Incentive mechanisms
Self-reward.
Obtaining a reward is considered to be an important contributor to compliance with an exercise regimen.
P10: “For me, I need to give myself a little reward to encourage me to keep moving. For example, if I swam for 1 h today, I would reward myself with a cup of low-sugar milky tea (laugh). In this way, I can keep doing exercise more easily.”
External incentives
Some platforms use incentive mechanisms to motivate their customers.
P14: “Do you know the Keep, the sports software? It can track and record the duration of exercise and display the number of calories I have burned. If you keep moving, you get some cute medals. On that platform, some people upload their fitness dynamics, which is very motivating for me… their figures are so charming!”
Preferences of professional and institutional support
Making full use of social media platform.
During the interviews, some women expressed a need for education by qualified health professionals over the internet, involving videos that improve their knowledge of diabetes following delivery and encourage them to undergo blood glucose screening.
P13: “I think there will be some promotional videos, which will tell me what I need to pay attention to when I go home. This method is more vivid and impressive.”
P2: “For example, if I haven’t visited for OGTT at about 42 days postpartum, I hope that my doctor will remind me and send messages about the risks of missing screening via telephone or WeChat.
Providing continuous health management
Regarding the timing of the support provided by healthcare workers following delivery, most women expected to obtain guidance prior to their discharge from hospital. In addition, during the routine examination of women 42 days following delivery, health professionals can provide education and guidance according to the results of OGTT, and continue to provide support through an online platform.
In the present study, we interviewed 16 Chinese women with a history of GDM to explore their health behaviors and related factors through the lens of TPB theory, during the inter-pregnancy period. We found that their behaviors varied substantially, and most were not optimal. Further exploration of the determinants of their behaviors revealed that in addition to some personal characteristics, a lack of awareness of the risks of diabetes, multiple-role conflicts, insufficient social support, and traditional cultural beliefs were repeatedly mentioned as factors that had negative impacts on the pursuit of a healthy lifestyle. In addition, some of the barriers were perceived to be beyond their control. In contrast, women who adhered to a healthy lifestyle believed that the incentive mechanisms and sufficient social support had positive impacts on their performance.
With the economic development and lifestyle changes occurring around the world, the prevalence of obesity is gradually increasing, and women of child-bearing age are no exception to this [ 29 ]. Obesity is associated with a range of health problems, including diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, and other chronic diseases, and weight loss can significantly reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases [ 30 ]. In the present study, women who developed conditions associated with obesity during the inter-pregnancy period were more willing to maintain good physical condition through lifestyle improvements, such as increases in physical exertion to achieve weight loss and a reduction in the consumption of foods that are rich in fat and sugar. In addition, the desire to improve body image is an important intrinsic motivation that increases the likelihood of women adopting a healthy diet and higher physical activity levels.
Of note, we found that women who were willing to prepare for their subsequent pregnancies were more likely to adopt a healthy lifestyle. However, a previous study showed that the unintended pregnancy rates, both in China and worldwide, remain high [ 31 ]. In the present study, only two of the women had a reproduction plan. A retrospective cohort study conducted in the United States showed that people who planned their pregnancies were less likely to smoke before becoming pregnant, were more likely to regularly take multivitamins, and were more likely to have undergone health checks during the preceding year [ 32 ]. In contrast, women with an unplanned pregnancy had higher body mass indexes and were less likely to take a folic acid supplement [ 33 ]. According to the guide “Optimizing Postnatal Care”, patients and their obstetricians/gynecologists or other obstetric care providers should discuss the woman’s reproductive life plans, beginning during prenatal care, and including a discussion regarding future pregnancies and their timing [ 34 ]. Therefore, medical staff in maternity hospitals may need to highlight the need for postpartum contraception and discuss future maternity plans with women who experience GDM and their partners, and encourage them to adopt healthy behaviors.
Furthermore, OGTT is time-consuming, involves the ingestion of unpalatable glucose syrup, and requires multiple blood samples to be collected. Therefore, this can be an unpleasant experience for women [ 35 ], and they may be reluctant to undergo this process again following delivery. As healthcare professionals, we should raise women’s awareness of the importance of postpartum OGTT and increase the rate of screening through telephone, emails and other internet platforms [ 36 , 37 ].
