Points About Ancient Greek History
Major Topics in Ancient Greek History You Should Know
- Figures & Events
- Ancient Languages
- Mythology & Religion
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
- M.A., Linguistics, University of Minnesota
- B.A., Latin, University of Minnesota
Greece, now a country in the Aegean, was a collection of independent city-states or poleis in antiquity that we know about archaeologically from the Bronze Age on. These poleis fought among one another and against bigger external forces, especially the Persians. Eventually, they were conquered by their neighbors to the north and then later became part of the Roman Empire. After the western Roman Empire fell, the Greek-speaking area of the Empire continued until 1453, when it fell to the Turks.

The Lay of the Land - Geography of Greece
Greece, a country in southeastern Europe whose peninsula extends from the Balkans into the Mediterranean Sea, is mountainous, with many gulfs and bays. Some areas of Greece are filled with forests. Much of Greece is stony and suitable only for pasturage, but other areas are suitable for growing wheat, barley, citrus, dates, and olives.
Prehistory: Before Greek Writing
Prehistoric Greece includes that period known to us through archaeology rather than writing. The Minoans and Mycenaeans with their bullfights and labyrinths come from this period. The Homeric epics—the Iliad and the Odyssey—describe valiant heroes and kings from the prehistoric Bronze Age of Greece. After the Trojan Wars, the Greeks were shuffled around the peninsula because of invaders the Greeks called Dorians.
- What Are the Letters of the Greek Alphabet?
- An Introduction to the Development of the Greek Alphabet
Greek Colonies
There were two main periods of colonial expansion among the ancient Greeks. The first was in the Dark Ages when the Greeks thought the Dorians invaded. See Dark Age Migrations . The second period of colonization began in the 8th century when Greeks founded cities in southern Italy and Sicily. The Achaeans founded Sybaris was an Achaean colony perhaps founded in 720 B.C. The Achaeans also founded Croton. Corinth was the mother city of Syracuse. The territory in Italy colonized by the Greeks was known as Magna Graecia (Great Greece). Greeks also settled colonies northward up to the Black (or Euxine) Sea.
Greeks set up colonies for many reasons, including trade and to provide land for the landless. They held close ties to the mother city.
The Social Groups of Early Athens
Early Athens had the household or oikos as its basic unit. There were also progressively larger groups, genos, phratry, and tribe. Three phratries formed a tribe (or phylai) headed by a tribal king. The earliest known function of the tribes was military. They were corporate bodies with their own priests and officials, as well as military and administrative units. There were four original tribes in Athens.
- Archaic Greece
- Classical Greece
The Acropolis - Athens' Fortified Hilltop
The civic life of ancient Athens was in the agora, like the Romans' forum. The Acropolis housed the temple of the patron goddess Athena, and had, since early times, been a protected area. Long walls extending to the harbor prevented the Athenians from starving in case they were besieged.
Democracy Evolves in Athens
Originally kings ruled the Greek states, but as they urbanized, the kings were replaced by a rule by the nobles, an oligarchy. In Sparta, the kings remained, possibly because they didn't have too much power since the power was split in 2, but elsewhere the kings were replaced.
Land Shortage was among the precipitating factors leading to the rise of democracy in Athens. So was the rise of the non-equestrian army. Cylon and Draco helped create a uniform law code for all Athenians that furthered the progress to democracy. Then came the poet-politician Solon , who set up a constitution, followed by Cleisthenes , who had to iron out the problems Solon left behind, and in the process increased from 4 to 10 the number of tribes.
Sparta - The Military Polis
Sparta started with small city-states (poleis) and tribal kings, like Athens, but it developed differently. It forced the native population on the neighboring land to work for the Spartans, and it maintained kings alongside an aristocratic oligarchy. The fact that it had two kings may have been what saved the institution since each king could have prevented the other from becoming too abusive of his power. Sparta was known for its lack of luxury and physically strong population. It was also known as the one place in Greece where women had some power and could own property.
The Greco-Persian Wars - Persian Wars Under Xerxes and Darius
The Persian Wars are usually dated 492-449/448 B.C. However, a conflict started between the Greek poleis in Ionia and the Persian Empire before 499 B.C. There were two mainland invasions of Greece, in 490 (under King Darius) and 480-479 B.C. (under King Xerxes). The Persian Wars ended with the Peace of Callias of 449, but by this time, and as a result of actions taken in Persian War battles, Athens had developed her own empire. Conflict mounted between the Athenians and the allies of Sparta. This conflict would lead to the Peloponnesian War.
Greeks were also involved in the conflict with the Persians when they hired on as mercenaries of King Cyrus (401-399) and Persians aided the Spartans during the Peloponnesian War.
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of mostly the city-states of the Peloponnese led by Sparta . Formed in the 6th century, it became one of the two sides fighting during the Peloponnesian War (431-404).
The Peloponnesian War - Greek Against Greek
The Peloponnesian War (431-404) was fought between two groups of Greek allies. One was the Peloponnesian League, which had Sparta as its leader and included Corinth. The other leader was Athens who had control of the Delian League. The Athenians lost, putting an effective end to the Classical Age of Greece. Sparta dominated the Greek world.
Thucydides and Xenophon are the major contemporary sources on the Peloponnesian War.
Philip and Alexander the Great - Macedonian Conquerors of Greece
Philip II (382 - 336 B.C.) with his son Alexander the Great conquered the Greeks and expanded the empire, taking Thrace, Thebes, Syria, Phoenicia, Mesopotamia, Assyria, Egypt, and on to the Punjab, in northern India. Alexander founded possibly more than 70 cities throughout the Mediterranean region and east to India, spreading trade and the culture of the Greeks wherever he went.
When Alexander the Great died, his empire was divided into three parts: Macedonia and Greece, ruled by Antigonus, founder of the Antigonid dynasty; the Near East, ruled by Seleucus , founder of the Seleucid dynasty ; and Egypt, where the general Ptolemy started the Ptolemid dynasty. The empire was wealthy thanks to the conquered Persians. With this wealth, building and other cultural programs were established in each region
Macedonian Wars - Rome Gains Power Over Greece
Greece was at odds with Macedonia, again, and sought the help of the budding Roman Empire. It came, helped them get rid of the northern menace, but when they were called back repeatedly, their policy gradually changed and Greece became part of the Roman Empire.
Byzantine Empire - The Greek Roman Empire
The fourth-century A.D. Roman emperor Constantine established a capital city in Greece, at Constantinople or Byzantium. When the Roman Empire "fell" in the following century, only the western emperor Romulus Augustulus was deposed. The Byzantine Greek-speaking part of the empire continued until it fell to the Ottoman Turks about a millennium later in 1453.
- 30 Maps of Ancient Greece Show How a Country Became an Empire
- Rise to Power of Sparta
- Political Aspects of the Classical Age of Greece
- The Peloponnesian War: Causes of the Conflict
- Formation of the Delian League
- 7 Points to Know About Ancient Greek Government
- A Short Summary of the Persian Wars
- Major Events in Ancient History
- The Thirty Tyrants After the Peloponnesian War
- Biography of Alcibiades, Ancient Greek Soldier-Politician
- Timeline of the Persian Wars 492-449
- Greece - Fast Facts About Greece
- How Athenian Democracy Developed in 7 Stages
- The Start of the Persian Wars
- The Age of Pericles and Periclean Athens
- The Heroes of Ancient Greece and Rome
Themes in Greek Society and Culture: An Introduction to Ancient Greece
John bloxham , the open university. [email protected].
Publisher’s Preview
This is an ambitious and extremely wide-ranging introduction to almost every aspect of ancient Greek studies encompassing a timespan from the Bronze Age to 31 BC and utilising approaches from archaeology, history, literature, art, philosophy and reception studies. The introduction does not claim to provide a narrative of the entire period and suggests that the authors will not ‘privilege’ political change (9). The volume contains two broad overviews of time periods, one chapter on the Bronze Age and another on the rest of Greek history down to the end of the Hellenistic period, as well as chapters giving thematic treatments of aspects of Greek life such as the polis, the economy, religion, law, slavery, gender, sport and so on.
As an introductory companion, each chapter aims to provide a clear overview of the topic, a window into current controversies and questions, and pointers towards further reading. At the end of each chapter there is a section titled ‘Questions for Review and Discussion’ which could be a useful resource for course designers. Some of these sections are quite basic, although the better ones will encourage more active students to reflect upon their learning. There are a range of useful illustrations in black and white, presumably to reduce the expense, and there are two maps, of Greece and the Aegean at the beginning of the book and Greece and the Middle East towards the end. However, it is quite a short book and the result is that some of the chapters are little more than superficial overviews of the topic under consideration.
