Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers.
- Clerc Center | PK-12 & Outreach
- KDES | PK-8th Grade School (D.C. Metro Area)
- MSSD | 9th-12th Grade School (Nationwide)
- Gallaudet University Regional Centers
- Parent Advocacy App
- K-12 ASL Content Standards
- National Resources
- Youth Programs
- Academic Bowl
- Battle Of The Books
- National Literary Competition
- Youth Debate Bowl
- Bison Sports Camp
- Discover College and Careers (DC²)
- Financial Wizards
- Immerse Into ASL
- Alumni Relations
- Alumni Association
- Homecoming Weekend
- Class Giving
- Get Tickets / BisonPass
- Sport Calendars
- Cross Country
- Swimming & Diving
- Track & Field
- Indoor Track & Field
- Cheerleading
- Winter Cheerleading
- Human Resources
- Plan a Visit
- Request Info

- Areas of Study
- Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- American Sign Language
- Art and Media Design
- Communication Studies
- Data Science
- Deaf Studies
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Programs
- Educational Neuroscience
- Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Information Technology
- International Development
- Interpretation and Translation
- Linguistics
- Mathematics
- Philosophy and Religion
- Physical Education & Recreation
- Public Affairs
- Public Health
- Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Theatre and Dance
- World Languages and Cultures
- B.A. in American Sign Language
- B.A. in Art and Media Design
- B.A. in Biology
- B.A. in Communication Studies
- B.A. in Communication Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Deaf Studies
- B.A. in Deaf Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Early Childhood Education
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Elementary Education
- B.A. in English
- B.A. in Government
- B.A. in Government with a Specialization in Law
- B.A. in History
- B.A. in Interdisciplinary Spanish
- B.A. in International Studies
- B.A. in Interpretation
- B.A. in Mathematics
- B.A. in Philosophy
- B.A. in Psychology
- B.A. in Psychology for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Social Work (BSW)
- B.A. in Sociology
- B.A. in Sociology with a concentration in Criminology
- B.A. in Theatre Arts: Production/Performance
- B.A. or B.S. in Education with a Specialization in Secondary Education: Science, English, Mathematics or Social Studies
- B.S in Risk Management and Insurance
- B.S. in Accounting
- B.S. in Accounting for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Biology
- B.S. in Business Administration
- B.S. in Business Administration for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Information Technology
- B.S. in Mathematics
- B.S. in Physical Education and Recreation
- B.S. In Public Health
- General Education
- Honors Program
- Peace Corps Prep program
- Self-Directed Major
- M.A. in Counseling: Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- M.A. in Counseling: School Counseling
- M.A. in Deaf Education
- M.A. in Deaf Education Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Cultural Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Language and Human Rights
- M.A. in Early Childhood Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Early Intervention Studies
- M.A. in Elementary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in International Development
- M.A. in Interpretation: Combined Interpreting Practice and Research
- M.A. in Interpretation: Interpreting Research
- M.A. in Linguistics
- M.A. in Secondary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Sign Language Education
- M.S. in Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- M.S. in Speech-Language Pathology
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ed.D. in Transformational Leadership and Administration in Deaf Education
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Critical Studies in the Education of Deaf Learners
- Ph.D. in Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Ph.D. in Linguistics
- Ph.D. in Translation and Interpreting Studies
- Ph.D. Program in Educational Neuroscience (PEN)
- Individual Courses and Training
- Summer On-Campus Courses
- Summer Online Courses
- Certificates
- Certificate in Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Educating Deaf Students with Disabilities (online, post-bachelor’s)
- American Sign Language and English Bilingual Early Childhood Deaf Education: Birth to 5 (online, post-bachelor’s)
- Peer Mentor Training (low-residency/hybrid, post-bachelor’s)
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Certificate
- Online Degree Programs
- ODCP Minor in Communication Studies
- ODCP Minor in Deaf Studies
- ODCP Minor in Psychology
- ODCP Minor in Writing
- Online Degree Program General Education Curriculum
- University Capstone Honors for Online Degree Completion Program
Quick Links
- PK-12 & Outreach
- NSO Schedule

Guide to Writing Introductions and Conclusions
202.448-7036
First and last impressions are important in any part of life, especially in writing. This is why the introduction and conclusion of any paper – whether it be a simple essay or a long research paper – are essential. Introductions and conclusions are just as important as the body of your paper. The introduction is what makes the reader want to continue reading your paper. The conclusion is what makes your paper stick in the reader’s mind.
Introductions
Your introductory paragraph should include:
1) Hook: Description, illustration, narration or dialogue that pulls the reader into your paper topic. This should be interesting and specific.
2) Transition: Sentence that connects the hook with the thesis.
3) Thesis: Sentence (or two) that summarizes the overall main point of the paper. The thesis should answer the prompt question.
The examples below show are several ways to write a good introduction or opening to your paper. One example shows you how to paraphrase in your introduction. This will help you understand the idea of writing sequences using a hook, transition, and thesis statement.
» Thesis Statement Opening
This is the traditional style of opening a paper. This is a “mini-summary” of your paper.
For example:
» Opening with a Story (Anecdote)
A good way of catching your reader’s attention is by sharing a story that sets up your paper. Sharing a story gives a paper a more personal feel and helps make your reader comfortable.
This example was borrowed from Jack Gannon’s The Week the World Heard Gallaudet (1989):
Astrid Goodstein, a Gallaudet faculty member, entered the beauty salon for her regular appointment, proudly wearing her DPN button. (“I was married to that button that week!” she later confided.) When Sandy, her regular hairdresser, saw the button, he spoke and gestured, “Never! Never! Never!” Offended, Astrid turned around and headed for the door but stopped short of leaving. She decided to keep her appointment, confessing later that at that moment, her sense of principles had lost out to her vanity. Later she realized that her hairdresser had thought she was pushing for a deaf U.S. President. Hook: a specific example or story that interests the reader and introduces the topic.
Transition: connects the hook to the thesis statement
Thesis: summarizes the overall claim of the paper
» Specific Detail Opening
Giving specific details about your subject appeals to your reader’s curiosity and helps establish a visual picture of what your paper is about.
» Open with a Quotation
Another method of writing an introduction is to open with a quotation. This method makes your introduction more interactive and more appealing to your reader.
» Open with an Interesting Statistic
Statistics that grab the reader help to make an effective introduction.
» Question Openings
Possibly the easiest opening is one that presents one or more questions to be answered in the paper. This is effective because questions are usually what the reader has in mind when he or she sees your topic.
Source : *Writing an Introduction for a More Formal Essay. (2012). Retrieved April 25, 2012, from http://flightline.highline.edu/wswyt/Writing91/handouts/hook_trans_thesis.htm
Conclusions
The conclusion to any paper is the final impression that can be made. It is the last opportunity to get your point across to the reader and leave the reader feeling as if they learned something. Leaving a paper “dangling” without a proper conclusion can seriously devalue what was said in the body itself. Here are a few effective ways to conclude or close your paper. » Summary Closing Many times conclusions are simple re-statements of the thesis. Many times these conclusions are much like their introductions (see Thesis Statement Opening).
» Close with a Logical Conclusion
This is a good closing for argumentative or opinion papers that present two or more sides of an issue. The conclusion drawn as a result of the research is presented here in the final paragraphs.
» Real or Rhetorical Question Closings
This method of concluding a paper is one step short of giving a logical conclusion. Rather than handing the conclusion over, you can leave the reader with a question that causes him or her to draw his own conclusions.
» Close with a Speculation or Opinion This is a good style for instances when the writer was unable to come up with an answer or a clear decision about whatever it was he or she was researching. For example:
» Close with a Recommendation
A good conclusion is when the writer suggests that the reader do something in the way of support for a cause or a plea for them to take action.
202-448-7036
At a Glance
- Quick Facts
- University Leadership
- History & Traditions
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- Our 10-Year Vision: The Gallaudet Promise
- Annual Report of Achievements (ARA)
- The Signing Ecosystem
- Not Your Average University
Our Community
- Library & Archives
- Technology Support
- Interpreting Requests
- Ombuds Support
- Health and Wellness Programs
- Profile & Web Edits
Visit Gallaudet
- Explore Our Campus
- Virtual Tour
- Maps & Directions
- Shuttle Bus Schedule
- Kellogg Conference Hotel
- Welcome Center
- National Deaf Life Museum
- Apple Guide Maps
Engage Today
- Work at Gallaudet / Clerc Center
- Social Media Channels
- University Wide Events
- Sponsorship Requests
- Data Requests
- Media Inquiries
- Gallaudet Today Magazine
- Giving at Gallaudet
- Financial Aid
- Registrar’s Office
- Residence Life & Housing
- Safety & Security
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- University Communications
- Clerc Center

Gallaudet University, chartered in 1864, is a private university for deaf and hard of hearing students.
Copyright © 2024 Gallaudet University. All rights reserved.
- Accessibility
- Cookie Consent Notice
- Privacy Policy
- File a Report
800 Florida Avenue NE, Washington, D.C. 20002
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
Introductions and Conclusions
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
Introductions and conclusions play a special role in the academic essay, and they frequently demand much of your attention as a writer. A good introduction should identify your topic, provide essential context, and indicate your particular focus in the essay. It also needs to engage your readers’ interest. A strong conclusion will provide a sense of closure to the essay while again placing your concepts in a somewhat wider context. It will also, in some instances, add a stimulus to further thought. Since no two essays are the same, no single formula will automatically generate an introduction and conclusion for you. But the following guidelines will help you to construct a suitable beginning and end for your essay.
Some general advice about introductions
- Some students cannot begin writing the body of the essay until they feel they have the perfect introduction. Be aware of the dangers of sinking too much time into the introduction. Some of that time can be more usefully channeled into planning and writing.
- You may be the kind of writer who writes an introduction first in order to explore your own thinking on the topic. If so, remember that you may at a later stage need to compress your introduction.
- It can be fine to leave the writing of the introduction for a later stage in the essay-writing process. Some people write their introduction only after they have completed the rest of the essay. Others write the introduction first but rewrite it significantly in light of what they end up saying in the body of their paper.
- The introductions for most papers can be effectively written in one paragraph occupying half to three-quarters of the first page. Your introduction may be longer than that, and it may take more than one paragraph, but be sure you know why. The size of your introduction should bear some relationship to the length and complexity of your paper. A twenty page paper may call for a two-page introduction, but a five-page paper will not.
- Get to the point as soon as possible. Generally, you want to raise your topic in your very first sentences. A common error is to begin too broadly or too far off topic. Avoid sweeping generalizations.
- If your essay has a thesis, your thesis statement will typically appear at the end of your introduction, even though that is not a hard-and-fast rule. You may, for example, follow your thesis with a brief road map to your essay that sketches the basic structure of your argument. The longer the paper, the more useful a road map becomes.
How do I write an interesting, effective introduction?
Consider these strategies for capturing your readers’ attention and for fleshing out your introduction:
- Find a startling statistic that illustrates the seriousness of the problem you will address.
- Quote an expert (but be sure to introduce him or her first).
- Mention a common misperception that your thesis will argue against .
- Give some background information necessary for understanding the essay.
- Use a brief narrative or anecdote that exemplifies your reason for choosing the topic. In an assignment that encourages personal reflection, you may draw on your own experiences; in a research essay, the narrative may illustrate a common real-world scenario.
- In a science paper, explain key scientific concepts and refer to relevant literature. Lead up to your own contribution or intervention.
- In a more technical paper, define a term that is possibly unfamiliar to your audience but is central to understanding the essay.
In fleshing out your introduction, you will want to avoid some common pitfalls:
- Don’t provide dictionary definitions, especially of words your audience already knows.
- Don’t repeat the assignment specifications using the professor’s wording.
- Don’t give details and in-depth explanations that really belong in your body paragraphs. You can usually postpone background material to the body of the essay.
Some general advice about conclusions
- A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your thesis. If you wish to summarize—and often you must—do so in fresh language. Remind the reader of how the evidence you’ve presented has contributed to your thesis.
- The conclusion, like much of the rest of the paper, involves critical thinking. Reflect upon the significance of what you’ve written. Try to convey some closing thoughts about the larger implications of your argument.
- Broaden your focus a bit at the end of the essay. A good last sentence leaves your reader with something to think about, a concept in some way illuminated by what you’ve written in the paper.
- For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion. In some cases, a two-or-three paragraph conclusion may be appropriate. As with introductions, the length of the conclusion should reflect the length of the essay.
How do I write an interesting, effective conclusion?
The following strategies may help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your essay:
- If your essay deals with a contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend a specific course of action.
- Use an apt quotation or expert opinion to lend authority to the conclusion you have reached.
- Give a startling statistic, fact, or visual image to drive home the ultimate point of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point with a relevant narrative drawn from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, example, or quotation that you introduced in your introduction, but add further insight that derives from the body of your essay.
- In a science or social science paper, mention worthwhile avenues for future research on your topic.
How does genre affect my introduction or conclusion?
Most of the advice in this handout pertains to argumentative or exploratory academic essays. Be aware, however, that different genres have their own special expectations about beginnings and endings. Some academic genres may not even require an introduction or conclusion. An annotated bibliography, for example, typically provides neither. A book review may begin with a summary of the book and conclude with an overall assessment of it. A policy briefing usually includes an introduction but may conclude with a series of recommendations. Check your assignment carefully for any directions about what to include in your introduction or conclusion.

