We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!

Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Case study research : design and methods
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
obscured text on back cover
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
1,356 Previews
24 Favorites
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station16.cebu on December 23, 2021
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (4th Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage

2013, The Canadian Journal of Action Research
Related Papers
rizwan gujjar
EmmsMt Ntuli
Simon Phelan
The Canadian Journal of Program Evaluation
Trista Hollweck
David E Gray
ZUHAL AHNAN
Yhonier Gonzalez
The Journal of Agricultural Sciences - Sri Lanka
rohitha rosairo
We receive a large number of manuscripts for possible publication in this journal. In reviewing them, we find that the bulk of them are from the area of crop sciences, livestock production and allied fields that have used experiments as the research strategy. The minority that falls in to the areas of agribusiness, agricultural economics and extension have used survey strategy. There is a lack of utilizing other research strategies in current research. Research has to be commenced with a clear direction and a clearly identified study process. These are primarily provided by its research strategy (Wedawatta, 2011). There are numerous strategies that a researcher can adopt to achieve the objectives of a particular research study. Some common research strategies are; experiment, survey, archival analysis, ethnography, action research, narrative inquiry, and the case study. This paper explains what a case study is and outlines the components of a case study. The Nature of a Case Study Yin (2003) defines case study as 'an empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident'. A phenomenon and context are not always distinguishable in real-life situations. Therefore, a case study uses a large number of variables of interest than data points; and essentially relies on multiple sources of evidence for data triangulation. A historical viewpoint on case study strategy is presented in Tellis (1997). According to Yin (2003), case studies can be exploratory, explanatory or descriptive. Research in social sciences deals with interactions between institutions and human behaviour. These can be best studied in real-life settings and contexts. Sometimes an inquiry may be undertaken on an individual organization with a limited or a narrow population. These suggest qualitative investigations which are assessments of attitudes, opinions and behaviour (Kothari and Garg, 2018). These qualitative investigations are characteristic with the case study strategy. Whilst often been identified as interpretivist, case studies can also be used in positivistic research (Saunders et al. 2012).
Rossad Ferdinand
RELATED PAPERS
Henry Cuascota
Takeshi Sakamoto
KUAT : Keuangan Umum dan Akuntansi Terapan
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry
RUIYANG XIAO
verena lepper
arXiv: Fluid Dynamics
Mingjun Wei
Cell Reports
Minghong Ma
Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union
Kebron Gurara
Applied Sciences
Dr. Uneb Gazder
Discurso & Sociedad
Patrick Charaudeau
Journal of Systems and Software
Jan Carlson
Medicinal and Aromatic plants
GUNJAN BHATT
Gastroenterology
Maria Freni
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
Alessandro Guida
Oscar Navarro Santos
Modern concepts in material science
Inge De Wandele
Technoscience Academy
Dr.(Mrs.)Kirubai D Computer Science-Aided
Fabrício Zera
Advances in Palliative Medicine
Małgorzata Krajnik
Revista Geográfica de América Central
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (4th Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- Trudie Aberdeen University of Alberta
Author Biography
Trudie aberdeen, university of alberta.
Copyrighted material allows the author to quote briefly (up to 100 words) for scholarly purposes from most published materials, providing the source is correctly cited within the manuscript. If the author wishes to use figures, tables, or longer quotations, written permission must be obtained from the writer or publisher to reprint the material. Under such circumstances, the author needs to provide a permission summary with their manuscript submission. Written permissions must also be provided by subjects in any photographs or audio or video segments. If the subjects are children, a signed release from a parent or guardian must be provided for each child visible in the photograph or video segment, or heard on an audio clip. In addition, although linking to another site does not require permission, replication (such as "screen shots") or description of a site within the manuscript requires permission to be sought from originator of web site, including those created by students, teachers, or schools.
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Make a Submission


- Politics & Social Sciences
- Social Sciences

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: .savingPriceOverride { color:#CC0C39!important; font-weight: 300!important; } .reinventMobileHeaderPrice { font-weight: 400; } #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPriceSavingsPercentageMargin, #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPricePriceToPayMargin { margin-right: 4px; } -24% $32.76 $ 32 . 76 FREE delivery Saturday, May 25 on orders shipped by Amazon over $35 Ships from: Amazon Sold by: HOSH LLC
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Save with Used - Good .savingPriceOverride { color:#CC0C39!important; font-weight: 300!important; } .reinventMobileHeaderPrice { font-weight: 400; } #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPriceSavingsPercentageMargin, #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPricePriceToPayMargin { margin-right: 4px; } $6.66 $ 6 . 66 FREE delivery Tuesday, May 28 on orders shipped by Amazon over $35 Ships from: Amazon Sold by: Vivé Liber Books LLC

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Follow the author

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Case Study Research: Design and Methods, 3rd Edition (Applied Social Research Methods, Vol. 5) 3rd Edition
There is a newer edition of this item:.

Purchase options and add-ons
This new edition of the best-selling Case Study Research has been carefully revised, updated, and expanded while retaining virtually all of the features and coverage of the Second Edition . Robert Yin′s comprehensive presentation covers all aspects of the case study method--from problem definition, design, and data collection, to data analysis and composition and reporting. Yin also traces the uses and importance of case studies to a wide range of disciplines, from sociology, psychology and history to management, planning, social work, and education.
- ISBN-10 0761925538
- ISBN-13 978-0761925538
- Edition 3rd
- Publisher SAGE Publications, Inc
- Publication date December 24, 2002
- Language English
- Dimensions 5.5 x 0.5 x 8.5 inches
- Print length 200 pages
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Customers who viewed this item also viewed

Editorial Reviews
About the author.
Robert K. Yin is President of COSMOS Corporation, an applied research and social science firm. Over the years, COSMOS has successfully completed hundreds of projects for federal agencies, state and local agencies, and private foundations.
Outside of COSMOS, Dr. Yin has assisted numerous other research groups, helping to train their field teams or to design research studies. The most recent such engagements have been with The World Bank, the Division of Special Education and disAbility Research at George Mason University, the Department of Nursing Research and Quality Outcomes at the Children’s National Health System (Washington, DC), and the School of Education, Southern New Hampshire University.
Dr. Yin has authored over 100 publications, including authoring or editing 11 books (not counting the multiple editions of any given book). Earlier editions of the present book have been translated into eight languages (Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Swedish, Romanian, Italian, Polish, and Portuguese), and a second book on Qualitative Research from Start to Finish (2016) is in its 2nd edition and has been translated into four languages (Chinese, Korean, Swedish, and Portuguese). Dr. Yin received his B.A. in history from Harvard College (magna cum laude) and his Ph.D. in brain and cognitive sciences from MIT.
Product details
- Publisher : SAGE Publications, Inc; 3rd edition (December 24, 2002)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 200 pages
- ISBN-10 : 0761925538
- ISBN-13 : 978-0761925538
- Item Weight : 3.84 ounces
- Dimensions : 5.5 x 0.5 x 8.5 inches
- #514 in Social Sciences Research
- #2,016 in Professional
- #2,950 in Social Sciences (Books)
About the author
Robert k. yin.
Robert K. Yin, Ph.D., serves as Chairman of the Board and CEO of COSMOS Corporation, an applied research and social science firm that has been in operation since 1980. Over the years, COSMOS has successfully completed hundreds of projects for government agencies, private foundations, and other entrepreneurial and non-profit organizations. At COSMOS, Dr. Yin actively leads various research projects, including those in which the case study method is used. He has authored numerous books and peer-reviewed articles, including Case Study Research and Applications of Case Study Research. In 1998 he founded the “Robert K. Yin Fund” at M.I.T., which supports seminars on brain sciences, as well as other activities related to the advancement of pre-doctoral students in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences.
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
- Find My Rep
You are here
Case Study Research and Applications Design and Methods
- Robert K. Yin - COSMOS Corporation
- Description
Supplements
Password-protected Instructor Resources include the following:
- An expanded glossary provided by the author in the form of downloadable Briefs.
- Additional tutorials written by the author which correspond to Chapters 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6.
- A selection of author Robert Yin's SAGE journal articles.
- Tables and figures from the book available for download.
“The book is filled with tips to the researcher on how to master the craft of doing research overall and specifically how to account for multi-layered cases.”
“Yin covers all of the basic and advanced knowledge for conducting case study and why they are useful for specific research studies without getting lost in the weeds.”
“The applications enhance the original material because it gives the reader concrete examples.”
“Yin is much more in-depth on case study methods both within a general qualitative text and any other case study text I have seen.”
On demand used as recommendation for basic literature for case study research
An essential reading for people doing case studies.
very thoruogh introduction
Very good introduction to Case Study design. I have used case study approach for my PhD study. I would recommend this book for an indepth understanding of case study design for research projects.
Dr Siew Lee School of Nursing, Midwifery and Paramedic Practice Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen.
The book is a really good introduction to case study research and is full of useful examples. I will recommend as the definitive source for students interested in pursuing this further in their projects.
In our Doctor of Ministerial Leadership (DML), Case Study is the Methodology that is required in this program. Robert Yin's book provides the foundational knowledge needed to conduct research using his Case Study design.
Sample Materials & Chapters
Preface: Spotlighting "Case Study Research"
Chapter 1: Getting Started
For instructors
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
- Electronic Order Options VitalSource Amazon Kindle Google Play eBooks.com Kobo
Related Products

The use of generative AI in research: a production management case study from the aviation industry
- Published: 10 May 2024
Cite this article

- R. O. Walton ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6630-4141 1 &
- D. V. Watkins 1
11 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) marks a groundbreaking shift in research. Unlike traditional AI, GAI can generate novel insights and content using natural language processing. Using case study methodology, this paper explored GAI's application in identifying research gaps in aviation's use of Additive Manufacturing (AM), focusing on Design Optimization. Recent advances, such as ChatGPT-4, enable GAI to process extensive data and recognize complex patterns. The research method includes paper selection, GAI-driven gap analysis, and thematic extraction. Generative AI uncovered research domains but has limitations in content attribution and accuracy. Nevertheless, GAI promises to revolutionize knowledge discovery and problem-solving across various fields.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Adetayo, A.J. 2023. Artificial Intelligence Chatbots in Academic Libraries: The Rise of ChatGPT. Library Hi Tech News 40 (3): 18–21. https://doi.org/10.1108/LHTN-01-2023-0007 .
Article Google Scholar
Agrawal, R., and S. Vinodh. 2019. Application of Total Interpretive Structural Modelling (TISM) for Analysis of Factors Influencing Sustainable Additive Manufacturing: A Case Study. Rapid Prototyping Journal 258 (7): 1198–1223. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-06-2018-0152 .
Brahmbhatt, A. 2023, Aug 7. GPT-3.5 vs GPT-4: An In-Depth Analysis of OpenAI’s Language Models . Auberginesolutions.com
Brown, T. B., B. Mann, N. Ryder, M. Subbiah, J. Kaplan, P. Dhariwal, A. Neelakantan, P. Shyam, G. Sastry, A. Askell, S. Agarwal, A. Herbert-Voss, G. Krueger, T. Henighan, R. Child, A. Ramesh, D.M. Ziegler, J. Wu, C. Winter, et al. 2020. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. Cornell University Library. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.14165
Debnath, B., M.S. Shakur, F. Tanjum, M.A. Rahman, and Z.H. Adnan. 2022. Impact of Additive Manufacturing on the Supply Chain of Aerospace Spare Parts Industry—A Review. Logistics . https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics6020028 .
Github.com. 2023. Hallucination-Leaderboard. Github.com. Accessed 28 November 2023
Jackson, K., P. Bazeley, and P. Bazeley. 2019. Qualitative data analysis with NVivo , 3rd ed. New York: Sage.
Google Scholar
Lawton, G. 2023, October. What is Generative AI? Everything You Need to Know. https://www.techtarget.com/ . Accessed 15 Oct 2023
Pant, M., P. Pidge, L. Nagdeve, and H. Kumar. 2020. A Review of Additive Manufacturing in Aerospace Application. Journal of Composite and Advanced Materials 31 (2): 109–115.
Wagner, S.M., and R.O. Walton. 2016. Additive Manufacturing’s Impact and Future in the Aviation Industry. Production Planning & Control 27: 1124–1130. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2016.1199824 .
Walton, R.O., and A. Gupta. 2023. Evaluating Additive Manufacturing Success Factors for the Aviation Industry: An Interpretive Structural Modeling Approach. International Journal of Logistics Systems and Management . https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLSM.2023.10054151 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, Daytona Beach, FL, USA
R. O. Walton & D. V. Watkins
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to R. O. Walton .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Walton, R.O., Watkins, D.V. The use of generative AI in research: a production management case study from the aviation industry. J Market Anal (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-024-00317-y
Download citation
Revised : 03 March 2024
Accepted : 08 April 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-024-00317-y
Research on trajectory control technology for L-shaped horizontal exploration wells in coalbed methane
- Xiugang Liu 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Zaibing Jiang 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Yi Wang 3 ,
- Haitao Mo 3 ,
- Haozhe Li 3 &
- Jianlei Guo 3
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 11343 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Energy science and technology
- Engineering
Horizontal wells have significant advantages in coal bed methane exploration and development blocks. However, its application in new exploration and development blocks could be challenging. Limited geological data, uncertain geological conditions, and the emergence of micro-faults in pre-drilled target coal seams make it hard to accurately control the well trajectory. The well trajectory prior to drilling needs to be optimized to ensure that the drilling trajectory is within the target coal seam and to prevent any reduction in drilling ratio (defined here as the percentage of the drilling trajectory in the entire horizontal section of the well located in the target coal seam) caused by faults. In this study, the well trajectory optimization is achieved by implementing the following process to drill pilot hole, acquire 2D resonance, and azimuthal gamma logging while drilling. The pilot hole drilling can obtain the characteristic parameters of the target coal seam and the top and bottom rock layers in advance, which can provide judgment values for the landing site design and real-time monitoring of whether the wellbore trajectory extends along the target coal seam; 2D resonance exploration can obtain the construction of set orientation before drilling and the development of small faults and formation fluctuations in the horizontal section, which can optimize the well trajectory in advance; the azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology can monitor the layers drilled by the current drill bit in real time, and can provide timely and accurate well trajectory adjustment methods.The horizontal well-Q in the Block-W of the Qinshui Basin was taken as a case study and underwent technical mechanism research and applicability analysis. The implementation of this new innovative process resulted in a successful drilling of a 711 m horizontal section, with a target coal seam drilling rate of 80%. Compared to previous L-type wells, the drilling rate increased by about 20%, and the drilling cycle shortened by 25%. The technical experience gained from this successful case provides valuable insight for low-cost exploration and development of new coalbed methane blocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
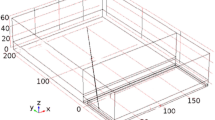

Study on optimization of layout parameters of high-level boreholes in Pingdingshan coal mine
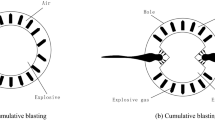
Study on parameter optimization of deep hole cumulative blasting in low permeability coal seams
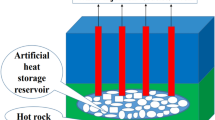
A new mathematical modeling approach for thermal exploration efficiency under different geothermal well layout conditions
Introduction.
