How to Create a Research Poster
- Poster Basics
- Design Tips
- Logos & Images

What is a Research Poster?
Posters are widely used in the academic community, and most conferences include poster presentations in their program. Research posters summarize information or research concisely and attractively to help publicize it and generate discussion.
The poster is usually a mixture of a brief text mixed with tables, graphs, pictures, and other presentation formats. At a conference, the researcher stands by the poster display while other participants can come and view the presentation and interact with the author.
What Makes a Good Poster?
- Important information should be readable from about 10 feet away
- Title is short and draws interest
- Word count of about 300 to 800 words
- Text is clear and to the point
- Use of bullets, numbering, and headlines make it easy to read
- Effective use of graphics, color and fonts
- Consistent and clean layout
- Includes acknowledgments, your name and institutional affiliation
A Sample of a Well Designed Poster
View this poster example in a web browser .

Image credit: Poster Session Tips by [email protected], via Penn State
Where do I begin?
Answer these three questions:.
- What is the most important/interesting/astounding finding from my research project?
- How can I visually share my research with conference attendees? Should I use charts, graphs, photos, images?
- What kind of information can I convey during my talk that will complement my poster?
What software can I use to make a poster?
A popular, easy-to-use option. It is part of Microsoft Office package and is available on the library computers in rooms LC337 and LC336. ( Advice for creating a poster with PowerPoint ).
Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and InDesign
Feature-rich professional software that is good for posters including lots of high-resolution images, but they are more complex and expensive. NYU Faculty, Staff, and Students can access and download the Adobe Creative Suite .
Open Source Alternatives
- OpenOffice is the free alternative to MS Office (Impress is its PowerPoint alternative).
- Inkscape and Gimp are alternatives to Adobe products.
- For charts and diagrams try Gliffy or Lovely Charts .
- A complete list of free graphics software .
A Sample of a Poorly Designed Poster
View this bad poster example in a browser.
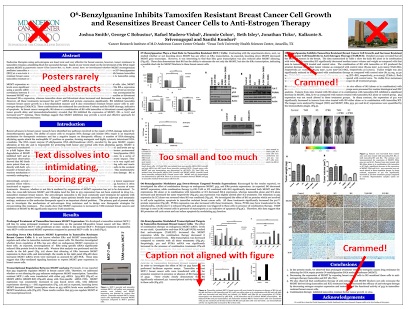
Image Credit: Critique by Better Posters
- Next: Design Tips >>
- Last Updated: Jul 11, 2023 5:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/posters
The Ultimate Guide: How to Create a Standout Research Poster
Craft standout research posters with this guide. Learn how to make research posters that captivate and inform effectively.
Are you a scientist or researcher looking to create a research poster that will grab attention and make an impact? Look no further – in this ultimate guide, we will walk you through the steps to make a research poster that stands out. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, Mind the Graph.com is an online platform designed to help you create visually appealing scientific figures, infographics, graphical abstracts, presentations, and posters. With its user-friendly interface and access to over 75,000 scientifically accurate illustrations in 80+ fields, Mind the Graph makes it easy for researchers to communicate their complex data in a visually engaging way. Say goodbye to the challenge of visualizing your research without specialized design skills – Mind the Graph is here to revolutionize scientific communication.
Understanding Research Posters
Importance of research posters.
In the world of scientific research, research posters play a crucial role. They are a popular medium for the presentation of scientific findings at scientific conferences, seminars, and symposia. Research posters provide a snapshot of your work, enabling fellow researchers, students, and the general public to understand the scope, methods, results, and implications of your research.
Moreover, research posters allow for interactive communication. Presenters get the opportunity to discuss their work one-on-one with interested viewers, explain complex concepts, generate discussion, and receive instant feedback. This interactive nature of poster presentations fosters scientific dialogue and collaboration.
Importantly, a well-designed research poster can attract attention and create a lasting impression on conference attendees. With so many posters on display at scientific gatherings, having a standout research poster is critical. It’s not just about presenting your research—it’s about making your research memorable.
What Constitutes a Good Research Poster?

