

Graphic Essays and Comics
Overview | Recommended Software | Student-Made Examples | Other Examples | Instructional Video
A graphic essay (sometimes called a visual essay) uses a combination of text and images to explore a specific topic. Graphic essays can look like comics, graphic novels, magazines, collages, artist books, textbooks, or even websites. Graphic essays often first take the form of written essays and then have graphic elements added to enrich the reader experience. Unlike infographics, which also combine text and images, graphic essays are often more text-based and usually have a narrative arc or specific reading order.
Comics are a genre used to express ideas through images combined with text or other visual information. Comics can take the form of a single panel or a series of juxtaposed panels of images, sometimes called a strip. Text is conveyed via captions below the panel(s), or speech bubbles and onomatopoeias within the panel(s), to indicate dialogue, narration, sound effects, or other information. Graphic novels are often considered to be a longer form of comics, typically in book form.
A web-based graphic essay can take the form of a blog or a single page website, such as a Microsoft Sway page or an interactive Prezi. For Microsoft Sway and Prezi graphic essays, see the examples below. If you are creating a blog we recommend visiting the Web-Based Projects page .
Graphic Essay Design Tip: Graphic essays can take many forms, so we recommend being creative within the scope of your project! Get some help from DesignLab to brainstorm options and talk through the various tools available!
Make an Appointment
Recommended Software
There are many different software programs that can be used to create graphic essays. Below is a list of the software that we recommend for making a graphic essay. We organized the software by category and put the software from top to bottom from best to worst. We recommend using a software you know well or learning the software well enough to establish an easy workflow, so you can spend less time troubleshooting and spend more time on your project. Check out our Software Support page for links to tutorials for all of these programs.
General Graphic Essay Software

Web-Based Graphic Essay Software

Comic-Specific Graphic Essay Software

Student-Made Examples
Print style graphic essay.
Becoming a Witness by Jessica Posnock

Creative Graphic Essay
Virtual Communication by Max Hautala *Award Winning*

Curb Magazine (2012) by Journalism 417

Web-Based (Magazine) Graphic Essay
Curb Magazine (Current) by Journalism 417

Web-Based (Sway) Graphic Essay
Language Influences Culture, Thoughts, and Identity by Kristen Luckow *Award Winning*

Dyslexia by Maria Swanke *Award Winning*

Other Examples
Web-based (blog) graphic essay.
Switch It Up: Graphic Essay by Amanda Zieba

Graphic Novel
Graphic Novels in the Classroom by Gene Yang

Instructional Video

Assigning a Graphic Essay as an Essay Alternative
One of my favorite ways to assess my students’ essay-writing skills without actually assigning a traditional essay is with the graphic essay . A graphic essay is an excellent essay alternative for the middle school ELA or high school English classroom.
A graphic essay is a graphic representation that contains all of the essential essay elements. It combines writing, visual elements, and design. When assigning a graphic essay, you can have students include any particular aspect from the essay that you want.

Getting Started
The first step to completing a graphic essay project in your classroom is to have a clear idea of the skills and content you want to assess. For example, if you are working on an argument and persuasive unit, are you looking to assess a counterargument? If you are working on an informative piece, are you looking for explanatory evidence?
Once you know what you want to assess, start mapping out the student requirements. I’m pretty old-school when it comes to things and prefer to draft out my notes with paper and pencil. When I do this, I make a list of all of the elements that I want my students to include. For a recent project, I wanted them to include a variety of features: introduction, big ideas with supporting evidence, counter argument, quick facts, visual data representation, and a Works Cited page.

Work Before Design
Once you have your graphic essay outlined, it is time to assign it to the students. However, and I cannot stress this enough, you don’t want them to focus on the visual and graphic elements first. That is just a hot mess waiting to happen. You know how it will go. Some students will spend the entire class period deciding between a blue or green spot color design element. By the time the class period ends, they’ll have a lovely purple box on their graphic essay, but that will probably all they have accomplished—one box.
Instead, try this. Have your students work on a brainstorming organizer first. You’ll want them to brainstorm, write, and curate all of the content for the graphic essay before they start the design process. When I complete this project in my classroom, I have them draft everything, find all of the images they want to include, and submit that work for a grade before they even start the design process.

Students either love or hate the graphic design process of this alternative essay project, and that is to be expected. When we get to the design process of this project, I try to give my students several different options for creating the final project that matches different graphic design comfort levels. A few of my students usually want to use Adobe Photoshop and design everything from scratch, a few need extra guidance working in a Google Slide, and the majority are excited to try a new online platform. Please note, this is not an ad. These websites did not pay to be included in this post.
One thing that I cannot emphasize enough for this type of project is that I grade content and not design. Let me repeat that: I assess the content of the work and not the quality of the design.
Here’s a look at some of the different platforms I suggest my students use to create their graphic essay. This list is in order from easiest to most advanced.
1. Google Docs – Most students are already familiar with Google Docs. Using the draw tool, students can create images, place text, and color to their Google Docs. For my students who need the most assistance with the design process, I have them use my initial template (which I created using the draw tool in Google Docs) and a plug and play template.
2. Google Slides – Some students might prefer Google Slides over Google Docs because they might feel like they have more freedom. Using Google Slides, students can change the dimensions of each slide to 8.5×11 inches (or larger), and use the textbox tool, shape tool, and other design tools to create the graphic essay.
3. Canva.com – I love Canva because it provides students with different design templates and elements. While there is a paid version, I tell all of my students to use the free option. Using Canva, students can select a flier because that is preset to 8.5×11 inch dimensions. Once students are in Canva, there are a ton of free design tools. Students can choose from a variety of options, including preset text designs, frames, shapes, data (which is excellent for inserting bar graphs and pie charts), and pictures. Students can even upload their own images to the site as well!
4. Adobe Spark – Adobe Spark is another great online tool for students to create graphic essays and other multimedia presentations. Students can choose a custom size to create an 8.5×11 inch poster, and Adobe Spark also has premade text elements and templates to choose from.
5. Piktochart.com – Personally, I like Piktochart more for having students create infographics instead of graphic essays, but Piktochart still works. Students can the custom size or letter size to create their graphic. Piktochart has more advanced design features, and one unique design feature is that students can design their project in blocks. Similar to Canva and Adobe Spark, students can also upload their own images to their creation.

Graphic Essay Sampler
Subscribe to receive a sample of the graphic essay assignment!
I won’t send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Powered By ConvertKit

Sharing the File
Once students finish creating their graphic essays, I like to have them upload their creations to one location so that all of my students can see the work that everyone created. My favorite site for this is Padlet. If you haven’t used Padlet before, it is like an online corkboard. Students can post their designs to your class’s board. Students can also comment on other students’ work if you want to add a gallery walk element to this project.

Subscribe to my email list.
Subscribe to receive freebies, teaching ideas, and my latest content by email.
Built with ConvertKit
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

SUBSCRIBE NOW

CRAFT: Let’s Get Graphic: A Look at the Visual Essay by Nicole Breit
August 1, 2018.

If you’re keen to tell new kinds of stories – or old stories in new ways – consider these ten “visual” approaches to writing short-form memoir.
1. The Photo Essay
The art of the photo essay lies in the writer’s careful selection of images balanced with the inclusion of text. Will the photos drive the narrative, or will they fill in textual “gaps” to move the story forward? Vivek Shraya strikes an elegant balance of “showing” and “telling” in her compelling photo narrative, “ Trisha .”
2. The Concrete Essay
This form is the next evolution of concrete poetry (A.K.A. shape or pattern poems), reincarnated as CNF. Jennifer Wortman’s “ Worst-Case Scenario ” presents the story of her husband’s 35-feet fall into a gap while rock climbing, visually – via text shaped like the rocks he fell through.
3. The Illustrated Essay
There’s something so charming about a notebook doodle – perhaps because sketches convey the character of the artist in such an immediate way. I love the narrator’s personality as it comes through Randon Billings’ Noble’s drawings in “ Accidental Notes on the Syllabus .”
4. The Graphic Essay
Check out the masters of graphic memoir – Maggie McKnight , Riad Sattouf , Alison Bechdel , Marjane Satrapi, Kristen Radtke, Nicole Georges and Ellen Forney – and understand how powerful comics can be as a medium for personal storytelling.
5. The Paper Craft Essay
If you’re wondering what to do with your stockpile of scrapbooking supplies, look no further than Erica’s Trabold’s “ Swedish Rye Bread ”– an essay constructed as a collage of typed index cards, digital scans, the pages of a vintage cookbook, and scrapbooking paper.
6. The Quilted Essay
Quilting has a long history of embodying narrative in carefully chosen patterns, colours, and symbols. Learn more about textile-based narratives in Sarah Minor’s article “ What Quilting and Embroidery Can Teach Us about Narrative Form ” and by reading her visual essay, “ Log Cabin Quilt .”
7. The Schematic Essay
The Process of Becoming Informed is a found schematic essay published by The Diagram and credited to Michael K. Buckland of Library Services in Theory and Context, Pergamon Press, 1983. Where might you find a visual essay just waiting to be discovered?
8. The Graphic Hermit Crab
The hermit crab essay appropriates a found text – also known as a “false document” – as a “shell” to protect the vulnerable story it contains. The textual form’s logical progression is visual, in which a found graphic is adopted as the essay’s structure. J. Robert Lennon’s “ Turnabout: A Story Game ” is a graphic hermit crab essay that can be read starting at any point, proceeding in any direction.
9. The Video Essay
Video is a natural medium for personal narrative, and John Breslund is known as a pioneer of the visual essay form. This article includes a Q and A with Bresland and his collaborator, poet and essayist, Eula Biss, with links to some of their groundbreaking work including “Ode to Every Thing.”
10. The Interactive Essay
“Hypertext is spatial in every direction, truly nonsequential—nothing follows by necessity anything else in the essay” write Brenda Miller and Suzanne Paola in Tell It Slant . Exemplary interactive hypertext CNF include Dinty W. Moore’s “ Mr. Plimpton’s Revenge: A Google Map Essay ,” Christine Wilks’ “ Fitting the Pattern ” and the work of Eric LeMay .
I hope this survey of the visual essay, in all its weird and wonderfully varied forms, inspires you to try a new approach to telling your stories. No matter your level of skill, experience, or talent with the visual arts, you can start including visuals in your work easily – and to great effect – incorporating images or multi-media collage.
Which visual essay format appeals to you the most? I’d love to hear which visual essays inspire your next project!
2 comments for “ CRAFT: Let’s Get Graphic: A Look at the Visual Essay by Nicole Breit ”
- Pingback: CRAFT: Life Writing Tips— How Asking Questions Can Spark New Stories by Nicole Breit | Hippocampus Magazine - Memorable Creative Nonfiction
- Pingback: CRAFT: Visual CNF Forms- A Look at the Concrete Essay by Nicole Breit | Hippocampus Magazine - Memorable Creative Nonfiction
Share a Comment Cancel reply
Contributor updates.