This review will assess the strengths and weaknesses of the book as a whole, whilst of necessity only looking in detail at a few chapters emblematic of broader issues. The work contains a number of solid if somewhat pedestrian surveys, such as those by A. Faulkner (‘Literature and Performance’), which manages to squeeze in discussions of epic, lyric, tragedy and comedy, and M. Haworth (‘Art and Architecture’). Chapter Two (‘The Ancient Greeks’), by R. Kroeker, is less successful. It provides an overview of the period from the Mycenaeans to 31 BC, and is concerned primarily with military and political developments on whose basis the later, more focused, chapters can be constructed. However, condensing such an expanse of history into a 20-page chapter (18 once the references, questions and so on are excluded) inevitably paints a simplistic picture. In addition, the ‘sources’ discussion for this section only lists authors concerned with the same small sliver of the chapter’s range (Herodotus, Thucydides and Xenophon), as does the ‘Further Reading’ section. Other periods are barely touched upon, including the Hellenistic period which is given just over a single page, and the interpretations are very much geared towards a traditional ‘Great Man’ view of history. The chapter also has a tendency towards vagueness (for example, providing no dates when talking about the emergence of the polis and providing population figures for a ‘typical’ polis). It may be heresy to suggest it, but it is difficult to see what this chapter offers that could not be gained by asking students to read the relevant Wikipedia page. Likewise, F. Pownall’s chapter on Macedonia provides just the sort of narrative political history that was disavowed by the editors in the introduction.
The volume is strongest where it sticks closest to the introductory aim of providing thematic treatments and avoiding political narrative. Sears’ chapter on the polis provides an excellent discussion which should really get students thinking about differences with the modern world where they might before have seen only similarities. That said, there is arguably too much emphasis placed upon the ‘specialness’ of the polis. A brief indication of the alternative views in existence (for example, Vlassopoulos’ Unthinking the Greek Polis 1 ) would have been useful, even if only added to the ‘Further Reading’ section. Sears also supplies the traditional account of the egalitarian nature of the polis being a consequence of the rise of hoplite warfare, but in this instance provides useful further reading suggestions which contest this view.
Kroeker’s chapter is not the only one to largely ignore the Hellenistic period, which merits a short postscript in most chapters. V. Provencal’s chapter on philosophy goes a step further and explicitly ignores all Greek philosophy after 300 BC. Chapter Four (‘War and Peace’) by S. Ager is one of the few chapters to give serious attention to the Hellenistic period. The chapter is also strong on hoplites and navies, although other important aspects of Greek warfare, such as sieges, logistics or irregular troops, are hardly mentioned. One small complaint is that she compares the period before the Peloponnesian War with the Cold War to argue that ‘bipolar alignments resulted in a dangerously combustible international situation’ (87), which oversimplifies the situation in Greece but might also leave the reader with the misleading impression that the Peloponnesian War was an aberration, whereas warfare was actually a fairly normal state of affairs in Greece.
A couple of points on especially good chapters are in order. ‘Sparta: Separating Reality from Mirage’, by N. Humble, is one of the strongest of the book. The question running throughout the chapter is whether Sparta can be classed as, ‘above all, a militaristic state?’ (106). Humble engages admirably with the scholarship of recent decades which has transformed Sparta by normalising it, whilst at the same time acknowledging the ‘othering of Sparta’ undertaken at times even by contemporaries such as Xenophon (109). In contrast to some of the more simplistic, narrative chapters, Humble does an excellent job of bringing out the complexity and ambiguity of both the literary and archaeological source material. B. Akrigg (‘Going to Market: the Economy and Society’) has also produced a thought-provoking introduction to his topic. He concisely lays out some of the main current and past debates concerning the Greek economy, acquainting students with the questions at issue between the primitivists and modernists, substantivists and formalists and so on. Akrigg adopts the position that Greece had a ‘high standard of living by historical standards’. A minor criticism arises from Akrigg’s argument that the Greek economy grew because Greeks became more productive (not just because there were more Greeks), for which he offers no real evidence in support.
Any study of ancient Greece will necessarily present a fairly unbalanced picture due to the preponderance of Athenian sources in the surviving evidence; however, this makes it all the more essential that non-Athenian evidence is utilised whenever available to establish a more inclusive representation of ancient Greece. Some of the best chapters make admirable efforts in this respect, such as those by J. Trevett (‘Status and Class’), R. Tordoff (‘Slaves and Slavery’) and C. Vester (‘Women and the Greek Household’). In contrast, a number of others are excessively Athenocentric, of which J. Fletcher’s chapter on law is a good example. The absence of any discussion of the Gortyn law code is especially regrettable, particularly as it is included in an illustration. There are a few references to non-Athenian evidence from Locri, Croton and so on, but no sustained comparison or discussion. This criticism notwithstanding, it is an excellent introduction to (largely) Athenian ideas of law and justice. Whilst a number of chapters can be criticised along similar lines for their overly narrow focus in terms of excluding the Hellenistic period or non-Athenian evidence, M. Liston’s chapter on disease and health suffers from the opposite ailment. Ignoring the scope of the volume, Liston frequently draws upon much later Roman authors as if Greeks and Romans are interchangeable and time has no meaning. Indeed, even Byzantine authors and evidence make an appearance. She is very good on different treatments given in the ancient world, but the chapter could have contained more on Greek attitudes to sickness and the body. Fortunately this drawback is rectified to some extent by Glazebrook’s stimulating discussion of the female body in her chapter on gender.
The work is largely free from editing errors (although an Egyptian statue illustrated on page 368 is mistakenly labelled as Greek). As I have indicated above, the volume occasionally oversimplifies, which can be further highlighted with a couple of examples concerning Sparta. Considering the importance that the falling number of Spartiates had in Sparta’s decline, and the controversies surrounding the extent and reasons for the fall in numbers, it is surprising that Sears simply describes the Spartiates as ‘typically around 5,000 in number’ (64). Sears also conflates different and occasionally contradictory ancient sources on Sparta to depict something close to the ‘Spartan Mirage’ discussed by Humble. A larger drawback is the frequent repetition of material. Chapters two and four both provide narrative outlines of the wars and changing political alliances of the Classical and Hellenistic periods and both cover the dynamics of warfare in a similar fashion; the structures of the polis are outlined in chapters two, three and four; and the Athenian attack on Melos is described in a large text box in chapter two and then again in chapter four. Likewise, chapters four and five each begin with discussions of the Battle of Thermopylae as the ‘hook’ to draw readers in. Both descriptions are fine in themselves, but a more assertive editor might have suggested that one of them be altered to avoid duplication.
The major strengths of the volume are its breadth of coverage and its straightforward readability. Additional selling points are the suggestions for further reading, which are largely current and authoritative, and the excellent introductions it provides to the types of evidence available and the different ways it can be interrogated. The glossary will also be a useful tool for students new to the ancient Greek world. However, whilst there are strong individual chapters, the volume as a whole tries to do too much. The result is that some of the periods which are ostensibly part of the work are barely touched upon. For example, every chapter includes a timeline sketching events from across the whole period covered by the book; however, the chapters themselves often concentrate almost entirely on the Archaic and Classical periods. By cutting out some of the chapters which do not fit with the book’s main thematic and chronological focus (the one on the Bronze Age, the political overview and the reception chapter), as well as each chapter’s sections on the Hellenistic period (usually the briefest of afterthoughts anyway) and the elements of repetition, the remaining chapters could have been made much more comprehensive.
Finally, it is worth adding a few words on the possible market for this work. For students intending to continue their studies of ancient Greece throughout their degrees, it is likely that even the introductory courses they take will demand more depth than many of the chapters in this volume provide. There are introductory works elsewhere which break the Greek world down into manageable units of time or theme, but delve much deeper into their chosen fields. Consequently, these alternatives are likely to be more suitable in many cases. However, the main market for a book like this one would be the large introductory survey courses popular in North America, in which ancient Greece might be just one part of a broader course on, for example, ‘Western Civilization’. Despite its drawbacks, this volume would serve as a very serviceable companion on such wide-ranging courses.
1 . Vlassopoulos, K., Unthinking the Greek Polis: Ancient Greek History beyond Eurocentrism , Cambridge; New York, Cambridge University Press, 2007.

Guide to Ancient Greek Art
(3 reviews)
Beth Harris
Steven Zucker
Copyright Year: 2019
Publisher: Smarthistory
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Caroline Wilson, Ed.D., Assistant Professor, Tidewater Community College on 7/27/22
This text covers a range and thorough summary of Greek periods in art history. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
This text covers a range and thorough summary of Greek periods in art history.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The authors have done effective research and applied their knowledge comprehensibly and interestingly for the reader.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The topic is a vital segment of the art historical timeline and the information provided is timeless.
Clarity rating: 5
Images selected in the text clarify the author’s point and provide helpful visual examples of Greek art historical trends described.
Consistency rating: 5
The writing styles of the authors are consistent.
Modularity rating: 5
The historical periods discussed build on one another.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The overall organization of the text is linear along the art history timeline and flows flawlessly.
Interface rating: 5
The text is free of interface issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is well written.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The text is not culturally offensive and is inclusive.
This text provides a “go-to” resource for a better understanding of the overview of ancient Greek art history. Highly recommended reading for the art history enthusiast.
