- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents

The 5 Steps of Problem Solving

Problem solving is a critical skill for success in business – in fact it’s often what you are hired and paid to do. This article explains the five problem solving steps and provides strategies on how to execute each one.
Defining Problem Solving
Before we talk about the stages of problem solving, it’s important to have a definition of what it is. Let’s look at the two roots of problem solving — problems and solutions.
Problem – a state of desire for reaching a definite goal from a present condition [1] Solution – the management of a problem in a way that successfully meets the goals set for treating it
[1] Problem solving on Wikipedia
One important call-out is the importance of having a goal. As defined above, the solution may not completely solve problem, but it does meet the goals you establish for treating it–you may not be able to completely resolve the problem (end world hunger), but you can have a goal to help it (reduce the number of starving children by 10%).
The Five Steps of Problem Solving
With that understanding of problem solving, let’s talk about the steps that can get you there. The five problem solving steps are shown in the chart below:
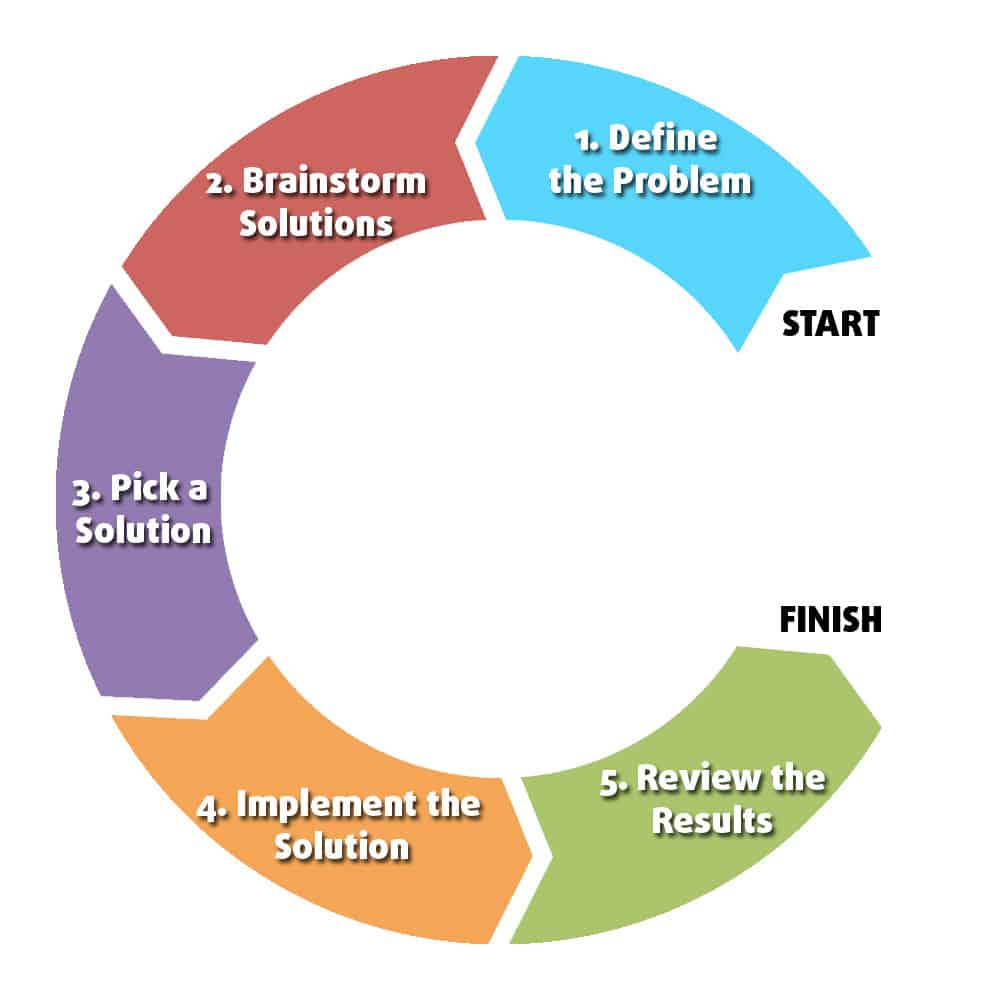
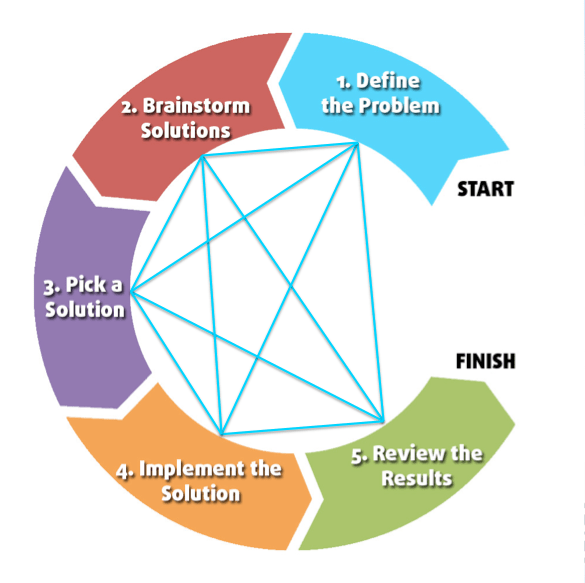
However this chart as is a little misleading. Not all problems follow these steps linearly, especially for very challenging problems. Instead, you’ll likely move back and forth between the steps as you continue to work on the problem, as shown below:
Let’s explore of these steps in more detail, understanding what it is and the inputs and outputs of each phase.
1. Define the Problem
aka What are you trying to solve? In addition to getting clear on what the problem is, defining the problem also establishes a goal for what you want to achieve.
Input: something is wrong or something could be improved. Output: a clear definition of the opportunity and a goal for fixing it.
2. Brainstorm Ideas
aka What are some ways to solve the problem? The goal is to create a list of possible solutions to choose from. The harder the problem, the more solutions you may need.
Input: a goal; research of the problem and possible solutions; imagination. Output: pick-list of possible solutions that would achieve the stated goal.
3. Decide on a Solution
aka What are you going to do? The ideal solution is effective (it will meet the goal), efficient (is affordable), and has the fewest side effects (limited consequences from implementation).
Input: pick-list of possible solutions; decision-making criteria. Output: decision of what solution you will implement.
4. Implement the Solution
aka What are you doing? The implementation of a solution requires planning and execution. It’s often iterative, where the focus should be on short implementation cycles with testing and feedback, not trying to get it “perfect” the first time.
Input: decision; planning; hard work. Output: resolution to the problem.
5. Review the Results
aka What did you do? To know you successfully solved the problem, it’s important to review what worked, what didn’t and what impact the solution had. It also helps you improve long-term problem solving skills and keeps you from re-inventing the wheel.
Input: resolutions; results of the implementation. Output: insights; case-studies; bullets on your resume.
Improving Problem Solving Skills
Once you understand the five steps of problem solving, you can build your skill level in each one. Often we’re naturally good at a couple of the phases and not as naturally good at others. Some people are great at generating ideas but struggle implementing them. Other people have great execution skills but can’t make decisions on which solutions to use. Knowing the different problem solving steps allows you to work on your weak areas, or team-up with someone who’s strengths complement yours.
Want to improve your problem solving skills? Want to perfect the art of problem solving? Check out our training programs or try these 20 problem solving activities to improve creativity .
THIS FREE 129 SECOND QUIZ WILL SHOW YOU
what is your humor persona?
Humor is a skill that can be learned. And when used correctly, it is a superpower that can be your greatest asset for building a happier, healthier and more productive life. See for yourself...
you might also be interested in...

