

PhD vs MD vs MD PhD – What’s right for you?
- Cracking Med School Admissions Team
For some students, choosing between a career in medicine and one in science seems like an impossible task. Many times, students will engage in research during college and develop an interest in medicine and do not want to give up the ability to do both by pursuing either a PhD or MD. Recognizing this desire, many medical schools have also created MD-PhD combined programs that allow students to get both degrees. With the plethora of options offered for graduate degrees coming out of college, many applicants are unsure of which program is best for them.
In this blog post, we will cover the following topics:
- PhD vs MD vs MD PhD?
What are the differences between PhD vs MD?
- MD vs MD PhD – which is right for a future doctor?
- Pros and Cons of MD PhD
- Complete List of MSTP Programs
- Resources for future MD PhD Applicants
Our Students Were Accepted at These MD PhD Programs!

PhD vs MD vs MD PhD
Before we analyze the differences between these programs, we will clearly define what each program consists of.
What is a PhD? PhD programs are funded graduate doctoral degree programs ranging from 4-8 years offered by research universities to teach and mentor graduates to contribute to research in their field, develop societal solutions, and train the next generation of scientists.
What is an MD? MD degrees are granted by allopathic medical schools in the United States, last four years, and prepare graduates to enter the world of medicine as physicians, usually through continued training in residency and fellowship programs.
What is an MD PhD program? MD/PhD programs are funded programs that last 7-9 years and train graduates to be clinical and academic leaders as both physicians and researchers who work closely with patients but also dedicate a significant amount of their time to researching areas adjacent to medicine to improve knowledge and treatment protocols.
When deciding PhD vs MD vs MD PhD, most students will first need to decide what aspects of science are most interesting to them – do they enjoy the interpersonal interactions or working with the biology itself to make new discoveries? First, let’s look at the differences between a PhD vs MD. There are three core differences between getting a PhD and an MD: career opportunities, admissions and training, and cost.
Career Options
As rigorous and prestigious degree programs, both MDs and PhDs have a plethora of career opportunities available to them. Most graduates from MD programs elected to continue their training by completing a residency and fellowship to become specialized and practice medicine. Nonetheless some graduates also choose to pursue alternative careers in public health, business, or education. In fact, 32% of graduates from Stanford’s MD program [1] chose not to a pursue a residency, many drawn by the allure of alternative ways to produce impact in society.
PhD graduates tend to have slightly more options, in both the academic and professional spheres. Many PhD candidates choose to pursue the established path of joining a research university to perform their research while teaching undergraduate and graduate students. This path often is best suited for those extremely passionate about their research topics who seek to mentor younger researchers and students but suffers from department politics attached to rising up professorial ranks and difficulties in receiving funding in certain disciplines.
Many other graduates choose to pursue non-academic work, whether it is joining an established industry company, starting their own companies, or working in public sector agencies. In these endeavors, they are able to leverage much of their subject matter expertise to conduct research, assess business operations and growth options, and contribute to public health or public works initiatives. At the same time, many graduates who take this path may find themselves drifting away from their academic routes and may find a slightly more fast-paced lifestyle than in academia.
Whether you pursue and MD degree or PhD degree, there are several post-graduate career options.
Admissions and Training
Admissions and training processes and timelines are also highly variable between MD and PhD paths, and require different planning for each.
MD Admissions and Training: MD programs often have extremely long admissions timelines, often starting two years before matriculation when many students begin studying for the MCAT (the medical school admissions exam). In addition, the increasing expectations of applicants has resulted in an increasing number of students taking gap years to adequately prepare to apply. After applying and matriculating, medical students have four years of medical school, followed by anywhere from 3-10 years of post-graduate specialization training. Furthermore, applications often have multiple components, require in-person interviews, and have delayed decision timelines.
PhD Admissions and Training: In contrast, PhD programs have relatively simpler timelines, with most students applying the winter before they plan to matriculate, with many schools not requiring standardized testing (GRE) to apply. After applying, many students receive interviews within a few weeks and an admissions decision soon after. After matriculating, program length can differ significantly, but usually consists of 5-8 years of graduate research and training before one is able to complete their degree.
Despite recruiting students with similar skillsets and backgrounds, medical school and graduate PhD programs have radically different cost structures. While pursuing an MD is a costly endeavor (often ranging from $200-400k), PhDs are usually fully funded and most students receive a generous living stipend. With this in mind, one would assume that most students would naturally gravitate to a PhD. However, while the median biology PhD starting salary is $100k [2] , the median starting salary for a physician is double – at $200k [2] – such that many physicians recoup the cost of their education in the long term. Although the ultimate decision will depend on your desire to take on loans and your career and training area preferences, cost is undoubtably an important component of this decision as well.
What are the differences between MD vs MD PhD
Differences between MD and MD-PhD admissions are neither widely discussed nor well understood, mostly because only 6-7% of students applying to medical school choose to pursue this path. [4]
MD-PhD programs are one of many dual-degree programs offered by medical schools and allow you to receive medical training while developing expertise in a particular research area. Your research focus can range from hard science like molecular biology and genetics to the social sciences like sociology. Since you would be getting two degrees, a MD-PhD program is designed to take 7-8 years, instead of 4 years for medical school and 5-6 years for a PhD. Usually, MD-PhD candidates will spend their first two years doing pre-clinical coursework with MD students. After completing their pre-medical requirements and taking the STEP 1 exam, MD-PhD students will usually take 3-5 years for their doctoral studies before they return for their final two years of clinical rotations.
In the United States, there are approximately 130 MD-PhD programs and 45 of these programs are known as Medical Scientist Training Programs (MSTP) programs. MSTP programs are funded by the National Institute of Health (NIH) and are very competitive as they offer full tuition coverage, support with living expenses, and a stipend. While some MD-PhD programs are funded by institutions, many of them may not offer the same financial support as an MSTP program.
Since the key difference between the MD and MD-PhD program is the emphasis on research, make sure that you will be able to demonstrate a longstanding commitment to research and that you have tangibly and significantly contributed to research projects, which can take the form of presentations or serving as an author on papers. Also, make sure that your research mentor is prepared to submit a strong recommendation to attest to your readiness for such a rigorous program.
Only 6-7% of medical school applicants apply as an MD PhD candidate
AMCAS most meaningful activity example #2: This applicant chose to write about his work in the emergency room. You can see both the 700 character AMCAS activity description and the 1325 character AMCAS most meaningful essay.
Pros and Cons of Applying MD PhD
Pros of applying md phd vs md, why md phd #1: tuition funding .
There is no doubting it – medical school is very expensive. Since many MD-PhD programs are fully funded with a living stipend on top, many MD-PhD candidates feel that they are being “paid” to pursue this education. While many of their medical school classmates will graduate with tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt, most MD-PhD candidates will not incur any cost during the course of their degree, attracting many looking to avoid accumulating further debt in addition to whatever was accrued during college. Although this funding seems attractive at first, it is important to remember that it comes at the cost of four more years, which could be time spent earning an attending’s salary. Depending on your choice of specialty, receiving this funding could actually be a negative if you aren’t interested in research.
Why MD PhD #2: Allows you to pursue 2 passions
If you are unable to decide between science and medicine, or want to pursue both, applying to an MD-PhD program will allow you to bridge these two disciplines and enjoy the best of both worlds. Many MD-PhD candidates believe that their professional careers would be incomplete without both research and medicine or seek to combine these two passions in their career. These are the exact candidates that MD-PhD programs exist for as they open up many opportunities that may not be available for regular MD students. Especially if you hope to have a career in academia or research-based medical universities, the skills and competencies of doing research and applying for grants is highly prized.
Why MD PhD #3: Receive great research and medical training in a shorter time period
It is undeniable that the condensed time frame of the MD-PhD program is highly appealing to those who seek to pursue both degrees. Instead of taking 9-10 years if completed separately, an MD-PhD program is highly integrated and structured to allow you to focus on one pursuit at a time while still providing continuity so that you can do research during your medical training and medical volunteering while completing your doctoral work. This blend allows for the shorter time period and still allows you to benefit from receiving high quality science and medical instruction.
Cons of Applying MD PhD vs MD
Why not apply md phd #1: time to complete degree .
Although the condensed format is ideal for those who have their hearts set on getting both an MD and a PhD, if you are unsure about pursuing both degrees or have a clear preference for one, the significantly longer educational period is a major factor to consider. A major aspect of the admission process for the MD-PhD is determining if you are prepared to make an almost decade-long commitment to a discipline, institution, and city. The projected 7-8 years to complete an MD-PhD is just that – a projection. Many times, there are factors both inside and outside of your control that can cause this number to vary greatly and increase to up to 10 years. Furthermore, since many people start their MD-PhDs at 23 or 24 years old, they often complete their residency in their late 30s, a fundamentally different time of your life where many of your friends from college may already have families and have been in the workforce for over a decade.
Why not apply MD PhD #2: You can still do research without a PhD
Although MD-PhD students learn how to apply for grants and the research skills necessary to drive their future academic careers, many MD students often pick up these skills if they take a research year, pursue a master’s degree, or spend a significant amount of time doing research in residency and beyond. In fact, while many researchers in academic institutions are PhDs or MD-PhDs, there are also numerous MDs who spend a large amount of their time dedicated to both clinical and basic science research. Furthermore, if your research interests are solely clinical in nature, you may be better served developing these skills in a residency or pursuing a master’s degree than pursuing an MD-PhD, which is usually more suited for basic scientists. Another downside to the MD-PhD is that while you will be focused on trying to pursue two separate paths as a clinician and scientists, many of your peers will be spending all of their time focusing on one of the two, which may put you at a disadvantage compared to them.
Why not apply MD PhD #3: May limit specialty choice
Finally, while MD-PhD students can technically pursue any residency after they graduate medical school, there is often a push to place them in less competitive and non-surgical specialties where they will have less clinical time and therefore more time to dedicate to their research work. Since surgical specialties are highly procedural, research is often a secondary consideration and usually not as prized as surgical dexterity. Furthermore, since you are more valuable to an academic center as a surgeon performing high value elective procedures than as a researcher, there is often a push to have surgeons focus on their clinical work. Similarly, many MD-PhDs may be encouraged to pursue less competitive specialties where they have more time to focus on their research work or where their research funding may be more valuable than the money they bring in from being a clinician. Although an MD-PhD student is free to pursue any specialty that they desire, these pressures are commonplace and often can stifle strong clinical preferences in favor of research potential.
List of MSTP Programs
As stated earlier, MSTP MD PhD programs are fully funded by the National Institutes of Health.
As of 2021, here is the list of MSTP MD PhD programs by state.
University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicine http://www.uab.edu/medicine/mstp
Stanford University http://med.stanford.edu/mstp.html
University of California, Davis School of Veterinary Medicine https://vstp.vetmed.ucdavis.edu/
University of California, Irvine School of Medicine http://www.mstp.uci.edu
University of California, Los Angeles & Cal Tech California Institute of Technology David Geffen School of Medicine http://mstp.healthsciences.ucla.edu
University of California, San Diego School of Medicine http://mstp.ucsd.edu
University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine https://mstp.ucsf.edu/
University of Colorado Denver http://www.ucdenver.edu/academics/colleges/medicalschool/education/degree_programs/mstp/pages/MSTP.aspx
Connecticut
Yale University School of Medicine http://medicine.yale.edu/mdphd
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine http://mdphd.med.miami.edu
Emory University School of Medicine M.D./Ph.D. Program http://med.emory.edu/MDPHD
Northwestern University Medical School http://www.feinberg.northwestern.edu/sites/mstp
University of Chicago Medical Scientist Training Program https://pritzker.uchicago.edu/academics/mstp-landing-page
University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine http://chicago.medicine.uic.edu/mstp
Indiana University School of Medicine, MSTP https://medicine.iu.edu/education/dual-degrees/
University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine https://medicine.uiowa.edu/mstp?
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine https://mdphd.johnshopkins.edu/
University of Maryland School of Medicine http://mdphd.umaryland.edu
Massachusetts
Harvard Medical School/Massachusetts Institute of Technology
There are two MD/PhD programs through Pathways and HST. Read more about Harvard Medical School here: https://crackingmedadmissions.com/how-to-get-into-harvard-medical-school/ http://www.hms.harvard.edu/md_phd
Tufts University School of Medicine http://sackler.tufts.edu/Academics/MSTP-Welcome
University of Massachusetts Medical School http://umassmed.edu/mdphd
University of Michigan Medical School http://medicine.umich.edu/medschool/education/mdphd-program
University of Minnesota Medical School http://www.med.umn.edu/mdphd
Mayo Medical School https://college.mayo.edu/academics/biomedical-research-training/medical-scientist-training-program-md-phd/
Washington University School of Medicine http://mstp.wustl.edu
Albert Einstein College of Medicine http://www.einstein.yu.edu/education/mstp
Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons http://www.cumc.columbia.edu/mdphd
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai http://icahn.mssm.edu/education/graduate/md-phd-program
New York University School of Medicine http://www.med.nyu.edu/sackler/mdphd-program
Stony Brook University https://medicine.stonybrookmedicine.edu/mstp
University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry http://www.urmc.rochester.edu/education/md/md-phd
Weill Cornell/Rockefeller/Sloan-Kettering Tri-Institutional MD PhD Program http://weill.cornell.edu/mdphd
North Carolina
Duke University Medical Center https://medschool.duke.edu/education/degree-programs-and-admissions/medical-scientist-training-program
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine http://www.med.unc.edu/mdphd
Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine http://mstp.cwru.edu
Ohio State University College of Medicine http://medicine.osu.edu/mstp
University of Cincinnati College of Medicine MSTP http://www.med.uc.edu/MSTP
Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine http://www.ohsu.edu/mdphd
Pennsylvania
Penn State College of Medicine http://www.pennstatehershey.org/web/mdphd
University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine http://www.med.upenn.edu/mstp
University of Pittsburgh http://www.mdphd.pitt.edu
South Carolina
Medical University of South Carolina https://education.musc.edu/colleges/graduate-studies/academics/dual-degree/mstp
Vanderbilt University School of Medicine MSTP https://medschool.vanderbilt.edu/mstp
Baylor College of Medicine MSTP https://www.bcm.edu/education/programs/md-phd-program
University of Texas Health Science Center Houston Department of Internal Medicine https://gsbs.uth.edu/mdphd/
University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Department of Neurology, Pharmacology, and Physiology https://lsom.uthscsa.edu/mimg/
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas https://www.utsouthwestern.edu/
University of Virginia Health System MSTP Program http://mstp.med.virginia.edu
University of Washington School of Medicine http://www.mstp.washington.edu
Medical College of Wisconsin MSTP https://www.mcw.edu/education/medical-scientist-training-program
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health http://mstp.med.wisc.edu
Read our medical school profiles to learn more about each individual school.
Now that we have reviewed what MD, PhD, and MD-PhD degrees consists of and how to apply, as well as some of the pros and cons of pursuing a MD-PhD program, we hope that you can make an informed decision about your graduate education! Even if you choose not to pursue an MD or PhD, many institutions have accelerated programs that allow MD or PhD graduates to complete the other degree in a shorter timeframe. Similarly, many medical schools even allow students to apply to add a PhD portion onto their education before they begin their clinical training. Regardless of whichever path is right for you, all three offer incredible opportunities to pursue scientific passions and work towards solving societal issues.
Here are some Cracking Med School Admissions Resources you will find helpful as you think about MD PhD programs:
- How To Shadow A Doctor
- Resume, CV, and Cover Letter Edits
- Premed Timeline: Planning For Medical School Applications
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us down below.
Questions? We're happy to help!
- Your Name *
- Your Email *
- Phone (optional)
- Leave us a Message or Question! We will email and call you back. *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Start typing and press enter to search

Sign up to our Newsletter
Md vs md phd: how to choose your best path.

Reviewed by:
Luke Hartstein
Former Admissions Committee Member, NYU Grossman School of Medicine
Reviewed: 10/16/23
You’re a prospective med student, and you’ve started your preliminary research on how to choose a medical school that will cultivate your interests and teach you the skills needed to be a leader in healthcare. Perhaps you greatly enjoy biomedical research and would like to combine your two passions: practicing medicine and conducting scientific research.
You may have noticed that many medical schools not only offer the traditional Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree but dual degrees as well. One of the most common of these dual degree programs is the MD PhD.
So, what is the MD versus the MD PhD, and how do you choose your best path? This blog will comprehensively review the similarities and differences between the MD and MD PhD degrees, including the application process and the education you can expect to receive for each program.
This blog will also cover important topics such as career outlook and salary. Finally, we will provide tips for choosing between the MD and MD PhD pathways, so that you can make the best decision for your unique career goals.
Get The Ultimate Guide on Writing an Unforgettable Personal Statement

What is an MD?
An MD is simply a Doctor of Medicine or physician who obtained their MD degree at an allopathic medical school accredited by the LCME (Liaison Committee of Medical Education). Allopathic medicine focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of disease. When people think of physicians, they generally think of MDs.
To become an MD, you must:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree at an accredited university and complete all required prerequisite courses for medical school . Your pre-med major doesn’t need to be in the sciences, but you need to complete science prerequisite coursework, including labs. Every school has specific requirements regarding which prerequisites to take, so check with the schools to ensure that you fulfill all undergrad requirements. If you need help with selecting and scheduling your prerequisite coursework, connect with a pre-health advisor.
- Take the MCAT and earn a competitive score . The MCAT is one of the most important selection factors for medical schools, and it is a strong indicator of your academic performance. Matriculated students often exceed the school’s minimum required MCAT score, so you should aim to fall within or exceed the school’s median MCAT score. In addition to the MCAT, some medical schools require the CASPer test .
- Graduate from an accredited allopathic medical school. Most MD programs are four years, with a few exceptions. For example, some schools have accelerated MD degrees that you can complete in just three years.
- Complete a residency . Residency programs typically last from three to eight years. Residents perform extensive duties in a clinical setting, such as interpreting charts and lab work, taking patient histories, attending conferences, and conducting physical exams. Residency applicants are matched to programs depending on their personal preferences via the National Resident Matching Program.
- Obtain licensure. MDs must obtain a license to practice medicine by passing the USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Examination). Each state has different requirements to become licensed. For example, some states limit the number of times you can take the USMLE, while other states have no such restrictions on exam attempts.
- Continue your education. Generally, physicians must complete state-required continuing education before renewing licensure every couple of years.
What is an MD PhD?
An MD PhD is also a Doctor of Medicine who additionally holds a PhD in scientific research. MD PhDs are known as physician-scientists or medical scientists. There are over 100 MD PhD programs affiliated with medical schools, and approximately 40 programs are partially supported by training grants known as MSTPs (Medical Science Training Programs).
Physician-scientists focus on both scientific research/discovery and treating patients in clinical settings. They have the unique skill set to research healthcare topics, including biomedical sciences, biochemistry, cell biology, microbiology, immunology, genetics, physiology, pharmacology, and neuroscience.
In short, MD PhDs blend scientific research with clinical medicine.
To become an MD PhD, you must:
- Complete all of the requirements for medical school to obtain your traditional MD degree.
- In addition to attending medical school for your MD, you must also attend graduate school for your PhD. Because you are completing both programs dually, the duration of your education is seven to eight years (four years for the MD; three to four years for the PhD).
- Complete medical training and conduct mentored, integrated, and mechanism-based research throughout the PhD program and for your thesis.
MD PhD programs actively seek applicants who exhibit the core competencies of entering medical students and have an aptitude for biomedical research. Applicants must have strong critical thinking and analytical skills to conduct and interpret research. Lastly, and most importantly, prospective candidates should have substantial research experience .

MD vs MD PhD: Application Process and Education
The application process for the MD and MD PhD programs is very similar. For most allopathic medical schools, you will use the AMCAS (American Medical College Application Service).
There are exceptions; for example, Texas medical schools use the TMDSAS (Texas Medical & Dental Schools Application Service). As always, follow every school’s individual requirements to use the appropriate application service portals.
In the AMCAS, you will have to select which degree you’re applying to and enter all required information. For the MD program, there are nine sections:
- Sections 1-3 are where you will input background information, such as your name, biographical information, identifiers, and the schools you’ve attended.
- Section 4 is where you will enter your school transcripts and undergraduate coursework.
- Section 5 is the work and activities section where you will enter relevant extracurricular activities , work experience, and appropriate hobbies .
- Section 6 is where you will upload your letters of evaluation.
- Section 7 is where you will enter the school’s information, such as the program to which you’re applying and whether you’re applying for an early decision.
- Section 8 is the personal statement .
- Section 9 is where you will enter your test scores, such as the MCAT.
To apply to the MD PhD program, you will have to complete all nine sections of the AMCAS. Additionally, you will have to complete two additional essays that describe your reasons for pursuing the MD PhD degree and your research experience.
Here is a general idea of what the MD PhD education looks like, year by year, according to the AAMC:

Discover how Patrick got into six fully funded MD/ Phd programs in the video below.
MD vs MD PhD: Career Outlook and Salary
Both MDs and MD PhDs enjoy lucrative, rewarding careers in medicine. Typically, MDs become physicians who practice medicine in hospitals, private practices, clinics, and other medical centers. MD PhDs become physician-scientists, and according to the AAMC , nearly 80% of them follow career paths consistent with their training, which include working in medical schools as faculty members or in other research institutions, such as the NIH (National Institutes of Health) and other federal agencies.
Physician-scientists are highly valued for both their medical training to treat patients and their extensive knowledge of public health, disease, treatment, and hot topics in healthcare. They can work in academia and teach, or they can combine clinical service with independent research. According to the AAMC, over 80% of graduates said that they would choose the MD PhD program again if given the chance. This should give you an idea of how passionate physician-scientists are about biomedical research.
For MDs , depending on their specialty and setting, the average annual salary is around $220k. For MD PhDs , depending on the type of role and place of employment, the average annual salary is about $100k.
Which is Better? Tips for Choosing Between the Two
So, now that you know a bit more about the MD and MD PhD degrees, which is better? To make the best decision for your goals, keep the following tips in mind:
Examine your passions honestly.
Are you excited to work with patients, but research doesn’t motivate you as much? Then you should stick with the traditional MD degree. Students who pursue the MD PhD do so because of their equal passion for clinical medicine and research. Keep in mind that the MD PhD has additional years of school, so it is not a decision that should be made lightly.
Use your experiences and extracurricular activities to guide you.
Think back to your medical shadowing or clinical experience . Compare your insights to your research experience. Which experience was the most rewarding to you? Which did you enjoy the most? Can you see yourself conducting research your entire career? It would be helpful to use your experiences and extracurricular activities as a measure of your interests.
In short, students who don’t absolutely love research should consider pursuing an MD degree, while those who do love research should look into the MD PhD dual degree.
1. What are the top MD programs in the United States?
According to the US News & World Report , the following medical schools consistently rank the highest:
- Harvard Medical School
- Perelman School of Medicine
- Grossman School of Medicine (NYU)
- Johns Hopkins University
- Stanford Medical School
- Columbia University
- Mayo Clinic School of Medicine
- David Geffen School of Medicine (UCLA)
- Washington University
- Cornell University
- Duke University
- University of California - San Francisco
- Vanderbilt University
- Yale University
2. How do I know which MD PhD program is right for me?
Ultimately, you will have to decide for yourself which program is the best fit for your particular interests and career goals. However, take a look at the US News & World Report’s list of signs that an MD PhD program is a great fit:
- There is ample funding.
- The location is desirable for your requirements.
- There is a good balance between clinics and research.
- The school has a history of strong publications/research.
- The program’s academic breadth is multi-disciplinary, ensuring that students will have a good selection of topics to research.
- Clinical training is introduced early in the program.
- There are numerous mentors available to oversee research projects.
- Current MD PhD students are satisfied with their program.
- The program’s alumni perform high-level research and publishing, which is a strong indicator of future success.
- The program’s mission and culture align with your academic and career goals.
3. Can I apply to the MD program and the MD PhD program at one school in the same cycle?
In the AMCAS, you must indicate the program to which you are applying, and it cannot be both for one school in the same application cycle. However, if you indicate that you are applying to the MD PhD program, most schools will first consider you for the dual degree program, and if you are not accepted, they will consider you for the MD program. Please reach out to your selection of schools to learn more about their application procedures regarding dual degrees and final decisions.
4. What topics in healthcare do MD PhDs research?
According to the AAMC , MD PhDs can research various topics in the following disciplines:
- Biochemistry and Macromolecular Biophysics
- Cell and Developmental Biology
- Immunology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Microbiology and Infectious Disease
- Neuroscience
- Pathology and Mechanisms of Disease
- Pharmacology
- Bioengineering and Biomedical Imaging
- Chemical and Physical Sciences
- Computational Biology and Bioinformatics
- Public Health, Epidemiology, and Preventative Medicine
- Social and Behavioral Sciences
There may be variations among different programs, so verify with the school before you apply.
5. Is financial assistance available for MD programs?
Generally, yes. The cost of attendance is an important consideration when applying to medical schools. There is federal assistance through FAFSA, in addition to scholarships, grants, and loans. To learn more about financial planning, please reach out to the Student Financial Services office for every school you apply to discuss your options.
6. Is financial assistance available for MD PhD programs?
One of the most significant perks of MD PhD programs is that most either partially cover or completely waive tuition for students. Stipends are also very common to cover the costs of living expenses for students. Because of this, many MD PhDs graduate with little to no debt. Although this shouldn’t be the only deciding factor for pursuing the MD PhD degree (remember to keep your goals in mind), it is a benefit that may spare you from, on average, $200k in debt.
7. What counts as a substantial research experience?
Substantial research experience involves some effort and commitment on your part. Before applying to the MD PhD program, be sure to have multiple summer research projects. You are also encouraged to have one or more years of pursuing research after completing your bachelor’s degree. This may mean that you have to take a gap year to bolster your application with research experience, but don’t worry.
Many students take a gap year for this very reason, to gain relevant experiences and strengthen their application. You should also strive to have publications, and it’s important to list them in your application materials. You must also have experience in accurately testing a hypothesis. It is also important to note that gaining more research experience will strengthen your skills in this field, but you will work with supervisors and mentors who can become potential letter writers for strong letters of recommendation .
8. Where can I find more information about the MD PhD degree?
For more information about the MD PhD degree , please visit AAMC’s MD PhD authority site .
Conclusion
As you can see, both the MD and MD PhD programs will lead to lucrative careers in medicine. Whether you pursue the MD degree or the MD PhD dual degree depends on your interests, motivations, passions, academic goals, and career aspirations. When you’re applying to either program, be sure to follow the medical school’s specific application guidelines and procedures.
Use the correct application service and select the program to which you’re applying. If you’re applying to the MD PhD program, be sure to complete all nine sections of the AMCAS in addition to the two essays that describe your reasons for pursuing the MD PhD program and your research experience.
Make sure your research experience is substantial. It’s important to have a competitive edge over other MD PhD candidates who undoubtedly will have their own strong research experiences and publications. No matter which path you choose, we wish you the best of luck in your efforts.
Schedule A Free Consultation
You may also like.

