Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.

What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Thesis Statement–Examples
What is a thesis statement? A thesis statement summarizes the main idea of a paper or an essay. Similar to the statement of the problem in research, it prepares the reader for what is to come and ties together the evidence and examples that are presented and the arguments and claims that are made later.
A good thesis statement can provoke thought, arouse interest, and is always followed up by exactly what it promises—if the focus or direction of your essay changes over time, you should go back to your statement and adapt it as well so that it clearly reflects what you are explaining or discussing.
Where does the thesis statement go in my paper?
Your thesis statement should be placed near the end of your introduction—after you have given the reader some background and before you delve into the specific evidence or arguments that support your statement.

Can you give me a thesis statement template?
Depending on the type of essay you are writing, your thesis statement will look different. The important thing is that your statement is specific and clearly states the main idea you want to get across. In the following, we will discuss different types of statements, show you a simple 4-step process for writing an effective thesis statement, and finish off with some not-so-good and good thesis statement examples.
Table of Contents:
- Types of Thesis Statements
- How to Write a Thesis Statement Step by Step
- Not-So-Good and Good Thesis Statements
Types of Thesis Statements
Depending on whether your paper is analytical, expository, or argumentative, your statement has a slightly different purpose.
Analytical thesis statements
An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its components, evaluates the pieces, and presents an evaluation of this breakdown to the reader. Such papers can analyze art, music, literature, current or historical events, political ideas, or scientific research. An analytical thesis statement is therefore often the result of such an analysis of, for example, some literary work (“Heathcliff is meant to be seen as a hero rather than a horrible person”) or a process (“the main challenge recruiters face is the balance between selecting the best candidates and hiring them before they are snatched up by competitors”), or even the latest research (“starving yourself will increase your lifespan, according to science”). In the rest of the paper, you then need to explain how you did the analysis that led you to the stated result and how you arrived at your conclusion, by presenting data and evidence.
Expository thesis statements
An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience, such as a historical development, a current phenomenon, or the effect of political intervention. A typical explanatory thesis statement is therefore often a “topic statement” rather than a claim or actual thesis. An expository essay could, for example, explain “where human rights came from and how they changed the world,” or “how students make career choices.” The rest of the paper then needs to present the reader with all the relevant information on the topic, covering all sides and aspects rather than one specific viewpoint.
Argumentative thesis statements
An argumentative paper makes a clear and potentially very subjective claim and follows up with a justification based on evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the author’s claim is true. A thesis statement for such a paper could be that “every student should be required to take a gap year after high school to gain some life experience”, or that “vaccines should be mandatory”. Argumentative thesis statements can be bold, assertive, and one-sided—you have the rest of the paper to convince the reader that you have good reasons to think that way and that maybe they should think like that, too.
How to Write a Thesis Statement Step-by-Step
If you are not quite sure how you get from a topic to a thesis statement, then follow this simple process—but make sure you know what type of essay you are supposed to write and adapt the steps to the kind of statement you need.
First , you will have to select a topic . This might have been done for you already if you are writing an essay as part of a class. If not, then make sure you don’t start too general—narrow the subject down to a specific aspect that you can cover in an essay.
Second , ask yourself a question about your topic, one that you are personally interested in or one that you think your readers might find relevant or interesting. Here, you have to consider whether you are going to explain something to the reader (expository essay) or if you want to put out your own, potentially controversial, opinion and then argue for it in the rest of your (argumentative) essay.
Third , answer the question you raised for yourself, based on the material you have already sifted through and are planning to present to the reader or the opinion you have already formed on the topic. If your opinion changes while working on your essay, which happens quite often, then make sure you come back to this process and adapt your statement.
Fourth and last, reword the answer to your question into a concise statement . You want the reader to know exactly what is coming, and you also want to make it sound as interesting as possible so that they decide to keep reading.
Let’s look at this example process to give you a better idea of how to get from your topic to your statement. Note that this is the development of a thesis statement for an argumentative essay .
- Choose a specific topic: Covid-19 vaccines
Narrow it down to a specific aspect: opposition to Covid-19 vaccines
- Ask a question: Should vaccination against Covid-19 be mandatory?
- Answer the question for yourself, by sorting through the available evidence/arguments:
Yes: vaccination protects other, more vulnerable people; vaccination reduces the spread of the disease; herd immunity will allow societies to go back to normal…
No: vaccines can have side-effects in some people; the vaccines have been developed too fast and there might be unknown risks; the government should stay out of personal decisions on people’s health…
- Form your opinion and reword it into your thesis statement that represents a very short summary of the key points you base your claim on:
While there is some hesitancy around vaccinations against Covid-19, most of the presented arguments revolve around unfounded fears and the individual freedom to make one’s own decisions. Since that freedom is offset by the benefits of mass vaccination, governments should make vaccines mandatory to help societies get back to normal.
This is a good argumentative thesis statement example because it does not just present a fact that everybody knows and agrees on, but a claim that is debatable and needs to be backed up by data and arguments, which you will do in the rest of your essay. You can introduce whatever evidence and arguments you deem necessary in the following—but make sure that all your points lead back to your core claim and support your opinion. This example also answers the question “how long should a thesis statement be?” One or two sentences are generally enough. If your statement is longer, make sure you are not using vague, empty expressions or more words than necessary .
Good and Bad Thesis Statement Examples
Not-so-good thesis statement : Everyone should get vaccinated against Covid-19.
Problem: The statement does not specify why that might be relevant or why people might not want to do it—this is too vague to spark anyone’s interest.
Good : Since the risks of the currently available Covid-19 vaccines are minimal and societal interests outweigh individual freedom, governments should make Covid-19 vaccination mandatory.
Not-so-good thesis statement : Binge drinking is bad for your health.
Problem: This is a very broad statement that everyone can agree on and nobody needs to read an article on. You need to specify why anyone would not think that way.
Good : Binge drinking has become a trend among college students. While some argue that it might be better for your health than regular consumption of low amounts of alcohol, science says otherwise.
Not-so-good thesis statement : Learning an instrument can develop a child’s cognitive abilities.
Problem: This is a very weak statement—”can” develop doesn’t tell us whether that is what happens in every child, what kind of effects of music education on cognition we can expect, and whether that has or should have any practical implications.
Good thesis statement : Music education has many surprising benefits on children’s overall development, including effects on language acquisition, coordination, problem-solving, and even social skills.
You could now present all the evidence on the specific effects of music education on children’s specific abilities in the rest of your (expository) essay. You could also turn this into an argumentative essay, by adding your own opinion to your statement:
Good thesis statement : Considering the many surprising benefits that music education has on children’s overall development, every child should be given the opportunity to learn an instrument as part of their public school education.
Not-so-good thesis statement : Outer space exploration is a waste of money.
Problem: While this is a clear statement of your personal opinion that people could potentially disagree with (which is good for an argumentative thesis statement), it lacks context and does not really tell the reader what to expect from your essay.
Good thesis statement : Instead of wasting money on exploring outer space, people like Elon Musk should use their wealth to solve poverty, hunger, global warming, and other issues we are facing on this earth.
Get Professional Thesis Editing Services
Now that you know how to write the perfect thesis statement for your essay, you might be interested in our free grammar checker , the Wordvice AI Proofreader. And after drafting your academic papers, be sure to get proofreading that includes manuscript editing , thesis editing , or dissertation editing services before submitting your work to journals for publication.
We have many more articles for you on all aspects of academic writing , tips and tricks on how to avoid common grammar mistakes , and resources on how to strengthen your writing style in general.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide
Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Thesis Statement
Definition:
Thesis statement is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of an essay, research paper, or any other written work.
It is usually located at the end of the introductory paragraph and provides a roadmap for the reader, indicating what the paper will be about and what the author’s position or argument is. The thesis statement should be clear, specific, and debatable, so that the reader knows what to expect and can evaluate the validity of the argument.
Structure of Thesis Statement
The structure of a thesis statement typically consists of two main parts: the topic and the argument or claim.
- Topic : The topic is the subject or issue that the paper will be addressing. It should be clear and specific, and should provide a context for the argument or claim that follows.
- Argument or claim: The argument or claim is the main point or position that the writer is taking on the topic. It should be clear and concise, and should be debatable or arguable, meaning that it can be supported with evidence and analysis.
For example, a thesis statement for an essay on the impact of social media on mental health could be:
“The excessive use of social media has a negative impact on individuals’ mental health as it leads to increased feelings of anxiety and depression, a distorted self-image, and a decline in face-to-face communication skills.”
In this example, the topic is the impact of social media on mental health, and the argument is that excessive social media use has negative effects on mental health, which will be supported by evidence throughout the essay.
How to Write Thesis Statement
Here are the steps to follow when writing a thesis statement:
- Identify your topic: Your thesis statement should be based on a clear understanding of your topic. Identify the key concepts, issues, and questions related to your topic.
- Research : Conduct research to gather information and evidence that supports your argument. Use reputable sources, such as academic journals, books, and websites.
- Brainstorm : Use brainstorming techniques to generate ideas and develop your argument. Consider different perspectives and opinions on your topic.
- Create a working thesis : Write a working thesis statement that expresses your argument or position on the topic. This statement should be concise and clear, and it should provide a roadmap for your paper.
- Refine your thesis : Revise your working thesis as you continue to research and develop your argument. Make sure your thesis is specific, debatable, and well-supported by evidence.
- Check for coherence : Ensure that your thesis statement is coherent with the rest of your paper. Make sure that your supporting arguments and evidence align with your thesis.
- Revisit your thesis statement : After completing your paper, revisit your thesis statement to ensure that it accurately reflects the content and scope of your work.
