

Oral Examinations
If you have questions about oral examinations, contact us at [email protected] .
Once your dissertation is nearing completion, it’s time to schedule your defense—your final oral examination.
You should begin making arrangements for your defense at the beginning of the semester (especially during the summer) in order to accommodate the schedules of your committee members.
Students must be currently enrolled in the dissertation course for the semester in which the defense is scheduled and held.
Committee Changes
Any changes to your dissertation committee must be approved by the Dean of the Graduate School. Changes should be approved at least 30 days prior to the date of the oral examination so that all new members have ample time to become familiar with your dissertation.
Defense Attendance
You, the student, and your supervisor, in negotiation with the dissertation committee members, should determine a time and date for the defense. Each member of your committee must receive a copy of your dissertation at least four weeks prior to your dissertation defense date. A defense cannot be held within two weeks of the last class day of the semester, unless the committee has consented to hold the defense within those last 2 weeks.
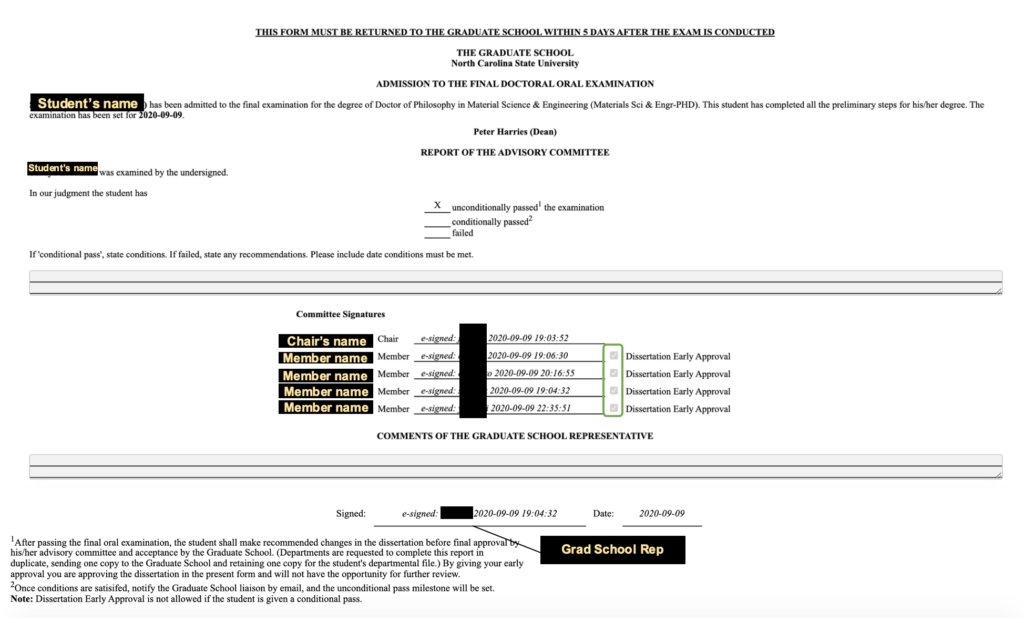
Request for Final Oral Examination Form
You must schedule the dissertation defense with the Graduate School at least two weeks prior to the defense date by completing the Request for Final Oral Examination form. All members of your committee must sign your request form indicating their intent to be present at your final oral. Your graduate adviser must also sign this form to indicate you have been approved to defend.
It is expected that all members of the committee attend the defense. The Graduate School does not distinguish between physical attendance or electronic/virtual attendance of the defense. One non-supervisory committee member may be absent from the defense in if necessary, but all members must read the dissertation and, when satisfied, sign the Report of Dissertation Committee form.
Contact for Questions
Email the Graduate School at the link above with any questions concerning defense attendance.
Format Check Requirements
When you submit the Request for Final Oral Examination form to the Graduate School, you should include one copy each of the dissertation abstract, title page and the committee membership page for a format check in separate PDF. You do not need to include the instructions page.
After the Defense
The official recommendation of your committee and your program is communicated to the Graduate School on the Report of Dissertation Committee. The Dean of the Graduate School depends on this document to determine your eligibility to receive the doctoral degree so it is essential that it be completed and returned in a timely fashion. A passing report signifies that your committee unanimously agrees that you have completed a dissertation that is an independent investigation in your major field.
In the event that revisions to your dissertation are necessary before your committee members approve your dissertation, the report will be retained by your supervisor until all revisions have been completed. After successful completion of your defense and any required revisions to your dissertation, the Report of Dissertation Committee should also be signed by all members of your committee and must be submitted to the Graduate School.
After you’ve made required or requested revisions to your dissertation, if any, check it carefully for grammar, spelling, punctuation, content and format, then convert it to the required PDF format and upload it.
Do not submit your report/thesis/dissertation via email . Final reports, theses and dissertations MUST be uploaded to the Texas Digital Library before your final paperwork and pages will be reviewed. After submission, no revisions or corrections will be allowed except for those required by the dean of the Graduate School.
Upcoming Oral Examinations
Doctoral students’ final oral examinations are open to all members of the University community and the public unless attendance is restricted by the Graduate Studies Committee. Scheduled oral examinations are published on the UT Grad School website.
- Mission & Vision
- Academic Calendar
- Doctoral Exam Schedule
- Graduate Programs
- Financial Support
- Priority Deadlines
- New Graduate Student Orientation
- Signature Events
- Degree Planning
- Embedded Counseling
- International Students
- Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETD)
- Graduate Peer Mentoring
- Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR)
- Catalog and Handbook
- Graduate Assistantships Overview
- Graduate Student Support Plan
- Tuition, Fees and Other Resources
- Fellowships and Grants
- Goodnight Doctoral Fellowship
- Professional Development
- Five Competencies
- Teaching Programs
- Wellness Program
- Career Readiness Program for Non-Academic Careers
- Writing Program
- Leadership Program
- Office of Postdoctoral Affairs (OPA)
- Faculty & Staff
- Forms and Data
- GSC Resources
- ABGS Resources
- Resources for Student Funding
- Curriculum Development
- Program Assessment
- Recruiting Resources
- Alliances for Graduate Education and the Professoriate (AGEP)
- Give Now
Oral Examination Information
Master’s oral examinations.
Candidates for master’s degrees, except those in Option B programs, must pass a comprehensive oral examination to demonstrate to the advisory committee that he/she possesses a reasonable mastery of the subject matter of the major and minor fields and that this knowledge can be used with promptness and accuracy.
This exam takes the form of a traditional defense of the thesis in those programs requiring theses. This examination may not be held until all other requirements, except completion of the course work taken during the final semester, are satisfied. After obtaining DGP approval, a student must file a Request for a Permit to Schedule the Master’s Oral Examination with the Dean of the Graduate School only after the above conditions are met (the request form can be found on the Graduate School Forms webpage).
Outcomes
Unconditional Pass. A unanimous vote of approval of the advisory committee is required for passing the final oral examination. An unconditional pass signifies that the student successfully defended and that the thesis/dissertation is complete, except for minor editing.
Conditional Pass. The student may be passed on condition of the student meeting specific requirements defined by the committee. The conditions may be based on the defense itself, or they may be connected directly to the thesis/dissertation. The examination is not complete until all conditions have been satisfied and that fact has been reported to the Graduate School.
Failure. Failure of a student to pass the examination terminates his or her work at this institution unless the advisory committee recommends a re-examination. No re-examination may be given until one full semester has elapsed and only one re-examination is permitted.
Students may appeal all committee actions according to the provisions in Grievance Procedure for Students (REG 11.40.1) .
Electronic Thesis Dissertation (ETD) Reminders
All theses and dissertations are submitted electronically to the Graduate School via the ETD Submission System for the ETD Review and final acceptance.
In order to graduate in a thesis program, the student must unconditionally pass the final oral exam, or clear all conditions associated with a conditional pass, AND submit a draft PDF file into the ETD Submission System for the ETD Review prior to the 5:00 p.m. ETD Review deadline for the semester in which s/he intends to graduate.
We encourage students to submit their ETD for review as soon as possible following the unconditional passing of the defense. This usually happens within 48 hours of receiving an unconditional pass or satisfying the conditions of a conditional pass.
The ETD submitted for initial review must contain all required components as specified in the ETD Guide (etd.ncsu.edu).
Once the conditions of a conditional pass of the defense are met, the committee chair must inform the Graduate School of the date the conditions were met.
Once a student submits their final error free file and it is accepted by the Graduate School, no edits may be made, unless the ETD is denied by a committee member.
Oral Examinations for Doctoral Candidates
Preliminary.
The preliminary oral examination is conducted by the student’s advisory committee, with the chair (or co-chairs) in charge, and a Graduate School Representative (if required). The exam is open to all graduate faculty members and is designed to test the student’s ability: 1) to relate factual knowledge to specific circumstances, 2) to use this knowledge with accuracy and promptness, and 3) to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the field of specialization and related areas.
As with the preliminary oral examination, the chair (co-chairs) of the student’s advisory committee is (are) in charge of conducting the final oral examination. Though the format of the doctoral examination may vary according to the culture of individual graduate programs, all examinations must include three elements.
- Presentation. The candidate typically presents the methodology used, the data collected, and the conclusions reached as reported in the dissertation. For the purpose of dissemination of research, it is required that the presentation of the dissertation be open to the university community.
- Questioning. Any member of the university community is allowed to ask questions of the candidate. If the need arises, graduate faculty members not on the advisory committee may meet in a restricted session after the presentation to ask additional questions of the student and express any concerns they have to the committee and student. The questioning phase may continue with a closed session in which the advisory committee questions the candidate.
- Deliberation and decision. Only the advisory committee and the Graduate School representative, if one has been appointed, are present.
The chair (co-chairs) of the candidate’s advisory committee has (have) the obligation to maintain a scholarly atmosphere and to keep academic integrity and the student’s best interest foremost.
Unconditional Pass. A unanimous vote of approval of the advisory committee is required for passing the final oral examination. An unconditional pass signifies that the student successfully defended and that the thesis/dissertation is complete, except for minor editing.
Failure. Failure of a student to pass the examination terminates his or her work at this institution unless the advisory committee recommends a re-examination. No re-examination may be given until one full semester has elapsed and only one re-examination is permitted.
Once a student submits their final error free file and the Graduate School accepts it, no edits can be made, unless a committee member denies the ETD.
To fulfill graduation requirements, each doctoral student must submit all the required forms and fee to the ETD Reviewer before the final thesis/dissertation will be accepted. All of the required forms are found under the Doctoral Required Forms link on the Electronic Thesis & Dissertation (ETD) Website, etd.ncsu.edu.
The Graduate School cannot authorize the release of the diploma or the inclusion of the statement of the awarded degree on the permanent record from which transcripts are made until the forms and fees have been received.
Exam Form Example
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to prepare an excellent thesis defense
What is a thesis defense?
How long is a thesis defense, what happens at a thesis defense, your presentation, questions from the committee, 6 tips to help you prepare for your thesis defense, 1. anticipate questions and prepare for them, 2. dress for success, 3. ask for help, as needed, 4. have a backup plan, 5. prepare for the possibility that you might not know an answer, 6. de-stress before, during, and after, frequently asked questions about preparing an excellent thesis defense, related articles.
If you're about to complete, or have ever completed a graduate degree, you have most likely come across the term "thesis defense." In many countries, to finish a graduate degree, you have to write a thesis .
A thesis is a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
Once you hand in your thesis, you will be assigned a date to defend your work. Your thesis defense meeting usually consists of you and a committee of two or more professors working in your program. It may also include other people, like professionals from other colleges or those who are working in your field.
During your thesis defense, you will be asked questions about your work. The main purpose of your thesis defense is for the committee to make sure that you actually understand your field and focus area.
The questions are usually open-ended and require the student to think critically about their work. By the time of your thesis defense, your paper has already been evaluated. The questions asked are not designed so that you actually have to aggressively "defend" your work; often, your thesis defense is more of a formality required so that you can get your degree.
- Check with your department about requirements and timing.
- Re-read your thesis.
- Anticipate questions and prepare for them.
- Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups.
- Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
How long your oral thesis defense is depends largely on the institution and requirements of your degree. It is best to consult your department or institution about this. In general, a thesis defense may take only 20 minutes, but it may also take two hours or more. The length also depends on how much time is allocated to the presentation and questioning part.
Tip: Check with your department or institution as soon as possible to determine the approved length for a thesis defense.
First of all, be aware that a thesis defense varies from country to country. This is just a general overview, but a thesis defense can take many different formats. Some are closed, others are public defenses. Some take place with two committee members, some with more examiners.
The same goes for the length of your thesis defense, as mentioned above. The most important first step for you is to clarify with your department what the structure of your thesis defense will look like. In general, your thesis defense will include:
- your presentation of around 20-30 minutes
- questions from the committee
- questions from the audience (if the defense is public and the department allows it)
You might have to give a presentation, often with Powerpoint, Google slides, or Keynote slides. Make sure to prepare an appropriate amount of slides. A general rule is to use about 10 slides for a 20-minute presentation.
But that also depends on your specific topic and the way you present. The good news is that there will be plenty of time ahead of your thesis defense to prepare your slides and practice your presentation alone and in front of friends or family.
Tip: Practice delivering your thesis presentation in front of family, friends, or colleagues.
You can prepare your slides by using information from your thesis' first chapter (the overview of your thesis) as a framework or outline. Substantive information in your thesis should correspond with your slides.
Make sure your slides are of good quality— both in terms of the integrity of the information and the appearance. If you need more help with how to prepare your presentation slides, both the ASQ Higher Education Brief and James Hayton have good guidelines on the topic.
