
What Are The Similarities Of Creative And Technical Writing?
Within the expansive universe of written expression, two seemingly divergent galaxies—creative writing and technical writing—find themselves orbiting around shared principles of communication. The question arises: What are the similarities of creative and technical writing? Beneath their apparent dichotomy lies a convergence of essential elements that serve as the cornerstone of effective writing.
Both realms demand clarity, structure, audience consideration, language mastery, and a commitment to revision. Creative writing, with its artistic tapestry of emotions and imagery, converges with technical writing’s precise architecture of information delivery. These disciplines, seemingly poles apart, intersect in various domains, often resulting in a fusion that marries creativity with technical precision.
Let’s know how both creative and technical writing contribute vital threads to the fabric of effective communication. As we delve deeper, the shared traits and intertwined nature of these writing forms emerge, illuminating a path to harness their combined strengths for comprehensive and impactful expression.
Also Like To Know: Technical writing examples in creative writing
Table of Contents
Meaning of Creative Writing
Creative writing, often seen as the artistic expression of thoughts and emotions, encompasses various forms, including fiction, poetry, drama, and creative nonfiction. It thrives on imagination, symbolism, and the ability to evoke emotions through language. The creative writer is an artist, painting vivid landscapes with words, and crafting narratives that captivate, inspire, and entertain.
Technical Writing Unveiled Meaning
On the other hand, technical writing stands as the backbone of structured communication, offering clarity and precision in conveying complex information. It’s the architect laying the blueprint for user manuals, reports, instructions, and documentation. The technical writer navigates through data, facts, and procedures, aiming for clarity and comprehension rather than artistic expression.
Is technical writing the same with creative writing?
No, technical writing and creative writing are not the same. They represent distinct styles and serve different purposes in the realm of writing.
Technical Writing :
- Purpose : Technical writing aims to convey information, instructions, or explanations in a clear, concise, and structured manner. It’s primarily used in fields such as science, technology, engineering, and business to communicate complex ideas to specific audiences.
- Style : It emphasizes clarity, accuracy, and precision. Technical writing often uses a formal tone, employs industry-specific terminology, and follows a structured format. The goal is to provide information that is easily understandable and actionable for the intended audience.
- Examples : User manuals, scientific reports, technical guides, instruction manuals, whitepapers, and any documentation that requires clarity and accuracy fall under technical writing.
Creative Writing :
- Purpose : Creative writing focuses on expressing emotions, imagination, storytelling, and literary artistry. It aims to entertain, inspire, or evoke emotions in readers through narrative, descriptive language, and storytelling.
- Style : It allows for artistic freedom, exploring various literary techniques like metaphors, similes, imagery, and unique narrative structures. Creative writing often involves character development, setting, themes, and plot development.
- Examples : Novels, short stories, poetry, plays, scripts, and any form of writing where the primary goal is to engage the audience through creativity and artistic expression fall under creative writing.
Here are the major differences between Creative And Technical Writing
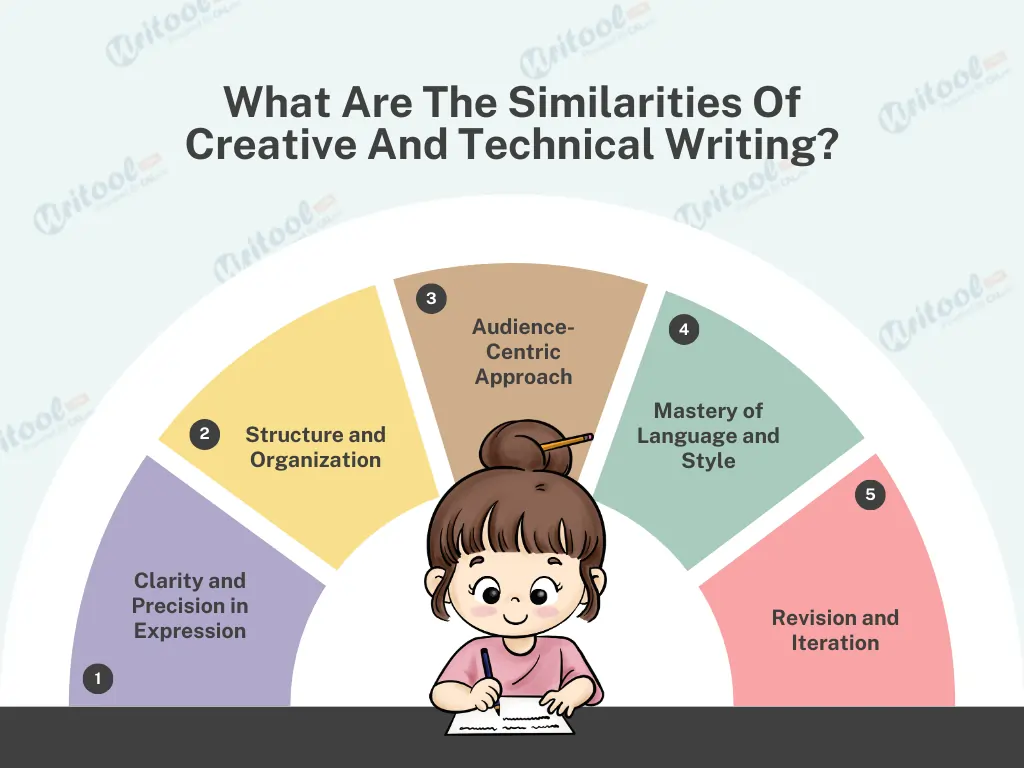
1. Clarity and Precision in Expression