Coal Bed Methane (CBM) is found in many parts of the world, and is considered as a clean and abundant source of energy 1 , 2 , 3 . In general, CBM wells mainly include three types; vertical, cluster and horizontal wells. The cluster and horizontal wells belong to directional wells. Moreover, horizontal wells could be further classified into; V-, U- and L-shaped wells. Which in turn could also be divided according to their radius, and branches. Figure 1 below provide an illustration for some of these wells.
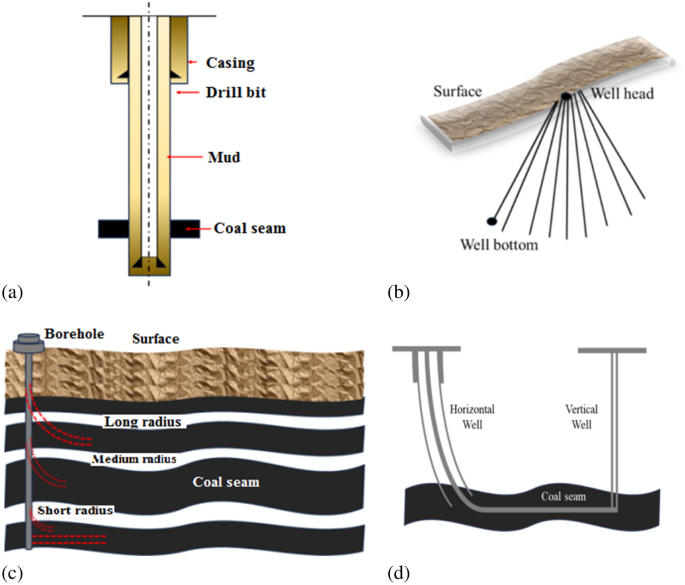
Illustration of well types; ( a ) Vertical well, ( b ) Cluster well, ( c ) Horizontal Well, and ( d ) Horizontal L-Shaped well with a vertical well forming a U-Shaped well.
In the development of CBM wells, L-shaped, U-shaped and multi-branch horizontal wells are usually used for new exploration and development blocks (defined here as new fields or area blocks in the oil and gas industry) 4 , 5 , 6 . However, complex formation structure, and small faults development have made it an extremely challenging task to achieve high output from newly developed CBM wells 7 . For instance, U-shaped wells (a well type in which a vertical well and a horizontal well are connected in the same target layer) face huge difficulties in accurate docking along the coal seam and have limited benefits in the presence of multiple faults in the horizontal Section 8 . Similarly, the applicability of multi-branch horizontal wells is poor, especially in complex stratigraphic structures and fault development of the block 9 .
On the other hand, L‑shaped horizontal wells are often adopted as the main type of wells for exploring and developing CBM in new blocks. The L-shaped horizontal wells exhibit uncomplicated drilling prerequisites, demonstrate a low probability of wellbore collapse or obstruction, and facilitate subsequent access for maintenance of the initial wellbore 10 . However, the drilling process of these wells are not free of challenges. L-shaped wells have a high requirement for wellbore trajectory control, and they are usually difficult to achieve one-time “soft landing” and ultra-long horizontal segment footage 10 . In addition, drainage equipment and method are another key restriction for the promotion and application of this type of well 11 . For example, reported completion data from several exploration wells indicated that the drilling ratio along the coal seam of the actual trajectory is less than 60%. The drilling cycle is nearly two months, and gas production is low 11 . Table 1 illustrates a tabulated analysis of the applicability and challenges associated with different well types in exploration blocks characterized by complex geological formations and the presence of micro-faults.
Various methods have been used to improve the drilling ratio, by improving the trajectory control. These methods, shown in Table 2 , include: geological guidance technology of adjacent well data, electromagnetic waves, natural gamma measurement, and three-dimensional seismic exploration technology. However, each method has its own limitations, such as high costs, difficulty in obtaining gamma values in specific directions, and signal loss when applied to drilling in complex formations 12 , 13 .
This study delves into trajectory control methods for Horizontal wells within Coalbed Methane (CBM) exploration and development blocks. The approach involves the utilization of pilot holes to determine the characteristics of the target coal seam and the surrounding upper and lower rock layers based on the magnitude of gamma values. This information serves as a predictive identification of marker layers, allowing real-time control and adjustment of the drilling trajectory within the target coal seam. This methodology enables the identification of whether the drilling trajectory is presently positioned within the target coal seam, the roof rock layer, or the floor rock layer. Additionally, a two-dimensional resonance exploration technology is employed for geological structure and fault detection prior to drilling, enabling pre-drilling trajectory optimization. Furthermore, azimuth gamma logging technology is utilized for real-time monitoring and correction of the drilling trajectory's horizontal positioning during the drilling process. Using L-shaped Short-Radius Well-Q in Block-W of the Qinshui Basin as a case study, a comprehensive assessment of the combined effectiveness of these three methods is conducted. Simultaneously, the research delves into the technical mechanisms and applicability analysis. This exploration of the technical mechanisms aims to enhance the understanding of the functions of these methods, their application conditions, and the analysis and utilization of their technical effects.
Trajectory control methodology
Pilot hole drilling, construction background and reasons.
The area formation structure and faults nature could be obtained by two-dimensional seismic data. Seismic surveys and exploratory drilling in the area could provide a good indication on the coal seam actual depth, coal seam distribution, layers, belts and interbeds. For the geological conditions of developing new blocks, such as less drilling data, less seismic exploration data, complex formation structure and micro-fault development, etc., before drilling, it is imperative to obtain the key parameters of the target coal seam, including its lithology, gas-bearing capacity, gamma value, etc., along with those of the rock layers above and below it. This will allow for the determination of the precise horizon of the coal seam and provide technical support for real-time monitoring and well trajectory control along the target coal seam. To achieve this, it is necessary to design and implement a pilot hole drilling program to obtain the characteristic parameters of the target coal seam and the surrounding strata 14 , 15 .
Pilot hole construction design
Once the goal of layer identification is achieved, the next step is to backfill and sidetrack the pilot hole to open branches and land according to the actual occurrence of the coal seam. To ensure the effectiveness of the pilot hole guidance in subsequent construction, it is advisable to minimize the distance between the coal-seem top point (the point where the drilling trajectory first drills into the target coal seam) and the landing point by increasing the well angle of inclination. Conversely, in order to enhance the construction efficiency of the pilot hole, it is preferable to keep the depth of the pilot hole to a minimum, which is indicated by a small well angle of inclination (70 degrees). Figure 2 illustrates this concept.
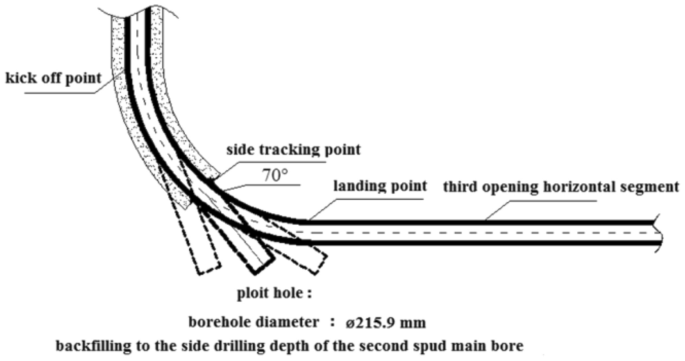
Optimization of pilot hole scheme.
Taking into account the underlying reasons and background for constructing a pilot hole, as well as the difficulty of side-tracking and the efficiency of construction, a comprehensive plan has been developed. The plan involves drilling the pilot hole at a steady angle of approximately 70° until the bottom of the target coal seam is reached.
- Two-dimensional resonance exploration
Resonance exploration mechanism
The seismic wave frequency resonance exploration technology is a novel geophysical exploration method that utilizes the frequency resonance principle prevalent in nature to investigate underground geological formations 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 . This technique enables the acquisition of geometric attributes of subsurface structures, such as fractures and faults. Figure 3 illustrates a typical resonance diagram of a seismic wave.
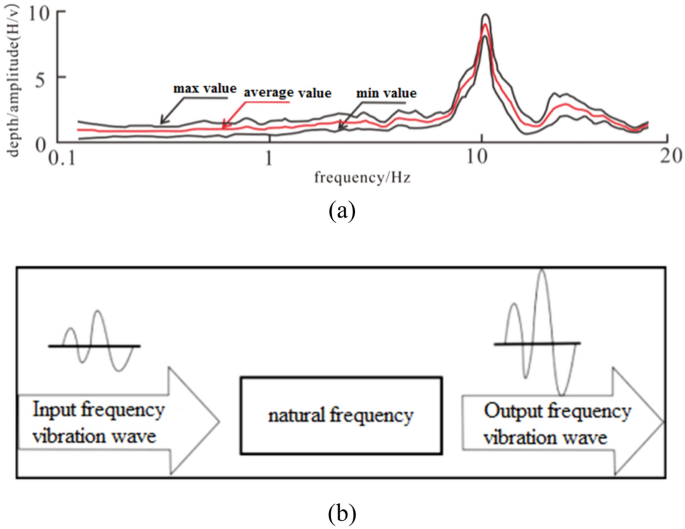
( a ) Typical resonance curve of seismic wave ( b ) self-excite resonance to vibration.
Resonance exploration technology boasts numerous advantages, including high sensitivity to density changes, exceptional vertical and horizontal resolution, and an exploration depth of up to 5000 m. Additionally, this technology can be acquired and processed passively, making it an economical and straightforward exploration method 20 .
Analysis of technical applicability
At this stage, the analysis of the existing two-dimensional seismic data in the exploration block would indicate the geological structure of the target coal seam in the block. In addition, it will reveal fault’s locations beside faults development status. The pilot hole drilling can accurately obtain the actual depth of the target coal seam and the characteristic parameter values of the target layer, as well as the roof and floor, but conventional means cannot predict structural conditions such as the development of micro faults in the horizontal section of the drilling along the designated direction. This increases the difficulty of well trajectory control and makes it challenging to ensure the coal seam drilling ratio. However, the two-dimensional resonance exploration technology can be used to infer the development of small faults in the horizontal section drilled along the specified direction by interpreting the resonance image. This enables the optimization of the well trajectory in advance to control the actual drilling trajectory and improve the drilling rate of the target coal seam.
Azimuth gamma control technology
Working principle of azimuth gamma.
The azimuth gamma logging tool is utilized to measure the width of gamma ray energy level 21 , 22 , 23 . The scintillation counter captures gamma rays from the stratum, and azimuth gamma logging while drilling offers unique advantages 24 , 25 . Firstly, it enables real-time calculation of the strata's apparent dip angle. It is convenient to calculate the apparent dip angle of the strata by utilizing the azimuth gamma data. The apparent dip angle at the current position can be obtained as long as it is required to cross an interface. The formula for calculating the apparent dip angle using the azimuth gamma 26 is as follows:
where α is the apparent strata dip; D is the well diameter; Δd is the distance between the upper and lower gamma value change points; β is the well deviation angle.
Second, measuring the natural gamma value in a specific direction. By transmitting up and down gamma data in real-time, it becomes possible to accurately determine the positions of different formation interfaces 27 , 28 . This information can then be used to ensure that the trajectory of the control well is precisely aligned with the target coal seam after drilling is complete. The specific process involved is illustrated in Fig. 4 .
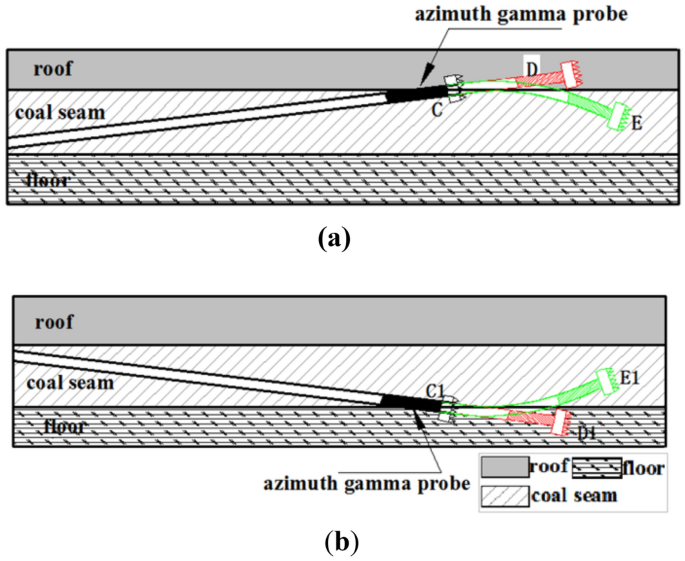
Trajectory control based on azimuth-while-drilling gamma logging. ( a ) Coal seam drilled out from the roof. ( b ) Coal seam drilled out from the floor.