MCAT Accommodations: What They Mean and How to Get Them
.png)
An In-Depth Look At The Top Caribbean Medical Schools

How to Decide Between an M.D. and M.D.-Ph.D.
The two medical programs differ in several ways, including time, expense and purpose.
M.D. vs. M.D.-Ph.D. Programs

Getty Images
While M.D. degree recipients typically go into some field of medical practice, M.D.-Ph.D. graduates tend to find jobs in medical research and academia.
Pursuing a medical degree is challenging and requires great familiarity and comfort with biomedical science. For those inclined to delve deeper into biomedical research, dual M.D.-Ph.D. programs offer an intriguing and unique pathway and should be carefully considered.
How Are M.D. and M.D.-Ph.D. Programs Different?
M.D.-Ph.D. programs differ from M.D.-only programs in several ways, including time, expense and purpose.
Time Commitment
While M.D. programs typically take four years to complete, M.D.-Ph.D. programs integrate heavy research training and last an average of four years longer than traditional medical school . This significant time commitment allows you to complete the requirements for a Ph.D. in a biological science, typically doing lab rotations before and during the first and second years of med school, followed by full-time lab work between the second and third years and culminating in thesis defense and awarding of the Ph.D. degree.
These joint programs typically are accelerated. Some medical students complete the Ph.D. requirements in three years, but most need four to five years. With the Ph.D. work done, the M.D. is earned upon completion of the third and fourth years of med school.
Cost Considerations
The average cost of medical school alone in the U.S. is $230,296, according to the Education Data Initiative, although it can range depending on the school and the student's state of residency.
Generally, M.D.-Ph.D. programs cost more because of the additional degree. However, the National Institutes of Health's dual M.D.-Ph.D. programs are divided into those that receive NIH Medical Scientist Training Program funding via a T32 research training grant for their students, and programs that don't. All MSTPs and many non-MSTPs waive med school tuition and provide stipends for M.D.-Ph.D. students.
Thus, many M.D.-Ph.D. students don't need to take out additional loans, which can be a significant advantage.
M.D. degree recipients tend to go into some field of medical practice, while M.D.-Ph.D. graduates veer more toward medical research and academia.
Typically for M.D.-Ph.D. studies, MSTP programs are better organized and more productive than their non-MSTP counterparts, and more effectively prepare students to compete for independent faculty positions at academic medical centers.
The career goal of becoming a physician scientist who practices medicine and runs an NIH-funded research laboratory drives M.D.-Ph.D. students through a long and difficult training period, which is the primary purpose of such programs.
What Is the M.D.-Ph.D. Application Process?
Applying to M.D.-Ph.D. programs, similar to M.D.-only programs, can be done through the American Medical College Application Service, known as AMCAS . The same application materials are required, plus two additional essays: an M.D.-Ph.D. essay detailing your motivation to apply and an essay describing your individual research experiences and accomplishments.
Throughout your application, your thoughtful consideration of the M.D.-Ph.D. pathway and a genuine passion for research must be evident. This is commonly the No. 1 component that admissions committees look for – does this applicant truly love biomedical research and demonstrate the commitment to science that will keep them motivated and on track during the arduous training process?
Passion and commitment can be communicated through the essays, work and activities section, personal statement , interviews and, critically, letters of recommendation – hopefully from accomplished faculty in biomedical sciences.
Significant research background is expected for M.D.-Ph.D. applicants, and it is extremely important to demonstrate high familiarity with research throughout the application.
A minimum of two years in a lab is generally considered significant research experience, and many applicants take one or more gap years to expand their research background and acquire further recommendation letters from scientists or doctors who can speak to both clinical and research potential. These recommendations take on added importance in the smaller biomedical research community.
What About an M.D. With Research vs. an M.D.-Ph.D.?
So, you’ve joined a lab as a premed and are enjoying research – at least more than you expected to. That’s great! At the very least, clinical medicine needs physicians with a strong background in scientific research.
But how do you know whether you should pursue an M.D.-Ph.D. program, with the goal of a lifelong career in research after graduation? Many med students, residents and attending physicians without a Ph.D. lead successful research endeavors, so pursuing an M.D. with research is feasible.
If you’re weighing such a choice, ask yourself if science brings out enough passion in you to sustain a lengthy training period. If the thought of watching your peers graduate and rise in their professions while you remain in training is outweighed by the thrill of scientific discovery, an M.D.-Ph.D. program may be a wise decision.
The benefits of a Ph.D. through a combined M.D.-Ph.D. program, compared to pursuing research later in your career as an M.D., are:
- Elevated familiarity with the methodology of basic science.
- More in-depth experience in carrying out experiments, compiling data, writing and publishing high-impact papers.
- Networking opportunities and the valuable connections they can create.
The protected research time of a Ph.D. is a rare and valuable commodity. Never in your career as a doctor will you have an opportunity to delve as deeply into a scientific subject as you will during Ph.D. studies. Although exceptions abound, researchers without a Ph.D. are frequently limited to clinical or translational science, and often do not feel comfortable enough with basic science methodologies to run a laboratory built around such techniques. With fewer publications and experience, the transition to an independently funded scientific career is typically harder.
Traditionally, this transition is accompanied by a K08 clinical investigator award, which provides funding for supervised research development as a final step before full independence, for example running a NIH R01-funded laboratory . K08 grants and other early-career funding opportunities are competitive, so it's a great benefit to have more publications and research experience.
Should I Apply to Traditional M.D. Programs as a Backup?
M.D.-Ph.D. programs are highly competitive, as you must demonstrate to a medical school that you are worth significant time and financial investment. Admissions committees must feel that you are a worthwhile investment and will contribute significantly to biomedical research as a future alumnus.
After deciding to apply to M.D.-Ph.D. programs, should you apply to traditional M.D.-only programs as a backup option? If you feel you have enough clinical experience to be competitive for M.D.-only programs and don't want to take a gap year, this is a realistic backup pathway. You can still pursue a meaningful research direction as an M.D., particularly if you dedicate several years to a postdoctoral position to learn research techniques.
A cautionary word of advice: Honestly self-reflect and try to understand and maintain focus on your primary interest.
If you are more excited to practice clinical medicine than research, you should heavily consider applying only to traditional M.D. programs. You can still pursue collaborations with basic science researchers and participate in clinical trials without a Ph.D., with a flexible level of involvement in basic science.
To make the right decision, consider your personal aspirations, long-term career goals and genuine level of commitment to biomedical research. Carefully evaluate these factors, as well as your qualifications.
Seek out mentorship from M.D.s and M.D.-Ph.D.s who know you and your application, and ask them whether you will be competitive for such programs. It can help to ask M.D.-Ph.D.s how they knew they wanted to apply, if they would make the same decision again and whether they can see you being fulfilled in a career using that degree.
Premed students commonly describe their affinity for medicine with a variation of the words, “I can’t imagine a fulfilling career outside of medicine.” The decision-making process for an M.D.-Ph.D. versus a traditional M.D. can often be broken down similarly: Can you imagine a fulfilling career without scientific research?
If the answer is yes, an M.D.-Ph.D. probably doesn’t align with your career goals. If the answer is no, this long but rewarding training path may indeed be for you.
As you embark on this application journey , know that regardless of the path you choose, you have likely already developed an appreciation for the importance of scientific discovery in furthering advancements in clinical care. Successful completion of either program will allow you to make valuable contributions to biomedical science, and it is a privilege to have the opportunity to advance understanding of medicine in such a unique and meaningful way.
10 Medical Schools With High Yield Rates

Tags: medical school , doctors , research , graduate schools , education , students
About Medical School Admissions Doctor
Need a guide through the murky medical school admissions process? Medical School Admissions Doctor offers a roundup of expert and student voices in the field to guide prospective students in their pursuit of a medical education. The blog is currently authored by Dr. Ali Loftizadeh, Dr. Azadeh Salek and Zach Grimmett at Admissions Helpers , a provider of medical school application services; Dr. Renee Marinelli at MedSchoolCoach , a premed and med school admissions consultancy; Dr. Rachel Rizal, co-founder and CEO of the Cracking Med School Admissions consultancy; Dr. Cassie Kosarec at Varsity Tutors , an advertiser with U.S. News & World Report; Dr. Kathleen Franco, a med school emeritus professor and psychiatrist; and Liana Meffert, a fourth-year medical student at the University of Iowa's Carver College of Medicine and a writer for Admissions Helpers. Got a question? Email [email protected] .
Popular Stories
Paying for Graduate School

Applying to College

Best Global Universities

Best Colleges

You May Also Like
How to win a fulbright scholarship.
Cole Claybourn and Ilana Kowarski April 26, 2024
What to Ask Law Students and Alumni
Gabriel Kuris April 22, 2024

Find a Strong Human Rights Law Program
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
M.D. vs. PhD. Degrees: What Are the Differences?

Cait Williams is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cait recently graduated from Ohio University with a degree in Journalism and Strategic Communications. During her time at OU, was active in the outdoor recreation community.
Learn about our editorial policies

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

Chances are, when you hear PhD and MD, you at least know that there is a difference between them. Since both are the titles of doctors, there’s still a lot of ambiguity as to what those specific differences are. In this article, we will look at how MDs and PhDs differ from one another and which one might be a better fit for you. Let’s jump in!
Doctor of Medicine (MD)
We’ll start by taking a separate look at MDs. An MD is a medical doctor. Their primary job is to work with patients in a variety of settings such as hospitals, clinics, and a variety of other places where having medical staff is necessary.
School
In order to become an MD, students must complete their undergraduate degree and then attend a four year medical school. Medical School is then followed by a residency, where a new doctor completes training under a senior physician. From start to finish, becoming a doctor takes around 8-12 years to finish undergrad, medical school, and residency.
Area of study
As a medical doctor, you will generally choose one area of medicine that you would like to focus on. Specialties can be based on a certain part of the body, such as cardiology, podiatry, or neurology. Aspiring medical doctors can also specialize in working with a select group of people, such as geriatrics or pediatrics, or finally, you can specialize in researching things like oncology. The possibilities are plentiful for MDs!
Where they work
Where you work will depend on what you choose to specialize in. Again, this could be in a hospital, a smaller clinic, or even across the globe with various organizations that work to provide medical care to underserved populations. Medical expertise is needed in many capacities, meaning that there is never a shortage of places that a medical degree could take you!
A word about DOs
Before we move on to PhDs, we have one more thing to clear up that you might have questions about. In addition to MDs, there is also another type of doctor called a DO, or a doctor of osteopathic medicine . DOs perform largely all the same functions as MDs, but with a more holistic approach. They attend undergrad just like MDs and then attend a four year DO program that is structured very similarly to a regular medical school.
The only difference between these two is where they receive their medical school training and how they approach studying medicine and treating patients. If you are thinking about becoming a medical doctor, you should take some time to explore DOs and what they do!
Doctorate of philosophy (PhD)
Okay, now onto PhDs! A doctorate of philosophy, known also as a PhD , doesn’t actually have anything to do with philosophy in most cases. A PhD can be completed in pretty much any field and is the highest level of education that one can receive.
In order to complete your PhD, you will need to first complete your undergrad, then a master’s program, and finally apply to PhD programs. Not all PhD programs require that you finish your masters. There are some schools that offer programs that allow you to complete both your masters and your doctorate at the same time.
Generally, schooling for your PhD takes anywhere from four to eight years to complete. The first year or two of your PhD is spent on coursework, while the remaining years are spent doing research and completing your dissertation.
There are endless areas of study that offer PhD programs. You can study everything from physical therapy, business management and psychology to health administration, engineering, social work, and so much more. The gist is pretty much that if you can think of a field of study, you can earn your PhD in it!
Based on the examples of fields you can study, it’s safe to say that what you study will determine where you decide to work. PhD holders are highly educated people, meaning that finding a job when you hold a PhD in your field will look pretty good to most employers.
Common places where you find a high concentration of PhDs are in hospitals, corporate offices, college campuses, and other educational institutions. Remember, though, that’s not a full list of where you could work–the list of places you could work is endless!
Tuition and Costs
It’s true, pursuing either one of these degrees is not the cheapest thing, but don’t let numbers scare you off! If anything in this article sounds like it is right for you, explore it thoroughly. There are lots of ways that you can pay for your education, including scholarships, organizations, and programs out there that want to help you do it!
Okay, so for some real talk, the price of either of these degrees can vary a lot. Medical school will generally cost between $45,000 – $65,000 a year, while PhD programs cost on average about $30,000 a year. But, again, this does not mean you have to be able to pay these costs out of pocket. There are a lot of programs for PhDs that work with you to help you pay for some of the costs. There are even some fully funded PhD programs !
Similarly, there are tons of medical scholarships and even tuition free medical schools that you can apply to help offset the costs of a medical degree. There are also options for student loans that you can take out as well. The point is, there are tons of ways to find your education. If a degree like this is right for you, it is possible to achieve with proper planning and determination.
Related: Top scholarships for graduate students
Shadowing
Before jumping all the way in with either of these degrees, shadowing is a great tool that can help you explore your intended field or job. It’s highly encouraged that students who want to attend medical school shadow at least a few different MDs and DOs prior to applying to medical school.
But the benefits of shadowing are not just for the medical world. You can ask to shadow just about anyone . Maybe you’d like to shadow a professor who you had during undergrad, a social worker, or someone you know of who works in business. There are no rules about who you can and can’t shadow, you simply have to ask and go from there!
What is right for you
Below are some basic questions to help you get your mind started thinking about whether an MD or PhD is right for you. The first set of questions pertains more to MD or DO degrees.
If you’re thinking about an MD or DO degree…
Questions to consider.
- Do you like working with people and helping them during difficult times?
- Do you love studying biological sciences ?
- Does working in a hospital or clinic sound like an environment you would enjoy?
If you’re thinking about a PhD…
- Is there a specific area or field you would like to study?
- Do you have a specific job in mind that you would like, and does it require a PhD?
The answers to these questions won’t instantly help you decide, but they should help you think a little deeper about these degrees.
Key Takeaways
- Both MDs and PhD holders are highly educated in their field of study, holding the highest degrees that you can earn
- The only way to become a practicing MD is to first obtain your bachelor’s degree, then attended a four year accredited medical school, and then successfully complete all the proper exams to practice medicine
- To earn a PhD, you do not have to attend medical school, but you will need to attend a PhD program, complete your undergrad, and usually complete your master’s degree before doing so
- There are lots of ways to fund both a PhD and an MD, including scholarships, grants, loans, and partially and fully funded programs for each
Frequently asked questions about the differences between MD and PhDs
Is a phd higher than an md, who gets paid more an md or a phd, is a phd harder than an md, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!

MD vs. MD/PhD: Key Differences and Choosing the Best Path
by internationalmedicalaid
MD/PhD vs. MD: Education
Both MDs and MD/PhDs are medical doctors, but MD/PhDs also hold a PhD and therefore are known as physician-scientists or medical scientists. If you want to obtain this additional title, you will need to take part in a program with a different structure and length than standard MD programs. MD/PhD programs are typically between seven to eight years in length and require one to attend both medical and graduate school. MD programs can be completed in four years (half the time of an MD/PhD program). During the first two years, both programs are classroom-based, but MD/PhD students will move on to grad school to complete their PhD thesis during years three and four. Afterward, they will return to medical school for one to two years to focus on completing clinical rotations. Both MD and MD/PhD students will take part in and spend around three to seven years in a residency program before obtaining their license to practice medicine.
MD/PhD vs. MD: Application and Tuition
The application for both programs is similar no matter which you decide to pursue. You will apply to the majority of these programs through the AMCAS , completing all sections of the application, including the AMCAS work and activities section , and uploading your coursework, letters of evaluation, and personal statement . Before submitting your application, it is important to check the requirements of each medical school, as some will require you to take the CASPer exam . If the program you want to apply to requires this exam, begin practicing for the exam by utilizing practice questions as soon as you can to best prepare yourself. In addition to the standard components of an MD program application, MD/PhD applicants will need to complete two additional essays. These essays will describe their reasons for pursuing an MD/PhD program and their previous research experience. Review each college’s application process and timeline to ensure you are aware of the process and any deadlines.
On average, the yearly medical school tuition for students enrolled in an MD program is around $37,000 in-state and $62,000 out-of-state or for those attending a private college. Students who are enrolled in MD/PhD programs often have the benefit of a largely reduced tuition or free tuition as some programs provide waivers and offer stipends to help students afford the cost of living expenses. Currently, forty-nine MD/PhD programs receive funding from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) through the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP).
MD/PhD vs. MD: Competition
It’s no surprise that both MD/PhD and MD programs are highly competitive. The average acceptance rate of these programs is between 1-4%. Compared to MD programs, there are considerably fewer MD/PhD programs available. The added benefit of tuition waivers makes the competition for these programs even higher. With such high levels of competition, it is a good idea to see how your grades and test scores compare to the average scores of students accepted into the program. Last year, matriculants of MD/PhD programs had an MCAT score of 516 and an average GPA of 3.8. The average MCAT and GPA of MD program students was 511.5 and 3.73, respectively. From this data, we can determine that to be a competitive applicant get into an MD/PhD program, one will need to possess a higher GPA and MCAT score than what is typically required for an MD program. Of course, each college will also have varying levels of competition as some receive a higher volume of applications each year than others.
If you are considering applying for an MD/PhD program and have already taken the MCAT but did not receive a score of 516 or higher, you may want to consider retaking the MCAT . Retaking the MCAT is not right for all students, but it may help boost your test score and give you an edge when applying to competitive programs. For further personalized help, consider seeking the guidance of medical school admissions consulting .
MD/PhD vs. MD: Salary and Career Outlook
While it may be obvious that those who graduate from an MD program go on to practice medicine as medical doctors within a hospital or clinic environment, some individuals are unsure of what post-grad life would look like for a physician-scientist. The majority of MD/PhD graduates choose to complete their residency in pediatrics, internal medicine, pathology, or neurology. However, many specialties are represented, from emergency medicine to surgery and radiology. Among MD graduates, internal medicine, pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine are the most common specialties. According to AAMC’s study, almost 80% of MD/PhD graduates hold positions at federal agencies, research institutes, medical schools, or the National Institute of Health. Of the 7,000 MD/PhD grads who took part in the study, 82% said they would take part in an MD/PhD program again.
Physician-scientist possess both in-depth knowledge of the medical field and knowledge of population health and disease. They are also trained to conduct thorough independent research and analysis. Physician-scientists with this dual degree are highly valued for their ability to treat patients, develop new treatments, and detect potential health threats. Those who choose to work in academia often teach and provide clinical services while also conducting their own research. The average annual MD/PhD salary is between $60k and $115k, depending on location and type of employment.
Physicians manage the health and well-being of patients in their care. This is done through physical exams, treatment, diagnostic testing, and communication. Depending on the type of physician, they may treat specific or general illnesses and diseases and perform surgical procedures. The annual salaries of physicians correspond to their level of training and specialization, but on average, a non MD/PhD salary for physicians ranges from $180k to $280k.
MD/PhD vs. MD: Which is a for You?
For some people, they knew what they wanted to be from the moment they first put on safety glasses in science class or gave their teddy bear an exam with a toy stethoscope. However, not everyone has the “aha” moment or an immediate passion for a field of work. Sometimes, one’s drive and passion for medicine and research develop later in their life. This passion may be formed by experiences, education, or overcoming hardships. What if you have a passion for both medicine and science? How does one choose whether to pursue a joint MD/PhD or an MD degree? You should only choose after you’ve taken the time to consider the variety of factors involved and are 100% confident in your decision. The reality is that neither choice will be easy, and both will require you to invest a lot of time, effort, and money.
Discover What Drives You
Begin by thinking about what you’re interested in and what motivates you—this will help you determine what your true passion is. If you discover that you are highly interested in medicine and want to help others, but you only have a small interest in the field of research, it may be best to pursue a career solely in medicine. With it being twice the length of an MD program, an MD/PhD program is no cakewalk. Students should only pursue this program if they have deep passions for both medicine and research. If you feel passionate about helping and treating patients and are interested in discovering more about the mechanisms behind diseases or can’t imagine a career that doesn’t involve some form of research, then the joint program may be right for you.
When deciding between these two career pathways, the first decision you will have to make is determining whether you are interested in becoming a physician-scientist or medical doctor. Those who are motivated by their passions are more likely to enjoy their career because they are doing something that they want to do. If you struggle to determine where your passions lie, consider participating in a pre-med shadowing study abroad program .
Let Your Experiences Guide You
What’s the best way to know which path is right for you? Gain experience in the field you are interested in before filling out your medical school applications. If you are struggling to choose between the two program options, be sure to gain experience in both fields before making your final decision. Getting hands-on experience in both fields is a great way to discover which career path truly sparks your interest. Some ways to gain this hands-on experience are by shadowing a doctor or participating in a healthcare internship. These experiences will be essential when it’s time to fill out your med school application, and through these unique experiences, you will discover your passion.
Consider Each Program’s Affordability
According to data from AAMC, approximately 76% of med school students graduate with some form of college-related debt. For students who take out student loans, the median debt is around $200k. Of course, physicians often earn a high salary, so this debt can be repaid after entering the workforce, but many students experience a rocky start as they begin their careers. One of the biggest benefits of an MD/PhD program is that most of these programs partially cover or waive tuition for students. Students may also receive a stipend to cover the cost of their living expenses. This allows some students to complete their training and graduate debt free. While you shouldn’t choose a program only based on the cost associated with the program, it is an important factor to consider. You should make a decision that best aligns with your passions, motivations, interests, and career goals.
International Medical Aid provides global internship opportunities for students and clinicians who are looking to broaden their horizons and experience healthcare on an international level. These program participants have the unique opportunity to shadow healthcare providers as they treat individuals who live in remote and underserved areas and who don’t have easy access to medical attention. International Medical Aid also provides medical school admissions consulting to individuals applying to medical school and PA school programs. We review primary and secondary applications, offer guidance for personal statements and essays, and conduct mock interviews to prepare you for the admissions committees that will interview you before accepting you into their programs. IMA is here to provide the tools you need to help further your career and expand your opportunities in healthcare.
Related Posts
All Posts

- Admissions Consulting
- Pre-Medicine
AMCAS Personal Statement Examples (2024)
Why is the AMCAS Personal Statement Important? Every year, thousands of graduates apply to medical school. Some of them have fantastic GPAs and MCAT...

