- Who’s Teaching What
- Subject Updates
- MEng program
- Opportunities
- Minor in Computer Science
- Resources for Current Students
- Program objectives and accreditation
- Graduate program requirements
- Admission process
- Degree programs
- Graduate research
- EECS Graduate Funding
- Resources for current students
- Student profiles
- Instructors
- DEI data and documents
- Recruitment and outreach
- Community and resources
- Get involved / self-education
- Rising Stars in EECS
- Graduate Application Assistance Program (GAAP)
- MIT Summer Research Program (MSRP)
- Sloan-MIT University Center for Exemplary Mentoring (UCEM)
- Electrical Engineering
- Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence + Decision-making
- AI and Society
- AI for Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Biological and Medical Devices and Systems
- Communications Systems
- Computational Biology
- Computational Fabrication and Manufacturing
- Computer Architecture
- Educational Technology
- Electronic, Magnetic, Optical and Quantum Materials and Devices
- Graphics and Vision
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Information Science and Systems
- Integrated Circuits and Systems
- Nanoscale Materials, Devices, and Systems
- Natural Language and Speech Processing
- Optics + Photonics
- Optimization and Game Theory
- Programming Languages and Software Engineering
- Quantum Computing, Communication, and Sensing
- Security and Cryptography
- Signal Processing
- Systems and Networking
- Systems Theory, Control, and Autonomy
- Theory of Computation
- Departmental History
- Departmental Organization
- Visiting Committee

Graduate programs
- Past Terms' Subject Updates and WTW
- Subject numbering
- FAQ about Fall 2024 Changes
- 2022 Curriculum Transition
- 6-1: Electrical Science and Engineering
- 6-2: Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- 6-3: Computer Science and Engineering
- 6-4: Artificial Intelligence and Decision Making
- 6-7: Computer Science and Molecular Biology
- 6-9: Computation and Cognition
- 11-6: Urban Science and Planning with Computer Science
- 6-14: Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science
- Requirements
- Application, Acceptance, and Deferral
- Thesis Proposal
- MEng Thesis
- UROP and SuperUROP
- Study Abroad
- USAGE Members, 2023-24
- 6-A Industrial Program
- Degree Audits and Departmental Petitions
- Space on Campus
- Resources for International Students
- Resources for Incoming Double Majors
- Resources for Advisors
- Graduate Admissions FAQs
- Graduate Admissions Information Letter
- What faculty members are looking for in a grad school application essay.
- Conditions of Appointment as a Teaching Assistant or Fellow
- RA Appointments
- Fellowship Appointments
- Materials and Forms for Graduate Students
- Subject Updates Spring 2024
- Subject Updates Fall 2023
- Subject Updates Spring 2023
- Subject Updates Fall 2022
- Subject Updates Spring 2022
- Subject Updates Fall 2021
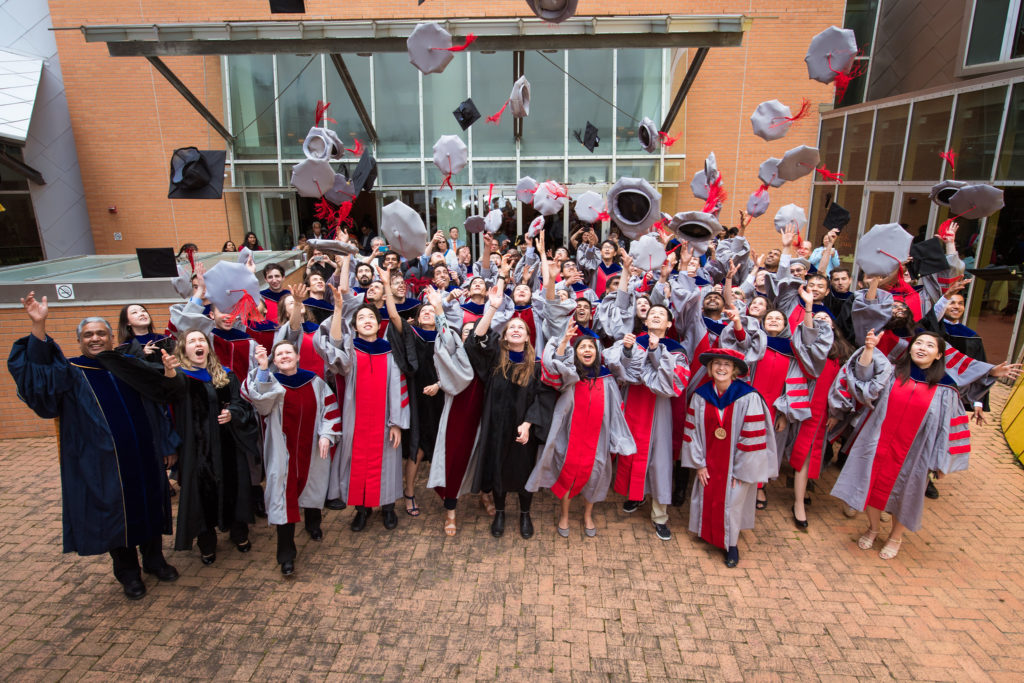

The largest graduate program in MIT’s School of Engineering, EECS has about 700 graduate students in the doctoral program at any given time. Those students conduct groundbreaking research across a wide array of fields alongside world-class faculty and research staff, build lifelong mentorship relationships and drive progress in every sector touched by electrical engineering, computer science, and artificial intelligence and decision-making.