Both creative and technical writing demand clarity and precision in their expression. While creative writing focuses on crafting imagery and emotions, technical writing aims for clear, concise language to convey information accurately. In both realms, the choice of words and their arrangement is deliberate, aiming to resonate with the intended audience.
2. Structure and Organization
Structure is the backbone of effective writing in both creative and technical spheres. Creative writers weave narratives with a well-defined structure, utilizing elements like plot, character development, and pacing. Similarly, technical writers employ logical structures, headings, bullet points, and numbered lists to organize information in a coherent and easily digestible manner.
3. Audience-Centric Approach
Understanding the audience is pivotal in both creative and technical writing. Creative writers craft stories to evoke emotions, engage readers, and create a connection. Likewise, technical writers analyze their audience to tailor content that meets their needs, ensuring information is accessible and comprehensible to the intended users.
4. Mastery of Language and Style
Both genres require a mastery of language and style, albeit with different objectives. Creative writers explore language for its aesthetic appeal, playing with metaphors, similes, and imagery. Meanwhile, technical writers employ a consistent and formal style, focusing on clarity and simplicity while adhering to industry-specific terminologies.
5. Revision and Iteration
Revision is a common thread in both creative and technical writing . The process of refining, editing, and polishing is integral to achieving the desired impact. Creative writers often undergo multiple drafts to refine their narratives, while technical writers meticulously review content to ensure accuracy and coherence.
The Intersection of Creativity and Technicality
Amidst their apparent disparities, creative and technical writing intersect in certain scenarios, resulting in a hybrid form that marries creativity with technical precision. Consider marketing copy, where creativity is employed to engage the audience, but technical accuracy is crucial in conveying product specifications or features.
Similarly, instructional manuals or scientific articles often demand a fusion of creativity to maintain reader interest while ensuring precise information delivery. The balance between engaging storytelling and factual accuracy exemplifies the amalgamation of these two writing domains.
Embracing the Fusion: Advantages and Opportunities
Understanding the similarities between creative and technical writing unveils a spectrum of advantages for writers venturing into both realms. A writer proficient in creative expression can infuse storytelling elements into technical content, making it more engaging and accessible to a broader audience.
Conversely, a technical writer well-versed in conveying complex information with clarity can lend precision and structure to creative narratives, enhancing readability and coherence.
Major Similarities of Creative and Technical Writing
These are the 13 key differences between creative writing and technical writing:
Conclusion: Bridging the Divide for Holistic Expression
So, that’s all about “What Are The Similarities of Creative and Technical Writing?” reveals an intricate web of shared elements within these seemingly distinct domains. Despite their apparent differences in purpose, style, and audience, creative and technical writing converge on essential aspects of effective communication.
Both creative and technical writing necessitate a profound understanding of audience needs, emphasizing clarity, precision, and effective organization. They share a commitment to language mastery, albeit with divergent objectives—one aiming for artistic expression and the other for informational delivery.
