Education articles from across Nature Portfolio

How to stop students cramming for exams? Send them to sea
An innovative proposal to stop exam over-preparation, plus William Bateson’s 1924 take on the previous century of biology, in the weekly dip into Nature ’s archive.
Latest Research and Reviews
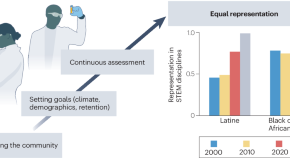
Framework for department-level accountability to diversify engineering
University departments may benefit from guidelines not only to craft effective diversity, equity and inclusion plans, but also to measure progress towards achieving specific goals. This Perspective presents a framework for building, assessing and continuously improving strategic plans to improve recruitment and retention and make departments more inclusive.
- Jacqueline C. Linnes
- Erika Moore
- Rebecca Kuntz Willits
Longitudinal trajectories of self-esteem, related predictors, and impact on depression among students over a four-year period at college in China
- Xinqiao Liu
- Yunfeng Luo
Why English? Exploring Chinese early career returnee academics’ motivations for writing and publishing in English
- Xiantong Zhao
Confidence of Emergency Department doctors in managing ophthalmic emergencies: a systematic review
- Jessica Mendall
- Abraham Tolley
- Victoria Nowak
From vocation to profession: multiple identities of Chinese management academics
- Qiuli Huang
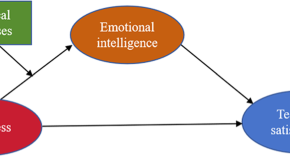
The moderating effect of physical exercises on job stress, emotional intelligence, and teaching satisfaction among Chinese University teachers
- Kuen Fung Sin
News and Comment
Teaching artificial intelligence in medicine.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is finding its way into healthcare. Therefore, medical students need to be trained to be ‘bilingual’ in both medical and computational terminology and concepts to allow them to understand, implement and evaluate AI-related research.
- Yosra Magdi Mekki
- Susu M. Zughaier
Reply to letter regarding ‘Descemet’s membrane or confirmation of a novel corneal structure: the layer of Dua’
- Yannis Athanasiadis
- Michael Tsatsos
- Georgios Labiris

Research culture in biomedicine: what we learned, and what we would like to do about it
This comment reports on work done at Harvard Medical School to identify areas for improvement in research rigor, reproducibility, and responsibility in pursuit of continued research excellence.
- Alexa T. McCray
- David Van Vactor
- Mary C. Walsh

The power of putting education first
From high school to distinguished professor of chemistry at Rhodes University, Tebello Nyokong discusses her inspiration and ambitions to promote science in South Africa.
- Tebello Nyokong
- Stephanie Greed
Beyond the microscope: embracing soft skills in ophthalmology for enhanced patient care and clinician well-being
- Gilles C. MARTIN
- Issam TANOUBI
- Frédéric MOURIAUX
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

On The Site
Harvard educational review.
Edited by Maya Alkateb-Chami, Jane Choi, Jeannette Garcia Coppersmith, Ron Grady, Phoebe A. Grant-Robinson, Pennie M. Gregory, Jennifer Ha, Woohee Kim, Catherine E. Pitcher, Elizabeth Salinas, Caroline Tucker, Kemeyawi Q. Wahpepah