How to Start a Thesis Statement
Here are some steps you can follow to start a thesis statement:
- Choose your topic: Start by selecting a topic that you are interested in and that is relevant to your assignment or research question.
- Narrow your focus : Once you have your topic, narrow it down to a specific aspect or angle that you will be exploring in your paper.
- Conduct research : Conduct some research on your topic to gather information and form an understanding of the existing knowledge on the subject.
- I dentify your main argument : Based on your research, identify the main argument or point you want to make in your paper.
- Write a draft thesis statement : Using the main argument you identified, draft a preliminary thesis statement that clearly expresses your point of view.
- Refine your thesis statement : Revise and refine your thesis statement to make sure it is clear, specific, and strong. Make sure that your thesis statement is supported by evidence and relevant to your topic.
Where is the Thesis Statement Located
In academic writing, the thesis statement is usually located in the introduction paragraph of an essay or research paper. It serves as a concise summary of the main point or argument that the writer will be making in the rest of the paper. The thesis statement is typically located towards the end of the introduction and may consist of one or two sentences.
How Long Should A Thesis Statement Be
Thesis Statement Should be between 1-2 sentences and no more than 25-30 words. It should be clear, concise, and focused on the main point or argument of the paper. A good thesis statement should not be too broad or too narrow but should strike a balance between these two extremes. It should also be supported by evidence and analysis throughout the paper.
For example, if you are writing a five-paragraph essay, your thesis statement should be one sentence that summarizes the main point of the essay. If you are writing a research paper, your thesis statement may be two or three sentences long, as it may require more explanation and support.
Thesis Statement Examples
Here are a few examples of thesis statements:
- For an argumentative essay: “The use of smartphones in classrooms should be banned, as it distracts students from learning and hinders their academic performance.”
- For a literary analysis essay: “In George Orwell’s 1984, the use of propaganda and censorship is a powerful tool used by the government to maintain control over the citizens.”
- For a research paper: “The impact of social media on mental health is a growing concern, and this study aims to explore the relationship between social media use and depression in young adults.”
- For a compare and contrast essay : “Although both American and British English are forms of the English language, they differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, and spelling.”
- For an expository essay: “The importance of regular exercise for overall health and well-being cannot be overstated, as it reduces the risk of chronic diseases, improves mood and cognitive function, and enhances physical fitness.”
- For a persuasive essay: “The government should invest in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, as they are more sustainable and environmentally friendly than fossil fuels.”
- For a history research paper: “The Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s was a pivotal moment in American history that paved the way for greater racial equality and social justice.”
- For a literary comparison essay: “In The Great Gatsby and Death of a Salesman, the theme of the American Dream is portrayed differently, with one exposing its emptiness and the other showing its destructive power.”
- For a science experiment report: “The hypothesis that increasing the amount of sunlight a plant receives will result in greater growth is supported by the results of this experiment.”
- For an analysis of a social issue : “The gender pay gap in the United States is a pervasive problem that is perpetuated by systemic discrimination and unequal access to education and opportunities.”
Good Thesis Statements Examples
Some Good Thesis Statements Examples are as follows:
- “The legalization of marijuana for medical use has proven to be a beneficial alternative to traditional pain management techniques, with numerous studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and provides specific information about the benefits of medical marijuana and the evidence supporting its use.
- “The rise of social media has fundamentally changed the way we communicate and interact with each other, with both positive and negative effects on our relationships and mental health.”
This thesis statement provides a clear argument and focus for the essay, exploring the impact of social media on communication and mental health.
- “The portrayal of women in advertising perpetuates harmful stereotypes and reinforces gender inequality, contributing to a larger societal issue of sexism and misogyny.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, analyzing the negative effects of advertising on women and the larger societal issue of gender inequality.
- “The implementation of renewable energy sources is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change and transitioning to a more sustainable future.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, emphasizing the importance of renewable energy sources in addressing climate change and promoting sustainability.
- “The American Dream is an illusion that perpetuates social and economic inequality, as it is based on the false notion of equal opportunity for all.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, critiquing the concept of the American Dream and its perpetuation of inequality.
Bad Thesis Statements Examples
Some Bad Thesis Statements Examples are as follows:
- “In this essay, I will talk about my favorite hobby.”
This thesis statement is too vague and does not give any specific information about the writer’s favorite hobby or what the essay will be about.
- “This paper will explore the benefits and drawbacks of social media.”
This thesis statement is too general and does not provide a clear argument or focus for the essay.
- “The world is a beautiful place.”
This thesis statement is an opinion and does not provide any specific information or argument that can be discussed or analyzed in an essay.
- “The impact of climate change is bad.”
This thesis statement is too broad and does not provide any specific information about the impacts of climate change or the focus of the essay.
- “I am going to write about the history of the United States.”
This thesis statement is too general and does not provide a specific focus or argument for the essay.
Applications of Thesis Statement
A thesis statement has several important applications in academic writing, including:
- Guides the reader: A thesis statement serves as a roadmap for the reader, telling them what to expect from the rest of the paper and helping them to understand the main argument or focus of the essay or research paper.
- Focuses the writer: Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Organizes the paper: A thesis statement provides a framework for organizing the paper, helping the writer to develop a logical and coherent argument that supports their main claim.
- Evaluates sources: A clear thesis statement helps the writer to evaluate sources and information, determining which information is relevant and which is not.
- Helps with revision: A strong thesis statement can help the writer to revise their paper, as they can use it as a reference point to ensure that every paragraph and piece of evidence supports their main argument or claim.
Purpose of Thesis Statement
The purpose of a thesis statement is to:
- Identify the main focus or argument of the essay or research paper: A thesis statement is typically a one or two-sentence statement that identifies the main argument or claim of the paper. It should be clear, specific, and debatable, and should guide the reader on what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- Provide direction and guidance to the reader: A thesis statement helps the reader to understand the main focus of the paper and what the writer is trying to convey. It also provides a roadmap for the reader to follow, making it easier for them to understand the structure and organization of the paper.
- Focus the writer and help with organization: Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information. Additionally, a clear thesis statement provides a framework for organizing the paper, helping the writer to develop a logical and coherent argument that supports their main claim.
- Provide a basis for evaluation and analysis: A clear thesis statement helps the writer to evaluate sources and information, determining which information is relevant and which is not. It also provides a basis for analyzing and evaluating the evidence presented in the paper, helping the writer to determine whether or not it supports their main argument or claim.
When to Write Thesis Statement
A thesis statement should be written early in the writing process, ideally before any significant research or drafting has taken place. This is because the thesis statement serves as the foundation for the rest of the paper, providing a clear and concise summary of the paper’s main argument or claim. By identifying the main argument or claim early in the writing process, the writer can stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
However, it is important to note that the thesis statement is not necessarily set in stone and may need to be revised as the paper is developed. As the writer conducts research and develops their argument, they may find that their original thesis statement needs to be modified or refined. Therefore, it is important to revisit and revise the thesis statement throughout the writing process to ensure that it accurately reflects the main argument or claim of the paper.
Characteristics of Thesis Statement
Some of the key characteristics of a strong thesis statement include:
- Clarity : A thesis statement should be clear and easy to understand, clearly conveying the main argument or claim of the paper.
- Specificity : A thesis statement should be specific and focused, addressing a single idea or topic rather than being overly broad or general.
- Debatable : A thesis statement should be debatable, meaning that there should be room for disagreement or debate. It should not be a statement of fact or a summary of the paper, but rather a statement that can be supported with evidence and analysis.
- Coherent : A thesis statement should be coherent, meaning that it should be logical and consistent with the rest of the paper. It should not contradict other parts of the paper or be confusing or ambiguous.
- Relevant : A thesis statement should be relevant to the topic of the paper and should address the main question or problem being investigated.
- Arguable : A thesis statement should present an argument that can be supported with evidence and analysis, rather than simply stating an opinion or belief.
Advantages of Thesis Statement
There are several advantages of having a strong thesis statement in academic writing, including:
- Focuses the writer : Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Establishes credibility: A strong thesis statement establishes the writer’s credibility and expertise on the topic, as it demonstrates their understanding of the issue and their ability to make a persuasive argument.
- Engages the reader: A well-crafted thesis statement can engage the reader and encourage them to continue reading the paper, as it presents a clear and interesting argument that is worth exploring.
Limitations of Thesis Statement
While a strong thesis statement is an essential component of academic writing, there are also some limitations to consider, including:
- Can be restrictive: A thesis statement can be restrictive if it is too narrow or specific, limiting the writer’s ability to explore related topics or ideas. It is important to strike a balance between a focused thesis statement and one that allows for some flexibility and exploration.
- Can oversimplify complex topics: A thesis statement can oversimplify complex topics, presenting them as black and white issues rather than acknowledging their complexity and nuance. It is important to be aware of the limitations of a thesis statement and to acknowledge the complexities of the topic being addressed.
- Can limit creativity: A thesis statement can limit creativity and experimentation in writing, as the writer may feel constrained by the need to support their main argument or claim. It is important to balance the need for a clear and focused thesis statement with the desire for creativity and exploration in the writing process.
- May require revision: A thesis statement may require revision as the writer conducts research and develops their argument, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. It is important to be flexible and open to revising the thesis statement as needed to ensure that it accurately reflects the main argument or claim of the paper.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
25 Thesis Statement Examples
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples


1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
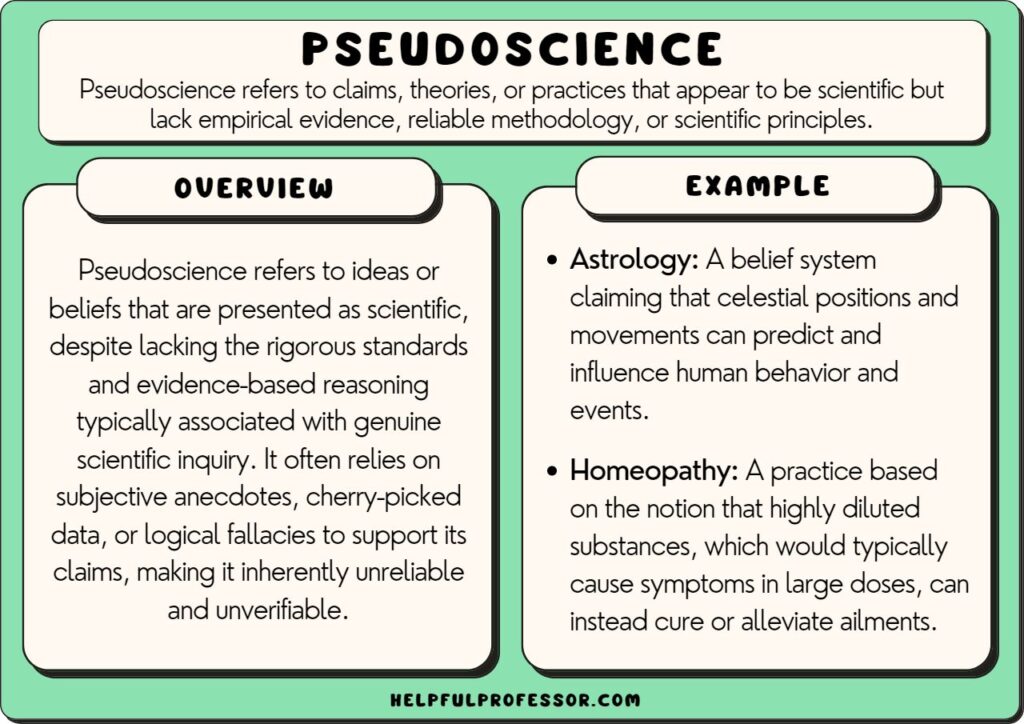
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
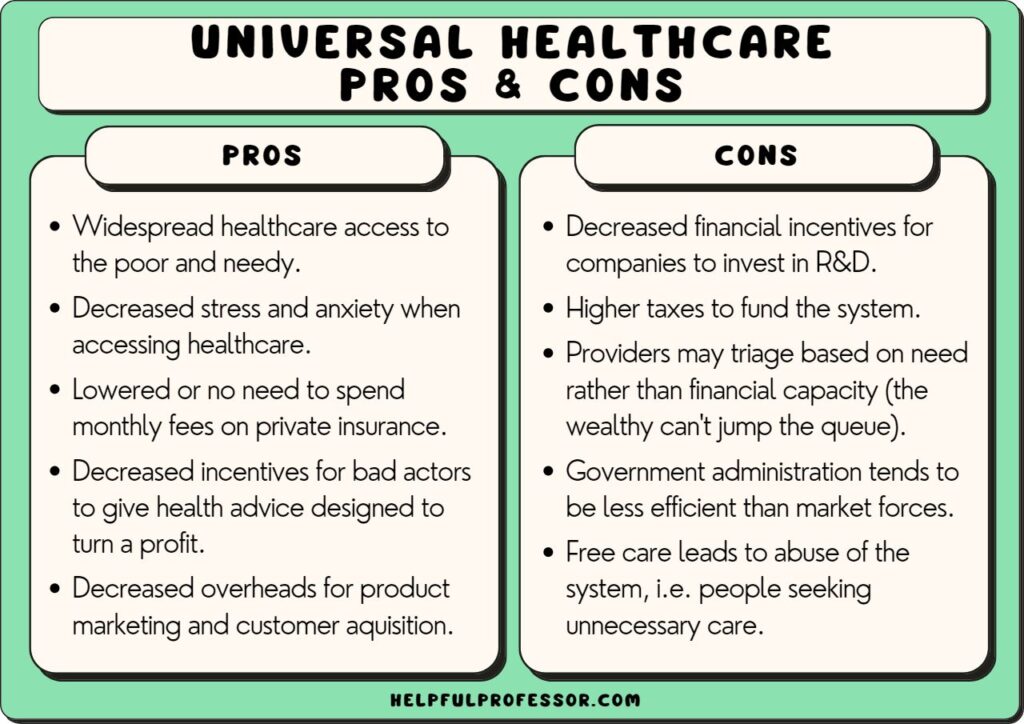
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
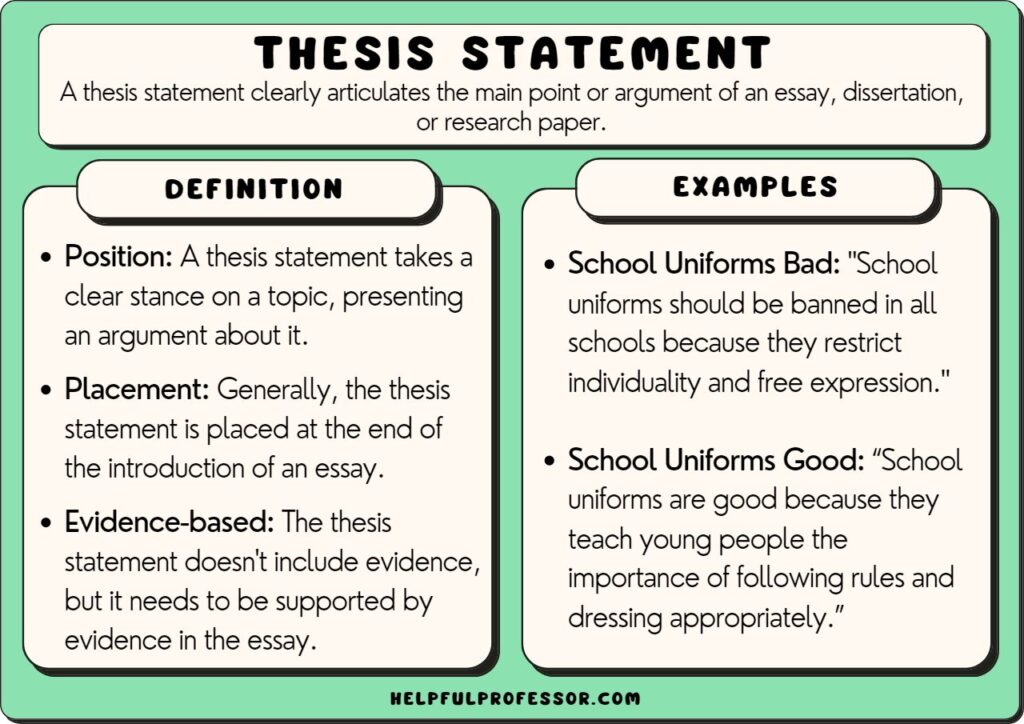
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Thesis Summary
Considering that you have finished writing your thesis, it is high time that you started working on your thesis summary or abstract as the last and final part of your research paper before submitting it to your instructor. Writing an abstract is actually the simplest way for your audience, the teachers and the panel of publishers (if you wish for it to be published) to know what your research paper is about without going through the bulk of your paper.
What is an Abstract?
According to an article found in the Simon Fraser University database, the abstract is deemed a critical part of your thesis and it is presented at the beginning of the thesis, as it is a summary of the whole thesis. The thesis summary is a substantive description of your work read by an external examiner by presenting all the major elements of your work in a highly condensed form.
Size and Structure
Normally, a thesis summary would only contain 120 or less (for undergraduate theses), 150 words (for Masters theses) and 350 words (for a doctoral dissertation).
- For doctoral dissertations, it is best to limit it to only 280 words with a format of one double-spaced page, to preserve visual coherence.
- The structure of the abstract should mirror the structure of the whole thesis, and should represent all its major elements.
- For instance, if your thesis has five chapters (rationale, literature review, methodology, results, conclusion), limit each chapter to only a sentence or two for each chapter in order to maximize some parts that need more substantial backing.
Clearly Specify Your Research Questions
- Research questions are important in making sure that the abstract is coherent and logically structured as they form the backbone to which other elements adhere; they should be presented near the beginning of the abstract.
- Depending on the length of your research paper, there is only room for one to three questions. If there are more than three major research questions in your thesis, try to rearrange them by reducing some to subsidiary status.
Don’t Forget the Results
- One of the most common mistakes in writing abstracts is the failure to indicate the results.
- The primary function of your thesis (and by extension your abstract) is not to tell readers what you did, it is to tell them what you discovered. Other information, such as the account of your research methods, is needed mainly to back the claims you make about your results.
- The final part of your thesis should be about summarizing your results as well as interpreting them.
- Although it is sometimes not necessary, you can choose to add keywords below your abstract as the most important terms that can be found in the thesis.
Listed below are some thesis summary examples:
This study aimed to analyze and identify the most frequent news category and rhetoric of the three local English dailies as well as assess whether they align to the readers’ news preference. These factors served as the sources of the data gathered by the researchers: ninety tertiary students, each local publication’s respective editorial board, and banner stories. Findings indicated that even though the editors would usually select their stories based on impact, the banner story content however focused more on news like crime and politics which are mostly conflict-based issues, instead of human interest stories that readers prefer the most. In conclusion, the respective editorial boards of each publication are not presenting the readers with their main interests in the banner story. Keywords: banner stories, news values, news categories, gatekeeping/gatekeepers, and readers’ preference
An example of a summary format The aim or goal or purpose of this graduation thesis (title) is to … (analyse, characterize, compare, examine, illustrate, present, survey, design, reconstruct) … The graduation thesis is composed of five chapters, each of them dealing with different aspect of … Chapter 1 is introductory and (defines, describes, reviews, deals with) … The chapter is subdivided into two parts. Part 1 describes … and explains … . Part 2 deals with … Chapter 2 examines … . The chapter consists of three parts. Part 1 focuses on … . Part 2 investigates … . Part 3 addresses the issue of … . Chapter 3 is subdivided into two parts and provides an outline of relevant … Part 1 illustrates … . Part 2 looks at … . Chapter 4 concentrates on problems resulting from … Part 1 describes …. Part 2 recommends changes to be made in legislation … Conclusions are drawn in Chapter 5. The main aim of the graduation thesis has been reached. The author suggests that …………………… should be changed/introduced/applied.
The aim of this graduation thesis entitled Development of Yamakawa Technologies to Ascertain the Existence of Cheese on the Moon is to test the use of Yamakawa technologies in ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. Yamakawa technologies have been successfully used to test the existence of water in Wakanda, but to date no further applications are known. For this reason the author decided to test further applications, with the aim of describing the technology’s suitability for further development. This thesis first examines the testing procedures for the water in Wakanda experiment, and presents the results. In a second stage several adaptations to Yamakawa for the testing of the existence of cheese on the moon are undertaken. Finally the technology is applied to the question of cheese on the moon, within a six-week testing phase. At the end of each week the testing apparatus is fine tuned, and experiment results are charted every twenty-four hours. The results of the experiment show that Yamakawa technologies are well suited to ascertaining the presence of water in Wakanda, but were unable to be sufficiently modified for the purpose of ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. The author recommends further modification to the technology before any other uses are considered.
After writing the said abstract in your research paper, then congratulations! You are now ready to move to the next step of your thesis journey, defending it. Just remember this, always know your thesis by heart. Believe me, if you do, you will not have a hard time and eventually, you will learn to enjoy it too. Good luck!
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
Thesis Summary: A Detailed Academic Writing Guide