Humor at Work TEDx talk
We are excited to announce that Drew’s TEDx talk on Humor at Work is available online. This talk dives deep […]
Inspiration from the Humor Project Conference 2012
I attended the 55th International Humor Project Conference this past weekend and learned from a number of great speakers. While […]

Do You Work in HR? Here’s How You Can Create A Positive Work Environment
Human Resources gets a bad rap. Among the Sales, Marketing, and IT departments, HR is sometimes seen as the “anti-fun […]
22 thoughts on “The 5 Steps of Problem Solving”
very helpful and informative training
Thank you for the information
YOU ARE AFOOL
I’m writing my 7th edition of Effective Security Management. I would like to use your circular graphic illustration in a new chapter on problem solving. You’re welcome to phone me at — with attribution.
Sure thing, shoot us an email at [email protected] .
i love your presentation. It’s very clear. I think I would use it in teaching my class problem solving procedures. Thank you
It is well defined steps, thank you.
these step can you email them to me so I can print them out these steps are very helpful
I like the content of this article, it is really helpful. I would like to know much on how PAID process (i.e. Problem statement, Analyze the problem, Identify likely causes, and Define the actual causes) works in Problem Solving.
very useful information on problem solving process.Thank you for the update.
Pingback: Let’s Look at Work Is Working with the Environment | #EnviroSociety
It makes sense that a business would want to have an effective problem solving strategy. Things could get bad if they can’t find solutions! I think one of the most important things about problem solving is communication.
Well in our school teacher teach us –
1) problem ldentification 2) structuring the problem 3) looking for possible solutions 4) lmplementation 5) monitoring or seeking feedback 6) decision making
Pleace write about it …
I teach Professional communication (Speech) and I find the 5 steps to problem solving as described here the best method. Your teacher actually uses 4 steps. The Feedback and decision making are follow up to the actual implementation and solving of the problem.
i know the steps of doing some guideline for problem solving
steps are very useful to solve my problem
The steps given are very effective. Thank you for the wonderful presentation of the cycle/steps/procedure and their connections.
I like the steps for problem solving
It is very useful for solving difficult problem i would reccomend it to a friend
this is very interesting because once u have learned you will always differentiate the right from the wrong.
I like the contents of the problem solving steps. informative.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Humor Persona - Template B2B
I make an effort to appreciate the humor of everyday life....
This question helps us further the advancement of humor research to make it more equitable.
Humor Persona - Main B2C

Level 5 Math Books

Level 5 Books Information
Designed in an engaging comic-book style format, our Level 5 curriculum includes the Guide books and Practice books for all four units (5A, 5B, 5C, 5D).
- The Guide book is a full-color paperback textbook, which teaches concepts in a comic-book style.
- The Practice book complements the Guide book and includes 300+ problems ranging from introductory-level exercises to challenging puzzles and word problems.

Level 5 has four units: A, B, C and D. Topics build upon each other from unit to unit.
We recommend taking the Level 5A Placement Test to determine if your student is ready to take Beast Academy Level 5.
Solutions to the placement test are found at the end of the test. Your student may also take the Level 5B , 5C , or 5D placement tests to determine readiness per unit.