Individuals
Institutions.
- Read the journal here
Journal Information
- ISSN: 0017-8055
- eISSN: 1943-5045
- Keywords: scholarly journal, education research
- First Issue: 1930
- Frequency: Quarterly
Description
The Harvard Educational Review (HER) is a scholarly journal of opinion and research in education. The Editorial Board aims to publish pieces from interdisciplinary and wide-ranging fields that advance our understanding of educational theory, equity, and practice. HER encourages submissions from established and emerging scholars, as well as from practitioners working in the field of education. Since its founding in 1930, HER has been central to elevating pieces and debates that tackle various dimensions of educational justice, with circulation to researchers, policymakers, teachers, and administrators.
Our Editorial Board is composed entirely of doctoral students from the Harvard Graduate School of Education who review all manuscripts considered for publication. For more information on the current Editorial Board, please see here.
A subscription to the Review includes access to the full-text electronic archives at our Subscribers-Only-Website .
Editorial Board
2023-2024 Harvard Educational Review Editorial Board Members
Maya Alkateb-Chami Development and Partnerships Editor, 2023-2024 Editor, 2022-2024 [email protected]
Maya Alkateb-Chami is a PhD student at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Her research focuses on the role of schooling in fostering just futures—specifically in relation to language of instruction policies in multilingual contexts and with a focus on epistemic injustice. Prior to starting doctoral studies, she was the Managing Director of Columbia University’s Human Rights Institute, where she supported and co-led a team of lawyers working to advance human rights through research, education, and advocacy. Prior to that, she was the Executive Director of Jusoor, a nonprofit organization that helps conflict-affected Syrian youth and children pursue their education in four countries. Alkateb-Chami is a Fulbright Scholar and UNESCO cultural heritage expert. She holds an MEd in Language and Literacy from Harvard University; an MSc in Education from Indiana University, Bloomington; and a BA in Political Science from Damascus University, and her research on arts-based youth empowerment won the annual Master’s Thesis Award of the U.S. Society for Education Through Art.
Jane Choi Editor, 2023-2025
Jane Choi is a second-year PhD student in Sociology with broad interests in culture, education, and inequality. Her research examines intra-racial and interracial boundaries in US educational contexts. She has researched legacy and first-generation students at Ivy League colleges, families served by Head Start and Early Head Start programs, and parents of pre-K and kindergarten-age children in the New York City School District. Previously, Jane worked as a Research Assistant in the Family Well-Being and Children’s Development policy area at MDRC and received a BA in Sociology from Columbia University.
Jeannette Garcia Coppersmith Content Editor, 2023-2024 Editor, 2022-2024 [email protected]
Jeannette Garcia Coppersmith is a fourth-year Education PhD student in the Human Development, Learning and Teaching concentration at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. A former public middle and high school mathematics teacher and department chair, she is interested in understanding the mechanisms that contribute to disparities in secondary mathematics education, particularly how teacher beliefs and biases intersect with the social-psychological processes and pedagogical choices involved in math teaching. Jeannette holds an EdM in Learning and Teaching from the Harvard Graduate School of Education where she studied as an Urban Scholar and a BA in Environmental Sciences from the University of California, Berkeley.
Ron Grady Editor, 2023-2025
Ron Grady is a second-year doctoral student in the Human Development, Learning, and Teaching concentration at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. His central curiosities involve the social worlds and peer cultures of young children, wondering how lived experience is both constructed within and revealed throughout play, the creation of art and narrative, and through interaction with/production of visual artifacts such as photography and film. Ron also works extensively with educators interested in developing and deepening practices rooted in reflection on, inquiry into, and translation of the social, emotional, and aesthetic aspects of their classroom ecosystems. Prior to his doctoral studies, Ron worked as a preschool teacher in New Orleans. He holds a MS in Early Childhood Education from the Erikson Institute and a BA in Psychology with Honors in Education from Stanford University.
Phoebe A. Grant-Robinson Editor, 2023-2024
Phoebe A. Grant-Robinson is a first year student in the Doctor of Education Leadership(EdLD) program at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Her ultimate quest is to position all students as drivers of their destiny. Phoebe is passionate about early learning and literacy. She is committed to ensuring that districts and school leaders, have the necessary tools to create equitable learning organizations that facilitate the academic and social well-being of all students. Phoebe is particularly interested in the intersection of homeless students and literacy. Prior to her doctoral studies, Phoebe was a Special Education Instructional Specialist. Supporting a portfolio of more than thirty schools, she facilitated the rollout of New York City’s Special Education Reform. Phoebe also served as an elementary school principal. She holds a BS in Inclusive Education from Syracuse University, and an MS in Curriculum and Instruction from Pace University.
Pennie M. Gregory Editor, 2023-2024
Pennie M. Gregory is a second-year student in the Doctor of Education Leadership (EdLD) program at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Pennie was born in Incheon, South Korea and raised in Gary, Indiana. She has decades of experience leading efforts to improve outcomes for students with disabilities first as a special education teacher and then as a school district special education administrator. Prior to her doctoral studies, Pennie helped to create Indiana’s first Aspiring Special Education Leadership Institute (ASELI) and served as its Director. She was also the Capacity Events Director for MelanatED Leaders, an organization created to support educational leaders of color in Indianapolis. Pennie has a unique perspective, having worked with members of the school community, with advocacy organizations, and supporting state special education leaders. Pennie holds an EdM in Education Leadership from Marian University.
Jennifer Ha Editor, 2023-2025
Jen Ha is a second-year PhD student in the Culture, Institutions, and Society concentration at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Her research explores how high school students learn to write personal narratives for school applications, scholarships, and professional opportunities amidst changing landscapes in college access and admissions. Prior to doctoral studies, Jen served as the Coordinator of Public Humanities at Bard Graduate Center and worked in several roles organizing academic enrichment opportunities and supporting postsecondary planning for students in New Haven and New York City. Jen holds a BA in Humanities from Yale University, where she was an Education Studies Scholar.
Woohee Kim Editor, 2023-2025
Woohee Kim is a PhD student studying youth activists’ civic and pedagogical practices. She is a scholar-activist dedicated to creating spaces for pedagogies of resistance and transformative possibilities. Shaped by her activism and research across South Korea, the US, and the UK, Woohee seeks to interrogate how educational spaces are shaped as cultural and political sites and reshaped by activists as sites of struggle. She hopes to continue exploring the intersections of education, knowledge, power, and resistance.
Catherine E. Pitcher Editor, 2023-2025
Catherine is a second-year doctoral student at Harvard Graduate School of Education in the Culture, Institutions, and Society program. She has over 10 years of experience in education in the US in roles that range from special education teacher to instructional coach to department head to educational game designer. She started working in Palestine in 2017, first teaching, and then designing and implementing educational programming. Currently, she is working on research to understand how Palestinian youth think about and build their futures and continues to lead programming in the West Bank, Gaza, and East Jerusalem. She holds an EdM from Harvard in International Education Policy.
Elizabeth Salinas Editor, 2023-2025
Elizabeth Salinas is a doctoral student in the Education Policy and Program Evaluation concentration at HGSE. She is interested in the intersection of higher education and the social safety net and hopes to examine policies that address basic needs insecurity among college students. Before her doctoral studies, Liz was a research director at a public policy consulting firm. There, she supported government, education, and philanthropy leaders by conducting and translating research into clear and actionable information. Previously, Liz served as a high school physics teacher in her hometown in Texas and as a STEM outreach program director at her alma mater. She currently sits on the Board of Directors at Leadership Enterprise for a Diverse America, a nonprofit organization working to diversify the leadership pipeline in the United States. Liz holds a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a master’s degree in higher education from the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Caroline Tucker Co-Chair, 2023-2024 Editor, 2022-2024 [email protected]