Moreover, structural elements like organization, revision processes, and audience engagement remain pivotal in both realms. The intersection of creativity and technicality, though manifesting differently, highlights their complementary roles in the broader spectrum of written expression.
What are the similarities and differences between creative writing and academic writing?
Both creative writing and academic writing involve the use of language, require clarity, and necessitate revision for effective communication.
What is the purpose of technical writing and creative writing?
The purpose of technical writing is to convey information, instructions, or explanations in a clear, concise, and structured manner, aiming for accuracy and comprehension in fields like science, technology, and business.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
APPLY NOW --> REQUEST INFO
Apply Today
Ready to apply to Penn LPS Online? Apply Now
Learn more about Penn LPS Online
Request More Information
The difference between academic and professional writing: a helpful guide

Whether you’re a current or prospective student at Penn LPS Online, you’ve likely written your fair share of academic papers and business emails. But you’re not alone if you still have questions about the differences and similarities between academic and professional writing. This overview contains a summary of everything you need to know about the intricacies of these critical forms of writing.
What is the difference between academic and professional writing?
One of the key differences between academic writing and business writing is the goal of each endeavor. Because the readers are often students, professors, or scholars in academic writing, the goal is to present and analyze information on a specific subject and increase understanding. With professional writing, the goal is generally to communicate information or influence the opinions of managers, coworkers, clients, or job prospects. While academic writing is strictly formal, it’s common to use the first-person point of view in many standard business communications. Lastly, academic writing requires adherence to strict formatting and source requirements, but there is generally more flexibility in this area when it comes to professional documents.
Read on to dive deeper into the ins and outs of academic and professional writing.
Academic writing
The hallmarks of academic writing include the use of the third-person point of view, a logical flow, an emphasis on facts and ideas, and an authoritative, formal tone. This writing style is objective, avoids casual language and slang, offers insightful analysis, and includes citations for research backed by reliable sources such as scientific studies or journal articles. While students and professors routinely use academic writing, scientists also use it to describe their research findings, as do literary critics. There are four distinct types of this formal writing style: descriptive, analytical, persuasive, and critical.
Descriptive writing
Descriptive writing is one of the most simple and ubiquitous types of scholarly writing. You can see examples of this writing style in essays, research papers, or lab reports for several fields of study. The primary goal of descriptive writing is to use precise language to summarize and describe information, such as the result of an experiment or a section of prose.
Analytical writing
An example of analytical writing is an academic paper that compares two or more complex ideas or theories. Although a part of analytical writing is descriptive, it requires going a step further to reorganize and deconstruct facts into categories, groups, types, or relationships that provide context. As such, to author a successful analytical essay, you need to start with a strong outline.
Persuasive writing
Persuasive writing takes analytical writing to the next level. Not only must you structure a coherent, fact-based argument, but you must also include your own point of view. This could be a recommendation, interpretation of findings, or an evaluation of someone else’s work, but the claims you make need to be credible and backed by evidence.
Critical writing
This formal style is commonly used in research, advanced undergraduate, or postgraduate writing. It includes the tenets of persuasive writing with the supplement of at least one other point of view (in addition to your own) on a topic or issue. For example, if you’re writing a thesis, you may explain a researcher’s analysis from a journal article, critique the merits of their argument, and provide your own alternative explanation.
Professional writing
Professional writing refers to any written communication that takes place in an organizational context. A primary objective of professional or business writing is to effectively educate, instruct, or persuade an audience via emails, newsletters, memos, press releases, project proposals, business plans, executive summaries, letters, and resumés. As is the case with all writing styles, proper grammar usage—including syntax, spelling, and parts of speech—is essential in professional writing, as are the three points below.
Clarity and concision
One of the main requirements for successful professional writing is to use clear, precise language so that your message is easily understood. It’s also important to avoid clichés and hyperbole and stick to simple, concise statements that efficiently share concrete information. Not only will this save you time, but it will also benefit the reader’s comprehension and enjoyment.
Active and purposeful
Whether you’re creating a quick email or preparing an in-depth report, every piece of business writing should start with a well-defined objective or purpose. To keep your communication to the point, you should use an active voice, choose strong action verbs, and avoid qualifiers or passive phrases such as “I think.”
Personal tone
Although professional writing should have a courteous tone, the level of formality does not need to be equal to that used in an academic setting. Documents such as business plans should have a formal structure, but with emails or online chats with colleagues, a friendly, polite tone and positive phrasing can go a long way.