A good research poster is a careful balance of content and design. It succinctly presents the results section your research in a visually appealing and easy-to-read format. Here are the key elements of how to make a research poster:
- Clarity : Your poster should concisely convey your research objective, methods, results, and conclusions. Avoid overly technical jargon and ensure your content is accessible to a broad audience.
- Structure : Your poster should have a logical flow. The layout should guide the viewer from the introduction and objectives, through the methods and results, to the conclusions and implications.
- Visual Appeal : Use figures, graphs, and diagrams to illustrate your points. These visuals should be simple yet informative, helping viewers understand your research at a glance.
- Readability : Choose fonts and colors that are easy on the eyes. Ensure there is sufficient contrast between the text and the background.
- Engagement : Aim to stimulate conversation. Pose thought-provoking questions or highlight surprising findings to draw in viewers and spark discussions.
Remember, the aim is not to cram as much information as possible onto the white space of the paper or poster. It’s about communicating your research effectively and engagingly.
Creating a Standout Research Poster
Essential elements of a research poster.

Creating a standout research poster involves incorporating several essential elements into your design:
- Title : Your title should be brief yet informative, clearly indicating the focus of your research. It’s the first thing viewers see, so make it captivating.
- Authors and Affiliations : List the names of all authors involved in the research and their respective affiliations. The lead author’s name is typically listed first.
- Introduction/Objectives : This section provides a context for your research, outlines your research question, and states your objectives.
- Methods : Describe your research design and the methods you used to collect and analyze data. Be succinct but clear.
- Results : Present your findings using clear and concise text, supplemented by graphs, charts, or images.
- Conclusions : Summarize the key findings and their implications. What does your research mean in the larger context?
- References : Cite any sources or research that informed your study.
- Acknowledgments : Recognize those who assisted in your research or funded your study.
- Contact Information : Include your email or other contact information for viewers who wish to follow up.
Remember, simplicity is key. Your poster’s content layout should be visually engaging, but not cluttered or overwhelming.
Designing with Mind the Graph
Designing a research poster can be a daunting task, especially if you don’t have a background in graphic design. That’s where Mind the Graph comes in. This online platform offers a user-friendly interface and a vast library of scientifically accurate illustrations, making it easy for researchers to create visually engaging scientific posters themselves.
To start, choose from a variety of pre-designed templates or create your own design from scratch. Then, drag and drop your desired illustrations onto your poster. With over 40,000 illustrations in 80+ fields, you’re sure to find images that perfectly represent your own research project.
Next, add your text. Mind the Graph allows you to customize the font, size, and color, ensuring your text complements your visuals and is easy to read.
Finally, use the platform’s tools to arrange your content in a logical, visually pleasing manner. You can easily adjust the size and position of each element, ensuring a balanced layout.
With Mind the Graph, you don’t need to be a design expert to create a professional, eye-catching research poster.
Making Use of Mind the Graph
Navigating the mind the graph platform.