A thesis summary is a highly condensed version of the longer paper. It highlights the main points that have been covered in the paper while concisely describing the content of the thesis. In most cases, the summary of a thesis and the abstract serve the same purpose. They provide an overview of all the major points of a thesis. Thus, a reader can quickly see the main content of your thesis when they read the summary. This enables them to determine whether they are interested in your work or not.
What is Included in a Thesis Summary?
When asked to summarize something, you’re simply required to condense the text to the main points. As such, a good summary of thesis research should include important elements only. It should capture the main idea in the paper and the supporting points that may be interwoven with content that is of lesser importance.
Many learners confuse a thesis statement summary with an analysis. An analysis is a discussion of the techniques, ideas, and meaning in the text. On the other hand, a summary does not entail responding or critiquing the ideas in the text. Analyzing a paper entails summarizing its content to establish the ideas that you will be analyzing. A summary does not substitute for analysis.
Here are some of the things that a Ph.D. or master thesis summary should include: A title that is similar to that of your thesis The main purpose of your thesis The main topic of your thesis The research methods used to gather the information The sub-sections of your thesis Recommendations, results, and conclusions
Essentially, a summary should present the points of the author in a straightforward structure. Therefore, read the thesis carefully to determine the major and minor components or points of the argument and summarize them in an organized manner.
A point that the author makes at the beginning and another one at the end should concisely be included in a summary of thesis to convey the main argument of the author. Thus, you should read, understand, and reconstruct the thesis into a more concise, shorter form.
How to Write an Executive Summary for Thesis
Perhaps, you have written a short thesis that is not longer than ten pages. In that case, follow these steps to write a summary thesis:
- Summarize every paragraph in one sentence
- Summarize the entire text in a single sentence
- Write a single paragraph that starts with a sentence that summarizes the entire text followed by a paragraph of summary sentences
- Rewrite and rearrange your paragraph to ensure that it’s concise and clear.
- Eliminate relatively minor and repetitive points and include transitions.
Make sure that the final summary is complete, coherent, and unified.
How to Write Summary of Ph.D. Thesis and Longer Texts
A longer text like a Ph.D. requires time to summarize. That’s because you have to read and understand the document before you summarize it. Here’s how to write a summary thesis for longer papers.
- Outline the thesis by breaking it down into different major sections. To do this, group the paragraphs that focus on a similar topic and then list down the supporting points for different sections.
- Write a sentence or two that summarizes every section.
- Create a single sentence that summarizes the entire text. Look for the topic sentence in the thesis to guide you.
- Write one paragraph or several to start the overall summary sentence. Follow it with sentences that summarize different sections.
- Rearrange and rewrite the paragraphs to make the text concise and clear while eliminating repetitious and relatively minor points. Also, include transitions in your summary.
The final summary should include the main supporting points of every idea. Make the final version coherent, unified, and complete.
When is the Summary of Findings in Thesis Necessary?
The summary and conclusion thesis serves the purpose of providing an overview of the paper. As such, students are required to write a summary in many instances. In some cases, an educator can assign learners to write a page or two after reading a paper or article. They can also be asked to come up with a summary of their text as part of their critique or response after reading a paper.
Students can also write article summaries as a part of their planning or note-taking process when writing a research paper. These summaries or their parts can be included in the final papers. When writing a research paper, an author can depend on the summary as their reference to source materials. A summary enables a writer to condense broad information so that they can explain and present the relevance of the sources that deal with a similar subject.
A paper can also be summarized in the introduction to present a precise and concise overview of the main ideas to be discussed in the rest of the text. The length of a summary should depend on the complexity and length of the paper. Additionally, the purpose of a summary should determine whether it will be a few sentences, a shorter paragraph, or even several paragraphs. You can even come across a thesis summary sample that looks like an entire paper.
Qualities of a Good Summary Thesis Sample
When learning how to write summary and conclusion in thesis, many students use samples as their guides. But, how do you know that you’re using a good thesis summary example? Here are the qualities to look for:
- Comprehensiveness : A good summary should be comprehensive. All important points should be isolated from the original passage and noted down in a brief list. These are the ideas that should form the summary because they are indispensable to the development of the thesis.
- Conciseness : An ideal summary should be free of repetitions. Do not repeat the same points even if they have been restated in the main document. The summary should be shorter while providing a brief overview of the paper. Therefore, avoid repetition of the main point and supporting ideas.
- Coherence : A good summary makes sense. It’s not a piece that looks like it’s been taken from the main document. It should also not sound like a collection of disjointed sentences from the main document that is being summarized.
- Independence : When writing a summary, your work is not to imitate the main text’s author. Instead, you are expected to showcase your style and voice in the summary. Thus, you should not just quote the main text’s author. Instead, express how you understand the document in your words. A summary should be based on your understanding and interpretation of the main ideas or points of the writer. Nevertheless, a good summary does not create distortion or misrepresentation through the introduction of criticisms or comments.
It’s also crucial to note that a good summary thesis example uses a structure that features an introduction, the body, and a conclusion. It presents the goal or purpose, results, and conclusion or recommendations. What’s more, it features logical connections of the included information without adding new information.
To write a great summary, work on this part after completing your thesis. Make sure that you’re guided by the main points of your thesis. What’s more, use a good executive summary for thesis sample to guide you. The length of your summary should depend on its purpose and the length of the main document. Once you have written the summary, read it carefully, and eliminate all errors when proofreading and editing it. Alternatively, ask our thesis editors to proofread the summary for you.

