- Other Guides
- How to Write a Position Paper: Definition, Outline & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

How to Write a Position Paper: Definition, Outline & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A position paper is a written statement that presents a particular perspective on any issue or topic. It typically argues a specific point of view and presents evidence to support that position. To write a position paper, you need to research and understand the topic, develop a supported argument, and address opposing viewpoints.
In this comprehensive guide, you will find all important information that will help you prepare this type of assignment. More specifically we will talk about:
- What is a position paper?
- How to write a position paper?
- Position paper example you could use for inspiration.
As an experienced paper writer team, we always come to support fellow students by providing them with helpful information and tips. Our readers can find detailed definitions and high-quality supporting materials on this website – all of that available for free!
What Is a Position Paper: Definition
First of all, let’s define it. Your position paper should clearly display and support your own view of a specific problem. Typically, position papers explore more or less controversial questions, which is why they must include argumentation supported by valid data. Providing evidence to the readers is the main distinctive feature of such an essay. Your work should demonstrate your ability to put up a strong case, not just describe your beliefs. Before you write a position paper, think it through and start with understanding your purpose. What do you try to tell your audience, and what is the best way to convey it? This helps with building good argumentation and structuring your essay.
Keep in mind that unlike a persuasive essay , convincing your readers to accept your point isn’t your primary task. Your piece should mainly focus on information that makes an argument strong. That’s why you should use supportive evidence that backs up your viewpoints.
Purpose of a Position Paper
Why do you need a position paper? First of all, it serves as great supporting material when talking about your viewpoint in front of an audience. Writing a position paper beforehand helps to organize your thoughts on the topic and set your defenses properly. Besides, you can use it when speaking to ensure you haven’t forgotten to mention something important. You might also be required to submit your paper before or after your speech. If it is your college or university assignment, this document will be your main output, which is why its structure and format are so important.
Position Paper Outline
One of the main first steps is preparing an outline for a position paper. After you’ve done some research and gathered enough data on your topic, spend additional time and create a concise draft. It should display your paper’s entire structure, including the key arguments, without going into much details. Your writing should follow a basic 5 paragraph essay outline . Once done with your plan, you can review it and easily spot major gaps or inconsistencies. Checking your work at this stage is typically much more productive than after writing the full text. Here is an example of position paper outline:
- Hook the reader with stats, numbers or facts
- Introduce the issue
- Include a thesis statement presenting your central idea and stand on the problem
- Present counterclaims
- Offer evidence that backs up counterarguments
- Refute the counter arguments using examples
- Strong opinion
- Supporting examples
- Restate your main claim
- Offer a course of action
Hopefully, this position paper template will speed up your progress with your own work. Check the attachments below – complete sample papers along with outlines are available there.
Position Paper Structure
What exactly does the structure of a position paper include? This is quite easy: similarly to any other scholarly essay, your position paper should contain three main parts:
Introduction
- Main body part
- Conclusion.
You’ll write a good position paper if you make it readable and concise in addition to preparing string argumentation backed by valid evidence. Otherwise, your poorly structured text won’t impress your readers. We’ve prepared more helpful information on how you should compose each of these sections. You can find it below, so please read it attentively. Also, check out the sample position papers available on this page. You can find more tips and ideas below.
Good introduction for a position paper should make your reader well familiar with the problem you are arguing about. This typically involves explaining why it is important for everyone or why you’ve decided to discuss it. Besides, the introduction must engage your audience so that they would be interested in hearing more about your position and evaluating its validity. This is how to start writing a position paper:
- Clearly state your position, giving the thesis statement.
- Give enough context about the problem and its background, explaining why you stand this ground.
- ‘Hook’ your readers by making it sound interesting.
The latter can be achieved by making some hints about upcoming evidence, using some kind of wordplay, or just making a suitable joke.
Body of a position paper is where its argumentation should be placed. When you make a position paper, be sure to divide it into logically interconnected paragraphs – each one for one of your major arguments expressed in the topic sentence . Make proper transitions between them. Leave at least one paragraph for the counter argumentation you may have faced and for its rebuttal. The evidence you’ve collected to support your claim should also be presented in the main body, together with quotes and references (if any). Remember to use solid and relevant data and avoid unnecessary facts, as they don’t bring value and may just make the text less readable. Pay attention to the consistency and readability of this section. Its structure and contents show how well you’ve built your argumentation. And that is what makes position papers persuasive.
This is how to write a conclusion for a position paper that adds real value to it:
- Properly summarize your argumentation, showing how it supports your take.
- Make it sound strong; ensure that it is logical and well-readable.
- Keep it brief, don’t repeat anything from the main part.
Remember that your proposition paper conclusion will be the last thing your audience reads, so making a strong and persuasive ending would help with leaving a good impression on it. You’ll find a conclusion template in one of the sections below.
How to Write a Position Paper in 9 Steps
Let’s get to the point – you must write a good position paper, and now you’re looking for some helpful tips on that. We’ve got your back! First and foremost, the best beginning is to set up a strong position. Otherwise, your essay will simply be uninteresting. Now make sure you can actually prove what it states. But that’s just the beginning: think about captivating headings, add some clever techniques and diligent work to that, keeping focus on your goal – and you’ll get an excellent paper. What should be added? Just keep reading. We’ve prepared an elaborate guide on how to write a position paper step by step. Let’s go and check it!
1. Choose a Topic
Creating position papers requires some hard work, but choosing a proper subject may save a lot of time and effort. If it is uninteresting or too narrow, that might result in an issue. Better to choose a topic that:
- Is relevant and controversial: this will draw your readers’ interest.
- Is understandable for you, so it would be easier for you to discuss some points about it.
- Has received some coverage in news, books, or other sources, making it simpler to find enough evidence about it.
Before commencing the writing process, search among good topics for position papers and select one most suitable for taking a point around it.
2. Do Research Before Writing a Position Paper
Conducting preliminary research for position papers is a key step before starting with actual writing. This is where you can collect evidence about your subject:
- Google it This is easier but remember to filter out results with low credibility.
- Media If this is a recent and big event, it should be mentioned in the news; make sure to pick the most credible resources.
- Check the sources used by books or articles written on the subject This way, you might find some ‘hidden gems’ that are difficult to google.
Don’t know if you’ll write a winning position paper? Follow the next steps closely. And don’t forget to explore the free samples available on this page, check their structure and style.
3. Draft a Position Paper Thesis
Thesis of a position paper is basically its foundation. Make it strong, and you’ll ensure your success. Don’t be too wordy. One sentence is enough to deliver your thesis and summarize your position on the topic. You can put it closer to the start or put it at the end of your introduction so that it summarizes the explanations you would give about the problem. Examples of a position paper thesis:
4. Create an Outline
Once you have decided about the direction you’re taking with your essay, proceed with the position essay outline. This step is often overlooked, but it will be much easier to find and correct mistakes and gaps at this early stage. So, writing a position paper outline actually saves you time. This is how to write a position paper outline:
- Keep it brief, just one sentence per idea. No need to always use full sentences, just make them readable.
- Include your thesis, mention the context, then write one sentence per each argument.
- Briefly summarize it, one sentence will suffice as well.
Don’t forget to review your outline carefully.
5. Begin Writing Your Position Paper
Once you’ve ensured the outline of an essay doesn’t have any gaps or logical flaws, go ahead and complete the full-text version. If you wonder how to start a position paper at this stage, begin with the introduction. You already have its shortened draft, so just add necessary details and list explanations if needed. But don’t give particular arguments or refute opposing opinions yet, those should come in the main body part. See how to write an introductory paragraph for a position paper in the next section.
Position Paper Introduction Example
Looking for introduction position paper examples? We’ve got one for you. Here’s how you can start your essay:
Check our sample position paper for introduction examples. They are available for free download.
6. Include Evidence in Your Position Paper
As we’ve already explained, position papers must be backed by solid evidence. You have to prove your point, and that requires addressing it with data, not just stating it with confidence. When you write your position paper, there are two main requirements for backing your claim:
- collect valid and relevant data;
- present it in your text properly.
Here’s an example of evidence in a position paper:
7. Provide Counterarguments and Refute Them
Still learning how to write position paper? If it is your first one, consider an important fact: ignoring evident contradictions to your claim doesn’t add credibility. Instead, you must work with counter arguments which is similar to writing an argumentative essay . You may be aware of the opposite opinions or think and assume which objections your opponents would make. Better mention them in your essay and show how you counter these claims. Here are some examples of counterarguments for position papers:
8. Summarize Your Position
When writing your position paper, it is important that you make it sound impressive in the end. Your position paper conclusion should properly summarize all arguments and rebuttal of counterarguments . Keep it brief, without repeating much, just highlight how all your findings support the claim. You can also add some extra notes, e.g., making additional assumptions, different predictions about this problem’s impact in the future, or hints about extra evidence you haven’t mentioned before to keep your text brief. This may help to make a lasting impression on your audience. Finally, review your conclusion once again, ensuring that it is logical and doesn’t contradict any claims, arguments, or assumptions provided above. Check the next section for an example of how to write a position paper conclusion.
Example of a Position Paper Conclusion
Need an actual conclusion for a position essay example? It can be something like this:
You can also find the conclusion of a position paper essay example if you check the free samples that are available on this page.
9. Proofread Your Position Paper
After your position essay is complete, you absolutely should spend some extra time and review it again. Try adopting a critical view, putting yourself in your potential opponent’s shoes. Are there any logical gaps or grammar mistakes left? Paper position is not clear enough? Wrong source mentioned? Nearly every text has some issues to correct. Sometimes even evident typos are left overlooked when writing. It is best to have someone else review a position paper since its writer may be biased toward their own text. Another way is reading it aloud to yourself prior to submission. Some flaws may be uncovered this way too.
Position Paper Format
Your position papers format is another element that shouldn’t be overlooked. Proper headline and paragraph styles make your text more readable. Also, there might be specific requirements for making citations. All your evidence must be presented correctly so that it doesn’t get mixed with your own opinions. Format depends on the discipline. You might need to use one of the popular styles: MLA, APA, or Chicago. If you don’t see which one of them is required, better ask your tutor. You can find some position paper format sample in our free attachments, available below.
Position Paper Examples
Need an example of a position paper so that you could learn how all these recommendations can be implemented? We’ve got some for you! Scroll down to the bottom of the page, and you’ll find sample of position papers available for free download. Each position paper example essay has been written by professional research writers and can be used for inspiration or as a reference. Just don’t copy any of those materials in your own text, as you should only submit 100% original works. Position paper example 1
Position paper example 2
Position paper example 3
Position Paper Sample 4
Tips for Writing a Position Paper
Finally, some extra tips on writing a position paper that is really persuasive:
- Choose topics that are interesting for you. This will motivate you to discuss them.
- Plan ahead and consider your deadlines. Don’t spend too much time conducting the preliminary research or perfecting your argumentation if it is already valid.
- Pay attention to your sources. Some books or research might be considered dubious by your opponents or might have some obvious gaps.
- Review your position papers as many times as possible. Ideally, ask a person with an opposite side on this issue to read and refute it.
- Keep it professional. Maintain a confident tone but stay logical and correct, avoid emotional or derogatory remarks.
More examples of position papers are available here – you can check them below.
Final Thoughts on How to Write a Position Paper
So, in order to write a position paper, you need to choose an appropriate topic and elaborate on your position regarding the specific problem. Then you should defend it using logic, facts, and confidence. Still not clear what are position papers and how one should write them? Check out this sample position paper for students available below, and you’ll find all our tips illustrated there. Follow its structure and style, just don’t copy anything to avoid plagiarizing.
If you are stuck in any stage of the writing process, don’t hesitate to use professional academic writing services. StudyCrumb is always here for you to solve any academic challenge you may have. Let us know your task, and we will match you with the most fitting expert who can write an excellent position paper for you.