The overlap between academic and professional writing
Although there are distinct differences, there are also many similarities between academic and professional writing. Both writing styles require that you use proper grammar and punctuation, clear and precise language, and a serious tone, along with well-developed ideas with clear objectives. Whether you’re writing for business or academic purposes, it’s also important to avoid exaggeration, emotionally charged expressions, and jargon, as they dilute the effectiveness of your communication. In everything from research papers and essays to memos and fundraising letters, it’s essential to ensure that the information you convey is both accurate and relevant. And you should always have a clearly defined goal for academic or business writing, such as to describe, inform, analyze, or persuade.
If you’re somewhat of a writing novice and looking to improve your skills, then consider PROW 1030: Introduction to Academic Reading, Writing, and Research and PROW 1000: Fundamentals of Professional Writing at Penn LPS Online. The former is designed to expand your abilities and build your confidence as you learn how to plan and execute a well-structured argument, write with logical coherence, and polish your work to ensure readability. The latter provides an introduction to critically analyzing any writing situation and creating purposeful messaging to address it. With targeted exercises to improve grammar, mechanics, and precision, you’ll work to enhance the quality and effectiveness of your writing practice.
If you want to expand and refine your existing repertoire, look to PROW 3030: Advanced Academic Writing and PROW 3010: The Power of Storytelling . The former focuses on improving your ability to translate readings, research, and findings into meaningful academic content. This includes employing time management and reading strategies and enhancing your understanding of the nuances of academic genres and writing styles. The latter explores storytelling as a means of conveying complex and memorable information. Learn how to use narrative studies as a research tool for gathering data and a rhetorical strategy for generating emotional appeal, action, and brand identity.
Explore the professional writing certificate at Penn LPS Online
The 4-course Certificate in Professional Writing at Penn LPS Online offers practical applications that provide an accelerated understanding of the art of effective business communication—and tips to help you become a master of grammar, concision, and clarity. As mentioned above, whether you’re looking to learn the fundamentals or you’re already a seasoned writer, these Ivy League writing courses will help you take your skills to the next level. Discover innovative findings in the field, receive extensive coaching and feedback, and learn how to incorporate your personal or corporate brand story into every piece of communication.
The Certificate in Professional Writing prepares you to:
- Analyze different audiences, scenarios, and contexts to better shape your messaging
- Develop effective rhetorical strategies and skills to persuade personal, professional, and social audiences
- Learn how use complex multimedia texts that incorporate language, image, and sound to produce a coherent, engaging message
- Grow your empathic and analytical skills to integrate and build upon other viewpoints
- Explore how to engage the senses to successfully convey information through social media
- Understand how to use effective visualization to make complex material more accessible
Ready to get started? If you have yet to do so, apply to Penn LPS Online today and enroll in the Certificate in Professional Writing . Or view our course guide to see what’s available in any upcoming term.
Soft Skills
11 minute read
Business Writing vs. Academic Writing: What’s the Difference?

Kat Boogaard
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Email
Regardless of particular style or format, written information has the same goal: to present information to an audience in a clear way.
So, that must mean good writing is good writing, right?
Not exactly. When you compare business writing to academic writing, for example, there are actually some significant differences that you should be aware of.
Familiarizing yourself with what separates these two distinct writing styles will help you write in a way that’s the most effective for your intended purpose and audience.
Think about it this way: You wouldn’t give a technical manual to a child and call it a children’s book. The same holds true for business and academic writing—there are key differences in style and structure.
So, what exactly makes business writing different from academic writing? Well, roll up your sleeves, because we’re diving into some of those key differentiators below.
What is business writing?
There’s a lot of writing that happens in the business world. But, if you think this means you need to be a skilled author capable of stringing together eloquent prose and flowery language, think again.
As this fact sheet from the University of Oregon explains, business writing is transactional. It describes what actions need to be taken to solve problems, achieve company goals, and so on.
From reports to emails to press releases, business writing comes in many shapes and sizes. The recipients of business writing also run the gamut—from board members to colleagues to customers to shareholders.
Because of that, there are tons of smaller details that separate business writing from academic writing. But, the overarching one you should remember is the purpose: Business writing is intended to direct action.