Introductions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid.
The role of introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when you sit down to respond to an assignment, you have at least some sense of what you want to say in the body of your paper. You might have chosen a few examples you want to use or have an idea that will help you answer the main question of your assignment; these sections, therefore, may not be as hard to write. And it’s fine to write them first! But in your final draft, these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to your reader.
Your introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis. If your readers pick up your paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of Chapel Hill, television, e-mail, and The Daily Tar Heel and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps your readers make a transition between their own world and the issues you will be writing about, you give your readers the tools they need to get into your topic and care about what you are saying. Similarly, once you’ve hooked your readers with the introduction and offered evidence to prove your thesis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. (See our handout on conclusions .)
Note that what constitutes a good introduction may vary widely based on the kind of paper you are writing and the academic discipline in which you are writing it. If you are uncertain what kind of introduction is expected, ask your instructor.
Why bother writing a good introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions of your argument, your writing style, and the overall quality of your work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of you, your analytical skills, your writing, and your paper.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper. Your introduction conveys a lot of information to your readers. You can let them know what your topic is, why it is important, and how you plan to proceed with your discussion. In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of your paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should capture your readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of your paper. Opening with a compelling story, an interesting question, or a vivid example can get your readers to see why your topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join you for an engaging intellectual conversation (remember, though, that these strategies may not be suitable for all papers and disciplines).
Strategies for writing an effective introduction
Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer. Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will likely be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction—start off with a big picture sentence or two and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it. (See our handout on understanding assignments for additional information on the hidden clues in assignments.)
Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. Imagine that you’re researching Chapel Hill. If what you want to find out is whether Chapel Hill is at roughly the same latitude as Rome, it might make sense to hit that little “minus” sign on the online map until it has zoomed all the way out and you can see the whole globe. If you’re trying to figure out how to get from Chapel Hill to Wrightsville Beach, it might make more sense to zoom in to the level where you can see most of North Carolina (but not the rest of the world, or even the rest of the United States). And if you are looking for the intersection of Ridge Road and Manning Drive so that you can find the Writing Center’s main office, you may need to zoom all the way in. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
Try writing your introduction last. You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know precisely what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper.
Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
Open with something that will draw readers in. Consider these options (remembering that they may not be suitable for all kinds of papers):
- an intriguing example —for example, Douglass writes about a mistress who initially teaches him but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery.
- a provocative quotation that is closely related to your argument —for example, Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other.” (Quotes from famous people, inspirational quotes, etc. may not work well for an academic paper; in this example, the quote is from the author himself.)
- a puzzling scenario —for example, Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote —for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”
- a thought-provoking question —for example, given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?
Pay special attention to your first sentence. Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and polished way.
How to evaluate your introduction draft
Ask a friend to read your introduction and then tell you what he or she expects the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will be. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately, you probably have a good introduction.
Five kinds of less effective introductions
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your question and will be reading many essays in response to it—he or she does not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question.
Example: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Webster’s Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. Anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what Webster says. If you want to open with a discussion of an important term, it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment. You may also be able to use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Instructors may see a great many papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time, throughout the world, etc. It is usually very general (similar to the placeholder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. It may employ cliches—the phrases “the dawn of man” and “throughout human history” are examples, and it’s hard to imagine a time when starting with one of these would work. Instructors often find them extremely annoying.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader probably already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave , in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
And now for the conclusion…
Writing an effective introduction can be tough. Try playing around with several different options and choose the one that ends up sounding best to you!
Just as your introduction helps readers make the transition to your topic, your conclusion needs to help them return to their daily lives–but with a lasting sense of how what they have just read is useful or meaningful. Check out our handout on conclusions for tips on ending your paper as effectively as you began it!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . New York: Dover.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 10:51 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Introductions and Conclusions
Have you ever read something that you couldn’t put down and then continued to think about it long after you finished? Good writing has that effect in general, but a strong introduction and conclusion are essential to engaging the reader from start to finish.
The introduction of a paper introduces the topic and scope of the discussion to prepare the reader for what follows, and the conclusion offers thoughtful analytic commentary or a synopsis that wraps up the discussion with final thoughts. In other words, the introduction and conclusion depend on everything that comes between them. With this in mind, an effective strategy for composing an introduction and a conclusion is to write everything that comes between them first. With the body of the paper drafted, you will know the topic well enough to introduce it effectively and you can also more readily determine where and how the discussion should end.
Consider the following characteristics of effective introductions and conclusions:
Characteristics of Effective Introductions
Provides relevant background information : Regardless of the topic, readers need a context to understand your remarks. A good introduction will include necessary background information about the topic that enables readers to understand the topic’s importance and why what you have to say about it matters. Providing context such as background information helps the reader feel grounded so that they can easily follow the development of the discussion.
Engages the reader : A good introduction will capture the attention of readers so that they want to read the paragraphs beyond the introduction. Enough specific information is presented so that readers are interested in the topic and what the writer plans to do with it. An engaging introduction invites readers into the world of the writing.
Sets the appropriate tone : The opening paragraph establishes the tone – the spirit and attitude behind the words – that the writer will use in a piece of writing. The tone should be a conscious choice as it reflects how the writer feels about the subject and about the audience, as well as the degree of formality of the writing. In most academic writing, the general tone is formal, but it may be more or less formal depending on the exact purpose of the writing. For example, a piece of writing with the purpose of introducing a new employee will probably be less formal and more personable than, say, a persuasive essay.
Establishes the focus and purpose : The introduction must make the focus and purpose of the paper clear to readers. Many writers include a thesis statement that establishes the focus and purpose and forecasts the main points. Even without an explicit thesis statement, the focus and purpose of the paper need to be just as clear. If readers do not understand the focus or what the writer hopes to accomplish, subsequent paragraphs may not make sense to readers.
Options for Introductions
The following is collection of some rhetorical strategies for writing introductions. Oftentimes an introduction will have characteristics of more than one strategy, so you should treat this list as a compilation of possibilities, not as a prescription of how certain types of beginnings must look. Try out a number of options to get a sense of the possibilities and then determine which would work best for your topic, purpose, and audience. The more you work on your introduction and think about what you are trying to say in your paper as a whole, the easier it will be to write an effective introduction.
Establish the Issue
Use the introduction to help make the case that the topic you are writing about is important and relevant and to provide context for your readers.
In the last decade or so, American culture has become increasingly tolerant of teenage sexuality. Many parents, too busy in their lives, are not proactive in educating their teens on issues related to sexuality. Educators are often left with the role of providing basic information about the subject even as more and more sexual education classes are cut from the curriculum. Where does this leave curious teens? Statistics show that 75 percent of teens have had sex by the time they are nineteen years old. The teenage birth rate continues to climb as do reported cases of sexually transmitted diseases (Healy, 2008). Cleary, it is imperative to develop intervention programs that teach adolescents the effective skills in delaying early sexual behaviors. Early education on delaying sexual activity for teens can drastically decrease teenage pregnancies, prevent the spread of STDs, and help teens to make the right choices that can impact the rest of their lives.
Asking relevant questions can be an excellent way to engage readers and get their attention. In the example below, the writer begins with a universal question that most readers can relate to.
Did you ever think that your life would change dramatically in a matter of twenty-four hours? One day you have a certain kind of life – a home, nearby schools for your kids, a wonderful neighborhood, good job, friends – and the next day it is all gone, irreversibly changed. As a resident of New Orleans, Louisiana, I had always known that a major hurricane could strike, but even knowing this fact could not prepare me for what happened in the wake of Hurricane Katrina. Hurricane Katrina demonstrated the need for residents to evacuate when mandated, for local and state authorities to work more efficiently together, and for the federal government to respond in a timely and responsible manner.
Use a narrative Most people enjoy reading a good story, so beginning with a narrative can be an effective way to connect with your readers.
It was a dark and stormy night. The wind whipped through the trees while lightening flashed and thunder boomed. Up ahead on a hill, a rickety old house stood. In an upstairs window, a single, solitary light shone, casting an eerie shadow across the yard. I was in Chattanooga, Tennessee, on business, and was driving to the outskirts of the city to visit my aunt, an old woman I hadn’t seen in nearly twenty years. According to my directions, that rickety old house was my aunt’s house, but I didn’t know if I had the nerve to knock on the door. In fact, I couldn’t remember a time I had been more scared. Everyone experiences fear just as everyone experiences happiness or sadness. Fear is a natural human emotion to the unknown and is characterized by physical changes to the body, an innate need to escape, and acute awareness of one’s surroundings.
Use an Attention Getter
Begin with a statement that will catch your readers’ attention and makes them want to continue reading.
Some children cannot sit still. They appear distracted by every little thing and do not seem to learn from their mistakes. These children disregard rules, even when they are punished repeatedly. It’s simple—their parents must not know how to control them. The truth is that attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder or ADHD is not understood appropriately. In fact, ADHD is a growing problem that requires more research to understand the issue, better intervention programs to help afflicted children, and improved training and support programs to help parents and educators.
Use an Extended Example or Series of Examples
Providing anecdotal examples can be a very effective way to capture your readers’ attention. Choose relevant, memorable examples.
According to the Federal Highway and Transportation Agency (2008), the majority of Americans, some 57%, do not regularly wear seat belts. Teddy Biro didn’t wear one when the car he was driving skidded on an icy road and hit a utility pole; Biro was catapulted through his front windshield and died of blood loss from a severed jugular vein. The coroner reported he had no other injuries besides minor abrasions. Bob Nettleblatt wasn’t wearing a seat belt when a car rear-ended him at a stop sign. Nettleblatt slammed his head into his front windshield and required 137 stitches to close up the laceration; investigators at the scene said if he had been wearing a seat belt, he would have been virtually unhurt from the 2 mph rear end collision (Fischer, 2007). Despite what is known about the safety of wearing seatbelts, too many Americans still do not buckle up, resulting in enormous emergency medical costs and fatalities that could be avoided. Despite what some people think, wearing a seatbelt is not a choice nor does it violate one’s personal rights. Wearing a seatbelt is the law and more needs to be done to enforce the law, punish those who break it, and educate young drivers to the dangers of not buckling up.
Define an Essential Term
To use this strategy, choose a term that is central to your paper and define it. This will help to engage your readers and make them want to continue reading. In the example below, the writer uses an extended example to define the term “collect.”
My friend George is a record fiend. Every room of his house contains floor-to-ceiling shelves filled entirely with record albums organized alphabetically regardless of genre. Stack after stack of record albums are piled high in the center of rooms, in corners, and in hallways. They are stacked under tables and in cupboards. One entire closet contains by George’s estimation over twenty-five hundred unsorted albums he purchased at flea markets, estate sales, and record shows. The parts of walls exposed contain framed original album covers—the Beatles’ Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band, Muddy Waters’ Electric Mud, John Coltrane’s Giant Steps. He owns commercially released albums, limited edition releases, reviewer copies, test pressings, and bootlegs. On most weekends, George travels to record shows and collectors conventions. He writes a weekly blog devoted to obscure records and another on the art of record collecting. His obsession with record collecting has cost him jobs, friends, and a wife. And still he collects.
Dramatize a Scene
Crafting a dramatic scene can go a long way toward making your readers want to read your work!
4 AM, March 28, 1979 and the floor of the control room at Three Mile Island nuclear power station jumps to life. The two control room operators are jolted from their mid-shift doldrums as alarms begin to sound, and the pounding in the auxiliary room is deafening. What those at the station did not know was that the “worst crisis yet experienced by the nation’s nuclear power industry” (Kemeny, 1979, p. 37) had just begun, and its impact wouldn’t be realized for years to come, if ever. Three Mile Island nuclear power station was located on an island in the middle of the Susquehanna River near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. It contained two separate nuclear power plants, TMI 1 and TMI 2. TMI 1 had been shut down for maintenance, but TMI 2 was operating at 97% of rated power providing electricity to the area (Carraway, 2000). Within seconds of the first alarm, a chain of events would commence to destroy the nuclear reactor and with it, the future of the nuclear power industry in this country.
Use a Quote
Using a relevant quotation, whether it is direct or indirect, can also help engage your reader.
An observer once said that New Orleanians are either having a party, recuperating from a party, or planning a party. The biggest and best party of all and the city’s most famous celebration is Mardi Gras, the greatest free show on earth. Despite the image the popular media displays to outsiders, Mardi Gras is a yearly celebration that is much tamer than most realize, brings family and friends together, and promotes unity among diverse groups of people.
Shocking but true statements or statistics can help draw your readers in.
McDonald’s has sold over 100 billion burgers. One hundred billion burgers with bun, stacked on top of one another would extend over 2.9 million miles into space–twelve times as far as the moon (Grimes, 2007). What is the secret of McDonald’s incredible success? To use the words of Ray Kroc, McDonald’s founder, the secret to McDonald’s success is that the fast-food giant produces “consistently mediocre food” (as cited in Thomas, 2001). The McDonald’s corporation has become a model of success due to its understanding of its market niche, its ability to redefine its image over time, and its ability to remain stable and produce a profit even in difficult economic times.
Characteristics of an Effective Conclusion
Brings the writing to a logical close : A conclusion provides the necessary signal to readers that the business of the essay is winding down, and the reader is being returned to the world outside of the essay. This transition should be fluid and the parting content thoughtful so that readers are prepared for and satisfied with the ending.
Reinforces the main idea in an engaging manner : Just as the introduction provides a first impression, the conclusion provides the last impression. The conclusion should reinforce the main idea of the work in a way that is fresh and not merely a perfunctory rehashing of what the essay discussed. Use the ending as your last chance to reach your audience and make sure the main point, its significance and/or its larger implications, are understood.
Leaves readers with something to think about : Ideally, a conclusion will bring the world of the essay to a close in such a way that even though the business of reading has ended, the audience does not stop thinking about what the essay said – its ideas. You don’t want an audience to end reading an essay, thinking “So what?” Provide some content that engages readers with what is important about the topic and your discussion of it so that the meaning of the writing stays with readers.
Options for Conclusions
What follows is a list of possible ways to conclude your writing. Depending on the purpose of the writing, some endings are more appropriate than others, so give careful thought to these techniques and try out a number of appropriate possibilities. Please also keep in mind that these options, like the offerings for introductions, can be combined so that a conclusion may have characteristics of more than one type of ending.
Most of the options for introductions can also be used for conclusions as well. Recall the introduction in which the writer was telling the story of the dark and stormy night he went to visit an aunt he hadn’t seen in decades. The conclusion could pick up where the introduction left off, or it could tell the story of another fearful situation the writer experienced, but the same general technique, a narrative in this case, could be used.
What follows is a list of additional ways in which you can compose a conclusion for your writing.
The idea of the echo is to repeat key words or phrases to create an “echo” that gets at a particular meaning or emphasizes a certain idea important to the writing. In the example below, note how the repetition of “Too many drivers” emphasizes the idea and, in essence, creates an echo readers will hear.
Too many drivers act in inappropriate ways when they get behind the wheel of a motor vehicle. Too many drivers are unnecessarily aggressive, darting in and out of traffic, running stop lights, putting everyone else on the road in peril. Too many drivers are just plain inconsiderate as if they are the only ones on the road. And too many of those drivers are just like you and me – good, decent people until we get in our cars.
Audience Appeal
The writer shows or points out directly to the audience how things are or the likely consequences if certain conditions remain the same. The content is presented in such a way that the burden of responsibility lies with the audience. This approach is well suited for writing that has a persuasive purpose.
The current political culture allows for staggering sums of money to be spent on campaigns. The basic idea is not so much about content as it is about getting the word out and creating a buzz. The more one hears about a candidate, the greater the buzz. And, of course, creating a buzz costs money, but, as advertisers have known for a long time, it is money well spent. Getting elected is a lot like selling laundry detergent, and until American citizens let their governmental advertisers know that they’ve had enough, that spending millions of dollars – even if it’s a candidate’s own money – to hold an office is ludicrous, then they have no one but themselves to blame.

State the “So What?”
With this ending, the writer essentially states the deeper meaning of the piece of writing so that the idea is not only clear, but it is also emphasized.
Today, Maine is one of only ten states that has not passed public charter school legislation. Maine’s current public school choice offerings are slim at best. Current choices include only traditional public schools or private schools. Whether the reason for wanting other alternatives is personal or educational, Maine families should be afforded another choice in public education. It’s time for Maine to recognize that public charter schools are a valuable choice in free public education.
Clinching Statement
With this type of conclusion, the writer uses a thought-provoking final statement that communicates the essence of the piece of writing and stays with readers.
For most residents living in hurricane-prone New Orleans, the first of June simply marks the beginning of another local season—hurricane season. The media quickly saturate the airwaves with hurricane season predictions, hurricane preparedness reminders and checklists, evacuation routes and guidelines, mini-lessons on the benefits of super Doppler imagery, and, certainly up until Katrina, doomsday predictions of what could happen if a major hurricane hit New Orleans. The information delivered was such standard fare that few gave it much thought. Hurricane Katrina changed all that. Katrina taught New Orleanians to be mindful of hurricane season and to pay attention—really pay attention—to what was swirling out near or in the Gulf. And even though by meteorological standards, Katrina was not the Big One, the apocalyptic aftermath of the storm and the physical and psychological damage it caused added up to something far greater than anyone expected.
Back to the Beginning
This ending uses content that in some way refers back to the beginning of the essay, not in a redundant way but in a manner that makes an important connection.
While friends will drift in and out of our lives, disappearing and maybe reappearing, some will be as constant as the stars in the sky. These friends – the essence of true friends – we will keep forever. These few friends will always be around, will see us through thick and thin, good and bad, no matter what, because that is what true friends do.
While the tendency when writing a conclusion is to offer a summary of what came before, now you have options for a conclusion that will move beyond a mere summary and bring the writing to a thoughtful and graceful exit.
Ernest Hemingway, the great 20th century American writer, claimed to have written 256 different endings for his short novel The Old Man and the Sea . According to Hemingway, he needed to get it right. While you may not have the time to try so many different conclusions, do keep in mind what Hemingway clearly knew: For a conclusion to be successful, it needs to be satisfying. Good endings create a sense of closure, a sense that the business of the essay has come to a completion; the reader is not expecting more. Like an introduction that makes a good first impression, the conclusion makes the final impression, and you want it to be lasting.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement Archive
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
Last Updated: June 29, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 42 testimonials and 82% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 2,257,835 times.
The conclusion of a research paper needs to summarize the content and purpose of the paper without seeming too wooden or dry. Every basic conclusion must share several key elements, but there are also several tactics you can play around with to craft a more effective conclusion and several you should avoid to prevent yourself from weakening your paper's conclusion. Here are some writing tips to keep in mind when creating a conclusion for your next research paper.
Sample Conclusions
Writing a basic conclusion.

- Do not spend a great amount of time or space restating your topic.
- A good research paper will make the importance of your topic apparent, so you do not need to write an elaborate defense of your topic in the conclusion.
- Usually a single sentence is all you need to restate your topic.
- An example would be if you were writing a paper on the epidemiology of infectious disease, you might say something like "Tuberculosis is a widespread infectious disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year."
- Yet another example from the humanities would be a paper about the Italian Renaissance: "The Italian Renaissance was an explosion of art and ideas centered around artists, writers, and thinkers in Florence."

- A thesis is a narrowed, focused view on the topic at hand.
- This statement should be rephrased from the thesis you included in your introduction. It should not be identical or too similar to the sentence you originally used.
- Try re-wording your thesis statement in a way that complements your summary of the topic of your paper in your first sentence of your conclusion.
- An example of a good thesis statement, going back to the paper on tuberculosis, would be "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease ."

- A good way to go about this is to re-read the topic sentence of each major paragraph or section in the body of your paper.
- Find a way to briefly restate each point mentioned in each topic sentence in your conclusion. Do not repeat any of the supporting details used within your body paragraphs.
- Under most circumstances, you should avoid writing new information in your conclusion. This is especially true if the information is vital to the argument or research presented in your paper.
- For example, in the TB paper you could summarize the information. "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease. In developing countries, such as those in Africa and Southeast Asia, the rate of TB infections is soaring. Crowded conditions, poor sanitation, and lack of access to medical care are all compounding factors in the spread of the disease. Medical experts, such as those from the World Health Organization are now starting campaigns to go into communities in developing countries and provide diagnostic testing and treatments. However, the treatments for TB are very harsh and have many side effects. This leads to patient non-compliance and spread of multi-drug resistant strains of the disease."

- Note that this is not needed for all research papers.
- If you already fully explained what the points in your paper mean or why they are significant, you do not need to go into them in much detail in your conclusion. Simply restating your thesis or the significance of your topic should suffice.
- It is always best practice to address important issues and fully explain your points in the body of your paper. The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed.

- Note that a call for action is not essential to all conclusions. A research paper on literary criticism, for instance, is less likely to need a call for action than a paper on the effect that television has on toddlers and young children.
- A paper that is more likely to call readers to action is one that addresses a public or scientific need. Let's go back to our example of tuberculosis. This is a very serious disease that is spreading quickly and with antibiotic-resistant forms.
- A call to action in this research paper would be a follow-up statement that might be along the lines of "Despite new efforts to diagnose and contain the disease, more research is needed to develop new antibiotics that will treat the most resistant strains of tuberculosis and ease the side effects of current treatments."

- For example, if you are writing a history paper, then you might discuss how the historical topic you discussed matters today. If you are writing about a foreign country, then you might use the conclusion to discuss how the information you shared may help readers understand their own country.
Making Your Conclusion as Effective as Possible

- Since this sort of conclusion is so basic, you must aim to synthesize the information rather than merely summarizing it.
- Instead of merely repeating things you already said, rephrase your thesis and supporting points in a way that ties them all together.
- By doing so, you make your research paper seem like a "complete thought" rather than a collection of random and vaguely related ideas.

- Ask a question in your introduction. In your conclusion, restate the question and provide a direct answer.
- Write an anecdote or story in your introduction but do not share the ending. Instead, write the conclusion to the anecdote in the conclusion of your paper.
- For example, if you wanted to get more creative and put a more humanistic spin on a paper on tuberculosis, you might start your introduction with a story about a person with the disease, and refer to that story in your conclusion. For example, you could say something like this before you re-state your thesis in your conclusion: "Patient X was unable to complete the treatment for tuberculosis due to severe side effects and unfortunately succumbed to the disease."
- Use the same concepts and images introduced in your introduction in your conclusion. The images may or may not appear at other points throughout the research paper.

- Include enough information about your topic to back the statement up but do not get too carried away with excess detail.
- If your research did not provide you with a clear-cut answer to a question posed in your thesis, do not be afraid to indicate as much.
- Restate your initial hypothesis and indicate whether you still believe it or if the research you performed has begun swaying your opinion.
- Indicate that an answer may still exist and that further research could shed more light on the topic at hand.

- This may not be appropriate for all types of research papers. Most research papers, such as one on effective treatment for diseases, will have the information to make the case for a particular argument already in the paper.
- A good example of a paper that might ask a question of the reader in the ending is one about a social issue, such as poverty or government policy.
- Ask a question that will directly get at the heart or purpose of the paper. This question is often the same question, or some version of it, that you may have started with when you began your research.
- Make sure that the question can be answered by the evidence presented in your paper.
- If desired you can briefly summarize the answer after stating the question. You could also leave the question hanging for the reader to answer, though.