Make PhD experience your own
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Summary

How to Write an Eighth Grade Book Report
Writing a thesis statement for a summary is important because it sums up the assertions or arguments of the writing. The key to a well-written summary is the thesis statement. The thesis should clearly communicate the theme of the summary. Your ability to develop a concise thesis statement and summary will depend on your ability to read critically. Even if your summary does not ask or address a specific question, your thesis needs to answer a question about the issue you will be exploring in the summary. A quality thesis statement can express either one main idea or assert your conclusions about the subject.
Investigation
To generate a thesis statement, thoroughly investigate your topic. Your thesis statement should be concise with clear ideas and conclusions. For example: "World hunger has many causes and effects" is a weak thesis, but "hunger persists in third world countries since jobs are scarce and farming is rarely profitable because of infertile soil" is a strong thesis example.
Test the strength of your thesis. Keep in mind a strong thesis statement takes a stand on an issue. The thesis should illustrate your conclusions in the summary. A strong thesis in a summary should indicate the point of the discussion and express one main idea. Those reading your summary need to be able to see that there is one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one main idea, your readers may become confused. Keep in mind the thesis statement should act as a road map for the paper and tell the reader what he can expect from the rest of the summary.
Expressing a precise opinion in a goal in the thesis statement. A quality thesis statement is not just an observation or question. It instead should be a specific claim that is supported by your summary. It includes a precise opinion and logical reasoning. Having a precise opinion will help you develop the answer to your question. Your opinion, either through argument or assertion, is vital to the reader’s comprehension of the goal of the summary. However, a thesis statement and opinion statement are not interchangeable. A good thesis statement may be based on your opinion and is not a statement of fact. It instead reads in a way that indicates the author has researched and understands the topic well and can defend the evidence presented.
Lay out the blueprint of your summary. For example, if your thesis statement introduces two theories, the reader will expect reasons to follow that support or refute the theories. The blueprint will help you not only think critically about your thesis statement, but will also act as a guide and introduce each section that will be outlined to support your thesis.
Check for accuracy. Reread your summary and thesis statement to be sure you have adequately represented the author’s key points and ideas. Make sure that you have cited anything that was quoted directly from the text.
Revise your thesis statement if necessary. Once you have read through your summary for accuracy, you may need to revise for style, punctuation and grammar. If time allows, give your summary to someone else to read. See if she can pick out your thesis statement. If she cannot identify your thesis statement within the summary, it may be too weak, and you should revise.
Related Articles

How to Start a Good Book Report
How to evaluate research.

How to Write an Introduction to a Reflective Essay

Importance of a Purpose Statement in Research

How to Write a Thesis Statement for "Robinson Crusoe"

How to Write an Introduction to an Analytical Essay

Writing a Summary Paper in APA Style

Tips on Writing an Explication Paper on a Short Story
- Indiana University: Thesis Statements
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Creating a Thesis Statement
Kesha Ward has been a professional writer since 2010. With a Bachelor of Science in applied economics, she brings more than a decade of experience in public finance.
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
Guide On How To Write a Thesis Summary In 2023

So, you just found out that you need to write a thesis summary. In most cases, students who encounter this requirement for the first time start to panic. Frankly, not everyone knows what this thesis summary is. And let’s not forget that most students have no clue how to write one. Don’t worry about it too much though.
What is a thesis summary?
Why use a thesis summary, how to write an effective thesis summary in 2023, master thesis summary example.
A thesis summary is a document that summarizes the points of a longer essay, thesis, or dissertation. Readers will often find a summary to be helpful as it offers a succinct overview of the document’s contents. A Thesis Summary should not be confused with an abstract as they both refer to separate documents that serve different purposes.
The steps involved in writing a Thesis Summary depend on what type of thesis you are summarizing. If you’re summarizing a text-based thesis, then your first step should be to read the Thesis and make note of any major key points and conclusions made by the author(s). You then assemble your notes into one coherent paragraph detailing each one of the major key points. Keep in mind that this initial paragraph will serve as an introduction to your Thesis Summary; therefore, it should not contain the thesis’ main points. Once you’ve completed this step, use these Main Points (identified in your thesis) as a guide for writing the body of your document.
If you’re developing a summary thesis that’s math-related, then you’ll first need to take note of the main conclusions. Second, you must determine how these conclusions were reached by noting each step in the proof. Finally, you’ll have to explain why each step is true using logic statements and definitions from the thesis.
These are the two standard ways to write a thesis summary. However, you can also include your insights, opinions, and comments if you choose.
The steps for writing a ‘ Thesis Summary in 2023’ are just about the same as they’ve always been. They’re pretty much set in stone because this is how students have written thesis summaries for decades.
For both types of thesis summaries, you should include a final paragraph that ties everything together with a brief conclusion. This final paragraph should highlight the key points and conclusions made throughout your document as well as offer a brief statement about why these points matter.
Step 1: Read the Text
The very first thing you’ll want to do is read the entire text. When you’re reading, make note of any major key points and conclusions made by the author(s). If you’re summarizing a text-based thesis, then these major points will form the basis for your introduction paragraph. However, don’t include these points in this introduction.
Step 2: Get to Work
After reading the entire document, it’s time to get started! Begin by taking notes on what you’ve learned from the text and organize them into one coherent paragraph. Make sure that this introduction doesn’t contain the thesis’ main points. Next, use these Main Points (identified in your thesis) as a guide for writing the rest of your thesis summary.
Step 3: Proof it Out
If you’re summarizing a math-related thesis, then you’ll first need to take note of the main conclusions and purposes stated within the document. Next, determine how these conclusions were reached by noting each statement or step in the proof. Finally, complete your Thesis Summary by explaining why each step is true using logical statements and definitions from the thesis.
Step 4: Wrap it Up
Once you’ve finished writing the body of your Thesis Summary, include a final paragraph that ties everything together with a brief conclusion. This final paragraph should highlight the key points and conclusions made throughout your document as well as offer a brief statement about why these points matter.
The best reasons to use a thesis summary are that it will both summarize the relevance of the document and add relevance to an argument. If someone is looking for a specific point or conclusion from the original text, then a Thesis Summary provides them with a quick breakdown of what they can find in the document’s introduction.
You should include a thesis summary in your writings when you believe that there may be too many arguments within your writing. It will help you put together the important points from the different arguments into one concise section.
If you’re summarizing a math-related thesis, they will ensure that you proof every step of the proof given in your paper. It will make sure that you do not miss any details.
There are a few key things that you should keep in mind when writing an effective thesis summary.
- When you’re summarizing a math-related paper, make sure to highlight the main conclusions and how they were arrived at.
- Tell the reader why these conclusions matter by explaining each one with logical statements and definitions from the original document.
- Include a brief conclusion paragraph that ties everything together and highlights the key points covered throughout your work.
- If your thesis is text-based, make sure to include important points throughout the body of your work.
- Last but not least, remember that you are writing a summary so don’t use big words or complex sentence structures! Your goal is to be understood by anyone who reads it in the future.
This Thesis Summary sample is based on a text-based document. Please note, as far as the format and structure are concerned, there’s not much difference between a summary of a bachelor thesis example, an example of a Ph.D. thesis summary, and a thesis chapter summary from a Master thesis summary.
The introduction to the original document should be written as such:
“In this thesis, we’d like to introduce a new framework for understanding how we learn and teach math. The topic of learning and teaching should be the focus of mathematics education.”
Then, point out the main points and conclusions made throughout the body of your work:
“One conclusion that we’ve drawn from our research is that children’s conceptions should be taken into account when designing an appropriate math curriculum for them.”
“A second conclusion that we’ve drawn from our research is that children are more likely to develop their ideas about math if they are encouraged to think critically.”
Finally, make a brief statement about why these points matter using logical statements and definitions from the thesis:
“These conclusions highlight how important it is to focus on children’s conceptions when designing curricula because if we don’t take them into account, we miss out on our student’s potential.”
“These conclusions also show that we need to emphasize critical thinking as a means for children to develop their ideas about math.”
Now, you’ve successfully written an effective thesis summary! Keep in mind that your goal is to highlight the main points and conclusions of the original document as well as boast about their significance. To make this process easier for you, we hope that our tips come in handy.
You should now have a good idea about what a thesis summary or dissertation summary is, why you should use them, and how to write one.
A thesis summary is an overview of the main points and conclusions made in a text-based document or simply put, a summary of the research paper. A Thesis Summary should be included when you believe there are too many arguments within your writing, or if you’re summarizing math-related papers for proofing purposes. Key things to keep in mind while writing one include highlighting important concepts that were previously mentioned, explaining why these new ideas matter with logical statements and definitions from the original work, and providing a brief conclusion paragraph that ties everything together. If you want thesis help with any part of this process from reading or understanding complex texts to organizing them into coherent paragraphs let us know! Our team of thesis writers will be happy to help you complete your thesis summary!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