Reviewed by Joyce Miller, Professor of Art, Mount Wachusett Community College on 5/24/21
Dry and informative read more
Dry and informative
Strong and content as expected with research and references
covers topics as expected
Clarity rating: 3
Reading written statements of recorded conversations or interviews is not an interesting format for students. Tedious at best. Interesting for faculty maybe.
Consistency rating: 3
Format is structured but when researching on how black figure pottery was made I got linked to smarthistory -a youtube video from Art Institute of Chicago that was terrific but then when I went back to text it was not listed in the resources nor could I find it again via the text online. Going back to "Search" in this textbook was problematic when download of page numbers does not correspond to actual page numbers on the scrolled through pages. Will just simply directly search Youtube, Google or other sites for such information . Easier.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
Content organized but as stated earlier the additional course materials and links not so clear or organized
Interface rating: 4
Just the hunt and seek too time consuming
Only reviewed a few chapters and the Table of Contents, all seemed well written from what I perused.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
Good images and overviews of Greek Pottery.
Reviewed by Tammy Cotton-Jennings, Lecturer/Art, Leeward Community College on 7/1/20
The textbook covers a lot of information, in a book of less than 200 pages. However, the content would be easier for those with some prior knowledge. This is more of a guide (as the title states), than an introduction to the subject. there is no... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The textbook covers a lot of information, in a book of less than 200 pages. However, the content would be easier for those with some prior knowledge. This is more of a guide (as the title states), than an introduction to the subject. there is no index or glossary, but I do appreciate the ability to click on titles of chapters and get taken easily to each section.
I found no inaccuracies in the book. The material appears to have been researched thoroughly and is error free.
The content of this textbook is mostly up to date. It appears that the last changes, or additions were made in 2017. It would be easy to insert new articles, citations, and research to the content.
I found most of the chapters missing Introductions. It is assumed that the reader has already been exposed to Greek history and literature, as in the first paragraph of the book: "Ancient Greece can feel strangely familiar. From the exploits of Achilles (hero of Homer’s epic poem, the Illiad, about the Trojan war) and Odysseus (also known as Ulysses, the hero in Homer’s other epic poem, the Odyssey), to the treatises of Aristotle.." The sections on ancient Greek architecture and Greek Vase-Painting, by Dr. Renee M. Gondek and Dr. Jeffey A. Becker are very well done, whereas the sections on Classical, Hellenistic styles have no introductions, just conversations between Dr. Beth Harris and Dr. Steven Zucker.
The terminology and framework are consistent, and the images are well chosen.
Modularity rating: 3
I would be happy to use parts of this textbook in my class, and there are sections that would work easily. In other instances, I would have to re-write introductions.
The topics in the text have been organized well.
Everything to do with the interface and navigation works well in this textbook. I especially would like to point out the excellent quality of the images and their explanations.
I found no significant errors.
My only criticism of the text is in relation to the assumption that all students would have prior knowledge of some of the philosophical or literary references. "...thanks largely to ..... well-known literary sources, ....this civilization is embedded in our collective consciousness—"
As already mentioned, for an introductory course perhaps the book would benefit from a clear concise introduction to the ancient world. Also, I think the conversations between Dr. Beth Harris and Dr. Steven Zucker. work very well in the smarthistory videos, but not as well in the textbook form.
Table of Contents
- Part I. A beginner's guide
- Part II. Pottery
- Part III. Daedalic and Archaic
- Part IV. Early Classical
- Part V. Classical
- Part VI. Late Classical
- Part VII. Hellenistic
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This book contains all of Smarthistory’s content for Ancient Greek art.
About the Contributors
Ruth Ezra is a doctoral candidate at Harvard University, where she specializes in the art of late-medieval and Renaissance Europe. Upon completion of her BA at Williams College, she studied in the UK on a Marshall Scholarship, earning an MPhil in history and philosophy of science from the University of Cambridge and an MA in history of art from the Courtauld Institute. A committed educator, Ruth has recently served as a Gallery Lecturer at both the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston and the National Galleries of Scotland, as well as a Teaching Fellow at Harvard.
Beth Harris is co-founder and executive director of Smarthistory. Previously, she was dean of art and history at Khan Academy and director of digital learning at The Museum of Modern Art, where she started MoMA Courses Online and co-produced educational videos, websites and apps. Before joining MoMA, Beth was Associate Professor of art history and director of distance learning at the Fashion Institute of Technology where she taught both online and in the classroom. She has co-authored, with Dr. Steven Zucker, numerous articles on the future of education and the future of museums, topics she regularly addresses at conferences around the world. She received her Master’s degree from the Courtauld Institute of Art in London, and her doctorate in Art History from the Graduate Center of the City University of New York.
Steven Zucker is co-founder and executive director of Smarthistory. Previously, Steven was dean of art and history at Khan Academy. He was also chair of history of art and design at Pratt Institute where he strengthened enrollment and lead the renewal of curriculum across the Institute. Before that, he was dean of the School of Graduate Studies at the Fashion Institute of Technology, SUNY and chair of their art history department. He has taught at The School of Visual Arts, Hunter College, and at The Museum of Modern Art. Dr. Zucker is a recipient of the SUNY Chancellor’s Award for Excellence in Teaching. He has co-authored, with Dr. Beth Harris, numerous articles on the future of education and the future of museums, topics he regularly addresses at conferences around the world. Dr. Zucker received his Ph.D. from the Graduate Center of the City University of New York.
Contribute to this Page
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Greek Mythology
By: History.com Editors
Updated: August 15, 2023 | Original: December 2, 2009

Ancient Greek mythology is a vast group of legends about gods and goddesses, heroes and monsters, warriors and fools, that were an important part of everyday life in the ancient world. Greek myths explained everything from religious rituals to the weather, and gave meaning to the world that people saw around them. While many of these myths are fanciful tales, such as the legends of greedy King Midas or heroic Hercules, other stories like the Trojan War epic have a basis in historical fact.
Sources of Greek Mythology
There is no single original text, like the Christian Bible or the Hindu Vedas, that introduces all Greek myths’ characters and stories. Instead, the earliest Greek myths were part of an oral tradition that began in the Bronze Age , and their plots and themes unfolded gradually in the written literature of the archaic and classical periods of the ancient Mediterranean world.
The poet Homer ’s 8th-century BC epics, The Iliad and The Odyssey , for example, tell the story of the Trojan War as a divine conflict as well as a human one. They do not, however, bother to introduce the gods and goddesses who are their main characters, since readers and listeners would already have been familiar with them.
Around 700 BC, the poet Hesiod’s Theogony offered the first written cosmogony, or origin story, of Greek mythology. The Theogony tells the story of the universe’s journey from nothingness (Chaos, a primeval void) into being, and details an elaborate family tree of elements, gods and goddesses who evolved from Chaos and descended from Gaia (Earth), Ouranos (Sky), Pontos (Sea) and Tartaros (the Underworld).
Later Greek writers and artists used and elaborated upon these sources in their own work. For instance, mythological figures and events appear in the 5th-century plays of Aeschylus, Sophocles and Euripides and the lyric poems of Pindar. Writers such as the 2nd-century BC Greek mythographer Apollodorus of Athens and the 1st-century BC Roman historian Gaius Julius Hyginus compiled the ancient myths and legends for contemporary audiences.
Did you know? Many consumer products get their names from Greek mythology. Nike sneakers are the namesake of the goddess of victory, for example, and the website Amazon.com is named after the race of mythical female warriors. Many high school, college and professional sports teams (Titans, Spartans and Trojans, for instance) also get their names from mythological sources.
Greek Gods and Goddesses
At the center of Greek mythology is the pantheon of gods and goddesses who were said to live on Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece. From their lofty perch, they ruled every aspect of human life. Olympian deities looked like men and women (though they could change themselves into animals and other things) and were — as many myths recounted — vulnerable to human foibles and passions..
The twelve main Olympians are:
- Zeus (Jupiter, in Roman mythology): the king of all the gods (and father to many) and god of weather, law and fate
- Hera (Juno): the queen of the gods and goddess of women and marriage
- Aphrodite (Venus): goddess of beauty and love
- Apollo (Apollo): god of prophesy, music and poetry and knowledge
- Ares (Mars): god of war
- Artemis (Diana): goddess of hunting, animals and childbirth
- Athena (Minerva): goddess of wisdom and defense
- Demeter (Ceres): goddess of agriculture and grain
- Dionysus (Bacchus): god of wine, pleasure and festivity
- Hephaestus (Vulcan): god of fire, metalworking and sculpture
- Hermes (Mercury): god of travel, hospitality and trade and Zeus’s personal messenger
- Poseidon (Neptune): god of the sea
Other gods and goddesses sometimes included in the roster of Olympians are:
- Hades (Pluto): god of the underworld
- Hestia (Vesta): goddess of home and family
- Eros (Cupid): god of sex and minion to Aphrodite
Greek Mythology: Heroes and Monsters
Greek mythology does not just tell the stories of gods and goddesses, however. Human heroes — including Heracles (aka Hercules), the adventurer who performed 12 impossible labors for King Eurystheus (and was subsequently worshipped as a god for his accomplishment); Pandora, the first woman, whose curiosity brought evil to mankind; Pygmalion, the king who fell in love with an ivory statue; Arachne, the weaver who was turned into a spider for her arrogance; handsome Trojan prince Ganymede who became the cupbearer for the gods; Midas, the king with the golden touch; Narcissus, the young man who fell in love with his own reflection; and Kratos, a god of strength and power—are just as significant.