Want to learn even more about business writing? Check out our business writing course !
What is academic writing?
So, what about academic writing? Take a minute to think about the various writing projects—like research papers and book reports—that you needed to complete during your schooling. You’ll quickly realize that the intention of academic writing is far different from business writing.
Rather than educating and informing others, the goal of academic writing is for students to educate themselves. They write to learn as well as to showcase what they’ve learned—and often earn a grade for doing so.
Some academic writing is then utilized to inform others (like a thesis, research paper, or dissertation). However, the original purpose of that writing work was to have the author learn something through the writing process.
In most cases, students write these academic pieces for one particular audience member: their professor or instructor.
Business writing vs. academic writing: how they differ
Obviously, the purposes behind business writing and academic writing are quite different. But what about those other details that we mentioned earlier?
Let’s dig into the numerous other differences that come up when you compare business writing to academic writing.
1. Tone and style
While both styles of writing can be somewhat formal from time to time, academic writing is typically much more so and is written from a third person perspective . Students often receive a grade on their academic writing, so you can bet there isn’t slang or jargon of any type.
However, because business writing is more oriented toward action, it leans less on long sentences and a complex vocabulary and instead focuses on short and clear sentences (and frequently, bullet points)—making it seem far less rigid and formal than academic writing.
With business writing, the audience needs to be able to extrapolate the meaning of the text and the resulting action steps without needing to wade through complicated sentences and lengthy paragraphs.
Tone and style of academic writing:
Formal, with longer sentences and well-developed paragraphs. Here’s an example:
According to recent research, audiences are far more responsive to advertising messages that portray models and actors within their own demographic. With this reasoning, one can assume that organizations should employ a diverse range of actors and models to appear in their advertising campaigns to ensure that these commercial messages resonate with a large percentage of viewers.
Tone and style of business writing:
Emphasis on keeping things short, clear, and as actionable as possible. Here’s an example:
Research shows that audiences connect more with advertising messages that showcase people in their own demographic. We should explore talent firms with diverse pools of models and actors.
2. Document structure
Reflect on most of the writing you did during your education, and this common essay format will probably pop into your head: introduction, body, conclusion. That was the tried and true formula you leaned on to complete most of your academic writing.
However, business writing has far more flexibility—mostly because there are so many different types and styles of business writing.
This means that writing in a business setting offers far more wiggle room to structure the writing to the appropriate purpose and audience. It doesn’t always stick to a specific approach the way most academic writing does.
Structure of academic writing:
Introduction, body of the written work, and a conclusion.
Structure of Business Writing:
Varies greatly depending on what you’re writing. An email will be structured much differently than a performance review, for example.
3. Audience
We touched on this briefly already, but the intended audience is another major component that separates business and academic writing.
With academic writing, students write for one crucial audience member: their instructor, who will be dishing out a grade on that written assignment. Occasionally other people will review that written work, but it’s almost always someone else who works within academia.
Business writing, in contrast, can be read and reviewed by a huge array of people—from colleagues to customers to board members to shareholders to competitors to regulatory agencies.
The list goes on and on. This is partly because the aim is to keep business writing simple and straightforward. When you aren’t sure whose eyeballs will eventually land on it, it’s best to make things explicitly clear, so that all parties can comprehend it.
Audience of academic writing:
Audience of business writing:
Almost anybody!
4. Document design
This is another area where academic writing is far more rigid than business writing—mostly because the design of these written works is often dictated by the instructor. You remember the good ol’ days of 12-point Times New Roman font, double spacing, and appropriately-sized margins, right?
Again, with business writing, authors have far more flexibility to design their work in a way that’s most suitable to their purpose and intended audience.
Perhaps that’s a highly-visual business report with lots of graphs and charts to illustrate a point. Or, maybe it’s a one-page document with headings, subheadings, and bullet points to allow for easy skimming and scanning.
The design of business writing comes in many shapes and sizes, while academic writing typically falls into a standardized mold.
Design of academic writing:
Highly standardized with requirements for text style, font size, spacing, and margins.
Design of business writing:
Flexible, depending on the purpose of the document and the audience.
5. Writing process
If you’d ask me what my writing process looked like for any academic papers, I’d tell you this: It was many late nights spent bleary-eyed alone in front of my computer, with a mug of lukewarm coffee by my side.
