
18 Qualitative Research Examples

Qualitative research is an approach to scientific research that involves using observation to gather and analyze non-numerical, in-depth, and well-contextualized datasets.
It serves as an integral part of academic, professional, and even daily decision-making processes (Baxter & Jack, 2008).
Methods of qualitative research encompass a wide range of techniques, from in-depth personal encounters, like ethnographies (studying cultures in-depth) and autoethnographies (examining one’s own cultural experiences), to collection of diverse perspectives on topics through methods like interviewing focus groups (gatherings of individuals to discuss specific topics).
Qualitative Research Examples
1. ethnography.
Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology , this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
Ethnographic research is characterized by extended observation of the group, often through direct participation, in the participants’ environment. An ethnographer typically lives with the study group for extended periods, intricately observing their everyday lives (Khan, 2014).
It aims to present a complete, detailed and accurate picture of the observed social life, rituals, symbols, and values from the perspective of the study group.
Example of Ethnographic Research
Title: “ The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity “
Citation: Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Overview: This study by Evans (2010) provides a rich narrative of young adult male identity as experienced in everyday life. The author immersed himself among a group of young men, participating in their activities and cultivating a deep understanding of their lifestyle, values, and motivations. This research exemplified the ethnographic approach, revealing complexities of the subjects’ identities and societal roles, which could hardly be accessed through other qualitative research designs.
Read my Full Guide on Ethnography Here
2. Autoethnography
Definition: Autoethnography is an approach to qualitative research where the researcher uses their own personal experiences to extend the understanding of a certain group, culture, or setting. Essentially, it allows for the exploration of self within the context of social phenomena.
Unlike traditional ethnography, which focuses on the study of others, autoethnography turns the ethnographic gaze inward, allowing the researcher to use their personal experiences within a culture as rich qualitative data (Durham, 2019).
The objective is to critically appraise one’s personal experiences as they navigate and negotiate cultural, political, and social meanings. The researcher becomes both the observer and the participant, intertwining personal and cultural experiences in the research.
Example of Autoethnographic Research
Title: “ A Day In The Life Of An NHS Nurse “
Citation: Osben, J. (2019). A day in the life of a NHS nurse in 21st Century Britain: An auto-ethnography. The Journal of Autoethnography for Health & Social Care. 1(1).
Overview: This study presents an autoethnography of a day in the life of an NHS nurse (who, of course, is also the researcher). The author uses the research to achieve reflexivity, with the researcher concluding: “Scrutinising my practice and situating it within a wider contextual backdrop has compelled me to significantly increase my level of scrutiny into the driving forces that influence my practice.”
Read my Full Guide on Autoethnography Here
3. Semi-Structured Interviews
Definition: Semi-structured interviews stand as one of the most frequently used methods in qualitative research. These interviews are planned and utilize a set of pre-established questions, but also allow for the interviewer to steer the conversation in other directions based on the responses given by the interviewee.
In semi-structured interviews, the interviewer prepares a guide that outlines the focal points of the discussion. However, the interview is flexible, allowing for more in-depth probing if the interviewer deems it necessary (Qu, & Dumay, 2011). This style of interviewing strikes a balance between structured ones which might limit the discussion, and unstructured ones, which could lack focus.
Example of Semi-Structured Interview Research
Title: “ Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review “
Citation: Puts, M., et al. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Overview: Puts et al. (2014) executed an extensive systematic review in which they conducted semi-structured interviews with older adults suffering from cancer to examine the factors influencing their adherence to cancer treatment. The findings suggested that various factors, including side effects, faith in healthcare professionals, and social support have substantial impacts on treatment adherence. This research demonstrates how semi-structured interviews can provide rich and profound insights into the subjective experiences of patients.
4. Focus Groups
Definition: Focus groups are a qualitative research method that involves organized discussion with a selected group of individuals to gain their perspectives on a specific concept, product, or phenomenon. Typically, these discussions are guided by a moderator.
During a focus group session, the moderator has a list of questions or topics to discuss, and participants are encouraged to interact with each other (Morgan, 2010). This interactivity can stimulate more information and provide a broader understanding of the issue under scrutiny. The open format allows participants to ask questions and respond freely, offering invaluable insights into attitudes, experiences, and group norms.
Example of Focus Group Research
Title: “ Perspectives of Older Adults on Aging Well: A Focus Group Study “
Citation: Halaweh, H., Dahlin-Ivanoff, S., Svantesson, U., & Willén, C. (2018). Perspectives of older adults on aging well: a focus group study. Journal of aging research .
Overview: This study aimed to explore what older adults (aged 60 years and older) perceived to be ‘aging well’. The researchers identified three major themes from their focus group interviews: a sense of well-being, having good physical health, and preserving good mental health. The findings highlight the importance of factors such as positive emotions, social engagement, physical activity, healthy eating habits, and maintaining independence in promoting aging well among older adults.
5. Phenomenology
Definition: Phenomenology, a qualitative research method, involves the examination of lived experiences to gain an in-depth understanding of the essence or underlying meanings of a phenomenon.
The focus of phenomenology lies in meticulously describing participants’ conscious experiences related to the chosen phenomenon (Padilla-Díaz, 2015).
In a phenomenological study, the researcher collects detailed, first-hand perspectives of the participants, typically via in-depth interviews, and then uses various strategies to interpret and structure these experiences, ultimately revealing essential themes (Creswell, 2013). This approach focuses on the perspective of individuals experiencing the phenomenon, seeking to explore, clarify, and understand the meanings they attach to those experiences.
Example of Phenomenology Research
Title: “ A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: current state, promise, and future directions for research ”
Citation: Cilesiz, S. (2011). A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: Current state, promise, and future directions for research. Educational Technology Research and Development, 59 , 487-510.
Overview: A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology by Sebnem Cilesiz represents a good starting point for formulating a phenomenological study. With its focus on the ‘essence of experience’, this piece presents methodological, reliability, validity, and data analysis techniques that phenomenologists use to explain how people experience technology in their everyday lives.
6. Grounded Theory
Definition: Grounded theory is a systematic methodology in qualitative research that typically applies inductive reasoning . The primary aim is to develop a theoretical explanation or framework for a process, action, or interaction grounded in, and arising from, empirical data (Birks & Mills, 2015).
In grounded theory, data collection and analysis work together in a recursive process. The researcher collects data, analyses it, and then collects more data based on the evolving understanding of the research context. This ongoing process continues until a comprehensive theory that represents the data and the associated phenomenon emerges – a point known as theoretical saturation (Charmaz, 2014).
Example of Grounded Theory Research
Title: “ Student Engagement in High School Classrooms from the Perspective of Flow Theory “
Citation: Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158–176.
Overview: Shernoff and colleagues (2003) used grounded theory to explore student engagement in high school classrooms. The researchers collected data through student self-reports, interviews, and observations. Key findings revealed that academic challenge, student autonomy, and teacher support emerged as the most significant factors influencing students’ engagement, demonstrating how grounded theory can illuminate complex dynamics within real-world contexts.
7. Narrative Research
Definition: Narrative research is a qualitative research method dedicated to storytelling and understanding how individuals experience the world. It focuses on studying an individual’s life and experiences as narrated by that individual (Polkinghorne, 2013).
In narrative research, the researcher collects data through methods such as interviews, observations , and document analysis. The emphasis is on the stories told by participants – narratives that reflect their experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
These stories are then interpreted by the researcher, who attempts to understand the meaning the participant attributes to these experiences (Josselson, 2011).
Example of Narrative Research
Title: “Narrative Structures and the Language of the Self”
Citation: McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative . American Psychological Association.
Overview: In this innovative study, McAdams et al. (2006) employed narrative research to explore how individuals construct their identities through the stories they tell about themselves. By examining personal narratives, the researchers discerned patterns associated with characters, motivations, conflicts, and resolutions, contributing valuable insights about the relationship between narrative and individual identity.
8. Case Study Research
Definition: Case study research is a qualitative research method that involves an in-depth investigation of a single instance or event: a case. These ‘cases’ can range from individuals, groups, or entities to specific projects, programs, or strategies (Creswell, 2013).
The case study method typically uses multiple sources of information for comprehensive contextual analysis. It aims to explore and understand the complexity and uniqueness of a particular case in a real-world context (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). This investigation could result in a detailed description of the case, a process for its development, or an exploration of a related issue or problem.
Example of Case Study Research
Title: “ Teacher’s Role in Fostering Preschoolers’ Computational Thinking: An Exploratory Case Study “
Citation: Wang, X. C., Choi, Y., Benson, K., Eggleston, C., & Weber, D. (2021). Teacher’s role in fostering preschoolers’ computational thinking: An exploratory case study. Early Education and Development , 32 (1), 26-48.
Overview: This study investigates the role of teachers in promoting computational thinking skills in preschoolers. The study utilized a qualitative case study methodology to examine the computational thinking scaffolding strategies employed by a teacher interacting with three preschoolers in a small group setting. The findings highlight the importance of teachers’ guidance in fostering computational thinking practices such as problem reformulation/decomposition, systematic testing, and debugging.
Read about some Famous Case Studies in Psychology Here
9. Participant Observation
Definition: Participant observation has the researcher immerse themselves in a group or community setting to observe the behavior of its members. It is similar to ethnography, but generally, the researcher isn’t embedded for a long period of time.
The researcher, being a participant, engages in daily activities, interactions, and events as a way of conducting a detailed study of a particular social phenomenon (Kawulich, 2005).
The method involves long-term engagement in the field, maintaining detailed records of observed events, informal interviews, direct participation, and reflexivity. This approach allows for a holistic view of the participants’ lived experiences, behaviours, and interactions within their everyday environment (Dewalt, 2011).
Example of Participant Observation Research
Title: Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics
Citation: Heemskerk, E. M., Heemskerk, K., & Wats, M. M. (2017). Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics. Journal of Management & Governance , 21 , 233-263.
Overview: This study examined how conflicts within corporate boards affect their performance. The researchers used a participant observation method, where they actively engaged with 11 supervisory boards and observed their dynamics. They found that having a shared understanding of the board’s role called a common framework, improved performance by reducing relationship conflicts, encouraging task conflicts, and minimizing conflicts between the board and CEO.
10. Non-Participant Observation
Definition: Non-participant observation is a qualitative research method in which the researcher observes the phenomena of interest without actively participating in the situation, setting, or community being studied.
This method allows the researcher to maintain a position of distance, as they are solely an observer and not a participant in the activities being observed (Kawulich, 2005).
During non-participant observation, the researcher typically records field notes on the actions, interactions, and behaviors observed , focusing on specific aspects of the situation deemed relevant to the research question.
This could include verbal and nonverbal communication , activities, interactions, and environmental contexts (Angrosino, 2007). They could also use video or audio recordings or other methods to collect data.
Example of Non-Participant Observation Research
Title: Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non-participant observation study
Citation: Sreeram, A., Cross, W. M., & Townsin, L. (2023). Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery‐oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non‐participant observation study. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing .
Overview: This study investigated the attitudes of mental health nurses towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units. The researchers used a non-participant observation method, meaning they observed the nurses without directly participating in their activities. The findings shed light on the nurses’ perspectives and behaviors, providing valuable insights into their attitudes toward mental health and recovery-focused care in these settings.
11. Content Analysis
Definition: Content Analysis involves scrutinizing textual, visual, or spoken content to categorize and quantify information. The goal is to identify patterns, themes, biases, or other characteristics (Hsieh & Shannon, 2005).
Content Analysis is widely used in various disciplines for a multitude of purposes. Researchers typically use this method to distill large amounts of unstructured data, like interview transcripts, newspaper articles, or social media posts, into manageable and meaningful chunks.
When wielded appropriately, Content Analysis can illuminate the density and frequency of certain themes within a dataset, provide insights into how specific terms or concepts are applied contextually, and offer inferences about the meanings of their content and use (Duriau, Reger, & Pfarrer, 2007).
Example of Content Analysis
Title: Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news .
Citation: Semetko, H. A., & Valkenburg, P. M. (2000). Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news. Journal of Communication, 50 (2), 93-109.
Overview: This study analyzed press and television news articles about European politics using a method called content analysis. The researchers examined the prevalence of different “frames” in the news, which are ways of presenting information to shape audience perceptions. They found that the most common frames were attribution of responsibility, conflict, economic consequences, human interest, and morality.
Read my Full Guide on Content Analysis Here
12. Discourse Analysis
Definition: Discourse Analysis, a qualitative research method, interprets the meanings, functions, and coherence of certain languages in context.
Discourse analysis is typically understood through social constructionism, critical theory , and poststructuralism and used for understanding how language constructs social concepts (Cheek, 2004).
Discourse Analysis offers great breadth, providing tools to examine spoken or written language, often beyond the level of the sentence. It enables researchers to scrutinize how text and talk articulate social and political interactions and hierarchies.
Insight can be garnered from different conversations, institutional text, and media coverage to understand how topics are addressed or framed within a specific social context (Jorgensen & Phillips, 2002).
Example of Discourse Analysis
Title: The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis
Citation: Thomas, S. (2005). The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis. Critical Studies in Education, 46 (2), 25-44.
Overview: The author examines how an education policy in one state of Australia positions teacher professionalism and teacher identities. While there are competing discourses about professional identity, the policy framework privileges a narrative that frames the ‘good’ teacher as one that accepts ever-tightening control and regulation over their professional practice.
Read my Full Guide on Discourse Analysis Here
13. Action Research
Definition: Action Research is a qualitative research technique that is employed to bring about change while simultaneously studying the process and results of that change.
This method involves a cyclical process of fact-finding, action, evaluation, and reflection (Greenwood & Levin, 2016).
Typically, Action Research is used in the fields of education, social sciences , and community development. The process isn’t just about resolving an issue but also developing knowledge that can be used in the future to address similar or related problems.
The researcher plays an active role in the research process, which is normally broken down into four steps:
- developing a plan to improve what is currently being done
- implementing the plan
- observing the effects of the plan, and
- reflecting upon these effects (Smith, 2010).
Example of Action Research
Title: Using Digital Sandbox Gaming to Improve Creativity Within Boys’ Writing
Citation: Ellison, M., & Drew, C. (2020). Using digital sandbox gaming to improve creativity within boys’ writing. Journal of Research in Childhood Education , 34 (2), 277-287.
Overview: This was a research study one of my research students completed in his own classroom under my supervision. He implemented a digital game-based approach to literacy teaching with boys and interviewed his students to see if the use of games as stimuli for storytelling helped draw them into the learning experience.
Read my Full Guide on Action Research Here
14. Semiotic Analysis
Definition: Semiotic Analysis is a qualitative method of research that interprets signs and symbols in communication to understand sociocultural phenomena. It stems from semiotics, the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation (Chandler, 2017).
In a Semiotic Analysis, signs (anything that represents something else) are interpreted based on their significance and the role they play in representing ideas.
This type of research often involves the examination of images, sounds, and word choice to uncover the embedded sociocultural meanings. For example, an advertisement for a car might be studied to learn more about societal views on masculinity or success (Berger, 2010).
Example of Semiotic Research
Title: Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia
Citation: Symes, C. (2023). Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia. Semiotica , 2023 (250), 167-190.
Overview: This study examines school badges in New South Wales, Australia, and explores their significance through a semiotic analysis. The badges, which are part of the school’s visual identity, are seen as symbolic representations that convey meanings. The analysis reveals that these badges often draw on heraldic models, incorporating elements like colors, names, motifs, and mottoes that reflect local culture and history, thus connecting students to their national identity. Additionally, the study highlights how some schools have shifted from traditional badges to modern logos and slogans, reflecting a more business-oriented approach.
15. Qualitative Longitudinal Studies
Definition: Qualitative Longitudinal Studies are a research method that involves repeated observation of the same items over an extended period of time.
Unlike a snapshot perspective, this method aims to piece together individual histories and examine the influences and impacts of change (Neale, 2019).
Qualitative Longitudinal Studies provide an in-depth understanding of change as it happens, including changes in people’s lives, their perceptions, and their behaviors.
For instance, this method could be used to follow a group of students through their schooling years to understand the evolution of their learning behaviors and attitudes towards education (Saldaña, 2003).
Example of Qualitative Longitudinal Research
Title: Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study
Citation: Hackett, J., Godfrey, M., & Bennett, M. I. (2016). Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study. Palliative medicine , 30 (8), 711-719.
Overview: This article examines how patients and their caregivers manage pain in advanced cancer through a qualitative longitudinal study. The researchers interviewed patients and caregivers at two different time points and collected audio diaries to gain insights into their experiences, making this study longitudinal.
Read my Full Guide on Longitudinal Research Here
16. Open-Ended Surveys
Definition: Open-Ended Surveys are a type of qualitative research method where respondents provide answers in their own words. Unlike closed-ended surveys, which limit responses to predefined options, open-ended surveys allow for expansive and unsolicited explanations (Fink, 2013).
Open-ended surveys are commonly used in a range of fields, from market research to social studies. As they don’t force respondents into predefined response categories, these surveys help to draw out rich, detailed data that might uncover new variables or ideas.
For example, an open-ended survey might be used to understand customer opinions about a new product or service (Lavrakas, 2008).
Contrast this to a quantitative closed-ended survey, like a Likert scale, which could theoretically help us to come up with generalizable data but is restricted by the questions on the questionnaire, meaning new and surprising data and insights can’t emerge from the survey results in the same way.
Example of Open-Ended Survey Research
Title: Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey
Citation: Hertlein, K. M., & Ancheta, K. (2014). Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey. The Qualitative Report , 19 (11), 1-11.
Overview: This article examines the advantages and disadvantages of technology in couple relationships through an open-ended survey method. Researchers analyzed responses from 410 undergraduate students to understand how technology affects relationships. They found that technology can contribute to relationship development, management, and enhancement, but it can also create challenges such as distancing, lack of clarity, and impaired trust.
17. Naturalistic Observation
Definition: Naturalistic Observation is a type of qualitative research method that involves observing individuals in their natural environments without interference or manipulation by the researcher.
Naturalistic observation is often used when conducting research on behaviors that cannot be controlled or manipulated in a laboratory setting (Kawulich, 2005).
It is frequently used in the fields of psychology, sociology, and anthropology. For instance, to understand the social dynamics in a schoolyard, a researcher could spend time observing the children interact during their recess, noting their behaviors, interactions, and conflicts without imposing their presence on the children’s activities (Forsyth, 2010).
Example of Naturalistic Observation Research
Title: Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study
Citation: Kaplan, D. M., Raison, C. L., Milek, A., Tackman, A. M., Pace, T. W., & Mehl, M. R. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study. PloS one , 13 (11), e0206029.
Overview: In this study, researchers conducted two studies: one exploring assumptions about mindfulness and behavior, and the other using naturalistic observation to examine actual behavioral manifestations of mindfulness. They found that trait mindfulness is associated with a heightened perceptual focus in conversations, suggesting that being mindful is expressed primarily through sharpened attention rather than observable behavioral or social differences.
Read my Full Guide on Naturalistic Observation Here
18. Photo-Elicitation
Definition: Photo-elicitation utilizes photographs as a means to trigger discussions and evoke responses during interviews. This strategy aids in bringing out topics of discussion that may not emerge through verbal prompting alone (Harper, 2002).
Traditionally, Photo-Elicitation has been useful in various fields such as education, psychology, and sociology. The method involves the researcher or participants taking photographs, which are then used as prompts for discussion.
For instance, a researcher studying urban environmental issues might invite participants to photograph areas in their neighborhood that they perceive as environmentally detrimental, and then discuss each photo in depth (Clark-Ibáñez, 2004).
Example of Photo-Elicitation Research
Title: Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study
Citation: Green, E. M., Spivak, C., & Dollahite, J. S. (2021). Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study. Appetite, 158 .
Overview: This study focused on early adolescents (ages 10-14) and their food routines. Researchers conducted in-depth interviews using a photo-elicitation approach, where participants took photos related to their food choices and experiences. Through analysis, the study identified various routines and three main themes: family, settings, and meals/foods consumed, revealing how early adolescents view and are influenced by their eating routines.
Features of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a research method focused on understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
Some key features of this method include:
- Naturalistic Inquiry: Qualitative research happens in the natural setting of the phenomena, aiming to understand “real world” situations (Patton, 2015). This immersion in the field or subject allows the researcher to gather a deep understanding of the subject matter.
- Emphasis on Process: It aims to understand how events unfold over time rather than focusing solely on outcomes (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). The process-oriented nature of qualitative research allows researchers to investigate sequences, timing, and changes.
- Interpretive: It involves interpreting and making sense of phenomena in terms of the meanings people assign to them (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011). This interpretive element allows for rich, nuanced insights into human behavior and experiences.
- Holistic Perspective: Qualitative research seeks to understand the whole phenomenon rather than focusing on individual components (Creswell, 2013). It emphasizes the complex interplay of factors, providing a richer, more nuanced view of the research subject.
- Prioritizes Depth over Breadth: Qualitative research favors depth of understanding over breadth, typically involving a smaller but more focused sample size (Hennink, Hutter, & Bailey, 2020). This enables detailed exploration of the phenomena of interest, often leading to rich and complex data.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative research centers on exploring and understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
It involves an in-depth approach to the subject matter, aiming to capture the richness and complexity of human experience.
Examples include conducting interviews, observing behaviors, or analyzing text and images.
There are strengths inherent in this approach. In its focus on understanding subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative research can yield rich and detailed data that quantitative research may overlook (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011).
Additionally, qualitative research is adaptive, allowing the researcher to respond to new directions and insights as they emerge during the research process.
However, there are also limitations. Because of the interpretive nature of this research, findings may not be generalizable to a broader population (Marshall & Rossman, 2014). Well-designed quantitative research, on the other hand, can be generalizable.
Moreover, the reliability and validity of qualitative data can be challenging to establish due to its subjective nature, unlike quantitative research, which is ideally more objective.
Compare Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methodologies in This Guide Here
In conclusion, qualitative research methods provide distinctive ways to explore social phenomena and understand nuances that quantitative approaches might overlook. Each method, from Ethnography to Photo-Elicitation, presents its strengths and weaknesses but they all offer valuable means of investigating complex, real-world situations. The goal for the researcher is not to find a definitive tool, but to employ the method best suited for their research questions and the context at hand (Almalki, 2016). Above all, these methods underscore the richness of human experience and deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Angrosino, M. (2007). Doing ethnographic and observational research. Sage Publications.
Areni, C. S., & Kim, D. (1994). The influence of in-store lighting on consumers’ examination of merchandise in a wine store. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 11 (2), 117-125.
Barker, C., Pistrang, N., & Elliott, R. (2016). Research Methods in Clinical Psychology: An Introduction for Students and Practitioners. John Wiley & Sons.
Baxter, P. & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13 (4), 544-559.
Berger, A. A. (2010). The Objects of Affection: Semiotics and Consumer Culture. Palgrave Macmillan.
Bevan, M. T. (2014). A method of phenomenological interviewing. Qualitative health research, 24 (1), 136-144.
Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2015). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Sage Publications.
Bryman, A. (2015) . The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage Publications.
Chandler, D. (2017). Semiotics: The Basics. Routledge.
Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing grounded theory. Sage Publications.
Cheek, J. (2004). At the margins? Discourse analysis and qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research, 14(8), 1140-1150.
Clark-Ibáñez, M. (2004). Framing the social world with photo-elicitation interviews. American Behavioral Scientist, 47(12), 1507-1527.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage Publications.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11(100), 1-9.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage.
Dewalt, K. M., & Dewalt, B. R. (2011). Participant observation: A guide for fieldworkers. Rowman Altamira.
Doody, O., Slevin, E., & Taggart, L. (2013). Focus group interviews in nursing research: part 1. British Journal of Nursing, 22(1), 16-19.
Durham, A. (2019). Autoethnography. In P. Atkinson (Ed.), Qualitative Research Methods. Oxford University Press.
Duriau, V. J., Reger, R. K., & Pfarrer, M. D. (2007). A content analysis of the content analysis literature in organization studies: Research themes, data sources, and methodological refinements. Organizational Research Methods, 10(1), 5-34.
Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Farrall, S. (2006). What is qualitative longitudinal research? Papers in Social Research Methods, Qualitative Series, No.11, London School of Economics, Methodology Institute.
Fielding, J., & Fielding, N. (2008). Synergy and synthesis: integrating qualitative and quantitative data. The SAGE handbook of social research methods, 555-571.
Fink, A. (2013). How to conduct surveys: A step-by-step guide . SAGE.
Forsyth, D. R. (2010). Group Dynamics . Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Fugard, A. J. B., & Potts, H. W. W. (2015). Supporting thinking on sample sizes for thematic analyses: A quantitative tool. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 18 (6), 669–684.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Aldine de Gruyter.
Gray, J. R., Grove, S. K., & Sutherland, S. (2017). Burns and Grove’s the Practice of Nursing Research E-Book: Appraisal, Synthesis, and Generation of Evidence. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Greenwood, D. J., & Levin, M. (2016). Introduction to action research: Social research for social change. SAGE.
Harper, D. (2002). Talking about pictures: A case for photo elicitation. Visual Studies, 17 (1), 13-26.
Heinonen, T. (2012). Making Sense of the Social: Human Sciences and the Narrative Turn. Rozenberg Publishers.
Heisley, D. D., & Levy, S. J. (1991). Autodriving: A photoelicitation technique. Journal of Consumer Research, 18 (3), 257-272.
Hennink, M. M., Hutter, I., & Bailey, A. (2020). Qualitative Research Methods . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15 (9), 1277–1288.
Jorgensen, D. L. (2015). Participant Observation. In Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary, Searchable, and Linkable Resource. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Jorgensen, M., & Phillips, L. (2002). Discourse Analysis as Theory and Method . SAGE.
Josselson, R. (2011). Narrative research: Constructing, deconstructing, and reconstructing story. In Five ways of doing qualitative analysis . Guilford Press.
Kawulich, B. B. (2005). Participant observation as a data collection method. Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 6 (2).
Khan, S. (2014). Qualitative Research Method: Grounded Theory. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy, 5 (4), 86-88.
Koshy, E., Koshy, V., & Waterman, H. (2010). Action Research in Healthcare . SAGE.
Krippendorff, K. (2013). Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology. SAGE.
Lannon, J., & Cooper, P. (2012). Humanistic Advertising: A Holistic Cultural Perspective. International Journal of Advertising, 15 (2), 97–111.
Lavrakas, P. J. (2008). Encyclopedia of survey research methods. SAGE Publications.
Lieblich, A., Tuval-Mashiach, R., & Zilber, T. (2008). Narrative research: Reading, analysis and interpretation. Sage Publications.
Mackey, A., & Gass, S. M. (2015). Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Marshall, C., & Rossman, G. B. (2014). Designing qualitative research. Sage publications.
McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative. American Psychological Association.
Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2015). Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation. Jossey-Bass.
Mick, D. G. (1986). Consumer Research and Semiotics: Exploring the Morphology of Signs, Symbols, and Significance. Journal of Consumer Research, 13 (2), 196-213.
Morgan, D. L. (2010). Focus groups as qualitative research. Sage Publications.
Mulhall, A. (2003). In the field: notes on observation in qualitative research. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 41 (3), 306-313.
Neale, B. (2019). What is Qualitative Longitudinal Research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
Nolan, L. B., & Renderos, T. B. (2012). A focus group study on the influence of fatalism and religiosity on cancer risk perceptions in rural, eastern North Carolina. Journal of religion and health, 51 (1), 91-104.
Padilla-Díaz, M. (2015). Phenomenology in educational qualitative research: Philosophy as science or philosophical science? International Journal of Educational Excellence, 1 (2), 101-110.
Parker, I. (2014). Discourse dynamics: Critical analysis for social and individual psychology . Routledge.
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage Publications.
Polkinghorne, D. E. (2013). Narrative configuration in qualitative analysis. In Life history and narrative. Routledge.
Puts, M. T., Tapscott, B., Fitch, M., Howell, D., Monette, J., Wan-Chow-Wah, D., Krzyzanowska, M., Leighl, N. B., Springall, E., & Alibhai, S. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Qu, S. Q., & Dumay, J. (2011). The qualitative research interview . Qualitative research in accounting & management.
Ali, J., & Bhaskar, S. B. (2016). Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 60 (9), 662–669.
Rosenbaum, M. S. (2017). Exploring the social supportive role of third places in consumers’ lives. Journal of Service Research, 20 (1), 26-42.
Saldaña, J. (2003). Longitudinal Qualitative Research: Analyzing Change Through Time . AltaMira Press.
Saldaña, J. (2014). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers. SAGE.
Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158-176.
Smith, J. A. (2015). Qualitative Psychology: A Practical Guide to Research Methods . Sage Publications.
Smith, M. K. (2010). Action Research. The encyclopedia of informal education.
Sue, V. M., & Ritter, L. A. (2012). Conducting online surveys . SAGE Publications.
Van Auken, P. M., Frisvoll, S. J., & Stewart, S. I. (2010). Visualising community: using participant-driven photo-elicitation for research and application. Local Environment, 15 (4), 373-388.
Van Voorhis, F. L., & Morgan, B. L. (2007). Understanding Power and Rules of Thumb for Determining Sample Sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 3 (2), 43–50.
Wodak, R., & Meyer, M. (2015). Methods of Critical Discourse Analysis . SAGE.
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (2018). Action research for developing educational theories and practices . Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Dissertations and research projects
- Book a session
- Planning your research
Developing a theoretical framework
Reflecting on your position, extended literature reviews, presenting qualitative data.
- Quantitative research
- Writing up your research project
- e-learning and books
- SkillsCheck This link opens in a new window
- ⬅ Back to Skills Centre This link opens in a new window
- Review this resource
What is a theoretical framework?
Developing a theoretical framework for your dissertation is one of the key elements of a qualitative research project. Through writing your literature review, you are likely to have identified either a problem that need ‘fixing’ or a gap that your research may begin to fill.
The theoretical framework is your toolbox . In the toolbox are your handy tools: a set of theories, concepts, ideas and hypotheses that you will use to build a solution to the research problem or gap you have identified.
The methodology is the instruction manual: the procedure and steps you have taken, using your chosen tools, to tackle the research problem.
Why do I need a theoretical framework?
Developing a theoretical framework shows that you have thought critically about the different ways to approach your topic, and that you have made a well-reasoned and evidenced decision about which approach will work best. theoretical frameworks are also necessary for solving complex problems or issues from the literature, showing that you have the skills to think creatively and improvise to answer your research questions. they also allow researchers to establish new theories and approaches, that future research may go on to develop., how do i create a theoretical framework for my dissertation.
First, select your tools. You are likely to need a variety of tools in qualitative research – different theories, models or concepts – to help you tackle different parts of your research question.