The drilling process in the horizontal section along the coal seam is susceptible to deviate from the target due to increased drilling pressure or the impact of the formation structure. The strata above and below the coal seam are usually mudstone or carbonaceous mudstone. When using azimuth gamma logging during drilling, the upper gamma value first increases, followed by the lower gamma value, indicating that the drilling has exited the coal seam roof at point C in Fig. 4 a. When the upper and lower gamma values become similar, it suggests that the drilling has left the layer, as shown at point D in Fig. 4 a. To correct the inclined drilling control track deviation, the trajectory correction process is initiated when drilling to point C using azimuth gamma measurement, as demonstrated at point E in Fig. 4 a. Similarly, when the lower gamma value increases first and the upper gamma value increases later, it indicates that the drilling trajectory is exiting the coal seam floor at point C1 in Fig. 4 b. When the upper and lower gamma values become similar, the drilling has left the layer, as shown at point D1 in Fig. 4 b. To correct the incremental drilling control track deviation, the trajectory correction process is initiated when drilling to point C1, as illustrated at point E1 in Fig. 4 b.
In terms of technical applicability, conventional natural single gamma logging technology cannot accurately determine the bit's position once it leaves the coal seam, making it challenging to provide precise corrective measures. This issue is particularly problematic wherever the geological structure of the target coal seam is complex, micro faults are developed, and the coal seam is thin. To ensure the penetration ratio of the target coal seam and ensure the safety of underground construction, azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology can be utilized. This technology allows for the real-time monitoring of the current drilling horizon and provides effective guidance during construction. As a result, the drill bit can efficiently drill into the coal seam, maximizing the penetration ratio of the target coal seam.
Technical applicability analysis
In the second drilling operation, if the targeted coal seam is complex due to its thinness or the presence of micro-faults, it will be very challenging to accurately determine the position of the drilling bit after it exits the coal seam. Therefore, it will be necessary to use azimuth gamma logging while drilling. This technology enables the real-time monitoring of the drilling bit's current horizon, guiding the construction process and ensuring that the bit drills to the maximum extent possible within the coal seam.
Trajectory control technology and case study
Geological setting.
In this study, the short radius, well-Q in Block-W of the Qinshui Basin is taken as an example. Based on the most recent exploration wells drilled in Block-W of Qinshui Basin, the geological horizons have been revealed. The strata in the block, from bottom to top, consist of Paleozoic Ordovician, Carboniferous, Permian, Mesozoic Triassic, Jurassic, and Cenozoic Quaternary. The stratum near Well-Q has a general inclination from northeast to northwest, and Coal Seam no.15 is the development target stratum. The coal seam is located in the lower part of the Taiyuan Formation and has a simple structure. It is a thick coal seam that is stable and easy to drill throughout the area and generally contains 0–2 layers of dirt shale. The effective thickness of the coal seam ranges from 0 to 5.30 m, with an average of 3.39 m. It is thicker in the east and thinner in the west. However, there is one exploration well in the block that did not drill into Coal Seam no.15, possibly due to fault interference resulting in the loss of the coal seam. The coal seam deposit depth ranges from 728 to 2002 m, with an average of 1479 m. The depth is shallow in the southeast of the block and gradually deepens towards the northwest. Due to the influence of the stratum tendency (Stratum dip), the depth of the coal seam reaches over 1500 m in the west 14 . The roof lithology of the coal seam mostly consists of sandy mudstone, mudstone, siltstone, and fine sandstone, while the floor is mostly sandy mudstone, mudstone, and siltstone.
Wellbore structure
Designing an optimized wellbore structure can greatly improve drilling efficiency and safety by reducing annular pressure loss and back pressure (the drilling tool back pressure phenomenon), especially for long well sections. In the case of Well-Q, the wellbore structure was designed with a three-opening sections to ensure gas production of the coal seam during subsequent fracturing development. The first section seals the formation prone to collapse and leakage in the upper part of the primary casing, creating a safe drilling environment for the second well section. The second section seals sandstone, mudstone, and sandy mudstone intervals at the upper part of the coal seam, with the second well section casing obliquely drilled to a depth of no less than 3 m from the target coal seam no.15.
The third section extends along coal seam no.15 and runs casing to form a stable gas production channel to prevent coal seam collapse in the horizontal section due to the influence of multiple factors such as fracturing in the later stage. Prior to drilling the second well section of the main borehole, pilot hole drilling was carried out to obtain relevant geological parameter information of the target coal seam and the adjacent marker bed. Specific design parameters and requirements are as follows:
In the first well section, a ø 346.1 mm drill bit was used to drill into the stable bedrock for 30 m. J55 grade steel ø 273.1 mm surface casing was then lowered and cementing cement slurry returned to the surface.
In the second well section, a ø 241.3 mm drill bit was used to drill to the roof of the target no.15 coal seam and then the drilling was stopped. The landing point was determined based on the lithology of the roof of the coal seam and the actual drilling process. N80 grade steel ø 193.7 mm technical casing was run to 3–5 m above the roof of the coal seam. Through variable density cementing process, high-density cement slurry was used to return to 300 m above the roof of Coal Seam no.15, while low-density cement slurry returned to the surface.
The third well section was drilled with a ø 171.5 mm drill bit. After entering the target coal seam no.15, the drilling followed the coal seam. Upon reaching the designed well depth, P110 grade steel ø 139.7 mm production casing was run, and the well was completed without cementing.
The pilot hole was drilled with a ø215.9 mm bit, and the inclination angle stabilizing drilling crossed the floor of the target coal seam for tens of meters. Subsequently, the bit was backfilled with pure cement slurry to the side drilling depth of the second well section. The specific wellbore structure is shown in Fig. 5 .

Well structure.
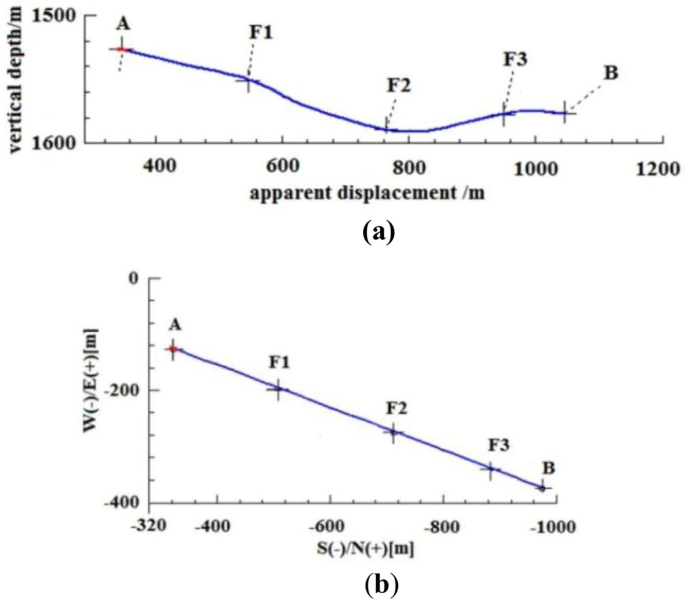
Case study: well-Q design optimization
Using Well-Q as a case study, the pilot hole trajectory design included the following: straight well section, kicking-off section, and stabilizing section. The stabilizing drilling passes through the floor of Coal Seam no.15 for approximately 30 m at an inclination angle of 70° to ensure accurate measurement of the gamma value, gas measurement value, and other characteristic parameters of the target coal seam bottom and floor using a simple gesturing instrument. The pilot hole is sealed by backfilling it with 42.5 grade Portland cement up to the well section with an inclination of about 25°, and the cement slurry has a specific gravity of 1.6–1.7 g/cm3. As the well deviation angle increases, the azimuth angle of directional and composite drilling becomes more stable, particularly when the well deviation angle exceeds 25°, resulting in a smaller azimuth drift 29 . This stability is beneficial for the subsequent inclined side-tracking in the main wellbore's second well section. The pilot hole and main borehole design trajectories are shown in Fig. 6 .
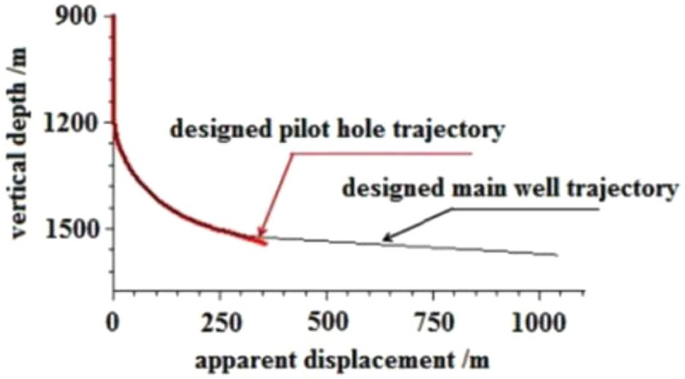
Design trajectory of pilot hole and main hole.
Significant data has been obtained through the pilot hole design and the actual drilling of Well-Q. This dataset is pivotal for precise trajectory control in Coalbed Methane (CBM) exploration. The acquisition process relies on several methods, including real-time drilling natural gamma logging for gamma values of marker layers, and downhole gas logging for coal seam gas characteristics. The examination of cuttings recorded in real-time during drilling operations further aids in the identification and differentiation of these marker layers.
The critical information gleaned encompasses the identification of the K2 marker bed, the longitudinal stratification of the target no.15 coal seam, as well as the lithological composition, gamma values, and gas-bearing attributes of the upper and lower rock layers. These specific parameters are thoughtfully presented in Fig. 7 , establishing a robust foundation for the meticulous control of trajectory and the rational design of the landing point within the target coal seam. This dataset also serves as a valuable point of reference, ensuring the seamless execution of the horizontal drilling phase within the coal seam. Consequently, these findings play a pivotal role in enhancing drilling efficiency, ultimately culminating in the realization of efficient drilling objectives.
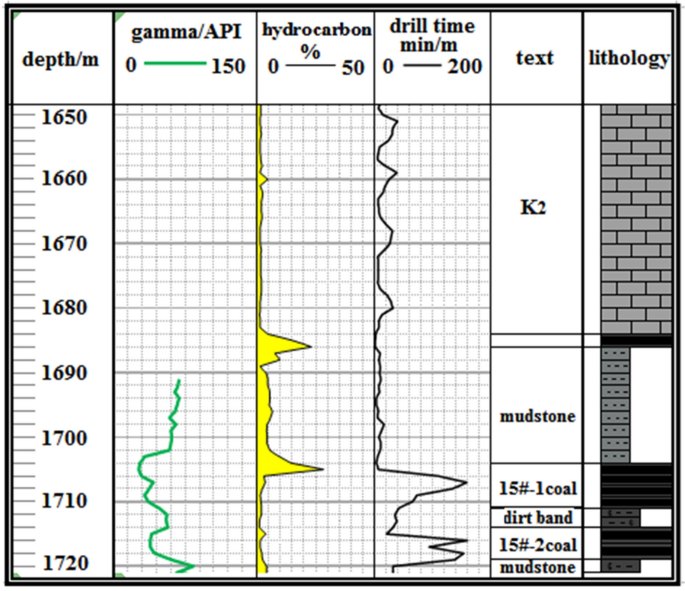
Characteristic parameters and lithology map of the marker layer, target, top, bottom layer.
The effect of two-dimensional resonance method
The horizontal section's overall drilling azimuth in the target coal seam is 200°. To identify minor faults in the coal seam azimuth direction, measurement points are arranged every 10 m from the landing point A to the final target point B along the 200° azimuth direction. Additionally, one exploration point is set every 20 m across the azimuth line perpendicular to the landing point A and 200° azimuth direction. Furthermore, exploration points are arranged 300 m along both sides of the landing point. Figure 8 shows the specific layout of the exploration points, where Line (L1) represents the 711 m long horizontal well section of the target coal seam in the 200° azimuth direction. Meanwhile, Line (L2) represents the 600 m long vertical section between the landing point A and L1. The obtained data from these exploration points are crucial in detecting potential faults and ensuring smooth drilling of the horizontal section of the coal seam. ultimately leading to improved drilling ratios and more efficient drilling.
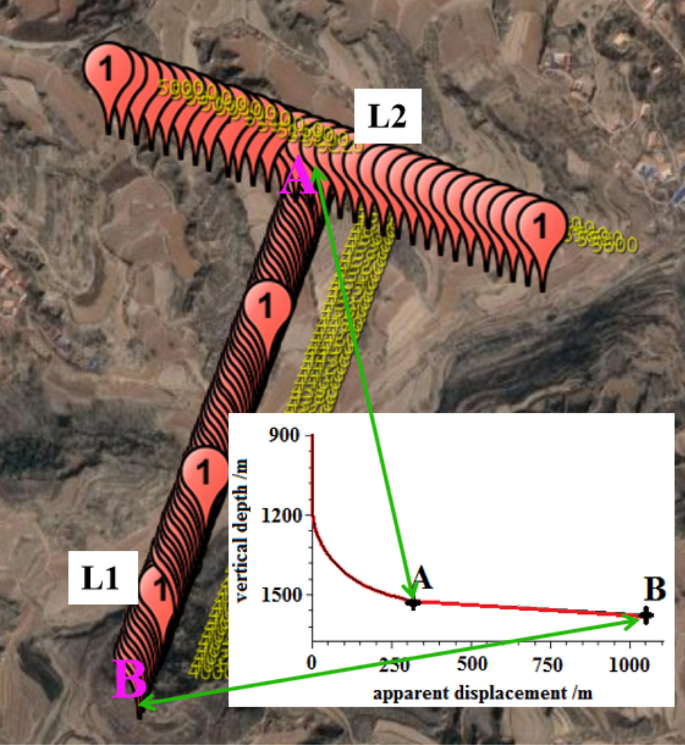
Two-dimensional resonance exploration layout points.
