
- 235,491 Views

HOW TO WRITE CHAPTER THREE OF YOUR RESEARCH PROJECT (RESEARCH METHODOLOGY) | ResearchWap Blog
- Posted: Friday, 17 April 2020
- By: ResearchWap Admin
How To Write Chapter Three Of Your Research Project (Research Methodology)
Methodology In Research Paper
Chapter three of the research project or the research methodology is another significant part of the research project writing. In developing the chapter three of the research project, you state the purpose of research, research method you wish to adopt, the instruments to be used, where you will collect your data, types of data collection, and how you collected it.
This chapter explains the different methods to be used in the research project. Here you mention the procedures and strategies you will employ in the study such as research design, study design in research, research area (area of the study), the population of the study, etc.
You also tell the reader your research design methods, why you chose a particular method, method of analysis, how you planned to analyze your data. Your methodology should be written in a simple language such that other researchers can follow the method and arrive at the same conclusion or findings.
You can choose a survey design when you want to survey a particular location or behavior by administering instruments such as structured questionnaires, interviews, or experimental; if you intend manipulating some variables.
The purpose of chapter three (research methodology) is to give an experienced investigator enough information to replicate the study. Some supervisors do not understand this and require students to write what is in effect, a textbook.
A research design is used to structure the research and to show how all of the major parts of the research project, including the sample, measures, and methods of assignment, work together to address the central research questions in the study. The chapter three should begin with a paragraph reiterating the purpose of research.
It is very important that before choosing design methods, try and ask yourself the following questions:
Will I generate enough information that will help me to solve the research problem by adopting this method?
Method vs Methodology
I think the most appropriate in methods versus methodology is to think in terms of their inter-connectedness and relationship between both. You should not beging thinking so much about research methods without thinking of developing a research methodology.
Metodologia or methodology is the consideration of your research objectives and the most effective method and approach to meet those objectives. That is to say that methodology in research paper is the first step in planning a research project work.
Design Methodology: Methodological Approach
Example of methodology in research paper, you are attempting to identify the influence of personality on a road accident, you may wish to look at different personality types, you may also look at accident records from the FRSC, you may also wish to look at the personality of drivers that are accident victims, once you adopt this method, you are already doing a survey, and that becomes your metodologia or methodology .
Your methodology should aim to provide you with the information to allow you to come to some conclusions about the personalities that are susceptible to a road accident or those personality types that are likely to have a road accident. The following subjects may or may not be in the order required by a particular institution of higher education, but all of the subjects constitute a defensible in metodologia or methodology chapter.
READ ALSO: HOW TO WRITE EFFECTIVE RESEARCH PROJECT ABSTRACT
Methodology
A methodology is the rationale for the research approach, and the lens through which the analysis occurs. Said another way, a methodology describes the “general research strategy that outlines the way in which research is to be undertaken” The methodology should impact which method(s) for a research endeavor are selected in order to generate the compelling data.
Example Of Methodology In Research Paper :
- Phenomenology: describes the “lived experience” of a particular phenomenon
- Ethnography: explores the social world or culture, shared beliefs and behaviors
- Participatory: views the participants as active researchers
- Ethno methodology: examines how people use dialogue and body language to construct a world view
- Grounding theory*: assumes a blank slate and uses an inductive approach to develop a new theory
A method is simply the tool used to answer your research questions — how, in short, you will go about collecting your data.
Methods Section Of Research Paper Example :
- Contextual inquiry
- Usability study
- Diary study
If you are choosing among these, you might say “what method should I use?” and settle on one or more methods to answer your research question.
READ ALSO: HOW TO DEVELOP EFFECTIVE AND UNIQUE PROJECT TOPICS
Research Design Definition: WRITING A RESEARCH DESIGN
A qualitative study does not have variables. A scientific study has variables, which are sometimes mentioned in Chapter 1 and defined in more depth in Chapter 3. Spell out the independent and dependent, variables. An unfortunate trend in some institutions is to repeat the research questions and/or hypotheses in both Chapter 1 and Chapter 3. Sometimes an operational statement of the research hypotheses in the null form is given to set the stage for later statistical inferences. In a quantitative study, state the level of significance that will be used to accept or reject the hypotheses.
Pilot Study
In a quantitative study, a survey instrument that the researcher designed needs a pilot study to validate the effectiveness of the instrument, and the value of the questions to elicit the right information to answer the primary research questions in. In a scientific study, a pilot study may precede the main observation to correct any problems with the instrumentation or other elements in the data collection technique. Describe the pilot study as it relates to the research design, development of the instrument, data collection procedures, or characteristics of the sample.
Instruments
In a research study, the instrument used to collect data may be created by the researcher or based on an existing instrument. If the instrument is the researcher created, the process used to select the questions should be described and justified. If an existing instrument is used, the background of the instrument is described including who originated it, and what measures were used to validate it.
If a Likert scale is used, the scale should be described. If the study involves interviews, an interview protocol should be developed that will result in a consistent process of data collection across all interviews. Two types of questions are found in an interview protocol: the primary research questions, which are not asked of the participants, and the interview questions that are based on the primary research questions and are asked of the participants.
In a qualitative study, this is the section where most of the appendices are itemized, starting with letters of permission to conduct the study and letters of invitation to participate with the attached consent forms. Sample: this has to do with the number of your participants or subjects as the case may be. Analysis (how are you planning to analyze the results?)
ALSO READ: TRENDING PROJECT TOPICS FOR FINAL YEAR STUDENTS AT A GLANCE
EFFECTIVE GUIDE AND METHODOLOGY SAMPLES
This chapter deals effectively with the research methods to be adopted in conducting the research, and it is organized under the following sub-headings:
- Research Design
- Area of Study
The population of the Study
- Sample and Sampling Techniques
- Instruments for Data Collection
The validity of the Instrument
Reliability of the Instrument
- Administration of the instruments
- Scoring the instruments
Method of Data Collection
Method of Data Analysis
Research Design:
This has to do with the structure of the research instrument to be used in collecting data. It could be in sections depending on different variables that form the construct for the entire topic of the research problems. A reliable instrument with a wrong research design will adversely affect the reliability and generalization of the research. The choice of design suitable for each research is determined by many factors among which are: kind of research, research hypothesis, the scope of the research, and the sensitive nature of the research.
Area of Study:
Research Area; this has to do with the geographical environment of the study area where the places are located, the historical background when necessary and commercial activities of that geographical area. For example, the area of the study is Ebonyi State University. At the creation of Ebonyi State in 1996, the Abakaliki campus of the then ESUT was upgraded to Ebonyi State University College by Edict no. 5 of Ebonyi State, 1998 still affiliated to ESUT with Prof. Fidelis Ogah, former ESUT Deputy Vice-Chancellor as the first Rector. In 1997, the Faculty of Applied and Natural Sciences with 8 departments was added to the fledging University, and later in 1998 when the ESUT Pre-Science Programme was relocated to Nsukka, the EBSUC Pre-Degree School commenced lectures in both Science and Arts in replacement of the former. This study focused on the students of the Business Education department in Ebonyi state university.
The population is regarded in research work as the type of people and the group of people under investigation. It has to be specific or specified. For example educational study teachers in Lagos state. Once the population is chosen, the next thing is to choose the samples from the population.
According to Uma (2007), the population is referred to as the totality of items or object which the researcher is interested in. It can also be the total number of people in an area of study. Hence, the population of this study comprised of all the students in the department of Business Education, Ebonyi State University which is made up of year one to four totaling 482. The actual number for the study was ascertained using Yaro-Yamane's formula which stated thus:
n = N
N is the Population
1 is constant
e is the error margin
Then, n = 482
1+482(0.05)2
= 214.35 approximately 214
Sample and sampling technique:
It may not be possible to reach out to the number of people that form the entire population for the study to either interview, observe, or serve them with copies of the questionnaire. To be realistic, the sample should be up to 20% of the total population. Two sampling techniques are popular among all the sampling techniques. These are random and stratified random sampling techniques. (A). in Random Sampling, the writers select any specific number from a place like a school, village, etc. (B). In Stratified Random Sampling, one has to indicate a specific number from a stratum which could be a group of people according to age, qualification, etc. or different groups from different locations and different considerations attached.
Instruments for Data Collection:
This is a device or different devices used in collecting data. Example: interview, questionnaire, checklist, etc. instrument is prepared in sets or subsections, each set should be an entity thus asking questions about a particular variable to be tested after collecting data. The type of instrument used will determine the responses expected. All questions should be well set so as to determine the reliability of the instrument.