What Is the Difference Between a Dissertation and a Thesis?

Transitioning from High School to College Academic Writing
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
Watch CBS News
RFK Jr. says he suffered from a parasitic brain worm and mercury poisoning
By Allison Novelo
Updated on: May 9, 2024 / 9:24 AM EDT / CBS News
The campaign of Robert F. Kennedy Jr. , the independent running for president, confirmed Wednesday that he contracted a parasite in his brain over a decade ago.
His campaign's comment came after The New York Times reported he said in a 2012 deposition that a parasitic worm "ate a portion" of his brain and may have caused cognitive issues.
Kennedy campaign spokesperson Stefanie Spear said in a statement to CBS News that he contracted a parasite after traveling "extensively in Africa, South America and Asia as his work as an environmental advocate."
"The issue was resolved more than 10 years ago, and he is in robust physical and mental health. Questioning Mr. Kennedy's health is a hilarious suggestion, given his competition," Spear said.
Kennedy quipped in a post on X Wednesday, "I offer to eat 5 more brain worms and still beat President Trump and President Biden in a debate."

During a deposition given by Kennedy in 2012 amid his divorce from his second wife, Mary Richardson Kennedy, The Times reports he stated that he faced "cognitive problems" and experienced memory loss and brain fog, leading one doctor to say he had a dead parasite in his brain in 2010.
The Times reported that Kennedy said in the deposition that a friend pushed him to seek out medical care after noticing his cognitive issues, initially thinking Kennedy might be suffering from a brain tumor.
It is possible that Kennedy could have contracted a parasitic worm in his brain, according to a medical expert, although it wouldn't have been "eating his brain." However, parasites such as tapeworms do not consume brain tissue, as Kennedy suggested during his deposition.
Tapeworm infections, or neurocysticercosis, can be contracted from consuming undercooked pork or drinking contaminated water, particularly in regions with poor sanitation such as parts of Latin America, sub-Saharan Africa and Asia. When individuals ingest tapeworm eggs, these can travel through the bloodstream and infest various organs including the brain, muscles, liver and other tissues.
Symptoms can include nausea, headaches and seizures, said CBS News medical contributor Dr. Celine Gounder on "CBS Mornings," although many people who suffer from this type of infection may not see symptoms.
Treatment for tapeworm infection typically involves medications such as anti-parasitic drugs to kill the worms.
In some cases, if the worm dies, the body's immune system may clear the dead worm from the brain tissue without requiring surgery, unless complications arise. It's unclear whether Kennedy underwent surgery for this diagnosis, though he informed the Times in a recent interview that he has fully recovered from the memory loss and brain fogginess and has experienced no other lingering effects. He also mentioned that no treatment was necessary for the parasitic condition.
According to The Times, during Kennedy's 2012 deposition, he also reported having been diagnosed with mercury poisoning, which he said was the result of a diet heavy on tuna and other fish. He reportedly said, "I have cognitive problems, clearly. I have short-term memory loss, and I have longer-term memory loss that affects me."
Memory loss is more commonly associated with mercury poisoning than with a parasitic worm, experts say.
Kennedy told the paper that he attributed his mercury poisoning diagnosis to his diet. He said medical tests showed his mercury levels were 10 times what the Environmental Protection Agency considers safe.
" I loved tuna fish sandwiches. I ate them all the time," Kennedy said to The Times.
Kennedy has long been an outspoken activist against vaccines containing thimerosal, a mercury-based preservative that was phased out of childhood vaccines two decades ago, falsely linking vaccinations in children to a rise in autism and other medical conditions. There is no evidence to suggest that low doses of thimerosal causes harm to people, but an excess consumption of mercury, found in fish, can be toxic to humans.
And while both parasitic infections and mercury poisoning can lead to long-term brain damage, it is also possible to make a full recovery, experts say.
Allison Novelo is a 2024 campaign reporter for CBS News.
More from CBS News

Elk Grove gives official go-ahead for new zoo. Next step is construction.

Passenger killed after DoorDash driver falls asleep and crashes near Grass Valley, CHP says

When will the new waterpark at Cal Expo open? Here's why it's been delayed

Fire burns at elder care facility in San Francisco's Japantown; residents evacuated
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Readout of President Joe Biden’s Call with Prime Minister Netanyahu of Israel
President Biden spoke this morning with Prime Minister Netanyahu. The President reaffirmed his message on Yom HaShoah, Holocaust Remembrance Day. The two leaders discussed the shared commitment of Israel and the United States to remember the six million Jews who were systematically targeted and murdered in the Holocaust, one of the darkest chapters in human history, and to forcefully act against antisemitism and all forms of hate-fueled violence. President Biden updated the Prime Minister on efforts to secure a hostage deal, including through ongoing talks today in Doha, Qatar. The Prime Minister agreed to ensure the Kerem Shalom crossing is open for humanitarian assistance for those in need. The President reiterated his clear position on Rafah.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Press Releases
DHS Announces Proposed Rule and Other Measures to Enhance Security, Streamline Asylum Processing
WASHINGTON – As part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s continued efforts to enhance the security of our border and deliver more timely consequences for those encountered who do not have a legal basis to remain in the United States, today the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), through U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), published a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that would allow statutory bars to asylum to be applied much earlier in the process. Even though the number of migrants who are subject to these bars is small, this rule would enable DHS to more quickly remove those who are subject to the bars and pose a risk to our national security or public safety.
Federal law bars individuals who pose a national security or public safety risk from asylum and withholding of removal, specifically those who have been convicted of a particularly serious crime, participated in the persecution of others, are inadmissible on national security or terrorism-related grounds, or for whom there are reasonable grounds to deem them a danger to the security of the United States. While anyone who is deemed to pose a public safety threat is taken into custody, the asylum eligibility determination is not currently made until later in the process – at the merits adjudication stage of the asylum and withholding of removal claims. Today’s proposed rule would permit Asylum Officers to consider these bars to asylum and withholding of removal during initial credible fear screening, which happens just days after an individual is encountered. This will allow DHS to expeditiously remove individuals who pose a threat to the United States much sooner than is currently the case, better safeguarding the security of our border and our country.
“The proposed rule we have published today is yet another step in our ongoing efforts to ensure the safety of the American public by more quickly identifying and removing those individuals who present a security risk and have no legal basis to remain here,” said Secretary of Homeland Security Alejandro Mayorkas . “We will continue to take action, but fundamentally it is only Congress that can fix what everyone agrees is a broken immigration system.”
Noncitizens who present a national security or public safety risk remain in DHS custody while their cases are referred for full immigration hearings before an immigration judge, a process that can take years and is resource intensive. The proposed rule would allow Asylum Officers to issue denial of claims within days after an individual is encountered when there is evidence that the individual is barred from asylum because of a terrorism, national security, or criminal bar, thereby significantly shortening the overall time between encounter and removal from the United States.
In addition to this proposed rule and in close coordination with vetting and law enforcement partners, DHS is updating its policy and procedures regarding the use of classified information in immigration proceedings. This updated guidance clarifies the circumstances in which classified information should be used in immigration proceedings. Consistent with longstanding practice, DHS will continue to screen and vet individuals prior to their entry to the United States to identify national security or public safety threats and take appropriate action.
The Department also continues enforcing the Circumvention of Lawful Pathways (CLP) rule. This rule incentivizes the use of orderly processes and imposes swifter consequences for those without a legal basis to remain in the United States. Today, USCIS issued revised guidance to Asylum Officers to consider whether an asylum seeker could reasonably relocate to another part of the country of feared persecution when assessing claims of future persecution in all credible fear cases. Internal relocation has always been a part of an analysis of future claims of harm, and this new guidance, consistent with the CLP rule, will ensure early identification and removal of individuals who would ultimately be found ineligible for protection because of their ability to remain safe by relocating elsewhere in the country from which they fled.
The Biden-Harris Administration has already taken numerous actions to address migration challenges in the region and at our border, while overseeing a historic expansion of lawful pathways. These efforts, with partner countries in the region and across the world, have made a significant impact. From May 12, 2023 through May 1, 2024, DHS has removed or returned more than 720,000 individuals, the vast majority of whom crossed the Southwest Border, including more than 109,000 individual family members. That includes removals to 170 countries around the world. Total removals and returns since mid-May 2023 exceed removals and returns in every full fiscal year since 2011. DHS has also significantly expanded the capacity to conduct the credible fear interviews needed to ultimately remove those without a legal basis to stay in the United States.
The Administration again calls on Congress to pass needed reforms and provide DHS the resources and tools it needs to fully implement expedited processing of all individuals encountered at the border. The public is invited to submit comments on the NPRM during the 30-day public comment period from May 13, 2024 to June 12, 2024.
- Border Security
- Citizenship and Immigration Services
- Secretary of Homeland Security
- Enforcement
- Immigration
- Lawful Pathways
- Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas
- U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS)
Screen Rant
Marvel permanently kills its 2 most powerful heroes in bold statement about new continuity.