View Sample Pages

Get the guide books for sure, because they are endearing and interesting and adorable and wonderful and they make your kid fall in love with doing math (even if they already love math). Kjersti, BA parent
Need help determining the right level for your student or finding a book? Want to know more about how Beast Academy differs from other curricula? Have your student take a Placement Test or visit our FAQs page for answers to popular questions.

The home of mathematics education in New Zealand.
- Forgot password ?
- Teaching material
- Problem solving activities
Level 5 Problems
The Ministry is migrating nzmaths content to Tāhurangi. Relevant and up-to-date teaching resources are being moved to Tāhūrangi (tahurangi.education.govt.nz). When all identified resources have been successfully moved, this website will close. We expect this to be in June 2024. e-ako maths, e-ako Pāngarau, and e-ako PLD 360 will continue to be available.
For more information visit https://tahurangi.education.govt.nz/updates-to-nzmaths
The problems have been grouped below by strand. Hover over each title to read the problem. Listed under 'Units' are extended problem solving investigations which aim to introduce students to an underlying idea of mathematics through a problem.
Choose a problem that involves your students in applying current learning. Remember that the context of most problems can be adapted to suit your students and your current class inquiry. Read more about using these problem solving activities.
EARLY BIRD PROMOTION: Register for the Masterclass by May 31 to secure lifetime(!) access. (Only 9 spots remaining)
5 Levels Of Problem Solving: A Framework For (First-Time) Managers

Leading people can be tough. Taking the reins for the first time? It can feel like navigating a maze blindfolded. Many first-time managers feel that pit in their stomach. Without the right guidance or training, they often turn, unintentionally, into micromanagers. Nobody's dream scenario. But, good news - help's at hand!
A few weeks ago, I interviewed two workplace pioneers for one of our monthly live events (part of the Corporate Rebels Academy ). In this extremely insightful conversation, I had the pleasure of interviewing Edwin Jansen and Luz Iglesias. They both work at Raise (formerly known as Ian Martin Group).
The company employs over 450 people and has offices in the US, Canada, India, Ghana, and the Philippines. It is a certified B Corp and has been reinventing its management practices for about 8 years.
Its business? Recruitment.
Avoid becoming the all-mighty fixer
In 2017, Edwin and Luz took the lead on changing the company's way of working. They started in one of the company's subsidiaries and used it as a test ground for finding a better way to work.
When I asked Edwin, who was the leader of the subsidiary back then, what their biggest challenge was, his answer was clear:
"It was me. I had to change."
Edwin: "At the time, Luz pointed out a significant flaw in my approach: I had become a 'fixer'. To be clear, this wasn't a compliment.
"It highlighted a dangerous trajectory where I had become the go-to person for every problem, failing to empower my team members to think critically and solve issues independently.
"Doing so, I robbed people of the opportunity to learn and grow."
In a self-managing organization, leaders have to let go and give others the opportunity to step up. Edwin was very honest about his shortcomings:
"I simply didn't know how to do that. I had to let people find their own solutions, support them to take more ownership, and stop solving their problems for them."
Edwin and Luz decided to change.
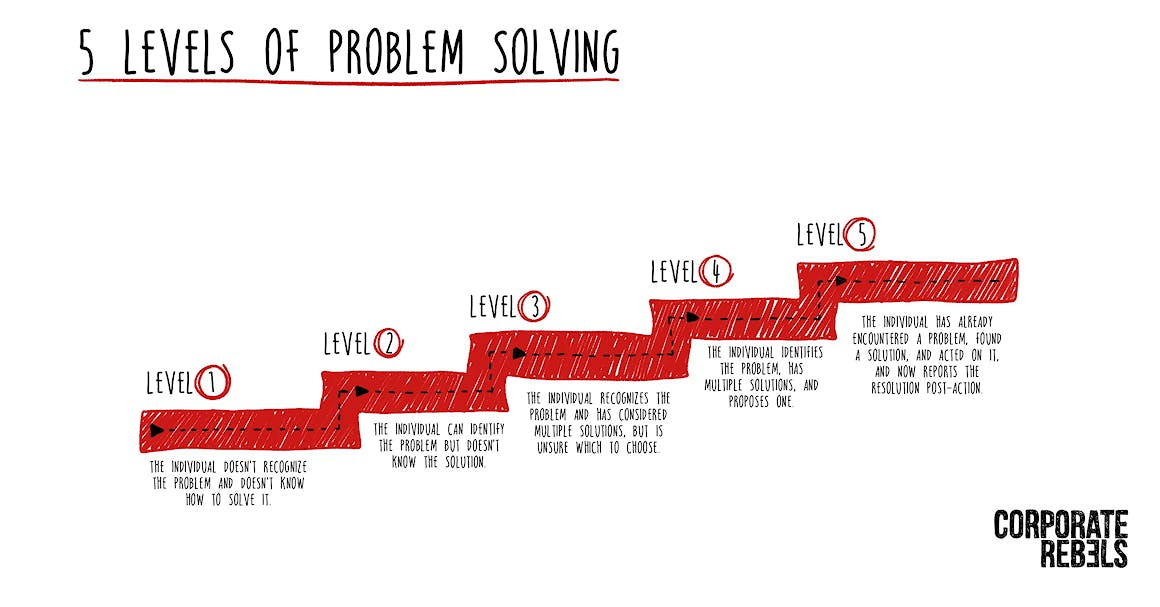
5 levels of problem solving
Along the way, Edwin encountered a framework that helped him become a better leader.
The framework details 5 levels of problem solving - moving from highly dependent to highly independent. The clarity of the various 'levels' of problem solving helped him and his colleagues to create awareness on how they were operating, while also providing clear opportunities for growth (for all involved).
Here's how Edwin explained it:
To summarize, here are the 5 levels Edwin talked about:
- Level 1: The individual doesn't recognize the problem and doesn't know how to solve it.
- Level 2: The individual can identify the problem but doesn't know the solution.
- Level 3: The individual recognizes the problem and has considered multiple solutions, but is unsure which to choose.
- Level 4: The individual identifies the problem, has multiple solutions, and proposes one.
- Level 5: The individual has already encountered a problem, found a solution, and acted on it, and now reports the resolution post-action.
Wanna improve? Here's Edwin's advice:
"At any point, if you're a manager and someone comes to you, whatever level they come to you at, ask them to go one level up.
"And if you're not a manager and you're coming with problems, make sure you're at the highest level that you possibly can be."
Solid (and practical) advice.
Start decentralizing decision-making now
Decision-making is an art, but with the right framework, it becomes a systematic process that fosters growth and innovation.
The '5 levels of problem solving' is one of those frameworks that has the power to change the way you work immediately. Print it out, share it with your team, and follow Edwin's advice.
Eager for more tips, tools, and frameworks to improve your decision-making? We've got you covered.
With an in-depth course, lots of pioneering practices, and powerful tools, our Academy has everything you need to radically reinvent the way you work.
Start now. Click here .