Caroline Tucker is a fourth-year doctoral student in the Culture, Institutions, and Society concentration at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Her research focuses on the history and organizational dynamics of women’s colleges as women gained entry into the professions and coeducation took root in the United States. She is also a research assistant for the Harvard and the Legacy of Slavery Initiative’s Subcommittee on Curriculum and the editorial assistant for Into Practice, the pedagogy newsletter distributed by Harvard University’s Office of the Vice Provost for Advances in Learning. Prior to her doctoral studies, Caroline served as an American politics and English teaching fellow in London and worked in college advising. Caroline holds a BA in History from Princeton University, an MA in the Social Sciences from the University of Chicago, and an EdM in Higher Education from the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Kemeyawi Q. Wahpepah Co-Chair, 2023-2024 Editor, 2022-2024 [email protected]
Kemeyawi Q. Wahpepah (Kickapoo, Sac & Fox) is a fourth-year doctoral student in the Culture, Institutions, and Society concentration at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Their research explores how settler colonialism is addressed in K-12 history and social studies classrooms in the United States. Prior to their doctoral studies, Kemeyawi taught middle and high school English and history for eleven years in Boston and New York City. They hold an MS in Middle Childhood Education from Hunter College and an AB in Social Studies from Harvard University.
Submission Information
Click here to view submission guidelines .
Contact Information
Click here to view contact information for the editorial board and customer service .
Subscriber Support
Individual subscriptions must have an individual name in the given address for shipment. Individual copies are not for multiple readers or libraries. Individual accounts come with a personal username and password for access to online archives. Online access instructions will be attached to your order confirmation e-mail.
Institutional rates apply to libraries and organizations with multiple readers. Institutions receive digital access to content on Meridian from IP addresses via theIPregistry.org (by sending HER your PSI Org ID).
Online access instructions will be attached to your order confirmation e-mail. If you have questions about using theIPregistry.org you may find the answers in their FAQs. Otherwise please let us know at [email protected] .
How to Subscribe
To order online via credit card, please use the subscribe button at the top of this page.
To order by phone, please call 888-437-1437.
Checks can be mailed to Harvard Educational Review C/O Fulco, 30 Broad Street, Suite 6, Denville, NJ 07834. (Please include reference to your subscriber number if you are renewing. Institutions must include their PSI Org ID or follow up with this information via email to [email protected] .)
Permissions
Click here to view permissions information.
Article Submission FAQ
Submissions, question: “what manuscripts are a good fit for her ”.
Answer: As a generalist scholarly journal, HER publishes on a wide range of topics within the field of education and related disciplines. We receive many articles that deserve publication, but due to the restrictions of print publication, we are only able to publish very few in the journal. The originality and import of the findings, as well as the accessibility of a piece to HER’s interdisciplinary, international audience which includes education practitioners, are key criteria in determining if an article will be selected for publication.
We strongly recommend that prospective authors review the current and past issues of HER to see the types of articles we have published recently. If you are unsure whether your manuscript is a good fit, please reach out to the Content Editor at [email protected] .
Question: “What makes HER a developmental journal?”
Answer: Supporting the development of high-quality education research is a key tenet of HER’s mission. HER promotes this development through offering comprehensive feedback to authors. All manuscripts that pass the first stage of our review process (see below) receive detailed feedback. For accepted manuscripts, HER also has a unique feedback process called casting whereby two editors carefully read a manuscript and offer overarching suggestions to strengthen and clarify the argument.
Question: “What is a Voices piece and how does it differ from an essay?”
Answer: Voices pieces are first-person reflections about an education-related topic rather than empirical or theoretical essays. Our strongest pieces have often come from educators and policy makers who draw on their personal experiences in the education field. Although they may not present data or generate theory, Voices pieces should still advance a cogent argument, drawing on appropriate literature to support any claims asserted. For examples of Voices pieces, please see Alvarez et al. (2021) and Snow (2021).
Question: “Does HER accept Book Note or book review submissions?”
Answer: No, all Book Notes are written internally by members of the Editorial Board.
Question: “If I want to submit a book for review consideration, who do I contact?”
Answer: Please send details about your book to the Content Editor at [email protected].
Manuscript Formatting
Question: “the submission guidelines state that manuscripts should be a maximum of 9,000 words – including abstract, appendices, and references. is this applicable only for research articles, or should the word count limit be followed for other manuscripts, such as essays”.
Answer: The 9,000-word limit is the same for all categories of manuscripts.
Question: “We are trying to figure out the best way to mask our names in the references. Is it OK if we do not cite any of our references in the reference list? Our names have been removed in the in-text citations. We just cite Author (date).”
Answer: Any references that identify the author/s in the text must be masked or made anonymous (e.g., instead of citing “Field & Bloom, 2007,” cite “Author/s, 2007”). For the reference list, place the citations alphabetically as “Author/s. (2007)” You can also indicate that details are omitted for blind review. Articles can also be blinded effectively by use of the third person in the manuscript. For example, rather than “in an earlier article, we showed that” substitute something like “as has been shown in Field & Bloom, 2007.” In this case, there is no need to mask the reference in the list. Please do not submit a title page as part of your manuscript. We will capture the contact information and any author statement about the fit and scope of the work in the submission form. Finally, please save the uploaded manuscript as the title of the manuscript and do not include the author/s name/s.
Invitations
Question: “can i be invited to submit a manuscript how”.
Answer: If you think your manuscript is a strong fit for HER, we welcome a request for invitation. Invited manuscripts receive one round of feedback from Editors before the piece enters the formal review process. To submit information about your manuscript, please complete the Invitation Request Form . Please provide as many details as possible. The decision to invite a manuscript largely depends on the capacity of current Board members and on how closely the proposed manuscript reflects HER publication scope and criteria. Once you submit the form, We hope to update you in about 2–3 weeks, and will let you know whether there are Editors who are available to invite the manuscript.
Review Timeline
Question: “who reviews manuscripts”.
Answer: All manuscripts are reviewed by the Editorial Board composed of doctoral students at Harvard University.
Question: “What is the HER evaluation process as a student-run journal?”
Answer: HER does not utilize the traditional external peer review process and instead has an internal, two-stage review procedure.
Upon submission, every manuscript receives a preliminary assessment by the Content Editor to confirm that the formatting requirements have been carefully followed in preparation of the manuscript, and that the manuscript is in accord with the scope and aim of the journal. The manuscript then formally enters the review process.
In the first stage of review, all manuscripts are read by a minimum of two Editorial Board members. During the second stage of review, manuscripts are read by the full Editorial Board at a weekly meeting.
Question: “How long after submission can I expect a decision on my manuscript?”
Answer: It usually takes 6 to 10 weeks for a manuscript to complete the first stage of review and an additional 12 weeks for a manuscript to complete the second stage. Due to time constraints and the large volume of manuscripts received, HER only provides detailed comments on manuscripts that complete the second stage of review.
Question: “How soon are accepted pieces published?”
Answer: The date of publication depends entirely on how many manuscripts are already in the queue for an issue. Typically, however, it takes about 6 months post-acceptance for a piece to be published.
Submission Process
Question: “how do i submit a manuscript for publication in her”.
Answer: Manuscripts are submitted through HER’s Submittable platform, accessible here. All first-time submitters must create an account to access the platform. You can find details on our submission guidelines on our Submissions page.
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Our Best Education Articles of 2020
In February of 2020, we launched the new website Greater Good in Education , a collection of free, research-based and -informed strategies and practices for the social, emotional, and ethical development of students, for the well-being of the adults who work with them, and for cultivating positive school cultures. Little did we know how much more crucial these resources would become over the course of the year during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Now, as we head back to school in 2021, things are looking a lot different than in past years. Our most popular education articles of 2020 can help you manage difficult emotions and other challenges at school in the pandemic, all while supporting the social-emotional well-being of your students.
In addition to these articles, you can also find tips, tools, and recommended readings in two resource guides we created in 2020: Supporting Learning and Well-Being During the Coronavirus Crisis and Resources to Support Anti-Racist Learning , which helps educators take action to undo the racism within themselves, encourage their colleagues to do the same, and teach and support their students in forming anti-racist identities.