The committee will ask questions about your work after you finish your presentation. The questions will most likely be about the core content of your thesis, such as what you learned from the study you conducted. They may also ask you to summarize certain findings and to discuss how your work will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
Tip: Read your entire thesis in preparation of the questions, so you have a refreshed perspective on your work.
While you are preparing, you can create a list of possible questions and try to answer them. You can foresee many of the questions you will get by simply spending some time rereading your thesis.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense:
You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions. In addition, since you will know who will be on the committee, look at the academic expertise of the committee members. In what areas would they most likely be focused?
If possible, sit at other thesis defenses with these committee members to get a feel for how they ask and what they ask. As a graduate student, you should generally be adept at anticipating test questions, so use this advantage to gather as much information as possible before your thesis defense meeting.
Your thesis defense is a formal event, often the entire department or university is invited to participate. It signals a critical rite of passage for graduate students and faculty who have supported them throughout a long and challenging process.
While most universities don't have specific rules on how to dress for that event, do regard it with dignity and respect. This one might be a no-brainer, but know that you should dress as if you were on a job interview or delivering a paper at a conference.
It might help you deal with your stress before your thesis defense to entrust someone with the smaller but important responsibilities of your defense well ahead of schedule. This trusted person could be responsible for:
- preparing the room of the day of defense
- setting up equipment for the presentation
- preparing and distributing handouts
Technology is unpredictable. Life is too. There are no guarantees that your Powerpoint presentation will work at all or look the way it is supposed to on the big screen. We've all been there. Make sure to have a plan B for these situations. Handouts can help when technology fails, and an additional clean shirt can save the day if you have a spill.
One of the scariest aspects of the defense is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. While you can prepare for some questions, you can never know exactly what the committee will ask.
There will always be gaps in your knowledge. But your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. You are not expected to know everything.
James Hayton writes on his blog that examiners will sometimes even ask questions they don't know the answer to, out of curiosity, or because they want to see how you think. While it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, but you would need to do [...] in order to find out.” This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
You will be nervous. But your examiners will expect you to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions, for example. Dora Farkas at finishyourthesis.com notes that it’s a myth that thesis committees are out to get you.
Two common symptoms of being nervous are talking really fast and nervous laughs. Try to slow yourself down and take a deep breath. Remember what feels like hours to you are just a few seconds in real life.
- Try meditational breathing right before your defense.
- Get plenty of exercise and sleep in the weeks prior to your defense.
- Have your clothes or other items you need ready to go the night before.
- During your defense, allow yourself to process each question before answering.
- Go to dinner with friends and family, or to a fun activity like mini-golf, after your defense.
Allow yourself to process each question, respond to it, and stop talking once you have responded. While a smile can often help dissolve a difficult situation, remember that nervous laughs can be irritating for your audience.
We all make mistakes and your thesis defense will not be perfect. However, careful preparation, mindfulness, and confidence can help you feel less stressful both before, and during, your defense.
Finally, consider planning something fun that you can look forward to after your defense.
It is completely normal to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions for example if needed. Slow yourself down, and take a deep breath.
Your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. James Hayton writes on his blog that it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", but he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, you would need to do [...] in order to find out".
Your Powerpoint presentation can get stuck or not look the way it is supposed to do on the big screen. It can happen and your supervisors know it. In general, handouts can always save the day when technology fails.
- Dress for success.
- Ask for help setting up.
- Have a backup plan (in case technology fails you).
- Deal with your nerves.

How to Prepare for the Oral Defense of Your Thesis/Dissertation
© Paul T. P. Wong , Ph.D., C.Psych., Former Research Director, Graduate Program in Counselling Psychology, Trinity Western University, Langley, BC, Canada
Use the following steps when preparing for the oral defense of your thesis/dissertation.
1. Evaluation of oral examination is based on your presentation and your answers to questions from the examining committee.
2. Be well prepared for your presentation—academically, mentally and physically. Try to be well rested and focused before your oral defense.
3. In your preparation, don’t try to memorize all the studies cited in your thesis, but you do need to know the details of the few key studies that form the basis of your investigation.
4. You need to be familiar with larger issues, such as the basic assumptions, theoretical framework, paradigm, cross-cultural perspectives, Christian integration, etc.
5. More importantly, you need to have a deep understanding of the nature of your research problem and the major issues involved.
6. You may bring with you important materials for easy reference in the course of your defense; these may include key articles, computer print-outs of results, etc.
7. Your presentation is evaluated in terms of content and clarity as well as style.
8. Don’t speak too fast and don’t read from your notes.
9. Treat your presentation as a public address because there may be non-psychologists present at your defense. Therefore, don’t use too many jargons and don’t pack it with details. You need to tell people in simple, concise language:
- What you did,
- Why you did it,
- How you did it,
- What you found, and
- What the results mean.
10. Prepare handouts or power-points. Typically, they should include
- An overview or outline of your presentation,
- Introduction (including research question, rationale and hypothesis, if any, and definition of key constructs),
- Method (including design, methodology, sample, instruments or questionnaires, and procedure,
- Results (including tables or figures summarizing your findings), and
- Discussion (including reasons for new or unexpected findings, contributions and limitations, and practical implications).
11. Make sure that you space yourself well. Don’t spend too much time on one section. For example, you should not spend more than 5 minutes on introduction, since you are allowed only 20 minutes for your presentation.
12. Most of the questions are rather general and broad, dealing with substantial methodological, theoretical and application issues. However, some questions focus on specific points regarding sampling, statistical analysis, or some questionable conclusions.
13. Be prepared to clarify or elaborate on your assumptions, theoretical positions, methods, and conclusions. Often, an examiner plays the devil’s advocate to see how well you can think on your feet and defend yourself.
14. Occasionally, an examiner may ask a question which is unfair or cannot be adequately answered. After a few futile attempts, feel free to say that you don’t know the answer. You may even be bold enough to say, “Since none of my answers are acceptable, I would really appreciate it if you could give me some pointers or tell me what would be a correct answer.”
15. Here are some common questions:
- If you were to do it all over again, what changes would you make?
- What specific aspects of your findings can be utilized by counselors or psychologists in their practice?
- What is the most important contribution of your thesis? Can you say it in one or two sentences?
- What are some of the competing hypotheses? Could you think of an alternative interpretation of your findings?
16. Don’t rush to any answers. It is perfectly acceptable to think for a couple of seconds, or ask if you are on the right track. If you are not clear about the question, you are entitled to ask for clarification.
17. Try to be concise and to the point, but at the same time demonstrate that you have a good grasp of the complex issues involved. In other words, do not give superficial answers, but at the same time, do not go all over the map.
18. Put up a good defense without being defensive. Be confident without being cocky. A good defense means that you can provide strong logical arguments as well as empirical support o defend your position or conclusion. However, don’t be defensive when people criticize your study. If they are able to point out some real flaws or weaknesses in your study, accept their criticisms with humility, grace and gratitude.
19. Before the oral defense, talk to your advisor about areas of concerns based on external examiner’s comments. Then, discuss with your advisor how to best address these concerns. (Your advisor cannot tell you the specific questions the examiners will ask, but s/he can direct your attention to issues or areas that require some thinking or additional research.)
20. After the oral defense, meet with your advisor for debriefing and seek advice on how to revise your thesis.
- Spring is Here Again
- My First Hospital Night
- Agency, hope, and wellbeing
- President’s Column: Is existential wellbeing the key to positive mental health?
- President’s Column: You can hope again
- FAQs for Prospective Students
- How to Apply
- Master’s & PhD Program
- Tuition & Fees
- Awards and Funding
- Role of the Supervisor
- Conflict within Committee
- Student Responsibilities
- Incoming Students
- Thesis, Defence and Graduation
- Master’s
- Doctoral (PhD)
- RES Forms & Policies
- Finance/HR Forms
- Core Faculty
- Administrative Staff
- Postdoctoral Fellows and Research Associates
- Master’s of Arts and Science Students
- PhD Students
- Alumni Interviews
- IRES Student Society
- Research Themes
- Theses & Dissertations
- IRES and Open Access
- Information for Authors
- Research Map
- RES Graduate Courses
- Methods Courses
- Undergraduate Courses taught by IRES Core Faculty
- Non-RES Courses
- Non-UBC Courses
- Vancouver Summer Program
- IRES Newsletter
- Seminar Videos
- Media Coverage
- External Opportunities
- Departmental Award Recipients
Graduate Program
Master’s thesis and final oral examination.
The Master’s thesis in Resources, Environment and Sustainability (RES) is a fundamental and essential component of the program. It is the main evidence that is available to the academic community by which the candidate is assessed in his/her abilities to synthesize and integrate biophysical and socio-economic sciences into new paradigms or knowledge.
Structure of an RES Master’s Thesis
Although there is debate about how research is done, the concept and structure of the RES Master’s thesis research is, in general, the same as in any graduate program. That is, there is:
- a statement of an issue
- a rationale of the significance of the issue
- a set of research questions (these may be presented as hypotheses, objectives, questions, propositions)
- a set of methods or tools from various disciplines that will be brought to bear to address the research questions
- a discussion of theoretical and analytical frameworks relevant to the issue
- research tools selected
- expected results
- a summary and/or conclusions of the research, and
- a discussion of how the research has contributed to the overall issue.
Specifics among the various sections will vary by the nature of the research topic, the graduate student and the supervisor/ supervisory committee. It is important that discussion take place early in a graduate student’s program on how to do the research and what will be expected from the thesis. These discussions should be re-examined at formal meetings of the graduate student’s supervisory committee.
All RES Master’s and Doctoral students must follow the G+PS formatting guidelines .
RES Master’s Thesis Defence Committee Requirements
Committee composition: The master’s thesis examination committee should be comprised of the members of the pre-approved RES supervisory committee plus one external examiner who has had no involvement in the thesis supervision. G+PS requires that the examination committee include, at minimum, the supervisor and one person not involved in the thesis supervision.
External (non-committee) member: An external (non-committee) examiner should be someone who was not involved in the thesis supervisory committee or research. In cases where the supervisory committee did not include an IRES core faculty member or core associate, the external (non-committee) member should be an IRES core or CA faculty member. Supervisors should endeavour to avoid calling upon an individual for service as an external examiner more than once per 12 months. (G+PS recommends that at least 1 member of the examining committee be from another graduate program.)
Examination chair: The chair of master’s thesis defence should be a member of the examination committee who is also an IRES core or CA faculty member. G+PS permits the thesis supervisor to also serve as Chair of the Master’s examination.
RES Master’s Thesis Final Oral Examination
The RES Master’s Final Oral Examination is an integral part of the RES Master’s Program and requires students defend their theses before they graduate. A successful defence of your Master’s thesis will depend on your ability to present your research effectively and confidently. Some basic skills and techniques which may be helpful for preparation can be found on the G+PS website .
The structure of the RES Master’s Final Oral Examination is as follows:
- A 25 minute (average) presentation made by the candidate.
- First round of questions from the Examining Committee in order of most distant from the candidate (generally begins with the External Examiner and ends with the Supervisor). Each committee member is given about 15 minutes for their questions.
- A second round of questions, generally about 5 minutes from each of the Examining Committee members.
- The audience is welcome to ask questions at this point.
- The candidate and audience leave the room and the Examining Committee decide whether the student has passed.
- The candidate is invited back into the room and informed of their result.
After the Master’s Thesis Final Oral Examination
You will need to complete any recommended revisions to your THesis before submitting it and some final administrative paperwork to G+PS to close your program.
- G+PS Final Thesis Submission Guidelines
Lastly, you will need to apply to Graduate via your SSC account!
Master’s Thesis Timeline
- Dissertation and Final Oral Exam
[Part of the Policies of the CHD, last updated fall 2021]
Dissertation
The dissertation must represent an original and significant contribution to knowledge. The dissertation should be a coherent document conforming with the customary standards of scholarly discourse and addressed to a broad audience in the corresponding subject rather than to a narrow audience of specialists in the field. SEAS does not follow the practice in which a collection of manuscripts published or intended for publication as technical papers constitutes an acceptable dissertation. It should be understood, however, that the student has an obligation to prepare the work for publication in the archival literature in timely fashion. The dissertation must meet the GSAS requirements available at https://gsas.harvard.edu/degree-requirements/dissertations/formatting-your-dissertation .
Final Oral Exam ("Defense")
The last two requirements are the final Ph.D. oral examination and an electronic copy of the dissertation submitted as a PDF file. The student must deliver a complete penultimate draft of the dissertation (except for the acknowledgments) to all members of the research committee at least two weeks prior to the final examination. Once the student has agreed upon a time for the examination with all members of the research committee, the student is responsible for contacting the Office of Academic Programs ( [email protected] ) at least two weeks in advance in order to prepare the exam paperwork, and, if needed, to schedule a room.
The final oral exam (i.e., the defense) is the culmination of a student’s years of effort and formally marks the candidate’s entry into the community of scholars . As such, the candidate and committee should strive to meet together in person for the exam. If after attempting to schedule a time for the full committee to meet together in person it appears that no such time can be found, the candidate should consult with the Office of Academic Programs about alternatives, possibly including that one or more committee members attend remotely.
SEAS encourages candidates to provide a videoconferencing (e.g., Zoom) option for remote attendance by guests, community members and the public who may not be able to attend in person.
The final examination is essentially a presentation and defense of the dissertation, though more general questions relating to the field of the dissertation are in order. At the end of the examination, the research committee may accept the dissertation, possibly subject to agreed-upon revisions, or specify further requirements. If other than minor revisions are involved, the nature of the conditions that need to be met should be reported to the DGS. The research advisor must certify in writing that these conditions have been met before award of the degree can formally be recommended by the Dean.