When deciding what tools would be best for the job of answering your research questions or problem, explore what existing research in your area has used. You may find that there is a ‘standard toolbox’ for qualitative research in your field that you can borrow from or apply to your own research.
You will need to justify why your chosen tools are best for the job of answering your research questions, at what stage they are most relevant, and how they relate to each other. Some theories or models will neatly fit together and appear in the toolboxes of other researchers. However, you may wish to incorporate a model or idea that is not typical for your research area – the ‘odd one out’ in your toolbox. If this is the case, make sure you justify and account for why it is useful to you, and look for ways that it can be used in partnership with the other tools you are using.
You should also be honest about limitations, or where you need to improvise (for example, if the ‘right’ tool or approach doesn’t exist in your area).
This video from the Skills Centre includes an overview and example of how you might create a theoretical framework for your dissertation:
How do I choose the 'right' approach?
When designing your framework and choosing what to include, it can often be difficult to know if you’ve chosen the ‘right’ approach for your research questions. One way to check this is to look for consistency between your objectives, the literature in your framework, and your overall ethos for the research. This means ensuring that the literature you have used not only contributes to answering your research objectives, but that you also use theories and models that are true to your beliefs as a researcher.
Reflecting on your values and your overall ambition for the project can be a helpful step in making these decisions, as it can help you to fully connect your methodology and methods to your research aims.
Should I reflect on my position as a researcher?
If you feel your position as a researcher has influenced your choice of methods or procedure in any way, the methodology is a good place to reflect on this. Positionality acknowledges that no researcher is entirely objective: we are all, to some extent, influenced by prior learning, experiences, knowledge, and personal biases. This is particularly true in qualitative research or practice-based research, where the student is acting as a researcher in their own workplace, where they are otherwise considered a practitioner/professional. It's also important to reflect on your positionality if you belong to the same community as your participants where this is the grounds for their involvement in the research (ie. you are a mature student interviewing other mature learners about their experences in higher education).
The following questions can help you to reflect on your positionality and gauge whether this is an important section to include in your dissertation (for some people, this section isn’t necessary or relevant):
- How might my personal history influence how I approach the topic?
- How am I positioned in relation to this knowledge? Am I being influenced by prior learning or knowledge from outside of this course?
- How does my gender/social class/ ethnicity/ culture influence my positioning in relation to this topic?
- Do I share any attributes with my participants? Are we part of a s hared community? How might this have influenced our relationship and my role in interviews/observations?
- Am I invested in the outcomes on a personal level? Who is this research for and who will feel the benefits?
One option for qualitative projects is to write an extended literature review. This type of project does not require you to collect any new data. Instead, you should focus on synthesising a broad range of literature to offer a new perspective on a research problem or question.
The main difference between an extended literature review and a dissertation where primary data is collected, is in the presentation of the methodology, results and discussion sections. This is because extended literature reviews do not actively involve participants or primary data collection, so there is no need to outline a procedure for data collection (the methodology) or to present and interpret ‘data’ (in the form of interview transcripts, numerical data, observations etc.) You will have much more freedom to decide which sections of the dissertation should be combined, and whether new chapters or sections should be added.
Here is an overview of a common structure for an extended literature review:

Introduction
- Provide background information and context to set the ‘backdrop’ for your project.
- Explain the value and relevance of your research in this context. Outline what do you hope to contribute with your dissertation.
- Clarify a specific area of focus.
- Introduce your research aims (or problem) and objectives.
Literature review
You will need to write a short, overview literature review to introduce the main theories, concepts and key research areas that you will explore in your dissertation. This set of texts – which may be theoretical, research-based, practice-based or policies – form your theoretical framework. In other words, by bringing these texts together in the literature review, you are creating a lens that you can then apply to more focused examples or scenarios in your discussion chapters.
Methodology
As you will not be collecting primary data, your methodology will be quite different from a typical dissertation. You will need to set out the process and procedure you used to find and narrow down your literature. This is also known as a search strategy.
Including your search strategy
A search strategy explains how you have narrowed down your literature to identify key studies and areas of focus. This often takes the form of a search strategy table, included as an appendix at the end of the dissertation. If included, this section takes the place of the traditional 'methodology' section.
If you choose to include a search strategy table, you should also give an overview of your reading process in the main body of the dissertation. Think of this as a chronology of the practical steps you took and your justification for doing so at each stage, such as:
- Your key terms, alternatives and synonyms, and any terms that you chose to exclude.
- Your choice and combination of databases;
- Your inclusion/exclusion criteria, when they were applied and why. This includes filters such as language of publication, date, and country of origin;
- You should also explain which terms you combined to form search phrases and your use of Boolean searching (AND, OR, NOT);
- Your use of citation searching (selecting articles from the bibliography of a chosen journal article to further your search).
- Your use of any search models, such as PICO and SPIDER to help shape your approach.
- Search strategy template A simple template for recording your literature searching. This can be included as an appendix to show your search strategy.
The discussion section of an extended literature review is the most flexible in terms of structure. Think of this section as a series of short case studies or ‘windows’ on your research. In this section you will apply the theoretical framework you formed in the literature review – a combination of theories, models and ideas that explain your approach to the topic – to a series of different examples and scenarios. These are usually presented as separate discussion ‘chapters’ in the dissertation, in an order that you feel best fits your argument.
Think about an order for these discussion sections or chapters that helps to tell the story of your research. One common approach is to structure these sections by common themes or concepts that help to draw your sources together. You might also opt for a chronological structure if your dissertation aims to show change or development over time. Another option is to deliberately show where there is a lack of chronology or narrative across your case studies, by ordering them in a fragmentary order! You will be able to reflect upon the structure of these chapters elsewhere in the dissertation, explaining and defending your decision in the methodology and conclusion.
A summary of your key findings – what you have concluded from your research, and how far you have been able to successfully answer your research questions.
- Recommendations – for improvements to your own study, for future research in the area, and for your field more widely.
- Emphasise your contributions to knowledge and what you have achieved.
Alternative structure
Depending on your research aims, and whether you are working with a case-study type approach (where each section of the dissertation considers a different example or concept through the lens established in your literature review), you might opt for one of the following structures:
Splitting the literature review across different chapters:

This structure allows you to pull apart the traditional literature review, introducing it little by little with each of your themed chapters. This approach works well for dissertations that attempt to show change or difference over time, as the relevant literature for that section or period can be introduced gradually to the reader.
Whichever structure you opt for, remember to explain and justify your approach. A marker will be interested in why you decided on your chosen structure, what it allows you to achieve/brings to the project and what alternatives you considered and rejected in the planning process. Here are some example sentence starters:
In qualitative studies, your results are often presented alongside the discussion, as it is difficult to include this data in a meaningful way without explanation and interpretation. In the dsicussion section, aim to structure your work thematically, moving through the key concepts or ideas that have emerged from your qualitative data. Use extracts from your data collection - interviews, focus groups, observations - to illustrate where these themes are most prominent, and refer back to the sources from your literature review to help draw conclusions.
Here's an example of how your data could be presented in paragraph format in this section:
Example from 'Reporting and discussing your findings ', Monash University .
- << Previous: Planning your research
- Next: Quantitative research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.shu.ac.uk/researchprojects

