- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

The Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Genetic and Environmental Influences and How They Interact
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Verywell / Joshua Seong
- Definitions
- Interaction
- Contemporary Views
Nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development. Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality and development is one of the oldest philosophical debates within the field of psychology .
Learn how each is defined, along with why the issue of nature vs. nurture continues to arise. We also share a few examples of when arguments on this topic typically occur, how the two factors interact with each other, and contemporary views that exist in the debate of nature vs. nurture as it stands today.
Nature and Nurture Defined
To better understand the nature vs. nurture argument, it helps to know what each of these terms means.
- Nature refers largely to our genetics . It includes the genes we are born with and other hereditary factors that can impact how our personality is formed and influence the way that we develop from childhood through adulthood.
- Nurture encompasses the environmental factors that impact who we are. This includes our early childhood experiences, the way we were raised , our social relationships, and the surrounding culture.
A few biologically determined characteristics include genetic diseases, eye color, hair color, and skin color. Other characteristics are tied to environmental influences, such as how a person behaves, which can be influenced by parenting styles and learned experiences.
For example, one child might learn through observation and reinforcement to say please and thank you. Another child might learn to behave aggressively by observing older children engage in violent behavior on the playground.
The Debate of Nature vs. Nurture
The nature vs. nurture debate centers on the contributions of genetics and environmental factors to human development. Some philosophers, such as Plato and Descartes, suggested that certain factors are inborn or occur naturally regardless of environmental influences.
Advocates of this point of view believe that all of our characteristics and behaviors are the result of evolution. They contend that genetic traits are handed down from parents to their children and influence the individual differences that make each person unique.
Other well-known thinkers, such as John Locke, believed in what is known as tabula rasa which suggests that the mind begins as a blank slate . According to this notion, everything that we are is determined by our experiences.
Behaviorism is a good example of a theory rooted in this belief as behaviorists feel that all actions and behaviors are the results of conditioning. Theorists such as John B. Watson believed that people could be trained to do and become anything, regardless of their genetic background.
People with extreme views are called nativists and empiricists. Nativists take the position that all or most behaviors and characteristics are the result of inheritance. Empiricists take the position that all or most behaviors and characteristics result from learning.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
One example of when the argument of nature vs. nurture arises is when a person achieves a high level of academic success . Did they do so because they are genetically predisposed to elevated levels of intelligence, or is their success a result of an enriched environment?
The argument of nature vs. nurture can also be made when it comes to why a person behaves in a certain way. If a man abuses his wife and kids, for instance, is it because he was born with violent tendencies, or is violence something he learned by observing others in his life when growing up?
Nature vs. Nurture in Psychology
Throughout the history of psychology , the debate of nature vs. nurture has continued to stir up controversy. Eugenics, for example, was a movement heavily influenced by the nativist approach.
Psychologist Francis Galton coined the terms 'nature versus nurture' and 'eugenics' and believed that intelligence resulted from genetics. Galton also felt that intelligent individuals should be encouraged to marry and have many children, while less intelligent individuals should be discouraged from reproducing.
The value placed on nature vs. nurture can even vary between the different branches of psychology , with some branches taking a more one-sided approach. In biopsychology , for example, researchers conduct studies exploring how neurotransmitters influence behavior, emphasizing the role of nature.
In social psychology , on the other hand, researchers might conduct studies looking at how external factors such as peer pressure and social media influence behaviors, stressing the importance of nurture. Behaviorism is another branch that focuses on the impact of the environment on behavior.
Nature vs. Nurture in Child Development
Some psychological theories of child development place more emphasis on nature and others focus more on nurture. An example of a nativist theory involving child development is Chomsky's concept of a language acquisition device (LAD). According to this theory, all children are born with an instinctive mental capacity that allows them to both learn and produce language.
An example of an empiricist child development theory is Albert Bandura's social learning theory . This theory says that people learn by observing the behavior of others. In his famous Bobo doll experiment , Bandura demonstrated that children could learn aggressive behaviors simply by observing another person acting aggressively.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
There is also some argument as to whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in the development of one's personality. The answer to this question varies depending on which personality development theory you use.
According to behavioral theories, our personality is a result of the interactions we have with our environment, while biological theories suggest that personality is largely inherited. Then there are psychodynamic theories of personality that emphasize the impact of both.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
One could argue that either nature or nurture contributes to mental health development. Some causes of mental illness fall on the nature side of the debate, including changes to or imbalances with chemicals in the brain. Genetics can also contribute to mental illness development, increasing one's risk of a certain disorder or disease.
Mental disorders with some type of genetic component include autism , attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), bipolar disorder , major depression , and schizophrenia .
Other explanations for mental illness are environmental. This includes being exposed to environmental toxins, such as drugs or alcohol, while still in utero. Certain life experiences can also influence mental illness development, such as witnessing a traumatic event, leading to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Health Therapy
Different types of mental health treatment can also rely more heavily on either nature or nurture in their treatment approach. One of the goals of many types of therapy is to uncover any life experiences that may have contributed to mental illness development (nurture).
However, genetics (nature) can play a role in treatment as well. For instance, research indicates that a person's genetic makeup can impact how their body responds to antidepressants. Taking this into consideration is important for getting that person the help they need.
Interaction Between Nature and Nurture
Which is stronger: nature or nurture? Many researchers consider the interaction between heredity and environment—nature with nurture as opposed to nature versus nurture—to be the most important influencing factor of all.
For example, perfect pitch is the ability to detect the pitch of a musical tone without any reference. Researchers have found that this ability tends to run in families and might be tied to a single gene. However, they've also discovered that possessing the gene is not enough as musical training during early childhood is needed for this inherited ability to manifest itself.
Height is another example of a trait influenced by an interaction between nature and nurture. A child might inherit the genes for height. However, if they grow up in a deprived environment where proper nourishment isn't received, they might never attain the height they could have had if they'd grown up in a healthier environment.
A newer field of study that aims to learn more about the interaction between genes and environment is epigenetics . Epigenetics seeks to explain how environment can impact the way in which genes are expressed.
Some characteristics are biologically determined, such as eye color, hair color, and skin color. Other things, like life expectancy and height, have a strong biological component but are also influenced by environmental factors and lifestyle.
Contemporary Views of Nature vs. Nurture
Most experts recognize that neither nature nor nurture is stronger than the other. Instead, both factors play a critical role in who we are and who we become. Not only that but nature and nurture interact with each other in important ways all throughout our lifespan.
As a result, many in this field are interested in seeing how genes modulate environmental influences and vice versa. At the same time, this debate of nature vs. nurture still rages on in some areas, such as in the origins of homosexuality and influences on intelligence .
While a few people take the extreme nativist or radical empiricist approach, the reality is that there is not a simple way to disentangle the multitude of forces that exist in personality and human development. Instead, these influences include genetic factors, environmental factors, and how each intermingles with the other.
Schoneberger T. Three myths from the language acquisition literature . Anal Verbal Behav . 2010;26(1):107-31. doi:10.1007/bf03393086
National Institutes of Health. Common genetic factors found in 5 mental disorders .
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response . Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci . 2022;2(2):115-126. doi:10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.07.008
Moulton C. Perfect pitch reconsidered . Clin Med J . 2014;14(5):517-9 doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.14-5-517
Levitt M. Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour . Life Sci Soc Policy . 2013;9:13. doi:10.1186/2195-7819-9-13
Bandura A, Ross D, Ross, SA. Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models . J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1961;63(3):575-582. doi:10.1037/h0045925
Chomsky N. Aspects of the Theory of Syntax .
Galton F. Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development .
Watson JB. Behaviorism .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Are Nature vs. Nurture Examples?
How is nature defined, how is nurture defined, the nature vs. nurture debate, nature vs. nurture examples, what is empiricism (extreme nurture position), contemporary views of nature vs. nurture.
Nature vs. nurture is an age-old debate about whether genetics (nature) plays a bigger role in determining a person's characteristics than lived experience and environmental factors (nurture). The term "nature vs. nature" was coined by English naturalist Charles Darwin's younger half-cousin, anthropologist Francis Galton, around 1875.
In psychology, the extreme nature position (nativism) proposes that intelligence and personality traits are inherited and determined only by genetics.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, the extreme nurture position (empiricism) asserts that the mind is a blank slate at birth; external factors like education and upbringing determine who someone becomes in adulthood and how their mind works. Both of these extreme positions have shortcomings and are antiquated.
This article explores the difference between nature and nurture. It gives nature vs. nurture examples and explains why outdated views of nativism and empiricism don't jibe with contemporary views.
Thanasis Zovoilis / Getty Images
In the context of nature vs. nurture, "nature" refers to genetics and heritable factors that are passed down to children from their biological parents.
Genes and hereditary factors determine many aspects of someone’s physical appearance and other individual characteristics, such as a genetically inherited predisposition for certain personality traits.
Scientists estimate that 20% to 60% percent of temperament is determined by genetics and that many (possibly thousands) of common gene variations combine to influence individual characteristics of temperament.
However, the impact of gene-environment (or nature-nurture) interactions on someone's traits is interwoven. Environmental factors also play a role in temperament by influencing gene activity. For example, in children raised in an adverse environment (such as child abuse or violence), genes that increase the risk of impulsive temperamental characteristics may be activated (turned on).
Trying to measure "nature vs. nurture" scientifically is challenging. It's impossible to know precisely where the influence of genes and environment begin or end.
How Are Inherited Traits Measured?
“Heritability” describes the influence that genes have on human characteristics and traits. It's measured on a scale of 0.0 to 1.0. Very strong heritable traits like someone's eye color are ranked a 1.0.
Traits that have nothing to do with genetics, like speaking with a regional accent ranks a zero. Most human characteristics score between a 0.30 and 0.60 on the heritability scale, which reflects a blend of genetics (nature) and environmental (nurture) factors.
Thousands of years ago, ancient Greek philosophers like Plato believed that "innate knowledge" is present in our minds at birth. Every parent knows that babies are born with innate characteristics. Anecdotally, it may seem like a kid's "Big 5" personality traits (agreeableness, conscientiousness, extraversion, neuroticism, and openness) were predetermined before birth.
What is the "Big 5" personality traits
The Big 5 personality traits is a theory that describes the five basic dimensions of personality. It was developed in 1949 by D. W. Fiske and later expanded upon by other researchers and is used as a framework to study people's behavior.
From a "nature" perspective, the fact that every child has innate traits at birth supports Plato's philosophical ideas about innatism. However, personality isn't set in stone. Environmental "nurture" factors can change someone's predominant personality traits over time. For example, exposure to the chemical lead during childhood may alter personality.
In 2014, a meta-analysis of genetic and environmental influences on personality development across the human lifespan found that people change with age. Personality traits are relatively stable during early childhood but often change dramatically during adolescence and young adulthood.
It's impossible to know exactly how much "nurture" changes personality as people get older. In 2019, a study of how stable personality traits are from age 16 to 66 found that people's Big 5 traits are both stable and malleable (able to be molded). During the 50-year span from high school to retirement, some traits like agreeableness and conscientiousness tend to increase, while others appear to be set in stone.
Nurture refers to all of the external or environmental factors that affect human development such as how someone is raised, socioeconomic status, early childhood experiences, education, and daily habits.
Although the word "nurture" may conjure up images of babies and young children being cared for by loving parents, environmental factors and life experiences have an impact on our psychological and physical well-being across the human life span. In adulthood, "nurturing" oneself by making healthy lifestyle choices can offset certain genetic predispositions.
For example, a May 2022 study found that people with a high genetic risk of developing the brain disorder Alzheimer's disease can lower their odds of developing dementia (a group of symptoms that affect memory, thinking, and social abilities enough to affect daily life) by adopting these seven healthy habits in midlife:
- Staying active
- Healthy eating
- Losing weight
- Not smoking
- Reducing blood sugar
- Controlling cholesterol
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure
The nature vs. nurture debate centers around whether individual differences in behavioral traits and personality are caused primarily by nature or nurture. Early philosophers believed the genetic traits passed from parents to their children influence individual differences and traits. Other well-known philosophers believed the mind begins as a blank slate and that everything we are is determined by our experiences.
While early theories favored one factor over the other, experts today recognize there is a complex interaction between genetics and the environment and that both nature and nurture play a critical role in shaping who we are.
Eye color and skin pigmentation are examples of "nature" because they are present at birth and determined by inherited genes. Developmental delays due to toxins (such as exposure to lead as a child or exposure to drugs in utero) are examples of "nurture" because the environment can negatively impact learning and intelligence.
In Child Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in child development is apparent when studying language development. Nature theorists believe genetics plays a significant role in language development and that children are born with an instinctive ability that allows them to both learn and produce language.
Nurture theorists would argue that language develops by listening and imitating adults and other children.
In addition, nurture theorists believe people learn by observing the behavior of others. For example, contemporary psychologist Albert Bandura's social learning theory suggests that aggression is learned through observation and imitation.
In Psychology
In psychology, the nature vs. nurture beliefs vary depending on the branch of psychology.
- Biopsychology: Researchers analyze how the brain, neurotransmitters, and other aspects of our biology influence our behaviors, thoughts, and feelings. emphasizing the role of nature.
- Social psychology: Researchers study how external factors such as peer pressure and social media influence behaviors, emphasizing the importance of nurture.
- Behaviorism: This theory of learning is based on the idea that our actions are shaped by our interactions with our environment.
In Personality Development
Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality development depends on different personality development theories.
- Behavioral theories: Our personality is a result of the interactions we have with our environment, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences.
- Biological theories: Personality is mostly inherited which is demonstrated by a study in the 1990s that concluded identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins.
- Psychodynamic theories: Personality development involves both genetic predispositions and environmental factors and their interaction is complex.
In Mental Illness
Both nature and nurture can contribute to mental illness development.
For example, at least five mental health disorders are associated with some type of genetic component ( autism , attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) , bipolar disorder , major depression, and schizophrenia ).
Other explanations for mental illness are environmental, such as:
- Being exposed to drugs or alcohol in utero
- Witnessing a traumatic event, leading to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood
In Mental Health Therapy
Mental health treatment can involve both nature and nurture. For example, a therapist may explore life experiences that may have contributed to mental illness development (nurture) as well as family history of mental illness (nature).
At the same time, research indicates that a person's genetic makeup may impact how their body responds to antidepressants. Taking this into consideration is important for finding the right treatment for each individual.
What Is Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)?
Innatism emphasizes nature's role in shaping our minds and personality traits before birth. Nativism takes this one step further and proposes that all of people's mental and physical characteristics are inherited and predetermined at birth.
In its extreme form, concepts of nativism gave way to the early 20th century's racially-biased eugenics movement. Thankfully, "selective breeding," which is the idea that only certain people should reproduce in order to create chosen characteristics in offspring, and eugenics, arranged breeding, lost momentum during World War II. At that time, the Nazis' ethnic cleansing (killing people based on their ethnic or religious associations) atrocities were exposed.
Philosopher John Locke's tabula rasa theory from 1689 directly opposes the idea that we are born with innate knowledge. "Tabula rasa" means "blank slate" and implies that our minds do not have innate knowledge at birth.
Locke was an empiricist who believed that all the knowledge we gain in life comes from sensory experiences (using their senses to understand the world), education, and day-to-day encounters after being born.
Today, looking at nature vs. nature in black-and-white terms is considered a misguided dichotomy (two-part system). There are so many shades of gray where nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to tease out how inherited traits and learned behaviors shape someone's unique characteristics or influence how their mind works.
The influences of nature and nurture in psychology are impossible to unravel. For example, imagine someone growing up in a household with an alcoholic parent who has frequent rage attacks. If that child goes on to develop a substance use disorder and has trouble with emotion regulation in adulthood, it's impossible to know precisely how much genetics (nature) or adverse childhood experiences (nurture) affected that individual's personality traits or issues with alcoholism.
Epigenetics Blurs the Line Between Nature and Nurture
"Epigenetics " means "on top of" genetics. It refers to external factors and experiences that turn genes "on" or "off." Epigenetic mechanisms alter DNA's physical structure in utero (in the womb) and across the human lifespan.
Epigenetics blurs the line between nature and nurture because it says that even after birth, our genetic material isn't set in stone; environmental factors can modify genes during one's lifetime. For example, cannabis exposure during critical windows of development can increase someone's risk of neuropsychiatric disease via epigenetic mechanisms.
Nature vs. nurture is a framework used to examine how genetics (nature) and environmental factors (nurture) influence human development and personality traits.
However, nature vs. nurture isn't a black-and-white issue; there are many shades of gray where the influence of nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to disentangle how nature and nurture overlap; they are inextricably intertwined. In most cases, nature and nurture combine to make us who we are.
Waller JC. Commentary: the birth of the twin study--a commentary on francis galton’s “the history of twins.” International Journal of Epidemiology . 2012;41(4):913-917. doi:10.1093/ije/dys100
The New York Times. " Major Personality Study Finds That Traits Are Mostly Inherited ."
Medline Plus. Is temperament determined by genetics?
Feldman MW, Ramachandran S. Missing compared to what? Revisiting heritability, genes and culture . Phil Trans R Soc B . 2018;373(1743):20170064. doi:10.1098/rstb.2017.0064
Winch C. Innatism, concept formation, concept mastery and formal education: innatism, concept formation and formal education . Journal of Philosophy of Education . 2015;49(4):539-556. doi:10.1111/1467-9752.12121
Briley DA, Tucker-Drob EM. Genetic and environmental continuity in personality development: A meta-analysis . Psychological Bulletin . 2014;140(5):1303-1331. doi:10.1037/a0037091
Damian RI, Spengler M, Sutu A, Roberts BW. Sixteen going on sixty-six: A longitudinal study of personality stability and change across 50 years . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology . 2019;117(3):674-695. doi:10.1037/pspp0000210
Tin A, Bressler J, Simino J, et al. Genetic risk, midlife life’s simple 7, and incident dementia in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study . Neurology . Published online May 25, 2022. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000200520
Levitt M. Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour . Life Sci Soc Policy . 2013;9(1):13. doi:10.1186/2195-7819-9-13
Ross EJ, Graham DL, Money KM, Stanwood GD. Developmental consequences of fetal exposure to drugs: what we know and what we still must learn . Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jan;40(1):61-87. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.14
World Health Organization. Lead poisoning .
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models . The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 1961; 63 (3), 575–582 doi:10.1037/h0045925
Krapfl JE. Behaviorism and society . Behav Anal. 2016;39(1):123-9. doi:10.1007/s40614-016-0063-8
Bouchard TJ Jr, Lykken DT, McGue M, Segal NL, Tellegen A. Sources of human psychological differences: the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart . Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):223-8. doi: 10.1126/science.2218526
National Institutes of Health. Common genetic factors found in 5 mental disorders .
Franke HA. Toxic Stress: Effects, Prevention and Treatment . Children (Basel). 2014 Nov 3;1(3):390-402. doi: 10.3390/children1030390
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response . Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci . 2022;2(2):115-126. doi:10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.07.008
National Human Genome Research Institute. Eugenics and Scientific Racism .
OLL. The Works of John Locke in Nine Volumes .
Toraño EG, García MG, Fernández-Morera JL, Niño-García P, Fernández AF. The impact of external factors on the epigenome: in utero and over lifetime . BioMed Research International . 2016;2016:1-17. doi:10.1155/2016/2568635
Smith A, Kaufman F, Sandy MS, Cardenas A. Cannabis exposure during critical windows of development: epigenetic and molecular pathways implicated in neuropsychiatric disease . Curr Envir Health Rpt . 2020;7(3):325-342. doi:10.1007/s40572-020-00275-4
By Christopher Bergland Bergland is a retired ultra-endurance athlete turned medical writer and science reporter. He is based in Massachusetts.
Nature vs. Nurture Debate In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual’s innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping behavior and development.
Key Takeaways
- Nature is what we think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors.
- Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception, e.g., the product of exposure, life experiences, and learning on an individual.
- Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture concerning specific psychological traits.
- Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways.
- For example, epigenetics is an emerging area of research that shows how environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
The nature-nurture debate is concerned with the relative contribution that both influences make to human behavior, such as personality, cognitive traits, temperament and psychopathology.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
Nature vs. nurture in child development.
In child development, the nature vs. nurture debate is evident in the study of language acquisition . Researchers like Chomsky (1957) argue that humans are born with an innate capacity for language (nature), known as universal grammar, suggesting that genetics play a significant role in language development.
Conversely, the behaviorist perspective, exemplified by Skinner (1957), emphasizes the role of environmental reinforcement and learning (nurture) in language acquisition.
Twin studies have provided valuable insights into this debate, demonstrating that identical twins raised apart may share linguistic similarities despite different environments, suggesting a strong genetic influence (Bouchard, 1979)
However, environmental factors, such as exposure to language-rich environments, also play a crucial role in language development, highlighting the intricate interplay between nature and nurture in child development.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in personality psychology centers on the origins of personality traits. Twin studies have shown that identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins, indicating a genetic component to personality (Bouchard, 1994).
However, environmental factors, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences, also shape personality.
For example, research by Caspi et al. (2003) demonstrated that a particular gene (MAOA) can interact with childhood maltreatment to increase the risk of aggressive behavior in adulthood.
This highlights that genetic predispositions and environmental factors contribute to personality development, and their interaction is complex and multifaceted.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in mental health explores the etiology of depression. Genetic studies have identified specific genes associated with an increased vulnerability to depression, indicating a genetic component (Sullivan et al., 2000).
However, environmental factors, such as adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood, also play a significant role in the development of depressive disorders (Dube et al.., 2002; Keller et al., 2007)
The diathesis-stress model posits that individuals inherit a genetic predisposition (diathesis) to a disorder, which is then activated or exacerbated by environmental stressors (Monroe & Simons, 1991).
This model illustrates how nature and nurture interact to influence mental health outcomes.
Nature vs. Nurture of Intelligence
The nature vs. nurture debate in intelligence examines the relative contributions of genetic and environmental factors to cognitive abilities.
Intelligence is highly heritable, with about 50% of variance in IQ attributed to genetic factors, based on studies of twins, adoptees, and families (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Heritability of intelligence increases with age, from about 20% in infancy to as high as 80% in adulthood, suggesting amplifying effects of genes over time.
However, environmental influences, such as access to quality education and stimulating environments, also significantly impact intelligence.
Shared environmental influences like family background are more influential in childhood, whereas non-shared experiences are more important later in life.
Research by Flynn (1987) showed that average IQ scores have increased over generations, suggesting that environmental improvements, known as the Flynn effect , can lead to substantial gains in cognitive abilities.
Molecular genetics provides tools to identify specific genes and understand their pathways and interactions. However, progress has been slow for complex traits like intelligence. Identified genes have small effect sizes (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Overall, intelligence results from complex interplay between genes and environment over development. Molecular genetics offers promise to clarify these mechanisms. The nature vs nurture debate is outdated – both play key roles.
Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)
It has long been known that certain physical characteristics are biologically determined by genetic inheritance.
Color of eyes, straight or curly hair, pigmentation of the skin, and certain diseases (such as Huntingdon’s chorea) are all a function of the genes we inherit.
These facts have led many to speculate as to whether psychological characteristics such as behavioral tendencies, personality attributes, and mental abilities are also “wired in” before we are even born.
Those who adopt an extreme hereditary position are known as nativists. Their basic assumption is that the characteristics of the human species as a whole are a product of evolution and that individual differences are due to each person’s unique genetic code.
In general, the earlier a particular ability appears, the more likely it is to be under the influence of genetic factors. Estimates of genetic influence are called heritability.
Examples of extreme nature positions in psychology include Chomsky (1965), who proposed language is gained through the use of an innate language acquisition device. Another example of nature is Freud’s theory of aggression as being an innate drive (called Thanatos).
Characteristics and differences that are not observable at birth, but which emerge later in life, are regarded as the product of maturation. That is to say, we all have an inner “biological clock” which switches on (or off) types of behavior in a pre-programmed way.
The classic example of the way this affects our physical development are the bodily changes that occur in early adolescence at puberty.
However, nativists also argue that maturation governs the emergence of attachment in infancy , language acquisition , and even cognitive development .
Empiricism (Extreme Nurture Position)
At the other end of the spectrum are the environmentalists – also known as empiricists (not to be confused with the other empirical/scientific approach ).
Their basic assumption is that at birth, the human mind is a tabula rasa (a blank slate) and that this is gradually “filled” as a result of experience (e.g., behaviorism ).
From this point of view, psychological characteristics and behavioral differences that emerge through infancy and childhood are the results of learning. It is how you are brought up (nurture) that governs the psychologically significant aspects of child development and the concept of maturation applies only to the biological.
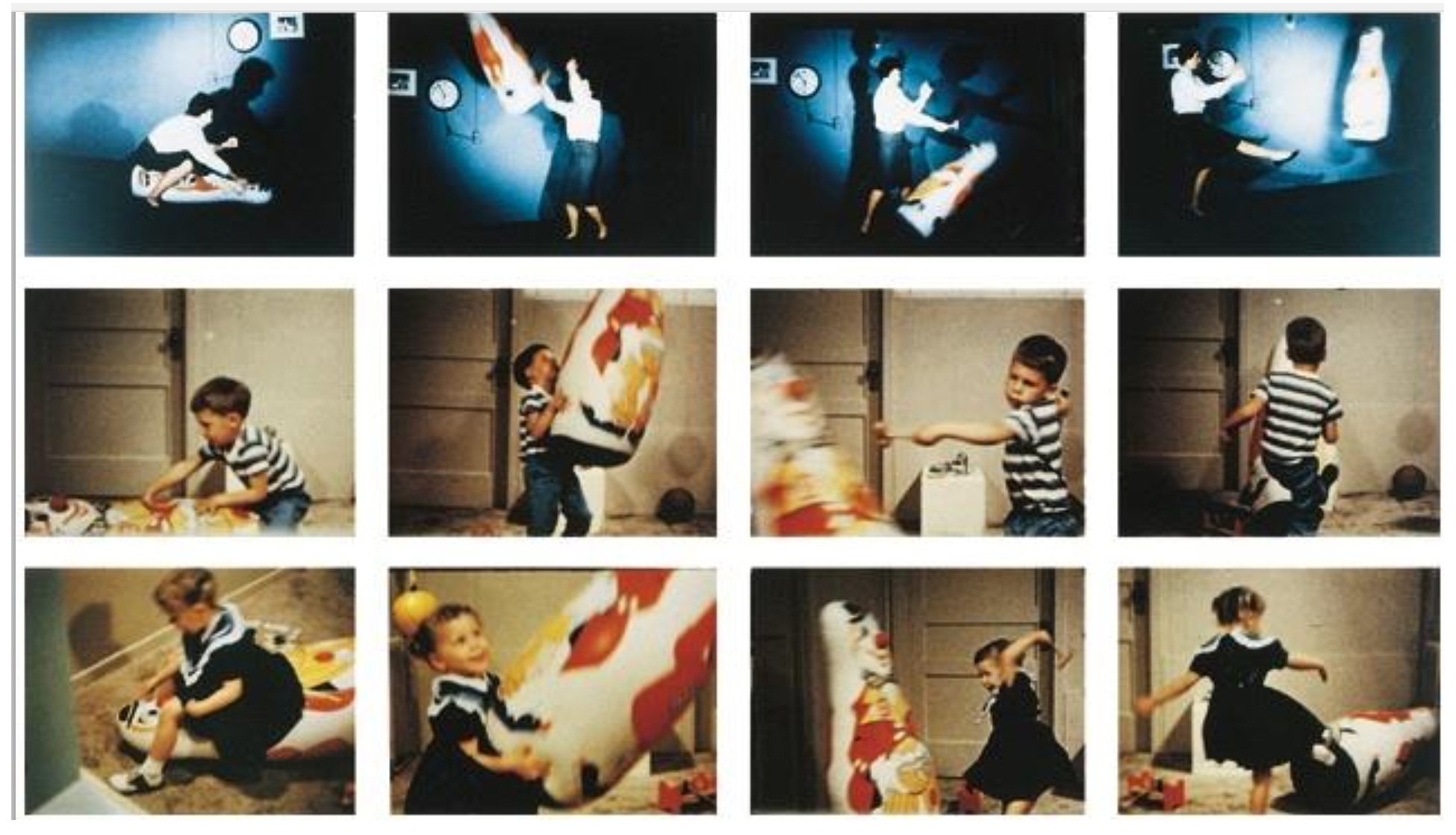
For example, Bandura’s (1977) social learning theory states that aggression is learned from the environment through observation and imitation. This is seen in his famous bobo doll experiment (Bandura, 1961).