Download: New Ways Of Working Guide
Unlock our in-depth guide spotlighting trends, tools, and best practices from over 150 pioneering organizations.
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.

Download: Free Guide
Unlock our in-depth guide on trends, tools, and best practices from over 150 pioneering organizations.
Subscribe below and receive it directly in your inbox.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at any time.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 13: Algebraic thinking
About this unit.
Math is all about problem solving, and this unit will challenge you to use your algebraic thinking skills in new ways. You'll learn how parentheses can change the whole meaning of an algebraic expression by practice evaluating, translating, and creating your own expressions.
Writing expressions
- Constructing numerical expressions (Opens a modal)
- Evaluating expressions with & without parentheses (Opens a modal)
- Translating expressions with parentheses (Opens a modal)
- Evaluate expressions with parentheses Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Translate expressions with parentheses Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Create expressions with parentheses Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Number patterns
- Graphing patterns on coordinate plane (Opens a modal)
- Interpreting patterns on coordinate plane (Opens a modal)
- Interpreting relationships in ordered pairs (Opens a modal)
- Graphing sequence relationships (Opens a modal)
- Algebraic thinking: FAQ (Opens a modal)
- Rules that relate 2 variables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Tables from rules that relate 2 variables Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Graphs of rules that relate 2 variables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Extend patterns Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Relationships between 2 patterns Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Problem Solving and Decision Making