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik aspers.
1 Department of Sociology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
2 Seminar for Sociology, Universität St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland
3 Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term “qualitative.” Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered across existing work, and based on Becker’s classic study of marijuana consumption, we formulate and illustrate a definition that tries to capture its core elements. We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. This formulation is developed as a tool to help improve research designs while stressing that a qualitative dimension is present in quantitative work as well. Additionally, it can facilitate teaching, communication between researchers, diminish the gap between qualitative and quantitative researchers, help to address critiques of qualitative methods, and be used as a standard of evaluation of qualitative research.
If we assume that there is something called qualitative research, what exactly is this qualitative feature? And how could we evaluate qualitative research as good or not? Is it fundamentally different from quantitative research? In practice, most active qualitative researchers working with empirical material intuitively know what is involved in doing qualitative research, yet perhaps surprisingly, a clear definition addressing its key feature is still missing.
To address the question of what is qualitative we turn to the accounts of “qualitative research” in textbooks and also in empirical work. In his classic, explorative, interview study of deviance Howard Becker ( 1963 ) asks ‘How does one become a marijuana user?’ In contrast to pre-dispositional and psychological-individualistic theories of deviant behavior, Becker’s inherently social explanation contends that becoming a user of this substance is the result of a three-phase sequential learning process. First, potential users need to learn how to smoke it properly to produce the “correct” effects. If not, they are likely to stop experimenting with it. Second, they need to discover the effects associated with it; in other words, to get “high,” individuals not only have to experience what the drug does, but also to become aware that those sensations are related to using it. Third, they require learning to savor the feelings related to its consumption – to develop an acquired taste. Becker, who played music himself, gets close to the phenomenon by observing, taking part, and by talking to people consuming the drug: “half of the fifty interviews were conducted with musicians, the other half covered a wide range of people, including laborers, machinists, and people in the professions” (Becker 1963 :56).
Another central aspect derived through the common-to-all-research interplay between induction and deduction (Becker 2017 ), is that during the course of his research Becker adds scientifically meaningful new distinctions in the form of three phases—distinctions, or findings if you will, that strongly affect the course of his research: its focus, the material that he collects, and which eventually impact his findings. Each phase typically unfolds through social interaction, and often with input from experienced users in “a sequence of social experiences during which the person acquires a conception of the meaning of the behavior, and perceptions and judgments of objects and situations, all of which make the activity possible and desirable” (Becker 1963 :235). In this study the increased understanding of smoking dope is a result of a combination of the meaning of the actors, and the conceptual distinctions that Becker introduces based on the views expressed by his respondents. Understanding is the result of research and is due to an iterative process in which data, concepts and evidence are connected with one another (Becker 2017 ).
Indeed, there are many definitions of qualitative research, but if we look for a definition that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature across the broad field of social science is meager. The main reason behind this article lies in the paradox, which, to put it bluntly, is that researchers act as if they know what it is, but they cannot formulate a coherent definition. Sociologists and others will of course continue to conduct good studies that show the relevance and value of qualitative research addressing scientific and practical problems in society. However, our paper is grounded in the idea that providing a clear definition will help us improve the work that we do. Among researchers who practice qualitative research there is clearly much knowledge. We suggest that a definition makes this knowledge more explicit. If the first rationale for writing this paper refers to the “internal” aim of improving qualitative research, the second refers to the increased “external” pressure that especially many qualitative researchers feel; pressure that comes both from society as well as from other scientific approaches. There is a strong core in qualitative research, and leading researchers tend to agree on what it is and how it is done. Our critique is not directed at the practice of qualitative research, but we do claim that the type of systematic work we do has not yet been done, and that it is useful to improve the field and its status in relation to quantitative research.
The literature on the “internal” aim of improving, or at least clarifying qualitative research is large, and we do not claim to be the first to notice the vagueness of the term “qualitative” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 ). Also, others have noted that there is no single definition of it (Long and Godfrey 2004 :182), that there are many different views on qualitative research (Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11; Jovanović 2011 :3), and that more generally, we need to define its meaning (Best 2004 :54). Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ), for example, as well as Nelson et al. (1992:2 cited in Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11), and Flick ( 2007 :ix–x), have recognized that the term is problematic: “Actually, the term ‘qualitative research’ is confusing because it can mean different things to different people” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :10–11). Hammersley has discussed the possibility of addressing the problem, but states that “the task of providing an account of the distinctive features of qualitative research is far from straightforward” ( 2013 :2). This confusion, as he has recently further argued (Hammersley 2018 ), is also salient in relation to ethnography where different philosophical and methodological approaches lead to a lack of agreement about what it means.
Others (e.g. Hammersley 2018 ; Fine and Hancock 2017 ) have also identified the treat to qualitative research that comes from external forces, seen from the point of view of “qualitative research.” This threat can be further divided into that which comes from inside academia, such as the critique voiced by “quantitative research” and outside of academia, including, for example, New Public Management. Hammersley ( 2018 ), zooming in on one type of qualitative research, ethnography, has argued that it is under treat. Similarly to Fine ( 2003 ), and before him Gans ( 1999 ), he writes that ethnography’ has acquired a range of meanings, and comes in many different versions, these often reflecting sharply divergent epistemological orientations. And already more than twenty years ago while reviewing Denzin and Lincoln’ s Handbook of Qualitative Methods Fine argued:
While this increasing centrality [of qualitative research] might lead one to believe that consensual standards have developed, this belief would be misleading. As the methodology becomes more widely accepted, querulous challengers have raised fundamental questions that collectively have undercut the traditional models of how qualitative research is to be fashioned and presented (1995:417).
According to Hammersley, there are today “serious treats to the practice of ethnographic work, on almost any definition” ( 2018 :1). He lists five external treats: (1) that social research must be accountable and able to show its impact on society; (2) the current emphasis on “big data” and the emphasis on quantitative data and evidence; (3) the labor market pressure in academia that leaves less time for fieldwork (see also Fine and Hancock 2017 ); (4) problems of access to fields; and (5) the increased ethical scrutiny of projects, to which ethnography is particularly exposed. Hammersley discusses some more or less insufficient existing definitions of ethnography.
The current situation, as Hammersley and others note—and in relation not only to ethnography but also qualitative research in general, and as our empirical study shows—is not just unsatisfactory, it may even be harmful for the entire field of qualitative research, and does not help social science at large. We suggest that the lack of clarity of qualitative research is a real problem that must be addressed.
Towards a Definition of Qualitative Research
Seen in an historical light, what is today called qualitative, or sometimes ethnographic, interpretative research – or a number of other terms – has more or less always existed. At the time the founders of sociology – Simmel, Weber, Durkheim and, before them, Marx – were writing, and during the era of the Methodenstreit (“dispute about methods”) in which the German historical school emphasized scientific methods (cf. Swedberg 1990 ), we can at least speak of qualitative forerunners.
Perhaps the most extended discussion of what later became known as qualitative methods in a classic work is Bronisław Malinowski’s ( 1922 ) Argonauts in the Western Pacific , although even this study does not explicitly address the meaning of “qualitative.” In Weber’s ([1921–-22] 1978) work we find a tension between scientific explanations that are based on observation and quantification and interpretative research (see also Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 ).
If we look through major sociology journals like the American Sociological Review , American Journal of Sociology , or Social Forces we will not find the term qualitative sociology before the 1970s. And certainly before then much of what we consider qualitative classics in sociology, like Becker’ study ( 1963 ), had already been produced. Indeed, the Chicago School often combined qualitative and quantitative data within the same study (Fine 1995 ). Our point being that before a disciplinary self-awareness the term quantitative preceded qualitative, and the articulation of the former was a political move to claim scientific status (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ). In the US the World War II seem to have sparked a critique of sociological work, including “qualitative work,” that did not follow the scientific canon (Rawls 2018 ), which was underpinned by a scientifically oriented and value free philosophy of science. As a result the attempts and practice of integrating qualitative and quantitative sociology at Chicago lost ground to sociology that was more oriented to surveys and quantitative work at Columbia under Merton-Lazarsfeld. The quantitative tradition was also able to present textbooks (Lundberg 1951 ) that facilitated the use this approach and its “methods.” The practices of the qualitative tradition, by and large, remained tacit or was part of the mentoring transferred from the renowned masters to their students.
This glimpse into history leads us back to the lack of a coherent account condensed in a definition of qualitative research. Many of the attempts to define the term do not meet the requirements of a proper definition: A definition should be clear, avoid tautology, demarcate its domain in relation to the environment, and ideally only use words in its definiens that themselves are not in need of definition (Hempel 1966 ). A definition can enhance precision and thus clarity by identifying the core of the phenomenon. Preferably, a definition should be short. The typical definition we have found, however, is an ostensive definition, which indicates what qualitative research is about without informing us about what it actually is :
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives. (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2)
Flick claims that the label “qualitative research” is indeed used as an umbrella for a number of approaches ( 2007 :2–4; 2002 :6), and it is not difficult to identify research fitting this designation. Moreover, whatever it is, it has grown dramatically over the past five decades. In addition, courses have been developed, methods have flourished, arguments about its future have been advanced (for example, Denzin and Lincoln 1994) and criticized (for example, Snow and Morrill 1995 ), and dedicated journals and books have mushroomed. Most social scientists have a clear idea of research and how it differs from journalism, politics and other activities. But the question of what is qualitative in qualitative research is either eluded or eschewed.
We maintain that this lacuna hinders systematic knowledge production based on qualitative research. Paul Lazarsfeld noted the lack of “codification” as early as 1955 when he reviewed 100 qualitative studies in order to offer a codification of the practices (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). Since then many texts on “qualitative research” and its methods have been published, including recent attempts (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) similar to Lazarsfeld’s. These studies have tried to extract what is qualitative by looking at the large number of empirical “qualitative” studies. Our novel strategy complements these endeavors by taking another approach and looking at the attempts to codify these practices in the form of a definition, as well as to a minor extent take Becker’s study as an exemplar of what qualitative researchers actually do, and what the characteristic of being ‘qualitative’ denotes and implies. We claim that qualitative researchers, if there is such a thing as “qualitative research,” should be able to codify their practices in a condensed, yet general way expressed in language.
Lingering problems of “generalizability” and “how many cases do I need” (Small 2009 ) are blocking advancement – in this line of work qualitative approaches are said to differ considerably from quantitative ones, while some of the former unsuccessfully mimic principles related to the latter (Small 2009 ). Additionally, quantitative researchers sometimes unfairly criticize the first based on their own quality criteria. Scholars like Goertz and Mahoney ( 2012 ) have successfully focused on the different norms and practices beyond what they argue are essentially two different cultures: those working with either qualitative or quantitative methods. Instead, similarly to Becker ( 2017 ) who has recently questioned the usefulness of the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research, we focus on similarities.
The current situation also impedes both students and researchers in focusing their studies and understanding each other’s work (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). A third consequence is providing an opening for critiques by scholars operating within different traditions (Valsiner 2000 :101). A fourth issue is that the “implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative paradigm” (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 :9). Relatedly, the National Science Foundation in the US organized two workshops in 2004 and 2005 to address the scientific foundations of qualitative research involving strategies to improve it and to develop standards of evaluation in qualitative research. However, a specific focus on its distinguishing feature of being “qualitative” while being implicitly acknowledged, was discussed only briefly (for example, Best 2004 ).
In 2014 a theme issue was published in this journal on “Methods, Materials, and Meanings: Designing Cultural Analysis,” discussing central issues in (cultural) qualitative research (Berezin 2014 ; Biernacki 2014 ; Glaeser 2014 ; Lamont and Swidler 2014 ; Spillman 2014). We agree with many of the arguments put forward, such as the risk of methodological tribalism, and that we should not waste energy on debating methods separated from research questions. Nonetheless, a clarification of the relation to what is called “quantitative research” is of outmost importance to avoid misunderstandings and misguided debates between “qualitative” and “quantitative” researchers. Our strategy means that researchers, “qualitative” or “quantitative” they may be, in their actual practice may combine qualitative work and quantitative work.
In this article we accomplish three tasks. First, we systematically survey the literature for meanings of qualitative research by looking at how researchers have defined it. Drawing upon existing knowledge we find that the different meanings and ideas of qualitative research are not yet coherently integrated into one satisfactory definition. Next, we advance our contribution by offering a definition of qualitative research and illustrate its meaning and use partially by expanding on the brief example introduced earlier related to Becker’s work ( 1963 ). We offer a systematic analysis of central themes of what researchers consider to be the core of “qualitative,” regardless of style of work. These themes – which we summarize in terms of four keywords: distinction, process, closeness, improved understanding – constitute part of our literature review, in which each one appears, sometimes with others, but never all in the same definition. They serve as the foundation of our contribution. Our categories are overlapping. Their use is primarily to organize the large amount of definitions we have identified and analyzed, and not necessarily to draw a clear distinction between them. Finally, we continue the elaboration discussed above on the advantages of a clear definition of qualitative research.
In a hermeneutic fashion we propose that there is something meaningful that deserves to be labelled “qualitative research” (Gadamer 1990 ). To approach the question “What is qualitative in qualitative research?” we have surveyed the literature. In conducting our survey we first traced the word’s etymology in dictionaries, encyclopedias, handbooks of the social sciences and of methods and textbooks, mainly in English, which is common to methodology courses. It should be noted that we have zoomed in on sociology and its literature. This discipline has been the site of the largest debate and development of methods that can be called “qualitative,” which suggests that this field should be examined in great detail.
In an ideal situation we should expect that one good definition, or at least some common ideas, would have emerged over the years. This common core of qualitative research should be so accepted that it would appear in at least some textbooks. Since this is not what we found, we decided to pursue an inductive approach to capture maximal variation in the field of qualitative research; we searched in a selection of handbooks, textbooks, book chapters, and books, to which we added the analysis of journal articles. Our sample comprises a total of 89 references.
In practice we focused on the discipline that has had a clear discussion of methods, namely sociology. We also conducted a broad search in the JSTOR database to identify scholarly sociology articles published between 1998 and 2017 in English with a focus on defining or explaining qualitative research. We specifically zoom in on this time frame because we would have expect that this more mature period would have produced clear discussions on the meaning of qualitative research. To find these articles we combined a number of keywords to search the content and/or the title: qualitative (which was always included), definition, empirical, research, methodology, studies, fieldwork, interview and observation .
As a second phase of our research we searched within nine major sociological journals ( American Journal of Sociology , Sociological Theory , American Sociological Review , Contemporary Sociology , Sociological Forum , Sociological Theory , Qualitative Research , Qualitative Sociology and Qualitative Sociology Review ) for articles also published during the past 19 years (1998–2017) that had the term “qualitative” in the title and attempted to define qualitative research.
Lastly we picked two additional journals, Qualitative Research and Qualitative Sociology , in which we could expect to find texts addressing the notion of “qualitative.” From Qualitative Research we chose Volume 14, Issue 6, December 2014, and from Qualitative Sociology we chose Volume 36, Issue 2, June 2017. Within each of these we selected the first article; then we picked the second article of three prior issues. Again we went back another three issues and investigated article number three. Finally we went back another three issues and perused article number four. This selection criteria was used to get a manageable sample for the analysis.
The coding process of the 89 references we gathered in our selected review began soon after the first round of material was gathered, and we reduced the complexity created by our maximum variation sampling (Snow and Anderson 1993 :22) to four different categories within which questions on the nature and properties of qualitative research were discussed. We call them: Qualitative and Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research, Fieldwork, and Grounded Theory. This – which may appear as an illogical grouping – merely reflects the “context” in which the matter of “qualitative” is discussed. If the selection process of the material – books and articles – was informed by pre-knowledge, we used an inductive strategy to code the material. When studying our material, we identified four central notions related to “qualitative” that appear in various combinations in the literature which indicate what is the core of qualitative research. We have labeled them: “distinctions”, “process,” “closeness,” and “improved understanding.” During the research process the categories and notions were improved, refined, changed, and reordered. The coding ended when a sense of saturation in the material arose. In the presentation below all quotations and references come from our empirical material of texts on qualitative research.
Analysis – What is Qualitative Research?
In this section we describe the four categories we identified in the coding, how they differently discuss qualitative research, as well as their overall content. Some salient quotations are selected to represent the type of text sorted under each of the four categories. What we present are examples from the literature.
Qualitative and Quantitative
This analytic category comprises quotations comparing qualitative and quantitative research, a distinction that is frequently used (Brown 2010 :231); in effect this is a conceptual pair that structures the discussion and that may be associated with opposing interests. While the general goal of quantitative and qualitative research is the same – to understand the world better – their methodologies and focus in certain respects differ substantially (Becker 1966 :55). Quantity refers to that property of something that can be determined by measurement. In a dictionary of Statistics and Methodology we find that “(a) When referring to *variables, ‘qualitative’ is another term for *categorical or *nominal. (b) When speaking of kinds of research, ‘qualitative’ refers to studies of subjects that are hard to quantify, such as art history. Qualitative research tends to be a residual category for almost any kind of non-quantitative research” (Stiles 1998:183). But it should be obvious that one could employ a quantitative approach when studying, for example, art history.
The same dictionary states that quantitative is “said of variables or research that can be handled numerically, usually (too sharply) contrasted with *qualitative variables and research” (Stiles 1998:184). From a qualitative perspective “quantitative research” is about numbers and counting, and from a quantitative perspective qualitative research is everything that is not about numbers. But this does not say much about what is “qualitative.” If we turn to encyclopedias we find that in the 1932 edition of the Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences there is no mention of “qualitative.” In the Encyclopedia from 1968 we can read:
Qualitative Analysis. For methods of obtaining, analyzing, and describing data, see [the various entries:] CONTENT ANALYSIS; COUNTED DATA; EVALUATION RESEARCH, FIELD WORK; GRAPHIC PRESENTATION; HISTORIOGRAPHY, especially the article on THE RHETORIC OF HISTORY; INTERVIEWING; OBSERVATION; PERSONALITY MEASUREMENT; PROJECTIVE METHODS; PSYCHOANALYSIS, article on EXPERIMENTAL METHODS; SURVEY ANALYSIS, TABULAR PRESENTATION; TYPOLOGIES. (Vol. 13:225)
Some, like Alford, divide researchers into methodologists or, in his words, “quantitative and qualitative specialists” (Alford 1998 :12). Qualitative research uses a variety of methods, such as intensive interviews or in-depth analysis of historical materials, and it is concerned with a comprehensive account of some event or unit (King et al. 1994 :4). Like quantitative research it can be utilized to study a variety of issues, but it tends to focus on meanings and motivations that underlie cultural symbols, personal experiences, phenomena and detailed understanding of processes in the social world. In short, qualitative research centers on understanding processes, experiences, and the meanings people assign to things (Kalof et al. 2008 :79).
Others simply say that qualitative methods are inherently unscientific (Jovanović 2011 :19). Hood, for instance, argues that words are intrinsically less precise than numbers, and that they are therefore more prone to subjective analysis, leading to biased results (Hood 2006 :219). Qualitative methodologies have raised concerns over the limitations of quantitative templates (Brady et al. 2004 :4). Scholars such as King et al. ( 1994 ), for instance, argue that non-statistical research can produce more reliable results if researchers pay attention to the rules of scientific inference commonly stated in quantitative research. Also, researchers such as Becker ( 1966 :59; 1970 :42–43) have asserted that, if conducted properly, qualitative research and in particular ethnographic field methods, can lead to more accurate results than quantitative studies, in particular, survey research and laboratory experiments.
Some researchers, such as Kalof, Dan, and Dietz ( 2008 :79) claim that the boundaries between the two approaches are becoming blurred, and Small ( 2009 ) argues that currently much qualitative research (especially in North America) tries unsuccessfully and unnecessarily to emulate quantitative standards. For others, qualitative research tends to be more humanistic and discursive (King et al. 1994 :4). Ragin ( 1994 ), and similarly also Becker, ( 1996 :53), Marchel and Owens ( 2007 :303) think that the main distinction between the two styles is overstated and does not rest on the simple dichotomy of “numbers versus words” (Ragin 1994 :xii). Some claim that quantitative data can be utilized to discover associations, but in order to unveil cause and effect a complex research design involving the use of qualitative approaches needs to be devised (Gilbert 2009 :35). Consequently, qualitative data are useful for understanding the nuances lying beyond those processes as they unfold (Gilbert 2009 :35). Others contend that qualitative research is particularly well suited both to identify causality and to uncover fine descriptive distinctions (Fine and Hallett 2014 ; Lichterman and Isaac Reed 2014 ; Katz 2015 ).
There are other ways to separate these two traditions, including normative statements about what qualitative research should be (that is, better or worse than quantitative approaches, concerned with scientific approaches to societal change or vice versa; Snow and Morrill 1995 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ), or whether it should develop falsifiable statements; Best 2004 ).
We propose that quantitative research is largely concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ); the analysis concerns the relations between variables. These categories are primarily not questioned in the study, only their frequency or degree, or the correlations between them (cf. Franzosi 2016 ). If a researcher studies wage differences between women and men, he or she works with given categories: x number of men are compared with y number of women, with a certain wage attributed to each person. The idea is not to move beyond the given categories of wage, men and women; they are the starting point as well as the end point, and undergo no “qualitative change.” Qualitative research, in contrast, investigates relations between categories that are themselves subject to change in the research process. Returning to Becker’s study ( 1963 ), we see that he questioned pre-dispositional theories of deviant behavior working with pre-determined variables such as an individual’s combination of personal qualities or emotional problems. His take, in contrast, was to understand marijuana consumption by developing “variables” as part of the investigation. Thereby he presented new variables, or as we would say today, theoretical concepts, but which are grounded in the empirical material.
Qualitative Research
This category contains quotations that refer to descriptions of qualitative research without making comparisons with quantitative research. Researchers such as Denzin and Lincoln, who have written a series of influential handbooks on qualitative methods (1994; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ; 2005 ), citing Nelson et al. (1992:4), argue that because qualitative research is “interdisciplinary, transdisciplinary, and sometimes counterdisciplinary” it is difficult to derive one single definition of it (Jovanović 2011 :3). According to them, in fact, “the field” is “many things at the same time,” involving contradictions, tensions over its focus, methods, and how to derive interpretations and findings ( 2003 : 11). Similarly, others, such as Flick ( 2007 :ix–x) contend that agreeing on an accepted definition has increasingly become problematic, and that qualitative research has possibly matured different identities. However, Best holds that “the proliferation of many sorts of activities under the label of qualitative sociology threatens to confuse our discussions” ( 2004 :54). Atkinson’s position is more definite: “the current state of qualitative research and research methods is confused” ( 2005 :3–4).
Qualitative research is about interpretation (Blumer 1969 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ), or Verstehen [understanding] (Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ). It is “multi-method,” involving the collection and use of a variety of empirical materials (Denzin and Lincoln 1998; Silverman 2013 ) and approaches (Silverman 2005 ; Flick 2007 ). It focuses not only on the objective nature of behavior but also on its subjective meanings: individuals’ own accounts of their attitudes, motivations, behavior (McIntyre 2005 :127; Creswell 2009 ), events and situations (Bryman 1989) – what people say and do in specific places and institutions (Goodwin and Horowitz 2002 :35–36) in social and temporal contexts (Morrill and Fine 1997). For this reason, following Weber ([1921-22] 1978), it can be described as an interpretative science (McIntyre 2005 :127). But could quantitative research also be concerned with these questions? Also, as pointed out below, does all qualitative research focus on subjective meaning, as some scholars suggest?
Others also distinguish qualitative research by claiming that it collects data using a naturalistic approach (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2; Creswell 2009 ), focusing on the meaning actors ascribe to their actions. But again, does all qualitative research need to be collected in situ? And does qualitative research have to be inherently concerned with meaning? Flick ( 2007 ), referring to Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ), mentions conversation analysis as an example of qualitative research that is not concerned with the meanings people bring to a situation, but rather with the formal organization of talk. Still others, such as Ragin ( 1994 :85), note that qualitative research is often (especially early on in the project, we would add) less structured than other kinds of social research – a characteristic connected to its flexibility and that can lead both to potentially better, but also worse results. But is this not a feature of this type of research, rather than a defining description of its essence? Wouldn’t this comment also apply, albeit to varying degrees, to quantitative research?
In addition, Strauss ( 2003 ), along with others, such as Alvesson and Kärreman ( 2011 :10–76), argue that qualitative researchers struggle to capture and represent complex phenomena partially because they tend to collect a large amount of data. While his analysis is correct at some points – “It is necessary to do detailed, intensive, microscopic examination of the data in order to bring out the amazing complexity of what lies in, behind, and beyond those data” (Strauss 2003 :10) – much of his analysis concerns the supposed focus of qualitative research and its challenges, rather than exactly what it is about. But even in this instance we would make a weak case arguing that these are strictly the defining features of qualitative research. Some researchers seem to focus on the approach or the methods used, or even on the way material is analyzed. Several researchers stress the naturalistic assumption of investigating the world, suggesting that meaning and interpretation appear to be a core matter of qualitative research.
We can also see that in this category there is no consensus about specific qualitative methods nor about qualitative data. Many emphasize interpretation, but quantitative research, too, involves interpretation; the results of a regression analysis, for example, certainly have to be interpreted, and the form of meta-analysis that factor analysis provides indeed requires interpretation However, there is no interpretation of quantitative raw data, i.e., numbers in tables. One common thread is that qualitative researchers have to get to grips with their data in order to understand what is being studied in great detail, irrespective of the type of empirical material that is being analyzed. This observation is connected to the fact that qualitative researchers routinely make several adjustments of focus and research design as their studies progress, in many cases until the very end of the project (Kalof et al. 2008 ). If you, like Becker, do not start out with a detailed theory, adjustments such as the emergence and refinement of research questions will occur during the research process. We have thus found a number of useful reflections about qualitative research scattered across different sources, but none of them effectively describe the defining characteristics of this approach.
Although qualitative research does not appear to be defined in terms of a specific method, it is certainly common that fieldwork, i.e., research that entails that the researcher spends considerable time in the field that is studied and use the knowledge gained as data, is seen as emblematic of or even identical to qualitative research. But because we understand that fieldwork tends to focus primarily on the collection and analysis of qualitative data, we expected to find within it discussions on the meaning of “qualitative.” But, again, this was not the case.
Instead, we found material on the history of this approach (for example, Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ; Atkinson et al. 2001), including how it has changed; for example, by adopting a more self-reflexive practice (Heyl 2001), as well as the different nomenclature that has been adopted, such as fieldwork, ethnography, qualitative research, naturalistic research, participant observation and so on (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ; Gans 1999 ).
We retrieved definitions of ethnography, such as “the study of people acting in the natural courses of their daily lives,” involving a “resocialization of the researcher” (Emerson 1988 :1) through intense immersion in others’ social worlds (see also examples in Hammersley 2018 ). This may be accomplished by direct observation and also participation (Neuman 2007 :276), although others, such as Denzin ( 1970 :185), have long recognized other types of observation, including non-participant (“fly on the wall”). In this category we have also isolated claims and opposing views, arguing that this type of research is distinguished primarily by where it is conducted (natural settings) (Hughes 1971:496), and how it is carried out (a variety of methods are applied) or, for some most importantly, by involving an active, empathetic immersion in those being studied (Emerson 1988 :2). We also retrieved descriptions of the goals it attends in relation to how it is taught (understanding subjective meanings of the people studied, primarily develop theory, or contribute to social change) (see for example, Corte and Irwin 2017 ; Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 :281; Trier-Bieniek 2012 :639) by collecting the richest possible data (Lofland et al. 2006 ) to derive “thick descriptions” (Geertz 1973 ), and/or to aim at theoretical statements of general scope and applicability (for example, Emerson 1988 ; Fine 2003 ). We have identified guidelines on how to evaluate it (for example Becker 1996 ; Lamont 2004 ) and have retrieved instructions on how it should be conducted (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ). For instance, analysis should take place while the data gathering unfolds (Emerson 1988 ; Hammersley and Atkinson 2007 ; Lofland et al. 2006 ), observations should be of long duration (Becker 1970 :54; Goffman 1989 ), and data should be of high quantity (Becker 1970 :52–53), as well as other questionable distinctions between fieldwork and other methods:
Field studies differ from other methods of research in that the researcher performs the task of selecting topics, decides what questions to ask, and forges interest in the course of the research itself . This is in sharp contrast to many ‘theory-driven’ and ‘hypothesis-testing’ methods. (Lofland and Lofland 1995 :5)
But could not, for example, a strictly interview-based study be carried out with the same amount of flexibility, such as sequential interviewing (for example, Small 2009 )? Once again, are quantitative approaches really as inflexible as some qualitative researchers think? Moreover, this category stresses the role of the actors’ meaning, which requires knowledge and close interaction with people, their practices and their lifeworld.
It is clear that field studies – which are seen by some as the “gold standard” of qualitative research – are nonetheless only one way of doing qualitative research. There are other methods, but it is not clear why some are more qualitative than others, or why they are better or worse. Fieldwork is characterized by interaction with the field (the material) and understanding of the phenomenon that is being studied. In Becker’s case, he had general experience from fields in which marihuana was used, based on which he did interviews with actual users in several fields.
Grounded Theory
Another major category we identified in our sample is Grounded Theory. We found descriptions of it most clearly in Glaser and Strauss’ ([1967] 2010 ) original articulation, Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ) and Charmaz ( 2006 ), as well as many other accounts of what it is for: generating and testing theory (Strauss 2003 :xi). We identified explanations of how this task can be accomplished – such as through two main procedures: constant comparison and theoretical sampling (Emerson 1998:96), and how using it has helped researchers to “think differently” (for example, Strauss and Corbin 1998 :1). We also read descriptions of its main traits, what it entails and fosters – for instance, an exceptional flexibility, an inductive approach (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :31–33; 1990; Esterberg 2002 :7), an ability to step back and critically analyze situations, recognize tendencies towards bias, think abstractly and be open to criticism, enhance sensitivity towards the words and actions of respondents, and develop a sense of absorption and devotion to the research process (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :5–6). Accordingly, we identified discussions of the value of triangulating different methods (both using and not using grounded theory), including quantitative ones, and theories to achieve theoretical development (most comprehensively in Denzin 1970 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Timmermans and Tavory 2012 ). We have also located arguments about how its practice helps to systematize data collection, analysis and presentation of results (Glaser and Strauss [1967] 2010 :16).
Grounded theory offers a systematic approach which requires researchers to get close to the field; closeness is a requirement of identifying questions and developing new concepts or making further distinctions with regard to old concepts. In contrast to other qualitative approaches, grounded theory emphasizes the detailed coding process, and the numerous fine-tuned distinctions that the researcher makes during the process. Within this category, too, we could not find a satisfying discussion of the meaning of qualitative research.
Defining Qualitative Research
In sum, our analysis shows that some notions reappear in the discussion of qualitative research, such as understanding, interpretation, “getting close” and making distinctions. These notions capture aspects of what we think is “qualitative.” However, a comprehensive definition that is useful and that can further develop the field is lacking, and not even a clear picture of its essential elements appears. In other words no definition emerges from our data, and in our research process we have moved back and forth between our empirical data and the attempt to present a definition. Our concrete strategy, as stated above, is to relate qualitative and quantitative research, or more specifically, qualitative and quantitative work. We use an ideal-typical notion of quantitative research which relies on taken for granted and numbered variables. This means that the data consists of variables on different scales, such as ordinal, but frequently ratio and absolute scales, and the representation of the numbers to the variables, i.e. the justification of the assignment of numbers to object or phenomenon, are not questioned, though the validity may be questioned. In this section we return to the notion of quality and try to clarify it while presenting our contribution.