Advice from health professionals is often thought to be the most important means of improving women’s knowledge regarding diabetes and the benefits of maintaining a healthy lifestyle postpartum. However, previous studies have shown that the information women receive regarding postpartum glucose management is too limited. A study conducted in Singapore showed that although women typically receive advice regarding healthy lifestyles from medical staff, this largely focuses on the prevention of obstetric complications, and includes little information regarding future diabetes risk [ 38 ]. After childbirth, the participants were transferred from tertiary hospitals to primary care facilities, but the staff in the latter did not know whether the women had previously experienced GDM, and therefore the continuity of maternal care, especially with regard to postpartum glucose management, was interrupted [ 38 ]. In China, the situation is similar. Healthcare professionals at maternity hospitals routinely help women who experience GDM during pregnancy and the early postpartum period to understand the severity of diabetes and the risk of developing diabetes in the future, and provide personalized health education to motivate them to make necessary lifestyle changes. In addition, maternity and primary hospitals can make use of information systems to affect a seamless handover. Specifically, they can make use of media including the telephone, email, WeChat, and other digital applications to continue the management of GDM [ 19 ]. This has been shown to be accepted by women in previous studies [ 19 , 39 ], and the women in the present study expressed similar opinions.
Of particular note, in China, the traditional month-long perinatal confinement period is considered to be a barrier to women’s engagement with a healthy lifestyle. Women are usually required to undergo confinement after giving birth and there are certain contraindications with respect to diet and activities during puerperium [ 40 ]. For example, women in some areas are prohibited from eating vegetables, fruit, and cold food; are required to consume substantial amounts of chicken soup and brown sugar water; and are not permitted to go out during the confinement period. Furthermore, some of these conventions, such as drinking a lot of soup and not performing vigorous physical activity, can even last until weaning. During this period, the women are cared for in general by their mothers or mothers-in-law, who may follow traditional customs. Furthermore, the birth of a baby engenders changes in the family structure and the social roles of its members. Mothers generally have to take the bulk of the responsibility for raising their babies, which may put them under substantial physical and psychological stress and reduce their concern for their own health. Many women say that postpartum fatigue and a lack of time, owing to the necessity to feed and care for the newborn, are the major barriers to maintaining a healthy lifestyle [ 19 , 20 , 38 ]. The necessity to rest or sleep is considered to be more important than exercise when women have some free time, and in their new role, they often prioritize the comfort and needs of their children over their personal health [ 38 , 41 ]. Moreover, when their maternity leave finishes, work and childcare occupy most of their time and energy, greatly reducing the amount of time they have available for regular exercise [ 19 ].
As reported in a systematic review, social support can improve an individual’s ability to change and maintain new lifestyle habits [ 42 ]. Similarly, the availability of adequate support has been identified as a significant element in the successful modification of the health-related behaviors of such women [ 18 , 38 ]. The foremost emotional motivating factor for these women is from their families, whose encouragement provides them with a sense of love and belonging. In particular, as we have shown in the present study, spouses with a high level of health awareness often accompany women and encourage them to do physical exercise, which is regarded as a strong incentive to achieve a healthy lifestyle [ 38 ]. In addition, peers can build a mutual aid system by sharing experiences and motivating one another [ 43 ], which empowers patients with diabetes to improve their self-efficacy [ 44 ]. In the present study, some women suggested the setting up of a WeChat group to share knowledge and skills regarding diabetes, based on their own personal experiences, a finding that was also made in another qualitative study [ 43 ]. This provides a reference for us to formulate more targeted and effective strategies to assist this high-risk population.