This has to do with different measures in order to determine the validity and reliability of the research instrument. For example, presenting the drafted questionnaire to the supervisor for scrutiny. Giving the questionnaire to the supervisor for useful comments and corrections would help to validate the instrument.
The test-retest reliability method is one of the simplest ways of testing the stability and reliability of an instrument over time. The test-retest approach was adopted by the researcher in establishing the reliability of the instrument. In doing this 25 copies of the questionnaire were administered on twenty-five selected respondents. After two weeks another 25 copies of the same questionnaire were re-administered on the same group. Their responses on the two occasions were correlated using Parsons Product Moment Correlation. A co-efficient of 0.81 was gotten and this was high enough to consider the instrument reliable.
Administration of the instruments:
Here, the writer states whether he or she administers the test personally or through an assistant. He also indicates the rate of return of the copies of the questionnaire administered.
Scoring the instruments:
Here items on the questionnaire or any other device used must be assigned numerical values. For example, 4 points to strongly agree, 3 points to agree, 2 points to disagree, and 1 point to strongly disagree.
Table of Analysis
The researcher collected data using the questionnaire. Copies of the questionnaire were administered by the researcher on the respondents. All the respondents were expected to give maximum co-operation, as the information on the questionnaire is all on things that revolve around their study. Hence, enough time was taken to explain how to tick or indicate their opinion on the items stated in the research questionnaire.
In this study, the mean was used to analyze the data collected. A four (4) point Likert scale was used to analyze each of the questionnaire items.
The weighing was as follows:
VGE—————- Very Great Extent (4 points)
GE—————– Great Extent (3 points)
LE—————– Little Extent (2 points)
VLE—————- Very Little Extent (1 point)
SA—————– Strongly Agree (4 points)
A——————- Agree (3 points)
D—————— Disagree (2 points)
SD—————- Strongly Disagree (1 point)
The mean of the scale will then be determined by summing up the points and dividing their number as follows with the formula:
Where; x= mean
f= frequency
X= Nominal value of the option
∑= summation
N= Total Number
Therefore, the mean of the scale is 2.5.
This means that any item statement with a mean of 2.50 and above is considered agreed by the respondents and any item statement below 2.5 is considered disagreed.
EDITORS SOURCE: How To Write Chapter Three Of Your Research Project (Research Methodology)
Tags: Research project, chapter three, methodology, project topics,
Project Categories
- AFRICAN LANGUAGES AND LINGUISTIC
- ACCOUNTING EDUCATION
- ACTUARIAL SCIENCE
- ADULT EDUCATION
- AGRICULTURAL ECONOMICS
- AGRICULTURAL EXTENSION
- ANIMAL SCIENCE
- ARCHITECTURE
- BANKING AND FINANCE
- BIBLICAL AND THEOLOGY
- BIOCHEMISTRY
- BREWING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- BUILDING TECHNOLOGY
- BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION
- BUSINESS EDUCATION
SEE MORE PROJECT CATEGORIES
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved researchwap.com - Free Project Topics, Research Materials, and Academic Resources
Chapter 3 The Research Process
In Chapter 1, we saw that scientific research is the process of acquiring scientific knowledge using the scientific method. But how is such research conducted? This chapter delves into the process of scientific research, and the assumptions and outcomes of the research process.
Paradigms of Social Research
Our design and conduct of research is shaped by our mental models or frames of references that we use to organize our reasoning and observations. These mental models or frames (belief systems) are called paradigms. The word “paradigm” was popularized by
Thomas Kuhn (1962) in his book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, where he examined the history of the natural sciences to identify patterns of activities that shape the progress of science. Similar ideas are applicable to social sciences as well, where a social reality can be viewed by different people in different ways, which may constrain their thinking and reasoning about the observed phenomenon. For instance, conservatives and liberals tend to have very different perceptions of the role of government in people’s lives, and hence, have different opinions on how to solve social problems. Conservatives may believe that lowering taxes is the best way to stimulate a stagnant economy because it increases people’s disposable income and spending, which in turn expands business output and employment. In contrast, liberals may believe that governments should invest more directly in job creation programs such as public works and infrastructure projects, which will increase employment and people’s ability to consume and drive the economy. Likewise, Western societies place greater emphasis on individual rights, such as one’s right to privacy, right of free speech, and right to bear arms. In contrast, Asian societies tend to balance the rights of individuals against the rights of families, organizations, and the government, and therefore tend to be more communal and less individualistic in their policies. Such differences in perspective often lead Westerners to criticize Asian governments for being autocratic, while Asians criticize Western societies for being greedy, having high crime rates, and creating a “cult of the individual.” Our personal paradigms are like “colored glasses” that govern how we view the world and how we structure our thoughts about what we see in the world.
Paradigms are often hard to recognize, because they are implicit, assumed, and taken for granted. However, recognizing these paradigms is key to making sense of and reconciling differences in people’ perceptions of the same social phenomenon. For instance, why do liberals believe that the best way to improve secondary education is to hire more teachers, but conservatives believe that privatizing education (using such means as school vouchers) are more effective in achieving the same goal? Because conservatives place more faith in competitive markets (i.e., in free competition between schools competing for education dollars), while liberals believe more in labor (i.e., in having more teachers and schools). Likewise, in social science research, if one were to understand why a certain technology was successfully implemented in one organization but failed miserably in another, a researcher looking at the world through a “rational lens” will look for rational explanations of the problem such as inadequate technology or poor fit between technology and the task context where it is being utilized, while another research looking at the same problem through a “social lens” may seek out social deficiencies such as inadequate user training or lack of management support, while those seeing it through a “political lens” will look for instances of organizational politics that may subvert the technology implementation process. Hence, subconscious paradigms often constrain the concepts that researchers attempt to measure, their observations, and their subsequent interpretations of a phenomenon. However, given the complex nature of social phenomenon, it is possible that all of the above paradigms are partially correct, and that a fuller understanding of the problem may require an understanding and application of multiple paradigms.
Two popular paradigms today among social science researchers are positivism and post-positivism. Positivism , based on the works of French philosopher Auguste Comte (1798-1857), was the dominant scientific paradigm until the mid-20 th century. It holds that science or knowledge creation should be restricted to what can be observed and measured. Positivism tends to rely exclusively on theories that can be directly tested. Though positivism was originally an attempt to separate scientific inquiry from religion (where the precepts could not be objectively observed), positivism led to empiricism or a blind faith in observed data and a rejection of any attempt to extend or reason beyond observable facts. Since human thoughts and emotions could not be directly measured, there were not considered to be legitimate topics for scientific research. Frustrations with the strictly empirical nature of positivist philosophy led to the development of post-positivism (or postmodernism) during the mid-late 20 th century. Post-positivism argues that one can make reasonable inferences about a phenomenon by combining empirical observations with logical reasoning. Post-positivists view science as not certain but probabilistic (i.e., based on many contingencies), and often seek to explore these contingencies to understand social reality better. The post -positivist camp has further fragmented into subjectivists , who view the world as a subjective construction of our subjective minds rather than as an objective reality, and critical realists , who believe that there is an external reality that is independent of a person’s thinking but we can never know such reality with any degree of certainty.
Burrell and Morgan (1979), in their seminal book Sociological Paradigms and Organizational Analysis, suggested that the way social science researchers view and study social phenomena is shaped by two fundamental sets of philosophical assumptions: ontology and epistemology. Ontology refers to our assumptions about how we see the world, e.g., does the world consist mostly of social order or constant change. Epistemology refers to our assumptions about the best way to study the world, e.g., should we use an objective or subjective approach to study social reality. Using these two sets of assumptions, we can categorize social science research as belonging to one of four categories (see Figure 3.1).
If researchers view the world as consisting mostly of social order (ontology) and hence seek to study patterns of ordered events or behaviors, and believe that the best way to study such a world is using objective approach (epistemology) that is independent of the person conducting the observation or interpretation, such as by using standardized data collection tools like surveys, then they are adopting a paradigm of functionalism . However, if they believe that the best way to study social order is though the subjective interpretation of participants involved, such as by interviewing different participants and reconciling differences among their responses using their own subjective perspectives, then they are employing an interpretivism paradigm. If researchers believe that the world consists of radical change and seek to understand or enact change using an objectivist approach, then they are employing a radical structuralism paradigm. If they wish to understand social change using the subjective perspectives of the participants involved, then they are following a radical humanism paradigm.