Broadly, research refers to the activity performed by people trained to obtain knowledge through systematic procedures. Notions such as “objectivity” and “reflexivity,” “systematic,” “theory,” “evidence” and “openness” are here taken for granted in any type of research. Next, building on our empirical analysis we explain the four notions that we have identified as central to qualitative work: distinctions, process, closeness, and improved understanding. In discussing them, ultimately in relation to one another, we make their meaning even more precise. Our idea, in short, is that only when these ideas that we present separately for analytic purposes are brought together can we speak of qualitative research.
Distinctions
We believe that the possibility of making new distinctions is one the defining characteristics of qualitative research. It clearly sets it apart from quantitative analysis which works with taken-for-granted variables, albeit as mentioned, meta-analyses, for example, factor analysis may result in new variables. “Quality” refers essentially to distinctions, as already pointed out by Aristotle. He discusses the term “qualitative” commenting: “By a quality I mean that in virtue of which things are said to be qualified somehow” (Aristotle 1984:14). Quality is about what something is or has, which means that the distinction from its environment is crucial. We see qualitative research as a process in which significant new distinctions are made to the scholarly community; to make distinctions is a key aspect of obtaining new knowledge; a point, as we will see, that also has implications for “quantitative research.” The notion of being “significant” is paramount. New distinctions by themselves are not enough; just adding concepts only increases complexity without furthering our knowledge. The significance of new distinctions is judged against the communal knowledge of the research community. To enable this discussion and judgements central elements of rational discussion are required (cf. Habermas [1981] 1987 ; Davidsson [ 1988 ] 2001) to identify what is new and relevant scientific knowledge. Relatedly, Ragin alludes to the idea of new and useful knowledge at a more concrete level: “Qualitative methods are appropriate for in-depth examination of cases because they aid the identification of key features of cases. Most qualitative methods enhance data” (1994:79). When Becker ( 1963 ) studied deviant behavior and investigated how people became marihuana smokers, he made distinctions between the ways in which people learned how to smoke. This is a classic example of how the strategy of “getting close” to the material, for example the text, people or pictures that are subject to analysis, may enable researchers to obtain deeper insight and new knowledge by making distinctions – in this instance on the initial notion of learning how to smoke. Others have stressed the making of distinctions in relation to coding or theorizing. Emerson et al. ( 1995 ), for example, hold that “qualitative coding is a way of opening up avenues of inquiry,” meaning that the researcher identifies and develops concepts and analytic insights through close examination of and reflection on data (Emerson et al. 1995 :151). Goodwin and Horowitz highlight making distinctions in relation to theory-building writing: “Close engagement with their cases typically requires qualitative researchers to adapt existing theories or to make new conceptual distinctions or theoretical arguments to accommodate new data” ( 2002 : 37). In the ideal-typical quantitative research only existing and so to speak, given, variables would be used. If this is the case no new distinction are made. But, would not also many “quantitative” researchers make new distinctions?
Process does not merely suggest that research takes time. It mainly implies that qualitative new knowledge results from a process that involves several phases, and above all iteration. Qualitative research is about oscillation between theory and evidence, analysis and generating material, between first- and second -order constructs (Schütz 1962 :59), between getting in contact with something, finding sources, becoming deeply familiar with a topic, and then distilling and communicating some of its essential features. The main point is that the categories that the researcher uses, and perhaps takes for granted at the beginning of the research process, usually undergo qualitative changes resulting from what is found. Becker describes how he tested hypotheses and let the jargon of the users develop into theoretical concepts. This happens over time while the study is being conducted, exemplifying what we mean by process.
In the research process, a pilot-study may be used to get a first glance of, for example, the field, how to approach it, and what methods can be used, after which the method and theory are chosen or refined before the main study begins. Thus, the empirical material is often central from the start of the project and frequently leads to adjustments by the researcher. Likewise, during the main study categories are not fixed; the empirical material is seen in light of the theory used, but it is also given the opportunity to kick back, thereby resisting attempts to apply theoretical straightjackets (Becker 1970 :43). In this process, coding and analysis are interwoven, and thus are often important steps for getting closer to the phenomenon and deciding what to focus on next. Becker began his research by interviewing musicians close to him, then asking them to refer him to other musicians, and later on doubling his original sample of about 25 to include individuals in other professions (Becker 1973:46). Additionally, he made use of some participant observation, documents, and interviews with opiate users made available to him by colleagues. As his inductive theory of deviance evolved, Becker expanded his sample in order to fine tune it, and test the accuracy and generality of his hypotheses. In addition, he introduced a negative case and discussed the null hypothesis ( 1963 :44). His phasic career model is thus based on a research design that embraces processual work. Typically, process means to move between “theory” and “material” but also to deal with negative cases, and Becker ( 1998 ) describes how discovering these negative cases impacted his research design and ultimately its findings.
Obviously, all research is process-oriented to some degree. The point is that the ideal-typical quantitative process does not imply change of the data, and iteration between data, evidence, hypotheses, empirical work, and theory. The data, quantified variables, are, in most cases fixed. Merging of data, which of course can be done in a quantitative research process, does not mean new data. New hypotheses are frequently tested, but the “raw data is often the “the same.” Obviously, over time new datasets are made available and put into use.
Another characteristic that is emphasized in our sample is that qualitative researchers – and in particular ethnographers – can, or as Goffman put it, ought to ( 1989 ), get closer to the phenomenon being studied and their data than quantitative researchers (for example, Silverman 2009 :85). Put differently, essentially because of their methods qualitative researchers get into direct close contact with those being investigated and/or the material, such as texts, being analyzed. Becker started out his interview study, as we noted, by talking to those he knew in the field of music to get closer to the phenomenon he was studying. By conducting interviews he got even closer. Had he done more observations, he would undoubtedly have got even closer to the field.
Additionally, ethnographers’ design enables researchers to follow the field over time, and the research they do is almost by definition longitudinal, though the time in the field is studied obviously differs between studies. The general characteristic of closeness over time maximizes the chances of unexpected events, new data (related, for example, to archival research as additional sources, and for ethnography for situations not necessarily previously thought of as instrumental – what Mannay and Morgan ( 2015 ) term the “waiting field”), serendipity (Merton and Barber 2004 ; Åkerström 2013 ), and possibly reactivity, as well as the opportunity to observe disrupted patterns that translate into exemplars of negative cases. Two classic examples of this are Becker’s finding of what medical students call “crocks” (Becker et al. 1961 :317), and Geertz’s ( 1973 ) study of “deep play” in Balinese society.
By getting and staying so close to their data – be it pictures, text or humans interacting (Becker was himself a musician) – for a long time, as the research progressively focuses, qualitative researchers are prompted to continually test their hunches, presuppositions and hypotheses. They test them against a reality that often (but certainly not always), and practically, as well as metaphorically, talks back, whether by validating them, or disqualifying their premises – correctly, as well as incorrectly (Fine 2003 ; Becker 1970 ). This testing nonetheless often leads to new directions for the research. Becker, for example, says that he was initially reading psychological theories, but when facing the data he develops a theory that looks at, you may say, everything but psychological dispositions to explain the use of marihuana. Especially researchers involved with ethnographic methods have a fairly unique opportunity to dig up and then test (in a circular, continuous and temporal way) new research questions and findings as the research progresses, and thereby to derive previously unimagined and uncharted distinctions by getting closer to the phenomenon under study.
Let us stress that getting close is by no means restricted to ethnography. The notion of hermeneutic circle and hermeneutics as a general way of understanding implies that we must get close to the details in order to get the big picture. This also means that qualitative researchers can literally also make use of details of pictures as evidence (cf. Harper 2002). Thus, researchers may get closer both when generating the material or when analyzing it.
Quantitative research, we maintain, in the ideal-typical representation cannot get closer to the data. The data is essentially numbers in tables making up the variables (Franzosi 2016 :138). The data may originally have been “qualitative,” but once reduced to numbers there can only be a type of “hermeneutics” about what the number may stand for. The numbers themselves, however, are non-ambiguous. Thus, in quantitative research, interpretation, if done, is not about the data itself—the numbers—but what the numbers stand for. It follows that the interpretation is essentially done in a more “speculative” mode without direct empirical evidence (cf. Becker 2017 ).
Improved Understanding
While distinction, process and getting closer refer to the qualitative work of the researcher, improved understanding refers to its conditions and outcome of this work. Understanding cuts deeper than explanation, which to some may mean a causally verified correlation between variables. The notion of explanation presupposes the notion of understanding since explanation does not include an idea of how knowledge is gained (Manicas 2006 : 15). Understanding, we argue, is the core concept of what we call the outcome of the process when research has made use of all the other elements that were integrated in the research. Understanding, then, has a special status in qualitative research since it refers both to the conditions of knowledge and the outcome of the process. Understanding can to some extent be seen as the condition of explanation and occurs in a process of interpretation, which naturally refers to meaning (Gadamer 1990 ). It is fundamentally connected to knowing, and to the knowing of how to do things (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ). Conceptually the term hermeneutics is used to account for this process. Heidegger ties hermeneutics to human being and not possible to separate from the understanding of being ( 1988 ). Here we use it in a broader sense, and more connected to method in general (cf. Seiffert 1992 ). The abovementioned aspects – for example, “objectivity” and “reflexivity” – of the approach are conditions of scientific understanding. Understanding is the result of a circular process and means that the parts are understood in light of the whole, and vice versa. Understanding presupposes pre-understanding, or in other words, some knowledge of the phenomenon studied. The pre-understanding, even in the form of prejudices, are in qualitative research process, which we see as iterative, questioned, which gradually or suddenly change due to the iteration of data, evidence and concepts. However, qualitative research generates understanding in the iterative process when the researcher gets closer to the data, e.g., by going back and forth between field and analysis in a process that generates new data that changes the evidence, and, ultimately, the findings. Questioning, to ask questions, and put what one assumes—prejudices and presumption—in question, is central to understand something (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ; Gadamer 1990 :368–384). We propose that this iterative process in which the process of understanding occurs is characteristic of qualitative research.
Improved understanding means that we obtain scientific knowledge of something that we as a scholarly community did not know before, or that we get to know something better. It means that we understand more about how parts are related to one another, and to other things we already understand (see also Fine and Hallett 2014 ). Understanding is an important condition for qualitative research. It is not enough to identify correlations, make distinctions, and work in a process in which one gets close to the field or phenomena. Understanding is accomplished when the elements are integrated in an iterative process.
It is, moreover, possible to understand many things, and researchers, just like children, may come to understand new things every day as they engage with the world. This subjective condition of understanding – namely, that a person gains a better understanding of something –is easily met. To be qualified as “scientific,” the understanding must be general and useful to many; it must be public. But even this generally accessible understanding is not enough in order to speak of “scientific understanding.” Though we as a collective can increase understanding of everything in virtually all potential directions as a result also of qualitative work, we refrain from this “objective” way of understanding, which has no means of discriminating between what we gain in understanding. Scientific understanding means that it is deemed relevant from the scientific horizon (compare Schütz 1962 : 35–38, 46, 63), and that it rests on the pre-understanding that the scientists have and must have in order to understand. In other words, the understanding gained must be deemed useful by other researchers, so that they can build on it. We thus see understanding from a pragmatic, rather than a subjective or objective perspective. Improved understanding is related to the question(s) at hand. Understanding, in order to represent an improvement, must be an improvement in relation to the existing body of knowledge of the scientific community (James [ 1907 ] 1955). Scientific understanding is, by definition, collective, as expressed in Weber’s famous note on objectivity, namely that scientific work aims at truths “which … can claim, even for a Chinese, the validity appropriate to an empirical analysis” ([1904] 1949 :59). By qualifying “improved understanding” we argue that it is a general defining characteristic of qualitative research. Becker‘s ( 1966 ) study and other research of deviant behavior increased our understanding of the social learning processes of how individuals start a behavior. And it also added new knowledge about the labeling of deviant behavior as a social process. Few studies, of course, make the same large contribution as Becker’s, but are nonetheless qualitative research.
Understanding in the phenomenological sense, which is a hallmark of qualitative research, we argue, requires meaning and this meaning is derived from the context, and above all the data being analyzed. The ideal-typical quantitative research operates with given variables with different numbers. This type of material is not enough to establish meaning at the level that truly justifies understanding. In other words, many social science explanations offer ideas about correlations or even causal relations, but this does not mean that the meaning at the level of the data analyzed, is understood. This leads us to say that there are indeed many explanations that meet the criteria of understanding, for example the explanation of how one becomes a marihuana smoker presented by Becker. However, we may also understand a phenomenon without explaining it, and we may have potential explanations, or better correlations, that are not really understood.
We may speak more generally of quantitative research and its data to clarify what we see as an important distinction. The “raw data” that quantitative research—as an idealtypical activity, refers to is not available for further analysis; the numbers, once created, are not to be questioned (Franzosi 2016 : 138). If the researcher is to do “more” or “change” something, this will be done by conjectures based on theoretical knowledge or based on the researcher’s lifeworld. Both qualitative and quantitative research is based on the lifeworld, and all researchers use prejudices and pre-understanding in the research process. This idea is present in the works of Heidegger ( 2001 ) and Heisenberg (cited in Franzosi 2010 :619). Qualitative research, as we argued, involves the interaction and questioning of concepts (theory), data, and evidence.
Ragin ( 2004 :22) points out that “a good definition of qualitative research should be inclusive and should emphasize its key strengths and features, not what it lacks (for example, the use of sophisticated quantitative techniques).” We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. Qualitative research, as defined here, is consequently a combination of two criteria: (i) how to do things –namely, generating and analyzing empirical material, in an iterative process in which one gets closer by making distinctions, and (ii) the outcome –improved understanding novel to the scholarly community. Is our definition applicable to our own study? In this study we have closely read the empirical material that we generated, and the novel distinction of the notion “qualitative research” is the outcome of an iterative process in which both deduction and induction were involved, in which we identified the categories that we analyzed. We thus claim to meet the first criteria, “how to do things.” The second criteria cannot be judged but in a partial way by us, namely that the “outcome” —in concrete form the definition-improves our understanding to others in the scientific community.
We have defined qualitative research, or qualitative scientific work, in relation to quantitative scientific work. Given this definition, qualitative research is about questioning the pre-given (taken for granted) variables, but it is thus also about making new distinctions of any type of phenomenon, for example, by coining new concepts, including the identification of new variables. This process, as we have discussed, is carried out in relation to empirical material, previous research, and thus in relation to theory. Theory and previous research cannot be escaped or bracketed. According to hermeneutic principles all scientific work is grounded in the lifeworld, and as social scientists we can thus never fully bracket our pre-understanding.
We have proposed that quantitative research, as an idealtype, is concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ). Variables are epistemically fixed, but can vary in terms of dimensions, such as frequency or number. Age is an example; as a variable it can take on different numbers. In relation to quantitative research, qualitative research does not reduce its material to number and variables. If this is done the process of comes to a halt, the researcher gets more distanced from her data, and it makes it no longer possible to make new distinctions that increase our understanding. We have above discussed the components of our definition in relation to quantitative research. Our conclusion is that in the research that is called quantitative there are frequent and necessary qualitative elements.
Further, comparative empirical research on researchers primarily working with ”quantitative” approaches and those working with ”qualitative” approaches, we propose, would perhaps show that there are many similarities in practices of these two approaches. This is not to deny dissimilarities, or the different epistemic and ontic presuppositions that may be more or less strongly associated with the two different strands (see Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ). Our point is nonetheless that prejudices and preconceptions about researchers are unproductive, and that as other researchers have argued, differences may be exaggerated (e.g., Becker 1996 : 53, 2017 ; Marchel and Owens 2007 :303; Ragin 1994 ), and that a qualitative dimension is present in both kinds of work.
Several things follow from our findings. The most important result is the relation to quantitative research. In our analysis we have separated qualitative research from quantitative research. The point is not to label individual researchers, methods, projects, or works as either “quantitative” or “qualitative.” By analyzing, i.e., taking apart, the notions of quantitative and qualitative, we hope to have shown the elements of qualitative research. Our definition captures the elements, and how they, when combined in practice, generate understanding. As many of the quotations we have used suggest, one conclusion of our study holds that qualitative approaches are not inherently connected with a specific method. Put differently, none of the methods that are frequently labelled “qualitative,” such as interviews or participant observation, are inherently “qualitative.” What matters, given our definition, is whether one works qualitatively or quantitatively in the research process, until the results are produced. Consequently, our analysis also suggests that those researchers working with what in the literature and in jargon is often called “quantitative research” are almost bound to make use of what we have identified as qualitative elements in any research project. Our findings also suggest that many” quantitative” researchers, at least to some extent, are engaged with qualitative work, such as when research questions are developed, variables are constructed and combined, and hypotheses are formulated. Furthermore, a research project may hover between “qualitative” and “quantitative” or start out as “qualitative” and later move into a “quantitative” (a distinct strategy that is not similar to “mixed methods” or just simply combining induction and deduction). More generally speaking, the categories of “qualitative” and “quantitative,” unfortunately, often cover up practices, and it may lead to “camps” of researchers opposing one another. For example, regardless of the researcher is primarily oriented to “quantitative” or “qualitative” research, the role of theory is neglected (cf. Swedberg 2017 ). Our results open up for an interaction not characterized by differences, but by different emphasis, and similarities.
Let us take two examples to briefly indicate how qualitative elements can fruitfully be combined with quantitative. Franzosi ( 2010 ) has discussed the relations between quantitative and qualitative approaches, and more specifically the relation between words and numbers. He analyzes texts and argues that scientific meaning cannot be reduced to numbers. Put differently, the meaning of the numbers is to be understood by what is taken for granted, and what is part of the lifeworld (Schütz 1962 ). Franzosi shows how one can go about using qualitative and quantitative methods and data to address scientific questions analyzing violence in Italy at the time when fascism was rising (1919–1922). Aspers ( 2006 ) studied the meaning of fashion photographers. He uses an empirical phenomenological approach, and establishes meaning at the level of actors. In a second step this meaning, and the different ideal-typical photographers constructed as a result of participant observation and interviews, are tested using quantitative data from a database; in the first phase to verify the different ideal-types, in the second phase to use these types to establish new knowledge about the types. In both of these cases—and more examples can be found—authors move from qualitative data and try to keep the meaning established when using the quantitative data.
A second main result of our study is that a definition, and we provided one, offers a way for research to clarify, and even evaluate, what is done. Hence, our definition can guide researchers and students, informing them on how to think about concrete research problems they face, and to show what it means to get closer in a process in which new distinctions are made. The definition can also be used to evaluate the results, given that it is a standard of evaluation (cf. Hammersley 2007 ), to see whether new distinctions are made and whether this improves our understanding of what is researched, in addition to the evaluation of how the research was conducted. By making what is qualitative research explicit it becomes easier to communicate findings, and it is thereby much harder to fly under the radar with substandard research since there are standards of evaluation which make it easier to separate “good” from “not so good” qualitative research.
To conclude, our analysis, which ends with a definition of qualitative research can thus both address the “internal” issues of what is qualitative research, and the “external” critiques that make it harder to do qualitative research, to which both pressure from quantitative methods and general changes in society contribute.
Acknowledgements
Financial Support for this research is given by the European Research Council, CEV (263699). The authors are grateful to Susann Krieglsteiner for assistance in collecting the data. The paper has benefitted from the many useful comments by the three reviewers and the editor, comments by members of the Uppsala Laboratory of Economic Sociology, as well as Jukka Gronow, Sebastian Kohl, Marcin Serafin, Richard Swedberg, Anders Vassenden and Turid Rødne.
Biographies
is professor of sociology at the Department of Sociology, Uppsala University and Universität St. Gallen. His main focus is economic sociology, and in particular, markets. He has published numerous articles and books, including Orderly Fashion (Princeton University Press 2010), Markets (Polity Press 2011) and Re-Imagining Economic Sociology (edited with N. Dodd, Oxford University Press 2015). His book Ethnographic Methods (in Swedish) has already gone through several editions.
is associate professor of sociology at the Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger. His research has been published in journals such as Social Psychology Quarterly, Sociological Theory, Teaching Sociology, and Music and Arts in Action. As an ethnographer he is working on a book on he social world of big-wave surfing.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Patrik Aspers, Email: [email protected] .
Ugo Corte, Email: [email protected] .
- Åkerström M. Curiosity and serendipity in qualitative research. Qualitative Sociology Review. 2013; 9 (2):10–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alford, Robert R. 1998. The craft of inquiry. Theories, methods, evidence . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Alvesson M, Kärreman D. Qualitative research and theory development . Mystery as method . London: SAGE Publications; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aspers, Patrik. 2006. Markets in Fashion, A Phenomenological Approach. London Routledge.
- Atkinson P. Qualitative research. Unity and diversity. Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2005; 6 (3):1–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Outsiders. Studies in the sociology of deviance . New York: The Free Press; 1963. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Whose side are we on? Social Problems. 1966; 14 (3):239–247. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Sociological work. Method and substance. New Brunswick: Transaction Books; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. The epistemology of qualitative research. In: Richard J, Anne C, Shweder RA, editors. Ethnography and human development. Context and meaning in social inquiry. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1996. pp. 53–71. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Tricks of the trade. How to think about your research while you're doing it. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker, Howard S. 2017. Evidence . Chigaco: University of Chicago Press.
- Becker H, Geer B, Hughes E, Strauss A. Boys in White, student culture in medical school. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers; 1961. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berezin M. How do we know what we mean? Epistemological dilemmas in cultural sociology. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):141–151. [ Google Scholar ]
- Best, Joel. 2004. Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , eds . Charles, Ragin, Joanne, Nagel, and Patricia White, 53-54. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf .
- Biernacki R. Humanist interpretation versus coding text samples. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):173–188. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blumer H. Symbolic interactionism: Perspective and method. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brady H, Collier D, Seawright J. Refocusing the discussion of methodology. In: Henry B, David C, editors. Rethinking social inquiry. Diverse tools, shared standards. Lanham: Rowman and Littlefield; 2004. pp. 3–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown AP. Qualitative method and compromise in applied social research. Qualitative Research. 2010; 10 (2):229–248. [ Google Scholar ]
- Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. London: Sage; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Corte, Ugo, and Katherine Irwin. 2017. “The Form and Flow of Teaching Ethnographic Knowledge: Hands-on Approaches for Learning Epistemology” Teaching Sociology 45(3): 209-219.
- Creswell JW. Research design. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches. 3. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidsson D. The myth of the subjective. In: Davidsson D, editor. Subjective, intersubjective, objective. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1988. pp. 39–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK. The research act: A theoretical introduction to Ssociological methods. Chicago: Aldine Publishing Company Publishers; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. Collecting and interpreting qualitative materials. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2003. pp. 1–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. The Sage handbook of qualitative research. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2005. pp. 1–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emerson RM, editor. Contemporary field research. A collection of readings. Prospect Heights: Waveland Press; 1988. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emerson RM, Fretz RI, Shaw LL. Writing ethnographic fieldnotes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Esterberg KG. Qualitative methods in social research. Boston: McGraw-Hill; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine, Gary Alan. 1995. Review of “handbook of qualitative research.” Contemporary Sociology 24 (3): 416–418.
- Fine, Gary Alan. 2003. “ Toward a Peopled Ethnography: Developing Theory from Group Life.” Ethnography . 4(1):41-60.
- Fine GA, Hancock BH. The new ethnographer at work. Qualitative Research. 2017; 17 (2):260–268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine GA, Hallett T. Stranger and stranger: Creating theory through ethnographic distance and authority. Journal of Organizational Ethnography. 2014; 3 (2):188–203. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. Qualitative research. State of the art. Social Science Information. 2002; 41 (1):5–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. Designing qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Frankfort-Nachmias C, Nachmias D. Research methods in the social sciences. 5. London: Edward Arnold; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Franzosi R. Sociology, narrative, and the quality versus quantity debate (Goethe versus Newton): Can computer-assisted story grammars help us understand the rise of Italian fascism (1919- 1922)? Theory and Society. 2010; 39 (6):593–629. [ Google Scholar ]
- Franzosi R. From method and measurement to narrative and number. International journal of social research methodology. 2016; 19 (1):137–141. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gadamer, Hans-Georg. 1990. Wahrheit und Methode, Grundzüge einer philosophischen Hermeneutik . Band 1, Hermeneutik. Tübingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
- Gans H. Participant Observation in an Age of “Ethnography” Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1999; 28 (5):540–548. [ Google Scholar ]
- Geertz C. The interpretation of cultures. New York: Basic Books; 1973. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert N. Researching social life. 3. London: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaeser A. Hermeneutic institutionalism: Towards a new synthesis. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 :207–241. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm L. Strauss. [1967] 2010. The discovery of grounded theory. Strategies for qualitative research. Hawthorne: Aldine.
- Goertz G, Mahoney J. A tale of two cultures: Qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goffman E. On fieldwork. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1989; 18 (2):123–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodwin J, Horowitz R. Introduction. The methodological strengths and dilemmas of qualitative sociology. Qualitative Sociology. 2002; 25 (1):33–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Habermas, Jürgen. [1981] 1987. The theory of communicative action . Oxford: Polity Press.
- Hammersley M. The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education. 2007; 30 (3):287–305. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley, Martyn. 2013. What is qualitative research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
- Hammersley M. What is ethnography? Can it survive should it? Ethnography and Education. 2018; 13 (1):1–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M, Atkinson P. Ethnography . Principles in practice . London: Tavistock Publications; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heidegger M. Sein und Zeit. Tübingen: Max Niemeyer Verlag; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heidegger, Martin. 1988. 1923. Ontologie. Hermeneutik der Faktizität, Gesamtausgabe II. Abteilung: Vorlesungen 1919-1944, Band 63, Frankfurt am Main: Vittorio Klostermann.
- Hempel CG. Philosophy of the natural sciences. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 1966. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hood JC. Teaching against the text. The case of qualitative methods. Teaching Sociology. 2006; 34 (3):207–223. [ Google Scholar ]
- James W. Pragmatism. New York: Meredian Books; 1907. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jovanović G. Toward a social history of qualitative research. History of the Human Sciences. 2011; 24 (2):1–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kalof L, Dan A, Dietz T. Essentials of social research. London: Open University Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Katz J. Situational evidence: Strategies for causal reasoning from observational field notes. Sociological Methods & Research. 2015; 44 (1):108–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane RO, Sidney S, Verba S. Scientific inference in qualitative research. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1994. Designing social inquiry. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamont M. Evaluating qualitative research: Some empirical findings and an agenda. In: Lamont M, White P, editors. Report from workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation; 2004. pp. 91–95. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamont M, Swidler A. Methodological pluralism and the possibilities and limits of interviewing. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):153–171. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lazarsfeld P, Barton A. Some functions of qualitative analysis in social research. In: Kendall P, editor. The varied sociology of Paul Lazarsfeld. New York: Columbia University Press; 1982. pp. 239–285. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lichterman, Paul, and Isaac Reed I (2014), Theory and Contrastive Explanation in Ethnography. Sociological methods and research. Prepublished 27 October 2014; 10.1177/0049124114554458.
- Lofland J, Lofland L. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. 3. Belmont: Wadsworth; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lofland J, Snow DA, Anderson L, Lofland LH. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. 4. Belmont: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Long AF, Godfrey M. An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2004; 7 (2):181–196. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lundberg G. Social research: A study in methods of gathering data. New York: Longmans, Green and Co.; 1951. [ Google Scholar ]
- Malinowski B. Argonauts of the Western Pacific: An account of native Enterprise and adventure in the archipelagoes of Melanesian New Guinea. London: Routledge; 1922. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manicas P. A realist philosophy of science: Explanation and understanding. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marchel C, Owens S. Qualitative research in psychology. Could William James get a job? History of Psychology. 2007; 10 (4):301–324. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McIntyre LJ. Need to know. Social science research methods. Boston: McGraw-Hill; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Merton RK, Barber E. The travels and adventures of serendipity . A Study in Sociological Semantics and the Sociology of Science. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mannay D, Morgan M. Doing ethnography or applying a qualitative technique? Reflections from the ‘waiting field‘ Qualitative Research. 2015; 15 (2):166–182. [ Google Scholar ]
- Neuman LW. Basics of social research. Qualitative and quantitative approaches. 2. Boston: Pearson Education; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin CC. Constructing social research. The unity and diversity of method. Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin, Charles C. 2004. Introduction to session 1: Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , 22, ed. Charles C. Ragin, Joane Nagel, Patricia White. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf
- Rawls, Anne. 2018. The Wartime narrative in US sociology, 1940–7: Stigmatizing qualitative sociology in the name of ‘science,’ European Journal of Social Theory (Online first).
- Schütz A. Collected papers I: The problem of social reality. The Hague: Nijhoff; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Seiffert H. Einführung in die Hermeneutik. Tübingen: Franke; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. Doing qualitative research. A practical handbook. 2. London: SAGE Publications; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. A very short, fairly interesting and reasonably cheap book about qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. What counts as qualitative research? Some cautionary comments. Qualitative Sociology Review. 2013; 9 (2):48–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Small ML. “How many cases do I need?” on science and the logic of case selection in field-based research. Ethnography. 2009; 10 (1):5–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Small, Mario L 2008. Lost in translation: How not to make qualitative research more scientific. In Workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research, ed in Michelle Lamont, and Patricia White, 165–171. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
- Snow DA, Anderson L. Down on their luck: A study of homeless street people. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Snow DA, Morrill C. New ethnographies: Review symposium: A revolutionary handbook or a handbook for revolution? Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1995; 24 (3):341–349. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL. Qualitative analysis for social scientists. 14. Chicago: Cambridge University Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL, Corbin JM. Basics of qualitative research. Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 2. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swedberg, Richard. 2017. Theorizing in sociological research: A new perspective, a new departure? Annual Review of Sociology 43: 189–206.
- Swedberg R. The new 'Battle of Methods'. Challenge January–February. 1990; 3 (1):33–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Timmermans S, Tavory I. Theory construction in qualitative research: From grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociological Theory. 2012; 30 (3):167–186. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trier-Bieniek A. Framing the telephone interview as a participant-centred tool for qualitative research. A methodological discussion. Qualitative Research. 2012; 12 (6):630–644. [ Google Scholar ]
- Valsiner J. Data as representations. Contextualizing qualitative and quantitative research strategies. Social Science Information. 2000; 39 (1):99–113. [ Google Scholar ]
- Weber, Max. 1904. 1949. Objectivity’ in social Science and social policy. Ed. Edward A. Shils and Henry A. Finch, 49–112. New York: The Free Press.
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Sign Up Free
Do you want a free Survey Software?
We have the #1 Online Survey Maker Software to get actionable user insights.
Qualitative Research Methods: Types, Examples, and Analysis