SEAS facilities are the usual location for the final defense. A student planning a defense to be held outside of SEAS must have the approval of all their committee members before finalizing the location of the defense. Arrangements as to location will be made by the student through the Office of Academic Programs. Public notice will be given. The Office of Academic Programs strongly encourages students to schedule their defense not later than two weeks before the GSAS Ph.D. Dissertation submission deadline.
In Academic Programs
- Non-Resident and Part-Time Study
- CHD Meeting Schedule
- PhD Overview and Timeline
- PhD Course Requirements
- PhD Program Plans
- Teaching: G2 year
- Qualifying Exam: by end of G2 year
- Research Advisors, Committees, and Meetings
- SM and ME Course Requirements
- SM and ME Program Plans
- Masters Thesis and Supervisor
- SM degree en route to the PhD
- Graduate Student Forms
- Teaching Fellows
- External Fellowships List
- COVID-19 Graduate Program Changes (archived)
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets & Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Social Impact
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Services
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Entering Class Profile
- Education & CV
- GMAT & GRE
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Letters of Recommendation
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Fields of Study
- Student Life
The oral examination is a defense of the dissertation work in progress.
The student orally presents and defends the thesis work in progress at a stage when it is one-half to two-thirds complete. The oral examination committee, composed of field and nonfield faculty, tests the student on the theory and methodology underlying the research, the areas of application and portions of the major field to which the research is relevant, and the significance of the dissertation research.
- Priorities for the GSB's Future
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Business Transformation
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships and Prizes
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Get Involved
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- Career Advancement
- Career Change
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- Information for Recommenders
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- After You’re Admitted
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- Videos, Code & Data
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Reading Materials
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
How to Prepare for an Oral Examination
by Prof Nora Tam, former Professor, Department of Biology and Chemistry
The oral exam is not just a formality. After you submit your MPhil or PhD thesis, the examiners judge whether it is worthy of an oral exam. The exam provides an opportunity for you to defend and clarify points that are not clear to the examiners. It allows the examiners to check whether you understand the topic properly. Most oral exam have two parts - an oral presentation by the student followed by a questions and discussion session.
Before the exam
As soon as you submit your thesis, prepare for your oral exam. Prepare your presentation in a clear and interesting way. Timing is crucial. You are asked to present for 20-25 minutes; if you go beyond thirty minutes it shows you cannot summarise your work. Give a brief introduction and outline your methodology. The most important parts are your key findings, your contribution to the topic and your originality.
Think about possible questions that may arise. Rehearse in front of your friends, or ask your supervisor for comments. Talk to students who have already sat their exams to find out exactly what happens. If you have already received feedback from your external examiner, look at these questions and comments very carefully and respond to them. You can even prepare written answers and table them for the examiners.
Ensure you are very familiar with your thesis. You need to be familiar with every page, table and figure. You should be able to elaborate a little on every statement it contains. Quite often after you submit your thesis you find typing errors and minor mistakes. Prepare a list of erratum and table it for the examiners.
During the exam
Dress appropriately to show respect to your examiners.
Make your oral presentation clear and interesting within the time allowed. Highlight your key findings and contribution to the area of study. Try to impress the panel members. A good oral presentation always leads to a friendlier environment and an open and meaningful discussion. After your presentation, questions usually start with the external examiner, followed by your internal examiner (usually from your department) and your supervisor.
Try to relax. The best way to approach it is as a discussion, an exchange of research findings and ideas, rather than just questions and answers.
Listen to each question very carefully. It is important that you understand each question fully and address the question that is being asked. You don't need to give your answer immediately, you can organise your thoughts first. If you think the answer is already in your thesis, you can remind the examiners to refer to certain pages, diagrams or figures.
The answers you give should be clear, concise and precise. If your answer is not precise, it will lead to a clarifying question, and this is when the questions become more difficult. If the exam is face-to-face, look at the facial expressions of your examiners to see if they are satisfied with your answer. If they appear satisfied then stop. You need to allow time for them to ask other questions.
Let the examiners see you are confident in your answers. If your answer does not agree with what the examiner says it doesn't matter. Different people can have different views. Give enough evidence to substantiate your arguments and convince the examiners that your way of thinking is acceptable. Don't become overly defensive and don't feel insulted if the examiner doesn't agree with what you say. Keep calm and stay in a discussion mood. If a question is raised that you don't know the answer to, just be honest and say that you have not yet come across this. Comment on whether it would be worthwhile exploring in the future.
You don't need to have all the answers but you do need to know the way to approach research questions. Examiners are looking for students who can work independently, identify research topics, consolidate research questions and can tackle and find answers for their research questions. Examiners may give you hypothetical questions, such as how would you tackle other aspects of your topic if you had time.
If your external examiner is overseas, the oral exam may be by telephone conference. You need to do the oral presentation slowly, and ensure that the examiner is following your presentation and knows which slide you are on (the examiner will have copies of the slides).
After the exam
There is no standard length for an oral exam. The discussion section can last from twenty minutes to over three hours. After the exam, you'll be asked to leave the room. The panel will decide the result and you'll be invited back. If you are successful, usually the first word you'll hear is "Congratulations!"
Go and talk to your classmates. As well as feeling relieved when you exam is over, you'll realise that you have learned a lot. Talk to your fellow classmates, especially those who haven't had their oral exam, because sharing your experience is very important.
PhD Oral Exam
Near the completion of the doctoral program, students must present a 30-45 minute public seminar on their dissertation research. Following the public presentation, the student is examined in private by a faculty committee of at least five examiners approved by the Electrical Engineering department.
The Oral Examination is intended to verify that the student’s research represents his or her own contribution to knowledge and understanding of the research. The oral examination is a dissertation defense in which the candidate is expected to:
- Demonstrate his or her ability to explain and defend the thesis and its contribution to knowledge before experts in the field;
- Present an understandable picture of the research and its setting to scholars whose special areas of interest lie outside the candidate's area of research;
- Answer satisfactorily any questions deemed pertinent by the examining committee.
The examination begins with a public presentation of research results by the PhD candidate, during which clarifying questions may be asked by members of the audience. This part of the examination is open to the public. After a brief recess, the examination continues in a private session with only the candidate and members of the examining committee in attendance. The examination, including the public portion, should not exceed three hours in length.
Students are advised to pass the oral examination within one year of the date of completion of the other requirements for the degree.
If the oral examination was passed more than one year prior to the date of graduation, the examination is void and the candidate may be asked to repeat the oral examination. The 12-month period of validity for the oral examination may be extended by petition to the Degree Progress Officer.
Students are responsible for creating Zoom meeting links and/or reserving a room for their exam. After students locate the room in Packard building or AllenX building, their faculty administrator can help to book that room. If their faculty administrator is not in EE (e.g., CS, Ginzton Lab, etc.), please have the administrator connect with Anna Lue ( [email protected] ) for assistance on scheduling a room. When the Registrar rooms are open to use for PhD defense, students can contact Laura Wuethrich ( [email protected] ) to schedule the room.
Students who plan to take the University Oral Examination need to submit the University Oral Examination form and an abstract to the Degree Progress Officer at least 1-2 weeks prior to the exam.
Related Information
- Oral Exam Procedures
- Notes on PhD Oral Exams
- Zoom Oral Exam Guidelines
- Oral Exam Abstract Template (Word document)
- University Oral Examination Form
Contact Information Laura Wuethrich Degree Progress Officer 650-723-3194 [email protected]
MIT Department of Biological Engineering
Search form.
- DEI Collaborative
- DEI Current Efforts
- DEI Newsletter
- Learning Resources
- Faculty Directory
- Staff Directory
- Open Faculty Positions
- Prospective Undergraduate
- Major Degree Requirements
- Minor Programs
- Undergraduate Thesis
- Research Prize
- BE Student Life
- Career Resources
- Master's Degree
- Graduate PhD Application
- Application Assistance Program
- Graduate FAQ
- Graduate Life
- Meet The Graduate Students
- PhD Course Requirements
- Advisor Selection
- PhD Written Exam
- Thesis Committee
- PhD Oral Exam
- PhD Dissertation Requirements
- BE Graduate Student Board
- Teaching Assistant Award Winners
- BE Communication Lab
- Research Areas
- Wishnok Prize
- BATS Resources
- BATS Archive
- For Undergraduate Students
- Professional Development
- For Post Docs
- Covid-19 Resources
- Laboratory Safety
- Faculty & Instructors
The formal presentation of the Thesis Proposal will serve as the Oral Examination. The purpose of the Oral Exam is to test the student’s ability to explain their thesis project, defend their scientific rationale, and propose alternate approaches, as necessary. The nature of the proposal may vary, depending on the project, but it should provide motivation as well as describe and justify the envisioned approach along with summarizing progress made to date. Preliminary results supporting the proposed research are beneficial, but not required, for the Thesis Proposal or the Oral Exam.
The Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam must take place by December 1 of the 3rd year, with the specific date scheduled before the beginning of the Fall Semester of the third year. If the student and advisor are convinced that a delay would serve the student's interests better, they must petition the Graduate Committee by August 1st of the summer following the 2nd year with their reasoning along with their commitment for a target date; the Graduate Committee will approve or deny the petition request. Failure to complete the Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam according to this policy will constitute unsatisfactory progress with respect to subsequent enrollment and funding support. Under these circumstances the student will not be able to register for the spring semester of their 3rd year.
The student is responsible for arranging the Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam meeting with the Thesis Committee Members and for reserving the location (plan for the meeting to take two hours). Generally, this meeting should be arranged at least two months in advance because it may be difficult to find a mutually agreeable time for all involved. Once this meeting has been scheduled, the Thesis Committee members and the Academic Office must be notified by e-mail about the day, time, and location of the presentation. The Thesis Committee constituted for the Oral Exam may change over the course of the student’s research, as determined by the student and advisor with approval by the Graduate Program Chair. Beyond administration of the Oral Exam, the Thesis Committee is meant to provide guidance on the various aspects of the student’s project; Thesis Committee members should therefore be selected with this goal in mind.
The student should be sure to register for Thesis Proposal (20.951) for 0-24-0 credit units during the term in which the Proposal is defended. At least one week prior to the Thesis Proposal presentation, the student should deliver a copy of the Thesis Proposal to each of the Oral Exam Committee Members and to the Academic Office.
The student should prepare a 30-minute presentation. The Oral Exam Committee members will have read and thought about the Proposal ahead of time. Given that the meeting lasts up to two hours, there will be ample time for questions/discussion during your presentation. If questions arise about the format or style of the presentation, the student should contact the Oral Exam Committee Chair. The student should expect to be examined in depth on subject matter directly and tangentially related to all aspects of the Proposal. The questioning need not be restricted to the Proposal itself, but may expand into areas impinging on the Thesis topic.
The day of the presentation, the student should give the thesis chair a “Report of Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam Meeting” form. The Committee Chair must complete this form to confirm the outcome of a Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam Presentation. The completed form should be submitted along with any comments or recommendations made by the Thesis Committee to the Academic Office. From there, copies will be distributed to the student, the advisor, and the Committee Chair. If the Proposal presentation is acceptable, a “Pass” grade will be recorded for 20.951.