Monsters and “hybrids” (human-animal forms) also feature prominently in the tales: the winged horse Pegasus, the horse-man Centaur, the lion-woman Sphinx and the bird-woman Harpies, the one-eyed giant Cyclops, automatons (metal creatures given life by Hephaestus), manticores and unicorns, Gorgons, pygmies, minotaurs, satyrs and dragons of all sorts. Many of these creatures have become almost as well known as the gods, goddesses and heroes who share their stories.
The Legacy of Greek Myths
The characters, stories, themes and lessons of Greek mythology have shaped art and literature for thousands of years. They appear in Renaissance paintings such as Botticelli ’s Birth of Venus and Raphael ’s Triumph of Galatea and writings like Dante ’s Inferno ; Romantic poetry and libretti; and scores of more recent novels, plays and movies. Much of the mythology was recorded in D'Aulaires' Book of Greek Myths , published in 1962 and still in print today.

HISTORY Vault: Clash of the Gods
Discover the history behind myths and legends.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Articles on Greek history
Displaying all articles.


Peter Polites maps war, migration, familial love and gay identity from mid-century Greece to western Sydney
Anthony Macris , University of Technology Sydney

The Ancient Greeks also lived through a plague, and they too blamed their leaders for their suffering
Joel Christensen , Brandeis University

Plagues and classical history – what the humanities will tell us about COVID in years to come
Christopher Smith , University of St Andrews

Ancient Greek desire to resolve civil strife resonates today – but Athenian justice would be a ‘bitter pill’ in modern America

How ancient cultures explained comets and meteors
Eve MacDonald , Cardiff University
Related Topics
- Ancient Greece
- Book reviews
- Bubonic plague
- Classical antiquity
- Greek mythology
- Roman history
- Western Sydney
Top contributors
Professor of Classical Studies, Brandeis University
Lecturer in Ancient History, Cardiff University
Executive Chair, Arts and Humanities Research Council, and Professor, School of Classics, University of St Andrews
Professor of Creative Writing, University of Technology Sydney
- X (Twitter)
- Unfollow topic Follow topic
Hellenic Studies
- Bibliographies
- Dictionaries
- Internet Links
Resources for Modern Greek History
- Modern Greek Literature
Below is a selection of books and databases that will lead you to in-depth information about a wide variety of topics in the history of modern Greece.
- A Concise History of Greece by Richard Clogg ISBN: 9781108953924 Publication Date: 2021 Now reissued in a fourth, updated edition, this book provides a concise, illustrated introduction to the modern history of Greece, from the first stirrings of the national movement in the late eighteenth century to the present day. As Greece emerges from a devastating economic crisis, this fourth edition offers analyses of contemporary political, economic and social developments.
- Historical Dictionary of Modern Greece by Dimitris Keridis ISBN: 9780810863125 Publication Date: 2009 This reference work explores the modern history of Greece through a chronology, an introductory essay, a bibliography, and hundreds of cross-referenced dictionary entries on important persons, places, events, and institutions, as well as on significant political, economic, social, and cultural aspects.
- Historical Dictionary of Greece by Thanos Veremēs Call Number: DF802 .V47 1995 (Reference, Non-circulating) Publication Date: 1995 Includes entries for individuals, organizations, place names, and important events. Focus is on the last two centuries of Greek history, including politics, economics, diplomatic relations, culture, and society. Detailed bibliography (pp. 185-243) lists resources in these and related areas.
- Historical Abstracts with Full Text (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Covers the history of the world (excluding the United States and Canada) from 1450 to the present, including world history, military history, women's history, history of education, and more. Indexes more than 1,700 academic historical journals in over 40 languages. Publication dates of coverage: 1955 to present.
- Iter Bibliography This link opens in a new window Comprised of secondary source material pertaining to the Middle Ages and Renaissance (400-1700). Citations for books and journal material (articles, reviews, review articles, bibliographies, catalogues, abstracts and discographies) are included, as are citations for dissertation abstracts and essays in books (including entries in conference proceedings, festschriften, encyclopedias and exhibition catalogues).
- << Previous: Internet Links
- Next: Modern Greek Literature >>
- Last Updated: Jan 23, 2024 11:41 AM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/hellenic-studies
122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples
Welcome to our list of Greek mythology essay topics! In you need good title ideas for your history paper or project, look no further. Here, you will find Greek mythology research topics that will help you learn more about gods like Zeus and Aphrodite. Check them out!
🔝 Top 10 Greek Mythology Essay Topics
🏆 best greek mythology topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 simple & easy greek mythology essay topics, 👍 good greek mythology topics for essays, 🔍 greek mythology research topics, ✅ greek mythology topics for presentation, ❓ research questions about greek mythology.
- The Hero’s Journey Archetypes
- What’s the Meaning of Pandora’s Box?
- Love Story of Orpheus and Eurydice
- Hades, Persephone, and the Afterlife
- The Twelve Olympian Gods and Their Roles
- Athena vs. Poseidon: The Contest for Athens
- Infidelity and Betrayal in Greek Mythology
- The Labors of Heracles and Divine Punishment
- The Myth of Narcissus and the Narcissistic Personality
- The Complexity of Medea’s Character in Greek Mythology
- “The Matrix” Trilogy and Greek Mythology: Comparison One of the exceptions of the previous statements is the Matrix trilogy directed by Larry and Andy Wachowski.”The Matrix”, The Matrix: Reloaded”, and “The Matrix: Revolution”, all of which gained a cult status among fans, […]
- Hercules in Greek Mythology The theme of his legends interpretation was to show the power of mythological heroes on the example of one of the most strong and powerful.
- Roman & Greek Mythology in Pop Culture: Examples, Referenses, & Allusions One of the most famous examples of the use of the characters taken from Greek mythology in pop culture must be the mentioning of the famous goddess, Venus, in advertising, which is, in fact, based […]
- Medusa in Greek Mythology So, it should be pointed out that Medusa was the great character of the Ancient mythology and remains to be the significant image in the world of modern literature and art.
- The Suffering Women in Greek Mythology Zeus told Hermes to go down to the underworld and bid the lord of it to let his bride to return to Demeter.
- Classical Mythology: Rats in Greek Mythology Hephaestus was the son of Zeus and Hera, and was the god of the creative fire, and was the divine artisan who worked with metals.
- The Issue of “Man’s Relationship with the Divine” in Greek Mythology As the reader explores the idea of divinity throughout most of the Greek mythologies and epics, it becomes clear that there is a strong connection between the people of Greece and their gods thus making […]
- Perseus: A Hero of Greek Mythology With the protection of Hermes and Athena, Perseus went ahead and beheaded Gorgon Medusa and took her head to the king of the island.
- Athena and Gender Roles in Greek Mythology According to Eicher and Roach-Higgins, the elements of her dress were important because they immediately communicated specific ideas about her character that was as contradictory as the physical gender of the birthing parent.”In appropriating the […]
- Greek Mythology: Story of Demeter and Persephone Review For example, Venus was the goddess of love, and her son Cupid was considered as the god of love; Pan was the god of the jungle, while Hymen was attributed to the domain of marriage, […]
- Greek Mythology Influence In fact, majority of the traditions that people in the modern society carry out have their origin in Greece. One Greek mythology that has influenced the whole world is the celebration of the Olympic Games.
- The Dichotomy of Women in Greek Mythology The male competitive spirit pushed women out of public life, and in the private sphere, the freedom of women was subjected to significant restrictions.
- Medea in Greek Mythology: Literary Analysis In this case, the position of kingship was the highest in political rankings, equivalent to the presidency in modern-day practices. Most importantly, the element of leadership in Greek mythology was characterized by concessions and plots.
- Political Concerns in Greek Mythology In other words, the ritual of killing the ruler to seize the throne is normal; it is the natural order of things for the Greeks and Romans.
- Ancient Greek Mythology: Deities of the Universe Hades is the eldest son of Kronos and Rhea, the god and the guardian of the Underworld, the realm of the dead.
- Owls in the Greek Mythology. A Lecture for Librarians They also believed that the owl was a keen full watcher of Athens trade, and that is why it was engraved at the back of their coins.
- Greek Mythology, Religion, Philosophy, and History The ancient religious stories of the Minoans and the Mycenaean were transmitted orally to the other parts of the Mediterranean region which later fused with the Greek traditions and religious practices.