Figure 9 shows the seismic frequency resonance inversion profile. The trajectory of the designed horizontal section coincides with the ground position of L1, with the no.4700 measuring point located at the ground projection position of the A target point, and the no.4000 measuring point located at the ground projection position of the B target point. Based on the interpretation of seismic frequency resonance line L1 profile, it is observed that the burial depth of the coal seam on the horizontal well section from target A to target B of the no.15 coal seam in the direction of 200° azimuth is shallow in the northeast and deep in the southwest. The overall trend of the burial depth of the coal seam indicates a shallow-to-deep trend. Furthermore, three small faults are expected to be encountered while drilling along this azimuth direction, located at no.4700, no.4280 and no.4096 measuring points, respectively, with a fault distance of approximately 5–10 m.
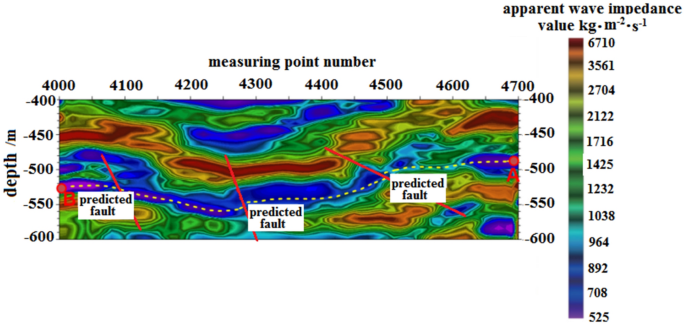
Design of horizontal section trajectory resonance exploration inversion profile.
The contour map of fault points found in the horizontal section is displayed in Fig. 10 . This map serves as a useful tool in guiding the vertical depth control of the horizontal section track.
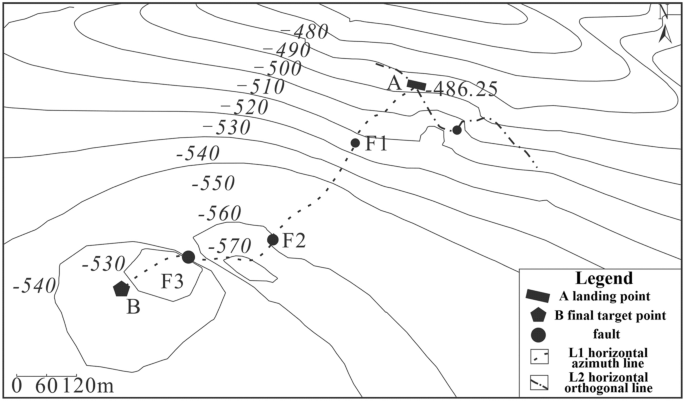
Contour map of fault points in the horizontal section.
To ensure that the drilling trajectory is within the target coal seam and to prevent any reduction in drilling ratio caused by the faults, it is necessary to optimize the well trajectory prior to drilling. Each fault point must be considered as a target point and their relative coordinate positions are presented in Table 3 .
Resonance exploration data is utilized to adjust the trajectory parameters every 10 to 20 m during the actual drilling process. This is before exploring the coal seam behind the fault following reasonable adjustment of the parameters. This method is simple and minimizes the length of the non-coal section during the coal chasing process after drilling through the fault. Based on the coordinate position of each target point, the design of the directional trajectory for the third well section is optimized, as shown in Fig. 11 .
optimized well trajectory for drilling reservoir section. ( a ) vertical section, ( b ) horizontal projection section.
The optimized design trajectory should be followed during actual drilling, ensuring that the dogleg degree ≤ 4°/30 m required by the management method for safe operations. Across the fault points F1, F2, and F3, the length of the non-coal section for coal tracking drilling was 56 m, 53 m, and 35 m, respectively. The total non-coal section for actual drilling was approximately 144 m, while achieving a drilling ratio of 80% for the target coal seam with an average thickness of 2.06 m. The entire drilling cycle takes approximately 45 days.
Azimuth gamma application
By analyzing the azimuth gamma data obtained during the drilling of the pilot hole and using the basic parameters of the pilot hole and formula ( 1 ), the apparent dip angle of the stratum near the designed landing point is determined to be α = 6.5°. The parameters of the landing point are shown in Fig. 12 , and the deviation angle of the actual main borehole trajectory of the second well section at the landing point β should be controlled at around 83.5° to ensure that the drilling ratio along the coal seam of the third well section is achieved and to reduce the frequency of directional trajectory adjustment.
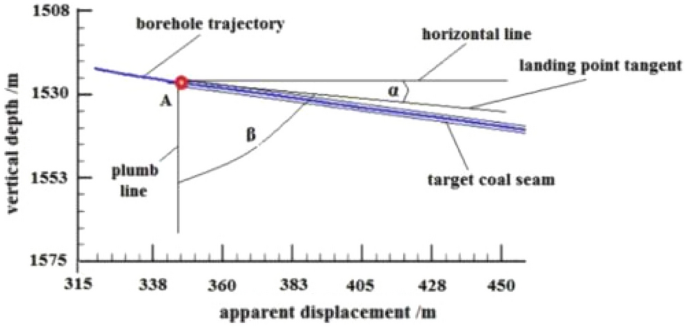
Parameters of the landing site.
During the drilling of the third horizontal section of Well-Q, a combination of Two-dimensional resonance exploration results and azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology was used to guide rapid coal tracking during the drilling of three faults. The process for each fault was as follows:
F1 Fault: The logging curve in Fig. 13 indicates that the F1 fault caused the drilling track of the 1920–1976 m well section to be drilled out from the coal seam roof. Geological logging revealed that the rock debris returning out of the hole bottom contained a large amount of mudstone. Based on the Two-dimensional resonance exploration inversion (Fig. 9 ) and fault contour (Fig. 10 ), the coal seam was traced by drilling with deviation correction through the lowering of well deviation. The actual drilling track during the pursuit of coal process is shown in Fig. 14 .
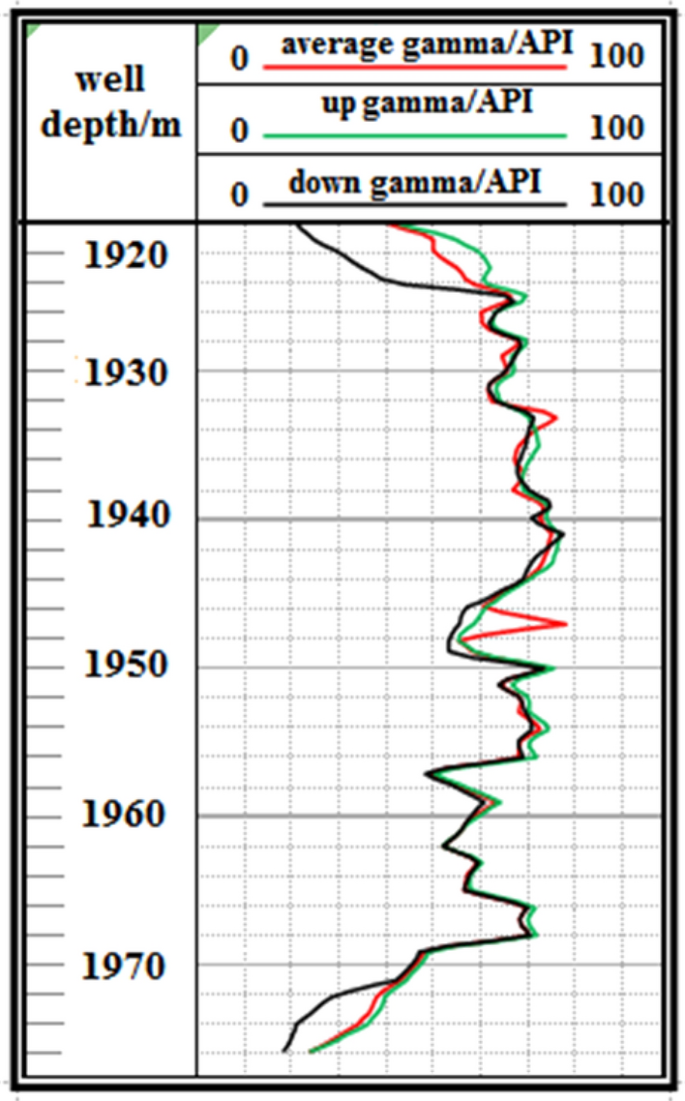
Non-coal seam section azimuth gamma logging curve crossing fault F 1 .
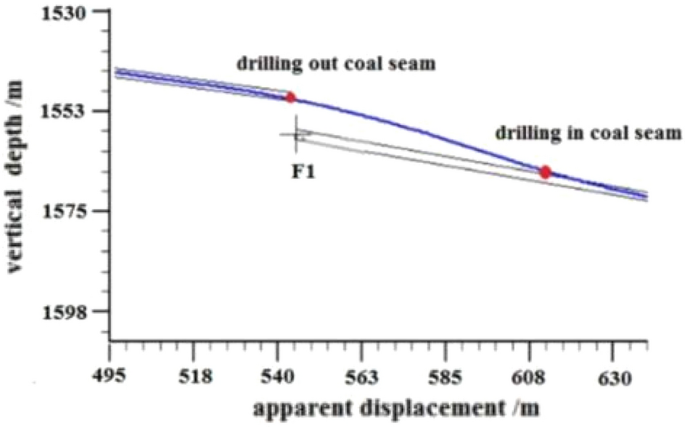
Actual drilling trajectory of fault F 1 in pursuit coal.
F2 Fault: The logging curve in Fig. 15 shows that the F2 fault caused the drilling trajectory of the 2130–2183 m well section to be drilled out from the coal seam roof. Geological logging revealed that the rock debris returning out of the hole bottom contained a large amount of mudstone. Based on the Two-dimensional resonance exploration inversion (Fig. 9 ), the back fault block of F2 fault in the direction of drilling trajectory of F2 fault shows a tendency of coal seam incline, so directly using lowering deviation correction drilling to trace the coal seam is not feasible and increases the length of the non-coal seam section. Therefore, the coal seam was pursued by increasing well deviation and rectifying drilling. The actual drilling track during the pursuit of coal process is shown in Fig. 16 .
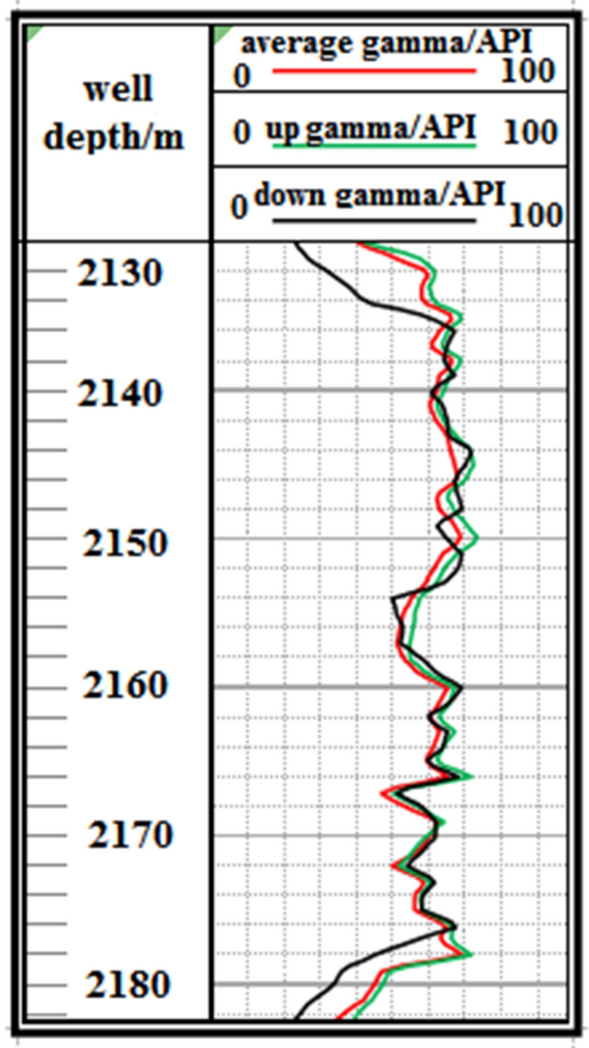
Non-coal seam section azimuth gamma logging curve crossing fault F 2 .
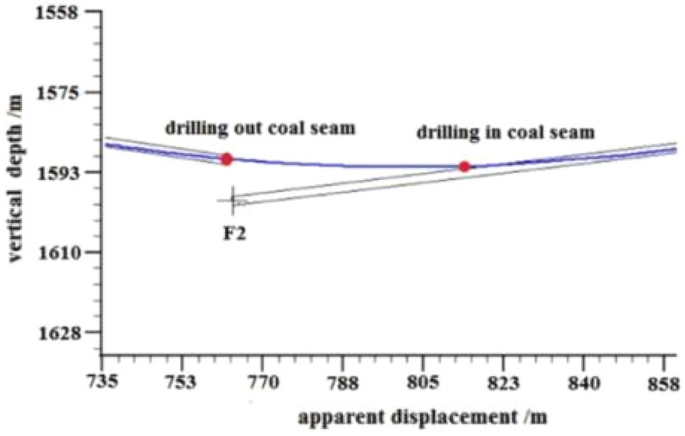
Actual drilling trajectory of fault F 2 in pursuit coal.
F3 Fault: The logging curve in Fig. 17 shows that the F3 fault caused the drilling trajectory of the 2315–2350 m well section to be drilled out from the coal seam roof floor. Geological logging revealed that the rock debris returning out of the hole bottom contained a large amount of carbonaceous mudstone. Using formula ( 1 ), the coal point well inclination angle was calculated as 96°. Based on the Two-dimensional resonance exploration inversion (Fig. 9 ) and fault contour (Fig. 10 ), the coal seam was pursued by slowly lowering the well inclination and correcting the deviation. The actual drilling track during the pursuit of coal process is shown in Fig. 18 . The well inclination angle was 91° upon returning back to the coal seam, after which drilling along the coal seam was continued normally.
