Speech Act Theory
FranksValli/Wikimedia Commons
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Speech act theory is a subfield of pragmatics that studies how words are used not only to present information but also to carry out actions.
The speech act theory was introduced by Oxford philosopher J.L. Austin in How to Do Things With Words and further developed by American philosopher J.R. Searle. It considers the degree to which utterances are said to perform locutionary acts , illocutionary acts , and/or perlocutionary acts .
Many philosophers and linguists study speech act theory as a way to better understand human communication. "Part of the joy of doing speech act theory, from my strictly first-person point of view, is becoming more and more remindful of how many surprisingly different things we do when we talk to each other," (Kemmerling 2002).

Searle's Five Illocutionary Points
Philosopher J.R. Searle is responsible for devising a system of speech act categorization.
"In the past three decades, speech act theory has become an important branch of the contemporary theory of language thanks mainly to the influence of [J.R.] Searle (1969, 1979) and [H.P.] Grice (1975) whose ideas on meaning and communication have stimulated research in philosophy and in human and cognitive sciences...
From Searle's view, there are only five illocutionary points that speakers can achieve on propositions in an utterance, namely: the assertive, commissive, directive, declaratory and expressive illocutionary points. Speakers achieve the assertive point when they represent how things are in the world, the commissive point when they commit themselves to doing something, the directive point when they make an attempt to get hearers to do something, the declaratory point when they do things in the world at the moment of the utterance solely by virtue of saying that they do and the expressive point when they express their attitudes about objects and facts of the world (Vanderkeven and Kubo 2002).
Speech Act Theory and Literary Criticism
"Since 1970 speech act theory has influenced...the practice of literary criticism. When applied to the analysis of direct discourse by a character within a literary work, it provides a systematic...framework for identifying the unspoken presuppositions, implications, and effects of speech acts [that] competent readers and critics have always taken into account, subtly though unsystematically.
Speech act theory has also been used in a more radical way, however, as a model on which to recast the theory of literature...and especially...prose narratives. What the author of a fictional work—or else what the author's invented narrator—narrates is held to constitute a 'pretended' set of assertions, which are intended by the author, and understood by the competent reader, to be free from a speaker's ordinary commitment to the truth of what he or she asserts.
Within the frame of the fictional world that the narrative thus sets up, however, the utterances of the fictional characters—whether these are assertions or promises or marital vows—are held to be responsible to ordinary illocutionary commitments," (Abrams and Galt Harpham 2005).
Criticisms of Speech Act Theory
Although Searle's theory of speech acts has had a tremendous influence on functional aspects of pragmatics, it has also received very strong criticism.
The Function of Sentences
Some argue that Austin and Searle based their work principally on their intuitions, focusing exclusively on sentences isolated from the context where they might be used. In this sense, one of the main contradictions to Searle's suggested typology is the fact that the illocutionary force of a concrete speech act cannot take the form of a sentence as Searle considered it.
"Rather, researchers suggest that a sentence is a grammatical unit within the formal system of language, whereas the speech act involves a communicative function separate from this."
Interactional Aspects of Conversation
"In speech act theory, the hearer is seen as playing a passive role. The illocutionary force of a particular utterance is determined with regard to the linguistic form of the utterance and also introspection as to whether the necessary felicity conditions —not least in relation to the speaker's beliefs and feelings—are fulfilled. Interactional aspects are, thus, neglected.
However, [a] conversation is not just a mere chain of independent illocutionary forces—rather, speech acts are related to other speech acts with a wider discourse context. Speech act theory, in that it does not consider the function played by utterances in driving conversation is, therefore, insufficient in accounting for what actually happens in conversation," (Barron 2003).
- Abrams, Meyer Howard, and Geoffrey Galt Harpham. A Glossary of Literary Terms . 8th ed., Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2005.
- Austin, J.l. “How To Do Things With Words.” 1975.
- Barron, Anne. Acquisition in Interlanguage Pragmatics Learning How to Do Things with Words in a Study Abroad Context . J. Benjamins Pub. Co., 2003..
- Kemmerling, Andreas. “Speech Acts, Minds, and Social Reality: Discussions with John r. Searle. Expressing an Intentional State.” Studies in Linguistics and Philosophy , vol. 79, 2002, pp. 83. Kluwer Academic Publishers .
- Vanderveken, Daniel, and Susumu Kubo. “Introduction.” Essays in Speech Act Theory , John Benjamins, 2001, pp. 1–21.
- Speech Acts in Linguistics
- Locutionary Act Definition in Speech-Act Theory
- Illocutionary Force in Speech Theory
- Illocutionary Act
- Performative Verbs
- Perlocutionary Act Speech
- Felicity Conditions: Definition and Examples
- The Power of Indirectness in Speaking and Writing
- Meaning Semantics
- Explicature (Speech Acts)
- What Is Relevance Theory in Terms of Communication?
- Reported Speech
- Information Content (Language)
- Examples of Indexicality (Language)
- Mental-State Verbs
- Pragmatics Gives Context to Language
- Media Studies
- Communication
- Linguistics
Speech Act Theory | How Words Shape Meaning & Interactions
- June 27, 2023 March 31, 2024
In the captivating world of media and communications, one theory that holds immense importance is the Speech Act Theory. Developed by philosophers J.L. Austin and John Searle, this theory helps us comprehend how our words possess the power to shape meaning. Also, how it influences our interactions with others. Let’s delve into this theory and explore its key concepts to unlock the secrets of effective communication.
The Power of Words
Words are not merely sounds or symbols; they carry profound power. Thus, they possess the ability to convey thoughts, express emotions, and influence others. Speech Act Theory enables us to comprehend that when we speak, we are not solely stating facts, but also performing actions through our words.
Understanding the power of words allows us to recognise the impact our speech has on others. It helps us become conscious of the choices we make in our language use. Thus, making us aware of the potential consequences they may have. By harnessing the power of words, we can express ourselves effectively and create meaningful connections with those around us.
Locution, Illocution & Perlocution
Speech acts can be understood through three levels: locution, illocution, and perlocution. Locution refers to the actual words and phrases we use. Illocution focuses on the intentions behind our words, such as making a request or giving an order. Perlocution refers to the impact our words have on others, like persuading or motivating them to take action.
By recognising these levels of speech acts, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of communication. We become aware that our words carry not only literal meanings but also implied intentions. We then need to consider the potential effects on the receiver. This awareness enables us to be more mindful of our speech and adapt it according to our communicative goals.
Types of Speech Acts
Speech Act Theory categorises speech acts into three main types: assertive, directive, and expressive. Assertive speech acts aim to convey information, such as stating facts or making claims. Directive speech acts involve issuing commands or requests. Expressive speech acts express emotions, attitudes, or feelings.
Understanding the different types of speech acts helps us navigate various communicative situations effectively. We learn to recognise when we need to provide information, give instructions, or express ourselves emotionally. This knowledge allows us to choose the appropriate speech acts to achieve our communication goals. Therefore, allowing us to convey our intended meanings accurately.
Felicity Conditions
For a speech act to be successful, certain conditions known as felicity conditions must be met. These conditions ensure that the act is performed appropriately and is understood by the intended audience. Felicity conditions may include factors such as sincerity, relevance, and the social context in which the speech act takes place. Understanding and adhering to these conditions contribute to effective communication.
Recognising felicity conditions helps us gauge the appropriateness and effectiveness of our speech acts. Therefore, we become more conscious of the importance of sincerity in our words. Furthermore, the relevance of our statements to the context, and finally the impact of social norms on communication. By considering these conditions, we enhance our ability to convey our messages successfully and build stronger connections with others.
Speech Act Theory & Performativity
Speech Act Theory emphasises the concept of performativity. This suggests that by uttering specific words, we bring about a change in the world. For example, saying “I now pronounce you husband and wife” during a wedding ceremony establishes a new marital status for the couple. Our words have the power to create realities and shape social structures. This aspect of speech acts highlights their transformative nature.
Understanding performativity allows us to appreciate the significant influence of our words on social and cultural contexts. As a result, we become aware of the role our speech plays in shaping perceptions, reinforcing norms, and constructing shared meanings. Also, by harnessing the power of performativity, we can contribute to positive social change and inspire others through our words.
Contextual Factors of Speech Act Theory
Context plays a vital role in comprehending speech acts. The same words can have different meanings depending on the context in which they are used. For instance, cultural norms, social relationships, and shared knowledge influence the interpretation of speech acts. Being aware of these contextual factors is essential for effective communication. Therefore, understanding the situational context helps to avoid miscommunication and ensures that the intended meaning is conveyed.
Considering contextual factors enhances our ability to adapt our communication to specific situations. We become sensitive to cultural nuances and adapt our language to different social relationships. Also, it allows us to utilise shared knowledge to convey our ideas effectively. By understanding context, we navigate diverse communication settings with ease and promote mutual understanding.
Pragmatics & Politeness
Speech Act Theory is closely intertwined with Pragmatics , the study of how language is used in real-life situations. Politeness is a significant aspect of pragmatics. Sociolinguists Penelope Brown and Stephen Levinson argue that Politeness Strategies , such as using indirect language or employing polite expressions, help maintain social harmony and prevent potential conflicts. Being aware of cultural and social norms of politeness aids in building positive interpersonal relationships.
Understanding pragmatics and politeness allows us to engage in effective and harmonious communication. Thus, we learn to adapt our speech to different social contexts, respect cultural norms, and demonstrate consideration for others. Therefore, by employing politeness strategies, we cultivate empathy, show respect, and foster healthy relationships with those around us.
Criticisms of Speech Act Theory
Despite its significant contributions to understanding communication, Speech Act Theory is not without its criticisms. Some scholars argue that the theory places excessive focus on the speaker’s intentions. Therefore, it neglects the role of the listener in interpreting speech acts. They suggest that meaning is a collaborative effort between the speaker and the listener. This is influenced by shared knowledge and social context.
Others criticise Speech Act Theory for its limited scope in accounting for non-verbal communication. Also, the impact of non-linguistic elements such as body language and facial expressions. They argue that meaning is not solely derived from words but also from non-verbal cues that accompany speech acts.
Additionally, critics point out that Speech Act Theory tends to overlook the role of power dynamics and social inequalities in communication. They argue that the ability to perform certain speech acts may be constrained by societal structures. Thus, not all individuals have equal opportunities to exercise their speech acts freely.
Speech Act Theory offers us a valuable framework for comprehending the power of words and the intricacies of human communication. By recognising the various levels of speech acts, the significance of felicity conditions, the transformative nature of performativity, the impact of context, and the importance of pragmatics and politeness, we can become more effective communicators. However, it is important to acknowledge the criticisms of the theory and consider alternative perspectives. This helps us to then develop a more comprehensive understanding of communication.
Austin, J.L. (1962). How to Do Things with Words . Oxford University Press.
Searle, J.R. (1969). Speech Acts: An Essay in the Philosophy of Language . Cambridge University Press.
Brown, P., & Levinson, S. C. (1987). Politeness: Some Universals in Language Usage . Cambridge University Press.
- Professional Development UPCOMING PROGRAMS Summer Institutes for Teachers Upcoming Conferences Presentations & Workshops PROFESSIONAL OPPORTUNITIES Advanced Practices Certificate CARLA Fellow Program RESOURCES & ARCHIVES Conference Organizing & Publishing Resources Presentation Recordings Conference Archives
- Publications CARLA Publications & Working Papers CARLA Bibliography Literacies in Language Education
- About CARLA CENTER INFORMATION Mission A Language Resource Center Funding History CARLA Update CONTACT INFORMATION Contact Us Mailing List Subscription CARLA Staff & Faculty OTHER INFORMATION Employment Opportunities Request Copyright Permission Document Use of CARLA Material
- Background Information
- American English
- Teaching Tips
- Teaching Materials
- Research Notes
- Australian English
- Functions and Classification
- British English
- Argentinean Spanish
- Canadian French
- Strategy Descriptions
- Marathi & Hindi
- Research Project
- Japanese Speech Acts
- Pragmatics & Speech Acts Bibliography
- Spanish Pragmatics
- CARLA Summer Institutes
- CARLA Bibliography
What is a Speech Act?
A speech act is an utterance that serves a function in communication. We perform speech acts when we offer an apology, greeting, request, complaint, invitation, compliment, or refusal. A speech act might contain just one word, as in "Sorry!" to perform an apology, or several words or sentences: "I’m sorry I forgot your birthday. I just let it slip my mind." Speech acts include real-life interactions and require not only knowledge of the language but also appropriate use of that language within a given culture.
Here are some examples of speech acts we use or hear every day:
Greeting: "Hi, Eric. How are things going?" Request: "Could you pass me the mashed potatoes, please?" Complaint: "I’ve already been waiting three weeks for the computer, and I was told it would be delivered within a week." Invitation: "We’re having some people over Saturday evening and wanted to know if you’d like to join us." Compliment: "Hey, I really like your tie!" Refusal: "Oh, I’d love to see that movie with you but this Friday just isn’t going to work."
Speech acts are difficult to perform in a second language because learners may not know the idiomatic expressions or cultural norms in the second language or they may transfer their first language rules and conventions into the second language, assuming that such rules are universal. Because the natural tendency for language learners is to fall back on what they know to be appropriate in their first language, it is important that these learners understand exactly what they do in that first language in order to be able to recognize what is transferable to other languages. Something that works in English might not transfer in meaning when translated into the second language. For example, the following remark as uttered by a native English speaker could easily be misinterpreted by a native Chinese hearer:
Sarah: "I couldn’t agree with you more. " Cheng: "Hmmm…." (Thinking: "She couldn’t agree with me? I thought she liked my idea!")
An example of potential misunderstanding for an American learner of Japanese would be what is said by a dinner guest in Japan to thank the host. For the invitation and the meal the guests may well apologize a number of times in addition to using an expression of gratitude (arigatou gosaimasu) -- for instance, for the intrusion into the private home (sumimasen ojama shimasu), the commotion that they are causing by getting up from the table (shitsurei shimasu), and also for the fact that they put their host out since they had to cook the meal, serve it, and will have to do the dishes once the guests have left (sumimasen). American guests might think this to be rude or inappropriate and choose to compliment the host on the wonderful food and festive atmosphere, or thank the host for inviting them, unaware of the social conventions involved in performing such a speech act in Japanese. Although such compliments or expression of thanks are also appropriate in Japanese, they are hardly enough for native speakers of Japanese -- not without a few apologies!
Back to Speech Acts .
- Twin Cities Campus:
- Parking & Transportation
- Maps & Directions
- Directories
- Contact U of M
- Privacy
- Corrections
J.L. Austin and John Searle on Speech Act Theory
J.L. Austin and John Searle developed Speech Act Theory and argued that our language does not only describe reality but that it can be used to perform acts.

The average number of words we speak on a daily basis remains a contested matter. Some have argued that the average is around 16,000 words, while more modest researchers refer to 5,000. Of course, culture, sample size, and sociodemographic variables influence the answer. One thing is certainly true: the number of spoken words we use is not trivial. And this is without adding the number of text messages, tweets, and other written posts that are part of our habits.
What do we do with these words? Some are historically memorable, like those of US president Ronald Regan during a speech in West Berlin in 1987: “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!”. Others are kept as literature treasures, like those found in Shakespeare or Gabriel García Márquez . It seems clear that with words we do not only describe the world and refer to things, but we transform reality. This was the intuition that J. L. Austin, a British philosopher of language, explored during his Harvard lectures in 1995. His philosophy became greatly influential and constituted the beginning of Speech Act Theory.
The Origins of Speech Act Theory: J. L. Austin and Wittgenstein
Austin and the later Wittgenstein were interested in how we use language rather than speculating about its abstract nature. In the Philosophical Investigations , published posthumously in 1953, Wittgenstein observed that language was like a toolbox: hammers and screwdrivers are an analogy to the different functions words can have (2009, op. § 11). What type of functions/usages can we find?
The Austrian philosopher believed there is no such thing as a static list of usages. From giving orders and describing a state of affairs, to making jokes and promises, the usages are countless : “Countless different kinds of use of what we call ‘symbols’, ‘words’, and ‘sentences’.” (Wittgenstein, 2009, op. § 23a). The emphasis on “countless” ( unzählige in German) means that one cannot simply make a taxonomy of usages; put differently, there are not easy to categorize.
Get the latest articles delivered to your inbox
Please check your inbox to activate your subscription.
Languages come into and go into existence. Some are born while others “become obsolete and forgotten” (Wittgenstein, 2009, op. § 23a). Historical linguists support this idea: it is only in historical practices that one finds the unfolding of language (Deutscher, 2006, p. 9 & 114). Contrary to Wittgenstein, J. L. Austin argued that classifying them could indeed be possible. That effort became the core of his Harvard lectures in 1995 from which Speech Act theory emerged.
What Are Speech Acts?