Alumni & Contributor Updates: Early 2024
Contributor Updates: Fall 2023
Contributor & Alumni Updates: Spring 2023
Contributor Updates: Spring 2022
Using Graphic Organizers for Writing Essays, Summaries and Research
Ask any student – essay writing is one of the most despised tasks of their educational career. Perhaps there is so much displeasure associated with the task because it’s perceived as too linear – there isn’t enough visual and creative appeal. But if you use graphic organizer for writing essays then you can make writing enjoyable – or at least less terrible.
Not only enjoyable but graphic organizers (or diagrams) can make the writing process a snap. They’ll help you think outside the box, draw conclusions you wouldn’t normally observe, and make the entire process faster and more efficient.
Why Use Graphic Organizers for Writing
The phrase “graphic organizer” is just a fancy way of saying “diagram” or “visual aid.” Basically, they are a visual representation of the information you’ve acquired in the research process. There are quite a few reasons why you should use them when writing essays or summaries.
- Helps you visualize your research and how elements connect with each other
- Enhance your essays, summaries and research papers with visual elements
- Track correlations between your thoughts, observations, facts or general ideas
When it comes to essay writing, the most common graphic organizers are webs, mind maps, and concept maps .
Using Webs for Brainstorming
Webbing is a great way to see how various topics are interrelated. This graphic organizer is particularly useful during the brainstorming step of the writing process.
A web can sometimes get a bit messy. Usually, there are lots of arrows to connect overlapping ideas. However, even with lines crisscrossing every which way, it is still a great way to visualize your thoughts. If you’re using an online diagramming software like Creately you can overcome some of this because we automatically arrange the object for you.
Once you’ve created a map to document all your ideas and establish connections, you can easily transition to other forms of diagramming to better organize the information.
For example if you’re writing a research paper about the food web of the Australian bushes you can start creating a food web diagram similar to the one below. This way you can easily visualize the web while writing the paper. This is a simple example but graphic organizers become even more important when the subject gets complex.
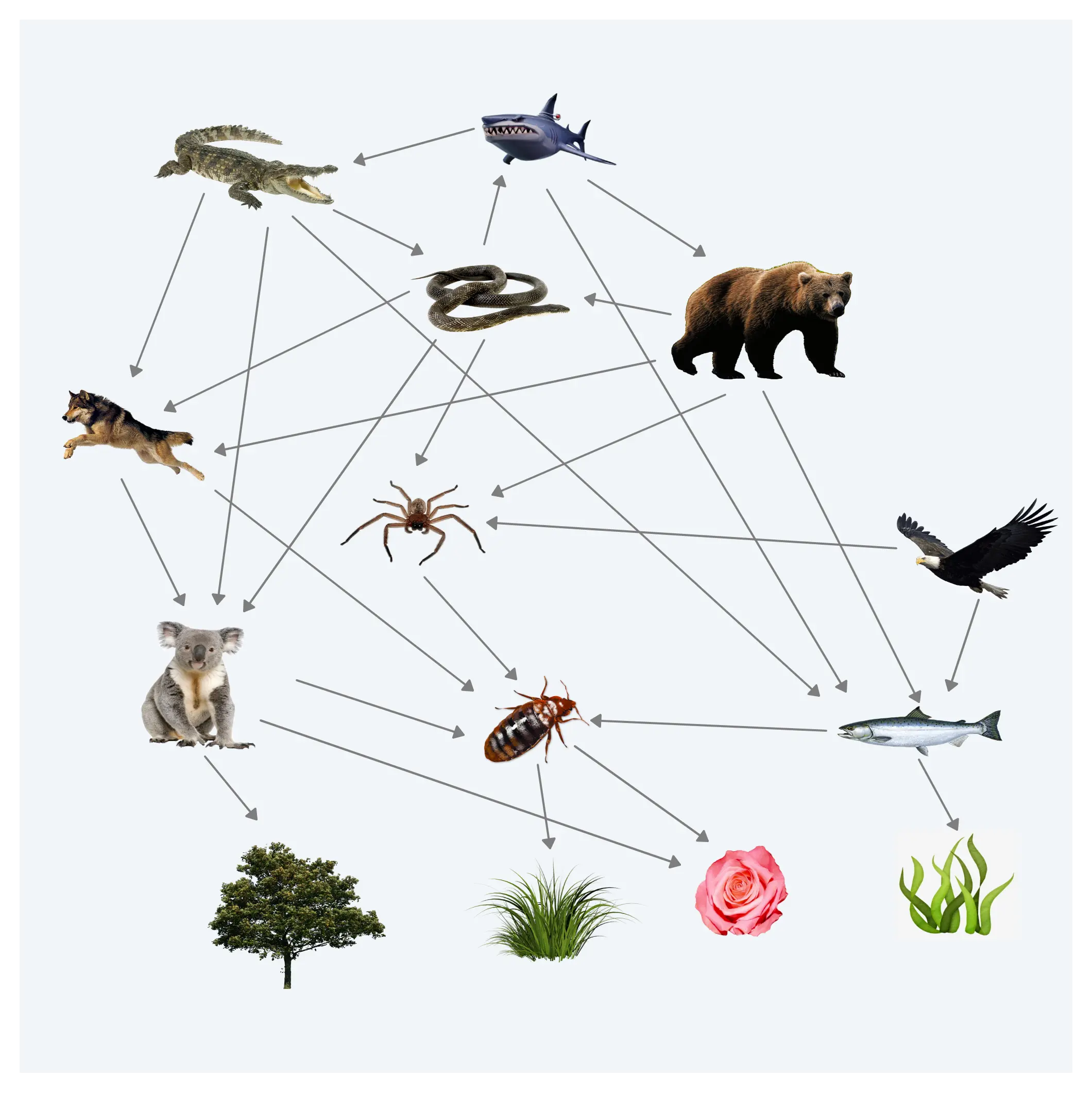
Although simple this example shows the importance of using graphic organizers for writing summaries. A comprehensive diagram pretty much does the summation for you.
Using Mind Maps as Graphic Organizers
Mind maps are a great way to depict a hierarchy. What is hierarchical organization ? The concept is simple: a singular topic dominates with each subsequent idea decreasing in importance.
Usually, the mind map starts with the thesis (or main idea) at the center. From there, you can branch out with your supporting evidence.
Use this process to replace your traditional note taking technique – note cards, outlines, whatever. You’ll quickly realize a mind map is a great way to formulate the structure of your essay. The thing to note here is that the nature of the mind maps force you think about sub topics and how to organize your ideas. And once the ideas are organized writing the essay become very easy.
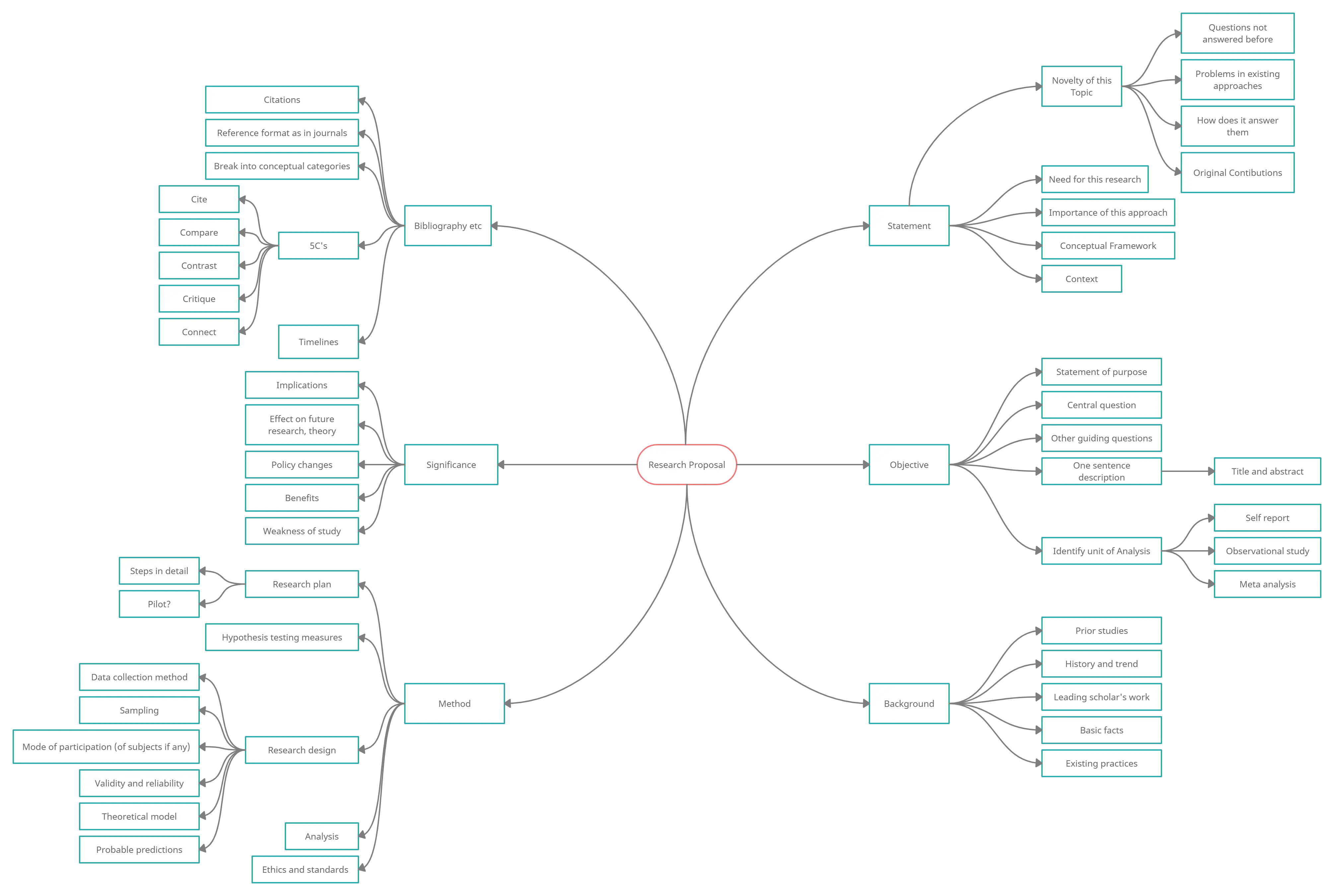
Above is a mind map of a research proposal. Click on it to see the full image or you can see the fully editable template via this link . As you can see in this mind map the difference areas of the research proposal is highlighted. Similarly when your writing the research paper you can use a mind map to break it down to sub topics. We have more mind map templates for you to get started.
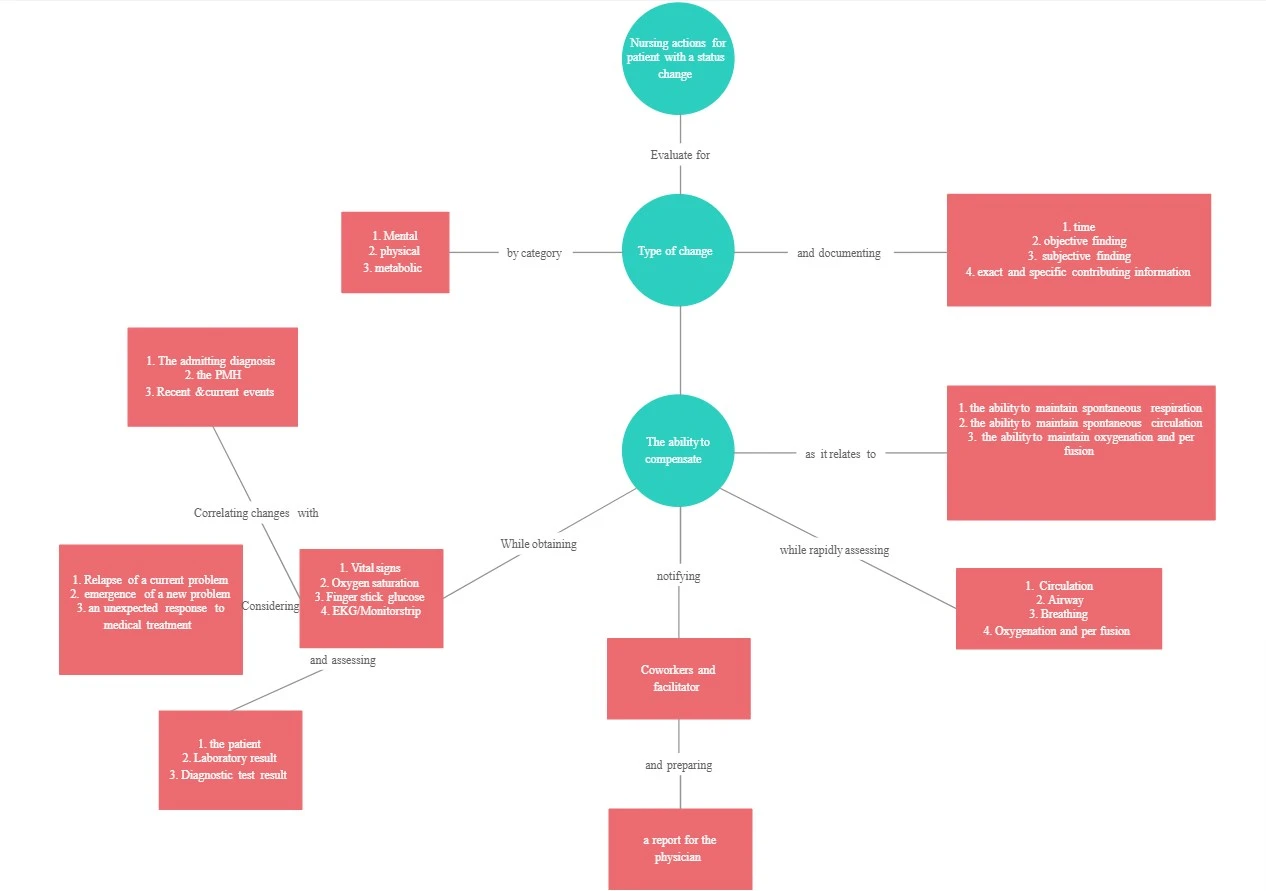
Concept Maps
A concept map will help you visualize the connection between ideas. You can easily see cause and effect – how one concept leads to another. Often times, concept mapping includes the use of short words or phrases to depict the budding relationship between these concepts.
If you look closely you can see that its very similar to a mind map. But a concept maps gives more of a free reign compares to the rigid topic structure of a mind map. I’d say it’s the perfect graphic organizer for writing research papers where you have the license to explore.
By creating a concept map , you can also see how a broad subject can be narrowed down into specific ideas. This is a great way to counter writers block. Often, we look at the big picture and fail to see the specifics that lead to it. Identifying contributing factors and supporting evidence is difficult. But with a concept map, you can easily see how the smaller parts add up to the whole.
Why Bother With Graphic Organizers?
If you already detest the writing process, adding another step might seem insane. However, there really are several advantages of using them. If you haven’t already accepted the benefits of each individual diagram style, here are some more perks of graphic organizers in general:
- Quality essays are based on detail. No one is going to accept your opinions and reasoning just because you say so. You’ll need proof. And organizing that proof will require attention to detail. Graphic organizers can help you see that detail and how it contributes to the overall concept.
- Graphic organizers are flexible. You don’t need one of those giant pink erasers. You don’t need to restructure your outline. All you have to do is draw a few arrows and bam – the relationship has totally changed.
- No matter what you are writing about, a graphic organizer can help. They can be used to structure an essay on the Great Wall, theoretical physics, or Spanish speaking countries.
- If you write an outline, can you easily see how point A influences point X? Probably not. But if little thought bubble A is sitting out there all by itself, you can visualize the way it ties into point R, T and X.
- Some of us find it difficult to put our opinions, thoughts, and ideas into writing. However, communicating our feelings with little doodles and sketches is far less threatening.
- As a writer, our brain often feels like a 2-year-old’s toy box – a big jumbled mess. Taking that mess and putting it onto paper with some semblance of organization is challenging. Rather than trying to take your thoughts from total chaos to a perfectly structured list, just try to get them out of your brain and onto paper in the form of a diagram.
- A graphic organizer helps you establish validity and relevance. You can easily nix the ideas that don’t support or enhance your thesis.
The next time you are faced with a writing project, take a few minutes to explore the efficiency of graphic organizers. You can find a wealth of templates here.
Have you ever used a graphic organizer to structure an essay? How did it go? Do you have a diagram suggestion for the writing process that wasn’t mentioned here? Let us know!
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
These are awesome guest posts contributed by our users and technology enthusiasts. Do you have something interesting to share? Want to get exposed to a massive tech audience? Check out our Guest Posting Guidelines to how to proceed.