Applying to Medical School with AMCAS: The Definitive Guide (2024)
Part 1: Introduction If you’re applying to medical school, chances are you’ve heard a lot of terms (like AMCAS) that you don’t understand. Like...

- Internships Abroad
How to Get Into an MD/MPH Program
Joint degree programs hold increasing prominence in the healthcare field and other professions. For instance, a lawyer with a medical degree (JD-MD) can tout...

Compelling vs Average Medical School Personal Statement
Did you know that almost 60% of medical school applicants are not accepted every year? Rejection should not worry you as long as you...

- Study Abroad
Why Pursue an MD/MBA?
If you're somebody who wants to change the medical field from the inside, you've likely thought about getting an MD/MBA degree. By being able...
Take the Next Step
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Mol Biol Cell
- v.29(8); 2018 Apr 15
Is an MD/PhD program right for me? Advice on becoming a physician–scientist
We are living in a golden age of biomedical research in which it is increasingly feasible to translate fundamental discoveries into new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to human illnesses. Inherited diseases are being cured with gene therapy. Cancer cells are being eliminated with less toxic small molecule inhibitors and reengineered T-cells. Direct connections are being made between the central nervous system and prosthetic devices. These efforts are being led by scientists and engineers, some of whom are also physicians. This article is intended to help anyone considering a career as a physician–scientist, but unsure about how best to begin. It is also intended for faculty, staff, and parents who are on the front lines of advising talented students about the options that they have for their future. With this in mind, I have tried to answer common questions about MD/PhD programs, but I have also included information about other paths to becoming a physician who does research.
INTRODUCTION
Because this is a perspectives piece, I will begin it with a confession: I have been a physician–scientist for more than 30 years and I like what I do. I am also a graduate of one of the earliest MD/PhD programs and have been director of the University of Pennsylvania’s MD/PhD program for 20 years. Being a physician who is also a scientist already makes me atypical. According to the American Medical Association, only 14,000 U.S. physicians (out of nearly 1 million) consider research to be their major job, and a search of National Institutes of Health (NIH) databases in 2012 turned up only 8200 physicians who were principal investigators on NIH research grants ( Ginsburg et al. , 2014 ). To put that number in context, there were 28,000 total investigators with NIH grants in 2012. In other words, most NIH principal investigators are PhD scientists, not physician–scientists (MD or MD/PhD).
My primary day (and sometimes night and weekend) job as a card-carrying physician–scientist is overseeing an NIH-funded research team. My clinical responsibilities include taking care of patients with the kinds of bleeding and blood clotting disorders that we study in the lab. Some of these patients have medical problems that are common in the United States. Some of them are true “zebras,” the kinds of patients who get referred to a well-respected academic medical center because physicians are unsure how best to proceed or lack the resources to manage the patient’s problem. I also teach medical students and graduate students, and I direct a very large MD/PhD program. In my spare time, I talk to lots of undergraduates and recent college graduates who are thinking about becoming physician–scientists and wondering whether they should be applying to MD/PhD programs. I meet them at Penn, but also on visits to other colleges and universities. This article is a distillation of some answers to questions that I am commonly asked. If you are an undergraduate trying to decide whether to go to medical school, graduate school, or both, this article may help you. Whatever you decide, I wish you success.
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF MD/PhD TRAINING?
MD/PhD programs were established in the 1950s to combine training in medicine and research. They were specifically designed for men and women who wanted to become research physicians, also known as physician–investigators or physician–scientists. Most of the graduates of MD/PhD programs in the 60-plus years since then have become faculty members at medical schools and universities, investigators at research institutes such as the NIH, or leaders in in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries ( Brass et al. , 2010 ). Regardless of where they eventually end up, MD/PhD trainees are being prepared for careers in which they will spend most of their time doing research or translating that research into new therapeutic and diagnostic approaches. It is a busy, challenging, and hugely rewarding career. A study of what has happened to MD/PhD program graduates from 24 schools appeared in Academic Medicine in 2010 and is worth reading not only for the data set, but also for the discussion of what the data mean ( Brass et al. , 2010 ). An even larger outcomes study that includes data on over 10,000 MD/PhD program graduates is scheduled for publication as a AAMC report in April 2018 ( Akabas et al. , 2018 ).
HOW CAN ONE PERSON DO TWO JOBS?
When I was an undergraduate and trying to decide what to do with my life, my mentors told me that I could become a doctor or a scientist, but that trying to combine two busy professions was futile. Many years later, I know that many current undergraduates are being told the same thing. However well-meant, that advice misses the point. The goal of MD/PhD program training is not to prepare you for two unrelated full time jobs. Instead, you should think of physician–scientists as chimeras—blends of a physician and a scientist with the two parts fitting closely together. A more relevant question is: if you are going to become a physician–scientist, do you have to go through an MD/PhD program? I will try to answer that one a bit later in this article. First, I’ll provide some definitions.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN AN MD/PhD PROGRAM, A COMBINED DEGREE PROGRAM, AND AN MSTP PROGRAM? A BIT OF HISTORY AND A WORD ABOUT FUNDING
None. Programs designed to train physician–scientists go by all of these names. For the most part, the terms are interchangeable, although at some schools “combined degree” programs can include MD/JD and MD/masters programs as well—also VMD/PhD programs, which train veterinary physician–scientists. A list of MD/PhD programs can be found at http://www.aamc.org/students/research/mdphd/applying_MD/PhD/61570/mdphd_programs.html . The NIH uses the term MSTP (short for “medical scientist training program”) to refer to programs at schools that have been competitively awarded special training funds to help support MD/PhD candidates. There are currently 46 MD/PhD programs that receive support from the National Institute of General Medical Studies. A list can be found at http://www.nigms.nih.gov/Training/InstPredoc/PredocOverview-MSTP.htm .
When they first started, there were only a handful of MD/PhD programs. I can clearly remember reading a small booklet about applying to medical school that had a single page at the back about MD/PhD programs. Over time, the number of programs has grown. Now there are ∼90 active MD/PhD programs that admit anywhere from a few students per year to 25 or more. The average size of an MD/PhD program in 2017 was ∼90 students in all stages of training. Compared with the many thousands who apply to medical school in each year, only 1900 (∼3%) apply to MD/PhD programs. About one-third of the applicants are accepted, which is similar to the acceptance rate for medical school. 1 When I began medical school, there were very few MD/PhD trainees—I was one of two in my entering class. That has changed considerably. There are currently ∼5500 men and women in training in MD/PhD programs.
Most MD/PhD programs provide tuition waivers for both medical school and graduate school plus a stipend to help cover living expenses. Such fellowships are exceedingly valuable for trainees and very expensive for medical schools and the NIH, so admissions committees work hard to pick the right students for their programs. Despite the high training costs, when I visit other MD/PhD programs to conduct reviews, it is not uncommon to hear deans refer to their MD/PhD program as “the jewel in the crown.” One can easily argue that the existence of MD/PhD programs is evidence of the high value that our society places on physician–scientists.
ARE MD/PhD PROGRAMS LIMITED TO THOSE INTERESTED IN LABORATORY RESEARCH?
The answer varies from school to school. Not all schools offer PhD programs in all disciplines. The majority of MD/PhD students receive their PhD in biomedical laboratory disciplines such as cell biology, biochemistry, genetics, immunology, pharmacology, neuroscience, and biomedical engineering. The names of departments and graduate programs vary from school to school. At some schools, MD/PhD trainees do their graduate work outside of the laboratory disciplines, in fields such as economics, epidemiology, health care economics, sociology, medical anthropology, or the history of science. This is not an exhaustive list, and you should check before you apply to see what is actually offered at any particular school.
Although there is no fully up-to-date and reliable list of which MD/PhD programs offer training in which graduate disciplines, a place to start is at the Website of the AAMC MD/PhD section (which is a good source for other types of information as well). 2
ARE THERE OTHER WAYS TO BECOME A PHYSICIAN–SCIENTIST?
Yes. Definitely. MD/PhD programs are a great choice for people who decide early that that they want to be physician–scientists and have built the necessary track record of academic success and research experience before they apply. Not everyone does this, however, either because he or she did not learn about the option early enough, he or she did not make a decision in time, or he or she does not have an academic and research experience record that supports an application. Not finding out early enough turns out to be a common problem. In my experience, college prehealth advisors know much less about MD/PhD training than MD training—not surprisingly, since only 3% of medical school applicants in the United States every year apply for MD/PhD training. As a result, some people choose (or are obliged) to do MD/PhD training in series, rather than parallel—finishing one degree and then starting the other. The disadvantages of this approach include taking longer to finish training and the likely need to cover the cost of medical school on your own.
I am frequently asked about the strategy of starting medical school and then applying to graduate school as a medical student. Some schools will consider you for transfer into their MD/PhD programs after you have completed a year or two of medical school or graduate school at the same university. Although it is very rare that an MD/PhD program will consider accepting a medical or graduate student from a different school, it does occasionally happen when faculty move from one institution to another and want to bring their students with them. The rules and requirements vary from school to school.
Other programs worth checking out include the NIH MD/PhD program that provides support for the PhD phase at the NIH campus or in Oxford/Cambridge, with the MD training taking place at one of the participating MSTP-designated programs. Note that not all of the MSTP programs have chosen to participate, so if you have your heart set on a specific medical school, you should be sure to ask. 3
Another option is to complete medical school and residency training before doing an extended period of supervised research. A number of Nobel Prize–winning physician–scientists did just that. However, with the increase in the number of MD/PhD training programs nationwide, most people who make the decision to become physician–scientists while still in college should think hard about doing both degrees together in an integrated MD/PhD program that combines graduate school and medical school into a joint program that currently takes 8 years on average to complete ( Akabas et al. , 2018 ).
DO I REALLY NEED A PhD TO DO RESEARCH? CAN I SAVE TIME BY SKIPPING IT?
The answer to the first of these questions is “Clearly not.” However, while medical school will put you firmly on the path to becoming an accomplished clinician, it does not provide training in how to do research. At some point you will benefit from that additional piece of your education if you intend to become a physician–scientist.
As noted above, in years past it was not uncommon to learn how to do research by doing an extended postdoctoral fellowship after (or instead of) a clinical residency. I am often asked whether it is possible to save time on the path to becoming a physician–scientist by skipping graduate school and just going to medical school. The available data suggest that the answer to this one is “No.” Physician–scientists get their first jobs in academia and their first independent NIH grants at approximately the same age regardless of whether they completed an MD/PhD program or went solely to medical school and then did a more extended postdoc ( Ginsburg et al. , 2014 ). As a result, I normally tell undergraduates that if they are ready to make the commitment before starting medical school, MD/PhD programs offer many advantages, including integrated training, mentored research training, and medical school tuition waivers. On the other hand, if you are sure you want to be a doctor, but less sure about being a scientist, then my advice is to go to medical school and figure out the rest of what you need when you know more about the opportunities that being a physician provides.
HOW DOES MD/PhD TRAINING WORK AND HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE?
The answer varies from school to school, but historically students begin with 2 years of medical school, switch to graduate school in the third year of the program, and then return to finish medical school after completing (and defending) a thesis research project. When I was an MD/PhD student in the 1970s, there was little, if any, communication between the medical and graduate phases of the program. That has changed considerably. Now most programs emphasize integration of the MD and PhD parts of the training, with graduate school courses during years 1 and 2 and clinical experiences during graduate school. Some programs allow completion of 3–12 months of clinical training before the start of full-time graduate training. Be sure to ask how things are organized at schools that you are considering. In programs leading to a PhD in laboratory science, MD/PhD trainees usually spend the summer between the first and second years of medical school working in the laboratory of the faculty member they are considering as a potential thesis advisor. Some programs also ask students to do one of these “lab rotations” in the summer before starting medical school classes as well. Depending on the number of clinical months completed before starting the thesis research, students returning to medical school will need 1–2 years to finish their training and meet the requirements for medical licensure. The stated goal is to complete an MD/PhD program in 7 or 8 years. However, numbers from across the country show that some students finish in 6 years, while others take 10 years (or more). The average currently is 8 years ( Akabas et al. , 2018 ). Note that medical education in the United States continues to evolve. One trend is away from the classic two years of preclinical education followed by 2 years of clinical education. The earlier start in clinical training made possible by shortening preclinical time enables some MD/PhD programs to offer full-time clinical experiences before the start of graduate school. However, some schools are choosing not to do this. The only way to find out what is being done is to ask, if it is not evident from the program’s Website.
HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE TO COMPLETE TRAINING AFTER GRADUATING FROM AN MD/PhD PROGRAM?
Corny as this may sound, the process is never really finished. Your education will continue throughout your career. A more pragmatic answer is that training will extend beyond medical school and graduate school as you complete your post graduate education. Here are some typical numbers: MD/PhD program, 8 years. Residency, 3–6 years. Postdoctoral fellowship, 3–6 years. For most people the term “postdoctoral fellowship” includes another year or two of clinical training, followed by a return to research for 2 or more years ( Figure 1 ). For example, I completed an MD/PhD program in 6 years, followed by a residency in internal medicine (3 years) and a fellowship in clinical hematology and oncology that was combined with postdoctoral training back in a lab (3 years). After that I became an assistant professor and started my own lab. That timing was fairly typical when I did it. Now it would be considered fast. On the other hand, my job description when I finished included running a research team, looking after postdocs and graduate students, and taking care of sick people with complicated medical problems, so maybe all of that training time was necessary.

Paths to becoming a physician who is also a scientist. Integrated MD/PhD training programs that combine research and medical training are not the only path to becoming a physician–scientist. Alternatives begin with doing a research year in medical school (MD+ in the figure) or just doing the standard four-year medical school education. These save time at the start, but usually require a longer period of postgraduate clinical and research training to reach the point where a job as a physician–scientist in academia becomes feasible. As a result, physician–scientists often arrive at the “get a job” point at about the same age whether they began as medical students, MD+ students, or MD/PhD students, although usually with greater student debt if they have not been in an MD/PhD program. See the text for details.
WHAT HAPPENS TO THE GRADUATES OF MD/PhD PROGRAMS?
Short-term, nearly all do additional clinical training. Those who do not are usually headed toward careers at research institutes or outside clinical medicine entirely. Those who do apply for residencies often find that their MD/PhD training makes them particularly appealing to residency programs at top institutions. Long-term, most program graduates end up with careers in which they combine patient care and research. The research may be lab-based, translational, or clinical. Most (75–80%) end up at academic medical centers, at research institutions such as the NIH, or in the pharmaceutical/biotech industry ( Figure 2 ; Brass et al. , 2010 ; Akabas et al. , 2018 ). A much higher percentage of MD/PhD program graduates have ended up in academia than of medical school graduates in general ( Brass et al. , 2010 ). Those who build research careers and apply for NIH research grants find that having the PhD in addition to the MD improves their chances of obtaining funding ( Ginsburg et al. , 2014 ).

Where are they working? Data from 2202 MD/PhD program alumni who have completed all phases of postgraduate clinical and research training. Adapted from Brass et al. (2010) . Industry includes the biotech and pharmaceutical industries. Pvt Practice refers to full-time clinical practice outside of an academic medical center.
HOW DO I APPLY?
The process of application varies from school to school. Some schools have an MD/PhD-focused committee that will screen your application and coordinate the interview and admission process. Other schools consider MD/PhD applicants only after a decision has been made about MD admissions. Finally, some schools consider students for the MD/PhD program only after they have completed a year or more of medical school. Schools that subscribe to AMCAS will ask you to indicate your interest in an MD/PhD program and then to provide additional information as part of a secondary application.
WHEN DO I APPLY?
Most people apply after finishing their junior year in college, but a growing number of applicants finish college and work for a year or more before applying. Some people use the time after college to take courses needed for medical school admission or to gain more full-time laboratory research experience. Some people simply were not ready to make decisions about their future careers and postponed choosing beyond the finish of college. It is a mistake to assume that MD/PhD programs are interested only in applicants who have worked in a lab for a year or more after college. That is clearly not the case, and some of us who direct MD/PhD programs are concerned about the growing percentage of applicants who have waited to apply after they graduate in the mistaken impression that it will improve their resumes. My advice is that for a training path that lasts as long as this one does, it is best to get started as soon as possible.
WHAT DO ADMISSIONS COMMITTEES LOOK FOR?
The answer clearly varies from school to school, but some basic principles apply. In general, admissions committees will look for evidence of academic success, extended research experience, letters of recommendation from people who know you well, and your plans for the future.
- Evidence of academic success. This includes your GPA and MCAT scores, but is not limited to them. Admission committees use a holistic approach and will undoubtedly consider where you went to college and what types of courses you took. They will not necessarily be dismayed if you got off to a slow start, as long as you did well later. They will place the greatest emphasis on courses that are relevant to your chosen area of graduate school training. I have not encountered a program director who seriously believed that the MCAT tests your ability to be a physician–scientist. Nonetheless programs use MCAT scores in a variety of ways, including seeing how you compare with the national pool of applicants and predicting how you will do on the numerous standardized tests that all of us have to take in medical school and beyond.
- Extensive research experience. If you plan to get a PhD in one of the laboratory sciences, then prior laboratory experience counts heavily, particularly if you spent a year or more in the same laboratory. Summer laboratory experience can be helpful because they are usually opportunities to do research full time, but summers are short. Whenever possible, you should try to do research during the academic year, or at least spend multiple summers in the same lab. If you are planning a PhD outside of the laboratory sciences, seek equivalent experiences. The idea is to be sure you like the experience and to create a track record upon which your past performance can be judged and your future success predicted.
- Letters of recommendation. The most important letter(s) are from the faculty members or other senior investigators with whom you worked. The letters should ideally comment on your talents, skills, and potential for success as an independent investigator. If you are working with a senior faculty member, it is very helpful if he or she can compare you with other students with whom he or she has worked. Note that such a letter is not necessarily the most appropriate for an MD-only application. MD/PhD program admissions committees are usually most interested in your talent and ability as a physician–scientist, although they will definitely also consider whether you are likely to become a successful and caring physician. Fortunately, medical schools allow you to submit more than one letter of recommendation.
- Your plans for the future. Because training to be a physician–investigator is so costly in terms of your time and the school’s resources, your career goals should be compatible with MD/PhD training. Becoming a full-time practitioner is a laudable goal, but does not require a PhD in addition to an MD. Your goal as a trained physician–investigator should be to spend at least 75% of your time on research. You do not need to know the specific problem you want to work on at this point (many do not, and it is likely to change), or with whom you would like to train, but your commitment to becoming an investigator should be clearly communicated in your essays and interviews, and you should have given thought to what will be required.
HOW DO I DECIDE WHERE TO APPLY?
Some applicants have decided that they want to work in a particular field or with a particular faculty member. For them, choosing where to apply is defined by where that faculty member works or where the field is best represented. Most applicants have only a general idea of what they might want to work on in the future and know that their interests are likely to evolve as they are exposed to new things. For them, choice will be defined by issues such as the reputation of the school (hopefully not based solely on U.S. News and World Report rankings!), the success of the graduates of the program (be sure to ask!), and geography. Schools vary in the difficulty of gaining admission. The directors and nonfaculty administrators of MD/PhD programs nationwide are a large pool of resources that you can tap. Most of us get e-mail from future applicants all the time. Take advantage of our willingness to talk with you. Ask questions about the things that are important to you.
FINAL THOUGHTS
I began this perspective with the confession that I am a physician–scientist and I like what I do. It is not unusual these days to encounter articles and opinion pieces that lament the difficulty of becoming and remaining a physician–scientist. I will not cite them here—you can find them on your own. Fortunately, our society is still willing to make a large investment in biomedical research through the NIH and through numerous foundations. If you want to become a physician who discovers the new stuff, there are jobs waiting to be filled. However, you will need good training and great mentorship as you learn the skills needed to be a physician and a research team leader. Good luck with your decision.
Acknowledgments
My thanks to my colleagues who direct MD/PhD programs, the NIH for supporting physician–scientist training (including my own), and the hundreds of MD/PhD candidates and alumni who have taught me so much over the past 20 years.
Abbreviations used:
DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-12-0721
1 www.aamc.org/data/facts/enrollmentgraduate/ .
2 www.aamc.org/students/research/mdphd/ .
3 http://mdphd.gpp.nih.gov .
- Akabas MH, Tartakovsky I, Brass LF. (2018). The National MD–PhD Program Outcomes Study. American Association of Medical Colleges Reports.
- Brass LF, Akabas MH, Burnley LD, Engman DM, Wiley CA, Andersen OS. (2010). Are MD–PhD programs meeting their goals? An analysis of career choices made by graduates of 24 MD–PhD programs . Acad Med , 692–701. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ginsburg D, Shurin SB, Mills S. (2014). NIH Physician–Scientist Workforce (PSW) Working Group Report. [ Google Scholar ]