Sound familiar? Much of the academic writing process takes place totally alone. The assignment is dished out by the professor, and the student is tasked with cranking out that document by the deadline in order to earn an individual grade.
Things don’t work that way in the business world, where writing is a far more collaborative process. When working on business writing, you’ll likely lean on the insights and expertise of numerous different people both inside and outside your organization to pull together something that makes sense.
Additionally, the process of writing an academic paper typically involved plenty of solo research. But, in a business environment, you usually tackle writing with far more existing context and background information received through meetings, previous projects, and other efforts. Most of the time, you aren’t approaching that subject totally cold.
Process for academic writing:
Research and writing is done mostly solo.
Process for Business Writing:
A collaborative effort, with plenty of groundwork already laid for the author.
6. Citations and sources
Sigh, citations. I remember cringing every time I needed to put together that detailed resources page for my academic papers. You remember the ones, right? They included everything from the authors' names, to the published date, to the volume number. The thought alone still sends a chill down my spine.
With academic writing, students are required to cite their sources using a highly standardized format—often MLA or APA style .
However, the rules for citing sources are far more lax with business writing and can often vary greatly depending on your company’s norms and regulations for quoting various sources.
Citations and sources for academic writing:
Highly standardized and regulated.
Citations and Sources for Business Writing:
Can vary based on the rules set by the individual company.
7. Legal considerations
While students who produce academic writing absolutely need to avoid plagiarism of any kind, it’s not often that their written work will be used in any sort of court cases, legal proceedings, or anything of the sort.
But, in a business setting? People should be aware that the written work they produce is likely now the property of their employer and thus could be used as evidence in this manner if the need arises—whether it’s something like a wrongful termination lawsuit or even an audit.
For that reason, ensuring accuracy is crucial whenever you’re writing, but particularly when you’re producing a document for your organization.
Legal considerations for academic writing:
Avoiding plagiarism is the top legal concern.
Legal Considerations for business writing:
Operate with the assumption that whatever you write could come back in a variety of legal matters. I won’t say it’s common, but it’s always better to play it safe!
Over to you
As we’ve highlighted here, there are plenty of differences between academic writing and business writing. In fact, this isn’t even all of them—we’ve barely scratched the surface.
You can dig into even more elements that separate these two styles with this fact sheet from the University of Oregon . It does a great job of breaking things down in an easily digestible way, and we used it as a resource for many of the differences we outlined here.
If you’re eager to learn even more about business writing in particular and how you can level up your own game at work? Make sure to check out our business writing course to dive into the nitty-gritty of how to be a top-notch writer in a business setting.
Gain the soft skills you need to succeed
Start learning for free with GoSkills courses
Loved this? Subscribe, and join 451,581 others.
Get our latest content before everyone else. Unsubscribe whenever.

Kat is a writer specializing in career, self-development, and productivity topics. When she escapes her computer, she enjoys reading, hiking, golfing, and dishing out tips for prospective freelancers on her website.

Recommended
How to Hire the Right Candidate for the Right Job
When using the right strategies, hiring the right job candidate can be seamless and effective.

7 Essential Skills To Help Startups Meet New Challenges
Startups and SMEs face specific challenges that threaten their survival. Make sure your business' growth doesn't lead to its downfall with these 7 tips.

The Future of Sales Careers: How Training, Methods, and Software are Changing
The nature of sales has evolved due to automation, specialization, and changing consumer expectations. This guide explores how such changes are reshaping sales careers.
© 2024 GoSkills Ltd. Skills for career advancement
The Librarian Parlor
Building a community of researchers

Reflections from a Young Writer: Academic vs. Creative Writing
LibParlor Contributor, Samantha Bise, reflects on the similarities and differences between academic and creative writing.
Samantha Bise is a Reference & Instruction Librarian at Central Penn College. Her research interests include critical information literacy, information bias, and educational barriers for vulnerable populations. Samantha spends a lot of her time volunteering in her community, and she is passionate about teaching, creating educational opportunities for adult learners, and writing poetry. Some of her recent poetry can be found at www.sambise.com , or here (2nd place in her county’s competition!), and here (published in a poetry journal). You can find her on Twitter: @sam_bise .