Also, Skinner (1957) believed that language is learned from other people via behavior-shaping techniques.
Evidence for Nature
- Biological Approach
- Biology of Gender
- Medical Model
Freud (1905) stated that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality.
He thought that parenting is of primary importance to a child’s development , and the family as the most important feature of nurture was a common theme throughout twentieth-century psychology (which was dominated by environmentalists’ theories).
Behavioral Genetics
Researchers in the field of behavioral genetics study variation in behavior as it is affected by genes, which are the units of heredity passed down from parents to offspring.
“We now know that DNA differences are the major systematic source of psychological differences between us. Environmental effects are important but what we have learned in recent years is that they are mostly random – unsystematic and unstable – which means that we cannot do much about them.” Plomin (2018, xii)
Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture with regard to specific psychological traits. One way to do this is to study relatives who share the same genes (nature) but a different environment (nurture). Adoption acts as a natural experiment which allows researchers to do this.
Empirical studies have consistently shown that adoptive children show greater resemblance to their biological parents, rather than their adoptive, or environmental parents (Plomin & DeFries, 1983; 1985).
Another way of studying heredity is by comparing the behavior of twins, who can either be identical (sharing the same genes) or non-identical (sharing 50% of genes). Like adoption studies, twin studies support the first rule of behavior genetics; that psychological traits are extremely heritable, about 50% on average.
The Twins in Early Development Study (TEDS) revealed correlations between twins on a range of behavioral traits, such as personality (empathy and hyperactivity) and components of reading such as phonetics (Haworth, Davis, Plomin, 2013; Oliver & Plomin, 2007; Trouton, Spinath, & Plomin, 2002).
Implications
Jenson (1969) found that the average I.Q. scores of black Americans were significantly lower than whites he went on to argue that genetic factors were mainly responsible – even going so far as to suggest that intelligence is 80% inherited.
The storm of controversy that developed around Jenson’s claims was not mainly due to logical and empirical weaknesses in his argument. It was more to do with the social and political implications that are often drawn from research that claims to demonstrate natural inequalities between social groups.
For many environmentalists, there is a barely disguised right-wing agenda behind the work of the behavioral geneticists. In their view, part of the difference in the I.Q. scores of different ethnic groups are due to inbuilt biases in the methods of testing.
More fundamentally, they believe that differences in intellectual ability are a product of social inequalities in access to material resources and opportunities. To put it simply children brought up in the ghetto tend to score lower on tests because they are denied the same life chances as more privileged members of society.
Now we can see why the nature-nurture debate has become such a hotly contested issue. What begins as an attempt to understand the causes of behavioral differences often develops into a politically motivated dispute about distributive justice and power in society.
What’s more, this doesn’t only apply to the debate over I.Q. It is equally relevant to the psychology of sex and gender , where the question of how much of the (alleged) differences in male and female behavior is due to biology and how much to culture is just as controversial.
Polygenic Inheritance
Rather than the presence or absence of single genes being the determining factor that accounts for psychological traits, behavioral genetics has demonstrated that multiple genes – often thousands, collectively contribute to specific behaviors.
Thus, psychological traits follow a polygenic mode of inheritance (as opposed to being determined by a single gene). Depression is a good example of a polygenic trait, which is thought to be influenced by around 1000 genes (Plomin, 2018).
This means a person with a lower number of these genes (under 500) would have a lower risk of experiencing depression than someone with a higher number.
The Nature of Nurture
Nurture assumes that correlations between environmental factors and psychological outcomes are caused environmentally. For example, how much parents read with their children and how well children learn to read appear to be related. Other examples include environmental stress and its effect on depression.
However, behavioral genetics argues that what look like environmental effects are to a large extent really a reflection of genetic differences (Plomin & Bergeman, 1991).
People select, modify and create environments correlated with their genetic disposition. This means that what sometimes appears to be an environmental influence (nurture) is a genetic influence (nature).
So, children that are genetically predisposed to be competent readers, will be happy to listen to their parents read them stories, and be more likely to encourage this interaction.
Interaction Effects
However, in recent years there has been a growing realization that the question of “how much” behavior is due to heredity and “how much” to the environment may itself be the wrong question.
Take intelligence as an example. Like almost all types of human behavior, it is a complex, many-sided phenomenon which reveals itself (or not!) in a great variety of ways.
The “how much” question assumes that psychological traits can all be expressed numerically and that the issue can be resolved in a quantitative manner.
Heritability statistics revealed by behavioral genetic studies have been criticized as meaningless, mainly because biologists have established that genes cannot influence development independently of environmental factors; genetic and nongenetic factors always cooperate to build traits. The reality is that nature and culture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways (Gottlieb, 2007; Johnston & Edwards, 2002).
Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact.
For example, in psychopathology , this means that both a genetic predisposition and an appropriate environmental trigger are required for a mental disorder to develop. For example, epigenetics state that environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
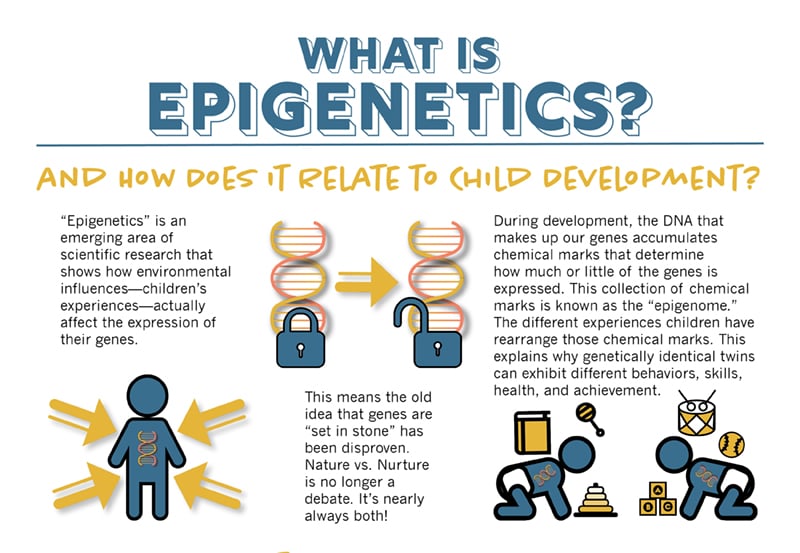
What is Epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the term used to describe inheritance by mechanisms other than through the DNA sequence of genes. For example, features of a person’s physical and social environment can effect which genes are switched-on, or “expressed”, rather than the DNA sequence of the genes themselves.
Stressors and memories can be passed through small RNA molecules to multiple generations of offspring in ways that meaningfully affect their behavior.
One such example is what is known as the Dutch Hunger Winter, during last year of the Second World War. What they found was that children who were in the womb during the famine experienced a life-long increase in their chances of developing various health problems compared to children conceived after the famine.
Epigenetic effects can sometimes be passed from one generation to the next, although the effects only seem to last for a few generations. There is some evidence that the effects of the Dutch Hunger Winter affected grandchildren of women who were pregnant during the famine.
Therefore, it makes more sense to say that the difference between two people’s behavior is mostly due to hereditary factors or mostly due to environmental factors.
This realization is especially important given the recent advances in genetics, such as polygenic testing. The Human Genome Project, for example, has stimulated enormous interest in tracing types of behavior to particular strands of DNA located on specific chromosomes.
If these advances are not to be abused, then there will need to be a more general understanding of the fact that biology interacts with both the cultural context and the personal choices that people make about how they want to live their lives.
There is no neat and simple way of unraveling these qualitatively different and reciprocal influences on human behavior.
Epigenetics: Licking Rat Pups
Michael Meaney and his colleagues at McGill University in Montreal, Canada conducted the landmark epigenetic study on mother rats licking and grooming their pups.
This research found that the amount of licking and grooming received by rat pups during their early life could alter their epigenetic marks and influence their stress responses in adulthood.
Pups that received high levels of maternal care (i.e., more licking and grooming) had a reduced stress response compared to those that received low levels of maternal care.
Meaney’s work with rat maternal behavior and its epigenetic effects has provided significant insights into the understanding of early-life experiences, gene expression, and adult behavior.
It underscores the importance of the early-life environment and its long-term impacts on an individual’s mental health and stress resilience.
Epigenetics: The Agouti Mouse Study
Waterland and Jirtle’s 2003 study on the Agouti mouse is another foundational work in the field of epigenetics that demonstrated how nutritional factors during early development can result in epigenetic changes that have long-lasting effects on phenotype.
In this study, they focused on a specific gene in mice called the Agouti viable yellow (A^vy) gene. Mice with this gene can express a range of coat colors, from yellow to mottled to brown.
This variation in coat color is related to the methylation status of the A^vy gene: higher methylation is associated with the brown coat, and lower methylation with the yellow coat.
Importantly, the coat color is also associated with health outcomes, with yellow mice being more prone to obesity, diabetes, and tumorigenesis compared to brown mice.
Waterland and Jirtle set out to investigate whether maternal diet, specifically supplementation with methyl donors like folic acid, choline, betaine, and vitamin B12, during pregnancy could influence the methylation status of the A^vy gene in offspring.
Key findings from the study include:
Dietary Influence : When pregnant mice were fed a diet supplemented with methyl donors, their offspring had an increased likelihood of having the brown coat color. This indicated that the supplemented diet led to an increased methylation of the A^vy gene.
Health Outcomes : Along with the coat color change, these mice also had reduced risks of obesity and other health issues associated with the yellow phenotype.
Transgenerational Effects : The study showed that nutritional interventions could have effects that extend beyond the individual, affecting the phenotype of the offspring.
The implications of this research are profound. It highlights how maternal nutrition during critical developmental periods can have lasting effects on offspring through epigenetic modifications, potentially affecting health outcomes much later in life.
The study also offers insights into how dietary and environmental factors might contribute to disease susceptibility in humans.
Bandura, A. Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 63, 575-582
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bouchard, T. J. (1994). Genes, Environment, and Personality. Science, 264 (5166), 1700-1701.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment. Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Loss . New York: Basic Books.
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., … & Poulton, R. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science , 301 (5631), 386-389.
Chomsky, N. (1957). Syntactic structures. Mouton de Gruyter.
Chomsky, N. (1965). Aspects of the theory of syntax . MIT Press.
Dube, S. R., Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Edwards, V. J., & Croft, J. B. (2002). Adverse childhood experiences and personal alcohol abuse as an adult. Addictive Behaviors , 27 (5), 713-725.
Flynn, J. R. (1987). Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: What IQ tests really measure. Psychological Bulletin , 101 (2), 171.
Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality . Se, 7.
Galton, F. (1883). Inquiries into human faculty and its development . London: J.M. Dent & Co.
Gottlieb, G. (2007). Probabilistic epigenesis. Developmental Science, 10 , 1–11.
Haworth, C. M., Davis, O. S., & Plomin, R. (2013). Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): a genetically sensitive investigation of cognitive and behavioral development from childhood to young adulthood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 16(1) , 117-125.
Jensen, A. R. (1969). How much can we boost I.Q. and scholastic achievement? Harvard Educational Review, 33 , 1-123.
Johnston, T. D., & Edwards, L. (2002). Genes, interactions, and the development of behavior . Psychological Review , 109, 26–34.
Keller, M. C., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2007). Association of different adverse life events with distinct patterns of depressive symptoms. American Journal of Psychiatry , 164 (10), 1521-1529.
Monroe, S. M., & Simons, A. D. (1991). Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: implications for the depressive disorders. Psychological Bulletin , 110 (3), 406.
Oliver, B. R., & Plomin, R. (2007). Twins” Early Development Study (TEDS): A multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems from childhood through adolescence . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 10(1) , 96-105.
Petrill, S. A., Plomin, R., Berg, S., Johansson, B., Pedersen, N. L., Ahern, F., & McClearn, G. E. (1998). The genetic and environmental relationship between general and specific cognitive abilities in twins age 80 and older. Psychological Science , 9 (3), 183-189.
Plomin, R., & Petrill, S. A. (1997). Genetics and intelligence: What’s new?. Intelligence , 24 (1), 53-77.
Plomin, R. (2018). Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . MIT Press.
Plomin, R., & Bergeman, C. S. (1991). The nature of nurture: Genetic influence on “environmental” measures. behavioral and Brain Sciences, 14(3) , 373-386.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1983). The Colorado adoption project. Child Development , 276-289.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1985). The origins of individual differences in infancy; the Colorado adoption project. Science, 230 , 1369-1371.
Plomin, R., & Spinath, F. M. (2004). Intelligence: genetics, genes, and genomics. Journal of personality and social psychology , 86 (1), 112.
Plomin, R., & Von Stumm, S. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence. Nature Reviews Genetics , 19 (3), 148-159.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal behavior . Acton, MA: Copley Publishing Group.
Sullivan, P. F., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2000). Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry , 157 (10), 1552-1562.
Szyf, M., Weaver, I. C., Champagne, F. A., Diorio, J., & Meaney, M. J. (2005). Maternal programming of steroid receptor expression and phenotype through DNA methylation in the rat . Frontiers in neuroendocrinology , 26 (3-4), 139-162.
Trouton, A., Spinath, F. M., & Plomin, R. (2002). Twins early development study (TEDS): a multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems in childhood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 5(5) , 444-448.
Waterland, R. A., & Jirtle, R. L. (2003). Transposable elements: targets for early nutritional effects on epigenetic gene regulation . Molecular and cellular biology, 23 (15), 5293-5300.
Further Information
- Genetic & Environmental Influences on Human Psychological Differences
Evidence for Nurture
- Classical Conditioning
- Little Albert Experiment
- Operant Conditioning
- Behaviorism
- Social Learning Theory
- Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
- Social Roles
- Attachment Styles
- The Hidden Links Between Mental Disorders
- Visual Cliff Experiment
- Behavioral Genetics, Genetics, and Epigenetics
- Epigenetics
- Is Epigenetics Inherited?
- Physiological Psychology
- Bowlby’s Maternal Deprivation Hypothesis
- So is it nature not nurture after all?
Evidence for an Interaction
- Genes, Interactions, and the Development of Behavior
- Agouti Mouse Study
- Biological Psychology
What does nature refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nature” refers to the influence of genetics, innate qualities, and biological factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of hereditary factors in shaping who we are.
What does nurture refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nurture” refers to the influence of the environment, upbringing, experiences, and social factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of external factors in shaping who we are.
Why is it important to determine the contribution of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture) in human development?
Determining the contribution of heredity and environment in human development is crucial for understanding the complex interplay between genetic factors and environmental influences. It helps identify the relative significance of each factor, informing interventions, policies, and strategies to optimize human potential and address developmental challenges.