Figure 3.1. Four paradigms of social science research (Source: Burrell and Morgan, 1979)

Figure 3.2. Functionalistic research process
The first phase of research is exploration . This phase includes exploring and selecting research questions for further investigation, examining the published literature in the area of inquiry to understand the current state of knowledge in that area, and identifying theories that may help answer the research questions of interest.
The first step in the exploration phase is identifying one or more research questions dealing with a specific behavior, event, or phenomena of interest. Research questions are specific questions about a behavior, event, or phenomena of interest that you wish to seek answers for in your research. Examples include what factors motivate consumers to purchase goods and services online without knowing the vendors of these goods or services, how can we make high school students more creative, and why do some people commit terrorist acts. Research questions can delve into issues of what, why, how, when, and so forth. More interesting research questions are those that appeal to a broader population (e.g., “how can firms innovate” is a more interesting research question than “how can Chinese firms innovate in the service-sector”), address real and complex problems (in contrast to hypothetical or “toy” problems), and where the answers are not obvious. Narrowly focused research questions (often with a binary yes/no answer) tend to be less useful and less interesting and less suited to capturing the subtle nuances of social phenomena. Uninteresting research questions generally lead to uninteresting and unpublishable research findings.
The next step is to conduct a literature review of the domain of interest. The purpose of a literature review is three-fold: (1) to survey the current state of knowledge in the area of inquiry, (2) to identify key authors, articles, theories, and findings in that area, and (3) to identify gaps in knowledge in that research area. Literature review is commonly done today using computerized keyword searches in online databases. Keywords can be combined using “and” and “or” operations to narrow down or expand the search results. Once a shortlist of relevant articles is generated from the keyword search, the researcher must then manually browse through each article, or at least its abstract section, to determine the suitability of that article for a detailed review. Literature reviews should be reasonably complete, and not restricted to a few journals, a few years, or a specific methodology. Reviewed articles may be summarized in the form of tables, and can be further structured using organizing frameworks such as a concept matrix. A well-conducted literature review should indicate whether the initial research questions have already been addressed in the literature (which would obviate the need to study them again), whether there are newer or more interesting research questions available, and whether the original research questions should be modified or changed in light of findings of the literature review. The review can also provide some intuitions or potential answers to the questions of interest and/or help identify theories that have previously been used to address similar questions.
Since functionalist (deductive) research involves theory-testing, the third step is to identify one or more theories can help address the desired research questions. While the literature review may uncover a wide range of concepts or constructs potentially related to the phenomenon of interest, a theory will help identify which of these constructs is logically relevant to the target phenomenon and how. Forgoing theories may result in measuring a wide range of less relevant, marginally relevant, or irrelevant constructs, while also minimizing the chances of obtaining results that are meaningful and not by pure chance. In functionalist research, theories can be used as the logical basis for postulating hypotheses for empirical testing. Obviously, not all theories are well-suited for studying all social phenomena. Theories must be carefully selected based on their fit with the target problem and the extent to which their assumptions are consistent with that of the target problem. We will examine theories and the process of theorizing in detail in the next chapter.
The next phase in the research process is research design . This process is concerned with creating a blueprint of the activities to take in order to satisfactorily answer the research questions identified in the exploration phase. This includes selecting a research method, operationalizing constructs of interest, and devising an appropriate sampling strategy.
Operationalization is the process of designing precise measures for abstract theoretical constructs. This is a major problem in social science research, given that many of the constructs, such as prejudice, alienation, and liberalism are hard to define, let alone measure accurately. Operationalization starts with specifying an “operational definition” (or “conceptualization”) of the constructs of interest. Next, the researcher can search the literature to see if there are existing prevalidated measures matching their operational definition that can be used directly or modified to measure their constructs of interest. If such measures are not available or if existing measures are poor or reflect a different conceptualization than that intended by the researcher, new instruments may have to be designed for measuring those constructs. This means specifying exactly how exactly the desired construct will be measured (e.g., how many items, what items, and so forth). This can easily be a long and laborious process, with multiple rounds of pretests and modifications before the newly designed instrument can be accepted as “scientifically valid.” We will discuss operationalization of constructs in a future chapter on measurement.
Simultaneously with operationalization, the researcher must also decide what research method they wish to employ for collecting data to address their research questions of interest. Such methods may include quantitative methods such as experiments or survey research or qualitative methods such as case research or action research, or possibly a combination of both. If an experiment is desired, then what is the experimental design? If survey, do you plan a mail survey, telephone survey, web survey, or a combination? For complex, uncertain, and multi-faceted social phenomena, multi-method approaches may be more suitable, which may help leverage the unique strengths of each research method and generate insights that may not be obtained using a single method.
Researchers must also carefully choose the target population from which they wish to collect data, and a sampling strategy to select a sample from that population. For instance, should they survey individuals or firms or workgroups within firms? What types of individuals or firms they wish to target? Sampling strategy is closely related to the unit of analysis in a research problem. While selecting a sample, reasonable care should be taken to avoid a biased sample (e.g., sample based on convenience) that may generate biased observations. Sampling is covered in depth in a later chapter.
At this stage, it is often a good idea to write a research proposal detailing all of the decisions made in the preceding stages of the research process and the rationale behind each decision. This multi-part proposal should address what research questions you wish to study and why, the prior state of knowledge in this area, theories you wish to employ along with hypotheses to be tested, how to measure constructs, what research method to be employed and why, and desired sampling strategy. Funding agencies typically require such a proposal in order to select the best proposals for funding. Even if funding is not sought for a research project, a proposal may serve as a useful vehicle for seeking feedback from other researchers and identifying potential problems with the research project (e.g., whether some important constructs were missing from the study) before starting data collection. This initial feedback is invaluable because it is often too late to correct critical problems after data is collected in a research study.
Having decided who to study (subjects), what to measure (concepts), and how to collect data (research method), the researcher is now ready to proceed to the research execution phase. This includes pilot testing the measurement instruments, data collection, and data analysis.
Pilot testing is an often overlooked but extremely important part of the research process. It helps detect potential problems in your research design and/or instrumentation (e.g., whether the questions asked is intelligible to the targeted sample), and to ensure that the measurement instruments used in the study are reliable and valid measures of the constructs of interest. The pilot sample is usually a small subset of the target population. After a successful pilot testing, the researcher may then proceed with data collection using the sampled population. The data collected may be quantitative or qualitative, depending on the research method employed.
Following data collection, the data is analyzed and interpreted for the purpose of drawing conclusions regarding the research questions of interest. Depending on the type of data collected (quantitative or qualitative), data analysis may be quantitative (e.g., employ statistical techniques such as regression or structural equation modeling) or qualitative (e.g., coding or content analysis).
The final phase of research involves preparing the final research report documenting the entire research process and its findings in the form of a research paper, dissertation, or monograph. This report should outline in detail all the choices made during the research process (e.g., theory used, constructs selected, measures used, research methods, sampling, etc.) and why, as well as the outcomes of each phase of the research process. The research process must be described in sufficient detail so as to allow other researchers to replicate your study, test the findings, or assess whether the inferences derived are scientifically acceptable. Of course, having a ready research proposal will greatly simplify and quicken the process of writing the finished report. Note that research is of no value unless the research process and outcomes are documented for future generations; such documentation is essential for the incremental progress of science.
Common Mistakes in Research
The research process is fraught with problems and pitfalls, and novice researchers often find, after investing substantial amounts of time and effort into a research project, that their research questions were not sufficiently answered, or that the findings were not interesting enough, or that the research was not of “acceptable” scientific quality. Such problems typically result in research papers being rejected by journals. Some of the more frequent mistakes are described below.
Insufficiently motivated research questions. Often times, we choose our “pet” problems that are interesting to us but not to the scientific community at large, i.e., it does not generate new knowledge or insight about the phenomenon being investigated. Because the research process involves a significant investment of time and effort on the researcher’s part, the researcher must be certain (and be able to convince others) that the research questions they seek to answer in fact deal with real problems (and not hypothetical problems) that affect a substantial portion of a population and has not been adequately addressed in prior research.
Pursuing research fads. Another common mistake is pursuing “popular” topics with limited shelf life. A typical example is studying technologies or practices that are popular today. Because research takes several years to complete and publish, it is possible that popular interest in these fads may die down by the time the research is completed and submitted for publication. A better strategy may be to study “timeless” topics that have always persisted through the years.
Unresearchable problems. Some research problems may not be answered adequately based on observed evidence alone, or using currently accepted methods and procedures. Such problems are best avoided. However, some unresearchable, ambiguously defined problems may be modified or fine tuned into well-defined and useful researchable problems.
Favored research methods. Many researchers have a tendency to recast a research problem so that it is amenable to their favorite research method (e.g., survey research). This is an unfortunate trend. Research methods should be chosen to best fit a research problem, and not the other way around.
Blind data mining. Some researchers have the tendency to collect data first (using instruments that are already available), and then figure out what to do with it. Note that data collection is only one step in a long and elaborate process of planning, designing, and executing research. In fact, a series of other activities are needed in a research process prior to data collection. If researchers jump into data collection without such elaborate planning, the data collected will likely be irrelevant, imperfect, or useless, and their data collection efforts may be entirely wasted. An abundance of data cannot make up for deficits in research planning and design, and particularly, for the lack of interesting research questions.
- Social Science Research: Principles, Methods, and Practices. Authored by : Anol Bhattacherjee. Provided by : University of South Florida. Located at : http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/oa_textbooks/3/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Welcome to Chapter 3
Chapter 3 Webinars
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Developing the Quantitative Research Design
- Qualitative Descriptive Design
- Qualitative Narrative Inquiry Research
- SAGE Research Methods
- Alignment of Dissertation Components for DIS-9902ABC
- IRB Resources This link opens in a new window
- Research Examples (SAGE) This link opens in a new window
- Dataset Examples (SAGE) This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
Need help ask us.

Was this resource helpful?
- Next: Developing the Quantitative Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Nov 2, 2023 10:17 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1007179