- Greek Deities in Primary Sources Hades is the god of the underworld, and he is the son of Cronus and Rhea. Dionysus is the god who represents wine-making, the fertility of the soil, drinking, and even theater; he is the […]
- Greek Mythology – Medea by Euripides While the character shares certain features with some of the female leads in other Ancient Greek plays, Euripides’ Medea stands on her own as a character and represents a new set of qualities, which used […]
- Greek Mythology: Historical and Factual Roots Greek mythology is a body of teachings used in ancient Greek to describe the human environment, the passing of time, and natural phenomena. The picture and the story behind it illustrate in many ways the […]
- The Struggles And Eventual Perseverance Of The Greek Mythology
- Comparing And Contrasting Rouse And Hamilton’s Books On Greek Mythology
- The Mysteries Surrounding How Man Was Created in Greek Mythology
- The Influence of Ancient Greek Mythology on Modern Society
- The Impact of Greek Mythology on the English Language
- Zeus’ Tyranny in Greek Mythology
- The Opposition Between Gods and Humans in Greek Mythology
- Persephone: Greek Mythology and Spring Persephone Returns
- An Analysis of Greek Mythology as a God of Wine and Vegetation
- The Myth of Atlas, the Strongest Titan in the Greek Mythology
- Understanding the Feminist Theory in Greek Mythology
- The Amazons, A Tribe Of Ancient Greek Mythology
- The Life And Power Of Zeus, King Of The Gods In Greek Mythology
- Confronting Death in Greek Mythology: Allegiance to Family or Empire
- Female Influence In Greek Mythology
- The Important Role of Hades in the History of Greek Mythology
- Ritualistic Sacrifice in Ancient Greek Mythology
- The Powers and Symbols of Polyphemus in the Greek Mythology
- The Role of Oracles in Chaldean and Greek Mythology
- Examining Self Exile In Greek Mythology As A Defense Mechanism
- The Portrayal of a Popular Greek Mythology in the Play Oedipus the King
- The Theme of Prophecy in Greek Mythology and Literature
- The Great Influences of Athene and Hermes in Greek Mythology
- The Portrait Of The Roman And Greek Mythology
- Story of Aphrodite and Her Son Cupid and Their Place in Greek Mythology
- The Effects Of Kleos On Greek Mythology
- The Role of Fate in Greek Mythology and Its Influence on American Society
- The Tragedy of Medea and Jason from Greek Mythology
- The Wise Old Man in the Story of Mentor in Greek Mythology
- The Relationship of Greek Mythology and Christianity
- The Essential Elements of Human Nature Illustrated through the Characters and Their Actions in the Greek Mythology
- Chaldean and Greek Mythology and the Roles Played by Oracles and Fate
- An Analysis of the Greek Mythology and the Concept of Creationism
- Star Wars, Episode II: Relation With Ancient Greek Mythology And Its Heroes
- The Elements of Change in Greek Mythology
- The Study and Interpretations of Greek Mythology
- The Hero of Athens, Theseus in Greek Mythology
- The Relationship between Love and Sex in Greek Mythology
- Greek Mythology and Immediate Satisfaction
- The Impact of Greek Mythology on Western Culture
- The Role of the Women in Greek Mythology
- Death And Its Personification In Greek Mythology And Other Cultures
- Greek Myths in Art and Literature
- The Trojan War in Greek Mythology
- Love and Desire in Greek Mythology
- Heroes and Heroines of Greek Mythology
- Greek Creation Myths of Chaos and Titans
- Underworld and Afterlife in Greek Mythology
- What Are the Moral Lessons of Greek Myths
- How Greek Mythology Influences Pop Culture
- The Powers and Stories of Greek Gods and Goddesses
- Medusa, Cerberus, and Other Monsters in Greek Mythology
- Chaoskampf as the Creation Myth
- An In-Depth Exploration of Zeus, Hera, and Poseidon
- Hercules, Perseus, and Their Legendary Quests
- Goddesses of Wisdom and Beauty in Greek Mythology
- The Trojan War: Myth and Reality
- Mythical Creatures in Greek Folklore
- Tragic Fates of Oedipus and Prometheus
- The Influence of Greek Mythology on Modern Cinema
- Greek Mythology in Sculptures, Pottery, and Temples
- Persephone, Orpheus, and the Themes of Death and Resurrection
- What Is the Role of Women in Greek Mythology? How Does It Differ From the Role of Women Today?
- How Do the Myths Differentiate Between Human and Divine Power?
- What Do the Greek Myths Suggest About Tragedy?
- How Does Author Publius Ovidius Naso Capture the Spirit of the Greek and Roman Mythology?
- Why Is Creon the Tragic Hero in Antigone?
- How Does Child Abuse Affect a Hero, a God, and a Monster in Greek Mythology?
- What Moral Lessons Do We Learn From the Greek Myths and Ancient Stories?
- How Are Egyptian and Greek Culture Reflected Through Their Respective Mythology?
- What Caused the Titanomachy War and Who Was Involved in It?
- How Did Greek Mythology Influence Christianity?
- Did Zeus and Apollo Have Anything in Common?
- How Does Fate and Destiny Work According to Greek Mythology?
- What Is the Story of Giants in Greek Mythology?
- How Was the Stonehenge Made According to the Myth?
- What Is the Most Unbelievable Myth You Find in the Greek Mythology?
- How Does Zeus Play Into Modern-Day Religion?
- What Is Something You Learned by Reading Homer’s Odyssey?
- Why Did the Goddess Athena Help the Hero Perseus Defeat Medusa?
- What Role Did Eros Play in the Life of Helen?
- Who Was the First Mortal to Be Made a God?
- Were the Trojan War and the Fall of Troy Necessary?
- What Is the Significance of Pandora’s Box?
- Did Jason Care for Medea or Exploit Her?
- What Was the Significance of Prometheus’ Gift to Man?
- Was the Trojan Horse a Clever Trick or an Act of Treachery?
- Who Were the Key Figures in the Trojan War, and Why Was It Fought?
- How Were Greek Myths Used to Keep Order in Society?
- Can We Criticize the Gods, or Are They Always Perfect in Their Actions and Behavior?
- Who Were the First Storytellers, and Why Were They Valued in Ancient Societies?
- What Is the Difference Between an Epic, a Legend, and a Myth?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 27). 122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/greek-mythology-essay-topics/
"122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 27 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/greek-mythology-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples'. 27 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/greek-mythology-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/greek-mythology-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/greek-mythology-essay-topics/.
- Ancient Greece Paper Topics
- Creation Myth Research Ideas
- Ancient History Topics
- Zeus Paper Topics
- Odyssey Questions
- Ancient Egypt Questions
- Antigone Ideas
- Poseidon Topics
- Pseudoscience Topics
- Medea Topics
- Homer Titles
- Allegory Essay Titles
- Culture Topics
- Roman Empire Ideas
- Achilles Topics
Best History Research Paper Topics

Dive into the world of historical scholarship with our comprehensive guide to the best history research paper topics . Primarily designed for students tasked with writing history research papers, this guide presents a curated list of 100 exceptional topics, divided into 10 distinct categories, each with a unique historical focus. The guide offers clear and practical advice on how to choose the most compelling history research paper topics, and provides 10 handy tips on crafting an outstanding research paper. In addition to academic guidance, the guide introduces the superior writing services of iResearchNet, a reliable option for students needing customized history research papers.