Environment
Nature versus nurture: where we are now, a short review of one of the most popular debates in behavioral science..
Posted October 6, 2017 | Reviewed by Kaja Perina
Note: This post has been adapted from a version published in Pediatric News.
The question of whether human behavior is driven by innate biological forces or the product of our learning and environment has been a popular discussion at cocktail parties and scientific conferences for many years. To many people, the longevity of this debate suggests that we haven’t actually learned that much. In reality, however, a tremendous number of scientific advances have drastically improved our level of understanding. The hope for this post is to offer a short narrative of how the answer to this question has shifted to its current state of knowledge. While admittedly an oversimplification, one useful way to track progress in the nature-nurture debate is to divide the evolution of our understanding into three main states.
Part 1: Nature Versus Nurture
The origins of nature versus nurture debate date back for thousands of years and across many cultures. The Greek philosopher Galen theorized that personality traits were the result of a person’s relative concentrations of four bodily fluids, or humours, namely blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. The actual term nature-nurture comes from Sir Francis Galton's 1874 publication of English Men of Science: Their Nature and Nurture, in which he argued that intelligence and character traits came from hereditary factors (this was well before the modern science of genetics ). His beliefs were in clear opposition to earlier scholars such as philosopher John Locke, who is well known for the theory that children are born a “blank slate” with their traits developing completely from experience and learning.
Fast forwarding to the 20th century, this debate continued in pretty much the same terms. For most of the 1900s, the two dominant schools of thought when it came to human behavior and psychiatric symptoms were behaviorism, which emphasized the importance of learning principles in shaping behavior, and psychoanalysis , which developed from the ideas of Sigmund Freud and focused on the ways that unconscious sexual and aggressive drives were channeled through various defense mechanisms . Despite the fact that these two perspectives were often in fierce opposition to each other, both shared the view that the environment and a person’s unique experiences, i.e. nurture, were the prevailing forces in development.
Part 2: Nature and Nurture
From about the 1970s to the end of the 20th century, a noticeable shift occurred as direct knowledge of the brain and genetics started to swing the pendulum back to an increased appreciation of nature as a critical influence on a person’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior. The Human Genome Project was launched in 1990 and the entire decade was designated as the “Decade of the Brain.” Neuroscience research exploded and many new psychiatric medications emerged and were used much more commonly than ever before.
Also during this time, the type of research design that had the most direct relevance to nature-nurture questions become popular. This was the twin study, which enabled researchers to calculate directly the degree to which a variable of interest (intelligence, height, anxiety level, etc.) could be attributed to genetic versus environmental factors. In doing this, a repeated finding when it came to behavioral variables was that both genetic and environmental influences were important, often at close to a 50/50 split in terms of magnitude.
These types of studies, combined with others, made it increasingly difficult to argue for the overwhelming supremacy of either nature or nurture as the primary driver of behavioral traits and disorders. Yet while many experts would now have to acknowledge the importance of both nature and nurture, the two worlds were generally treated as being quite independent. For example, terms such as “endogenous depression ” were employed to differentiate people who had depressive symptoms from what were presumed to be more autonomously operating biological factors from those whose depression resulted from “psychological” causes, with different treatments being recommended based on that determination. Looking back, what appears now as the fatal flaw in this perspective was the assumption that if something was brain-based or “biological” then it, therefore, implied a kind of automatic wiring of the brain that was generally driven by genes and beyond the reach of environmental factors.
Part 3: Nature Is Nurture (and vice versa)
Today, most scientists who carefully examine the ever-expanding research base have come to appreciate that the nature and nurture domains are hopelessly interwoven with one another. Genes have an influence on the environments we experience. At the same time, a person’s environment and experience can directly change the level at which certain genes are expressed (a rapidly evolving area of research called epigenetics ), which in turn alters both the physical structure and activity of the brain.
Given this modern understanding, the question of nature versus nurture ceases even to make sense in many ways. As an example, consider the developmental pathway a 10-year-old boy might have taken to eventually presenting to a mental health professional for high levels of aggressive behavior. He may have inherited a genetically-based temperamental predisposition to being aggressive. As a young child, that tendency to become irritable and angry would then often evoke more negative responses in other people such as parents, who may themselves struggle with controlling their own anger . These interactions begin to snowball, affecting his schoolwork and friendships and, through epigenetic mechanisms, all of these experiences cause this child’s brain to grow differently.
Yet there is also a hopeful message in this example, as an appreciation of these complicated interacting genetic and environmental factors give us many places in this cycle to intervene to stop this progression and even change the direction of the momentum. Now, we understand that not only are medications biological treatments but also things like psychotherapy , parenting guidance, mindfulness practices, exercise, and good eating habits.

In the end, when the families of children like this ask me whether or not their child’s struggles are behavioral or psychological, the best answer I can give them these days is “yes.”
@copyright by David Rettew, MD

David Rettew, M.D. , is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and faculty at the Oregon Health and Science University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
Introduction, general overviews.
- Conceptual Problems
- Biological Constraints, Predispositions, and Preparedness in Learning
- Critical Periods
- Innate Knowledge
- Heritability
- Behavioral Epigenetics
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Life-Span Development
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Remote Work
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology by Hunter Honeycutt LAST REVIEWED: 12 January 2023 LAST MODIFIED: 12 January 2023 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0305
The nature-nurture dichotomy is a long-standing and pervasive framework for thinking about the causal influences believed to be operating during individual development. In this dichotomy, nature refers to factors (e.g., genes, genetic programs, and/or biological blueprints) or forces (e.g., heredity and/or maturation) inherent to the individual that predetermine the development of form and function. Nurture generally refers to all the remaining, typically “external,” causal factors (e.g., physical and social conditions) and processes (e.g., learning and experience) that influence development. The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to recognize instead that both nature and nurture work together or “interact” to produce outcomes, although exactly how to view the interaction is a matter of much debate. While acknowledging the interaction of nature and nurture, one’s theoretical models and research focus might emphasize the prominence of one over the other. Thus, nativists focus more on the importance of innate factors or forces operating on development, whereas empiricists focus more on experiential or environmental factors. However, not everyone finds value in thinking about development in terms of nature and nurture. By the middle of the twentieth century, some psychologists, biologists, and philosophers began to view nature-nurture as a conceptually deficient and biologically implausible dichotomy that oversimplifies the dynamics of behavior and development. Such people espouse some variant of “developmental systems theory” and seek to eliminate or otherwise fuse the nature-nurture division.
The works in this section are mostly trade books that provide general introductions to the nature-nurture debate across a variety of topical areas in psychology, all of which would be suitable for use in classes with undergraduate students at all levels. Goldhaber 2012 contrasts four popular perspectives on the nature-nurture issue and would be a good place to start for anyone unfamiliar with the nature-nurture debate in psychology. Nativist perspectives are represented by Pinker 2002 , Plomin 2018 , and Vallortigara 2021 . An empiricist-leaning position on behavior development is put forth in Schneider 2012 . Developmental systems theory is promoted in Blumberg 2005 and Moore 2002 . Two edited books are included and both are better suited for advanced undergraduate- or graduate-level students. The first edited book, Coll, et al. 2013 , focuses on the nature-nurture issue across a range of topics and perspectives in psychology. The other, Mayes and Lewis 2012 , presents empiricist (or environmentalist) perspectives on child development.
Bateson, P. 2017. Behaviour, development and evolution . Cambridge, UK: OpenBook Publishers.
DOI: 10.11647/OBP.0097
Written by a distinguished ethologist who draws extensively from his work on animal behavior, this book argues that the nature-nurture division is neither valid nor helpful in capturing the complex system of factors that influence behavioral development. Topics include imprinting and attachment, parent-offspring relations, the influence of early-life experiences on later-life outcomes, problems with genetic determinism, and the role of behavior in evolutionary change.
Blumberg, M. S. 2005. Basic instinct: The genesis of novel behavior . New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press.
Consistent with developmental systems theory, Blumberg presents an overview of the conceptual and empirical limitations of nativism in explanations of behavioral and neural development in animals and cognitive development in humans.
Coll, C. G., E. L. Bearer, and R. M. Lerner, eds. 2013. Nature-nurture: The complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences on human behavior and development . New York: Psychology Press.
The contents of this edited volume are almost entirely original works with commentary that span multiple disciplines (psychology, biology, economics, philosophy) and multiple perspectives (behavioral genetics and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue.
Goldhaber, D. 2012. The nature-nurture debates: Bridging the gap . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
DOI: 10.1017/CBO9781139022583
Goldhaber reviews four major perspectives (behavior genetics, environmentalism, evolutionary psychology, and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue. He argues we should reject reductionist views based on either genetic determinism or environmental determinism in favor of more holistic, interactionist approaches.
Mayes, L. C., and M. Lewis, eds. 2012. The Cambridge handbook of environment in human development . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
This handbook explores a wide variety of ways in which the environment influences child development. Chapters cover conceptual frameworks and methodological issues in thinking about and studying environmental influences as well reviewing ways in which environmental contexts and systems influence specific aspects of child development.
Moore, D. S. 2002. The dependent gene: The fallacy of nature vs. nurture . New York: Henry Holt.
This book provides an introduction to the developmental systems theory take on the nature-nurture issue particularly as it relates to genetic determinism, heritability and heredity.
Pinker, S. 2002. The blank slate: The modern denial of human nature . New York: Viking.
In this best-selling book, Pinker draws on evidence from behavioral genetics, evolutionary psychology, and cognitive psychology to argue for a nativist position concerning human nature.
Plomin, R. 2018. Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Plomin reviews traditional and more modern evidence from behavioral genetics to argue that genes are the primary factor in bringing about psychological differences between people. Moreover, he argues that many “environmental” factors operating on development are themselves strongly influenced by genetic differences.
Schneider, S. M. 2012. The science of consequences: How they affect genes, change the brain, and impact our world . Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Schneider presents a view grounded in behavior analysis to argue for the critical role that the consequences of genetic activity, neural activity, and behavioral activity play in individual development. While emphasizing environmental (or experiential) factors influencing development, this book also highlights the systemic and interactive nature of developmental systems across multiple levels of analysis.
Vallortigara, G. 2021. Born knowing: Imprinting and the origins of knowledge . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
DOI: 10.7551/mitpress/14091.001.0001
Drawing upon research in comparative cognition and comparative neuroscience, much of it his own, Vallortigara argues that animals, including humans, enter the world with a set of unlearned, innate or instinctive behaviors and neural circuits that bias or predispose subsequent learning and development.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Action Research
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Effect Size
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- Heuristics and Biases
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Item Response Theory
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Mediation Analysis
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Meta-Analysis
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Path Models
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Person-Centered and Experiential Psychotherapies: From Car...
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Protocol Analysis
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.39.149.46]
- 185.39.149.46
Nature Vs. Nurture: What Matters Most?
Have you ever questioned how much of your personality or difficulties you’ve faced may be due to your biology, and how much may be due to the environment you’ve lived in and learned from? If so, you aren’t alone. This is one of the fundamental bases of nature vs nurture psychology, which has been studied by experts for decades. It’s even been featured in countless articles from publishers as prominent as the New York Times for decades.
The debate over what drives human culture, personality, and behavior is actually believed by many to go back thousands of years to Ancient Greece. It can involve cultural, philosophical, and scientific elements to identify a variant or a hypothesis of the primary force behind human nature. Understanding this element of scope and pursuing ongoing education in this area can help you to determine how either element affects your present-day experience and how you can live well in your current situation.
Read on to learn more about the nature vs nurture debate in psychology and how both can affect your daily experiences.
Nature vs. nurture psychology
Nature refers to inherent characteristics while nurture refers to outside factors. The topic has been debated for millennia, and many have found that science has yet to arrive at a definitive answer—possibly suggesting that human nature is complex and not easy to define with labels.
The history of the nature vs. nurture debate
Galen, a philosopher in Ancient Greece, is thought by many to have first proposed that a person’s personality can arise from the levels of four types of bodily fluids (or “humors”), also known by many as the humorism or humoralism theory.
Later on, in the 1870s, Sir Francis Galton is quoted in historical texts using the terms “nature” and “nurture” when explaining his theory that traits, like intelligence and personality, could be developed by genetics and inherited at birth. During the same period, philosopher John Locke proposed that children were born as blank slates, and their characters developed from what they learned.
According to medical history, many behavioral and psychoanalytic theories in the early 1900s relied on the assumption that learning, environment and experience might be the most critical elements that can contribute to a person’s mental health. However, as time progressed to the later years of the 20th century, genetics and neuroscience gained popularity—and many medical professionals may have shifted back toward the nature “side” of the argument.
Current research generally indicates that individual differences in personality, behavior patterns, and mental health can all have intricate ties to genetic and environmental factors.
The interactionist position in the nature–nurture debate
Many field experts appear to support the interactionist position in the nature vs nurture debate—which is thought to state that genetics and environmental factors work within a fully interactive system that can determine a person’s personality and overall mental well-being.
As parents can provide someone with both genetic makeup and early environment and childhood lessons, in most cases, it can be argued that one of the most influential factors in human and child development—childhood caregivers—is, by definition, driven by both nature and nurture.
“Nature vs nurture is one of the oldest questions in science. The answer is not an either/or, but rather it is both nature and nurture, acting in various degrees”. — Grand Challenge: Nature Versus Nurture
Why does the nature vs nurture debate matter?
Your opinion on what matters most may affect how you approach your mental health. For example: If you stand firmly on the nature side, you may feel powerless to change something you believe was determined before birth. If nurture is the basis of your philosophy, however, you may feel powerless in pursuit or ownership of your unique fusion of personality traits.
Understanding both sides of the debate can give you an open mind regarding mental health treatment options, as you can change your experience in a range of ways. Those who favor the interactionist position may work with all the factors that could influence them—possibly empowering them to make an informed decision about improving their well-being with varied methods.
To help you to determine your own set of personal beliefs, we’ve listed a summary of both nature- and nurture-related elements below.
Nature: Biological factors
Nature can refer to your genetics and other biological factors that can influence your mental health and personality development.
Elements included on the nature side of the debate
While there can be a range of elements included in this area of the nature vs nurture argument, some of the most includes:
- Genetic diseases and disorders
- Appearance-related elements, such as eye, hair or skin color
How does nature affect you?
In a 2021 study, researchers sought to determine genetic influence on one’s experience and understanding of self with the removal of the environmental factors provided by parents to avoid errors related to causation. As a result, they suggested using the Familial Control Method as a workaround when genetically sensitive information isn’t available.
This could be a plausible measure to determine how nature truly can affect you. Per current psychological understanding, your genetic code is thought to be the source of your nature—while your genes might determine your brain structure, and your individual neurochemistry may shape your thought patterns, emotions and behaviors.
Nurture: Environmental factors
Nurture generally refers to the environmental factors, such as relationships, experiences and culture, which can impact who you are and how your mental health develops.
Elements included on the nurture side of the debate
Many people might have common nurture-related experiences, such as:
- Parenting and attachment style variations during childhood
- Learned experiences (facilitated by school or extracurricular activities)
- Social relationships
- Culture-related achievements (variable)
How does nurture affect you?
As you might imagine, your experiences and everything you’ve been through can impact your life and experiences. For example: Your experiences as an infant and throughout childhood substantially influence who you become, from your attachment style affecting how you form and maintain relationships to traumatic experiences changing how you react to certain situations.
Can nurture be changed?
Psychotherapy is generally defined as a proven method to help change one’s behavior and thought patterns. It can be regarded as an effective treatment for various mental health conditions.
Many may have nearly limitless ways to alter your environment—and psychotherapy can help you rebuild your cognitive pathways , according to data presented in a 2017 study. This published work alone shows the potential of change that nurture can hold, encouraging those who may wish to change facets of their personality or thought processes over time.
What are examples of nature vs. nurture in psychology?
You can see practical examples of nature vs nurture in everyday life, specifically in the area of behavioral psychology. Many believe that rather than showing definitive evidence for one side or the other, the evidence can show how integral and widespread the connection between nature and nurture truly is.
Nature vs nurture: Abusive behaviors
If a person exhibits abusive behavior, is it because they learned it by observing violence during their formative years, or is it due to being born with violent tendencies? This can be a common topic that’s brought up in the nature vs nurture debate.
If you or a loved one is experiencing abuse, contact the Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-SAFE (7233). Support is available 24/7.
If you are experiencing trauma, support is available. Please see our Get Help Now page for more resources.
Nature vs nurture: Intelligence
Does a person who demonstrates a high level of intelligence owe that to their genetic makeup or years of studying? How do we account for people who are born geniuses?
Looking to improve your mental health? Speak with a licensed therapist
Nature vs nurture: personality.
Twins can offer a unique view into how genetics and environment can shape your personality, mental health and emotional stability. For example, why would identical twins develop separate personalities and interests when they have the exact same genetics? Or how could children adopted into a home develop personality characteristics like their non-biological siblings?
Nature vs nurture: Mental health conditions
Some mental health conditions, like schizophrenia, might have a significant genetic component, while others can be directly caused by experiences—such as post-traumatic stress disorder. There are several brain issues, like Huntington’s disease, known to be passed on through genetics as well. What role would nature vs nurture have in these instances? How would one account for that?
Nature vs. nurture debate status
According to a 2018 study the medical community suggests that there’s not a single answer to the nature vs. nurture debate. The solution for many may be to allow both nature and nurture to interact throughout your life, shaping you into the person you are and influencing your mental health and stability in many complex ways.
How can online therapy help you establish mental stability
Mental health conditions can often leave you feeling overwhelmed. This level of overwhelm can make it difficult for you to leave the home, especially to confront your nervousness head on through in-person therapeutic intervention. Working with a licensed therapist online through virtual therapy platforms like BetterHelp can empower you to work on your mental health from the convenience and comfort of your own home—possibly offering a sense of safety when speaking about vulnerable topics.