- Dean’s Office
- External Advisory Council
- Computing Council
- Extended Computing Council
- Undergraduate Advisory Group
- Break Through Tech AI
- Building 45 Event Space
- Infinite Mile Awards: Past Winners
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Educating Computing Bilinguals
- Online Learning
- Industry Programs
- AI Policy Briefs
- Envisioning the Future of Computing Prize
- SERC Symposium 2023
- SERC Case Studies
- SERC Scholars Program
- SERC Postdocs
- Common Ground Subjects
- For First-Year Students and Advisors
- For Instructors: About Common Ground Subjects
- Common Ground Award for Excellence in Teaching
- New and Incoming Faculty
- Faculty Resources
- Faculty Openings
- Search for: Search
- MIT Homepage
3 Questions: A new PhD program from the Center for Computational Science and Engineering
Co-directors Youssef Marzouk and Nicolas Hadjiconstantinou describe how the standalone degree aims to train students in cross-cutting aspects of computational science and engineering.
This fall, the Center for Computational Science and Engineering (CCSE), an academic unit in the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing, is introducing a new standalone PhD degree program that will enable students to pursue research in cross-cutting methodological aspects of computational science and engineering. The launch follows approval of the center’s degree program proposal at the May 2023 Institute faculty meeting.
Doctoral-level graduate study in computational science and engineering (CSE) at MIT has, for the past decade, been offered through an interdisciplinary program in which CSE students are admitted to one of eight participating academic departments in the School of Engineering or School of Science. While this model adds a strong disciplinary component to students’ education, the rapid growth of the CSE field and the establishment of the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing have prompted an exciting expansion of MIT’s graduate-level offerings in computation.
The new degree, offered by the college, will run alongside MIT’s existing interdisciplinary offerings in CSE, complementing these doctoral training programs and preparing students to contribute to the leading edge of the field. Here, CCSE co-directors Youssef Marzouk and Nicolas Hadjiconstantinou discuss the standalone program and how they expect it to elevate the visibility and impact of CSE research and education at MIT.
Q: What is computational science and engineering?
Marzouk: Computational science and engineering focuses on the development and analysis of state-of-the-art methods for computation and their innovative application to problems of science and engineering interest. It has intellectual foundations in applied mathematics, statistics, and computer science, and touches the full range of science and engineering disciplines. Yet, it synthesizes these foundations into a discipline of its own — one that links the digital and physical worlds. It’s an exciting and evolving multidisciplinary field.
Hadjiconstantinou: Examples of CSE research happening at MIT include modeling and simulation techniques, the underlying computational mathematics, and data-driven modeling of physical systems. Computational statistics and scientific machine learning have become prominent threads within CSE, joining high-performance computing, mathematically-oriented programming languages, and their broader links to algorithms and software. Application domains include energy, environment and climate, materials, health, transportation, autonomy, and aerospace, among others. Some of our researchers focus on general and widely applicable methodology, while others choose to focus on methods and algorithms motivated by a specific domain of application.
Q: What was the motivation behind creating a standalone PhD program?
Marzouk: The new degree focuses on a particular class of students whose background and interests are primarily in CSE methodology, in a manner that cuts across the disciplinary research structure represented by our current “with-departments” degree program. There is a strong research demand for such methodologically-focused students among CCSE faculty and MIT faculty in general. Our objective is to create a targeted, coherent degree program in this field that, alongside our other thriving CSE offerings, will create the leading environment for top CSE students worldwide.