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Undergraduate and Postgraduate Taught
- Postgraduate examinations
- Writing, submitting and examination
- PhD, EdD, MSc, MLitt
- Cambridge students
- New students overview
- Pre-arrival courses
- Student registration overview
- Information for New Students
- Information for Continuing Students
- Frequently Asked Questions overview
- Who needs to register
- When to register
- Received registration in error/not received registration email
- Problems creating an account
- Problems logging in
- Problems with screen display
- Personal details changed/incorrectly displayed
- Course details changed/incorrectly displayed
- Accessing email and other services
- Miscellaneous questions
- Contact Form
- First few weeks
- Manage your student information overview
- Student record overview
- Camsis overview
- Extended Self-Service (ESS)
- Logging into CamSIS
- What CamSIS can do for you
- Personal information overview
- Changing your name
- Changing Colleges
- Residing outside the University's precincts
- Applying for person(s) to join you in Cambridge
- Postgraduate students overview
- Code of Practice for Master's students
- Code of Practice for Research Students
- Postgraduate student information
- Requirements for research degrees
- Terms of study
- Your progress
- Rules and legal compliance overview
- Freedom of speech
- Public gatherings
- Disclosure and barring service overview
- Cambridge life overview
- Student unions
- Extra-curricular activities overview
- Registering societies
- Military, air, and sea training
- Food and accommodation
- Transport overview
- Bicycles and boats
- Your course overview
- Undergraduate study
- Postgraduate study overview
- Changes to your student status (postgraduates only) overview
- Applying for a change in your student status (postgraduates only)
- Changing your mode of study
- Withdrawing from the University
- Allowance/exemption of research terms
- Withdrawal from Study
- Reinstatement
- Changing your course registration
- Changing your department/faculty
- Changing your supervisor
- Exemption from the University composition fee
- Confirmation of Study: Academic Verification Letters
- Extending your submission date
- Medical intermission (postgraduates)
- Non-medical intermission (postgraduates)
- Returning from medical intermission
- Working away
- Working while you study
- Postgraduate by Research Exam Information
- Research passports
- Engagement and feedback
- Student elections
- Graduation and what next? overview
- Degree Ceremonies overview
- The ceremony
- Academical dress
- Photography
- Degree ceremony dates
- Eligibility
- The Cambridge MA overview
- Degrees Under Statute B II 2
- Degree certificates and transcripts overview
- Academic Transcripts
- Degree Certificates
- After Graduation
- Verification of Cambridge degrees
- After your examination
- Exams overview
- Undergraduate and Postgraduate Taught overview
- All students timetable
- Undergraduate exam information overview
- Postgraduate examinations overview
- Examination access arrangements overview
- Research programmes
- Taught programmes
- Writing, submitting and examination overview
- PhD, EdD, MSc, MLitt overview
- Research Best Practice
- Preparing to submit your thesis
- Submitting your thesis
- Word limits
- The oral examination (viva)
- After the viva (oral examination)
- After the examination overview
- Degree approval and conferment overview
- Final thesis submission
- Examination allowances for certain Postgraduate degrees (except PhD, MSc, MLitt and MPhil by thesis degrees)
- Requesting a review of the results of an examination (postgraduate qualifications)
- Higher degrees overview
- Higher doctorates
- Bachelor of divinity
- PhD under Special Regulations
- Faith-provision in University exams
- Publication of Results
- Exam Support
- Postgraduate by Research
- EAMC overview
- Annual Reports of the EAMC
- Dates of meetings
- Frequently asked questions
- Guidance notes and application forms
- Resources overview
- Build your skills
- Research students
- Fees and financial assistance overview
- Financial assistance overview
- General eligibility principles and guidance
- Cambridge Bursary Scheme funding overview
- What you could get
- Scottish students
- EU students
- Clinical medics and vets
- Independent students
- Extra scholarships and awards
- Undergraduate Financial Assistance Fund
- Postgraduate Financial Assistance Fund
- Realise Financial Assistance Fund
- The Crane Fund
- Loan Fund I
- External Support
- Support from your Funding Sponsor
- Guidance for Academic Supervisors and College Tutors
- Fees overview
- Funding overview
- Mosley, Worts, and Frere Travel Funds
- Support for UKRI Studentship Holders overview
- Student loans overview
- US loans overview
- Application procedure
- Entrance and Exit Counselling
- Cost of attendance
- What type of loan and how much you can borrow
- Interest rates for federal student loans
- Proof of funding for visa purposes
- Disbursement
- Satisfactory academic progress policy
- In-School Deferment Forms
- Leave of absence
- Withdrawing and return to Title IV policy
- Rights and Responsibilities as a Borrower
- Managing Repayment
- Consumer information
- Submitting a thesis — information for PhD students
- Private loans
- Veteran affairs benefits
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Student support
- Complaints and appeals
The Oral Examination (viva) - Doctoral degrees, MSc and MLitt
If you have not been advised of the date for your viva within six weeks of submitting your thesis, you should contact your Degree Committee.
Location of the viva
The viva will normally take place in-person in Cambridge, but you may choose to be examined remotely by video conference. You should inform your Degree Committee of your preference when you notify them of your intention to submit/apply for appointment of examiners. Please also make your supervisor aware of your preference as it may affect the choice of available examiners.
Arrangements where you and one examiner are co-located in Cambridge, with the second examiner participating by video conference, where both examiners are co-located and you participate by video conference, or where you and the examiners are all in separate locations, are permissible provided all parties agree.
In-person oral examination: In-person examinations may be delayed depending on the availability of the examiners as travel time will need to be factored in. Students who are overseas and returning to Cambridge for their viva should contact the International Student Office for visa advice if their student visa has expired or will be expiring soon.
Video conference oral examination: A guide to conducting vivas by video conference can be found here .
The choice of in-person or video conference viva does not constitute procedural irregularity grounds for complaint should you fail the examination.
Adjustments to the oral examination on the grounds of disability
If you wish to notify examiners of a disability or request adjustments on account of a disability for your viva (either your first year assessment or final examination), you can do this via your Degree Committee by completing and submitting the voluntary disclosure form . It is recommended you do this at least four weeks before your expected date of examination to allow time for appropriate recommendations and adjustments to be made.
Once you have submitted the form, your Degree Committee will contact the University’s Accessibility and Disability Resource Centre (ADRC) who will advise the Degree Committee on the appropriate course of action. You may be contacted by the ADRC if additional information is required or to provide you with an offer of additional support.
The information provided on the voluntary disclosure form will be kept confidential and will not be used for any other purpose.
If you already have a Student Support Document (SSD) that includes recommendations for adjustments to the viva , and you have given permission for the SSD to be shared with the Degree Committee, you do not have to complete the voluntary disclosure form but may do so if you wish.
What happens at the viva?
- The viva will normally take place in Cambridge, although some may take place via video-conference (please see above)
- It is carried out between yourself and the two examiners and is conducted in English
- It may include an Independent Chairperson if the Degree Committee requires this
- There is no set duration, but a viva will normally last between 90 minutes and three hours
- You may be required to do a presentation - please check with your Department whether this is the case. If you are required to give a presentation, you should be informed at least two weeks in advance of the viva
- The viva cannot be recorded
- Your supervisor cannot attend the viva
Your Department should advise on any department-specific conventions or procedures.
Purpose of the viva
The viva gives the opportunity for:
- you to defend your thesis and clarify any matters raised by your examiners
- the examiners to probe your knowledge in the field
- the examiners to assure themselves that the work presented is your own and to clarify matters of any collaboration
- the examiners to come to a definite conclusion about the outcome of the examination
Possible outcomes of the viva
The possible outcomes are:
- Conditional approval - pass without correction (but for doctoral degrees subject to submission of hardbound and electronic copies of the thesis ); or pass, subject to minor or major corrections
- Revision and resubmission of the work for a fresh examination
- Revision and resubmission of the work for a fresh examination or acceptance of the MSc/MLitt without further examination (but possibly subject to corrections)
- Not to be allowed to revise the thesis, but offered the MSc/MLitt without further revision or examination (but possibly subject to corrections)
- Outright failure
Notification of the result of the viva
Your examiners are asked not to give any direct indication of the likely outcome of the examination as the official result can be confirmed only by Student Registry on behalf of the Postgraduate Committee. Following your Degree Committee's meeting they will forward their decision to the Student Registry who will email your reports to you, copying in your Supervisor.
Process following the viva
Information about the process following your viva can be found here.
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
- Graduate School
- Current Students
- Final Doctoral Exam
Doctoral Exam Guide
Final oral defence, purpose of the final oral defence.
- To ensure that the candidate is able to present and defend the dissertation and its underlying assumptions, methodology, results, and conclusions in a manner consistent with the doctoral degree being sought;
- To communicate the results of the work to the campus community.
Structure of the Final Oral Defence
The detailed Final Oral Defence procedures are outlined in the Exam Instructions . A copy of these instructions is provided to the examining committee approximately one week before the Oral Defence.
The basic structure of the Oral Defence is:
- Candidate makes a public presentation of the dissertation (maximum 30 minutes)
- Examining committee members question the candidate
- Members of the audience are invited to ask questions of the candidate
- Examining committee holds an in-camera discussion where it decides on the overall recommendation it will make to Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies (see Evaluation Protocol below)
- Chair conveys the recommendations of the examining committee to the candidate
Candidates are encouraged to arrive 30 minutes early to get comfortable and set-up in the exam room. Exams start promptly at the official start time. The doors to the exam room are closed at the start of the exam and no one may enter the exam room, either physical or virtual, once the Final Oral Defence has begun. The Oral Defence usually takes two to two and a half hours.
Audiovisual Equipment
The examination rooms in the Graduate Student Centre come equipped with a projector and screen (room 200) or a large monitor and auxiliary screen (room 203), a white board, and a podium. Most candidates prefer to bring their own laptops to the examination; it is possible to use the wall mounted PC in either room, in which case candidates should either have their presentations available on cloud storage or bring a thumb drive.
The displays in rooms 200 and 203 are equipped with VGA and HDMI inputs. Candidates using laptops without these outputs must bring the appropriate adaptors.
Candidates planning to use Zoom to enable remote attendance should indicate their preference when making the exam booking.
Language Requirement
Candidates for the Final Doctoral Examination must have fulfilled all course and/or language requirements of the degree program. It is the responsibility of the candidate's graduate program to ensure these requirements have been met, and that the candidate's oral language proficiency is adequate for full communication between the examination committee and the candidate.
The Final Doctoral Examination is a public event at UBC and as such will be conducted in English. The candidate's oral proficiency in the language of the examination must be adequate for full communication between the examination committee and the candidate. For theses in language programs, some questions can be posed or answered in the language concerned, provided the examination committee can follow proceedings (by translation if necessary) in this other language.
Remote Attendance at in-person Exams
For information regarding Virtual Defences held entirely on Zoom, see Schedulng the Oral Defence, and the Virtual Exam Protocol .
Managing remote attendees can pose both technological challenges and challenges for candidates in managing divided attention. For these reasons, Hybrid Defences with more than one remote attendee should be discussed with the doctoral exams team in advance. We will work with candidates and supervisors to make sure these defences run smoothly .
Normally, examiners required for quorum at an in-person defence should be physically present in the room. The external examiner or a third member of the supervisory committee may attend the defence remotely.
Doctoral exams team use a Meeting OWL to support videoconferencing with Zoom. Candidates who wish to have remote attendees should indicate this on their Booking Request. The OWL can be used in either room.
For exams in other suitable rooms on campus, the research supervisor should verify that appropriate equipment is available in the room. Devices such as an OWL, or other mobile AV device may be used.
Should any technological issues arise during the course of the exam, the exam may be paused for a reasonable amount of time to resolve them. Only those examining committee members who have been present for the full duration of the exam can cast a vote in the proceedings. If members required for quorum lose connection and it cannot be restored, the exam will need to be rescheduled.
Please also note that the examination chair has the right to discontinue a remote connection if it is interfering with the proper conduct of the examination.
Attendance of the External Examiner
The external examiner's participation in a candidate's Final Oral Defence offers the opportunity for a valuable dialogue about the dissertation and the research it presents. Therefore, the participation of the external examiner in the Final Oral Defence is encouraged, but it is not required.
Inviting the external examiner to participate in the Final Oral Defence is at the discretion of the research supervisor; Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies will not extend such an invitation. For information about inviting the external examiner, please see Scheduling the Oral Defence .
Recording the Examination
See Recording the Examination .
Evaluation Protocol for the Oral Defence
The examining committee is asked to make an overall recommendation after evaluating two aspects of the candidate's performance:
- The Oral Defence : The committee should evaluate the candidate’s performance while presenting the synopsis, responding to questions, and defending the work. The committee must decide whether or not the performance met the standard of excellence expected of a doctoral candidate at UBC.
- The Dissertation: The committee should evaluate the overall merit of the dissertation, considering scholarship, scope and impact of the contribution made, and the quality of writing. They are asked to take into consideration the external examiner’s report, the assessments of the other examining committee members, and candidate's responses to questions during the Oral Defence. The committee will decide what revisions, if any, will be required before the dissertation can be considered fully acceptable.
Evaluation options available to the examining committee are:
- No revision or only minor revisions are required. The committee charges the research supervisor to verify that the required changes have been made.
- Substantive revisions are required. The committee chooses two or more of its members, including the research supervisor, to verify that the required changes have been made.
- The dissertation is unsatisfactory. Major rewriting and rethinking are required.
- The dissertation is unacceptable; it is fundamentally flawed and therefore beyond revision.
The examining committee is then asked to select one of the following overall recommendations:
- Pass. Pending final submission of the dissertation to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies, the University should award the doctoral degree to this candidate.
- Re-examination required. The candidate should be allowed a second attempt to pass the Final Doctoral Examination. (No more than one subsequent attempt is permitted.)
- Fail. The University should not grant the doctoral degree to this candidate.
In any category where the committee's judgment is unanimous, or nearly so (in that at most one examiner dissents), the chair will express it using the check-boxes on the chair's Report form. Dissenting opinions will be noted in the text of the Chair’s Report. In any category where two or more examiners disagree with the majority view, the chair will select a box labelled “No Decision” and provide a written description of the differing views in the text of the report. If this occurs, the chair will inform Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies as soon as possible (typically within one business day of the examination). The Dean of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies will review the Chair's Report and promptly determine an appropriate course of action, in consultation with the examination chair and the examining committee.
The examination chair is responsible for completing the Chair's Report form and submitting it to Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies within one week of the Oral Defence.
- Why Grad School at UBC?
- Graduate Degree Programs
- Application & Admission
- Info Sessions
- Research Supervisors
- Research Projects
- Indigenous Students
- International Students
- Tuition, Fees & Cost of Living
- Newly Admitted
- Student Status & Classification
- Student Responsibilities
- Supervision & Advising
- Managing your Program
- Health, Wellbeing and Safety
- Professional Development
- Dissertation & Thesis Preparation
- Final Dissertation & Thesis Submission
- Life in Vancouver
- Vancouver Campus
- Graduate Student Spaces
- Graduate Life Centre
- Life as a Grad Student
- Graduate Student Ambassadors
- Meet our Students
- Award Opportunities
- Award Guidelines
- Minimum Funding Policy for PhD Students
- Killam Awards & Fellowships
- Policies & Procedures
- Information for Supervisors
- Dean's Message
- Leadership Team
- Strategic Plan & Priorities
- Vision & Mission
- Equity, Diversity & Inclusion
- Initiatives, Plans & Reports
- Graduate Education Analysis & Research
- Media Enquiries
- Newsletters
- Giving to Graduate Studies
Strategic Priorities
- Strategic Plan 2019-2024
- Improving Student Funding
- Promoting Excellence in Graduate Programs
- Enhancing Graduate Supervision
- Advancing Indigenous Inclusion
- Supporting Student Development and Success
- Reimagining Graduate Education
- Enriching the Student Experience
Initiatives
- Public Scholars Initiative
- 3 Minute Thesis (3MT)
- PhD Career Outcomes

Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam
Oral examination, thesis proposal document.