- Even without a call to action, you can still make a recommendation to your reader.
- For instance, if you are writing about a topic like third-world poverty, you can various ways for the reader to assist in the problem without necessarily calling for more research.
- Another example would be, in a paper about treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis, you could suggest donating to the World Health Organization or research foundations that are developing new treatments for the disease.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls

- These sayings usually sound stiff, unnatural, or trite when used in writing.
- Moreover, using a phrase like "in conclusion" to begin your conclusion is a little too straightforward and tends to lead to a weak conclusion. A strong conclusion can stand on its own without being labeled as such.

- Always state the main argument or thesis in the introduction. A research paper is an analytical discussion of an academic topic, not a mystery novel.
- A good, effective research paper will allow your reader to follow your main argument from start to finish.
- This is why it is best practice to start your paper with an introduction that states your main argument and to end the paper with a conclusion that re-states your thesis for re-iteration.

- All significant information should be introduced in the body of the paper.
- Supporting evidence expands the topic of your paper by making it appear more detailed. A conclusion should narrow the topic to a more general point.
- A conclusion should only summarize what you have already stated in the body of your paper.
- You may suggest further research or a call to action, but you should not bring in any new evidence or facts in the conclusion.

- Most often, a shift in tone occurs when a research paper with an academic tone gives an emotional or sentimental conclusion.
- Even if the topic of the paper is of personal significance for you, you should not indicate as much in your paper.
- If you want to give your paper a more humanistic slant, you could start and end your paper with a story or anecdote that would give your topic more personal meaning to the reader.
- This tone should be consistent throughout the paper, however.

- Apologetic statements include phrases like "I may not be an expert" or "This is only my opinion."
- Statements like this can usually be avoided by refraining from writing in the first-person.
- Avoid any statements in the first-person. First-person is generally considered to be informal and does not fit with the formal tone of a research paper.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/724/04/
- ↑ http://www.crlsresearchguide.org/18_Writing_Conclusion.asp
- ↑ http://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html#conclusion
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/conclusions/
- ↑ http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/conclude.html
About This Article

To write a conclusion for a research paper, start by restating your thesis statement to remind your readers what your main topic is and bring everything full circle. Then, briefly summarize all of the main points you made throughout your paper, which will help remind your readers of everything they learned. You might also want to include a call to action if you think more research or work needs to be done on your topic by writing something like, "Despite efforts to contain the disease, more research is needed to develop antibiotics." Finally, end your conclusion by explaining the broader context of your topic and why your readers should care about it, which will help them understand why your topic is relevant and important. For tips from our Academic co-author, like how to avoid common pitfalls when writing your conclusion, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ummay Aimen
Sep 30, 2016
Did this article help you?
Oct 22, 2017
Sally Larrin
Mar 17, 2018
Maya Loeven
Jun 4, 2017
Sep 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, a two-or-three paragraph conclusion may be required.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with several important opportunities to demonstrate your overall understanding of the research problem to the reader. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key points in your analysis or findings.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger implications of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly answer the "so what?" question by placing the study within the context of past research about the topic you've investigated.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers you a chance to elaborate on the significance of your findings.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing/contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2018/07/conclusions_uwmadison_writingcenter_aug2012.pdf I. General Rules
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- State your conclusions in clear, simple language.
- Do not simply reiterate your results or the discussion.
- Indicate opportunities for future research, as long as you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Make sure, however, that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings because this reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your essay.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data.
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented, or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have done will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way.
NOTE : Don't delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply not to guess at possible outcomes.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following.
- If your essay deals with a contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion to lend authority to the conclusion you have reached [a good place to look is research from your literature review].
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to drive home the ultimate point of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point with a relevant narrative drawn from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you introduced in your introduction, but add further insight that is derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results to reframe it in new ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a strong, succient statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid Failure to be concise The conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too long often have unnecessary detail. The conclusion section is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, etc. that you make. Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from general [the field of study] to specific [your research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from specific [your research problem] back to general [your field, i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In other words, the conclusion is where you place your research within a larger context. Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. Problems, drawbacks, and challenges encountered during your study should be included as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative results [findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section of your paper. In the conclusion, use the negative results as an opportunity to explain how they provide information on which future research can be based. Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits back into your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize it briefly and directly. Often this element of your conclusion is only a few sentences long. Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine your original objectives in your introduction, as these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you now know a good deal about it, perhaps even more than your professor! Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches...."
Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions . Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization . Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining to read, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your Conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. If you have new information to present, add it to the Discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no actual new information is introduced, the conclusion is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; it's where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate your understanding of the material that you’ve presented, and locate your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Writing the Introduction/Background of a Research Article
Writing the introduction and background of a research article can be daunting. Where do you start? What information should you include?
A great place to start is creating an argument structure for why your research topic is relevant and important. This structure should clearly walk the reader through current, relevant literature and lead them to the gap in the literature that your topic fills. To do this I use the following 4-step argument creation structure.
- Create argument funnel questions/statements
- Harvest article quotes that explain/backup each of the argument funnel questions/statements
- Organize article quotes to best support each section of the argument funnel
- Write prose that utilizes the article quotes to progress your argument from most well known to your specific topic
1. Argument Funnel Creation
Create an argument funnel with statements that take the reader form the most well known and widely accepted knowledge connected to my topic down to your specific research topic.
Completed Argument Funnel Example
When creating your funnel statements think about what research exists related to your topic. Where are the gaps in the existing literature? How do you know those are the gaps? If you get stuck, think about the 50,000 ft view of your topic and how you would explain the necessity of your research to people not in your field.
2. Harvesting Article Quotes
Find research articles that pertain to each of your funnel statements to back them up with evidence. As you find the articles put them into a citation manager (e.g., Zotero) now to save yourself time later. While reading the articles, pull (copy and paste) article quotes/excerpts that MAY be relevant. Pull more than you think you need, especially duplicates of the same idea by different authors to strengthen your argument. Store your quotes/excerpts in a document organized by your funnel statements with in-text citations with the page number you pulled it from. The National Academy of Engineering reports can be valuable top of funnel resources.
3. Organizing Article Quotes
Once you have harvested many article quotes for each of your funnel statements, organized them in an order that walks your reader through the literature landscape in a logical way. As you do this assume the reader doesn’t know anything about your topic so start at the beginning. Chronological order is a good place to start but may not always fit your argument. Think about your quotes/excerpts as puzzle pieces, where do they logically fit together?
4. Writing Prose
Now that your article quotes are organized, summarize the quotes in your own voice with appropriate citations. This is the time to begin including transition/connecting words and phrases between summarized quotes to bring your reader through your argument. Don’t forget to include “so what?” sentences and phrases after summarized quotes. In other words don’t only report what other authors said or found, tell the reader why that is important to your argument.

Essay Conclusion Generator
Ai-powered essay conclusion tool.
- Finish a school essay: Create a compelling conclusion that summarizes your arguments and restates your thesis.
- Conclude a research paper: Generate a succinct conclusion that wraps up your findings and leaves a lasting impression.
- Close a persuasive essay: Craft a powerful conclusion that reinforces your arguments and persuades your readers.
- Conclude a narrative essay: Create a memorable conclusion that ties together your story and leaves your readers satisfied.
- Finish a college application essay: Generate a compelling conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on the admissions committee.
New & Trending Tools
Ai text generator, webpage text extractor ai.
< Main ILO website