Is online therapy effective?
Studies published by the American Psychological Association (APA) suggest that online therapy can be a viable, affordable option for many mental health conditions. It can also effectively boost the overall mental well-being of people who are not currently diagnosed with a mental condition. The APA has been quoted stating that virtual options for therapy can make treatment available in areas that did not previously have in-person option, possibly maximizing the amount of benefit that a larger pool of people can gain.
Why is Nature Vs Nurture important to psychology?
The nature versus nurture debate is the extent to which aspects of our behavior are the product of either inherited (i.e., nature) or learned (i.e., nurture) influences. Nature is what we think of as what we are pre-destined to become and is influenced by genetic inheritance (i.e., hair color). On the other hand, nurture is the influence of external factors after conception (i.e., personality characteristics).
Breaking down nature versus nurture within the psychological science disciplines involves a discussion around the two extreme schools of thought – Nativism and Empiricism. The first is nativism. Eye color, hair texture, skin pigmentation and predisposition to genetic diseases are all a function of the genes we inherit. These facts have led nativists to speculate whether psychological characteristics such as behavioral tendencies, personality attributes, and mental abilities are also genetically influenced. The basic assumption amongst nativists is that the characteristics of the human species is entirely a product of evolution and individual differences can be explained by each person’s unique genetic code.
Empiricism is the opposite of nativism in that it takes the extreme nurture position. Their basic assumption is that at birth, the human mind is a blank slate, or a tabula rasa, and that it is gradually filled as a result of experience. Psychological characteristics and behavioral differences that emerge from birth through childhood are the results of learning and being part of an environment.
Researchers in the field of behavioral genetics study how genes affect behavior and therefore relate variation in behavior between people. Behavioral genetics allows psychology to quantify just how much nature and nurture impact specific psychological traits. Adoption also acts a natural experiment that allows researchers to determine whether certain traits are more or less a product of either nature or nurture or a combination of the two. Studies have consistently shown that adopted children show greater physical resemblance to their biological parents, rather than their adoptive parents.
Another way researchers have studied nature versus nurture is through twin studies. Like adoption studies, twin studies support that psychological traits are extremely inheritable, about 50% on average. In a Twins in Early Development Study , there was found to be correlations between twins on a range of behavioral traits such as personality (empathy and hyperactivity) and the reach of phonetics.
Nature versus nurture is just one way that developmental psychology tries to explain and understand the differences in human behavior and how genetic and environmental factors contribute to those differences.
Is Developmental Psychology a nature or nurture?
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of changes that occur in human beings over the course of their lives and examines change and development across a broad range of topics, such as motor skills, cognitive development, problem-solving skills, personality and emotional development, among others.
When explaining development, considering both nature and nurture is important. Developmental psychology seeks to answer two big questions around nature versus nurture. The first is how much weight does each contribute? And the second is how do nature and nurture interact? Developmental psychology considers both nature and nurture when it comes to explaining human development since they are both seen as playing a crucial role in determining the development of personality and other behaviors.
Was Freud nature or nurture?
Sigmund Freud stated that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality characteristics. Freud was of the belief that parenting is of primary importance to a child’s development. These aspects of the theory led Freud to believe early childhood was crucial to the development of personality as an adult. In fact, he focused primarily on the first five years of life as being critical to healthy outcomes.
While Freud was primarily interested in how nurture influences a person’s behavior, Freud’s theory of aggression is steeped in nature. Freud believed that aggression was an innate drive propelled by thoughts and feelings of the subconscious mind. Unlike his belief that personality traits are influenced by a person’s environment during early childhood, he saw aggression as something that was innate in everyone.
Despite Freud’s flourishing success and contributions to the psychology field, it is clear that even he struggled with the nature versus nurture debate.
How does nature and nurture affect personality?
As discussed above, there are various schools of thoughts around whether nature or nurture influence personality. However, the contemporary school of thought is that person’s personality is multi-faceted and is therefore a combination of both influences, rather than one being solely responsible.
Personality is not determined by any single gene. Rather, genes work together to determine certain actions. There is no “IQ gene” that determines intelligence. Genes are also not so powerful that they can control or create our personalities solely by themselves. In the same way that personality is not determined solely by genes, it is also not solely determined by environmental influences. Personality is affected by both genetic and environmental influences and because of this, it is something that can continue to be shaped throughout a person’s life.
How does nature and nurture affect intelligence?
Intelligence is a complex, multi-faceted phenomenon that cannot simply be boiled down to whether one’s genetics or environment influence intelligence.
Throughout the history of psychology, the nature versus nurture debate has caused quite a bit of controversy. Eugenics, for example, was a movement heavily influenced by the nativist approach.
Psychologist Francis Galton , a cousin of naturalist Charles Darwin, coined the terms nature versus nurture as well as eugenics and believes that intelligences were the result of genetics. Galton believed that intelligent individuals should be encouraged to marry and have many children, while less intelligent individuals should be prevented from reproducing.
Today, the majority of experts believe that a combination of nature and nurture impact behavior and development, including intelligence.
How does nature and nurture influence child development?
In the past, children were viewed as blank slates, which led to parents believing they could mod their child’s development solely through their actions. The idea put a lot of pressure on parents as it suggested that any decision would impact their child. We now know that this is not the case as their genetic makeup influences aspects of their behavior and personality. Beginning at conception, how a child develops and behaviors is partly influenced by the genes they inherit. Examples of nature influencing characteristics include sleeping behavior and parts of a child’s personality. However, the child’s environment plays a crucial role in influencing which genetic influences play a prominent role.
The reality is that nature and nurture both play a crucial role in influencing child development. In fact, new research demonstrates that environmental influences can actually affect genetic expression and whether or how the genes are expressed in the first place. The research found that adverse fetal and early childhood experiences can, and oftentimes do, lead to physical and chemical changes in the brain that can last a lifetime. Additionally, the study found that variations in DNA sequences between individuals influences the way genes are expressions, but the environment in which one develops, before and soon after birth, provides an impactful experience that chemically modify certain genes.
What are the 6 principles of nurture?
The six principles of nurture include: environmental variables, childhood experiences, how we were raised, social relationships, surrounding culture, and having a sense of belonging.
Is anxiety caused by nature or nurture
Around 40 million people are diagnosed with anxiety annually. When it comes to mental illness, the nature nurture debate can be quite helpful in shedding light on why some people develop issues whereas others do not. Anxiety researchers cite social learning theory as significant to the development of clinical anxiety conditions. Four ways the development of anxiety can be explained is:
- Exposure to a traumatic event can lead to fear and anxiety.
- Anxiety and fear are learned by people through watching the reactions and experiences of those around them.
- Simply talking about situations, objects, or people can lead to fear or anxiety.
- Children may negatively reinforce anxiety by avoiding it, which can lead to the development of a clinically significant anxiety condition.
On the other side of the debate, nature plays a pivotal role in understanding anxiety. Twin studies on anxiety disorders have found a genetic foundation for developing anxiety . However, gene-mapping findings have been less clear. This has led researchers to believe that there may be different genes responsible for the development of specific anxiety disorders, such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
When it comes to the nature nurture discussion for just about any topic, it becomes clear that both likely play a role in determining why certain behaviors and health problems arise.
Is aggression Nature or nurture?
Examples of nature influencing aggression include Sigmund Freud’s belief that aggression is innate and therefore is influenced by nature. In contrast to this view, Albert Bandura’s social learning theory states that aggression is learned from the environment through observation and imitation. In 1961, Bandura sought to prove this through his famous Bobo Doll experiment. During the experiment, 24 children were shown an aggressive model, 24 children were shown a non-aggressive model, and 24 children were shown no model. The study found that children are able to learn social behavior such as aggression through the process of observing another person’s behavior.
Is high IQ nature or nurture?
A high IQ is not determined by nature or nurture, rather it is a combination of the two. As stated previously, there is no single “IQ gene” that will predetermine whether a person is destined to have a higher IQ than someone else. Rather, it is a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental influences that truly impact a person’s IQ.
Does nature affect intelligence?
Intelligence is a complex trait that is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Intelligence is strongly influenced by the environment a person grows up in. Many psych reports show that factors related to a child’s home environment and parenting, education and availability of learning resources, and nutrition are just some of the environmental contributions to a person’s intelligence. Examples of nature influencing intelligence have been studied extensively , however the studies have not conclusively identified any genes that play a major role in differences in intelligence.
Which one is more important between nature and nurture?
The current school of thought is that nature and nurture are equally important and that both influence a person’s overall behavior and personality.
Why is nurture important?
While certain genetic factors may create an increased chance for a particular illness or behavior, the probability that a person develops either is oftentimes dependent on environment. One example of this is that the basis for addiction is not thought to be entirely genetic by most researchers. Environmental aspects, such as the habits of parents, friends, or a partner might also be significant factors contributing to whether a person develops an addiction. Similarly, researchers found that while a family history of mental health conditions was the second strongest predictor of mental illness, the strongest predictors were life events and experiences, such as childhood bullying, abuse, or other trauma. Nurture plays a crucial role in how we develop and evolve into who we are in the world.
How do you nurture yourself?
There are many ways to nurture yourself and doing so will have many positive impacts. A technique for treating yourself better is by developing your “ Inner Nurturing Parent .” Even if you did not have the most nurturing of familial relationships, you can create your inner nurturing parent by forgiving your past mistakes, making every effort to keep yourself healthy and safe,to love and support yourself. Some tips to get started include telling yourself “I love you and appreciate who you are” at the end of each day or saying “I believe in you” when you’ve had a particularly tough day. Making time each day for things you enjoy and prioritizing your health and well-being by starting a weekly exercise routine are other ways to begin to nurture yourself.
What is a nurturing woman?
There is no one “right” way to be a nurturing person. However, some characteristics of a nurturing person is someone who makes an effort to keep loved ones healthy and safe, listens to and acknowledges their feelings, forgives mistakes, and lets their loved ones know how loved they are. A nurturing person makes mistakes, lets others know when they have made a mistake and accepts responsibility for those mistakes.
- Evolutionary Psychology: Explaining Human Behavior Medically reviewed by Dr. April Brewer , DBH, LPC
- What Is A Military Psychologist And How To Become One Medically reviewed by Melissa Guarnaccia , LCSW
- Psychologists
- Relationships and Relations
Take 10% OFF— Expires in h m s Use code save10u during checkout.
Chat with us
- Live Chat Talk to a specialist
- Self-service options
- Search FAQs Fast answers, no waiting
- Ultius 101 New client? Click here
- Messenger
International support numbers
For reference only, subject to Terms and Fair Use policies.
- How it Works
Learn more about us
- Future writers
- Explore further
Ultius Blog
Sample critical essay on nature vs. nurture.