Problem Solving
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
- Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
- Identifying and Structuring Problems
- Investigating Ideas and Solutions
- Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
- Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Everybody can benefit from having good problem solving skills as we all encounter problems on a daily basis. Some of these problems are obviously more severe or complex than others.
It would be wonderful to have the ability to solve all problems efficiently and in a timely fashion without difficulty, unfortunately though there is no one way in which all problems can be solved.
You will discover, as you read through our pages on problem solving, that the subject is complex.
However well prepared we are for problem solving, there is always an element of the unknown. Although planning and structuring will help make the problem solving process more likely to be successful, good judgement and an element of good luck will ultimately determine whether problem solving was a success.
Interpersonal relationships fail and businesses fail because of poor problem solving.
This is often due to either problems not being recognised or being recognised but not being dealt with appropriately.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after by employers as many companies rely on their employees to identify and solve problems.
A lot of the work in problem solving involves understanding what the underlying issues of the problem really are - not the symptoms. Dealing with a customer complaint may be seen as a problem that needs to be solved, and it's almost certainly a good idea to do so. The employee dealing with the complaint should be asking what has caused the customer to complain in the first place, if the cause of the complaint can be eliminated then the problem is solved.
In order to be effective at problem solving you are likely to need some other key skills, which include:
Creativity. Problems are usually solved either intuitively or systematically. Intuition is used when no new knowledge is needed - you know enough to be able to make a quick decision and solve the problem, or you use common sense or experience to solve the problem. More complex problems or problems that you have not experienced before will likely require a more systematic and logical approach to solve, and for these you will need to use creative thinking. See our page on Creative Thinking for more information.
Researching Skills. Defining and solving problems often requires you to do some research: this may be a simple Google search or a more rigorous research project. See our Research Methods section for ideas on how to conduct effective research.
Team Working. Many problems are best defined and solved with the input of other people. Team working may sound like a 'work thing' but it is just as important at home and school as well as in the workplace. See our Team-Working page for more.
Emotional Intelligence. It is worth considering the impact that a problem and/or its solution has on you and other people. Emotional intelligence, the ability to recognise the emotions of yourself and others, will help guide you to an appropriate solution. See our Emotional Intelligence pages for more.
Risk Management. Solving a problem involves a certain amount of risk - this risk needs to be weighed up against not solving the problem. You may find our Risk Management page useful.
Decision Making . Problem solving and decision making are closely related skills, and making a decision is an important part of the problem solving process as you will often be faced with various options and alternatives. See Decision Making for more.
The measure of success is not whether you have a tough problem to deal with, but whether it is the same problem you had last year.
John Foster Dulles, Former US Secretary of State.
What is a Problem?
The Concise Oxford Dictionary (1995) defines a problem as:
“ A doubtful or difficult matter requiring a solution ”
“ Something hard to understand or accomplish or deal with.”
It is worth also considering our own view of what a problem is.
We are constantly exposed to opportunities in life, at work, at school and at home. However many opportunities are missed or not taken full advantage of. Often we are unsure how to take advantage of an opportunity and create barriers - reasons why we can't take advantage. These barriers can turn a potentially positive situation into a negative one, a problem.
Are we missing the 'big problem'? It is human nature to notice and focus on small, easy to solve problems but much harder to work on the big problems that may be causing some of the smaller ones.
It's useful to consider the following questions when faced with a problem.
Is the problem real or perceived?
Is this problem really an opportunity?
Does the problem need solving?
All problems have two features in common: goals and barriers.
Problems involve setting out to achieve some objective or desired state of affairs and can include avoiding a situation or event.
Goals can be anything that you wish to achieve, or where you want to be. If you are hungry then your goal is probably to eat something. If you are the head of an organisation (CEO), then your main goal may be to maximise profits and this main goal may need to be split into numerous sub-goals in order to fulfil the ultimate aim of increasing profits.
If there were no barriers in the way of achieving a goal, then there would be no problem. Problem solving involves overcoming the barriers or obstacles that prevent the immediate achievement of goals.
Following our examples above, if you feel hungry then your goal is to eat. A barrier to this may be that you have no food available - so you take a trip to the supermarket and buy some food, removing the barrier and thus solving the problem. Of course for the CEO wanting to increase profits there may be many more barriers preventing the goal from being reached. The CEO needs to attempt to recognise these barriers and remove them or find other ways to achieve the goals of the organisation.
Our problem solving pages provide a simple and structured approach to problem solving.
The approach referred to is generally designed for problem solving in an organisation or group context, but can also be easily adapted to work at an individual level at home or in education.
Trying to solve a complex problem alone however can be a mistake. The old adage " A problem shared is a problem halved " is sound advice.
Talking to others about problems is not only therapeutic but can help you see things from a different point of view, opening up more potential solutions.
Stages of Problem Solving
Effective problem solving usually involves working through a number of steps or stages, such as those outlined below.
Problem Identification:
This stage involves: detecting and recognising that there is a problem; identifying the nature of the problem; defining the problem.
The first phase of problem solving may sound obvious but often requires more thought and analysis. Identifying a problem can be a difficult task in itself. Is there a problem at all? What is the nature of the problem, are there in fact numerous problems? How can the problem be best defined? By spending some time defining the problem you will not only understand it more clearly yourself but be able to communicate its nature to others, which leads to the second phase.
Structuring the Problem:
This stage involves: a period of observation, careful inspection, fact-finding and developing a clear picture of the problem.
Following on from problem identification, structuring the problem is all about gaining more information about the problem and increasing understanding. This phase is all about fact finding and analysis, building a more comprehensive picture of both the goal(s) and the barrier(s). This stage may not be necessary for very simple problems but is essential for problems of a more complex nature.
Looking for Possible Solutions:
During this stage you will generate a range of possible courses of action, but with little attempt to evaluate them at this stage.
From the information gathered in the first two phases of the problem solving framework it is now time to start thinking about possible solutions to the identified problem. In a group situation this stage is often carried out as a brain-storming session, letting each person in the group express their views on possible solutions (or part solutions). In organisations different people will have different expertise in different areas and it is useful, therefore, to hear the views of each concerned party.
Making a Decision:
This stage involves careful analysis of the different possible courses of action and then selecting the best solution for implementation.
This is perhaps the most complex part of the problem solving process. Following on from the previous step it is now time to look at each potential solution and carefully analyse it. Some solutions may not be possible, due to other problems like time constraints or budgets. It is important at this stage to also consider what might happen if nothing was done to solve the problem - sometimes trying to solve a problem that leads to many more problems requires some very creative thinking and innovative ideas.
Finally, make a decision on which course of action to take - decision making is an important skill in itself and we recommend that you see our pages on decision making .
Implementation:
This stage involves accepting and carrying out the chosen course of action.
Implementation means acting on the chosen solution. During implementation more problems may arise especially if identification or structuring of the original problem was not carried out fully.
Monitoring/Seeking Feedback:
The last stage is about reviewing the outcomes of problem solving over a period of time, including seeking feedback as to the success of the outcomes of the chosen solution.
The final stage of problem solving is concerned with checking that the process was successful. This can be achieved by monitoring and gaining feedback from people affected by any changes that occurred. It is good practice to keep a record of outcomes and any additional problems that occurred.
Continue to: Identifying and Structuring Problems Social Problem Solving
See also: Project Management Risk Management Effective Decision Making
- Apps for the IWB
- Early Place Value
- Early Subtraction
- Hands-on Activities
- Linear Measurement
- Multiplicative Strategies
- No Worksheet Required
- Place Value
Problem Solving
- Strategy Mats
Receive news, product launches and course info via subscribing to our mailing list here .