In the present study, most of the participants had a poor understanding of health information and limited knowledge regarding the association between GDM and long-term disease risk, and these were the primary obstacles to compliance with healthy lifestyle behaviors in women after giving birth, consistent with the findings of other studies [ 18 , 38 ]. Because the abnormalities in glucose metabolism disappear soon after delivery, some of the women believed that their blood glucose status had returned to normal, and therefore they resumed their pre-pregnancy lifestyle [ 45 , 46 ]. This was particularly the case in the women who did not administer insulin or maintain a strict diet and exercise regimen to control their blood glucose concentrations during pregnancy. In contrast, the women who understood the risk of developing T2DM or other metabolic diseases because of online education, information provided by healthcare providers, or the experience of family members were more likely to return to the hospital for glucose screening and to change their unhealthy lifestyles [ 35 ]. In addition, knowledge of the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle is related to the health status of women themselves.
Women’s perception of the ease or difficulty of consuming a balanced diet, undertaking regular activity, and participating in health screening also makes a difference. We found that the poor taste of coarse grains was one of the reasons why mothers were unwilling to continue eating this food after giving birth. Especially for women whose dietary preferences conflict with the recommendations, the maintenance of a healthy diet is not easy [ 47 , 48 ]. Therefore, we suggest that healthcare providers should encourage women to consult a dietitian, to develop a diverse range of recipes, taking into account their food preferences. In addition, the outcomes of the present study show that women can increase their motivation by preparing a “self-reward checklist” regarding a healthy lifestyle for the long term. This technique helps reinforce particular behaviors, and has been successfully applied to weight loss, the management of diabetes, the cessation of smoking, and broader changes in health behaviors [ 49 ].
In addition to personal and interpersonal factors, the external environment affects lifestyle. The present study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, and therefore the participants were locked down at home and it was difficult for them to obtain a diverse range of foods. At the same time, the closure of gyms and sports venues restricted the activity of pregnant women and caused many of them to put on weight. A rapid review revealed that there were significant decreases in the availability and utilization of postnatal care services during and after the COVID-19 lockdown [ 50 ], owing to the postponement of non-urgent treatments and changes in the care delivered [ 51 ]. In addition to environmental changes owing to unexpected events, current societal practices are generally not attuned to people with diabetes, and specifically with respect to the provision of healthy diets. In China, very few restaurants and canteens provide special meals for people with diabetes. Instead, fast food and foods high in fat and sugar are more accessible, meaning that women face great challenges in maintaining a healthy diet. Therefore, public awareness should be raised to facilitate the provision of a more convenient and optimized eating environment for this group.
Strengths and limitations of the present study
To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the perceptions and attitudes, and the influences on these, regarding health-related behaviors in Chinese women with a history of GDM during their second pregnancy. We have obtained an abundance of data regarding their health-related behaviors during the inter-pregnancy period, which includes both the postpartum and preconception periods. Furthermore, the interviewees in the study had experienced the lockdown of the city owing to COVID-19, which was a unique experience for the women with a history of GDM. In addition, the combination of the inductive and deductive approaches used for the data analysis facilitated the making of synergistic findings regarding the influences on and determinants of women’s behaviors. The present study also had several limitations. First, because all the participants were recruited from one center in Shanghai, the findings may be context-specific and not readily generalizable. Second, only the views and attitudes of patients regarding their health-related behaviors were captured. Future studies should explore the views of healthcare professionals and policymakers regarding the support of women with a history of GDM, and especially regarding those who want to become pregnant again, in the Chinese context.
In the present qualitative study, we have shown that health-related behaviors are affected by multiple factors in women with a history of GDM. As shown in Fig. 2 , healthcare professionals should provide enough information regarding the disease and help women, as well as their families, to understand the associated future risks, to facilitate the development of a positive attitude toward healthy behaviors. In addition, the power of family and other social support networks to improve women’s subjective norms, as well as their intentions to actively adopt a healthy lifestyle, should be taken into account.