Select network
There has long been a debate about whether nature or nurture matters more in determining the traits an individual will have. In other words, do genetics or environment play a more formative role in the development of one’s personality? Nature says that our traits are influenced by genetic inheritance and similar biological factors while nurture is meant as the influence of environmental factors after conception.
We know that physical characteristics like eye color, hair color, and height can be attributed to specific genes within our DNA. But what about emotional or behavioral traits? This sample biological essay from the essay writing services at Ultius examines the question that while some behavioral traits can be traced to certain genes, does our environment play a role in activating those genes?
Our genetic makeup
Science tells us that certain traits are most definitely attributed to genetic causes. Our eye color, skin pigmentation, and certain diseases like Tay-Sachs or Huntingdon’s chorea are all direct results of the genes we inherit from our parents. Other traits to which we can be genetically predisposed include weight, height, life expectancy, hair loss, and vulnerability to certain illnesses (McLeod 2007). Because these characteristics can be definitively connected to our biology, many speculate on whether or not genetic factors can contribute to behavioral tendencies, mental abilities, and personality traits .
Nativists, those who believe that every characteristic we have is determined only by nature, assume that the characteristics of the human species as a whole are simply a product of evolution and that the things that make us unique are a result of our own specific genetic code. They believe that the characteristics that are not observable at birth, such as personality traits, emerge later as the product of maturation.
We each have a biological clock inside us that turns certain behaviors on and off in a way that is preprogrammed from birth. An example of this would be the way our bodies change during puberty. Nativists also believe that:
“maturation governs the emergence of attachment in infancy, language acquisition, and even cognitive development as a whole” (McLeod 2007).
Bowlby’s theory of attachment views the bond between the mother and child as being an innate process that aids in our survival as a species. Likewise, Chomsky believed that language is learned through the use of an innate language acquisition device that all humans are born with (McLeod 2007). In addition, Freud speculated that traits like aggression are engrained in our DNA.
Fraternal twins as evidence of nature over nurture
Similarly, it is often debated whether or not criminal activity can be linked to a genetic disposition. One of the biggest pieces of supporting evidence for the nature over nurture is the fact that fraternal twins exhibit similar characteristics even when they are raised apart. Often times, these twins will share behavioral traits as if they were raised together in the same place. Mental health is undoubtedly affected by our biological dispositions.
For example, bipolar is approximately five times as likely to develop when there is a family history of the condition (“Nature vs. Nurture Debate”). There are similar statistics available for a wide number of mental health conditions . Researchers also tend to place more emphasis on nature when it comes to addiction. Alcoholism, for example, can recur in families and it has been found that certain genes may influence the development of alcoholism and the way alcohol effects the body.
Alternatively, to nativists, empiricists believe that the human mind is a blank slate at birth and any characteristics we develop are a result of our experiences and environment. With point of view speculates that psychological characteristics and our behavioral tendencies are things we learned during our development. While the concept of maturation applies to the biological development we experience, any psychological growth is a result of the way we are brought up.
Attachment of infants as evidence of nurturing
An example of this would be the way infants form attachment. The formation of attachment is a direct result of the love and attention a child receives. If they are not given love and attention, the attachment will not develop. Similarly, we learn language by mirroring the speech we hear from others.
Our cognitive development is dependent on the environment and civilization in which we are reared (“Nature vs. Nurture”). Bandura’s social learning theory states that aggression is a characteristic that we learn through observation and imitation. In addition, Skinner believed that language is something individuals learn from others via behavioral shaping techniques.
Watson's ideas on environmental learning
John Watson, one of the most well-known psychologists to propose environmental learning as the dominating factor in the nature versus nurture debate, feels that our behavioral traits are purely a result of our surroundings and experiences. He felt that he could condition a new behavior in a child or alter an already existing behavior that is considered to be unfavorable (Sincero 2016).
Watson believed that he could randomly choose any baby out of a group of twelve infants and raise the child to become any type of specialist he chose. He stated that he could train any child to be anything, regardless of the individual’s talents, potentialities, and social groups.
Benefits of nurturing on mental health
Just like nature, nurture affects our mental health, as well. While someone may have a genetic disposition for one condition or another, there still needs to be an environmental trigger for that condition to develop. If there is a genetic indication that a mental condition may develop, the individual can be ‘nurtured’ in a way that can prevent the condition from developing or lessen its severity.
A neuroscientist named James Fallon discovered that he possessed the brain of a psychopath and believed that being raised in a loving and nurturing environment helped ensure that he never fully developed enough sociopathic traits for them to affect his success (“Nature vs. Nurture Debate”).
The foundations of addiction
In a similar way, the basis for addiction is not entirely determined by genetics. Certain environmental aspects, such as the habits of our friends, partners, and parents, can contribute significantly to the development of addiction. A genetic predisposition to alcoholism becomes entirely more significant when the individual in question is frequently exposed to alcohol abuse and comes to view the harmful behavior as normal.
A study conducted at the University of Liverpool found that a family history of mental health conditions was only the second strongest indicator that a mental condition would develop (“Nature vs. Nurture Debate”). The strongest predictor was life events and experiences that contributed to the development of the mental condition, such as abuse, bullying, or childhood trauma.
Meeting in the middle
Today, most people agree that our characteristics are a result of a combination of both nature and nurture. There is enough support for both sides to completely count either side out. For example, if one twin develops schizophrenia gene , the other twin has only a fifty percent chance of also developing the same condition (“Nature vs. Nurture Debate”). Clearly, both nature and nurture can affect the development of certain disorders.
The question then shifted from ‘which one’ to ‘how much?’ We know that both play a role, but which force is more important? Francis Galton was the first to pose this question during the late nineteenth century. A relative of Charles Darwin, he felt that intellectual ability was mostly attributed to genetics and that the tendency for genius to be a familial trait was the result of natural superiority (McLeod 2007).
Like what you're reading? Consider buying an essay from Ultius.
Arthur Jenson on intelligence testing
Many others have agreed throughout history, which has spurred an influx of intelligence testing; in particular, on separated twins and adopted children. Arthur Jenson is an American psychologist who is a modern proponent of nature over nurture. Jenson cites average IQ scores in which black Americans scored significantly lower than white participants and suggested that as much as eighty percent of intelligence is inherited (McLeod 2007).
Not surprisingly, controversy developed surrounding Jenson’s claims due to the logical weakness of his argument. It was widely agreed that his study was tainted by social and political implications that are often drawn from various studies that claim to represent natural inequalities between race and other social groups. Differences in IQ scores between various ethnic groups can be explained by biases in testing methods and social inequalities in access to resources and opportunities (McLeod 2007). Similarly, it is hotly debated whether or not alleged intelligence difference in male versus female results is a consequence of biology or culture.
The importance of both nature and nurture
Now, however, the scientific world has come to understand that trying to place a numerical value on nature and nurture to judge which is more important is not really the right approach (Davies 2001). Intelligence, for example, is a complex human characteristic that can exhibit itself in a wide variety of ways from genius to basic common sense .
By attempting to place quantitative values on the separate factors, we fail to focus on the fact that biology and environment interact in a host of important and intricate ways (Ridley 2003). Today, most people agree that neither biology nor environment act independently of one another. Both are necessary for any characteristic to manifest. Because they are dependent on each other and interact in such a complex manner, it is illogical to attempt to think of them separately.
How nature and nurture combine in the individual
Rather than defending nativists or empiricists, most psychologists are now more interested in researching the ways in which nature and nurture interact with each other to develop characteristics and traits. In psychotherapy, this means that not only does there need to be a genetic disposition required for mental disorders to develop, but there also needs to be an environmental trigger, as well (Feller 2015).
The recognition of this important relationship is especially important given the genetic advancements made during the twenty-first century. The Human Genome Project and advent of bioengineering sparked wide interest in tracing types of behavior to particular strands of DNA found on certain chromosomes (McLeod 2007). Scientists expect to soon find specific genes that are linked to criminality, alcoholism, and other characteristics.
Stuck with writing?
Ultius can help
Ordering takes 5 minutes
Conclusion
Psychologists have been debating the influence of nature versus nurture over human characteristics for a very long time. After the scientific world came to recognize that biology and environment both play a role, the emphasis shifted to determining which was more important. Now though, as we have come to truly understand the complexity of the relationship between our genetic dispositions and environmental triggers, we no longer focus on one versus the other, but rather the way they interact with and affect each other.
While it is certainly helpful in the development of certain conditions for there to be a genetic disposition, there almost always needs to be an environmental trigger that causes the characteristic to manifest in an individual. This is only a small part of this complex discussion and an example of what you can expect when you buy a critical essay from Ultius.
Davies, Kevin. “Nature vs. Nurture Revisited.” PBS . WGBH Educational Foundation, 17 Apr. 2001. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
Feller, Stephen. “Nature vs. Nurture: It’s a tie, study finds.” UPI . United Press International, Inc., 19 May 2015. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
McLeod, S.A. “Nature vs. Nurture in Psychology.” Simply Psychology . Simple Psychology, 2007. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
“Nature vs. Nurture.” Diffen . Diffen, 2016. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
“Nature vs. Nurture Debate”. GoodTherapy.org . GoodTherapy.org, 2016. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
Ridley, Matt. “Nature via nurture: Genes, experience, and what makes us human.” APA PsycNET . HarperCollins Publishers, 2003. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
Sincero, Sarah Mae. “Nature and Nurture Debate” Explorable . Explorable.com, 2016. Web. 14 Apr. 2016.
https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-critical-essay-on-nature-vs-nurture.html
- Chicago Style
Ultius, Inc. "Sample Critical Essay on Nature vs. Nurture." Ultius | Custom Writing and Editing Services. Ultius Blog, 22 Apr. 2016. https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-critical-essay-on-nature-vs-nurture.html
Copied to clipboard
Click here for more help with MLA citations.
Ultius, Inc. (2016, April 22). Sample Critical Essay on Nature vs. Nurture. Retrieved from Ultius | Custom Writing and Editing Services, https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-critical-essay-on-nature-vs-nurture.html
Click here for more help with APA citations.
Ultius, Inc. "Sample Critical Essay on Nature vs. Nurture." Ultius | Custom Writing and Editing Services. April 22, 2016 https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-critical-essay-on-nature-vs-nurture.html.
Click here for more help with CMS citations.
Click here for more help with Turabian citations.
Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions and matches customers with highly qualified writers for sample writing, academic editing, and business writing.

Tested Daily
Click to Verify
About The Author
This post was written by Ultius.

- Writer Options
- Custom Writing
- Business Documents
- Support Desk
- +1-800-405-2972
- Submit bug report
- A+ BBB Rating!
Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions for consumers around the world. Connect with great American writers and get 24/7 support.
© 2024 Ultius, Inc.
- Refund & Cancellation Policy
Free Money For College!
Yeah. You read that right —We're giving away free scholarship money! Our next drawing will be held soon.
Our next winner will receive over $500 in funds. Funds can be used for tuition, books, housing, and/or other school expenses. Apply today for your chance to win!
* We will never share your email with third party advertisers or send you spam.
** By providing my email address, I am consenting to reasonable communications from Ultius regarding the promotion.
Past winner

- Name Samantha M.
- From Pepperdine University '22
- Studies Psychology
- Won $2,000.00
- Award SEED Scholarship
- Awarded Sep. 5, 2018
Thanks for filling that out.
Check your inbox for an email about the scholarship and how to apply.
Essay Sample: Nature Versus Nurture
26 March, 2020
7 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
This sample is a great example of the compare and contrast essay writing. It presents two points of view on what influences the development of a personality the most - genetics or environmental factors. Don't hesitate to read it to see what such a type of essay should look like when written professionally!

Nature and nurture is a hotly contested argument concerning what influences the behavior and personality attributes of individuals. Nature is entirely dependent on the genetic combination of an individual which dictates their character and appearance. On the other hand, nurture is dependent on the environmental factors that an individual gets exposed to which end up shaping his or her personality. Nature and nurture influence individuals to a certain extent because individuals get exposed to both of them in one way or the other dictating their development process.

Nature principle holds that biological characteristics of individuals get inherited from the genetic makeup in their lineage. Character traits such as height, weight, vulnerability to certain illnesses and skin complexion are inherited and determined by the genetic combination of individuals. Such biological combination is usually similar amongst individuals who are blood relatives, and for this reason, they tend to have almost a uniform genetic combination. Moreover, other behavioral, mental and personality attributes are also a reflection of our genetic makeup and usually inherited from individuals’ close blood relatives (Kong et al. 2018). Through the traits, it is easier to identify closely related individuals just by looking at their appearance and conduct.
Besides, specific characteristics do not become evident during birth, and when a person reaches a certain age, for instance, during puberty, that is when the hidden attributes begin showing up. The biological clock guides such characteristics, and when the right time comes, the physical and behavioral attributes mature and become conspicuous. Such traits get programmed in a way that for them to grow visible, they will take a certain period to develop. Moreover, they are also dependent on other biological factors within our bodies for them to manifest. However, the traits still maintain the genetic combination and the similarity of a specific lineage.
Note that our company provides academic writing help. You can buy a narrative essay (or any other type) written from scratch by our essay writer .
On the contrary, through nurture, an individual acquires specific attributes from the environment that surrounds them. When a child is born, for instance, its mind is black and empty. It is through its interaction with the surrounding and the people around it that will make the infant acquire some of their traits through learning, observation and aping their conducts. In other words, nurturing is dependent on the environment, experience, and learning as the individual interacts with the environment with time (Vazsonyi, Roberts, Huang & Vaughn, 2015). The way an individual was nurtured or brought up will influence their aspect of child development. Maturation will only affect biological development. The environment plays a vital role in the development process.
Similarly, the type of relationships also plays a crucial role in the nurturing, especially during child development. For instance, an infant develops an emotional attachment to its parents because of the love and affection it receives. Moreover, children who are given proper care and affection will reciprocate the same while growing up. On the contrary, infants who receive harsh treatment from their parents will develop withdrawal symptoms while growing up. Also, the infants also try and learn how and what to talk by studying the speech of those around them. The cognitive development comes from the exposer that the infant receives and conditions surrounding it.
Correspondingly, certain traits are acquired based on what an individual went through. Children who got abused or molested when growing up develop specific antisocial characteristics, for instance, being high tempered, harsh and develops particular disorders. For example, bipolar disorders manifest because an individual underwent harsh treatment which affects their psychological stability after that. Some of them become abusers and molesters in their future relationships as a way of imitating and justifying what they experienced while growing up. Imitation is a way of implementing what the individual has learned during the nurturing process by putting the lessons into practice.
Striking a Balance
However, after careful analysis, psychologists have discovered that both nature and nurture are responsible for the development of an individual. Both factors interact with each other and play a crucial role in shaping up the conduct of an individual (Lux, 2014). For example, in psychopathology, it is argued that both hereditary factors and environmental conditions contribute to the development of mental disorders in individuals. The biological combinations of people closely interact with the socio-cultural set up surrounding them. Individuals are now left to make their own choices in dictating what is suitable for them and what should be left out. Nature and nurture complement each other in shaping an individual.
Conclusively, nature and nurture are broiling discussion, and both sides have valid points to justify their stands. Nature is purely based on the fact that genetic makeup influence how an individual behaves and thinks. Similarly, the natives hold that genetic factors dictate factors such as the appearance, particular illness, and intelligence levels. On the contrary, individuals who believe in nurturing hold that environmental factors are majorly involved in the development process of individuals. Children acquire traits through learning from the people surrounding them and will try to imitate the behavior after that. However, psychologists are trying their level best to strike a balance between the two school of thoughts since both sides hold valid arguments, but both nurture and nature interact with each other during the development process. Nature and nurture cannot get treated in isolation.

Lux, V. (2014). Nature and nurture. Encyclopedia of Critical Psychology , 1225-1231.
Kong, A., Thorleifsson, G., Frigge, M. L., Vilhjalmsson, B. J., Young, A. I., Thorgeirsson, T. E., … & Gudbjartsson, D. F. (2018). The nature of nurture: Effects of parental genotypes. Science , 359 (6374), 424-428.
Vazsonyi, A. T., Roberts, J. W., Huang, L., & Vaughn, M. G. (2015). Why focusing on nurture made and still makes sense: The biosocial development of self-control. The Routledge international handbook of biosocial criminology , 263-280.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

Nature vs Nurture Examples: Genes or Environment
Categories Development
The nature versus nurture debate focuses on the question of whether genetic or environmental factors matter most in the course of human development.
What is it that makes you who you are? Some might say that it is your genes that have the greatest influence in controlling your personality and preferences. Others might say that it is your environment and the unique experiences you have had over the course of your life that have a greater role.
In this article, learn more about the nature vs. nurture debate and what research has found about the contributions of genetic and environmental factors.
Table of Contents
What Is the Nature vs Nurture Debate?
The nature vs. nurture debate is often described as one of the big philosophical and scientific questions facing psychologists. So what exactly does this debate mean? Why is it important for understanding the human mind and behavior?
Let’s start by learning more about each of these factors.
- Nature: This side of the debate argues that genes have the greatest influence over who we are, from the way we look to the way we behave. Genes determine physical traits such as height, eye color, hair color, and face shape, but they can also contribute to other attributes such as your personality traits and cognitive abilities.
- Nurture: This side of the debate argues that environmental variables such as upbringing, individual experiences, and other social relationships play a more important role. Your upbringing, early social interactions, school, and peers all shape who you are and how you behave.
Let’s consider an example. If a student excels at math, is it because they inherited that ability from their parents or because they work hard to learn the subject?
Nature would suggest that they do well because they are genetically inclined to do so, while nature argues that their talent stems from their upbringing and educational background.
History of Nature vs. Nurture
The debate over nature and nurture predates psychology and goes back to the days of the ancient philosophers. In philosophy, this is often referred to as the nativism versus empiricism debate. What do these terms mean and how do they relate to nature and nurture?
The nativist approach suggests that inheritance plays the greatest role in determining characteristics. Nativism proposes that people’s characteristics, both physical and mental, are innate. These are things that are passed down genetically from our ancestors. The nativist approach essentially espouses the nature side of the argument.
Noam Chomsky’s theory of language acquisition is one of the best-known examples of nativism in psychology. Chomsky suggested that language develops as a result of an innate language acquisition device. He believed that people are able to learn language because they have an innate, hard-wired capacity for what he referred to as universal grammar.
Empiricism represents the nurture side of the debate. The empiricist approach suggests that all learning is the result of experience and environmental factors.
The philosopher John Locke took an empiricist approach and proposed a concept known as tabula rasa, which means “blank slate.” This approach that the mind is essentially that —a blank slate—and that it is through learning and experience that all knowledge, skill, and behavioral patterns are acquired.
Behaviorism is one example of an empirical approach to understanding human behavior. Behaviorists such as John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner believed that all human behavior was the result of conditioning, either classical (associative) or operant ( reinforcement and punishment ).
Watson was famously known for proclaiming that he could train anyone to be anything using the principles of conditioning, regardless of that individual’s genetics and background.
Approaches to Psychology
While few contemporary psychologists take an extreme, hard-lined empiricist or nativist approach, different branches of psychology do sometimes tend to emphasize one influence over the other.
Biological Psychology
Biological psychology, for example, tends to focus more on the nature side of the debate. This area of psychology focuses on how biological factors influence human behavior, so things such as the brain, neurons, and neurotransmitters are of greater interest than external factors.
Behavioral Psychology
Behavioral psychology tends to take the nurture side of the debate, focusing on how environmental factors and learned associations contribute to how people think and act.
Health Psychology
Health psychology is an example of an approach that tends to lie somewhere in the middle. Health psychologists are focused on understanding how both biological and environmental factors contribute and interact to affect an individual’s health.
Nature vs. Nurture Examples
Looking at examples can be helpful to understand why the nature vs nurture debate has been so crucial throughout psychology’s history. The topic is not just an important philosophical debate. It has been critical for understanding what factors influence different aspects of human behavior and has been the source of considerable controversy at times.
Consider the long debate over the factors that influence intelligence. Those on the nature side of the debate suggest that the greatest influence on IQ is inheritance. Some early thinkers such as Francis Galton believed that intelligence could largely be attributed to genetic factors.
Such views have been used to justify discriminatory social policies and attitudes. When some research suggested that some groups of people had lower IQ scores, for example, some researchers interpreted these results to suggest that these individuals scored lower as a result of genetics.
Those taking the nurture side of the debate point out that other factors, including biased test construction, racism, and systemic discrimination impacting educational access and quality, play a more important role.
Inequality, discrimination, and lack of access play a role in shaping how well people perform on intelligence tests and other assessments of educational outcomes.
Gender Differences and Education
Sex differences in school performance and attainment is another area where the debate between the contributions of nature vs nurture comes into play. Girls often perform better on verbal tests but less well on math. As they advance in school, girls also become less likely to enter STEM courses and STEM fields.
Those taking a nature perspective might suggest that girls are inherently less capable in these subjects. Nature advocates, however, would point out that social variables, including gender stereotypes and discrimination, have a greater influence.
Many researchers today believe that human behavior is influenced by both nature and nurture, and that it is often the interaction of the two variables that is even more important.
Examples of the Impact of the Nature and Nurture Debate
Few modern psychologists would take an extreme nature or nurture position. Rather than asking which one controls specific variables, researchers are more likely to wonder about the degree to which each of these forces plays a role. So what exactly are the relative contributions of nature and nurture?
According to the research, the answer is about 50/50. Researchers collected the results of nearly every twin study conducted over the last half-century. Doing this allowed them to determine which factors played a role in determining certain characteristics.
Twin studies examine similarities and differences by looking at twins who are either raised together or raised apart. This allows researchers to determine the impact of genes versus the environment.
Researchers analyzed more than 2,700 twin studies involving a whopping 14.5 million pairs of twins from 39 different countries and discovered that genes and environment share a roughly equal role in determining who we are.
Variations in personality traits and disease were determined to be 49% due to genetics and 51% due to environment.
One important thing to note is that while the research suggests a 50/50 split, the findings did reveal that genes do play a greater role in the risk of certain diseases. Bipolar disorder, for example, was found to be approximately 70% heritable.
Examples of How Nature and Nurture Interact
Today, many experts suggest that we should be more concerned with how nature and nurture interact to determine how we develop. For example, we might be genetically inclined toward a certain trait, but our experiences can determine to what degree that trait is expressed.
Height is a good example of how genes and the environment can interact to make you who you are. Even if you inherit genes for tallness, proper nourishment is important for reaching that height. Kids who come from tall families might not become tall if they do not receive proper nutrition during their childhood.
So while we know that both factors are equally important, the question we are left to ponder is just how much of a role each factor plays in the development of certain characteristics. As the research suggests, some diseases are more strongly linked to genetics than to the environment.
As researchers continue to explore how nature and nurture interact, we will continue to gain a deeper understanding of the factors that contribute to who we are.
Haworth CM, Davis OS, Plomin R. Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): a genetically sensitive investigation of cognitive and behavioral development from childhood to young adulthood . Twin Res Hum Genet . 2013;16(1):117-125. doi:10.1017/thg.2012.91
Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Neuroscience and Nervous System Disorders. From Molecules to Minds: Challenges for the 21st Century: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2008. Grand challenge: Nature versus nurture: How does the interplay of biology and experience shape our brains and make us who we are ? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK50991/
Sravanti L. (2017). Nurture the nature . Indian journal of psychiatry , 59 (3), 385. https://doi.org/10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_341_17