As Anne Lamott says in her book Bird by Bird, “…good writing is about telling the truth. We are a species that needs and wants to understand who we are.” What is humanity if not collectively sharing our experiences, anyway? I believe writing is one of the best ways to use our voices, share our experiences, work through difficult concepts, and contribute to the world.
“I believe writing is one of the best ways to use our voices, share our experiences, work through difficult concepts, and contribute to the world.”
As an early-career academic librarian, I am often writing about education for scholarly publications and presentations. As a lifelong poet who recently began submitting poetry for publication, I spend a lot of my time writing poetry and sending my work to editors. Throughout the writing and publication processes, I’ve noticed key differences and fundamental parallels in academic and creative writing. Below are reflections from me, a young academic and creative writer, along with suggestions for other beginners.
Writing to learn
Writing is at the root of my learning style, meaning I cannot see a way through difficult topics and issues without writing about it first. When I’m introduced to a new pedagogical idea, I research it and write about it. When somebody suggests a new library program or project, I research similar projects and write about my findings Results The section of a research article where researchers share the results from the research. This section takes the results and directly connects them to the research questions or hypotheses posed at the start of the article. Also can be called “Findings.” . Similarly, when I am struggling to understand something about the world around me, I write poetry about it.
Just like learning, writing is a messy business. I tell my students that research and writing are not linear processes, and this holds true for us, too. It’s messy and personal. Researching and writing are like doing a puzzle—some people start with the edges, some people sort by color, and others dive right in. We all have our ways of organizing ourselves. When writing academically or creatively, organize yourself in your way.
Choosing your topic
I made the decision years ago only to write what I am passionate about. If you haven’t made this promise to yourself yet, do it now. I spent too much of my time trying to be excited about library marketing when education and teaching information literacy was actually what I loved most. Once I began researching things that I felt a connection to, excitement and a desire to learn more kept me committed.
This holds true in my poetry, too. I spent most of my undergraduate years trying to be a romantic writer by writing very vague metaphors about nature. This is the genre of poetry I found myself reading, so I forced it into my writing. In direct contrast, I learned that I am more passionate about the raw realities of social issues, like drug addiction, mental illness, and poverty; this is now what most of my poetry focuses on. Don’t make writing more difficult by forcing a topic that doesn’t align with your passions, interests, or goals. Choosing to write only what you care about may be the best thing you ever do for your writer-self.
Adhering to a style
When writing for an academic audience, I learned the hard way to read the publisher’s guidelines or conference requirements before planning the way I shape my research findings. Scholarly publishers and academic conferences have specific styles they expect you to adhere to. Writing an article or proposal before finding a publisher has proven to be more time consuming than necessary.
When writing poetry, I was taught the opposite—don’t think about the audience. Writing creatively lends itself to, well, more creativity. When I write poetry, I write first and find appropriate publications later. This gives me more control over the final product, compared to the academic publishing process.
Supporting your claim and giving credit
As an academic librarian, I am constantly drawing a line between what ideas are mine and what concepts I’ve borrowed from others to help strengthen my point. The scholarly writing process relies heavily on expert voices and textual evidence to support my claims. This is necessary to help make a strong case and to contribute to the scholarly conversation. There’s a certain anxiety that comes along with responding to and critiquing the claims of other scholars.
On the other hand, the creative writing process focuses on my own experiences and perceptions of the world around me. An uncomfortable, yet liberating, part of creative writing is that I get to own [almost] every experience that happens to me without thinking about citation styles, copyright ethics, and intellectual freedom. However, similar to the anxieties in academic writing, writing creatively about personal experiences and observations lends itself to some discomfort, too.
Building community
One of the best parts about working in librarianship is that it’s a profession rooted in sharing. There are professional networks available for most interests in our field. I can share my work with my greater library community, and receive valuable feedback and support.
Similarly, in my creative writing communities, there is an abundance of mutual sharing and support. The difference is, people are less likely to harshly critique creative writing than they are academic writing. Outside of academia, poetry that is based on personal perceptions of the world does not lend itself to formal criticism. My creative writing communities value the act of sharing over the need for critique, which is in direct contrast to the mission of academic writing.
Coping with critiques
When you use your voice, people will have opinions about your work. This holds true for academic works and creative projects. When I finish a piece of writing—be it an article, conference proposal, or poem—the self-doubt sets in. I begin to have unrealistically high expectations for my writing. I suddenly believe that this one piece of writing should be simultaneously timeless, indisputable, and groundbreaking. But the truth is, most ideas are not unique, and all ideas should be open to critique.