Austin made a provisional division between constative and performative sentences. While constative sentences had truth value (can be true or false), performatives were successful or not, or like Austin wrote, happy or unhappy (2020, p. 18).
Consider the sentence: ‘A water molecule is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom”. Clearly, this sentence is describing the world. It is stating a fact that can be true or false. But what fact is being described by Ronald Regan’s “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall”? The second utterance is performative because it is neither true nor false. As a request, it could be either felicitous or infelicitous (another terminology for happy or unhappy). A request is felicitous when it changes the future such that the request is observed.
We can now define speech acts as, precisely, the act of uttering performative sentences. Later in his lectures, Austin realized that everything we say is, to various extents, performative, so he abandoned the distinction to develop a general theory of speech acts (Huang, 2014, p. 126). Austin introduced new distinctions to elucidate what is happening when someone says something: every utterance (locution) has an illocutionary act and a perlocutionary effect . Let us consider them quickly.
The Illocutionary and Perlocutionary Force of a Speech Act

The illocutionary act refers to the type of speech act that is being performed, this is, the function that the speaker intends to fulfill. The perlocutionary part, on the other hand, is the effect that an utterance could have on the hearer or addressee (Huang, 2014, p. 128).
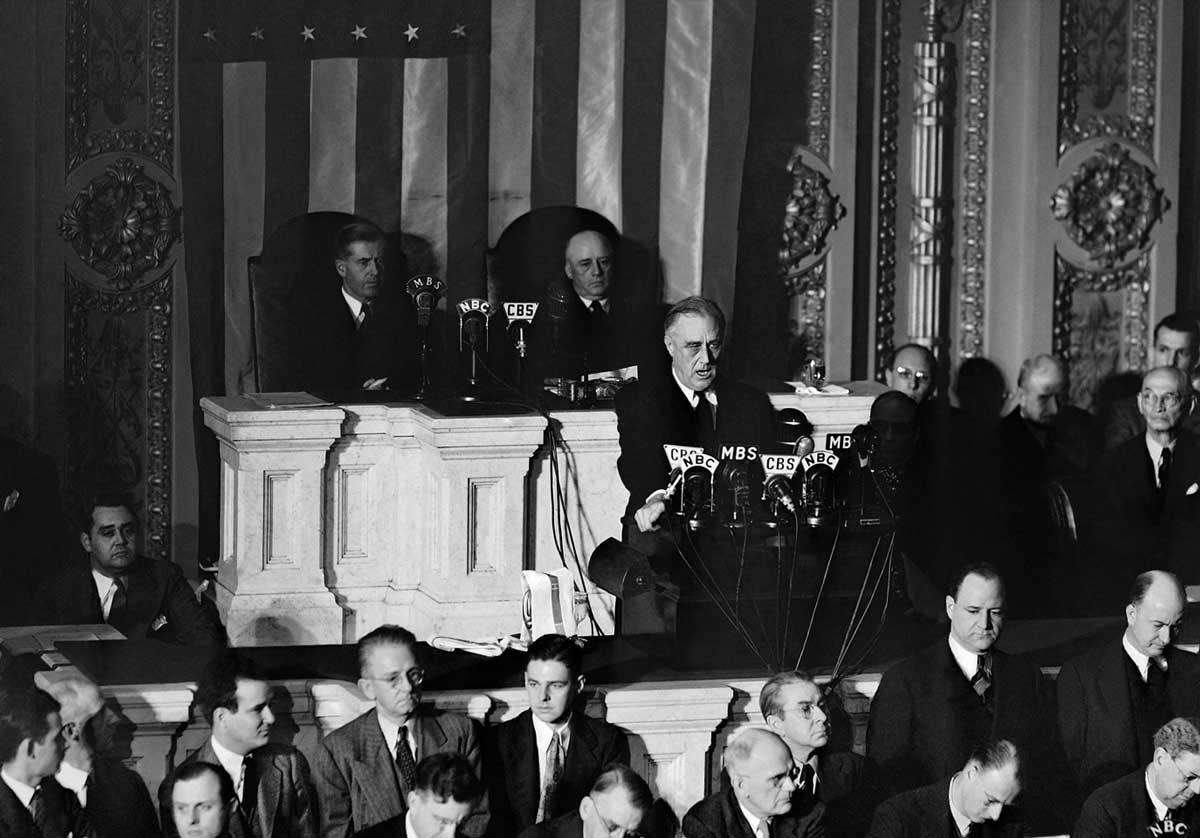
As an illustration, recall that on December 8, 1941, the US Congress declared war on the Empire of Japan responding to the previous attack on Pearl Harbor . President Franklin D. Roosevelt addressed congress. In his discourse, one can distinguish illocutionary acts: promises (to the US) and warnings (to Japan), also including his requests for the state of war to be recognized.
We can speculate about the perlocutionary effects: some people were moved and excited, while others could have experienced fear and anxiety, as it was now clear that the United States would join World War II . The perlocutionary effect, therefore, does not depend on the intention of the speaker. I cannot say “I hereby scare you” or “I hereby convince you”.
Classifying Speech Acts

Focusing on the illocutionary act, J.L. Austin was ready to classify speech acts. He did this by using performative verbs that make the illocutionary act explicit (e.g., ‘I declare’, ‘I promise’). He ended up with six types: verdictives, exercitives, commissives, behabitives, and expositives (Austin, 2020, p. 166). The following table summarizes and explains his classification.
John Searle’s Speech Act Theory

Austin’s classification of speech acts was closely examined and greatly improved by his student John Searle. In his book Expression and Meaning (1979), instead of focusing on performative verbs, he distinguishes twelve dimensions of variation in which illocutionary acts differ from one another. However, he decides to build his taxonomy mainly around two: the illocutionary point and the direction of fit (Searle, 1979, p. 5) 1 .
To begin, the illocutionary point is the purpose of the utterance. The illocutionary point of a description is different from, let us say, a command ; but a request and a command have the same illocutionary point: “both are attempts to get the hearer to do something” (Searle, 1979, p. 3). Searle’s illocutionary point is part of Austin’s illocutionary act. In any case, there is something more that distinguishes illocutionary acts, namely, their direction of fit. To explain it Searle uses an example made by Elizabeth Anscombe.

Imagine that a husband goes to the grocery store with a list of things to buy. At the same time, he is being followed by a detective who is observing which products he is acquiring and writing them on a list as well. In the end, both the husband and the detective will have the same list (both contain the same items). Yet, they are different:
“In the case of the shopper’s list, the purpose of the list is, so to speak, to get the world to match the words; the man is supposed to make his actions fit the list. In the case of the detective, the purpose of the list is to make the words match the world; the man is supposed to make the list fit the actions of the shopper.” (Searle, 1979, p. 3).
What Searle is stressing by using Anscombe’s example, is that speech acts (words) relate in different ways to reality (the world). Searle introduces a notation, such that ‘(↓)’ represents a word-to-world direction of fit (that of the detective), and ‘(↑)’ stands for a world-to-word direction of fit (that of the husband). Considering the illocutionary point and the direction of fit I can now summarize Searle’s taxonomy.

Searle is conscious of the additional requirement for non-linguistic institutions to exist so that ‘directive speech acts’ are successful (happy). A command, for example, is obeyed once the speaker is in a position of authority over the hearer (Searle, 1969, p. 66). This point was made in the Harvard Lectures as well (Austin, 2020, p. 18). In the case of ‘Expressives’ the direction of fit is presupposed because when one congratulates or expresses condolence there is already an antecedent speech act that is being assumed (Searle, 2010, p. 12).
For Searle, the most interesting speech acts are ‘Declarations”. Declarations bring about correspondence between the propositional content of an utterance and reality, this is, they create reality by representing it . In this sense when the proper authority in an appropriate context says “I declare you husband and wife” the content of that utterance is now real; this is why there is a double direction of fit (↕).
The Future of Speech Act Theory

Speech Act Theory is deeply influential in the modern philosophy of language, linguistics, social theory, Critical Theory , and discourse studies, among others. Some have tried to extend the classification of speech acts based on Searle (Ballmer & Brennenstuhl, 1981). The most challenging part about speech acts is, nevertheless, that they are not necessarily linguistic, this is, one can perform a speech act by gesture or by pointing at things. Additionally, some speech acts can be nested, such that the question ‘where is the salt?’ contains, in the context of dinner, a nested directive: ‘pass the salt’ or ‘please pass the salt’.
The most important idea to remember from speech act theory is this: in speaking we are not only describing things, but we are also performing actions and interacting with reality. We can commit ourselves to promises, we can influence the behavior of others, and we can choose to declare war.
Austin, J. L. (2020). How to do things with words (Kindle Ver). Barakaldo Books.
Ballmer, T., & Brennenstuhl, W. (1981). Speech Act Classification . Springer Verlag.
Deutscher, G. (2006). The Unfolding of Language. The evolution of mankind’s greatest invention . London: Arrow Books.
Huang, Y. (2014). Pragmatics (Second). Oxford University Press.
Searle, J. (1979). Expression and Meaning . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Searle, J. (2010). Making the Social World . Oxford University Press.
Wittgenstein, L. (2009). Philosophical Investigations . (G. E. M. Anscombe, Ed.) (4th ed.). Oxford: Wiley Blackwell.
1 The third dimension is also relevant although we will not discuss it here: the expressed psychological state.

The Economic Effects of the Cold War: Conservatism Plus Deficit Spending

By Andres Felipe Barrero MA Philosophy, MSc Philosophy, Ph.D. Candidate Andrés has a background in philosophy from Universidad de la Salle in Bogotá, Colombia, where he finished his undergraduate and master`s studies. He completed a second master's at Universität Hamburg, Germany, where he wrote about philosophical theories of Modernity and Secularization. Currently, he is a Ph.D. Candidate at Universität Bremen. His fields of interest include the Philosophy of Language, Philosophy of Religion, Philosophy of Science, Social Theory, Discourse Studies, Corpus Linguistics, and Natural Language Processing.

Frequently Read Together


6 Artworks Inspired by Gabriel García Márquez’s Famous Novel

Ludwig Wittgenstein: The Turbulent Life of a Philosophical Pioneer

What Is the Significance of Ludwig Wittgenstein’s Philosophical Investigations?
- List of Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Opt-out preferences
SPEECH ACT THEORY
INTRODUCTION
The speech act theory considers language as a sort of action rather than a medium to convey and express. The contemporary Speech act theory developed by J. L. Austin a British philosopher of languages, he introduced this theory in 1975 in his well-known book of ‘How do things with words’. Later John Searle brought the aspects of theory into much higher dimensions. This theory is often used in the field of philosophy of languages. Austin is the one who came up with the findings that people not only uses that language to assert things but also to do things. And people who followed him went to greater depths based on this point.
All sort of linguist communication are comprised of linguistic actions. Previously it was conceived that the very basic unit of communication is words, Symbols, sentences or some kind of token of all of these, but it was speech act theory which suggested that production or issuances if words, symbols are the basic units of communication. This issuance happens during the process of performance of speech act. The meaning of these basic units was considered as the building blocks of mutual understanding between the people intend to communicate.
“ A theory of language is a theory of action”- Greig E. Henderson and Christopher Brown.
The theory emphasis that the utterances have a different or specific meaning to its user and listener other than its meaning according to the language. The theory further identify that there are two kinds of utterances, they are called constative and performative utterances. In his book of ‘How do things with words’ Austin clearly talks about the disparities between the constative and performative utterances.
A constative utterances is something which describes or denotes the situation, in relation with the fact of true or false.
Example: The teacher asked Olivia whether she had stolen the candy. Olivia replies “mmmmmm”. Here the utterances of Olivia describes the event in pact of answering her teacher whether the situation was true or false.
The performative utterances is something which do not describes anything at all. The utterances in the sentences or in the part of sentences are normally considered as having a meaning of its own. The feelings, attitudes, emotions and thoughts of the person performing linguistic act are much of a principal unit here.
Example: Bane and Sarah have been dating for the past four years. One fine evening Bane took Sarah to the most expensive restaurant in town. And he ordered the most expensive wine available in the restaurant. Then he moved closer to her and asked her that “ will you marry me?”. Sarah burst with contentment and replied “I will”. Here the “I will” of Sarah express her feelings, attitudes and emotional towards the context. This utterances have its specific meaning only in relation to it specific context.
Further Austin divides his linguistic act into three different categories. They are,
- Locutionary act – This is the act of saying something. It has a meaning and it creates an understandable utterly to convey or express
- Illocutionary act – It is performed as an act of saying something or as an act of opposed to saying something. The illocutionary utterance has a certain force of it. It well well-versed with certain tones, attitudes, feelings, or emotions. There will be an intention of the speaker or others in illocutionary utterance. It is often used as a tone of warning in day today life
- Perlocutionary act – It normally creates a sense of consequential effects on the audiences. The effects may be in the form of thoughts, imaginations, feelings or emotions. The effect upon the addressee is the main charactership of perlocutionary utterances
For example
The locutionary act describes a dangerous situation, the illocutionary act acts as a force of the warning and perlocutionary acts frighten the addressee.
Austin himself admits that these three components of utterances are not altogether separable.“We must consider the total situation in which the utterance is issued- the total speech act – if we are to see the parallel between statements and performative utterance, and how each can go wrong. Perhaps indeed there is no great distinction between statements and performative utterances.” Austin.
Searle suggested that the basic unit of linguistic communication is speech act. It can be a word, a phrase, a sentence or a sound, it should fulfil the task of expressing the intention of the user. Understanding the user’s intention can lead to complete understanding of the speech act.
The context of speech act is in the context of situation than explanation. The speech act borrows it ideas from structuralism. The indirect speech act of John Searle was developed based on Austin’s speech act.
Related Posts:
- MEDIUM THEORY
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Computer Mediated Communication
It has written in fabulous manner!!
lookie here
It is a nice script
very triggering to think more about language as cognition, languange as emotion, and language as action
please give us more example of the three levels of speech acts
The simplest and easiest explanation there is. Brief but direct to the point. 🙂
Till now i cannot get it,dod Austen devide Speech acts into constative and performative OR locutionary,illocutionary ,perlocutionary???
It’s a wonderful piece and wish to get more
learned a lot. Thanks!
Article is insightful and straight forward. Thumbs up.
Learned great from it
I do agree with Mari that more specific example is needed for each classification. Without such example, we are still hanging with those philosophical words.
Very impressive!
Thank you, for your contribution.
İ needed to read this twice to understand. The theory isn’t easy to understand in my opinion.
I got a little confusion on locutionary , illocutionary & perlocutionar also in the perforamtive & constative I’ m asking for more examples that I can be well on it.. but the rest are perfect understandable..
Very impressive, direct to the point hence easy to understand,, thanks much…!!
Nicely explained in precise manner.
Nice material
Really helpful for my graduation research and quoted some of it, I’m very grateful.
Paul C. Hoffman dice
Really helpful for my research Nice material
Thank you for this explanation!
Good explanation
Well develop and simple
Leave a Comment
Next post: SYMBOLIC INTERACTIONISM THEORY
Previous post: Attribution Theory
- Advertising, Public relations, Marketing and Consumer Behavior
- Business Communication
- Communication / General
- Communication Barriers
- Communication in Practice
- Communication Models
- Cultural Communication
- Development Communication
- Group Communication
- Intercultural Communication
- Interpersonal Communication
- Mass Communication
- Organisational Communication
- Political Communication
- Psychology, Behavioral And Social Science
- Technical Communication
- Visual Communication
Communication Theory