Here are the 10 best education articles of 2020, based on a composite ranking of pageviews and editors’ picks.
Can the Lockdown Push Schools in a Positive Direction? , by Patrick Cook-Deegan: Here are five ways that COVID-19 could change education for the better.
How Teachers Can Navigate Difficult Emotions During School Closures , by Amy L. Eva: Here are some tools for staying calm and centered amid the coronavirus crisis.
Six Online Activities to Help Students Cope With COVID-19 , by Lea Waters: These well-being practices can help students feel connected and resilient during the pandemic.
Help Students Process COVID-19 Emotions With This Lesson Plan , by Maurice Elias: Music and the arts can help students transition back to school this year.
How to Teach Online So All Students Feel Like They Belong , by Becki Cohn-Vargas and Kathe Gogolewski: Educators can foster belonging and inclusion for all students, even online.
How Teachers Can Help Students With Special Needs Navigate Distance Learning , by Rebecca Branstetter: Kids with disabilities are often shortchanged by pandemic classroom conditions. Here are three tips for educators to boost their engagement and connection.
How to Reduce the Stress of Homeschooling on Everyone , by Rebecca Branstetter: A school psychologist offers advice to parents on how to support their child during school closures.
Three Ways to Help Your Kids Succeed at Distance Learning , by Christine Carter: How can parents support their children at the start of an uncertain school year?
How Schools Are Meeting Social-Emotional Needs During the Pandemic , by Frances Messano, Jason Atwood, and Stacey Childress: A new report looks at how schools have been grappling with the challenges imposed by COVID-19.
Six Ways to Help Your Students Make Sense of a Divisive Election , by Julie Halterman: The election is over, but many young people will need help understanding what just happened.
Train Your Brain to Be Kinder (video), by Jane Park: Boost your kindness by sending kind thoughts to someone you love—and to someone you don’t get along with—with a little guidance from these students.
From Othering to Belonging (podcast): We speak with john a. powell, director of the Othering & Belonging Institute, about racial justice, well-being, and widening our circles of human connection and concern.
About the Author
Greater good editors.
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Education →

- 13 May 2024
- Research & Ideas
Picture This: Why Online Image Searches Drive Purchases
Smaller sellers' products often get lost on large online marketplaces. However, harnessing images in search can help consumers find these products faster, increasing sales and customer satisfaction, finds research by Chiara Farronato and colleagues.

- 26 Mar 2024
How Humans Outshine AI in Adapting to Change
Could artificial intelligence systems eventually perform surgeries or fly planes? First, AI will have to learn to navigate shifting conditions as well as people do. Julian De Freitas and colleagues pit humans against machines in a video game to study AI's current limits and mine insights for the real world.

- 12 Mar 2024
Publish or Perish: What the Research Says About Productivity in Academia
Universities tend to evaluate professors based on their research output, but does that measure reflect the realities of higher ed? A study of 4,300 professors by Kyle Myers, Karim Lakhani, and colleagues probes the time demands, risk appetite, and compensation of faculty.

- 25 Jan 2024

Being a Team Player: Why College Athletes Succeed in Business
Forget rocks for jocks. A study by Paul Gompers of more than 400,000 Ivy League athletes probes how the rigors of college sports can help people climb the corporate ladder faster and into higher-paying positions.

- 19 Dec 2023
$15 Billion in Five Years: What Data Tells Us About MacKenzie Scott’s Philanthropy
Scott's hands-off approach and unparalleled pace—helping almost 2,000 organizations and counting—has upended the status quo in philanthropy. While her donations might seem scattershot, an analysis of five years of data by Matthew Lee, Brian Trelstad, and Ethan Tran highlights clear trends and an emerging strategy.

- 21 Nov 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
Cold Call: Building a More Equitable Culture at Delta Air Lines
In December 2020 Delta Air Lines CEO Ed Bastian and his leadership team were reviewing the decision to join the OneTen coalition, where he and 36 other CEOs committed to recruiting, hiring, training, and advancing one million Black Americans over the next ten years into family-sustaining jobs. But, how do you ensure everyone has equal access to opportunity within an organization? Professor Linda Hill discusses Delta’s decision and its progress in embedding a culture of diversity, equity, and inclusion in her case, “OneTen at Delta Air Lines: Catalyzing Family-Sustaining Careers for Black Talent.”

- 16 Oct 2023
Advancing Black Talent: From the Flight Ramp to 'Family-Sustaining' Careers at Delta
By emphasizing skills and expanding professional development opportunities, the airline is making strides toward recruiting and advancing Black employees. Case studies by Linda Hill offer an inside look at how Delta CEO Ed Bastian is creating a more equitable company and a stronger talent pipeline.