Navigating the Mind the Graph platform is straightforward, even for beginners. Here’s a simple guide to help you get started:
First, sign up for a free account on the Mind the Graph website. Once logged in, you’ll be directed to the dashboard. From here, you can create a new project, view your saved projects, or explore the platform’s vast library of scientific illustrations.
To create a new research poster, click on the “New Infographic” button. You’ll be prompted to choose a template. Mind the Graph offers a variety of templates tailored to different scientific fields and presentation types.
Once you’ve selected a template, you’ll be taken to the editor. Here, you can add text, change fonts and colors, and insert illustrations. The platform’s drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to add and rearrange elements on your poster.
On the left-hand side, you’ll find the tools menu. Here, you can access more design options, such as shapes, lines, and backgrounds.
Remember, the Mind the Graph team is always ready to assist if you have any questions or need help navigating the platform.
Utilizing Scientific Illustrations
Scientific illustrations are a powerful tool for visualizing complex research data. Mind the Graph offers a wealth of scientifically accurate illustrations to enhance your research poster.
To access the illustrations library, navigate to the “Illustrations” tab in the editor. Here, you can browse through over 40,000 illustrations in 80+ fields. You can search for specific illustrations using the search bar at the top or filter by categories.
Once you’ve found an illustration you’d like to use, simply click on it and drag it onto your poster. You can resize and reposition the print, entire poster or illustration as needed.
Using illustrations can help break up text-heavy sections well-designed posters, making your poster more engaging and easier to digest. They can also help to highlight key points, demonstrate processes, and represent results visually.
Remember, while illustrations can greatly enhance your poster, they should not be overly complex or confusing. The goal of visual representation is to aid understanding, not to complicate it. Use illustrations judiciously and ensure they directly support your research message.
Advantages of Using Mind the Graph
Using Mind the Graph to create your research poster has several key advantages.
Firstly, it democratizes great poster design for scientists and researchers. With its user-friendly interface, you don’t need to be a graphic design expert to create a professional-looking scientific poster either.
Secondly, it offers a vast library of scientifically accurate illustrations good poster make. This resource saves you the time and effort of creating visuals from scratch and ensures your poster is both visually appealing and scientifically sound.
Thirdly, it’s customizable. You can easily adjust the font, color, size, and positioning of every element on your poster, ensuring your poster design aligns with your research and personal style.
Lastly, it’s efficient. With Mind the Graph, you can create a poster in less time than it would take using traditional design software. Plus, with the ability to save and edit your project, you can work on your poster at your own pace.
In short, Mind the Graph equips you with the tools to effectively communicate your research in a visually engaging way.
Finalizing Your Research Poster
Reviewing your research poster.
Once you’ve completed your initial design, it’s essential to take the time to review your research poster thoroughly. Here are some points to consider:
- Clarity : Is your message clear and concise? Does your poster effectively communicate your research objective, methods, results, and conclusions?
- Flow : Check the logical progression of your content. Can viewers easily follow the flow from the introduction to the conclusion?
- Visuals : Review your illustrations and charts. Do they accurately represent your data and enhance understanding?
- Typography : Check your text for readability. Is the font size large enough? Is there sufficient contrast between the text and the background?
- Errors : Proofread your text for any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Also, check your data for any inaccuracies.
- Feedback : Consider getting feedback from colleagues or mentors. They can provide a fresh perspective and may spot errors or areas for improvement that you might have missed.
Remember, a little extra time spent reviewing and refining your poster can make a significant difference in the poster display final outcome. It’s worth the effort.
Making Your Research Poster Accessible
Accessibility should be a priority when finalizing your research poster. Ensuring your effective poster presentation is accessible to all viewers, regardless of their ability, is not just ethical – it enhances the reach and impact of your research.
Here are some simple ways to make your poster more accessible:
- Color Contrast : Use colors that contrast well to ensure your text and illustrations are clear and distinguishable. Avoid using color as the only means of conveying important information, as this can be problematic for viewers with color vision deficiencies.
- Font Size : Use a large, easy-to-read font size. This not only helps viewers with visual impairments but also makes your poster easier to read from a distance.
- Clear Language : Use clear, concise language and avoid unnecessary jargon. This makes your research accessible to viewers from different backgrounds and knowledge levels.
- Captioning : Provide captions or alternative text for images and diagrams. This helps viewers with visual impairments understand the content of your visuals.
- Layout : Arrange the elements of your poster in a logical, linear order. This helps viewers with cognitive impairments follow your content more easily.
Remember, an accessible academic poster, is an effective poster. Make sure the poster title of your research can be appreciated by everyone.
Promoting Your Research Poster with Mind the Graph
Once you’ve created your standout research poster, it’s time to share it with the world. Mind the Graph can aid in promoting your research poster to a wider audience.
Firstly, you can download your poster in a high-resolution format suitable for printing or digital viewing. You can also share a direct link to your online poster or embed it in your website or blog.
Furthermore, Mind the Graph has a continually growing community of scientists and researchers from around the world. Becoming part of this community allows you to share your work, get feedback, and engage in scientific discussions. You can also explore and get inspired by the work of others.
Remember, promoting your research is an integral part of the scientific process. It’s not enough to do good research; you need to communicate it effectively and make it accessible to others. Whether you’re presenting at a conference, a poster session, a seminar, or online, Mind the Graph is here to help you make your research and poster sessions stand out and be seen.
Enhance your research with compelling visuals through Mind the Graph
The Mind the Graph platform provides customizable scientific illustrations, templates, and design tools, empowering scientists to create engaging figures that convey findings effectively. With features for data integration and customization of colors, fonts, and styles, researchers can personalize their visuals to match their unique research style, ensuring broader accessibility and memorability.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Fabricio Pamplona
Fabricio Pamplona is the founder of Mind the Graph - a tool used by over 400K users in 60 countries. He has a Ph.D. and solid scientific background in Psychopharmacology and experience as a Guest Researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (Germany) and Researcher in D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR, Brazil). Fabricio holds over 2500 citations in Google Scholar. He has 10 years of experience in small innovative businesses, with relevant experience in product design and innovation management. Connect with him on LinkedIn - Fabricio Pamplona .
Content tags
University Library, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign

Research Posters
- Elements of a poster
CREATING YOUR POSTER
Color scheme choices.
- WHAT TO INCLUDE IN YOUR POSTER
- More helpful tips
- Visualizations & images
- Illinois logo
- Archiving - Grad Students
- More Resources
- Oral Presentations
- 2024 Undergraduate Research Symposium This link opens in a new window
You have two choices when creating a research poster:
- You can create your poster from scratch by using PowerPoint, Adobe InDesign, or a similar design program.
- You can use one of the University of Illinois Research Poster Templates .
Sizing your Poster
- If you are presenting for the Undergraduate Research Symposium , resize your slide to width 48 inches by height 36 inches.
- If you are presenting at a professional conference , your instructions should indicate the size limits of your poster. Standard U.S. conference poster size is 48" by 36".
IMPORTANT: You must change the size of your slide before you start working on your poster. This will ensure that your images and text do not become pixilated when the poster is printed. See below for specific instructions.
How to correctly size your poster in PowerPoint:
- Select the "Design" tab
- Click "Slide Size"
- Select "Page Setup"
- Under the "Slides sized for:" dropdown menu, select "Custom"
- Set the "Width" and "Height" to what is needed for your poster
- Click "OK"

How to correctly size your poster in Adobe InDesign:
When a new document is created in Adobe InDesign, a dialogue box prompts you to enter dimensions:

- Change the dimension metric to inches from the drop down box.
- Margins are intentional space from an object to the edge of the poster, intended not to be trimmed. You can set this to 0 inches on all sides unless you have a specific plan to use margins in your design.
- Bleed shows the printer where to trim white space that occurs when printing color onto white poster paper. If you are printing your poster, include at least a 0.25 inch bleed on each side; remember not to place any content in the bleed as it will be trimmed by the printer.
- Slug is a space for the creator to leave any notes for the printer. You can set this to 0 inches unless you have notes.
If you ever want to change your poster dimensions after starting the poster, you can do so through the Document Setup Menu .
Using multiple font styles can really make your poster stand out and look professional. Consult this graphic to understand different font styles, what fonts work best together, and what fonts to avoid.
Sticking to a color scheme can help your poster look professional. Consistent use of color can help your viewer understand how information is organized on your poster. Not sure where to start with color?
- Pick colors from an image (including a custom one you're planning to use on your poster)
- Use Illinois branding colors
Not sure what to do with the hex code from a brand guide or color palette generator?
- Adobe InDesign
Always check that your text is accessible on background colors using WebAIM's free contrast checker.
If printing your poster, it's a good idea to do a small-scale test print of your poster before getting it printed. Colors often appear brighter and more vibrant on a screen than when printed. There still might be some variation in color depending on the color scale the printer uses, but it will be a closer match on paper than what you see on screen.
- << Previous: Examples
- Next: Visualizations & images >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 2:05 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinois.edu/poster

Research Posters
What are research posters, what should a research poster look like, what software can i use to make one, where can i print my poster.
- Themes, Colors, and Emphasis
- Text Formatting
- Writing Style
- Hyperlinks and URLs
- Including Images
- Actual Examples
- How to Present Posters
Acknowledgements
This guide is based off of Librarian Professor Ashley Orehek Rossi's presentation at the 2024 Student Scholar Showcase Workshop series .
Research posters provide general (or detailed) overviews about research either you are currently working on or already completed. Think of them like "mini research papers" or a summarized version of your research -- You want to discuss your research project in a short, concise narrative (with pictures!).

- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Google Slides
- Microsoft Publisher
PowerPoint is versatile! You have the freedom to place objects wherever you want on a page. It will also help you line up and space content evenly. PowerPoint is a very popular software to make posters in.
How do I adjust the slide size to my poster size?
For example, let's say you need a poster that is 36 inches by 48 inches. In the menu ribbon:
Design > Slide Size > Custom Slide Size. Change the Slides sized for: to Custom . Enter the dimensions as 36 inches wide by 48 inches high. Click OK .
Just like PowerPoint, Google Slides is versatile and you have the freedom to place objects wherever on a page.
File > Page Setup > Custom. Change the Page Setup to Custom . Enter the dimensions as 36 inches wide by 48 inches high. Click Apply .
Publisher is a graphic design app from Microsoft. It allows users to create various types of documents using templates provided, downloaded templates, or starting from a blank canvas. Like PowerPoint, you can place objects anywhere you want on a page.
PRO: What makes it preferred than Microsoft Word is that page layout is emphasized, so you don't need to fret about adjusting alignments or line spacing -- You have the freedom to place objects wherever you need to on the document.
CON: It is only available on desktop or laptop computers - You cannot access it from Microsoft 365 online.
How do I resize my Publisher page?
Page Design > Page Setup > Change Width and Height values and/or units.
Canva is like an online version of Microsoft Publisher. It allows user to make designs for both online content and printed materials. Media types include, but not limited to, videos, social media posts, documents, and websites. You can also invite others to collaborate on projects, just like Google Docs.
Canva offers two plans for account holders: Free and Pro.
Information from Canva.com (Accessed 25 Oct 2023).
The WKU Print Center (ground floor DSU) can print posters for you for a fee. You can also check with your academic major department if they have a poster printer available.
Stores like Staples and Office Depot / OfficeMax offer poster printing services.
- Next: Themes, Colors, and Emphasis >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 3:15 PM
- URL: https://libguides.wku.edu/posters
Learn more about how the Cal Poly Humboldt Library can help support your research and learning needs.
Stay updated at Campus Ready .