Speech Acts
Speech acts are a staple of everyday communicative life, but only became a topic of sustained investigation, at least in the English-speaking world, in the middle of the Twentieth Century. [ 1 ] Since that time “speech act theory” has been influential not only within philosophy, but also in linguistics, psychology, legal theory, artificial intelligence, literary theory and many other scholarly disciplines. [ 2 ] Recognition of the importance of speech acts has illuminated the ability of language to do other things than describe reality. In the process the boundaries among the philosophy of language, the philosophy of action, the philosophy of mind and even ethics have become less sharp. In addition, an appreciation of speech acts has helped lay bare an implicit normative structure within linguistic practice, including even that part of this practice concerned with describing reality. Much recent research aims at an accurate characterization of this normative structure underlying linguistic practice.
1. Introduction
2.1 the independence of force and content, 2.2 can saying make it so, 2.3 seven components of illocutionary force, 3. illocutions and perlocutions, and indirect speech acts, 4. force, fit and satisfaction, 5.1 force conventionalism, 5.2. an objection to force conventionalism, 6.1 grice's account of speaker meaning, 6.2 objections to grice's account, 6.3 force as an aspect of speaker meaning, 7.1 speech acts and conversation analysis, 7.2 speech acts and scorekeeping, 8. force-indicators and the logically perfect language, 9. do speech acts have a logic, further reading, other internet resources, related entries.
One way of appreciating the distinctive features of speech acts is in contrast with other well-established phenomena within the philosophy of language. Accordingly in this entry I will consider the relation among speech acts and: semantic content, grammatical mood, speaker-meaning, logically perfect languages, perlocutions, performatives, presuppositions, and implicature. This will enable us to situate speech acts within their ecological niche.
Above I shuddered with quotation marks around the expression ‘speech act theory’. It is one thing to say that speech acts are a phenomenon of importance for students of language and communication; another to say that we have a theory of them. While, as we shall see below, we are able to situate speech acts within their niche, having a theory of them would enable us to explain (rather than merely describe) some of their most significant features. Consider a different case. Semantic theory deserves its name: For instance, with the aid of set-theoretic tools it helps us tell the difference between good arguments and bad arguments couched in ordinary language. By contrast, it is not clear that “speech act theory” has comparable credentials. One such credential would be a delineation of logical relations among speech acts, if such there be. To that end I close with a brief discussion of the possibility, envisioned by some, of an “illocutionary logic”.
2. Content, Force, and How Saying Can Make It So
Construed as a bit of observable behavior, a given act may be done with any of a variety of aims. I bow deeply before you. So far you may not know whether I am paying obeisance, responding to indigestion, or looking for a wayward contact lens. So too, a given utterance, such as ‘You'll be more punctual in the future,’ may leave you wondering whether I am making a prediction or issuing a command or even a threat. The colloquial question, “What is the force of those words?” is often used to elicit an answer. In asking such a question we acknowledge a grasp of what those words mean. However, given the dizzying array of uses of ‘meaning’ in philosophy and related cognitive sciences, I will here refer instead to content. While different theories of content abound (as sets of possible worlds, sets of truth conditions, Fregean senses, ordered n -tuples, to name a few), the phenomenon is relatively clear: What the speaker said is that the addressee will be more punctual in the future. The addressee or observer who asks, “What is the force of those words?” is asking, of that content, how it's to be taken–as a threat, as a prediction, or as a command. The addressee is not asking for a further elucidation of that content.
Or so it seems. Perhaps whether the utterance is meant as a threat, a prediction or a command will depend on some part of her content that was left unpronounced? According to this suggestion, really what she said was, “I predict you'll be more punctual,” or “I command you to be more punctual,” as the case may be. Were that so, however, she'd be contradicting herself in uttering ‘You'll be more punctual in the future’ as a prediction while going on to point out, ‘I don't mean that as a prediction.’ While such a juxtaposition of utterances is surely odd, it is not a self-contradiction, any more than “It's raining but I don't believe it,” is a self-contradiction when the left conjunct is put forth as an expression of belief. What is more, ‘I predict you'll be more punctual,’ is itself a sentence with a content, and will be being put forth with some force or other when–as per our current suggestion—the speaker says it in the course of making a prediction. So that sentence, ‘I predict you'll be more punctual’ is put forth with some force–say as an assertion. This implies, according to the present suggestion, that really the speaker said, ‘I assert that I predict that you'll be more punctual.’ Continuing this same style of reasoning will enable us to infer that performance of a single speech act requires saying–though perhaps not pronouncing—infinitely many things. That is reason for rejecting the hypothesis that implied it, and for the rest of this entry I will assume that force is no part of content.
In chemical parlance, a radical is a group of atoms normally incapable of independent existence, whereas a functional group is the grouping of those atoms in a compound that is responsible for certain of the compound's properties. Analogously, it is often remarked that a proposition is itself communicatively inert; for instance, merely expressing the proposition that snow is white is not to make a move in a “language game”. Rather, such moves are only made by putting forth a proposition with an illocutionary force such as assertion, conjecture, command, etc. The chemical analogy gains further plausibility from the fact that just as a chemist might isolate radicals held in common among various compounds, the student of language may isolate a common element held among ‘Is the door shut?’, ‘Shut the door!’, and ‘The door is shut’. This common element is the proposition that the door is shut, queried in the first sentence, commanded to be made true in the second, and asserted in the third. According to the chemical analogy, then:
Illocutionary force : propositional content :: functional group : radical
In light of this analogy we may see, following Stenius 1967, that just as the grouping of a set of atoms is not itself another atom or set of atoms, so too the forwarding of a proposition with a particular illocutionary force is not itself a further component of propositional content.
Encouraged by the chemical analogy, a central tenet in the study of speech acts is that content may remain fixed while force varies. Another way of putting the point is that the content of one's communicative act underdetermines the force of that act. That's why, from the fact that someone has said, “You'll be more punctual in the future,” we cannot infer the utterance's force. The force of an utterance also underdetermines its content: Just from the fact that a speaker has made a promise, we cannot deduce what she has promised to do. For these reasons, students of speech acts contend that a given communicative act may be analyzed into two components: force and content. While semantics studies the contents of speech acts, pragmatics studies, inter alia , their force. The bulk of this entry may be seen as an elucidation of force.
Need we bother with such an elucidation? That A is an important component of communication, and that A underdetermines B , do not justify the conclusion that B is an important component of communication. Content also underdetermines the decibel level at which we speak but this fact does not justify adding decibel level to our repertoire of core concepts for the philosophy of language. Why should force be thought any more worthy of admission to this set of core concepts than decibel level? One reason for an asymmetry in our treatment of force and decibel level is that the former, but not the latter, seems to be a component of speaker meaning : Force is a feature not of what is meant but of how it is meant; decibel level, by contrast, is a feature at most of the way in which something is said. This point is developed in Section 6 below.
Speech acts are not to be confused with acts of speech. One can perform a speech act such as issuing a warning without saying anything: A gesture or even a minatory facial expression will do the trick. So too, one can perform an act of speech, say by uttering words in order to test a microphone, without performing a speech act. [ 3 ] For a first-blush delineation of the range of speech acts, then, consider that in some cases we can make something the case by saying that it is. Alas, I can't lose ten pounds by saying that I am doing so, nor can I persuade you of a proposition by saying that I am doing so. On the other hand I can promise to meet you tomorrow by uttering the words, “I promise to meet you tomorrow,” and if I have the authority to do so, I can even appoint you to an office by saying, “I hereby appoint you.” (I can also appoint you without making the force of my act explicit: I might just say, “You are now Treasurer of the Corporation.” Here I appoint you without saying that I am doing so.) A necessary and, perhaps, sufficient condition of a type of act's being a speech act is that acts of that type can–whether or not all are—be carried out by saying that one is doing so.
Saying can make it so, but that is not to suggest that any old saying by any speaker constitutes the performance of a speech act. Only an appropriate authority, speaking at the appropriate time and place, can: christen a ship, pronounce a couple married, appoint someone to an administrative post, declare the proceedings open, or rescind an offer. Austin, in How To Do Things With Words, spends considerable effort detailing the conditions that must be met for a given speech act to be performed felicitously . Failures of felicity fall into two classes: misfires and abuses . The former are cases in which the putative speech act fails to be performed at all. If I utter, before the QEII, “I declare this ship the Noam Chomsky,” I have not succeeded in naming anything simply because I lack the authority to do so. My act thus misfires in that I've performed an act of speech but no speech act. Other attempts at speech acts might misfire because their addressee fails to respond with an appropriate uptake : I cannot bet you $100 on who will win the election unless you accept that bet. If you don't accept that bet, then I have tried to bet but have not succeeded in betting.
Some speech acts can be performed–that is, not misfire—while still being less than felicitous. I promise to meet you for lunch tomorrow, but haven't the least intention of keeping the promise. Here I have promised all right, but the act is not felicitous because it is not sincere. My act is, more precisely, an abuse because although it is a speech act, it fails to live up to a standard appropriate for a speech act of its kind. Sincerity is a paradigm condition for the felicity of speech acts. Austin foresaw a program of research in which individual speech acts would be studied in detail, with felicity conditions elucidated for each one. [ 4 ]
Here are three further features of the “saying makes it so” condition. First, the saying appealed to in the “saying makes it so” test is not an act of speech: My singing in the shower, “I promise to meet you tomorrow for lunch,” when my purpose is simply to enjoy the sound of my voice, is not a promise, even if you overhear me. Rather, the saying (or singing) in question must itself be something that I mean. We will return in Section 6 to the task of elucidating the notion of meaning at issue here.
Second, the making relation that this “saying makes it so” condition appeals to needs to be treated with some care. My uttering, “I am causing molecular agitation,” makes it the case that I am causing molecular agitation. Yet causing molecular agitation is not a speech act on any intuitive understanding of that notion. One might propose that the notion of making at issue here marks a constitutive relation rather than a causal relation. That may be so, but as we'll see in Section 5, this suggests the controversial conclusion that all speech acts depend for their existence on conventions over and above those that imbue our words with meaning.
Finally, the saying makes it so condition has a flip side. Not only can I perform a speech act by saying that I am doing so, I can also rescind that act later on by saying (in the speech act sense) that I take it back. I cannot, of course, change the past, and so nothing I can do on Wednesday can change the fact that I made a promise or an assertion on Monday. However, on Wednesday I may be able to retract a claim I made on Monday. I can't take back a punch or a burp; the most I can do is apologize for one of these infractions, and perhaps make amends. By contrast, not only can I apologize or make amends for a claim I now regret; I can also take it back. Likewise, you may allow me on Wednesday to retract the promise I made to you on Monday. In both these cases of assertion and promise, I am no longer beholden to the commitments that the speech acts engender in spite of the fact that the past is fixed. Just as one can, under appropriate conditions, perform a speech act by saying that one is doing so, so too one can, under the right conditions, retract that very speech act.
Searle and Vanderveken 1985 distinguish between those illocutionary forces employed by speakers within a given linguistic community, and the set of all possible illocutionary forces. While a certain linguistic community may make no use of a force such as conjecturing or appointing, these two are among the set of all possible forces. (These authors appear to assume that while the set of possible forces may be infinite, it has a definite cardinality.) Searle and Vanderveken go on to define illocutionary force in terms of seven features, claiming that every possible illocutionary force may be identified with a septuple of such values. The features are:
1. Illocutionary point : This is the characteristic aim of each type of speech act. For instance, the characteristic aim of an assertion is to describe how things are; the characteristic point of a promise is to commit oneself to a future course of action.
2. Degree of strength of the illocutionary point : Two illocutions can have the same point but differ along the dimension of strength. For instance, requesting and insisting that the addressee do something both have the point of attempting to get the addressee to do that thing; however, the latter is stronger than the former.
3. Mode of achievement : This is the special way, if any, in which the illocutionary point of a speech act must be achieved. Testifying and asserting both have the point of describing how things are; however, the former also involves invoking one's authority as a witness while the latter does not. To testify is to assert in one's capacity as a witness. Commanding and requesting both aim to get the addressee to do something; yet only someone issuing a command does so in her capacity as a person in a position of authority.
4. Propositional content conditions : Some illocutions can only be achieved with an appropriate propositional content. For instance, I can only promise what is in the future and under my control. I can only apologize for what is in some sense under my control and already the case. For this reason, promising to make it the case that the sun did not rise yesterday is not possible; neither can I apologize for the truth of Snell's Law.
5. Preparatory conditions : These are all other conditions that must be met for the speech act not to misfire. Such conditions often concern the social status of interlocutors. For instance, a person cannot bequeath an object unless she already owns it or has power of attorney; a person cannot marry a couple unless she is legally invested with the authority to do so.
6. Sincerity conditions : Many speech acts involve the expression of a psychological state. Assertion expresses belief; apology expresses regret, a promise expresses an intention, and so on. A speech act is sincere only if the speaker is in the psychological state that her speech act expresses.
7. Degree of strength of the sincerity conditions : Two speech acts might be the same along other dimensions, but express psychological states that differ from one another in the dimension of strength. Requesting and imploring both express desires, and are identical along the other six dimensions above; however, the latter expresses a stronger desire than the former.
Searle and Vanderveken suggest, in light of these seven characteristics, that each illocutionary force may be defined as a septuple of values, each of which is a “setting” of a value within one of the seven characteristics. It follows, according to this suggestion, that two illocutionary forces F 1 and F 2 are identical just in case they correspond to the same septuple.
I cannot lose ten pounds by saying that I am doing so, and I cannot convince you of the truth of a claim by saying that I am doing so. However, these two cases differ in that the latter, but not the former, is a characteristic aim of a speech act. One characteristic aim of assertion is the production of belief in an addressee, whereas there is no speech act one of whose characteristic aims is the reduction of adipose tissue. A type of speech act can have a characteristic aim without each speech act of that type being issued with that aim: Speakers sometimes make assertions without aiming to produce belief in anyone, even themselves. Instead, the view that a speech act-type has a characteristic aim is akin to the view that a biological trait has a function. The characteristic role of wings is to aid in flight, but some flightless creatures have wings.
Austin called these characteristic aims of speech acts perlocutions (1962, p. 101). I can both urge and persuade you to shut the door, yet the former is an illocution while the latter is a perlocution. How can we tell the difference? We can do this by noting that one can urge by saying, “I urge you to shut the door,” while there are no circumstances in which I can persuade you by saying, “I persuade you to shut the door.” A characteristic aim of urging is, nevertheless, the production of a resolution to act. (1962, p. 107)
Perlocutions are characteristic aims of one or more illocution, but are not themselves illocutions. Nevertheless, a speech act can be performed by virtue of the performance of another one. For instance, my remark that you are standing on my foot is normally taken as, in addition, a demand that you move; my question whether you can pass the salt is normally taken as a request that you do so. These are examples of so-called indirect speech acts (Searle 1975b).
Indirect speech acts are less common than might first appear. In asking whether you are intending to quit smoking, I might be taken as well to be suggesting that you quit. However, while the embattled smoker might indeed jump to this interpretation, we do well to consider what evidence would mandate it. After all, while I probably would not have asked whether you intended to quit smoking unless I hoped you would quit, I can evince such a hope without suggesting anything. Similarly, the advertiser who tells us that Miracle Cream reversed hair loss in Bob, Mike, and Fred, also most likely hopes that I will believe it will reverse my own hair loss. That does not show that he is (indirectly) asserting that it will. Whether he is asserting this depends, it would seem, on whether he can be accused of being a liar if in fact he does not believe that Miracle Cream will staunch my hair loss.
Whether, in addition to a given speech act, I am also performing an indirect speech act would seem to depend on my intentions. My question whether you can pass the salt is also a request that you do so only if I intend to be so understood. My remark that Miracle Cream helped Bob, Mike and Fred is also an assertion that it will help you only if I intend to be so committed. What is more, these intentions must be feasibly discernible on the part of one's audience. Even if, in remarking on the fine weather, I intend as well to request that you pass the salt, I have not done so. I need to make that intention manifest in some way.
How might I do this? One way is by virtue of inference to the best explanation. All else being equal, the best explanation of my asking whether you can pass the salt is that I mean to be requesting that you do so. All else equal, the best explanation of my remarking that you are standing on my foot, particularly if I use a stentorian tone of voice, is that I mean to be demanding that you desist. By contrast, it is doubtful that the best explanation of my asking whether you intend to quit smoking is my intention to suggest that you do so. Another explanation at least as plausible is my hope that you do so. Bertolet 1994, however, develops an even more skeptical position than that suggested here, arguing that any alleged case of an indirect speech act can be construed just as an indication, by means of contextual clues, of the speaker's intentional state–hope, desire, etc., as the case may be. Postulation of a further speech act beyond what has been (relatively) explicitly performed is explanatorily unmotivated.
These considerations suggest that indirect speech acts, if they do occur, can be explained within the framework of conversational implicature–that process by which we mean more than we say, but in a way not due exclusively to the conventional meanings of our words. Conversational implicature, too, depends both upon communicative intentions and the availability of inference to the best explanation. (Grice, 1989). In fact, Searle's 1979b account of indirect speech acts was in terms of conversational implicature. The study of speech acts is in this respect intertwined with the study of conversations; we return to this connection in Section 7.
Force is often characterized in terms of the notions of direction of fit and conditions of satisfaction. The first of these may be illustrated with an example derived from Anscombe (1963). A woman sends her husband to the grocery store with a list of things to get; unbeknownst to him he is also being trailed by a detective concerned to make a list of what the man buys. By the time the husband and detective are in the checkout line, their two lists contain exactly the same items. The contents of the two lists is the same, yet they differ along another dimension. For the contents of the husband's list guide what he puts in his shopping cart. Insofar, his list exhibits world-to-word direction of fit : It is, so to speak, the job of the items in his cart to conform to what is on his list. By contrast, it is the job of the detective's list to conform with the world, in particular to what is in the husband's cart. As such, the detective's list has word-to-world direction of fit : The onus is on those words to conform to how things are. Speech acts such as assertions and predictions have word-to-world direction of fit, while speech acts such as commands have world-to-word direction of fit.
Not all speech acts appear to have direction of fit. I can thank you by saying “Thank you,” and it is widely agreed that thanking is a speech act. However, thanking seems to have neither of the directions of fit we have discussed thus far. Similarly, asking who is at the door is a speech act, but it does not seem to have either of the directions of fit we have thus far mentioned. Some would respond by construing questions as a form of imperative (e.g., “Tell me who is at the door!”), and then ascribing the direction of fit characteristic of imperatives to questions. This leaves untouched, however, banal cases such as thanking or even, “Hooray for Arsenal!” Some authors, such as Searle and Vanderveken 1985, describe such cases as having “null” direction of fit. That characterization is evidently distinct from saying such speech acts have no direction of fit at all. (The characterization is thus analogous to the way in which some non-classical logical theories describe some proposition as being neither True nor False, but as having a third truth value, N : Evidently that is not to say that such propositions are bereft of truth value.) It is difficult to discern from such accounts how one sheds light on a speech act in characterizing it as having a null direction of fit, as opposed to having no direction of fit at all. [ 5 ]
Direction of fit is also not so fine-grained as to enable us to distinguish speech acts meriting different treatment. Consider asserting that the center of the Milky Way is inhabited by a black hole, as opposed to conjecturing that the center of the Milky Way is so inhabited. These two acts seem subject to norms: The former purports to be a manifestation of knowledge, while the latter does not. This is suggested by the fact that it is appropriate to reply to the assertion with, “How do you know?”, while that is not an appropriate response to the conjecture. (Williamson 1996) Nevertheless, both the assertion and conjecture have word-to-world direction of fit. Might there be other notions enabling us to mark differences between speech acts with the same direction of fit? This is not to say that the difference between assertion and conjecture cannot be expressed as a difference among Searle and Vanderveken's seven components of illocutionary force; for instance that difference might be thought of as a difference in parameter 2, namely the degree of strength of illocutionary point. Rather, what we are seeking is an account of, rather than a label for, that difference.
One suggestion might come from the related notion of conditions of satisfaction . This notion generalizes that of truth. As we saw in 2.3, it is internal to the activity of assertion that it aims to capture how things are. When an assertion does so, not only is it true, it has hit its target; the aim of the assertion has been met. A similar point may be made of imperatives: It is internal to the activity of issuing an imperative that the world is enjoined to conform to it. The imperative is satisfied just in case it is fulfilled. Assertions and imperatives both have conditions of satisfaction–truth in the first place, and conformity in the second. In addition, it might be held that questions have answerhood as their conditions of satisfaction: A question hits its target just in case it finds an answer, typically in a speech act, performed by an addressee, such as an assertion that answers the question posed. Like the notion of direction of fit, however, the notion of conditions of satisfaction is too coarse-grained to enable us to make some valuable distinctions among speech acts. Just to use our earlier case again: An assertion and a conjecture that P have identical conditions of satisfaction, namely that P be the case. May we discern features distinguishing these two speech acts, and that may enable us to make finer-grained distinctions among other speech acts as well? I shall return to this question in Section 7.
5. Mood, Force and Convention
Just as content underdetermines force and force underdetermines content; so too even grammatical mood together with content underdetermine force. ‘You'll be more punctual in the future’ is in the indicative grammatical mood, but as we have seen that fact does not determine its force. The same may be said of other grammatical moods. Although I overhear you utter the words, ‘shut the door’, I cannot infer yet that you are issuing a command. Perhaps instead you are simply describing your own intention, in the course of saying, “I intend to shut the door.” If so, you've used the imperative mood without issuing a command. So too with the interrogative mood: I overhear your words, ‘who is on the phone.’ Thus far I don't know whether you've asked a question. After all, you may have so spoken in the course of stating, “John wonders who is on the phone.” Might either or both of initial capitalization or final punctuation settle the issue? Apparently not: What puzzles John is the following question: Who is on the phone?
Mood together with content underdetermine force. On the other hand it is a plausible hypothesis that grammatical mood is one of the devices we use, together with contextual clues, intonation and so on to indicate the force with which we are expressing a content. Understood in this weak way, it is unexceptionable to construe the interrogative mood as used for asking questions, the imperatival mood as used for issuing commands, and so on. So understood, we might go on to ask how speakers indicate the force of their speech acts given that grammatical mood and content cannot be relied on alone to do so.
One well known answer we may term force conventionalism . According to a strong version of this view, for every speech act that is performed, there is some convention that will have been invoked in order to make that speech act occur. This convention transcends those imbuing words with their literal meaning. Thus, force conventionalism implies that in order for use of ‘I promise to meet you tomorrow at noon,’ to constitute a promise, not only must the words used possess their standard conventional meanings, there must also exist a convention to the effect that the use, under the right conditions, of some such words as these constitutes a promise. J.L. Austin, who introduced the English-speaking world to the study of speech acts, seems to have held this view. For instance in his characterization of “felicity conditions” for speech acts, Austin holds that for each speech act
There must exist an accepted conventional procedure having a certain conventional effect, that procedure to include the uttering of certain words by certain persons in certain circumstances… (1962, p. 14).
Austin's student Searle follows him in this, writing
…utterance acts stand to propositional and illocutionary acts in the way in which, e.g., making an X on a ballot paper stands to voting. (1969, p. 24)
Searle goes on to clarify this commitment in averring,
…the semantic structure of a language may be regarded as a conventional realization of a series of sets of underlying constitutive rules, and …speech acts are acts characteristically performed by uttering sentences in accordance with these sets of constitutive rules. (1969, p. 37)
Searle espouses a weaker form of force conventionalism than does Austin in leaving open the possibility that some speech acts can be performed without constitutive rules; Searle considers the case of a dog requesting to be let outside (1969, p. 39). Nevertheless Searle does contend that speech acts are characteristically performed by invoking constitutive rules.
Force-conventionalism, even in the weaker form just adumbrated, has been challenged by Strawson, who writes,
I do not want to deny that there may be conventional postures or procedures for entreating: one can, for example, kneel down, raise one's arms, and say, “I entreat you.” But I do want to deny that an act of entreaty can be performed only as conforming to such conventions….[T]o suppose that there is always and necessarily a convention conformed to would be like supposing that there could be no love affairs which did not proceed on lines laid down in the Roman de la Rose or that every dispute between men must follow the pattern specified in Touchstone's speech about the countercheck quarrelsome and the lie direct. (1964, p. 444)
Strawson contends that rather than appealing to a series of extra-semantic conventions to account for the possibility of speech acts, we explain that possibility in terms of our ability to discern one another's communicative intentions. What makes an utterance of a sentence in the indicative mood a prediction rather than a command, for instance, is that it is intended to be so taken; likewise for promises rather than predictions. This position is compatible with holding that in special cases linguistic communities have instituted conventions for particular speech acts such as entreating and excommunicating.
Intending to make an assertion, promise, or request, however, is not enough to perform one of these acts. Those intentions must be efficacious. The same point applies to cases of trying to perform a speech act, even when what one is trying to do is clear to others. This fact emerges from reflecting on an oft-quoted passage from Searle:
Human communication has some extraordinary properties, not shared by most other kinds of human behavior. One of the most extraordinary is this: If I am trying to tell someone something, then (assuming certain conditions are satisfied) as soon as he recognizes that I am trying to tell him something and exactly what it is I am trying to tell him, I have succeeded in telling it to him. (1969, p. 47.)
An analogous point would not apply to the act of sending : Just from the facts that I am trying to send my addressee something, and that he recognizes that I am trying to do so (and what it is I am trying to send him), we cannot infer that I have succeeded in sending it to him. However, while Searle's point about telling looks more plausible at first glance than would a point about sending, it also is not accurate. Suppose I am trying to tell somebody that I love her, and that she recognizes this fact on the basis of background knowledge, my visible embarrassment, and my inability to get past the letter ‘l’. Here we cannot infer that I have succeeded in avowing my love for her. Nothing short of coming out and saying it will do. Similarly, it might be common knowledge that my moribund uncle is trying, as he breathes his last, to bequeath me his fortune; still, I won't inherit a penny if he expires before saying what he was trying to. [ 6 ]
The gist of these examples is not the requirement that words be uttered in every speech act–we have already observed that speech acts can be performed silently. Rather, its gist is that speech acts involve intentional undertaking of one or another form of commitment; further, that commitment is not undertaken simply by virtue of my intending to undertake it, even when it is common knowledge that this is what I am trying to do. Can we, however, give a more illuminating characterization of the relevant intentions than merely saying that, for instance, to assert P one must intentionally put forth P as an assertion? [ 7 ] Strawson (1964) proposes that we can do so with aid of the notion of speaker meaning–a topic to which I now turn.
6. Speaker-Meaning and Force
As we have seen, that A is an important component of communication, and that A underdetermines B , do not justify the conclusion that B is an important component of communication. One reason for an asymmetry in our treatment of force and decibel level is that the former, but not the latter, seems to be a component of speaker meaning. I intend to speak at a certain volume, and sometimes succeed, but in most cases it is no part of what I mean that I happen to be speaking at the volume that I do. On the other hand, the force of my utterance is part of what I mean. It is not, as we have seen, part of what I say–that notion being closely associated with content. However, whether I mean what I say as an assertion, a conjecture, a promise or something else will be a feature of how I mean what I do.
Let us elucidate this notion of speaker meaning (née non-natural meaning). In his influential 1957 article, Grice distinguished between two senses of ‘mean’. One sense is exemplified by remarks such as ‘Those clouds mean rain,’ and ‘Those spots mean measles.’ The notion of meaning in play in such cases Grice dubs ‘natural meaning’. Grice suggests that we may distinguish this sense of ‘mean’ from another sense of the word more relevant to communication, exemplified in such utterances as