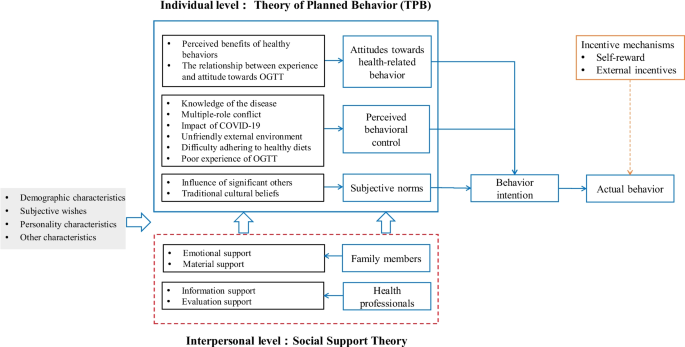
Intervention hypothesis, based on the results identified during the study. The red dotted line indicates the intervention hypothesis that is derived from the study data and the social support theory
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author Na Wang, upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Gestational diabetes mellitus
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Oral glucose tolerance testing
- Theory of planned behavior
Petersmann A, Muller-Wieland D, Muller UA, Landgraf R, Nauck M, Freckmann G, et al. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2019;127(S 01):S1–7. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1018-9078 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wang H, Li N, Chivese T, Werfalli M, Sun H, Yuen L, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: estimation of global and regional gestational diabetes mellitus prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group’s Criteria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109050 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mistry SK, Das GR, Alam S, Kaur K, Shamim AA, Puthussery S. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and adverse pregnancy outcome in South Asia: a systematic review. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2021;4(4):e285. https://doi.org/10.1002/edm2.285 .
Article Google Scholar
Vounzoulaki E, Khunti K, Abner SC, Tan BK, Davies MJ, Gillies CL. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;369:m1361. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1361 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pintaudi B, Di Vieste G, Corrado F, Lucisano G, Pellegrini F, Giunta L, et al. Improvement of selective screening strategy for gestational diabetes through a more accurate definition of high-risk groups. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014;170(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-13-0759 .
Lowe WJ, Lowe LP, Kuang A, Catalano PM, Nodzenski M, Talbot O, et al. Maternal glucose levels during pregnancy and childhood adiposity in the hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcome follow-up study. Diabetologia. 2019;62(4):598–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4809-6 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Moon JH, Jang HC. Gestational diabetes mellitus: diagnostic approaches and maternal-offspring complications. Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0335 . Epub 2022 Jan 27.
Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, Wang JX, Yang WY, An ZX, et al. Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and diabetes study. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):537–44. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.20.4.537 .
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(6):393–403. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012512 .
Lewey J, Beckie TM, Brown HL, Brown SD, Garovic VD, Khan SS, et al. Opportunities in the postpartum period to reduce cardiovascular disease risk after adverse pregnancy outcomes: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149(7):e330–46. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001212 .
Elsayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 15. Management of diabetes in pregnancy: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(Suppl 1):S254–66. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc23-S015 .
Rotem R, Salem-Yaniv S, Sandler-Rahat H, Yohay D, Sade S, Yahav L, et al. Adherence to postpartum diabetes mellitus screening, do associated pregnancy complications make a difference? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;159:107972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107972 .
Liu ZY, Zhao JJ, Gao LL, Wang AY. Glucose screening within six months postpartum among Chinese mothers with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2276-9 .
Ward RJ, Fryer AA, Hanna FW, Spencer N, Mahmood M, Wu P, et al. Inadequate postpartum screening for type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestation diabetes mellitus: a retrospective audit of practice over 17 years. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(9):e14447. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.14447 . Epub 2021 Jul 14.
Daly B, Toulis KA, Thomas N, Gokhale K, Martin J, Webber J, et al. Increased risk of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus, a target group in general practice for preventive interventions: a population-based cohort study. Plos Med. 2018;15(1):e1002488. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002488 .
Persson M, Winkvist A, Mogren I. Lifestyle and health status in a sample of Swedish women four years after pregnancy: a comparison of women with a history of normal pregnancy and women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015;15:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0487-2 .
Retnakaran R, Qi Y, Sermer M, Connelly PW, Zinman B, Hanley AJ. Gestational diabetes and postpartum physical activity: evidence of lifestyle change 1 year after delivery. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010;18(7):1323–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.329 .
Neven A, Lake AJ, Williams A, O’Reilly SL, Hendrieckx C, Morrison M, et al. Barriers to and enablers of postpartum health behaviours among women from diverse cultural backgrounds with prior gestational diabetes: a systematic review and qualitative synthesis applying the theoretical domains framework. Diabet Med. 2022;39(11):e14945. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14945 .