- PhD vs MD – Differences explained
- Types of Doctorates
A MD is a Doctor of Medicine, whilst a PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy. A MD program focuses on the application of medicine to diagnose and treat patients. A PhD program research focuses on research (in any field) to expand knowledge.
Introduction
This article will outline the key differences between a MD and a PhD. If you are unsure of which degree is suitable for you, then read on to find out the focuses and typical career paths of both. Please note this article has been written for the perspective of a US audience.
What is a MD?
MD (also seen stylized as M.D and M.D.) comes from the Latin term Medicīnae Doctor and denotes a Doctor of Medicine.
MDs practice allopathic medicine (they use modern medicine to treat symptoms and diseases). A common example would be your physician, though there are numerous types of medical doctors, with different areas of speciality and as such may be referred to differently.
What is a PhD?
A PhD (sometimes seen stylized as Ph.D.) comes from the Latin term Philosophiae Doctor and denotes a Doctor of Philosophy.
A PhD can be awarded for carrying out original research in any field, not just medicine. In comparison to an MD, a PhD in a Medicinal field is focused on finding out new knowledge, as opposed to applying current knowledge.
A PhD in Medicine therefore does not require you to attend medical school or complete a residency program. Instead, you are required to produce a thesis (which summarizes your research findings) and defend your work in an oral examination.
What is the difference between a MD and a PhD?
Both are Doctoral Degrees, and someone with either degree can be referred to as a doctor. But for clarity, MDs are awarded to those with expertise in practicing medicine and are therefore more likely to be found in clinical environments. PhDs are awarded to researchers, and are therefore more likely to be found in academic environments.
This does not mean that MDs cannot pursue a research career, nor does it mean that a PhD cannot pursue clinical practice. It does mean, however, that PhDs are more suited to those who would wish to pursue a career in research, and that MDs are more suited to those who prefer the clinical aspects of medicine or aspire to become a practicing physician.
It should also be noted that a medical PhD doctorates possess transferable skills which make them desirable to various employers. Their familiarity with the scientific method and research experience makes them well suited to industry work beyond medical research.
Program structure and time
The standard MD program structure sees students undertake 2 years of coursework and classroom-based learning, before undertaking 2 years of rotational work in a clinical environment (such as a hospital). Getting an MD requires attending a medical school (accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education) and completing a residency program. Both of which prepare students to diagnose patients and practice clinical medicine.
The standard PhD program lasts 5 to 7 years and sees students undertake original research (monitored by a supervisor). Getting a PhD requires the contribution of novel findings, which leads to the advancement of knowledge within your field of research. With the exception of some clinical PhDs, a PhD alone is not enough to be able to prescribe medicine.
PhD doctorates are required to summarize the purpose, methodology, findings and significance of their research in a thesis. The final step is the ‘ Viva Voce ’ where the student must defend their thesis to a panel of examiners.
To summarize, a MD program usually lasts 4 years, whilst a PhD program lasts 5 to 7 years. Before being licensed to practice medicine, however, you must first complete a residency program which can last between 3 to 7 years.
What is a MD/PhD?
A MD/PhD is a dual doctoral degree. The program alternates between clinical focused learning and research focused work. This is ideal for those who are interested in both aspects of medicine. According to the Association of American Medical Colleges, an estimated 600 students matriculate into MD-PhD programs each year .
The typical length of a MD/PhD program is 7 to 8 years, almost twice the length of a MD alone. As with a MD, MD/PhDs are still required to attend medical school and must complete a residency program before being able to practice medicine.
In comparison to PhD and MD programs, MD/PhD positions in the United States are scarce and consequently more competitive. The tuition fees for MD/PhD positions are typically much lower than MD and PhD positions are sometimes waived completely.
Those who possess a MD/PhD are commonly referred to as medical scientists. The ability to combine their medical knowledge with research skills enables MD/PhDs to work in a wide range of positions from academia to industrial research.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Pros and Cons of the MD-PhD Degree
- By Lawrence Wang
- August 17, 2018
- Medical Student , Pre-med
- Clinical Rotations , Dual Degree , Research , Residency
“Two roads diverged in a wood, and I— I took the one less traveled by, And that has made all the difference.” -Robert Frost
Do you have an interest/background in medicine and research , but balk at the prospect of spending eight years getting the MD-PhD degree? You can theoretically do all the same things (i.e. see patients and run a research lab) with only an MD degree. There are plenty of MD’s out there who are successful physician-scientists, and the MD-PhD is certainly the less common path, the road less traveled. So why bother getting a PhD as well?
These are all great questions, worth a fair amount of thought and reflection. Pursuing the rewarding, competitive, and singular pathway of a combined MD-PhD degree is a major decision that warrants a critical evaluation of its associated pros and cons. So without further ado, let’s dive right in.

Pros of the MD-PhD Degree
1 | fully funded.
Medical school is expensive, with the average medical student graduating in 2017 with a debt of nearly $200,000 . In contrast, many MD-PhD students graduate debt-free and may even have a small nest egg saved away. This is because Medical Scientist Training Programs (MSTP) and many non-MSTP MD-PhD programs waive tuition and provide stipends to their students that are comparable to a biology graduate student stipend (~$30,000 of disposable income a year). The stipend is adjusted to match the cost of living in the city in which your school is located.
2 | Options for Fast-Tracking
MD-PhD’s enjoy specialized tracks that enable them to shorten their PhD and residency training. The PhD portion of the dual degree is an average of 4 years (vs. an average of 5-6 years for single degree PhD’s in the biomedical sciences).
Furthermore, MD-PhD graduates can “short-track” their residency into fellowship training. In the case of the three-year internal medicine residency, the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) has a pathway that enables residents with a demonstrated potential for basic science or clinical research to spend only two years doing clinical training before returning to full-time research . These so-called “research residencies” are typically populated by MD-PhD’s, with a few MD-MPH/MD-MS/MD graduates that have strong research credentials thrown into the mix.
3 | Competitiveness for Funding to Start a Lab
According to an NIH report about physician-scientists , MD-PhD’s overall had higher award rates for research program grants (RPGs) (24.6%) than MD’s (21.7%, p<0.01) or PhD’s (21.4%, p<0.01). Furthermore, the award rate for MD-PhD’s from an MSTP program was nearly three times higher than that for MD/PhD’s not from an MSTP program (36.2% vs. 12.3%). If you are interested in more details, there is a wealth of outcomes data in this report as well as the AAMC National MD-PhD Program Outcomes Study .

Cons of the MD-PhD Degree
1 | delayed autonomy.
The additional four years that an MD-PhD student invests in obtaining a PhD represent a significant opportunity cost (time and money). The ramifications of this can be broad. For example, an MD-PhD student living on a graduate student stipend may not have the financial autonomy to start a family until after they obtain an income (and free time!) commensurate to their training level. Furthermore, the average age of young investigators obtaining their first RPG’s continues to rise (44.3 years for MD-PhD’s, 43.8 years for MD’s, and 41.9 years for PhD’s in 2014) . The path of an academic researcher, especially an MD-PhD, creates an extreme delay in full professional autonomy.
2 | Disjointed Training
MD-PhDs are often likened to chimeras in their duality, which is exemplified by the disjointed path to obtaining the MD-PhD degree.
Students typically complete the first two pre-clinical years of medical school, transition to a 4-year PhD program, and then return to medical school to finish the last two clinical years before graduating with their dual degree. Subsequently, most pursue residency and fellowship training in their chosen medical specialties before finally becoming principal investigators (PIs) of a lab. This disjointed pathway forces many MD-PhD’s to play catch-up when they inevitably fall behind in either medicine or research. For instance, a common issue for MD-PhD’s is that their research skills become outdated when they return to clinical training for a number of years during the latter half of medical school and residency.
3| Balancing Clinical and Research Commitments
Juggling the considerable responsibilities of caring for patients and managing research projects can be challenging. Physician-scientists working at academic medical centers may be incentivized (or even pressured) to spend more time seeing patients, a task that earns more revenue for both the physician-scientist and the medical center. It also requires significant time and money for physician-scientists to maintain their clinical skills and board certifications. Consequently, many MD-PhD’s eventually dedicate themselves to either medicine or research and unfortunately let their less-used skill set fade into irrelevance.
Final Remarks
Any aspiring student considering a dual MD-PhD degree should think deeply and critically about whether this demanding career path is right for them. There are pros and cons to getting the MD-PhD degree, some of which may be deal-makers or deal-breakers. Ultimately, I see MD-PhD’s as chimeras walking a road less traveled, obtaining unique toolkits to address gaps in the existing body of medical knowledge and therapies. If this aligns with your goals, it can be an outstanding career!
If you are considering an MD-PhD degree but are unsure, please consider the Med School Insiders general advising services . We have advisers who have completed this degree and can give you detailed, real-world advice and feedback!
Lawrence Wang

6 Shocking Facts From the 2024 NRMP Match
Let’s dive into the results of the 2024 NRMP Residency Match. Did emergency medicine make a comeback, or is it still a declining specialty? Why are more DOs applying?

Medical School vs Residency Comparison
The transition from Medical School to Residency is often misunderstood. Learn about the key differences between med school and residency so that you can best prepare yourself for both types of training.

2024-2025 ERAS Residency Application Guide
Read our ERAS residency application guide, which covers the ideal application timeline, what you need to include, mistakes to avoid, and FAQs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Join the Insider Newsletter
Receive regular exclusive MSI content, news, and updates! No spam. One-click unsubscribe.
Customer Note Premed Preclinical Med Student Clinical Med Student
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Complimentary 1-hour tutoring consultation Schedule Now
What’s the Difference Between MD and PhD Programs?
What’s the difference between MD and PhD programs? Both an MD and a Ph.D. are doctorates awarded to people who finish the highest level of graduate education. However, MD and Ph.D. holders have quite distinct professional paths. Understanding the difference between MD and Ph.D. will help you choose the one that best matches your academic and career goals. Here, we’ll go through the similarities and distinctions between an MD and a Ph.D., as well as some pointers on how to decide between the two. Here are these medical degrees explained:
The Difference Between MD and Ph.D.
MDs are medical doctors who treat patients, whereas PhDs are researchers who specialize in a particular field of study. The Latin phrase medicinae doctor , which translates to teacher of medicine , is where we get the English acronym MD. People who have earned an MD, also known as a Doctor of Medicine, have participated in clinical training during their time in graduate school in order to become physicians upon completion of their studies.
The title philosophiae doctor , from which we get the name Ph.D., literally translates to teacher of philosophy . However, the term is applicable to a wider variety of people than merely philosophy teachers. Students pursuing a Doctor of Philosophy degree, sometimes known as a Ph.D., follow a curriculum distinct from that followed by those pursuing a Doctor of Medicine. Ph.D. candidates are required to undertake research in their respective fields of study rather than getting experience in the workforce. Graduates with PhDs usually find employment in a field relevant to their major or the specialized field they studied.
Dual MD/Ph.D. Programs
An MD/Ph.D. is a dual doctorate. The curriculum alternates between clinical and research-oriented components. This is perfect for people who want to learn both clinical and research-focused aspects of medicine. Approximately 600 students enter MD-PhD programs annually, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
MD/ Ph.D. vs MD
MD Ph.D. graduates are also known as physician-scientists or medical scientists since they hold a Ph.D. in addition to their MD degree. Medical professionals with an MD degree and a Ph.D. are both considered medical doctors. To obtain this additional degree, you will need to participate in a program that is longer and structured differently than MD programs. MD Ph.D. programs typically last anywhere from seven to eight years and require students to attend both medical school and graduate school. On the other hand, medical doctor (MD) programs can be finished in just four years, which is just half the amount of time required for MD Ph.D. students.
Although the initial two years of instruction in both programs take place in classrooms, MD Ph.D. students continue to graduate school to work on their dissertations for an additional three to four years after those first two years. After that, they will return to medical school to complete their clinical training for another year or two. To obtain a license to practice medicine, graduates with an MD or MD Ph.D. degree must first finish a residency program that lasts between three and seven years.
Application and Cost
The application process is the same whether you are interested in an MD Ph.D. or an MD program. Most programs require you to apply through AMCAS. You will fill out all application sections (including the AMCAS work and activities section) and upload your coursework, letters of recommendation, and medical school personal statement. Find out if the CASPer test is required for admission to the schools of your choice. If so, begin practicing with CASPer sample questions as soon as possible. Students will be required to write two additional essays to explain why they want to pursue an MD Ph.D. degree as well as their research experience.
In public medical schools, the annual tuition and fees for MD students are about $37,000; in private or out-of-state medical schools, the annual tuition and fees are about $62,000. In contrast, students enrolled in MD-PhD programs have access to reduced or even free tuition, as many programs waive tuition and provide financial aid to cover living costs. The National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) funds 49 MD Ph.D. programs through the highly competitive Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP).
Competition
Both MD Ph.D. and MD programs are notoriously difficult to get into, with acceptance rates ranging on average from 1 percent to 4 percent. The number of available MD Ph.D. programs is significantly lower than the number of MD programs, and the advantage of significantly reduced or waived tuition contributes to an even higher level of competition, particularly in MSTPs compared to MD programs.
To be a competitive MD Ph.D. applicant, you should have a higher GPA and MCAT score than if you applied as an MD applicant. MD programs have varying levels of competition, and there are MD programs that receive a large number of applicants competing for a limited number of spots. It is entirely dependent on the school, the program, and the application cycle to determine whether or not some MD programs are more competitive than MD-PhD programs.
Salary and Career Prospects
Although it may appear obvious that students who graduate from MD programs become medical doctors and the majority of them practice medicine in hospitals, clinics, medical centers, and private practices, some students are unsure of what a career as a physician-scientist entails. Although many MD Ph.D. graduates choose to complete their residency training in internal medicine, pathology, pediatrics, and neurology, there are also graduates working in a wide variety of other medical specialties, including surgery, radiology, and emergency medicine. Other typical specialties for MD graduates include pediatrics, emergency medicine, and family medicine. One study by the American Association for Medical Education and Research (AAMC) found that nearly 80 percent of MD Ph.D. graduates are employed as professors at medical schools or in research institutions such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), pharmaceutical companies, and other government agencies. More than 7,000 MD-PhD alumni participated in this study, and 82% said they would do it all over again, even if they could go back in time and do it all over again.
Physician-scientists are trained to not only have in-depth knowledge of the medical field but also of population health and disease, as well as the ability to conduct research and analysis independently. With a dual degree, physician-scientists can treat patients, detect health threats, and develop new treatments, therapies, or cures. When employed in academic settings, physician-scientists have the opportunity to teach, provide clinical services, and conduct their own or joint research. Physician-scientists typically earn between $60,000 and $115,000 per year, depending on the type and location of employment.
Physicians are responsible for managing and supporting the health and wellbeing of the patients in their care. They can manage and significantly improve their patients’ health through physical exams, diagnostic tests, treatment, and communication. Surgical procedures and treatment of illness and disease, either on a general or a specific level, may be performed by doctors of different specialties. The range of annual salaries is usually between $180,000 and $280,000, depending on the level of specialization.
Which Option Is the Most Suitable for You? MD or MD-PhD?
For some students putting on the safety glasses in science class or reviving a childhood teddy bear was a defining moment in choosing the medical field as their future path. However, not everyone is blessed with an immediate passion or the typical “aha” moment. Sometimes, a student’s interest in medicine or research develops later in life through experiences or education, which is perfectly normal. So what if your interests lie somewhere between the two fields of science and medicine? What factors should you consider when deciding between obtaining a degree in medicine (MD) and a joint degree (MD-PhD)? It is essential to choose only after you have considered various factors and are one hundred percent sure about your decision. The reality is that neither choice will be easy, and you’ll need to be willing to invest the necessary amount of time, money, and effort to achieve success.
Why Do Some Students Choose an MD-PhD?
Here are some reasons why people want to be both doctors and scientists.
As a physician-scientist, you’ll have a unique career path. One of the most rewarding aspects of working as a medical researcher is solving a patient’s medical issues while pursuing scientific research that could lead to a clinical cure for that particular disease.
MD-PhD trainees are medical researchers who also have a strong desire to practice medicine in a clinical setting.
The MD-PhD curriculum is designed to integrate the scientific and medical education of the future physician-scientist effectively and efficiently.
In the years leading up to their Ph.D., MD-PhD students complete coursework and receive formal training in research methodology.
Most MD-PhD programs offer trainees financial support in the form of stipends and scholarships to cover tuition costs. This financial support acknowledges the amount of time a student must devote to training in order to pursue a career in both medicine and research (MD-PhD). However, each program’s level of financial assistance varies, and some may provide assistance to only United States citizens and permanent residents.
MD-PhD Training Areas of Research
When applying to specific MD-PhD Programs, one essential factor to consider is the variety of the available graduate degree programs.
Most candidates for MD-PhD programs earn their Ph.D. in a biomedical laboratory discipline like cell biology, biochemistry, genetics, immunology, pharmacology, physiology, neuroscience, or biomedical engineering.
Students in some MD-PhD programs may also complete graduate work in non-laboratory disciplines such as computer science, economics, epidemiology, health care policy, or even the history of medicine and its social and cultural influences.
How to Choose Between an MD and a Ph.D.
Figure out what motivates you the most.
It would help if you first consider what you’re interested in and what drives you. This will help you figure out what you’re passionate about. Suppose you are confident that you are interested in medicine and assisting other people but are only slightly interested in research. In that case, it is probably a good idea to pursue medicine on its own rather than research. The MD Ph.D. program isn’t easy because it takes almost twice as long as an MD program. Students should only go for this joint degree if they are serious about both medicine and research. The joint program may be a good fit for you if you have a strong interest in disease mechanisms, are curious about the unknown, and can’t imagine a career that doesn’t involve research in some capacity.
First and foremost, decide if you want to become a medical doctor or a physician-scientist. People driven by their passions are more likely to find fulfillment in their work because they are doing what they truly want to do. You’ll have a rewarding career only when you have enough motivation to put in the necessary time and effort.
Think About the Dynamics of Your Preferred Job
Doctors spend a lot of time talking to their patients and families, and they need good communication skills. In hospitals, doctors may work unusual hours, even on weekends and holidays; in offices, they can have a more conventional schedule. If you decide to get a Ph.D., you might spend a lot of time working alone in a lab, or you might decide to teach students in your field. Whether you want an MD or a Ph.D. can depend on what kind of work environment and schedule you want.
Trust Your Own Experience
Is it possible to know for sure which path is the best for you? Before submitting your applications, get some hands-on experience in the field. This is the best opportunity to see whether you’ll like your future career path. If you’re torn between an MD and an MD Ph.D. program, make sure you get some clinical and research experience before making a decision. This is an excellent opportunity for you to gain practical experience in both fields and determine which ones pique your interest the most. You could sign up for volunteering opportunities that will give you first-hand experience in medicine or research. These experiences will be crucial when applying to medical school, but they’ll also help you narrow your interests.
Finally, remember that if you are still unsure which path is the best, you could always reach out to our Academic Advisors and seek their guidance.
By setting up a free one-on-one meeting with our friendly and knowledge advisors, you will be able to gain the valuable insight as to which career path you would like to take and how to get there. CLICK HERE TO GET STARTED .
Your Notifications Live Here
{{ notification.creator.name }} Spark
{{ announcement.creator.name }}
Trial Session Enrollment
Live trial session waiting list.

Next Trial Session:
{{ nextFTS.remaining.months }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.months > 1 ? 'months' : 'month' }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.days }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.days > 1 ? 'days' : 'day' }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.days === 0 ? 'Starts Today' : 'remaining' }} Starts Today
Recorded Trial Session
This is a recorded trial for students who missed the last live session.
Waiting List Details:
Due to high demand and limited spots there is a waiting list. You will be notified when your spot in the Trial Session is available.
- Learn Basic Strategy for CARS
- Full Jack Westin Experience
- Interactive Online Classroom
- Emphasis on Timing
Next Trial:
Free Trial Session Enrollment
Daily mcat cars practice.
New MCAT CARS passage every morning.
You are subscribed.
{{ nextFTS.remaining.months }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.months > 1 ? 'months' : 'month' }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.days }} {{ nextFTS.remaining.days > 1 ? 'days' : 'day' }} remaining Starts Today
Welcome Back!
Please sign in to continue..