Samples Requested

Problem Solving at Level 5
Grade level, lesson materials.
2 Mental Routines 20 Problematized Situations 3 Games
Compressed Zip File 8 MB 65 printable pages 4 FLASH programs 4 Slide Shows 1 Spreadsheet Planning Sheet
Select Licence:

- Description
- Australian Curriculum Links
- Sample Activity
The package comprises a series of problem solving activities and related problem solving strategies that young students can begin to apply. The package comprises:
- Two mental routines to develop student’s confidence and fluency with making an organized list or table and with spotting patterns.
- Strategy lessons and problems designed to develop strategic approaches, reasoning and to provide engaging situations for their application.
- Explicit use of the STAR model designed to help students unpack and understand what problems are asking them to find out as well as to find the important information and select a problem solving strategy that will allow them to get started on it.
- Suggestions for reflection to deepen understanding, share strategies and compare and formalize learning support materials in the form of interactive whiteboard (IWB) slide sequences to introduce many of the strategies and the essential vocabulary of the lessons and games.
- FLASH programs that help students explore a number of mathematical problems.
The mental routines, problems and games in this book cover almost all aspects of the ACM for Year 5. A Planning Sheet is included that shows how the coverage is achieved.
Download Sample
Similar Products You may also be interested in...
Problem solving at level 1.
The package comprises a series of problem-solving activities and related problem-solving strategies.
Problem Solving at Level 2
The package comprises a series of problem-solving activities and related problem-solving strategies suitable for Year 2 students.
STAR Posters for Problem Solving
The package comprises three posters sets, Lower Primary, Middle Primary and Upper Primary, that explain the STAR model of problem solving.
POWER UP Posters for Problem Solving
The POWER UP posters are intended to help with the issue of students 'giving up', by providing suggestions that support stickability and endurance.
Problem Solving at Level 3
The package comprises a series of problem-solving activities and related problem-solving strategies suitable for Year 3 students.
Problem Solving at Level 4
The package comprises a series of problem-solving activities and related problem-solving strategies suitable for Year 4 students.
Dominoes – Lower Primary
The package comprises a series of problem-solving activities for Year 1 and Year 2 students.
Dominoes – Middle and Upper Primary
The package comprises a series of problem-solving activities for Year 3 - Year 6 students.
Product is added
Want to ask a question.
- Ask a question *
- Product Title
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Natural Maths © 2019. All rights reserved.
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

KS3 Worksheet – Level 5 Problem Solving
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
16 December 2011
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Tes classic free licence
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
i liked this very much as a student but it would help me more if I would to explain how to get the answers <br />
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions

- Education & Teaching
- Schools & Teaching

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Return this item for free
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Problem Solving: Grade Level 5-6 (Basic Skills & Beyond) Paperback – January 1, 2005
Purchase options and add-ons.
- Print length 48 pages
- Language English
- Publisher Carson Dellosa Pub Co Inc
- Publication date January 1, 2005
- ISBN-10 9780887241819
- ISBN-13 978-0887241819
- See all details

Product details
- ASIN : 0887241816
- Publisher : Carson Dellosa Pub Co Inc; Workbook edition (January 1, 2005)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 48 pages
- ISBN-10 : 9780887241819
- ISBN-13 : 978-0887241819
- Item Weight : 4.8 ounces
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