Hadjiconstantinou: One of CCSE’s most important functions is to recruit exceptional students who are trained in and want to work in computational science and engineering. Experience with our CSE master’s program suggests that students with a strong background and interests in the discipline prefer to apply to a pure CSE program for their graduate studies. The standalone degree aims to bring these students to MIT and make them available to faculty across the Institute.
Q: How will this impact computing education and research at MIT?
Hadjiconstantinou: We believe that offering a standalone PhD program in CSE alongside the existing “with-departments” programs will significantly strengthen MIT’s graduate programs in computing. In particular, it will strengthen the methodological core of CSE research and education at MIT, while continuing to support the disciplinary-flavored CSE work taking place in our participating departments, which include Aeronautics and Astronautics; Chemical Engineering; Civil and Environmental Engineering; Materials Science and Engineering; Mechanical Engineering; Nuclear Science and Engineering; Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences; and Mathematics. Together, these programs will create a stronger CSE student cohort and facilitate deeper exchanges between the college and other units at MIT.
Marzouk: In a broader sense, the new program is designed to help realize one of the key opportunities presented by the college, which is to create a richer variety of graduate degrees in computation and to involve as many faculty and units in these educational endeavors as possible. The standalone CSE PhD will join other distinguished doctoral programs of the college — such as the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science PhD; the Operations Research Center PhD; and the Interdisciplinary Doctoral Program in Statistics and the Social and Engineering Systems PhD within the Institute for Data, Systems, and Society — and grow in a way that is informed by them. The confluence of these academic programs, and natural synergies among them, will make MIT quite unique.
Related Stories


Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
77 Massachusetts Avenue Building 38-444 Cambridge MA, 02139
617-253-4603 [email protected]
Website: Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Application Opens: September 16
Deadline: December 15 at 11:59 PM Eastern Time
Fee: $75.00
Terms of Enrollment
Master of Engineering in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (MEng)*
Interdisciplinary Programs
Standardized tests.
Graduate Record Examination (GRE)
- Not required
International English Language Testing System (IELTS)
- Minimum score required: 7
- Electronic scores send to: MIT Graduate Admissions
Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL)
- Minimum score required: 100 (iBT) 600 (PBT)
- Institute code: 3514
- Department code: 78 or 66
IELTS exam is preferred over the TOEFL. Waiver of TOEFL/IELTS may be available.
Areas of Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bioelectrical Engineering
- Circuit Design
- Communications
- Computational Biology
- Computer Architecture
- Computer Graphics and Vision
- Computer Networks
- Control and Decisions Systems
- Electromagnetics, Energy, and Power
- Human Computer Interaction
- Machine Learning
- Materials, Devices, and Photonics
- Natural Language and Speech Processing
- Programming Languages
- Signal Processing
- Theoretical Computer Science
Financial Support
In the EECS PhD program, students are supported with a fellowship, research assistantship or teaching assistantship. The financial support provides full tuition, a monthly living stipend and medical insurance. When needed, additional departmental support is available.
Decisions on support are made after decisions on admission and are based on the information supplied in the application for admission. Any newly admitted student will automatically be considered for Department fellowships and assistantship support. Newly admitted students are also encouraged to apply to outside government and private agencies for fellowship support. Please see the EECS website for more information.
Application Requirements
- Online application
- Statement of objectives
- Three letters of recommendation
- Transcripts
- English proficiency exam scores
Special Instructions
*The Master of Engineering degrees are available to MIT undergraduates only.
**The Master of Science degree is required of students pursuing a doctoral degree. If you do not have a master’s degree when you apply, you will receive that degree first before proceeding to the PhD. A terminal master’s degree is not offered.
Applicants should not send published papers or theses. Admitted students will be required to submit official transcript(s) to the EECS Graduate Office.
This site uses cookies to give you the best possible experience. By browsing our website, you agree to our use of cookies.
If you require further information, please visit the Privacy Policy page.

Doctoral Programs in Computational Science and Engineering
- Current MIT Graduate Students
Please login to continue
This content is restricted.
CS PhD Course Guidelines
The following program guidelines (a.k.a model pogram) serve as a starting point for a discussion with the faculty about areas of interest. This description of the Computer Science PhD course guidelines augments the school-wide PhD course requirements . Students should make themselves familiar with both.