Rachel R. Hill is a real educational devotee. She prides in writing exceptional general guides while listening to every need of students.
You may also like

• Online education is cost-effective, being more affordable for both students and educational institutions. • Schools should offer low-income pupils summertime educational resources.
Traditional education is commonly regarded as a better alternative since live interaction with teachers often facilitates the learning process. However, given the ever-growing problem with student loans, the affordability of online education has become an important factor. Additionally, when studying online, people don’t have to commute, thus saving extra time and money. So, we can see that online education is more effective for common students.
As shown by many researchers (particularly by Kim and Norton in their work, 2018), more than 60% of students in the US attend online courses on a regular basis.
Evidently, e-learning doesn’t allow face-to-face interaction with your tutor, which may make it harder to exchange experience. However, the affordability factor still makes it a better choice, especially for motivated students. The price difference between traditional and online education might not be that big. But if we add the price of commuting and time spent on that, this difference becomes much bigger.
According to the statistical data presented above, e-learning is already gaining increasing popularity among students below 25 ages all over the globe. Since it is better compatible with the part-time work schedule most students have to follow, this format has actually proven its efficiency in recent years. And it is quite safe to assume it will become a new dominant way of education within the next decade or two.
FAQ About a Position Paper
1. how long should a position paper be.
The length of a position paper is usually limited to one page and a half (up to 350 words). Don’t make it too long, stick to the facts and brief statements. When given with confidence, concise claims are more persuasive. At the same time better include all necessary evidence, not rely just on confidence. So don’t make it less than one page.
2. What are the kinds of support in a position paper?
You can use these support types in your position paper:
- Factual knowledge: either well-known facts (e.g., historical or biological) or data retrieved from credible sources;
- Statistical trends: always helpful for making assumptions but also need to be backed by sources;
- Informed opinion: citations from renowned specialists in fields related to your topic.
3. What is forbidden in a position paper?
When writing a position paper, avoid the following:
- Taking opinions for facts.
- Using threats or derogatory language as a means of persuasion.
- Comparing unrelated situations and making some conclusions from that.
- Copying other works without citing them.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Position Paper
Definition:
Position paper is a written document that presents an argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. It outlines the author’s position on the issue and provides support for that position with evidence and reasoning. Position papers are commonly used in academic settings, such as in Model United Nations conferences or debates, but they can also be used in professional or political contexts.
Position papers typically begin with an introduction that presents the issue and the author’s position on it. The body of the paper then provides evidence and reasoning to support that position, often citing relevant sources and research. The conclusion of the paper summarizes the author’s argument and emphasizes its importance.
Types of Position Paper
There are several types of position papers, including:
- Advocacy Position Paper : This type of position paper presents an argument in support of a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to persuade the reader to take a particular action or adopt a particular perspective.
- Counter-Argument Position Paper: This type of position paper presents an argument against a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to convince the reader to reject a particular perspective or course of action.
- Problem-Solution Position Paper : This type of position paper identifies a problem and presents a solution to it. It seeks to convince the reader that the proposed solution is the best course of action to address the identified problem.
- Comparative Position Paper : This type of position paper compares and contrasts two or more options, policies, or proposals. It seeks to convince the reader that one option is better than the others.
- Historical Position Paper : This type of position paper examines a historical event, policy, or perspective and presents an argument based on the analysis of the historical context.
- Interpretive Position Paper : This type of position paper provides an interpretation or analysis of a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to persuade the reader to adopt a particular perspective or understanding of the topic.
- Policy Position Paper: This type of position paper outlines a specific policy proposal and presents an argument in support of it. It may also address potential objections to the proposal and offer solutions to address those objections.
- Value Position Paper: This type of position paper argues for or against a particular value or set of values. It seeks to convince the reader that a particular value or set of values is more important or better than others.
- Predictive Position Paper : This type of position paper makes predictions about future events or trends and presents an argument for why those predictions are likely to come true. It may also offer suggestions for how to prepare for or respond to those events or trends.
- Personal Position Paper : This type of position paper presents an individual’s personal perspective or opinion on a particular issue. It may draw on personal experiences or beliefs to support the argument.
Position Paper Format
Here is a format you can follow when writing a position paper:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide a brief overview of the topic or issue being discussed. It should also provide some background information on the issue and state the purpose of the position paper.
- Definition of the problem : This section should describe the problem or issue that the position paper addresses. It should explain the causes and effects of the problem and provide evidence to support the claims made.
- Historical perspective : This section should provide a historical perspective on the issue or problem, outlining how it has evolved over time and what previous attempts have been made to address it.
- The organization’s stance : This section should present the organization’s stance on the issue or problem. It should provide evidence to support the organization’s position and explain the rationale behind it. This section should also address any counterarguments or alternative perspectives.
- Proposed solutions: This section should provide proposed solutions or recommendations to address the problem or issue. It should explain how the proposed solutions align with the organization’s stance and provide evidence to support their effectiveness.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the organization’s position on the issue or problem and restate the proposed solutions or recommendations. It should also encourage further discussion and action on the issue.
- References: Include a list of references used to support the claims made in the position paper.
How to Write Position Paper
Here are the steps to write a position paper:
- Choose your topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or have knowledge of. It could be related to social, economic, environmental, political, or any other issues.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on the topic to gather relevant information and supporting evidence. This could include reading scholarly articles, reports, books, and news articles.
- Define your position: Once you have gathered sufficient information, identify the main arguments and formulate your position. Consider both the pros and cons of the issue.
- Write an introduction : Start your position paper with a brief introduction that provides some background information on the topic and highlights the key points that you will discuss in the paper.
- Present your arguments: In the body of your paper, present your arguments in a logical and coherent manner. Each argument should be supported by evidence from your research.
- Address opposing views : Acknowledge and address the opposing views on the issue. Provide counterarguments that refute these views and explain why your position is more valid.
- Conclusion : In the conclusion, summarize your main points and reiterate your position on the topic. You can also suggest some solutions or actions that can be taken to address the issue.
- Edit and proofread : Finally, edit and proofread your position paper to ensure that it is well-written, clear, and free of errors.
Position Paper Example
Position Paper Example structure is as follows:
- Introduction:
- A brief overview of the issue
- A clear statement of the position the paper is taking
- Background:
- A detailed explanation of the issue
- A discussion of the history of the issue
- An analysis of any previous actions taken on the issue
- A detailed explanation of the position taken by the paper
- A discussion of the reasons for the position taken
- Evidence supporting the position, such as statistics, research, and expert opinions
- Counterarguments:
- A discussion of opposing views and arguments
- A rebuttal of those opposing views and arguments
- A discussion of why the position taken is more valid than the opposing views
- Conclusion:
- A summary of the main points of the paper
- A call to action or recommendation for action
- A final statement reinforcing the position taken by the paper
- References:
- A list of sources used in the paper, cited in an appropriate citation style
Purpose of Position Paper
Here are some of the most common purposes of position papers:
- Advocacy: Position papers are often used to promote a particular point of view or to advocate for a specific policy or action.
- Debate : In a debate, participants are often required to write position papers outlining their argument. These papers help the debaters clarify their position and provide evidence to support their claims.
- Negotiation : Position papers can be used as part of negotiations to establish each party’s position on a particular issue.
- Education : Position papers can be used to educate the public, policymakers, and other stakeholders about complex issues by presenting a clear and concise argument supported by evidence.
- Decision-making : Position papers can be used by decision-makers to make informed decisions about policies, programs, or initiatives based on a well-reasoned argument.
- Research : Position papers can be used as a starting point for further research on a particular topic or issue.
When to Write Position Paper
Here are some common situations when you might need to write a position paper:
- Advocacy or lobbying : If you are part of an organization that is advocating for a specific policy change or trying to influence decision-makers, a position paper can help you articulate your organization’s position and provide evidence to support your arguments.
- Conferences or debates: In academic or professional settings, you may be asked to write a position paper to present your perspective on a particular topic or issue. This can be a useful exercise to help you clarify your thoughts and prepare for a debate or discussion.
- Public relations: A position paper can also be used as a tool for public relations, to showcase your organization’s expertise and thought leadership on a particular issue.
- Internal communications: Within an organization, a position paper can be used to communicate a particular stance or policy to employees or stakeholders.
Advantages of Position Paper
There are several advantages to writing a position paper, including:
- Organizing thoughts : Writing a position paper requires careful consideration of the issue at hand, and the process of organizing thoughts and arguments can help you clarify your own position.
- Demonstrating expertise: Position papers are often used in academic and professional settings to demonstrate expertise on a particular topic. Writing a well-researched and well-written position paper can help establish your credibility and expertise in a given field.
- Advocacy: Position papers are often used as a tool for advocacy, whether it’s advocating for a particular policy or for a specific point of view. Position papers can help persuade others to adopt your position on an issue.
- Facilitating discussion : Position papers can be used to facilitate discussion and debate on a particular issue. By presenting different perspectives on an issue, position papers can help foster dialogue and lead to a better understanding of the topic at hand.
- Providing a framework for action: Position papers can also be used to provide a framework for action. By outlining specific steps that should be taken to address an issue, a position paper can help guide decision-making and policy development.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

What is Art – Definition, Types, Examples

What is Anthropology – Definition and Overview

What is Literature – Definition, Types, Examples

Economist – Definition, Types, Work Area

Anthropologist – Definition, Types, Work Area

What is History – Definitions, Periods, Methods
A Brief Guide to Writing a Position Paper
13 July, 2020
13 minutes read
Author: Mathieu Johnson
Speaking your thoughts out loud happens to be easier than doing the same in writing. Why is that so? Every time you prepare a speech, you need to write it down first. And your writing needs to be precise because readers are about to know what you’ve put down on a paper. When it comes to a position paper, your mission is to express your opinion on a controversial topic. You will have to take a side on a specific topic and make up a case based on your opinion. To succeed in this writing task, you may need some guidelines.

What Is Position Paper?
A position paper is a kind of essay in which you express your opinion or position regarding a particular subject matter. It can be used for different purposes, from a discussion of international challenges to an analysis of business strategies. As a result, a position paper format is widely used in business and politics. Also, it can take a form of a report revealing your plans for the subject matter at hand. A position paper should contain a smooth flow of thoughts and ideas that provide a rock-solid evidence for your line of reasoning.