Please sign up to continue.
{{ detailingplan.name }}.
- {{ feature }}
Is an MD/PhD Program Right for You?
MD-PhD programs may be right for you if you are interested in a career path that melds both clinical practice and in-depth scientific research. MD-PhD graduates aren’t simply doctors; they are “physician-scientists” or “medical scientists.”
MD-PhD programs offer a dual-degree track that combines the clinical training of a standard MD degree with the added coursework of a PhD. The PhD training is particularly rigorous and includes classes usually in the realm of biomedical sciences, as well as advanced research training, lab rotations, and intensive investigative work.
The payoff for choosing an MD-PhD program is that these clinical medicine graduates are equipped to treat patients while also participating in the discovery and development of innovative healthcare solutions.
Here are a few reasons you might want to pursue an MD/PhD career:
- You want to participate in cutting-edge medical research.
- You want career options beyond clinical medical practice.
- You want to help train future generations of medical doctors.
- You want more collaborative research opportunities with colleagues.
- You want funding opportunities only available to MD/PhD students.
The Difference Between MD & MD/PhD
The difference between MD and MD-PhD is that graduates with an MD-PhD receive PhD training and hold a PhD degree in addition to their MD degree.
The cost of an MD-PhD program varies widely depending on the institution. Still, the stipend and tuition-free training make many of these programs significantly less financially burdensome compared to standalone MD or PhD programs.
MD/PhD students will complete graduate school and medical school qualified to hold positions in academic medicine and biomedical research (in addition to being qualified to practice clinical medicine.
What Is an MD?
A medical doctor has earned a standard medical degree or MD and is skilled to practice clinical medicine. Medical students must complete 4 years of medical school to earn their degree, followed by 3-7 years of residency and fellowship training to practice medicine.
What Is a PhD?
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy in reference to their critical knowledge and research experience in a particular field of study. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree.
Earning a PhD is often considered harder than earning an MD due to the scientific research required to stimulate original thought and develop quality hypotheses.
How Competitive Are MD/PhD Programs?
Physician-scientist programs are slightly more selective and competitive than the average medical program.
Between 2018 and 2023, a little more than one-third of students who applied to an MD/PhD program (37.7%) were accepted. The acceptance rate for medical school applicants in general was 41.2% for the 2022-23 application cycle.
The test scores of these programs also indicate how much more competitive these programs are. The average MCAT score of MD/PhD matriculants in the 2022-23 cycle was 516.2, and their mean GPA was 3.82. In comparison, medical school matriculants overall had an average MCAT score of 511.9 and average GPA of 3.75 during the same cycle.
How Long Are MD/PhD Programs?
The MD-PhD dual degree takes approximately 7-8 years of coursework to complete, followed by an additional 3-7 years of residency to be eligible to practice medicine.
Generally, MD coursework is emphasized in years 1-2, followed by research training in years 3-5, and ending with medical training and clinicals in years 6-8.
Requirements for MD/PhD Applicants
If you are considering applying to an MD/PhD program , know that having strong essays and letters is more important than incrementally higher MCAT test scores and GPAs. Numbers get your foot in the door; storytelling gets you a seat at the table.
In general, the requirements for MD/PhD applicants include:
- MCAT score in the 90th percentile: Specific MCAT requirements for MD/PhD programs vary by school. However, in general, most students have the best chance at success with an MCAT score in the 90th percentile or higher. In the 2022-23 application cycle, MD/PhD applicants had an average MCAT score of 511.3, while matriculants averaged 516.2.
- GPA of 3.7 or higher: Like MCAT scores, the GPA requirements for MD/PhD programs differ by program. But your chances are highest with an average GPA of at least 3.7. In the 2022-23 application cycle, MD/PhD applicants averaged a science GPA of 3.61 and overall GPA of 3.68, while matriculants averaged a 3.78 science GPA and 3.82 overall.
- Compelling personal statement: Your personal statement essay should explain why you want to become a physician and is required for both MD & MD/PhD applications . All prospective doctors must write a personal statement that stands out, and this is doubly true for MD/PhD applicants.
- 2 additional essays: You’ll write one essay conveying your personal interest in pursuing an MD/PhD dual degree specifically, and one essay covering your substantive experiences in the field of research . These may include multiple summer projects, senior thesis research, or 1+ years of post-undergrad research programs and activities.
- 2-3 letters from research mentors who can praise your scientific potential.
- 1-2 letters from clinical mentors who know your aptitude for patient care.
- 1 letter from the premed committee.
- 1 letter from a mentor who can discuss your leadership skills and personal traits in an extracurricular setting.
Questions to Ask Yourself When Considering an MD/PhD Program
By answering these questions, you can choose the graduate program that is the best fit for you over the next 8 years.
- What skills do you want to develop? Choose a program that has ample opportunities to explore your field of interest and in which you can identify potential mentors for rotations and thesis projects.
- What is your preferred MD/PhD program size? Choose a smaller program of MD-PhD students if you prefer hands-on guidance with individualized attention and a larger program if you prefer a larger community with more networking opportunities.
- Where do you want to live for 8 years of medical school ? Choose a location that fits your needs for cost of living, housing, transportation, extracurriculars, as well as opportunities for fun and making friends.
- Does the program offer financial aid? Choose a program that meets your financial needs in the form of stipends and tuition waivers. It’s important to note that if you drop out of an MD-PhD program, some schools require you to pay back the investment that the school made in you.
- Will you fit into the school’s culture? Choose a program after you’ve visited the campus, talked with the current students and faculty, and asked about opportunities in your field of interest as well as other’s experiences at the school and living in the city.
- Does the MD/PhD Program align with your timeline? Choose a program with coursework that allows you to graduate in your preferred timeline, which could be sooner or longer than eight years.
Possible Career Paths for MD/PhD Graduates
A career choice often depends on an individual’s specific interests, such as which medical specialties they are drawn to, whether they prefer working with patients or in a laboratory, and how they want to contribute to advancing medical science.
The salary range for MD/PhD graduates varies significantly by position and type of work. Policy analysts’ starting salary is around $57,000 per year, while attending physicians who do research can make upwards of $500,000.
Below are careers someone with an MD-PhD might pursue:
Attending Physician with Research Responsibilities
An MD/PhD holder in this position would have a traditional medical role seeing and treating patients, but they might also have dedicated time for research. This role allows one to continue practicing medicine while contributing to academic or clinical research.
Individuals in this role often split their time among patient care, research activities, and instructional duties. Typically, they are found in educational hospitals or medical schools.
Physicians’ salaries can vary significantly based on specialty and experience, but generally, they are well-compensated. An attending physician in a specialized field can expect to earn upwards of $200,000 to $500,000 or more, especially if they have dual responsibilities that include research.
Translational Medicine Specialist
These specialists work at the intersection of basic research and patient care, focusing on turning research insights into practical medical applications.
This role may exist within academia, industry, or clinical settings and is tailored for those who understand both the clinical and research aspects of medicine.
The salary for this role can also vary based on industry, location, and level of experience but would likely fall in the range of $150,000 to $250,000 or more.
Biomedical Researcher
Those with MD-PhD qualifications commonly secure jobs as researchers within biomedical science. Employment settings can range from academic institutions and drug companies to governmental agencies like the NIH.
Salaries for biomedical researchers typically fall somewhere between $85,000 and $104,000 per year.
Clinical Research Director
These are medical doctors responsible for overseeing clinical trials and research projects, usually within a hospital, academic institution, or pharmaceutical/biotech company. This role leverages both the clinical insights from an MD and the research methodology of a PhD.
Salaries can vary widely depending on the setting (academia, private industry, etc.) and geographic location. In general, a Clinical Research Director could expect to earn a six-figure salary, often ranging from around $150,000 to $250,000 or more per year.
Pharmaceutical/Biotech Industry Professional
A significant number of MD-PhDs join the pharmaceutical or biotech sectors. Responsibilities might include roles in the development of new medications, overseeing clinical trials, regulatory compliance, or managing medical affairs.
The average salary for this position will likely differ quite a bit depending on the exact role and company, but the average is generally between $125,000 and $133,00 per year.
Medical Director
In this capacity, a person is in charge of the medical elements of a healthcare facility or a specific department within a hospital. The role usually calls for expertise in both medical practice and research.
This position is likely to be one of the most lucrative of the MD/PhD field, with an average salary from $319,000 to $329,000 per year.
Science Policy Analyst/Advisor
Individuals in this role often find themselves in governmental or nonprofit settings, where they influence policy decisions related to scientific research and healthcare.
The typical salary for a science policy analyst starts at around $57,000 per year. Advisors have a slightly higher upper salary range and may make as much as $75,000.
Public Health Official
Some MD-PhDs opt for roles in the public sector where they focus on health concerns at a societal level. They may be employed by organizations such as the CDC or WHO.
In many cases, public health officials can expect to make a yearly salary of between $101,000 and $111,000.
Medical Science Liaison
This role typically serves as an intermediary between pharmaceutical enterprises and medical professionals. These liaisons disseminate information about new treatments and scientific advancements to doctors, researchers, and other medical stakeholders.
This role also typically commands a six-figure salary, usually ranging from approximately $100,000 to $200,000, depending on experience, location, and the hiring organization.
Medical Educator
Professors teach medical students, residents, and fellows in an academic setting while also conducting research. These doctors often have clinical responsibilities as well. An MD/PhD is especially well-suited for this role due to the dual focus on clinical care and research.
They may teach various medical subjects like pharmacology or genetics and actively participate in the educational goals of their institutions.
In academia, salaries can vary widely based on rank (Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Full Professor), institution, and geographic location. Salaries may range from $100,000 to well over $200,000 for senior roles or those at prestigious institutions.
Best MD/PhD Programs in the US
There are 122 different American Universities that offer MD/PhD degree programs, according to the AAMC list of MD-PhD Programs by State . A further 13 Canadian programs also use the AMCAS application system.
Some MD-PhD programs in the United States are funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP). This means that students receive full tuition remission, health insurance, and a living stipend throughout their training.
Medical schools with fully funded MD-PhD programs :
- Dartmouth University, Geisel School of Medicine
- Duke University School of Medicine
- Harvard/M.I.T MD-PhD Program, Harvard Medical School
- John Hopkins University School of Medicine
- Mayo Clinic College of Medicine & Science
- University of Florida College of Medicine
- University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine
- University of Southern California (USC), Keck School of Medicine
- Yale University School of Medicine
Medical schools with the most MD-PhD spots historically:
- Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
- University of Illinois College of Medicine
- Weill Cornell Medical College
- Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine
- Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
- Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University
- University of California, Los Angeles David Geffen School of Medicine
- University of Michigan Medical School
- Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons
- University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
- Harvard Medical School
- Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
- Northwestern University The Feinberg School of Medicine
- Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
- University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine
- Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
- Ohio State University College of Medicine
- University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
- New York University School of Medicine
- Stanford University School of Medicine
- Yale School of Medicine
Medical schools with MD/PhD programs that accept international students:
- Emory University School of Medicine
- Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine
- University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine
- University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine/California Institute of Technology
- University of Texas Southwestern Medical School
- Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
The MD/PhD Application Process
The application process for MD-PhD programs is similar to that of typical MD programs. The two major differences are that you’ll designate yourself as an MD/PhD candidate on the AMCAS application, and you’ll submit 2 additional essays on that primary.
The Application Timeline
- AMCAS (submit by end of May): You’ll fill out a primary application through AMCAS in the spring of the first year of your application cycle (e.g., to matriculate in fall 2026, you’ll submit AMCAS in spring 2025). AMCAS opens at the end of May each year. Aim to submit the primary application no later than the end of June, as early applications are more likely to be reviewed and accepted.
- Secondaries (submit by end of August): You’ll respond to secondary applications in the summer after your primary application is reviewed by each school you submitted it to. Each program sends secondary applications to students who generally meet their minimum requirements.
- Interviews (October-March): You’ll then attend interviews as invited between October and March. Some schools won’t contact you at all to reject your application; others will offer conflicting invites. You must prioritize your options and prepare for the opportunities that do come.
- Final decisions (December-March): Final decisions are made by schools between December and March. Schools with a rolling admissions cycle (most of them) accept students after completing interviews and determining a student is a fit. A smaller number of programs wait to send acceptances until after all interviews are complete.
- Choose your program (March-April): Students choose where to matriculate between March and April.
- Programs start (June-August): Programs begin between June and August, depending on the school.
How to Prepare for an MD/PhD interview
You should prepare for your MD/PhD interview by practicing mock interviews to rid yourself of the jitters and fine-tune your responses in various scenarios. In addition to developing your personal narrative, you must be able to explain your research training at multiple levels.
If you’re interested in participating in a mock interview with a physician who has served on an admissions committee, consider a mock interview with MedSchoolCoach .
What to Do if You Get Waitlisted
Finding out that you’ve been waitlisted for the MD/PhD program of your dreams is never a good feeling. However, you are not helpless in the wait. It’s a good idea to remain in contact with program leaders and administrators by sending a Letter of Intent or a Letter of Interest.
Listen: An MD/PHD’s Journey to Medicine [PODCAST]
What is a Letter of Intent vs. a Letter of Interest?
A Letter of Intent is a formal statement that you would commit to matriculating into a program if you are accepted. A Letter of Interest conveys that you are strongly interested in the program, but it does not indicate any commitment or explicitly state that a program is your first choice.
Both letters should summarize why you believe the program and school are a great fit for your interests and how you will be able to uniquely contribute to the school, in under one page.
Finding Out You’ve Been Accepted!
The day you receive that phone call or email — the one from the MD-PhD program director contacting you to say you have officially been offered acceptance into their program — provides a feeling of joy worth being patient for!
Our Physician Advisors can support you through the application process for your best shot at getting into the school of your choice.
What specialties can MD/PhD graduates earn their PhD in?
PhD students commonly choose to specialize in topics such as:
- Cell Biology
- Biochemistry
- Pharmacology
- Neuroscience
- Biomedical Engineering
What is the salary range for an MD/PhD graduate?
MD/PhD graduates can expect an average annual salary of about $100K, depending on the type of work and place of employment.
What is the difference between a PhD and a Postdoctorate?
A Postdoctoral Fellowship is a temporary period of mentorship and research training for graduates with doctoral degrees, offered by the National Institutes of Health, to acquire skills needed for a chosen career. A PhD thesis must be successfully defended, whereas a postdoc is a non-defendable temporary employment assignment from an organization such as a university.
Can an MD/PhD be a doctor?
Graduates who earn an MD/PhD are fully qualified doctors and may practice medicine in a clinical setting upon completing their residency training.
Can an MD/PhD graduate be a surgeon?
While an MD/PhD graduate CAN be a surgeon if they choose surgery specialties in their residency programs, a surgical resident is not required to obtain a PhD in addition to their MD.
Schedule a free 15-minute consultation with MedSchoolCoach to learn how we can help boost your chances of success getting into medical school .
Related posts:
- What Does DO Mean?
- What Kind of Students are Successful in Getting into Medical School?
- What Counts as Clinical Experience for Medical School?
- Should I Delete My Social Media When Applying to Medical School?

Renee Marinelli MD
Related articles.

Use MSAR To Choose Which Medical Schools You’ll Apply To

How to Hold on to the Med School Dream

The Healing Capacity of Empathic Curiosity in Medicine

The Path to Earning a Dual Degree
- Medical School Application
MD-PhD Programs: The Definitive Guide
Including a list of md-phd programs in the us and canada.
Featured Expert: Dr. Jacquelyn Paquet, MD