Shang J, Henry A, Zhang P, Chen H, Thompson K, Wang X, et al. Chinese women’s attitudes towards postpartum interventions to prevent type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes: a semi-structured qualitative study. Reprod Health. 2021;18(1):133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-021-01180-1 .
Saligheh M, Mcnamara B, Rooney R. Perceived barriers and enablers of physical activity in postpartum women: a qualitative approach. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-016-0908-x .
Li H, Nawsherwan FC, Yin S, Haq IU, Mubarik S, et al. Changes in adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with advanced maternal age (AMA) after the enactment of China’s universal two-child policy. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):5048. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08396-6 .
Zhu H, Zhao Z, Xu J, Chen Y, Zhu Q, Zhou L, et al. The prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus before and after the implementation of the universal two-child policy in China. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:960877. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.960877 .
Young HM, Lierman L, Powell-Cope G, Kasprzyk D, Benoliel JQ. Operationalizing the theory of planned behavior. Res Nurs Health. 1991;14(2):137–44.
Bosnjak M, Ajzen I, Schmidt P. The theory of planned behavior: selected recent advances and applications. Eur J Psychol. 2020;16(3):352–6. https://doi.org/10.5964/ejop.v16i3.3107 .
Mceachan RRC, Conner M, Taylor NJ, Lawton RJ. Prospective prediction of health-related behaviours with the theory of planned behaviour: a meta-analysis. Health Psychol Rev. 2011;5(2):97–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2010.521684 .
Metzger BE, Gabbe SG, Persson B, Buchanan TA, Catalano PA, Damm P, et al. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(3):676–82. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1848 .
Elo S, Kyngas H. The qualitative content analysis process. J Adv Nurs. 2008;62(1):107–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x .
Mcgowan LJ, Powell R, French DP. How can use of the theoretical domains framework be optimized in qualitative research? A rapid systematic review. Br J Health Psychol. 2020;25(3):677–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12437 . Epub 2020 Jun 19.
World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Geneva; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight . Accessed 10 Jan 2023.
Piche ME, Tchernof A, Despres JP. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 2020;126(11):1477–500. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101 .
Che Y, Li Y, Gu X, Jiang L, Zhou Y, Hu X, et al. Contraception, unintended pregnancy, and induced abortion within 24 months of delivery in China: a retrospective cohort study. Contraception. 2021;103(3):144–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2020.12.014 .
Green-Raleigh K, Lawrence JM, Chen H, Devine O, Prue C. Pregnancy planning status and health behaviors among nonpregnant women in a California managed health care organization. Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2005;37(4):179–83. https://doi.org/10.1363/psrh.37.179.05 .
Cheng TS, Loy SL, Cheung YB, Godfrey KM, Gluckman PD, Kwek K, et al. Demographic characteristics, health behaviors before and during pregnancy, and pregnancy and birth outcomes in mothers with different pregnancy planning status. Prev Sci. 2016;17(8):960–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0694-8 .
Mckinney J, Keyser L, Clinton S, Pagliano C. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132(3):784–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000002633 .
Sunny SH, Malhotra R, Ang SB, Lim C, Tan Y, Soh Y, et al. Facilitators and barriers to post-partum diabetes screening among mothers with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus-a qualitative study from Singapore. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:602. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00602 . eCollection 2020.
Carolan-Olah M, Sayakhot P. A randomized controlled trial of a web-based education intervention for women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Midwifery. 2019;68:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2018.08.019 .
Carmody L, Egan AM, Dunne FP. Postpartum glucose testing for women with gestational diabetes mellitus: Improving regional recall rates. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;108(3):e38–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2015.04.005 .
Teh K, Quek IP, Tang WE. Postpartum dietary and physical activity-related beliefs and behaviors among women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus: a qualitative study from Singapore. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021;21(1):612. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-021-04089-6 .
Ekezie W, Dallosso H, Saravanan P, Khunti K, Hadjiconstantinou M. Experiences of using a digital type 2 diabetes prevention application designed to support women with previous gestational diabetes. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):772. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-06791-9 .