How to Use Graphic Organizers to Write Better Essays
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 6 min
If you’re a student, there’s no way around the inevitable: You’re going to have to write essays. Lots of essays. In fact, the five-paragraph essay is so fundamental to the high school curriculum that it’s still used on the ACTs, and knowing how to recognize the organizational structure of essays will help you score higher on the SATs.
Even though it seems like a chore, knowing how to organize and write an essay can have a lasting effect on your life, from getting into a better college to scoring a better job to performing better in that job long after your high school days are over.
Here’s a secret: Using graphic organizers for writing essays can help you write better essays faster. (And don’t count yourself out if you’re an educator—you can offer these tools to help your students succeed.) We’ll show you exactly how to do it.
Why use graphic organizers
When ACT graders or teachers are looking your essay, they’re looking for very specific criteria; essentially, they’re looking at how well you’ve organized your thoughts. Many students don’t take the time to outline their essay structure before writing, and that always means a lower score on a test and a lower grade on the essay in class.
Using a writing template can feel like an unnecessary step in an already complicated process. If you need extra motivation to implement these organizers into your writing routine, consider all of their benefits. Graphic organizers can help you:
- Save time by showing you where each piece of the essay “lives.”
- Have more productive brainstorming sessions, either by yourself or with a group.
- Make connections between ideas and create a more cohesive argument.
- Pinpoint holes in your arguments and either adjust the thesis or find supporting statements.
- Keep track of your research.
- Organize your thoughts and come to interesting, more compelling conclusions.
- Stay in the right direction when you feel lost in a sea of words.
- Manage anxiety by converting the fear of a blank assignment into an action plan with a clear map.
With all those benefits, it’s hard to ignore how useful and vital graphic organizers are to writing. And once you’ve become adept at organizing your thoughts for something like a school essay, you’ll find that skill carries with you throughout your life, whether you’re trying to become a more intelligent debater to negotiate prices. It goes beyond just the essay to becoming a better thinker. And it starts with a simple template.
We’ll walk you through several use cases for graphic organizers and provide templates for you to download and fill in when you’re ready to write.
Brainstorming graphic organizers
Brainstorming is important, not only to come up with ideas for topics but to determine what information you need to include in the essay once you’ve determined your topic. Though many think of brainstorming as just freeflow thinking, brainstorming is most productive when you work within specific parameters.
That’s why essay brainstorming graphic organizers are useful, whether you’re using one to brainstorm on your own or you’re working with a group.
In Lucidchart, our mind map shapes and templates double as brainstorming graphic organizers. Start with an essay prompt as your central shape and then fill in the shapes that branch off your prompt with topic ideas. Alternatively, you can add your selected topic to the center and start brainstorming the different ideas you need to cover in your paper.
When the template is filled in, you’ll have a clear starting point for your essay or research paper.
Research paper graphic organizers
Nothing paralyzes students with fear quite like a research paper. These long-form papers require—as the name implies—quite a bit of research, and their purpose is to teach students how to look for valid sources to support their arguments.
But keeping track of all those sources and tying them into your argument can be tricky. That’s where a research paper graphic organizer can be a student’s greatest ally.