Comprehensive List of Best History Research Paper Topics
The following comprehensive list of the best history research paper topics is crafted to stimulate your curiosity and ignite your passion for historical study. These topics cover a range of historical periods and geographical locations to cater to the diverse interests of history students.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Ancient History Topics
- The Causes and Effects of the Fall of the Roman Empire
- Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
- The Influence of Alexander the Great’s Conquests on the Hellenistic World
- The Role of Women in Spartan Society
- The Construction and Significance of the Great Wall of China
- The Impact of Confucianism on Ancient Chinese Society
- Trade Routes and their Role in the Expansion of Ancient Civilizations
- The Cultural and Political Influence of the Phoenician Civilization
- Comparing Democracy in Ancient Greece to Modern Democracy
- The Religious Practices and Beliefs of the Mayans
Medieval History Topics
- The Role of the Catholic Church in Medieval Europe
- The Impact of the Black Death on Medieval Society
- The Cultural Significance of the Knights Templar
- Gender Roles and Family Structure in Medieval Japan
- The Causes and Consequences of the Hundred Years War
- The Political Structure of the Byzantine Empire
- The Influence of the Carolingian Renaissance on Europe
- The Role of Vikings in European Trade and Exploration
- The Crusades: Causes, Events, and Consequences
- The Architecture and Symbolism of Gothic Cathedrals
Early Modern History Topics
- The Causes and Effects of the Protestant Reformation
- The Role of the Enlightenment in the French Revolution
- The Impact of the Scientific Revolution on European Society
- The Socioeconomic Consequences of the Industrial Revolution
- The Influence of the Ottoman Empire on Southeast Europe
- The Role of Slavery in the Colonial Economies
- The Politics and Culture of the Renaissance in Italy
- European Imperialism in Africa and Asia
- The Cultural and Political Impacts of the Mughal Empire
- The American Revolution: Causes, Events, and Legacy
Modern History Topics
- The Causes and Global Consequences of World War I
- The Great Depression: Causes and Effects
- The Role of Propaganda in World War II
- The Impact of the Cold War on International Relations
- The Civil Rights Movement in the United States
- The Fall of the Berlin Wall and the End of the Cold War
- The Effects of Decolonization in the 20th Century
- The Role of Women in the World Wars
- The Formation and Impact of the European Union
- The Causes and Consequences of the Arab Spring
Asian History Topics
- The Cultural Impact of the Silk Road in Asia
- The Effects of Colonial Rule in India
- The Legacy of the Mongol Empire in Asia
- The Cultural and Political Changes in China’s Cultural Revolution
- The Korean War: Causes, Events, and Consequences
- The Role of Samurai in Feudal Japan
- The Impact of the Opium Wars on China
- The Influence of Buddhism on Asian Cultures
- The Cambodian Genocide under the Khmer Rouge
- The Role of Gandhi in India’s Independence
American History Topics
- The Impact of the New Deal on the American Economy
- The Vietnam War: Causes, Events, and Legacy
- The Influence of the Beat Generation on American Culture
- The Role of Manifest Destiny in Westward Expansion
- The Cuban Missile Crisis and Its Effects on the Cold War
- The Women’s Suffrage Movement in the United States
- The Native American Civil Rights Movement
- The Role of the Transcontinental Railroad in American Expansion
- The Civil War: Causes, Events, and Aftermath
- The Immigration Wave at Ellis Island: Causes and Effects
European History Topics
- The Impacts of the Russian Revolution
- The Influence of Martin Luther’s Theses on Europe
- The British Empire: Rise, Dominance, and Fall
- The Role of Art in the French Revolution
- The Impact of the Spanish Inquisition on Spain and its Colonies
- The Rise and Influence of Fascism in Europe
- The Role of the Catholic Church in the Middle Ages
- The Consequences of the Treaty of Versailles
- The Formation and Impact of NATO
- The Role of the Media in the Fall of the Berlin Wall
African History Topics
- The Effects of Apartheid in South Africa
- The Influence of the Trans-Saharan Trade on West African Societies
- The Role of Nelson Mandela in Ending Apartheid
- The Scramble for Africa and its Effects on the Continent
- The Impact of the Atlantic Slave Trade on West Africa
- The Rwandan Genocide: Causes and Consequences
- The Role of the African Union in Continental Politics
- The Impact of Islam on North Africa
- The Decolonization of Africa in the 20th Century
- The Role of Women in Pre-Colonial African Societies
Military History Topics
- The Influence of Technological Innovations on Warfare
- The Role of the French Foreign Legion in Global Conflicts
- The Impact of the Manhattan Project on World War II and Beyond
- The Role of the Spartans in Ancient Greek Warfare
- The Impact of Drones on Modern Warfare
- The Influence of the English Longbow on Medieval Warfare
- The Role of the Maginot Line in World War II
- The Impact of Naval Power on the British Empire
- The Influence of Nuclear Weapons on International Politics
- The Role of Propaganda in World War I
This expansive list of best history research paper topics offers a comprehensive exploration of the past, crossing different eras, regions, and themes. They form a rich tapestry of human experience and a foundation for understanding our present and future. Choose a topic that piques your interest, ignites your curiosity, and promises a journey of intellectual discovery. Remember that the exploration of history is a journey into the roots of our shared humanity and an exploration of the forces that shape our world.
History and What Range of Best Research Paper Topics it Offers
As a subject of study, history is more than a chronological list of events, dates, and prominent figures. History is the exploration of human experiences, societal changes, political upheavals, cultural transformations, economic shifts, and technological advancements across different periods and regions. This exploration allows us to understand how the past has shaped our present and how it can potentially shape our future. It teaches us to appreciate the complexities and nuances of human nature and society, making history a rich field for research paper topics.
History is an interdisciplinary field, interweaving elements from various areas of study, including politics, sociology, economics, anthropology, geography, and literature. This interdisciplinary nature provides a wide array of best history research paper topics. Moreover, the global scope of history further broadens the pool of topics, as it encompasses every region of the world and every period from the dawn of human civilization to the present day.
Exploring Different Periods
Historical research often focuses on specific periods, each offering unique topics for exploration. For instance, Ancient History provides topics related to ancient civilizations like Rome, Greece, Egypt, China, and India, and key events such as Alexander the Great’s conquests or the fall of the Roman Empire.
The Medieval Period offers topics related to the socio-political structure of societies, the influence of religion, the impact of plagues, and the role of significant historical figures. Researching the Renaissance can focus on cultural, artistic, and scientific revolutions that have shaped the modern world.
The Modern History category contains topics related to significant events and transformations, such as world wars, the Great Depression, the Cold War, decolonization, and various national and international movements.
Geographical Perspectives
Geographical focus is another common approach in historical research. Asian history encompasses topics ranging from the influence of Confucianism in China to the impact of colonial rule in India. European history explores events such as the Enlightenment, the French and Russian revolutions, and the formation of the European Union. American history topics can cover everything from Manifest Destiny to the Civil Rights Movement. African history can delve into the effects of the Atlantic Slave Trade, the apartheid era, and decolonization.
Thematic Approaches
In addition to period- and region-based topics, history offers an extensive range of thematic topics. These themes often intersect with other disciplines, leading to exciting interdisciplinary research opportunities.
Social and cultural history, for instance, covers diverse topics such as the influence of the Harlem Renaissance on African American culture, the counterculture movement of the 1960s, the role of film and television in shaping societies, or the impacts of the Internet on global culture.
Military history provides a wide range of topics related to warfare, strategy, technological developments, and the influence of military conflicts on societies and politics. From the use of the English longbow in medieval warfare to the impact of drones on modern warfare, this field offers a variety of fascinating topics.
Making the Right Choice
The choice of a research paper topic in history should ideally be guided by your interest, the available resources, and the requirements of your assignment. With such a wide range of topics, it can be challenging to make a choice. But remember, a good history research paper topic is not just about the past; it should also engage with the present and potentially shed light on the future. The best research paper topics are those that not only delve deep into the annals of history but also resonate with current issues and debates.
The study of history is a gateway into the vast narrative of human civilization. With an extensive range of periods, regions, and themes to choose from, history offers a rich reservoir of research paper topics. As we delve into the past, we discover the forces that have shaped our world, gain insights into the human experience, and glean lessons for our future. This journey of exploration makes history an incredibly exciting field for research papers.
How to Choose Best History Research Paper Topics
Choosing the best history research paper topic can be the first step towards a rewarding intellectual journey. It’s not just about meeting academic requirements; it’s about uncovering facets of the past that intrigue you and may potentially contribute to the broader understanding of history. Here are twenty in-depth tips that will guide you through the process and help you select the best topic for your history research paper.
- Understand the Assignment: Understanding your assignment’s requirements is the primary and most critical step in selecting a topic. Take time to carefully read the guidelines given by your instructor. Are there any specific historical periods, geographical regions, or themes you are required to focus on? Do the instructions indicate the scope or complexity level of the topic? Comprehending the parameters set by your instructor will significantly narrow down your options.
- Choose a Time Period: One way to approach the topic selection is by focusing on a particular time period that sparks your interest. It could be anything from the Bronze Age, to the Renaissance, to World War II. The more interested you are in the chosen time period, the more engaged you will be in the research process.
- Pick a Region: Similar to choosing a time period, selecting a particular region or country can also help narrow down potential topics. Are you fascinated by the history of East Asia, intrigued by ancient Egypt, or drawn to the socio-political history of Europe? Starting with a geographic focus can provide a strong foundation for your research.
- Identify a Theme: In addition to or instead of a time period or region, you might want to choose a theme that you wish to explore. Themes can range from political history, cultural history, history of science and technology, to gender history, among others. A thematic approach can offer a unique perspective and can even allow you to cross over different time periods or regions.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Even before you have a firm topic in hand, engage in some preliminary research. This could involve reviewing textbooks, scholarly articles, or reputable online resources related to your chosen period, region, or theme. Preliminary research can give you a general sense of the historical context and inspire potential topics.
- Seek Inspiration from Existing Works: As part of your preliminary research, look at other research papers, theses, or dissertations in your area of interest. This can give you a good idea of what has been done, what gaps exist in the research, and where your research could potentially fit in.
- Scope Your Topic: The scope of your topic should be proportionate to the length and depth of your paper. If your paper is relatively short, a narrow, focused topic would be more suitable. For a longer and more complex paper, a broader topic that explores multiple facets or perspectives would be more appropriate.
- Consider the Relevance: Another aspect to consider when selecting a topic is its relevance. Does the topic have any relation to the course you are undertaking? Does it reflect on current historical or social debates? A topic that connects your historical research to broader academic or social issues can make your paper more impactful and engaging.
- Look for Unique Angles: While not every research paper can revolutionize the field, striving for some degree of originality in your work is always a good practice. Look for unique angles, underexplored areas, or new perspectives on a well-trodden topic. Presenting a fresh approach can make your paper more interesting for both you and your readers.