Introduction
Principles of the “high road”, the return of theory x using artificial intelligence, the pluses and minuses of ai in the workplace, managing the transition: why the “wrong” choices are made, policy responses to the ai-related and other technological challenges.
See all ILO working papers
Artificial intelligence in human resource management: a challenge for the human-centred agenda?
(no footnote loaded)
Peter Cappelli
Nikolai Rogovsky
The ILO human-centred agenda puts the needs, aspirations and rights of all people at the heart of economic, social and environmental policies. At the enterprise level, this approach calls for broader employee representation and involvement that could be powerful factors for productivity growth. However, the implementation of the human-centred agenda at the workplace level may be challenged by the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in various areas of corporate human resource management (HRM). While firms are enthusiastically embracing AI and digital technology in a number of HRM areas, their understanding of how such innovations affect the workforce often lags behind or is not viewed as a priority. This paper offers guidance as to when and where the use of AI in HRM should be encouraged, and where it is likely to cause more problems than it solves.
Sustainable development is at the core of national and international discussions on development issues. At the enterprise level, the ILO defines sustainability as “operating a business so as to grow and earn profit, and recognition of the economic and social aspirations of people inside and outside the organization on whom the enterprise depends, as well as the impact on the natural environment” (ILO 2007). According to the ILO, “sustainable enterprises should innovate, adopt environmentally friendly technologies, develop skills and human resources, and enhance productivity to remain competitive in national and international markets” (ILO 2007).
The ILO Centenary Declaration for the Future of Work emphasizes “the role of sustainable enterprises as generators of employment and promoters of innovation and decent work” and, in this regard, underlines the importance of “supporting the role of the private sector as a principal source of economic growth and job creation by promoting an enabling environment for entrepreneurship and sustainable enterprises […] in order to generate decent work, productive employment and improved living standards for all”. Creating “productive workplaces” and “productive and healthy conditions” of work are critical in achieving this goal (ILO 2019a).
At both the macro- and micro-levels, the ILO promotes the “high road” approach to productivity which “seeks to enhance productivity through better working conditions and the full respect for labour rights as compared to the “low road” which consists of the exploitation of the workforce” (ILO, n.d.). The “high road” is related to the ILO’s “human-centred agenda,” which is a key part of the ILO human-centred approach to the future of work highlighted in the ILO Centenary Declaration for the Future of Work and described in-depth in the related Work for a brighter future – Global Commission on the Future of Work report. This approach puts “workers’ rights and the needs, aspirations and rights of all people at the heart of economic, social and environmental policies” (ILO 2019a) and calls for investments in people’s capabilities, institutions of work and in decent and sustainable work (ILO 2019b). It is expected that such investments would be combined with people-centred approach to business practices at the workplace level.
This paper is aimed at exploring when and how AI is used in HRM, and when its impact on firm and individual performance is positive, negative or cannot be properly accessed. We start by looking at the principles of high road approach and how these principles are related to the use of AI in HRM. Then we specifically look at the pluses of minuses of AI in the workplace focusing on such aspects of HRM as hiring and work organization. We conclude with a brief overview of some possible policy responses to the AI-related and other technological challenges.
Since the Western Electric studies that were carried out in the 1920s and 1930s (Landsberger 1958), evidence has accumulated year-by-year about the advantages of taking employee management seriously: look after employees, and they will look after the employer’s interests; empower employees to make decisions, from quality circles to lean production to agile management, and performance and quality improves.
In the 1950s and early 1960s, Douglas McGregor described the developing literature on the effectiveness of management practices as “Theory Y” and contrasted it with “Theory X” which essentially views employees as simply another factor of production like raw materials in manufacturing (McGregor 1960). Frederick Taylor and his scientific management approach were arguably the originators of a sophisticated view of Theory X, which is rooted in a simple, conservative (with a small “c”) notion that employees are mainly motivated by money, need to be told what to do by experts, and will shirk their responsibilities if not watched closely. Theory Y has the much more complex but more accurate assumption that employees have many complicated motivations and if managed correctly would do the right thing for the employer even if they are not monitored or incentivized by financial rewards and punishments. The contemporary incarnation of Theory X and Y with a few new twists is the idea of a “high road” approach for Theory Y practices and a “low road” for Theory X.
In recent decades, evidence has accumulated about the advantages of Theory Y approach of taking employee management seriously and the most fundamental element of that approach, reciprocity: if employers look after the interests of their employees, then the employees in turn will be inclined to look after the interests of their employer.
The ILO data from the Better Work and Sustaining Competitive and Responsible Enterprises (SCORE) programmes 1 provides evidence of the positive effects of such an approach, showing that “improved workplace cooperation, effective workers’ representation, quality management, clean production, human resource management and occupational safety and health, as well as supervisory skills training, particularly among female supervisors, all increase productivity”. Moreover, “better management also helps to lower accidents at work 2 and employee turnover and reduces the occurrence of unbalanced production lines (where work piles up on one line while other workers are sitting idle)”. Evidence also points to “increased productivity and profitability associated with a reduction in verbal abuse and sexual harassment.” 3
Evidence has even moved past showing reductions in turnover and improvements in individual and organizational productivity to financial performance. The strongest of these studies is arguably Edmans (2011) which finds that companies making the “best places to work” ranking have higher than anticipated share prices in future years. A different study finds a similar market-beating performance for companies that have greater managerial integrity and ethics (Guiso, Sapienza and Zingales 2015). Another global study shows that companies that have better management (including more sophisticated human resource practices) perform better on a wide range of economic dimensions (Bloom and Van Reenen 2010).
None of this is to suggest that tracking employee performance, setting standards for their work efforts, and rewarding and punishing are irrelevant. However, relying solely on those tactics is not enough.
At the same time, it is important to note that at least in the short term the “low road” approach to management can allow firms to break-even or even improve economic performance (but not social outcomes) where the initial practices are simplistic. In those countries and sectors where labour standards and laws are not always respected and workers are often not organized and represented, the “low road” approach to productivity is still common, in part because it is simpler for management and may appeal to their world view that focuses on their roles. However, the “low road” approach is seeing something of a resurgence even in the most sophisticated sectors of the world leading economies as we note below.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in HRM can challenge the implementation of the ILO-led human-centred agenda at the workplace level. While firms are enthusiastically embracing artificial intelligence and digital technology in a number of their HRM areas, their understanding of how such innovations affect the workforce is often not viewed as a priority or lags behind (Rogovsky and Cooke 2021).
Many enterprises in both developing and developed countries are replacing the employee empowerment approach, such as quality circles and lean production, with an “optimization” approach where experts and the algorithms associated with artificial intelligence (AI) they create take back the decision-making that empowerment had created. Optimization seems to appeal to many managers as it sounds per se to be more efficient. As a result, the evidence of employee empowerment as a productivity driver is largely ignored (Cappelli 2020).
The application of data science as well as an increase in computer power in worker-related questions have spawned a huge number of applications, indeed an entire industry of vendors, offering solutions to virtually every human resource question. It takes the decision-making out of the hands of employees and their supervisors as well, turning it over to the software and ultimately the vendors and their programmers who generate answers to human resource problems. In 2020, 28 per cent of US employers report that they were using data science tools to “replace line manager duties in assigning tasks and managing performance.” 39 per cent were planning to start doing so the following year (Mercer 2020).
The use of AI in the form of data science in workforce management is not per se a bad thing. As with AI in other contexts, it may allow us to answer questions that have not been addressed before: not every AI solution is taking decisions away from humans. For example, advice to employees about possible career paths can be generated for them by machine-learning algorithms based on what has been best in the past for other workers like them. Rigorous advice on questions like this has simply not been available before. It is also the case that decisions currently made by managers and supervisors are often so poor, driven by subjectivity and bias, which makes it easier for data science solutions to do better. In hiring, for example, it is easier for data-based algorithms to do a better job than line managers who have no relevant training and base their decisions largely on subjective opinion. More generally, the lag in productivity growth across most industrialized countries has been caused, at least in part, because not enough investment was made in solutions where “capital,” which includes software, takes over tasks from workers and perform them at less cost. Consider, for example, what it would cost for a large employer that receives thousands of job applications every year if it had to do the initial classification of applications by hand instead of by applicant tracking software.
The issue in terms of guidance is knowing when the application of these AI techniques is useful (i.e. they solve new problems and handle tasks better than humans do) and where they are counterproductive (i.e. they offer no advantage over human decisions and may actually make employment relationships worse).
Finding such a mix is a challenge that involves managerial as well as moral dimensions. At the very least, we believe that when there is a choice between options that are equal in terms of organizational outcomes, employers should choose the one that is better for employees. This principle coincides with standard utilitarian views of ethics and with economic interpretations of Pareto improvements. 4 Perhaps more importantly, it draws on the legal principle in civil law of “abuse of right”, which means that simply because one party has the legal right to do something does not create the right to do it if by doing so it damages other parties without creating benefits (Mughal, unpublished).
There are still very few studies that examine the implications of artificial intelligence for corporate HRM. Tambe, Cappelli and Yakubovich (2019) noted “a substantial gap between the promise and reality of artificial intelligence” in the area of HRM. They identified four major challenges in using artificial intelligence as part of HRM:
complexity of HR phenomena, which make it difficult to model;
limitations of small data sets;
accountability issues associated with fairness and other ethical and legal constraints when decisions are made by algorithms; and
potentially negative employee reactions to managerial decisions taken based on data-based algorithms.
In particular, from both economic and social points of view there is a growing concern over the use of artificial intelligence algorithms for hiring (Cappelli 2019) and for work organization (Cappelli 2020). These issues will be considered next.
It may be easiest to grasp the general principles behind the use of AI through some common examples. Before we look into the “optimization” policies and practices per se , let us focus on hiring which is perhaps the most basic, time-consuming, and important of the employee management questions. The evidence increasingly points to the fact that we do not handle this process well even without AI: we rely on ad hoc methods of finding recruits, mainly just hoping that the right ones come to us, and then we hope that hiring managers, typically untrained in the process who rely on off-the-cuff interviews, will somehow find the best candidates to hire. Then we do not check to see whether the ones we have hired are good or bad so we do not learn from the process. What we do know is that this process gives ample room for biases to influence decisions: my personal views on what constitutes a good cultural “fit” shape who gets hired as does how much I like candidates, which is strongly correlated with how similar they are to me.
Hiring is actually a context where the prospects for algorithms are best. The way data science ideally works starts with machine learning, where the software (the “machine” in this case) looks at the attributes of as many current and past employees as possibly to see how their attributes relate to their quality as employees. The software is agnostic as to what should matter and how it should matter: relationships could be non-linear, simultaneous, in any form. It generates a single equation to measure the attributes that are associated with a good performer, not as with prior “best practice” approaches where there is one score for say IQ, one for prior experience, one for interviews, and so forth. The machine learning algorithm looks at any potential candidate and tells you how similar they are to those in the past who were your best performing employees.
The plus of this approach is that it is objective. Unlike human assessors, it will not give higher scores to more attractive applicants or those most similar to us. Algorithms have the advantage of treating all similar observations the same way: if it is counting a college degree a certain way, it does not give extra credit to the college where the boss is an alumnus. Cowgill (2020) finds that an algorithm used to predict who should advance to short-list status did a better job than human recruiters did in part because it did not over-value credentials that had higher social status such as degrees from elite universities. 5 An algorithm will also find factors that predict that humans with our more limited experience would never find. Another plus is that once set up, using algorithms to hire is remarkably cheaper than relying on humans.
The downside that is common to human assessors is that if prior experience was shaped by bias, then the algorithm will be as well. Amazon’s hiring algorithm, for example, gave higher scores to men because in the past Amazon managers had given higher scores to male employees (Cappelli 2019). Another downside is the issue now known as “explainability”: can we explain to the candidates why they were not hired when they ask why their scores were low? It is difficult for machine learning algorithms to address those questions. Complaints from gig workers that the algorithms managing them are biased have led organizations like the UK-based Workers Info Exchange to press those gig companies to explain to their contractors why and how their algorithms made the decisions they did (Murgia 2021). It also takes very large data sets to generate machine learning algorithms, and few employers hire enough employees to build their own. They are likely as a result to rely on the algorithms produced by vendors with no guarantee or even reason to believe that the vendor’s algorithm will predict hiring success for their jobs.
A related issue is that some of the factors that have been used in generating these algorithms might give us qualms. For example, the commuting distance from one’s home to a job has been shown to be a good predictor of turnover and some aspects of performance. Where one lives, therefore, shapes the likelihood of getting a job. Social media postings are sometimes used in building hiring algorithms as well. Most employers would probably want limits placed on the kind of information on which the algorithms are based, something that is not possible when one uses algorithms produced elsewhere.
From the human-centred point of view, these practices are not only potentially discriminatory as Amazon case shows, but they also prevent decent candidates getting the jobs they deserve.
If hiring is amongst the most promising uses of AI, perhaps the most troublesome is the use of software to determine workers’ schedules. This is not a new idea, but its use has expanded considerably to a wide range of jobs. 6 42 per cent of US companies now use it (Harris and Gurchensky 2020). The goal is a sensible one, to “optimize” work scheduling process in order to minimize total amount of labor needed to cover assignments and make sure that everyone is doing roughly the same amount of work allocated across similar schedules. The reason this approach is troublesome, though, is because we have other approaches that work even better where the employees themselves work out schedules through a process of negotiations and social exchange: I’ll cover for you this weekend if you take my shift next week, for example. Scheduling algorithms cut both employees and supervisors out of the process and end up being quite rigid and unable to respond to last-minute adjustments. 7 A study of optimization approaches in scheduling discovered that it increased turnover and turnover costs while adding nothing to performance outcomes (Kesavan and Kuhnen 2017). The effort to cut costs in one category (headcount) increased them in another (turnover).
The evidence that the flexible approach works is, by the standards of rigorous research, about as good as it gets. It improves a range of outcomes for employees, such as better job attitudes (Baltes et al. 1999), as well as better accommodation of life challenges outside of work including evidence that it is worth extra salary to employees (Kelly et al. 2008). For employers, it leads to higher productivity 8 . Software, in contrast, assumes that the workers are interchangeable, it imposes schedules without any consideration as to the varying needs of individual employees, and it is not at all flexible when last-minute problems pop up. As with many of these new practices, the question is, what problem is it really solving, and is the solution worse than the original problem?
Then we have situations where existing practices that involve empowering employees have worked extremely well yet there is a push to replace them with software. Beginning in the 1970s, efforts to involve employees in solving workplace problems borrowed from Japan by North American and West European companies worked so well that they spread systematically throughout industrialized countries and beyond, starting union-based cooperative programmes on safety problems, to quality circles where workers identified the causes of quality problems, and then to lean production where workers took over some of the tasks of the industrial engineers, redesigning their own jobs to improve productivity and quality. The evidence that lean production in the form of Toyota’s operating model worked so much better than anything else, especially the efforts at GM and Volkswagen to deal with productivity and quality problems with automation, was so clear that it was impossible to ignore (MacDuffie and Pil 1997). Lean production spread from there to other industries including healthcare.
Recently, though, we have seen efforts to replace the employee involvement that was at the heart of lean production with machine learning software. The new approach is called “machine vision.” Rather than having employees figure out what is wrong with their work processes, it captures what employees are doing now with cameras. Some of the new software ends there, monitoring assembly line workers constantly to make sure that they perform the tasks exactly as designed. Another software called Robotic Process Automation takes those video images and figures out how to redesign tasks to make them more efficient. In other words, it takes over the tasks the workers used to do in lean production (Simonite 2020). Other vendors reassemble jobs to push simpler tasks down to cheaper labour, 9 the classic “deskilling” practice with the classic pushback, that the narrow, simple tasks that result are so boring that engagement, commitment, and performance ultimately decline. They are performing the same tasks that workers had done before with the difference being that now, the most and possibly only interesting part of those jobs is gone. That control is what made the boring jobs tolerable.
More generally, it is also difficult to argue that paying vendors to take over a task that employees either were already doing or could do – updating the performance of tasks through lean production - is going to be cheaper, especially because lean production is a never-ending process that has to be recalibrated whenever there are changes anywhere in the system.
A final especially illustrative example comes from earlier days in IT technology and the introduction of numerically controlled machines in machining work. Here the question was, who will perform the tasks of setting up and programming those machines, something that has to be done frequently, whenever they switch over to a new product or new specifications for it. One option was to hire engineers who were skilled programmers and have them learn the context of machining that was done in different organizations. That would mean getting rid of many of the machinists. The other was to take the machinists who had the knowledge for the latter tasks and teach them programming. It was easier to do the former, but it was far cheaper in the long run to do the latter not only by avoiding the churning costs of laying off one group of workers and hiring in another or even because machinists were paid less than engineers but because the employer then created a cadre of employees with skills unique to them: unlike the programming engineers, who could easily leave for jobs elsewhere, these machinist-programmers now had the best jobs they likely could find anywhere (Kelley 1996).
There is sometimes a view stemming from simple economic assumptions that “firms” always make the most efficient choices because if they do not, they go out of business. But most businesses do fail, and it is possible for larger companies to make the wrong decisions for some time and yet stay in business. There are also so many decisions to be made in businesses that it is inevitable that we will make the wrong ones in some area.
Employers are not rational calculating machines, they are humans with the same limitations in ability to make decisions as all of us have. In the workplace, though, there are systematic reasons why employers might choose the “low road” approach even when alternatives objectively make more sense. One reason is that high road approaches that require engaging employees and soliciting their best efforts are not easy to pursue. They require sustained efforts at communication, building trust, and so forth. Not every business leader has the inclination to pursue that path. Nor do they have the knowledge base to do so. Leaders who come from engineering backgrounds are taught optimization approaches to business problems that, when focused on worker issues, come down to minimizing the costs of using them. That approach per se is not the issue as long as we have complete and accurate measures of costs and benefits 10 . But few if any employers have those measures.
Consider, for example, the cost of turnover, which is one of the most basic facts necessary to operate efficiently. Organizations that are focused on making money need to know what those costs are in order to determine how much investment is efficient to head them off. We also need to know where those costs occur. It is common if they are measured at all to simply count the administrative costs of hiring a replacement. A very careful look at these costs found that even in front-line retail jobs, two-thirds of the costs of turnover come between the time when the employee gives their notice to leave and before they actually depart. That happens in part because of negative effects on peers who remain, in part because of the demands on them of recruiting, hiring, and onboarding replacements. Those costs are massively greater than the administrative costs (Kuhn and Yu 2021). What most employers do instead is use a rough measure of the administrative costs of hiring a new worker as a proxy, which vastly undercounts the true costs. Why employers had not calculated them is in part because it is difficult to do but ultimately because of the unspoken assumption that, unlike say the costs of missing inventory, they are not big enough to bother.
At the same time, employers’ incorrect assumptions can also be explained by a lack of understanding about how humans actually behave. Many employers are simply convinced that in order to be productive the employees must be tightly controlled and refuse to accept the notion that the employees can contribute more when they are given freedom to express their views, contribute to the decision making process and are expected to take initiative 11 . Another reason, which is investor driven, is the quirkiness of financial accounting: Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) are more likely to invest in software but not in employees because software is an asset that can be depreciated – paid off over time – whereas training and other investments in employees are current expenses that must be paid off completely in the year they are “purchased” (Cappelli 2023).
To summarize, we offer some practical suggestions on the use of AI in corporate HRM (see Box 1). The choices as to whether to use AI tools or rely on employees depend in part – but only in part - on the nature of the tasks in question. The traditional view that we should automate the simplest tasks is not necessarily the right advice as we saw earlier with lean production where simple tasks were bundled together into jobs that workers largely controlled. There they were able to take over supervisory tasks and proved more adaptable (e.g., they did not need to be reprogrammed) than robots. Beyond the nature of the tasks, the context also determines the choice of using AI or humans.
Box 1. AI and HRM: Q&A
Governments and social partners can come up with a number of policies and practices that help guide corporate HR functions to respond to the AI-related opportunities as well as other technological challenges. Many of them are in line with the ILO-driven human-centred agenda, in particular with its pillars related to “harnessing and managing technology for decent work”, and “universal entitlement to lifelong learning that enables people to acquire skills and to reskill and upskill” 12 (ILO 2019b).
Many governments have been active in promoting a knowledge economy, the development of high-tech firms and technological upgrading in the manufacturing sector through smart manufacturing underpinned by innovations (Cooke, forthcoming). For example, in 2015, the Chinese government launched “Made in China 2025”, which is one of the national strategic initiatives aimed at transitioning China from a “large manufacturing country” to a “strong manufacturing country” through innovations related to digital technology and artificial intelligence (Kania 2019). The success of such a strategic initiative largely depends on the development of a well-educated workforce equipped with the skills and knowledge required by employers. In this case, the industrial policy of making more use of AI went together with upgrading the education and skills of workers.
Technological challenges may imply that workers will experience more transitions – as some jobs get automated. They will need more than ever support to go through a growing number of labour market transitions throughout their lives. In particular, younger workers will need help in “navigating increasingly difficult school-to-work transition” (Cooke, forthcoming). Older workers will need to be able to stay economically active as long as they want. 13 Lifelong learning policies will definitely help to be prepared for these transitions. Interestingly, data science algorithms may actually be useful here first in creating a more efficient labour market for matching workers and jobs and second by making better predictions as to what kind of skills individuals will need next based on their current experiences and jobs.
In this paper we identified some of the key challenges for high-road approach to employee management that are associated with rapid technological development and, in particular, with the use of AI. While the use of AI in HRM, in particular for hiring and work organization, is promising, still low-road approach is rather common and many suboptimal decisions are being made. The situation can be improved by broader employee engagement in HR-related decision-making process, training of managers on the principles and examples of high-road approach, as well as smart government policies. Particular attention should be paid to the development of “knowledge economy”, harnessing and managing technology for decent work, and universal entitlement to lifelong learning that enables people to acquire skills and to reskill and upskill.
As far as research is concerned, we call for more research to be done on:
pluses and minuses of using the AI in HRM;
the “natural boundaries” between the humans and AI;
how to ensure that the AI does not inherit mistakes made by the humans in the past (for example when it comes to hiring);
how AI products can become truly self-learning;
the ways to encourage fruitful collaboration of data scientists and HRM professionals in the development of the AI products; and
the role of policy makers in encouraging the use of “people-friendly” AI and in promoting high-road corporate practices.
Baltes, Boris B., Thomas E. Briggs, Joseph W. Huff, Julie A. Wright, and George A. Neuman. 1999. “Flexible and Compressed Workweek Schedules: A Meta-Analysis of Their Effects on Work-Related Criteria”. Journal of Applied Psychology 84 (4): 496–513.
Bernstein, Ethan, Saravanan Kesavan, and Bradley Staats. 2014. “How to Manage Scheduling Software Fairly”. Harvard Business Review, December 2014.
Bloom, Nicholas, and John Van Reenen. 2010. “Why Do Management Practices Differ across Firms and Countries?” Journal of Economic Perspectives 24 (1): 203–224.
Cappelli, Peter. 2019. “Your Approach to Hiring Is All Wrong”. Harvard Business Review, May–June 2019.
———. 2020. “Stop Overengineering People Management: The Trend toward Optimization Is Disempowering Employees”. Harvard Business Review, September–October 2020.
———. 2023. Our Least Important Asset: Why the Relentless Focus on Finance and Accounting Is Bad for Business and Employees. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cooke, Fang Lee. Forthcoming. “Towards a Human-Centred Approach to Increasing Workplace Productivity: A Multi-Level Analysis of China”. In The Human-Centred Approach to Increasing Workplace Productivity: Evidence from Asia, edited by Nikolai Rogovsky and Fang Lee Cooke. Geneva: ILO.
Cowgill, Bo. 2020. “Bias and Productivity in Humans and Algorithms: Theory and Evidence from Résumé Screening”. Research paper. Columbia Business School.
Edmans, Alex. 2011. “Does the Stock Market Fully Value Intangibles? Employee Satisfaction and Equity Prices”. Journal of Financial Economics 101 (3): 621–640.
Ghosheh, N.S., Jr., Sangheon Lee, and Deirdre McCann. 2006. “Conditions of Work and Employment for Older Workers in Industrialized Countries: Understanding the Issues”, ILO Conditions of Work and Employment Series No. 15.
Guiso, Luigi, Paola Sapienza, and Luigi Zingales. 2015. “The Value of Corporate Culture”. Journal of Financial Economics 117 (1): 60–76.
Harris, Stacey, and Amy L. Gurchensky. 2020. Sierra-Cedar 2019–2020 HR Systems Survey: 22nd Annual Edition. Sierra-Cedar.
ILO. 2007. Conclusions concerning the promotion of sustainable enterprises. International Labour Conference. 96th Session.
———. 2019a. ILO Centenary Declaration for the Future of Work.
———. 2019b. Work for a Brighter Future – Global Commission on the Future of Work.
———. 2021. Decent Work and Productivity. GB.341/POL/2.
———. n.d. “Productivity”. https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/dw4sd/themes/productivity/lang--en/index.htm .
Kania, Elsa B. 2019. “Made in China 2025, Explained: A Deep Dive into China’s Techno-Strategic Ambitions for 2025 and Beyond”. The Diplomat, 1 February 2019.