Students are required to pass an oral examination to qualify for the doctoral degree. This proposal consists of a document submitted to an approved Thesis Committee at least one week prior to an oral presentation of the proposal to the Committee.
The nature of the proposal may vary, depending on the project, but it should provide motivation as well as describe and justify the envisioned approach along with summarizing progress made to date. Preliminary results supporting the proposed research are beneficial, but not required, for the Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam.
Each committee is free to choose its own criteria by which to judge the quality of thesis proposal. These criteria tend to include:
- a proposal document that conforms to the BE Handbook’s guidelines,
- a feasible research plan proposed and defended by the student that will result in a body of work that will meet the committee’s criteria for graduation, and
- scholarship in the research field demonstrating that the student is capable of executing original, informed research in that field.
Thesis Committee
The Thesis Committee must be approved prior to the scheduling of the thesis proposal/oral exam presentation. See the Thesis Committee page for more information on assembling a committee.
The Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam must take place by December 1 of the 3rd year, with the specific date scheduled before the beginning of the Fall Semester of the third year.
If the student and advisor are convinced that a delay would serve the student’s interests better, they must petition the Graduate Committee by August 1st of the summer following the 2nd year with their reasoning along with their commitment for a target date; the Graduate Committee will approve or deny the petition request. Failure to complete the Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam according to this policy will constitute unsatisfactory progress with respect to subsequent enrollment and funding support. Under these circumstances the student will not be able to register for the spring semester of their 3rd year.
Registration
The student should be sure to register for Thesis Proposal (20.951) for 0-24-0 credit units during the term in which the Proposal is defended.
The formal presentation of the Thesis Proposal will serve as the Oral Examination. The purpose of the Oral Exam is to test the student’s ability to explain their thesis project, defend their scientific rationale, and propose alternate approaches, as necessary. BE’s oral examination is focused on subject matter in the proposal and related to the proposal. It is not intended as a general examination on biology.
Format of the exam
The student should prepare a 30-minute presentation based on the research plan outlined in the Thesis Proposal Document . The Thesis Committee members will have read and thought about the Thesis Proposal Document ahead of time. Given that the meeting lasts up to 2 hours, there will be ample time for questions/discussion during your presentation. If questions arise about the format or style of the presentation, the student should contact the Thesis Committee Chair.
The student is responsible for arranging the Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam meeting with the Thesis Committee Members. Students should plan for the meeting to take 2 hours. Generally, this meeting should be scheduled at least two months in advance because it may be difficult to find a mutually agreeable time for all involved. Students are also responsible for reserving the location; they may contact the BE Academic Office for help reserving a room. Once this meeting has been scheduled, the Thesis Committee members and the Academic Office must be notified by e-mail about the day, time, and location of the presentation.
The student should hand out printouts of their presentation slides to the Thesis Committee Members on the day of the meeting.
Evaluation Form
The day of the presentation, the student should provide the Committee Chair with an “ Oral Examination for the Doctoral Degree ” form. The Committee Chair must complete this form to confirm the outcome of a Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam Presentation. The completed form should be submitted along with any comments or recommendations made by the Thesis Committee to the Academic Office. From there, copies will be distributed to the student, the advisor, and the Committee Chair.
If the proposal as presented is acceptable, a Pass grade will be recorded for 20.951, the student changes status from a graduate student to a PhD candidate, and the student is expected to begin a schedule of regular meetings with their thesis committee.
If the proposal requires changes or improvements to be considered acceptable, a Pass grade will be recorded and the student will advance to PhD candidacy but the student will be expected to improve the proposal according to the committee’s specifications before their next meeting.
If the proposal is unacceptable, the student will not be admitted to PhD candidacy. The student may either leave the program or complete a Master’s thesis . A student that completes a Master’s may apply for reinstatement into the PhD program or graduate with a Master’s degree.
At least one week prior to the Thesis Proposal presentation, the student should deliver a copy of the Thesis Proposal Document to each of the Oral Exam Committee Members and to the BE Academic Office. A signature from the Academic Office is required to confirm that the proposal adheres to the format described below.
Students who would like assistance in improving their writing skills or in any stage of writing a thesis proposal should contact the BE Communication Lab or the MIT Writing and Communications Center .
Thesis Proposal Guidelines
Title Page (One page) Include the title, the date, your name and signature, the advisor’s name and signature, and the notation “Thesis Proposal”.
Abstract (Less than 300 words on One page) State the significance of the proposed research. Include long-term objectives and specific aims. Describe concisely the research design and methods for achieving these objectives. Highlight the specific hypotheses to be tested, goals to be reached, or technology to be developed, which are intended to be your original contributions. Avoid summaries of past accomplishments.
Overall & Objective Specific Aims (One page Maximum) Articulate the overall objective of your thesis project, and outline a set of specific aims by which your work is intended to accomplish this objective. Be sure to clearly state the hypotheses to be tested, goals to be reached, or technology to be developed.
Background & Significance (Three to Five pages) Sketch the background leading to the present research, critically evaluate existing knowledge, and specifically identify the gaps that your research is intended to fill. State concisely the importance of the research described in this proposal by relating the specific aims to the broad, long-term objectives.
Research Design & Methods (Six to Eight pages) Along with the Objective & Aims section, this is the most important part of the proposal. The majority of your time should be spent making this part of your proposal strong, direct, and completely clear. Describe the research design and the procedures to be used to accomplish the specific aims of the project; it is generally most effective to do this according to the same outline as in the Objective & Aims section. Include how the data will be collected, analyzed, and interpreted. Describe any new methodology and its advantage over existing methodologies. Discuss the potential difficulties and limitations of the proposed procedures and alternative approaches to achieve the aims. As part of this section, provide a tentative timetable for the project. Point out any procedures, situations or materials that may be hazardous and the precautions to be exercised.
Preliminary Studies (Three to Four pages) This section may alternatively be located before the Research Design & Methods section) Use this section to provide an account of your preliminary studies that are pertinent to your research project and that support your specific aims. Note: it is not necessary to have obtained a substantial amount of preliminary data in order to submit or defend the proposal, although it will be expected that you have begun to undertake some of the key methods to assess their feasibility.
Literature Cited (No page limits) List all references. Each reference must include the title, names of authors, book or journal, volume number, starting and ending page numbers, and year of publication. References should be limited to relevant literature. References are not included in the page limits. However, only references pertinent to the proposed research should be included.
Appendix (No page limits) Copies of published or submitted articles pertinent to the proposed research for which you are an author may be included. Such publications are neither expected nor required at the time of Thesis Proposal presentation.
Format and Page Limitations
Proposals must be single spaced using 12 pt font and 1 inch margins. Figures may be embedded into the text, but they must be readable. The font within figures must be at least 9 point and the figure captions must be at least 10 point.
- Devote one page each for the title page, abstract and specific aims.
- Use between 13–17 pages for the remaining sections (Background & Significance, Preliminary Results, and Research Design & Methods). Note that although the maximum recommended page limits for these sections add up to a total of 17 pages, you are expected to expand and contract these sections as you see fit so that the total is no more than 17 pages.
- Page limits include both text and figures. References are not included in the page limits.
- The total length of the document should not exceed 20 pages (including 3 pages for the title page, abstract and specific aims; not including references or appendices).
Preparing For Your Dissertation Defense
13 Key Questions To Expect In The Viva Voce
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & David Phair (PhD) . Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2021
Preparing for your dissertation or thesis defense (also called a “viva voce”) is a formidable task . All your hard work over the years leads you to this one point, and you’ll need to defend yourself against some of the most experienced researchers you’ve encountered so far.
It’s natural to feel a little nervous.
In this post, we’ll cover some of the most important questions you should be able to answer in your viva voce, whether it’s for a Masters or PhD degree. Naturally, they might not arise in exactly the same form (some may not come up at all), but if you can answer these questions well, it means you’re in a good position to tackle your oral defense.

Viva Voce Prep: 13 Essential Questions
- What is your study about and why did you choose to research this in particular?
- How did your research questions evolve during the research process?
- How did you decide on which sources to include in your literature review?
- How did you design your study and why did you take this approach?
- How generalisable and valid are the findings?
- What were the main shortcomings and limitations created by your research design?
- How did your findings relate to the existing literature?
- What were your key findings in relation to the research questions?
- Were there any findings that surprised you?
- What biases may exist in your research?
- How can your findings be put into practice?
- How has your research contributed to current thinking in the field?
- If you could redo your research, how would you alter your approach?
#1: What is your study about and why did you choose to research this in particular?
This question, a classic party starter, is pretty straightforward.
What the dissertation or thesis committee is assessing here is your ability to clearly articulate your research aims, objectives and research questions in a concise manner. Concise is the keyword here – you need to clearly explain your research topic without rambling on for a half-hour. Don’t feel the need to go into the weeds here – you’ll have many opportunities to unpack the details later on.
In the second half of the question, they’re looking for a brief explanation of the justification of your research. In other words, why was this particular set of research aims, objectives and questions worth addressing? To address this question well in your oral defense, you need to make it clear what gap existed within the research and why that gap was worth filling.

#2: How did your research questions evolve during the research process?
Good research generally follows a long and winding path . It’s seldom a straight line (unless you got really lucky). What they’re assessing here is your ability to follow that path and let the research process unfold.
Specifically, they’ll want to hear about the impact that the literature review process had on you in terms of shaping the research aims, objectives and research questions . For example, you may have started with a certain set of aims, but then as you immersed yourself in the literature, you may have changed direction. Similarly, your initial fieldwork findings may have turned out some unexpected data that drove you to adjust or expand on your initial research questions.
Long story short – a good defense involves clearly describing your research journey , including all the twists and turns. Adjusting your direction based on findings in the literature or the fieldwork shows that you’re responsive , which is essential for high-quality research.

#3: How did you decide on which sources to include in your literature review?
A comprehensive literature review is the foundation of any high-quality piece of research. With this question, your dissertation or thesis committee are trying to assess which quality criteria and approach you used to select the sources for your literature review.
Typically, good research draws on both the seminal work in the respective field and more recent sources . In other words, a combination of the older landmark studies and pivotal work, along with up-to-date sources that build on to those older studies. This combination ensures that the study has a rock-solid foundation but is not out of date.
So, make sure that your study draws on a mix of both the “classics” and new kids on the block, and take note of any major evolutions in the literature that you can use as an example when asked this question in your viva voce.
#4: How did you design your study and why did you take this approach?
This is a classic methodological question that you can almost certainly expect in some or other shape.
What they’re looking for here is a clear articulation of the research design and methodology, as well as a strong justification of each choice . So, you need to be able to walk through each methodological choice and clearly explain both what you did and why you did it. The why is particularly important – you need to be able to justify each choice you made by clearly linking your design back to your research aims, objectives and research questions, while also taking into account practical constraints.
To ensure you cover every base, check out our research methodology vlog post , as well as our post covering the Research Onion .

#5: How generalizable and valid are the findings?
This question is aimed at specifically digging into your understanding of the sample and how that relates to the population, as well as potential validity issues in your methodology.
To answer question this well, you’ll need to critically assess your sample and findings and consider if they truly apply to the entire population, as well as whether they assessed what they set out to. Note that there are two components here – generalizability and validity . Generalizability is about how well the sample represents the population. Validity is about how accurately you’ve measured what you intended to measure .
To ace this part of your dissertation defense, make sure that you’re very familiar with the concepts of generalizability , validity and reliability , and how these apply to your research. Remember, you don’t need to achieve perfection – you just need to be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of your research (and how the weaknesses could be improved upon).
Need a helping hand?
#6: What were the main shortcomings and limitations created by your research design?
This question picks up where the last one left off.
As I mentioned, it’s perfectly natural that your research will have shortcomings and limitations as a result of your chosen design and methodology. No piece of research is flawless. Therefore, a good dissertation defense is not about arguing that your work is perfect, but rather it’s about clearly articulating the strengths and weaknesses of your approach.
To address this question well, you need to think critically about all of the potential weaknesses your design may have, as well as potential responses to these (which could be adopted in future research) to ensure you’re well prepared for this question. For a list of common methodological limitations, check out our video about research limitations here .
#7: How did your findings relate to the existing literature?
This common dissertation defense question links directly to your discussion chapter , where you would have presented and discussed the findings in relation to your literature review.
What your dissertation or thesis committee is assessing here is your ability to compare your study’s findings to the findings of existing research . Specifically, you need to discuss which findings aligned with existing research and which findings did not. For those findings that contrasted against existing research, you should also explain what you believe to be the reasons for this.
As with many questions in a viva voce, it’s both the what and the why that matter here. So, you need to think deeply about what the underlying reasons may be for both the similarities and differences between your findings and those of similar studies.

#8: What were your key findings in relation to the research questions?
This question is similar to the last one in that it too focuses on your research findings. However, here the focus is specifically on the findings that directly relate to your research questions (as opposed to findings in general).
So, a good way to prepare for this question is to step back and revisit your research questions . Ask yourself the following:
- What exactly were you asking in those questions, and what did your research uncover concerning them?
- Which questions were well answered by your study and which ones were lacking?
- Why were they lacking and what more could be done to address this in future research?
Conquering this part dissertation defense requires that you focus squarely on the research questions. Your study will have provided many findings (hopefully!), and not all of these will link directly to the research questions. Therefore, you need to clear your mind of all of the fascinating side paths your study may have lead you down and regain a clear focus on the research questions .