- Assess the Availability of Sources: Your research paper is only as good as your sources. Before finalizing your topic, make sure there are enough primary and secondary sources available to you. This could be in the form of books, academic articles, documentary films, archives, databases, or digital resources.
- Evaluate the Feasibility: Beyond the availability of sources, consider other practical aspects of your chosen topic. Is it feasible to conduct the research within the given time frame? Is the topic too complex or too simplistic for your current academic level? A realistic evaluation of these factors at an early stage can save you a lot of time and effort down the line.
- Reflect on Your Interests: Above all, select a topic that genuinely piques your curiosity. A research paper is a significant undertaking, and your interest in the topic will sustain you through potential challenges. If you are passionate about the topic, it will reflect in your writing and make your paper more compelling.
- Solicit Feedback: Seek advice from your instructor, classmates, or any other knowledgeable individuals. They may be able to provide valuable feedback, point out potential pitfalls, or suggest different perspectives that can enrich your research.
- Be Flexible: Be prepared to tweak, adjust, or even overhaul your topic as you delve deeper into the research process. New information or insights may emerge that shift your focus or challenge your initial assumptions.
- Bridge the Past and Present: Try to find topics that allow you to connect historical events or phenomena with contemporary issues. This can provide additional depth to your paper and may also appeal to a broader audience.
- Consult Specialized Encyclopedias and Guides: These can provide overviews of various topics and can often suggest areas for research. They also offer bibliographies which can serve as a starting point for your research.
- Draft a Preliminary Thesis Statement: Once you have a potential topic, try drafting a preliminary thesis statement. This can help you focus your ideas and give you a clear direction for your research.
- Ensure Your Topic Meets the Assignment Goals: Check back with your assignment guidelines to make sure your chosen topic meets all the requirements. It’s a good idea to do this before you start your in-depth research.
- Be Ready to Invest Time and Effort: Choose a topic that you are ready to spend time on. Remember, you will be working on this topic for an extended period, so choose something that you find interesting and engaging.
- Enjoy the Process: Finally, remember that the process of researching and writing a history paper can be a source of enjoyment and intellectual satisfaction. Choose a topic that not only meets academic requirements but also gives you a sense of accomplishment and discovery.
Choosing the best history research paper topic is not merely about fulfilling an academic requirement. It’s about setting the stage for a journey into the past, an exploration of humanity’s collective memory. The right topic will not only make this journey enjoyable but also deeply enlightening. By considering these tips, you can select a topic that resonates with you and holds the potential for a meaningful scholarly contribution.
How to Write a Best History Research Paper
Writing a history research paper can be a rewarding experience, providing an opportunity to delve into the past and explore the events, ideas, and personalities that have shaped our world. However, crafting a high-quality paper requires more than just an interest in the subject matter. It involves thorough research, analytical thinking, and clear, persuasive writing. Here are twenty comprehensive tips on how to write a best history research paper.
- Understand the Assignment: Begin by thoroughly understanding the assignment. Ensure you grasp the requirements, the scope of the paper, the format, and the deadline. Clear any doubts with your professor or peers before you start.
- Select a Suitable Topic: As discussed earlier, choosing an appropriate topic is crucial. It should be engaging, manageable, and meet the assignment’s requirements. Consider your interests, the available resources, and the paper’s scope when choosing the topic.
- Conduct In-Depth Research: Once the topic is decided, embark on thorough research. Use a variety of sources, such as books, academic journals, credible online sources, primary sources, and documentaries. Remember to take notes and record the sources for citation purposes.
- Formulate a Thesis Statement: The thesis statement is the central argument or point of your paper. It should be clear, concise, and debatable, providing a roadmap for your entire paper. The thesis statement should guide your research and each main point you make in your paper should support this central idea.
- Create an Outline: An outline helps organize your thoughts and arguments. Typically, it should include an introduction (with the thesis statement), body paragraphs (with topic sentences), and a conclusion. Each point in your outline should be a reflection of your thesis statement.
- Start with a Strong Introduction: The introduction should be engaging, provide some background on the topic, and include the thesis statement. It sets the tone for the rest of your paper, so make it compelling and informative.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on one main idea that supports your thesis. Begin with a topic sentence, provide evidence or arguments, and then conclude the paragraph by linking it back to your thesis. Be clear and concise in your arguments.
- Use Evidence Effectively: Support your arguments with evidence from your research. This could include quotations, statistics, or primary source materials. Remember to interpret the evidence and explain its relevance to your argument.
- Maintain a Logical Flow: The ideas in your paper should flow logically from one point to the next. Use transitional words and phrases to maintain continuity and help guide your reader through your paper.
- Write a Compelling Conclusion: Your conclusion should sum up your main points, restate the thesis in light of the evidence provided, and possibly offer areas for further research or a concluding insight. It should leave the reader with something to think about.
- Cite Your Sources: Always cite your sources properly. This not only gives credit where it’s due but also strengthens your argument by indicating the breadth of your research. Ensure you follow the required citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Revise for Clarity and Coherence: After finishing your initial draft, revise your work. Check for clarity, coherence, and consistency of argument. Ensure each paragraph has a clear focus, and that the paragraphs flow smoothly from one idea to the next.
- Proofread: Proofread your paper for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors. Such errors can distract from the content and undermine your credibility as a writer. Reading your paper aloud or having someone else read it can help catch errors you might have missed.
- Seek Feedback: Before finalizing your paper, consider seeking feedback from your professor, peers, or a writing center tutor. They can provide valuable perspectives and suggestions for improvement that you might not have considered.
- Write in a Formal Academic Style: Your paper should be written in a formal academic style. Avoid slang, colloquialisms, and overly complex language. Be clear, concise, and precise in your expression.
- Avoid Plagiarism: Plagiarism is a serious academic offense. Ensure that all ideas and words that are not your own are properly cited. When in doubt, it’s better to over-cite than to under-cite.
- Stay Objective: A good history paper is objective and does not include personal opinions or biases. It relies on facts and evidence, and presents balanced arguments. Stick to the evidence and avoid emotional language.
- Be Original: Strive for originality in your argument and interpretation. While your topic might not be entirely new, your perspective on it can be. Don’t be afraid to challenge established interpretations if you have evidence to support your argument.
- Use Primary Sources Wisely: Primary sources are invaluable in historical research. However, remember that they should be used to support your argument, not to construct it. Your analysis and interpretation of the sources are what matters.
- Enjoy the Process: Finally, remember to enjoy the process. Writing a research paper is not just an academic exercise, but a journey into the past. It’s a chance to learn, explore, and contribute to our understanding of history.
In conclusion, writing a best history research paper requires careful planning, thorough research, clear writing, and detailed revision. However, the process can be highly rewarding, leading to new insights and a deeper understanding of history. These tips provide a comprehensive guide to help you craft a top-notch history research paper. Remember, history is a continually evolving dialogue, and your paper is your chance to join the conversation.
Custom Writing Services
When it comes to academic writing, particularly in the realm of history, the challenges are manifold. Selecting a suitable topic, conducting thorough research, forming persuasive arguments, and structuring your thoughts in a coherent and scholarly manner can often be a daunting task. This is where iResearchNet comes to your aid. As a premier academic writing service, iResearchNet provides students with the opportunity to order a custom history research paper on any topic. The goal is to alleviate your academic stress while ensuring that you meet your educational goals.
Key features of iResearchNet’s services include:
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers: Our team consists of professionals who are not just well-versed in various historical topics, but also have extensive experience in academic writing.
- Custom Written Works: Every paper we deliver is created from scratch, tailored to your specific requirements and instructions, ensuring originality and uniqueness.
- In-Depth Research: Our writers are committed to conducting meticulous and comprehensive research to gather relevant information and provide insightful perspectives for your paper.
- Custom Formatting: Whether your paper requires APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, or Harvard style, our team is proficient in all these citation formats.
- Top Quality: Quality is not negotiable for us. We strive to provide superior writing services that align with the highest academic standards.
- Customized Solutions: Every student is unique, and so are our solutions. We customize our approach based on your individual needs and the demands of your project.
- Flexible Pricing: We understand the financial constraints students may face, and therefore, we offer a variety of pricing plans to suit different budgets.
- Short Deadlines: We accept orders with deadlines as short as 3 hours, always delivering on time without compromising the quality of work.
- Timely Delivery: We understand the importance of meeting deadlines in academia and ensure timely delivery of all assignments.
- 24/7 Support: Our customer service team is available round the clock to assist you with any queries or issues you may have.
- Absolute Privacy: We maintain strict confidentiality and privacy policies to protect your personal information.
- Easy Order Tracking: With our seamless order tracking system, you can easily monitor the progress of your paper.
- Money Back Guarantee: We offer a money-back guarantee if our work does not meet the agreed-upon standards, giving you peace of mind when using our services.