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 4. Genetics and Evolution
4.1 The Nature-Nurture Question
Eric Turkheimer
People have a deep intuition about what has been called the “nature–nurture question.” Some aspects of our behavior feel as though they originate in our genetic makeup, while others feel like the result of our upbringing or our own hard work. The scientific field of behavior genetics attempts to study these differences empirically, either by examining similarities among family members with different degrees of genetic relatedness, or, more recently, by studying differences in the DNA of people with different behavioral traits. The scientific methods that have been developed are ingenious, but often inconclusive. Many of the difficulties encountered in the empirical science of behavior genetics turn out to be conceptual, and our intuitions about nature and nurture get more complicated the harder we think about them. In the end, it is an oversimplification to ask how “genetic” some particular behavior is. Genes and environments always combine to produce behavior, and the real science is in the discovery of how they combine for a given behavior.
Learning Objectives
- Understand what the nature–nurture debate is and why the problem fascinates us.
- Understand why nature–nurture questions are difficult to study empirically.
- Know the major research designs that can be used to study nature–nurture questions.
- Appreciate the complexities of nature–nurture and why questions that seem simple turn out not to have simple answers.
Introduction
There are three related problems at the intersection of philosophy and science that are fundamental to our understanding of our relationship to the natural world: the mind–body problem, the free will problem, and the nature–nurture problem. These great questions have a lot in common. Everyone, even those without much knowledge of science or philosophy, has opinions about the answers to these questions that come simply from observing the world we live in. Our feelings about our relationship with the physical and biological world often seem incomplete. We are in control of our actions in some ways, but at the mercy of our bodies in others; it feels obvious that our consciousness is some kind of creation of our physical brains, at the same time we sense that our awareness must go beyond just the physical. This incomplete knowledge of our relationship with nature leaves us fascinated and a little obsessed, like a cat that climbs into a paper bag and then out again, over and over, mystified every time by a relationship between inner and outer that it can see but can’t quite understand.
It may seem obvious that we are born with certain characteristics while others are acquired, and yet of the three great questions about humans’ relationship with the natural world, only nature–nurture gets referred to as a “debate.” In the history of psychology, no other question has caused so much controversy and offense: We are so concerned with nature–nurture because our very sense of moral character seems to depend on it. While we may admire the athletic skills of a great basketball player, we think of his height as simply a gift, a payoff in the “genetic lottery.” For the same reason, no one blames a short person for his height or someone’s congenital disability on poor decisions: To state the obvious, it’s “not their fault.” But we do praise the concert violinist (and perhaps her parents and teachers as well) for her dedication, just as we condemn cheaters, slackers, and bullies for their bad behavior.
The problem is, most human characteristics aren’t usually as clear-cut as height or instrument-mastery, affirming our nature–nurture expectations strongly one way or the other. In fact, even the great violinist might have some inborn qualities—perfect pitch, or long, nimble fingers—that support and reward her hard work. And the basketball player might have eaten a diet while growing up that promoted his genetic tendency for being tall. When we think about our own qualities, they seem under our control in some respects, yet beyond our control in others. And often the traits that don’t seem to have an obvious cause are the ones that concern us the most and are far more personally significant. What about how much we drink or worry? What about our honesty, or religiosity, or sexual orientation? They all come from that uncertain zone, neither fixed by nature nor totally under our own control.

One major problem with answering nature-nurture questions about people is, how do you set up an experiment? In nonhuman animals, there are relatively straightforward experiments for tackling nature–nurture questions. Say, for example, you are interested in aggressiveness in dogs. You want to test for the more important determinant of aggression: being born to aggressive dogs or being raised by them. You could mate two aggressive dogs—angry Chihuahuas—together, and mate two nonaggressive dogs—happy beagles—together, then switch half the puppies from each litter between the different sets of parents to raise. You would then have puppies born to aggressive parents (the Chihuahuas) but being raised by nonaggressive parents (the Beagles), and vice versa, in litters that mirror each other in puppy distribution. The big questions are: Would the Chihuahua parents raise aggressive beagle puppies? Would the beagle parents raise non aggressive Chihuahua puppies? Would the puppies’ nature win out, regardless of who raised them? Or… would the result be a combination of nature and nurture? Much of the most significant nature–nurture research has been done in this way (Scott & Fuller, 1998), and animal breeders have been doing it successfully for thousands of years. In fact, it is fairly easy to breed animals for behavioral traits.
With people, however, we can’t assign babies to parents at random, or select parents with certain behavioral characteristics to mate, merely in the interest of science (though history does include horrific examples of such practices, in misguided attempts at “eugenics,” the shaping of human characteristics through intentional breeding). In typical human families, children’s biological parents raise them, so it is very difficult to know whether children act like their parents due to genetic (nature) or environmental (nurture) reasons. Nevertheless, despite our restrictions on setting up human-based experiments, we do see real-world examples of nature-nurture at work in the human sphere—though they only provide partial answers to our many questions.
The science of how genes and environments work together to influence behavior is called behavioral genetics . The easiest opportunity we have to observe this is the adoption study . When children are put up for adoption, the parents who give birth to them are no longer the parents who raise them. This setup isn’t quite the same as the experiments with dogs (children aren’t assigned to random adoptive parents in order to suit the particular interests of a scientist) but adoption still tells us some interesting things, or at least confirms some basic expectations. For instance, if the biological child of tall parents were adopted into a family of short people, do you suppose the child’s growth would be affected? What about the biological child of a Spanish-speaking family adopted at birth into an English-speaking family? What language would you expect the child to speak? And what might these outcomes tell you about the difference between height and language in terms of nature-nurture?

Another option for observing nature-nurture in humans involves twin studies . There are two types of twins: monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ). Monozygotic twins, also called “identical” twins, result from a single zygote (fertilized egg) and have the same DNA. They are essentially clones. Dizygotic twins, also known as “fraternal” twins, develop from two zygotes and share 50% of their DNA. Fraternal twins are ordinary siblings who happen to have been born at the same time. To analyze nature–nurture using twins, we compare the similarity of MZ and DZ pairs. Sticking with the features of height and spoken language, let’s take a look at how nature and nurture apply: Identical twins, unsurprisingly, are almost perfectly similar for height. The heights of fraternal twins, however, are like any other sibling pairs: more similar to each other than to people from other families, but hardly identical. This contrast between twin types gives us a clue about the role genetics plays in determining height. Now consider spoken language. If one identical twin speaks Spanish at home, the co-twin with whom she is raised almost certainly does too. But the same would be true for a pair of fraternal twins raised together. In terms of spoken language, fraternal twins are just as similar as identical twins, so it appears that the genetic match of identical twins doesn’t make much difference.
Twin and adoption studies are two instances of a much broader class of methods for observing nature-nurture called quantitative genetics , the scientific discipline in which similarities among individuals are analyzed based on how biologically related they are. We can do these studies with siblings and half-siblings, cousins, twins who have been separated at birth and raised separately (Bouchard, Lykken, McGue, & Segal, 1990; such twins are very rare and play a smaller role than is commonly believed in the science of nature–nurture), or with entire extended families (see Plomin, DeFries, Knopik, & Neiderhiser, 2012, for a complete introduction to research methods relevant to nature–nurture).
For better or for worse, contentions about nature–nurture have intensified because quantitative genetics produces a number called a heritability coefficient , varying from 0 to 1, that is meant to provide a single measure of genetics’ influence of a trait. In a general way, a heritability coefficient measures how strongly differences among individuals are related to differences among their genes. But beware: Heritability coefficients, although simple to compute, are deceptively difficult to interpret. Nevertheless, numbers that provide simple answers to complicated questions tend to have a strong influence on the human imagination, and a great deal of time has been spent discussing whether the heritability of intelligence or personality or depression is equal to one number or another.
One reason nature–nurture continues to fascinate us so much is that we live in an era of great scientific discovery in genetics, comparable to the times of Copernicus, Galileo, and Newton, with regard to astronomy and physics. Every day, it seems, new discoveries are made, new possibilities proposed. When Francis Galton first started thinking about nature–nurture in the late-19th century he was very influenced by his cousin, Charles Darwin, but genetics per se was unknown. Mendel’s famous work with peas, conducted at about the same time, went undiscovered for 20 years; quantitative genetics was developed in the 1920s; DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in the 1950s; the human genome was completely sequenced at the turn of the 21st century; and we are now on the verge of being able to obtain the specific DNA sequence of anyone at a relatively low cost. No one knows what this new genetic knowledge will mean for the study of nature–nurture, but as we will see in the next section, answers to nature–nurture questions have turned out to be far more difficult and mysterious than anyone imagined.
What Have We Learned About Nature–Nurture?
It would be satisfying to be able to say that nature–nurture studies have given us conclusive and complete evidence about where traits come from, with some traits clearly resulting from genetics and others almost entirely from environmental factors, such as childrearing practices and personal will; but that is not the case. Instead, everything has turned out to have some footing in genetics. The more genetically-related people are, the more similar they are—for everything : height, weight, intelligence, personality, mental illness, etc. Sure, it seems like common sense that some traits have a genetic bias. For example, adopted children resemble their biological parents even if they have never met them, and identical twins are more similar to each other than are fraternal twins. And while certain psychological traits, such as personality or mental illness (e.g., schizophrenia), seem reasonably influenced by genetics, it turns out that the same is true for political attitudes, how much television people watch (Plomin, Corley, DeFries, & Fulker, 1990), and whether or not they get divorced (McGue & Lykken, 1992).

It may seem surprising, but genetic influence on behavior is a relatively recent discovery. In the middle of the 20th century, psychology was dominated by the doctrine of behaviorism, which held that behavior could only be explained in terms of environmental factors. Psychiatry concentrated on psychoanalysis, which probed for roots of behavior in individuals’ early life-histories. The truth is, neither behaviorism nor psychoanalysis is incompatible with genetic influences on behavior, and neither Freud nor Skinner was naive about the importance of organic processes in behavior. Nevertheless, in their day it was widely thought that children’s personalities were shaped entirely by imitating their parents’ behavior, and that schizophrenia was caused by certain kinds of “pathological mothering.” Whatever the outcome of our broader discussion of nature–nurture, the basic fact that the best predictors of an adopted child’s personality or mental health are found in the biological parents he or she has never met, rather than in the adoptive parents who raised him or her, presents a significant challenge to purely environmental explanations of personality or psychopathology. The message is clear: You can’t leave genes out of the equation. But keep in mind, no behavioral traits are completely inherited, so you can’t leave the environment out altogether, either.
Trying to untangle the various ways nature-nurture influences human behavior can be messy, and often common-sense notions can get in the way of good science. One very significant contribution of behavioral genetics that has changed psychology for good can be very helpful to keep in mind: When your subjects are biologically-related, no matter how clearly a situation may seem to point to environmental influence, it is never safe to interpret a behavior as wholly the result of nurture without further evidence. For example, when presented with data showing that children whose mothers read to them often are likely to have better reading scores in third grade, it is tempting to conclude that reading to your kids out loud is important to success in school; this may well be true, but the study as described is inconclusive, because there are genetic as well as environmental pathways between the parenting practices of mothers and the abilities of their children. This is a case where “correlation does not imply causation,” as they say. To establish that reading aloud causes success, a scientist can either study the problem in adoptive families (in which the genetic pathway is absent) or by finding a way to randomly assign children to oral reading conditions.
The outcomes of nature–nurture studies have fallen short of our expectations (of establishing clear-cut bases for traits) in many ways. The most disappointing outcome has been the inability to organize traits from more – to less -genetic. As noted earlier, everything has turned out to be at least somewhat heritable (passed down), yet nothing has turned out to be absolutely heritable, and there hasn’t been much consistency as to which traits are more heritable and which are less heritable once other considerations (such as how accurately the trait can be measured) are taken into account (Turkheimer, 2000). The problem is conceptual: The heritability coefficient, and, in fact, the whole quantitative structure that underlies it, does not match up with our nature–nurture intuitions. We want to know how “important” the roles of genes and environment are to the development of a trait, but in focusing on “important” maybe we’re emphasizing the wrong thing. First of all, genes and environment are both crucial to every trait; without genes the environment would have nothing to work on, and too, genes cannot develop in a vacuum. Even more important, because nature–nurture questions look at the differences among people, the cause of a given trait depends not only on the trait itself, but also on the differences in that trait between members of the group being studied.
The classic example of the heritability coefficient defying intuition is the trait of having two arms. No one would argue against the development of arms being a biological, genetic process. But fraternal twins are just as similar for “two-armedness” as identical twins, resulting in a heritability coefficient of zero for the trait of having two arms. Normally, according to the heritability model, this result (coefficient of zero) would suggest all nurture, no nature, but we know that’s not the case. The reason this result is not a tip-off that arm development is less genetic than we imagine is because people do not vary in the genes related to arm development—which essentially upends the heritability formula. In fact, in this instance, the opposite is likely true: the extent that people differ in arm number is likely the result of accidents and, therefore, environmental. For reasons like these, we always have to be very careful when asking nature–nurture questions, especially when we try to express the answer in terms of a single number. The heritability of a trait is not simply a property of that trait, but a property of the trait in a particular context of relevant genes and environmental factors.
Another issue with the heritability coefficient is that it divides traits’ determinants into two portions—genes and environment—which are then calculated together for the total variability. This is a little like asking how much of the experience of a symphony comes from the horns and how much from the strings; the ways instruments or genes integrate is more complex than that. It turns out to be the case that, for many traits, genetic differences affect behavior under some environmental circumstances but not others—a phenomenon called gene-environment interaction, or G x E. In one well-known example, Caspi et al. (2002) showed that among maltreated children, those who carried a particular allele of the MAOA gene showed a predisposition to violence and antisocial behavior, while those with other alleles did not. Whereas, in children who had not been maltreated, the gene had no effect. Making matters even more complicated are very recent studies of what is known as epigenetics (see module, “Epigenetics” http://noba.to/37p5cb8v), a process in which the DNA itself is modified by environmental events, and those genetic changes transmitted to children.