What Are The 3 Parts of a Position Paper?
A position paper consists of three main parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Here is an explanation of what you can write in each part:
Introduction
The introductory part aims to attract the reader’s attention to the covered subject matter. Ideally, you should begin with several opening sentences about the specific issue to hook the reader.
The body part involves background information, evidence to back up your opinion, and analysis of both sides of the subject matter. By conducting thorough research, you will collect enough data to support your claims. The main point is to address both aspects of the argument. That way, you will show the reader that you are objective in your statements.
In the conclusion part, you need to restate the key points of your essay without adding anything new. Depending on your topic, it makes sense to suggest a solution to the problem.
How to Write a Position Paper?
To start writing a position paper , you should have a clearly stated topic that is debatable with logical details. While writing a paper, you should examine your vision of the problem through the prism of available arguments. Consider practicability, cost-effectiveness, and local environment when evaluating possible solutions and necessary actions. In other words, you should express, explain, and back up your opinion. And don’t forget to be specific in stating and supporting your arguments.
Select a Position Paper Topic
If you want to create a good position paper, you should focus on a subject matter that has enough findings to support it as well as some controversy to produce an argument. If you are dealing with a position paper assignment, you will want to skip your personal values and focus on something that can get you the highest grade. Here are some of the position paper topics to consider:
- Should reality TV shows be regulated?
- What are the positive and negative sides of video gaming?
- Are there any parallels between video gaming and addiction?
- Can beauty contests have a positive impact on women?
- Should children have a schedule for school and after-school activities or be given more free time for playing?
- What affects the rapid increase in child obesity?
- How to reduce the number of abortions without legislation?
- How can pro-life and pro-choice groups cooperate?
- Should the production of Barbie dolls be banned?
- What is the meaning of true beauty?
- Should young children be forced to compete at athletics?
- What are the reasons for blood cancer?
- How does COVID-19 pandemic affect the business sector?
- Is COVID-19 a real problem or a huge fake?
- How does COVID-19 affect our lives?
- Should media coverage be taken under control?
- Is private school tuition really worth it?
- How can the country’s school system be amended?
- What role should technology play in the business sector?
- Should college athletes receive a salary?
- Should college athletes be allowed to skip classes?
- Technologies are changing the way people think.
- How are online technologies affecting the way we live?
- What laws should regulate the use of cell phones in cars?
- Should parents limit teenagers’ use of social media?
- Should scientists be allowed to experiment on human embryos?
- What causes people to immigrate illegally?
- Is there any way to reduce the immigration rate?
- Can illegal immigration be justified?
- How do people justify war?
- How significant is race to American identity?
- What is the world culture?
- What is the value of knowing your cultural background?
- Should schools teach multiculturalism?
- Is global warming a problem?
- Is racism the problem of the modern community?
- How can clean water be provided to everyone?
- Is the problem of air pollution exaggerated?
- What needs to be done to reduce the level of air pollution?
- Who should take responsibility for air pollution?
- Will the worldwide population increase?
- What needs to be done to stop poaching of endangered species?
- Is hunting good for the environment?
- Are citizens responsible for their local environment?
- What can manufacturers do to reduce the air and water pollution across the world?
- What is the real importance of clean water?
- Is there any connection between health and pollution?
- What can people do to stop global pollution?
- How can people be encouraged to recycle more?
- How does global warming increase?
Preliminary Research
How do you write a position paper? Where to start from? Preliminary research requires you to find sufficient evidence for the covered subject matter. At the same time, you don’t need to rely on a subject matter that falls apart under a challenge of hefty research. You will also need to specify the sources you are planning to use. Follow them in bibliography and make some notes about every particular book, journal, or document you take information from. Thus, you will save a lot of time in the writing process.
By searching a couple of education and social sites, you will be able to find professional research data. Our professional essay writer recommends to narrow your focus, you will develop a list of questions that you have to answer in your paper. If you find no valuable information after spending several hours on research, you should understand that your position cannot be supported by sufficient findings on trustworthy sites.
Challenge Your Topic and Collect Supporting Evidence
You will need to dispute the truth or validity of your topic by finding supporting evidence. If you have some doubts, you may need some time to identify all the possible challenges that you have to deal with. Your position paper will address the opposing view and address it with counterevidence. It will make sense to have some discussions with friends, colleagues, or family about the topic. That way, you will be able to learn some additional thoughts and ideas that can be used for further research. As soon as you find some counterarguments, you will need to analyze them. Once it is done, you will see whether they are sound or not.
Another useful approach to challenging the topic requires you to mention your arguments on one side and opposing arguments on the other one. In which part of the paper do you have more points collected? Which points are stronger? If counterarguments seem to outnumber your arguments, you will have to reconsider your subject matter or your opinion on it .
Position Paper Outline
Before taking action, you’ll need to develop a position paper outline to organize your thoughts and ideas. With an outline, you will find it easier to write a position paper. So how will you do that? It depends on your personal preferences. Some writers find it easier to apply pictures and diagrams, others just follow a template offered by the teacher. If you feel like writing an outline yourself from scratch, don’t hesitate to do so. You can create it on your computer or write it down in your notebook. After all, there is no right or wrong approach to developing an outline. The main point is that an outline contains all the key points that you have to add to your position paper. You may want to look at a position paper sample before starting the writing process. Here is the format to be followed:
Decide on your topic with some background details. Develop a thesis sentence that addresses your position. Some examples are as follows:
- Smoking is a bad habit causing breathing problems.
- Fast food packages should be marked with health warnings .
- Air pollution requires certain actions from the national governments.
Decide on potential contradictions to your position. Here are some examples: :
- A medical examination needs to be conducted on an annual basis to monitor the possible negative health conditions .
- Health warnings can affect the companies’ revenues.
- The national program can be quite costly.
Cover the opposing points. Make sure that you aren’t contradicting your own thoughts and ideas. Sample points are as follows:
- It can be hard to determine the monitoring process.
- Citizens don’t want their government to abuse its power.
- Program funding will fall on the shoulders of average taxpayers.
Explain your position through the prism of counterarguments. This is how you can contradict some of the counterarguments and back up your own one. Sample points are as follows:
- The government has already tried to reduce smoking statistics in the country.
- Restaurants will enhance the quality of food in case of using health warnings .
- The government’s primary role is to protect citizens.
Sum up your arguments and express your opinion in different words. You should finish your paper by focusing on your arguments and responding to the counterarguments. You need your reader to understand and accept your opinion on the covered subject matter.
When you create a position paper, you should act with confidence. In the end, your mission is to reveal your position from the best side.
Tips on Writing a Position Paper from Our Experts
Even if you have a position paper example, you still may need some practical recommendations to make things easier for you. Here are some tips you need to follow during the writing process:
- Decide on a topic. While choosing the topic for discussion, you should find the one you have a clear idea of. You can broaden your outlook by reading some literature on the desired subject matter. Ideally, you should embark on different viewpoints to consider them for further analysis.
- Express your position idea. Focus on one specific aspect of the topic in order to express it in a one-sentence opinion. Make sure you have found a really arguable idea. If the topic cannot be debated, then it can hardly be used for writing a good position paper.
- Be precise in your statement. Try to express your opinion briefly and clearly. A position paper is not meant to be vague.
- Lead the narrative in the present tense. You are discussing the topic here and now, so the use of the past tense is quite inappropriate.
- Minimize the use of superlatives . Avoid using superlatives such as biggest, major, extremely, and so on because they make the context sound exaggerated.
- Use frequently used terms. To make the content look appealing and well-written , you should use the most common thematic terms such as world community, member states, recommendations, development, realization, regulations, international, and so on.
- Use commonly used verbs . You should include some commonly used verbs such as comprehend, enable, recognize, acknowledge, believe, suggest, consider, addresse, highlight, and so on.
- Proceed with final proofreading . You cannot consider your position paper as completed unless a successful spelling and grammar check is done. To achieve the maximum result, you should read your paper aloud a couple of times. That way, you will find it easier to indicate and fix mistakes.
While there is no universal formula for writing a perfect position paper, you can still follow some simple tips that’ll make you closer to the desired result. Just think analytically and act logically throughout the writing process.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
In a position paper assignment, your charge is to choose a side on a particular topic, sometimes controversial, and build up a case for your opinion or position. You will use facts, opinion, statistics, and other forms of evidence to convince your reader that your position is the best one. To do this, you'll collect research for your position paper and craft an outline in order to create a well-constructed argument.
Select a Topic for Your Paper
Your position paper centers around a topic that is supported by research. Your topic and position have to hold up when challenged, so it's helpful to research a few topics and pick the one you can best argue, even if it may not reflect your personal beliefs. In many cases, the subject matter and your topic are not as important as your ability to make a strong case. Your topic can be simple or complex, but your argument must be sound and logical.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Preliminary research is necessary to determine whether sufficient evidence is available to back up your stance. You don’t want to get too attached to a topic that falls apart under a challenge.
Search a few reputable sites, like education (.edu) sites and government (.gov) sites, to find professional studies and statistics. If you come up with nothing after an hour of searching, or if you find that your position doesn’t stand up to the findings on reputable sites, choose another topic. This could save you from a lot of frustration later.
Challenge Your Own Topic
You must know the opposite view as well as you know your own stance when you take a position. Take the time to determine all the possible challenges that you might face as you support your view. Your position paper must address the opposing view and chip away at it with counter-evidence. Consider having friends, colleagues, or family debate the topic with you to get alternative points of view that you might not have readily considered yourself. When you find arguments for the other side of your position, you can address them in a fair manner, and then state why they are not sound.
Another helpful exercise is to draw a line down the middle of a plain sheet of paper and list your points on one side and list opposing points on the other side. Which argument is really better? If it looks like your opposition might outnumber you with valid points, you should reconsider your topic or your stance on the topic.
Continue to Collect Supporting Evidence
Once you’ve determined that your position is supportable and the opposite position is (in your opinion) weaker than your own, you are ready to branch out with your research. Go to a library and conduct a search, or ask the reference librarian to help you find more sources. You can, of course, conduct online research as well, but it's important to know how to properly vet the validity of the sources you use. Ensure that your articles are written by reputable sources, and be wary of singular sources that differ from the norm, as these are often subjective rather than factual in nature.
Try to collect a variety of sources, and include both an expert’s opinion (doctor, lawyer, or professor, for example) and personal experience (from a friend or family member) that can add an emotional appeal to your topic. These statements should support your own position but should read differently than your own words. The point of these is to add depth to your argument or provide anecdotal support.
Create an Outline
A position paper can be arranged in the following format:
1. Introduce your topic with some basic background information. Build up to your thesis sentence , which asserts your position. Sample points:
- For decades, the FDA has required that warning labels should be placed on certain products that pose a threat to public health.
- Fast food restaurants are bad for our health.
- Fast food packages should contain warning labels.
2. Introduce possible objections to your position. Sample points:
- Such labels would affect the profits of major corporations.
- Many people would see this as overreaching government control.
- Whose job is it to determine which restaurants are bad? Who draws the line?
- The program would be costly.
3. Support and acknowledge the opposing points. Just be sure you aren't discrediting your own views. Sample points:
- It would be difficult and expensive for any entity to determine which restaurants should adhere to the policy.
- Nobody wants to see the government overstepping its boundaries.
- Funding would fall on the shoulders of taxpayers.
4. Explain that your position is still the best one, despite the strength of counter-arguments. This is where you can work to discredit some of the counter-arguments and support your own. Sample points:
- The cost would be countered by the improvement of public health.
- Restaurants might improve the standards of food if warning labels were put into place.
- One role of the government is to keep citizens safe.
- The government already does this with drugs and cigarettes.
5. Summarize your argument and restate your position. End your paper focusing on your argument and avoid the counter-arguments. You want your audience to walk away with your view on the topic being one that resonates with them.
When you write a position paper, write with confidence and state your opinion with authority. After all, your goal is to demonstrate that your position is the correct one.
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- Choosing a Strong Research Topic
- Preparing an Argument Essay: Exploring Both Sides of an Issue
- The Five Steps of Writing an Essay
- What Is Expository Writing?
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- LSAT Writing: What You Need to Know
- Persuasive Writing: For and Against
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- What Is a Literature Review?