Course Guidelines for Ph.D. Students in Computer Science
We expect students to obtain broad knowledge of computer science by taking graduate level courses in a variety of sub-areas in computer science, such as systems, networking, databases, algorithms, complexity, hardware, human-computer interaction, graphics, or programming languages.
Within our school, CS courses are roughly organized according to sub-area by their middle digit, so we expect students to take courses in a minimum of three distinct sub-areas, one of which should be theory (denoted by the middle digit of 2, or CS 231). Theory is specifically required as we expect all students to obtain some background in the mathematical foundations that underlie computer science. The intention is not only to give breadth to students, but to ensure cross-fertilization across different sub-disciplines in Computer Science.
Just as we expect all students obtaining a Ph.D. to have experience with the theoretical foundations of computer science, we expect all students to have some knowledge of how to build large software or hardware systems , on the order of thousands of lines of code, or the equivalent complexity in hardware. That experience may be evidenced by coursework or by a project submitted to the CHD for examination. In almost all cases a course numbered CS 26x or CS 24x will satisfy the requirement (exceptions will be noted in the course description on my.harvard). Students may also petition to use CS 161 for this requirement. For projects in other courses, research projects, or projects done in internships the student is expected to write a note explaining the project, include a link to any relevant artifacts or outcomes, describe the student's individual contribution, and where appropriate obtain a note from their advisor, their class instructor, or their supervisors confirming their contributions. The project must include learning about systems concepts, and not just writing many lines of code. Students hoping to invoke the non-CS24x/26x/161 option must consult with Prof. Mickens , Prof, Kung, or Prof. Idreos well in advance of submitting their Program Plan to the CHD.
Computer science is an applied science, with connections to many fields. Learning about and connecting computer science to other fields is a key part of an advanced education in computer science. These connections may introduce relevant background, or they may provide an outlet for developing new applications.
For example, mathematics courses may be appropriate for someone working in theory, linguistics courses may be appropriate for someone working in computational linguistics, economics courses may be appropriate for those working in algorithmic economics, electrical engineering courses may be appropriate for those working in circuit design, and design courses may be appropriate for someone working in user interfaces.
Requirements
The Graduate School of Arts & Sciences (GSAS) requires all Ph.D. students to complete 16 half-courses (“courses”, i.e., for 4 units of credit) to complete their degree. Of those 16 courses, a Ph.D. in Computer Science requires 10 letter-graded courses. (The remaining 6 courses are often 300-level research courses or other undergraduate or graduate coursework beyond the 10 required courses.)
The requirements for the 10 letter-graded courses are as follows:
- Of the 7 technical courses, at least 3 must be 200-level Computer Science courses, with 3 different middle digits (from the set 2,3,4,5,6,7,8), and with one of these three courses either having a middle digit of 2 or being CS 231 (i.e., a “theory” course). Note that CS courses with a middle digit of 0 are valid technical courses, but do not contribute to the breadth requirement.
- At least 5 of the 8 disciplinary courses must be SEAS or SEAS-equivalent 200-level courses. A “SEAS equivalent” course is a course taught by a SEAS faculty member in another FAS department.
- For any MIT course taken, the student must provide justification why the MIT course is necessary (i.e. SEAS does not offer the topic, the SEAS course has not been offered in recent years, etc.). MIT courses do not count as part of the 5 200-level SEAS/SEAS-equivalent courses.
- 2 of the 10 courses must constitute an external minor (referred to as "breadth" courses in the SEAS “ Policies of the Committee on Higher Degrees [CHD] ”) in an area outside of computer science. These courses should be clearly related; generally, this will mean the two courses are in the same discipline, although this is not mandatory. These courses must be distinct from the 8 disciplinary courses referenced above.
- Students must demonstrate practical competence by building a large software or hardware system during the course of their graduate studies. This requirement will generally be met through a class project, but it can also be met through work done in the course of a summer internship, or in the course of research.
- In particular, for Computer Science graduate degrees, Applied Computation courses may be counted as 100-level courses, not 200-level courses.
- Up to 2 of the 10 courses can be 299r courses, but only 1 of the up to 2 allowed 299r courses can count toward the 8 disciplinary courses. 299r courses do not count toward the 5 200-level SEAS/SEAS-equivalent courses. If two 299r’s are taken, they can be with the same faculty but the topics must be sufficiently different.
- A maximum of 3 graduate-level transfer classes are allowed to count towards the 10 course requirement.