In a universe swarming with data, numbers, and algorithms, lies a lesser-known realm where emotions, stories, and intimate revelations take center stage. When you want to get inside your customers’ heads to understand their thoughts, feelings, perceptions, beliefs, and emotions, numbers are unlikely to provide a complete picture.
Let’s set the scene: picture a cozy bakery buzzing with conversations. People from different walks of life gather, each carrying a unique story to tell. You observe that your sale of pancakes is more than that of pastries, numerical data will tell you that much. But numbers won’t tell you why.
This is exactly where qualitative surveys come into play; they take you right to the heart of people’s minds and experiences – the “why” behind the statistics.
Quantitative data may offer a bird’s-eye view of the crowd, but qualitative surveys open the doorways to your audience’s individual tales. In this blog, we are going to explore qualitative research, its types, analytical procedures, positive and negative aspects, and examples.
Here we go!
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is a branch of market research that involves collecting and analyzing qualitative data through open-ended communication. The primary purpose of conducting qualitative research is to understand the individual’s thoughts, feelings, opinions, and reasons behind these emotions.
It is used to gather in-depth and rich insights into a particular topic. Understanding how your audience feels about a specific subject helps make informed decisions in research.
As opposed to quantitative research, qualitative research does not deal with the collection of numerical data for statistical analysis. The application of this research method is usually found in humanities and social science subjects like sociology, history, anthropology, health science, education, etc.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative research methods are designed to understand the behavior and perception of the target audience about a particular subject.
Qualitative research methods include observations, one-on-one interviews, case study research, focus groups, ethnographic research, phenomenology, and grounded theory.
Let’s discuss them one by one.
1. Observations
Observation is one of the oldest qualitative methods of research used to collect systematic data using subjective methodologies. It is based on five primary sense organs – smell, sight, taste, touch, and hearing, and their functioning. This method focuses on characteristics and qualities rather than numbers.
The qualitative observation technique involves observing the interaction patterns in a particular situation. Researchers collect data by closely watching the behaviors of others. They rely on their ability to observe the target audience rather than communicating with people about their thoughts on a particular subject.
2. One-on-One Interviews
Conducting one-on-one interviews is one of the most common types of qualitative research methods. Although both open-ended and closed-ended questions can be a part of these interviews, open-ended conservation between researchers and participants related to a particular subject is still the preferred mode of communication. This is to gather in-depth qualitative data for the research purpose.
Here, the researcher asks pre-determined questions to the participants to collect specific information about their research topic. Interviews can be conducted face-to-face, by email, or by phone. The drawback of this method is that sometimes the participants feel uncomfortable sharing honest answers with the researcher.
3. Focus Groups
A Focus group involves collecting qualitative data by conducting a group discussion of 6-12 members along with a moderator related to a particular subject. Here the moderator asks respondents a set of predetermined questions so that they can interact with each other and form a group discussion. It helps researchers to collect rich qualitative data about their market research.
However, it is essential to ensure that the moderator asks open-ended questions like “how,” “what,” and “why” that will enable participants to share their thoughts and feelings.
Close-ended questions like “yes” and “no” should be avoided as they do not lead to engagement among participants.
4. Case Study Research
A case study is another example of qualitative research that involves a comprehensive examination of a particular subject, person, or event.