In conclusion, iResearchNet offers a comprehensive suite of academic writing services designed to support students in their academic journey. From expert writers and custom written works to in-depth research and timely delivery, iResearchNet is equipped to handle any history research paper with excellence and dedication. We believe in delivering high-quality, original, and impactful research papers that can elevate your academic experience and success. So why wait? Avail of iResearchNet’s services today and experience the relief and satisfaction of handing in a top-quality history research paper.
You’re One Step Away From Your Perfect History Research Paper!
Students often find themselves at a crossroads when it comes to writing a history research paper. With so many topics to explore and limited time to do so, this can seem like an insurmountable challenge. But it doesn’t have to be. iResearchNet is here to transform this challenge into a remarkable academic journey.
Imagine handing in a meticulously researched and perfectly structured history research paper, crafted by an expert writer with a deep understanding of your topic. Picture the relief as you submit a top-quality assignment, knowing that you’ve fulfilled all the requirements to the highest standard. And visualize the sense of achievement when you receive the grade you’ve been striving for.
This is more than a possibility – it’s a reality with iResearchNet. Our expert writing services provide a path to academic success that’s both straightforward and stress-free. You can say goodbye to the anxiety of looming deadlines and the stress of achieving the perfect balance in your paper.
Why waste precious time and energy struggling with complex historical data, grappling with the perfect argument, or wrestling with formatting guidelines? Instead, invest in your future with iResearchNet, where we turn your academic challenges into milestones of success.
So, are you ready to excel in your history research paper and make a lasting impression on your professors? Click on the order button, provide your paper details, and let our expert writers do the rest. Success in your history class is just a click away with iResearchNet!
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

MDMA (Ecstasy/Molly)

- MDMA, also called Molly or Ecstasy, is a lab-made (synthetic) drug that has effects similar to stimulants like methamphetamine. Some researchers and organizations consider MDMA to be a psychedelic drug because it can also mildly alter visual and time perception.
- MDMA’s effects may include feeling more energetic and alert and having an increased sense of well-being, warmth, and openness toward others.
- However, MDMA can also cause a number of negative health effects. For example, while deaths from MDMA are rare, overdoses can potentially be life threatening—with symptoms including high blood pressure, faintness, panic attacks, and in severe cases, a loss of consciousness and seizures.
MDMA (Ecstasy) Abuse Research Report
Describes the science behind MDMA (ecstasy) abuse, including what it does to the brain, whether it is addictive, and the latest research regarding prevention and treatment of MDMA.
Latest from NIDA
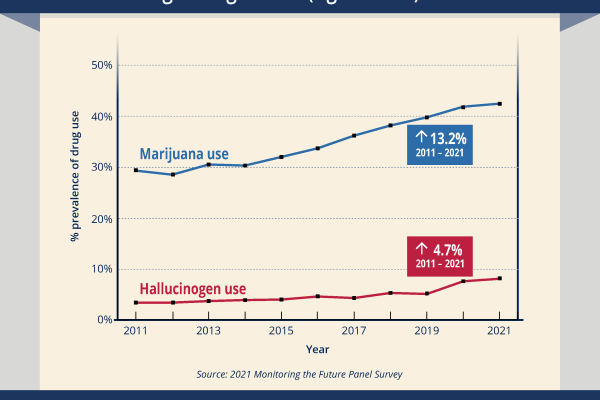
Marijuana and hallucinogen use among young adults reached all time-high in 2021
Find more resources on mdma.
- Find basic information from MedlinePlus , a service of NIH’s National Library of Medicine (NLM).
- Learn more about MDMA from the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
- Read more about MDMA research from the National Institutes of Health.

COMMENTS
Greek Jewelry and Adornment: Materials, Designs, and Symbolism. Greek Textile Art: Weaving, Dyeing, and Pattern-making. The comprehensive list of ancient Greece research paper topics provides students with a wide range of fascinating subjects to explore within the realm of Greek history, culture, and civilization.
The Byzantine Greek-speaking part of the empire continued until it fell to the Ottoman Turks about a millennium later in 1453. Topics in the History of Ancient Greece, including the major wars, government, conquerors, and lay of the land.
BBC Ancient Greece: The Greatest Show on Earth. The presenter of this video talks about the importance of theater culture to the people of ancient Athens. In the days of the ancient Greeks, the people of Athens learned the latest news from theatrical […] The Architecture of Ancient Greece Found in Los Angeles.
The term Ancient, or Archaic, Greece refers to the years 700-480 B.C. The period is known for its art, architecture and philosophy. Ancient Greece saw advances in art, poetry and technology, and ...
Ancient Greek civilization, the period following Mycenaean civilization, which ended about 1200 BCE, to the death of Alexander the Great, in 323 BCE. It was a period of political, philosophical, artistic, and scientific achievements that formed a legacy with unparalleled influence on Western civilization.
The Acropolis, Athens. ancient Greek civilization, The period between the end of the Mycenaean civilization (1200 bce) and the death of Alexander the Great (323 bce) that significantly influenced later Western culture in politics, philosophy, and art. Little is known about the earliest period of ancient Greek civilization, and many extant ...
The gradual elimination of deities and a quest for accurate and reliable sources from historians such as Herodotus, Thucydides, and Polybius shaped the writing and reporting of history in Greece. The historiography of Ancient Greece arguably traces its roots back to the bards who would recite epic tales most notably the ones accredited to Homer.
They lived in a world of constant economic crises, wars, destruction of entire cities, and social instability. The remedies for these pressing problems and their causes were the subject of public deliberation and theoretical reflection in the constant search for a more stable and viable existence. To seek answers in ancient Greece to the kind ...
Greek History - Volume 69 Issue 2. ... which offer an excellent overview of past scholarship and new paths of research. A third important topic is that of the changing history of statuses like those of Lacedaemonian perioikoi and Athenian metics. Finally, the volume includes a series of excellent essays on slavery in Hellenistic Greece, which ...
Publisher's Preview. This is an ambitious and extremely wide-ranging introduction to almost every aspect of ancient Greek studies encompassing a timespan from the Bronze Age to 31 BC and utilising approaches from archaeology, history, literature, art, philosophy and reception studies. The introduction does not claim to provide a narrative of ...
History of Archaic and Classical Greece | Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on ANCIENT GREEK HISTORY. Find methods information, sources ...
The topic is a vital segment of the art historical timeline and the information provided is timeless. ... Strong and content as expected with research and references. Relevance/Longevity rating: 5 covers topics as expected ... It is assumed that the reader has already been exposed to Greek history and literature, as in the first paragraph of ...
From ancient Greece to now, the bravado of athletes transcends centuries. Peter J. Miller, University of Winnipeg. Without the internet, television, radio or any widespread means of communication ...
Hera (Juno): the queen of the gods and goddess of women and marriage. Aphrodite (Venus): goddess of beauty and love. Apollo (Apollo): god of prophesy, music and poetry and knowledge. Ares (Mars ...
on these questions, and trying to identify other huge black holes in the study of Greek. history, has a value of its own. The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens, edited by Jenifer Neils and ...
Browse Greek history news, research and analysis from The Conversation Greek history - News, Research and Analysis - The Conversation - page 1 Menu Close
Dark Age is the period in Greek history between 1200 BC and 800 BC. During this period, the Greek generations passed on tales from the poems of Homer. It is believed that Homer was blind and hence the name "dark age.". The Dark Age symbolizes the fall of civilization. In this duration, there was famine, little trade with foreigners and the ...
View sample Ancient Greece research paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of history research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a history research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A!
Embarking on a journey through the labyrinth of ancient history research paper topics, this comprehensive guide has been expertly crafted for students tasked with writing a research paper in history.The page unveils an extensive array of 100 topics, divided into ten distinct categories, thus providing a wealth of options for exploration.
ISBN: 9780810863125. Publication Date: 2009. This reference work explores the modern history of Greece through a chronology, an introductory essay, a bibliography, and hundreds of cross-referenced dictionary entries on important persons, places, events, and institutions, as well as on significant political, economic, social, and cultural aspects.
A report on Greek history education. October 2019. History Education Research Journal 16 (2):179-181. Authors: George Kokkinos. Discover the world's research.
122 Greek Mythology Essay Topics & Examples. Welcome to our list of Greek mythology essay topics! In you need good title ideas for your history paper or project, look no further. Here, you will find Greek mythology research topics that will help you learn more about gods like Zeus and Aphrodite. Check them out!
Get 10% OFF with 24START discount code. Ancient History Topics. The Causes and Effects of the Fall of the Roman Empire. Daily Life in Ancient Egypt. The Influence of Alexander the Great's Conquests on the Hellenistic World. The Role of Women in Spartan Society.
MDMA, also called Molly or Ecstasy, is a lab-made (synthetic) drug that has effects similar to stimulants like methamphetamine. Some researchers and organizations consider MDMA to be a psychedelic drug because it can also mildly alter visual and time perception.; MDMA's effects may include feeling more energetic and alert and having an increased sense of well-being, warmth, and openness ...
The British poet Lord Byron arrived in Greece on Christmas Eve 1823 to join the country's fight for independence from the Ottoman Empire. A mere hundred days later, on April 19, 1824, he died ...