Kelley, Maryellen R. 1996. “Participative Bureaucracy and Productivity in the Machined Products Sector”. Industrial Relations: A Journal of Economy and Society 35 (3): 374–399.
Kelly, Erin L., Ellen Ernst Kossek, Leslie B. Hammer, Mary Durham, Jeremy Bray, Kelly Chermack, Lauren A. Murphy, and Dan Kaskubar. 2008. “Getting There from Here: Research on the Effects of Work–Family Initiatives on Work–Family Conflict and Business Outcomes”. The Academy of Management Annals 2 (1): 305–349.
Kesavan, Saravanan, and Camelia M. Kuhnen. 2017. “Demand Fluctuations, Precarious Incomes, and Employee Turnover”. Working paper. Kenan‑Flagler Business School.
Kuhn, Peter, and Lizi Yu. 2021. “How Costly is Turnover? Evidence from Retail”. Journal of Labor Economics 39 (2).
Landsberger, Henry A. 1958. Hawthorne Revisited: Management and the Worker, Its Critics, and Developments in Human Relations in Industry. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University.
Lee, Byron Y., and Sanford E. DeVoe. 2012. “Flextime and Profitability”. Industrial Relations: A Journal of Economy and Society 51 (2): 298–316.
Liem, Cynthia C.S, Markus Langer, Andrew Demetriou, Annemarie M.F. Hiemstra, Achmadnoer Sukma Wicaksana, Marise Ph. Born, and Cornelius J. König. 2018. “Psychology Meets Machine Learning: Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Algorithmic Job Candidate Screening”. In Explainable and Interpretable Models in Computer Vision and Machine Learning, edited by Hugo Jair Escalante, Sergio Escalera, Isabelle Guyon, Xavier Baró, Yağmur Güçlütürk, Umut Güçlü and Marcel van Gerven, 197–253. Cham: Springer.
MacDuffie, John Paul, and Frits K. Pil. 1997. “Changes in Auto Industry Employment Practices: An International Overview”. In After Lean Production: Evolving Employment Practices in the World Auto Industry, edited by Thomas A. Kochan, Russell D. Landsbury and John Paul MacDuffie, 9–44. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University.
McGregor, Douglas. 1960. The Human Side of Enterprise. New York: McGraw‑Hill.
Mercer. 2020. 2020 Global Talent Trends Study.
Mughal, Munir Ahmad. Unpublished. “What is Abuse of Rights Doctrine?” 8 September 2011.
Murgia, Madhumita. 2021. “Workers Demand Gig Economy Companies Explain their Algorithms”. Financial Times, 13 December 2021.
Rogovsky, Nikolai, and Fang Lee Cooke, eds. 2021. Towards a Human-Centred Agenda: Human Resource Management in the BRICS Countries in the Face of Global Challenges. Geneva: ILO.
Simonite, Tom. 2020. “When AI Can’t Replace a Worker, It Watches Them Instead”. WIRED, 27 February 2020.
Tambe, Prasanna, Peter Cappelli, and Valery Yakubovich. 2019. “Artificial Intelligence in Human Resources Management: Challenges and a Path Forward”. California Management Review 61 (4): 15–42.
Van den Bergh, Jorne, Jeroen Beliën, Philippe De Bruecker, Erik Demeulemeester, and Liesje De Boeck. 2013. “Personnel Scheduling: A Literature Review”. European Journal of Operational Research 226 (3): 367–385.
WTW. n.d. “WorkVue”. https://www.wtwco.com/en-ch/solutions/products/work-vue .
Peter Cappelli is the George W. Taylor Professor of Management at the Wharton School and Director of Wharton’s Center for Human Resources, University of Pennsylvania
Nikolai Rogovsky is a Senior Economist, Research Department, International Labour Office
Copyright © International Labour Organization 2023
This is an open access work distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 IGO License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/igo/deed.en ). Users can reuse, share, adapt and build upon the original work, even for commercial purposes, as detailed in the License. The ILO must be clearly credited as the owner of the original work. The use of the emblem of the ILO is not permitted in connection with users’ work.
Translations – In case of a translation of this work, the following disclaimer must be added along with the attribution: This translation was not created by the International Labour Organization (ILO) and should not be considered an official ILO translation. The ILO is not responsible for the content or accuracy of this translation.
Adaptations – In case of an adaptation of this work, the following disclaimer must be added along with the attribution: This is an adaptation of an original work by the International Labour Organization (ILO). Responsibility for the views and opinions expressed in the adaptation rests solely with the author or authors of the adaptation and are not endorsed by the ILO.
This CC license does not apply to non-ILO copyright materials included in this publication. If the material is attributed to a third party, the user of such material is solely responsible for clearing the rights with the right holder.
All queries on rights and licensing should be addressed to ILO Publishing (Rights and Licensing), CH-1211 Geneva 22, Switzerland, or by email to [email protected] .
ISBN: 9789220394045
https://doi.org/10.54394/OHVV4382
ILO/International Finance Corporation, “Better Work”. ILO, “Sustaining Competitive and Responsible Enterprises (SCORE): Programme at a Glance”. Cited from ILO (2021).
ILO, “Looking Back to Look Forward – Impact Evaluation of ILO SCORE Training in Peru”, ILO SCORE Impact Study, August 2020. Cited from ILO (2021).
ILO, SCORE (Sustaining Competitive and Responsible Enterprises): Phase II Final Report 2017, 2017, 36–37. Cited from ILO (2021).
Pareto improvement occurs when a change in allocation does not harm anyone and helps at least one agent, given an initial allocation of goods for a set of agents.
For a very detailed discussion of how machine learning treats hiring tasks as opposed to the more traditional approach from psychology, see Liem et al. (2018).
For a review of this literature, see Van den Bergh et al. (2013).
Bernstein, Kesavan and Staats (2014) note that it is possible to try to balance the recommendations of the algorithms, but for most employers, the reason for using them is to eliminate the time needed for that process.
See, e.g., Lee and DeVoe (2012).
The software is WorkVue. See WTW (n.d.).
This includes intangible costs (such as workers’ views on firm’s reputation as an employer, job quality or equity in decision-making, etc.) that might not be fully addressed or calculated.
As noted earlier these are the two conflicting views of Theory X and Theory Y by Douglas McGregor in his seminal book The Human Side of Enterprise (1960).
Ghosheh, Lee and McCann (2006) provide an overview of the factors that need to be considered for older workers to effectively and constructively continue to contribute to the labour market.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 27 April 2024
Spatial non-parametric Bayesian clustered coefficients
- Wala Draidi Areed 1 ,
- Aiden Price 1 ,
- Helen Thompson 1 ,
- Reid Malseed 2 &
- Kerrie Mengersen 1
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 9677 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Health care
- Mathematics and computing
In the field of population health research, understanding the similarities between geographical areas and quantifying their shared effects on health outcomes is crucial. In this paper, we synthesise a number of existing methods to create a new approach that specifically addresses this goal. The approach is called a Bayesian spatial Dirichlet process clustered heterogeneous regression model. This non-parametric framework allows for inference on the number of clusters and the clustering configurations, while simultaneously estimating the parameters for each cluster. We demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed algorithm using simulated data and further apply it to analyse influential factors affecting children’s health development domains in Queensland. The study provides valuable insights into the contributions of regional similarities in education and demographics to health outcomes, aiding targeted interventions and policy design.
Similar content being viewed by others
Predictive limitations of spatial interaction models: a non-Gaussian analysis
Measuring inequality beyond the Gini coefficient may clarify conflicting findings
Functional data analysis characterizes the shapes of the first COVID-19 epidemic wave in Italy
Introduction.
Spatial data analysis in public health often involves statistical models for areal data, which aggregate health outcomes over administrative units like states, counties, or zip codes 1 . Statistical models for areal data typically aim to provide estimates of geospatial outcomes of interest, find boundaries between abrupt changes in spatial patterns, describe smoothly varying spatial trends, identify and characterise spatial clusters, and so on. These models have been extensively employed in various fields, including geography, econometrics, ecology, epidemiology and public health.
When spatial dependence is present in the data, traditional statistical models that assume independent observations are inadequate and can produce biased estimates of outcomes of interest. This necessitates the use of alternative spatial models that incorporate this dependence 2 . There is a very wide range of spatial models tailored to the inferential aim, the nature of the spatial dependence, and the type of data.
Recent advancements in methods for spatial boundary detection have focused on model-based approaches which focus on probabilistic uncertainty quantification 3 , 4 . An exemplar paper is by Lee 5 , who employs stochastic models for adjacency matrices in order to identify edges between regions with significant differences in health outcomes. Elaborations of this method have included control for multiple comparisons 6 and Bayesian hierarchical approaches 7 . Other approaches in boundary detection include integrated stochastic processes 8 , stochastic edge mixed-effects models 9 , and methods for estimating adjacencies in areal modelling contexts 10 , 11 . This modelling introduces spatial dependence using stochastic models on graphs, where nodes represent regions, and edges connect neighbouring regions 12 . Other methods include Markov random fields using undirected graphs 13 , 14 or directed acyclic graphical autoregression (DAGAR) models 15 .
The most common regression methods for geographically referenced data are spatial linear regression 16 and spatial generalized linear regression 17 . However, these models assume that the coefficients of the explanatory variables are constant across space, which can be overly restrictive for large regions where the regression coefficients may vary spatially. Many methods include longitude and latitude coordinates as location variables, while others account for spatial variability in the model by including an additive spatial random effect for each location. This technique has been applied to linear models by Cressie 16 , and generalized linear models by Diggle 17 .
Numerous methods have been developed to identify and describe smoothly varying patterns of regression coefficients, such as Gelfand’s 18 spatially varying coefficient processes (SVCM ) and the spatial expansion methods proposed by Casetti 19 . In a follow-up paper, Casetti and Jones 20 treat the regression coefficients that vary spatially as a function of expansion variables.
An alternative popular method for capturing smoothly varying spatial patterns is through geographically weighted regression (GWR) 21 . The GWR fits a local weighted regression model at the location of each observation and captures spatial information by accounting for nearby observations, using a weight matrix defined by a kernel function 21 . This approach has been extended in a variety of ways, for example to a Cox survival model for spatially dependent survival data to explore how geographic factors impact time-to-event outcomes 22 . Unlike SVCM, GWR does not assume a specific functional form for the relationship between covariates and the response variable. This flexibility is advantageous when dealing with complex spatial data where relationships may vary across space 23 . The GWR can also be computationally more efficient, especially for large datasets, and the results from GWR are often more interpretable as they provide localized parameter estimates for each spatial location 23 . This allows for a deeper understanding of how relationships between variables vary across space, which may be more intuitive for practitioners and policymakers.
The traditional GWR models are typically fit using a frequentist framework. A critical limitation of this approach is the violation of the usual assumption of non-constant variation between observations, and the resultant normality assumption for the errors 24 . Additionally, the usual frequentist approach struggles to address issues of model complexity, overfitting, variable selection and multicollinearity 24 . The stability and reliability of frequentist GWR might also yield unstable results or high variance when dealing with small sample sizes 25 .
Bayesian GWR (BGWR) provides an appealing solution to these problems 26 . An exemplar paper is by Gelfand 27 , who built a Bayesian model with spatially varying coefficients by applying a Gaussian process to the distribution of regression coefficients. Lesage 28 suggested an early version of BGWR, where the prior distribution of the parameters depends on expert knowledge. More recently, Ma 29 proposed BGWR based on the weighted log-likelihood and Liu 30 proposed BGWR based on a weighted least-squares approach. Spline approaches have been explored to estimate bivariate regression functions 31 and to accommodate irregular domains with complex boundaries or interior gaps 32 . Other studies, including those by Li et al. 30 and Wang et al. 33 , also address this problem over irregular domains. However, all of these methods have a significant limitation, in that they cannot handle the possibility of a spatially clustered pattern in the regression coefficients. A recent development by Li et al. 34 is the spatially clustered coefficient (SCC) regression, which employs the fused LASSO to automatically detect spatially clustered patterns in the regression coefficients. Ma et al. 35 and Luo et al. 36 have proposed spatially clustered coefficient models using Bayesian approaches. Ma et al. 35 identified coefficient clusters based on the Dirichlet process, whereas Luo et al. 36 used a hierarchical modelling framework with a Bayesian partition prior model from spanning trees of a graph. Sugasawa et al. proposed spatially clustered regression (SCR) 37 . The selection of the appropriate number of clusters is a crucial aspect of clustering analysis. Most traditional methods require the number of clusters to be specified beforehand, which can limit their applicability in practice. This applies for K-means 38 , hierarchical clustering 39 and Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) 40 . These constraints pose challenges in scenarios where the optimal number of clusters isn’t obvious from the start or varies across datasets, limiting the flexibility and adaptability of these clustering approaches in real-world applications. Dirichlet process mixture models (DPMM) have gained popularity in Bayesian statistics as they allow for an unknown number of clusters, increasing the flexibility of clustering analysis. However the DPMM does not account for the spatial information in the clusters.
In this paper, we synthesise two approaches, namely, a Bayesian GWR and a Bayesian spatial DPMM, to create a new method called the Bayesian spatial Dirichlet process clustered heterogeneous regression model. This method can detect spatially clustered patterns while considering the smoothly varying relationship between the response and the covariates within each group. We used a Bayesian geographically weighted regression algorithm to model the varying coefficients over the geographic regions and incorporated spatial neighbourhood information of regression coefficients. We then combined the regression coefficient and a spatial Dirichlet mixture process to perform the clustering. The approach is demonstrated using simulated data and then applied to a real-world case study on children’s development in Queensland, Australia.
This approach meets the inferential aims of clustering and localised regression, for areal data. The clustering approach is preferred over the boundary detection approach in this context, since abrupt explainable changes in the spatial process are not anticipated and the prioritisation is to identify and profile broadly similar geospatial areas. The proposed use of GWR is also preferred over SCR, since GWR explicitly accounts for spatial variation in relationships between variables by estimating separate regression parameters for different locations, whereas SCR typically assumes spatial homogeneity within clusters and estimates a single set of parameters for each cluster. GWR is therefore capable of capturing fine-scale spatial variation, as it estimates parameters at the level of individual spatial areal units, whereas SCR aggregates data into clusters, potentially smoothing out fine-scale variation and overlooking localized patterns.
The strength of the proposed clustering method lies in several key features that set it apart from traditional clustering algorithms. Unlike K-Means and hierarchical clustering, which lack uncertainty measures, the proposed method provides clusters with associated uncertainty measures, enhancing interpretability and making them more valuable for decision-making and analysis. Additionally, the proposed method incorporates spatial neighbourhood information. This ensures that the resulting clusters not only reflect data similarity but also account for spatial heterogeneity. Furthermore, this Bayesian framework allows for better handling of outliers and uncertainties in the data by incorporating prior information. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in scenarios where data quality varies or is incomplete. The paper proceeds as follows: In Sect. " Results ", we present the results obtained from applying the proposed algorithm to both simulated and real case studies. Following this, Sect. " Methods " provides a detailed explanation of the proposed algorithm. Section " Discussion " includes the discussion for the results and its limitation. In Sect. " Bayesian estimation and inference ", we delve into the sampling procedure utilized in the proposed algorithms, along with an analysis of cluster accuracy. Finally, Sect. " Conclusion " concludes the paper by summarizing the findings.
The proposed method, described in detail in the " Methods " section below, is evaluated through a simulation study and applied to a real-world case study. These applications demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach in simultaneously estimating and clustering spatially varying regression coefficients, with associated measures of uncertainty.
Simulation study
The simulation was structured based on the Georgia dataset with 159 regions introduced by Ma 35 , where spatial sampling locations represented geographical positions for data collection. Specifically, we used centroids of geographical areas as the sampling locations.
For the simulation, six covariates ( \(X_1\) to \(X_6\) ) were introduced as independent variables, each representing distinct features or characteristics at each sampling location. To incorporate spatial autocorrelation, we generated the covariates using multivariate normal distributions with spatial weight matrices derived from the distance matrix and parameter bandwidth.
The response variable ( Y ) in the simulation was generated using the GWR model 21 :
It is noteworthy that the true parameters ( \(\beta _1\) to \(\beta _6\) ) of the GWR model varied spatially, implying that they differed across sampling locations based on the spatial weight matrices. This spatial variation allowed us to capture spatially dependent effects in the simulation 37 . We generate simulated spatial data with six covariates using the following steps. First, we generate 159 spatial locations, denoted as \( s_1, \ldots , s_n \) , based on the centroids of geographic areas. The locations are determined based on specific conditions related to the x and y coordinates of the centroids. Next, six covariates, \( x_1(s_i), x_2(s_i), \ldots , x_6(s_i) \) , are generated for each spatial location \( s_i \) . These covariates are derived from a spatial Gaussian process with mean zero and a covariance matrix defined by an exponential function \( w_{ij} = \exp \left( -\frac{{\Vert s_i - s_j \Vert }}{{\phi }} \right) \) , where \( \phi \) is the bandwidth parameter with \( \phi = 0.9 \) . This parameter influences the strength of spatial correlation in the covariates. Finally, the response at each location, \( y(s_i) \) , is generated according to a spatially varying linear model. This model includes the coefficients \( \beta _1(s_i), \beta _2(s_i), \ldots , \beta _6(s_i) \) corresponding to the six covariates \( x_1(s_i), x_2(s_i), \ldots , x_6(s_i) \) , respectively. The error terms \( \epsilon (s_i) \) are mutually independent.
To create distinct spatial patterns in the data, we visually partitioned the counties of Georgia into three large regions based on the spatial coordinates of centroids, defining true clustering settings. This approach enabled us to incorporate spatial autocorrelation, spatial variability, and true clustering effects in the simulated data. Figure 1 visualizes partition of the counties into three large regions with sizes, 51, 49 and 59 areas.
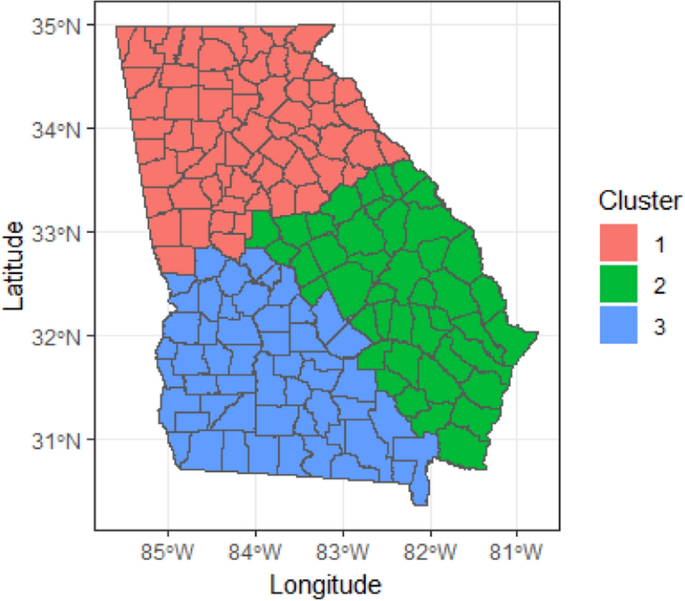
Regional cluster assignment for Georgia counties used for simulation study.
The code for the proposed algorithm can be found in the first author’s GitHub https://github.com/waladraidi/Spatial-stick-breaking-BGWR .
The simulation was repeated 100 times. Figure 2 illustrates the spatial distribution of the posterior mean parameter coefficients for each location over the 100 replicates. This figure showcases the diverse spatial patterns and disparities in these parameter coefficients across the study area, providing insights into the geographical variation.
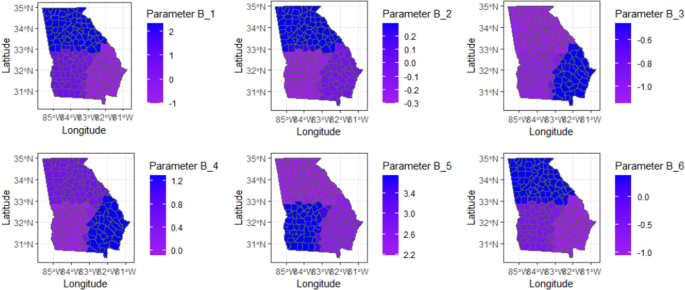
The spatial distribution of the posterior mean for the parameters obtained from the proposed model.
The performance of these posterior estimates was evaluated by mean absolute bias (MAB), mean standard deviation (MSD), mean of mean squared error (MMSE), as follows:
where \(\bar{\hat{\beta }}_{s, k}\) , is the average parameter estimate and has been calculated by the average of \(\hat{\beta }_{s,k}\) ( \(s = 1, \ldots , 159; \quad k = 1, \ldots , 6\) ) in 100 simulations, and \(\hat{\beta }_{s, k, r}\) denotes the posterior estimate for the k -th coefficient of county s in the r -th replicate. In each replicate, the MCMC chain length is set to be 10,000, and the first 2000 samples are discarded as burn-in. Therefore, we have 8000 samples for posterior inference. Table 1 reports the the three performance measures in Eqs. ( 2 )–( 4 ) for the simulated data. The parameter estimates are very close to the true underlying values and have a small MAB, MSD, and MMSE.
Three distinct clusters were found within the 159 regions. The spatial layout of these clusters is visualized in Fig. 3 , where two cluster configurations are described in the later section on cluster configurations. Notably, when examining Fig. 3 , it is clear that the cluster assignments derived from Dahl’s and mode allocation approaches (see " Methods " section below) exhibit a high degree of similarity. The corresponding parameter estimates are shown in Table 2 .
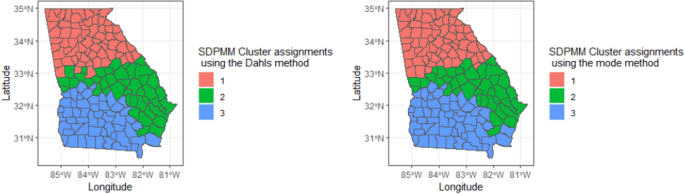
(LHS) Cluster assignment for Georgia counties using Dahl’s method from the proposed algorithm. (RHS) The cluster assignment obtained from the proposed algorithm using the mode method.
Since the kernel type, bandwidth prior and the number of knots play a crucial role in the spatial stick-breaking construction of the the proposed mode for the DPMM, the priors and kernel functions from Table 8 (" Methods " section) were utilised to test the accuracy of the proposed model. We explored different options to determine the optimal fit for the data using the Watanabe-Akaike onformation criterion (WAIC) 39 , and we performed a sensitivity analysis on the proposed model with respect to number of knots. The results are summarized in Table 3 .
According to the Table 3 , the optimal number of knots for the simulated data as 9, as evidenced by the lowest WAIC value. In Table 4 , we present a sensitivity analysis for our proposed algorithm, discussing its performance under various bandwidth priors and kernel functions. This table categorizes the results under two primary kernel types: uniform and squared exponential.
For each kernel type, two bandwidth priors were evaluated. Based on the WAIC values, the squared exponential kernel with a bandwidth prior of \(\varepsilon _{1i}, \varepsilon _{2i} \equiv \frac{\lambda ^2}{2}\) emerged as the most effective. Importantly, our algorithm not only demonstrated the stability of clusters when compared to two established methods but also managed to accurately assign clusters with an accuracy of 0.87. In the simulated dataset, our method effectively identified three distinct clusters.
Real data analysis
Children’s Health Queensland (CHQ) has developed the CHQ Population Health Dashboard, a remarkable resource providing data on health outcomes and socio-demographic factors for a one-year period (2018-2019) across 528 small areas (Statistical area level 2 (SA2) in Queensland, Australia. The dashboard presents over 40 variables in a user-friendly format, with a focus on health outcomes, particularly vulnerability indicators measuring children’s developmental vulnerability across five Australian Early Development Census (AEDC) domains. These domains include physical health, social competence, emotional maturity, language and cognitive skills, and communication skills with general knowledge.
The AEDC also includes two additional domain indicators: vulnerable on one or more domains (Vuln 1) and vulnerable on two or more domains (Vuln 2). Socio-demographic factors, including Socio-Economic Indexes for Areas (SEIFA) score, preschool attendance, and remoteness factors are also incorporated, offering insights into potential links to health outcomes. The SEIFA score summarizes socio-economic conditions in an area, while remoteness factors categorize regions into cities, regional, and remote areas.
In the field of population health, publicly available data are often grouped according to geographical regions, such as the statistical areas (SA) defined in the Australian Statistical Geography Standard (ASGS). These areas, called SA1, SA2, SA3, and SA4, range respectively from the smallest to the largest defined geographical regions. Due to privacy and confidentiality concerns, personal-level information is typically not released. Therefore, in this paper, we focus on group-level data, and in the case study, we use data that have been aggregated at the SA2 level 41 .
Data for the analysis are sourced from the 2018 AEDC, and focus on the proportion of vulnerable children in each SA2. Some missing data is handled through imputation using neighboring SA2s, with two islands having no contiguous neighbors excluded from the analysis. The study utilises the remaining data from 526 SA2 areas to conduct the analysis.
Our study uses the proposed methodology to analyse the influential factors affecting the development of children who are vulnerable in one or more domains (Vuln 1) in the Queensland SA2 regions. Data were found on the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) official website and the AEDC. For each SA2 region, we considered several dependent variables, including the proportion of attendance at preschool, the remoteness factor which is converted using the one hot coding to three variables including zero and one and the index of relative socio-economic disadvantage (IRSD) factor which is considered continuous in this case study. Before fitting the model, we scaled the variables using the logarithm. As a result, all the models are fitted without an intercept term. In our Bayesian Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) analysis, we illustrate substantively important regions by plotting the 95% credible intervals for each coefficient. With (BGWR), a separate parameter estimate is indeed generated for each region. This means that the credible intervals obtained are specific to each region and its corresponding parameter. Therefore, the 95% credible interval associated with each region reflects the uncertainty in the parameter estimate for that particular geographical area. This is illustrated in the Fig. 4 , where the blue line represents the mean.
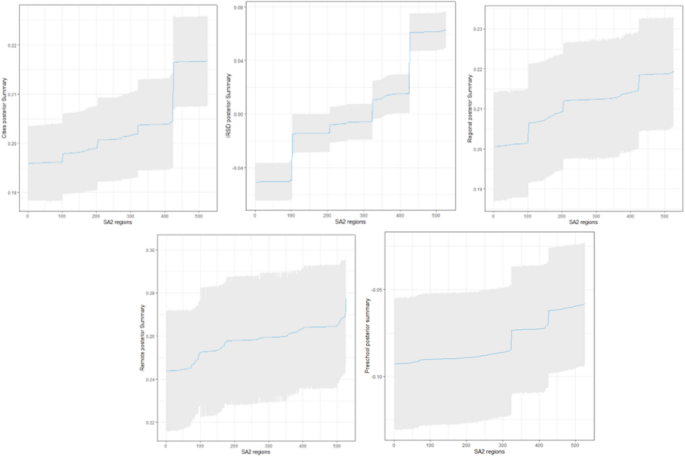
95% posterior credible interval form the proposed algorithm.
Spatial cluster inferences
Figure 5 offers a geographical representation of five posterior mean parameters plotted on a map of Queensland. These values have been obtained through the proposed method, revealing that the relationship between the response variable (Vuln 1) and the covariates varies across different locations.
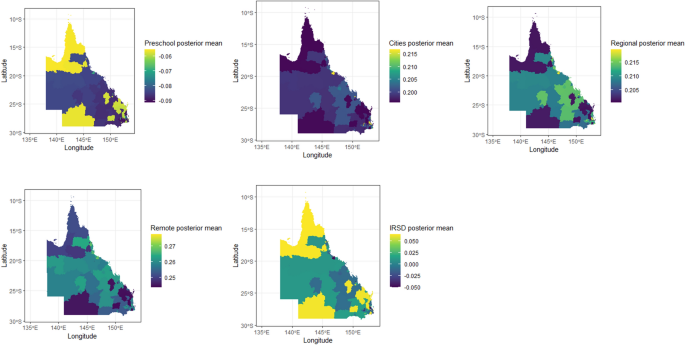
The spatial distribution of the posterior mean parameters derived from the proposed model.
To find the suitable structure of spatial weighs kernel for SDPMM for the case study, we used the WAIC. The WAIC values of the uniform and exponentially weighted kernels associated with different bandwidth priors can be found in Table 5 . Comparison of the WAIC value leads to the conclusion that the exponential kernel is the most suitable for the real dataset. Additionally, Table 6 shows that as the complexity of the model (in terms of the number of knots) increases, the fit of the model to the data (WAIC) also improves. However, since the total number of SA2 is just 526, in this case study we assumed the number of knots to be 9.
Figure 6 showed the cluster distribution on the map obtained from the proposed algorithm with 6 clusters using Dahl’s method. The cluster sizes are 124, 103, 90, 101 , 101 and 7. The strength of the proposed algorithm lies in its capability to create smaller cluster sizes compared to other cluster algorithms. This is beneficial for policy interventions targeting specific regions in Queensland, especially for identifying regions with high developmental vulnerabilities. Further, we provide a summary (Table 7 ) for each of these clusters according to the parameter estimation and 95% highest posterior density (HPD) interval.
Cluster 1 (124 out of 526) stands out due to its negative effect on the regression parameters for “Attendance at Preschool” with a narrow credible interval. The positive effects for the three levels of “Remoteness” are reliable, with the broadest uncertainty observed for the “Cities” parameters in comparison with the rest of the clusters. There’s also some uncertainty in the “IRSD” parameters, which exhibit a negative effect, although they remain influential. Cluster 2 (103 out of 526) is characterized by a significant negative effect for “Attendance at Preschool” with a narrowest credible interval across the six clusters, indicating a strong impact and high confidence. Additionally, There are more positive effects for the “Cities”, “Regional” and “Remote” parameters compared to Cluster 1, there is a more negative relationship for “IRSD” parameters compared to Cluster 1. Cluster 3 (90 out of 526) also exhibits a significant negative effect for “Attendance at Preschool” parameters but with a broader credible interval, indicating a strong impact with more uncertainty. The positive effects for “Remoteness” parameters are still significant and confident, with the broadest uncertainty for the “Regional” parameters across the six clusters, “IRSD” exhibits the most negative parameters in this cluster in comparison with the rest. Cluster 4 (101 out of 526) maintains a significant negative effect for “Attendance at Preschool” with a narrow credible interval, with a positive effects for “Remoteness” parameters. In this cluster “IRSD” has a positive effect with a narrow credible interval in comparison with clusters 1, 2 and 3. Cluster 5 (101 out of 526) has a negative effect for “Attendance at Preschool” and a narrow credible interval. Similar to Cluster 4, the positive effects for “Remoteness”. But in this cluster “IRSD” has more positive effect in comparison with cluster 4. Cluster 6 (7 out of 526) stands out with it negative effect for “Attendance at Preschool” even though it has a wider credible interval. The positive effects for “Remoteness” are similar to the previous clusters, with the narrowest credible intervals for the “Cities, Regional, and Remote” parameters, also the “IRSD” has a negative effect with a narrow credible interval.
These clusters are distinguished primarily by the magnitude and certainty of the effect of “Attendance at Preschool” and the reliability of the “Remoteness” and “IRSD”. Cluster 1, 4,5, and 6 share a strong negative impact of “Attendance at Preschool” with narrow credible intervals. Cluster 2 , with a broader credible interval, indicates more uncertainty in the impact of “Attendance at Preschool”. Cluster 3, despite having a wider credible interval for “Attendance at Preschool” still shows a significant negative effect. Additionally, the “IRSD” exhibits variations across clusters, adding another layer of distinction.
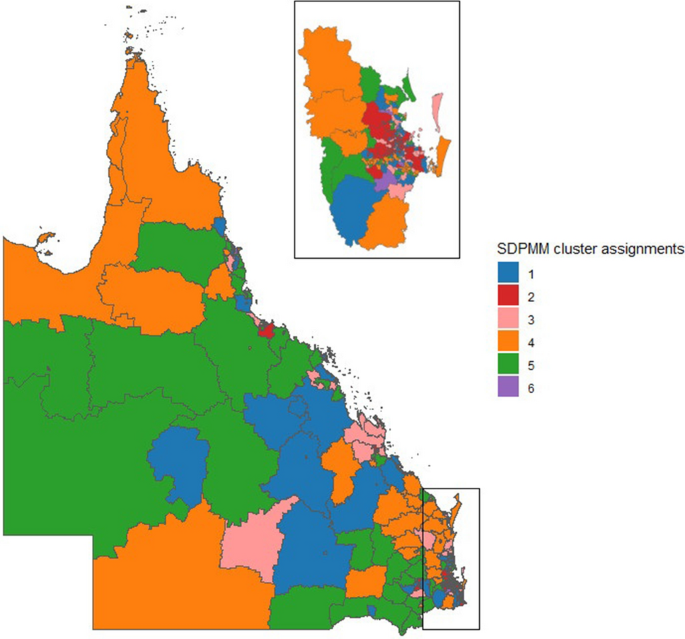
Cluster distribution from the proposed algorithm for the case study.