- All CS Ph.D. program plans must adhere to the SEAS-wide Ph.D. requirements, which are stated in the SEAS Policies of the Committee on Higher Degrees (CHD) . These SEAS-wide requirements are included in the items listed above, though students are encouraged to read the CHD document if there are questions, as the CHD document provides further explanation/detail on several of the items above.
- All program plans must be approved by the CHD. Exceptions to any of these requirements require a detailed written explanation of the reasoning for the exception from the student and the student’s research advisor. Exceptions can only be approved by the CHD, and generally exceptions will only be given for unusual circumstances specific to the student’s research program.
Requirement Notes
- Courses below the 100-level are not suitable for graduate credit.
- For students who were required to take it, CS 2091/2092 (formerly CS 290a/b or 290hfa/hfb may be included as one of the 10 courses but it does not count toward the 200-level CS or SEAS/SEAS-equivalent course requirements nor toward the SM en route to the PhD.
Your program plan must always comply with both our school's General Requirements, in addition to complying with the specific requirements for Computer Science. All program plans must be approved by the Committee on Higher Degrees [CHD]. Exceptions to the requirements can only be approved by the CHD, and generally will only be given for unusual circumstances specific to the student’s research program
In Computer Science
- First-Year Exploration
- Concentration Information
- Secondary Field
- Senior Thesis
- AB/SM Information
- Student Organizations
- How to Apply
- PhD Timeline
- PhD Course Requirements
- Qualifying Exam
- Committee Meetings (Review Days)
- Committee on Higher Degrees
- Research Interest Comparison
- Collaborations
- Cross-Harvard Engagement
- Lecture Series
- Clubs & Organizations
- Centers & Initiatives
- Alumni Stories
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Admissions Requirements
The following are general requirements you should meet to apply to the MIT Sloan PhD Program. Complete instructions concerning application requirements are available in the online application.
General Requirements
- Bachelor's degree or equivalent
- A strong quantitative background (the Accounting group requires calculus)
- Exposure to microeconomics and macroeconomics (the Accounting group requires microeconomics)
A Guide to Business PhD Applications by Abhishek Nagaraj (PhD 2016) may be of interest.
Application Components
Statement of purpose.
Your written statement is your chance to convince the admissions committee that you will do excellent doctoral work and that you have the promise to have a successful career as an academic researcher.
GMAT/GRE Scores
We require either a valid GMAT or valid GRE score. At-home testing is allowed. Your unofficial score report from the testing institution is sufficient for application. If you are admitted to the program, you will be required to submit your official test score for verification.
We do not have a minimum score requirement. We do not offer test waivers. Registration information for the GMAT (code X5X-QS-21) and GRE (code 3510) may be obtained at www.mba.com and www.ets.org respectively.
TOEFL/IELTS Scores
We require either a valid TOEFL (minimum score 577 PBT/90 IBT ) or valid IELTS (minimum score 7) for all non-native English speakers. Your unofficial score report from the testing institution is sufficient for application. If you are admitted to the program, you will be required to submit your official test score for verification. Registration information for TOEFL (code 3510) and IELTS may be obtained at www.toefl.org and www.ielts.org respectively.
The TOEFL/IELTS test requirement is waived only if you meet one of the following criteria:
- You are a native English speaker.
- You attended all years of an undergraduate program conducted solely in English, and are a graduate of that program.
Please do not contact the PhD Program regarding waivers, as none will be discussed. If, upon review, the faculty are interested in your application with a missing required TOEFL or IELTS score, we may contact you at that time to request a score.
Transcripts
We require unofficial copies of transcripts for each college or university you have attended, even if no degree was awarded. If these transcripts are in a language other than English, we also require a copy of a certified translation. In addition, you will be asked to list the five most relevant courses you have taken.
Letters of Recommendation
We require three letters of recommendation. Academic letters are preferred, especially those providing evidence of research potential. We allow for an optional fourth recommendation, but no more than four recommendations are allowed.
Your resume should be no more than two pages. You may chose to include teaching, professional experience, research experience, publications, and other accomplishments in outside activities.
Writing Sample(s)
Applicants are encouraged to submit a writing sample. For applicants to the Finance group, a writing sample is required. There are no specific guidelines for your writing sample. Possible options include (but are not limited to) essays, masters’ theses, capstone projects, or research papers.