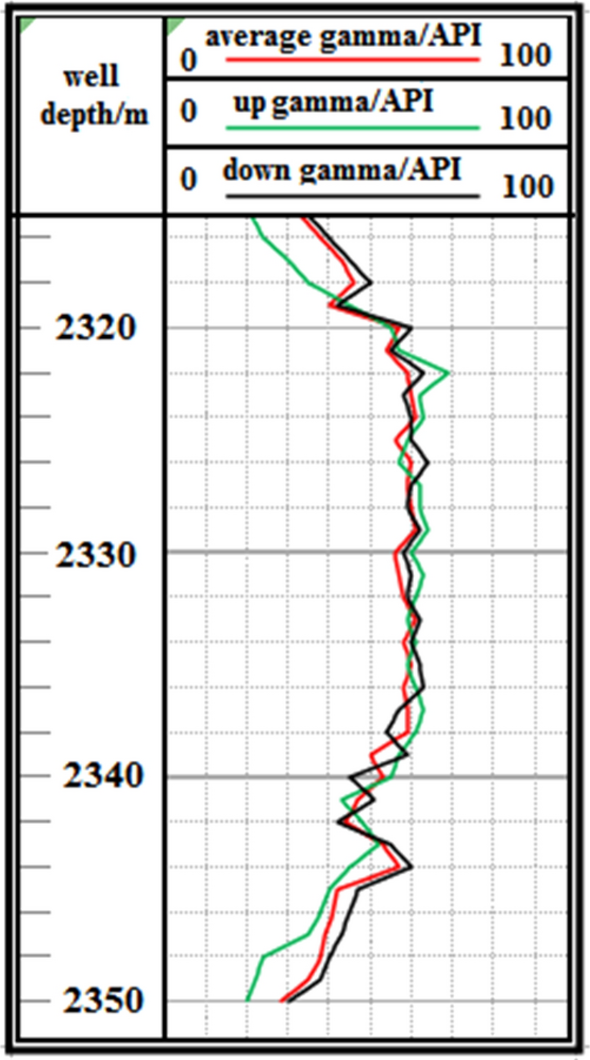
Non-coal seam section azimuth gamma logging curve crossing fault F 3 .
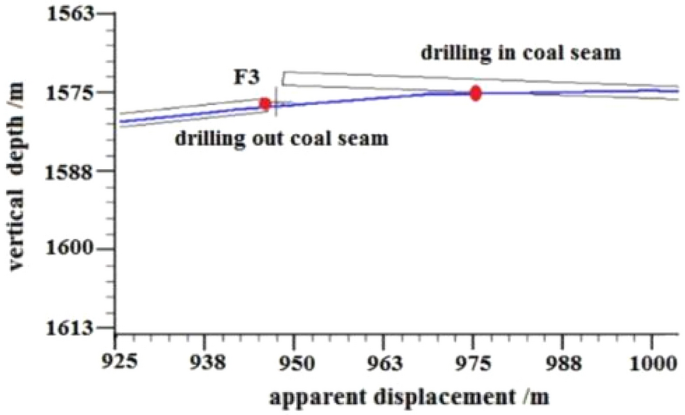
Actual drilling trajectory of fault F 3 in pursuit coal.
In conclusion, for the exploration block of CBM, the combined use of pilot hole drilling, two-dimensional resonance exploration technology, and azimuth gamma logging technology has proven effective in controlling the drilling of short-radius horizontal sections along the seam and ensuring the coal seam drilling ratio. Two major points can be drawn from this:
The two-dimensional resonance exploration technology detected the development of micro faults in the horizontal section of the drilling, enabling trajectory optimization before drilling. The azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology monitored the current drill bit drilling horizon in real-time, ensuring timely and accurate well trajectory adjustment.
The comprehensive use of these technologies has led to a 20% improvement in the coal seam drilling ratio and a 25% reduction in drilling cycle time in tested short-radius wells in the new exploration and development block-W in Qinshui Basin. This provides technical experience for low-cost exploration and development of CBM in new blocks.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Sun, W. L., Chen, Z. Y., Chen, X., Wang, S. H. & Fu, X. Y. Geological features and resource potentials of coalbed methane basins in China. Oil Gas Geol. 26 (2), 141–146 (2005).
Google Scholar
Qin, Y. Evaluation and production technology of coalbed methane reservoir. China University of Mining and Technology Press, (1996).
Men, X. Y., Han, Z., Gong, H. J. & Wang, X. Y. Challenges and opportunities of CBM exploration and development in China under new situations. Nat. Gas. Ind. 38 (09), 10–16 (2018).
Zhang, P. Y., Sun, J. M. & Cheng, Z. G. Application of azimuthal gamma ray imaging logging while drilling to geosteering in horizontal wells of H area, Ordos Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 21 (23), 9713–9724 (2021).
Dai, Y. J., Li, S. Q., Xia, L. Y., Li, J. X. & Lv, Y. A CBM development well type optimization method based on the long-run marginal cost. Nat. Gas. Ind. 38 (07), 113–119 (2018).
CAS Google Scholar
Liu, Y. K., Wang, F. J., Tang, H. M. & Liang, S. Well type and pattern optimization method based on fine numerical simulation in coalbed methane reservoir. Environ. Earth Sci. 73 (10), 5877–5890 (2015).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar
Jia, H. M., Hu, Q. J., Fan, B., Mao, C. H. & Zhang, Q. Causes for low CBM production of vertical wells and efficient development technology in northern Zhengzhuang Block in Qinshui Basin. Coal Geol. Explor. 49 (2), 34–42 (2021).
Liu, C. C., Jia, H. M., Mao, S. F., Cui, X. R. & Peng, H. The development characteristics and main control factors of the open-hole multi-branch CBM horizontal wells. Coal Geol. Explor. 46 (5), 140–145 (2018).
Huang, W. et al. Construction technologies and stimulation of U-shape well for CBM development—with 2014ZX-U-05V/H well of coal 15 in SiHe mine as an example. Coal Geol. Explor. 43 (6), 133–136 (2015).
Hu, Q. J. et al. Discussion of the geological adaptability of coal-bed methane horizontal wells of high-rank coal formation in southern Qinshui Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 44 (4), 1178–1187 (2019).
Liu, C. C., Jia, H. M. & Mao, S. F. The development characteristics and main control factors of the open-hole multi-branch CBM horizontal wells. Coal Geol. Explor. 46 (5), 140–145 (2018).
Wang, L., Li, L., Sheng, L. M., Dou, X. R. & Zhang, L. C. Electromagnetic wave DREMWD system and its field test. Oil Drill Prod. Technol. 35 (02), 20–23 (2013).
Pang, Q., Feng, Q. H., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y. Y. & Peng, X. H. The application of three-dimensional geological modeling technology in horizontal well geologic steering: A case from X3–8 horizontal well development zone. Nat. Gas Geosci. 28 (3), 473–478 (2017).
Song, H. B. et al. Controlling geological factors and coalbed methane enrichment areas in Southern Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 46 (12), 3974–3987 (2019).
Liu, C. H., Liu, S. C., Yan, S., Liu, Y. & Su, L. Application of integrated geophysical exploration techniques to detecting shallow coal gob. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 8 (1), 51–54 (2021).
Zhang, Q. Key technologies for drilling and completion of No.15 coal L-shaped horizontal well in Zhengzhuang block. Qinshui Basin. Coal Eng. 53 (11), 61–66 (2021).
Xue, A. M., Li, D., Song, H. X. & Zhang, A. J. Image the earth with the frequency resonance effect of vibration noise. Geol. Rev. 65 (supplement1), 47–48 (2021).
Li, H. et al. Application of shallow seismic exploration combining mixed source surface waves and three-component frequency resonance method in fine detection of urban shallow geological structure. Prog. Geophys. 35 (3), 1149–1155 (2020).
Liu, X. G., Li, J. F., Zhang, Q. & Zhang, J. Practice of accurate control technology for multi-branch horizontal grouting well trajectory of coal seam floor limestone reinforcement in Zhaogu No.1 Mine. Saf. Coal Mines 52 (11), 100–103 (2021).
Zhu, C. C. & Li, H. Application of seismic frequency resonance technique in goaf detection of heavy-cover coal seams. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 18 (5), 774–779 (2021).
Du, Z. Q., Hao, Y. L., Zhang, G. L., Yang, Z. B. & Lu, D. The application of the azimuth gamma logging while drilling for the geosteering in the horizontal wells in Jidong Oil field. Mud. Logging Eng. 19 (1), 18–21 (2008).
Tang, H. Q. Image processing method of LWD azimuthal gamma data. Lithol. Reserv. 29 (1), 110–115 (2017).
Zheng, Y. T., Fang, F., Wu, J. P., Li, J. B. & Zhang, W. Development and application of near-bit gamma-ray imaging system during drilling. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 44 (3), 70–76 (2020).
Liu, X. P., Fang, J. & Jin, Y. H. Application status and prospect of LWD data transmission technology. Well Logging Technol. 32 (3), 249–253 (2008).
Sun, D. J. & Sun, L. Application of geosteering technology in construction of CBM horizontal well. Coal Geol. Explor. 43 (02), 106–108 (2015).
Zhang, J. Q. et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method in detecting goaf of thick overburden coal mine. Geol. Rev. 65 (supplement1), 52–54 (2021).
Wu, C. L. Application of azimuth gamma in coal bed methane horizontal wells. J. Drill. Eng. 48 (5), 69–75 (2021).
Chen, G., Wang, K. B., Jiang, B. C. & Wang, X. L. Comparison and application of LWD lithology identification method. Coal Geol. Explor. 46 (01), 165–169 (2018).
Liu, H. B., Fan, Z. X. & Gao, M. Study on decreasing the azimuth drift in the directional well. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field. 2 (10), 80–82 (2003).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The financial support by the Found of the National Key Research and Development Program and Key Special Fund Project (No.2018YFC0808202) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, 100083, China
Xiugang Liu & Zaibing Jiang
China Coal Research Institute, Beijing, 100013, China
Xi’an Research Institute Co. Ltd., China Coal Technology and Engineering Group Corp., Xi’an, 710077, China
Xiugang Liu, Zaibing Jiang, Yi Wang, Haitao Mo, Haozhe Li & Jianlei Guo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
X.L. conceived the study and, together with Z.J., Y.W., and H.M. did the literature search, selected the studies. X.L. and H.L. extracted the relevant information. X.L. synthesised the data. J.G. drawed pictures. X.L.and Z.J.wrote the first drafts of the paper.Y.W.and H.M.critically revised successive drafs of the paper. All authors approved the final drafts of the manuscript. X.L. is the guarantor of the study.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiugang Liu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Liu, X., Jiang, Z., Wang, Y. et al. Research on trajectory control technology for L-shaped horizontal exploration wells in coalbed methane. Sci Rep 14 , 11343 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60550-4
Download citation
Received : 17 January 2024
Accepted : 24 April 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60550-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coalbed methane (CBM)
- Short-radius wells
- Trajectory control
- Azimuth gamma logging while drilling (LWD)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Developing a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD): a mixed method modified e-Delphi study
- Jocelyn Schroeder 1 ,
- Barbara Pesut 1 , 2 ,
- Lise Olsen 2 ,
- Nelly D. Oelke 2 &
- Helen Sharp 2
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 326 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
150 Accesses
Metrics details
Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) was legalized in Canada in 2016. Canada’s legislation is the first to permit Nurse Practitioners (NP) to serve as independent MAiD assessors and providers. Registered Nurses’ (RN) also have important roles in MAiD that include MAiD care coordination; client and family teaching and support, MAiD procedural quality; healthcare provider and public education; and bereavement care for family. Nurses have a right under the law to conscientious objection to participating in MAiD. Therefore, it is essential to prepare nurses in their entry-level education for the practice implications and moral complexities inherent in this practice. Knowing what nursing students think about MAiD is a critical first step. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to develop a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in MAiD in the Canadian context.
The design was a mixed-method, modified e-Delphi method that entailed item generation from the literature, item refinement through a 2 round survey of an expert faculty panel, and item validation through a cognitive focus group interview with nursing students. The settings were a University located in an urban area and a College located in a rural area in Western Canada.
During phase 1, a 56-item survey was developed from existing literature that included demographic items and items designed to measure experience with death and dying (including MAiD), education and preparation, attitudes and beliefs, influences on those beliefs, and anticipated future involvement. During phase 2, an expert faculty panel reviewed, modified, and prioritized the items yielding 51 items. During phase 3, a sample of nursing students further evaluated and modified the language in the survey to aid readability and comprehension. The final survey consists of 45 items including 4 case studies.
Systematic evaluation of knowledge-to-date coupled with stakeholder perspectives supports robust survey design. This study yielded a survey to assess nursing students’ attitudes toward MAiD in a Canadian context.
The survey is appropriate for use in education and research to measure knowledge and attitudes about MAiD among nurse trainees and can be a helpful step in preparing nursing students for entry-level practice.
Peer Review reports
Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) is permitted under an amendment to Canada’s Criminal Code which was passed in 2016 [ 1 ]. MAiD is defined in the legislation as both self-administered and clinician-administered medication for the purpose of causing death. In the 2016 Bill C-14 legislation one of the eligibility criteria was that an applicant for MAiD must have a reasonably foreseeable natural death although this term was not defined. It was left to the clinical judgement of MAiD assessors and providers to determine the time frame that constitutes reasonably foreseeable [ 2 ]. However, in 2021 under Bill C-7, the eligibility criteria for MAiD were changed to allow individuals with irreversible medical conditions, declining health, and suffering, but whose natural death was not reasonably foreseeable, to receive MAiD [ 3 ]. This population of MAiD applicants are referred to as Track 2 MAiD (those whose natural death is foreseeable are referred to as Track 1). Track 2 applicants are subject to additional safeguards under the 2021 C-7 legislation.