In saying “You make a better door than a window”, George meant that you should move,
In gesticulating that way, Salvatore means that there's quicksand over there,
Grice used the term ‘non-natural meaning’ for this sense of ‘mean’, and in more recent literature this jargon has been replaced with the term ‘speaker meaning’. [ 8 ] After distinguishing between natural and (what we shall heretofore call) speaker meaning, Grice attempts to characterize the latter. It is not enough that I do something that influences the beliefs of an observer: In putting on a coat I might lead an observer to conclude that I am going for a walk. Yet in such a case it is not plausible that I mean that I am going for a walk in the sense germane to speaker meaning. Might performing an action with an intention of influencing someone's beliefs be sufficient for speaker meaning? No: I might leave Smith's handkerchief at the crime scene to make the police think that Smith is the culprit. However, whether or not I am successful in getting the authorities to think that Smith is the culprit, in this case it is not plausible that I mean that Smith is the culprit.
What is missing in the handkerchief example is the element of overtness. This suggests another criterion: Performing an action with the, or an, intention of influencing someone's beliefs, while intending that this very intention be recognized. Grice contends that even here we do not have enough for speaker meaning. Herod presents Salome with St. John's severed head on a charger, intending that she discern that St. John is dead and intending that this very intention of his be recognized. Grice observes that in so doing Herod is not telling Salome anything, but is instead deliberately and openly letting her know something. Grice concludes that Herod's action is not a case of speaker meaning either. The problem is not that Herod is not using words; we have already considered hunters who mean things wordlessly. The problem seems to be that to infer what Herod intends her to, Salome does not have to take his word for anything. She can see the severed head for herself if she can bring herself to look. By contrast, in its central uses, telling requires a speaker to intend to convey information (or alleged information) in a way that relies crucially upon taking her at her word. Grice appears to assume that at least for the case in which what is meant is a proposition (rather than a question or an imperative), speaker meaning requires a telling in this central sense. What is more, this last example is a case of performing an action with an intention of influencing someone's beliefs, even while intending that this very intention be recognized; yet it is not a case of telling. Grice infers that it is not a case of speaker meaning either.
Grice holds that for speaker meaning to occur, not only must one (a) intend to produce an effect on an audience, and (b) intend that this very intention be recognized by that audience, but also (c) one must intend this effect on the audience to be produced at least in part by their recognition of the speaker's intention. The intention to produce a belief or other attitude by means (at least in part) of recognition of this very intention, has come to be called a reflexive communicative intention .
It has, however, been shown that intentions to produce cognitive or other effects on an audience are not necessary for speaker meaning. Davis 1992 offers many cases of speaker meaning in the absence of reflexive communicative intentions. Indeed, he forcefully argues that speaker meaning can occur without a speaker intending to produce any beliefs in an audience. [ 9 ] [ 10 ] Instead of intentions to produce certain effects in an audience, some authors have proposed that speaker meaning is a matter of overtly indicating some aspect of oneself. (Green, 2007). Compare my going to the closet to take out my overcoat (not a case of speaker meaning), with the following case: After heatedly arguing about the weather, I march to the closet while beadily meeting your stare, then storm out the front door while ostentatiously donning the coat. Here it's a lot more plausible that I mean that it's raining outside, and the reason seems to be that I am making some attitude of mine overt: I am not only showing it, I am making clear my intention to do just that.
How does this help to elucidate the notion of force? One way of asserting that P , it seems, is overtly to manifest my commitment to P , and indeed commitment of a particular kind: commitment to defend P in response to challenges of the form, “How do you know that?” I must also overtly manifest my liability to be either right or wrong on the issue of P depending on whether P is the case. By contrast, I conjecture P by overtly manifesting my commitment to P in this same “liability to error” way; but I am not committed to responding to challenges demanding justification. I must, however, give some reason for believing P ; this much cannot, however, be said of a guess.
We perform a speech act, then, when we overtly commit ourselves in a certain way to a content–where that way is an aspect of how we speaker-mean that content. One way to do that is to invoke a convention for undertaking commitment; another way is overtly to manifest one's intention to be so committed. We may elucidate the relevant forms of commitment by spelling out the norms underlying them. We have already adumbrated such an approach in our discussion of the differences among asserting and conjecturing. Developing that discussion a bit further, compare
- conjecturing
All three of these acts have word-to-world direction of fit, and all three have conditions of satisfaction mandating that they are satisfied just in case the world is as their content says it is. Further, one who asserts, conjectures, or guesses that P is right or wrong on the issue of P depending on whether P is in fact so. However, as we move from left to right we find a decreasing order of stringency in commitment. One who asserts P lays herself open to the challenge, “How do you know that?”, and she is obliged to retract P if she is unable to respond to that challenge adequately. By contrast, this challenge is inappropriate for either a conjecture or a guess. On the other hand, we may justifiably demand of the conjecturer that she give some reason for her conjecture; yet not even this much may be said of one who makes a guess. (The “educated guess” is intermediate between these two cases.)
We may think of this illocutionary dimension of speaker meaning as characterizing not what is meant, but rather how it is meant. Just as we may consider your remark, directed toward me, “You're tired,” and my remark, “I'm tired,” as having said the same thing but in different ways; so too we may consider my assertion of P , followed by a retraction and then followed by a conjecture of P , as two consecutive cases in which I speaker-mean that P but do so in different ways. This idea will be developed a bit further in Section 9 under the rubric of “mode” of illocutionary commitment.
Speaker meaning, then, applies not just to content but also to force, and we may elucidate that claim with a further articulation of the normative structure characteristic of each speech act: When you overtly display a commitment characteristic of that speech act, you have performed that speech act. Is this a necessary condition as well? That depends on whether I can perform a speech act without intending to do so—a topic for Section 9 below. For now, however, compare the view at which we have arrived with Searle's view that one performs a speech act when others become aware of one's intention, or at least one's attempt, to perform that act. What is missing from Searle's characterization is the notion of overtness: The agent in question must not only make her intention to undertake a certain commitment manifest; she must also intend that that very intention be manifest. There is more to overtness than wearing one's heart (or mind) on one's sleeve.
7. Force, Norms, and Conversation
In elucidating this normative dimension of force, we have brought speech acts into their conversational context. That is not to say that speech acts can only be performed in the setting of a conversation: I can approach you, point out that your vehicle is blocking mine, and storm off. Here I have made an assertion but have not engaged in a conversation. Perhaps I can ask myself a question in the privacy of my study and leave it at that–not continuing into a conversation with myself. However, it might reasonably be held that a speech act's ecological niche is nevertheless the conversation. In that spirit, while we may be able to remove it from its environment and scrutinize it in isolated captivity, doing so may leave us blind to some of its distinctive features.
This ecological analogy sheds light on a dispute over the question whether speech acts can profitably be studied in isolation from the conversations in which they occur. An empiricist framework, exemplified in John Stuart Mill's, A System of Logic , suggests attempting to discern the meaning of a word, for instance a proper name, in isolation. By contrast, Gottlob Frege (1884) enjoins us to understand a word's meaning in terms of the contribution it makes to an entire sentence. Such a method is indispensable for a proper treatment of such expressions as quantifiers, and represents a major advance over empiricist approaches. Yet students of speech acts have espoused going even further, insisting that the unit of significance is not the proposition but the speech act. Vanderveken writes,
Illocutionary acts are important for the purpose of philosophical semantics because they are the primary units of meaning in the use and comprehension of natural language. (Vanderveken, 1990, p. 1.)
Why not go even further, since speech acts characteristically occur in conversations? Is the unit of significance really the debate, the colloquy, the interrogation?
Students of so-called conversation analysis have contended precisely this, remarking that many speech acts fall naturally into pairs. [ 11 ] For instance, questions pair naturally with assertions when the latter purport to be answers. Likewise, offers pair naturally with acceptances or rejections, and it is easy to multiply examples. Searle, who favors studying speech acts in isolation, has replied to these considerations (Searle 1992). There he issues a challenge to students of conversation to provide an account of conversations parallel to that of speech acts, arguing as well that the prospects for such an account are dim. One of his reasons is that unlike speech acts conversations do not as such have a point or purpose. More recently, Asher and Lascardes 2003 have defended a more systematic treatment of speech acts in their conversational setting that responds to Searle's challenge.
Much literature concerned with speech acts is curiously disconnected from certain traditions flowing from work in the semantics of natural language emphasizing pragmatic factors. For instance, Stalnaker (1972, 1973, 1974) Lewis (1979, 1980), Thomason (1990) and others have developed models of the evolution of conversations aimed at understanding the role of quantification, presupposition (both semantic and pragmatic), anaphora, deixis, and vagueness in discourse. Such models typically construe conversations as involving an ever-developing set of propositions (construed as the conversational “common ground”) that can be presupposed by interlocutors. (Such propositions may, but need not be, understood as sets of possible worlds.) Other parameters characterizing a conversation at a given point include the domain of discourse, a set of salient perceptible objects, standards of precision, time, world or situation, speaker, addressee, and so forth. The set of all values for these items at a given conversational moment is often referred to as “conversational score”.
“Scorekeeping” approaches to language use typically construe a contribution to a conversation as a proposition: If that “assertion” is accepted, then the score is updated accordingly. Little attention is paid to the question whether that proposition is put forth as a conjecture, guess, assertion, or supposition for the sake of argument. An enrichment of the scorekeeping model would do just this. Accordingly Green 1999 attempts a synthesis of some aspects of this scorekeeping model, Gricean pragmatics, and concepts pertaining to speech acts.
Frege's Begriffschrift constitutes history's first thoroughgoing attempt to formulate a rigorous formal system. However, Frege did not see his Begriffschrift as merely a tool for assessing the validity of arguments. Rather, he appears to have seen it as an organon for the acquisition of knowledge from unquestionable first principles; in addition he wanted to use it in order to help make clear the epistemic foundations on which our knowledge rests. To this end his formal system contains not only symbols indicating the content of propositions (including logical constants), but also symbols indicating the force with which they are put forth. In particular, Frege insists that when using his formal system to acquire new knowledge from proposition already known, we use an assertion sign to indicate our acknowledgment of the truth of the proposition used as axioms or inferred therefrom. Frege thus employs what would now be called a force indicator : an expression whose use indicates the force with which an associated proposition is being put forth. (Green 2002).
Reichenbach expands upon Frege's idea in his 1947. In addition to using an assertion sign, Reichenbach also uses indicators of interrogative and imperatival force. Hare similarly introduces force indicators to lay bare the way in which ethical and cognate utterances are made (Hare 1970). Davidson, however, challenges the value of this entire enterprise, arguing that since natural language already contains many devices for indicating the force of one's speech act, the only interest in a force indicator would be if it could guarantee the force of one's speech act. But nothing could: Any device purporting to be, say, an infallible indicator of assertoric force is liable to being used by a joker or actor to heighten the realism of her performance:
It is easy to see that merely speaking the sentence in the strengthened mood cannot be counted on to result in an assertion; every joker, storyteller, and actor will immediately take advantage of the strengthened mood to simulate assertion. There is no point, then, in the strengthened mood; the available indicative does as well as language can do in the service of assertion (Davidson 1979, p. 311).
Dummett 1993 and Hare 1989 reply to Davidson. Hare in particular remarks that there could be a society with a convention that utterance of a certain expression constituted performance of a certain illocutionary act. Green 1997 questions the relevance of this observation to the issue of illocutionary acts, which, as we have seen, seem to require intentions for their performance. Just as no convention could make it the case that I believe that P (though perhaps a convention could make it the case that people say I believe that P ), so too no convention could make it the case that I intend to put forth a certain sentence as an assertion.
On the other hand, Green 1997 and Green 2000 also observe that even if there can be no force indicator in the sense Davidson criticizes, nothing prevents natural language from containing devices that indicate force conditional upon one's performing a speech act: Such a force indicator would not show whether one is performing a speech act, but, given that one is doing so, which speech act one is performing. For instance, parenthetical expressions such as, ‘as is the case’ can occur in the antecedent of conditionals, as in: ‘If, as is the case, the globe is warming, then Greenland will melt.’ Use of the parenthetical cannot guarantee that the sentence or any part of it is being asserted, but if the entire sentence is being asserted, then, Green claims, use of the parenthetical guarantees that the speaker is committed to the content of the antecedent. If that claim is correct, natural language already contains force indicators in this qualified sense. Whether it is worth introducing such force indicators into a logical notation remains an open question.
Students of speech acts contend, as we have seen, that the unit of communicative significance is the speech act rather than the proposition. This attitude prompts the question whether logic itself might be enriched by incorporating inferential relations among speech acts rather than just inferential relations among propositions. Since particulars cannot stand in inferential relations to one another, no such relations could obtain between individual speech acts. However, just as two events E 1 and E 2 (such as running quickly and running) could be logically related to one another in that it is not possible for one to occur without the other; so too speech act types S 1 and S 2 could be inferentially related to one another if it is not possible to perform one without performing the other. A warning that the bull is about to charge is also an assertion that the bull is about to charge but the converse is not true. This is in spite of the fact that these two speech acts have the same propositional content: That the bull is about to charge. If, therefore, warning implies asserting but not vice versa, then that inferential relation is not to be caught within the net of inferential relations among propositions.
In their Foundations of Illocutionary Logic (1985), Searle and Vanderveken attempt a general treatment of logical relations among speech acts. They describe their central question in terms of commitment:
A theory of illocutionary logic of the sort we are describing is essentially a theory of illocutionary commitment as determined by illocutionary force. The single most important question it must answer is this: Given that a speaker in a certain context of utterance performs a successful illocutionary act of a certain form, what other illocutions does the performance of that act commit him to? (1985, p. 6)
To explicate their notion of illocutionary commitment, these authors invoke their definition of illocutionary force in terms of the seven values mentioned in Section 2.3 above. On the basis of this definition, they define two notions pertinent to entailment relations among speech acts, namely strong illocutionary commitment and weak illocutionary commitment . According to the former definition, an illocutionary act S 1 commits a speaker to another illocutionary act S 2 iff it is not possible to perform S 1 without performing S 2 . Whether that relation holds between a pair of illocutionary acts depends on the particular septuples with which they are identified. Thus suppose that S 1 is identical with <IP 1 , Str " , Mode 1 , Cont 1 , Prep 1 , Sinc 1 , Stresinc 1 > (corresponding to illocutionary point, strength, mode of achievement, propositional content, preparatory condition, sincerity condition, and strength of sincerity condition, respectively); and suppose that S 2 is identical with <IP 1 , Str $ , Mode 1 , Cont 1 , Prep 1 , Sinc 1 , Stresinc 1 >. Suppose further that Str " and Str $ differ only in that " is stronger than $. Then it will not be possible to perform S 1 without performing S 2 ; whence the former strongly illocutionarily implies the latter. (This definition of strong illocutionary commitment generalizes in a straightforward way to the case in which a set of speech acts S 1 , …, S n -1 implies a speech act S n .)
Performance of a speech act or set of speech acts can also commit an agent to a distinct content, and do so relative to some force. If P and Q jointly imply R , then my asserting both P and Q commits me to R . That is not to say that I have also asserted R : If assertion were closed under deduction I would assert infinitely many things just by virtue of asserting one. By contrast, if I conjecture P and Q , then I am once again committed to R but not in the way that I would have been had I asserted P and Q . For instance, in the assertion case, once my further commitment to R is made clear, it is within the rights of my addressee to ask how I know that R holds; this would not have been an acceptable reply to my merely conjecturing P and Q .
To explicate this relation, Searle and Vanderveken define weak illocutionary commitment: S 1 weakly illocutionarily implies S 2 iff every performance of S 1 commits an agent to meeting the conditions laid down in the septuple identical to S 2 (1985, p. 24). Searle and Vanderveken infer that this implies that if P logically entails Q , and an agent asserts P , then she is committed to believing that Q . These authors stress, however, that this does not mean that the agent who asserts P is committed to cultivating the belief Q when P implies Q . In lieu of that explication, however, it is unclear just what notion of commitment is at issue. It is unclear, for instance, what it could mean to be committed to believing Q (rather than just being committed to Q ) if this is not to be explicated as being committed to cultivating the belief that Q .
Other approaches attempt to circumvent such problems by reductively defining the notion of commitment in terms of obligations to action and liability to error and/or vindication. Let S be an arbitrary speaker, < ⊢ l A l , …, ⊢ n A n , ⊢ B > a sequence of force/content pairs; then:
<⊢ l A l , …, ⊢ n A n , ⊢ B > is illocutionarily valid iff if speaker S is committed to each A i under mode ⊢ i , then S is committed to B under mode ⊢. [ 12 ]
Because it concerns what force/content pairs commit an agent to what others, illocutionary validity is an essentially deontic notion: It will be cashed out in terms either of obligation to use a content in a certain way conversationally, or liability to error or vindication depending upon how the world is.
Our discussion of the possibility of an illocutionary logic answers one question posed at the end of Section 6.3, namely whether it is possible to perform a speech act without intending to do so. This seems likely given Searle and Vanderveken's definition of strong illocutionary commitment: We need only imagine an agent performing some large number of speech acts, S 1 , …, S n -1 , which, unbeknownst to her, jointly guarantee that she fulfills the seven conditions defining another speech act S n . Evidently such a “strict liability” conception still requires that one performs S n only by virtue of intentionally performing some other set of speech acts S 1 , …, S n -1 ; it is difficult to see how one can perform S n while having no intention of performing a speech act at all.
We have also made progress on a question raised in Section 1, namely whether “speech act theory” deserves its name. An appropriate definition of illocutions would enable us to explain, rather than merely describe, some features of speech acts. Vanderveken 1990 offers a set of tableaux depicting inferential relations among speech acts. For instance, the following is a fragment of his tableaux for assertives–speech acts whose illocutionary point is to describe how things are:
castigate reprimand accuse blame criticize assert suggest
where strong illocutionary validity moves from left to right. This is because all these speech acts have the illocutionary point of describing how things are, but the propositional content conditions and degree of strength of illocutionary point conditions become increasingly less stringent as we move from left to right. Accounts of this sort offer hope of our being able informatively answer such questions whether someone who castigates an addressee for some state of affairs is also assertorically committed to the obtaining of that state of affairs. Might we discover “illocutionary tautologies”, “illocutionary absurdities” and other phenomena that could shed light on such utterances as “This very utterance is an assertion”, “I doubt this very claim”? Affirmative answers to such questions will be needed if we are to justify our use of “speech act theory”.
Bibliography
- Alston, W. (2000) Illocutionary Acts and Sentence Meaning . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- –––. 1994: ‘Illocutionary Acts and Linguistic Meaning,’ in Tsohatzidis (ed.), pp. 29-49.
- Anscombe, G.E.M. (1963) Intention, 2 nd Edition. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Armstrong, D. (1971) ‘Meaning and communication’. The Philosophical Review 80 : 427-47.
- Asher, N. and A. Lascarides 2003: Logics of Conversation . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Austin, J.L. (1962). How To Do Things With Words , 2 nd Edition, ed. J.O. Urmson and M. Sbisá. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––. (1970) Philosophical Papers , Edited by J. Urmson, and G. Warnock. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Avramides, A. (1989) Meaning and Mind: An Examination of the Gricean Account of Language . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Bach, K. 1975: ‘Performatives are statements too’, Philosophical Studies 28 : 229-36.
- –––. 1994: ‘Conversational impliciture,’ Mind and Language 9 : 124-162.
- –––, and R. Harnish (1979) Linguistic Communication and Speech Acts, Cambridge: M.I.T. Press.
- Barker, S. (2004). Renewing Meaning: A Speech-Act Theoretic Approach . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Belnap, N., T. Steel, 1976: The Logic of Questions and Answers. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Bennett, J. (1976) Linguistic Behaviour . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Bertolet, R. 1994: ‘Are There Indirect Speech Acts?’ in in S. Tsohatzidis (ed.) Foundations of Speech Act Theory: Philosophical and Linguistic Perspectives (London: Routledge), pp. 335-49.
- Brandom, R. (1983). ‘Asserting.’ Noûs 17: 637-650.
- Brandom, R (1994) Making It Explicit , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Carston, R. (2003) Thoughts and Utterances . Oxford: Blackwell.
- Clark, H. (1996) Using Language , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Cohen, ‘Do Illocutionary Forces Exist?’ The Philosophical Quarterly 14 : 18-137.
- Davidson, D. (1979) ‘Moods and Performances’. Reprinted in Davidson (1984) Inquiries into Truth and Interpretation . (Oxford: Oxford University Press).
- Davis, W. 1992: ‘Speaker meaning,’ Linguistics and Philosophy 15 : 223-53.
- –––. (2003) Meaning, Expression and Thought . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Dummett, M.A.E. (1973) Frege: Philosophy of Language. London: Duckworth.
- –––. (1993) ‘Mood, force and convention,’ in his The Seas of Language (Oxford: Oxford University Press), pp. 202-23.
- Forguson, L.W. 1973. “Locutionary and illocutionary acts”. In G. Warnock (ed), Essays on J. L. Austin . Oxford: Clarendon Press, 160–185.
- Dummett, M. 1993: “Mood, Force and Convention”, in his The Seas of Language (Oxford), pp. 202-23.
- Frege, G. [1879] 1976: Begriffsschrift in van Heijenoort (ed.) From Frege to Gödel: A Sourcebook in Mathematical Logic. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, pp. 1-82.
- Frege, G. (1884) The Foundations of Arithmentic , trans. J.L. Austen. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- –––. (1979) Posthumous Writings H. Hermes, F. Kambartel and F. Kaulbach (eds.) (Blackwell).
- –––. (1980) Philosophical and Mathematical Correspondence , G. Gabriel, et al eds. (Chicago).
- –––. (1984) ‘The thought: A logical inquiry.’ Collected Papers on Mathematics Logic and Philosophy . Edited by B. McGuinness, trans. by M. Black et al . Oxford: Blackwell.
- Frye, M. 1976. “On saying”. American Philosophical Quarterly 13: 123–127.
- –––. 1973: ‘Force and meaning,’ Journal of Philosophy 70 : 281-94.
- Geach, P. (1972) ‘Assertion.’ Reprinted in his Logic Matters , Oxford: Blackwell: pp. 254-269.
- Gorman, D. (1999) The Use and Abuse of Speech-act Theory in Criticism. Poetics Today 20 : 93-119.
- Ginet, C. (1979) ‘Performativity’. Linguistics and Philosophy 3 : 245-65.
- Green, M. (1997) ‘On the Autonomy of Linguistic Meaning’. Mind , 106 : 217-244.
- –––. (1999) ‘Illocutions, Implicata, and What a Conversation Requires’. Pragmatics & Cognition 7 : 65-92.
- –––. (2000) ‘Illocutionary Force and Semantic Content’. Linguistics and Philosophy 23 : 435-473.
- –––. (2002) ‘The Inferential Significance of Frege's Assertion Sign’. Facta Philosophica , 4 : 201-29.
- –––. (2007). Self-Expression . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Grice, H.P. (1957) “Meaning”, The Philosophical Review 66, No. 3: 377-88.
- ––– (1989) Studies in the Way of Words. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Hajdin, M. (1991) ‘Is There More to Speech Acts Than Illocutionary Force and Propositional Content?’ Nous, 25 : 353-7.
- Hamblin, C.L. (1987) Imperatives. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Hare, R. (1970) ‘Meaning and Speech Acts’. The Philosophical Review , 79 , pp. 3-24.
- –––. (1989) ‘Some Subatomic Particles of Logic’, Mind , 98 , pp. 23-37.
- Harrah, D. (1980) ‘On speech acts and their logic,’ Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 61 : 204-11.
- –––. (1994) ‘On the vectoring of speech acts,’ in S. Tsohatzidis (ed.) Foundations of Speech Act Theory: Philosophical and Linguistic Perspectives (London: Routledge), pp. 374-392.
- Holdcroft, D. (1994): ‘Indirect Speech Acts and Propositional Content,’ in S. Tsohatzidis (ed.) Foundations of Speech Act Theory: Philosophical and Linguistic Perspectives (London: Routledge), pp. 350-64.
- Humberstone, L. (1992) ‘Direction of fit’. Mind 101: 59–83.
- Kearns, J. (1997) ‘Propositional Logic of Supposition and Assertion’, Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic 38 : 325–349.
- –––. (1999) ‘An Illocutionary Logical Explanation of the Surprise Execution’, History and Philosophy of Logic 20 : 195-214.
- –––. (2006) ‘Conditional Assertion, Denial, and Supposition as Illocutionary Acts,’ Linguistics and Philosophy 29 : 455-85.
- Lewis, D. (1979) ‘Scorekeeping in a Language Game’. Journal of Philosophical Logic 8, pp. 339-59. Reprinted in Lewis 1983.
- Lewis, D. (1980) ‘Index, Context, and Content’. In Stig Kanger and Sven Ohman (Eds.), Philosophy and Grammar . Dordrecht: Reidel. Reprinted in David Lewis, 1998, Papers in Philosophical Logic, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Lewis, D. (1983) Philosophical Papers Volume I . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- McDowell, J. (1980) ‘Meaning, communication, and knowledge.’ Reprinted in Meaning, Knowledge and Reality . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Meggle, G. (1985) ‘To hell with speech act theory,’ in M. Dascal (ed.) Dialogue (Benjamins): 205-11.
- Mulligan, K. (ed) (1987) Speech Act and Sachverhalt: Reinach and the Foundations of Realist Phenomenology . Dordrecht: Martinus Nijhof.
- Parret, H. and J. Verschueren (eds.) (1991) (On) Searle on Conversation . Amsterdam: J. Benjamins.
- Pendlebury, M. (1986) ‘Against the power of force: reflections on the meaning of mood,’ Mind 95 : 361-372.
- Recanati, F. (1987) Meaning and Force: The Pragmatics of Performative Utterances. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Reichenbach, H. (1947): Elements of Symbolic Logic . New York: Macmillan.
- Reinach, A. (1913) ‘Die apriorischen Grunglagen des bürgerlichen Rechtes,’ Jahrbuch fur Philosophie und phänomenologische Forschung 2 : 685-847.
- Sbisa, M. (1995) ‘Speech act theory,’ in J. Verschueren, J. Östman, and J. Blommaert (eds.) Handbook of Pragmatics . John Benjamins, 495-506.
- Schiffer, S. (1972) Meaning . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Schuhmann, K. and Smith, B. 1990. ‘Elements of speech act theory in the philosophy of Thomas Reid,’ History of Philosophy Quarterly 7 : 47–66.
- Searle, J. (1968) ‘Austin on locutionary and illocutionary acts’. The Philosophical Review 77 : 405–424.
- –––. (1969). Speech Acts: An Essay in the Philosophy of Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- –––. (1975a) ‘A taxonomy of illocutionary acts’. In K. Gunderson (ed), Language, Mind and Knowledge . Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press, 344–369.
- –––. (1975b) ‘Indirect speech acts’. In Syntax and Semantics, 3: Speech Acts , ed. P. Cole & J. L. Morgan, pp. 59–82. New York: Academic Press.
- –––. (1979) ‘Indirect Speech Acts,’ in his Expression and Meaning: Studies in the Theory of Speech Acts . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- –––. (1986a). ‘Meaning, communication, and representation’. In R. Grandy and R. Warner (eds), Philosophical Grounds of Rationality: Intentions, Categories, Ends . Oxford: Clarendon Press, 209–226.
- –––. (1986b) ‘Notes on conversation’. In D.G. Ellis and W. A. Donohue (eds), Contemporary Issues in Language and Discourse Processes . Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates 7–19.
- –––. (1989) ‘How performatives work’. Linguistics and Philosophy 12 : 535–558.
- –––. (1992) ‘Conversation’. In H. Parrett and J. Verschueren (eds.) (On) Searle on Conversation . New York: Benjamins, 7-30.
- –––. (1999) Mind, Language, and Society: Doing Philosophy in the Real World . London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
- –––. ,and D. Vanderveken (1985) Foundations of Illocutionary Logic . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Smith, B. (1990) ‘Toward a history of speech act theory’. In A. Burkhardt (ed), Speech Acts, Meaning and Intentions: Critical Approaches to the Philosophy of John Searle . Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, 29–61.
- –––. (ed). 2003. John Searle . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Stalnaker, R. (1972) ‘Pragmatics’. In D. Davidson and G. Harman (eds.) Semantics of Natural Language . Dordrecht: D. Reidel, 380-397.
- –––. (1973) ‘Presuppositions’. Journal of Philosophical Logic 2: 447-457.
- –––. (1974) ‘Pragmatic Presuppositions’. In M. Munitz and P. Unger (eds.) Semantics and Philosophy . New York: NYU Press, 197-213.
- –––. (1984) Inquiry . Cambridge, MA: MIT.
- Stenius, E. (1967) ‘Mood and language-game’, Synthese 17 : 254-274.
- Strawson, P. (1950). ‘On referring’. Mind 59: 320-44.
- –––(1964) ‘Intention and convention in speech acts’, The Philosophical Review 73 : 439-60, reprinted in Strawson, Logico-Linguistic Papers . London: Methuen, 1971.
- –––. (1970) Meaning and truth. Reprinted in Strawson, Logico-Linguistic Papers . London: Methuen 1971.
- –––. (1973) ‘Austin and ‘locutionary meaning’’. In G.Warnock (ed), Essays on J. L. Austin , Oxford: Clarendon Press, 46–68.
- Thomason, R. (1990) ‘Accommodation, meaning and implicature: interdisciplinary foundations for pragmatics’. In Cohen, Morgan and Pollock (eds.), Intentions in Communication . Cambridge, MA: MIT. 325-364.
- Tsohatzidis, S.L. (ed.) (1994) Foundations of Speech Act Theory: Philosophical and Linguistic Perspectives (Routledge)
- Vanderveken, D. (1990). Meaning and Speech Acts, Vols I and II (Cambridge).
- Vendler, Z. 1972: Res Cogitans (Cornell).
- Watson, G. 2004: ‘Asserting and Promising,’ Philosophical Studies 117 : 57-77
- Williamson, T. (1996). ‘Knowing and asserting.’ The Philosophical Review 105: 489-523.
- Dummett, M. Origins of Analytic Philosophy (Harvard).
- Furberg, M. 1971. Saying and Meaning: A Main Theme in J. L. Austin's Philosophy . Oxford: Blackwell.
- Grewendorf, G. and G. Meggle (eds.) 2002: Speech Acts, Mind and Social Reality (Dordrecht: Kluwer).
- Holdcroft, D. 1978. Words and Deeds: Problems in the Theory of Speech Acts. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Lepore, E. and van Gulick, R. (eds). 1991. John Searle and his Critics . Oxford: Blackwell.
- Warnock, G. Ed. 1973: Essays on J. L. Austin . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Warnock, G. 1989: J. L. Austin . New York: Routledge.
- Research project in the philosophy of language , maintained at the University of Berne, Switzerland. This site is devoted to some main themes of research stemming from Grices' work on speaker meaning and implicature.
- Working Papers in Lingustics , University College London.
- ‘ Toward a history of speech act theory ’, a paper by Barry Smith (SUNY/Buffalo).
anaphora | assertion | Frege, Gottlob | Grice, Paul | implicature | -->meaning, theories of --> | pragmatics | -->presupposition --> | propositional attitude reports | propositions | vagueness