Top 10 Tips for Writing a Strong Position Paper
As scientists and researchers, you might be familiar with objective research papers, which tend to consider both sides of an argument and present findings based on facts. But are you aware of another important piece of academic writing known as the position paper? In this article, we will discuss different aspects that make position paper share expert tips on writing a great position paper that clearly presents an argument or opinion.
Table of Contents
What Is a Position Paper?
A position paper discusses a controversial issue and focuses on one aspect of an argument, providing valuable insights on how to interpret issues where science is ambiguous. It can also act as a medium for scientists and researchers to put forth solutions to resolve problems. Similar to objective research papers, position papers are still rooted in facts, statistics, evidence, and data. Additionally, they further enable authors to take a position on what these facts and data are telling us.
The purpose of a position paper is to gather support for an opinion on an issue by explaining the author’s stance and providing factual evidence to back it up. It critically evaluates the position, acknowledging its strengths and weaknesses.
Types of Position Paper
There are several types of position papers, each serving a unique purpose.
Ready to gauge your understanding of position papers? Take our short quiz today!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

How to Write a Position Paper?
1. choosing a good topic.
Selecting a good topic for your position paper is just as important as having a well-structured paper that presents a strong argument. A well-written paper about an uninteresting or uncontroversial topic is simply a waste of time and effort. So how can you best choose a topic for your argument ?
Like all types of research, you should begin with preliminary research. A good topic for a position paper will answer yes to the following questions :
- Does the topic represent a genuine controversy?
- Are there two clear positions?
- Do you care enough to argue for one of those positions?
- Is the scope of the topic manageable?
Once you have found a topic that meets these criteria, you will need to conduct research to build a solid case in favor of your argument. This means finding supporting evidence (for both sides!) just as you would for an ordinary research paper . By including supporting evidence for the opposing side, you will be able to more clearly refute the conflicting arguments. In other words, you can point out weaknesses in the evidence cited by the opposing side or highlight strengths of evidence that supports your stand in comparison.
2. Conducting a Preliminary Research
Conducting preliminary research is crucial before delving into any topic. Evaluate evidence quality from reputable sources institutional websites, white papers, policies, scholarly articles, research reports, etc. Stay objective, dedicating some time for research. Be adaptable; reconsider your topic if evidence is lacking or contradictory. Prioritize quality over quantity in source selection. This ensures a well-supported and credible argument.
3. Crafting and Testing Your Thesis Statement
Crafting a thesis statement is a pivotal step in developing a coherent paper. This statement depicts your stance on the topic. A clear and focused thesis statement serves as the backbone of your argument, guiding the reader and shaping the trajectory of your analysis. Once established, subject it to rigorous examination by challenging it.
While it may seem counterintuitive, actively challenging your own thesis statement is a vital exercise in academic integrity and intellectual rigor. By earnestly considering opposing viewpoints and potential counterarguments, you not only demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter but also fortify your position through logical reasoning and evidence-based support.
4. Collecting Supporting Evidence
When gathering evidence for your position paper, prioritize relevance and credibility. Use expert quotes sparingly, ensuring they directly support your argument. Prefer research-based evidence over anecdotes, focusing on quality rather than quantity. Verify the credibility of sources and regularly update evidence to reflect the latest research. Following these guidelines enhances the credibility and persuasiveness of your paper.
5. Drafting and Structuring the Position paper
The structure of a position paper is flexible, but it should generally follow a simple flow that clearly conveys the problem and the position of the author(s). A position paper should begin by clearly stating the problem and its relevance to the scientific community or even to the society as a whole. It should then address the main position of the author. For example:
a. Background: For decades, the WHO has urged the adoption of a tax on unhealthy foods to discourage the consumption of products that are harmful to our health.
b. Relevance: Sugar has been shown to have a negative impact on health, and play a major role in the rising obesity rates in America.
c. Position: The United States should adopt a tax on drinks with added sugar, to reduce the consumption of sugar, and promote healthier eating habits.
The author should then clearly list the common arguments and possible objections against this position. To continue with our example:
Argument 1: A sugary drink tax that focuses on soda may not impact other products that have an equally negative health impact such as fruit juice or candy.
Argument 2: A sugary drink tax is regressive and places a financial burden on the poorest consumers.
A strong position paper acknowledges the validity of the counter-arguments and then puts forth reasons why the author’s position is still the correct one. In our example paper, the author can address the counter-arguments in the next section like so:
Counter-argument 1: It is true that a sugary drink tax would not impact all sources of added sugar in the average American diet. However, it would still have a significant impact on a major source of added sugar to achieve its goal of reducing overall sugar consumption.
Counter-argument 2: All consumption taxes are regressive. A sugary drink tax would be most effective accompanied by subsidies for healthy foods such as fruit and vegetables.
Finally, summarize your main points and re-state your position in your conclusion. All arguments in the paper should be backed up by facts, data, and evidence , with proper citation attributed to your sources. In this way, a position paper is no different from an ordinary research paper . If you wish, you can include a brief literature review in your discussion of the background of the issue. While such a literature review is not essential, it can make your paper stronger.
Ten Tips for Writing a Strong Position Paper
Now that we know what a position paper is, let us review some tips to write a great position paper.
- Select a timely, relevant topic with two clear opposing sides.
- Conduct thorough preliminary research, collecting evidence supporting arguments for and against your position.
- Identify your intended audience. You should tailor your tone depending on who the paper is written for (the public, other scientists, policymakers, etc.).
- Clearly state your position on the topic.
- List and refute the counter-arguments to your position.
- Include supporting data and evidence to back up your argument.
- Properly attribute your sources using correct citation .
- Keep it simple! Position papers don’t need to go into excessive detail . Present your points clearly and briefly.
- Each paragraph in the paper should discuss a single idea.
- Have someone proofread your paper to ensure it reads well and looks professional.
A position paper can be a great way to expand your horizons and write a new type of research paper. Use these ten tips to write an effective position paper!
Are you seeking advice on writing a position paper? Seek professional assistance to craft a compelling argument in your position paper that effectively communicates your perspective to the scientific community.
Frequently Asked Questions
The length of a position paper can vary depending on the requirements set by the institution or conference. However, typically, position papers are concise and focused documents, usually ranging from 1,000 to 2,000 words.
The purpose of a position paper is to articulate an author's stance on a particular issue or topic, backed by factual evidence and logical reasoning.
Characteristics of a position paper include: 1.Focus on a controversial issue or topic. 2.Clear statement of author's stance or position. 3.Incorporation of factual evidence, statistics, and data. 4.Acknowledgment of counterarguments and addressing them effectively. 5.Concise and well-structured presentation of arguments.
Very informative
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Intersectionality in Academia: Dealing with diverse perspectives
Meritocracy and Diversity in Science: Increasing inclusivity in STEM education
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
VII. Researched Writing
7.2 Researched Position Paper
Terri Pantuso
Now that you have found a topic to research, it is time to begin the research process. Though you may have an idea of what you think your argument will be at this point, it’s important to start your research with an open mind. It’s often helpful to formulate your topic as a research question. Research questions are open-ended questions that you explore as you figure out the direction your topic will go and inform or shape your thesis statement. For example, if your topic is on first-generation students and financial aid, you might have a research question such as “What is the long-term impact of student loans on first-generation college students?” Using such a question as you begin your research leaves you a lot of flexibility to adjust your position, and therefore your thesis, as you uncover new information.
Using that research question as the foundation for your research, you can begin your proposal. This is oftentimes the first step in the process of writing a researched position paper. Basically, a researched position paper is one where you take a stance on a chosen topic and defend your position with qualitative and quantitative research found in scholarly or academic sources. While you might also include popular sources, you’ll want to make certain you incorporate evidence from a body of scholars whose work can be used to support the position you are taking. The difference between a descriptive or narrative research paper and a position paper is the argument – you are doing more than simply reporting facts. In a researched position paper, you are placing yourself in dialogue with a scholarly community and taking a stance on a topic about which you feel strongly. The first formal step is the proposal.
A proposal is quite simply a method for thinking out loud on paper. While all instructors have their own specifications, typically a proposal is less formal than the rough draft and can range in length from ½-1 full page in length. In the proposal, you state the topic about which you are researching and why you are interested in it. Since this is the preliminary stage, it’s okay to say that you do not know if you can defend your chosen position. The proposal is the place to begin exploration. It’s a good place to talk about your research question and, based on the information that you’ve found so far, where your thesis begins to grow. Some instructors may ask that you also state what you know about the topic, what potential sources you might use, and what you think you need to learn before fully developing your selected topic. In some courses, the proposal serves as a written dialogue between students and instructors and provides some foundational plans for the research process.
The next step is the annotated bibliography. Later in this section, we detail for you how to write an annotated bibliography which is basically the step where you locate sources to defend your position and then summarize those sources for their strengths and weaknesses as applied to your topic.
After the annotated bibliography, the formal writing process begins with a first rough draft. Typically, you will be given a page length or word count specification within the assignment parameters so that you’ll have an idea of how much is expected of you at this stage. In the first rough draft, your focus should be on developing your thesis and supporting it throughout the body of your paper. While many students get stuck on the introduction, this isn’t really the place to start your research. For this stage of the paper, you want to make sure the content surrounding your topic is strong with topic sentences connecting back to the thesis in every paragraph.
Sometimes, your instructor may ask for a second rough draft before final submission. If so, this is the place for you to take feedback from a peer reviewer or writing center tutor and fine tune your essay. Use the feedback you receive to check that your position is consistently supported throughout the essay and that you are using evidence correctly to support your position. Reading the draft out loud can also help you find missing elements or spaces for enrichment before the final draft submission, or the backwards/reverse outlining method discussed in section 2.4 might be helpful.
The final draft will be your best polished effort at defending your chosen topic and position after going through the rhetorical strategies defined by your instructor. Depending upon style format, you may or may not need an abstract in the final draft. An abstract is a brief summary of the topic you are discussing in the paper, but it does not give your conclusion. At the end of your final draft you’ll need to include your Works Cited/References page. This will be easily compiled from your annotated bibliography but remember – the annotations do NOT go into the final Works Cited/References page. Only the citations are included in the final draft. Keep in mind that nothing is ever perfect, but you want to strive to present a solid essay that utilizes scholarly, peer reviewed sources to defend and support the position you are taking on your chosen topic. For the rest of this section, we will provide information on how to find the best sources for your paper as well as how to develop the annotated bibliography.
A statement, usually one sentence, that summarizes an argument that will later be explained, expanded upon, and developed in a longer essay or research paper. In undergraduate writing, a thesis statement is often found in the introductory paragraph of an essay. The plural of thesis is theses .
Research that is based on the interpretation of open-ended, non-numeric data, such as writings, interviews, focus groups, and surveys.
Research that is based on numerical data and analyzing it using statistical or mathematical analyses.
When something is described as scholarly, that means that has been written by and for the academic community. The term scholarly is commonly used as shorthand to indicate that information that has been peer reviewed or examined by other experts of the same academic field or discipline. Sometimes, the terms academic, scholarly, and peer reviewed are confused as synonyms; peer reviewed is a narrower term referring to an item that has been reviewed by experts in the field prior to publication, while academic is a broader term that also includes works that are written by and for academics, but that have not been peer reviewed.
The sentence that relays the main idea or the point of the paragraph in which it is contained; usually the first sentence of a body paragraph which gives the reader an idea of what ideas will be discussed in that paragraph.
7.2 Researched Position Paper Copyright © 2022 by Terri Pantuso is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
10.5 Writing Process: Creating a Position Argument
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Demonstrate brainstorming processes and tools as means to discover topics, ideas, positions, and details.
- Apply recursive strategies for organizing drafting, collaborating, peer reviewing, revising, rewriting, and editing.
- Compose a position argument that integrates the writer’s ideas with those from appropriate sources.
- Give and act on productive feedback to works in progress.
- Apply or challenge common conventions of language or grammar in composing and revising.
Now is the time to try your hand at writing a position argument. Your instructor may provide some possible topics or a singular topic. If your instructor allows you to choose your own topic, consider a general subject you feel strongly about and whether you can provide enough support to develop that subject into an essay. For instance, suppose you think about a general subject such as “adulting.” In looking back at what you have learned while becoming an adult, you think of what you wish you had known during your early teenage years. These thoughts might lead you to brainstorm about details of the effects of money in your life or your friends’ lives. In reviewing your brainstorming, you might zero in on one topic you feel strongly about and think it provides enough depth to develop into a position argument. Suppose your brainstorming leads you to think about negative financial concerns you or some of your friends have encountered. Thinking about what could have helped address those concerns, you decide that a mandated high school course in financial literacy would have been useful. This idea might lead you to formulate your working thesis statement —first draft of your thesis statement—like this: To help students learn how to make sensible financial decisions, a mandatory class in financial literacy should be offered in high schools throughout the country.
Once you decide on a topic and begin moving through the writing process, you may need to fine-tune or even change the topic and rework your initial idea. This fine-tuning may come as you brainstorm, later when you begin drafting, or after you have completed a draft and submitted it to your peers for constructive criticism. These possibilities occur because the writing process is recursive —that is, it moves back and forth almost simultaneously and maybe even haphazardly at times, from planning to revising to editing to drafting, back to planning, and so on.
Summary of Assignment
Write a position argument on a controversial issue that you choose or that your instructor assigns to you. If you are free to choose your own topic, consider one of the following:
- The legal system would be strengthened if ______________________.