Problem Solving Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 – 5)
By Status.net Editorial Team on July 21, 2023 — 4 minutes to read
Problem solving is an important skill in any work environment: it includes the ability to identify, understand, and develop solutions to complex issues while maintaining a focus on the end goal. Evaluating this skill in employees during performance reviews can be highly beneficial for both the employee and the organization.
Questions that can help you determine an employee’s rating for problem solving skills:
- How well does the employee define the problem and identify its root cause?
- How creative is the employee in generating potential solutions?
- How effective is the employee in implementing the chosen solution?
- How well does the employee evaluate the effectiveness of the solution and adjust it if necessary?
Related: Best Performance Review Examples for 48 Key Skills
2000+ Performance Review Phrases: The Complete List (Performance Feedback Examples)
Performance Review Phrases and Paragraphs Examples For Problem Solving
5 – outstanding.
Phrases examples:
- Consistently demonstrates exceptional problem-solving abilities
- Proactively identifies issues and offers innovative solutions
- Quickly adapts to unforeseen challenges and finds effective resolutions
- Exceptional problem-solving ability, consistently providing innovative solutions
- Regularly goes above and beyond to find creative solutions to complicated issues
- Demonstrates a keen understanding of complex problems and quickly identifies effective solutions
Paragraph Example 1
“Jane consistently demonstrates outstanding problem-solving skills. She proactively identifies issues in our department and offers innovative solutions that have improved processes and productivity. Her ability to quickly adapt to unforeseen challenges and find effective resolutions is commendable and has proven invaluable to the team.”
Paragraph Example 2
“Sarah has demonstrated an outstanding ability in problem solving throughout the year. Her innovative solutions have significantly improved our department’s efficiency, and she consistently goes above and beyond expectations to find creative approaches to complicated issues.”
4 – Exceeds Expectations
- Demonstrates a strong aptitude for solving complex problems
- Often takes initiative in identifying and resolving issues
- Effectively considers multiple perspectives and approaches before making decisions
- Displayed a consistently strong ability to tackle challenging problems efficiently
- Often takes the initiative to solve problems before they escalate
- Demonstrates a high level of critical thinking when resolving issues
“John exceeds expectations in problem-solving. He has a strong aptitude for solving complex problems and often takes initiative in identifying and resolving issues. His ability to consider multiple perspectives and approaches before making decisions has led to valuable improvements within the team.”
“Sam consistently exceeded expectations in problem solving this year. His efficient handling of challenging issues has made a positive impact on our team, and he often takes the initiative to resolve problems before they escalate. Sam’s critical thinking ability has been a valuable asset to our organization, and we appreciate his efforts.”
3 – Meets Expectations
- Displays adequate problem-solving skills when faced with challenges
- Generally able to identify issues and propose viable solutions
- Seeks assistance when necessary to resolve difficult situations
- Demonstrates a solid understanding of problem-solving techniques
- Capable of resolving everyday issues independently
- Shows perseverance when facing difficult challenges
“Mary meets expectations in her problem-solving abilities. She displays adequate skills when faced with challenges and is generally able to identify issues and propose viable solutions. Mary also seeks assistance when necessary to resolve difficult situations, demonstrating her willingness to collaborate and learn.”
“Sarah meets expectations in her problem-solving abilities. She demonstrates a solid understanding of problem-solving techniques and can resolve everyday issues independently. We value her perseverance when facing difficult challenges and encourage her to continue developing these skills.”
2 – Needs Improvement
- Struggles to find effective solutions to problems
- Tends to overlook critical details when evaluating situations
- Reluctant to seek help or collaborate with others to resolve issues
- Struggles to find effective solutions when faced with complex issues
- Often relies on assistance from others to resolve problems
- May lack confidence in decision-making when solving problems
“Tom’s problem-solving skills need improvement. He struggles to find effective solutions to problems and tends to overlook critical details when evaluating situations. Tom should work on being more willing to seek help and collaborate with others to resolve issues, which will ultimately strengthen his problem-solving abilities.”
“Mark’s problem-solving skills need improvement. He often struggles to find effective solutions for complex issues and seeks assistance from others to resolve problems. We encourage Mark to build his confidence in decision-making and focus on developing his problem-solving abilities.”
1 – Unacceptable
- Fails to identify and resolve problems in a timely manner
- Lacks critical thinking skills necessary for effective problem-solving
- Often creates additional issues when attempting to resolve problems
- Demonstrates a consistent inability to resolve even basic issues
- Often avoids responsibility for problem-solving tasks
- Fails to analyze problems effectively, leading to poor decision-making
“Sally’s problem-solving skills are unacceptable. She consistently fails to identify and resolve problems in a timely manner, and her lack of critical thinking skills hinders her ability to effectively solve challenges. Additionally, her attempts to resolve problems often create additional issues, resulting in a negative impact on the team’s overall performance.”
“Susan’s problem-solving performance has been unacceptable this year. She consistently demonstrates an inability to resolve basic issues and avoids taking responsibility for problem-solving tasks. Her ineffectiveness in analyzing problems has led to poor decision-making. It is crucial that Susan improve her problem-solving skills to succeed in her role.”
- Job Knowledge Performance Review Phrases (Examples)
- Cooperation Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- 100 Performance Review Phrases for Job Knowledge, Judgment, Listening Skills
- What Are Analytical Skills? [Examples]
- Collaboration Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- Critical Thinking: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)