Video Essay
A video essay is required for the Accounting research group and optional for the Marketing and System Dynamics research groups. The essay is a short and informal video answering why you selected this research group and a time where you creatively solved a problem. The video can be recorded with your phone or computer, and should range from 2 to 5 minutes in length. There is no attention — zero emphasis! — on the production value of your video.
Nondiscrimination Policy: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is committed to the principle of equal opportunity in education and employment. For complete text of MIT’s Nondiscrimination Statement, please click here .
- Skip to Content
- Bulletin Home

- Degree Charts >
- Computational Science and Engineering (SM)
- Around Campus
- Academic Program
- Administration
- Arts at MIT
- Campus Media
- Fraternities, Sororities, and Independent Living Groups
- Medical Services
- Priscilla King Gray Public Service Center
- Religious Organizations
- Student Government
- Work/Life and Family Resources
- Advising and Support
- Digital Learning
- Disability and Access Services
- Information Systems and Technology
- Student Financial Services
- Writing and Communication Center
- Major Course of Study
- General Institute Requirements
- Independent Activites Period
- Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program
- First-Year Advising Seminars
- Interphase EDGE/x
- Edgerton Center
- Grading Options
- Study at Other Universities
- Internships Abroad
- Career Advising and Professional Development
- Teacher Licensure and Education
- ROTC Programs
- Financial Aid
- Medical Requirements
- Graduate Study at MIT
- General Degree Requirements
- Other Institutions
- Registration
- Term Regulations and Examination Policies
- Academic Performance and Grades
- Policies and Procedures
- Privacy of Student Records
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab
- Art, Culture, and Technology Program
- Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard
- Center for Archaeological Materials
- Center for Bits and Atoms
- Center for Clinical and Translational Research
- Center for Collective Intelligence
- Center for Computational Science and Engineering
- Center for Constructive Communication
- Center for Energy and Environmental Policy Research
- Center for Environmental Health Sciences
- Center for Global Change Science
- Center for International Studies
- Center for Real Estate
- Center for Transportation & Logistics
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Concrete Sustainability Hub
- D-Lab
- Deshpande Center for Technological Innovation
- Division of Comparative Medicine
- Haystack Observatory
- Initiative on the Digital Economy
- Institute for Medical Engineering and Science
- Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies
- Institute for Work and Employment Research
- Internet Policy Research Initiative
- Joint Program on the Science and Policy of Global Change
- Knight Science Journalism Program
- Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research
- Laboratory for Financial Engineering
- Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems
- Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity
- Laboratory for Nuclear Science
- Legatum Center for Development and Entrepreneurship
- Lincoln Laboratory
- Martin Trust Center for MIT Entrepreneurship
- Materials Research Laboratory
- McGovern Institute for Brain Research
- Microsystems Technology Laboratories
- MIT Center for Art, Science & Technology
- MIT Energy Initiative
- MIT Environmental Solutions Initiative
- MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research
- MIT Media Lab
- MIT Office of Innovation
- MIT Open Learning
- MIT Portugal Program
- MIT Professional Education
- MIT Sea Grant College Program
- Nuclear Reactor Laboratory
- Operations Research Center
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Plasma Science and Fusion Center
- Research Laboratory of Electronics
- Simons Center for the Social Brain
- Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology Centre
- Sociotechnical Systems Research Center
- Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
- Women's and Gender Studies Program
- Architecture (Course 4)
- Art and Design (Course 4-B)
- Art, Culture, and Technology (SM)
- Media Arts and Sciences
- Planning (Course 11)
- Urban Science and Planning with Computer Science (Course 11-6)
- Aerospace Engineering (Course 16)
- Engineering (Course 16-ENG)
- Biological Engineering (Course 20)
- Chemical Engineering (Course 10)
- Chemical-Biological Engineering (Course 10-B)
- Chemical Engineering (Course 10-C)
- Engineering (Course 10-ENG)
- Engineering (Course 1-ENG)
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (Course 6-2)
- Electrical Science and Engineering (Course 6-1)
- Computation and Cognition (Course 6-9)
- Computer Science and Engineering (Course 6-3)
- Computer Science and Molecular Biology (Course 6-7)