- The growing use of technology in college classrooms is weakening _____________.
- For safety reasons, public signage should be _________________.
- For entrance into college, standardized testing _________________________.
- In relation to the cost of living, the current minimum wage _______________________.
- During a pandemic, America __________________________.
- As a requirement to graduate, college students __________________________.
- To guarantee truthfulness of their content, social media platforms have the right to _________________.
- To ensure inclusive and diverse representation of people of all races, learning via virtual classrooms _________________.
- Segments of American cultures have differing rules of acceptable grammar, so in a college classroom ___________________.
In addition, if you have the opportunity to choose your own topic and wish to search further, take the lead from trailblazer Charles Blow and look to media for newsworthy “trends.” Find a controversial issue that affects you or people you know, and take a position on it. As you craft your argument, identify a position opposing yours, and then refute it with reasoning and evidence. Be sure to gather information on the issue so that you can support your position sensibly with well-developed ideas and evidence.
Another Lens. To gain a different perspective on your issue, consider again the people affected by it. Your position probably affects different people in different ways. For example, if you are writing that the minimum wage should be raised, then you might easily view the issue through the lens of minimum-wage workers, especially those who struggle to make ends meet. However, if you look at the issue through the lens of those who employ minimum-wage workers, your viewpoint might change. Depending on your topic and thesis, you may need to use print or online sources to gain insight into different perspectives.
For additional information about minimum-wage workers, you could consult
- printed material available in your college library;
- databases in your college library; and
- pros and cons of raising the minimum wage;
- what happens after the minimum wage is raised;
- how to live on a minimum-wage salary;
- how a raise in minimum wage is funded; and
- minimum wage in various U.S. states.
To gain more insight about your topic, adopt a stance that opposes your original position and brainstorm ideas from that viewpoint. Begin by gathering evidence that would help you refute your previous stance and appeal to your audience.
Quick Launch: Working Thesis Frames and Organization of Ideas
After you have decided on your topic, the next step is to arrive at your working thesis. You probably have a good idea of the direction your working thesis will take. That is, you know where you stand on the issue or problem, but you are not quite sure of how to word your stance to share it with readers. At this point, then, use brainstorming to think critically about your position and to discover the best way to phrase your statement.
For example, after reading an article discussing different state-funded community college programs, one student thought that a similar program was needed in Alabama, her state. However, she was not sure how the program worked. To begin, she composed and answered “ reporters’ questions ” such as these:
- What does a state-funded community college program do? pays for part or all of the tuition of a two-year college student
- Who qualifies for the program? high school graduates and GED holders
- Who benefits from this? students needing financial assistance, employers, and Alabama residents
- Why is this needed? some can’t afford to go to college; tuition goes up every year; colleges would be more diverse if everyone who wanted to go could afford to go
- Where would the program be available? at all public community colleges
- When could someone apply for the program? any time
- How can the state fund this ? use lottery income, like other states
The student then reviewed her responses, altered her original idea to include funding through a lottery, and composed this working thesis:
student sample text To provide equal educational opportunities for all residents, the state of Alabama should create a lottery to completely fund tuition at community colleges. end student sample text
Remember that a strong thesis for a position should
- state your stance on a debatable issue;
- reflect your purpose of persuasion; and
- be based on your opinion or observation.
When you first consider your topic for an argumentative work, think about the reasoning for your position and the evidence you will need—that is, think about the “because” part of your argument. For instance, if you want to argue that your college should provide free Wi-Fi for every student, extend your stance to include “because” and then develop your reasoning and evidence. In that case, your argument might read like this: Ervin Community College should provide free Wi-Fi for all students because students may not have Internet access at home.
Note that the “because” part of your argument may come at the beginning or the end and may be implied in your wording.
As you develop your thesis, you may need help funneling all of your ideas. Return to the possibilities you have in mind, and select the ideas that you think are strongest, that recur most often, or that you have the most to say about. Then use those ideas to fill in one of the following sentence frames to develop your working thesis. Feel free to alter the frame as necessary to fit your position. While there is no limit to the frames that are possible, these may help get you started.
________________ is caused/is not caused by ________________, and _____________ should be done.
Example: A declining enrollment rate in college is caused by high tuition rates, and an immediate freeze on the cost of tuition should be applied.
______________ should/should not be allowed (to) ________________ for a number of reasons.
Example: People who do not wear masks during a pandemic should not be allowed to enter public buildings for a number of reasons.
Because (of) ________________, ___________________ will happen/continue to happen.
Example: Because of a lack of emphasis on STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, the Arts, and Mathematics) education in public schools, America will continue to lag behind many other countries.
_____________ is similar to/nothing like ________________ because ______________.
Example: College classes are nothing like high school classes because in college, more responsibility is on the student, the classes are less frequent but more intense, and the work outside class takes more time to complete.
______________ can be/cannot be thought of as __________________ because ______________.
Example: The Black Lives Matter movement can be thought of as an extension of the Civil Rights movement from the 1950s and 1960s because it shares the same mission of fighting racism and ending violence against Black people.
Next, consider the details you will need to support your thesis. The Aristotelian argument structure, named for the Greek philosopher Aristotle , is one that may help you frame the draft of your position argument. For this method, use something like the following chart. In Writing Process: Creating a Position Argument, you will find a similar organizer that you can copy and use for your assignment.
Drafting: Rhetorical Appeals and Types of Supporting Evidence
To persuade your audience to support your position or argument, consider various rhetorical appeals— ethos, logos, pathos, and kairos—and the types of evidence to support your sound reasoning. See Reasoning Strategies: Improving Critical Thinking for more information on reasoning strategies and types of evidence.
Rhetorical Appeals
To establish your credibility, to show readers you are trustworthy, to win over their hearts, and to set your issue in an appropriate time frame to influence readers, consider how you present and discuss your evidence throughout the paper.
- Appeal to ethos . To establish credibility in her paper arguing for expanded mental health services, a student writer used these reliable sources: a student survey on mental health issues, data from the International Association of Counseling Services (a professional organization), and information from an interview with a campus mental health counselor.
- Appeal to logos . To support her sound reasoning, the student writer approached the issue rationally, using data and credible evidence to explain the current situation and its effects.
- Appeal to pathos . To show compassion and arouse audience empathy, the student writer shared the experience of a student on her campus who struggled with anxiety and depression.
- Appeal to kairos . To appeal to kairos, the student emphasized the immediate need for these services, as more students are now aware of their particular mental health issues and trying to deal with them.
The way in which you present and discuss your evidence will reflect the appeals you use. Consider using sentence frames to reflect specific appeals. Remember, too, that sentence frames can be composed in countless ways. Here are a few frames to get you thinking critically about how to phrase your ideas while considering different types of appeals.
Appeal to ethos: According to __________________, an expert in ______________, __________________ should/should not happen because ________________________.
Appeal to ethos: Although ___________________is not an ideal situation for _________________, it does have its benefits.
Appeal to logos: If ____________________ is/is not done, then understandably, _________________ will happen.
Appeal to logos: This information suggests that ____________________ needs to be investigated further because ____________________________.
Appeal to pathos: The story of _____________________ is uplifting/heartbreaking/hopeful/tragic and illustrates the need for ____________________.
Appeal to pathos: ___________________ is/are suffering from ________________, and that is something no one wants.
Appeal to kairos: _________________ must be addressed now because ________________ .
Appeal to kairos: These are times when ______________ ; therefore, _____________ is appropriate/necessary.
Types of Supporting Evidence
Depending on the point you are making to support your position or argument, certain types of evidence may be more effective than others. Also, your instructor may require you to include a certain type of evidence. Choose the evidence that will be most effective to support the reasoning behind each point you make to support your thesis statement. Common types of evidence are these:
Renada G., a junior at Powell College South, worked as a waitress for 15 hours a week during her first three semesters of college. But in her sophomore year, when her parents were laid off during the pandemic, Renada had to increase her hours to 35 per week and sell her car to stay in school. Her grades started slipping, and she began experiencing symptoms of depression and anxiety. When she called the campus health center to make an appointment for counseling, Renada was told she would have to wait two weeks before she could be seen.
Here is part of how Lyndon B. Johnson defined the Great Society: “But most of all, the Great Society is not a safe harbor, a resting place, a final objective, a finished work. It is a challenge constantly renewed, beckoning us toward a destiny where the meaning of our lives matches the marvelous products of our labor.”
Bowen Lake is nestled in verdant foothills, lush with tall grasses speckled with wildflowers. Around the lake, the sweet scent of the purple and yellow flowers fills the air, and the fragrance of the hearty pines sweeps down the hillsides in a westerly breeze. Wood frogs’ and crickets’ songs suddenly stop, as the blowing of moose calling their calves echoes across the lake’s soundless surface. Or this was the scene before the deadly destruction of fires caused by climate change.
When elaborating on America’s beauty being in danger, Johnson says, “The water we drink, the food we eat, the very air that we breathe, are threatened with pollution. Our parks are overcrowded, our seashores overburdened. Green fields and dense forests are disappearing.”
Speaking about President Lyndon B. Johnson and the Vietnam War, noted historian and Johnson biographer Doris Kearns Goodwin said, “It seemed the hole in his heart from the loss of work was too big to fill.”
Charles Blow has worked at the Shreveport Times , The Detroit News , National Geographic , and The New York Times .
When interviewed by George Rorick and asked about the identities of his readers, Charles Blow said that readers’ emails do not elaborate on descriptions of who the people are. However, “the kinds of comments that they offer are very much on the thesis of the essay.”
In his speech, Lyndon B. Johnson says, “The Great Society is a place where every child can find knowledge to enrich his mind and to enlarge his talents.”
To support the need for change in classrooms, Johnson uses these statistics: “Each year more than 100,000 high school graduates, with proved ability, do not enter college because they cannot afford it. And if we cannot educate today’s youth, what will we do in 1970 when elementary school enrollment will be five million greater than 1960?”
- Visuals : graphs, photographs, charts, or maps used in addition to written or spoken information.
Brainstorm for Supporting Points
Use one or more brainstorming techniques, such as a web diagram as shown in Figure 10.8 or the details generated from “because” statements, to develop ideas or particular points in support of your thesis. Your goal is to get as many ideas as possible. At this time, do not be concerned about how ideas flow, whether you will ultimately use an idea (you want more ideas than will end up in your finished paper), spelling, or punctuation.
When you have finished, look over your brainstorming. Then circle three to five points to incorporate into your draft. Also, plan to answer “ reporters’ questions ” to provide readers with any needed background information. For example, the student writing about the need for more mental health counselors on her campus created and answered these questions:
What is needed? More mental health counseling is needed for Powell College South.
Who would benefit from this? The students and faculty would benefit.
- Why is this needed? The college does not have enough counselors to meet all students’ needs.
- Where are more counselors needed? More counselors are needed at the south campus.
- When are the counselors needed? Counselors need to be hired now and be available both day and night to accommodate students’ schedules.
- How can the college afford this ? Instead of hiring daycare workers, the college could use students and faculty from the Early Childhood Education program to run the program and use the extra money to pay the counselors.
Using Logic
In a position argument, the appropriate use of logic is especially important for readers to trust what you write. It is also important to look for logic in material you read and possibly cite in your paper so that you can determine whether writers’ claims are reasonable. Two main categories of logical thought are inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning .
- Inductive reasoning moves from specific to broad ideas. You begin by collecting details, observations, incidents, or facts; examining them; and drawing a conclusion from them. Suppose, for example, you are writing about attendance in college classes. For three weeks, you note the attendance numbers in all your Monday, Wednesday, and Friday classes (specific details), and you note that attendance is lower on Friday than on the other days (a specific detail). From these observations, you determine that many students prefer not to attend classes on Fridays (your conclusion).
- Deductive reasoning moves from general to specific ideas. You begin with a hypothesis or premise , a general concept, and then examine possibilities that would lead to a specific and logical conclusion. For instance, suppose you think that opportunities for foreign students at your college are inadequate (general concept). You examine the specific parts of that concept (e.g., whether your college provides multicultural clubs, help with language skills, or work-study opportunities) and determine that those opportunities are not available. You then determine that opportunities for foreign students are lacking at your college.
Logical Fallacies and Propaganda
Fallacies are mistakes in logic. Readers and writers should be aware of these when they creep into writing, indicating that the points the writers make may not be valid. Two common fallacies are hasty generalizations and circular arguments. See Glance at Genre: Rhetorical Strategies for more on logical fallacies.
- A hasty generalization is a conclusion based on either inadequate or biased evidence. Consider this statement: “Two students in Math 103 were nervous before their recent test; therefore, all students in that class must have text anxiety.” This is a hasty generalization because the second part of the statement (the generalization about all students in the class) is inadequate to support what the writer noted about only two students.
- A circular argument is one that merely restates what has already been said. Consider this statement: “ The Hate U Give is a well-written book because Angie Thomas, its author, is a good novelist.” The statement that Thomas is a good novelist does not explain why her book is well written.
In addition to checking work for fallacies, consider propaganda , information worded so that it endorses a particular viewpoint, often of a political nature. Two common types of propaganda are bandwagon and fear .
- In getting on the bandwagon , the writer encourages readers to conform to a popular trend and endorse an opinion, a movement, or a person because everyone else is doing so. Consider this statement: “Everyone is behind the idea that 7 a.m. classes are too early and should be changed to at least 8 a.m. Shouldn’t you endorse this sensible idea, too?”
- In using fear, the writer presents a dire situation, usually followed by what could be done to prevent it. Consider this statement: “Our country is at a turning point. Enemies threaten us with their power, and our democracy is at risk of being crushed. The government needs a change, and Paul Windhaus is just the man to see we get that change.” This quotation appeals to fear about the future of the country and implies that electing a certain individual will solve the predicted problems.