Could Indiana’s Kel’el Ware solve the Sixers’ problem at backup center? The draft prospect thinks so.
CHICAGO — Standing at 6-foot-11 ¾ with a 230-pound frame, Kel’el Ware has the ideal size to back up Joel Embiid .
But his stature isn’t the only reason the Indiana center thinks he’s a solid fit for the 76ers or any other NBA team.
“I’m able to space the floor,” Ware said Tuesday at the NBA Draft Combine. “The NBA game is getting to that level where the bigs are not just back to the basket. I’m able to pick and pop. I’m able to be a lob threat. I’m able to move my feet. I’m able to defend on the perimeter. That’s why I feel I’m ready.”
There’s a chance the Sixers may trade their first-round pick in June’s NBA draft. However, multiple mock drafts have them selecting the 20-year-old if they keep the No. 16 selection. And that would be fine for the Arkansas native.
“That would be great to learn from [Embiid], especially since he’s a vet and has been in the league for a while,” Ware said of the possibility of backing up the 2023 MVP. “So if that did happen, I wouldn’t be opposed to that.”
Ware averaged 15.9 points, 9.9 rebounds, and 1.9 blocks during his lone season with the Hoosiers. That came after he averaged 6.6 points, 4.1 rebounds, and 1.3 blocks as a freshman at Oregon during the 2022-23 season. His ability to shoot the ball from the outside was one of his biggest improvements since transferring.
He shot 42.5% on college three-pointers this past season after making just 27.3% with the Ducks. Ware credits Indiana coach Mike Woodson for his improved shooting.
“Coach Woodson allowed me to play,” he said, “and trusting me on the court and playing through my mistakes.”
On Monday, Ware displayed his athleticism during the combine testing, finishing the three-quarter-court sprint in 3.29 seconds. He also made 10 of 25 shots in the three-point star drill. The 2022 McDonald’s All American will not compete in the five-on-five scrimmages here. He will, however, have meetings with various NBA front office executives and coaches this week in the Windy City.
“It’s just a blessing to be here, especially the hard work I put in to get here,” he said.
Edey’s mission
Zach Edey is out to prove that his game translates to the NBA.
Despite being the two-time national college player of the year at Purdue, the 7-4 center isn’t projected to be a lottery pick.
Critics have questioned his speed and believe his back-to-the basket playing style is outdated. But Edey made 14 of 25 three-pointers to finish tied for second in the three-point star drill. He also finished the three-quarter-court sprint in 3.51 seconds.
“I think it’s a tough thing, obviously, when people want to take down your game when you play a certain way,” he said. “But at the end of the day, I think teams are going to value what I do. …
“It doesn’t matter what people say. Teams put stock into rebounding. Teams put stock into having strength in the paint, strength and length, all that stuff. People are going to say what they are going to say. But I know who I am, and I know what I’m good at.”
Edey averaged 25.2 points, 12.2 rebounds, and 2.2 blocks this past season as a senior.
©2024 The Philadelphia Inquirer. Visit inquirer.com. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
The implementation of a solution requires planning and execution. It's often iterative, where the focus should be on short implementation cycles with testing and feedback, not trying to get it "perfect" the first time. Input: decision; planning; hard work. Output: resolution to the problem. 5.
Art of Problem Solving. AoPS Online. Math texts, online classes, and more for students in grades 5-12. Visit AoPS Online j. Books for Grades 5-12 Online Courses . ... Designed in an engaging comic-book style format, our Level 5 curriculum includes the Guide books and Practice books for all four units (5A, 5B, 5C, 5D).
Level 5 Problems. The Ministry is migrating nzmaths content to Tāhurangi. Relevant and up-to-date teaching resources are being moved to Tāhūrangi (tahurangi.education.govt.nz). When all identified resources have been successfully moved, this website will close. We expect this to be in June 2024.
Level 5 Math Games Game Spotlight: Puppy Chase Decimals Advertisement. Multiplayer Math Games Advertisement. Exponents. Hungry Decimals. Tug Fractions. ... Logic and Problem Solving Games Icy Super Slide. Arcade Golf. Rabbit Samurai 2. Duck Life 4. Icy Purple Head 2. Duck Life Space. Doctor Acorn 3. Doctor Acorn 2. Purple Mole. Fox Adventurer.
The 5 Levels of Problem Solving. To summarize, here are the 5 levels Edwin talked about: Level 1: The individual doesn't recognize the problem and doesn't know how to solve it. Level 2: The individual can identify the problem but doesn't know the solution. Level 3: The individual recognizes the problem and has considered multiple solutions, but ...
PROBLEM SOLVING SCQF Level 5 4 can be carried out simultaneously and the candidates will identify who is to carry out the tasks. In devising the action plan, the candidates will take into account any workplace limitations and issues relating to managing time and people. The candidates will identify the resources needed to carry out the action plan.
Graphing sequence relationships. Algebraic thinking: FAQ. Math is all about problem solving, and this unit will challenge you to use your algebraic thinking skills in new ways. You'll learn how parentheses can change the whole meaning of an algebraic expression by practice evaluating, translating, and creating your own expressions.
Our problem solving pages provide a simple and structured approach to problem solving. The approach referred to is generally designed for problem solving in an organisation or group context, but can also be easily adapted to work at an individual level at home or in education. Trying to solve a complex problem alone however can be a mistake.
Li Fanglan. FAN-Math Process Skills in Problem Solving L5 - is developed for pupils in grade 5 to 6. This series of books will help pupils to be aware of and develop a set of good habits of mind and acquire the necessary process skills involved in reasoning, communication and connections. In addition, The challenging sums and activities trains ...
The package comprises a series of problem solving activities and related problem solving strategies that young students can begin to apply. The package comprises: Two mental routines to develop student's confidence and fluency with making an organized list or table and with spotting patterns. Strategy lessons and problems designed to develop ...
Problem-Solving Skills Definition. Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to ...
How to Develop Problem Solving Skills: 4 Tips. Learning problem-solving techniques is a must for working professionals in any field. No matter your title or job description, the ability to find the root cause of a difficult problem and formulate viable solutions is a skill that employers value. Learning the soft skills and critical thinking ...
KS3 Worksheet - Level 5 Problem Solving. Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 11-14. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. doc, 23.5 KB. Worksheet of KS3 questions based on Number - Level 5 - Problem Solving Good in class as a worksheet for consolidation, working together in groups during whole class teaching or for independent homework.
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
4. Implement the Solution. At this stage of problem solving, be prepared for feedback, and plan for this. When you roll out the solution, request feedback on the success of the change made. 5. Review, Iterate, and Improve. Making a change shouldn't be a one time action.
Problem Solving offers students practice in reading and interpreting word and logic problems. Information needed to solve each problem can be found in the form of stories, tables, graphs, recipes, pictures, and more. The questions cover basic math facts appropriate for each grade level and require students to use higher level thinking skills.
Problem-solving skills are important in every career at every level. As a result, effective problem-solving may also require industry or job-specific technical skills. For example, a registered nurse will need active listening and communication skills when interacting with patients but will also need effective technical knowledge related to ...
Problem solving is an important skill in any work environment: it includes the ability to identify, understand, and develop solutions to complex issues while maintaining a focus on the end goal. ... Demonstrates a high level of critical thinking when resolving issues Goal Setting: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5) Paragraph Example 1
Reflect Regularly. Be the first to add your personal experience. 6. Stay Positive. Be the first to add your personal experience. 7. Here's what else to consider. Be the first to add your ...
The 2024 NBA Draft prospect thinks so. CHICAGO — Standing at 6-foot-11 ¾ with a 230-pound frame, Kel'el Ware has the ideal size to back up Joel Embiid. But his stature isn't the only reason ...