#9: Were there any findings that surprised you?
This question is two-pronged.
First, you should discuss the surprising findings that were directly related to the original research questions . Going into your research, you likely had some expectations in terms of what you would find, so this is your opportunity to discuss the outcomes that emerged as contrary to what you initially expected. You’ll also want to think about what the reasons for these contrasts may be.
Second, you should discuss the findings that weren’t directly related to the research questions, but that emerged from the data set . You may have a few or you may have none – although generally there are a handful of interesting musings that you can glean from the data set. Again, make sure you can articulate why you find these interesting and what it means for future research in the area.
What the committee is looking for in this type of question is your ability to interpret the findings holistically and comprehensively , and to respond to unexpected data. So, take the time to zoom out and reflect on your findings thoroughly.

#10: What biases may exist in your research?
Biases… we all have them.
For this question, you’ll need to think about potential biases in your research , in the data itself but also in your interpretation of the data. With this question, your committee is assessing whether you have considered your own potential biases and the biases inherent in your analysis approach (i.e. your methodology). So, think carefully about these research biases and be ready to explain how these may exist in your study.
In an oral defense, this question is often followed up with a question on how the biases were mitigated or could be mitigated in future research. So, give some thought not just to what biases may exist, but also the mitigation measures (in your own study and for future research).
#11: How can your findings be put into practice?
Another classic question in the typical viva voce.
With this question, your committee is assessing your ability to bring your findings back down to earth and demonstrate their practical value and application. Importantly, this question is not about the contribution to academia or the overall field of research (we’ll get to that next) – it is specifically asking about how this newly created knowledge can be used in the real world.
Naturally, the actionability of your findings will vary depending on the nature of your research topic. Some studies will produce many action points and some won’t. If you’re researching marketing strategies within an industry, for example, you should be able to make some very specific recommendations for marketing practitioners in that industry.
To help you flesh out points for this question, look back at your original justification for the research (i.e. in your introduction and literature review chapters). What were the driving forces that led you to research your specific topic? That justification should help you identify ways in which your findings can be put into practice.
#12: How has your research contributed to current thinking in the field?
While the previous question was aimed at practical contribution, this question is aimed at theoretical contribution . In other words, what is the significance of your study within the current body of research? How does it fit into the existing research and what does it add to it?
This question is often asked by a field specialist and is used to assess whether you’re able to place your findings into the research field to critically convey what your research contributed. This argument needs to be well justified – in other words, you can’t just discuss what your research contributed, you need to also back each proposition up with a strong why .
To answer this question well, you need to humbly consider the quality and impact of your work and to be realistic in your response. You don’t want to come across as arrogant (“my work is groundbreaking”), nor do you want to undersell the impact of your work. So, it’s important to strike the right balance between realistic and pessimistic .
This question also opens the door to questions about potential future research . So, think about what future research opportunities your study has created and which of these you feel are of the highest priority.

#13: If you could redo your research, how would you alter your approach?
This question is often used to wrap up a viva voce as it brings the discussion full circle.
Here, your committee is again assessing your ability to clearly identify and articulate the limitations and shortcomings of your research, both in terms of research design and topic focus . Perhaps, in hindsight, it would have been better to use a different analysis method or data set. Perhaps the research questions should have leaned in a slightly different direction. And so on.
This question intends to assess whether you’re able to look at your work critically , assess where the weaknesses are and make recommendations for the future . This question often sets apart those who did the research purely because it was required, from those that genuinely engaged with their research. So, don’t hold back here – reflect on your entire research journey ask yourself how you’d do things differently if you were starting with a blank canvas today.
Recap: The 13 Key Dissertation Defense Questions
To recap, here are the 13 questions you need to be ready for to ace your dissertation or thesis oral defense:
As I mentioned, this list of dissertation defense questions is certainly not exhaustive – don’t assume that we’ve covered every possible question here. However, these questions are quite likely to come up in some shape or form in a typical dissertation or thesis defense, whether it’s for a Master’s degree, PhD or any other research degree. So, you should take the time to make sure you can answer them well.
If you need assistance preparing for your dissertation defense or viva voce, get in touch with us to discuss 1-on-1 coaching. We can critically review your research and identify potential issues and responses, as well as undertake a mock oral defense to prepare you for the pressures and stresses on the day.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

12 Comments
Very interesting
Interesting. I appreciate!
Really appreciating
My field is International Trade
Interesting
This is a full course on defence. I was fabulously enlightened and I gained enough confidence for my upcoming Masters Defence.
There are many lessons to learn and the simplicity in presentationmakes thee reader say “YesI can”
This is so helping… it has Enlightened me on how to answer specific questions. I pray to make it through for my upcoming defense
Lovely to hear that 🙂
Really educative and beneficial
Interesting. On-point and elaborate. And comforting too! Thanks.
Thank you very much for the enlightening me, be blessed
Thankyou so much. I am planning to defend my thesis soon and I found this very useful
Very interesting and useful to all masters and PhD students
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Candidates with oral examination
Process overview.
The external examination of a HDR candidate is a 2-part process consisting of a thesis evaluation and an oral examination.
Each of these parts is linked to the following outputs:
- Thesis evaluation: a summary and a written report from each examiner.
- Oral examination: a Chair’s report summarising the feedback of the examiners and recommendation of the examination panel.
These outcomes inform a decision by the Dean of the Graduate School on the final outcome of the candidate’s examination and whether an award (Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) or Master of Philosophy (MPhil)) will be conferred.
The oral examination will take place between 2 weeks to 3 months after scheduling, depending on the availability of the participants.
Thesis evaluation
Read the entire thesis and provide a summary and written report, based on the following criteria.
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) candidate:
- Does the candidate demonstrate a significant and original contribution to knowledge?
- Does the candidate engage with the literature and the work of others?
- Does the candidate show an advanced knowledge of research principles and methods relating to the applicable discipline?
- Is there a clear and discernible coherence in the presented research, its arguments and conclusions?
- Is the thesis clearly, accurately, and cogently written?
Master of Philosophy (MPhil) candidate
- Does the candidate show originality in the application of knowledge?
Your written report should provide sufficient detail to allow the candidate to prepare responses for the oral examination.
If you express significant concerns about the thesis, then the oral examination, which usually takes place approximately 1 month after your reports are returned, may be postponed at the Dean’s discretion in order to give the student more time to prepare.
Evaluation timeframe
Your report should be submitted to the UQ Graduate School no later than 5 weeks after you receive the thesis for evaluation. If you require additional time, contact the Graduate School’s progressions and examinations team outlining your requirements at [email protected] .
Once your report has been reviewed by the Dean of the Graduate School, it will be released to the candidate and their principal advisor so that the candidate can prepare for the oral examination.
Oral examination
The oral examination is the second part of the HDR candidate examination process. Only once the oral examination has taken place can an outcome of the candidate’s examination be determined.
The oral examination usually involves 4 participants:
- the candidate
- the Chair of examiners (appointed by UQ)
- 2 external examiners who provided written reports.
The Chair of examiners and the 2 examiners constitute the oral examination panel.
The main objectives are to:
- provide a developmental learning opportunity
- authenticate the contribution made by the candidate to the thesis
- establish that the candidate fully understands the work and its wider implications
- provide the candidate with an opportunity to reply to criticism or challenge
- enable the candidate and examiners to clarify issues, corrections, and revisions.
Assessment and report
The oral examination will include assessment of the candidate’s ability to:
- demonstrate detailed knowledge of the thesis
- locate their research in the broader context of their discipline
- demonstrate the originality of the thesis and the contribution it makes to the state of knowledge in the field
- defend the methodology and conclusions of the thesis
- display awareness of the limitations of the thesis.
The outcome of this second component is a Chair’s report which:
- summarises the feedback of the examination panel
- provides the recommendation of the panel on the outcome of the oral examination.
The report should:
- be clear and concise
- detail any revisions required
- justify the final recommendation.
Oral examination process
The Chair of examiners is responsible for scheduling and conducting the oral examination. Once the examiners’ reports have been returned, the Chair will be informed that the oral examination is ready to be scheduled. You’ll then be invited to respond to an online poll to help establish the date and time of the oral examination. Once a date and time have been finalised, you will receive a Zoom link for the examination.
By this stage in the examination process, the candidate is aware of the examiners’ identities, but is not allowed to contact them. Similarly, you are requested not to contact the candidate or their advisors. All communication should be conducted through the Chair of examiners.
Day of examination
It is recommended that, on the day of the oral examination, the Chair and examiners meet in the first 20 minutes of the scheduled session to discuss their reports and set an agenda with points for discussion and issues requiring clarification. Any potential areas of disagreement between examiners should be discussed at this meeting and a resolution should be sought. (If the examination panel wishes to begin these preparatory discussions earlier via email, it’s welcome to do so.)
The oral examination may take up to 3 hours.
All discussion should take place in English.
Possible recommendations are:
- Pass with changes
- Repeat oral examination
- Revise and resubmit thesis for examination.
At the conclusion of the oral examination, the Chair’s report containing the panel’s recommendation will be forwarded to the Dean of the Graduate School for a final decision.
Examination format
The examination typically begins with the candidate presenting a short overview of the thesis and its main findings. The thesis should be discussed, and questions asked and answered, in a respectful and fair manner.
Questions should focus on the areas of concern raised in the written reports provided by the examiners. The candidate may rebut some of the feedback with sound academic arguments and justifications or may concede that further revisions would enhance the thesis.
Examiners may ask questions tangential to the work carried out in the thesis, but the ability or inability of the candidate to answer such questions should not influence the examiners’ recommendation on the final outcome of the examination.
At the conclusion of the oral examination, the candidate will temporarily leave the room (or Zoom meeting). The examiners (with the guidance of the Chair) will decide on a recommendation to the Dean regarding the outcome of the oral examination.
The candidate will then be invited back into the room (or Zoom meeting) and given a verbal summary of the outcome of the oral examination.

- PhD Viva Voces – A Complete Guide
- Doing a PhD
- A PhD viva involves defending your thesis in an oral examination with at least two examiners.
- The aim of a PhD viva is to confirm that the work is your own , that you have a deep understanding of your project and, overall, that you are a competent researcher .
- There are no standard durations, but they usually range from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours .
- There are six outcomes of a PhD viva: (1) pass without corrections (2) pass subject to minor corrections, (3) pass subject to major corrections, (4) downgrade to MPhil with no amendments, (5) downgrade to MPhil subject to amendments, (6) immediate fail.
- Almost all students who sit their viva pass it, with the most common outcome being ‘(2) – pass subject to minor corrections’.
What Is a PhD Viva?
A viva voce , more commonly referred to as ‘viva’, is an oral examination conducted at the end of your PhD and is essentially the final hurdle on the path to a doctorate. It is the period in which a student’s knowledge and work are evaluated by independent examiners.
In order to assess the student and their work around their research question, a viva sets out to determine:
- you understand the ideas and theories that you have put forward,
- you can answer questions about elements of your work that the examiners have questions about,
- you understand the broader research in your field and how your work contributes to this,
- you are aware of the limitations of your work and understand how it can be developed further,
- your work makes an original contribution, is your own and has not been plagiarised.
Note: A viva is a compulsory procedure for all PhD students, with the only exception being when a PhD is obtained through publication as opposed to the conventional route of study.
Who Will Attend a Viva?
In the UK, at least two examiners must take part in all vivas. Although you could have more than two examiners, most will not in an attempt to facilitate a smoother questioning process.
One of the two examiners will be internal, i.e. from your university, and the other will be external, i.e. from another university. Regardless, both will be knowledgeable in your research field and have read your thesis beforehand.
In addition to your two examiners, two other people may be present. The first is a chairperson. This is an individual who will be responsible for monitoring the interview and for ensuring proper conduct is followed at all times. The need for an external chairperson will vary between universities, as one of the examiners can also take on this role. The second is your supervisor, whose attendance is decided upon by you in agreement with your examiners. If your supervisor attends, they are prohibited from asking questions or from influencing the outcome of the viva.
To avoid any misunderstandings, we have summarised the above in a table:
Note: In some countries, such as in the United States, a viva is known as a ‘PhD defense’ and is performed publicly in front of a panel or board of examiners and an open audience. In these situations, the student presents their work in the form of a lecture and then faces questions from the examiners and audience which almost acts as a critical appraisal.
How Long Does a Viva Last?
Since all universities have different guidelines , and since all PhDs are unique, there are no standard durations. Typically, however, the duration ranges from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours.
Your examiners will also influence the duration of your viva as some will favour a lengthy discussion, while others may not. Usually, your university will consult your examiners in advance and notify you of the likely duration closer to the day of your viva.
What Happens During a Viva?
Regardless of the subject area, all PhD vivas follow the same examination process format as below.
Introductions
You will introduce yourselves to each other, with the internal examiner normally introducing the external examiner. If an external chairperson is present, they too are introduced; otherwise, this role will be assumed by one of the examiners.
Procedure Explained
After the introductions, the appointed chair will explain the viva process. Although it should already be known to everyone, it will be repeated to ensure the viva remains on track during the forthcoming discussion.
Warm-Up Questions
The examiners will then begin the questioning process. This usually starts with a few simple opening questions, such as asking you to summarise your PhD thesis and what motivated you to carry out the research project.
In-Depth Questions
The viva questions will then naturally increase in difficulty as the examiners go further into the details of your thesis. These may include questions such as “What was the most critical decision you made when determining your research methodology ?”, “Do your findings agree with the current published work?” and “How do your findings impact existing theories or literature? ”. In addition to asking open-ended questions, they will also ask specific questions about the methodology, results and analysis on which your thesis is based.