Organize the Paper
To begin, write your thesis at the top of a blank page. Then select points from your brainstorming and reporters’ questions to organize and develop support for your thesis. Keep in mind that you can revise your thesis whenever needed.
To begin organizing her paper on increased mental health services on her college campus, the student wrote this thesis at the top of a page:
student sample text Because mental health is a major concern at Powell College South, students could benefit from expanding the services offered . end student sample text
Next she decided the sequence in which to present the points. In a position or an argument essay, she could choose one of two methods: thesis-first organization or delayed-thesis organization.
Thesis-First Organization
Leading with a thesis tells readers from the beginning where you stand on the issue. In this organization, the thesis occupies both the first and last position in the essay, making it easy for readers to remember.
Introduce the issue and assert your thesis. Make sure the issue has at least two debatable sides. Your thesis establishes the position from which you will argue. Writers often state their thesis as the last sentence in the first paragraph, as the student writer has done:
student sample text The problem of mental health has become front-page news in the last two months. Hill’s Herald , Powell College South’s newspaper, reported 14 separate incidents of students who sought counseling but could not get appointments with college staff. Since mental health problems are widespread among the student population, the college should hire more health care workers to address this problem. end student sample text
Summarize the counterclaims . Before elaborating on your claims, explain the opposition’s claims. Including this information at the beginning gives your argument something to focus on—and refute—throughout the paper. If you ignore counterclaims, your argument may appear incomplete, and readers may think you have not researched your topic sufficiently. When addressing a counterclaim, state it clearly, show empathy for those who have that view, and then immediately refute it with support developed through reasoning and evidence. Squeezing the counterclaims between the thesis and the evidence reserves the strongest places—the opening and closing—for your position.
student sample text Counterclaim 1 : Powell College South already employs two counselors, and that number is sufficient to meet the needs of the student population. end student sample text
student sample text Counterclaim 2 : Students at Powell College South live in a metropolitan area large enough to handle their mental health needs. end student sample text
Refute the counterclaims. Look for weak spots in the opposition’s argument, and point them out. Use your opponent’s language to show you have read closely but still find problems with the claim. This is the way the writer refuted the first counterclaim:
student sample text While Powell College South does employ two counselors, those counselors are overworked and often have no time slots available for students who wish to make appointments. end student sample text
State and explain your points, and then support them with evidence. Present your points clearly and precisely, using Reasoning Strategies: Improving Critical Thinking to explain and cite your evidence. The writer plans to use a problem-solution reasoning strategy to elaborate on these three points using these pieces of evidence:
student sample text Point 1: Wait times are too long. end student sample text
student sample text Kay Payne, one of the campus counselors, states that the wait time for an appointment with her is approximately 10 days. end student sample text
student sample text Point 2: Mental health issues are widespread within the student community. end student sample text
student sample text In a recent on-campus student survey, 75 percent of 250 students say they have had some kind of mental health issues at some point in their life. end student sample text
student sample text Point 3: The staff-to-student ratio is too high. end student sample text
student sample text The International Accreditation of Counseling Services states that the recommended ratio is one full-time equivalent staff member for every 1,000 to 1,500 students. end student sample text
Restate your position as a conclusion. Near the end of your paper, synthesize your accumulated evidence into a broad general position, and restate your thesis in slightly different language.
student sample text The number of students who need mental health counseling is alarming. The recent news articles that attest to their not being able to schedule appointments add to the alarm. While Powell College South offers some mental health counseling, the current number of counselors and others who provide health care is insufficient to handle the well-being of all its students. Action must be taken to address this problem. end student sample text
Delayed-Thesis Organization
In this organizational pattern, introduce the issue and discuss the arguments for and against it, but wait to take a side until late in the essay. By delaying the stance, you show readers you are weighing the evidence, and you arouse their curiosity about your position. Near the end of the paper, you explain that after carefully considering both pros and cons, you have arrived at the most reasonable position.
Introduce the issue. Here, the writer begins with action that sets the scene of the problem.
student sample text Tapping her foot nervously, Serena looked at her watch again. She had been waiting three hours to see a mental health counselor at Powell College South, and she did not think she could wait much longer. She had to get to work. end student sample text
Summarize the claims for one position. Before stating which side you support, explain how the opposition views the issue. This body paragraph presents evidence about the topic of more counselors:
student sample text Powell College South has two mental health counselors on staff. If the college hires more counselors, more office space will have to be created. Currently Pennington Hall could accommodate those counselors. Additional counselors would allow more students to receive counseling. end student sample text
Refute the claims you just stated. Still not stating your position, point out the other side of the issue.
student sample text While office space is available in Pennington Hall, that location is far from ideal. It is in a wooded area of campus, six blocks from the nearest dorm. Students who would go there might be afraid to walk through the woods or might be afraid to walk that distance. The location might deter them from making appointments. end student sample text
Now give the best reasoning and evidence to support your position. Because this is a delayed-thesis organization, readers are still unsure of your stance. This section should be the longest and most carefully documented part of the paper. After summarizing and refuting claims, the writer then elaborates on these three points using problem-solution reasoning supported by this evidence as discussed in Reasoning Strategies: Improving Critical Thinking, implying her position before moving to the conclusion, where she states her thesis.
student sample text The International Association of Counseling Services states that one full-time equivalent staff member for every 1,000 to 1,500 students is the recommended ratio. end student sample text
State your thesis in your conclusion. Your rhetorical strategy is this: after giving each side a fair hearing, you have arrived at the most reasonable conclusion.
student sample text According to the American Psychological Association, more than 40 percent of all college students suffer from some form of anxiety. Powell College South students are no different from college students elsewhere: they deserve to have adequate mental health counseling. end student sample text
Drafting begins when you organize your evidence or research notes and then put them into some kind of written form. As you write, focus on building body paragraphs through the techniques presented in Reasoning Strategies: Improving Critical Thinking that show you how to support your position and then add evidence. Using a variety of evidence types builds credibility with readers. Remember that the recursiveness of the writing process allows you to move from composing to gathering evidence and back to brainstorming ideas or to organizing your draft at any time. Move around the writing process as needed.
Keep in mind that a first draft is just a beginning—you will revise it into a better work in later drafts. Your first draft is sometimes called a discovery draft because you are discovering how to shape your paper: which ideas to include and how to support those ideas. These suggestions and graphic organizer may be helpful for your first draft:
- Write your thesis at the top of the paper.
- Compose your body paragraphs: those that support your argument through reasoning strategies and those that address counterclaims.
- Leave your introduction, conclusion, and title for later drafts.
Use a graphic organizer like Table 10.1 to focus points, reasoning, and evidence for body paragraphs. You are free to reword your thesis, reasoning, counterclaim(s), refutation of counterclaim(s), concrete evidence, and explanation/elaboration/clarification at any time. You are also free to adjust the order in which you present your reasoning, counterclaim(s), and refuting of counterclaim(s).
Develop a Writing Project through Multiple Drafts
Your first draft is a kind of experiment in which you are concerned with ideas and with getting the direction and concept of the paper clear. Do not think that your first draft must be perfect; remind yourself that you are just honing your work. In most serious writing, every phase of the process can be considered recursive, helping you shape the best paper possible.
Peer Review: Critical Thinking and Counterclaims
After you have completed the first draft, begin peer review. Peer reviewers can use these sentence starters when thinking critically about overall strengths and developmental needs.
- One point about your position that I think is strong is ______ because ________.
- One point about your position that I think needs more development is _____ because _______.
- One area that I find confusing is _____________; I was confused about _______.
- One major point that I think needs more explanation or detail is _______.
- In my opinion, the purpose of your paper is to persuade readers _______.
- In my opinion, the audience for your paper is _______.
- One area of supporting evidence that I think could use more development is _______.
- One counterclaim you include is ________________.
- Your development of the counterclaim is __________________ because ________________.
Refuting Counterclaims
Peer reviewers are especially helpful with position and argument writing when it comes to refuting counterclaims. Have your peer reviewer read your paper again and look for supporting points and ideas to argue against , trying to break down your argument. Then ask your reviewer to discuss the counterclaims and corresponding points or ideas in your paper. This review will give you the opportunity to think critically about ways to refute the counterclaims your peer reviewer suggests.
As preparation for peer review, match each of the following arguments with their counterarguments.
Revising: Reviewing a Draft and Responding to Counterclaims
Revising means reseeing, rereading, and rethinking your thoughts on paper until they fully match your intention. Mentally, it is conceptual work focused on units of meaning larger than the sentence. Physically, it is cutting, pasting, deleting, and rewriting until the ideas are satisfying. Be ready to spend a great deal of time revising your drafts, adding new information and incorporating sources smoothly into your prose.
The Revising Process
To begin revising, return to the basic questions of topic ( What am I writing about? ), purpose ( Why am I writing about this topic? ), audience ( For whom am I writing? ), and culture ( What is the background of the people for whom I am writing? ).
- What is the general scope of my topic? __________________________________
- What is my thesis? __________________________________________________
- Does my thesis focus on my topic? ______________________________________
- Does my thesis clearly state my position? ______________________
- What do I hope to accomplish in writing about this topic? ____________________
- Do all parts of the paper advance this purpose? ____________________________
- Does my paper focus on my argument or position? _________________________
- What does my audience know about this subject? _______________________
- What does my audience need to know to understand the point of my paper? _______________________________________________________________
What questions or objections do I anticipate from my audience? ___________
________________________________________________________________
- What is the culture of the people for whom I am writing? Do all readers share the same culture? ________________________________________________________
How do my beliefs, values, and customs differ from those of my audience?
____________________________________________________________________
- How do the cultures of the authors of sources I cite differ from my culture or the culture(s) of my audience? ______________________________________________
Because of the recursivity of the writing process, returning to these questions will help you fine-tune the language and structure of your writing and target the support you develop for your audience.
Responding to Counterclaims
The more complex the issue, the more opposing sides it may have. For example, a writer whose position is that Powell College South Campus should offer daycare to its students with children might find opposition for different reasons. Someone may oppose the idea out of concern for cost; someone else may support the idea if the daycare is run on a volunteer basis; someone else may support the idea if the services are offered off campus.
As you revise, continue studying your peer reviewer’s comments about counterclaims. If you agree with any counterclaim, then say so in the paragraph in which you address counterclaims. This agreement will further establish your credibility by showing your fairness and concern for the issue. Look over your paper and peer review comments, and then consider these questions:
- In what ways do you address realistic counterclaims? What other counterclaims should you address? Should you add to or replace current counterclaims?
- In what ways do you successfully refute counterclaims? What other refutations might you include?
- Are there any counterclaims with which you agree? If so, how do you concede to them in your paper? In what ways does your discussion show fairness?
After completing your peer review and personal assessment, make necessary revisions based on these notes. See Annotated Student Sample an example of a student’s argumentative research essay. Note how the student
- presents the argument;
- supports the viewpoint with reasoning and evidence;
- includes support in the form of facts, opinions, paraphrases, and summaries;
- provides citations (correctly formatted) about material from other sources in the paper;
- uses ethos, pathos, and logos throughout the paper; and
- addresses counterclaims (dissenting opinions).
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/10-5-writing-process-creating-a-position-argument
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Parts of a Paper / How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis can be found in many places—a debate speech, a lawyer’s closing argument, even an advertisement. But the most common place for a thesis statement (and probably why you’re reading this article) is in an essay.
Whether you’re writing an argumentative paper, an informative essay, or a compare/contrast statement, you need a thesis. Without a thesis, your argument falls flat and your information is unfocused. Since a thesis is so important, it’s probably a good idea to look at some tips on how to put together a strong one.
Guide Overview
What is a “thesis statement” anyway.
- 2 categories of thesis statements: informative and persuasive
- 2 styles of thesis statements
- Formula for a strong argumentative thesis
- The qualities of a solid thesis statement (video)
You may have heard of something called a “thesis.” It’s what seniors commonly refer to as their final paper before graduation. That’s not what we’re talking about here. That type of thesis is a long, well-written paper that takes years to piece together.
Instead, we’re talking about a single sentence that ties together the main idea of any argument . In the context of student essays, it’s a statement that summarizes your topic and declares your position on it. This sentence can tell a reader whether your essay is something they want to read.
2 Categories of Thesis Statements: Informative and Persuasive
Just as there are different types of essays, there are different types of thesis statements. The thesis should match the essay.
For example, with an informative essay, you should compose an informative thesis (rather than argumentative). You want to declare your intentions in this essay and guide the reader to the conclusion that you reach.
To make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, you must procure the ingredients, find a knife, and spread the condiments.
This thesis showed the reader the topic (a type of sandwich) and the direction the essay will take (describing how the sandwich is made).
Most other types of essays, whether compare/contrast, argumentative, or narrative, have thesis statements that take a position and argue it. In other words, unless your purpose is simply to inform, your thesis is considered persuasive. A persuasive thesis usually contains an opinion and the reason why your opinion is true.
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are the best type of sandwich because they are versatile, easy to make, and taste good.
In this persuasive thesis statement, you see that I state my opinion (the best type of sandwich), which means I have chosen a stance. Next, I explain that my opinion is correct with several key reasons. This persuasive type of thesis can be used in any essay that contains the writer’s opinion, including, as I mentioned above, compare/contrast essays, narrative essays, and so on.
2 Styles of Thesis Statements
Just as there are two different types of thesis statements (informative and persuasive), there are two basic styles you can use.
The first style uses a list of two or more points . This style of thesis is perfect for a brief essay that contains only two or three body paragraphs. This basic five-paragraph essay is typical of middle and high school assignments.
C.S. Lewis’s Chronicles of Narnia series is one of the richest works of the 20th century because it offers an escape from reality, teaches readers to have faith even when they don’t understand, and contains a host of vibrant characters.
In the above persuasive thesis, you can see my opinion about Narnia followed by three clear reasons. This thesis is perfect for setting up a tidy five-paragraph essay.
In college, five paragraph essays become few and far between as essay length gets longer. Can you imagine having only five paragraphs in a six-page paper? For a longer essay, you need a thesis statement that is more versatile. Instead of listing two or three distinct points, a thesis can list one overarching point that all body paragraphs tie into.
Good vs. evil is the main theme of Lewis’s Narnia series, as is made clear through the struggles the main characters face in each book.
In this thesis, I have made a claim about the theme in Narnia followed by my reasoning. The broader scope of this thesis allows me to write about each of the series’ seven novels. I am no longer limited in how many body paragraphs I can logically use.
Formula for a Strong Argumentative Thesis
One thing I find that is helpful for students is having a clear template. While students rarely end up with a thesis that follows this exact wording, the following template creates a good starting point:
___________ is true because of ___________, ___________, and ___________.
Conversely, the formula for a thesis with only one point might follow this template:
___________________ is true because of _____________________.
Students usually end up using different terminology than simply “because,” but having a template is always helpful to get the creative juices flowing.
The Qualities of a Solid Thesis Statement
When composing a thesis, you must consider not only the format, but other qualities like length, position in the essay, and how strong the argument is.
Length: A thesis statement can be short or long, depending on how many points it mentions. Typically, however, it is only one concise sentence. It does contain at least two clauses, usually an independent clause (the opinion) and a dependent clause (the reasons). You probably should aim for a single sentence that is at least two lines, or about 30 to 40 words long.
Position: A thesis statement always belongs at the beginning of an essay. This is because it is a sentence that tells the reader what the writer is going to discuss. Teachers will have different preferences for the precise location of the thesis, but a good rule of thumb is in the introduction paragraph, within the last two or three sentences.
Strength: Finally, for a persuasive thesis to be strong, it needs to be arguable. This means that the statement is not obvious, and it is not something that everyone agrees is true.
Example of weak thesis:
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are easy to make because it just takes three ingredients.
Most people would agree that PB&J is one of the easiest sandwiches in the American lunch repertoire.
Example of a stronger thesis:
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are fun to eat because they always slide around.
This is more arguable because there are plenty of folks who might think a PB&J is messy or slimy rather than fun.
Composing a thesis statement does take a bit more thought than many other parts of an essay. However, because a thesis statement can contain an entire argument in just a few words, it is worth taking the extra time to compose this sentence. It can direct your research and your argument so that your essay is tight, focused, and makes readers think.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Introduction
Course Overview and Policy Statements
CO301 as a Core Course
Core Detail: Instructional Modes
Core Detail: Course Objectives
Core Detail: Weekly Schedule
Core Detail: Methods of Evaluation
Sample Weekly Outline
Portfolios?
Portfolio Overview - Thomas
Portfolio Process Requirements - Thomas
Portfolio Grading (Holtcamp)
Portfolios: Promises, Problems, Practices (Kiefer)
Traditional And/Or Portfolio Grading? (Gogela)
Defining the Humanities
Collaborative Activity - Myers
Humanities Defined - Myers
Text Analysis
Text Analysis Assignments
Individual Topics
Individual Topic Assignments
Individual Topic Activities
Reflective Writing
Position Paper - Myers