- 26 Jul 2023
STEM Needs More Women. Recruiters Often Keep Them Out
Tech companies and programs turn to recruiters to find top-notch candidates, but gender bias can creep in long before women even apply, according to research by Jacqueline Ng Lane and colleagues. She highlights several tactics to make the process more equitable.

- 14 Jun 2023
Four Steps to Building the Psychological Safety That High-Performing Teams Need
Struggling to spark strategic risk-taking and creative thinking? In the post-pandemic workplace, teams need psychological safety more than ever, and a new analysis by Amy Edmondson highlights the best ways to nurture it.

- 23 May 2023
The Entrepreneurial Journey of China’s First Private Mental Health Hospital
The city of Wenzhou in southeastern China is home to the country’s largest privately owned mental health hospital group, the Wenzhou Kangning Hospital Co, Ltd. It’s an example of the extraordinary entrepreneurship happening in China’s healthcare space. But after its successful initial public offering (IPO), how will the hospital grow in the future? Harvard Professor of China Studies William C. Kirby highlights the challenges of China’s mental health sector and the means company founder Guan Weili employed to address them in his case, Wenzhou Kangning Hospital: Changing Mental Healthcare in China.

- 28 Feb 2023
Can Apprenticeships Work in the US? Employers Seeking New Talent Pipelines Take Note
What if the conventional college-and-internship route doesn't give future employees the skills they need to build tomorrow's companies? Research by Joseph Fuller and colleagues illustrates the advantages that apprenticeships can provide to employees and young talent.

- 15 Aug 2022
University of the Future: Finding the Next World Leaders in Higher Ed
Which universities will step into the void as American colleges decline? In the book Empires of Ideas, William Kirby explores how the history of higher education in the US, China, and Germany might shape its future.

- 11 Aug 2022
When Parents Tell Kids to ‘Work Hard,’ Do They Send the Wrong Message?
It takes more than grit to succeed in a world rife with systemic inequity. So why don't we tell children that? Research by Ashley Whillans and colleagues shows how honest talk about social barriers could empower kids to break them down.

- 02 May 2022
- What Do You Think?
Can the Case Method Survive Another Hundred Years?
The case method pioneered by Harvard Business School has weathered a hundred years of controversy and criticism. However, is the approach the best way to teach people to lead in a world that demands more agility and adaptability? James Heskett asks. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 18 Nov 2021
5 Principles for Scaling Change from IBM’s High School Innovation
P-TECH has bolstered graduation rates for students of color while creating a new tech hiring pipeline. Rosabeth Moss Kanter and program architect Stanley Litow discuss the social impact lessons for other organizations. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 09 Aug 2021
OneTen: Creating a New Pathway for Black Talent
A new organization aims to help 1 million Black Americans launch careers in the next decade, expanding the talent pool. Rawi E. Abdelal, Katherine Connolly Baden, and Boris Groysberg explain how. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 19 May 2021
Why America Needs a Better Bridge Between School and Career
As the COVID-19 pandemic wanes, America faces a critical opportunity to close gaps that leave many workers behind, say Joseph Fuller and Rachel Lipson. What will it take? Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 18 May 2021
How Georgia State University Increased Graduation Rates
Georgia State University was facing a growing "summer melt" problem, where nearly 20 percent of incoming students never actually enrolled. The university used a data-based approach to retain students of all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic backgrounds and help them graduate. Professor Mike Toffel> and Harvard Advanced Leadership Initiative fellow Robin Mendelson discuss what the university learned about improving student success, while scaling its efforts to help other universities, in their case, “Student Success at Georgia State University.” Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 13 Apr 2021
- Working Paper Summaries
Population Interference in Panel Experiments
In panel experiments, units are exposed to different interventions over time. This article introduces a unifying framework for studying panel experiments with population interference, in which a treatment assigned to one experimental unit affects another experimental unit's outcome. Findings have implications for fields as diverse as education, economics, and public health.

- 23 Mar 2021
Managing Future Growth at an Innovative Workforce Education Startup
Guild Education is an education marketplace that connects employers and universities to provide employees with “education as a benefit.” Now CEO and co-founder Rachel Carlson must decide how to manage the company’s future growth. Professor Bill Sahlman discusses this unique startup and Carlson’s plans for its growth in his case, “Guild Education: Unlocking Opportunity for America's Workforce.” Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
70 years after brown v. board of education, new research shows rise in school segregation.