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Discrimination Experiences Shape Most Asian Americans’ Lives
3. asian americans and the ‘model minority’ stereotype, table of contents.
- Key findings from the survey
- Most Asian Americans have been treated as foreigners in some way, no matter where they were born
- Most Asian Americans have been subjected to ‘model minority’ stereotypes, but many haven’t heard of the term
- Experiences with other daily and race-based discrimination incidents
- In their own words: Key findings from qualitative research on Asian Americans and discrimination experiences
- Discrimination in interpersonal encounters with strangers
- Racial discrimination at security checkpoints
- Encounters with police because of race or ethnicity
- Racial discrimination in the workplace
- Quality of service in restaurants and stores
- Discrimination in neighborhoods
- Experiences with name mispronunciation
- Discrimination experiences of being treated as foreigners
- In their own words: How Asian Americans would react if their friend was told to ‘go back to their home country’
- Awareness of the term ‘model minority’
- Views of the term ‘model minority’
- How knowledge of Asian American history impacts awareness and views of the ‘model minority’ label
- Most Asian Americans have experienced ‘model minority’ stereotypes
- In their own words: Asian Americans’ experiences with the ‘model minority’ stereotype
- Asian adults who personally know an Asian person who has been threatened or attacked since COVID-19
- In their own words: Asian Americans’ experiences with discrimination during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Experiences with talking about racial discrimination while growing up
- Is enough attention being paid to anti-Asian racism in the U.S.?
- Acknowledgments
- Sample design
- Data collection
- Weighting and variance estimation
- Methodology: 2021 focus groups of Asian Americans
- Appendix: Supplemental tables
In the survey, we asked Asian Americans about their views and experiences with another stereotype: Asians in the U.S. being a “model minority.” Asian adults were asked about their awareness of the label “model minority,” their views on whether the term is a good or bad thing, and their experiences with being treated in ways that reflect the stereotype.
What is the ‘model minority’ stereotype?
Amid the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s, another narrative about Asian Americans became widespread: being characterized as a “model” minority. In 1966, two articles were published in The New York Times Magazine and U.S. News and World Report that portrayed Japanese and Chinese Americans as examples of successful minorities. Additionally, in 1987 Time magazine published a cover story on “those Asian American whiz kids.” The model minority stereotype has characterized the nation’s Asian population as high-achieving economically and educationally, which has been attributed to Asians being hardworking and deferential to parental and authority figures, among other factors. The stereotype generalizes Asians in the U.S. as intelligent, well-off, and able to excel in fields such as math and science. Additionally, the model minority myth positions Asian Americans in comparison with other non-White groups such as Black and Hispanic Americans.
For many Asians living in the United States, these characterizations do not align with their lived experiences or reflect their diverse socioeconomic backgrounds . Among Asian origin groups in the U.S., there are wide differences in economic and social experiences. Additionally, academic research has investigated how the pressures of the model minority stereotype can impact Asian Americans’ mental health and academic performance . Critics of the myth have also pointed to its impact on other racial and ethnic groups, especially Black Americans. Some argue that the myth has been used to minimize racial discrimination and justify policies that overlook the historical circumstances and impacts of colonialism, slavery and segregation on other non-White racial and ethnic groups.
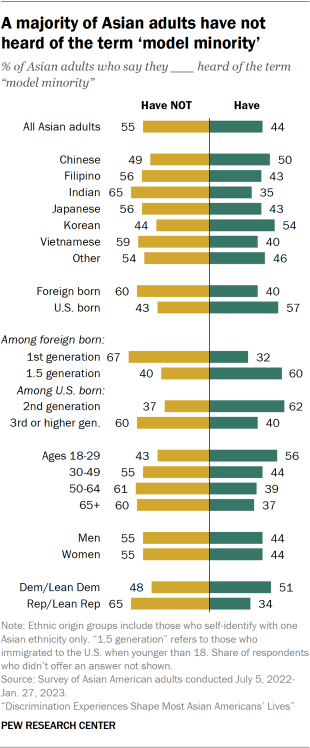
More than half of Asian adults (55%) say they have not heard of the term “model minority.” Just under half (44%) say they have heard of the term.
There are some differences in awareness of the term across demographic groups:
- Ethnic origin: About half of Korean and Chinese adults say they have heard of the term, while only about one-third of Indian adults say the same.
- Nativity: 57% of U.S.-born Asian adults have heard the term “model minority,” compared with 40% of immigrants.
- Immigrant generation: Among immigrants, 60% of those who came to the U.S. as children (“1.5 generation” in this report) say they have heard of the term “model minority,” compared with 32% of those who came to the U.S. as adults (first generation). And among U.S.-born Asian Americans, those who are second generation are more likely than those who are third or higher generation to say the same (62% vs. 40%).
- Age: 56% of Asian adults under 30 say they have heard of the term, compared with fewer than half among older Asian adults.
- Party: 51% of Asian adults who identify with or lean to the Democratic Party say they’ve heard the term, compared with 34% of those who identify with or lean to the Republican Party.
Awareness of the term ‘model minority’ varies across education and income
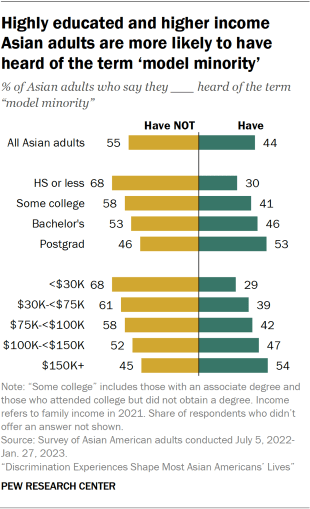
Asian adults with higher levels of formal education and higher family income are more likely to say they have heard of the term “model minority”:
- 53% of Asian adults with a postgraduate degree say they have heard the term, compared with smaller shares of those with a bachelor’s degree or less.
- 54% of Asian adults who make $150,000 or more say they have heard the term, higher than the shares among those with lower incomes. Among Asian Americans who make less than $30,000, only 29% say they have heard of the term “model minority.”
Notably, awareness of the term is higher among those born in the U.S. than immigrants across all levels of education and income.
Among Asian adults who have heard of the term “model minority,” about four-in-ten say using it to describe Asians in the U.S. is a bad thing. Another 28% say using it is neither good nor bad, 17% say using it is a good thing, and 12% say they are not sure.
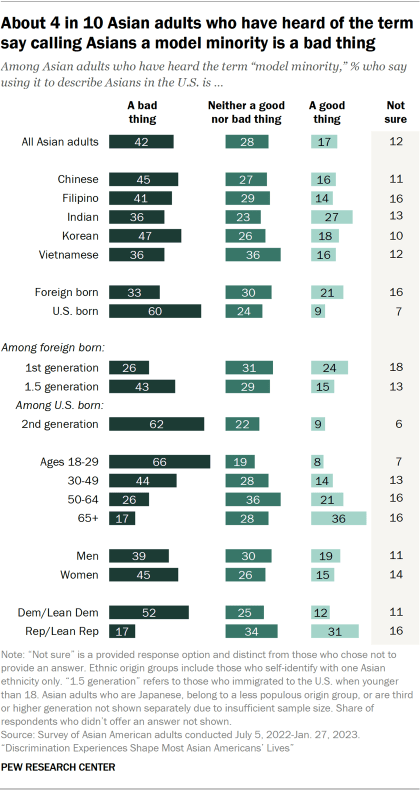
These views vary by ethnic origin, nativity, age and party. Among those who have heard of the term:
- Ethnic origin: Among Indian adults, the gap between those who say the term “model minority” is a bad thing and those who say it is a good thing (36% vs. 27%) is smaller than among other ethnic origin groups.
- Nativity: 60% of U.S.-born Asian adults say describing Asians as a model minority is a bad thing, while 9% say it is a good thing. Meanwhile, immigrants’ views of the model minority stereotype are more split (33% vs. 21%, respectively).
- Immigrant generation: Among immigrants, 43% of 1.5-generation Asian adults say using the term “model minority” is a bad thing, compared with 26% of first-generation Asian adults.
- Age: Asian adults under 30 are far more likely to say the model minority label is a bad thing than a good thing (66% vs. 8%). Meanwhile, Asian adults 65 and older are more likely to say describing Asian Americans as a model minority is a good thing (36%) than a bad thing (17%).
- Party: 52% of Asian Democrats say describing Asians as a model minority is a bad thing, about three times the share of Asian Republicans who say the same (17%).
Among those who know the term “model minority,” views of whether using it to describe Asians in the U.S. is a good or bad thing does not vary significantly across education levels. By income, Asian adults who make less than $30,000 are somewhat less likely to say it is a bad thing than those with higher incomes. 18
Views of the ‘model minority’ label are linked to perceptions of the American dream
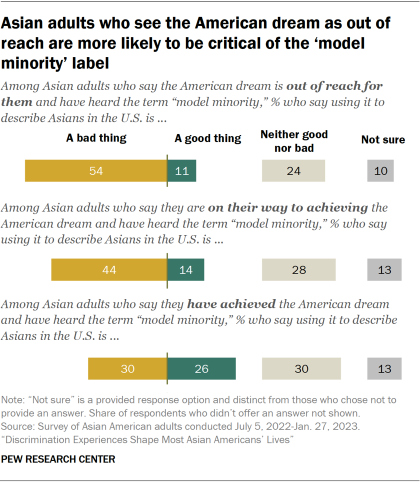
In the survey, we asked Asian Americans if they believe they have achieved the American dream, are on their way to achieving it, or if they believe the American dream is out of their reach. Among those who have heard of the term “model minority”:
- 54% of Asian adults who believe the American dream is out of their reach say describing Asian Americans as a model minority is a bad thing. This is higher than the shares among those who believe they are on their way to achieving (44%) or believe they have already achieved the American dream (30%).
- Meanwhile, 26% of Asian adults who believe they have achieved the American dream say the model minority label is a good thing. In comparison, 14% of those who believe they are on their way to achieving the American dream and 11% of those who believe that the American dream is out of their reach say the same.
In this survey, we asked Asian Americans how informed they are about the history of Asians in the U.S.
Whether Asian adults have heard of the model minority label is linked to their knowledge of Asian American history:
- 62% of Asian adults who are extremely or very informed of U.S. Asian history have heard of the term “model minority.”
- Smaller shares of those who are somewhat informed (44%) or a little or not at all informed (29%) about U.S. Asian history say they are aware of the term.
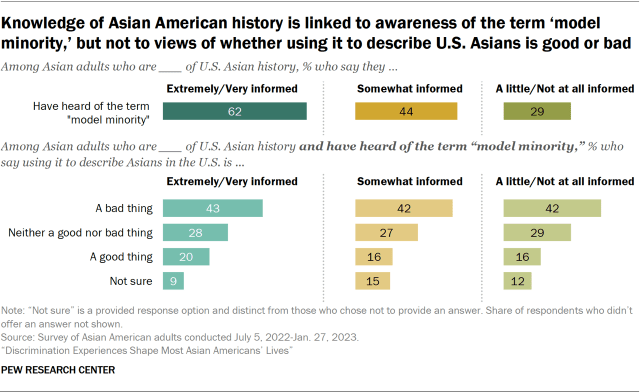
However, among those who have heard of the “model minority” label, views on whether using it to describe Asian Americans is good or bad are similar regardless of how informed they are on Asian American history. About four-in-ten across knowledge levels say describing Asian Americans as a model minority is a bad thing.
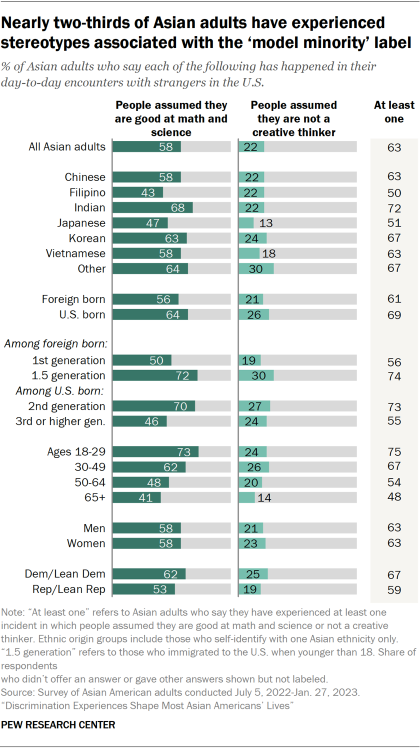
The model minority stereotype often paints Asian Americans as intellectually and financially successful, deferential to authority, and competent but robotic or unemotional , especially in comparison with other racial and ethnic groups. Additionally, some stereotypes associated with the model minority characterize Asian Americans as successful in fields such as math and science, as well as lacking in creativity.
Nearly two-thirds of Asian adults (63%) say that in their day-to-day encounters with strangers, they have at least one experience in which someone assumed they are good at math and science or not a creative thinker.
Broadly, Asian adults are far more likely to say someone has assumed they are good at math and science (58%) than not a creative thinker (22%).
Across these experiences, there are some differences by demographic groups:
- Ethnic origin: 68% of Indian adults say strangers have assumed they are good at math and science, a higher share than among most other origin groups. Meanwhile, about half or fewer of Japanese (47%) and Filipino (43%) adults say people have made this assumption about them.
- Immigrant generation: About seven-in-ten Asian adults who are 1.5 generation and second generation each say people have assumed they are good at math and science, compared with 50% among the first generation and 46% among third or higher generations.
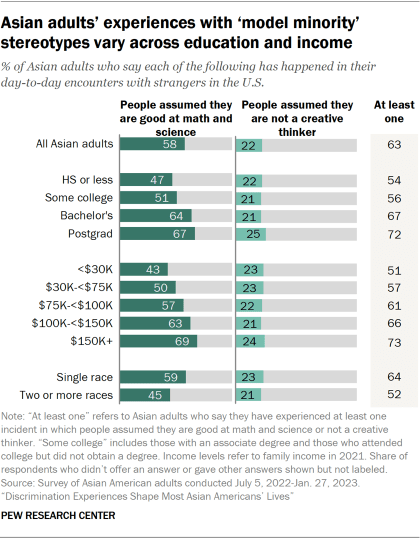