Three additional proposed changes to the legislation have been extensively studied by Canadian Expert Panels (Council of Canadian Academics [CCA]) [ 4 , 5 , 6 ] First, under the legislation that defines Track 2, individuals with mental disease as their sole underlying medical condition may apply for MAiD, but implementation of this practice is embargoed until March 2027 [ 4 ]. Second, there is consideration of allowing MAiD to be implemented through advanced consent. This would make it possible for persons living with dementia to receive MAID after they have lost the capacity to consent to the procedure [ 5 ]. Third, there is consideration of extending MAiD to mature minors. A mature minor is defined as “a person under the age of majority…and who has the capacity to understand and appreciate the nature and consequences of a decision” ([ 6 ] p. 5). In summary, since the legalization of MAiD in 2016 the eligibility criteria and safeguards have evolved significantly with consequent implications for nurses and nursing care. Further, the number of Canadians who access MAiD shows steady increases since 2016 [ 7 ] and it is expected that these increases will continue in the foreseeable future.
Nurses have been integral to MAiD care in the Canadian context. While other countries such as Belgium and the Netherlands also permit euthanasia, Canada is the first country to allow Nurse Practitioners (Registered Nurses with additional preparation typically achieved at the graduate level) to act independently as assessors and providers of MAiD [ 1 ]. Although the role of Registered Nurses (RNs) in MAiD is not defined in federal legislation, it has been addressed at the provincial/territorial-level with variability in scope of practice by region [ 8 , 9 ]. For example, there are differences with respect to the obligation of the nurse to provide information to patients about MAiD, and to the degree that nurses are expected to ensure that patient eligibility criteria and safeguards are met prior to their participation [ 10 ]. Studies conducted in the Canadian context indicate that RNs perform essential roles in MAiD care coordination; client and family teaching and support; MAiD procedural quality; healthcare provider and public education; and bereavement care for family [ 9 , 11 ]. Nurse practitioners and RNs are integral to a robust MAiD care system in Canada and hence need to be well-prepared for their role [ 12 ].
Previous studies have found that end of life care, and MAiD specifically, raise complex moral and ethical issues for nurses [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. The knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs of nurses are important across practice settings because nurses have consistent, ongoing, and direct contact with patients who experience chronic or life-limiting health conditions. Canadian studies exploring nurses’ moral and ethical decision-making in relation to MAiD reveal that although some nurses are clear in their support for, or opposition to, MAiD, others are unclear on what they believe to be good and right [ 14 ]. Empirical findings suggest that nurses go through a period of moral sense-making that is often informed by their family, peers, and initial experiences with MAID [ 17 , 18 ]. Canadian legislation and policy specifies that nurses are not required to participate in MAiD and may recuse themselves as conscientious objectors with appropriate steps to ensure ongoing and safe care of patients [ 1 , 19 ]. However, with so many nurses having to reflect on and make sense of their moral position, it is essential that they are given adequate time and preparation to make an informed and thoughtful decision before they participate in a MAID death [ 20 , 21 ].
It is well established that nursing students receive inconsistent exposure to end of life care issues [ 22 ] and little or no training related to MAiD [ 23 ]. Without such education and reflection time in pre-entry nursing preparation, nurses are at significant risk for moral harm. An important first step in providing this preparation is to be able to assess the knowledge, values, and beliefs of nursing students regarding MAID and end of life care. As demand for MAiD increases along with the complexities of MAiD, it is critical to understand the knowledge, attitudes, and likelihood of engagement with MAiD among nursing students as a baseline upon which to build curriculum and as a means to track these variables over time.
Aim, design, and setting
The aim of this study was to develop a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in MAiD in the Canadian context. We sought to explore both their willingness to be involved in the registered nursing role and in the nurse practitioner role should they chose to prepare themselves to that level of education. The design was a mixed-method, modified e-Delphi method that entailed item generation, item refinement through an expert faculty panel [ 24 , 25 , 26 ], and initial item validation through a cognitive focus group interview with nursing students [ 27 ]. The settings were a University located in an urban area and a College located in a rural area in Western Canada.
Participants
A panel of 10 faculty from the two nursing education programs were recruited for Phase 2 of the e-Delphi. To be included, faculty were required to have a minimum of three years of experience in nurse education, be employed as nursing faculty, and self-identify as having experience with MAiD. A convenience sample of 5 fourth-year nursing students were recruited to participate in Phase 3. Students had to be in good standing in the nursing program and be willing to share their experiences of the survey in an online group interview format.
The modified e-Delphi was conducted in 3 phases: Phase 1 entailed item generation through literature and existing survey review. Phase 2 entailed item refinement through a faculty expert panel review with focus on content validity, prioritization, and revision of item wording [ 25 ]. Phase 3 entailed an assessment of face validity through focus group-based cognitive interview with nursing students.
Phase I. Item generation through literature review
The goal of phase 1 was to develop a bank of survey items that would represent the variables of interest and which could be provided to expert faculty in Phase 2. Initial survey items were generated through a literature review of similar surveys designed to assess knowledge and attitudes toward MAiD/euthanasia in healthcare providers; Canadian empirical studies on nurses’ roles and/or experiences with MAiD; and legislative and expert panel documents that outlined proposed changes to the legislative eligibility criteria and safeguards. The literature review was conducted in three online databases: CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Medline. Key words for the search included nurses , nursing students , medical students , NPs, MAiD , euthanasia , assisted death , and end-of-life care . Only articles written in English were reviewed. The legalization and legislation of MAiD is new in many countries; therefore, studies that were greater than twenty years old were excluded, no further exclusion criteria set for country.
Items from surveys designed to measure similar variables in other health care providers and geographic contexts were placed in a table and similar items were collated and revised into a single item. Then key variables were identified from the empirical literature on nurses and MAiD in Canada and checked against the items derived from the surveys to ensure that each of the key variables were represented. For example, conscientious objection has figured prominently in the Canadian literature, but there were few items that assessed knowledge of conscientious objection in other surveys and so items were added [ 15 , 21 , 28 , 29 ]. Finally, four case studies were added to the survey to address the anticipated changes to the Canadian legislation. The case studies were based upon the inclusion of mature minors, advanced consent, and mental disorder as the sole underlying medical condition. The intention was to assess nurses’ beliefs and comfort with these potential legislative changes.
Phase 2. Item refinement through expert panel review
The goal of phase 2 was to refine and prioritize the proposed survey items identified in phase 1 using a modified e-Delphi approach to achieve consensus among an expert panel [ 26 ]. Items from phase 1 were presented to an expert faculty panel using a Qualtrics (Provo, UT) online survey. Panel members were asked to review each item to determine if it should be: included, excluded or adapted for the survey. When adapted was selected faculty experts were asked to provide rationale and suggestions for adaptation through the use of an open text box. Items that reached a level of 75% consensus for either inclusion or adaptation were retained [ 25 , 26 ]. New items were categorized and added, and a revised survey was presented to the panel of experts in round 2. Panel members were again asked to review items, including new items, to determine if it should be: included, excluded, or adapted for the survey. Round 2 of the modified e-Delphi approach also included an item prioritization activity, where participants were then asked to rate the importance of each item, based on a 5-point Likert scale (low to high importance), which De Vaus [ 30 ] states is helpful for increasing the reliability of responses. Items that reached a 75% consensus on inclusion were then considered in relation to the importance it was given by the expert panel. Quantitative data were managed using SPSS (IBM Corp).
Phase 3. Face validity through cognitive interviews with nursing students
The goal of phase 3 was to obtain initial face validity of the proposed survey using a sample of nursing student informants. More specifically, student participants were asked to discuss how items were interpreted, to identify confusing wording or other problematic construction of items, and to provide feedback about the survey as a whole including readability and organization [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. The focus group was held online and audio recorded. A semi-structured interview guide was developed for this study that focused on clarity, meaning, order and wording of questions; emotions evoked by the questions; and overall survey cohesion and length was used to obtain data (see Supplementary Material 2 for the interview guide). A prompt to “think aloud” was used to limit interviewer-imposed bias and encourage participants to describe their thoughts and response to a given item as they reviewed survey items [ 27 ]. Where needed, verbal probes such as “could you expand on that” were used to encourage participants to expand on their responses [ 27 ]. Student participants’ feedback was collated verbatim and presented to the research team where potential survey modifications were negotiated and finalized among team members. Conventional content analysis [ 34 ] of focus group data was conducted to identify key themes that emerged through discussion with students. Themes were derived from the data by grouping common responses and then using those common responses to modify survey items.
Ten nursing faculty participated in the expert panel. Eight of the 10 faculty self-identified as female. No faculty panel members reported conscientious objector status and ninety percent reported general agreement with MAiD with one respondent who indicated their view as “unsure.” Six of the 10 faculty experts had 16 years of experience or more working as a nurse educator.
Five nursing students participated in the cognitive interview focus group. The duration of the focus group was 2.5 h. All participants identified that they were born in Canada, self-identified as female (one preferred not to say) and reported having received some instruction about MAiD as part of their nursing curriculum. See Tables 1 and 2 for the demographic descriptors of the study sample. Study results will be reported in accordance with the study phases. See Fig. 1 for an overview of the results from each phase.
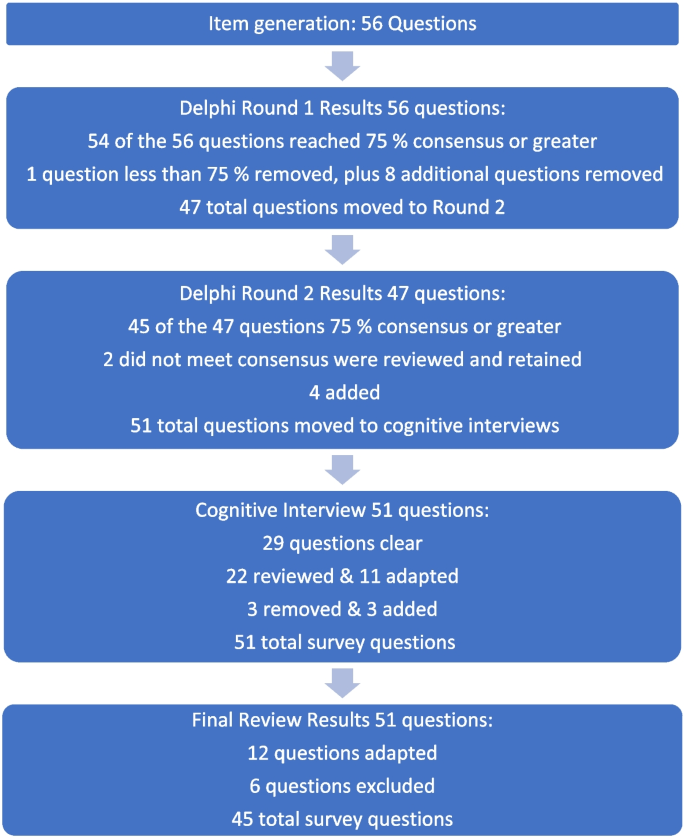
Fig. 1 Overview of survey development findings
Phase 1: survey item generation
Review of the literature identified that no existing survey was available for use with nursing students in the Canadian context. However, an analysis of themes across qualitative and quantitative studies of physicians, medical students, nurses, and nursing students provided sufficient data to develop a preliminary set of items suitable for adaptation to a population of nursing students.
Four major themes and factors that influence knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about MAiD were evident from the literature: (i) endogenous or individual factors such as age, gender, personally held values, religion, religiosity, and/or spirituality [ 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ], (ii) experience with death and dying in personal and/or professional life [ 35 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 44 , 45 ], (iii) training including curricular instruction about clinical role, scope of practice, or the law [ 23 , 36 , 39 ], and (iv) exogenous or social factors such as the influence of key leaders, colleagues, friends and/or family, professional and licensure organizations, support within professional settings, and/or engagement in MAiD in an interdisciplinary team context [ 9 , 35 , 46 ].
Studies of nursing students also suggest overlap across these categories. For example, value for patient autonomy [ 23 ] and the moral complexity of decision-making [ 37 ] are important factors that contribute to attitudes about MAiD and may stem from a blend of personally held values coupled with curricular content, professional training and norms, and clinical exposure. For example, students report that participation in end of life care allows for personal growth, shifts in perception, and opportunities to build therapeutic relationships with their clients [ 44 , 47 , 48 ].
Preliminary items generated from the literature resulted in 56 questions from 11 published sources (See Table 3 ). These items were constructed across four main categories: (i) socio-demographic questions; (ii) end of life care questions; (iii) knowledge about MAiD; or (iv) comfort and willingness to participate in MAiD. Knowledge questions were refined to reflect current MAiD legislation, policies, and regulatory frameworks. Falconer [ 39 ] and Freeman [ 45 ] studies were foundational sources for item selection. Additionally, four case studies were written to reflect the most recent anticipated changes to MAiD legislation and all used the same open-ended core questions to address respondents’ perspectives about the patient’s right to make the decision, comfort in assisting a physician or NP to administer MAiD in that scenario, and hypothesized comfort about serving as a primary provider if qualified as an NP in future. Response options for the survey were also constructed during this stage and included: open text, categorical, yes/no , and Likert scales.
Phase 2: faculty expert panel review
Of the 56 items presented to the faculty panel, 54 questions reached 75% consensus. However, based upon the qualitative responses 9 items were removed largely because they were felt to be repetitive. Items that generated the most controversy were related to measuring religion and spirituality in the Canadian context, defining end of life care when there is no agreed upon time frames (e.g., last days, months, or years), and predicting willingness to be involved in a future events – thus predicting their future selves. Phase 2, round 1 resulted in an initial set of 47 items which were then presented back to the faculty panel in round 2.
Of the 47 initial questions presented to the panel in round 2, 45 reached a level of consensus of 75% or greater, and 34 of these questions reached a level of 100% consensus [ 27 ] of which all participants chose to include without any adaptations) For each question, level of importance was determined based on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = very unimportant, 2 = somewhat unimportant, 3 = neutral, 4 = somewhat important, and 5 = very important). Figure 2 provides an overview of the level of importance assigned to each item.