Closing the Viva
Once the examiners are satisfied that they have thoroughly evaluated your knowledge and thesis, they will invite you to ask any questions you may have, and then bring the oral examination to a close.
What Happens After the Viva?
Once your viva has officially ended, your examiners will ask you to leave the room so that they can discuss your performance. Once a mutual agreement has been reached, which can take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour, you will be invited back inside and informed of your outcome.
PhD Viva Outcomes
There are six possible outcomes to a viva:
- Immediate award of degree: A rare recommendation – congratulations, you are one of the few people who completely satisfied your examiners the first time around. You do not have to do anything further at this point.
- Minor amendments required: The most common recommendation – you obtain a pass on the condition that you make a number of minor amendments to your thesis, such as clarifying certain points and correcting grammatical errors. The time you have to make these changes depends on the number of them, but is usually one to six months.
- Major amendments required: A somewhat uncommon recommendation – you are requested to make major amendments to your thesis, ranging from further research to collecting more data or rewriting entire sections. Again, the time you have to complete this will depend on the number of changes required, but will usually be six months to one year. You will be awarded your degree once your amended thesis has been reviewed and accepted.
- Immediate award of MPhil: An uncommon recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree but meets the standard for an MPhil (Master of Philosophy), a lower Master’s degree.
- Amendments required for MPhil: A rare recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree, but with several amendments will meet the standard for an MPhil.
- Immediate fail: A very rare recommendation – you are given an immediate fail without the ability to resubmit and without entitlement to an MPhil.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Is the Pass Rate for Vivas?
Based on an analysis of 26,076 PhD students who took their viva exam between 2006 and 2017, the PhD viva pass rate in the UK is 96%; of those who passed, about 80% were required to make minor amendments to their thesis. The reason for this high pass rate is that supervisors will only put their students forward for a viva once they confidently believe they are ready for it. As a result, most candidates who sit a viva are already well-versed in their PhD topic before they even start preparing for the exam.
How Do I Arrange a Viva?
Your viva will be arranged either by the examiners or by the chairperson. The viva will be arranged at least one to two months after you have submitted your thesis and will arrange a viva date and venue that is suitable for all participants.
Can I Choose My Examiners?
At most universities, you and your supervisor will choose the internal and external examiners yourselves. This is because the examiners must have extensive knowledge of the thesis topic in order to be able to examine you and, as the author of the thesis in question, who else could better determine who they might be than you and your supervisor. The internal examiner is usually quite easy to find given they will be from your institution, but the external examiner may end up being your second or third preference depending on availability.
Can I Take Notes Into a Viva?
A viva is about testing your competence, not your memory. As such, you are allowed to take notes and other supporting material in with you. However, keep in mind that your examiners will not be overly impressed if you constantly have to refer to your notes to answer each question. Because of this, many students prefer to take an annotated copy of their thesis, with important points already highlighted and key chapters marked with post-it notes.
In addition to an annotated copy of a thesis, some students also take:
- a list of questions they would like to ask the examiners,
- notes that were created during their preparation,
- a list of minor corrections they have already identified from their viva prep work.
How Do I Prepare for a PhD Viva?
There are several ways to prepare for a PhD viva, one of the most effective being a mock viva voce examination . This allows you to familiarise yourself with the type of viva questions you will be asked and identify any weak areas you need to improve. They also give you the opportunity to practise without the pressure, giving you more time to think about your answers which will help to make sure that you know your thesis inside out. However, a mock viva exam is just one of many methods available to you – some of the other viva preparation methods can be found on our “ How to Prepare for a PhD Viva ” page.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
The University of Manitoba campuses are located on original lands of Anishinaabeg, Ininew, Anisininew, Dakota and Dene peoples, and on the National Homeland of the Red River Métis. More
Faculty of Graduate Studies
University of manitoba.
University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba Canada, R3T 2N2
The PhD oral examination
Doctoral students must pass an oral examination on the subject of their thesis and matters relating to it before they may obtain their Ph.D. degree. This page outlines the key tasks for preparing for and conducting the Ph.D. oral examination.
On this page
Examination attendees, scheduling the oral examination, advertising the oral examination, documentation for the conduct of the examination, conduct of the examination, following completion of the examination, video conference capabilities for examinations, guidelines for phd oral examinations (pdf).
- The examination will be conducted by the Dean of Graduate Studies or the Dean's designate chosen from among scholars of the University (the "Chair").
- In most cases, the examining committee will consist of the same members as that of the candidate’s advisory committee, plus an examiner external to the University of Manitoba selected by the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
- The doctoral candidate, advisor, and all internal members of the examining committee must be present.
- The presence of the external examiner is strongly encouraged but not mandatory.
- The oral examination is open to all members of the University community. Graduate students are especially encouraged to attend.
It is the responsibility of the department to reserve the room for the oral examination (if hybrid or in-person) and notify the Faculty of Graduate Studies of the following no later than two weeks (10 business days) prior to the date of the examination via email to [email protected] :
- Date and time of the examination
- Location and/or virtual platform to be used, if applicable
- The name and email address of an eligible Chair who has agreed to serve for the examination
In addition to the scheduling details, the Faculty of Graduate Studies must receive the candidate’s examination program information (i.e., previous degrees, awards, and publications) and updated thesis abstract via email to [email protected] at least two weeks (10 business days) prior to the proposed date of the examination.
The Faculty will not accept examination information before all reports have been received from the internal and external members of the examining committee.
If the examination is to be held in-person or using a blended format, the examination must be held at one of the following:
- University of Manitoba Fort Garry campus
- University of Manitoba Bannatyne campus
- St. Boniface Hospital Albrechtsen Research Centre
All internal members of the examining committee must be present in real time at the defence, unless exceptional circumstances prevent this and prior approval has been given by the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
Departments/Units may choose to conduct Ph.D. Oral Examinations in-person, remotely, or using a hybrid model. Note that for in-person and hybrid examinations, Departments/Units will be responsible for providing appropriate space and technology for their chosen delivery method(s) (e.g., sufficient space for adequate distancing of all in-person attendees and reliable technology to facilitate hybrid participation) and aiding in securing a chair.
Once the oral examination has been scheduled by the department, the Faculty of Graduate Studies must be notified. A minimum of two weeks' notice is required. Notices of the examination, including the invitation to graduate students, should be posted within the department/unit. A template for examination notices is available on the Faculty of Graduate Studies intranet site (faculty and staff only - University of Manitoba account login required) for use by all department/units.
Approximately one week prior to the oral examination, FGS will provide the chair of the examination with an electronic package containing:
- Guidelines for Ph.D. Oral Examinations;
- Sample Chair Script;
- Candidate Bio, Thesis Title, and Thesis Abstract;
- Copies of all of the examiner's reports, both internal and external;
- The questions and expected answers, if provided, from the external examiner if not attending;
- Approval Form; and
- Link to the Chair Report Form
The individual chairing the oral examination bears a very important responsibility. A thorough examination and defence of the thesis serves as the University's guarantee that the standards of the Ph.D. are maintained. To this end, the procedures for the conduct of the examination must be consistent and adhered to strictly.
The Chair is responsible for:
- Note: All internal examiners must attend unless otherwise approved by the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies. If any of the expected members of the examining committee are absent, the Chair must seek approval for the examination to proceed from the Faculty of Graduate Studies;
- Ensuring that the examination follows the procedure detailed below in a professional and collegial manner;
- Monitoring the examining committee's deliberations and conducting a vote to determine the rest of the examination;
- Informing the candidate of the result of the examination and outlining the post-examination procedures for both the candidate and the examining committee; and
- Completing and submitting the Chair Report Form to the Faculty of Graduate Studies
General introduction and welcome
The chair welcomes all of those in attendance. The chair impresses upon the candidate, the examiners, and the audience that this occasion is the senior academic event in the Faculty of Graduate Studies and is a formal examination process prior to awarding the highest academic degree of the University of Manitoba.
Introduction of candidate and examiners
The Chair:
- Introduces the candidate, noting previous degrees obtained, awards, special achievements, and publications
- Introduces the examining committee, beginning with a special welcome to the external examiner (if present) and proceeding with introductions of the non-departmental examiner, departmental examiners, and finally the advisor.
The chair should note that all members of the examining committee have read the thesis and submitted written reports. The advisor may or may not have submitted a report.
Outline of procedures for the oral examination
- The candidate will give a 20 to 25-minute presentation of the major objectives, content, results, and conclusions of their thesis. The candidate’s ability to present the thesis clearly and concisely is an essential part of the examination process.
- External Examiner (or Chair on the External Examiner's behalf)
- Internal Examiners and Knowledge Keeper (if applicable)
- Advisor (and Co-Advisor, if applicable)
- A second round of questions may be offered to the examining committee if time permits.
- The Invited Member (if applicable) and audience will be invited to ask questions if time permits.
- Once the question periods are completed, the candidate, audience, and Invited Member (if applicable) will be asked to leave the room/virtual meeting. The examining committee will discuss the candidate’s performance and determine the outcome of the oral examination.
- The candidate will be invited to return once the examining committee reaches a decision.
For virtual and Hybrid Examinations, the Chair must also state the following:
- All remote audience members must keep their microphone and video off for the duration of the examination. If time permits questions from the audience, members may turn their video on only when speaking;
- All participants and attendees may only use the chat function to communicate technical difficulties to the meeting host, or to indicate that they would like to pose a question during the appropriate time.
Professionalism and collegiality are expected of all participants and attendees. Any who behave inappropriately will be removed from the meeting.
In addition, note that:
- In no case should the questioning exceed two hours;
- The Chair must remain neutral, and consequently is not permitted to pose any questions of their own; and
- The examiners should keep comments and discussion on the subject matter of the thesis to a minimum, unless they are essential to the questions being posed. Otherwise, such comments and discussions should occur only during the examiners deliberations.
After the candidate’s presentation and questioning period
The chair conducts the remainder of the oral examination as follows:
- The audience (and Invited Member, if applicable) is thanked for their attendance and support of the candidate and, along with the candidate, is asked to leave so that a confidential meeting of the examining committee may be held
- Each examiner is asked, in sequence to comment on the candidate's performance with respect to the answers to the questions and on whether the candidate should pass or fail the oral examination. If the external examiner or two or more internal examiners indicate a fail, the candidate fails the examination.
- The candidate is invited back into the room and informed of the results of the examination, the nature of revisions, and the method of approval of the revisions.
- The candidate is reminded of the procedures for submission of the thesis to the UM's digital repository, MSpace .The candidate is congratulated (if appropriate) and members of the examining committee are thanked.
The decision of the Examination Committee is reported on the Chair Report Form. The members of the examining committee are asked to sign the approval form and indicate whether they assign the candidate a vote of “Pass” or “Fail” on their oral defence. If the oral examination is failed, a second attempt at the oral defence of the thesis may be scheduled in accordance with Academic Guide.
The nature of required revisions, prior to submission of the final copy of the thesis to MSpace as well as the procedures for their completion is determined by the chair, in discussion with the examining committee.
After the examination is complete, these participants are responsible for the following tasks.
The chair shall:
- Communicate the result of the examination, nature of revisions (if any), participant attendance methods (for hybrid examinations only), and revision procedure to the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies through the submission of the Chair Report Form.
- Sign the Final Oral Examination of the Ph.D. Thesis Approval Form and email it to the Advisor.
The Advisor/Co-Advisor (if applicable) shall:
- Ensure that any required revisions to the thesis have been approved according to the agreed upon procedure;
- Obtain the signature of all committee members who participated in the oral examination on the Approval Form; and
- Submit the Approval Form via email to the Faculty of Graduate Studies ([email protected]) in time to meet relevant deadlines.
The candidate shall:
- Revise the thesis as required by the examining committee and follow the agreed upon approval procedure;
- Upload a digital (pdf) version of the final thesis to the MSpace website once all required revisions have been made and approved.
The Dean of Graduate Studies shall:
- Ensure that the external examiner is thanked for their services
The Faculty of Graduate Studies encourages units to have external examiners participate in the Ph.D. oral examination. This can be accomplished by video conference if it is too expensive or not possible for the external examiner to be present. The University of Manitoba has excellent videoconferencing facilities. They may be used:
- for University of Manitoba oral examinations with an external examiner at another institution
- for University of Manitoba faculty members who are external examiners when the examination is held at another institution.
Please contact Information Services & Technology (IST) to ask about current videoconferencing rates for oral examinations. Please refer to video recording and productions services for more information.
You may also want
Submit your thesis or practicum.
- 3. Thesis examination
- Information and services
- Higher Degree by Research
If you have submitted your thesis for examination via UQ eSpace please read this document for information on how your examination will progress.
You can track the progress of your examination via the HDR Thesis examination request in my.UQ.
- Receiving examiner reports
- Oral examinations (viva voce)
- Examination outcomes
- After the examination process
- Thesis completion
1. Receiving examiner reports
Once your thesis is submitted, the Dean of the Graduate School will invite two examiners from the list of examiners nominated by your Principal Advisor.
Each examiner is asked to provide a written report with feedback about your thesis. Examiners are requested to return their written reports within:
- four weeks for an MPhil, or
- five weeks for a PhD.
You will receive your examination reports only when both examiners have completed and returned their reports and the Dean has determined the outcome. Following the receipt of these reports you will then either:
- proceed to an oral examination, or
- receive your examination outcome.
Role of Chair of Examiners
Once your thesis has been submitted for examination, your school will appoint a Chair of Examiners who will ensure any changes requested by examiners are implemented.