This method is used to obtain in-depth data and complete knowledge of the subject. The data is collected from various sources like interviews and observation to supplement the conclusion.
This qualitative approach is extensively used in the field of social sciences, law, business, and health. Many companies use this technique when marketing their products/services to new customers. It tells them how their business offerings can solve a particular problem. Let’s discuss an example of this method of qualitative research.
5. Digital Ethnography
This is an innovative form of qualitative research that focuses on understanding people and their cultures in the context of the digital realm. Digital ethnography aims to study individuals’ behavior, interactions, and social dynamics within online environments and digital communities.
In digital ethnography, the researcher acts as both an observer and a participant in these said online communities to gain firsthand insight into the lifestyles, cultures, and traditions of people navigating these digital landscapes.
Unlike traditional ethnography, digital ethnography is more efficient and accessible. The studies are conducted remotely, reducing the need for extended physical presence in a specific location, and the data collection process is often more streamlined.
6. Grounded Theory
This is another data collection method of qualitative research used across various disciplines. The Grounded Theory aims to provide the reasons, theories, and explanations behind an event. It focuses on why a course of action has happened the way it did.
The grounded theory model collects and analyzes the data to develop new theories about the subject. The data is collected using different techniques like observation, literature review, and document analysis.
This qualitative method is majorly used in business for conducting user satisfaction surveys to explain why a customer purchases a particular product or service. It helps companies in managing customer loyalty.
Watch: How to Create a Customer Satisfaction Survey
7. Phenomenology
Phenomenology is another qualitative research example that describes how an individual experiences or feels about a particular event. It also explores the experience of a specific event in a community.
Here, the researcher interviews people who have experienced a particular event to find similarities between their experiences. The researcher can also record what they learn from the target audience to maintain the credibility of the data.
Although this qualitative technique depends majorly on interviews, other data collection methods like observation, interviews, and survey questionnaires are also used to supplement the findings. The application of this method is found in psychology, philosophy, and education.
For example, to prompt a participant to share their experience around an event they encountered, you can ask:
“What was your experience like when you first encountered [a specific phenomenon or event]?”
8. Record Keeping
This approach involves using existing trustworthy documents and other reliable sources as the basis of data for new research. It’s comparable to visiting a library, where you can explore books and reference materials to gather relevant data that might be helpful for your research.
How Do You Analyze Qualitative Data?

1. Arranging the Data
Qualitative data is collected in different forms like audio recordings, interviews, video transcriptions, etc. This step involves arranging all the collected data in the text format in the spreadsheet. This can be done either manually or with the help of data analysis tools.
2. Organizing the Data
Even after putting the data into a spreadsheet, the data is still messy and hard to read. Due to this, the data needs to be organized in a readable and understandable pattern.
For example, you can organize data based on questions asked. Organize your data in such a way that it appears visually clear. Data organization can be tedious, but it is essential for the next step.
3. Assigning Codes
Developing codes for the data helps simplify the data analysis methods in qualitative research. Assigning code implies categorizing and setting patterns and properties to the collected data. It helps in compressing the vast amount of information collected. By developing codes for your data, you can gather deep insight into the data to make informed business decisions.
4. Analyzing the Data
Qualitative data cannot be analyzed based on any universally accepted equation like quantitative data. Qualitative data analysis depends on the thinking and logical skill of the researcher.

However, there are a few techniques by which you can easily interpret data by identifying themes and patterns between sample responses:
- Checking the data for repetitive words and phrases commonly used by the audience in their answers.
- Comparing the primary and secondary data collection to find the difference between them.
- Scanning the data for expected information that has not been included in answers provided by respondents.
5. Summarizing the Data
The final stage is to link the qualitative data to the hypothesis. Highlight significant themes, patterns, and trends by using essential quotes from the data, as well as any possible contradictions.

One of the main things about qualitative data is that there isn’t a single, formal way to collect and analyze data. Each research project will have its own set of methods and techniques that it needs to use.
The key is to look at the specific needs of each project and change the research method accordingly.
Advantages and Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative market research techniques offer a more comprehensive and complete picture of the subject than quantitative research, which focuses on specific and narrow areas. Other advantages of using qualitative research methods are:
- Explore the subject in-depth: Qualitative research is personal and offers a deep understanding of the respondent’s feelings, thoughts, and actions so that the researcher can perform an in-depth analysis of the subject.
- Promotes discussion: Qualitative research methods are open-ended in approach rather than rigorously following a predetermined set of questions. It adds context to the research rather than just numbers.
- More flexibility: The interviewer can study and ask questions on the subject they feel is pertinent or had not previously thought about during the discussions. Moreover, open-ended questions enable respondents to be free to share their thoughts, leading to more information.
- Capture trends as they change: Qualitative research can track how people’s feelings and attitudes change over time. Respondents’ opinions can change during the conversation, and qualitative research can show this.
With that being said, however, we do not mean that qualitative data is entirely devoid of flaws. Like most things, it, too, has its fair share of limitations, the prime among them being:
- Subjectivity: Qualitative data can be influenced by the researcher’s bias or interpretation, potentially affecting the objectivity of the findings. The absence of strict guidelines in qualitative research can lead to variations in data collection and analysis too.
- Time-Consuming & Resource-Intensive: Conducting qualitative research can be a lengthy process, from data collection through transcription and analysis. It also often requires skilled researchers, making it more resource-intensive compared to some quantitative methods.
- Difficulty in Analysis: Analyzing qualitative data can be complex, as it involves coding, categorizing, and interpreting open-ended responses. This data category often does not lend itself well to traditional statistical tests, limiting the depth of statistical analysis as well.
- Challenges in Replication: Replicating qualitative studies can be challenging due to the unique context and interactions involved.