This template lays out the writing process itself. After you come up with a general topic, like “the disappearance of honey bees,” fill in the “Research Paper Topic” box.
Then, start looking for reputable sources (Wikipedia doesn’t count) and use the five sources boxes to hold the most relevant quotes and statistics you find. Using those quotes and statistics, you can then fill out a thesis statement that is supported by the research.
Then, you’ll be able to focus your paragraphs on a single topic each that supports the thesis statement and your overarching argument. After you’ve filled out the template, the backbone of the research paper is complete: All that’s left to do is fill in the spaces between sources and arguments.
5-paragraph essay graphic organizer
When it comes to writing the five-paragraph essay, writing diagrams are key. By using graphic organizers for writing, you’re no longer staring at a giant blank piece of paper with no idea how or where to begin. Your graphic organizer is your map.
Although using writing diagrams may seem time-consuming, the fact is that taking the time to fill a graphic organizer in before writing actually saves time. If there’s a problem with the argument, it will show up on the diagram, or if there’s not enough evidence to support your argument, you’ll know before you’ve wasted time writing the paper. And, as we said before, even if your writing is terrible, if your argument is sound, you’ll still score a decent grade.
Try this 5-paragraph essay template to get you started.

Don’t feel pressured to come up with a compelling title right away. Instead, it’s more important that you come up with a thesis statement that can be supported by three solid arguments. Fill in that thesis statement and your arguments. Then, for each argument, figure out three supporting details to support your case.
That’s it! You’ve got the most essential parts of your 5-paragraph essay completed.
Now, come up with an introduction that sets the stage for your argument and a conclusion that wraps up and restates your thesis and supporting arguments in a compelling way. Now you have a solid plan for your paper and can approach it with confidence.
If you’d like a more linear graphic that exactly follows the structure of the 5-paragraph, use the writing template below and follow the same process.

Visuals, such as graphic organizers for writing, can help you better understand concepts, think creatively, and collaborate with your classmates—and there are plenty of other templates where these came from.
Lucidchart offers hundreds of templates to help you through your studies, including timelines, Venn diagrams, word maps, and more. Sign up for Lucidchart and upgrade to an Educational account for free.
Resources for teachers
Providing graphic resources to students is essential; after all, many of your students will be visual learners, so while you may beautifully explain how the process works, there will be some who won’t understand until they see a template of the essay itself.
Lucidchart has many resources for teachers, from lesson plans to writing templates. While you’re teaching your students how to write essays or research papers, it’s useful to print out the templates and fill them out together (even using a completed template as a separate assignment with a separate grade) so that your students can get a feel for properly filling out graphic organizers before attempting it on their own.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles

Check out how Annika, a recent English graduate of the University of Michigan, used mind mapping in Lucidchart to develop her honors thesis.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered visual tool ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Tools
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Visual Academy
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
12 Graphic Organizer Examples for Teachers and Students
Every teacher wants their students to fully understand the concepts taught in class. However, you may encounter topics that are difficult to teach and understand. It is necessary to employ an innovative approach in order to assist students in comprehending a challenging subject.
Graphic organizers are powerful tools that make complex concepts easier to teach and understand. They also help students develop visual literacy skills . Teachers find graphic organizers helpful for explaining difficult concepts, and students find them engaging. Graphic organizers are also great for presenting research data if, for example, the teacher wants to share a case study with students.
Now, what if you could quickly find and customize graphic organizers without spending hours brainstorming from scratch?Because there is a sea of engaging templates to choose from, you can create compelling visuals with just a few clicks. These graphics can be used for a number of different purposes, including teaching. With Piktochart, you can access and customize engaging graphic organizer templates in minutes – no design skills required. Simply create a free account to get started.
In this article, we will look at the 12 graphic organizer examples that greatly assist teachers and help students retain information for a longer period of time.
What is a Graphic Organizer?
Graphic organizers are tools that help visually organize information and complex concepts in a way that is easy to understand and memorize. Graphic organizers effectively organize and visualize information by creating links between concepts or facts. By visually illustrating the relationships between concepts, graphic organizers make it easier to analyze and internalize information.
We know that every mind works differently. Presenting information in a systematic, visual format enables students to follow along at their own pace and grasp relationships more easily than via verbal explanation alone. They can also be an invaluable tool for visual learners.
12 Graphic Organizer Examples for Different Learning Objectives
There are countless types of graphic organizers out there, as information can be organized and visualized in many different ways. We’ll focus on 12 of the most helpful types of graphic organizers for teachers and students, organized by the primary purpose each one serves.
Graphic Organizers for Brainstorming and Organizing Ideas
Some graphic organizers are specifically great for organizing ideas for brainstorming. Here are three examples.
Mind maps are graphic organizers that organize information in a structured and visually attractive fashion. When a mind map is finished, you will get a structure that looks like a spider web. An example of the graphic organizer is the following mind map on Piktochart . It shows the values of a company, with different values branching out from the central idea, that is, company values .
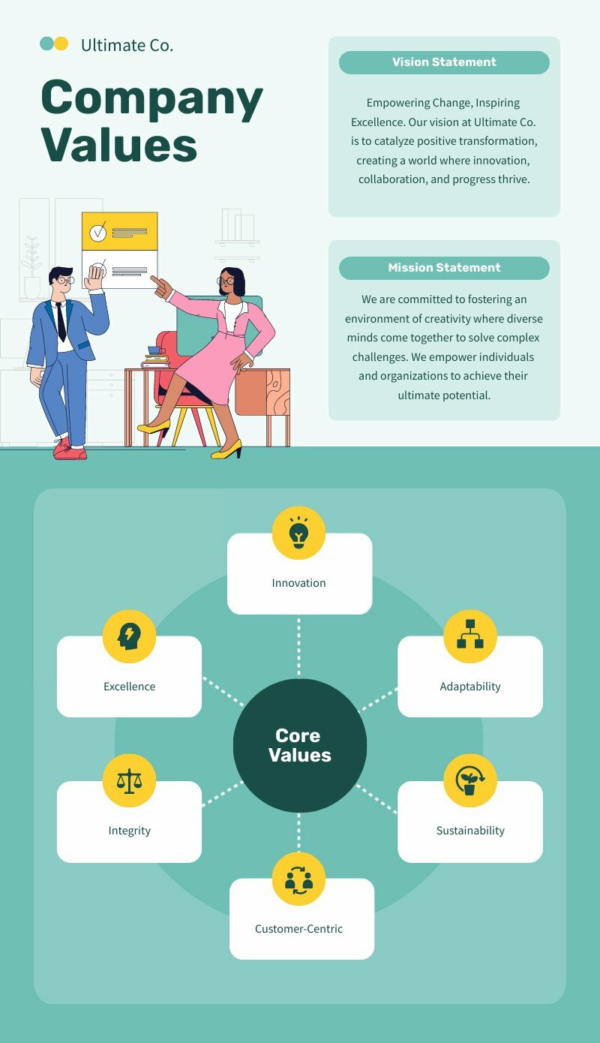
We all know that information retention can become quite difficult, especially when a number of different subtopics link to one main topic. A student could use a mind map to break down the taxonomy of living things, with ‘Organisms’ in the center, ‘Kingdoms’ branching out one level, ‘Phyla’ branching out from each ‘Kingdom’ and so on.
Concept Map
Concept maps are another type of graphic organizer that excels at representing hierarchical information. They use boxes or circles to represent different concepts, with lines or arrows labeled to illustrate the relationships between them.
Concept maps have many uses in educational settings. They help in the sequential understanding of different concepts for students. For example, if a teacher has to break down a country’s government structure, he or she will most likely use a concept map to show the branches and subbranches of different government institutions systematically.
Cluster Diagram
Cluster or cloud diagrams help brainstorm different ideas around a main concept. This type of graphic organizer is called a cluster because the topic or ideas related to the main idea form a cluster around it. For example, a cluster diagram can assist students determine how much they know about a topic and what areas need further research.
This type of graphic organizer is very useful when generating ideas for a project or planning its different phases. Cluster diagrams break down a complex subject into smaller parts, both for individuals and for groups, for example, during defining scope of a project in its early stage.
Graphic Organizers for Comparing and Contrasting
The next type of graphic organizer helps you to compare two or more concepts. You can use this organizer to compare and contrast ideas, people, events, and policies. For instance, say you’re teaching a unit on different forms of government. You could use a compare and contrast graphic organizer to help students parse out key similarities and differences between a democracy and a dictatorship. This type of graphic organizer will be your go-to option.
It is important to know that when you use this type of graphic organizer to compare two concepts, you are covering both the similarities and differences between those concepts. However, with contrast, only the differences are mentioned. Some examples of this category of graphic organizers are given below.
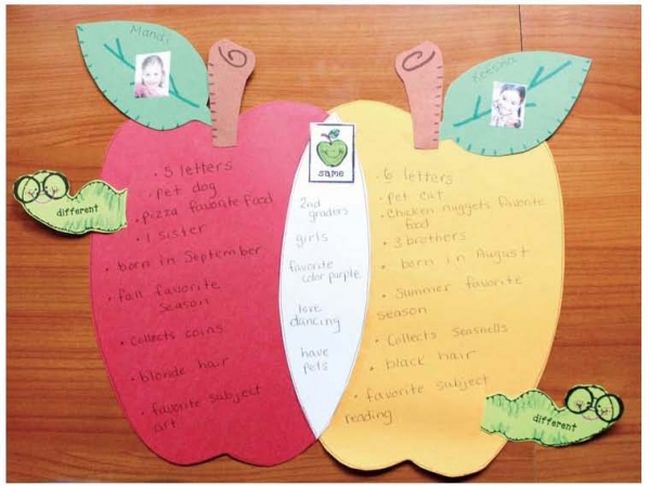
Venn Diagram
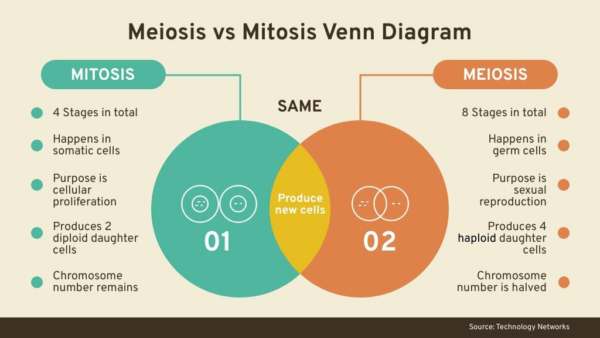
A Venn Diagram usually comprises two to three overlapping circles. The commonalities between the concepts are written in the shared or overlapping area, whereas all the distinct or unique features are mentioned in the part of the circle that does not overlap with any other circle.
For example, you could have your students draw Venn diagram for the fruits and vegetables that red or orange. The common area between the two circles will contain vegetables like tomatoes that come in both these categories. The Venn diagram below shows the comparison of mitosis and meiosis.
Another brilliant graphic organizer for comparing and contrasting is the “T Chart.” A T-chart is simply a table with two columns, usually comparing two items or ideas, or sorting data into categories. This type of graphic organizer is super quick to create and easy to understand, especially for students. T charts can also be used to categorize and jot down pros and cons.
The T chart is a popular option for both teachers and students because its layout is straightforward, and it offers a wide array of functions. For example, if the students are planning to go on a field trip but are not able to choose a location, then T charts can help a great deal.
Teachers can ask the students to make a T chart of potential places and list the advantages and disadvantages of each of the locations in their respective columns. Also, a T chart is a great graphic organizer to show upsides and downsides of a topic.
Graphic Organizers for Sequencing and Cause-Effect
Next on the list are graphic organizers, which show the sequence or timeline of events. Sequence and timeline graphic organizers are particularly useful for teachers when presenting events in chronological order is important. Some of the graphic organizers that help students visualize the relationships between steps in a process or links in a chain of events are as follows.
A timeline graphic organizer shows a sequence of events in chronological order. History subjects make great use of timelines . Because major historical events can be shown in a proper sequence using a timeline. Along with dates, timelines give the flexibility to mention locations as well. For example, a timeline of the American Revolution could chart major turning points like the Boston Tea Party, the signing of the Declaration of Independence, and the Battle of Yorktown.
Timelines can also be used to show how a certain phenomenon has progressed over time, such as a business’s growth. The Piktochart timeline template below charts key events in the life and reign of Queen Elizabeth II. Notice how the combination of images and concise text makes the chronology engaging and easy to follow.