- Education: About two-thirds of Asian adults with a postgraduate degree or a bachelor’s degree say strangers have assumed they are good at math and science, compared with roughly half of those with some college experience or less. Similar shares regardless of education say people have assumed they are not a creative thinker.
- Income: 69% of those who make $150,000 or more say strangers have assumed they are good at math and science, compared with 43% of those who make less than $30,000.
- Race: 59% of single-race Asian adults (those who identify as Asian and no other race) say someone assumed they are good at math and science, compared with 45% of Asian adults who identify with two or more races (those who identify as Asian and at least one other race).
In our 2021 focus groups of Asian Americans, participants talked about their views of and experiences with the “model minority” stereotype.
Many U.S.-born Asian participants shared how it has been harmful , with some discussing the social pressures associated with it. Others spoke about how the stereotype portrays Asians as monolithic and compares them with other racial and ethnic groups.
“You have to be polished. There’s no room for failure. There’s no room for imperfections. You have to be well-spoken, well-educated, have the right opinions, be good-looking, be tall. [You] have to have a family structure. There’s no room for any sort of freedom in identity except for the mold that you’ve been painted as – as a model citizen.”
–U.S.-born man of Pakistani origin in early 30s
“As an Asian person, I feel like there’s a stereotype that Asian students are high achievers academically. They’re good at math and science. … I was a pretty mediocre student, and math and science were actually my weakest subjects, so I feel like it’s either way you lose. Teachers expect you to fit a certain stereotype and if you’re not, then you’re a disappointment, but at the same time, even if you are good at math and science, that just means that you’re fitting a stereotype. It’s [actually] your own achievement, but your teachers might think ‘Oh, it’s because they’re Asian,’ and that diminishes your achievement.”
–U.S.-born woman of Korean origin in late 20s
“The model minority myth … mak[es] us as Asians [and] South Asians monoliths. … I’ve had people go, ‘Oh, so your dad’s a doctor? Is he a lawyer? Do you have money? Do you have this? Do you have that? Are you [in] an arranged marriage?’ And just the kind of image that portrays and gives us. But the expectations put on us as being high performing and everyone assumes you’re going to be smart. … I am a black sheep in many ways, not only within my family, but within Asian [and] South Asian culture, being [in my profession], someone who’s not a doctor, who hasn’t gone the professional, traditional, educational route. So, it’s very harmful, that too, for those communities within the Asian diaspora who have come to the United States. … [M]any of them come from impoverished and underrepresented communities and the expectations put on them to produce or the types of jobs and menial labor they have to take on as a result is really a very poisonous mythos to have out there.”
–U.S.-born woman of Indian origin in early 40s
“One of the reasons the model minority fallacy works so well as an argument against affirmative action [for Indians is] they are a newer immigrant group that has come here and … [t]here’s a lot of education [in India]. People have opportunity there that then they can come [to America] and continue with those connections. Whereas Blacks and Hispanics have had generations of oppression, so they don’t have anything to build off of. So when you bucket everybody – Black, Hispanics and Asians – into one group, then you can make those arguments of, ‘Oh, [Asians] are the model minority, they can do it.’”
Some participants talked about having mixed feelings about being called the “model minority” and how they felt like it put them in a kind of “middle ground.”
“I feel like Asians are kind of known as the model minority. That kind of puts us in an interesting position where I feel like we’re supposed to excel and succeed in the media, or we’re seen in the media as exceeding in all these things as smart. All of us are not by any means. Yeah, I feel like we’re in this weird middle ground.”
–U.S.-born man of Chinese origin in early 20s
“A lot of people believe that Japanese are the most humble and honest people, even among other Asians. I feel like I need to live up to that. I have to try hard when people say things like that. Of course, it is good, but it’s a lot of work sometimes. As Japanese, and for my family, I try hard.”
–Immigrant man of Japanese origin in mid-40s (translated from Japanese)
Others had more positive impressions of the model minority label, saying it made them proud to be Asian and have others see them that way:
“Whenever I apply for any job, in the drop-down there is an option to choose the ethnicity, and I write Asian American proudly because everyone knows us Asians as hardworking, they recognize us as loyal and hardworking.”
–Immigrant woman of Nepalese origin in mid-40s (translated from Nepali)
“I think any model is a good thing. I mean the cognitive, the word ‘model,’ when you model after somebody it’s a positive meaning to it. So personally for me I have no issues with being called the model minority because it only tells me that I’m doing something right.”
–U.S.-born man of Hmong origin in early 40s
- Some of these groups had relatively small sample sizes. For shares of Asian adults who have heard of the term “model minority” and say using the term to describe the U.S. Asian population is a good or bad thing, by education and income, refer to the Appendix . ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings

Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Asian Americans
- Discrimination & Prejudice
- Immigration Issues
- Race Relations
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
Key facts about Asian Americans living in poverty
Methodology: 2023 focus groups of asian americans, 1 in 10: redefining the asian american dream (short film), the hardships and dreams of asian americans living in poverty, key facts about asian american eligible voters in 2024, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Advancing social justice, promoting decent work ILO is a specialized agency of the United Nations

Forced labour is a severe violation of human rights affecting 28 million of men, women and children in all countries and all economic sectors. It is rooted in poverty, discrimination and lack of social protection, and it disrupts fair competition between businesses. The issue has been at the heart of the ILO mandate to promote Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work, leaving no one behind.

What is forced labour?

Data and research

Our impact, their voices

Forced Labour Observatory
Facts and figures
men, women and children are in forced labour
of forced labour happens in the private economy
236 billion US$
generated in illegal profits every year
countries ratified the ILO Forced Labour Protocol
International Labour Standards on Forced Labour
- Convention No. 29 (C29)
- Convention No. 105 (C105)
- Protocol No. 29 (P29)
- Recommendation 203 (R203)
The Forced Labour Convention (No. 29), adopted in 1930, contains the definition of forced labour and provides that it should be punished as a crime. This is one of the most ratified ILO standards.
- Text of the Convention
- Ratifications
- Countries that have not ratified yet
The Abolition of Forced Labour Convention (No. 105), adopted in 1957, deals with state-imposed forms of forced labour. This is one of the most ratified ILO standards.
The Protocol to the Forced Labour Convention, (P029), adopted in 2014, requires ratifying countries to take effective measures to prevent forced labour, protect victims and ensure their access to justice.
The Protocol complements the Convention No. 29, therefore only countries that have ratified this Convention can ratify the Protocol.
- Text of the Protocol
The Forced Labour Recommendation (No. 203), adopted in 2014, provides further guidance on how to implement the Protocol.
It is a non-binding document that does not require ratification.
- Text of the Recommendation
What can the ILO offer and how?
- Eradicating Forced Labour: Partnering strategically with ILO
- Good practices in addressing Forced Labour (forthcoming)
- Developing National Action Plans on Forced Labour