- #WalangPasok
- Breaking News
- Photography
- ALS Exam Results
- Aeronautical Engineering Board Exam Result
- Agricultural and Biosystem Engineering Board Exam Result
- Agriculturist Board Exam Result
- Architecture Exam Results
- BAR Exam Results
- CPA Exam Results
- Certified Plant Mechanic Exam Result
- Chemical Engineering Exam Results
- Chemical Technician Exam Result
- Chemist Licensure Exam Result
- Civil Engineering Exam Results
- Civil Service Exam Results
- Criminology Exam Results
- Customs Broker Exam Result
- Dental Hygienist Board Exam Result
- Dental Technologist Board Exam Result
- Dentist Licensure Exam Result
- ECE Exam Results
- ECT Board Exam Result
- Environmental Planner Exam Result
- Featured Exam Results
- Fisheries Professional Exam Result
- Geodetic Engineering Board Exam Result
- Guidance Counselor Board Exam Result
- Interior Design Board Exam Result
- LET Exam Results
- Landscape Architect Board Exam Result
- Librarian Exam Result
- Master Plumber Exam Result
- Mechanical Engineering Exam Results
- MedTech Exam Results
- Metallurgical Engineering Board Exam Result
- Midwives Board Exam Result
- Mining Engineering Board Exam Result
- NAPOLCOM Exam Results
- Naval Architect and Marine Engineer Board Exam Result
- Nursing Exam Results
- Nutritionist Dietitian Board Exam Result
- Occupational Therapist Board Exam Result
- Ocular Pharmacologist Exam Result
- Optometrist Board Exam Result
- Pharmacist Licensure Exam Result
- Physical Therapist Board Exam
- Physician Exam Results
- Principal Exam Results
- Professional Forester Exam Result
- Psychologist Board Exam Result
- Psychometrician Board Exam Result
- REE Board Exam Result
- RME Board Exam Result
- Radiologic Technology Board Exam Result
- Real Estate Appraiser Exam Result
- Real Estate Broker Exam Result
- Real Estate Consultant Exam Result
- Respiratory Therapist Board Exam Result
- Sanitary Engineering Board Exam Result
- Social Worker Exam Result
- UPCAT Exam Results
- Upcoming Exam Result
- Veterinarian Licensure Exam Result
- X-Ray Technologist Exam Result
- Programming
- Smartphones
- Web Hosting
- Social Media
- SWERTRES RESULT
- EZ2 RESULT TODAY
- STL RESULT TODAY
- 6/58 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/55 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/49 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/45 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/42 LOTTO RESULT
- 6-Digit Lotto Result
- 4-Digit Lotto Result
- 3D RESULT TODAY
- 2D Lotto Result
- English to Tagalog
- English-Tagalog Translate
- Maikling Kwento
- EUR to PHP Today
- Pounds to Peso
- Binibining Pilipinas
- Miss Universe
- Family (Pamilya)
- Life (Buhay)
- Love (Pag-ibig)
- School (Eskwela)
- Work (Trabaho)
- Pinoy Jokes
- Tagalog Jokes
- Referral Letters
- Student Letters
- Employee Letters
- Business Letters
- Pag-IBIG Fund
- Home Credit Cash Loan
- Pick Up Lines Tagalog
- Pork Dishes
- Lotto Result Today
- Viral Videos
Types Of Speech Act – Locution, Illocution, and Perlocution
Locution, illocution, and perlocution are the types of speech act and here’s a brief discussion about each..
TYPES OF SPEECH ACT – The three types of speech act are Locution, Illocution, and Perlocution, and here’s an explanation about them.
Speech act in linguistics is defined in the terms of the intention of the speaker and the effect it would take on the listener. And this is an important part of communication. These verbal actions do accomplish acts like greeting, insulting, complimenting, pleading, giving information, and expressing requests, warnings, promises, apologies, greetings, or any declarations.