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Iron Lad, Illuminati, and The Parkers: Every Promise Marvel Needs To Keep From 2023’s Ultimate Universe Reboot
Marvel's new juggernaut officially debuts, with 1 huge difference to the original, darth maul's new series confirms a core truth about the sith and the dark side.
- The new Ultimate Universe just killed off two god-tier heroes in Marvel Comics canon: Black Bolt and Sentry.
- The Ultimates discover this upon investigating the Maker's Damage Control facility, where they find the corpses of these heroes on display.
- Killing Black Bolt and Sentry is a bold statement by Marvel, as it tells fans that there will be no easy solutions or god-level allies in the Ultimates' fight against the Maker.
Warning: Contain SPOILERS for Free Comic Book Day: Spider-Man/Ultimate Universe! Marvel Comics has expanded its continuity beyond just Earth-616, as a new Ultimate Universe takes center-stage as its own separate, ongoing canon. While a future crossover between Earth-616 and the newly established Earth-6160 seems inevitable (especially given the circumstances of Earth-6160’s origin), the new Ultimate Universe is currently totally separate, with a storyline that’s in the beginning stages of shaping its entire continuity. And as that storyline unfolds, it will have to do so without two of Marvel’s most powerful heroes.
In Free Comic Book Day: Spider-Man/Ultimate Universe ( Ultimate Universe storyline titled “Forgotten Marvels” by Deniz Camp and Juan Frigeri), the Ultimates - consisting of Earth-6160’s Captain America, Tony Stark (Iron Lad), and Doctor Doom (Reed Richards) - break into a Damage Control facility in order to rescue a WWII-era hero that has seemingly been forgotten to time: the original Human Torch, Jim Hammond . While they were successful in rescuing the old-school hero, the Ultimates came across some other familiar faces that they were too late to save.
The Damage Control facility was littered with the corpses of heroes that were some of Marvel’s heaviest hitters in Earth-616, along with others that proved to be powerful allies during any given storyline. Ka-Zar and the original Vision are two such heroes who aren’t exactly god-tier powerhouses, but still would have made strong allies for the Ultimates just as they did to the X-Men or Avengers in Earth-616. However, the two greatest losses the Ultimates come across are Black Bolt and Sentry.
Killing Black Bolt and Sentry before the Ultimate Universe really takes off is a bold statement about this new continuity: there will be no easy-answer or god-level allies in this fight.
The new Ultimate Universe launches its first ongoing titles in 2024, and fans have many expectations for these books, from plot, to tone, to themes.
Why Black Bolt & Sentry Being Dead Is Terrible News for the Ultimates
Blackagar Boltagon aka Black Bolt is famously the leader of the Inhumans, who possesses the superhuman ability to manipulate energy, manifesting in his Quasi-Sonic Voice (among other applications of his power). A mere whisper from Black Bolt is enough to utterly obliterate anyone it's directed toward, and his scream has the potential to impact an entire planet. In other words, Black Bolt would have been a god-tier ally to the Ultimates, which is exactly why he was deliberately targeted - smothered as an infant in his crib.
Similarly, Robert Reynolds aka Sentry is an immensely powerful hero in Marvel Comics canon, and is often referred to as ‘Marvel’s Superman’ by fans. After taking the Golden Sentry Serum, Reynolds became this nearly unstoppable hero, gaining the powers of super strength, super speed, and flight, along with a healing factor and self-sustaining power that makes Sentry nigh-invulnerable. Like Black Bolt, Sentry would have been a powerful ally to the Ultimates, which is exactly why his fate was the same as Boltagon’s.
Why These Marvel Powerhouses are Dead in the New Ultimate Universe
Ultimate invasion by jonathan hickman and bryan hitch.
As described in Ultimate Invasion (the prelude to the new Ultimate Universe continuity), the Maker invades Earth-6160 with the intention of using his interdimensional/time-travel technology to shape the universe in his image. The Maker (an evil version of Reed Richards from the original Ultimate Universe, Earth-1610 ) systematically murdered or otherwise erased every superhero that would have risen to prominence if he allowed events to transpire as they should have. The Maker became the ruler of this new world, and practically every threat to his power was accounted for - including Black Bolt and Sentry.
While this universe seems overwhelmingly bleak, the Ultimate Invasion storyline ends with the Maker effectively neutralized (if just for a relatively short time), which gives the newly-formed Ultimates the advantage they need to finish assembling all the remaining heroes of Earth in order to undo what the Maker has done to their world. Unfortunately, however, they’ll have to do so without Black Bolt or Sentry, which is a bold statement on Marvel Comics ’ part about this new Ultimate Universe continuity.
Free Comic Book Day: Spider-Man/Ultimate Universe by Marvel Comics is available now.
Ultimate Marvel
Created in 2000, the Ultimate Marvel imprint redesigned the entire Marvel Comics universe with a new set of origin stories and relationships. The reboot reinterpreted Marvel continuity from scratch in an attempt to simplify and update the company's 60-year history for modern audiences. With famous comic book writers such as Brian Michael Bendis, Warren Ellis, and Mark Millar at the helm, the Ultimate universe (named Earth-1610 within the Marvel multiverse) lasted 15 years and provided plenty of inspiration for the MCU.
- Marvel Comics
Advertisement
Stormy Daniels Delivers Intense Testimony in Trump’s Trial: 6 Takeaways
A long day on the stand put Ms. Daniels’s credibility to the test as defense lawyers challenged her motives.
- Share full article

By Kate Christobek and Jesse McKinley
- Published May 7, 2024 Updated May 10, 2024
Follow our live coverage of Trump’s hush money trial in Manhattan.
“The people call Stormy Daniels.”
So began the intense and often uncomfortable testimony of Ms. Daniels, who spent almost five hours in a Manhattan courtroom on Tuesday recounting her story of a 2006 encounter with Donald J. Trump and the ensuing hush-money cover-up that has become the bedrock of the prosecution’s case.
Ms. Daniels spoke quickly and at length about her first meeting with Mr. Trump at a celebrity golf tournament near Lake Tahoe in Nevada.
After the lunch break, Mr. Trump’s lawyer Todd Blanche moved for a mistrial, arguing that the prosecution’s questions had been designed to embarrass Mr. Trump and prejudice the jury.
The judge, Justice Juan M. Merchan of State Supreme Court, agreed that some of Ms. Daniels’s testimony might have “been better left unsaid,” but he denied a mistrial.
The former president is accused of falsifying business records to cover up a $130,000 payment to Ms. Daniels just before the 2016 election. Mr. Trump, 77, has denied the charges and says he did not have sex with Ms. Daniels. If convicted, he could face prison time or probation.
Here are six takeaways from Mr. Trump’s 13th day on trial.
Prosecutors took a risk with their witness.
Jurors heard a vivid account of the Lake Tahoe encounter and met the woman who had received the hush-money payment. This could have presented a risk for prosecutors, depending on whether the jury viewed Ms. Daniels’s story as prurient or powerful.
Ms. Daniels described meeting Mr. Trump at the golf event and accepting his dinner invitation after her publicist said, “What could possibly go wrong?”
She recalled that Mr. Trump had been wearing pajamas when she met him at his hotel suite and that she asked him to change. They discussed the porn industry, and he asked about residuals, unions and testing for sexually transmitted diseases, she said.
She said they had talked about his family, including his daughter, whom he likened to Ms. Daniels — “People underestimate her as well,” Ms. Daniels recalled him as saying. They also discussed his wife; Mr. Trump said they did not “even sleep in the same room.” He suggested that Ms. Daniels might appear on “The Apprentice.”
When she later emerged from the bathroom, Ms. Daniels found Mr. Trump partially undressed, she said. The sex was consensual, she said, but there was a power “imbalance.”