As the nation prepares to mark the 70th anniversary of the landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education , a new report from researchers at Stanford and USC shows that racial and economic segregation among schools has grown steadily in large school districts over the past three decades — an increase that appears to be driven in part by policies favoring school choice over integration.
Analyzing data from U.S. public schools going back to 1967, the researchers found that segregation between white and Black students has increased by 64 percent since 1988 in the 100 largest districts, and segregation by economic status has increased by about 50 percent since 1991.
The report also provides new evidence about the forces driving recent trends in school segregation, showing that the expansion of charter schools has played a major role.
The findings were released on May 6 with the launch of the Segregation Explorer , a new interactive website from the Educational Opportunity Project at Stanford University. The website provides searchable data on racial and economic school segregation in U.S. states, counties, metropolitan areas, and school districts from 1991 to 2022.
“School segregation levels are not at pre- Brown levels, but they are high and have been rising steadily since the late 1980s,” said Sean Reardon , the Professor of Poverty and Inequality in Education at Stanford Graduate School of Education and faculty director of the Educational Opportunity Project. “In most large districts, school segregation has increased while residential segregation and racial economic inequality have declined, and our findings indicate that policy choices – not demographic changes – are driving the increase.”
“There’s a tendency to attribute segregation in schools to segregation in neighborhoods,” said Ann Owens , a professor of sociology and public policy at USC. “But we’re finding that the story is more complicated than that.”
Assessing the rise
In the Brown v. Board decision issued on May 17, 1954, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that racially segregated public schools violated the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment and established that “separate but equal” schools were not only inherently unequal but unconstitutional. The ruling paved the way for future decisions that led to rapid school desegregation in many school districts in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Though segregation in most school districts is much lower than it was 60 years ago, the researchers found that over the past three decades, both racial and economic segregation in large districts increased. Much of the increase in economic segregation since 1991, measured by segregation between students eligible and ineligible for free lunch, occurred in the last 15 years.
White-Hispanic and white-Asian segregation, while lower on average than white-Black segregation, have both more than doubled in large school districts since the 1980s.
Racial-economic segregation – specifically the difference in the proportion of free-lunch-eligible students between the average white and Black or Hispanic student’s schools – has increased by 70 percent since 1991.
School segregation is strongly associated with achievement gaps between racial and ethnic groups, especially the rate at which achievement gaps widen during school, the researchers said.
“Segregation appears to shape educational outcomes because it concentrates Black and Hispanic students in higher-poverty schools, which results in unequal learning opportunities,” said Reardon, who is also a senior fellow at the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research and a faculty affiliate of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning .
Policies shaping recent trends
The recent rise in school segregation appears to be the direct result of educational policy and legal decisions, the researchers said.
Both residential segregation and racial disparities in income declined between 1990 and 2020 in most large school districts. “Had nothing else changed, that trend would have led to lower school segregation,” said Owens.
But since 1991, roughly two-thirds of districts that were under court-ordered desegregation have been released from court oversight. Meanwhile, since 1998, the charter sector – a form of expanded school choice – has grown.
Expanding school choice could influence segregation levels in different ways: If families sought schools that were more diverse than the ones available in their neighborhood, it could reduce segregation. But the researchers found that in districts where the charter sector expanded most rapidly in the 2000s and 2010s, segregation grew the most.
The researchers’ analysis also quantified the extent to which the release from court orders accounted for the rise in school segregation. They found that, together, the release from court oversight and the expansion of choice accounted entirely for the rise in school segregation from 2000 to 2019.
The researchers noted enrollment policies that school districts can implement to mitigate segregation, such as voluntary integration programs, socioeconomic-based student assignment policies, and school choice policies that affirmatively promote integration.
“School segregation levels are high, troubling, and rising in large districts,” said Reardon. “These findings should sound an alarm for educators and policymakers.”
Additional collaborators on the project include Demetra Kalogrides, Thalia Tom, and Heewon Jang. This research, including the development of the Segregation Explorer data and website, was supported by the Russell Sage Foundation, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- New! Member Benefit New! Member Benefit
- Featured Analytics Hub
- Resources Resources
- Member Directory
- Networking Communities
- Advertise, Exhibit, Sponsor
- Find or Post Jobs
- Learn and Engage Learn and Engage
- Bridge Program
- Compare AACSB-Accredited Schools
- Explore Programs
- Advocacy Advocacy
- Featured AACSB Announces 2024 Class of Influential Leaders
- Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging
- Influential Leaders
- Innovations That Inspire
- Connect With Us Connect With Us
- Accredited School Search
- Accreditation
- Learning and Events
- Advertise, Sponsor, Exhibit
- Tips and Advice
- Is Business School Right for Me?
Recognizing the Value of Educational Research
- A recent survey shows that research on teaching and learning is not valued at many AACSB-accredited schools across the U.S. and Canada.
- One reason that business schools might not recognize research on teaching and learning is that the journal quality lists they commonly use to assess faculty intellectual contributions focus primarily on discipline-based scholarship.
- STEM fields already place equal value on research on teaching and learning within individual disciplines. By following their lead, two Canadian scholars argue, business schools will enrich their students’ learning experiences.
If business educators were asked to define the purpose of business schools, they likely would emphasize the need to “prepare the next generation of leaders.” But if this is the case, why do so few business schools prioritize research that advances teaching and curricular design?
Researcher Sanobar Siddiqui first explored this question as the subject of her doctoral dissertation. “One of my thesis findings was that the tenure system’s lack of rewards impedes business academics from pursuing research in teaching and learning,” she explains.
Now an assistant professor of accounting at the University of Regina’s Faculty of Business Administration in Canada, Siddiqui wanted to learn why so many business schools do not value research on teaching and learning (RoTL). This response is puzzling, she says, given that Standard 7 of the AACSB Business Accreditation Standards accepts “scholarship of teaching and learning” as documentation to indicate a business school’s teaching effectiveness and impact.
She and Camillo Lento, a professor with the Faculty of Business Administration at Lakehead University in Thunder Bay, Ontario, published a paper on the status of RoTL in the April 2022 edition of the International Journal of Educational Management . The paper’s findings are based on a survey in which Siddiqui and Lento asked educators two questions:
- How do AACSB-accredited business schools in the U.S. and Canada define “teaching effectiveness,” according to AACSB’s Standard 7?
- Do these schools consider research on teaching and learning in their promotion and tenure decisions?
This topic is particularly important, says Siddiqui, because business schools serve such diverse student audiences. Moreover, learner success is integral to every business school’s mission. Many of the instructional strategies “that we use in class are not research-informed or evidence-based. Hence, we are shortchanging our students,” she says. “Our teaching needs to catch up with the changes we see in our classroom.”
‘A Last Priority’
Siddiqui and Lento received 78 responses to their survey; in the second phase of their study, they conducted semi-structured interviews with 11 educators in the U.S. and Canada.
Among survey respondents, 42 percent noted that they were “unaware of an explicit teaching effectiveness definition” at their schools, but 58 percent said the policies in place at their schools communicated “an implied definition.” Only one respondent could quote a definition of teaching effectiveness from the school’s website.
Respondents noted a lack of “perceived respect and value” for RoTL, describing this line of scholarship as “a last priority” at their schools. As one educator put it, “Our department does not really care about teaching as long as you are cranking out strong scholarship.”
Schools that consider educational research for tenure and faculty qualification tend to focus on journal quality alone, not on whether published articles are discipline-based.
The good news is that 55 percent of respondents noted that their schools did take RoTL into account when making tenure decisions. Siddiqui and Lento found that these schools have two things in common. First, they focus on journal quality alone for the purposes of tenure and faculty qualification, not on whether faculty’s published articles are discipline-based.
Second, these schools are more likely to consider RoTL when faculty include this work “as part of a larger research plan that includes discipline-based research.” Only faculty following teaching tracks are likely to receive tenure based solely on publications in education-focused journals.
Additionally, teaching-oriented schools are more likely than research-oriented schools to recognize RoTL. While this makes outward sense, Siddiqui wonders why prolific faculty who produce innovative scholarship on pedagogical issues that are critical to business education cannot “be hired, promoted, and awarded just like discipline-based researchers” at research-oriented institutions.
What Perpetuates the Stigma?
Siddiqui and Lento point to several factors that could be driving the lack of recognition of RoTL among AACSB-accredited schools:
No consensus about teaching quality. Although many individual educational institutions have defined teaching effectiveness based on existing research, business schools have not yet established a shared definition of what constitutes effective teaching. However, the co-authors emphasize, more dedicated research could produce findings that inspire a common language around teaching and learning.
The complex nature of determining teaching quality. Schools often evaluate the quality of faculty’s research by whether the work appears in academic journals that are rated highly by certain journal quality lists . However, they find they cannot use a similar approach to evaluate the quality of faculty’s teaching, says Lento. “The evaluation of teaching effectiveness is much more complex and requires many more sources of information, possibly compiled into a teaching dossier that is unique to an educator.”
A lack of attention in business doctoral programs. Most doctoral programs train young researchers to study topics related to their disciplines of choice. As a result of this early training, RoTL “may come with a stigma as it is outside of traditional discipline-specific research,” Lento says.
Lento admits that the reasons listed above are speculative. He and Siddiqui would like to see other researchers conduct follow-up studies that take deeper dives into the broader stigma surrounding RoTL.
Changing Mindsets, Taking Action
In the meantime, Siddiqui and Lento call on business school administrators and faculty to work together to create a “shared and precise definition of teaching effectiveness.” Educators can start by defining teaching quality within their own institutions.
From there, Siddiqui and Lento say that schools can take any or all the following actions to change mindsets about RoTL:
- Set appropriate objectives, incentives, and evaluation mechanisms.
- Create and nurture communities of practice that help like-minded faculty pursue research focused on solving issues they face in their classrooms.
- Consider weighing education research in peer-reviewed articles more heavily, particularly for faculty in teaching-focused roles.
- Recognize RoTL for accreditation and tenure and normalize it as a legitimate form of scholarship.
- Make seed funds available to faculty who pursue RoTL.
- Give awards and incentives to faculty who use research-informed teaching in their classrooms.
- Consider hiring tenure-track academics who also are expert educators with an expressed interest in pursuing RoTL. These scholars can investigate and develop “research-informed teaching tools ready to be put into practice in almost any business classroom,” says Siddiqui. This outcome, she emphasizes, is an indication of how RoTL contributes to the advancement of business disciplines.
- Encourage and teach RoTL in doctoral programs, with the aim of improving and advancing the quality of teaching at business schools.
Siddiqui points out that information on the websites of AACSB-accredited schools “are replete with research centers, research chairs and scholars, core research focus areas, research awards, annual research celebration reports, intellectual contributions, and grant-funding awards.”
There is no reason, she says, that schools could not also highlight information about their teaching philosophies, teaching awards, student feedback, educational leadership and professional development, and faculty research on teaching and learning.
Two B-School Perspectives
So far, Siddiqui and Lento’s paper has captured the attention of other like-minded educators in the business school community. This includes Nicola Charwat, associate dean of teaching and learning and senior lecturer of business law and taxation at Monash University’s Monash Business School (MBS) in Caulfield East, Australia.
MBS prioritizes scholarship on teaching and learning (SoTL) where appropriate, she says, through efforts that include identifying quality education-oriented journals and valuing publication in those journals equally to publication in discipline-based journals. The school uses “a consultative process” to identify journals specializing in teaching and learning that are equivalent to discipline-based journals rated as A*, A, B, and C on the quality list compiled by the Australian Business Deans Council.
“We have also instituted a Business Education and Research Group, which has been awarding both practice- and research-output-focused grants to staff for three years,” Charwat says. “Alongside these efforts, of course, there are moves in the university in line with the broader trend of raising the profile of teaching and ensuring its status is on par with other work of the university.”
Educators in STEM disciplines have long recognized educational research in tenure decisions and regularly reward academics who pursue RoTL in their disciplines.
Despite these changes, Charwat notes that the perception remains that accomplishments related to educational research are “somehow lesser” than those related to discipline-related scholarship. Additionally, many faculty remain uncertain about how to approach educational research. In response, MBS has built communities of practice dedicated to teaching and is now working “to increase awareness of and opportunities to undertake SoTL and education research,” Charwat says.
Charwat says that the questions raised in Siddiqui and Lento’s paper are “essential” to business education, and that their article “has prompted us to start exploring the patterns of our own SoTL and education research.” MBS faculty, she adds, might also pursue a similar study focused on AACSB-accredited schools in Australia.
Another educator who read the article with interest is Martin Lockett, former dean and professor of strategic management at Nottingham University Business School China (NUBS China) in Zhejiang. Lockett explains that NUBS China uses the Academic Journal Guide , which is produced by the Chartered Association of Business Schools (CABS), to support tenure decisions and to classify faculty under AACSB accreditation standards.
But in the CABS guide, only four journals focused on teaching and learning are rated as 3, 4, or 4*, which are the targets that NUBS China uses to qualify faculty as Scholarly Academics under AACSB accreditation or for internal recognition of quality research, Lockett says.
This has led to worry among the school’s teaching-oriented faculty that if they focus on RoTL, they risk being classified as “additional faculty,” unless they can consistently publish in the few education-focused journals listed by CABS. That concern, Lockett says, deters most faculty from pursuing RoTL in any substantial way.
While this scenario is all too common at institutions with research-focused missions, it is not mandated by AACSB accreditation standards, emphasizes Stephanie Bryant, AACSB’s chief accreditation officer. She clarifies that whether a business school considers educational scholarship for the purpose of accreditation or tenure is its choice, based on the parameters it has set for its individual mission. “The standards do not say anywhere, or imply, that educational research is not valued,” Bryant stresses. The devaluation of RoTL, she adds, “is a school perspective.”
Time to ‘Balance the Scales’
The stigma surrounding RoTL at AACSB-accredited business schools could be lifted, say Siddiqui and Lento, if administrators acknowledge the benefits that fostering cultures of teaching and learning bring to all business school stakeholders. These advantages include a wider scope of scholarship and more evidence-based pedagogical tools for faculty, richer learning experiences and better learning outcomes for students, and more well-rounded job candidates for employers.
Educators in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines already know this, says Siddiqui. STEM departments have long recognized educational research in tenure decisions and regularly reward academics who pursue RoTL in their disciplines.
As one example, Siddiqui points to Carl Edwin Wieman, winner of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize in Physics. Wieman established the Carl Wieman Science Education Initiative at the University of British Columbia in Canada to encourage evidence-based teaching methods focused on improving undergraduate science education. Since its inception, the initiative has hired fellows who are interested in conducting education research, particularly based in the disciplines in which they have earned their doctorates. It also has inspired the creation of teaching materials in science education, a dedicated website, and a sister initiative at the University of Colorado Boulder in the United States.
Business schools, says Siddiqui, could achieve comparable results by raising awareness of the importance of RoTL, disseminating RoTL findings beyond peer-reviewed journals, and driving research-informed teaching methods that advance business education.
This year, the co-authors published a second paper that finds that scholarly and practice academics who developed rigorous research skills in their doctoral programs and who publish discipline-based research are more likely to pursue RoTL research. Here, Siddiqui and Lento more directly call on business school deans to reward and incentivize this line of research by creating communities of practice and expanding their journal ranking frameworks to include relevant peer-reviewed publications.
It is imperative, Siddiqui and Lento argue, that business schools place studies based on classroom settings on equal footing with studies based on corporate settings. “Research on teaching and learning balances the scales,” Siddiqui says, “by utilizing evidence-based, efficient, and effective teaching to foster deep learning amongst diverse student audiences.”
- accreditation
- administration
- faculty engagement
- Our Mission