This type of graphic organizer shows the steps of a process and how all the steps combine in a sequence to make the process happen. Flowcharts systematically and clearly document and communicate how a process works and what steps are involved in it, from start to finish. When a process is mapped using a flowchart , potential areas or steps of improvement can be identified.
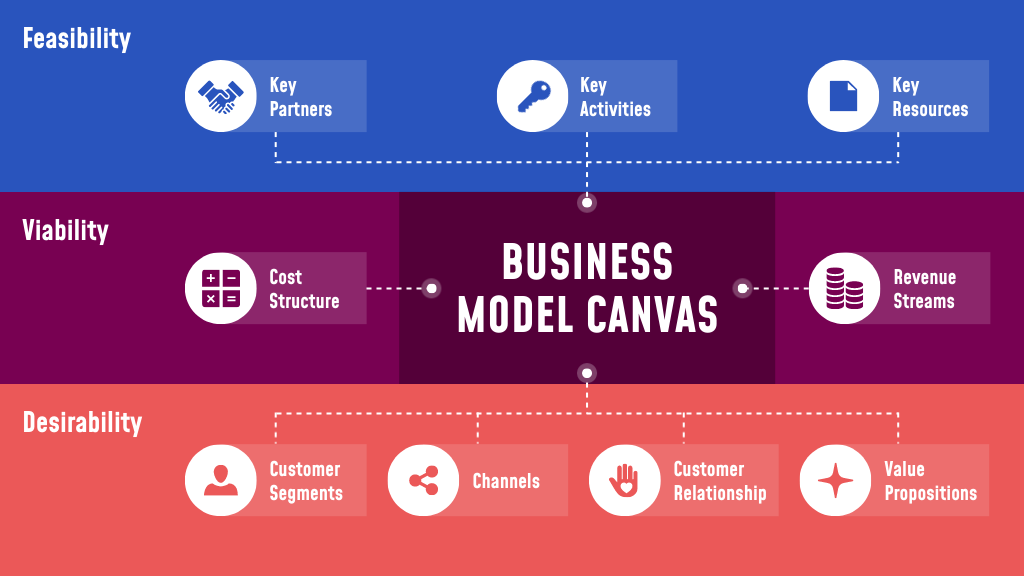

Cause and Effect Diagram
As the name suggests, a cause-and-effect diagram groups those causes of a problem that either have already happened or might happen. Relationships between different contributing factors can also be shown using a cause-and-effect diagram.
Often referred to as an Ishikawa diagram, or a fishbone diagram, a cause-and-effect visual is one of the basic tools of quality . While often associated with root cause analysis in business and manufacturing, cause-and-effect diagrams are equally powerful for getting to the bottom of issues in the classroom. By mapping out all the potential contributing factors to a problem, students can start to identify patterns and actionable solution.
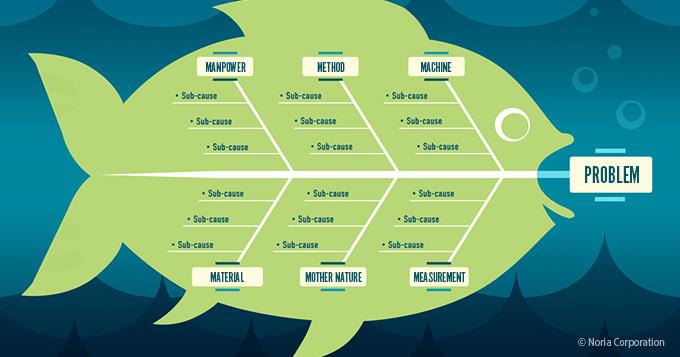
Source: Noria Corporation
Graphic Organizers for Main Idea and Supporting Details
This category of graphic organizers shows a main idea and its supporting ideas. It defines and visualizes a core concept and all its supporting details. It is a great tool that helps students develop an outline of a topic for better understanding. Some of the examples are given below.
Main Idea Web
This type of graphic organizer starts with a main idea and branches out into related sub-ideas. The key point behind web graphic organizers is sometimes referred to as a light bulb. It is predominantly used to brainstorm ideas for writing purposes. For example, if a student wrote a report on photosynthesis, they could put “photosynthesis” in the center, then branch out to related subtopics like ‘chloroplasts’, ‘light-dependent reactions’, etc.
Herringbone Diagram
A herringbone diagram is used when processes are involved. This type of web organizer helps you break down variations in a process or causes that lead up to an effect. A herringbone diagram is particularly important for avoiding an event before it happens.
Graphic Organizers for Writing and Note-taking
Another group of graphic organizers we’ll explore focuses on writing and note-taking. Writing, especially essays, proves challenging for many students as they struggle with arranging ideas. Here are a couple of graphic organizers for writing, which can be of great help to you.
Essay writing is an important skill that students use throughout their lives. An essay map graphic organizer is a brilliant tool for students, as it helps them to chalk out the outline in a systematic manner without missing any detail. Once a student is done with his or her essay map, writing becomes a walk in the park.
Cornell Map
This graphic organizer is a popular technique for note-taking. Particularly during lectures and textbook reading, the Cornell Map template comes in handy as it helps students to jot down all the important ideas and information systematically. It usually has a cue column, a note-taking column, and a summary section.
When students are taking notes, the key ideas, important dates, formulas and other such details would go into the “note-taking” column. They will add questions, cues, and headings in the “cue” column. Whereas, the “summary” section will include a summary of the notes as one or two key learning outcomes. This helps students identify important details when they revise their notes later on.
Tips for Using Graphic Organizers Effectively
It is important for teachers to use graphic organizers in a manner that maximizes the chances of effective learning. Some of the tips to make sure a graphic organizer effective are given below.
- Simple is Always Better —Your graphic organizers must always be simple. This will help students learn quickly. For example, avoid complete sentences unless absolutely necessary.
- Offer a Variety of Graphic Organizers – Expose your students to different types of graphic organizers day-to-day. This will bring out the best in them in terms of creativity.
- Use the to Assess Student Learning – Give the students a task along with a graphic organizer focused on the skill in focus. Use their graphic organizers to assess their standing in the class.
- Use them Frequently —Using graphic organizers frequently helps students internalize what is being taught. The more often students use these tools to engage with content, the more adept they’ll become at using them independently.
A graphic organizer is a tool for teachers to explain complex problems to their students. Similarly, graphic organizers help students visualize the information being taught in class.
There are different graphic organizers, each suited to a specific purpose or thinking process. Whether it’s brainstorming ideas, comparing and contrasting, sequencing events, mapping out an essay, or taking structured notes, there’s a graphic organizer that can help.Teachers can encourage their students to generate ideas by using graphic organizers in their lessons. Students can use graphic organizers to enhance their writing skills.
Piktochart is a one-stop solution that lets you create your own graphic organizer within seconds. It has both one-pager templates and multi-pager templates to cater to all kinds of requirements. Sign up on Piktochart now and make learning fun!

Other Posts

The World Map

5 Best AI Chart And Graph Makers in 2024 (Free and Paid)

Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your First Custom Map
ELA Brave and True by Marilyn Yung
Teach Theme with Graphic Essays: The Old Man and the Sea

Here’s how I’ve used graphic essays and what I’ll tweak for next time.
My junior English classes recently read the short story, “In Another Country” by Ernest Hemingway as a follow-up to reading “The Old Man and the Sea.” Because they had just completed a traditional written thematic analysis of the novel, I opted to have them produce a graphic essay instead focused again on a theme revealed in the text.
I’ve assigned graphic essays before at my last school where I asked my eighth-graders to create these at the conclusion of a study of Frederick Douglass’ narrative. Click here for a post about that graphic essay assignment. It was a successful project; however, since it was the first time I had tackled the graphic essay, it left room for improvement. And by the way, that need for improvement always happens, and it doesn’t matter if it’s a new assignment or a tried-and-true one, I always discover things I want to “fix” for next time.
And, of course, our “In Another Country” graphic essays followed that trusty pattern.
Regardless, I’ve decided to write this post about this project based on a short story I wasn’t even sure I wanted to approach with students. In my view, there are other more interesting pieces by Hemingway (think “The Short Happy Life of Francis Macomber,” but now in retrospect, I am SO GLAD I plowed ahead and experienced “In Another Country” with my students because this story is rich with themes and historical context and it paves the way for good discussions about World War I (and by extension World War II), the Lost Generation, the birth of modernism, and even more specifically the influence of avant garde art on writers.