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (MEng)
- Computer Science and Molecular Biology (MEng)
- Health Sciences and Technology
- Archaeology and Materials (Course 3-C)
- Materials Science and Engineering (Course 3)
- Materials Science and Engineering (Course 3-A)
- Materials Science and Engineering (PhD)
- Mechanical Engineering (Course 2)
- Mechanical and Ocean Engineering (Course 2-OE)
- Engineering (Course 2-A)
- Nuclear Science and Engineering (Course 22)
- Engineering (Course 22-ENG)
- Anthropology (Course 21A)
- Comparative Media Studies (CMS)
- Writing (Course 21W)
- Economics (Course 14-1)
- Mathematical Economics (Course 14-2)
- Data, Economics, and Design of Policy (MASc)
- Economics (PhD)
- Global Studies and Languages (Course 21G)
- History (Course 21H)
- Linguistics and Philosophy (Course 24-2)
- Philosophy (Course 24-1)
- Linguistics (SM)
- Literature (Course 21L)
- Music (Course 21M-1)
- Theater Arts (Course 21M-2)
- Political Science (Course 17)
- Science, Technology, and Society/Second Major (STS)
- Business Analytics (Course 15-2)
- Finance (Course 15-3)
- Management (Course 15-1)
- Biology (Course 7)
- Chemistry and Biology (Course 5-7)
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences (Course 9)
- Chemistry (Course 5)
- Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (Course 12)
- Mathematics (Course 18)
- Mathematics with Computer Science (Course 18-C)
- Physics (Course 8)
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- Institute for Data, Systems, and Society
- Chemistry and Biology
- Climate System Science and Engineering
- Computation and Cognition
- Computer Science and Molecular Biology
- Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science
- Humanities and Engineering
- Humanities and Science
- Urban Science and Planning with Computer Science
- African and African Diaspora Studies
- American Studies
- Ancient and Medieval Studies
- Applied International Studies
- Asian and Asian Diaspora Studies
- Biomedical Engineering
- Energy Studies
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Environment and Sustainability
- Latin American and Latino/a Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Polymers and Soft Matter
- Public Policy
- Russian and Eurasian Studies
- Statistics and Data Science
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Advanced Urbanism
- Computational and Systems Biology
Computational Science and Engineering
- Design and Management (IDM & SDM)
- Joint Program with Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
- Leaders for Global Operations
- Microbiology
- Music Technology and Computation
- Operations Research
- Real Estate Development
- Social and Engineering Systems
- Supply Chain Management
- Technology and Policy
- Transportation
- School of Architecture and Planning
- School of Engineering
- Aeronautics and Astronautics Fields (PhD)
- Artificial Intelligence and Decision Making (Course 6-4)
- Biological Engineering (PhD)
- Nuclear Science and Engineering (PhD)
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Humanities (Course 21)
- Humanities and Engineering (Course 21E)
- Humanities and Science (Course 21S)
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences (PhD)
- Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences Fields (PhD)
- Interdisciplinary Programs (SB)
- Climate System Science and Engineering (Course 1-12)
- Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science (Course 6-14)
- Interdisciplinary Programs (Graduate)
- Computation and Cognition (MEng)
- Computational Science and Engineering (PhD)
- Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science (MEng)
- Leaders for Global Operations (MBA/SM and SM)
- Music Technology and Computation (SM and MASc)
- Real Estate Development (SM)
- Statistics (PhD)
- Supply Chain Management (MEng and MASc)
- Technology and Policy (SM)
- Transportation (SM)
- Aeronautics and Astronautics (Course 16)
- Aerospace Studies (AS)
- Civil and Environmental Engineering (Course 1)
- Comparative Media Studies / Writing (CMS)
- Comparative Media Studies / Writing (Course 21W)
- Computational and Systems Biology (CSB)
- Computational Science and Engineering (CSE)
- Concourse (CC)
- Data, Systems, and Society (IDS)
- Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences (Course 12)
- Economics (Course 14)
- Edgerton Center (EC)
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (Course 6)
- Engineering Management (EM)
- Experimental Study Group (ES)
- Global Languages (Course 21G)
- Health Sciences and Technology (HST)
- Linguistics and Philosophy (Course 24)
- Management (Course 15)
- Media Arts and Sciences (MAS)
- Military Science (MS)
- Music and Theater Arts (Course 21M)
- Naval Science (NS)
- Science, Technology, and Society (STS)
- Special Programs
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Urban Studies and Planning (Course 11)
- Women's and Gender Studies (WGS)
Master of Science in Computational Science and Engineering
Restricted electives.

Print this page.