I’ve learned to cope with the critiques by not attaching my professional or personal self-worth to others’ opinions of my work. If we make claims that are later deemed incorrect or invaluable, that’s okay. Research evolves, and so do we. Defend your work as you see fit, but also allow yourself to recognize and admit when your work has room for improvement. Stop holding your work to an impossible standard of perfection, and realize that using your voice as productively as you can is often enough. If you publish something you later regret, do better next time.
Using your voice
Researching and writing for academia is an important way to contribute to the progress of human knowledge. Similarly, writing creatively—in my case, writing poetry—is also a practice in using our voices, sharing our stories, and trying to help make sense of humanity. Contributing to the greater conversation by sharing your own experiences and expertise is challenging, rewarding, and necessary.
Above all else, I believe using our voices productively is one of the best things we can do for the world. Writing is one way to do this. Often times us beginners feel like we have nothing to offer, but simply the experiences of being new are perspectives worth sharing. When you use your voice, know that you will both formally and informally receive criticism, you will be told your voice doesn’t align with the standards or desires of certain publications or communities, and you will sometimes wonder why you are even trying to use your voice at all. I’d like to tell you that your voice and your contributions do matter.
Keep the Conversation Going
- Do you have a creative outlet that allows you to use your voice productively and express yourself?
- What are some ways you’ve learned to cope with critiques of your work?
- How do you stay committed to the scholarly writing process?
- What professional networks or communities have helped you find your place within librarianship?
Featured image [ CC0 ], via Pexels

The expressions of writer do not reflect anyone’s views but their own
Share this:
2 comments on “ reflections from a young writer: academic vs. creative writing ”.
Remember that the writing style of an academic research paper is tightly defined by three factors: 1) the discipline; 2) the type of research you are reporting (qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research create expectations in reporting styles (see http://www.equator-network.com ); and 3) the style expectations of the journal. Adhere closely to those and remember that academic research writing is very formalized and structured. Use classic, proper English at all times. Yes, your own voice will come through to some extent, but that’s actually more expressed in the choice of research topic and research method Research Method The approach taken by the researcher to collect data. Examples include in-depth interviews, focus groups, surveys, experiments, etc. . Writing for a scholarly, peer-reviewed journal is about as formalized as it gets. Peer-reviewers will be tough on you. Sometimes you have to rewrite multiple times and submit to multiple journals. You don’t have to accept everything a peer-reviewer tells you, but you should have a good reason for why you didn’t. Forget creative writing, there is nothing creative about this type of writing except for trying to persuade editors buried in submissions and busy peer-reviewers that you have something novel and useful enough to contribute to the journal and the discipline.
See Also: http://www.phrasebank.manchester.ac.uk/ https://ori.hhs.gov/avoiding-plagiarism-self-plagiarism-and-other-questionable-writing-practices-guide-ethical-writing http://www.mhhe.com/mayfieldpub/tsw/toc.htm http://www.ease.org.uk/publications/author-guidelines-authors-and-translators/ https://www.aacc.org/publications/clinical-chemistry/clinical-chemistry%C2%A0guide-to-scientific-writing# https://cgi.duke.edu/web/sciwriting/index.php
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from the librarian parlor.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Academic Writing vs. Professional Writing: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between academic writing and professional writing is that academic writing is aimed at an academic or scholarly audience whereas professional writing targets a broader audience in a professional context.
Before we move to more differences, let’s first understand Academic Writing and Professional Writing:
- Academic Writing : Academic writing refers to the style of writing used in academic settings, such as universities, research institutions, and scholarly publications.
- Professional Writing : Professional writing is a broader term that encompasses various forms of writing used in professional contexts, such as business, industry, government, and organizations.
Now, let’s get to Academic Writing vs Professional Writing:
Major differences between Academic Writing and Professional Writing
So, these are the main differences between the entities.
- Laptop vs. Notebook
- Goods vs. Services
- DVD vs. Blu-Ray
You can see other “differences between…” posts by clicking here .
If you have a related query, kindly feel free to let me know in the comments below.
- Colleges and Institutes
- Accessibility --> Accessibility tools
- --> Subjects -->