To culminate our reading of “In Another Country,” the graphic essay project was intended to:
- offer my students a break from traditional essay writing;
- help them discuss theme with evidence and their own commentary;
- allow students to discuss symbolism; and
- allow students to get creative and apply their artistic skills.
I found the graphic essay idea a little over a year ago in a post by teacher and author Buffy Hamilton at her blog, Living in the Layers. Hamilton’s post references projects created by students at North Atlanta High School, including the graphic essay project created by teacher Casey Christenson. Her students created graphic essays based around Henry David Thoreau’s Walden Pond .
Last year, I modified my Frederick Douglass graphic essay project to conform itself to a shorter work. Douglass’ narrative runs 175 pages or so depending on the edition you read, and can support a more extensive graphic essay. “In Another Country” is quite short. It covered four pages in our Glencoe Literature textbook.

The only change I did make, however, was to have students use one piece of textual evidence to support their chosen theme instead of three. I like this modification; it compels students to find the absolute best passage from the story instead.

I also allowed students to look outside the story for their symbols, which were to symbolize in some way their chosen theme. This is one detail of the project I may modify next time, but the jury is still out on that one. In short, due to the brevity of the story, there really aren’t that many possibilities for symbols used within the text; however, maybe I need to read the story more closely with that precise need in mind for the next time I plan for this project.
Even so, for this graphic essay, I did scaffold the theme identification process and provided five specific themes from the story that students could explore.
Here are the five specific themes:
- dislocation/being a foreigner
- the technology dilemma (For example, technological progress can both help and harm mankind; the machines of war can be destructive (as in weapons and artillery) but they can also heal (as in the physical therapy “machines” in the story).
Maybe I made this project too easy by providing students with predetermined themes. After all, in our recent essays written for “The Old Man and the Sea,” we read articles that addressed specific themes in that novel. Those articles (here’s my post about those five articles) assisted students in identifying themes within the book to write about. It will be interesting to see how well students are able to notice and discuss themes next year when I have them as seniors. Perhaps at that time I’ll have them recall these two thematic essay projects to jog their memories.
Anyway, I provided them with these five choices for themes and then let them run with it, following the guidelines provided on a printed handout. Here’s a screenshot of the assignment sheet. Here’s a link to the Google doc of this handout.

This project took my students two to three work sessions of thirty to forty minutes each.
I assigned this project on a Friday with about twenty minutes of work time available and scheduled it to be due at the end of class the following Tuesday. After vocabulary bell work and a mini-lesson, students had about thirty to forty minutes on Monday and Tuesday. Looking back on it, two and half class periods were just about right. Most students were able to finish without needing time outside of class; some were finished by the beginning of class Tuesday, which fortunately just happened to be our last day of school before closing for COVID-19.
Overall, I’m satisfied with this project.
Am I happy with the final products? Mostly.
Many of my students are more concerned with getting the project finished quickly, and so could have spent more time on their graphic essays.
Here’s what I would change for next time:
- Have students spend more time developing thesis statements. I provided an example on the sheet as a guide, but many students basically copied it, swapping out the theme provided for theirs, if needed.
- Stipulate that symbols need to be objects and not illustrations. For example, a stick figure drawing is an illustration, not a symbol. I might need to explain the difference: a symbol represents something; an illustration shows something.
- Call for students to add a sentence or two near their symbols that explains the symbol and how it represents the theme discussed.
- Require color and lots of it. While this isn’t an art project, I would still like them to create an interesting, eye-catching layout.
- Require that handwriting be done in pen, i.e. no pencil.
Without further ado, here are the rest of the graphic essays I’ve chosen to include in this post. I’ve included two photos for each of the five themes discussed. These graphic essays below tended to be a representative sample of the quality of work my juniors turned in. See the captions for more thoughts.

Thanks for reading! I haven’t seen students since the day these projects were turned in and, as of the latest, we will be out of school until Tuesday, April 28. This project will seem so far in the past at that time that I doubt if many constructive comments will arise. But that’s one of the downsides of distance learning and the passage of time.
Regardless, have you tried graphic essays with your students let me know of your experience. and follow my blog for a future post about my lack of success — so far, anyway — with the popular one-pager., share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Published by Marilyn Yung
Writes | Teaches | Not sure where one ends and the other begins. View more posts
3 thoughts on “ Teach Theme with Graphic Essays: The Old Man and the Sea ”
- Pingback: How to make student writing more specific – ELA Brave and True by Marilyn Yung
Extremely interesting. Thank you for giving such an informative blog.
You are welcome! Thanks for reading!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from ela brave and true by marilyn yung.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Get Your Free Field Trip Reflection Sheet 🦁!
Graphic Organizers 101: Why and How To Use Them
An incredibly valuable tool for every student, every subject.

Even if you’ve never heard of graphic organizers, chances are good you’ve been using them in one form or another all your life. That pros and cons list you made before making a big purchase? The family tree you’re working on? Your school’s org chart? They’re all graphic organizers. Here’s what you need to know about using this powerful tool with students of all ages.
What are graphic organizers?

Source: @thecomfortableclassroom
Put simply, graphic organizers are a way of organizing information visually to help students understand and remember it. They’re tools that let kids make connections, create a plan, and communicate effectively. A good organizer simplifies complex information and lays it out in a way that makes it easier for a learner to digest. Graphic organizers may include text and images, depending on the purpose and student’s learning style.
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
How do I use them?
Source: @yourteacherbestie
You can provide students with pre-printed organizers or encourage them to draw their own. Either way, teach students how to use them by modeling the behavior first. Consider making anchor charts for commonly used types so students can refer back to them as they work.
With younger students, work to help them understand how to choose certain types of organizers depending on their goals. For instance, students taking notes while they study may find a concept map most helpful. When comparing two topics, a Venn diagram or T chart is probably the best choice. Here are some ways to use graphic organizers in various subjects (and explanations of them below).
Language Arts
- Use a story map or story mountain to diagram the characters, setting, and key plot points.
- Try a web organizer to keep track of character relations and connections.
- Learn vocabulary words with a Frayer model that lays out meaning, synonyms, examples, and illustrations.
- Map out the topic, main ideas, and supporting facts of an essay before you start writing.
- Use a story map or mountain to plan creative writing.
Math and Science
- Use a Frayer model to define and understand terms and formulas.
- Compare two or more concepts with a Venn diagram (like area and perimeter).
- Create a visual representation to solve a story problem.
- Plan an experiment with a sequence organizer.
- Start the exploration of a new topic with a KWL organizer to understand what students already know, what they want to learn, and what they do learn.
- Draw a timeline to understand the order of events in history.
- Use idea webs or concept maps to keep track of information as you read and help you study.
- Dig deeper into a topic with a cause and effect organizer.
What types of graphic organizers should I use in my classroom?
Graphic organizers come in a wide array of styles. Here are some of the most common types to try with your students.

Source: Mrs. Byrd’s Learning Tree
This is one of the first organizers many kids learn to use. For little ones, story maps are simple, laying out the setting, characters, and beginning, middle, and end. Older students can expand the map to take in more details.
Timeline and Sequence of Events

Source: Growing Kinders
Here are two more common organizers kids will recognize. Timelines are generally used in history and social studies classes, though they can be helpful when reading books too. Use sequencing organizers to lay out the steps of a procedure or science experiment.
Story Mountain
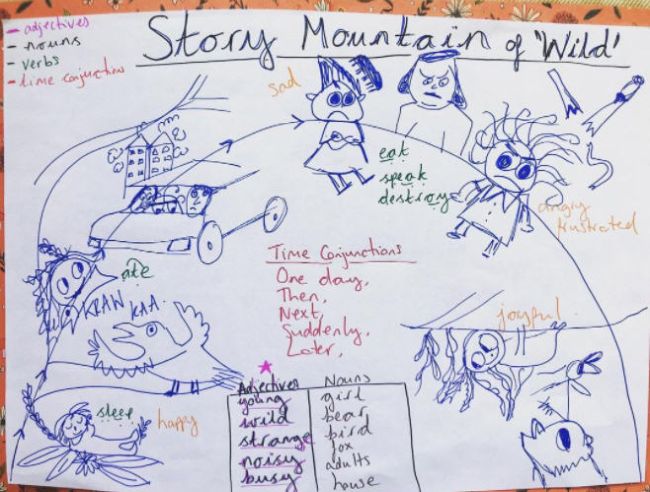
Source: @goodmorningmissbagge
A story mountain is helpful both when reading and preparing to write. Students map out a story from start to finish, building up to a climax and back down to the conclusion.

Source: Mrs. Kurt’s All Star Kindergarten Blog
KWL (What I K now, What I W onder, What I L earned) charts are a terrific way to help kids think about what they want to learn about a topic and hold them responsible for actually finding out that information. The first column is a list of everything they already know. The second column lists what they’d like to learn, and the third one provides new information acquired along the way.
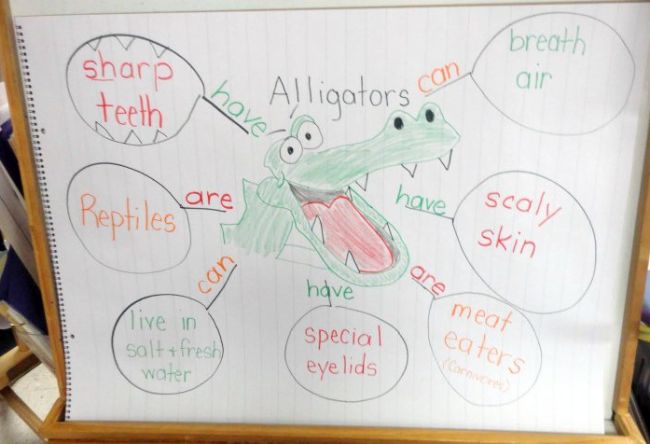
Source: Krazy for Kindergarten Goes to Third Grade
When there’s a lot of information to remember about a subject, idea webs are a terrific way to organize it all. It’s a more interesting way to explore a subject than just making a list or taking notes and one that’s more likely to help kids actually remember the information.
Concept Map
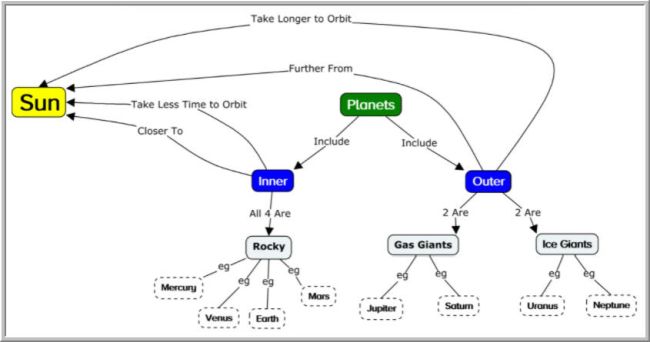
Source: Evidence-Based Teaching
A concept map takes an idea web to the next level. It’s really a series of idea webs, with connections drawn between. These can get very large, so encourage older students to explore online programs that can help them create useful diagrams.