In this paper, we introduce a new statistical framework aimed at addressing the challenges in clustering posed by spatially varying relationships within regression analysis. Specifically, we present a Bayesian model that integrates geographically weighted regression with a spatial Dirichlet process to cluster relevant model parameters. This solution therefore not only identifies clusters of the model parameters but effectively captures the inherent heterogeneity present in spatial data. Our exploration encompasses various weighting schemes designed to effectively model the complex spatial interaction between neighborhood characteristics and the positioning of key points (or “knots”). This modelling is supported by a discussion of Bayesian model selection criteria, a crucial step in the analysis process that ensures selection of an appropriate and well-fitted model. Spatial variation in the effects of covariates empowers our model to provide a better fit to spatial data compared to conventional models, offering insights into the complex patterns of heterogeneity across diverse geographical locations. Additionally, making smaller group sizes helps decision-makers identify which regions need more help. To demonstrate the efficacy of our methodology, we have presented a simulation study. Moreover, we have extended our investigation to a real-world application: a thorough analysis of the factors influencing children’s development indicators in Queensland. Through this practical example, we showcase the benefits of our proposed approach, emphasizing its ability to find hidden dynamics that might otherwise remain obscured.
In our case study, we aimed to explore the influential factors affecting child development vulnerability in Queensland’s statistical area level 2 (SA2) regions. Our analysis utilised a dataset consisting of 526 observations, each corresponding to one of Queensland’s SA2 regions. The dataset included various explanatory variables, including preschool attendance, remoteness factors, and socio-economic factors. The primary objective was to identify spatial clusters of children’s vulnerability and gain insights into the regional disparities in children’s development domains. To select the appropriate spatial weights kernel for our model, we employed WAIC and found the uniform kernel, suggesting that it provides a better fit for our real dataset. Furthermore, we performed a sensitivity analysis to determine the optimal number of knots in the spatial stick-breaking process and found increasing the complexity of the model by adding more knots improved its fit to the data. We selected 9 knots as the optimal number for our analysis. Using the selected model with an exponential kernel and 10 knots, we applied the proposed algorithm to identify spatial clusters of child vulnerability. Our analysis revealed a total of 6 clusters across Queensland’s SA2 regions. These clusters vary in size, with the largest containing 124 regions and the smallest comprising only 7 regions. The ability of the proposed algorithm to create smaller cluster sizes is noteworthy, as it allows for more targeted policy interventions in regions with specific developmental needs. Moreover, we conducted a detailed analysis of the clusters to understand their characteristics and implications. For instance, the presence of smaller clusters may indicate isolated areas with unique developmental challenges that require tailored interventions. In contrast, larger clusters could represent regions with similar vulnerabilities, suggesting the need for broader policy strategies. These findings offer valuable insights for policymakers and stakeholders interested in addressing child development disparities in Queensland.
Both the Bayesian Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) and the Bayesian Spatially Varying Coefficient Model (Bayesian SVCM) offer powerful tools for understanding spatially varying relationships within data. Comparing and contrasting these two approaches can help in justifying the consideration of Bayesian GWR.
Firstly, both Bayesian GWR and Bayesian SVCM operate within a Bayesian framework, allowing for the incorporation of prior knowledge and uncertainty into the modelling process. However, they differ in their approaches to capturing spatial variation. Bayesian GWR explicitly models spatial heterogeneity by allowing regression coefficients to vary across space, making it well-suited for exploring localized relationships between variables. On the other hand, Bayesian SVCM focuses on estimating spatially varying coefficients for a global regression model, which may overlook finer-scale variations present in the data.
Furthermore, it is important to note that coefficients obtained from these methods may differ. Bayesian GWR produces coefficients that are specific to each geographic location, reflecting the spatially varying nature of relationships within the data. In contrast, Bayesian SVCM estimates coefficients that represent spatially varying effects within the context of a global model. These differences in coefficient estimation highlight the distinct strengths and interpretation nuances of each approach, the Bayesian GWR approach can complement existing non-Bayesian techniques such as the Spatial Clustered Regression (SCR) proposed by Sugasawa and Murakami 37 While SCR provides an alternative for capturing spatial clustering effects, it may lack the flexibility to adequately model spatially varying relationships. Bayesian GWR, with its emphasis on local estimation, can offer additional insights into how relationships between variables change across different geographic areas .
Bayesian SVCM and our method have their computational challenges. Our proposed algorithm is not computationally intensive, in comparison with other clustering Bayesian methods. The time to run the simulated data was around 25 minutes, while for the real data set it took around 2:23 hours using the high performance computer (HPC).
While our paper represents a step forward in the field of spatial regression, it is essential to acknowledge the avenues for further exploration that our research did not study. For instance, while we thoroughly examined the full model that incorporates all relevant covariates, we did not delve into methodologies for variable selection within the context of clustered regression. This presents a clear direction for future research, where approaches for selecting the most influential variables among a clustered regression could enhance the performance of our model even further. Additionally, our work touched upon the utilisation of the spatial Dirichlet process mixture model (SDPMM) to derive cluster information for regression coefficients. However, we acknowledge that the posterior distribution of the cluster count might not always be accurately estimated through the SDPMM, as demonstrated by Miller and Harrison 42 . Our simulation studies confirm this observation. This area emerges as a critical focus for future studies. Another area for future work involves expanding our methodology to accommodate non-Gaussian data distributions, a direction that holds promise for a wider range of applications. Moreover, the pursuit of adapting our model to handle multivariate response scenarios represents an essential avenue for future exploration, offering the potential to unlock insights and applications across various domains. Lastly, extend the proposed algorithm to a semi-parametric GWR scenario where certain exploratory variables remain fixed while others vary spatially 43 . Further, GWR allows regression coefficients to vary by location; it typically assumes a linear relationship between all predictor variables and the response within each location. However, in some real-world scenarios, not all predictor variables may exhibit linear relationships with the response variable. Some variables might have non-linear patterns or lack a certain discernible pattern altogether. These features could be included in the linear model through polynomials, splines, interactions, and so on, and alternative non-parametric regression models could be developed. It would be interesting to extend the proposed algorithm to allow for more flexibility in modeling complex relationships between predictor variables and the response 44 .
This section outlines the proposed model called the spatial Dirichlet process clustered heterogeneous regression model. The model utilises a non-parametric spatial Dirichlet mixture model applied to the regression coefficients of the geographically weighted regression model. The model is cast in a Bayesian framework.
Bayesian geographical weighted regression
The Bayesian geographically weighted regression (BGWR) model can be described as follows. Given diagonal weight matrix \( W(s) \) for a location s , the likelihood for each \( y(s) \) is:
where \( y(s) \) is the \(i\) th observation of the dependent variable, \( x(s) \) is the \(i\) th row (or observation) from the design matrix \( X \) and \( W_i(s) \) is the \(i\) th diagonal element from the spatial weight matrix \( W(s) \) . The weighted matrix W ( s ) is constructed to identify the relative influence of neighbouring regions on the parameter estimates at locations.
When working with areal data, the graph distance is an alternative distance metric that can be used. It is based on the concept of a graph, where \(V=\{v_1,...,v_m\}\) represents the set of nodes (locations) and \(E(G)=\{e_1,...,e_n\}\) represents the set of edges connecting these nodes. The graph distance is defined as the distance between any two nodes in the graph 35 .
where | V ( e )| is the number of edges in e 45 . The graph distance-based weighted function is given as:
where \(d_i(s)^ b\) is the graph distance between locations i and s , f is a weighting function, and b represents the bandwidth. In this study, we suppose that f () is a negative exponential function 29 , so,
where b represents the bandwidth that controls the decay with respect to distance 46 . Here, \(d_i(s)\) indicates that an observation far away from the location of interest contributes little to the estimate of parameters at that location. In this paper, we used the graph distance and the greater circle distances 47 and both of these methods show consistent parameters. The proposed model is constructed in a Bayesian framework with conjugate priors on the regression parameters and other model terms. The full model is given in the (Full Bayesian spatial Dirichlet process mixture prior cluster heterogeneous regression) section.
Heterogeneous regression with spatial Dirichlet process mixture prior
In a Bayesian framework, coefficient clustering can be achieved by using a Dirichlet process mixture model (DPMM). This approach links the response variable to the covariates through cluster membership. The DPMM is defined by a probability measure G that follows a Dirichlet process, denoted as \(G \sim (\alpha , G_0)\) , where \(\alpha \) is the concentration parameter and \(G_0\) is the base distribution 35 . Hence,
where \((A_1,...,A_k)\) is a finite measurable partition of the space \(\Omega \) , and the variable k represents the number of components or clusters in a (DPMM). Several formulas have been proposed in the literature for specifying the DPMM’s parameters and incorporating spatial dependencies 48 , 49 . A popular approach is the spatial stick-breaking algorithm 50 , 51 , which in a BGWR setup is applied at each location as follows:
where \(\delta (\theta _i)\) is the Dirac distribution with a point mass at ( \(\theta _i)\) , and \(p_i (s)\) is a random probability weight between 0 and 1. The distribution of G ( s ) depends on \(V_i\) and \(\theta _i\) ; the distribution varies according to the kernel function \(l_i(s)\) . However, the spatial distributions of the kernel function \(l_i(s)\) vary, constrained within the interval [0, 1]. These functions are centered at knots \(\psi _i=(\psi _{1i}, \psi _{2i})\) , and the degree of spread is determined by the bandwidth parameter \(\epsilon _i=(\epsilon _{1i}, \epsilon _{2i})\) . Both the knots and bandwidths are treated as unknown parameters with independent prior distributions, unrelated to \(V_i\) and \(\theta _i\) . The knots \(\psi _i\) are assigned independent uniform priors, covering the bounded spatial domain. The bandwidths can be modelled to be uniform for all kernel functions or can vary across kernel functions, following specified prior distributions 50 , 52 . The most common kernels are the uniform and the square exponential functions. This kernel can take different formats. Table 8 provides examples of the most popular kernels used for the spatial stick-breaking configuration.
A vector of latent allocation variables Z is generated to characterize the clustering explicitly. Let \(Z_{n,k}=\{z_1.,...,z_n\}\) , where \(z_i \in \{1,...,k\}\) and \(1\le i \le n\) represents all possible clustering of n observations into K clusters.
Full Bayesian spatial dirichlet process mixture prior cluster heterogeneous regression
Adapting the spatial Dirichlet process to the heterogeneous regression model, we focus on clustering of spatial coefficients \(\beta (s_1),...,\beta (s_n)\) and \(\beta (s_i)=\beta _{{z_i}} \in \{\beta _1,...,\beta _k\}\) . The full model is described as follows with the most commonly adopted priors:
Here, the response variable \(Y\) is assumed to follow a Gaussian distribution; the design matrix representing the predictors is denoted by X , and the spatial weight matrix W ( s ) depends on two key aspects: the distance between observations, represented as \(d_i\) , and a parameter \(b\) , which controls the bandwidth. This bandwidth is assumed to follow a uniform distribution between 0 and a certain value \(D\) , which represents the bandwidth parameter. A common prior for the bandwidth is given by: b-Uniform(0,D), where D > 0. Without any prior knowledge, D can be selected to be large enough that we begin to approximate with a non-informative prior; i.e. we begin with an approximate global model in which all observations are weighted equally. We used a bandwidth parameter D set to 100. The maximum great circle distance in the spatial structure of the 159 regions is 10, so using a bandwidth of 100 induces a weighting scheme that ensures relative weights are assigned appropriately. If the distance between two regions is considerable, the relative weight is approximately exp(-10/100) = 0.904. This approximation thus allows the model to behave similarly to a global model where every observation is equally weighted, ensuring a sufficiently non-informative prior bandwidth b. please see the method section. f is the graph weighting function. The regression coefficients \(\beta _{z_i}\) are associated with a specific group, or cluster, \(z_i\) , for a particular observation. The mean and spread of cluster \(z_i\) are denoted as \(\mu \) and \(\Sigma _{z_i}\) , respectively, and the maximum number of possible clusters is \(K\) .
The hyper-parameter \(m_k\) is a prior mean value for the \(\mu _{z_i}\) and \(\Sigma _k\) is a way to express how different a cluster can be. Similarly, \(D_k\) is the scale matrix, and \(c_k >p-1\) is the degrees of freedom. Another important aspect is the variation in the data, which is \(\sigma ^2(s)\) . This variation changes across locations and follows a specific prior pattern, which is assumed to be an inverse Gamma distribution with parameters \(\alpha _1\) and \(\alpha _2\) .
we focus on the probability \(P(z_i = k)\) that observation \(i\) belongs to cluster \(k\) . This assignment probability at a specific location \(s\) is denoted as \(p_k(s)\) . For the clusters, we also consider “stick-breaking weights”, denoted by \(V_k(s)\) , which change across locations. The values \(a_v\) and \(b_v\) are related to how these weights are determined using a beta distribution. Here \(\sum _{j=1}^{k} p_k (s) = 1\) almost surely under the constraint that \(V_k (s) = 1\) for all locations s 53 .
Bayesian estimation and inference
This section covers using MCMC to obtain samples from posterior distributions of model parameters. It explains the sampling scheme, covers the use of posterior inference for cluster assignments, and methods for evaluating accuracy.
The MCMC sampling schemes
The main R function for the model is implemented using the nimble package 54 . This function encapsulates the model and provides an interface for executing the MCMC sampling scheme, performing posterior inference, and evaluating estimation performance and clustering accuracy. The model itself is wrapped within a nimbleCode function, which allows the nimble package to generate and compile C++ code to execute the MCMC sampling scheme efficiently. This can result in substantial speed improvements over pure R implementations, especially for models with large datasets or complex parameter space. In the context of the proposed algorithm, the nimble package provides several MCMC sampling methods, including the popular Gibbs and Metropolis-Hasting algorithms for inferring the posterior distribution of the regression and other model parameters. Nimble also allows for the specification of priors and likelihood functions for the parameters to customise the MCMC sampling process. In our study, the Gibbs sampling algorithm was used to obtain the clusters of the parameters.
Block Gibbs sampling is a MCMC technique used for sampling from the joint distribution of multiple random variables. The primary idea behind block sampling is to group related variables together into “blocks” and sample them jointly, which can improve the efficiency and convergence of the sampling process 55 . An explanation of this sampling algorithm for the proposed algorithm can be found in the Appendix .
Cluster configurations
Two methods are used to determine cluster configurations. In the first, the estimated parameters, together with the cluster assignments \(Z_{n,k}\) are determined for each replicate from the best post-burn-in iteration selected using Dahl’s method 56 , which involves estimating the clustering of observations through a least-squares model-based approach that draws from the posterior distribution. In this method, membership matrices for each iteration, denoted as \(B^{(1)}, \ldots , B^{(M)}\) , with \(M\) being the number of post-burn-in MCMC iterations, are computed. The membership matrix for the \(c\) -th iteration, \(B^{(c)}\) is defined as:
where \(\textbf{1}(\cdot )\) represents the indicator function. The entries \(B^{(c)}(i, j)\) take values in \(\{0, 1\}\) for all \(i, j = 1, \ldots , n\) and \(c = 1, \ldots , M\) . When \(B^{(c)}(i, j) = 1\) , it indicates that observations i , and j belong to the same cluster in the c th iteration.
To obtain an empirical estimate of the probability for locations i and j being in the same cluster, the average of \(B^{(1)}, \ldots , B^{(M)}\) can be calculated as:
where \(\sum \) denotes the element-wise summation of matrices. The ( i , j )th entry of \(\overline{B}\) provides this empirical estimate.
Subsequently, the iteration that exhibits the least squared distance to \(\overline{B}\) is determined as:
where \(B^{(c)}(i, j)\) represents the ( i , j )th entry of B ( c ), and \(\overline{B}(i, j)\) denotes the ( i , j )th entry of \(\overline{B}\) . The least-squares clustering offers an advantage in that it leverages information from all clusterings through the empirical pairwise probability matrix \(\overline{B}\) .
The second method utilised here is the posterior mode method. This method leverages posterior samples from iterations associated with \(z_i\) , where z denotes the cluster assignments specific to each region. Each iteration generates a new set of cluster assignments z , which are dependent on the parameters. Consequently, following multiple iterations, each region will have an empirical posterior distribution of cluster assignments z . The mode indicates the cluster with the highest probability of assignment for a given region.
Cluster accuracy
In order to assess the accuracy of the proposed algorithm, we compared the cluster configurations with the true labels provided for the simulated data. It is important to note that while the true labels are available for the simulated data, such information is not readily available for real-world datasets. In practice, true labels are often unknown, which poses a challenge for the evaluation of clustering accuracy. In this study, we utilised the Rand index (RI) 57 . This index measures the level of similarities between two sets of cluster assignments, labelled as \(C\) and \(C'\) , with respect to a given dataset \(X = \{x_1, x_2, \ldots , x_n\}\) . Each data point \(x(s)\) is assigned a cluster label \(c_i\) in \(C\) and \(c'_i\) in \(C'\) . The RI is computed using the following formula:
Hhere \(a\) , represents the number of pairs of data points that are in the same cluster in both \(C\) and \(C'\) (true positives); \(b\) indicates the number of pairs of data points that are in different clusters in both \(C\) and \(C'\) (true negatives); \(c\) represents the number of pairs of data points that are in the same cluster in \(C\) but in different clusters in \(C'\) (false positives); and \(d\) stands for the number of pairs of data points that are in different clusters \(C\) but in the same cluster in \(C'\) (false negatives).
The Rand index ranges from 0 to 1, with a value of 1 denoting a complete concordance between the two clusterings (both C and \(C'\) perfectly agree on all pairs of data points). Conversely, a value close to 0 indicates a weak level of agreement between the two clusterings.
This paper introduces a method called the spatial Dirichlet process clustered heterogeneous regression model. The method employs a non-parametric Bayesian clustering approach to group the spatially varying regression parameters of a Bayesian geographically weighted regression, and also determines the best number and arrangement of clusters. The model uses advanced Bayesian techniques to cluster the parameters and determine the best number and arrangement of clusters. The model’s abilities were demonstrated using simulated data and then applied to actual data related to children’s development vulnerabilities in their first year of school. In this application, the model successfully identified key factors. This approach enhances our understanding of how children develop in various regions, revealing the factors that impact their health and well-being. With these insights, policymakers can create targeted policies that are suited to each area’s unique characteristics. As a result, this innovative method not only improves the suite of analytical tools but also contributes to the broader goal of enhancing the health and development prospects of children in different places.
Data availibility
All the datasets used in this article are publicly accessible and free to download. Anyone interested can access them without special privileges. Likewise, the authors did not have any special privileges when accessing the data for analysis in this article. The datasets can be obtained from the following sources: Children’s Health Data is sourced from the Australian Early Development Census, available upon request at https://www.aedc.gov.au/data-explorer/ . The Explanatory Data is obtained from the Australian Bureau of Statistics and is publicly available at https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/quickstats/2021/3 .
Lawson, A. B., Banerjee, S., Haining, R. P. & Ugarte, M. D. Handbook of Spatial Epidemiology (CRC Press, 2016).
Book Google Scholar
Anselin, L. Spatial dependence and spatial structural instability in applied regression analysis. J. Reg. Sci. 30 , 185–207 (1990).
Article Google Scholar
Hanson, T., Banerjee, S., Li, P. & McBean, A. Spatial boundary detection for areal counts. Nonparametric Bayesian Inference Biostat. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19518-6_19 (2015).
Ma, H., Carlin, B. P. & Banerjee, S. Hierarchical and joint site-edge methods for medicare hospice service region boundary analysis. Biometrics 66 , 355–364 (2010).
Article MathSciNet PubMed Google Scholar
Lee, D. & Mitchell, R. Boundary detection in disease mapping studies. Biostatistics 13 , 415–426 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Storey, J. D. A direct approach to false discovery rates. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 64 , 479–498 (2002).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Aiello, L. & Banerjee, S. Detecting spatial health disparities using disease maps. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2309.02086 (2023).
Riley, D. D., Koutsoukos, X. & Riley, K. Simulation of stochastic hybrid systems using probabilistic boundary detection and adaptive time stepping. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 18 , 1397–1411 (2010).
Gao, H. & Bradley, J. R. Bayesian analysis of areal data with unknown adjacencies using the stochastic edge mixed effects model. Spat. Stat. 31 , 100357 (2019).
Lu, H., Reilly, C. S., Banerjee, S. & Carlin, B. P. Bayesian areal wombling via adjacency modeling. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 14 , 433–452 (2007).
Lu, H. & Carlin, B. P. Bayesian areal wombling for geographical boundary analysis. Geogr. Anal. 37 , 265–285 (2005).
Dale, M. & Fortin, M.-J. From graphs to spatial graphs. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evolut. Syst. 41 , 21–38 (2010).
Besag, J. Spatial interaction and the statistical analysis of lattice systems. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 36 , 192–225 (1974).
Rue, H. & Held, L. Gaussian Markov Random Fields: Theory and Applications (CRC Press, 2005).
Datta, A., Banerjee, S., Hodges, J. S. & Gao, L. Spatial disease mapping using directed acyclic graph auto-regressive (Dagar) models. Bayesian Anal. 14 , 1221 (2019).
Article MathSciNet PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cressie, N. Statistics for Spatial Data Vol. 4 (Wiley, Terra Nova, 1992).
Google Scholar
Diggle, P. J., Tawn, J. A. & Moyeed, R. A. Model-based geostatistics. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 47 , 299–350 (1998).
Gelfand, A. E., Kim, H.-M.J., Sirmans, C. F. & Banerjee, S. Spatial modeling with spatially varying coefficient processes. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 98 , 387–396 (2003).
Casetti, E. Generating models by the expansion method: Applications to geographical research. Geogr. Anal. 4 , 81–91 (1972).
Casetti, E. & Jones, J. P. Spatial aspects of the productivity slowdown: An analysis of us manufacturing data. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 77 , 76–88 (1987).
Fotheringham, A. S., Charlton, M. E. & Brunsdon, C. Geographically weighted regression: A natural evolution of the expansion method for spatial data analysis. Environ. Plan. A 30 , 1905–1927 (1998).
Xue, Y., Schifano, E. D. & Hu, G. Geographically weighted Cox regression for prostate cancer survival data in Louisiana. Geogr. Anal. 52 , 570–587 (2020).
Finley, A. O. Comparing spatially-varying coefficients models for analysis of ecological data with non-stationary and anisotropic residual dependence. Methods Ecol. Evolut. 2 , 143–154 (2011).
Chan, H. S. R. Incorporating the Concept of Community into a Spatially-weighted Local Regression Analysis (University of New Brunswick, 2008).
Dormann, F. C. et al. Methods to account for spatial autocorrelation in the analysis of species distributional data: A review. Ecography 30 , 609–628 (2007).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Sodikin, I., Pramoedyo, H. & Astutik, S. Geographically weighted regression and Bayesian geograpically weighted regression modelling with adaptive Gaussian kernel weight function on the poverty level in West Java province. Int. J. Humanit. Relig. Soc. Sci. 2 , 21–30 (2017).
Gelfand, A. E. & Schliep, E. M. Spatial statistics and Gaussian processes: A beautiful marriage. Spat. Stat. 18 , 86–104 (2016).
LeSage, J. P. A family of geographically weighted regression models. In Advances in Spatial Econometrics (ed. LeSage, J. P.) 241–264 (Springer, 2004).
Chapter Google Scholar
Ma, Z., Xue, Y. & Hu, G. Geographically weighted regression analysis for spatial economics data: A Bayesian recourse. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 44 , 582–604 (2021).
Liu, Y. & Goudie, R. J. Generalized geographically weighted regression model within a modularized bayesian framework. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00996 (2021).
Opsomer, J. D., Claeskens, G., Ranalli, M. G., Kauermann, G. & Breidt, F. J. Non-parametric small area estimation using penalized spline regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 70 , 265–286 (2008).
Wang, H. & Ranalli, M. G. Low-rank smoothing splines on complicated domains. Biometrics 63 , 209–217 (2007).
Wang, L., Wang, G., Lai, M.-J. & Gao, L. Efficient estimation of partially linear models for data on complicated domains by bivariate penalized splines over triangulations. Stat. Sin. 30 , 347–369 (2020).
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Li, X., Wang, L., Wang, H. J. & Initiative, A. D. N. Sparse learning and structure identification for ultrahigh-dimensional image-on-scalar regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 116 , 1994–2008 (2021).
Article MathSciNet CAS Google Scholar
Ma, Z., Xue, Y. & Hu, G. Heterogeneous regression models for clusters of spatial dependent data. Spat. Econ. Anal. 15 , 459–475 (2020).
Luo, Z. T., Sang, H. & Mallick, B. A Bayesian contiguous partitioning method for learning clustered latent variables. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 22 , 1748–1799 (2021).
Sugasawa, S. & Murakami, D. Adaptively robust geographically weighted regression. Spat. Stat. 48 , 100623 (2022).
Liu, F. & Deng, Y. Determine the number of unknown targets in open world based on elbow method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 29 , 986–995 (2020).
Watanabe, S. A widely applicable Bayesian information criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 14 , 867–897 (2013).
Bouguila, N. & Fan, W. Mixture Models and Applications (Springer, 2020).
Buchin, K. et al. Clusters in aggregated health data. In Headway in Spatial Data Handling (eds Buchin, K. et al. ) 77–90 (Springer, 2008).
Miller, J. W. & Harrison, M. T. A simple example of Dirichlet process mixture inconsistency for the number of components. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems Vol. 26 (eds Miller, J. W. & Harrison, M. T.) (Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc, 2013).
Laome, L., Budiantara, I. N. & Ratnasari, V. Estimation curve of mixed spline truncated and Fourier series estimator for geographically weighted nonparametric regression. Mathematics 11 , 152 (2022).
Laome, L., Budiantara, I. N. & Ratnasari, V. Construction of a geographically weighted nonparametric regression model fit test. MethodsX 12 , 102536 (2024).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gao, X., Xiao, B., Tao, D. & Li, X. A survey of graph edit distance. Pattern Anal. Appl. 13 , 113–129 (2010).
Cho, S.-H., Lambert, D. M. & Chen, Z. Geographically weighted regression bandwidth selection and spatial autocorrelation: An empirical example using Chinese agriculture data. Appl. Econ. Lett. 17 , 767–772 (2010).
Bullock, R. Great circle distances and bearings between two locations. MDT 5 , 1–3 (2007).
Quintana, F. A., Müller, P., Jara, A. & MacEachern, S. N. The dependent Dirichlet process and related models. Stat. Sci. 37 , 24–41 (2022).
Yamato, H. Dirichlet process, Ewens sampling formula, and Chinese restaurant process. In Statistics Based on Dirichlet Processes and Related Topics (ed. Yamato, H.) 7–28 (Springer, 2020).
Reich, B. J. & Fuentes, M. A multivariate semiparametric Bayesian spatial modeling framework for hurricane surface wind fields. Ann. Appl. Stat. 1 , 249–264 (2007).
Sethuraman, J. A constructive definition of Dirichlet priors. Stat. Sin. 4 , 639–650 (1994).
Hosseinpouri, M. & Khaledi, M. J. An area-specific stick breaking process for spatial data. Stat. Pap. 60 , 199–221 (2019).
Ishwaran, H. & James, L. F. Gibbs sampling methods for stick-breaking priors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96 , 161–173 (2001).
de Valpine, P. et al. Programming with models: Writing statistical algorithms for general model structures with nimble. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 26 , 403–413 (2017).
Yu, G., Huang, R. & Wang, Z. Document clustering via Dirichlet process mixture model with feature selection. In Proc. of the 16th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining , 763–772 (2010).
Dahl, D. B. Model-based clustering for expression data via a Dirichlet process mixture model. Bayesian Inference Gene Expr. Proteomics 4 , 201–218 (2006).
Rand, W. M. Objective criteria for the evaluation of clustering methods. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 66 , 846–850 (1971).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the team at Children’s Health Queensland and the Centre for Data Science for their invaluable assistance and support in this project.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mathematical Science, Centre for Data Science, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
Wala Draidi Areed, Aiden Price, Helen Thompson & Kerrie Mengersen
Children’s Health Queensland, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
Reid Malseed
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: Wala Draidi Areed, Aiden Price, Helen Thompson, Kerrie Mengersen. Data curation: Wala Draidi Areed, Aiden Price, Reid Malseed, Kerrie Mengersen. Formal analysis: Wala Draidi Areed. Investigation: Wala Draidi Areed. Methodology: Wala Draidi Areed, Kerrie Mengersen. Software: Wala Draidi Areed. Supervision: Aiden Price, Helen Thompson, Reid Malseed, Kerrie Mengersen. Validation: Wala Draidi Areed. Visualization: Wala Draidi Areed. Writing – original draft: Wala Draidi Areed. Writing - review and editing: Wala Draidi Areed, Aiden Price, Helen Thompson, Reid Malseed, Kerrie Mengersen.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wala Draidi Areed .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Areed, W.D., Price, A., Thompson, H. et al. Spatial non-parametric Bayesian clustered coefficients. Sci Rep 14 , 9677 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-59973-w
Download citation
Received : 21 November 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 27 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-59973-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: AI and Robotics newsletter — what matters in AI and robotics research, free to your inbox weekly.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
About 1 in 5 U.S. teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork

Roughly one-in-five teenagers who have heard of ChatGPT say they have used it to help them do their schoolwork, according to a new Pew Research Center survey of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17. With a majority of teens having heard of ChatGPT, that amounts to 13% of all U.S. teens who have used the generative artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot in their schoolwork.
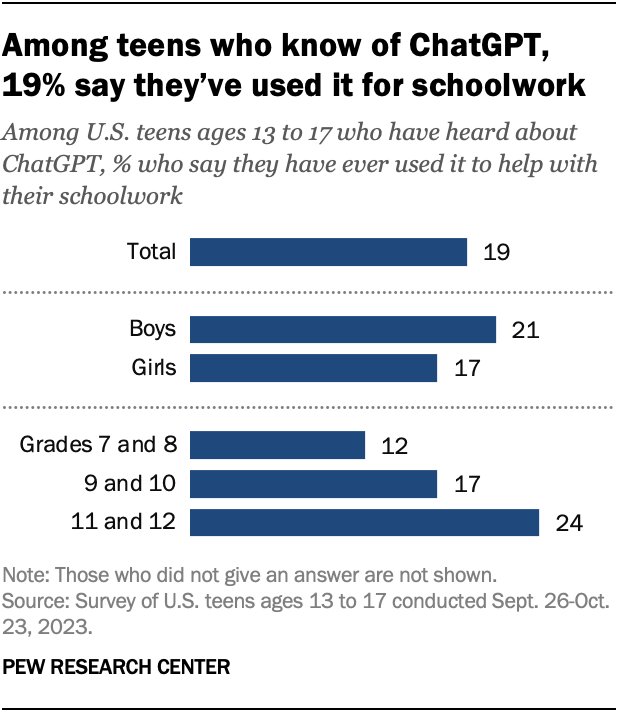
Teens in higher grade levels are particularly likely to have used the chatbot to help them with schoolwork. About one-quarter of 11th and 12th graders who have heard of ChatGPT say they have done this. This share drops to 17% among 9th and 10th graders and 12% among 7th and 8th graders.
There is no significant difference between teen boys and girls who have used ChatGPT in this way.
The introduction of ChatGPT last year has led to much discussion about its role in schools , especially whether schools should integrate the new technology into the classroom or ban it .
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand American teens’ use and understanding of ChatGPT in the school setting.
The Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, via Ipsos. Ipsos recruited the teens via their parents, who were part of its KnowledgePanel . The KnowledgePanel is a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey was weighted to be representative of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 who live with their parents by age, gender, race and ethnicity, household income, and other categories.
This research was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, an independent committee of experts specializing in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
Teens’ awareness of ChatGPT
Overall, two-thirds of U.S. teens say they have heard of ChatGPT, including 23% who have heard a lot about it. But awareness varies by race and ethnicity, as well as by household income:
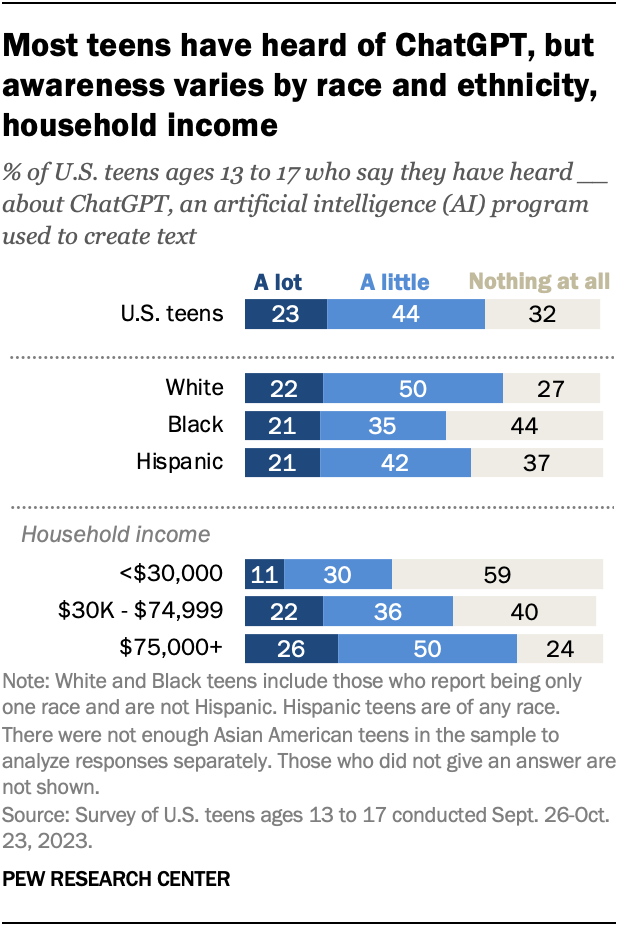
- 72% of White teens say they’ve heard at least a little about ChatGPT, compared with 63% of Hispanic teens and 56% of Black teens.
- 75% of teens living in households that make $75,000 or more annually have heard of ChatGPT. Much smaller shares in households with incomes between $30,000 and $74,999 (58%) and less than $30,000 (41%) say the same.
Teens who are more aware of ChatGPT are more likely to use it for schoolwork. Roughly a third of teens who have heard a lot about ChatGPT (36%) have used it for schoolwork, far higher than the 10% among those who have heard a little about it.
When do teens think it’s OK for students to use ChatGPT?
For teens, whether it is – or is not – acceptable for students to use ChatGPT depends on what it is being used for.
There is a fair amount of support for using the chatbot to explore a topic. Roughly seven-in-ten teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use when they are researching something new, while 13% say it is not acceptable.
However, there is much less support for using ChatGPT to do the work itself. Just one-in-five teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use it to write essays, while 57% say it is not acceptable. And 39% say it’s acceptable to use ChatGPT to solve math problems, while a similar share of teens (36%) say it’s not acceptable.
Some teens are uncertain about whether it’s acceptable to use ChatGPT for these tasks. Between 18% and 24% say they aren’t sure whether these are acceptable use cases for ChatGPT.
Those who have heard a lot about ChatGPT are more likely than those who have only heard a little about it to say it’s acceptable to use the chatbot to research topics, solve math problems and write essays. For instance, 54% of teens who have heard a lot about ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use it to solve math problems, compared with 32% among those who have heard a little about it.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
- Artificial Intelligence
- Technology Adoption
- Teens & Tech