Ranking level of importance for survey items
After round 2, a careful analysis of participant comments and level of importance was completed by the research team. While the main method of survey item development came from participants’ response to the first round of Delphi consensus ratings, level of importance was used to assist in the decision of whether to keep or modify questions that created controversy, or that rated lower in the include/exclude/adapt portion of the Delphi. Survey items that rated low in level of importance included questions about future roles, sex and gender, and religion/spirituality. After deliberation by the research committee, these questions were retained in the survey based upon the importance of these variables in the scientific literature.
Of the 47 questions remaining from Phase 2, round 2, four were revised. In addition, the two questions that did not meet the 75% cut off level for consensus were reviewed by the research team. The first question reviewed was What is your comfort level with providing a MAiD death in the future if you were a qualified NP ? Based on a review of participant comments, it was decided to retain this question for the cognitive interviews with students in the final phase of testing. The second question asked about impacts on respondents’ views of MAiD and was changed from one item with 4 subcategories into 4 separate items, resulting in a final total of 51 items for phase 3. The revised survey was then brought forward to the cognitive interviews with student participants in Phase 3. (see Supplementary Material 1 for a complete description of item modification during round 2).
Phase 3. Outcomes of cognitive interview focus group
Of the 51 items reviewed by student participants, 29 were identified as clear with little or no discussion. Participant comments for the remaining 22 questions were noted and verified against the audio recording. Following content analysis of the comments, four key themes emerged through the student discussion: unclear or ambiguous wording; difficult to answer questions; need for additional response options; and emotional response evoked by questions. An example of unclear or ambiguous wording was a request for clarity in the use of the word “sufficient” in the context of assessing an item that read “My nursing education has provided sufficient content about the nursing role in MAiD.” “Sufficient” was viewed as subjective and “laden with…complexity that distracted me from the question.” The group recommended rewording the item to read “My nursing education has provided enough content for me to care for a patient considering or requesting MAiD.”
An example of having difficulty answering questions related to limited knowledge related to terms used in the legislation such as such as safeguards , mature minor , eligibility criteria , and conscientious objection. Students were unclear about what these words meant relative to the legislation and indicated that this lack of clarity would hamper appropriate responses to the survey. To ensure that respondents are able to answer relevant questions, student participants recommended that the final survey include explanation of key terms such as mature minor and conscientious objection and an overview of current legislation.
Response options were also a point of discussion. Participants noted a lack of distinction between response options of unsure and unable to say . Additionally, scaling of attitudes was noted as important since perspectives about MAiD are dynamic and not dichotomous “agree or disagree” responses. Although the faculty expert panel recommended the integration of the demographic variables of religious and/or spiritual remain as a single item, the student group stated a preference to have religion and spirituality appear as separate items. The student focus group also took issue with separate items for the variables of sex and gender, specifically that non-binary respondents might feel othered or “outed” particularly when asked to identify their sex. These variables had been created based upon best practices in health research but students did not feel they were appropriate in this context [ 49 ]. Finally, students agreed with the faculty expert panel in terms of the complexity of projecting their future involvement as a Nurse Practitioner. One participant stated: “I certainly had to like, whoa, whoa, whoa. Now let me finish this degree first, please.” Another stated, “I'm still imagining myself, my future career as an RN.”
Finally, student participants acknowledged the array of emotions that some of the items produced for them. For example, one student described positive feelings when interacting with the survey. “Brought me a little bit of feeling of joy. Like it reminded me that this is the last piece of independence that people grab on to.” Another participant, described the freedom that the idea of an advance request gave her. “The advance request gives the most comfort for me, just with early onset Alzheimer’s and knowing what it can do.” But other participants described less positive feelings. For example, the mature minor case study yielded a comment: “This whole scenario just made my heart hurt with the idea of a child requesting that.”
Based on the data gathered from the cognitive interview focus group of nursing students, revisions were made to 11 closed-ended questions (see Table 4 ) and 3 items were excluded. In the four case studies, the open-ended question related to a respondents’ hypothesized actions in a future role as NP were removed. The final survey consists of 45 items including 4 case studies (see Supplementary Material 3 ).
The aim of this study was to develop and validate a survey that can be used to track the growth of knowledge about MAiD among nursing students over time, inform training programs about curricular needs, and evaluate attitudes and willingness to participate in MAiD at time-points during training or across nursing programs over time.
The faculty expert panel and student participants in the cognitive interview focus group identified a need to establish core knowledge of the terminology and legislative rules related to MAiD. For example, within the cognitive interview group of student participants, several acknowledged lack of clear understanding of specific terms such as “conscientious objector” and “safeguards.” Participants acknowledged discomfort with the uncertainty of not knowing and their inclination to look up these terms to assist with answering the questions. This survey can be administered to nursing or pre-nursing students at any phase of their training within a program or across training programs. However, in doing so it is important to acknowledge that their baseline knowledge of MAiD will vary. A response option of “not sure” is important and provides a means for respondents to convey uncertainty. If this survey is used to inform curricular needs, respondents should be given explicit instructions not to conduct online searches to inform their responses, but rather to provide an honest appraisal of their current knowledge and these instructions are included in the survey (see Supplementary Material 3 ).
Some provincial regulatory bodies have established core competencies for entry-level nurses that include MAiD. For example, the BC College of Nurses and Midwives (BCCNM) requires “knowledge about ethical, legal, and regulatory implications of medical assistance in dying (MAiD) when providing nursing care.” (10 p. 6) However, across Canada curricular content and coverage related to end of life care and MAiD is variable [ 23 ]. Given the dynamic nature of the legislation that includes portions of the law that are embargoed until 2024, it is important to ensure that respondents are guided by current and accurate information. As the law changes, nursing curricula, and public attitudes continue to evolve, inclusion of core knowledge and content is essential and relevant for investigators to be able to interpret the portions of the survey focused on attitudes and beliefs about MAiD. Content knowledge portions of the survey may need to be modified over time as legislation and training change and to meet the specific purposes of the investigator.
Given the sensitive nature of the topic, it is strongly recommended that surveys be conducted anonymously and that students be provided with an opportunity to discuss their responses to the survey. A majority of feedback from both the expert panel of faculty and from student participants related to the wording and inclusion of demographic variables, in particular religion, religiosity, gender identity, and sex assigned at birth. These and other demographic variables have the potential to be highly identifying in small samples. In any instance in which the survey could be expected to yield demographic group sizes less than 5, users should eliminate the demographic variables from the survey. For example, the profession of nursing is highly dominated by females with over 90% of nurses who identify as female [ 50 ]. Thus, a survey within a single class of students or even across classes in a single institution is likely to yield a small number of male respondents and/or respondents who report a difference between sex assigned at birth and gender identity. When variables that serve to identify respondents are included, respondents are less likely to complete or submit the survey, to obscure their responses so as not to be identifiable, or to be influenced by social desirability bias in their responses rather than to convey their attitudes accurately [ 51 ]. Further, small samples do not allow for conclusive analyses or interpretation of apparent group differences. Although these variables are often included in surveys, such demographics should be included only when anonymity can be sustained. In small and/or known samples, highly identifying variables should be omitted.
There are several limitations associated with the development of this survey. The expert panel was comprised of faculty who teach nursing students and are knowledgeable about MAiD and curricular content, however none identified as a conscientious objector to MAiD. Ideally, our expert panel would have included one or more conscientious objectors to MAiD to provide a broader perspective. Review by practitioners who participate in MAiD, those who are neutral or undecided, and practitioners who are conscientious objectors would ensure broad applicability of the survey. This study included one student cognitive interview focus group with 5 self-selected participants. All student participants had held discussions about end of life care with at least one patient, 4 of 5 participants had worked with a patient who requested MAiD, and one had been present for a MAiD death. It is not clear that these participants are representative of nursing students demographically or by experience with end of life care. It is possible that the students who elected to participate hold perspectives and reflections on patient care and MAiD that differ from students with little or no exposure to end of life care and/or MAiD. However, previous studies find that most nursing students have been involved with end of life care including meaningful discussions about patients’ preferences and care needs during their education [ 40 , 44 , 47 , 48 , 52 ]. Data collection with additional student focus groups with students early in their training and drawn from other training contexts would contribute to further validation of survey items.
Future studies should incorporate pilot testing with small sample of nursing students followed by a larger cross-program sample to allow evaluation of the psychometric properties of specific items and further refinement of the survey tool. Consistent with literature about the importance of leadership in the context of MAiD [ 12 , 53 , 54 ], a study of faculty knowledge, beliefs, and attitudes toward MAiD would provide context for understanding student perspectives within and across programs. Additional research is also needed to understand the timing and content coverage of MAiD across Canadian nurse training programs’ curricula.
The implementation of MAiD is complex and requires understanding of the perspectives of multiple stakeholders. Within the field of nursing this includes clinical providers, educators, and students who will deliver clinical care. A survey to assess nursing students’ attitudes toward and willingness to participate in MAiD in the Canadian context is timely, due to the legislation enacted in 2016 and subsequent modifications to the law in 2021 with portions of the law to be enacted in 2027. Further development of this survey could be undertaken to allow for use in settings with practicing nurses or to allow longitudinal follow up with students as they enter practice. As the Canadian landscape changes, ongoing assessment of the perspectives and needs of health professionals and students in the health professions is needed to inform policy makers, leaders in practice, curricular needs, and to monitor changes in attitudes and practice patterns over time.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to small sample sizes, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
British Columbia College of Nurses and Midwives
Medical assistance in dying
Nurse practitioner
Registered nurse
University of British Columbia Okanagan
Nicol J, Tiedemann M. Legislative Summary: Bill C-14: An Act to amend the Criminal Code and to make related amendments to other Acts (medical assistance in dying). Available from: https://lop.parl.ca/staticfiles/PublicWebsite/Home/ResearchPublications/LegislativeSummaries/PDF/42-1/c14-e.pdf .
Downie J, Scallion K. Foreseeably unclear. The meaning of the “reasonably foreseeable” criterion for access to medical assistance in dying in Canada. Dalhousie Law J. 2018;41(1):23–57.
Nicol J, Tiedeman M. Legislative summary of Bill C-7: an act to amend the criminal code (medical assistance in dying). Ottawa: Government of Canada; 2021.
Google Scholar
Council of Canadian Academies. The state of knowledge on medical assistance in dying where a mental disorder is the sole underlying medical condition. Ottawa; 2018. Available from: https://cca-reports.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/The-State-of-Knowledge-on-Medical-Assistance-in-Dying-Where-a-Mental-Disorder-is-the-Sole-Underlying-Medical-Condition.pdf .
Council of Canadian Academies. The state of knowledge on advance requests for medical assistance in dying. Ottawa; 2018. Available from: https://cca-reports.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/The-State-of-Knowledge-on-Advance-Requests-for-Medical-Assistance-in-Dying.pdf .
Council of Canadian Academies. The state of knowledge on medical assistance in dying for mature minors. Ottawa; 2018. Available from: https://cca-reports.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/The-State-of-Knowledge-on-Medical-Assistance-in-Dying-for-Mature-Minors.pdf .
Health Canada. Third annual report on medical assistance in dying in Canada 2021. Ottawa; 2022. [cited 2023 Oct 23]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/medical-assistance-dying/annual-report-2021.html .
Banner D, Schiller CJ, Freeman S. Medical assistance in dying: a political issue for nurses and nursing in Canada. Nurs Philos. 2019;20(4): e12281.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pesut B, Thorne S, Stager ML, Schiller CJ, Penney C, Hoffman C, et al. Medical assistance in dying: a review of Canadian nursing regulatory documents. Policy Polit Nurs Pract. 2019;20(3):113–30.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
College of Registered Nurses of British Columbia. Scope of practice for registered nurses [Internet]. Vancouver; 2018. Available from: https://www.bccnm.ca/Documents/standards_practice/rn/RN_ScopeofPractice.pdf .
Pesut B, Thorne S, Schiller C, Greig M, Roussel J, Tishelman C. Constructing good nursing practice for medical assistance in dying in Canada: an interpretive descriptive study. Global Qual Nurs Res. 2020;7:2333393620938686. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333393620938686 .
Article Google Scholar
Pesut B, Thorne S, Schiller CJ, Greig M, Roussel J. The rocks and hard places of MAiD: a qualitative study of nursing practice in the context of legislated assisted death. BMC Nurs. 2020;19:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-020-0404-5 .
Pesut B, Greig M, Thorne S, Burgess M, Storch JL, Tishelman C, et al. Nursing and euthanasia: a narrative review of the nursing ethics literature. Nurs Ethics. 2020;27(1):152–67.
Pesut B, Thorne S, Storch J, Chambaere K, Greig M, Burgess M. Riding an elephant: a qualitative study of nurses’ moral journeys in the context of Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD). Journal Clin Nurs. 2020;29(19–20):3870–81.
Lamb C, Babenko-Mould Y, Evans M, Wong CA, Kirkwood KW. Conscientious objection and nurses: results of an interpretive phenomenological study. Nurs Ethics. 2018;26(5):1337–49.
Wright DK, Chan LS, Fishman JR, Macdonald ME. “Reflection and soul searching:” Negotiating nursing identity at the fault lines of palliative care and medical assistance in dying. Social Sci & Med. 2021;289: 114366.
Beuthin R, Bruce A, Scaia M. Medical assistance in dying (MAiD): Canadian nurses’ experiences. Nurs Forum. 2018;54(4):511–20.
Bruce A, Beuthin R. Medically assisted dying in Canada: "Beautiful Death" is transforming nurses' experiences of suffering. The Canadian J Nurs Res | Revue Canadienne de Recherche en Sci Infirmieres. 2020;52(4):268–77. https://doi.org/10.1177/0844562119856234 .
Canadian Nurses Association. Code of ethics for registered nurses. Ottawa; 2017. Available from: https://www.cna-aiic.ca/en/nursing/regulated-nursing-in-canada/nursing-ethics .