Source: Joyful Learning in KC
Circle maps are terrific for brainstorming or thoroughly understanding a specific concept. In some cases, circles can continue to expand outward. For instance, a circle map could begin with your hometown in the middle, with a larger circle for your state, another for your country, then your continent, and so on. Inside each circle, students write info relevant to that subject.

Source: A Learning Journey
Graphic organizers are especially useful when planning any kind of writing. OREO and Hamburger models are common, but you’ll find a lot of other options out there too. The key is to make sure the organizer helps students define their main idea, gather supporting evidence, and draw a conclusion supported by the facts.
Frayer Model (Vocabulary)

Source: What I Have Learned
The Frayer model has a lot of uses but is most often applied to vocabulary. The term goes in the middle, with four sections surrounding it for definition, characteristics, examples, and non-examples. Another version has sections for definition, synonym, an illustration, and using the term in a sentence.
Cause and Effect Graphic Organizer

Source: Around the Kampfire
When you want students to dig deeper into the material, try a cause and effect organizer. You can use it in pretty much any subject to make connections between actions and results.

Source: @ducksntigers13
A T chart is a very simple way to compare two related subjects. Many people use these all the time, especially when writing pros and cons lists.
Venn Diagram
Source: Teach With Me
A Venn diagram is another way to compare and contrast material, looking for similarities and differences. The simplest version has two overlapping circles, with more overlapping circles added for more complex subjects.
Where can I find free graphic organizer printables?
While you don’t need to use a pre-printed organizer every time, they can be especially helpful with younger students as they learn how this valuable tool works. The internet is full of graphic organizer printables, both free and for purchase on sites like Teachers Pay Teachers. Here are some free options we’ve created for teachers to try.
- Summary Graphic Organizer
- Summarizing Graphic Organizers (Grades 2-4)
- Predictions and Inferences Organizer
- Scientific Method Graphic Organizer
- Continents Graphic Organizer
Get all the latest free printables and teaching ideas when you sign up for our newsletters .
Plus, anchor charts 101: why and how to use them ..

You Might Also Like
11 Helpful Note-Taking Strategies Your Students Should Know
It's a skill they can use later in life too. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
EL Education Curriculum
You are here.
- ELA 2019 G8:M3:U2:L3
Write an Informative Essay: Plan Introduction and Body Paragraphs
In this lesson, daily learning targets, ongoing assessment.
- Technology and Multimedia
Supporting English Language Learners
Materials from previous lessons, new materials, closing & assessments, you are here:.
- ELA 2019 Grade 8
- ELA 2019 G8:M3
- ELA 2019 G8:M3:U2
Like what you see?
Order printed materials, teacher guides and more.
How to order
Help us improve!
Tell us how the curriculum is working in your classroom and send us corrections or suggestions for improving it.
Leave feedback
Focus Standards: These are the standards the instruction addresses.
- RL.8.1, RL.8.2, W.8.2a, W.8.2b, W.8.4, W.8.5, L.8.1a
Supporting Standards: These are the standards that are incidental—no direct instruction in this lesson, but practice of these standards occurs as a result of addressing the focus standards.
- RL.8.10, W.8.10
- I can identify the purpose of each part of the introduction of a model literary analysis and use this understanding to plan the introduction of my own literary analysis. ( W.8.2 )
- I can identify the structure and purpose of each part of a Proof Paragraph and use this understanding to plan the Proof Paragraphs of my own literary analysis. ( W.8.2 )
- Opening A: Entrance Ticket
- Work Times B and C: Informative Writing Plan graphic organizer ( W.8.2 )
- Work Time C: Analyze a Model: Proof Paragraphs 1a and 1b ( W.8.2 )
- Closing and Assessment A: Informative Writing Checklist ( W.8.2 )
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 3
- Literary Analysis Informative Essay directions
- Proof Paragraphs 1a and 1b handout
- Informative Writing Plan graphic organizer
- Ensure there is a copy of Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 3 at each student's workspace.
- Strategically pair students for the peer critique in Closing and Assessment A with at least one strong reader per pair.
- Review the Informative Writing Plan graphic organizer (example for teacher reference) to become familiar with an example of the planning students will be doing today and in the next lesson.
- Post the learning targets and applicable anchor charts (see Materials list).
Tech and Multimedia
- Work Times A and B: Convert Informative Writing Plan graphic organizers and invite students to complete them in an online format—for example, http://eled.org/0158 .
- Continue to use the technology tools recommended throughout previous modules to create anchor charts to share with families; to record students as they participate in discussions and protocols to review with students later and to share with families; and for students to listen to and annotate text, record ideas on note-catchers, and word-process writing.
Supports guided in part by CA ELD Standards 8.I.B.6 and 8.I.B.8.
Important Points in the Lesson Itself
- To support ELLs, this lesson includes time spent analyzing a model informative essay that compares a familiar text, Summer of the Mariposas , with a poem before then writing an essay that focuses on analyzing the similarities and differences in theme and structure in Maus I and "Often a Minute" and the way in which these contribute to meaning. The lesson also includes time for peer feedback and collaborative discussion to help students improve their writing while also practicing oral skills.
- ELLs may find it challenging to understand portions of the model essay. While Summer of the Mariposas will be quite familiar to students, the poem that this text is compared to in the model is not something students will have a deep understanding of. Encourage students to focus on the structure of the essay and the way in which the author crafts points about similarities and differences. Remind students that for their own essays, they will be working with texts that they know well.
- Homework: Language, Structure, and Theme (example for teacher reference) (from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 2, Homework A)
- Characteristics of a Literary Analysis Essay anchor chart (one for display; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 1, Work Time A)
- Model Literary Analysis Essay: Relationship of Structure to Meaning (example for teacher reference) (from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 1, Work Time A)
- Informative Writing checklist (for teacher reference) (from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 1, Work Time B)
- Homework: Language, Structure, and Theme (one per student; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 2, Homework A)
- Model Literary Analysis Essay: Relationship of Structure to Meaning (one per student; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 1, Work Time A)
- Informative Writing checklist (one per student; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 1, Work Time B)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 3 (answer for teacher reference)
- Literary Analysis Informative Essay: Sample Student Response (example for teacher reference)
- Informative Writing Plan graphic organizer (example for teacher reference)
- Analyze a Model: Proof Paragraphs 1a and 1b (example for teacher reference)
- Homework: Structure and Meaning: "The Owl" (answers for teacher reference) (see Homework Resources)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 3 (one per student)
- Literary Analysis Informative Essay directions (one per student and one for display)
- Informative Writing Plan graphic organizer (one per student and one for display)
- Analyze a Model: Proof Paragraphs 1a and 1b (one per student and one for display)
- Homework: Structure and Meaning: "The Owl" (one per student; see Homework Resources)
Each unit in the 6-8 Language Arts Curriculum has two standards-based assessments built in, one mid-unit assessment and one end of unit assessment. The module concludes with a performance task at the end of Unit 3 to synthesize students' understanding of what they accomplished through supported, standards-based writing.
Copyright © 2013-2024 by EL Education, New York, NY.
Get updates about our new K-5 curriculum as new materials and tools debut.
Help us improve our curriculum..
Tell us what’s going well, share your concerns and feedback.
Terms of use . To learn more about EL Education, visit eleducation.org
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
A Dangerous Game Is Underway in Asia