Zheng X, Watts K, Morrell J. Chinese primiparous women’s experience of the traditional postnatal practice of “Doing the month”: a descriptive method study. Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2019;16(3):253–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/jjns.12232 .
Svensson L, Nielsen KK, Maindal HT. What is the postpartum experience of Danish women following gestational diabetes? A qualitative exploration. Scand J Caring Sci. 2018;32(2):756–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/scs.12506 .
Kwasnicka D, Dombrowski SU, White M, Sniehotta F. Theoretical explanations for maintenance of behaviour change: a systematic review of behaviour theories. Health Psychol Rev. 2016;10(3):277–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2016.1151372 .
Dennison RA, Griffin SJ, Usher-Smith JA, Fox RA, Aiken CE, Meek CL. “Post-GDM support would be really good for mothers”: a qualitative interview study exploring how to support a healthy diet and physical activity after gestational diabetes. PLoS One. 2022;17(1):e262852. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262852 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Sathish T, Williams ED, Pasricha N, Absetz P, Lorgelly P, Wolfe R, et al. Cluster randomised controlled trial of a peer-led lifestyle intervention program: study protocol for the Kerala diabetes prevention program. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:1035. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-1035 .
Rafii F, Rahimparvar S, Mehrdad N, Keramat A. Barriers to postpartum screening for type 2 diabetes: a qualitative study of women with previous gestational diabetes. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;26:54. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2017.26.54.11433 .
Bernstein JA, Mccloskey L, Gebel CM, Iverson RE, Lee-Parritz A. Lost opportunities to prevent early onset type 2 diabetes mellitus after a pregnancy complicated by gestational diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2016;4(1):e250. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000250 .
Hui AL, Sevenhuysen G, Harvey D, Salamon E. Food choice decision-making by women with gestational diabetes. Can J Diabetes. 2014;38(1):26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2014.07.001 .
Hui AL, Sevenhuysen G, Harvey D, Salamon E. Barriers and coping strategies of women with gestational diabetes to follow dietary advice. Women Birth. 2014;27(4):292–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2014.07.001 .
Brown EM, Smith DM, Epton T, Armitage CJ. Do self-incentives and self-rewards change behavior? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Ther. 2018;49(1):113–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2017.09.004 .
Dzinamarira T, Moyo E, Pierre G, Mpabuka E, Kahere M, Tungwarara N, et al. Postnatal care services availability and utilization during the COVID-19 era in sub-Saharan Africa: a rapid review. Women Birth. 2023;36(3):e295–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2022.10.002 .
Jensen NH, Nielsen KK, Dahl-Petersen IK, Maindal HT. The experience of women with recent gestational diabetes during the COVID-19 lockdown: a qualitative study from Denmark. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022;22(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-022-04424-5 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the participants who took part in this study. We appreciate the help from Liang Xu for participant recruitment.
This study was supported by the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health Foundation (grant number: 202150050); the Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Fudan University (grant number: FC2021CR203).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nursing Department, Obstetrics and Gynaecology Hospital of Fudan University, No. 128 Shenyang Road, Shanghai, 200090, China
Xiaoxia Ma, Yun Yang, Shuhua Qian, Yan Ding, Qiping Lin & Na Wang
School of Nursing, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
NW and QL designed the study, oversaw the study implementation; XM, NW and YY conducted interviews, analysed and interpreted the data; XM drafted the main parts of manuscript; NW worked on the manuscript revision until the version for submission is finalized; SQ, QL and YD participated in the study implementation and data translation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Qiping Lin or Na Wang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by the Ethical committee of the Obstetrics and Gynaecology Hospital of Fudan University (approval no. 202123). And all participants provided written informed consent to participate in the study prior to data collection.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ma, X., Yang, Y., Qian, S. et al. Perceptions of Chinese women with a history of gestational diabetes regarding health behaviors and related factors: a directed qualitative content analysis. BMC Public Health 24 , 1237 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18731-3
Download citation
Received : 16 February 2024
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 06 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18731-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Diabetes, gestational
- Health behavior
- Qualitative research
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes.2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed ...
research questions remain fixed throughout the study. Use open-ended questions without reference to the literature or theory unless otherwise indicated by a qualitative strategy of inquiry. Specify the participants and the research sitefor the study, if the infor-mation has not yet been given. Here is a script for a qualitative central question:
6. Write a null hypothesis. If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing, you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0, while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. ... The positing of a hypothesis is often the first step in quantitative research but not in qualitative ...