Advantages of Using Website Surveys for Qualitative Research
The role of surveys and questionnaires in collecting quantitative data is pretty obvious, but how exactly would you use them to capture qualitative data, and why? Well, for starters, website surveys offer numerous advantages here, such as letting researchers explore diverse perspectives, collect rich and detailed data, conduct cost-effective and time-efficient studies, etc.
Let’s have a brief rundown of the significant benefits below:
Reach and Diversity: Website surveys enable researchers to engage with a diverse and global audience. They break geographical barriers, allowing participation from individuals residing in different regions, cultures, and backgrounds, leading to a richer pool of perspectives.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Conducting traditional face-to-face qualitative research can be expensive and time-consuming. In contrast, website surveys are cost-effective, as they eliminate the need for travel, venue rentals, and other logistical expenses.
- Convenience and Flexibility: Website surveys offer unparalleled convenience to both researchers and participants. Respondents can take part in the study at their own pace and preferred time, promoting higher response rates and reducing non-response bias.
- Anonymity and Honesty: Participants often feel more comfortable expressing themselves honestly in online surveys. Anonymity ensures confidentiality, encouraging candid responses, and allowing researchers to gain deeper insights into personal experiences and opinions.
- Rich Data Collection: Website surveys can accommodate various question types, including open-ended questions, allowing respondents to elaborate on their thoughts. This results in the collection of rich, detailed, and nuanced data, enriching the qualitative analysis.
- Time-Efficient Data Collection: Website surveys facilitate efficient data collection, reaching a large number of participants in a short span. Researchers can access real-time data, enabling quick analysis and timely decision-making.
- Ease of Analysis: Online survey platforms often provide tools for automated data analysis, simplifying the coding and categorization process. Researchers can swiftly identify themes and patterns, expediting the interpretation of qualitative findings.
- Longitudinal Studies: Website surveys are well-suited for longitudinal studies, as they allow researchers to follow up with the same participants over an extended period. This longitudinal approach enables the exploration of changes in attitudes or behaviors over time.
- Integration with Multimedia: Website surveys can seamlessly incorporate multimedia elements, such as images, videos, or audio clips, enabling respondents to provide more context and depth to their responses.
- Eco-Friendly Approach: By reducing the need for paper and physical materials, website surveys promote a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to data collection, aligning with responsible research practices.
Most website survey tools are equipped with features that efficiently collect and analyze diverse perspectives, ultimately furthering your data collection process. For example:
- Question Customization: These tools allow users to create and customize a wide range of questions, including open-ended, closed-ended, rating scale, and more. This flexibility allows participants to express their thoughts and feelings in their own words, paving the way for gathering diverse qualitative data.
- Anonymity and Confidentiality: Ensuring confidentiality in qualitative research is crucial for building trust and obtaining more accurate and sensitive data. Participants can often remain anonymous when using website survey tools, which can encourage them to provide honest and candid responses.
- Data Analysis Support: Many website survey tools offer built-in data analysis features, such as basic statistical summaries and visualizations. While these features are more suited for quantitative data, they can still aid in organizing and understanding qualitative responses, making the analysis process more manageable.
- Flexibility in Survey Design: Researchers can use skip logic and branching features in these tools to create dynamic surveys that adapt based on participants’ responses. This can be greatly valuable in qualitative research, where participants’ experiences might vary widely.
- Ease of Participation: Participants can access website surveys using various devices like computers, tablets, or smartphones, making it convenient and accessible for them to take part in the research. This ease of participation can contribute to a higher response rate and a more diverse participant pool.
- Data Storage and Security: Many website survey tools offer secure data storage and backup, ensuring the safety of the collected qualitative data. This feature is essential for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of participants’ responses.
Examples of Website Survey Questions for Qualitative Research
These examples can greatly help in targeting customers through Click-to-WhatsApp Ads on various social media platforms. Crafting effective survey questions is crucial for qualitative research. Ensuring clarity, avoiding leading questions, and maintaining a balanced mix of question types is paramount if you are looking to gather comprehensive and valuable qualitative data.
With well-designed website survey questions, you can delve deep into participants’ thoughts, emotions, and experiences, providing a solid foundation for insightful qualitative analysis.
Let’s explore some of the prime examples:
1. Open-Ended Questions (Exploratory):
- “Please describe your experience with our product/service in your own words.”
- “What are the main challenges you face in your daily work?”

2. Multiple-Choice Questions (Categorization):
“Which age group do you belong to?”
- 18-25 years
- 26-35 years
- 36-45 years
- 46-55 years

3. Likert Scale Questions (Rating/Opinion): “On a scale of 1 to 5, how satisfied are you with our customer support?” 1 (Not satisfied at all) 2 (Slightly satisfied) 3 (Moderately satisfied) 4 (Very satisfied) 5 (Extremely satisfied)

4. Ranking Questions (Preference):
“Please rank the following factors in order of importance for choosing a smartphone:”
- Battery life
- Camera quality
- Processor speed
- Display resolution
5. Semantic Differential Questions (Contrast): “How would you describe our website’s user interface?”
- Difficult _ Easy Unattractive Attractive
- Confusing ___ Clear
6. Picture Choice Questions (Visual Feedback):
“Which logo do you find more appealing for our brand?”
- Option A (Image)
- Option B (Image)
7. Demographic Questions (Participant Profiling):
“Which of the following best describes your occupation?”
- Professional
8. Dichotomous Questions (Yes/No):
- “Have you ever purchased products from our online store?”

9. Follow-Up Probing Questions (In-depth Insight):
- “You mentioned facing challenges at work. Could you please elaborate on the specific challenges you encounter?”
10. Experience-Based Questions (Narrative):
- “Tell us about a memorable customer service experience you’ve had, whether positive or negative.”
Ready to Obtain Quality Data Using Qualitative Research?
So, there you have it all about qualitative research methods: their types, examples, use, and importance. Quantitative research is one of the most effective instruments to understand individuals’ thoughts and feelings or identify their needs and problems.
After figuring out the problem, quantitative research is used to make the conclusion and offer a reliable solution for business.
You can also supplement your qualitative market research with ProProfs Survey Maker to reach your target audience more effectively and in a shorter duration. Use the 15-day free trial to enhance your qualitative research – no commitment, no credit card details!

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Popular Posts in This Category

10 Best Formstack Alternatives in 2024 (Pricing + Features)

What Is a Good Net Promoter Score?

Market Research Surveys – Types, Steps, Tips, & 20+ Questions

How to Collect Website Feedback

What are the Advantages of NPS to My Business
Event Surveys: Survey Questions, Examples & Best Practices
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
The qualitative research process, end-to-end

.css-1nrevy2{position:relative;display:inline-block;} The qualitative research process: step by step guide
Although research processes may vary by methodology or project team, some fundamentals exist across research projects. Below outlines the collective experience that qualitative researchers undertake to conduct research.
Step 1: Determine what to research
Once a researcher has determined a list of potential projects to tackle, they will prioritize projects based on the business's impact, available resourcing, timelines & dependencies to create a research roadmap. For each project, they will also identify the key questions they need to answer in the research.
The researcher should identify the participants they plan to research, and any key attributes that are a 'must-have' or 'nice to have' as these can be influential in determining the research approach (e.g. a niche group may require a longer timeline to recruit).
Researchers will generally aim for a mix of project types. Some may be more tactical or requests from stakeholders, and some will be projects that the researcher has proactively identified as opportunities for strategic research.

Step 2: Identify how to research it
Once the researcher has finalized the research project, they will need to figure out how they will do the work.
Firstly, the researcher will look through secondary data and research (e.g. analytics, previous research reports). Secondary analysis will help determine if there are existing answers to any of the open questions, ensuring that any net-new study doesn't duplicate current work (unless previous research is out of date).
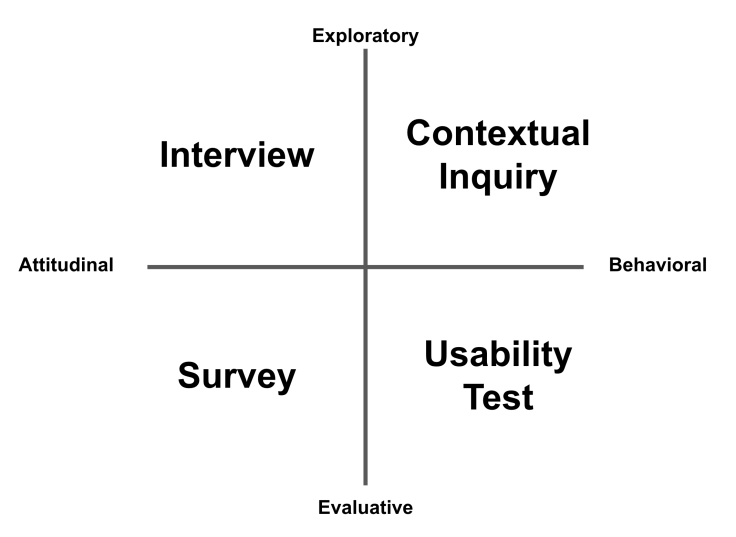
After scoping the research, researchers will determine if the research input needs to be attitudinal (i.e. what someone says) or behavioral (i.e. what someone does); as well as if they need to explore a problem space or evaluate a product – these help determine the methodology to use. There are many methodologies out there, but the main ones you generally will find from a qualitative perspective are:
Interviews [Attitudinal / Exploratory] – semi-structured conversation with a participant focused on a small set of topics. Runs for 30-60 minutes.
Contextual Inquiry [Behavioral / Exploratory] – observation of a participant in their environment. Probing questions may be asked during the observation. Runs for 2-3 hours.
Survey [Attitudinal / Evaluative] – gathering structured information from a sample of people, traditionally to generalize the results to a larger population. Surveys should generally not take participants more than 10 minutes to complete.
Usability Test [Behavioral / Evaluative] – evaluating how representative users are, or are not, able to achieve critical tasks within an experience.
Check out these articles for more information about different methodologies:
When to Use Which User-Experience Research Methods
UX Research Cheat Sheet
Usability.gov
Design Research Kit
Step 3: Get buy-in and alignment from others
Once a researcher has determined what they will be researching and how they will research it, they will generally write up a research plan that includes additional information about the research goals, participant scope, timelines, and dependencies. The plan is typically either a document or presentation shared with stakeholders depending on the company and how they work.
After the research plan is complete, researchers will share the plan for feedback and input from their stakeholders to ensure that the stakeholders have the right expectations going into the research. Stakeholders may ask for additional question topics to be added, ensure that research will be executed against specific timelines, or provide recommendations on how the study will help make product decisions.
At organizations where there is a research team, researchers may also share their plan with other researchers informally or through a 'crit' process. Generally, researchers will provide feedback on the research craft, such as methodologies, participant mixes, and the research goals or questions.
Once the researcher feels confident in their plan, they will either begin to plan the research, or in the case of more junior researchers, get approval from their manager to begin the study.
Step 4: Prepare research
This step is where the researcher will get all of their ducks in a row to execute the research. Preparation activities include:
Equipment: Booking venues, labs, observation rooms, and procuring any appropriate equipment needed to run the study (e.g. cameras, mobile devices).
Participants: Sourcing participants from internal / external databases, reaching out/scheduling participants, managing schedule changes.
Incentives: Find budget, identify incentive type (e.g. Amazon gift card? customer credit? gift baskets), and purchasing.
Assets: Building relevant designs / prototypes (with design or design technologists), creating interview / observation guides and other research tools needed for sessions (e.g. physical cards for in-person card sorts).
Legal & Procurement: Participant waivers or NDAs preparation to ensure they are sent in advance of the research session to participants, vendor procurement, and management.
If Research Operations exists within an organization, they will generally take on most of the load in this area. The researcher will focus on assets required for executing research, such as interview guides.
In some cases, vendors may be engaged for some of these requirements (e.g. labs, participants, and incentive management) if resourcing is not available internally or if a researcher wants a blinded study (i.e. the participant doesn't know what company is running the research). In this case, additional time is incorporated to brief, onboard, and get approvals to work with the vendor.
Step 5: Execute research
Now the researcher gets to research!
Researchers will generally aim to execute research activities for 1–2 weeks, depending on the methodology to ensure they can be efficient in execution. In some more longitudinal methods (e.g., diary studies), or if a participant type is harder to recruit, it may take longer.
In consumer research, there will usually be back up participants available in case of no shows. However, in business or enterprise research, researchers will engage will all recruited participants as participants will generally have relationships with other parts of the company (e.g. sales). It is essential to maintain those relationships post-research.
During sessions, in a perfect world, there is one facilitator (principal researcher). In some cases, a secondary attendee who takes notes – this can be a stakeholder or a more junior researcher who can then learn soft skills from the primary researcher. By delegating note-taking, the principal researcher can focus on driving and managing the participant's conversation.
However, in most cases (especially if there is a "research team of one"), researchers will try to have to do both facilitation and documentation – this can lead to a clunkier conversation as the facilitator attempts to quickly write notes between trying to think of the next question. If a researcher decides to record a session instead, they will have to spend additional time after the research listening to the full recordings and writing notes.
In qualitative research, researchers may begin to see patterns in the findings after five sessions . They may start to tailor the research questions to be more specific to gaps in their understanding.
Researchers may also set up an observation room for stakeholders (or share links to remote sessions) to attend live. Generally, researchers will have a backchannel (e.g., slack, chat, or SMS), so if a stakeholder has a follow-up question to an answer, the researcher can dig deeper. In some cases, researchers will give stakeholders an input form to take their notes that can be shared with the researcher afterward - this can be useful for the researcher to understand how the stakeholder views the research and what the stakeholder perceives as necessary to the research insights.
Step 6: Synthesize and find insights
Once the research capture is complete, the researcher will then aggregate findings to begin to look for common themes (in exploratory) or success rates (in evaluative). Both of these will then lead to insight generation that researchers will then look to tie back to the project's original research goals.
As analysis can be one of the most high-effort tasks in research, researchers will lean towards how to be efficient in their study, generally using digital tools, hacks, or workarounds. Researchers will usually create the analysis process they refine throughout their careers to help them become more efficient.
In cases where researchers are looking to get buy-in for research or capture stakeholder input, they may seem to more visual approaches (e.g. post-it affinity analysis) in war rooms. This process can take longer to process (especially if there is a high volume of data). Still, there can be a higher impact on analyzing research in this way – especially if the researcher is looking to get buy-in for future projects.
Step 7: Create research outputs
After a researcher identifies the key themes and insights, the researcher will reframe these findings to a relevant research output to ensure that stakeholders understand and buy-in to the outcomes. Outputs may include:
Report: Outlines vital findings from research in a document or presentation format. Will most likely include an executive summary, insight themes, and supporting evidence.
Videos: A highlight reel of supporting evidence from crucial findings. Generally seen as more useful and engaging compared to just a report. In most cases, the video will help the research report.
Personas : A written representation of a product's intended users to understand different types of user goals, needs, and behaviors. Also used to help stakeholders build empathy for the end-user of the product.
Journey Map : A visualization of the process that a person goes through to accomplish a goal. Generally created in conjunction with a persona.
Concepts / Wireframes / Designs: If research is evaluative, designs can visualize recommendations.
Storyboarding
Before a researcher makes the output, researchers will spend time planning the structure and storyboarding. Storyboarding is incredibly essential to help researchers define information requirements and ensure they present their findings in the most impactful way to stakeholders.
Having a point of view in outputs
Historically, researchers have tried to stay neutral to the data and not try to have a strong opinion or perspective to let the data speak. However, as researchers become more embedded in the industry, this has shifted to stakeholders wanting a strong point of view or recommendations from researchers that can help other stakeholders (especially product managers and designers) decide the knowledge captured as part of the research.
Having a strong perspective helps researchers have a seat at the table and appear as a trusted advisor/partner in cross-functional settings.
Step 8: Share and follow up on findings
After the research outputs are complete, some researchers will do a "pre-share" or walkthrough with key stakeholders or potential detractors to the research. The purpose of these meetings is to align with stakeholders' expectations and find potential 'watch-outs' (things that may derail a presentation).
Researchers will generally have to share their findings out multiple times to different stakeholder groups and tailor them for each audience. For example, executive meetings will be more higher level than a meeting with a product manager.
After sharing, researchers will follow up with key stakeholders (especially those who provided input to the research) to confirm they understand the findings and identify next steps. Next steps may include incorporating results in product strategy documents, proposals / PRDs, or user stories to ensure that the recommendations or findings have been reflected or sourced.
Keep reading