By Mike M. Mochizuki and Michael D. Swaine
Dr. Mochizuki is a professor at George Washington University. Dr. Swaine is a senior research fellow at the Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft.
This month, President Biden threw one of the most lavish state dinners in Washington’s recent memory. Celebrities and billionaires flocked to the White House to dine in honor of Prime Minister Fumio Kishida of Japan, posing for photos in front of an elaborate display of Japanese fans. Jeff Bezos dropped by; Paul Simon provided the entertainment.
The spectacle was part of a carefully orchestrated series of events to showcase the renewed U.S.-Japan relationship — and the notable transformation of the United States’ security alliances in Asia. The next day, President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. of the Philippines was also in the U.S. capital for a historic U.S.-Japan-Philippines summit, during which a new trilateral security partnership was announced.
Both events were directed at the same audience: China.
Over the past several years, Washington has built a series of multilateral security arrangements like these in the Asia-Pacific region. Although U.S. officials claim that the recent mobilization of allies and partners is not aimed at China, don’t believe it. Indeed, Mr. Kishida emphasized in a speech to Congress on April 11 that China presents “the greatest strategic challenge” both to Japan and to the international community.
China’s recent activity is, of course, concerning. Its military has acquired ever more potent ways to counter U.S. and allied capabilities in the Western Pacific and has behaved aggressively in the South China Sea, the Taiwan Strait and elsewhere, alarming its neighbors.
But Washington’s pursuit of an increasingly complex lattice of security ties is a dangerous game. Those ties include upgrades in defense capabilities, more joint military exercises, deeper intelligence sharing, new initiatives on defense production and technology cooperation and the enhancement of contingency planning and military coordination. All of that may make Beijing more cautious about the blatant use of military force in the region. But the new alliance structure is not, on its own, a long-term guarantor of regional peace and stability — and could even increase the risk of stumbling into a conflict.
The security partnership rolled out this month in Washington is only the latest in a string of new defense configurations that reach across Asia and the Pacific. In 2017 the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, known as the Quad, was revived, promoting collaboration among the United States, Japan, Australia and India. In September 2021, Australia, Britain and the United States began their partnership, known as AUKUS, and the United States, Japan and South Korea committed to closer cooperation in a summit at Camp David last August.
All of these moves have been motivated primarily by concern over Beijing, which has, in turn, castigated these countries as being part of a U.S.-led effort to create an Asian version of NATO designed to contain China. None amount to a collective defense pact like the NATO treaty, whose Article 5 considers an armed attack on one member as “an attack against them all.” But China will nevertheless almost certainly regard the latest agreement among the United States, Japan and the Philippines — with which it is engaged in an active territorial dispute — as further confirmation of a Washington-led attempt to threaten its interests.
It’s not yet clear how Beijing will respond. But it may double down on the expansion of its military capabilities and intensify its use of military and paramilitary force to assert its territorial claims in the region, especially regarding the sensitive issue of Taiwan. Beijing could also promote further Chinese military cooperation with Russia in the form of enhanced military exercises and deployments.
The net result may be an Asia-Pacific region that is even more divided and dangerous than it is today, marked by a deepening arms race. In this increasingly contentious and militarized environment, the chance of some political incident or military accident triggering a devastating regional war is likely to grow. This is especially likely, given the absence of meaningful U.S. and allied crisis communication channels with China to prevent such an incident from spiraling out of control.
To prevent this nightmare, the U.S. and its allies and partners must invest much more in diplomacy with China, in addition to bolstering military deterrence.
For a start, the United States and key allies like Japan should make a sustained effort to establish a durable crisis prevention and management dialogue with China involving each nation’s foreign policy and security agencies. So far, such dialogues have been limited primarily to military channels and topics. It is critical that both civilian and military officials understand the many possible sources of inadvertent crises and develop ways to prevent them or manage them if they occur. This process should include the establishment of an agreed-upon set of leaders’ best practices for crisis management and a trusted but unofficial channel through which the relevant parties can discuss crisis-averting understandings.
The immediate focus for the United States and Japan should be on avoiding actions that add to tensions across the Taiwan Strait. The deployment of American military trainers to Taiwan on what looks like a permanent basis and suggestions by some U.S. officials and policy analysts that Taiwan be treated as a security linchpin within the overall U.S. defense posture in Asia are needlessly provocative. They also openly contradict America’s longstanding “one China” policy , under which the United States ended the deployment of all U.S. military forces to Taiwan and does not view Taiwan as a key U.S. security location, caring only that the Taiwan issue be handled peacefully and without coercion.
Japan, for its part, has also become more circumspect about its own “one China” policy by being reluctant to reaffirm explicitly that Tokyo does not support Taiwan’s independence. Recent statements by some political leaders in Tokyo about Japanese military forces being ready to help defend Taiwan will almost certainly inflame Chinese leaders, who remember that Japan seized Taiwan after the Sino-Japanese War of 1894 and ’95.
Washington and Tokyo should clearly reaffirm their previous commitments on the China-Taiwan dispute. Tokyo also should confirm that it does not support any unilateral move by Taiwan toward independence and resist U.S. efforts to compel Japan to commit to Taiwan’s defense. Although American officials have reportedly been prodding Japan to join military planning for a Taiwan conflict, a large majority of Japanese residents do not favor fighting to defend Taiwan. Tokyo can best contribute to deterring China by focusing on strengthening its ability to defend its own islands.
Washington and its allies should shift to a more positive approach to China, aimed at fostering accommodation and restraint. This could include working to secure credible mutual assurances regarding limits on Chinese military deployments, such as amphibious forces and missile capabilities relevant to Taiwan, in return for U.S. limits on the levels and types of arms that it sells to the island. They could also explore increasing security cooperation with China regarding cyberattacks, the defense of sea lanes and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, as well as better collaboration to combat climate change and the outbreak of another pandemic.
China, of course, has its own role to play. In the end, Beijing, like the United States, wants to avoid a crisis and conflict in the region. Given that, it should respond to a more cooperative American and allied approach by moderating its own coercive behavior regarding maritime disputes.
None of this will be easy, given the intense suspicion that now exists between Beijing and Washington and its allies. But new thinking and new diplomatic efforts could incentivize China to reciprocate in meaningful ways. At the very least, it’s necessary to try. Focusing on military deterrence alone won’t work. Trying to find a way to cooperate with China is the best way — perhaps the only way — to steer the world away from disaster.
Mike M. Mochizuki is a professor at George Washington University and a nonresident fellow at the Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft. Michael D. Swaine is a senior research fellow focusing on China-related security topics at the Quincy Institute.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A graphic essay (sometimes called a visual essay) uses a combination of text and images to explore a specific topic. Graphic essays can look like comics, graphic novels, magazines, collages, artist books, textbooks, or even websites. Graphic essays often first take the form of written essays and then have graphic elements added to enrich the ...
Adobe Spark - Adobe Spark is another great online tool for students to create graphic essays and other multimedia presentations. Students can choose a custom size to create an 8.5×11 inch poster, and Adobe Spark also has premade text elements and templates to choose from. 5. Piktochart.com - Personally, I like Piktochart more for having ...
A graphic essay is an essay that uses images and graphics to complement the writing. This could be an essay that is explained via comic book panels or in the style of infographics (but as an essay). ( How to Create a Narrative Arc for Personal Essays .) As such, a graphic essay is more visual and design based, which can make it fun.
Step-by-Step Instructions. Step One: You need to brainstorm, plan, and research for your essay. Follow my steps below to plan your essay. I also give you links on where to find images to put in your essay and quotes to use. Step Two: Gather your images and video.
The great University of Wisconsin Madison defines it like this. " A graphic essay uses text and images to explore a specific topic. Graphic essays often look like graphic novels, magazines or artist books, but like theory comix they generally convey nonfictional histories, cases and/or arguments. — University Of Wisconsin Design Lab.
This Essay Map helps students with those challenges by providing them with an organized format that will help them generate and outline their ideas. When you introduce this graphic organizer to your students, model its use by creating an essay of a topic that is very familiar to students. Using a projector so students can watch, fill in the ...
Grades. 3 - 12. Launch the tool! Expository writing is an increasingly important skill for elementary, middle, and high school students to master. This interactive graphic organizer helps students develop an outline that includes an introductory statement, main ideas they want to discuss or describe, supporting details, and a conclusion that ...
© 1998-2020 NCTE. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy; Links Policy; Terms of Use
Use Essay Map to plan and organize your essays with an interactive graphic organizer. Learn expository writing skills and improve your grades.
J. Robert Lennon's "Turnabout: A Story Game" is a graphic hermit crab essay that can be read starting at any point, proceeding in any direction. 9. The Video Essay. Video is a natural medium for personal narrative, and John Breslund is known as a pioneer of the visual essay form.
Helps you visualize your research and how elements connect with each other. Enhance your essays, summaries and research papers with visual elements. Track correlations between your thoughts, observations, facts or general ideas. When it comes to essay writing, the most common graphic organizers are webs, mind maps, and concept maps.
In Lucidchart, our mind map shapes and templates double as brainstorming graphic organizers. Start with an essay prompt as your central shape and then fill in the shapes that branch off your prompt with topic ideas. Alternatively, you can add your selected topic to the center and start brainstorming the different ideas you need to cover in your ...
Essay Map. Essay writing is an important skill that students use throughout their lives. An essay map graphic organizer is a brilliant tool for students, as it helps them to chalk out the outline in a systematic manner without missing any detail. Once a student is done with his or her essay map, writing becomes a walk in the park.
Enter title of your graphic map. Enter author (s) of your graphic map.
This graphic essay used three quotes from the text when the assignment requested one. I actually see more value in students using and interpreting one piece of evidence (especially when the text is short to begin with). This student's work shows a thorough thought process, creativity, and neatness.
Essay Map. Source: A Learning Journey. Graphic organizers are especially useful when planning any kind of writing. OREO and Hamburger models are common, but you'll find a lot of other options out there too. The key is to make sure the organizer helps students define their main idea, gather supporting evidence, and draw a conclusion supported ...
Essay Map Introduction: Write one or two sentences that introduce your topic, including a brief description of the main ideas. Main Ideas: List the main ideas about your topic that you will include in your essay. There can be important facts you'd like to describe, points you'd like to explain, or elements you'd like to define.
Graphic organizers are incredibly versatile. Students can use a graphic organizer for writing an essay, creating a story map, or studying a scientific concept. Teachers can also create a graphic organizer to discuss the main topic or guide students through a lab procedure.
Practice Argument Essay directions (one per student) Practice Argument Essay Writing Plan graphic organizer (one per student) Strategically pair students for work in Opening A with at least one strong reader per pair. Create strategic partners for the partner collaboration on the practice essay. Students will be in these partnerships from ...
Display and distribute Literary Analysis Informative Essay directions. Read the directions aloud and ask students to follow along, annotating the text. Ask students to Think- Pair-Share: ... distribute a copy of the Informative Writing Plan graphic organizer with information from the introduction and Proof Paragraphs of Model Literary Analysis ...
Apr 18th 2024. W HEN THE Bharatiya Janata Party ( BJP) won India's general election in 2019, its campaign slogans also set its target: "ab ki baar, 300 paar" (this time 300 seats). It worked ...
Launch the tool! This interactive graphic organizer helps students develop an outline for one of three types of comparison essays: whole-to-whole, similarities-to-differences, or point-to-point. A link in the introduction to the Comparison and Contrast Guide give students the chance to get definitions and look at examples before they begin working.
Although U.S. officials claim that the recent mobilization of allies and partners is not aimed at China, don't believe it. Indeed, Mr. Kishida emphasized in a speech to Congress on April 11 that ...
The Comparison and Contrast Guide includes an overview, definitions and examples. The Organizing a Paper section includes details on whole-to-whole (block), point-by-point, and similarities-to-differences structures. In addition, the Guide explains how graphic organizers are used for comparison and contrast, provides tips for using transitions ...
Israel says it has killed at least 13,000 members of Hamas. Columbia President Minouche Shafik has given students a deadline of Friday night to remove all tents from the school's main campus ...
The Persuasion Map is an interactive graphic organizer that enables students to map out their arguments for a persuasive essay or debate. Students begin by determining their goal or thesis. They then identify three reasons to support their argument, and three facts or examples to validate each reason. The map graphic in the upper right-hand ...