5 Popular Education Beliefs That Aren’t Backed by Research
Making adjustments to these common misconceptions can turn dubious strategies into productive lessons, the research suggests.
Not every learning myth requires teachers to pull up stakes and start all over again—at least not entirely. There are some commonly held misconceptions that contain a nugget of wisdom but need to be tweaked in order to align with the science of learning.
Sometimes, in other words, you’re already halfway there. Here are five mostly myths, from the power of doodling to the motivating role of grades, that educators can quickly adjust and turn to their advantage.
1. Doodling Improves Focus and Learning
When we write about the power of drawing to learn, we often hear from readers who feel compelled to defend an old habit: “See, I told you that when I was doodling, I was still paying attention!” But doodling—which is commonly defined as “an aimless or casual scribble or sketch” and often consists of marginalia like cartoon characters, geometric patterns, or pastoral scenes—is distinct from what researchers call “task-related drawing.” And doodling, in this sense, is not associated with improvements in focus or academic outcomes.
In fact, both cognitive load theory and experimental studies are generally downbeat on doodling. Students who sketch complicated scenes or designs as they try to process a lesson on plate tectonics, according to the first theory, are engaging in competitive cognitive tasks and will generally underperform on both. Doodling, like all drawing, is cognitively intensive, involving complex feedback loops between visual, sensorimotor, attentional, and planning regions of the brain and body. Because our ability to process information is finite, drawing and learning about different things at the same time is a simple question of too much.
Research confirms the theory. A 2019 study pitted off-task doodling against typical learning activities like “task-related drawing” and writing. In three separate but related experiments, task-related drawing and writing beat out doodling in terms of recall—by margins as large as 300 percent. How to fix it: Sketching what you are actually learning—from representational drawings of cells or tectonic boundaries to the creation of concept maps and organizational drawings—is, in fact, a powerful learning strategy (see research here , here , and here ), and that applies “regardless of one’s artistic talent,” a 2018 study confirms. Try to harness a student’s passion for doodling by allowing them to submit academic sketches as work products. To get even more bang for your buck, ask them to annotate their drawings, or talk you through them—which will encode learning even more deeply, according to research .
2. Reading Aloud In Turn Improves Fluency
Often called round robin reading (RRR), I resorted to it when I taught years ago—and it appears that it’s still frequently used, judging from a 2019 blog by literacy expert Timothy Shanahan and comments on a 2022 Cult of Pedagogy post on the topic. Teachers deploy RRR—during which the whole class follows a text while students read sections consecutively—for good reasons: Arguably, the practice encourages student engagement, gives teachers the opportunity to gauge oral reading fluency, and has a built-in classroom management benefit as well. Students are generally silent and (superficially) attentive when a peer is reading.
But according to Shanahan, and the literacy professors Katherine Hilden and Jennifer Jones, the practice has long been frowned upon. In an influential 2012 review of relevant literature , Hilden and Jones cut straight to the point: “We know of no research evidence that supports the claim that RRR actually contributes to students becoming better readers, either in terms of their fluency or comprehension.”
In fact, RRR has plenty of problems. Individual students using RRR may accumulate less than three hours of oral reading time over the course of a year, according to Shanahan—and Hilden and Jones say that students who are following along during the activity tend to “subvocalize” as they track the reader, reducing their own internal reading speed unnecessarily. RRR also has the unfortunate effects of stigmatizing struggling readers, exposing new readers to dysfluent modeling, and failing to incorporate meaningful comprehension strategies.
How to fix it: Yes, reading out loud is necessary to teach fluency, according to Shanahan, but there are better methods. Pairing kids together to “read sections of the text aloud to each other (partner reading) and then discuss and answer your questions” is a good approach, he says, especially if teachers circulate to listen for problems.
More generally, reading strategies that model proper reading speed, pronunciation, and affect—while providing time for vocabulary review, repeated exposure to the text, and opportunities to summarize and discuss—can improve both fluency and comprehension.
A 2011 study , for example, demonstrated that combining choral reading—teachers and students read a text in unison (similar to echo reading )—with other activities like vocabulary review, teacher modeling, and follow-up discussion improved students’ decoding and fluency.
3. Talent Beats Persistence
It’s a common trap: Observers tend to rate people who appear to be naturally gifted at something more highly than those who admit they’ve worked hard to achieve success. Researchers call this the “ naturalness bias ,” and it shows up everywhere, from teachers evaluating students to bosses evaluating employees.
In reality, the opposite is more often true. “Popular lore tells us that genius is born, not made,” writes psychologist and widely cited researcher of human potential K. Anders Ericsson for the Harvard Business Review . “Scientific research, on the other hand, reveals that true expertise is mainly the product of years of intense practice and dedicated coaching.”
Experimental studies extend the point to academics: An influential 2019 study led by psychologists Brian Galla and Angela Duckworth, for example, found that high school GPA is a better predictor than the SAT of how likely students are to complete college on time. That’s because “grades are a very good index of your self-regulation—your ability to stick with things, your ability to regulate your impulses, your ability to delay gratification and work hard instead of goofing off,” said Duckworth in a 2020 interview with Edutopia .
How to fix it: All kids—even the ones who already excel in a discipline—benefit when teachers emphasize the importance of effort, perseverance, and growth. Consider praising students for their improvement instead of their raw scores; have students read about and then discuss the idea of neural plasticity; and consider assigning reports on the mistakes and growing pains of accomplished writers, scientists, and artists.
Try to incorporate rough-draft thinking in class, and think about taking risks yourself: The renowned writing teacher Kelly Gallagher, author of Readicide , regularly composes in front of his class to model his own tolerance for errors and redrafting.
4. Background Music (Always) Undermines Learning
It’s a fascinating and complex question: Can students successfully learn while background music is playing?
In some cases, it appears, background music can be a neutral to positive influence; in other scenarios, it’s clearly distracting. There are several factors at play in determining the outcomes.
A 2021 study clarifies that because music and language use some of the same neural circuitry—a finding that appears as early as infancy —“listening to lyrics of a familiar language may rely on the same cognitive resources as vocabulary learning,” and that can “lead to an overload of processing capacity and thus to an interference effect.” Other features of the music probably matter, too: Dramatic changes in a song’s rhythm, for example, or transitions from one song to the next often force the learning brain to reckon with irrelevant information. A 2018 research review confirms the general finding: Across 65 studies, background music consistently had a “small but reliably detrimental effect” on reading comprehension.
In some cases, however, music may aid learning. Neuroscience suggests that catchy melodies, for example, can boost a student’s mood—which might lead to significant positive effects on learning when motivation and concentration are paramount, a 2023 study found.
How to fix it: Basically, “music has two effects simultaneously that conflict with one another,” cognitive psychologist Daniel Willingham told Edutopia in 2023 —one distracting and the other arousing.
“If you’re doing work that’s not very demanding, having music on is probably fine”—and likely to motivate students to keep going, Willingham says . In those cases, try to stick to music that’s instrumental or familiar, in order to decrease the cognitive resources needed to process it. “But if you’re doing work that’s just somewhat difficult, the distraction is probably going to make music a negative overall,” Willingham adds.
5. Grades Are Motivating
Teachers are well aware that grading, as a system, has many flaws—but at least grades motivate students to try their hardest, right? Unfortunately, the research suggests that that’s largely not the case.
“Despite the conventional wisdom in education, grades don’t motivate students to do their best work, nor do they lead to better learning or performance,” write motivation researcher Chris Hulleman and science teacher Ian Kelleher in an article for Edutopia . A 2019 research review , meanwhile, revealed that when confronted by grades, written feedback, or nothing at all—students preferred the latter two to grades, suggesting that A–F rankings might actually have a net negative impact on motivation.
In another blow to grades, a 2018 analysis of university policies like pass/fail grading or narrative evaluations concluded that “grades enhanced anxiety and avoidance of challenging courses” but didn’t improve student motivation. Providing students with specific, actionable feedback, on the other hand, “promot[ed] trust between instructors and students,” leading to greater academic ambition.
How to fix it: While grades are still mandatory in most schools—and some form of rigorous assessment remains an imperative—educators might consider ways to de-emphasize them.
Some teachers choose to drop every student’s lowest grade , for example; allow students to retake a limited number of assessments each unit; or periodically give students the discretion to turn in “their best work” from a series of related assignments.
At King Middle School, in Portland, Maine , educators delay their release of grades until the end of the unit, an approach backed by a 2021 study that found that delayed grading—handing back personalized feedback days before releasing number or letter grades—can boost student performance on future assignments by two-thirds of a letter grade.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support