The Chair of Examiners is an academic staff member at UQ who is familiar with your research discipline and will advise the Graduate School on the outcomes of your thesis examination.
Further details regarding the Chair of Examiners can be found in the Higher Degree by Research Examination Policy .
Late Examiner Reports
The Graduate School sends regular reminders to examiners to ensure reports are returned in good time. We email before the report is due and follow up twice over two weeks if a report is overdue.
If the report is not received after this time, the Dean of the Graduate School may choose to replace an examiner. The Dean of the Graduate School may contact the examiner directly prior to making the decision to appoint a third examiner.
For more information see the Higher Degree by Research Examination (with Oral Examination) Procedure and Higher Degree by Research Examination (without Oral Examination) Procedure . A timeline of the entire examination process is also available:
- Examination process timeline (PDF, 383.2 KB)
- 1. Thesis preparation
- 2. Thesis submission
- 4. Award of degree
- Thesis submission date and scholarship extension
Need assistance?
Chat to the Graduate School Team
- Utility Menu
Senior Thesis & Undergraduate Research
Every year, approximately 45%-55% of senior History concentrators choose to cap their Harvard careers by writing a senior honors thesis.
The senior thesis tutorial is a two-semester sequence comprising Hist 99a and Hist 99b . While the overwhelming majority of students who start a thesis choose to complete it, our process allows students to drop the thesis at the end of the fall semester after History 99a (in which case they are not eligible for departmental honors).
The senior thesis in History is a year-long project involving considerable primary- and secondary-source research and a good deal of writing; finished theses are expected to be between 60 and 130 pages in length , and to make an original contribution to historical knowledge.
The department’s senior thesis program is one of the strongest in Harvard College. In recent years, one quarter or more of our thesis writers have received Hoopes Prizes , which is well over the College average.
History 99 Syllabus 2022–2023
History 99: Senior Thesis Writers’ Tutorial Wednesdays, 6–7 and 7-8 PM Robinson Conference Room
Click here to view the History 99 syllabus for this year.
A Sampling of Past History Thesis Titles
For a list of thesis titles from the past five years, please click here .
Senior Thesis Conference
The History Department's annual Senior Thesis Writer's Conference is an opportunity for thesis writers to present their projects as members of three-to-four person panels moderated by a faculty member or advanced graduate student, to an audience of other faculty and graduate students. Their aim is to get the critical and constructive feedback they need to clarify their arguments, refine their methods, and ultimately transform their research projects into theses.
Like our faculty, our student presenters are conscious of their reliance on other disciplines in almost every aspect of their work. This conference supplies opportunities to engage in cross-disciplinary dialogues. Audience members also learn from these dedicated and talented young scholars even as they teach them new ways of conceiving and pursuing their projects.
For more information about the conference or the Department's thesis program as a whole, please write to the Assistant Director of Undergraduate Studies in History, or visit the Senior Thesis Writers Conference and History 99a website. The Conference is open to all active members of the Harvard community.
All seniors writing theses receive as part of the History 99a and 99b seminar materials a Timetable for Thesis Writers which lists approximate deadlines for staying current with work on this large-scale project. (For current copies of these documents, please click here .) Many thesis writers will submit work in advance of the deadlines listed on the timetable, following schedules worked out with their individual advisers. Several of the deadlines listed on the timetable must be met:
- Students who wish to enroll in History 99 must attend the first meeting of the seminar on Wednesday, September 5th at 6:00 pm in the Robinson Lower Library.
- By the beginning of the fall reading period, students must submit substantial proof of research to both their adviser and the 99 History instructors. This usually takes the form of a chapter or two of the thesis (20–30 pages).
- Theses are due to the History Undergraduate Office (Robinson 101) on Thursday, March 10, 2022 before 5:00 pm. Theses that are handed in late will be penalized.
Thesis Readings
Each History thesis is read by at least two impartial members of the Board of Tutors, assigned by the Department. The Board of Tutors consists of (1) all department faculty in residence and (2) all graduate students teaching History 97 and/or a Research Seminar, as well as those advising senior theses. If History is the secondary field of a joint concentration, there is only one History reader. Each reader assigns an evaluation to the thesis (highest honors, highest honors minus, high honors plus, high honors, high honors minus, honors plus, honors, or no distinction), and writes a report detailing the special strengths and weaknesses of the thesis. Theses by students with a highest honors-level concentration GPA and one highest-level reading will automatically be assigned three readers. Additionally, a thesis by any student may be sent to a third reader when the first two evaluations are three or more distinctions apart (e.g., one high honors plus and one honors plus).
Department Standards for the Thesis Program
Seniors who wish to write a thesis must meet certain prerequisites:
- a ‘B+’ average in the concentration;
- a ‘B+’ average on a 20-page research seminar paper
- the recommendation of their Research Seminar tutor(s).
Students who do not meet the above standards may petition the History Undergraduate Office for admission to the senior thesis; successful petitions must include a detailed thesis proposal, and will be evaluated at the discretion of the Assistant Director of Undergraduate Studies (Asst. DUS).
The Awarding of Departmental Honors in History
THE AWARDING OF DEPARTMENTAL HONORS IN HISTORY
Nominations for departmental honors are made by the Board of Examiners at the degree meeting each spring. In making its nominations, the Board first takes two elements into account: the average of course grades in History and thesis readings. All students who may be eligible for a recommendation of highest honors will then be given an oral examination by the Board of Examiners; performance on this exam will be considered in determining the final recommendation. The standing of those students at the border of two different degrees may also be determined through an oral examination administered by the Board of Examiners.
To be considered eligible for highest honors in history, a student will ordinarily have a grade point average greater than or equal to 3.85 in courses taken for departmental credit, and have received at least two highest -level thesis readings. In addition, the student must convince the Board of Examiners of their qualifications for the highest recommendation through their performance on the oral examination. Whether any particular student falling into this numerical range receives highest honors in history will be determined in part by the performance on the oral examination.
To be considered eligible for high honors in history, a student will ordinarily have a grade point average greater than or equal to 3.7, and will ordinarily have received two high -level readings on the thesis.
To be considered eligible for honors in history, a student will ordinarily have a grade point average greater than or equal to 3.3, and will ordinarily have received two honors -level readings on the thesis.
Please note that the Department recommends students’ English honors (highest, high, honors, no honors) and sends these recommendations to the College which determines students’ Latin honors based on total GPA. Please visit: https://handbook.fas.harvard.edu/book/requirements-honors-degrees for more information on how the College awards Latin honors (summa cum laude, magna cum laude, cum laude, no honors). In addition, you should consult with your Resident Dean. Any degree candidate who does not receive the A.B. degree with honors in History will be considered by the FAS for the degree of cum laude.
Departmental Support
Students who do decide to enter the thesis program benefit from a great deal of departmental support. The Department encourages its thesis writers to consider the possibility of devoting the summer prior to their senior year to thesis research, whether on campus or around the world. Each year a large number of rising seniors find funding for summer thesis research. The Undergraduate Office holds a meeting to advise students on how to write a successful fellowship proposal. In addition, we maintain a listing of organizations that have supported concentrators’ thesis research.
The Department also supports its senior thesis writers through two semesters of a Senior Thesis Seminar, History 99a and 99b , which provide a useful framework for thesis writers as they work through the intermittent difficulties that all thesis students inevitably encounter. For many seniors, their thesis will turn out to be the best piece of writing done while at Harvard. It will also be the longest and most complicated. Consequently, the seminars will focus much attention on the unique challenges of writing an extended, multi-chapter work. History 99a and 99b also provide a common forum in which seniors can share with thesis-writing colleagues their feedback, successes, frustrations, interests, and techniques. This kind of collegiality and exchange of ideas is at the heart of the academic seminar, and it can be the most rewarding aspect of the seminar series.
Students must enroll in the Thesis Seminars in order to write a thesis by obtaining approval from the Asst. DUS on their study cards.
- Thinking about a History Concentration?
- Undergraduate Alumni Profiles
- Concentration Guidelines and Requirements
- Senior Thesis Grants
- Office Hours
- Research & Employment Opportunities
- Tempus: Undergraduate History Journal
- Graduate Program

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
PhD students are required to sit an oral examination, called a viva voce, as part of the assessment procedure for their degree. This video lecture gives an i...
Request for Final Oral Examination Form. You must schedule the dissertation defense with the Graduate School at least two weeks prior to the defense date by completing the Request for Final Oral Examination form. All members of your committee must sign your request form indicating their intent to be present at your final oral.
In order to graduate in a thesis program, the student must unconditionally pass the final oral exam, or clear all conditions associated with a conditional pass, AND submit a draft PDF file into the ETD Submission System for the ETD Review prior to the 5:00 p.m. ETD Review deadline for the semester in which s/he intends to graduate.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense: 1. Anticipate questions and prepare for them. You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions.
Use the following steps when preparing for the oral defense of your thesis/dissertation. 1. Evaluation of oral examination is based on your presentation and your answers to questions from the examining committee. 2. Be well prepared for your presentation—academically, mentally and physically. Try to be well rested and focused before your oral ...
RES Master's Thesis Final Oral Examination. The RES Master's Final Oral Examination is an integral part of the RES Master's Program and requires students defend their theses before they graduate. A successful defence of your Master's thesis will depend on your ability to present your research effectively and confidently.
The last two requirements are the final Ph.D. oral examination and an electronic copy of the dissertation submitted as a PDF file. The student must deliver a complete penultimate draft of the dissertation (except for the acknowledgments) to all members of the research committee at least two weeks prior to the final examination.
Each time you give a presentation, even a poster presentation, at a conference or department meeting, you're preparing for your ultimate oral exam. Prepare your act. Because a thesis defense is a formal ceremony as well as an examination, you will have to play the highly scripted part expected of you.
The oral examination is a defense of the dissertation work in progress. The student orally presents and defends the thesis work in progress at a stage when it is one-half to two-thirds complete. The oral examination committee, composed of field and nonfield faculty, tests the student on the theory and methodology underlying the research, the ...
Before the exam. As soon as you submit your thesis, prepare for your oral exam. Prepare your presentation in a clear and interesting way. Timing is crucial. You are asked to present for 20-25 minutes; if you go beyond thirty minutes it shows you cannot summarise your work. Give a brief introduction and outline your methodology.
The oral examination is a dissertation defense in which the candidate is expected to: Answer satisfactorily any questions deemed pertinent by the examining committee. The examination begins with a public presentation of research results by the PhD candidate, during which clarifying questions may be asked by members of the audience.
PhD Oral Exam. The formal presentation of the Thesis Proposal will serve as the Oral Examination. The purpose of the Oral Exam is to test the student's ability to explain their thesis project, defend their scientific rationale, and propose alternate approaches, as necessary. The nature of the proposal may vary, depending on the project, but ...
In-person oral examination: In-person examinations may be delayed depending on the availability of the examiners as travel time will need to be factored in. Students who are overseas and returning to Cambridge for their viva should contact the International Student Office for visa advice if their student visa has expired or will be expiring soon.
The detailed Final Oral Defence procedures are outlined in the Exam Instructions. A copy of these instructions is provided to the examining committee approximately one week before the Oral Defence. The basic structure of the Oral Defence is: Candidate makes a public presentation of the dissertation (maximum 30 minutes) Examining committee ...
The dissertation and final public oral examination together serve as a culminating experience that showcases a doctoral candidate's mastery of and emerging contributions to their field. Students are encouraged to visit the Advanced Degree Application page for a detailed outline of steps both prior to and following the FPO that culminate in ...
The Thesis Proposal/Oral Exam must take place by December 1 of the 3rd year, with the specific date scheduled before the beginning of the Fall Semester of the third year. If the student and advisor are convinced that a delay would serve the student's interests better, they must petition the Graduate Committee by August 1st of the summer ...
If you need assistance preparing for your dissertation defense or viva voce, get in touch with us to discuss 1-on-1 coaching. We can critically review your research and identify potential issues and responses, as well as undertake a mock oral defense to prepare you for the pressures and stresses on the day.
The external examination of a HDR candidate is a 2-part process consisting of a thesis evaluation and an oral examination. Each of these parts is linked to the following outputs: Thesis evaluation: a summary and a written report from each examiner. Oral examination: a Chair's report summarising the feedback of the examiners and recommendation ...
Summary. A PhD viva involves defending your thesis in an oral examination with at least two examiners.; The aim of a PhD viva is to confirm that the work is your own, that you have a deep understanding of your project and, overall, that you are a competent researcher.; There are no standard durations, but they usually range from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours.
If the oral examination is failed, a second attempt at the oral defence of the thesis may be scheduled in accordance with Academic Guide. The nature of required revisions, prior to submission of the final copy of the thesis to MSpace as well as the procedures for their completion is determined by the chair, in discussion with the examining ...
Thesis examination is a core assessment required in all higher degree research (HDR) programs. This procedure outlines the processes for preparation, submission and examination of the thesis component of all HDR programs. It also includes the roles and responsibilities of higher degree research (HDR) candidates, supervisors, Postgraduate ...
Thesis examination - my.UQ - University of Queensland. 3. Thesis examination. If you have submitted your thesis for examination via UQ eSpace please read this document for information on how your examination will progress. You can track the progress of your examination via the HDR Thesis examination request in my.UQ. 1. Receiving examiner reports.
Senior Thesis & Undergraduate Research. Every year, approximately 45%-55% of senior History concentrators choose to cap their Harvard careers by writing a senior honors thesis. The senior thesis tutorial is a two-semester sequence comprising Hist 99a and Hist 99b. While the overwhelming majority of students who start a thesis choose to complete ...