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
25 Thesis Statement Examples
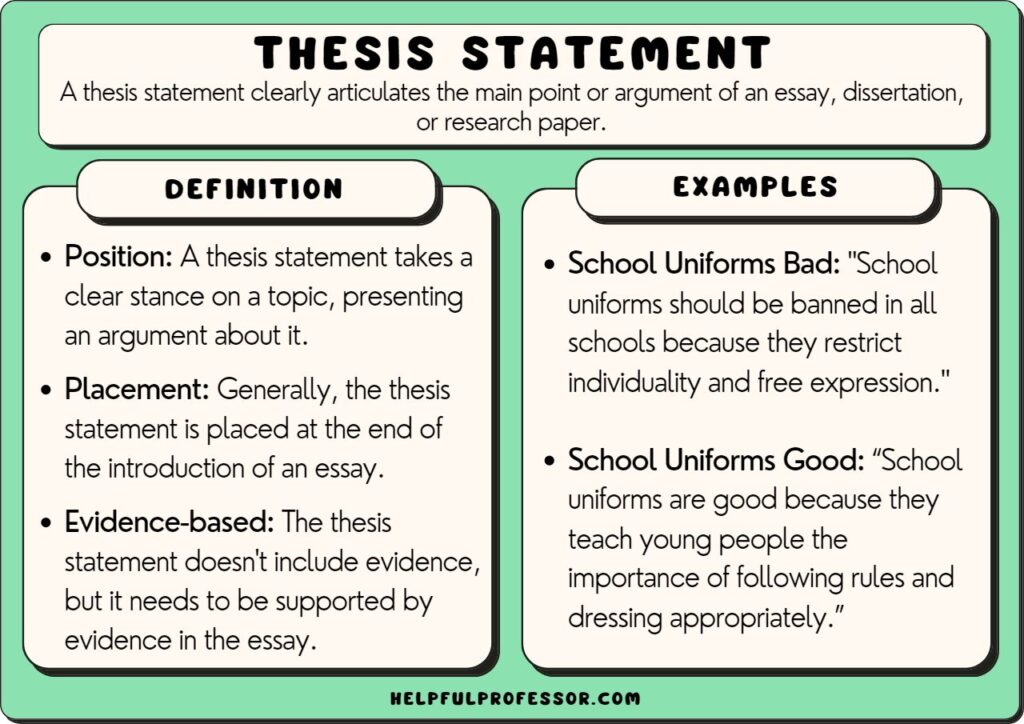
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