Canadian Nurses Association. National nursing framework on Medical Assistance in Dying in Canada. Ottawa: 2017. Available from: https://www.virtualhospice.ca/Assets/cna-national-nursing-framework-on-maidEng_20170216155827.pdf .
Pesut B, Thorne S, Greig M. Shades of gray: conscientious objection in medical assistance in dying. Nursing Inq. 2020;27(1): e12308.
Durojaiye A, Ryan R, Doody O. Student nurse education and preparation for palliative care: a scoping review. PLoS ONE. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286678 .
McMechan C, Bruce A, Beuthin R. Canadian nursing students’ experiences with medical assistance in dying | Les expériences d’étudiantes en sciences infirmières au regard de l’aide médicale à mourir. Qual Adv Nurs Educ - Avancées en Formation Infirmière. 2019;5(1). https://doi.org/10.17483/2368-6669.1179 .
Adler M, Ziglio E. Gazing into the oracle. The Delphi method and its application to social policy and public health. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers; 1996
Keeney S, Hasson F, McKenna H. Consulting the oracle: ten lessons from using the Delphi technique in nursing research. J Adv Nurs. 2006;53(2):205–12.
Keeney S, Hasson F, McKenna H. The Delphi technique in nursing and health research. 1st ed. City: Wiley; 2011.
Willis GB. Cognitive interviewing: a tool for improving questionnaire design. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, Calif: Sage; 2005. ISBN: 9780761928041
Lamb C, Evans M, Babenko-Mould Y, Wong CA, Kirkwood EW. Conscience, conscientious objection, and nursing: a concept analysis. Nurs Ethics. 2017;26(1):37–49.
Lamb C, Evans M, Babenko-Mould Y, Wong CA, Kirkwood K. Nurses’ use of conscientious objection and the implications of conscience. J Adv Nurs. 2018;75(3):594–602.
de Vaus D. Surveys in social research. 6th ed. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge; 2014.
Boateng GO, Neilands TB, Frongillo EA, Melgar-Quiñonez HR, Young SL. Best practices for developing and validating scales for health, social, and behavioral research: A primer. Front Public Health. 2018;6:149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00149 .
Puchta C, Potter J. Focus group practice. 1st ed. London: Sage; 2004.
Book Google Scholar
Streiner DL, Norman GR, Cairney J. Health measurement scales: a practical guide to their development and use. 5th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2015.
Hsieh H-F, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15(9):1277–88.
Adesina O, DeBellis A, Zannettino L. Third-year Australian nursing students’ attitudes, experiences, knowledge, and education concerning end-of-life care. Int J of Palliative Nurs. 2014;20(8):395–401.
Bator EX, Philpott B, Costa AP. This moral coil: a cross-sectional survey of Canadian medical student attitudes toward medical assistance in dying. BMC Med Ethics. 2017;18(1):58.
Beuthin R, Bruce A, Scaia M. Medical assistance in dying (MAiD): Canadian nurses’ experiences. Nurs Forum. 2018;53(4):511–20.
Brown J, Goodridge D, Thorpe L, Crizzle A. What is right for me, is not necessarily right for you: the endogenous factors influencing nonparticipation in medical assistance in dying. Qual Health Res. 2021;31(10):1786–1800.
Falconer J, Couture F, Demir KK, Lang M, Shefman Z, Woo M. Perceptions and intentions toward medical assistance in dying among Canadian medical students. BMC Med Ethics. 2019;20(1):22.
Green G, Reicher S, Herman M, Raspaolo A, Spero T, Blau A. Attitudes toward euthanasia—dual view: Nursing students and nurses. Death Stud. 2022;46(1):124–31.
Hosseinzadeh K, Rafiei H. Nursing student attitudes toward euthanasia: a cross-sectional study. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(2):496–503.
Ozcelik H, Tekir O, Samancioglu S, Fadiloglu C, Ozkara E. Nursing students’ approaches toward euthanasia. Omega (Westport). 2014;69(1):93–103.
Canning SE, Drew C. Canadian nursing students’ understanding, and comfort levels related to medical assistance in dying. Qual Adv Nurs Educ - Avancées en Formation Infirmière. 2022;8(2). https://doi.org/10.17483/2368-6669.1326 .
Edo-Gual M, Tomás-Sábado J, Bardallo-Porras D, Monforte-Royo C. The impact of death and dying on nursing students: an explanatory model. J Clin Nurs. 2014;23(23–24):3501–12.
Freeman LA, Pfaff KA, Kopchek L, Liebman J. Investigating palliative care nurse attitudes towards medical assistance in dying: an exploratory cross-sectional study. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(2):535–45.
Brown J, Goodridge D, Thorpe L, Crizzle A. “I am okay with it, but I am not going to do it:” the exogenous factors influencing non-participation in medical assistance in dying. Qual Health Res. 2021;31(12):2274–89.
Dimoula M, Kotronoulas G, Katsaragakis S, Christou M, Sgourou S, Patiraki E. Undergraduate nursing students’ knowledge about palliative care and attitudes towards end-of-life care: A three-cohort, cross-sectional survey. Nurs Educ Today. 2019;74:7–14.
Matchim Y, Raetong P. Thai nursing students’ experiences of caring for patients at the end of life: a phenomenological study. Int J Palliative Nurs. 2018;24(5):220–9.
Canadian Institute for Health Research. Sex and gender in health research [Internet]. Ottawa: CIHR; 2021 [cited 2023 Oct 23]. Available from: https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/50833.html .
Canadian Nurses’ Association. Nursing statistics. Ottawa: CNA; 2023 [cited 2023 Oct 23]. Available from: https://www.cna-aiic.ca/en/nursing/regulated-nursing-in-canada/nursing-statistics .
Krumpal I. Determinants of social desirability bias in sensitive surveys: a literature review. Qual Quant. 2013;47(4):2025–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9640-9 .
Ferri P, Di Lorenzo R, Stifani S, Morotti E, Vagnini M, Jiménez Herrera MF, et al. Nursing student attitudes toward dying patient care: a European multicenter cross-sectional study. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parmensis. 2021;92(S2): e2021018.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Beuthin R, Bruce A. Medical assistance in dying (MAiD): Ten things leaders need to know. Nurs Leadership. 2018;31(4):74–81.
Thiele T, Dunsford J. Nurse leaders’ role in medical assistance in dying: a relational ethics approach. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(4):993–9.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the faculty and students who generously contributed their time to this work.
JS received a student traineeship through the Principal Research Chairs program at the University of British Columbia Okanagan.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Health and Human Services, Selkirk College, Castlegar, BC, Canada
Jocelyn Schroeder & Barbara Pesut
School of Nursing, University of British Columbia Okanagan, Kelowna, BC, Canada
Barbara Pesut, Lise Olsen, Nelly D. Oelke & Helen Sharp
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and drafting and substantively revising the work. JS has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. BP made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and drafting and substantively revising the work. BP has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. LO made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and substantively revising the work. LO has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. NDO made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and substantively revising the work. NDO has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. HS made substantial contributions to drafting and substantively revising the work. HS has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature.
Authors’ information
JS conducted this study as part of their graduate requirements in the School of Nursing, University of British Columbia Okanagan.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Barbara Pesut .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research was approved by the Selkirk College Research Ethics Board (REB) ID # 2021–011 and the University of British Columbia Behavioral Research Ethics Board ID # H21-01181.
All participants provided written and informed consent through approved consent processes. Research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Schroeder, J., Pesut, B., Olsen, L. et al. Developing a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD): a mixed method modified e-Delphi study. BMC Nurs 23 , 326 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01984-z
Download citation
Received : 24 October 2023
Accepted : 28 April 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01984-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical assistance in dying (MAiD)
- End of life care
- Student nurses
- Nursing education
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Providing a complete portal to the world of case study research, the Fourth Edition of Robert K. Yin's bestselling text Case Study Research offers comprehensive coverage of the design and use of the case study method as a valid research tool. This thoroughly revised text now covers more than 50 case studies (approximately 25% new), gives fresh attention to quantitative analyses, discusses ...
This new edition of the best-selling Case Study Research has been carefully revised, updated, and expanded while retaining virtually all of the features and coverage of the Second Edition. Robert Yin's comprehensive presentation covers all aspects of the case study method--from problem definition, design, and data collection, to data analysis and composition and reporting.
Providing a complete portal to the world of case study research, the Fifth Edition of Robert K. Yin's bestselling text offers comprehensive coverage of the design and use of the case study method as a valid research tool. The book offers a clear definition of the case study method as well as discussion of design and analysis techniques.
The components of the research design are provided in chapter 2. After discussing the art of developing research questions in case study research, Yin makes a strong plea for using propositions. This is often confused with grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967) or with case study design by Eisenhardt (1989) and Eisenhardt and Graebner
Providing a complete portal to the world of case study research, the Fifth Edition of Robert K. Yin's bestselling text offers comprehensive coverage of the design and use of the case study method as a valid research tool. The book offers a clear definition of the case study method as well as discussion of design and analysis techniques. The Fifth Edition has been updated with nine new case ...
Case study research : design and methods by Yin, Robert K. Publication date 2014 Topics Case method, Social sciences -- Research -- Methodology Publisher Los Angeles : SAGE Collection printdisabled; internetarchivebooks; inlibrary Contributor Internet Archive Language English. xxviii, 282 pages : 24 cm
Foreword, by Donald T. Campbell Preface 1. INTRODUCTION: How to Know Whether and When to Use Case Studies as a Research Method The Case Study as a Research Method Comparing Case Studies With Other Research Methods in the Social Sciences Different Kinds of Case Studies, But a Common Definition Summary 2. DESIGNING CASE STUDIES: Identifying Your Case(s) and Establishing the Logic of Your Case ...
PDF | On Mar 1, 2016, Trista Hollweck published Robert K. Yin. (2014). Case Study Research Design and Methods (5th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. 282 pages. | Find, read and cite all the research ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
12-1-2008 Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers ... research methods course, we have listened to novice researchers describe their views of ... According to Yin (2003) a case study design should be considered when: (a) the focus of the study is to answer "how" and "why" questions; (b ...
Case study research: Design and methods (4th Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Reviewed by Trudie Aberdeen, PhD candidate in Educational Psychology, University of Alberta Yin begins the fourth edition of his 6 chapter book by explaining that case study research is a "linear, but iterative process."
The case study method is particularly useful for researching educational interventions because it provides a rich description of all the interrelated factors. ... Baxter P., Jack S (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. ... Case study research and applications: Design and methods (6th ...
Yin (2009Yin ( , 2014 defines case study research design as the in-depth investigation of contemporary phenomena, within a real-life context, by making use of multiple evidentiary sources that ...
Yin begins the fourth edition of his 6 chapter book by explaining that case study research is a "linear, but iterative process." This statement is supported by a visual which is displayed on the first page of each chapter. Each chapter contains one step in the linear process of case design (planning, designing, preparing, collecting, analyzing, and sharing) as well as it highlights how ...
This new edition of the best-selling Case Study Research has been carefully revised, updated, and expanded while retaining virtually all of the features and coverage of the Second Edition.Robert Yin′s comprehensive presentation covers all aspects of the case study method--from problem definition, design, and data collection, to data analysis and composition and reporting.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
A case study is an empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon in depth and within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident" (18). The components of the research design are provided in chapter 2.
The Sixth Edition of Robert K. Yin's bestseller provides a complete portal to the world of case study research. Offering comprehensive coverage of the design and use of the case study method in addition to an integration of applications, the book gives readers access to exemplary case studies drawn from a wide variety of academic and applied fields.
Orienting Case Study Research to an Audience's Needs 223 Communicating With Case Studies 224 Varieties of Case Study Compositions 225 Compositional Formats 226 Illustrative Structures for the Substance of Your Case Study 229 Methods and Research Literature Portions of a Case Study 232 Case Studies as Part of Larger, Mixed-Methods Studies 235
Books. Case Study Research: Design and Methods. Robert K. Yin. SAGE Publications, Mar 18, 1994 - Social Science - 170 pages. This best-selling book focuses on case study design and analysis as a distinct research tool with wide applicability. It has now been carefully revised, updated, and expanded to include a discussion of the debate in ...
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) marks a groundbreaking shift in research. Unlike traditional AI, GAI can generate novel insights and content using natural language processing. Using case study methodology, this paper explored GAI's application in identifying research gaps in aviation's use of Additive Manufacturing (AM), focusing on Design Optimization. Recent advances, such as ...
Robert K. Yin. SAGE Publications, Feb 1, 1989 - Social Science - 168 pages. Taking a unique approach to case studies research -- specifically that case studies are a useful tool for hypothesis testing on social phenomena -- Yin introduces the research professional or graduate student to the case study method. He shows the reader how to use the ...
Case study: well-Q design optimization Using Well-Q as a case study, the pilot hole trajectory design included the following: straight well section, kicking-off section, and stabilizing section.
Dul and Hak (2008) categorize the case study research as the single case study and comparative case study. All in all, we believe that in using the case study research as a methodology we have two types: single case study or multiple case study which follows a replication logic. ... Case study research: Design and methods (4th ed.). Paper ...
Community green spaces (CGSs) constitute a crucial element of urban land use, playing a pivotal role in maintaining the stability of urban ecosystems and enhancing the overall quality of the urban environment. Through the post-occupancy evaluation (POE) of green spaces, we can gain insights into residents' actual needs and usage habits, providing scientific evidence for the planning, design ...
We present a novel explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) method to assess the associations between the temporal patterns in the patient trajectories recorded in longitudinal clinical data and the adverse outcome risks, through explanations for a type of deep neural network model called Hybrid Value-Aware Transformer (HVAT) model. The HVAT models can learn jointly from longitudinal and non ...
The design was a mixed-method, modified e-Delphi method that entailed item generation from the literature, item refinement through a 2 round survey of an expert faculty panel, and item validation through a cognitive focus group interview with nursing students. ... The survey is appropriate for use in education and research to measure knowledge ...