Here are the three types:
- Locutionary Speech Act According to “Philosophy of Language: The Central Topics” of Susana Nuccetelli and Gary Seay, is the “mere act of producing some linguistic sounds or marks with a certain meaning and reference”. The utterance is a sound, a word, or a phrase that follows the rules of language. This is simply just an utterance.
- Illocutionary Speech Act This is a directive to the audience which could be a promise, an order, an apology, or an expression of thanks. This is an act of saying something that has an intention of stating an opinion, a confirmation, or a denial, giving an advise, making a promise, and among others. This is the act of saying something with an intention.
- Perlocutionary Speech Act This act carries out an effector consequence to the listener. One could be inspiring or insulting, persuading, convincing, and scaring. The main goal is to change feelings, thoughts, or actions. This happens when the listener is being affected by what the speaker has said.
- Types Of Speech Style – A Brief Explanation According To Martin Joos
- Antas Ng Wika – Mga Halimbawa At Kahulugan Ng Antas Ng Wika
What can you say about this? Let us know!
For more news and updates, follow us on Twitter: @ philnews_ph Facebook: @PhilNews and; YouTube channel Philnews Ph .
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous
- Next chapter >
Introduction: Assertion among the Speech Acts
- Published: November 2018
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Consider the sorts of act one performs when one makes a statement or report, gives one’s testimony, or tells another person something. There are various ways we might try to characterize the nature of acts like these. They (typically) involve the utterance of a declarative sentence in an ordinary conversational context; they are acts in which the speaker makes as if to express a belief of hers, or in which she commits herself to the truth of the relevant propositional content, or in which she (characteristically) aims to induce a belief with that content in her audience. However we characterize acts of these sorts, to have this class of speech act in mind is a good initial way to approach what philosophers and linguists have in mind when they speak of assertions . Work in this area typically proceeds on the assumptions, first, that there is an interesting and unified type of speech act here, and second, that acts of this type have features that are of some theoretical interest—not only in linguistics and in philosophy of language, but also in psychology, law, sociology, political science, education theory, computer science, and elsewhere.
It turns out to be a difficult matter to fix the contours of the class of acts precisely. Indeed, one might even doubt that this can be done in a theory-neutral way. 1 Even so, many philosophers and linguists have thought that this sort of taxonomic project is worth pursuing. The simplest explanation for this project is this: a speech act with something like the profile described earlier appears to be related to various other phenomena of theoretical interest, and we might hope to appeal to our understanding of the act itself to shed light on these other phenomena. If we give the label “assertion” to the (alleged) type of speech act in question, we might pursue the hypothesis that assertion is a type of speech act that
is apt for the expression of judgment and belief; 2
is apt for the transmission of knowledge; 3
commits one to the truth of a proposition; 4
makes possible lies and acts of incompetence, and so renders one prone to a distinctive type of ethical assessment bound up with issues of trust and trustworthiness. 5
And we might appeal to the nature of this act in an attempt to spell out such things as
how language can be used to represent a worldly state of affairs; 6
what it is for an expression to have a meaning, or to have the distinct meaning that it has; 7
what is involved in being trustworthy; 8
how we should think about communication itself; 9
how language use is bound up with many of the ways in which we hold one another accountable; 10
how bias and relations of oppression might distort this sort of accountability. 11
The prospect of a route to illuminating these and other matters is part of what leads many philosophers to attend to the nature of assertion itself.
It is no wonder, then, that as a speech act, assertion has loomed large in the philosophical imagination. Arguably, the category of assertion itself, as a distinctive way in which one presents a proposition as true, was not clearly framed until the late nineteenth or early twentieth century. 12 Even so, topics in the vicinity have been on the philosophical agenda for centuries. Ancient and medieval logicians were very interested in the act of judgement itself, thereby manifesting an interest in what many contemporaries regard as the mental analogue of assertion. So, too, in early modern Europe the English philosopher Thomas Reid was very interested in the use of speech to express belief and spread knowledge. In the more recent history of philosophy, in the late nineteenth century the German philosopher Gottlob Frege felt the need to represent (something like) the act of assertion in his attempted formalization of logic ( Begriffschrift ). In the early twentieth century the English philosopher G. E. Moore saw in the nature of assertion one way to diagnose the paradoxicality of sentences such as “It’s raining but I don’t believe that it is raining”—sentences whose sincere use appears to be self-undermining, even as the state of affairs they describe is a possible one. More recently still, the mid-century English philosopher J. L. Austin, taking a stand against the long tradition in philosophy that focused most of its attention on the statement (a category of speech act arguably coextensive with assertion), railed against the central role philosophers ascribed to this act. A bit later, the English philosopher Paul Grice argued that so-called nonnatural meaning —the sort of meaning involved in acts of communication—could be understood in terms of an act very much like, if not the same as, the act of assertion. (Grice somewhat misleadingly called this act the act of saying .)
Perhaps it is no surprise, then, that assertion has received the attention it has. Somewhat more surprising is the extent to which there has been a resurgence of interest among philosophers for this type of act. According to Google Scholar, in the one hundred years between 1895 and 1995, there were just under seventy-five published papers that use or mention “the nature of assertion,” whereas in the approximately twenty-five years since then there have been over four hundred. No doubt some of this discrepancy is owed to a greater number of publishing venues in the last several decades as well as the professionalization of philosophy itself (putting pressure on people to publish). But part of it is owed to a renewed interest in the act itself.
This handbook aims to explore various dimensions of the act of assertion: its nature; its place in a theory of speech acts, and in semantics and meta-semantics; its role in epistemology; and the various social, political, and ethical dimensions of the act. While it does not aim at exhaustiveness, the handbook presents some of the best work done on the core issues pertaining to assertion. These issues should be of interest not only to philosophers but also linguists, psychologists, anthropologists, lawyers, computer scientists, and theorists from communication studies. Although it is broken up into parts, all of the papers can be read in isolation by those interested only in a single topic. The entries themselves, written by leading theorists, offer opinionated introductions to the topics.
Part 1 explores the nature of assertion. What distinguishes assertion as a speech act? A traditional way to approach this question is in terms of the familiar distinction between (illocutionary) force and content. While this distinction is not entirely uncontroversial, 13 it provides the standard way to address the distinctiveness of speech act types, namely, by treating each distinct type as individuated by the distinctive force of acts of that type. On this approach, assertions are those speech acts with a distinctive (assertoric) force, and our question becomes: under what conditions does an utterance have a force of that kind? But however we frame the question, our topic is the individuation of assertion as a speech act. The seven papers in Part 1 explore the seven leading accounts. A rather loose but informative taxonomy of these accounts is in terms of four main ways one might try to capture the nature of the act itself. (Where accounts might be placed under more than one category, I place it under the category that is most characteristic of the account.)
The first category includes those accounts that characterize assertion in terms of the contextual effects of performing speech acts of this type. This handbook has chapters devoted to two distinct varieties of this sort of account. Lenny Clapp presents an account, owed to Robert Stalnaker and often developed as part of “discourse dynamics,” according to which the “essential effect” of an assertion is to update the context of conversation by adding the proposition asserted to the set of propositions that have been mutually presupposed in the conversation. An alternative account within this same general category, deriving from the work of Robert Brandom and presented in the chapter by Lionel Shapiro, holds that to assert a proposition is to perform a speech act in which the speaker undertakes a commitment to defend that proposition (if called upon to do so) and authorizes others to believe the proposition in question.
A second category includes those accounts that see the nature of the act as closely linked with the declarative (grammatical) mood. Once again, this handbook has chapters devoted to two distinct varieties of this sort of account. In his chapter, Mark Jary defends a view on which to assert a proposition is to undertake a commitment to defend the proposition by way of uttering a sentence in the declarative mood. Peter Pagin develops a view on which assertion is the type of speech act that is prima facie informative, where prima facie informativeness is linked in an indirect way with the declarative mood.
A third category includes those accounts that construe assertions in terms of the rule (or norm) that governs acts of this type. This type of account, which is described in the chapter by Mona Simion and Chris Kelp, might be seen as deriving from the work of John Searle. In any case it has become significantly more popular, owing to a recent defense of a version of this sort of account by Tim Williamson, according to which assertion is the unique speech act governed by a knowledge norm, to the effect that one must assert only what one knows.
A fourth category includes those broadly Gricean accounts that approach the nature of assertion in terms of the communicative intentions that inform acts of that type. If we think of communicative intentions as the sort of intentions to achieve an effect on an audience by way of the audience’s recognition of this intention, then the Gricean approach to assertion holds that assertions are those acts performed with the communicative intention to get the audience to believe that the speaker believes the proposition in question. This sort of view is developed in the chapter by Mark Siebel.
The last of the chapters in this first part, by Herman Cappelen, does not fall into any of these categories, as it challenges the theoretical utility of the speech act category assertion itself. On Cappelen’s view, this category is “defective” and does not pick out any interesting kind of speech act.
Part 2 collects three essays which, broadly speaking, address the place of assertion within speech act theory more generally. In her contribution, Marina Sbisà addresses whether the speech act is to be granted any special place within speech act theory, and she considers how this question might be answered from the perspective of various types of account of the speech acts themselves (Austinian, Gricean, normative-pragmatic, Alstonian). Mark van Roojen asks about the role assertion might play in an account of promising, with special attention to the commitment one incurs in the act of promising. And in her contribution Hallie Liberto argues that contrary to the view deriving from John Searle’s taxonomy of speech acts, threats and warnings are themselves illocutionary acts, and she uses assertion in her analysis of those acts.
Part 3 addresses variations within the category of assertion itself. Several such variations are explored in the papers in this part. One variation involves assertions that in some sense or other are qualified, as in the contribution by Matthew Benton and Peter van Elswyk focusing on what they call “hedged assertion.” In addition, it includes assertions that are made in nonstandard ways. This topic is explored in Marga Reimer’s contribution, where she focuses on the category of indirect assertion—for example, the sort of speech act that is made when one asks a rhetorical question. It includes as well assertions that are “marked” in some way. Thus, in his contribution, Ben Kotzee is keen to see how bullshit (in Harry Frankfurt’s sense) might be seen as a distinctive type of perversion of the speech act of assertion, using this analysis in turn to shed light on the nature of assertion itself. And Christopher Hom explores those assertions that constitute slurring speech, offering an account on which a slur and its neutral counterpart differ in their Fregean senses. Finally, it includes an exploration of cases involving what we might call nonstandard agents of the act of assertion itself. Thus, Kirk Ludwig is interested in cases in which assertions are made by proxy, and Deborah Tollefsen explores what is involved when a group (rather than an individual) is said to make an assertion.
The four papers of Part 4 address what we might call methodological issues in the study of assertion. Mitch Green’s contribution addresses the issue of the conventionality of assertion, arguing that the act of assertion does not require the existence of a conventional means of expression (even as making an assertion is something that can be aided by such conventions). In his paper, Martin Montminy argues that there is no theory-neutral way to identify assertions, and he uses the freedom that this indeterminacy provides to defend a belief-based account of assertion. Sid Horton’s contribution explores the roles that mindreading plays in the production and comprehension of assertions, suggesting that these will be significant if speech acts are intended to obey the maxim of relevance. In their contribution, Boaz Miller and Ori Freiman ask whether devices or machines can be said to make assertions, and they conclude with a qualified affirmative answer (describing the outputs of devices as “quasi-assertions”).
Part 5 takes up issues pertaining to the content of assertions. Manuel García-Carpintero argues that there can be genuine assertions about matters of fiction and that fiction itself can be seen as making assertions, and that both of these claims are compatible with the fictional status of the content of such assertions. In her contribution, Isidora Stojanovic explores how various theses in the philosophy of mind (concerning the distinctively first-person nature of de se attitudes) might relate to the assertions in which such attitudes are expressed. Corine Besson and Anandi Hattiangati discuss whether the conception of the future as open causes difficulty for the thesis that some assertions about future contingents are true, arguing that those who see these claims as incompatible face some unmet challenges. Fabrizio Cariani explores how the contents of assertions of epistemic modals might be rendered within a Stalnakerian framework. Tim McCarthy discusses the role of assertibility in the generation of various paradoxes.
In recent years, the speech act of assertion has been connected to a host of topics in epistemology, philosophy of mind, and philosophy of action, and Part 6 explores these topics. Ted Hinchman’s contribution explores the relationship between assertion and testimony, arguing that the latter category is the more explanatorily fundamental one, and that this highlights the important interpersonal dimension of assertion itself. Patrick Rysiew focuses on assertions involving ascriptions of knowledge, exploring the role such assertions play as evidence for theories of knowledge, the social roles they play, and the pragmatics and psychology of such ascriptions. In his paper, Rik Peels addresses the extent to which one’s own ignorance is assertable, arguing that of the many types of ignorance, only two can be properly ascribed to oneself in an assertion. Jennifer Lackey criticizes familiar approaches to the standard for proper assertion by developing her notion of the (epistemic) quality of assertion, something she distinguishes from more familiar “quantitative” epistemic properties such as reliability or likelihood on one’s evidence. Robert Fiengo develops Austin’s view of assertion, exploring how our common assertive practices are linked to the knowledge that informs speech acts of this type. Erik Olsson’s paper develops various formal models of an assertion—Bayesian models, game-theoretic models, social network models, logical models, public announcement models—in an attempt to explore the variety of ways in which the speech act can be of interest to epistemologists. Mikkel Gerken and Esben Petersen survey the work on epistemic norms of action, practical deliberation, and assertion, in an attempt to characterize how these norms are interrelated. And Clayton Littlejohn’s paper discusses the role of assertion in Moore’s Paradox, and he explores the prospects for appealing to an account of assertion in order to illuminate the paradoxicality of the phenomenon itself (whether in speech or in thought).
Recent years have also seen a dramatic increase in recognition of and interest in the more social dimensions of assertion; the six papers in Part 7 explore some of these. Peter Graham’s paper borrows Ruth Millikan’s notion of a proper function, arguing that assertion has the proper function of inducing true hearer belief, and that this is so in part because of our social norms for truth-telling. Alessandra Tanesini discusses how individuals from disadvantaged or oppressed groups can be “silenced” when they attempt to make assertions, and she explores the recent literature on these and related topics. In her contribution, Casey Johnson examines how one’s social identity makes a difference to one’s ability to use assertions, indicating in this way how recent work on the speech act is connected to work on such things as race, gender, and sexual orientation. Terence Cuneo argues that ethics is of central importance to the very existence of the illocutionary act of assertion, claiming that it is the possibility of lying that explains the possibility of performing the act of assertion. Jessica Brown addresses a recent defense of the knowledge norm of assertion, according to which norm conformity and blamelessness come apart, and finds this response wanting. And Jessica Pepp defends the traditional thought that there is an ethically significant difference between lying and deliberately misleading (through implication).
Beyond aiming to capture the state of the art on the topic at issue, one of the hopes often associated with a handbook of this sort is to indicate potentially fruitful future lines of research. I want to close this introduction with a brief plea for one such line.
Whether in speech act theory or in philosophy of language and epistemology more generally, theorizing about the act of assertion has tended to focus on face-to-face speech exchanges. To be sure, those with an interest in knowledge transmission have broadened the scope of their interests to include written language as well. But it seems that neither paradigm is entirely happy when we explore the nature of the communicative language-involving acts performed online. This point itself has been made by others. I can only encourage continued reflection on those sorts of acts. In this regard the various accounts of assertion contained herein may prove helpful—if only to make clear a range of questions we might ask as we characterize our online exchanges, and to enable us to understand the full contrast of these exchanges with ordinary face-to-face conversations.
See the contributions in this handbook by Cappelen (chapter 7 ), Sbisà (chapter 8 ), and Montminy (chapter 18 ).
See Siebel (chapter 5 ) and Horton (chapter 19 ), this volume.
See Simion and Kelp (chapter 3 ), Hinchman (chapter 26 ), Rysiew (chapter 27 ), Lackey (chapter 29 ), and Fiengo (chapter 30 ), this volume.
See Shapiro (chapter 4 ) and McCarthy (chapter 25 ), this volume.
See Hinchman (chapter 26 ), Liberto (chapter 10 ), Cuneo (chapter 37 ), and Pepp (chapter 39 ), this volume.
See Pagin (chapter 6), this volume.
See García-Carpintero (chapter 21), Stojanovic (chapter 22), Besson and Hattiangati (chapter 23), and Cariani (chapter 24), this volume.
See Hinchman (chapter 26) and Pepp (chapter 39), this volume.
See Graham (chapter 34) and Olsson (chapter 31), this volume.
See Shapiro (chapter 4), Gerken and Pedersen (chapter 32), Cuneo (chapter 37), and Brown (chapter 38), this volume.
See Hom (chapter 14), Tanesini (chapter 35), and Johnson (chapter 36), this volume.
I thank Rob Stainton for suggesting this (private communication).
Some recent work in speech act theory has called this distinction into question. For discussion, see, e.g., New Work on Speech Acts , eds. Fogal, Harris, and Moss (Oxford University Press, 2018).
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- My Research
- Books/Edited Volumes
- Reviews of My Books
- 500 Years Later
- UNAM/IU, May 17-18
- My Teaching
- Service Encounters
- Implicature
- Invitations
- Disinvitations
- Compliments
- Politeness 1
- Politeness 2
- Impoliteness
- North America
- Central America
- South America
- Voces Hispanas
- Refusals (Eng)
- Refusals (Span)
- Compliments (Span)
- Capítulo 10
- Recursos para instructores
- Respuestas de los ejercicios del libro
- Actos de habla
- Encuentros de servicio
Pragmatics & Discourse at IU
- Speech Acts
A complaint is an expressive speech act that can be expressed directly or indirectly.
An indirect complaint is defined as “the expression of dissatisfaction to an interlocutor about oneself or someone/something that is not present” (Boxer, 1996: 219). The following exchange between two graduate students who express their dissatisfaction with a course is an example of an indirect complaint (Boxer, 1996):
A: I sat through yesterday's class with total non-comprehension!
B: Oh, yesterday was the worst!
In a direct complaint a speaker expresses displeasure or annoyance as a result of a past or ongoing action that affects him/her unfavorably. Unlike other speech acts such as expressions of apology or compliments, the speaker who complains addresses an interlocutor directly and uses various strategies of displeasure that precede or follow a direct complaint. Although the strategies used to express a complaint may vary with the situation and among languages, complaints are generally realized by means of the following strategies proposed by Olshtain & Weinbach (1988):
- Below the level of reproach . The speaker avoids explicit mention of the offensive event by means of various remarks without directly blaming the interlocutor. For example, if someone breaks a wine glass at a party, the interlocutor may mention a remark such as: ‘don't worry about it; such things happen.' Here the speaker does not intend to reprimand the interlocutor too strongly.
- Expression of annoyance or disapproval . These are realizations of disapproval by means of indirect or vague indications that something has been violated without holding the interlocutor directly responsible. In these cases, the speaker avoids direct confrontation with the interlocutor and makes general remarks that something has happened expressing some kind of annoyance at the violation. For example, a ‘complaint' such as ‘this is unacceptable behavior' does not hold the interlocutor responsible and makes indirect mention of the violation.
- Explicit complaint. The speaker explicitly states a direct complaint holding the interlocutor responsible for such a violation. This is often a direct or unmitigated complaint addressed to the interlocutor's face: ‘you're such an inconsiderate person; you should've consulted with me first.'
- Accusation and warning. The direct action taken by the speaker making an explicit complain carries potential consequences for the interlocutor: ‘Next time, you'll pay for it with your own money.'
In addition to the aforementioned classification, a complaint may be realized by means of three additional strategies (DeCapua, 1998): 6. Requests for repair . These include questions that ask the hearer to remediate the problem: ‘Please see if you can fix this as soon as possible.' 7. Justifications . These include reasons expressed when complaining to defend or lend support to the speaker's position or request for demand. 8. Criticisms . A person who expresses a complaint may offer an evaluation of the situation that directly affects the interlocutor's face: You've ruined my car!
Complaints across cultures
Research has shown that the realization of complaints varies across speakers from different cultures. For example, when complaining to a professor about an unfair grade, Americans expressed a direct complaint (‘I think …in my opinion, maybe the grade was a little low'), while Koreans learners of English preferred a criticism over an explicit complaint (‘…. You don't recognize my point') (Murply & Neu, 1996). In another study of different situations expressing complaints, Germans showed a preference for requests for repair, justifications, and criticism than Americans who tended to avoid these strategies (DeCapua, 1998).
Complaints in Spanish
Although not much research has been conducted on complaints in Spanish, there is at least one study that examined complaints among female university students in Caracas (Venezuela) (Bolivar 2002). Overall, complaints in Spanish incorporate several of the strategies mentioned before, as shown in the examples from Bolivar (2002) (cited in Márquez Reiter & Placencia 2005, p. 73): (1) To a friend who has borrowed a car and returned it with an empty tank: Eres un inconsciente! / dame dinero para llenarlo yo / no te lo presto más . (2) To a stranger whose dog has fouled the speaker's front entrance: Disculpe pero / este no es sitio para que su perro haga sus necesidades, / por favor, retire eso de mi entrada Example (1) is realized by means of an evaluation or a justification, a request for repair, and a warning, and example (2) contains an alerter in the form of an apology, a moralizing instruction, and a request for repair.
Complaining in Spanish
Complaining about Final Grade in Mexican Spanish (Student-Professor)
Complaining in English
Complaining about Final Grade in US English (Student-Professor)
Pragmatics & Discourse at IU resources
- César Félix-Brasdefer, Ph.D. - [email protected]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Speech Act Theory and Filipino Idioms