An MD-PhD program might be the right choice for you if the question “ Why do you want to be a doctor? ” leaves you feeling excited but a little unsure. Are you inspired to work in medicine but not interested in concentrating exclusively on clinical work? MD-PhD programs accept applicants who want to become physician-scientists, a career path that focuses on scientific innovation and research.
In this definitive guide to MD-PhD programs, you will learn everything you need to know about applying, medical schools in North America that offer this program, admission requirements, funding for MD-PhD programs, and tips to help you get accepted!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 1 min read
List of md-phd programs.
Many schools offer the MD-PhD program in Canada and the United States, and the number of available programs is growing. Here is an up-to-date list, which is also available on the AAMC website. Schools funded through MTSP are starred.
· University of Alabama School of Medicine*
· University of Arizona College of Medicine *
· University of Arizona College of Medicine - Phoenix
· University of Arkansas College of Medicine
· Loma Linda University School of Medicine
· Stanford University School of Medicine*
· University of California, Davis School of Medicine *
· University of California, Irvine School of Medicine*
· University of California, Los Angeles David Geffen School of Medicine*
· University of California, San Diego School of Medicine*
· University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine*
· Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine
· Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California
· University of Colorado Health Sciences Center
· University of Colorado Denver*
· Colorado State University College of Veterinary Medicine and Biological Sciences*
· University of Connecticut School of Medicine
· Yale University School of Medicine*
· Georgetown University School of Medicine
· Howard University College of Medicine
· University of Florida College of Medicine
· University of Miami Miller School of Medicine*
· University of South Florida College of Medicine
· University of Central Florida College of Medicine
· Emory University School of Medicine*
· Morehouse School of Medicine
· Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University
· Loyola University of Chicago - Stritch School of Medicine
· Northwestern University Medical School *
· Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science - Chicago Medical School
· University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine (MTSP) *
· University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine *
· Carle Illinois College of Medicine
· Indiana University School of Medicine *
· University of Iowa College of Medicine *
· University of Kansas School of Medicine
· University of Kentucky College of Medicine
· University of Louisville School of Medicine
· Louisiana State University, New Orleans School of Medicine
· Louisiana State University, Shreveport School of Medicine
· Tulane University School of Medicine
· Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine *
· National Institutes of Health Intramural MD-PhD Partnership
· Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
· University of Maryland at Baltimore School of Medicine *
· Boston University School of Medicine
· Harvard Medical School *
· Tufts University School of Medicine *
· University of Massachusetts Medical School *
· Michigan State University College of Medicine
· University of Michigan Medical School *
· Wayne State University School of Medicine
· Western Michigan University Homer Stryker M.D. School of Medicine
· Mayo Medical School *
· University of Minnesota Medical School *
· University of Mississippi School of Medicine
· Saint Louis University School of Medicine
· University of Missouri - Columbia School of Medicine
· Washington University School of Medicine *
· University of Nebraska College of Medicine
· Creighton University School of Medicine
· University of Nevada School of Medicine
· Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth
· University of Medicine & Dentistry of New Jersey - New Jersey Medical School
· University of Medicine & Dentistry of New Jersey - Robert Wood Johnson Medical School
· Cooper Medical School of Rowan University
· University of New Mexico School of Medicine
· Albany Medical College
· Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University *
· Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons *
· Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell
· Weill Cornell/Rockefeller/Sloan-Kettering Tri-Institutional MD/PhD Program
· Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai *
· New York Medical College
· New York University Grossman School of Medicine *
· Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at the University at Buffalo
· SUNY at Stony Brook Health Sciences Center *
· SUNY Downstate Medical Center College of Medicine
· SUNY Upstate Medical University
· University of Rochester School of Medicine *
· Wake Forest School of Medicine
· Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University
· Duke University School of Medicine *
· University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine *
· University of North Dakota School of Medicine
· Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine *
· Northeastern Ohio College of Medicine
· Ohio State University College of Medicine *
· University of Cincinnati College of Medicine *
· University of Toledo College of Medicine
· Wright State University School of Medicine
· University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
· Oregon Health & Science University School of Medicine *
· Drexel University College of Medicine
· Penn State University College of Medicine *
· Perelman School of Medicine School of Medicine *
· Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
· University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine *
· University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine
· Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Philadelphia, Pa.
· University of Puerto Rico School of Medicine
· Brown University School of Medicine
· Medical University of South Carolina College of Medicine *
· University of South Carolina School of Medicine
· University of South Dakota School of Medicine
· Meharry Medical College School of Medicine
· East Tennessee State University James H. Quillen College of Medicine
· University of Tennessee, Memphis College of Medicine
· Vanderbilt University School of Medicine *
· Baylor College of Medicine *
· Texas A&M University Health Sciences Center College of Medicine
· Texas Tech University School of Medicine
· University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston
· McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center *
· University of Texas, San Antonio Medical School *
· University of Texas, Southwestern Med Center - Dallas *
· University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine
· University of Utah School of Medicine
· University of Vermont College of Medicine
· Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine
· University of Virginia School of Medicine *
· University of Washington School of Medicine *
· Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine
· West Virginia University School of Medicine
· Medical College of Wisconsin *
· University of Wisconsin Medical School *
· McGill University Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Montreal, Quebec
· McMaster University of Faculty of Health Sciences Hamilton, Ontario
· Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John’s, Newfoundland
· Queen’s University School of Medicine Kingston, Ontario
· Universite de Montreal Faculte de Medecine Montréal, Québec
· Universite de Sherbrooke Faculte de Medecine Sherbrooke, Quebec
· Universite Laval Faculte de Medecine Québec, Québec
· University of Alberta Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry Edmonton, Alberta
· University of Calgary Faculty of Medicine Calgary, Alberta
· University of British Columbia Faculty of Medicine Vancouver, British Columbia
· University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba
· University of Ottawa Faculty of Medicine Ottawa
· University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine Toronto, Ontario
· University of Western Ontario London, Ontario
MD-PhD programs allow you to obtain a dual degree in medicine and research. When deciding between MD-PhD vs MD programs, it is important to know what MD-PhD programs entail. Upon graduation, students receive a combined degree with advanced, hands-on research training and expertise in a field of their choice.
“MD-PhD … students enter their first year of medical school and complete their pre-clerkship years. During this period they are likely exploring what they are interested in, solidifying their focus in research and seeking supervisors. Then they will take approximately 5 years off of their medical training to complete their PhD. They will then re-engage in their medical training completing their clerkship training, which will complete their program. MD-PhD is a rigorous program and the committee is looking for individuals who are academically strong and possess research skills to succeed in the PhD program. Applicants should be strong clinicians, thus having a breadth of leadership, extracurricular, volunteerism and research experience.” - Dr Jacquelyn Paquet, MD, University of Alberta Faculty of Medicine
Is the md-phd program right for me.
The MD-PhD program is for exceptional students interested in a career in medical research, but you’ll still need to be a well-rounded medical school applicant.
“For the MD-PhD they are wanting individuals to possess additional research skills, however recognizing the unique leadership positions of those with doctoral degrees, they are often situated in academic centers, thus involved in administrative and teaching roles as well! They are still wanting applicants to be strong clinicians, thus having a breadth of leadership, extracurricular, volunteerism and research experience are sought.” – Dr. Jacquelyn Paquet, MD.
Keep in mind that even if you choose not to pursue a dual degree program, MDs can still earn their PhDs—and vice versa!
“I pursued a PhD during residency. I had considered doing a MD-PhD as it would provide more opportunities to focus on research prior to initiating my residency training. I opted to complete my MD first and pursue my MSc and PhD during residency as I was concerned about having 5 years off between my pre-clerkship and clerkship years would impact my clinical skills.” – Dr. Jacquelyn Paquet, MD.
Finally, ask yourself, \u201c What is your greatest weakness? \u201d If the answer is research, an MD-PhD program might not be for you. However, if you are determined to pursue medicine and research simultaneously, the MD-PhD program is perfect! ","label":"Question to Ask Yourself","title":"Question to Ask Yourself"}]" code="tab4" template="BlogArticle">
Struggling to decide between MD-PhD and MD programs? Check out our video below!
The most important admission requirements and prerequisites for MD-PhD programs are your research background and lab experience. MD-PhD programs require the completion of a four-year undergraduate degree and background in the following disciplines:
2 years of clinical training to prepare you for residency. After clerkships, you will complete the USMLE Step 2 exam and any other MD requirements of your program. "}]">
These medical school prerequisites are the baseline. Your academic record should include a variety of science and non-science courses. Admissions committees will note your coursework’s difficulty levels and academic improvement over time.
Check with your program of choice for specific course requirements.
We’ve compiled a list of our top tips for getting accepted into an MD-PhD program, based on expert advice and experience:
GPA and MCAT
According to the latest AAMC statistics, the average GPA of MD-PhD matriculants is 3.7, while the average MCAT score is 511. If your academic record does not reflect these numbers, you need to get your grades up. Here are four ways you can start to get into medical school with a low GPA.
- Re-enroll in classes you performed poorly in and get a higher grade.
- Ask your instructors and teaching assistants for extra credit assignments.
- Find a tutor to help with areas where you struggle.
- Plan your school schedule to include subjects in which you excel.
Your MCAT score is an indicator of your academic prowess. Before you take the test, make sure you know what is a good MCAT score and when to start studying for the MCAT . Here are four strategies that can help your MCAT score.
- Give yourself ample time to prepare.
- Start by taking an MCAT practice test to determine areas for improvement.
- Create an MCAT study schedule.
- Take multiple practice tests to monitor improvement. If you consistently score at the 90% percentile in your practice tests, you can start planning to take the actual MCAT.
If you’re still wondering “ When should I take the MCAT ?”, read our blog for tips.
CASPer Test
If your schools require the completion of the Acuity Insights Suite, you will complete the Duet profile and CASPer test. Preparing for each component is challenging, but CASPer remains the most intimidating.
The CASPer test is an online situational judgment test designed to assess the suitability of students applying to professional schools. The timed format is challenging, so knowing how the CASPer test is scored is helpful. Learn how to prepare for CASPer and review these CASPer practice questions to ace your test!
“Thanks to BEMO I got a 4th quartile on my casper test!!!!! It took me long to understand the BEMO structure but practice and great coaching made the difference. Without BEMO I would of probably gotten a 2. So don’t hesitate signing up with them, if you are committed, you will also get a 4! Also, buy the BEMO casper book!” - Mike, Former BeMo Student
You will need to submit a total of three essays for the MD-PhD program:
- Your personal statement,
- The research interest statement , and
- The MD PhD essay .
Note: If you’re applying through TMDSAS, you will need to submit the Dual Degree essay along with the other essay application components.
“In your personal statement you want to highlight your breadth and skillset in research and areas of interest. You also want to highlight how completing a PhD will make you a stronger clinician and if you are aware, how you see yourself fulfilling the roles of researcher and clinician.” – Dr. Jacquelyn Paquet, MD.
While your medical school personal statement answers the question “Why do you want to be a doctor?”, the MD-PhD specific essays demonstrate your research expertise and explain why you have chosen to pursue an MD-PhD. The significant research experience essay outlines your most valuable research experiences, including the nature of the work, your role and contributions, project length, and details about the principal investigators. Your MD-PhD essay tells the story of how you became involved in scientific research and how you want to apply your research to medical practice.
“I used BeMo consulting when applying to my MD/PhD programs this year. As a first time applicant to these programs, it can be overwhelming. Luckily, BeMo’s services are helpful and easy-to-use. They have a fast response and helped me greatly in writing my essays." -- Zhinan Liu, former BeMo student.
Want to know how to write an MD-PhD essay? Check out our video below!
Research Experience
As an MD-PhD program applicant, you must have research experience to demonstrate your exposure to research methods and techniques.
Dr. Monica Taneja, BeMo expert and Psychiatry resident at Harvard South Shore, reminds students that it is important to consider your own passion when finding research opportunities, not focusing solely on what you think the admission committee is looking for.
“I definitely felt that public health gave me a lot of unique opportunities to delve into research related to the social determinants of health and health equity. I noticed that research in this area was not as common compared to basic science or clinical research.” - Dr. Monica Taneja, MD, Harvard South Shore – Psychiatry.
Make sure you can identify what you learned from your research experiences – you will have to outline valuable lessons and skills you acquired in multiple parts of your MD-PhD application and interviews. To bolster your research background, try looking for research assistant positions.
- Talk to your instructors and teaching assistants about participating in their research projects.
- Check for research position postings on your school’s website.
- Reach out to former instructors and ask about research opportunities.
- Contact physicians you volunteered with or shadowed to find out if they are involved in research projects. Even if they are not, physicians can often recommend research-oriented organizations and medical professionals.
You need a strong application, including a research assistant cover letter and CV, to apply to research positions. If academia is your passion, you might want to look into special master’s programs . These graduate degrees are designed to enhance students’ medical school applications and may improve the quality of your research background.
Clinical experience is one of the essential extracurriculars for medical school , and having no clinical background will decrease your chances of being accepted to an MD-PhD program.
You can gain clinical experience through:
- Working and volunteering in clinics, hospitals, and hospices.
- Volunteering in long-term care and retirement homes.
- Working as a health professional’s assistant.
- Volunteering as a medical scribe or a personal caretaker.
Shadowing a physician can also increase your knowledge of clinical practice. Take note of memorable lessons you learn – they may be invaluable sources for your MD-PhD essays. Make sure you know how many shadowing hours are required for medical school to fulfill the requirement and how to ask to shadow a doct or.
Dr. Neel Mistry, MD, a graduate from the University of Ottawa medical school and a BeMo admissions expert, says this about his clinical experience:
“These experiences helped solidify my passion for medicine and why I wanted to become a doctor. I was able to draw on these experiences during my medical school application and the interview process.” - Dr Neel Mistry, MD, University of Ottawa Faculty of Medicine
Md-phd residency.
As an MD-PhD student, you need to find residencies developed to train physician-scientists by fully integrating research into clinical training. The number of residency programs for MD-PhDs is growing, and a wide range of clinical specialty choices exist. During your dual degree program, you’ll have plenty of opportunities to explore research in different medical specialties.
“By having an area of focus, it allows you to explore if you do want to indeed be a clinician-scientist in the area you have considered or if you have a different scope of the project that might lend itself better to a complimentary specialty. For instance, someone who is interested in head and neck cancers may be quite interested in pursuing otolaryngology however when they focus on their project, they recognize that they prefer the radiology or oncologic treatments and thus pursue interventional radiology, radiation oncology or oncology.” – Dr. Jacquelyn Paquet, MD.
You will use the ERAS application to apply to American residency programs and CaRMS to apply to programs in Canada.
1. WHAT ARE MY CAREER OPTIONS WITH AN MD-PHD?
Individuals with an MD-PhD have career options across academia, research institutions, healthcare organizations, and private industry. The versatility of an MD-PhD equips graduates to make significant contributions to medical practice and scientific innovation.
Career paths for MD-PhDs include:
- Academic careers, working in universities or medical schools, where time is shared between patient care, teaching, and conducting research.
- Leadership roles within healthcare organizations, directing research programs or shaping healthcare policy.
- Private industry, such as pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, or healthcare consulting.
- Government agencies, advancing medical research and public health initiatives.
2. HOW LONG ARE MOST MD-PHD PROGRAMS?
MD-PhD programs can take up to 8 years to complete. Factors influencing the duration include clinical and PhD requirements and research progress. Two common tracks are the 2-3-2 or 2-4-2, involving initial MD coursework, followed by PhD research, and concluding with clinical training.
3. IS IT HARDER TO GET INTO AN MD-PHD PROGRAM?
Getting into an MD-PhD program can be harder because you have to meet the admission requirements for both the MD and PhD programs, and have research experience. MD-PhD programs can be very selective and highly competitive.
4. ARE THERE ANY FUNDED MD-PHD PROGRAMS?
MD-PhD program funding can include tuition waivers and a stipend to help cover the costs of living expenses. The National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) provides financial support to dozens of MD-PhD programs through the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP). These programs are extremely competitive as the funding offers a tuition allowance and a basic stipend, with most institutions supplementing the stipend.
5. DO I STILL NEED TO GET CLINICAL AND SHADOWING EXPERIENCE IF I AM APPLYING TO THE COMBINED PROGRAM?
While research is going to be the major focus of the MD-PhD, you must still have sufficient clinical and shadowing experience to assure that medicine is also a desired component of your career.
6. SHOULD I GET A MASTER’S DEGREE BEFORE I APPLY TO MD-PHD?
Most applicants do not have master’s degrees. However, some students pursue a special master’s program to gain valuable research experience and bolster their MD-PhD applications.
7. WHAT IS A GOOD RESEARCH EXPERIENCE FOR MD-PHD?
You do not need to have research experience in the medical field to qualify for MD-PhD. Many research skills are transferable across disciplines. As long as you learn valuable research skills and understand the process, your research experience can come from any field you like.
8. HOW MUCH RESEARCH EXPERIENCE DO I NEED TO GET ACCEPTED?
The quality of your research experience is most important. It is not necessary to be involved in dozens of research projects or make any ground-breaking scientific discoveries to enter the MD-PhD program. In your application, focus on what you have learned and accomplished and don't be afraid to discuss your setbacks in addition to your accomplishments.
9. DO I NEED TO BE A PUBLISHED RESEARCHER TO ENTER THE MD-PHD PROGRAM?
Having published research can give you a competitive edge as not every applicant will have this experience. Keep in mind that you must have an in-depth understanding of this research because you will be asked about it during your interviews. However, many students apply directly out of undergrad and admissions committees understand that it is difficult to contribute to publication at such an early stage in your education.
10. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MD-PHD AND MSTP?
Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) is an MD-PhD program that has been awarded a training grant (T32) from the National Institute of General Medical Science that financially supports trainees in the program. There are currently about 49 MD-PhD programs that have T32 awards. Non-MSTP MD-PhD programs also provide environments where students obtain outstanding dual-degree training.
11. WHO SHOULD WRITE MY RECOMMENDATION LETTERS FOR THIS TYPE OF PROGRAM?
Ideally, at least one of your writers will be the head of a research project in which you participated. It is important to have a person who can speak to your research skills and progress. Other writers can include professors and instructors, volunteer and work supervisors, athletics coaches, or a physician you worked with or whom you shadowed.
12. CAN I CHANGE MY RESEARCH INTERESTS DURING MY STUDIES, OR WILL I HAVE TO STICK TO THE RESEARCH FIELD I IDENTIFIED IN MY PERSONAL STATEMENT AND MY MD PHD ESSAY?
It is completely normal to change direction in your research throughout your studies and many students change their research fields after they gain more research experience.
13. CAN I BECOME A PHYSICIAN-SCIENTIST WITHOUT OBTAINING AN MD-PHD DEGREE?
It is certainly possible to become a physician-scientist without obtaining an MD-PhD degree. However, the joint program is the most effective way to become a physician-scientist. You can also complete an MD and PhD separately, but this route takes much longer. Some schools will let you transfer into their MD-PhD program if you've completed a year or two in their medical program.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee your acceptance to med school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
- Doctor of Medicine and Doctor of Philosophy (MD/PhD)
- MAS Application Fee Waiver Requirements
- Master of Arts (MA) in Geography and Environmental Engineering
- Master of Arts and Master of Science in Public Health (MA/MSPH)
- Master of Arts in Public Health Biology (MAPHB)
- Master of Bioethics (MBE)
- MHA Frequently Asked Questions
- Mission, Vision, and Values
- MHA Executive in Residence and Alumni
- Student Experience
- Program Outcomes
- Bachelor's/MHA Program
- Master of Health Science (MHS) - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Master of Health Science (MHS) - Department of Epidemiology
- Alumni Update
- MHS Combined with a Certificate Program
- Master of Health Science (MHS) - Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Alumni Highlights
- Post-Baccalaureate Program in Environmental Health for Pre-Medicine Students
- Bachelor's/MHS in Health Economics and Outcomes Research
- MHS HEOR Careers
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Master of Health Science (MHS)
- Concurrent School-Wide Master of Health Science Program in Biostatistics
- Master of Health Science - Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Master of Health Science Online (MHS) - Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Careers in Health Economics
- Core Competencies
- Meet the Director
- What is Health Economics
- MPH Capstone Schedule
- Concentrations
- Online/Part-Time Format
- Requirements
- Tuition and Funding
- Executive Board Faculty
- Master of Science (MS) in Geography and Environmental Engineering
- Independent Professional Project and Final Essay
- Program Objectives and Outcomes
- Internships
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Biostatistics
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Epidemiology
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- ScM Faculty Advisers
- Master of Science in Engineering (MSE) in Geography and Environmental Engineering
- Bachelor's/MSPH in Health Policy
- FAQ for MSPH in Health Policy
- Field Placement Experience
- MSPH Capstone
- MSPH Practicum
- Required and Elective Courses
- Student Timeline
- Career Opportunities
- 38-Week Dietetics Practicum
- Completion Requirements
- MSPH/RD Program FAQ
- Program Goals
- Master's Essay Titles
- Application Fee Waiver Requirements
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Biostatistics
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Epidemiology
- Program Goals and Expectations
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Clinical Investigation
- Track in Environmental Sustainability, Resilience, and Health
- Track in Exposure Sciences and Environmental Epidemiology
- Track in Health Security
- Track in Toxicology, Physiology and Molecular Mechanisms
- PhD in Geography and Environmental Engineering Faculty Advisers
- Recent Graduates and Dissertation Titles
- PhD Funding
- PhD TA Requirement
- Recent Dissertation Titles
- JHU-Tsinghua Doctor of Public Health
- Core Course Requirements
- Concentration in Women’s and Reproductive Health
- Custom Track
- Concentration in Environmental Health
- Concentration in Global Health: Policy and Evaluation
- Concentration in Health Equity and Social Justice
- Concentration in Health Policy and Management
- Concentration in Implementation Science
- Meet Current Students
- Combined Bachelor's / Master's Programs
- Concurrent MHS Option for BSPH Doctoral Students
- Concurrent MSPH Option for JHSPH Doctoral students
- Adolescent Health Certificate Program
- Bioethics Certificate Program
- Climate and Health Certificate Program
- Clinical Trials Certificate Program
- Community- Based Public Health Certificate Program
- Demographic Methods Certificate Program
- Environmental and Occupational Health Certificate Program
- Epidemiology for Public Health Professionals Certificate Program
- Evaluation: International Health Programs Certificate Program
- Food Systems, the Environment and Public Health Certificate Program
- Frequently Asked Questions for Certificate Programs
- Gender and Health Certificate Program
- Gerontology Certificate Program
- Global Digital Health Certificate Program
- Global Health Certificate Program
- Global Health Practice Certificate Program
- Health Communication Certificate Program
- Health Disparities and Health Inequality Certificate Program
- Health Education Certificate Program
- Health Finance and Management Certificate Program
- Health and Human Rights Certificate Program
- Healthcare Epidemiology and Infection Prevention and Control Certificate Program
- Humane Sciences and Toxicology Policy Certificate Program
- Humanitarian Health Certificate Program
- Implementation Science and Research Practice Certificate Program
- Injury and Violence Prevention Certificate Program
- International Healthcare Management and Leadership Certificate Program
- Leadership for Public Health and Healthcare Certificate Program
- Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) Public Health Certificate Program
- Maternal and Child Health Certificate Program
- Mental Health Policy, Economics and Services Certificate Program
- Non-Degree Students General Admissions Info
- Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety Certificate Program
- Population Health Management Certificate Program
- Population and Health Certificate Program
- Product Stewardship for Sustainability Certificate Program
- Public Health Advocacy Certificate Program
- Public Health Economics Certificate Program
- Public Health Informatics Certificate Program
- Public Health Practice Certificate Program
- Declaration of Intent - Public Health Preparedness
- Public Health Training Certificate for American Indian Health Professionals
- Public Mental Health Research Certificate Program
- Quality, Patient Safety and Outcomes Research Certificate Program
- Quantitative Methods in Public Health Certificate Program
- Requirements for Successful Completion of a Certificate Program
- Rigor, Reproducibility, and Responsibility in Scientific Practice Certificate Program
- Risk Sciences and Public Policy Certificate Program
- Spatial Analysis for Public Health Certificate Program
- Training Certificate in Public Health
- Tropical Medicine Certificate Program
- Tuition for Certificate Programs
- Vaccine Science and Policy Certificate Program
- Online Student Experience
- Online Programs for Applied Learning
- Barcelona Information
- Fall Institute Housing Accommodations
- Participating Centers
- Registration, Tuition, and Fees
- Agency Scholarship Application
- General Scholarship Application
- UPF Scholarship Application
- Course Evaluations
- Online Courses
- Registration
- General Institute Tuition Information
- International Students
- Directions to the Bloomberg School
- All Courses
- Important Guidance for ONSITE Students
- D.C. Courses
- Registration and Fees
- Cancellation and Closure Policies
- Application Procedures
- Career Search
- Current Activities
- Current Trainees
- Related Links
- Process for Appointing Postdoctoral Fellows
- Message from the Director
- Program Details
- Admissions FAQ
- Current Residents
- Elective Opportunities for Visiting Trainees
- What is Occupational and Environmental Medicine?
- Admissions Info
- Graduates by Year
- Compensation and Benefits
- How to Apply
- Academic Committee
- Course Details and Registration
- Tuition and Fees
- ONLINE SOCI PROGRAM
- Principal Faculty
- Johns Hopkins RAPID Psychological First Aid
- General Application
- JHHS Application
- Areas of Study
- Important Dates
- Our Faculty
- Welcome Letter
- Descripción los Cursos
- Programa en Epidemiología para Gestores de Salud, Basado en Internet
- Consultants
- Britt Dahlberg, PhD
- Joke Bradt, PhD, MT-BC
- Mark R. Luborsky, PhD
- Marsha Wittink, PhD
- Rebekka Lee, ScD
- Su Yeon Lee-Tauler, PhD
- Theresa Hoeft, PhD
- Vicki L. Plano Clark, PhD
- Program Retreat
- Mixed Methods Applications: Illustrations
- Announcements
- 2023 Call for Applications
- Jennifer I Manuel, PhD, MSW
- Joke Bradt, PhD
- Josiemer Mattei, PhD, MPH
- Justin Sanders, MD, MSc
- Linda Charmaran, PhD
- Nao Hagiwara, PhD
- Nynikka R. A. Palmer, DrPH, MPH
- Olayinka O. Shiyanbola, BPharm, PhD
- Sarah Ronis, MD, MPH
- Susan D. Brown, PhD
- Tara Lagu, MD, MPH
- Theresa Hoft, PhD
- Wynne E. Norton, PhD
- Yvonne Mensa-Wilmot, PhD, MPH
- A. Susana Ramírez, PhD, MPH
- Animesh Sabnis, MD, MSHS
- Autumn Kieber-Emmons, MD, MPH
- Benjamin Han, MD, MPH
- Brooke A. Levandowski, PhD, MPA
- Camille R. Quinn, PhD, AM, LCSW
- Justine Wu, MD, MPH
- Kelly Aschbrenner, PhD
- Kim N. Danforth, ScD, MPH
- Loreto Leiva, PhD
- Marie Brault, PhD
- Mary E. Cooley, PhD, RN, FAAN
- Meganne K. Masko, PhD, MT-BC/L
- PhuongThao D. Le, PhD, MPH
- Rebecca Lobb, ScD, MPH
- Allegra R. Gordon, ScD MPH
- Anita Misra-Hebert, MD MPH FACP
- Arden M. Morris, MD, MPH
- Caroline Silva, PhD
- Danielle Davidov, PhD
- Hans Oh, PhD
- J. Nicholas Dionne-Odom, PhD RN ACHPN
- Jacqueline Mogle, PhD
- Jammie Hopkins, DrPH, MS
- Joe Glass, PhD MSW
- Karen Whiteman, PhD MSW
- Katie Schultz, PhD MSW
- Rose Molina, MD
- Uriyoán Colón-Ramos, ScD MPA
- Andrew Riley, PhD
- Byron J. Powell, PhD, LCSW
- Carrie Nieman MD, MPH
- Charles R. Rogers, PhD, MPH, MS, CHES®
- Emily E. Haroz, PhD
- Jennifer Tsui, Ph.D., M.P.H.
- Jessica Magidson, PhD
- Katherine Sanchez, PhD, LCSW
- Kelly Doran, MD, MHS
- Kiara Alvarez, PhD
- LaPrincess C. Brewer, MD, MPH
- Melissa Radey, PhD, MA, MSSW
- Sophia L. Johnson, PharmD, MPH, PhD
- Supriya Gupta Mohile, MD, MS
- Virginia McKay, PhD
- Andrew Cohen, MD, PhD
- Angela Chen, PhD, PMHNP-BC, RN
- Christopher Salas-Wright, PhD, MSW
- Eliza Park MD, MS
- Jaime M. Hughes, PhD, MPH, MSW
- Johanne Eliacin, PhD, HSPP
- Lingrui Liu ScD MS
- Meaghan Kennedy, MD
- Nicole Stadnick, PhD, MPH
- Paula Aristizabal, MD
- Radhika Sundararajan, MD
- Sara Mamo, AuD, PhD
- Tullika Garg, MD MPH FACS
- Allison Magnuson, DO
- Ariel Williamson PhD, DBSM
- Benita Bamgbade, PharmD, PhD
- Christopher Woodrell MD
- Hung-Jui (Ray) Tan, MD, MSHPM
- Jasmine Abrams, PhD
- Jose Alejandro Rauh-Hain, MD
- Karen Flórez, DrPH, MPH
- Lavanya Vasudevan, PhD, MPH, CPH
- Maria Garcia, MD, MPH
- Robert Brady, PhD
- Saria Hassan, MD
- Scherezade Mama, DrPH
- Yuan Lu, ScD
- 2021 Scholars
- Sign Up for Our Email List
- Workforce Training
- Cells-to-Society Courses
- Course/Section Numbers Explained
- Pathway Program with Goucher College
- The George G. Graham Lecture
In partnership with the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine , the Bloomberg School offers students the opportunity to earn a Doctor of Medicine (MD) alongside a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) – a rigorous combination that prepares graduates for prestigious careers in academic medicine.
The long-lasting relationship between the School of Medicine and the Bloomberg School – both situated along the same city block here in Baltimore – fosters the ideal environment for this combined six or eight year program.
Students complete two years of medical school before devoting themselves full-time to their PhD studies. After completion of the PhD degree requirements, students then complete their MD degree.
Interested “physician-scientists” should contact the MD/PhD program administrator, Sharon Welling ( [email protected] or 410-955-8008), and visit the MD/PhD Program's website for full details on admission requirements and application procedures.
MD-PhD Degree Programs by State
New section.
Combined MD-PhD degree programs provide students the opportunity to earn both the MD and the PhD in areas pertinent to medicine.
Combined MD-PhD degree programs provide students the opportunity to earn both the MD and the PhD in areas pertinent to medicine. Below is a list of schools offering a combined MD-PhD degree, with links to their web sites. Please contact the institutions directly for curriculum information and admission requirements. School administrators may contact [email protected] with any omissions or corrections to this listing.
University of Alabama School of Medicine Birmingham, Ala.
University of South Alabama College of Medicine Mobile, Ala.
University of Arizona College of Medicine Tucson, Ariz.
University of Arizona College of Medicine - Phoenix Phoenix, Ariz.
University of Arkansas College of Medicine Little Rock, Ark.
Loma Linda University School of Medicine Loma Linda, Calif.
Stanford University School of Medicine Stanford, Calif.
University of California, Davis School of Medicine Davis, Calif.
University of California, Irvine School of Medicine Irvine, Calif.
University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine Los Angeles, Calif.
University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, Calif.
University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine San Francisco, Calif.
Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California Los Angeles, Calif.
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center Denver, Colo.
Connecticut
University of Connecticut School of Medicine Farmington, Conn.
Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, Conn.
District of Columbia
Georgetown University School of Medicine Washington, D.C.
Howard University College of Medicine Washington, D.C.
University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Fla.
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Fla.
University of South Florida College of Medicine Tampa, Fla.
Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, Ga.
Medical College of Georgia Augusta, Ga.
Morehouse School of Medicine Atlanta, Ga.
Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University Augusta, Ga.
Loyola University of Chicago - Stritch School of Medicine Maywood, Ill.
Northwestern University Medical School Chicago, Ill.
Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science - Chicago Medical School North Chicago, Ill.
University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine (MTSP) Chicago, Ill.
University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine (MD/PhD) Chicago, Ill.
University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine Chicago, Ill.
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign College of Medicine Urbana, Ill.
Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, Ind.
University of Iowa College of Medicine Iowa City, Iowa
University of Kansas School of Medicine Kansas City, Kan.
University of Kentucky College of Medicine Lexington, Ky.
University of Louisville School of Medicine Louisville, Ky.
Louisiana State University, New Orleans School of Medicine New Orleans, La.
Louisiana State University, Shreveport School of Medicine Shreveport, La.
Tulane University School of Medicine New Orleans, La.
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, Md.
National Institutes of Health Intramural MD-PhD Partnership Bethesda, Md.
Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences Bethesda, Md.
University of Maryland at Baltimore School of Medicine Baltimore, Md.
Massachusetts
Boston University School of Medicine Boston, Mass.
Harvard Medical School Boston, Mass.
Tufts University School of Medicine Boston, Mass.
University of Massachusetts Medical School Worcester, Mass.
Michigan State University College of Human Medicine East Lansing, Mich.
University of Michigan Medical School Ann Arbor, Mich.
Wayne State University School of Medicine Detroit, Mich.
Mayo Medical School Rochester, Minn.
University of Minnesota Medical School Minneapolis, Minn.
Mississippi
University of Mississippi School of Medicine Jackson, Miss.
Saint Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Mo.
University of Missouri - Columbia School of Medicine Columbia, Mo.
University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine Kansas City, Mo.
Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, Mo.
Creighton University School of Medicine Omaha, Neb.
University of Nebraska College of Medicine Omaha, Neb.
University of Nevada School of Medicine Reno, Nev.
New Hampshire
Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Hanover, N.H.
Rutgers - New Jersey Medical School Newark, N.J.
Rutgers - Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, N.J.
University of New Mexico School of Medicine Albuquerque, N.M.
Albany Medical College Albany, N.Y.
Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University Bronx, N.Y.
Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons New York, N.Y.
Hofstra North Shore - LIJ School of Medicine Hempstead, N.Y.
Weill Cornell/Rockefeller/Sloan-Kettering Tri-Institutional MD/PhD Program New York, N.Y.
Mount Sinai School of Medicine New York, N.Y.
New York Medical College Valhalla, N.Y.
New York University School of Medicine New York, N.Y.
SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine Buffalo, N.Y.
SUNY at Stony Brook Health Sciences Center Stony Brook, N.Y.
SUNY Downstate Medical Center College of Medicine Brooklyn, N.Y.
SUNY Upstate Medical University Syracuse, N.Y.
University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, N.Y.
North Carolina
Wake Forest School of Medicine Winston-Salem, N.C.
Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University Greenville, N.C.
Duke University School of Medicine Durham, N.C.
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine Chapel Hill, N.C.
North Dakota
University of North Dakota School of Medicine Grand Forks, N.D.
Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Cleveland, Ohio
Northeastern Ohio College of Medicine Rootstown, Ohio
Ohio State University College of Medicine Columbus, Ohio
University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio
University of Toledo College of Medicine Toledo, Ohio
Wright State University School of Medicine Dayton, Ohio
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Oklahoma City, Okla.
Oregon Health Sciences University School of Medicine Portland, Ore.
Pennsylvania
Drexel University College of Medicine Philadelphia, Pa.
Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, Pa.
Penn State University College of Medicine Hershey, Pa.
University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Philadelphia, Pa.
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Pittsburgh, Pa.
Temple University School of Medicine Philadelphia, Pa.
Rhode Island
Brown University School of Medicine Providence, R.I.
South Carolina
Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, S.C.
University of South Carolina School of Medicine Columbia, S.C.
South Dakota
University of South Dakota School of Medicine Vermillion, S.D.
East Tennessee State University James H. Quillen College of Medicine Johnson City, Tenn.
Meharry Medical College School of Medicine Nashville, Tenn.
University of Tennessee, Memphis College of Medicine Memphis, Tenn.
Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tenn.
Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas
McGovern Medical School at UTHealth/MD Anderson Cancer Center/University of Puerto Rico Tri-Institutional Program Houston, Texas
Texas A&M University Health Sciences Center College of Medicine College Station, Texas
Texas Tech University School of Medicine Lubbock, Texas
University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston Galveston, Texas
University of Texas Health San Antonio, Long School of Medicine San Antonio, Texas
University of Texas, Southwestern Med Center - Dallas Dallas, Texas
University of Utah School of Medicine Salt Lake City, Utah
University of Vermont College of Medicine Burlington, Vt.
Eastern Virginia Medical School Norfolk, Va.
Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine Richmond, Va.
University of Virginia School of Medicine Charlottesville, Va.
University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, Wash.
West Virginia
Marshall University School of Medicine Huntington, W.Va.
West Virginia University School of Medicine Morgantown, W.Va.
Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, Wisc.
University of Wisconsin Medical School Madison, Wisc.
McGill University Faculty of Medicine Montreal, Quebec
McMaster University of Faculty of Health Sciences Hamilton, Ontario
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Medicine St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador
Universite de Montreal Faculte de Medecine Montreal, Quebec
Universite de Sherbrooke Faculte de Medecine Sherbrooke, Quebec
Universite Laval Faculte de Medecine Quebec, Quebec
University of Alberta Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry Edmonton, Alberta
University of Calgary Faculty of Medicine Calgary, Alberta
University of British Columbia Faculty of Medicine Vancouver, British Columbia
University of Manitoba Faculty of Medicine Winnipeg, Manitoba
University of Saskatchewan College of Medicine Saskatoon, Saskatchewan
University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine Toronto, Ontario
University of Western Ontario London, Ontario
Related Programs
NIH MD-PhD Partnership Program
- Like AAMC Pre-Med
- Follow @AAMCpremed
Information on how to become a research physician, also known as a physician-investigator or a physician-scientist.