The Fair Recruitment Initiative

The ILO Global Business Network on Forced Labour

8.7 Accelerator Lab
News and articles

Prospects to achieve decent work in cocoa supply chain

Making innovation work for decent work
The ILO 8.7 Accelerator Lab launches vision for innovation, knowledge sharing and scaling up
Publications
Nigeria Forced Labour Survey 2022
8.7 Accelerator Lab: Theory of change for the fishing sector
8.7 Accelerator Lab: Theory of change for the mining sector
Social safety nets
ILO/Japan Fund for Building Social Safety Nets in Asia and the Pacific (SSN Fund)
Ship to Shore Rights South East Asia - Indonesia
Want to know more about Forced Labour? You can contact us at [email protected] and follow us on social media:
Explaining the Department of Labor’s new overtime rule that will benefit 4.3 million workers
The U.S. Department of Labor issued a final rule today making changes to the regulations about who is eligible for overtime pay. Here’s why this matters:
How the overtime threshold works
Overtime pay protections are included in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) to ensure that most workers who put in more than 40 hours a week get paid 1.5 times their regular pay for the extra hours they work. Almost all hourly workers are automatically eligible for overtime pay. But workers who are paid on a salary basis are only automatically eligible for overtime pay if they earn below a certain salary. Above that level, employers can claim that workers are “exempt” from overtime pay protection if their job duties are considered executive, administrative, or professional (EAP) —essentially managers or highly credentialed professionals.
The current overtime salary threshold is too low to protect many workers
The pay threshold determining which salaried workers are automatically eligible for overtime pay has been eroded both by not being updated using a proper methodology, and by inflation. Currently, workers earning $684 per week (the equivalent of $35,568 per year for a full-time, full-year employee) can be forced to work 60-70 hours a week for no more pay than if they worked 40 hours. The extra 20-30 hours are completely free to the employer, allowing employers to exploit workers with no consequences.
The Department of Labor’s new final rule will phase in the updated salary threshold in two steps over the next eight months, and automatically update it every three years thereafter.
- This is the equivalent of $43,888 per year for a full-time, full-year worker.
- In 2019, the Department updated the salary threshold to a level that was inappropriately low. Further, that threshold has eroded substantially in the last 4+ years as wages and prices have risen over that period, leaving roughly one million workers without overtime protections who would have received those protections under the methodology of even that inappropriately weak rule. This first step essentially adjusts the salary threshold set in the 2019 rule for inflation.
- This is the equivalent of $58,656 per year for a full-time, full-year worker.
- This level appropriately sets the threshold at the 35th percentile of weekly wages for full-time, salaried workers in the lowest-wage Census region, currently the South.
- The salary threshold will automatically update every three years thereafter, based on the methodology laid out in the rule, to ensure that the strength of the rule does not erode over time as prices and wages rise.
The final rule will benefit 4.3 million workers
- 2.4 million of these workers (56%) are women
- 1.0 million of these workers (24%) are workers of color
- The largest numbers of impacted workers are in professional and business services, health care and social services, and financial activities.
- The 4.3 million represents 3.0% of workers subject to the FLSA.
Expanding overtime protections is good for workers and manageable for employers
- The final rule will result in a transfer of $1.5 billion annually from employers to workers in increased pay.
- While that increase in wages will be enormously impactful to affected workers, it represents well under one-tenth of one-percent of total wages and salaries in the U.S. economy. Employers will be more than able to adjust to the rule without negatively impacting the overall economy.
- In addition to increasing pay for many workers, the overtime rule will also reduce excessive hours of unpaid work. Before this update to the salary threshold, the cost to employers of overworking salaried EAP workers who make more than $684 weekly was effectively zero. The concept of overtime pay is designed to protect workers’ most valuable asset—their time—and to push employers to value it too.
- Automatic updating is a smart and easy way to simply maintain the labor standard established in the proposal. If the threshold is not updated automatically over time, it will steadily weaken as a labor standard until the next rulemaking, covering fewer and fewer workers as the salary distribution naturally rises over time with inflation and productivity growth.
- With automatic updating, employers will know exactly what to expect and when to expect it. They will also be able to get a reasonable sense well in advance of what the next threshold will be, because they will be able to track on a dedicated Bureau of Labor Statistics website how the 35th percentile of full-time salaried worker earnings in the lowest-wage Census region is evolving over time.
Enjoyed this post?
Sign up for EPI's newsletter so you never miss our research and insights on ways to make the economy work better for everyone.
Track us on Twitter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Chapter 3. Research Design and Methodology. Chapter 3 consists of three parts: (1) Purpose of the. study and research design, (2) Methods, and (3) Statistical. Data analysis procedure. Part one ...
Dissertation Chapter 3 Sample. be be 1. Describe. quantitative, CHAPTER III: METHOD introduce the qualitative, the method of the chapter and mixed-methods). used (i.e. The purpose of this chapter is to introduce the research methodology for this. methodology the specific connects to it question(s). research.
The purpose of chapter three (research methodology) is to give an experienced investigator enough information to replicate the study. Some supervisors do not understand this and require students to write what is in effect, a textbook. A research design is used to structure the research and to show how all of the major parts of the research ...
qualitative research, in general, and in your tra-dition or genre, in particular; hence, it is written in future tense. In the dissertation's chapter 3, you report on what you have already done. You write after the fact; hence, you write in past tense. As such, many of the sections of chapter 3 can be written only after you have
Instruments. This section should include the instruments you plan on using to measure the variables in the research questions. (a) the source or developers of the instrument. (b) validity and reliability information. •. (c) information on how it was normed. •. (d) other salient information (e.g., number of. items in each scale, subscales ...
The methodology section, chapter three should reiterate the research questions and hypotheses, present the research design, discuss the participants, the instruments to be used, the procedure, the data analysis plan, and the sample size justification. Research Questions and Null Hypotheses. Chapter three should begin with a portion that ...
Chapter 3 The Research Process. In Chapter 1, we saw that scientific research is the process of acquiring scientific knowledge using the scientific method. ... This multi-part proposal should address what research questions you wish to study and why, the prior state of knowledge in this area, theories you wish to employ along with hypotheses to ...
methods will be explained independently from the research design section. In a nutshell, the following is the procedure of research design: 1. Dene the purpose of your project. Determine whether it will be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory. 2. Specify the meanings of each concept you want to study. 3. Select a research method. 4.
3.1 Research Strategies A research strategy is an overall plan for conducting a research study. A research strategy guides a researcher in planning, executing, and monitoring the study. While the research strategy provides useful support on a high level, it needs to be complemented with research methods that can guide the research work on a more
To gain the approval of a supervisor. The proposal plays an important rôle in justifying the research to a supervisor. It is the vehicle that you use to argue the case for the research, demonstrating that it is important that you are capable of undertaking - and successfully completing - the work, and that the work will enable you to ...
Chapter 3. Chapter 3 explains the research method being used in the study. It describes the instruments associated with the chosen research method and design used; this includes information regarding instrument origin, reliability, and validity. Chapter 3 details the planned research approach, design, and analysis. An outline of the assumptions ...
This chapter presents the following: (1) Purpose of the Study and Research Design, (2) Method, and (3) Statistical Data Analysis Procedure. Part One, Purpose of the Study and Research Design ...
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Introduction . This Chapter presents the description of the research process. It provides information concerning the method that was used in undertaking this research as well as a justification for the use of this method. The Chapter also describes the various stages of the research, which includes the selection of ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
3.1 Introduction: the qualitative research paradigm This chapter discusses the planning and execution of the study and the overall ... As part of the extended-case studies methodology, in chapter 2 and later chapters the importance and significance of news agencies is discussed. This study therefore seeks not to "prove" the existence of
Part 7 of Chapter 3 (Research methods) on research design stage 6 and 7 will cover . the following topics: Adopting a skeptical approach to explanations; causal connection and .
Led by teacher-leaders, the IPI-T process is implemented school-wide, collecting data about student cognitive engagement to show how students are thinking when using technology. Within a week after the collection of data, the teacher-leaders facilitate faculty collaborative sessions in an effort to disaggregate the data and participate in ...
Chapter 3: Method (Phenomenological Study) This workbook is intended to help you to write Chapter 3 of your dissertation proposal. Each part of the workbook contains information that will help you understand what should be ... Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation (2nd ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
2. RESEARCH DESIGN. This research is exploratory in nature as it attempts to explore the experiences of mothers of incest survivors. Their subjective perceptions formed the core data of the study; hence it needed the method that would deal with the topic in an exploratory nature. For the purpose of this study, the research paradigm that was ...
research oneself (or as a part of a team) or as an end in itself. ©SAGE Publications. Chapter 3 ... 3. Research may have been conducted on a different population from the one in . which you are interested, thus justifying your work with a different population. For example, Strassman and Schirmer (2013) reported that an evidence-based schema ...
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. As it is indicated in the title, this chapter includes the research methodology of. the dissertation. In more details, in this part the author ...
Sample Chapter 3 chapter methodology this chapter reveals the methods of research to be employed the researcher in conducting the study which includes the. ... This sampling method is conducted where each member of a population has a capability to become part of the sample. The chosen respondents are containing of eighty (80) respondents from ...
The 10 principles are: 1/ Participants in research must voluntarily consent to participating. 2/ The aims of the research project must benefit society. 3/ The research that is being undertaken must be based upon sound theory and must previously have employed animal testing. 4/ Any unnecessary physical and mental suffering must be avoided during ...
In their own words: Key findings from qualitative research on Asian Americans and discrimination experiences; 1. Asian Americans' experiences with discrimination in their daily lives. Discrimination in interpersonal encounters with strangers; Racial discrimination at security checkpoints; Encounters with police because of race or ethnicity
More data and research on forced labour. International Labour Standards on Forced Labour. Convention No. 29 (C29) Convention No. 105 (C105) Protocol No. 29 (P29) Recommendation 203 (R203) The Forced Labour Convention (No. 29), adopted in 1930, contains the definition of forced labour and provides that it should be punished as a crime. This is ...
The final rule will benefit 4.3 million workers. 2.4 million of these workers (56%) are women; 1.0 million of these workers (24%) are workers of color; The largest numbers of impacted workers are in professional and business services, health care and social services, and financial activities. The 4.3 million represents 3.0% of workers subject ...