.css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} Decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next
Decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Open access
- Published: 16 April 2024
How does the external context affect an implementation processes? A qualitative study investigating the impact of macro-level variables on the implementation of goal-oriented primary care
- Ine Huybrechts ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0288-1756 1 , 2 ,
- Anja Declercq 3 , 4 ,
- Emily Verté 1 , 2 ,
- Peter Raeymaeckers 5 na1 &
- Sibyl Anthierens 1 na1
on behalf of the Primary Care Academy
Implementation Science volume 19 , Article number: 32 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
599 Accesses
8 Altmetric
Metrics details
Although the importance of context in implementation science is not disputed, knowledge about the actual impact of external context variables on implementation processes remains rather fragmented. Current frameworks, models, and studies merely describe macro-level barriers and facilitators, without acknowledging their dynamic character and how they impact and steer implementation. Including organizational theories in implementation frameworks could be a way of tackling this problem. In this study, we therefore investigate how organizational theories can contribute to our understanding of the ways in which external context variables shape implementation processes. We use the implementation process of goal-oriented primary care in Belgium as a case.
A qualitative study using in-depth semi-structured interviews was conducted with actors from a variety of primary care organizations. Data was collected and analyzed with an iterative approach. We assessed the potential of four organizational theories to enrich our understanding of the impact of external context variables on implementation processes. The organizational theories assessed are as follows: institutional theory, resource dependency theory, network theory, and contingency theory. Data analysis was based on a combination of inductive and deductive thematic analysis techniques using NVivo 12.
Institutional theory helps to understand mechanisms that steer and facilitate the implementation of goal-oriented care through regulatory and policy measures. For example, the Flemish government issued policy for facilitating more integrated, person-centered care by means of newly created institutions, incentives, expectations, and other regulatory factors. The three other organizational theories describe both counteracting or reinforcing mechanisms. The financial system hampers interprofessional collaboration, which is key for GOC. Networks between primary care providers and health and/or social care organizations on the one hand facilitate GOC, while on the other hand, technology to support interprofessional collaboration is lacking. Contingent variables such as the aging population and increasing workload and complexity within primary care create circumstances in which GOC is presented as a possible answer.
Conclusions
Insights and propositions that derive from organizational theories can be utilized to expand our knowledge on how external context variables affect implementation processes. These insights can be combined with or integrated into existing implementation frameworks and models to increase their explanatory power.
Peer Review reports
Contributions to literature
Knowledge on how external context variables affect implementation processes tends to be rather fragmented. Insights on external context in implementation research often remain limited to merely describing macro-context barriers and facilitators.
Organizational theories contribute to our understanding on the impact of external context to an implementation process by explaining the complex interactions between organizations and their environments.
Findings can be utilized to help explain the mechanism of change in an implementation process and can be combined with or integrated into existing implementation frameworks and models to gain a broader picture on how external context affects implementation processes.
In this study, we integrate organizational theories to provide a profound analysis on how external context influences the implementation of complex interventions. There is a growing recognition that the context in which an intervention takes place highly influences implementation outcomes [ 1 , 2 ]. Despite its importance, researchers are challenged by the lack of a clear definition of context. Most implementation frameworks and models do not define context as such, but describe categories or elements of context, without capturing it as a whole [ 2 , 3 ]. Studies often distinguish between internal and external context: micro- and meso-level internal context variables are specific to a person, team, or organization. Macro-level external context variables consist of variables on a broader, socio-economic and policy level that are beyond one’s control [ 4 ].
Overall, literature provides a rather fragmented and limited perspective on how external context influences the implementation process of a complex intervention. Attempts are made to define, categorize, and conceptualize external context [ 5 , 6 ]. Certain implementation frameworks and models specifically mention external context, such as the conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors [ 7 ], the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research [ 8 ], or the i-PARiHS framework [ 9 ]. However, they remain limited to identifying and describing external context variables. Few studies are conducted that specifically point towards the actual impact of macro-level barriers and facilitators [ 10 , 11 , 12 ] but only provide limited insights in how these shape an implementation process. Nonetheless, external contextual variables can be highly disruptive for an organization’s implementation efforts, for example, when fluctuations in funding occur or when new legislation or technology is introduced [ 13 ]. In order to build a more comprehensive view on external context influences, we need an elaborative theoretical perspective.
Organizational theories as a frame of reference
To better understand how the external context affects the implementation process of a primary care intervention, we build upon research of Birken et al. [ 13 ] who demonstrate the explanatory power of organizational theories. Organizational theories can help explain the complex interactions between organizations and their environments [ 13 ], providing understanding on the impact of external context on the mechanism of change in an implementation process. We focus on three of the theories Birken et al. [ 8 ] put forward: institutional theory, resource dependency theory, and contingency theory. We also include network theory in recognition of the importance of interorganizational context and social ties between various actors, especially in primary care settings which are characterized by a multitude of diverse actors (meaning: participants of a process).
These four organizational theories demonstrate the ways in which organizations interact with their external environment in order to sustain and fulfill their core activities. All four of them do this with a different lens. Institutional theory states that an organization will aim to fulfil the expectations, values, or norms that are posed upon them in order to achieve a fit with their environment [ 14 ]. This theory helps to understand the relationships between organizations and actors and the institutional context in which they operate. Institutions can broadly be defined as a set of expectations for social or organizational behavior that can take the form formal structures such as regulatory entities, legislation, or procedures [ 15 ]. Resource dependency theory explains actions and decisions of organizations in terms of their dependence on critical and important resources. It postulates that organizations will respond to their external environment to secure the resources they need to operate [ 16 , 17 ]. This theory helps to gain insight in how fiscal variables can shape the adoption of an innovation. Contingency theory presupposes that an organizations’ effectiveness depends on the congruence between situational factors and organizational characteristics [ 18 ]. External context variables such as social and economic change and pressure can impact the way in which an innovation will be integrated. Lastly, network theory in its broader sense underlines the strength of networks: collaborating in networks can establish an effectiveness in which outcomes are achieved that could not be realized by individual organizations acting independently. Networks are about connecting or sharing information, resources, activities, and competences of three or more organizations aiming to achieve a shared goal or outcome [ 19 , 20 ]. Investigating networks helps to gain understanding of the importance of the interorganizational context and how social ties between organizations affect the implementation process of a complex intervention.
Goal-oriented care in Flanders as a case
In this study, we focus on the implementation of the approach goal-oriented care (GOC) in primary care in Flanders, the Dutch-speaking region in Belgium. Primary care is a highly institutionalized and regulated setting with a high level of professionalism. Healthcare organizations can be viewed as complex adaptive systems that are increasingly interdependent [ 21 ]. The primary care landscape in Flanders is characterized by many primary care providers (PCPs) being either self-employed or working in group practices or community health centers. They are organized and financed at different levels (federal, regional, local). In 2015–2019, a primary care reform was initiated in Flanders in which the region was geographically divided into 60 primary care zones that are governed by care councils. The Flemish Institute of Primary Care was created as a supporting institution aiming to strengthen the collaboration between primary care health and welfare actors. The complex and multisectoral nature of primary care in Flanders forms an interesting setting to gain understanding in how macro-level context variables affect implementation processes.
The concept of GOC implies a paradigm shift [ 22 ] that shifts away from a disease or problem-oriented focus towards a person-centered focus that departs from “what matters to the patient.” Boeykens et al. [ 23 ] state in their concept analysis that GOC could be described as a healthcare approach encompassing a multifaceted, dynamic, and iterative process underpinned by the patient’s context and values. The process is characterized by three stages: goal elicitations, goal setting, and goal evaluation in which patients’ needs and preferences form the common thread. It is an approach in which PCPs and patients collaborate to identify personal life goals and to align care with those goals [ 23 ]. An illustration of how this manifests at individual level can be found in Table 1 . The concept of GOC was incorporated in Flemish policies and included in the primary care reform in 2015–2019. It has gained interest in research and policy as a potential catalyst for integrated care [ 24 ]. As such, the implementation of GOC in Flanders provides an opportunity to investigate the external context of a complex primary care intervention. Our main research question is as follows: what can organizational theories tell us about the influence of external context variables on the implementation process of GOC?
We assess the potential of four organizational theories to enrich our understanding of the impact of external context variables on implementation processes. The organizational theories assessed are as follows: institutional theory, resource dependency theory, network theory, and contingency theory. Qualitative research methods are most suitable to investigate such complex matters, as they can help answer “how” and “why” questions on implementation [ 25 ]. We conducted online, semi-structured in-depth interviews with various primary care actors. These actors all had some level of experience at either meso- or micro-level with GOC implementation efforts.
Sample selection
For our purposive sample, we used the following inclusion criteria: 1) working in a Flemish health/social care context in which initiatives are taken to implement GOC and 2) having at least 6 months of experience. For recruitment, we made an overview of all possible stakeholders that are active in GOC by calling upon the network of the Primary Care Academy (PCA) Footnote 1 . Additionally, a snowballing approach was used in which respondents could refer to other relevant stakeholders at the end of each interview. This leads to respondents with different backgrounds (not only medical) and varying roles, such as being a staff member, project coordinator, or policy maker. We aimed at a maximum variation in the type of organizations which were represented by respondents, such as different governmental institutions and a variety of healthcare/social care organizations. In some cases, paired interviews were conducted [ 26 ] if the respondents were considered complementary in terms of expertise, background, and experience with the topic. An information letter and a request to participate was send to each stakeholder by e-mail. One reminder was sent in case of nonresponse.
Data collection
Interviews were conducted between January and June 2022 by a sociologist trained in qualitative research methods. Interviewing took place online using the software Microsoft Teams and were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. A semi-structured interview guide was used, which included (1) an exploration of the concept of GOC and how the respondent relates to this topic, (2) questions on how GOC became a topic of interest and initiatives within the respondent’s setting, and (3) the perceived barriers and facilitators for implementation. An iterative approach was used between data collection and data analysis, meaning that the interview guide underwent minor adjustments based on proceeding insights from earlier interviews in order to get richer data.
Data analysis
All data were thematically analyzed, both inductively and deductively, supported by the software NVivo 12©. For the inductive part, implicit and explicit ideas within the qualitative data were identified and described [ 27 ]. The broader research team, with backgrounds in sociology, medical sciences, and social work, discussed these initial analyses and results. The main researcher then further elaborated this into a broad understanding. This was followed by a deductive part, in which characteristics and perspectives from organizational theories were used as sensitizing concepts, inspired by research from Birken et al. [ 13 ]. This provided a frame of reference and direction, adding interpretive value to our analysis [ 28 ]. These analyses were subject of peer debriefing with our cooperating research team to validate whether these results aligned with their knowledge of GOC processes. This enhances the trustworthiness and credibility of our results [ 29 , 30 ]. Data analysis was done in Dutch, but illustrative quotes were translated into English.
In-depth interviews were performed with n = 23 respondents (see Table 2 ): five interviews were duo interviews, and one interview took place with n = 3 respondents representing one organization. We had n = 6 refusals: n = 3 because of time restraints, n = 1 did not feel sufficiently knowledgeable about the topic, n = 1 changed professional function, and there was n = 1 nonresponse. Respondents had various ways in which they related towards the macro-context: we included actors that formed part of external context (e.g., the Flemish Agency of Care and Health), actors that facilitate and strengthen organizations in the implementation of GOC (e.g., the umbrella organization for community health centers), and actors that actively convey GOC inside and outside their setting (e.g., an autonomous and integral home care service). Interviews lasted between 47 and 72 min. Table 3 gives an overview on the main findings of our deductive analysis with their respective links to the propositions of each of the organizational theories that we applied as a lens.
Institutional theory: laying foundations for a shift towards GOC
For the implementation of GOC in primary care, looking at the data with an institutional theory lens helps us understand the way in which primary care organizations will respond to social structures surrounding them. Institutional theory describes the influence of institutions, which give shape to organizational fields: “organizations that, in the aggregate, constitute a recognized area of institutional life [ 31 ], p. 148. Prevailing institutions within primary care in Flanders can affect how organizations within such organizational fields fulfil their activities. Throughout our interviews, we recognized several dynamics that are being described in institutional theory.
First of all, the changing landscape of primary care in Flanders (see 1.2) was often brought up as a dynamic in which GOC is intertwined with other changes. Respondents mention an overall tendency to reform primary care to becoming more integrated and the ideas of person-centered care becoming more upfront. These expectations in how primary care should be approached seem to affect the organizational field of primary care: “You could tell that in people’s minds they are ready to look into what it actually means to put the patient, the person central. — INT01” Various policy actors are committed to further steer towards these approaches: “the government has called it the direction that we all have to move towards. — INT23” It was part of the foundations for the most recent primary care reform, leading to the creation of demographic primary care zones governed by care councils and the Flemish Institute of Primary Care as supporting institution.
These newly established actors were viewed by our respondents as catalysts of GOC. They pushed towards the aims to depart from local settings and to establish connections between local actors. Overall, respondents emphasized their added value as they are close to the field and they truly connect primary care actors. “They [care councils] have picked up these concepts and have started working on it. At the moment they are truly the incubators and ecosystems, as they would call it in management slang. — INT04” For an innovation such as GOC to be diffused, they are viewed as the ideal actors who can function as a facilitator or conduit. They are uniquely positioned as they are closely in contact with the practice field and can be a top-down conduit for governmental actors but also are able to address the needs from bottom-up. “In this respect, people look at the primary care zones as the ideal partners. […] We can start bringing people together and have that helicopter view: what is it that truly connects you? — INT23” However, some respondents also mentioned their difficult governance structure due to representation of many disciplines and organizations.
Other regulatory factors were mentioned by respondents were other innovations or changes in primary care that were intentionally linked to GOC: e.g., the BelRAI Footnote 2 or Flemish Social Protection Footnote 3 . “The government also provides incentives. For example, family care services will gradually be obliged to work with the BelRAI screener. This way, you actually force them to start taking up GOC. — INT23” For GOC to be embedded in primary care, links with other regulatory requirements can steer PCPs towards GOC. Furthermore, it was sometimes mentioned that an important step would be for the policy level to acknowledge GOC as quality of care and to include the concept in quality standards. This would further formalize and enforce the institutional expectation to go towards person-centered care.
Currently, a challenge on institutional level as viewed by most respondents is that GOC is not or only to a limited extent incorporated in the basic education of most primary care disciplines. This leads to most of PCPs only having a limited understanding of GOC and different disciplines not having a shared language in this matter. “You have these primary health and welfare actors who each have their own approach, history and culture. To bring them together and to align them is challenging. — INT10” The absence of GOC as a topic in basic education is mentioned by various respondents as a current shortcoming in effectively implementing GOC in the wider primary care landscape.
Overall, GOC is viewed as our respondents as a topic that has recently gained a lot interest, both by individual PCPS, organizations, and governmental actors. The Flemish government has laid some foundations to facilitate this change with newly created institutions and incentives. However, other external context variables can interfere in how the concept of GOC is currently being picked up and what challenges arise.
Resource dependency theory: in search for a financial system that accommodates interprofessional collaboration
Another external context variable that affects how GOC can be introduced is the financial system that is at place. To analyze themes that were raised during the interviews with regard to finances, we utilized a resource dependency perspective. This theory presumes that organizations are dependent on financial resources and are seeking ways to ensure their continued functioning [ 16 , 17 ]. To a certain extent, this collides with the assumptions of institutional theory that foregrounds organization’s conformity to institutional pressures [ 32 ]. Resource dependency theory in contrast highlights differentiation of organizations that seek out competitive advantages [ 32 ].
In this context, respondents mention that their interest and willingness to move towards a GOC approach are held back by the current dominant system of pay for performance in the healthcare system. This financial system is experienced as restrictive, as it does not provide any incentive to PCPs for interprofessional collaboration, which is key for GOC. A switch to a flat fee system (in which a fixed fee is charged for each patient) or bundled payment was often mentioned as desirable. PCPs and health/social care organizations working in a context where they are financially rewarded for a trajectory or treatment of a patient in its entirety ensure that there is no tension with their necessity to obtain financial resources, as described in the resource dependency theory. Many of our respondents voice that community health centers are a good example. They cover different healthcare disciplines and operate with a fixed price per enrolled patient, regardless of the number of services for that patient. This promotes setting up preventive and health-promoting actions, which confirms our finding on the relevance of dedicated funding.
At the governmental level, the best way to finance and give incentives is said to be a point of discussion: “For years, we have been arguing about how to finance. Are we going to fund counsel coordination? Or counsel organization? Or care coordination? — INT04” Macro-level respondents do however mention financial incentives that are already in place to stimulate interprofessional collaboration: fees for multidisciplinary consultation being the most prominent. Other examples were given in which certain requirements were set for funding (e.g., Impulseo Footnote 4 , VIPA Footnote 5 ) that stimulate actors or settings in taking steps towards more interprofessional collaboration.
Nowadays, financial incentives to support organizations to engage in GOC tend to be project grants. However, a structural way to finance GOC approaches is currently lacking, according to our respondents. As a consequence, a long-term perspective for organizations is lacking; there is no stable financing and organizations are obliged to focus on projects instead of normalizing GOC in routine practice. According to a resource dependency perspective, the absence of financial incentives for practicing GOC hinders organizations in engaging with the approach, as they are focused on seeking out resources in order to fulfil their core activities.
A network-theory perspective: the importance of connectedness for the diffusion of an innovation
Throughout the interviews, interorganizational contextual elements were often addressed. A network theory lens states that collaborating in networks can lead to outcomes that could not be realized by individual organizations acting independently [ 19 , 20 ]. Networks consist of a set of actors such as PCPs or health/social care organizations along with a set of ties that link them [ 33 ]. These ties can be state-type ties (e.g., role based, cognitive) or event-type ties (e.g., through interactions, transactions). Both type of ties can enable a flow in which information or innovations can pass, as actors interact [ 33 ]. To analyze the implementation process of GOC and how this is diffused through various actors, a network theory perspective can help understand the importance of the connection between actors.
A first observation throughout the interviews in which we notice the importance of networks was in the mentioning of local initiatives that already existed before the creation of the primary care zones/care councils. In the area around Ghent, local multidisciplinary networks already organized community meetings, bringing together different PCPs on overarching topics relating to long-term care for patients with chronic conditions. These regions have a tradition of collaboration and connectedness of PCPs, which respondents mention to be highly valuable: “This ensures that we are more decisive, speaking from one voice with regards to what we want to stand for. — INT23” Respondents voice that the existence of such local networks has had a positive effect on the diffusion of ideas such as GOC, as trust between different actors was already established.
Further mentioning of the importance of networks could be found in respondents acknowledging one of the presumptions of network theory: working collaboratively towards a specific objective leads to outcomes that cannot be realized independently. This is especially true for GOC, an approach that in essence requires different disciplines to work together: “When only one GP, nurse or social worker starts working on it, it makes no sense. Everyone who is involved with that person needs to be on board. Actually, you need to finetune teams surrounding a person — INT11.” This is why several policy-level respondents mentioned that emphasis was placed on organizing GOC initiatives in a neighborhood-oriented way, in which accessible, inclusive care is aimed at by strengthening social cohesion. This way, different types of PCPs got to know each other through these sessions an GOC and would start to get aligned on what it means to provide GOC. However, in particular, self-employed PCPs are hard to reach. According to our respondents, occupational groups and care councils are suitable actors to engage these self-employed PCPs, but they are not always much involved in such a network .
To better connect PCPs and health/social care organizations, the absence of connectedness through the technological landscape is also mentioned. Current technological systems and platforms for documenting patient information do not allow for aligning and sharing between disciplines. In Flanders, there is a history of each discipline developing its own software, which lacks centralization or unification: “For years, they have decided to just leave it to the market, in such a way that you ended up with a proliferation of software, each discipline having its own package. — INT06” Most of the respondents mentioning this were aware that Flanders government is currently working on a unified digital care and support platform and were optimistic about its development.
Contingency theory: how environmental pressure can be a trigger for change
Our interviews were conducted during a rather dynamic and unique period of time in which the impact of social change and pressure was clearly visible: the Flemish primary care reform was ongoing which leads to the creation of care councils and VIVEL (see 3.1.1), and the COVID crisis impacted the functioning of these and other primary care actors. These observed effects of societal changes are reminiscent of the assumptions that are made in contingency theory. In essence, contingency theory presupposes that “organizational effectiveness results from fitting characteristics of the organization, such as its structure, to contingencies that reflect the situation of the organization [ 34 ], p. 1.” When it comes to the effects of the primary care reform and the COVID crisis, there were several mentions on how primary care actors reorganized their activities to adapt to these circumstances. Representatives of care councils/primary care zones whom we interviewed underlined that they were just at the point where they could again engage with their original action plans, not having to take up so many COVID-related tasks anymore. On the one hand, the COVID crisis had however forced them to immediately become functional and has also contributed that various primary care actors quickly got to know them. On the other hand, the COVID crisis has also kept them from their core activities for a while. On top of that, the crisis has also triggered a change the overall view towards data sharing. Some respondents mention a rather protectionist approach towards data sharing, while data sharing has become more normalized during the COVID crisis. This discussion was also relevant for the creation of a unified shared patient record in terms of documenting and sharing patient goals.
Other societal factors that were mentioned having an impact on the uptake of GOC are the demographic composition of a certain area. It was suggested that areas that are characterized by a patient population with more chronic care needs will be more likely to steer towards GOC as a way of coping with these complex cases. “You always have these GPs who blow it away immediately and question whether this is truly necessary. They will only become receptive to this when they experience needs for which GOC can be a solution — INT11.” On a macro-level, several respondents have mentioned how a driver for change is to have the necessity for change becoming very tangible. As PCPs are confronted with increasing numbers of patients with complex, chronic needs and their work becomes more demanding, the need for change becomes more acute. This finding is in line with what contingency theory underlines: changes in contingency (e.g., the population that is increasingly characterized by aging and multimorbidity) are an impetus for change for health/social care organizations to resolve this by adopting a structure that better fits the current environmental characteristics [ 34 ].
Our research demonstrates the applicability of organizational theories to help explain the impact that macro-level context variables have on an implementation process. These insights can be integrated into existing implementation frameworks and models to add the explanatory power of macro-level context variables, which is to date often neglected. The organizational theories demonstrate the ways in which organizations interact with their external environment in order to sustain and fulfill their core activities. As demonstrated in Fig. 1 , institutional theory largely explains how social expectations in the form of institutions lead towards the adoption or implementation of innovation, such as GOC. However, other organizational theories demonstrate how other macro-context elements on different areas can either strengthen or hamper the implementation process.
How organizational theories can help explain the way in which macro-level context variables affect implementation of an intervention
Departing from the mechanisms that are postulated by institutional theory, we observed that the shift towards GOC is part of a larger Flemish primary care reform in which and new institutions have been established and polices have been drawn up to go towards more integrated, person-centered care. To achieve this, governmental actors have placed emphasis on socialization of care, the local context, and establishing ties between organizations in order to become more complementary in providing primary health care [ 35 ]. With various initiatives surrounding this aim, the Flemish government is steering towards GOC. This is reminiscent of the mechanisms that are posed within institutional theory: organizations adapt to prevailing norms and expectations and mimic behaviors that are surrounding them [ 15 , 36 ].
Throughout our data, we came across concrete examples of how institutionalization takes place. DiMaggio and Powell [ 31 ] describe the subsequent process of isomorphism: organizations start to resemble each other as they are conforming to their institutional environment. A first mechanism through which this change occurs is coercive isomorphism and is clearly noticeable in our data. This type of isomorphism results from both formal and informal pressure coming from organizations from which a dependency relationship exists and from cultural expectations in the society [ 31 ]. Person-centered, GOC care is both formally propagated by governmental institutions and procedures and informally expected by current social tendencies. Care councils within primary care zones explicitly propagate and disseminate ideas and approaches that are desirable on policy level. Another form of isomorphism is professional isomorphism and relates to our finding that incorporation of GOC in basic education is currently lacking. The presumptions of professional isomorphism back up the importance of this: values, norms, and ideas that are developed during education are bound to find entrance within organizations as professionals start operating along these views.
Although many observations in our data back up the assumptions of institutional theory, it should be noticed that new initiatives such as the promotion of person-centered care and GOC can collide with earlier policy trends. Martens et al. [ 12 ] have examined the Belgian policy process relating three integrated care projects and concluded that although there is a strong support for a change towards a more patient-centered system, the current provider-driven system and institutional design complicate this objective. Furthermore, institutional theory tends to simplify actors as passive adopters of institutional norms and expectations and overlook the human agency and sensemaking that come with it [ 37 ]. For GOC, it is particularly true that PCPs will actively have to seek out their own style and fit the approach in their own way of working. Moreover, GOC was not just addressed as a governmental expectation but for many PCPs something they inherently stood behind.
Resources dependency theory poses that organizations are dependent on critical resources and adapt their way of working in response to those resources [ 17 ]. From our findings, it seems that the current financial system does not promote GOC, meaning that the mechanisms that are put forward in resources dependency theory are not set in motion. A macro-level analysis of barriers and facilitators in the implementation of integrated care in Belgium by Danhieux et al. [ 10 ] also points towards the financial system and data sharing as two of the main contextual determinants that affect implementation.
Throughout our data, the importance of a network approach was frequently mentioned. Interprofessional collaboration came forward as a prerequisite to make GOC happen, as well as active commitment on different levels. Burns, Nembhard, and Shortell [ 38 ] argue that research efforts on implementing person-centered, integrated care should have more focus on the use of social networks to study relational coordination. In terms of interprofessional collaboration, to date, Belgium has a limited tradition of working team-based with different disciplines [ 35 ]. However, when it comes to strengthening a cohesive primary care network, the recently established care councils have become an important facilitator. As a network governance structure, they resemble mostly a Network Administrative Organization (NAO): a separate, centralized administrative entity that is externally governed and not another member providing its own services [ 19 ]. According to Provan and Kenis [ 19 ], this type of governance form is most effective in a rather dense network with many participants, when the goal consensus is moderately high, characteristics that are indeed representative for the Flemish primary care landscape. This strengthens our observation that care councils have favorable characteristics and are well-positioned to facilitate the interorganizational context to implement GOC.
Lastly, the presumptions within contingency theory became apparent as respondents talked about how the need for change needs to become tangible for PCPs and organizations to take action, as they are increasingly faced with a shortage of time and means and more complex patient profiles. Furthermore, De Maeseneer [ 39 ] affirms our findings that the COVID-19 crisis could be employed as an opportunity to strengthen primary health care, as health becomes prioritized and its functioning becomes re-evaluated. Overall, contingency theory can help gain insight in how and why certain policy trends or decisions are made. A study of Bruns et al. [ 40 ] found that modifiable external context variables such as interagency collaboration were predictive for policy support for intervention adoption, while unmodifiable external context variable such as socio-economic composition of a region was more predictive for fiscal investments that are made.
Strengths and limitations
This study contributes to our overall understanding of implementation processes by looking into real-life implementation efforts for GOC in Flanders. It goes beyond a mere description of external context variables that affect implementation processes but aims to grasp which and how external context variables influence implementation processes. A variety of respondents from different organizations, with different backgrounds and perspectives, were interviewed, and results were analyzed by researchers with backgrounds in sociology, social work, and medical sciences. Results can not only be applied to further develop sustainable implementation plans for GOC but also enhance our understanding of how the external context influences and shapes implementation processes. As most research on contextual variables in implementation processes has until now mainly focused on internal context variables, knowledge on external context variables contributes to gaining a bigger picture of the mechanism of change.
However, this study is limited to the Flemish landscape, and external context variables and their dynamics might differ from other regions or countries. Furthermore, our study has examined and described how macro-level context variables affect the overall implementation processes of GOC. Further research is needed on the link between outer and inner contexts during implementation and sustainment, as explored by Lengninck-Hall et al. [ 41 ]. Another important consideration is that our sample only includes the “believers” in GOC and those who are already taking steps towards its implementation. It is possible that PCPs themselves or other relevant actors who are more skeptical about GOC have a different view on the policy and organizational processes that we explored. Furthermore, data triangulations in which this data is complemented with document analysis could have expanded our understanding and verified subjective perceptions of respondents.
Insights and propositions that derive from organizational theories can be utilized to expand our knowledge on how external context variables affect implementation processes. Our research demonstrates that the implementation of GOC in Flanders is steered and facilitated by regulatory and policy variables, which sets in motion mechanisms that are described in institutional theory. However, other external context variables interact with the implementation process and can further facilitate or hinder the overall implementation process. Assumptions and mechanisms explained within resource dependency theory, network theory, and contingency theory contribute to our understanding on how fiscal, technological, socio-economic, and interorganizational context variables affect an implementation process.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to confidentiality guaranteed to participants but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
The Primary Care Academy (PCA) is a research and teaching network of four Flemish universities, six university colleges, the White and Yellow Cross (an organization for home nursing), and patient representatives that have included GOC as one of their main research domains.
BelRAI, the Belgian implementation of the interRAI assessment tools; these are scientific, internationally validated instruments enabling an assessment of social, psychological, and physical needs and possibilities of individuals in different care settings. The data follows the person and is shared between care professionals and care organizations.
The Flemish Social Protection is a mandatory insurance established by the Flemish government to provide a range of concessions to individuals with long-term care and support needs due to illness or disability.
Impulseo, financial support for general practitioners who start an individual practice or join a group practice
VIPA, grants for the realization of sustainable, accessible, and affordable healthcare infrastructure
Abbreviations
- Goal-oriented care
Primary care provider
Primary Care Academy
Squires JE, Graham ID, Hutchinson AM, Michie S, Francis JJ, Sales A, et al. Identifying the domains of context important to implementation science: a study protocol. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):1–9.
Article Google Scholar
Nilsen P, Bernhardsson S. Context matters in implementation science: a scoping review of determinant frameworks that describe contextual determinants for implementation outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):1–21.
Rogers L, De Brún A, McAuliffe E. Defining and assessing context in healthcare implementation studies: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):1–24.
Huybrechts I, Declercq A, Verté E, Raeymaeckers P, Anthierens S. The building blocks of implementation frameworks and models in primary care: a narrative review. Front Public Health. 2021;9:675171.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hamilton AB, Mittman BS, Eccles AM, Hutchinson CS, Wyatt GE. Conceptualizing and measuring external context in implementation science: studying the impacts of regulatory, fiscal, technological and social change. Implement Sci. 2015;10 BioMed Central.
Watson DP, Adams EL, Shue S, Coates H, McGuire A, Chesher J, et al. Defining the external implementation context: an integrative systematic literature review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):1–14.
Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors. Adm Policy Ment Health Ment Health Serv Res. 2011;38:4–23.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4(1):1–15.
Harvey G, Kitson A. PARIHS revisited: from heuristic to integrated framework for the successful implementation of knowledge into practice. Implement Sci. 2015;11(1):1–13.
Danhieux K, Martens M, Colman E, Wouters E, Remmen R, Van Olmen J, et al. What makes integration of chronic care so difficult? A macro-level analysis of barriers and facilitators in Belgium. International. J Integr Care. 2021;21(4).
Hamilton AB, Mittman BS, Campbell D, Hutchinson C, Liu H, Moss NJ, Wyatt GE. Understanding the impact of external context on community-based implementation of an evidence-based HIV risk reduction intervention. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):1–10.
Martens M, Danhieux K, Van Belle S, Wouters E, Van Damme W, Remmen R, et al. Integration or fragmentation of health care? Examining policies and politics in a Belgian case study. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2022;11(9):1668.
PubMed Google Scholar
Birken SA, Bunger AC, Powell BJ, Turner K, Clary AS, Klaman SL, et al. Organizational theory for dissemination and implementation research. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):1–15.
Powell WW, DiMaggio PJ. The new institutionalism in organizational analysis. University of Chicago Press; 2012.
Google Scholar
Zucker LG. Institutional theories of organization. Annu Rev Sociol. 1987;13(1):443–64.
Hillman AJ, Withers MC, Collins BJ. Resource dependence theory: a review. J Manag. 2009;35(6):1404–27.
Nienhüser W. Resource dependence theory-how well does it explain behavior of organizations? Management Revue; 2008. p. 9–32.
Lammers CJ, Mijs AA, Noort WJ. Organisaties vergelijkenderwijs: ontwikkeling en relevantie van het sociologisch denken over organisaties. Het Spectrum. 2000;6.
Provan KG, Kenis P. Modes of network governance: structure, management, and effectiveness. J Public Adm Res Theory. 2008;18(2):229–52.
Kenis P, Provan K. Het network-governance-perspectief. Business performance management Sturen op prestatie en resultaat; 2008. p. 296–312.
Begun JW, Zimmerman B, Dooley K. Health care organizations as complex adaptive systems. Adv Health Care Org Theory. 2003;253:288.
Mold JW. Failure of the problem-oriented medical paradigm and a person-centered alternative. Ann Fam Med. 2022;20(2):145–8.
Boeykens D, Boeckxstaens P, De Sutter A, Lahousse L, Pype P, De Vriendt P, et al. Goal-oriented care for patients with chronic conditions or multimorbidity in primary care: a scoping review and concept analysis. PLoS One. 2022;17(2):e0262843.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gray CS, Grudniewicz A, Armas A, Mold J, Im J, Boeckxstaens P. Goal-oriented care: a catalyst for person-centred system integration. Int J Integr Care. 2020;20(4).
Hamilton AB, Finley EP. Qualitative methods in implementation research: an introduction. Psychiatry Res. 2019;280:112516.
Wilson AD, Onwuegbuzie AJ, Manning LP. Using paired depth interviews to collect qualitative data. Qual Rep. 2016;21(9):1549.
Guest G, MacQueen KM, Namey EE. Applied thematic analysis. Sage Publications; 2011.
Bowen GA. Grounded theory and sensitizing concepts. Int J Qual Methods. 2006;5(3):12–23.
Connelly LM. Trustworthiness in qualitative research. Medsurg Nurs. 2016;25(6):435.
Morse JM, Barrett M, Mayan M, Olson K, Spiers J. Verification strategies for establishing reliability and validity in qualitative research. Int J Qual Methods. 2002;1(2):13–22.
DiMaggio PJ, Powell WW. The iron cage revisited: institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. Am Sociol Rev. 1983;147-60.
de la Luz F-AM, Valle-Cabrera R. Reconciling institutional theory with organizational theories: how neoinstitutionalism resolves five paradoxes. J Organ Chang Manag. 2006;19(4):503–17.
Borgatti SP, Halgin DS. On network theory. Organ Sci. 2011;22(5):1168–81.
Donaldson L. The contingency theory of organizations. Sage; 2001.
Book Google Scholar
De Maeseneer J, Galle A. Belgium’s healthcare system: the way forward to address the challenges of the 21st century: comment on “Integration or Fragmentation of Health Care? Examining Policies and Politics in a Belgian Case Study”. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2023;12.
Dadich A, Doloswala N. What can organisational theory offer knowledge translation in healthcare? A thematic and lexical analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):1–20.
Jensen TB, Kjærgaard A, Svejvig P. Using institutional theory with sensemaking theory: a case study of information system implementation in healthcare. J Inf Technol. 2009;24(4):343–53.
Burns LR, Nembhard IM, Shortell SM. Integrating network theory into the study of integrated healthcare. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114664.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
De Maeseneer J. COVID-19: using the crisis as an opportunity to strengthen primary health care. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2021;22:e73.
Bruns EJ, Parker EM, Hensley S, Pullmann MD, Benjamin PH, Lyon AR, Hoagwood KE. The role of the outer setting in implementation: associations between state demographic, fiscal, and policy factors and use of evidence-based treatments in mental healthcare. Implement Sci. 2019;14:1–13.
Lengnick-Hall R, Stadnick NA, Dickson KS, Moullin JC, Aarons GA. Forms and functions of bridging factors: specifying the dynamic links between outer and inner contexts during implementation and sustainment. Implement Sci. 2021;16:1–13.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the partnership with the Primary Care Academy (academie-eerstelijn.be) and want to thank the King Baudouin Foundation and Fund Daniël De Coninck for the opportunity they offer us for conducting research and have impact on the primary care of Flanders, Belgium. The consortium of the Primary Care Academy consists of the following: lead author: Roy Remmen—[email protected]—Department of Primary Care and Interdisciplinary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium; Emily Verté—Department of Primary Care and Interdisciplinary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium, and Department of Family Medicine and Chronic Care, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussel, Belgium; Muhammed Mustafa Sirimsi—Centre for Research and Innovation in Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium; Peter Van Bogaert—Workforce Management and Outcomes Research in Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Belgium; Hans De Loof—Laboratory of Physio-Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Biomedical and Veterinary Sciences, University of Antwerp, Belgium; Kris Van den Broeck—Department of Primary Care and Interdisciplinary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium; Sibyl Anthierens—Department of Primary Care and Interdisciplinary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium; Ine Huybrechts—Department of Primary Care and Interdisciplinary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium; Peter Raeymaeckers—Department of Sociology, Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Antwerp, Belgium; Veerle Bufel—Department of Sociology, Centre for Population, Family and Health, Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Antwerp, Belgium; Dirk Devroey—Department of Family Medicine and Chronic Care, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussel; Bert Aertgeerts—Academic Centre for General Practice, Faculty of Medicine, KU Leuven, Leuven, and Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine, KU Leuven, Leuven; Birgitte Schoenmakers—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium; Lotte Timmermans—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium; Veerle Foulon—Department of Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Sciences, Faculty Pharmaceutical Sciences, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium; Anja Declercq—LUCAS-Centre for Care Research and Consultancy, Faculty of Social Sciences, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium; Dominique Van de Velde, Department of Rehabilitation Sciences, Occupational Therapy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium, and Department of Occupational Therapy, Artevelde University of Applied Sciences, Ghent, Belgium; Pauline Boeckxstaens—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium; An De Sutter—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium; Patricia De Vriendt—Department of Rehabilitation Sciences, Occupational Therapy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium, and Frailty in Ageing (FRIA) Research Group, Department of Gerontology and Mental Health and Wellbeing (MENT) Research Group, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Vrije Universiteit, Brussels, Belgium, and Department of Occupational Therapy, Artevelde University of Applied Sciences, Ghent, Belgium; Lies Lahousse—Department of Bioanalysis, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium; Peter Pype—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium, End-of-Life Care Research Group, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Vrije Universiteit Brussel and Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium; Dagje Boeykens—Department of Rehabilitation Sciences, Occupational Therapy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium, and Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium; Ann Van Hecke—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium, University Centre of Nursing and Midwifery, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium; Peter Decat—Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Ghent, Belgium; Rudi Roose—Department of Social Work and Social Pedagogy, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, University Ghent, Belgium; Sandra Martin—Expertise Centre Health Innovation, University College Leuven-Limburg, Leuven, Belgium; Erica Rutten—Expertise Centre Health Innovation, University College Leuven-Limburg, Leuven, Belgium; Sam Pless—Expertise Centre Health Innovation, University College Leuven-Limburg, Leuven, Belgium; Anouk Tuinstra—Expertise Centre Health Innovation, University College Leuven-Limburg, Leuven, Belgium; Vanessa Gauwe—Department of Occupational Therapy, Artevelde University of Applied Sciences, Ghent, Belgium; Didier ReynaertE-QUAL, University College of Applied Sciences Ghent, Ghent, Belgium; Leen Van Landschoot—Department of Nursing, University of Applied Sciences Ghent, Ghent, Belgium; Maja Lopez Hartmann—Department of Welfare and Health, Karel de Grote University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Antwerp, Belgium; Tony Claeys—LiveLab, VIVES University of Applied Sciences, Kortrijk, Belgium; Hilde Vandenhoudt—LiCalab, Thomas University of Applied Sciences, Turnhout, Belgium; Kristel De Vliegher—Department of Nursing–Homecare, White-Yellow Cross, Brussels, Belgium; and Susanne Op de Beeck—Flemish Patient Platform, Heverlee, Belgium.
This research was funded by fund Daniël De Coninck, King Baudouin Foundation, Belgium. The funder had no involvement in this study. Grant number: 2019-J5170820-211,588.
Author information
Peter Raeymaeckers and Sibyl Anthierens have contributed equally to this work and share senior last authorship.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Family Medicine and Population Health, University of Antwerp, Doornstraat 331, 2610, Antwerp, Belgium
Ine Huybrechts, Emily Verté & Sibyl Anthierens
Department of Family Medicine and Chronic Care, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Laarbeeklaan 103, 1090, Jette/Brussels, Belgium
Ine Huybrechts & Emily Verté
LUCAS — Centre for Care Research and Consultancy, KU Leuven, Minderbroedersstraat 8/5310, 3000, Leuven, Belgium
Anja Declercq
Center for Sociological Research, Faculty of Social Sciences, KU Leuven, Parkstraat 45/3601, 3000, Leuven, Belgium
Department of Social Work, University of Antwerp, St-Jacobstraat 2, 2000, Antwerp, Belgium
Peter Raeymaeckers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
- , Emily Verté
- , Muhammed Mustafa Sirimsi
- , Peter Van Bogaert
- , Hans De Loof
- , Kris Van den Broeck
- , Sibyl Anthierens
- , Ine Huybrechts
- , Peter Raeymaeckers
- , Veerle Bufel
- , Dirk Devroey
- , Bert Aertgeerts
- , Birgitte Schoenmakers
- , Lotte Timmermans
- , Veerle Foulon
- , Anja Declerq
- , Dominique Van de Velde
- , Pauline Boeckxstaens
- , An De Sutter
- , Patricia De Vriendt
- , Lies Lahousse
- , Peter Pype
- , Dagje Boeykens
- , Ann Van Hecke
- , Peter Decat
- , Rudi Roose
- , Sandra Martin
- , Erica Rutten
- , Sam Pless
- , Anouk Tuinstra
- , Vanessa Gauwe
- , Leen Van Landschoot
- , Maja Lopez Hartmann
- , Tony Claeys
- , Hilde Vandenhoudt
- , Kristel De Vliegher
- & Susanne Op de Beeck
Contributions
IH wrote the main manuscript text. AD, EV, PR, and SA contributed to the different steps of the making of this manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ine Huybrechts .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study protocol was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the University of Antwerp/Antwerp University Hospital (reference: 2021-1690). All participants received verbal and written information about the purpose and methods of the study and gave written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Huybrechts, I., Declercq, A., Verté, E. et al. How does the external context affect an implementation processes? A qualitative study investigating the impact of macro-level variables on the implementation of goal-oriented primary care. Implementation Sci 19 , 32 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-024-01360-0
Download citation
Received : 03 January 2024
Accepted : 28 March 2024
Published : 16 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-024-01360-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Contingency theory
- External context
- Institutional theory
- Primary care
- Implementation process
- Macro-context
- Network theory
- Organizational theories
- Resource dependency theory
Implementation Science
ISSN: 1748-5908
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
VASA-1: Lifelike Audio-Driven Talking Faces Generated in Real Time
- Follow on Twitter
- Like on Facebook
- Follow on LinkedIn
- Subscribe on Youtube
- Follow on Instagram
- Subscribe to our RSS feed
Share this page:
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative Research Examples. 1. Ethnography. Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology, this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
For students conducting their first qualitative research project, the choice of approach and subsequent alignment among problem, research questions, data collection, and data analysis can be particularly difficult. ... We follow the comparative overview with examples of the different approaches applied to familiar research contexts to highlight ...
38 jump starting your qualitative research project (e.g., good or evil), conditions (e.g., happy or sad) or its relative quality (e.g., better or worse). Equally important is to avoid language that implies direction (e.g., affect) or hierarchical ordering (e.g., more than). Example 1: Assumptions about nature, condition or quality
Developing a theoretical framework for your dissertation is one of the key elements of a qualitative research project. Through writing your literature review, you are likely to have identified either a problem that need 'fixing' or a gap that your research may begin to fill. ... Example 2: This project will analyse and compare three films ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Table 1: Examples of data sources used in qualitative research and the types of research question they might answer What the research question is about Source of data Beliefs, feelings, perceptions, ideas about a particular topic or concept or intervention or illness Interviews and focus groups, websites and fora, media articles
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive, allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.. Example: Qualitative research If you want to generate new ideas for online teaching strategies, a qualitative approach would make the most sense. You can use this type of research to explore exactly what teachers and students ...
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being "qualitative," the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
In most quantitative studies, the sample size is calculated before the study is implemented. However, in qualitative research, the sample size is determined by two critical factors: (1) access to diverse participants aware of the research topic and (2) getting to a saturation point. ... This paper's qualitative research project mapping tool ...
word guidelines to highlight the flexibility of this qualitative analytic method. These guidelines. are (1) familiarizing yourself with your data, (2) generating initial codes, (3) The researcher read. throughout each transcript to immerse in the data, (4) reviewing themes, (5) defining and naming.
Qualitative research methods are designed to understand the behavior and perception of the target audience about a particular subject. Qualitative research methods include observations, one-on-one interviews, case study research, focus groups, ethnographic research, phenomenology, and grounded theory. Let's discuss them one by one.
Revised on 30 January 2023. Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which ...
Step 2: Identify how to research it. Once the researcher has finalized the research project, they will need to figure out how they will do the work. Firstly, the researcher will look through secondary data and research (e.g. analytics, previous research reports). Secondary analysis will help determine if there are existing answers to any of the ...
For many researchers unfamiliar with qualitative research, determining how to conduct qualitative analyses is often quite challenging. Part of this challenge is due to the seemingly limitless approaches that a qualitative researcher might leverage, as well as simply learning to think like a qualitative researcher when analyzing data. From framework analysis (Ritchie & Spencer, 1994) to content ...
Research Proposal Format Example. Following is a general outline of the material that should be included in your project proposal. I. Title Page II. Introduction and Literature Review (Chapters 2 and 3) A. Identification of specific problem area (e.g., what is it, why it is important). B. Prevalence, scope of problem.
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PAPER 1 Sample of the Qualitative Research Paper In the following pages you will find a sample of the full BGS research qualitative paper with each section or chapter as it might look in a completed research paper beginning with the title page and working through each chapter and section of the research paper.
This chapter will outline the qualitative data collection methods used, describe the analytic techniques employed as well as presenting the findings from this phase of the research study. The findings will be fully discussed with links to current literature identified in Chapter 1. The characteristics of the research participants have been ...
For example, graphic elicitation is a frequently used qualitative approach in which research participants are asked to create drawings or other visual media according to different prompts and then the products are analyzed alongside other data collected (Copeland & Agosto, 2012).
For example, the Flemish government issued policy for facilitating more integrated, person-centered care by means of newly created institutions, incentives, expectations, and other regulatory factors. ... Interviews were conducted between January and June 2022 by a sociologist trained in qualitative research methods. Interviewing took place ...
VASA-1: Lifelike Audio-Driven Talking Faces Generated in Real Time. Opens in a new tab. Follow us: Follow on Twitter; Like on Facebook
Our experience in a recent qualitative research project was similar to that of Wax and Shapiro. In the project Crime in Latin America (CRIMLA), which had a high-intensity, repeat-interview research design, over 350 incarcerated persons in seven Latin American countries were interviewed three times with up to a week between sessions.Analyzing the fieldwork notes, logs, and interview excerpts ...
Attention to researcher positionality is an important component of qualitative research, particularly in research done with and for communities. ... with deep ties linking American and Israeli settler projects (Barakat, 2018; Khalidi, ... and illustrates ethical dilemmas that can emerge in relational approaches to research. In another example ...