A Personal Plea to Premeds
Trisha Kaundinya | January 13, 2021
When I was in college, I was in a premed “bubble” a lot of the time. I took many of my courses and labs alongside hundreds of other aspiring physicians. I would see the same people throughout my academic day, and sometimes even outside of the lecture hall. Because of this, I unintentionally overheard conversations […]
Get important information, resources, and tips to help you on your path to medical school—delivered right to your inbox each month.
MD-PhD in the City
Pursuing an MD and PhD while finding the best burger in NYC
- Privacy Policy
Dual MD-PhD Program , Grad School , MD+PhD , Med School · August 29, 2021
What is the difference between MD, MD-PhD, and PhD?

MD, MD PhD, and PhD programs differ in a number of ways including:
- Training goals
- Length of training
- Career path and outcomes
- Cost of programs
In this article, we will cover these differences in depth.
What is an MD, MD PhD, and PhD?
MD is the abbreviation of Doctor of Medicine . It is a medical degree. For instance, you’ve likely encountered an MD when you visited the doctor’s office for a physical examination or when you are sick.
Ph.D. is the abbreviation of Doctor of Philosophy and is awarded for a breadth of academic fields – from biology to ethnomusicology. This doctorate degree is an academic degree focused on original research, data analysis, and the evaluation of theory. For this article, we will be focusing on STEM PhDs.
For example, during the pandemic, you may have encountered media headlines describing scientists who were investigation the delta variant or studying the virus’ resistance. PhDs collect facts and evidence through their research and provide important foundations for the medicine we know and practice today.
MD-PhD is a dual doctorate degree where you get a medical degree and an academic degree. In particular, programs awarding MD-PhD are for students who intend to pursue careers as physician-scientists where they’ll straddle the roles of both an MD and a Ph.D.
After completing training, physician-scientists may spend part of their week practicing in the clinic or hospital. Along with this, an MD-PhD may spend the rest of their week conducting research on a specific topic such as the microbiome or cancer.

Training Goals Differences: MD vs. MD PhD vs. PhD
Md programs.
MD programs aim to train students to treat patients as a physician.
Firstly, trainees will gain fundamental knowledge in topics such as anatomy, physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. This occurs during pre-clerkship years. Following are the clerkship years. These are typically years 3 and 4 of medical school. which students learn patient bedside manners and clinical skills. Importantly, medical students will also rotate in various departments of the hospital. These rotations help medical students decide on which medical specialties that they want to specialize in.
Additionally, their medical school years will also help them prepare applications for residency where they will further hone their clinical skills and knowledge in their chosen specialty. Examples of specialties include but are not limited to:
- Family Medicine
- Emergency Medicine
- General Surgery
- Plastic Surgery
- Eyes, Nose, Throat
- Dermatology
PhD Programs
Ph.D. programs train students to develop and apply critical thinking and technical skills to conduct research problems and pursue a career as an independent scientist . For example, disciplines that stem Ph.D. candidates perform research in include but are not limited to:
- Cancer Biology
- Computational Biology and Bioinformatics
- Molecular Biology
- Meuroscience
- Biochemistry
- Cell and Developmental Biology
- Pharmacology
MD-PhD Programs
MD-PhD programs equip students with the skills generally learned from sole MD and sole Ph.D. training programs described above, but with the aim to integrate skills from both doctorate degrees to pursue the path of a physician-scientist. The clinical specialties and research disciplines that they pursue are similar to those described above for MD-only and PhD-only programs.

Length of Training
It typically takes four years to earn an MD.
At my institution, it takes about 5-6 years to complete a Ph.D. in virology, immunology, cancer biology, microbiology, etc.
A typical MD-PhD program length is 8 years – 4 years of the MD and 4 years of the Ph.D.
Again, these are averages as certain institutions may differ and individuals may vary in their training timeline.
Also note that for all these degrees, there is more training involved before degree-holding individuals gain their permanent position of employment.

Bottom line is that earning an MD typically takes 4 years, Ph.D. takes 5 years, and MD-PhD takes 8 years.
Career Paths and Outcomes
Md graduates.
When medical students graduate with their MD, the vast majority will continue their medical training in residency. In my anecdotal experience, a few individuals will not go onto residency from each class. For example, I know of someone who wanted to become a writer and therefore did not want to pursue residency after medical school.
After residency, some trainees will go onto fellowship. All the training combined, from medical school to fellowship, may involve 10 years. Eventually, the majority of MD-holding individuals will practice clinical medicine in a range of settings, including an academic hospital and private clinic. Some will also go into academic and industry positions.
MD-PhD graduates
After earning both doctorate degrees, most MD-PhD trainees go into residency programs as well. Eventually, their career will likely be in academia where they do a mix of medicine and research.
2018 National MD-PhD outcomes study surveyed graduates from 80 MD-PhD programs. It collected information from 6,786 respondents and was combined with data for all MD-PhD program alumni. This publication highlights key outcomes for MD-PhD program alumni including the following:
“Nearly 60% of all program alumni show up in the AAMC Faculty Roster as full-time faculty at U.S. medical schools. Among survey respondents, nearly 80% are either full-time faculty members or work for the NIH, research institutes, industry, and federal agencies. 91.2% of 2,109 survey respondents still in postgraduate training reported that their expected first workplace will be in academia, the NIH, federal agencies, research institutes, or industry. Notably, these numbers were not significantly different for men and women.” 2018 National MD-Phd Outcome study, AAMC
Another research study conducted by Akabas & Brass (2019) utilized data from the National MD-PhD Programs Outcome Study to ask and answer questions about the career paths of program graduates.
They found that among women and men, 63% and 66% went into academia full-time, respectively. 16% and 14% of women and men went into private practice, while 5% and 7% of women and men took on industry roles, respectively.

The 2018 National MD-PhD outcome also found that 77% of program alumni were doing some level of research activity. Research time for physician-scientists in academic institutions varies widely.
52.7% of survey respondents with full-time academic appointments reported devoting at least half of their time to research. Only 22.7% reported devoting most of their time to clinical activities.” 2018 National MD-Phd Outcome study, AAMC
PhD graduates
Once Ph.D. students earn their degree, they will likely go into a post-doctoral position in an academic institution for further training. Eventually, they will apply for professor positions to run their own lab and teach.
Some Ph.D. graduates may go into industry to work at pharmaceutical or biotech companies. Post-doctoral positions also exist in some companies.
There’s a surprising dearth of outcomes post-PhD training. Science covered this gap in data and the need to address this. For now, there are a few institutions that cover their training outcomes.
The University of Toronto in Canada has an online database, 10,000 PhDs Project , which follows the professional outcomes of 15 years of doctoral graduates.
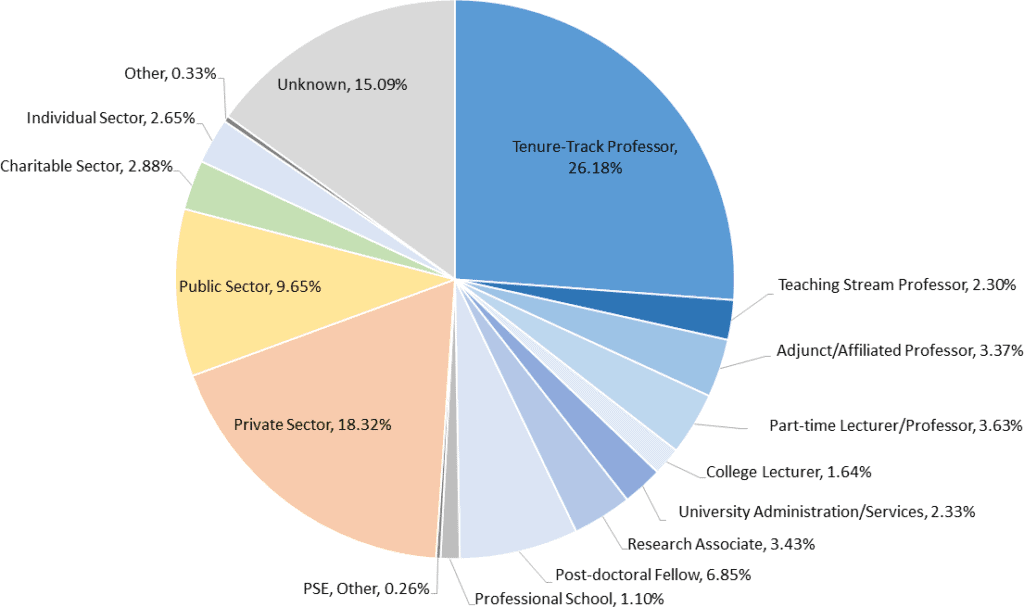
This graph shows that 26.18% of graduates go on to a multitude of professionals roles with the top identified employment sectors as follows: tenure-track professors (26.18%), private sector (18.32%), public sector (9.65%). The article later goes on to differentiate employment sectors of life science PhDs.
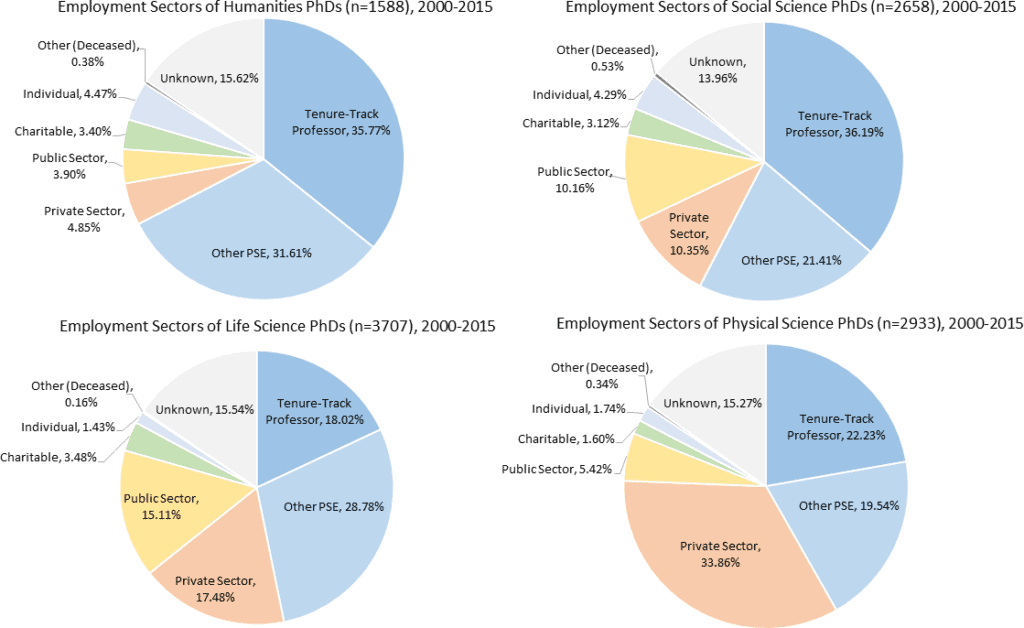
Finance
In 2020-2021, AAMC reported that tuition at public medical schools for state residents was an average annual cost of $32,384 and $57,394 for non-residents. Tuition at private medical schools was an average annual cost of $57,394. With additional fees and health insurance, the total cost at a private medical institution averages out to $61,490 per year. Tuition, fees, and health insurance included resulted in an average of $62,230 for non-residents and $61,858 for residents at private universities. For example, the following 2020-2021 medical school education cost data was pulled from the 2013-2021 Tuition and Student Fees Report :
Ph.D. students typically receive a stipend and a scholarship to cover the cost of tuition. At my institution, students don’t pay for tuition and receive ~$40,000 stipend and get health insurance.
For example, here is a table of a few PhD programs and their stipend that is published on their website at the time of this article’s publication.
MD-PhD Costs
The typical MD-PhD student receives a stipend, insurance, and full coverage of medical and graduate school tuition. The level of financial support differs by program, but this support helps trainees avoid debts that would deter them from becoming physician-scientists. MD-PhD students typically receive a stipend and health insurance. Moreover, trainees do not pay for medical school or graduate school.
For example, at my institution, the trainees don’t pay for tuition and receive a ~$40,000 stipend and health insurance.
Here is a table of a few MD-PhD programs and their stipend that is published on their website at the time of this article’s publication:

Application Process
Md and md-phds.
Applying to MD and MD PhD programs overlap in many parts and look very similar. For testing, you take the MCAT. To apply to programs, you apply to MD and MD PhD programs using the same portal and application called AMCAS (American Medical College Application Service).
Exceptions include Texas Medical School TMDAS). Look at those schools’ websites to see how the TMDAS schools process MD-PhD programs. For example, when I applied only to UT-Health MD Anderson’s MD-PhD program I didn’t need to fill out the TMDAS. Again, check the school’s individual requirements and make sure to follow these instructions.
The AMCAS primary application requires the following components:
After primary application, you will receive secondary applications. If you are invited, you will then attend interviews. MD-PhD interviews are longer than MD interviews. I had an MD-PhD interview spread across 2 days. MD interview can be a full day or only two hours.
For graduate school, you take the GRE. You then apply to the PhD program using the school-specific portal. Each program has its own deadline so plan accordingly. In general, the application will ask for basic biographical information, GRE score, GPA, personal statement, and potentially additional essay prompts.
Choosing between MD, MD PhD, and PhD
Ultimately it comes down to what you are passionate about and what your goals are . The most important considerations include r esearch, patient care, and length of training.
Do you desire a career where you treat patients? Then that narrows down to MD and MD PhD.
Do you desire a career that balances treating patients with a significant research component? Then MD PhD could provide the training to be an independent scientist.
Do the extra 4 years of MD PhD programs make it worth pursuing the research training? While MD-PhD programs provide an excellent choice for individuals who want to become physician-scientists, there are certainly other ways to become one.
Some ways include transferring into the MD/PhD program after applying as a medical student at schools that allow this. There are also shorter programs such as the CCLM program within Case Western Reserve University of Medicine . This is a five-year program that awards an MD and special qualifications in biomedical research upon graduation.
Harvard Medical School’s Health Sciences and Technology (HST) program prepare students for a research career in academic medicine. This program offers an opportunity to spend a minimum of 4-6 years working as a research professor but can elect to do research full-time for an additional year.
The questions and goals are important to consider when deciding on which path to pursue. MD, PhD, and MD-PhD programs are rigorous and prestigious programs with a wealth of career opportunities awaiting after training. Good luck with your decision-making process!
Suggested Readings:
What is an MD-PhD?
How to Secure a Lab Position as a High School or College Student
How to Email a Research Professor to Secure a Lab Position – Templates Included
18 Important Medical School Interview Questions to Prepare For
Receive the FREE AMCAS Application Planner
Everything you need to fill out
for the AMCAS is in one place
You’ll Also Love

Copyright © 2024 MD-PhD in the City · Theme by 17th Avenue
- 2023 FACTS: Applicants and Matriculants Data
2023 FACTS: Enrollment, Graduates, and MD-PhD Data
- 2023 FACTS: Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) Data
- FACTS Glossary
By Institution
By gender and race/ethnicity, md-phd and other dual degrees, summary data, additional resources.
Graduation Rates and Attrition Rates of U.S. Medical Students (PDF) This AAMC Data Snapshot provides information on the graduation and attrition rates of U.S. Medical Students.
- Medical Education
Tri-Institutional PhD Programs
The Tri-Institutional PhD Programs at Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences (WCGS) offer interdisciplinary graduate training in various fields of biomedical research. These programs are part of the collaborative effort between Weill Cornell Medicine, Rockefeller University, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. Each program provides rigorous training in research methodologies, critical thinking, and scientific communication, preparing students for careers in academia, industry, and more. Below are the three Tri-I PhD programs available:

Chemical Biology
The Tri-Institutional PhD Program in Chemical Biology (TPCB) at WCGS is a dynamic interdisciplinary graduate program focused on elucidating biological processes through chemical principles. This program integrates chemical synthesis, biophysical techniques, and molecular biology to address fundamental questions in biology and develop novel therapeutic strategies. Students in the CB program engage in rigorous coursework, collaborative research projects, and hands-on training, benefiting from the expertise and resources of Weill Cornell Medicine, The Rockefeller University, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. By combining diverse scientific perspectives, graduates of the CB program are well-equipped to make significant contributions to both basic science and translational research, ultimately advancing our understanding of biology and improving human health.

Computational Biology & Medicine
The Tri-Institutional Computational Biology and Medicine (CBM) program at Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences is a multidisciplinary graduate program that integrates computational approaches with biological and medical sciences. This program equips students with the computational and analytical skills necessary to tackle complex biological questions and address challenges in medicine. Through a combination of coursework, research rotations, and thesis work, students explore topics such as genomics, bioinformatics, systems biology, and medical informatics. The collaborative nature of the program, involving Weill Cornell Medicine, The Rockefeller University, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, provides students with access to cutting-edge research facilities and a vibrant scientific community. Graduates of the CBM program are well-prepared for careers at the intersection of computational biology and medicine, making impactful contributions to both fields.
The Tri-Institutional MD-PhD Program at Weill Cornell Medicine is a joint program between Weill Cornell Medicine, The Rockefeller University, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. It offers an integrated curriculum that allows students to pursue both medical and graduate research training concurrently, leading to both an MD degree from Weill Cornell Medicine and a PhD degree from either Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Rockefeller University, or Gerstner Sloan Kettering Graduate School . This program aims to train physician-scientists who can bridge the gap between clinical medicine and scientific research.
Weill Cornell Medicine Graduate School of Medical Sciences 1300 York Ave. Box 65 New York, NY 10065 Phone: (212) 746-6565 Fax: (212) 746-8906
- MD | PhD Program
- Master's Programs
- PhD Programs
- Postdoctoral Fellows
- Residency & Fellowship
- Non-Degree Programs
- Visiting Students
- Campus Life at U-M
- Health & Wellness
- Building Your Community
- Accessibility & Disability
- Departments
- Centers & Institutes
- Interdisciplinary Programs
- Facts & Figures
- Medical School Leadership
- Research at the U-M Medical School
- News & Stories
- Requirements
- Interview Day
- Admissions Chats
- AAMC Michigan's 35 Answers
- AAMC Michigan's 10 Financial Aid Answers
- Admitted Students
- Overview & Highlights
- Patient Interaction
- Chief Concern
- Years 3 & 4
- Learning Informatics
- Training Sites
- Leadership Program
- Global Health & Disparities
- Health Policy
- Healthcare Innovation
- Medical Humanities
- Patient Safety & Quality Improvement
- Scientific Discovery
- Doctoring Course
- Evidence-Based Medicine
- Interprofessional Education
- DEIAJ Curriculum
- Language Opportunities
- Curriculum Diagrams
- Grading & Assessments
- Guideline Budget
- Loans & Eligibility
- Financial Aid Application Timeline
- Scholarships & Grants
- Documents & Forms
- Tips & Links
- Tuition Refund Policies
- Consumer Information
- Disbursement & Repayment
- MD Emergency Student Aid Fund
- MD Travel Grant
- Child Care Subsidy
- Residency Interviewing Loans and Resources
- Short-Term University Loan
- Contact the Office of Financial Aid
- Profiles & Demographics
- Culinary Connections
- Students with Disabilities
- Arts & Humanities
- Diversity & Health Equity
- Dual Degrees
- More Possibilities
- Commencement
- Available PhD Programs
- Academic & Social Events
- MSTP Fellows
- Application Process
- Application Requirements
- MD | PhD Curriculum
- Undergrad Summer Program
- Contact the MD | PhD Program
- Bioinformatics
- Biological Chemistry
- Cancer Biology
- Cell & Developmental Biology
- Cellular & Molecular Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Health Infrastructures & Learning Systems
- Microbiology & Immunology
- Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology
- Molecular & Cellular Pathology
- Molecular & Integrative Physiology
- Neuroscience
- Pharmacology
- Recruitment Events
- Interview Weekends
- Certificates & Dual Degrees
- Quantitative & Computational Biology Emphasis
- Training Grants
- Facilities & Resources
- Stipend & Benefits
- Professional Development
- Finding a Position
- Funding Your Postdoc
- Hiring Process
- Postdoc Preview
- International Postdocs
- ACGME Fellowships
- Non-Accredited Fellowships
- Postdoctoral Physician Scientist Training
- Salary & Benefits
- Prerequisites
- Visiting Residents & Fellows
- Application Overview & Requirements
- Tuition & Fees
- Timeline & Curriculum
- Information Sessions
- Program Details
- Undergrad Summer Research
- First Days Survival Guide
- Health Services
- Mental Health
- Health, Spirituality & Religion Program
- For Partners & Families
- Things to Do in Ann Arbor
- Getting Around
- Graduate Medical Education
- Office of Continuing Medical Education
- Office of Faculty Affairs & Faculty Development
- Office of Graduate & Postdoctoral Studies
- Physician Scientist Education & Training
- Office of Medical Student Education
- Points of Blue
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Department Outings
- PhD Program
- Accelerated MS Program
- PhD | MS Dual Degree Program
- Course Descriptions
- BIDS Training Program
- Proteogenomics Training Program
- Student Organizations
- Applications to Complex Genetic Diseases
- Biomedical Data Science, Translational Bioinformatics & Pharmacogenomics
- 4D Nucleome
- Genomics, Regulatory Genomics & Epigenomics
- Methodological Development in Computational Biology
- Multi-“omics” Integrative Bioinformatics
- Protein Structure, Proteomics & Alternative Splicing
- Systems Biology & Networks Analysis
- Software & Bioinformatics Tools