Olivia Sidoti is a research assistant focusing on internet and technology research at Pew Research Center

Jeffrey Gottfried is an associate director focusing on internet and technology research at Pew Research Center
Many Americans think generative AI programs should credit the sources they rely on
Americans’ use of chatgpt is ticking up, but few trust its election information, q&a: how we used large language models to identify guests on popular podcasts, striking findings from 2023, what the data says about americans’ views of artificial intelligence, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Delegation Process and Recommendations Coursework
Introduction, purpose of delegation.
In management, delegation can be defined as assigning other members of staff responsibilities and authority to complete certain tasks. It can be differentiated from dumping tasks or abdicating duty because delegation shows that the leader trusts the employees, which enhances teamwork (Akinola et al., 2018). Another aspect is that how to delegate effectively is an important core competency for all leaders. Leaders who apply delegation of tasks demonstrate that they care, which is essential in developing the work environment. Therefore, delegation can be considered as the process of allocating employees’ responsibilities and authority to work on certain tasks.
Delegation is a common occurrence in most workplaces as it serves different objectives. One of the purposes of delegating is that it frees time for other tasks, which enables the leader to deal with other crucial issues. Another purpose is that it helps develop management skills because leaders learn more about people management. The delegation also assists employees to enhance their skills when they handle different tasks at the workplace. Managers can handle the workload at the workplace by delegating tasks to staff members (Akinola et al., 2018). Delegation encourages open communication and trust, which increases motivation and builds morale in the work environment.
Delegation also encourages and stimulates the creativity of employees, which allows them to take initiative. The employees contribute to the success of the company by being assigned different responsibilities and authority. The use of delegation ensures the creation of an efficient and confident team and retains skilled employees at the workplace, which saves resources. Employees who receive responsibilities at the workplace are more inclined to remain at the workplace (Akinola et al., 2018). Another purpose of delegation is that it maximizes the potential of employees by ensuring that staff members are involved in the collective success of the organization.
One of the ways to delegate effectively is to understand the tasks to delegate. For example, activities such as performance reviews and recruitment should not be delegated. Another aspect is that delegation should be based on the strengths and goals of employees. This is because employees are motivated to pursue goals that enhance their skills. Managers need to provide employees with the desired outcomes and ensure they have the right level of authority and resources to complete the tasks (Akinola et al., 2018). For example, tasks involving access to confidential company information cannot be delegated to junior staff without providing them with access. Leaders are also required to allow failure, provide feedback, and recognize the success of employees. For example, if a task is not completed successfully, the manager can offer constructive criticism to the employee and encourage them to develop their skills.
Akinola, M., Martin, A. E., & Phillips, K. W. (2018). To delegate or not to delegate: Gender differences in affective associations and behavioral responses to delegation . Academy of Management Journal, 61(4), 1467- 1491. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, April 28). Delegation Process and Recommendations. https://ivypanda.com/essays/delegation-process-and-recommendations/
"Delegation Process and Recommendations." IvyPanda , 28 Apr. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/delegation-process-and-recommendations/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Delegation Process and Recommendations'. 28 April.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Delegation Process and Recommendations." April 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/delegation-process-and-recommendations/.
1. IvyPanda . "Delegation Process and Recommendations." April 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/delegation-process-and-recommendations/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Delegation Process and Recommendations." April 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/delegation-process-and-recommendations/.
- Therapeutic Reduction as Responsibility Abdication
- Developing Delegating Skills
- Delegation and Empowerment
- Delegation: Business Term Definition
- BM and Leadership: Delegation
- Delegation in the Health Care Setting
- Empowerment and Delegation
- Delegation: Definition and Importance
- Encouraging Managers to Delegate
- The Correct Use of Authority in Nursing Delegation
- Southwest Airlines: Talent Management Plan
- Exploring the Concept of Remote Work
- The Importance of a Leadership Succession Plan
- Working Committee: Hiring Process
- Brown's Hardware & Company Limited: Employee Dynamics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Conclusions for academic papers. An academic conclusion paragraph reminds your reader of the main points of your paper and summarizes the "take away" or significance of the conversation. Think of your conclusion as an upside-down introduction paragraph. Returning to the triangle analogy from academic introductions: Specific
The conclusion in a research paper is the final section, where you need to summarize your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. ... However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
Guide to Writing Introductions and Conclusions. First and last impressions are important in any part of life, especially in writing. This is why the introduction and conclusion of any paper - whether it be a simple essay or a long research paper - are essential. Introductions and conclusions are just as important as the body of your paper.
Introductions and conclusions can be the hardest parts of a paper to write. In research, many scholars solely look at introductions and conclusions to quickly find out whether or not a publication is useful for their research. The Introduction Starting an introduction can be a daunting task. You have to think about the whole paper and create ...
Introductions and Conclusions. Introductions and conclusions play a special role in the academic essay, and they frequently demand much of your attention as a writer. A good introduction should identify your topic, provide essential context, and indicate your particular focus in the essay. It also needs to engage your readers' interest.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don't have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don't really say much. They exist just to take up the "introduction space" in your paper.
Research Paper Introduction. Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question(s) or hypothesis(es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. ... They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions. Advantages of Research Paper. Research papers have many advantages, both for ...
Writing Centre Learning Guide. Good essays, reports or theses start with good introductions and end with good conclusions. The introduction leads your reader into the main text, while the conclusion leaves your reader with a final impression. Although introductions and conclusions have some similarities, they also have many differences.
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion: Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study. Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results ...
The introduction of a paper introduces the topic and scope of the discussion to prepare the reader for what follows, and the conclusion offers thoughtful analytic commentary or a synopsis that wraps up the discussion with final thoughts. In other words, the introduction and conclusion depend on everything that comes between them.
The introduction and conclusion allow a writer to address the overall purpose and significance of an essay. In general terms, the introduction states the intention, while the conclusion defines the achievement of an essay. Together they constitute the frame for your paper, providing the first and last opportunities to convince your reader of ...
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed. 5. Make a call to action when appropriate. If and when needed, you can state to your readers that there is a need for further research on your paper's topic.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion ...
Writing the introduction and background of a research article can be daunting. Where do you start? What information should you include? A great place to start is creating an argument structure for why your research topic is relevant and important. This structure should clearly walk the reader through current, relevant literature and lead them ...
Generate a compelling conclusion for your essay based on your introduction and key points. HyperWrite's Essay Conclusion Generator is an AI-powered tool that creates compelling conclusions for your essays. By analyzing the introduction and key points of your essay, this tool generates a unique and high-quality conclusion that restates your thesis, summarizes your arguments, and leaves a ...
Introductions and conclusions can be the hardest parts of a paper to write. In research, many scholars solely look at introductions and conclusions to quickly find out whether or not a publication is useful for their research. The Introduction Starting an introduction can be a daunting task. You have to think about the whole paper and create ...
Introduction. Sustainable development is at the core of national and international discussions on development issues. ... The evidence that the flexible approach works is, by the standards of rigorous research, about as good as it gets. ... Conclusion. In this paper we identified some of the key challenges for high-road approach to employee ...
On the other hand, research is also concerned with how deforestation drives people out of rural areas, leading to overurbanization. Other research, often in demography conversations, focuses more on theories of overurbanization, specifically the rural-push and urban-pull perspectives (Harper 2009; Hawley 1971; Weeks 2020).According to these perspectives, demographic transitions, like ...
Finally, Sect. "Conclusion" concludes the paper by summarizing the findings. Results The proposed method, described in detail in the " Methods " section below, is evaluated through a simulation ...
It contains thousands of paper examples on a wide variety of topics, all donated by helpful students. You can use them for inspiration, an insight into a particular topic, a handy source of reference, or even just as a template of a certain type of paper. The database is updated daily, so anyone can easily find a relevant essay example.
The introduction of ChatGPT last year has led to much ... How we did this. Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand American teens' use and understanding of ChatGPT in the school setting. The Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, via Ipsos. ... Just one-in-five teens who have ...
It contains thousands of paper examples on a wide variety of topics, all donated by helpful students. You can use them for inspiration, an insight into a particular topic, a handy source of reference, or even just as a template of a certain type of paper. The database is updated daily, so anyone can easily find a relevant essay example.