Some common questions about nature–nurture are, how susceptible is a trait to change, how malleable is it, and do we “have a choice” about it? These questions are much more complex than they may seem at first glance. For example, phenylketonuria is an inborn error of metabolism caused by a single gene; it prevents the body from metabolizing phenylalanine. Untreated, it causes intellectual disability and death. But it can be treated effectively by a straightforward environmental intervention: avoiding foods containing phenylalanine. Height seems like a trait firmly rooted in our nature and unchangeable, but the average height of many populations in Asia and Europe has increased significantly in the past 100 years, due to changes in diet and the alleviation of poverty. Even the most modern genetics has not provided definitive answers to nature–nurture questions. When it was first becoming possible to measure the DNA sequences of individual people, it was widely thought that we would quickly progress to finding the specific genes that account for behavioral characteristics, but that hasn’t happened. There are a few rare genes that have been found to have significant (almost always negative) effects, such as the single gene that causes Huntington’s disease, or the Apolipoprotein gene that causes early onset dementia in a small percentage of Alzheimer’s cases. Aside from these rare genes of great effect, however, the genetic impact on behavior is broken up over many genes, each with very small effects. For most behavioral traits, the effects are so small and distributed across so many genes that we have not been able to catalog them in a meaningful way. In fact, the same is true of environmental effects. We know that extreme environmental hardship causes catastrophic effects for many behavioral outcomes, but fortunately extreme environmental hardship is very rare. Within the normal range of environmental events, those responsible for differences (e.g., why some children in a suburban third-grade classroom perform better than others) are much more difficult to grasp.
The difficulties with finding clear-cut solutions to nature–nurture problems bring us back to the other great questions about our relationship with the natural world: the mind-body problem and free will. Investigations into what we mean when we say we are aware of something reveal that consciousness is not simply the product of a particular area of the brain, nor does choice turn out to be an orderly activity that we can apply to some behaviors but not others. So it is with nature and nurture: What at first may seem to be a straightforward matter, able to be indexed with a single number, becomes more and more complicated the closer we look. The many questions we can ask about the intersection among genes, environments, and human traits—how sensitive are traits to environmental change, and how common are those influential environments; are parents or culture more relevant; how sensitive are traits to differences in genes, and how much do the relevant genes vary in a particular population; does the trait involve a single gene or a great many genes; is the trait more easily described in genetic or more-complex behavioral terms?—may have different answers, and the answer to one tells us little about the answers to the others.
It is tempting to predict that the more we understand the wide-ranging effects of genetic differences on all human characteristics—especially behavioral ones—our cultural, ethical, legal, and personal ways of thinking about ourselves will have to undergo profound changes in response. Perhaps criminal proceedings will consider genetic background. Parents, presented with the genetic sequence of their children, will be faced with difficult decisions about reproduction. These hopes or fears are often exaggerated. In some ways, our thinking may need to change—for example, when we consider the meaning behind the fundamental American principle that all men are created equal. Human beings differ, and like all evolved organisms they differ genetically. The Declaration of Independence predates Darwin and Mendel, but it is hard to imagine that Jefferson—whose genius encompassed botany as well as moral philosophy—would have been alarmed to learn about the genetic diversity of organisms. One of the most important things modern genetics has taught us is that almost all human behavior is too complex to be nailed down, even from the most complete genetic information, unless we’re looking at identical twins. The science of nature and nurture has demonstrated that genetic differences among people are vital to human moral equality, freedom, and self-determination, not opposed to them. As Mordecai Kaplan said about the role of the past in Jewish theology, genetics gets a vote, not a veto, in the determination of human behavior. We should indulge our fascination with nature–nurture while resisting the temptation to oversimplify it.
Outside Resources
Web: Institute for Behavioral Genetics http://www.colorado.edu/ibg/
Discussion Questions
- Is your personality more like one of your parents than the other? If you have a sibling, is his or her personality like yours? In your family, how did these similarities and differences develop? What do you think caused them?
- Can you think of a human characteristic for which genetic differences would play almost no role? Defend your choice.
- Do you think the time will come when we will be able to predict almost everything about someone by examining their DNA on the day they are born?
- Identical twins are more similar than fraternal twins for the trait of aggressiveness, as well as for criminal behavior. Do these facts have implications for the courtroom? If it can be shown that a violent criminal had violent parents, should it make a difference in culpability or sentencing?
Image Attributions
Figure 4.1: Sebastián Dario, https://goo.gl/OPiIWd, CC BY-NC 2.0, https://goo.gl/FIlc2e
Figure 4.2: CCO Creative Commons https://pixabay.com/en/baby-twins-brother-sister-siblings-772439/
Figure 4.3: EMSL, https://goo.gl/IRfn9g, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0, https://goo.gl/fbv27n
Figure 4.4: Paul Altobelli, https://goo.gl/SWLwm2, CC BY 2.0, https://goo.gl/9uSnqN
Figure 4.5: Sundaram Ramaswamy, https://goo.gl/Bv8lp6, CC BY 2.0, https://goo.gl/9uSnqN
Bouchard, T. J., Lykken, D. T., McGue, M., & Segal, N. L. (1990). Sources of human psychological differences: The Minnesota study of twins reared apart. Science, 250(4978), 223–228.
Caspi, A., McClay, J., Moffitt, T. E., Mill, J., Martin, J., Craig, I. W., Taylor, A. & Poulton, R. (2002). Role of genotype in the cycle of violence in maltreated children. Science, 297(5582), 851–854.
McGue, M., & Lykken, D. T. (1992). Genetic influence on risk of divorce. Psychological Science, 3(6), 368–373.
Plomin, R., Corley, R., DeFries, J. C., & Fulker, D. W. (1990). Individual differences in television viewing in early childhood: Nature as well as nurture. Psychological Science, 1(6), 371–377.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., Knopik, V. S., & Neiderhiser, J. M. (2012). Behavioral genetics. New York, NY: Worth Publishers.
Scott, J. P., & Fuller, J. L. (1998). Genetics and the social behavior of the dog. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Turkheimer, E. (2000). Three laws of behavior genetics and what they mean. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9(5), 160–164.
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2019 by Eric Turkheimer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Home — Essay Samples — Psychology — Nature Versus Nurture — Nature Vs Nurture in Psychology
Nature Vs Nurture in Psychology
- Categories: Nature Versus Nurture
About this sample

Words: 644 |
Published: Mar 20, 2024
Words: 644 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Introduction

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Psychology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1762 words
2 pages / 962 words
3 pages / 1195 words
3 pages / 1549 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Nature Versus Nurture
Victor Frankenstein, the titular character in Mary Shelley's classic novel "Frankenstein," is a complex and enigmatic figure whose actions and motivations are the subject of much debate and analysis. One of the key themes that [...]
Have you ever felt a surge of energy and determination that propels you towards your goals, despite challenges and obstacles in your way? This powerful force is known as motivation, a driving factor that inspires individuals to [...]
Leadership is a complex and multifaceted concept that has been the subject of extensive study and debate. There are two contrasting views on the nature of leadership - some believe that leadership is an innate quality that [...]
Throughout history, philosophers and scholars have grappled with the concept of human nature. This essay will explore the three major views of human nature: Tabula Rasa, Innate Goodness, and Evil Inclination. By examining the [...]
Nature can be defined as to what abilities we present with at birth, ability can be determined by our genes; including those that we develop with age. Both a biological and evolutionary perspective support the model that our [...]
In the movie The Blind Side by John Lee Hancock, the true story of Michael Oher and his interesting path to NFL stardom help shine light on many topics related to educational psychology. Michael is a 17-year-old African American [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
21 Nature vs Nurture Examples

The nature vs. nurture debate is the long-standing argument over whether heredity (nature) or environment (nurture) plays a greater role in developing human characteristics and behaviors.
Nature refers to the biological characteristics we are born with, including genetic predispositions toward certain traits. In contrast, nurture includes external influences that shape us, such as culture, relationships, and everyday experiences.
For example, when it comes to personality development, some people believe that genetics play a stronger role than environmental factors; this would be considered a nature-focused perspective.
Others may view the environment as more important. In this case, a nurturing upbringing could help individuals develop their personalities. Therefore, both sides can have valid arguments for their respective positions in the debate.
The Nature Perspective
In the context of the nature vs. nurture debate, nature refers to biological heredity and genetic predispositions inherited by individuals from their parents at birth.
Buheji (2018) states that:
“in the “nature vs. nurture” debate, nature refers to an individual’s innate qualities (nativism)” (p. 221).
This includes physical characteristics such as eye color, facial features, personality traits, and behavioral tendencies.
Genes determine the unique physical characteristics of each individual while also influencing psychological and social behavior.
Some research implies that roughly 50% of an individual’s personality and disposition are pre-determined by genetics (Bouchard & Loehlin, 2001).
However, Krueger and colleagues (2008) state that the interplay between gene-environment interactions has a consequential effect on one’s character traits. Hence, the heritability of personality isn’t always precisely 50%.
So, nature is the hereditary and genetic characteristics pre-determined at birth and influence a person’s behavior.
The Nurture Perspective
Nurture, in the context of the nature vs. nurture debate, is used to describe environmental factors that influence an individual’s development.
According to Coon and Mitterer (2014), nurture:
“…refers to the sum of all external conditions that affect a person” (p. 100).
This includes a variety of influences such as parenting style, educational experiences, cultural background, and exposure to different environmental conditions over time.
While “nurture” may naturally invoke ideas of childhood and parental care, environmental components and life experience can shape human mental, emotional, and physical health throughout their lives (Harsha et al., 2020).
For example, lifestyle choices have been found to impact a person’s risk for developing certain diseases and their level of immunity against illness.
Furthermore, addiction susceptibility can be impacted by environmental factors such as peer group that has been observed throughout an individual’s life (Ducci & Goldman, 2012).
Simply, nurture is an umbrella term for any environmental influences that shape the development of a person’s mental, physical, and emotional health.
Examples of Nature vs Nurture
Nature examples.
- Eye color : A person’s eye color is determined by their genetic makeup and inherited from their parents.
- Height : As with eye color, height is a physical trait that is determined by a person’s genes and largely determines an individual’s adult height.
- Risk of D iseases : A person’s risk for developing certain diseases can be partially attributed to their genetic predisposition for that illness and influenced by lifestyle factors and personal environment.
- Immune S ystem F unctionality : Genetic predisposition plays an important role in determining an individual’s resistance to disease through the strength of their immune system. However, lifestyle choices can also influence this trait over time (e.g., diet and exercise).
- Hair Color: Hair color is determined by genetic factors. Recessive genes, like the red hair gene, generally have to be present in both parents for the recessive gene to become dominant.
- Balding: Going bald is an inherited trait. Some groups – such as male British Anglo-Saxons – are more likely to go bald in their 30s than the average.
- Adrenaline response : An individual’s ability to react quickly in dangerous situations—their “fight or flight” response—tends to be innate in all of us.
Nurture Examples
- Ethics and Parenting style : An individual’s upbringing and the parenting style they are exposed to can shape their behavior, emotional reactions, and psychological outlook throughout life.
- Linguistic Determinism Theory : In this theory, the language we are taught as a child will determine the ways we think and interact with the world. It goes some way to explaining how people of differing language groups may have differing values and belief systems .
- Values and Cultural background : Depending on their cultural background, different individuals may be exposed to different values and belief systems, which can impact their attitudes toward certain issues or topics/ideas/beliefs.
- Anxiety and Exposure to T rauma : Experiences with violence or traumatic events can have long-term effects on an individual’s psychology which could manifest outwardly as symptoms of anxiety or difficulty coping under pressure in later stages of life.
- Positivity and Social E nvironment : The people an individual interacts with can either positively or negatively affect their development. Individuals need to surround themselves with positive influences while avoiding those that might lead them down the wrong path in life.
- Relationship E xperiences and Sense of Security : Positive relationships throughout a person’s life will tend to improve outlook and well-being. In contrast, unhealthy relationships could leave long-term psychological damage that might need professional help before it can be addressed adequately by an individual suffering firsthand.
Nature and Nurture Examples
- Personality traits: The role of genetics (nature) in determining personality traits, such as extraversion or conscientiousness is balanced against the influence of upbringing and life experiences (nurture).
- Aggression: There is debate over whether aggressive behavior is primarily influenced by genetic factors (nature) or by environmental factors, such as upbringing, social learning , and exposure to violence (nurture).
- Athletic ability: The role of genetics (nature) determines a lot of our natural talent in sports but the importance of training, motivation, and exposure to physical activity (nurture) takes us the rest of the way.
- Musical talent: Musical ability may be affected by genetic predisposition (nature) but also environmental factors, such as exposure to music at a young age, education, and practice (nurture).
- Attachment styles: It is debatable whether a person’s attachment style (secure, anxious, or avoidant) is impacted by genetics (nature) versus the influence of early childhood experiences and caregiver relationships (nurture).
- Empathy and emotional intelligence: The capacity for empathy and emotional intelligence is debatably determined by both genetics (nature) and the result of upbringing, social exposure, and life experiences (nurture).
- Spiritual beliefs: Theological determinism holds that god has pre-selected his chosen people who will be true believers (nature) while others think that belief in god is a choice and we must raise our children to maintain a belief in god (nurture).
- Learning styles: In the 1980s, there was extensive debate over whether preferred learning styles, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, are determined by genetic factors (nature) or influenced by educational experiences and personal development (nurture). Today, most education theorists believe that learning preferences are based on nurture over nature.
- Addiction susceptibility : Scientists have identified genes related to addiction susceptibility, even though this trait is also heavily influenced by the environment (Ducci & Goldman, 2012).
- Intelligence : Education can significantly impact traits such as intelligence levels and knowledge base, with certain experiences inspiring curiosity or creativity in individuals later in life.
Origins of Nature vs. Nurture Debate
The debate surrounding the extent to which human development is influenced by nature (heredity) or nurture (environmental factors) has been around since ancient times.
Plato, the renowned Greek philosopher, argued that beneficial traits in humans were attributable to both nature and nurture. He believed people could adapt to external occurrences throughout their lifetime (Englander, 2010).
However, his mentor Socrates leaned more towards genetics as the primary factor of human development – a notion known as Nativism, which was coined by both philosophers together.
In the late 1800s, Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution and Sir Francis Galton’s article “Hereditary Talent and Character” sparked a resurgence in interest in this topic (Galton, 1865)
So, Galton (1865) suggested hereditary influences to be at least as important as the environment when determining an individual’s outcomes in life.
The debate continued through subsequent decades, with psychologist John B. Watson’s revolutionary suggestion that environment—what he called “nurture”—was more important than hereditary factors or biology (Herrnstein, 1998).
In recent years, researchers have realized that both internal (genetic) and external (environmental) factors play a role in how individuals develop physically and psychologically.
As such, most experts now subscribe to an approach that looks at how both genetic inheritance and environmental influences work together throughout life to shape each person’s unique character traits and behaviors.
The Role of Epigenetics in the Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression caused by environmental factors, such as diet and exposure to toxins, without altering the underlying sequences of DNA .
It is an emerging field of research that has been gaining prominence in recent years as scientists try to uncover how and to what extent the environment can shape genetic expression (Harvard University, 2019).
Epigenetic influences are now considered a significant factor in the nature vs. nurture debate, particularly in how individuals develop physically and psychologically throughout life.
Evidence suggests that epigenetic mechanisms can be used to modulate gene expression depending on the environment, thus having a direct influence on an individual’s characteristics and behaviors (Harvard University, 2019).
This means that while both genetics and environment may play a role in determining an individual’s outcomes in life, epigenetics provides an additional layer of complexity by allowing environmental factors to interact with gene expression.
Nature vs. nurture is a decades-old debate that continues to be studied in various fields.
Nativists state that genetics play a major role in determining characteristics and behaviors. For example, a person may have inherited certain traits from their family.
However, empiricists suggest that external factors, such as upbringing and lifestyle choices, can also have a significant influence.
From ancient philosophers to modern-day scientists, this debate has gone through various iterations and continues to evolve today with the introduction of epigenetics.
More recently, epigenetics have emerged as a key factor in the debate. Its mechanisms can be used to modulate gene expression depending on the environment, thus having a direct influence on an individual.
So, it appears that both nature and nurture are important factors in determining an individual’s outcomes in life.
Bouchard, T. J., & Loehlin, J. C. (2001). Genes, evolution, and personality. Behavior Genetics , 31 (3), 243–273. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1012294324713
Buheji, M. (2018). Understanding the power of resilience economy . Mohamed Buheji.
Coon, D., & Mitterer, J. O. (2014). Psychology: A journey . Wadsworth/Cengage Learning.
Ducci, F., & Goldman, D. (2012). The genetic basis of addictive disorders. Psychiatric Clinics of North America , 35 (2), 495–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2012.03.010
Englander, M. (2010). The nature and nurture of learners . AuthorHouse.
Galton, F. (1865). Hereditary talent and character . University of Bristol Library.
Harsha, N., Ziq, L., Lynch, M. A., & Giacaman, R. (2020). Assessment of parental nurturing and associated social, economic, and political factors among children in the West Bank of the occupied Palestinian territory. BMC Pediatrics , 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-020-02317-0
Harvard University. (2019). What is epigenetics? The answer to the nature vs. nurture debate . Center on the Developing Child at Harvard University; Harvard University. https://developingchild.harvard.edu/resources/what-is-epigenetics-and-how-does-it-relate-to-child-development/
Herrnstein, R. J. (1998). Nature as nurture: Behaviorism and the instinct doctrine. Behavior and Philosophy , 26 (1/2), 73–107. https://www.jstor.org/stable/27759383
Krueger, R. F., South, S., Johnson, W., & Iacono, W. (2008). The heritability of personality is not always 50%: Gene-environment interactions and correlations between personality and parenting. Journal of Personality , 76 (6), 1485–1522. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.2008.00529.x

Viktoriya Sus (MA)
Viktoriya Sus is an academic writer specializing mainly in economics and business from Ukraine. She holds a Master’s degree in International Business from Lviv National University and has more than 6 years of experience writing for different clients. Viktoriya is passionate about researching the latest trends in economics and business. However, she also loves to explore different topics such as psychology, philosophy, and more.
- Viktoriya Sus (MA) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Free Enterprise Examples
- Viktoriya Sus (MA) #molongui-disabled-link 21 Sunk Costs Examples (The Fallacy Explained)
- Viktoriya Sus (MA) #molongui-disabled-link Price Floor: 15 Examples & Definition
- Viktoriya Sus (MA) #molongui-disabled-link Linguistic Relativity: 10 Examples and Definition

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Nature Vs Nurture Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on nature vs nurture.
The topic of nature vs nurture is always a great topic of debate among people. There are great men who did work hard to achieve great heights . But still, they are some people who didn’t work that hard yet still managed to be successful.