Related Papers
JOPR IAIN Salatiga
Dialogue and Universalism, 1, 2013, 129-142.
Maciej Witek
The paper reconstructs and discusses three different approaches to the study of speech acts: (i) the intentionalist approach, according to which most illocutionary acts are to be analysed as utterances made with the Gricean communicative intentions, (ii) the institutionalist approach, which is based on the idea of illocutions as institutional acts constituted by systems of collectively accepted rules, and (iii) the interactionalist approach, the main tenet of which is that performing illocutionary acts consists in making conventional moves in accordance with patterns of social interaction. It is claimed that, first, each of the discussed approaches presupposes a different account of the nature and structure of illocutionary acts, and, second, all those approaches result from one-sided interpretations of Austin’s conception of verbal action. The first part of the paper reconstructs Austin's views on the functions and effects of felicitous illocutionary acts. The second part reconstructs and considers three different research developments in the post-Austinian speech act theory—the intentionalist approach, the institutionalist approach, and the interactionalist approach.
sahar ommar
Stina Bäckström
Language and Dialogue
Razvan Saftoiu
Anton Didikin
Reconsideration of legal phenomena by legal language means is a typical feature of analytical tradition in the legal philosophy, since legal regulations are expressed not only in language, but are inextricably linked with the linguistic content of rules whilst applying them. Language as a form of communication and representation of the world is a holistic and specific phenomenon, that is localized in speech acts that form subject's intentions and his further actions. It is necessary to count the meaningful use of signs for the reality perception, that form the language. Legal reality and its language forms are inseparable, and thus, we can learn more deeply the essence of legal phenomena by interpreting legal texts and speech acts that illustrate legal intentions and actions. So in the speech acts theory of J.L. Austin introduces the category of com missives , denoting the obligations declared by the intentions of the person (promise, agree, intend, plan, provide, allow, swear, etc.). In legal language speech acts are used with the purposes of execution, prohibition, coercion for maintenance of a social order, therefore legal discourse has performative character. Performative expressions in legal language are characterized by speech stereotypes due to repetitive procedures (for example, procedural actions in criminal proceedings or court hearings). If it is a question of acts of application of the right, from the point of view of their performative form they have declarative character, that is contain instructions and obligations of legal character. The illocutionary function of these proposals is to form a respectful attitude to the established norms, and the perlocutive force is to impose compliance with these norms. The question of the relation of speech acts and actions in a different context was considered by Gilbert Ryle.
Pragmatics of Speech Actions ed. M. Sbisà, K. Turner, Mouton de Gruyter
Marina Sbisa'
Il capitolo presenta e discute le nozioni originarie di atto locutorio, illocutorio e perlocutorio (Austin) e le riformulazioni cui sono andate incontro nello sviluppo della teoria degli atti linguistici. L'esposizione mostra come diversi background filosofici possano generare differenze nell'analisi dell'atto linguistico e nelle definizioni dei suoi aspetti o componenti, con ricadute importanti sull'applicazione delle nozioni di atto locutorio, illocutorio e perlocutorio nel contesto dell'analisi del discorso o della conversazione. This chapter expounds and discusses the original Austinian notionf of the locutionary, illocutionary, and perlocutionary acts and their reformulations in the subsequent developments of speech act theory. It is shown how different philosophical backgrounds yield differences in the analysis of the speech act and in the definitions of its aspects or components, which affect in important ways the employment of the notions of the locutionary, illocutionary, and perlocutionary acts in the analysis of discourse or conversation.
FAIZAL RISDIANTO
Asia Pacific Journal of Education Perspective
The fundamental role of legislators is to make laws which would bring about positive changes in the lives of the electorates whom they represent. Consequently, it is expected that every legislator's utterances are made with the intention to bring about a " change in the existing state of affairs " in the country. One linguistic theory which has demonstrated that speaking is acting is Speech Act Theory. This theory states that speakers perform three communicative acts: locutionary, illocutionary and performative acts. Illocutionary acts could be performed either implicitly or explicity. Therefore, using Speech Act Theory, this study sets out to identify and explain the various illocutionary acts performed by Nigerian legislators during bill debates. The data for the analysis were taken from Nigeria Senate Hansard of the 6 th National Assembly. The study is constrained by the fact that the Hansard which is a verbatim recordings of the senate official interactions is devoid of phonological and other non-verbal pragmatic clues. The study reveals that Nigerian legislators perform mostly four types of explicit illocutionary acts – representative, affective, effective and conditional acts. The study concludes that the speakers' utterances are characterized by two levels: surface and deep levels. The surface level of the locution is the act of representative, affective, effective and conditional and the deep level is the act of persuading the other senators to accept the speaker's view on the topic of discussion.
RELATED PAPERS
Inorganic Chemistry
José A. Olabe
Rev. med. vet.(Bogota)
camilo ramirez
Dharmendra kumar Sinha
Solrun Oladottir
Emil Stanev
Kahramanmaraş Ansiklopedisi 5. Cilt (K-N)
oktay dumankaya
Journal of Cardiology and Catheterization
Leandro Assunção
Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control
Nikhil Bajaj
Paradigmi del fotografico (a cura di Claudio Marra e Daniel Borselli)
Raffaele De Berti
Forest Ecology and Management
Nilda Amiotti
International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies in Heritage Research
Irfan Helmy
Rui Ning Chia
Journal of the American Chemical Society
Joaquin C Garcia Martinez
Ma. Luisa Magaña
JACC. Cardiovascular interventions
Anna Palmisano
Luis Cabrera
Nuclear Medicine Communications
Förvaltningsrättslig Tidskrift
Christina Allard
Mohan Sridharan
Frontiers in Psychology
Kimberly Arthur
Estudios de historia moderna y contemporánea de México, Nº. 55
Roberto Breña
Farukh Gill
BMC Medicine
Tony Cassidy
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics
Aloisi Somer
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