Medical research is increasingly informed by recognition of diversity’s key role in addressing health equity. But when it comes to medical education, there’s a group that has remained not just underrepresented but also under-researched: first-generation (first-gen) medical students — those whose parents have not earned bachelor’s degrees. These students are more likely to be older, identify as racial or ethnic minorities, be immigrants or children of immigrants, or come from low-income families. Along with anecdotal evidence, the minimal previous research indicates that these students face some unique struggles on top of the common challenges most medical students encounter.
“It became clear to me that schools — even the great ones that are intentional and diligent about building diverse classes — are not truly ready to receive first-gen students,” said Catherine Havemann, MD, an emergency medicine chief resident at UChicago Medicine. “Admission isn’t the same as full access to the institution. Sometimes support doesn’t exist, and other times it’s off-target.”
To increase understanding of the first-gen experience and identify opportunities for educators and administrators to provide the most meaningful support, Havemann helped lead a team of researchers to perform an in-depth qualitative study. They analyzed data collected in interviews with a diverse group of medical students recruited from 27 medical schools across the U.S. The results, published in JAMA , have the potential to inform efforts at increasing educational equity at both the institutional and individual level.
Struggles shared amongst a diverse first-gen population
Overall, the study confirmed that first-gen medical students feel that they face disproportionate adversity throughout their education and do not receive the support they need to compensate for that. Participants identified 4 main themes: feelings of isolation and exclusion; difficulties accessing basic resources such as food, rent, transportation and textbooks; a general lack of institutional support; and pressure to rely on personal “grit” and resilience for survival.
Some issues highlighted in the data were relatively unsurprising, such as financial difficulties.
“No matter which subset of first-gen students we talk to, money is a foundational part of the challenges they face — even if they're not technically low-income,” said Havemann, the paper’s first author. “Within the medical community, we need to talk more about the discomfort of disadvantaged students entering incredibly wealthy institutions with mostly wealthy peers. What does it mean to create some basic degree of equity?”
Other issues emerged as more persistent than the researchers had anticipated. For example, interviewees frequently mentioned transportation problems, such as situations where student loans don’t cover the cost of having a car but medical school necessitates one. An especially striking theme was that many students reported being overtly discouraged by mentors or teachers during their education.
“People who meet the criteria for medical school admission are being told ‘This is not for you,’” Havemann said. “It’s disheartening to see, and it makes me think differently about my career as an aspiring educator. Saying ‘Yes’ — even in a small way — to someone who has heard a lifetime of ‘No’ can make all the difference. To think there are people out there discouraging others is frankly appalling.”
Responding to the findings
Havemann said the paper resonated strongly with student communities online following its publication.
“Responses ranged from ‘This is obvious’ and ‘Water is wet’ to ‘Why doesn't my school understand this?’ or "We knew this already — where are the solutions?’” she said.
As a former first-gen student herself, she was struck by the consistency of experience revealed by the study’s results. “It was validating as a researcher but also profoundly validating as a person.”
But while the student response online served as important confirmation that the study’s findings are representative, the real target audience is the educators who have the power to make a difference.
“I would love for them to read this paper and feel what a powerful position they're in to make a more equitable world,” Havemann said. “Even the little things matter a lot.”
Even as she and others conduct more research on this topic, Havemann said institutions can and should already be taking steps to provide better support for first-generation medical students.
“People like to talk about using holistic review in admissions to look at the whole student — we also have to look at holistic support once they enroll,” she said.
Future studies will dive deeper into themes like professional identity formation, financial challenges, burnout and sense of belonging. Now that the qualitative groundwork has been laid, researchers can design more nuanced quantitative and mixed-method studies.
“For example, I’d like to quantify the percentage of first-gen students who are not only trying to support themselves but also keeping the lights on for their parents,” Havemann said. “I think the answers would be gutting.”
The article, “ Challenges Facing First-Generation College Graduates in Medical School: A Qualitative Analysis ,” was published in JAMA in December 2023. Authors included Catherine Havemann, Hyacinth R. C. Mason, Regina G. Russell, Alejandra Casillas, Mytien Nguyen, Dowin Boatright, Alexis Webber, Jon Andre Parilla, Abraham Gallegos and Tasha R. Wyatt.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ERIC is an online library of education research and information, sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education.
The American Educational Research Journal (AERJ) is the flagship journal of AERA, with articles that advance the empirical, theoretical, and methodological understanding of education and learning. It publishes original peer-reviewed analyses spanning the field of education research across all subfields and disciplines and all levels of analysis, all levels of education throughout the life span ...
Ranked #414 out of 1,469 "Education" journals. The American Journal of Education seeks to bridge and integrate the intellectual, methodological, and substantive diversity of educational scholarship and to encourage a vigorous dialogue between educational scholars and policy makers. It publishes empirical research, from a wide range of ...
A curated list of must-read research from 2021 on topics such as school quality, social and emotional learning, classroom management, and learning strategies. Learn how to reframe our notion of "good" schools, mine the magic of expert teachers, confront an old myth about immigrant students, and more.
Research in Education provides a space for fully peer-reviewed, critical, trans-disciplinary, debates on theory, policy and practice in relation to Education. International in scope, we publish challenging, well-written and theoretically innovative contributions that question and explore the concept, practice and institution of Education as an object of study.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
The Review of Educational Research (RER) publishes critical, integrative reviews of research literature bearing on education, including conceptualizations, interpretations, and syntheses of literature and scholarly work in a field broadly relevant to education and educational research. View full journal description
Metrics. The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make ...
More is more: exploring the relationship between young people's experiences of school-based career education, information, advice and guidance at age 14-16 and wider adult outcomes at age 21-22 in England. Julie Moote, Louise Archer, Morag Henderson, Emma Watson, Jennifer DeWitt, Becky Francis & Henriette Holmegaard. Published online: 22 ...
Lucinda Soltero-González. Sakura Kamioka. Frontiers in Education. doi 10.3389/feduc.2024.1347503. A multidisciplinary journal that explores research-based approaches to education for human development. It focuses on the global challenges and opportunities education faces, ultimately aiming to i...
Latest Research and Reviews Longitudinal trajectories of self-esteem, related predictors, and impact on depression among students over a four-year period at college in China Xinqiao Liu
Description. The Harvard Educational Review (HER) is a scholarly journal of opinion and research in education. The Editorial Board aims to publish pieces from interdisciplinary and wide-ranging fields that advance our understanding of educational theory, equity, and practice. HER encourages submissions from established and emerging scholars, as ...
Future in Educational Research (FER) focuses on new trends, theories, methods, and policies in the field of education. We're a double anonymized peer-reviewed journal. Our original articles advance empirical, theoretical, and methodological understanding of education and learning. We deliver high quality research from developed and emerging ...
Learn more about Research Topics. A multidisciplinary journal that explores research-based approaches to education for human development. It focuses on the global challenges and opportunities education faces, ultimately aiming to i...
In February of 2020, we launched the new website Greater Good in Education, a collection of free, research-based and -informed strategies and practices for the social, emotional, and ethical development of students, for the well-being of the adults who work with them, and for cultivating positive school cultures.
10. An Authoritative Study of Two High-Impact Learning Strategies. Spacing and retrieval practices are two of the most effective ways to drive long-term retention, confirms an authoritative 2022 review spanning hundreds of studies on the topic—and students should know how and why the strategies are effective. In the review, researchers ...
Exploring what student teachers do when preparing their lessons: four planning profiles. Agnès Deprit et al. Article | Published online: 18 Mar 2024. View all latest articles. Explore the current issue of Research Papers in Education, Volume 39, Issue 2, 2024.
This article introduces a unifying framework for studying panel experiments with population interference, in which a treatment assigned to one experimental unit affects another experimental unit's outcome. Findings have implications for fields as diverse as education, economics, and public health. 23 Mar 2021.
Review of Research in Education (RRE), published annually, provides a forum for analytic research reviews on selected education topics of significance to the field.Each volume addresses a topic of broad relevance to education and learning, and publishes articles that critically examine diverse literatures and bodies of knowledge across relevant disciplines and fields.
Review of Education is an official BERA journal publishing educational research from throughout the world, and papers on topics of international interest. Abstract This article reports on a systematic review of the evidence concerning the impact of citizenship education, specifically focusing on the effect of different teaching activities on a ...
Educational Research is an international peer-reviewed research journal which, since its inception in 1958, has contributed as a leading international forum for informed thinking on all issues of contemporary concern in education.. As the journal of the National Foundation for Educational Research (NFER), Educational Research is committed to publishing research of interest to academics ...
As the nation prepares to mark the 70th anniversary of the landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v.Board of Education, a new report from researchers at Stanford and USC shows that racial and economic segregation among schools has grown steadily in large school districts over the past three decades — an increase that appears to be driven in part by policies favoring school choice over ...
Consider weighing education research in peer-reviewed articles more heavily, particularly for faculty in teaching-focused roles. Recognize RoTL for accreditation and tenure and normalize it as a legitimate form of scholarship. Make seed funds available to faculty who pursue RoTL.
Research confirms the theory. A 2019 study pitted off-task doodling against typical learning activities like "task-related drawing" and writing. In three separate but related experiments, task-related drawing and writing beat out doodling in terms of recall—by margins as large as 300 percent.
Developing a school-based nutrition education programme to transform the nutritional behaviours of basic-level schoolchildren: a case from participatory action research in Nepal. Yadu R. Upreti, Bhimsen Devkota, Sheri Bastien & Bal Chandra Luitel. Published online: 10 May 2023.
As schools reconsider cursive, research homes in on handwriting's brain benefits : Shots - Health News Researchers are learning that handwriting engages the brain in ways typing can't match ...
Medical research is increasingly informed by recognition of diversity's key role in addressing health equity. But when it comes to medical education, there's a group that has remained not just underrepresented but also under-researched: first-generation (first-gen) medical students — those whose parents have not earned bachelor's degrees.
The oldest educational publication in the country, the Journal of Education's mission is to disseminate knowledge that informs practice in PK-12, higher, and professional education. A refereed publication, the Journal offers three issues each calendar year.. The Journal publishes original research reports, explications of theory, and reflections.
Washington — If you tend to do other things or get distracted while eating dinner, you may be running the risk of overconsuming everyday pleasures later, possibly because the distraction caused you to enjoy yourself less, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.. The study looked at how distraction affects "hedonic consumption," or buying and using ...