The PDF includes all information on this page and its related tabs. Subject (course) information includes any changes approved for the current academic year.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The standalone CSE PhD program is intended for students who plan to pursue research in cross-cutting methodological aspects of computational science. The resulting doctoral degree in Computational Science and Engineering is awarded by CCSE via the the Schwarzman College of Computing. In contrast, the interdisciplinary Dept-CSE PhD program is ...
The standalone CSE PhD program is intended for students who intend to pursue research in cross-cutting methodological aspects of computational science. The resulting doctoral degree in Computational Science and Engineering is awarded by CCSE via the the Schwarzman College of Computing. In contrast, the interdisciplinary CSE PhD program is ...
279-399. 1. A program of study comprising subjects in the selected core areas and the computational concentration must be developed in consultation with the student's doctoral thesis committee and approved by the CCSE graduate officer. Programs Offered by CCSE in Conjunction with Select Departments in the Schools of Engineering and Science.
Program Overview. The standalone doctoral program in Computational Science and Engineering ( PhD in CSE) enables students to specialize at the doctoral level in fundamental, methodological aspects of computational science via focused coursework and a thesis. The emphasis of thesis research activities is the development and analysis of broadly ...
The DMSE-CSE doctoral program of study consists of at least five graduate subjects in computational science and engineering selected from the approved list of Computational Concentration Subjects.The CSE five-course requirement can be satisfied through courses that simultaneously satisfy the DMSE core, post-core electives, and/or minor requirements.
77 Massachusetts Avenue. Building 35-434B. Cambridge MA, 02139. 617-253-3725. [email protected]. Website: Computational Science and Engineering PhD. Apply here. Application Opens:
MIT Graduate Admissions Statement March 26, 2020. In response to the challenges of teaching, learning, and assessing academic performance during the global COVID-19 pandemic, MIT has adopted the following principle: MIT's admissions committees and offices for graduate and professional schools will take the significant disruptions of the COVID-19 outbreak in 2020 into account when reviewing ...
The largest graduate program in MIT's School of Engineering, EECS has about 700 graduate students in the doctoral program at any given time. Those students conduct groundbreaking research across a wide array of fields alongside world-class faculty and research staff, build lifelong mentorship relationships and drive progress in every sector ...
This fall, the Center for Computational Science and Engineering (CCSE), an academic unit in the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing, is introducing a new standalone PhD degree program that will enable students to pursue research in cross-cutting methodological aspects of computational science and engineering. The launch follows approval of the center's degree program proposal at […]
Inquiries. Additional information concerning graduate academic and research programs, admissions, financial aid, and assistantships may be obtained from the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Graduate Office, Room 38-444, 617-253-4605, or visit the EECS website.
The application and additional information may be found on the Advanced Study Program website. Admission is valid only for one term; a student must seek readmission each term to continue at the Institute. Those applying for special graduate student status for the first time must pay an application fee. To be allowed to continue as a special ...
A doctoral degree requires the satisfactory completion of an approved program of advanced study and original research of high quality. Please note that the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) and Doctor of Science (ScD) degrees are awarded interchangeably by all departments in the School of Engineering and the School of Science, except in the fields of biology, cognitive science, neuroscience, medical ...
Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. 77 Massachusetts Avenue. Building 38-444. Cambridge MA, 02139. 617-253-4603. [email protected]. Website: Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. Apply here.
77 Massachusetts Ave. 45-421.2 Cambridge, MA 02139. [email protected] Accessibility
Summary of Subject Requirements Subjects; Science Requirement: 6: Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences (HASS) Requirement [two subjects can be satisfied by 6.3260[J] and 6.4590[J] (taken as part of a track) in the Departmental Program]; at least two of these subjects must be designated as communication-intensive (CI-H) to fulfill the Communication Requirement.
The requirements for the 10 letter-graded courses are as follows: 8 of the 10 courses must be disciplinary, and at least 7 of those must be technical courses drawn from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, FAS or MIT. Of the 7 technical courses, at least 3 must be 200-level Computer Science courses, with 3 ...
Admissions Requirements. The following are general requirements you should meet to apply to the MIT Sloan PhD Program. Complete instructions concerning application requirements are available in the online application. General Requirements. Bachelor's degree or equivalent. A strong quantitative background (the Accounting group requires calculus)
CSE.999. Experiential Learning in Computational Science and Engineering. IDS.131 [J] Statistics, Computation and Applications. 12. 1. Restricted elective credit can only be given for one of 6.7900, 15.077, or IDS.147. 2. Students cannot receive credit without simultaneous completion of a 6-unit Common Ground disciplinary module.