In other words, it is a debate between hard work and talent. In the grooming of a person, the nurturing is essential. However, still, there are some individuals who were never born in a great environment . Yet by their sense of knowledge and intellectualism created a special place in the hearts of people.
Nature has given us many things in life and one of them is talents. Either we are born as the only individual in our family or it is in our genes. Furthermore, nature plays a vital role in deciding the future of a child. Many singers in this era are born with beautiful voices. They did not need any nurturing. Their talent took them to heights they couldn’t even imagine.
For instance, some of the great legends like Lata Mangeshkar, Asha Bhosle, Kishor Kumar had soulful voices. Also, they were the ones who sang from their childhood days. They started their careers and became successful at a very early age. Moreover, they did not get much teaching but still are the legends of all time.
Apart from singing, there are other talents that nature has given us. Various scientists like Albert Einstein , Isaac Newton , Galileo Galilei, started their work in their teenage years. They had amazing intellectualism, because of which they got recognition in their entire world. Furthermore, these scientists did not get any mentoring. They did everything on their own. Because they had extraordinary intelligence and ambition in life.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
On the other hand, the nurturing of a person is important. Because hard work beats talent. With proper mentoring and practice, a person can achieve success in life. If a person has an environment in which everybody is in the same profession and are successful in it.
Then there is a great chance that the person will land up in the same profession and will achieve heights. Because in that environment he will get proper nurturing.
Furthermore, he will also be able to perform better over the years. “ Hard work always pays off ”. This idiom is always true and nobody can deny that. If a person has true dedication then it can beat talent. Various singers, dancers, musicians, businessmen, entrepreneurs did work really hard for years.
And because of that, they got recognition in the entire world. In these categories, musicians are who achieved heights only with their hard work and constant practice.
It is true that there are no shortcuts to success. Various known legends like Bob Dylon. Lou Reed, Elvis Persley, Michael Jackson worked hard throughout their lives. As a result, they were some of the great personalities in the entire world.
Q1. What is the meaning of nurture?
A1. Nurture means the way a person grooms himself. This is done in order to achieve success. Nurturing is essential in a person’s life because it can be a way a person can cross the barrier and do something great. Moreover nurture also means the mentoring and care a person is getting in an environment.
Q2. What is the difference between Nature and Nurture?
A2. The main difference between nature and nurture is, nature is the talent a person inherits from his parents or is God gifted. While nurturing is hard work and mentoring of a person in a particular field. So that he may excel in that field.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
One-And-Done Guide To A-Grade Worthy Essays On Nature

Table of Contents

At least once in your life from elementary school you will find yourself having to talk or having to write about the inspiring relationship between man and nature that has been there since us humans started walking this planet.
You better be inspired and get a feel for it before you start gnawing at your pen. You’ll see that this topic, apart from being so ubiquitous and beloved by teachers of all kinds and calibers, is rather fun to explore and write about.
Essays on nature: how to structure?
The topic of essays on nature is blissfully broad unless narrowed down by your teacher’s specifications. Not that we will break any major news saying that you should start your essay with a catchy introduction.
Do not underestimate the importance of that short introductory piece : written well, it will set the right tone to your essay, make your own voice heard and make that first impression on your readers.
The contextual diversity stems from the very definition of nature. Quoting Merriam Webster , nature can be defined as
- The inherent character or basic constitution … of a person or thing.
- A creative and controlling force in the universe.
- Natural scenery.
We have picked here only the most distinct definitions that would send your essay in three different directions, but you certainly get the drift.
As often as not, tasking students with an essay on nature, an educator expects a charming piece on scenic beauty with lots of descriptive passages.
But before you knock yourself out waxing lyrical on that breathtaking view from the mountain top that opened itself to your eyes as you were hitchhiking with your family during your Colorado trip, let not a premature sigh of relief escape your lips: there is more depth to it than may initially seem.
Depending on what the actual topic at hand is, you should:
- Make a concise presentation of the topic.
- Outline the problems you are going to solve in your essay.
- Introduce a clear thesis statement.
Normally, you are not expected to come up with any laboriously picked and analyzed sources of information other than your own experiences with nature that inspired you into deep contemplations, profound emotions and filled other spiritual gaps in your perception of the world.
However, a good quote here and there is a must – just to show that you are familiar with the background and the efforts your fellow-writers have made in the field.
Proceed to the core of your writing, speaking about the moments when the presence of nature in your life overpowered you, the thoughts and ideas this feeling sparkled in you, and the impact it has had on your way of thinking and living.
Remember that drawing unexpected parallels is a mark of genius. How about you compare natural phenomena to the way you express your own emotions? What in the way you express your feelings through beaming, smiling – or tears and yelling – can be paralleled to weather changes?
…Go full-on allegorical!
Writing about nature, we suggest that you pick such tried-and-true fellow-writers as Henry David Thoreau , who is commonly referred to as “the godfather of American nature writing,” as an environmental educator and a travel/naturalist writer Heidi Zillie put it, and a harbinger of all go-green enthusiasts.
Speaking of environmentalists: as far as the cornerstone idea of your essay is concerned, it would score you a lot of points to jump on the naturalist bandwagon and make a strong call to protect natural resources.
The use of nature essay examples
Depending on what your primary focus in the essay is, you should pick a specific set of arguments to back up the viewpoints you express in your writing.
While describing and processing the imprint that nature sceneries have had on you is not about debating, since it is a purely subjective description of your own emotions, you still can present your feelings as contradictory and conflicting.
For instance, speak about the impact a sunny spell has on you when you are happy as opposed to when you are depressed. By contrasting your own emotions, sunshine from a clear blue sky can make you feel worse – although it can do the opposite and pick you up.
Um… or not?
Provide arguments to support both stances and illustrate with an example from your life.
Don’t be afraid to channel your inner Hemingway; we mean, the topic is pretty corny in its nature – bad pun intended!
What to write in essays on human nature?
Essays on human nature open up new horizons still.
Here once again it would be great to make a reference to Thoreau who advocated for
“the importance of leaving nature undisturbed, the need for all humans to have contact with nature, and the relationship between humans and other living things”
Speak about the contradictory nature of humans: we are part of nature, but we constantly seek to outsmart it.
What do we get as benefits, and are they compared to the damage we do the environment in the process?
One thing is for sure, and it is that it is human nature to defy mother nature, and our own nature whilst at it.
For centuries, from the earliest forms of human life on Earth, man has been trying to interpret, explain and even control nature and its phenomena, it is not by chance that the first explanations of meteorological phenomena that is rain can already be found in the first primitive men.
The wind, the sun, the snow, which, however, lacking any logical or scientific connection , gave an answer through the omnipotent presence of gods who controlled these temporal impacts.
But not only that, being peoples who based their entire survival on agriculture, they introduced the first songs and dances of the rain, of the sun, and in doing so they were convinced that the gods could hear them and that they could control and “send” what could be used to harvest to be prosperous.

Essays on nature vs. nurture
Merriam-Webster defines nurture as
– as opposed to those predetermined by genes, or nature.
The debates about to what extension we are influenced by our genetics that is nature, and to what – by environmental factors.
The supporters of the “nature” camp study the behavioral development in twins to prove their point, and we suggest you get the most out of citing some of them.
On the other side of the equation, scientists prove that there is a link between the events in our lives and our bodily functions; some events or actions can actually make us pass on genes to our offspring, like for instance substance abusing or smoking.
A study like this one under the supervision of Dr. Linda J. Luecken proves some meaningful connections between our biography facts and health condition.
Nature vs. nurture essay topics
Here are some of the most fruitful and inspiring topics for an essay on nature versus nurture you can dig into because every essay topic needs to be narrowed down for you to be able to make a clear and logical presentation of your standpoint:
- Nature vs. Nurture In Personal Development.
- Nature Vs. Nurture In Children.
- The Nurture Assumption.
- Nature vs. Nurture: From Elizabethan Times Till Now.
- Frankenstein: Nature vs. Nurture.
- Nature vs. Nurture Debate.
- Nature vs. Nurture In Medicine.
- Intelligence Quotient.
- Nature vs. Nurture From A Psychological Standpoint.
- Human Nature.
- Obligate vs. Facultative Adaptations.
- Social Pre-Wiring.
- Heritability Of Intelligence.
- Nature vs. Nurture in Genomics.
- Personality Traits: Nature Or Nurture?
- The Fallacy Of Nature vs. Nurture.
- Darwinian Ethics In Nature Vs. Nurture Debate.
- Biological Determinism.
- Stability And Change In Nature Vs. Nurture Discourse.
- The Nature And Nurture Of Genius.
Bottom line
Science is progressing with increasingly surprising innovations and technologies day by day, but people in some way continue to not fully grasp the benefits nature offers.
Exemplary is the case of houses built at the foot of Vesuvius, an area considered to be at risk of eruptions.
There are laws that prevent building in those areas, but at the same time in those areas, you always see more architectures, houses, and buildings that endanger human life.
Then the question arises of who is to blame in the end, and the necessary answer is that man, as in many things, is the main cause of own flaws!
…You get the drift?
Got questions or feel a bit lost? You don’t have to do this on your own; there is expertly help to get you all set for a maximal educational outcome!
Speaking of that… How about trying an expert help right now? Any topic, tightest deadline, complete safety! Click the button below to save your evening!

Guide on Writing a Death Penalty Research Paper
Psychology essay topics, how to write a discussion post that fetches excellent marks.
“Nature vs. Nurture” Debate in Education Essay
The ‘Nature vs. Nurture’ debate holds in several areas of psychology and refers to the question of whether our genes (‘nature’) determine attributes such as intelligence or language aptitude or whether such attributes can be acquired and improved through experience (‘nurture’). The outcome is of great importance for educators since education – together with parental influence – is the main source of experiential learning (Bulmer 2003). In this essay, the concept will be explained based on my own experience and academic research.
Historically, the nature vs. nurture debate began with the publication of Galton’s (1869) study in which he promoted inherited ability in the faculties of thinking and learning. On the same side of the argument, the more recent work by Herrnstein and Murray (1994) was significant in arguing that intelligence is, at least to some extent, inherited.
The theory is based on the assumption that aptitude is dominant in learning and that it is mainly hereditary. Therefore, the aim of education is to separate the naturally able from the less able and to provide each group of students with programs adapted to their talents. In other words, schools should function as if the ‘Bell Curve’ is a natural phenomenon that must be obtained in all learning results and that effort makes little difference (Resnick 1995: 55-62).
IQ tests are there to spread students out on a scale rather than to define what each one should actually work at learning. Teachers assign grades believing that – if everyone were to get an A or B – standards must be too low (and not that uniformly high grades mean everyone worked hard and managed to learn what was taught).
In my high school years, I certainly witnessed how belief in inherited aptitude was self-fulfilling. Students who were held to low expectations did not try to break through that barrier but often accepted the idea that aptitude is what matters and that they have not inherited enough of it – and their performance stayed low.
On the ‘nurture’ side of the argument is the theory of learning behind most educational practices today, based on the work of Thorndike (Faulkner 1998). Thorndike developed practical learning tools (textbooks, tests, curricula, and teacher training) in the belief that knowledge consists of a collection of bonds i.e. links between pairs of mental entities or between an external stimulus and an internal mental response. Learning is just trying to change the strengths of the bonds i.e. increasing the strength of ‘correct’ bonds and decreasing the strength of ‘incorrect’ ones.
In practice, correct bonds are strengthened by rewards, and incorrect ones are weakened through punishment or withholding rewards and create a system where the ‘stamping in’ of correct bonds and the ‘stamping out’ of incorrect ones is enhanced. In my experience, whenever teachers used positive feedback to create ‘enjoyment’ in the learning environment it certainly motivated me to work harder.
Recent evidence from developmental biology claims to have resolved the ‘Nature vs. Nurture’ issue and what this might mean for education practice. According to the Education Commission of the States (1996), research on brain development provides insight for improving the education of young children. The Carnegie Corporation (1994) highlights the fact that the environment affects not only the number of brain cells and the number of connections between them but also the way they are ‘wired’ and evidence points to the negative impact of early stress (a ‘nurture’ factor) on brain function (Carnegie Corporation 1994: 2)
While the brain connections developed before birth are vital, their main purpose is biological and it is during the child’s first months and years of growth and development that nature and nurture combine until they become ‘ intertwined and inseparable’ (Simmons & Sheehan 1997: 6).
At birth, the brain has around 100 billion neurons, which then link together in over 50 trillion synapses (Begley 1997). Afterward – especially in the first three years of life – the brain goes through a number of important changes. Over this period, many more connections among neurons are created than the brain can ever use. Over time, the connections that are rarely or never used disappear (Nash 1997). However, which connections are eliminated is not predetermined and the way in which a child is raised affects how the brain chooses to wire itself for life (Simmons & Sheehan 1997).
I have always believed that children should be encouraged to take advantage of the various windows of opportunity presented to them for healthy development. The research above shows that a child’s brain development suffers if the child is denied the opportunity to live in a stimulating environment. In other words, the research stresses the positive effects of active parenting – something I believe in very strongly – in order to provide children with stimulating experiences (Nash 1997).
In conclusion, this essay has explained the ‘Nature vs. Nurture’ issue providing arguments and evidence for the primacy of both inheritance and environment in learning and thinking. Each side leads to a different approach to education. If we accept the primacy of inheritance, this gives rise to the streaming of students based on their ‘aptitudes’ as revealed by their scores in, for example, IQ tests. Each stream is then taught at a level suitable for their supposed inherited aptitude.
On the other hand, the primacy of the environment leads to education based on ‘associationist’ learning achieved through effort, motivation, and rewards. Recent evidence from developmental biology clearly points to the greater importance of ‘nurture’ in preparing children successfully for thinking and learning. The more stimulating, enjoyable, and interesting we can make their environment, the more they will learn.
Works Cited
Begley, S. “Your child’s brain.” Newsweek 127.8 (1996): 55-61.
Begley, S. “How to build a baby’s brain.” Newsweek 129 (1997): 28-32.
Black, P. “Dreams, Strategies and Systems: portraits of assessment past, present and future.” Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice 8.1 (2001): 65-85.
Bulmer, M. Francis Galton: Pioneer of Heredity and Biometry . John Hopkins University Press. 2003.
Carnegie Corporation. “Starting points: Meeting the needs of our youngest children.” Corporation of New York . 1994. Web.
Education Commission of the States . “Brain research and education: Bridging the gap between neuroscience & education.” 1996. Web.
Faulkner, D. Learning Relationships in the Classroom . London: Routledge. 1998.
Galton, Francis. Hereditary Genius, Its Laws and Consequences. London: Macmillan. 1869.
Herrnstein, R. J., and Murray, C. The Bell Curve: Intelligence and Class Structure in American Life . New York: Free Press. 1996.
Nash, J. M. “Fertile minds.” Time 149.5 (1997): 48-56.
Resnick, L. Education and Learning to Think Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press. 2009.
Simmons, T., & Sheehan, R. “Brain research manifests importance of first years” The News & Observer. 1997. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, February 5). "Nature vs. Nurture" Debate in Education. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nature-vs-nurture-debate-in-education/
""Nature vs. Nurture" Debate in Education." IvyPanda , 5 Feb. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/nature-vs-nurture-debate-in-education/.
IvyPanda . (2021) '"Nature vs. Nurture" Debate in Education'. 5 February.
IvyPanda . 2021. ""Nature vs. Nurture" Debate in Education." February 5, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nature-vs-nurture-debate-in-education/.
1. IvyPanda . ""Nature vs. Nurture" Debate in Education." February 5, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nature-vs-nurture-debate-in-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . ""Nature vs. Nurture" Debate in Education." February 5, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nature-vs-nurture-debate-in-education/.
- A Summary of Operations at Oregon
- Data Protection: Securing Information System
- Scholastic Aptitude Test for College Admissions
- The Efficiencies of Educational Policies
- "Before Teaching Ethics, Stop Kidding Yourself" by Marino Gordon
- Differentiated Instruction and Universal Design of Learning
- Literacy Standards and Reading Instruction Theory
- Montessori Educational Philosophy, Its Pros and Cons

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nature vs. Nurture Essay. Nature is the influence of genetics or hereditary factors in determining the individual's behavior. In other words, it is how natural factors shape the behavior or personality of an individual. In most cases, nature determines the physical characteristics which in effect influence the behavior of an individual.
The Nature vs. Nurture Debate. Nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development. Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality and development is one of the oldest philosophical debates within ...
Summary. Nature vs. nurture is a framework used to examine how genetics (nature) and environmental factors (nurture) influence human development and personality traits. However, nature vs. nurture isn't a black-and-white issue; there are many shades of gray where the influence of nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to disentangle how ...
The relationship between nature and nurture has constantly raised controversial debates about the roles of the two factors in heredity and external behavior of a person. As a result, there has been confusion about the functions of nature and nurture in shaping human personality. Some psychologists have shown strong support for nature as a ...
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual's innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping ...
The expression "nature vs. nurture" describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either "nature" or "nurture." "Nature" means innate biological ...
The nature vs. nurture debate has both been influenced by and has influenced psychology, sociology, and genetics. Psychology is largely concerned with the mind and behavior of the individual. Sociology is concerned with the collective experiences and behavior of society. Genetics studies how genes and traits are passed down through families.
At first glance, a nature vs nurture essay seems to be easy. However, a limited view of the subject matter may cost you marks, which is why it is crucial to offer a well-rounded account of the debate. Here are some of the aspects that you might want to include in your essay on nature vs nurture. The importance of the topic.
The "Middle Ground" Perspective on Nature-Nurture. Twenty-first-century psychology textbooks often state that the nature-nurture debates have been resolved, and the tension relaxed, because we have moved on from emphasizing nature or nurture to appreciating that development necessarily involves both nature and nurture. In this middle-ground position, one asks how nature and nurture ...
Part 1: Nature Versus Nurture. The origins of nature versus nurture debate date back for thousands of years and across many cultures. The Greek philosopher Galen theorized that personality traits ...
The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to ...
Elements included on the nature side of the debate. While there can be a range of elements included in this area of the nature vs nurture argument, some of the most includes: Genetic diseases and disorders. Appearance-related elements, such as eye, hair or skin color. Behavior.
Ultius. Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions and matches customers with highly qualified writers for sample writing, academic editing, and business writing. Nature vs Nurture is an ongoing debate in human development. This sample essay looks at both sides as well as the two working in conjunction with one another.
Essay Sample: Nature Versus Nurture. This sample is a great example of the compare and contrast essay writing. It presents two points of view on what influences the development of a personality the most - genetics or environmental factors. Don't hesitate to read it to see what such a type of essay should look like when written professionally!
The nature versus nurture debate focuses on the question of whether genetic or environmental factors matter most in the course of human development. What is it that makes you who you are? Some might say. The debate between nature vs nurture is one of the oldest in psychology and centers on the relative contributions of genes and environment. ...
Eric Turkheimer. People have a deep intuition about what has been called the "nature-nurture question.". Some aspects of our behavior feel as though they originate in our genetic makeup, while others feel like the result of our upbringing or our own hard work. The scientific field of behavior genetics attempts to study these differences ...
The debate between nature and nurture has been a long-standing one in the field of psychology. It pertains to the relative importance of an individual's innate qualities (nature) versus their personal experiences and environment (nurture) in determining behavior and mental processes. This essay aims to delve into this debate, exploring the ...
Step 1: Choose a Topic. Understand the nature vs nurture debate: Before picking a topic for your essay, it's important to know what the nature vs nurture debate is all about. It covers various areas like intelligence, personality traits, mental health, addiction, and wrong behavior.
Buheji (2018) states that: "in the "nature vs. nurture" debate, nature refers to an individual's innate qualities (nativism)" (p. 221). This includes physical characteristics such as eye color, facial features, personality traits, and behavioral tendencies. Genes determine the unique physical characteristics of each individual while ...
A1. Nurture means the way a person grooms himself. This is done in order to achieve success. Nurturing is essential in a person's life because it can be a way a person can cross the barrier and do something great. Moreover nurture also means the mentoring and care a person is getting in an environment. Q2.
Essays on nature vs. nurture. Merriam-Webster defines nurture as. "the sum of the environmental factors influencing the behavior and traits expressed by an organism.". - as opposed to those predetermined by genes, or nature. The debates about to what extension we are influenced by our genetics that is nature, and to what - by ...
The 'Nature vs. Nurture' debate holds in several areas of psychology and refers to the question of whether our genes ('nature') determine attributes such as intelligence or language aptitude or whether such attributes can be acquired and improved through experience ('nurture'). The outcome is of great importance for educators since ...
Essay Sample: Being yourself, being who you are. When you hear those two expression it may seem that they mean the same affair but they do not. You were bear into this ... Such questions are what wind to the great argument between nature vs nurture. If you believe you were born already with a personality, then you take the side of nature.