Want to Master Your Synthesis Essay Assignment? Here's How.

The Write Stuff
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college

Developing a Thesis Statement: The Heart of Successful Paper Writing
Introduction.
A thesis declaration is the cornerstone of any scholastic paper, succinctly summing up the bottom line or claim of the essay in a clear, concise manner. It is not merely a statement of truth, but a claim that needs evidence and elaboration as part of the paper. This foundational aspect not just informs the reader of what to anticipate but also guides the author's own research and writing process. Comprehending how to craft a compelling thesis statement is important for any student aiming to write clear, convincing scholastic documents, desiring to become the very best of the best paper writer in their scholastic field.
Understanding the Purpose of a Thesis Statement
The primary function of a thesis statement is to offer a clear, specific assertion that demonstrates your position concerning the topic at hand. It functions as the assisting force of your paper, directing logical reasoning and argumentation. A well-formulated thesis statement sets the tone and instructions of an essay, allowing you to build a coherent and organized argument. It acts as the roadmap for your essay, assisting to guarantee that each section contributes toward the argument or claim being made.
Elements of a Reliable Thesis Declaration
Clearness is vital in a thesis statement. It ought to be devoid of unclear terms like "excellent," "successful," "interesting," etc. Instead, it needs to be precise and articulate the specific focus of your essay. This clarity helps prevent the reader from becoming confused about your position.
Conciseness
While a thesis declaration needs to be broad enough to cover the whole argument of your paper, it ought to be concise sufficient to be understood in a single, clear sentence. Balancing information and brevity makes sure that your thesis statement is both helpful and manageable.
A thesis statement should reflect a clear position on the subject. Instead of merely specifying a basic truth, it ought to argue a point that demands proof and defense. This assertive nature welcomes analysis and argument, which is main to scholastic writing.
Crafting Your Thesis Statement
Brainstorming key concepts.
Begin by conceptualizing to create a list of ideas or questions associated with your topic. This preliminary stage is important for determining the instructions of your research study and the angle of your argument.
Refining Ideas
Filter through the ideas produced throughout brainstorming to separate those that are most considerable and pertinent to your research study objectives. This refined focus will help in preparing a more directed and potent thesis declaration.
Preparing the Thesis
Start drafting your thesis by stating your primary argument in a simple sentence. Then refine this declaration by including uniqueness and complexity to mirror the depth of your analysis.
Examples of Strong Thesis Statements
Examining examples from different fields can offer a blueprint for what makes a reliable thesis statement:
- " Environment change develops unpredictable weather patterns that significantly impact the natural and human-made environments."
- " Technological developments in the 21st century have more separating than connecting effects on society."
These examples demonstrate clearness and take a conclusive position on a topic, providing a clear direction for supporting arguments.
Common Mistakes to Prevent in Thesis Declaration Development
Avoid uncertainty, overly broad statements, or extremely simplistic assertions that do not challenge the status quo. A thesis statement need to not be a summary of an obvious point but rather an assertion that supplies the reader with insights into your analysis and analysis.
Revising Your Thesis Statement
As your composing advances, revisit your thesis statement. Research may lead you to tweak it to better show the instructions and nuances of your argument. This iterative process ensures that your thesis remains relevant and robust throughout your writing.
Establishing a strong thesis statement is vital for successful paper writing. It not only shapes your research study and writing direction but likewise plays an important function in engaging your reader. By investing time in crafting a detailed and assertive thesis declaration, you set the stage for a clear, well-argued paper that demonstrates your understanding of the subject matter.
Note: This article is for information purposes only and does not contain any recommendation.
This article may contain affiliate links that Microsoft and/or the publisher may receive a commission from if you buy a product or service through those links.

COMMENTS
4. Create an Outline. Once you have decided about the direction you're taking with your essay, proceed with the position essay outline. This step is often overlooked, but it will be much easier to find and correct mistakes and gaps at this early stage. So, writing a position paper outline actually saves you time.
Position Paper Example. Position Paper Example structure is as follows: Introduction: A brief overview of the issue. A clear statement of the position the paper is taking. Background: A detailed explanation of the issue. A discussion of the history of the issue. An analysis of any previous actions taken on the issue.
A position paper requires three basic parts: an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Follow these seven steps to help write a position paper on any topic: 1. Choose a topic. In some classes or jobs, you can choose the topic of a position paper. If you're choosing your topic, consider ones relevant to your industry or academic interests.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
The thesis is located in the two strongest places, first and last. 3. It is the most common form of academic argument used. ... Sample Outline for a Position Paper I. Introduction A. Introduce the topic B. Provide background on the topic C. Assert the thesis (your view of the issue) II. Counter Argument A. Summarize the counterclaims B. Provide ...
Express your position idea. Focus on one specific aspect of the topic in order to express it in a one-sentence opinion. Make sure you have found a really arguable idea. If the topic cannot be debated, then it can hardly be used for writing a good position paper. Be precise in your statement.
5. Summarize your argument and restate your position. End your paper focusing on your argument and avoid the counter-arguments. You want your audience to walk away with your view on the topic being one that resonates with them. When you write a position paper, write with confidence and state your opinion with authority.
4. Collecting Supporting Evidence. When gathering evidence for your position paper, prioritize relevance and credibility. Use expert quotes sparingly, ensuring they directly support your argument. Prefer research-based evidence over anecdotes, focusing on quality rather than quantity. Verify the credibility of sources and regularly update ...
In a researched position paper, you are placing yourself in dialogue with a scholarly community and taking a stance on a topic about which you feel strongly. The first formal step is the proposal. A proposal is quite simply a method for thinking out loud on paper. While all instructors have their own specifications, typically a proposal is less ...
What is an Argumentative or Position Paper? In this type of assignment, you take a stand on a particular topic that is debatable. You present a clear and strong statement usually at the start of your paper that asserts your position on the topic. (See the Writing Center's handout on thesis statements for more help with this stage!).
student sample text To provide equal educational opportunities for all residents, the state of Alabama should create a lottery to completely fund tuition at community colleges. end student sample text. Remember that a strong thesis for a position should. state your stance on a debatable issue; reflect your purpose of persuasion; and
The thesis should match the essay. For example, with an informative essay, you should compose an informative thesis ... Position: A thesis statement always belongs at the beginning of an essay. This is because it is a sentence that tells the reader what the writer is going to discuss. Teachers will have different preferences for the precise ...
Position Paper - Myers. A Position Paper is a common type of academic argument writing assignment. Typically, a Position Paper is written after reading about and discussing a particular issue. Quite often, the readings cover more than one issue, and as a writer you must choose a particular area of focus. The central goal of writing a position ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right. Example of a thesis that is too broad:
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
Position Statements. A position statement is like a thesis or goal. It describes one side of an arguable viewpoint. To write a position statement, gather a list of reasons to support a particular viewpoint. Next, write a sentence or two that pulls all the information together and makes your stand clear to the audience.
A thesis statement is a sentence used in academic or professional writing that states your position on a certain topic. Your thesis statement explains what the rest of your essay is about in clear, detailed terms. Thesis statements often appear in expository essays, compare and contrast essays, persuasive essays and research papers.
A thesis declaration is the cornerstone of any scholastic paper, succinctly summing up the bottom line or claim of the essay in a clear, concise manner. It is not merely a statement of truth, but ...
The thesis or dissertation conclusion should be 5-7% of your paper's overall word count. For example, if your thesis is 30,000 words, the conclusion can be 1,500-2100 words. The conclusion for empirical or scientific theses or dissertations is often brief.