The Bioinformatics PhD | MS Dual Degree Program is designed for PhD or Master’s students who wish to pursue a dual Master’s degree in Bioinformatics.
- How to Apply
- Diversity Information for Applicants
- Application Materials
- Application Fees
- Funding Sources
- Frequently Asked Questions
Ph.D. students who wish to pursue a dual Master’s degree in Bioinformatics must apply by August 1 directly to the Bioinformatics Program through the Rackham Graduate School . List the upcoming Fall term as your proposed term of enrollment.
Students who are interested in obtaining a Bioinformatics Master’s degree, while pursuing a PhD are strongly encouraged to consult with Master's Program Director, Dr. Alla Karnovsky before applying for the program.
Interested students should consult with Dr. Alla Karnovsky before enrolling in classes, as applicants with limited computer programming may be required to take preparatory courses in their first year. Grades obtained in these first-year bioinformatics courses will be considered during the evaluation of applicants for suitability for the MS Program.
If a PhD student applies after August 1 of their first year, a written justification of why the student waited before applying is required. Applications from candidate-level PhD students are discouraged, as the ability to take additional classes is limited for candidates.
The application deadline is August 1. If a PhD student applies after August 1 of their first year, a written justification of why the student waited before applying is required. Applications from candidate-level PhD students are discouraged, as the ability to take additional classes is limited for candidates.
The Bioinformatics Graduate Program encourages applications from traditionally underrepresented minorities, students with disabilities, and those from disadvantaged backgrounds. There are funding opportunities and resources both from the program and other campus units to contribute to students' overall well-being while pursuing studies. Several resources available to students can be found on the Rackham Graduate School Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion website .
In addition, DCMB’s faculty members participate at events around the country, such as the Annual Biomedical Research Conference for Minority Students ( ABRCMS ).
Diversity is a key component of excellence, especially for solving the complex biomedical challenges that our field of computational medicine and bioinformatics faces. We believe that all people—regardless of background, race, religion, sexual/gender orientation, age or disability—deserve an equitable opportunity to pursue the education and career of their choice.
All application materials should be submitted electronically when possible. Applicants must meet Rackham's Minimum Requirements for Admission . The online application form can be found on the Rackham Admissions webpages. The application is available in early September through the deadline.
- GPA, minimum 3.2/4.0 (exceptions may be made if deemed appropriate)
- Letters of recommendation (3 required): Please be aware that submitting only the Rackham Recommendation for Admission Form is insufficient; forms must be accompanied by a letter from the recommender. All letters are due by the application deadline. Without them, applications will not be considered complete or reviewed by the Program Admissions Committee.
- Statement of Purpose: The Statement of Purpose should be a concise, well-written statement about your academic and research background, your career goals, and how Michigan's graduate program will help you meet your career and educational objectives.
- Personal Statement: The Personal Statement should be a concise, well-written statement about how your personal background and life experiences, including social, cultural, familial, educational, or other opportunities or challenges, motivated your decision to pursue a graduate degree at the University of Michigan. This is not an Academic Statement of Purpose, but a discussion of the personal journey that has led to your decision to seek a graduate degree.
- Transcripts: Please submit unofficial transcripts electronically with your online application
- GRE scores are no longer included as part of admission
- Applicants whose native language is not English must demonstrate English proficiency via either the TOEFL or IELTS exam. The institution code is 1839. Other exams may not be substituted. Rackham Graduate School offers a full explanation of this requirement , including exemption criteria. Please contact Rackham directly ( [email protected] ) with questions.
We find a new reason to love Ann Arbor nearly every day — year-round outdoor activities, cultural experiences, a growing food scene, and a welcoming, family-friendly atmosphere are just a few that come to mind. Explore all that Ann Arbor and our surrounding communities have to offer.
While we cannot waive the application fees, in rare cases the Bioinformatics Graduate Program can cover the cost.
In order to qualify you have to
- Be a U.S. citizen, permanent resident, or undocumented student with Deferred Action for Childhood Arrival (DACA);
- Have a record of superior academic achievement (e.g., grade point average, honors, or other designation);
- Come from an educational, cultural, or geographic background that is underrepresented in graduate study in their discipline in the United States or at the University of Michigan;
- Have demonstrated a sustained commitment to diversity in the academic, professional, or civic realm through their work experience, volunteer engagement, or leadership of student or community organizations. By commitment to diversity, we mean efforts in the U.S. to reduce social, educational, or economic disparities based on race, ethnicity, or gender, or to improve race relations in the U.S.;
- Have experienced financial hardship as a result of family economic circumstances;
- Are first-generation U.S. citizens or are the first generation in their families to graduate from a four-year college.
If you believe that you meet these criteria, please submit your unofficial transcript and a brief description of your qualifications to the Bioinformatics Graduate Office ( [email protected] ).
Please note that we can only accommodate a limited number of requests.
Please be aware that the Bioinformatics Program does not guarantee financial support to Master’s students. There are occasional work opportunities that may help defray your expenses; however, we cannot guarantee the availability of such opportunities, and most will not cover tuition and living expenses in full.
Sources of Aid on Campus
Our Master students are largely self-funded. You may apply for teaching or research assistantships, but there is no guarantee. Please note that the Bioinformatics Program offers few positions and priority is given to PhD students. A student may obtain a teaching position (GSI) in another unit.
While many Master's students get some funding, rarely is a student fully funded without some type of external award or fellowship. If interested in research assistantships, you need to contact specific faculty for those positions. Having significant programming experience is helpful.
Yes. Some students take coursework while working full time. A student is expected to complete all coursework within five years from the date of first enrollment in the program.
Bioinformatics consists of a mathematical and/or statistical analysis of a biomedical problem using computation. We define bioinformatics widely and include traditional bioinformatics areas such as for examples, systems biology, genomics, proteomics, plus statistical and evolutionary genetics, clinical informatics, and protein modeling.
As an interdisciplinary field, Bioinformatics attracts graduate students from mathematics, statistics, physics, computer science, biomedical engineering, chemistry, biochemistry and biology. Most incoming students have both a major in one and a minor in another discipline. In recent years students have entered with undergraduate training in bioinformatics or computational biology.
We transform lives through bold discovery, compassionate care and innovative education.
- Find a Doctor
- Conditions & Treatments
- Patient & Visitor Guide
- Patient Portal
- Clinical Trials
- Research Labs
- Research Centers
- Cores and Resources
- Programs & Admissions
- Our Community
- Departments, Centers & Offices
- About the Medical School
Global Footer Secondary Navigation
The IU School of Medicine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology is proud to offer the Clinical Research and Academic Success in Obstetrics and Gynecology course . The course will take place in Stowe, Vermont, at the Topnotch Resort, from Aug. 26–29, 2024. Vermont was selected because it welcomes, affirms, and respects reproductive rights. We look forward to seeing you in Vermont! Questions should be directed to the course director, Dr. Jeffery Peipert, MD, PhD, Clarence E. Ehrlich Professor and Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Chair at IU School of Medicine.
Who the program is for
What learners will gain.
- List the key attributes of an appropriate research question
- Describe the advantages and disadvantages of longitudinal cohort studies, case-control studies and randomized clinical trials
- Use the basic functions of a statistical software package
- Understand the basic principles of article publication and manuscript review processes
- Critically read research papers by understanding the main sources of bias and confounding
- List the attributes of a good mentor and the key principles of a successful mentor-mentee relationship
- Describe the process for promotion from Assistant to Full Professor and the “currency” of academic faculty for career advancement
Submit an application
To apply, please email Dr. Peipert the following:
- A brief statement (one page or less) indicating your reason for applying
- Potential clinical research interests
- A letter of commitment for funding from chair or division director.
Participants and their departments will be responsible for travel, accommodations and tuition ($4,000).
Applications are due by May 15, 2024.
Email your application now
Course faculty

Kavita Nanda, MD, MHS
Director of Medical Research at FHI360
Kavita Nanda, MD, MS, is an internationally recognized expert in contraception. She is the director of medical research at FHI360, where she has worked as an obstetrician gynecologist, epidemiologist and scientist for almost 25 years.
For the past 18 years, she has worked as a temporary advisor to WHO, working to update the WHO Medical Eligibility Criteria and Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use. She is also a member of the CDC guidelines development group for contraception.
Nanda received her medical degree from Albany Medical College, completed her residency at Thomas Jefferson University, and did a Women’s Health Research Fellowship and Master of Health Sciences (Clinical Research) at Duke University.

Christina M. Scifres, MD
Associate Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology
Christina Scifres, MD, is a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Indiana University School of Medicine. She joined the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology faculty as an associate professor in 2018 and was named the maternal-fetal medicine division director in 2020.
Her clinical and research interests include gestational diabetes, ovarian cysts, and improving outcomes in pregnancies complicated by diabetes and obesity. She was a co-investigator for an NIH-funded randomized clinical trial comparing two screening strategies for gestational diabetes.
Scifres graduated from the University of Oklahoma College of Medicine and completed residency and a fellowship at Washington University School of Medicine.
Read Bio Christina M. Scifres, MD

Jeffrey F. Peipert, MD, PhD
Chair, Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology
Jeffrey F. Peipert, MD, PhD, is the Clarence E. Ehrlich Professor and chair of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Indiana University School of Medicine. He is board-certified in obstetrics and gynecology and has a doctorate in epidemiology.
He has conducted numerous studies including: NICHD-funded randomized trial of a computer-based intervention to encourage dual method contraceptive use to prevent unplanned pregnancy and STIs; randomized trial of therapy for pelvic inflammatory disease (PEACH Study). He was also the principal investigator of a large prospective study, the Contraceptive CHOICE Project, which recruited 9,256 women and successfully followed them for two to three years for contraceptive effectiveness, satisfaction, and continuation rates.
Read Bio Jeffrey F. Peipert, MD, PhD
UMD Ph.D. Student Snehesh Shrestha's Software Uses AI to Teach You How to Play the Violin

On the ground floor of one of the new computer buildings at the University of Maryland, Anna Kelleher played her centuries-old violin while a program running on a laptop in front of her told her to do things such as raise her chin or widen her stance.
These were common mistakes that Kelleher knows not to do. After all, she’s a graduate student studying violin performance. But she also teaches violin to others, and the program she was demonstrating might someday help those she teaches to play even better.
Believers in artificial intelligence say the program will radically transform our lives in so many ways.
It’s designed by Snehesh Shrestha , a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Computer Science, and is the perfect example of how the University of Maryland is building bridges between AI and every other academic program on campus.
A simple webcam found on your laptop, or even your phone, captures enough movement and audio from your performance that the AI program can tell what you’re doing wrong. Whether your stance is too wide or narrow, to whether or not your chin is in the right spot, it can see and also hear everything you’re doing right and wrong.
The program was designed to try “to understand the whole space, not just blindly building a technology, but understanding how can we fill the gaps that are currently there in the entire music learning process,” Shrestha said. “And by identifying gaps where we can empower the teacher and the students, we could really build something a lot more powerful than just building a single technology. And that really was like the starting point of exploring into what the technology can provide towards the future direction of music education.”
On the monitor, the teacher can see the student in 3D — every angle imaginable — to see how they stand and how they move. Technology, including a piece that looks sort of like a smartwatch, can also send cues to the student through vibrations in the wrist.
Click HERE to read the full article
The Department welcomes comments, suggestions and corrections. Send email to editor [-at-] cs [dot] umd [dot] edu .
Popular Search Resources for
Grand Rounds Speaker | Oluyinka O. Olutoye, MD, PhD
Apr 3, 2024

Dr. Olutoye is a surgeon-scientist leader with expertise in fetal and neonatal medicine and surgery. His research focuses on fetal wound healing, correcting congenital malformations before birth, and detecting necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants.
Previously, Dr. Olutoye served as a co-director of the Fetal Center and president of the medical staff at Texas Children's Hospital. He was a tenured Professor of Surgery, Obstetrics & Gynecology, and Pediatrics, and chair of the Faculty Senate at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas. Currently, Dr. Olutoye leads Nationwide Children’s Hospital, which is one of the largest and most comprehensive children’s hospitals in the United States.
During his presentation entitled " Fetal Therapy: Su rgical Correction and Much More ", Dr. Olutoye emphasized the significance of surgical innovation, research, multidisciplinary collaboration, and the pursuit of patient care excellence. He provided an overview of his approach to state-of-the-art fetoscopic surgery and discussed the complexities of managing the mother and the fetus.
Dr. Olutoye's presentation included amazing photos and videos of fetoscopic surgery.
Additionally, Dr. Olutoye also commended Francisca Velcek MD FACS FAAP MAMSE , Director of Pediatric Surgery and Professor of Surgery, for her incredible decades of dedication to the pediatric patients at Downstate, as well as her mentor Dr. Peter K. Kottmeier , who was the Director of Pediatric Surgery at Downstate from 1961 to 1991.

Downstate Pediatric Surgeons Dr. Reck and Dr. Velcek with Dr. Olutoye standing beside the
Dr. Peter K. Kottmeier Surgical Library plaque.
After the Grand Rounds session, Dr. Olutoye met with residents and faculty. He talked about his life journey, from being a medical student in Nigeria to becoming a globally recognized leader in surgery. He shared his philosophy of focusing on excellence, perseverance, gratitude, and humility.

We are grateful to Dr. Olutoye for sharing his knowledge and expertise with our SUNY Downstate Department of Surgery team.
Tags: Residency , Surgery , fetal , iNSPIRe , Research , Pediatric
Related Posts
- Downstate General Surgery Residency Match 2024
- Highlights of 2024 Chief Residents
- Grand Rounds Speaker | Kamal M.F. Itani, MD
- Grand Rounds Speaker | Robert Rhee, MD
School of Medicine M.D./Ph.D. Training Program
- Enter keyword Search
M.D./Ph.D. Training Program
Rick mathews.
Current Program Year: Grad 4 Current Student, Biomedical Engineering Graduate Program, School of Medicine M.D./Ph.D. Program Students, School of Medicine
Monica Hinds Lab
I completed my undergraduate degree in biomedical engineering at the William E. Macaulay Honors College at the City College of New York. After graduation, I worked as a project manager for an electronic health records company, Epic Systems, in Verona, Wisconsin. I came to OHSU to complete my MD/ PhD training and to study cardiovascular physiology.
Outside of school, I enjoy learning to cook, swimming regularly, and hiking.
Education and training
B.S.E., 2017, The William E. Macaulay Honors College at the City College of New York
Memberships and associations:
- American Physician Scientist Association
- National Engineering Honor Society, Tau Beta Pi
Areas of interest
Endothelial Dysfunction Cardiovascular Disease
Additional information
ORCiD Google Scholar PubMed
Publications
Selected publications.
Bartosch AMW, Mathews R , Mahmoud MM, Cancel LM, Haq ZS, Tarbell JM. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan glypican-1 and PECAM-1 cooperate in shear-induced endothelial nitric oxide production. Sci Rep. 2021 May 31;11(1):11386. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90941-w. PMID: 34059731; PMCID: PMC8166914. ( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-90941-w )

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cost of attendance. Most MD-PhD programs grant entrants tuition-free training. In addition, most students in those tracks earn a stipend, which according to the AAMC report, can be as high as $38,000 annually. Harvey believes that the potential savings on education shouldn't be your top motivation for entering an MD-PhD program.
MD PhD vs MD: Competition. It's no secret that both MD PhD and MD programs are extremely competitive, with acceptance rates on average between 1-4%. There are far fewer MD PhD programs available compared with MD programs and the large benefit of reduced or waived tuition makes for even higher competition, especially in MSTPs vs MD programs.
Your research focus can range from hard science like molecular biology and genetics to the social sciences like sociology. Since you would be getting two degrees, a MD-PhD program is designed to take 7-8 years, instead of 4 years for medical school and 5-6 years for a PhD. Usually, MD-PhD candidates will spend their first two years doing pre ...
MD vs MD PhD: Application Process and Education. The application process for the MD and MD PhD programs is very similar. For most allopathic medical schools, you will use the AMCAS (American Medical College Application Service).. There are exceptions; for example, Texas medical schools use the TMDSAS (Texas Medical & Dental Schools Application Service). As always, follow every school's ...
M.D. degree recipients tend to go into some field of medical practice, while M.D.-Ph.D. graduates veer more toward medical research and academia. Typically for M.D.-Ph.D. studies, MSTP programs ...
Okay, so for some real talk, the price of either of these degrees can vary a lot. Medical school will generally cost between $45,000 - $65,000 a year, while PhD programs cost on average about $30,000 a year. But, again, this does not mean you have to be able to pay these costs out of pocket. There are a lot of programs for PhDs that work with ...
MD/PhD vs. MD: Competition. It's no surprise that both MD/PhD and MD programs are highly competitive. The average acceptance rate of these programs is between 1-4%. Compared to MD programs, there are considerably fewer MD/PhD programs available. The added benefit of tuition waivers makes the competition for these programs even higher.
Now there are ∼90 active MD/PhD programs that admit anywhere from a few students per year to 25 or more. The average size of an MD/PhD program in 2017 was ∼90 students in all stages of training. Compared with the many thousands who apply to medical school in each year, only 1900 (∼3%) apply to MD/PhD programs.
The typical length of a MD/PhD program is 7 to 8 years, almost twice the length of a MD alone. As with a MD, MD/PhDs are still required to attend medical school and must complete a residency program before being able to practice medicine. In comparison to PhD and MD programs, MD/PhD positions in the United States are scarce and consequently ...
Most MD-PhD programs provide: stipend to cover housing, food, and other, living expenses. full-ride scholarship for all medical school tuition and fees (graduate school is also covered) Research mentorship & Career advising. NOTE: Funding typically comes from either the Medical Scientist Training Program or private, institutional funds.
MD-PhD programs are designed to be completed in 7 to 8 years. A minority of students complete the program in 6 or 10 years. Here's what the typical MD-PhD curriculum looks like: Years 1-2 will be spent mostly on completing medical school coursework. Years 3-6 will consist mostly of PhD research. Years 7-8 will be spent mostly completing ...
MD-PhD programs provide training for the dual degree by integrating research and clinical training experiences where students learn to conduct hypothesis driven research in a mentored environment. There are over 100 MD-PhD programs affiliated with U.S. medical schools, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences partially supports ...
Furthermore, the award rate for MD-PhD's from an MSTP program was nearly three times higher than that for MD/PhD's not from an MSTP program (36.2% vs. 12.3%). If you are interested in more details, there is a wealth of outcomes data in this report as well as the AAMC National MD-PhD Program Outcomes Study. Cons of the MD-PhD Degree
MD Ph.D. programs typically last anywhere from seven to eight years and require students to attend both medical school and graduate school. On the other hand, medical doctor (MD) programs can be finished in just four years, which is just half the amount of time required for MD Ph.D. students. Although the initial two years of instruction in ...
An M.D. is a medical doctor who treats patients, while a Ph.D. is an academic with a doctoral degree in a specific field. The abbreviation M.D. comes from the Latin term medicinae doctor, which means teacher of medicine. People who have an M.D., or Doctor of Medicine, undergo practical training during graduate school to become physicians upon ...
In the 2022-23 application cycle, MD/PhD applicants had an average MCAT score of 511.3, while matriculants averaged 516.2. GPA of 3.7 or higher: Like MCAT scores, the GPA requirements for MD/PhD programs differ by program. But your chances are highest with an average GPA of at least 3.7. In the 2022-23 application cycle, MD/PhD applicants ...
What is an MD-PhD Program? MD-PhD programs allow you to obtain a dual degree in medicine and research. When deciding between MD-PhD vs MD programs, it is important to know what MD-PhD programs entail. Upon graduation, students receive a combined degree with advanced, hands-on research training and expertise in a field of their choice.
According to the AAMC, out of the 22,000 students per year who matriculate at allopathic US medical schools, about 700 are in the MD/PhD program, which is 3% of all students. The number dwindles closer to 600 by the time of graduation. Most programs pay for tuition (~$60,000) and living expenses ($30,000-$40,000) for both the MD and PhD ...
After completion of the PhD degree requirements, students then complete their MD degree. Interested "physician-scientists" should contact the MD/PhD program administrator, Sharon Welling ([email protected] or 410-955-8008), and visit the MD/PhD Program's website for full details on admission requirements and application procedures.
Funding. The Harvard/MIT MD-PhD Program at Harvard Medical School (HMS) has been sponsored in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through its Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) since 1974. All MD-PhD student applicants to our program compete on equal footing for MSTP support, regardless of scientific interest.
Combined MD-PhD degree programs provide students the opportunity to earn both the MD and the PhD in areas pertinent to medicine. Below is a list of schools offering a combined MD-PhD degree, with links to their web sites. Please contact the institutions directly for curriculum information and admission requirements.
Welcome to the Harvard/MIT MD-PhD Program " Training the next-generation of premier and diverse physician-scientist leaders " Welcome! Program Overview, Loren Walensky, MD-PhD Program Director. Support our Students! The Linda Burnley Fund for MD-PhD Education at Harvard and MIT.
A typical MD-PhD program length is 8 years - 4 years of the MD and 4 years of the Ph.D. Again, these are averages as certain institutions may differ and individuals may vary in their training timeline. Also note that for all these degrees, there is more training involved before degree-holding individuals gain their permanent position of ...
MD-PhD Matriculants to U.S. Medical Schools by Race/Ethnicity and State of Legal Residence, 2023-2024: PDF: Excel: B-10: MCAT Scores and GPAs for MD-PhD Applicants and Matriculants to U.S. Medical Schools, 2019-2020 through 2023-2024: PDF: Excel: B-11.1: Total MD-PhD Enrollment by U.S. Medical School and Gender, 2014-2015 through 2018-2019: PDF ...
The Tri-Institutional MD-PhD Program at Weill Cornell Medicine is a joint program between Weill Cornell Medicine, The Rockefeller University, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. It offers an integrated curriculum that allows students to pursue both medical and graduate research training concurrently, ...
MD | PhD Program Master's Programs PhD Programs Postdoctoral Fellows Residency & Fellowship ... first-year bioinformatics courses will be considered during the evaluation of applicants for suitability for the MS Program. If a PhD student applies after August 1 of their first year, a written justification of why the student waited before ...
Questions should be directed to the course director, Dr. Jeffery Peipert, MD, PhD, Clarence E. Ehrlich Professor and Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Chair at IU School of Medicine. ... Who the program is for The course is intended for OBGYN fellows and junior faculty interested in advancing their skills in clinical and medical education ...
Believers in artificial intelligence say the program will radically transform our lives in so many ways. It's designed by Snehesh Shrestha, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Computer Science, and is the perfect example of how the University of Maryland is building bridges between AI and every other academic program on campus.
The SUNY Downstate Department of Surgery was pleased to host a Grand Rounds session with Oluyinka O. Olutoye, MD, PhD, FACS, FAAP, FWACS, Surgeon-in-Chief at Nationwide Children's Hospital and the E. Thomas Boles Jr. Chair of Pediatric Surgery of The Ohio State University College of Medicine.
I completed my undergraduate degree in biomedical engineering at the William E. Macaulay Honors College at the City College of New York. After graduation, I worked as a project manager for an electronic health records company, Epic Systems, in Verona, Wisconsin. I came to OHSU to complete my MD/ PhD training and to study cardiovascular physiology.