COMMENTS
Speech act theory is a subfield of pragmatics that studies how words are used not only to present information but also to carry out actions. The speech act theory was introduced by Oxford philosopher J.L. Austin in How to Do Things With Words and further developed by American philosopher J.R. Searle. It considers the degree to which utterances ...
effects those speech acts can have. It's a highly uncertain, context-dependent process that has important social and legal consequences. 2 Locutionary act A locutionary act is an instance of using language. (This seems mundane, but it hides real com-plexity, since it is all wrapped up with speaker intentions.) 3 Illocutionary act An ...
The contemporary use of the term "speech act" goes back to J. L. Austin 's development of performative utterances and his theory of locutionary, illocutionary, and perlocutionary acts. Speech acts serve their function once they are said or communicated. These are commonly taken to include acts such as apologizing, promising, ordering, answering ...
The latter (but not the former) is a case of speaker meaning. Accordingly, a speech act is a type of act that can be performed by speaker meaning that one is doing so. This conception still counts resigning, promising, asserting and asking as speech acts, while ruling out convincing, insulting and whispering.
How Words Shape Meaning & Interactions. In the captivating world of media and communications, one theory that holds immense importance is the Speech Act Theory. Developed by philosophers J.L. Austin and John Searle, this theory helps us comprehend how our words possess the power to shape meaning. Also, how it influences our interactions with ...
speech act theory, Theory of meaning that holds that the meaning of linguistic expressions can be explained in terms of the rules governing their use in performing various speech acts (e.g., admonishing, asserting, commanding, exclaiming, promising, questioning, requesting, warning).In contrast to theories that maintain that linguistic expressions have meaning in virtue of their contribution ...
A speech act is an utterance that serves a function in communication. We perform speech acts when we offer an apology, greeting, request, complaint, invitation, compliment, or refusal. A speech act might contain just one word, as in "Sorry!" to perform an apology, or several words or sentences: "I'm sorry I forgot your birthday.
The essential insight of speech act theory was that when we use language, we perform actions—in a more modern parlance, core language use in interaction is a form of joint action. Over the last thirty years, speech acts have been relatively neglected in linguistic pragmatics, although important work has been done especially in conversation ...
The illocutionary act refers to the type of speech act that is being performed, this is, the function that the speaker intends to fulfill. The perlocutionary part, on the other hand, is the effect that an utterance could have on the hearer or addressee (Huang, 2014, p. 128).
ABSTRACT. The conception of language as a means o f action has becom e a top ic of sustained investigation by. philosophers of language and linguists w ithin the theory of sp eech acts. The ...
The speech act theory is a theory in the philosophy of language which rigorously attempts. to systematically explain the workings of language. Its wide influence has transcended the confines. of ...
The speech act theory considers language as a sort of action rather than a medium to convey and express. The contemporary Speech act theory developed by J. L. Austin a British philosopher of languages, he introduced this theory in 1975 in his well-known book of 'How do things with words'. Later John Searle brought the aspects of theory into ...
Befehl is a speech act label. 2.1.1 speech acts and illocutionary acts The characterization of speech acts that was given at the beginning of this section ('the verbal action which a speaker performs by means of an utterance') is, in fact, a characterization of speech acts in a restricted sense. In this restricted sense in 3.
Speaker meaning, then, encompasses not just content but also force, and we may elucidate this in light of the normative structure characteristic of each speech act: When you overtly display a commitment characteristic of that speech act, you have performed that speech act.
Speech acts are a staple of everyday communicative life, but only became a topic of sustained investigation, at least in the English-speaking world, in the middle of the Twentieth Century. [] Since that time "speech act theory" has been influential not only within philosophy, but also in linguistics, psychology, legal theory, artificial intelligence, literary theory and many other ...
Speech Act Theory is the level of analysis that goes beyond naming entities or judging linguistic structures. ... li ng uistic and non ... Expressions, meaning and speech acts 3. The structure of ...
MEANING AND SPEECH ACTS. I. INTRODUCTION. AA CONTROVERSY has been brewing up for some time. now between those who want to explain the meanings. of certain words in terms of the speech acts which those words (or sentences containing them) are standardly used to perform, and those who say that this is a mistake. Let us call these two.
Locutionary Speech Act According to "Philosophy of Language: The Central Topics" of Susana Nuccetelli and Gary Seay, is the "mere act of producing some linguistic sounds or marks with a certain meaning and reference". The utterance is a sound, a word, or a phrase that follows the rules of language. This is simply just an utterance. ...
If we give the label "assertion" to the (alleged) type of speech act in question, we might pursue the hypothesis that assertion is a type of speech act that. •. is apt for the expression of judgment and belief; 2. •. is apt for the transmission of knowledge; 3. •. commits one to the truth of a proposition; 4. •.
Complaints. A complaint is an expressive speech act that can be expressed directly or indirectly. An indirect complaint is defined as "the expression of dissatisfaction to an interlocutor about oneself or someone/something that is not present" (Boxer, 1996: 219). The following exchange between two graduate students who express their ...
A speech act is an utterance considered as an action, particularly with regard to its intention, purpose, or effect. Isang Teorya ng Wika. Ang speech act theory ay isang teoryang batay sa aklat na How to Do Things with Words ni J.L. Austin (1975). Pinapaniwalaan sa teoryang ito na ang yunit ng komunikasyong linggwistik ay hindi ang simbulo, salita o ang pangungusap mismo, kundi ang produksyon ...
Speech act belongs to the domain of pragmatics, and its study, called speech act theory, is a. prominent part of that discipline. At this level, speech act theory and utterances are essential ...
In the speech act theory, there is what is called a direct speech act. This happens when a speaker means exactly what their words might entail. More often, however, an utterance is said indirectly. This is called an indirect speech act. The indirect speech act has an implied meaning, along with its literal (Paltridge, 2006).