The Links Between Trump and 3 Hush-Money Deals
Here’s how key figures involved in making hush-money payoffs on behalf of Donald J. Trump are connected.
Trump received another warning.
Justice Merchan has already held the former president in contempt 10 times, fined him $10,000 and twice threatened to send him to jail. On Tuesday, Mr. Trump again drew the judge’s ire after Justice Merchan said he had been “cursing audibly” and “shaking his head.”
The judge asked Mr. Trump’s lawyers privately to talk to their client, saying Mr. Trump’s actions might intimidate the witness, Ms. Daniels.
“You need to speak to him,” the judge said. “I won’t tolerate that.”
The motive for the payoff is a point of contention.
Prosecutors asked Ms. Daniels about a 2018 statement in which she denied the sexual encounter. Ms. Daniels said she had not wanted to sign it and that it was not true.
Defense lawyers, capitalizing on what they seem to perceive as Ms. Daniels’s shortcomings as a witness, came out blazing. One of them, Susan Necheles, implied in her cross-examination that Ms. Daniels was trying to “extort money” from Mr. Trump.
Ms. Daniels replied sharply, “False.”
Daniels’s story bothers Trump.
Before court even started Tuesday morning, Trump telegraphed his frustration with Ms. Daniels in an angry post on Truth Social, saying he had just learned about a coming witness and that his lawyers had “no time” to prepare. The post was removed shortly thereafter, possibly because of concerns over violating the gag order.
Mr. Trump, who has spent much of the trial with his eyes closed, remained attentive for part of the day, often with a sour expression on his face. He continually whispered to his lawyers and at one point mouthed an expletive.
But by the afternoon, he had returned to his habit of closing his eyes, even during a combative cross-examination.
Daniels’s credibility is a hurdle for prosecutors.
Ms. Daniels’s motivations are a major focus of the defense. In a sharp moment, Ms. Necheles confronted her about what Ms. Necheles described as her hatred of the former president and asked whether she wanted him to go to jail. Ms. Daniels responded, “I want him to be held accountable.”
Ms. Necheles also asked Ms. Daniels about making money by claiming to have had sex with Mr. Trump. Ms. Daniels responded, “I have been making money by telling my story,” and later added, “It has also cost me a lot of money.”

Who Are Key Players in the Trump Manhattan Criminal Trial?
The first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump is underway. Take a closer look at central figures related to the case.
Trump’s words haunt him.
Prosecutors have tried several times to use Mr. Trump’s prior statements against him.
Before Ms. Daniels testified Tuesday, a witness read aloud passages from books by Mr. Trump. Some spoke to his frugality. Others spoke to his penchant for revenge.
“For many years I’ve said that if someone screws you, screw them back,” the witness read. The passage continued, “When somebody hurts you, just go after them as viciously and as violently as you can.”
Not long after, one of his enemies — Ms. Daniels — took the stand. Her cross-examination resumes on Thursday.
Kate Christobek is a reporter covering the civil and criminal cases against former president Donald J. Trump for The Times. More about Kate Christobek
Jesse McKinley is a Times reporter covering upstate New York, courts and politics. More about Jesse McKinley
Our Coverage of the Trump Hush-Money Trial
News and Analysis
Ahead of Michael Cohen’s testimony on Monday, Justice Juan M. Merchan told prosecutors to keep Mr. Cohen from speaking about the case .
Several witnesses have mentioned Keith Schiller , Donald Trump’s bodyguard, during their testimony. Where is he?
Custodial witnesses, who have discussed FedEx labels, Sharpies and stapling protocol, have made for little spectacle in the trial. But they’ve provided basic information about the documents at the heart of the case.
More on Trump’s Legal Troubles
Key Inquiries: Trump faces several investigations at both the state and the federal levels, into matters related to his business and political careers.
Case Tracker: Keep track of the developments in the criminal cases involving the former president.
What if Trump Is Convicted?: Could he go to prison ? And will any of the proceedings hinder Trump’s presidential campaign? Here is what we know , and what we don’t know .
Trump on Trial Newsletter: Sign up here to get the latest news and analysis on the cases in New York, Florida, Georgia and Washington, D.C.
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Edit, Fill & eSign PDF Documents Online. No Downloads Needed. Get Started Now. Best PDF Fillable Form Builder. Professional Toolset. Quick and Simple. Subscribe for more
Improve your text interactively and quickly get ideas on how to improve your text. Write better articles and essays with Advanced AI writing checker and sentence corrector.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
Elaborate a thesis statement. The thesis statement. is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics.
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper. ... A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
A Thesis Statement: Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results. Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic. Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it.
Form your opinion and reword it into your thesis statement that represents a very short summary of the key points you base your claim on:; While there is some hesitancy around vaccinations against Covid-19, most of the presented arguments revolve around unfounded fears and the individual freedom to make one's own decisions.
thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you'll make in the rest of your paper. What is a thesis statement? A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of ...
Think of the thesis statement as a one-sentence summary that tells the reader exactly what an essay says. Rather than writing your essay like a puzzle, keeping the reader in suspense about what conclusion you'll reach by the end, use the thesis statement like a treasure map to give the reader a sense of your essay's direction.
It serves as a concise summary of the main point or argument that the writer will be making in the rest of the paper. The thesis statement is typically located towards the end of the introduction and may consist of one or two sentences. How Long Should A Thesis Statement Be. Thesis Statement Should be between 1-2 sentences and no more than 25 ...
Generally, the summary is about 200-350 words long, but you should verify this with your supervisor. Also, it generally follows an introduction-body-conclusion structure. Related reading: The basics of converting your PhD thesis into journal articles. Answered by Editage Insights on 13 Sep, 2017.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
The thesis summary is a substantive description of your work read by an external examiner by presenting all the major elements of your work in a highly condensed form. Size and Structure Normally, a thesis summary would only contain 120 or less (for undergraduate theses), 150 words (for Masters theses) and 350 words (for a doctoral dissertation).
Many learners confuse a thesis statement summary with an analysis. An analysis is a discussion of the techniques, ideas, and meaning in the text. On the other hand, a summary does not entail responding or critiquing the ideas in the text. Analyzing a paper entails summarizing its content to establish the ideas that you will be analyzing.
The thesis should illustrate your conclusions in the summary. A strong thesis in a summary should indicate the point of the discussion and express one main idea. Those reading your summary need to be able to see that there is one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one main idea, your readers may become confused.
A thesis summary is a document that summarizes the points of a longer essay, thesis, or dissertation. Readers will often find a summary to be helpful as it offers a succinct overview of the document's contents. A Thesis Summary should not be confused with an abstract as they both refer to separate documents that serve different purposes.
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
Summary: The signs of economic stabilization are strengthening, with gradual disinflation underway and external pressures easing further since the first review on the back of improved fiscal balances. However, the outlook remains challenging, with downside risks remaining exceptionally high. Series:
Kennedy campaign spokesperson Stefanie Spear said in a statement that "the issue was resolved more than 10 years ago, and he is in robust physical and mental health."
President Biden spoke this morning with Prime Minister Netanyahu. The President reaffirmed his message on Yom HaShoah, Holocaust Remembrance Day. The two leaders discussed the shared commitment of ...
As part of the Biden-Harris Administration's continued efforts to enhance the security of our border and deliver more timely consequences for those encountered who do not have a legal basis to remain in the United States, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), through U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), published a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that would allow ...
The new Ultimate Universe just killed off two god-tier heroes in Marvel Comics canon: Black Bolt and Sentry. The Ultimates discover this upon investigating the Maker's Damage Control facility, where they find the corpses of these heroes on display. Killing Black Bolt and Sentry is a bold statement by Marvel, as it tells fans that there will be ...
The judge, Justice Juan M. Merchan of State Supreme Court, agreed that some of Ms. Daniels's testimony might have "been better left unsaid," but he denied a mistrial. The former president is ...
SUMMARY: The Department of State has submitted the information collection described below to the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) for approval. In accordance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995 we are requesting comments on this collection from all interested individuals and organizations.