Unlike in quantitative research, where hypotheses are only developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. Concerning how qualitative research works for hypothesis-generation, Auerbach and Silverstein (p. 7) explained that it could, with the aid of grounded theory, allow the ...
The literature review thus offered the theoretical foundation for the first, exploratory research step, where qualitative research methods were applied subsequently to further specify the preliminary conceptual model and the hypotheses derived. Qualitative research is a means to focus on people's perceptions and meanings in order to explore ...
First, stating a prior hypothesis that is to be tested deductively is quite rare in qualitative research. One way this can be done is to divide the the total set of participants into so ...
There are at least three primary applications of theory in qualitative research: (1) theory of research paradigm and method (Glesne, 2011), (2) theory building as a result of data collection (Jaccard & Jacoby, 2010), and (3) theory as a framework to guide the study (Anfara & Mertz, 2015). Differentiation and clarification between these ...
What Is Qualitative Research? This book is primarily about quantitative research.Quantitative researchers typically start with a focused research question or hypothesis, collect a small amount of data from each of a large number of individuals, describe the resulting data using statistical techniques, and draw general conclusions about some large population.
in qualitative research. Based on its objective of creating an understanding of qualitative research to provide guidelines on how qualitative researchers can use (include formulate, write and test) hypotheses, this study uses the evidence available in the literature to explore and present arguments in support of hypothesis-driven qualitative ...
It lies rather in reflecting on how embeddedness affects qualitative research, and on what is the most appropriate reaction to this fundamental condition. ... One should, however, distinguish between allowing for more engaged and hypothesis-driven phenomenological qualitative research and championing a more esoteric or subjectivist approach ...
Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable. ... In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses. Reply. Samia on July 14, 2023 at 7:40 pm could you please elaborate it more.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
A qualitative research design incorporating one-on-one interviews was conducted. The conceptual framework guiding this study was informed and developed by integrating three respected models ...
This study aligns with the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) checklist and was conducted between December 2021 and April 2022. ... Before the prevalence of the COVID-19 virus, the hypothesis of the negative effect of respiratory masks on the mental state of people was investigated and confirmed by some studies .
Open-Science Guidance for Qualitative Research: An Empirically Validated Approach for De-Identifying Sensitive Narrative Data Rebecca Campbell, McKenzie Javorka, Jasmine Engleton, Kathryn Fishwick, Katie Gregory, and Rachael Goodman-Williams ... The primary analyses failed to support the core hypothesis: No significant difference in attitude ...
Family Relations is an international journal publishing original research on all aspects of psychology related to health and illness. Abstract Objective This study examined family dynamics that are common in families experiencing elder family financial exploitation (EFFE) using an innovative analytical protocol, qualitative genog...
The article discusses the theoretical and data analysis implications of using the Hypothesis Tester for qualitative research. Future additions to the program are presented that promise to revolutionize the way that qualitative research is conducted. Get full access to this article.
Quantitative Research Qualitative research is a method of testing hypotheses and being able to measure variables using numerical data qualitative research finds trend patterns and correlations between variables qualitative research is objective and able to use standardized methods. Qualitative research uses statistical approaches to analyze ...
The sample size was selected based on the principle of saturation of qualitative research data, and 16 women were finally interviewed. ... Intervention hypothesis, based on the results identified during the study. The red dotted line indicates the intervention hypothesis that is derived from the study data and the social support theory.
Data transparency is fundamental to scholarly research. Beugelsdijk, van Witteloostuijn, and Meyer (2020: 887) define data transparency in quantitative empirical studies, including hypothesis-testing studies, "as comprised of an easy-to-follow explanation of the way in which data are generated or collected and also of the procedures used to reach conclusions."