- Cal Poly Humboldt Library
- Research Guides
Creating a Research Poster
- Creating your poster step by step
- Getting Started
- Citing Images
- Creative Commons Images
- Printing options
- More Resources
Preparing your poster
There are three components to your poster session:
- Your poster
All three components should complement one another, not repeat each other.
Poster: Your poster should be an outline of your research with interesting commentary about what you learned along the way.
You: You should prepare a 10-30 second elevator pitch and a 1-2 minute lightning talk about your research. This should be a unique experience or insight you had about your research that adds depth of understanding to what the attendee can read on your poster.
Handout: Best practices for handouts - Your handout should be double-sided. The first side of the paper should include a picture of your poster (this can be in black and white or color). The second side of the handout should include your literature review, cited references, further information about your topic and your contact information.
Creating your poster by answering 3 questions:
- What is the most important and/or interesting finding from my research project?
- How can I visually share my research with conference attendees? Should I use charts, graphs, images, or a wordcloud?
- What kind of information do I need to share during my lightning talk that will complement my poster?
- *Title (at least 72 pt font).
- Research question or hypothesis (all text should be at least 24 pt font).
- Methodology. What is the research process that you used? Explain how you did your research.
- Your interview questions.
- Observations. What did you see? Why is this important?
- *Findings. What did you learn? Summarize your conclusions.
- Pull out themes in the literature and list in bullet points.
- Consider a brief narrative of what you learned - what was the most interesting/surprising part of your project?
- Interesting quotes from your research.
- Turn your data into charts or tables.
- Use images (visit the "Images" tab in the guide for more information). Take your own or legally use others.
- Recommendations and/or next steps for future research.
- You can include your list of citations on your poster or in your handout.
- *Make sure your name, and Cal Poly Humboldt University is on your poster.
*Required. Everything else is optional - you decide what is important to put on your poster. These are just suggestions. Use the tabs in this guide for more tips on how to create your poster.
Poster Sizes
You can create your poster from scratch by using PowerPoint or a similar design program.
Resize the slide to fit your needs before you begin adding any content. Standard poster sizes range from 40" by 30" and 48" by 36" but you should check with the conference organizers. If you don't resize your design at the beginning, when it is printed the image quality will be poor and pixelated if it is sized up to poster dimensions.
The standard poster sizes for ideaFest are 36" x 48" and 24" by 36".
To resize in PowerPoint, go to "File" then "Page Setup..." and enter your dimensions in the boxes for "width" and "height". Make sure to select "OK" to save your changes.
To resize in Google Slides, go to "File" then "Page setup" and select the "Custom" option in the drop down menu. Enter the dimensions for your poster size and then select "Apply" to save your changes.
Step Four: Final checklist
Final checklist for submitting your poster for printing:.
- Proofread your poster for spelling and grammar mistakes. Ask a peer to read your poster, they will catch the mistakes that you miss. Print your poster on an 8 1/2" by 11" sheet of paper - it is easier to read for mistakes and to judge your design.
- Make sure you followed Step 3 and resized your PPT slide correctly.
- Does your poster have flow? Did you "chunk" information into easily read pieces of information?
- Do your visualizations (e.g. charts, graphs, tag clouds, etc.) tell a story? Are they properly labeled and readable?
- Make sure that your images we not resized in PPT. You should use the original size of the image or try an image editor (e.g. Photoshop). Did you cite your image?
- Is your name, department, and affiliation on your poster?
- Did you want to include acknowlegments on your poster? This may be appropriate if your advisor and a graduate student provided leadership during the research process.
- Most importantly- Save your PPT slide to PDF before you send to the printer in order to avoid any printing mishaps. You should also double-check the properties to make sure it is still sized correctly in PDF.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Images >>

How to Create an Academic Poster
- Designing Effective Research Posters
- Poster Templates
- Poster Printing Guidelines
How to Write a Poster Abstract or Proposal
- More Research Help
Little Memorial Library Printing Guidelines
How to print a poster:.
- Submit your poster print request here: https://midway.libwizard.com/f/posterprinting
- Submit your poster print request at least one week in advance of when you need it
- Go to the Business Office in LRC and pay for the poster (You may also call them at 859-846-5402 .)
- Wait for an email from The Center@Midway telling you to come pick up your poster
Printing specifications:
- Make your poster 36" x 48".
- Save your poster as a PDF. Only PDF files will be accepted.
- Use at least 300 dpi (but no more than 1200 dpi)
- File size should be no more than 10MB
- Poster must be school/study-related.
- Cost: $20 per poster (you will incur an additional $20 charge every time you want your poster re-printed because of a typo, wanting to change information, etc.).
- Poster Abstracts
What is an abstract/proposal and why should I write one?
If you want to submit your paper/research at a conference, you must first write a proposal. A poster proposal tells the conference committee what your poster is about and, depending on the conference guidelines, might include a poster abstract, your list of contributors, and/or presentation needs.
The poster abstract is the most important part of your proposal. It is a summary of your research poster, and tells the reader what your problem, method, results, and conclusions are. Most abstracts are only 75 -- 250 words long.
- << Previous: Poster Printing Guidelines
- Next: More Research Help >>
- Last Updated: Mar 23, 2021 11:17 AM
- URL: https://midway.libguides.com/AcademicPoster
RESEARCH HELP
- Research Guides
- Databases A-Z
- Journal Search
- Citation Help
LIBRARY SERVICES
- Accessibility
- Interlibrary Loan
- Study Rooms
INSTRUCTION SUPPORT
- Course Reserves
- Library Instruction
- Little Memorial Library
- 512 East Stephens Street
- 859.846.5316
- [email protected]


How to create a research poster
- Getting Started
- Planning your Poster
- Designing a Poster
- Poster Templates & Examples
- Printing your Poster
- Additional Guides
What is a research poster?
A research poster is a visual way to summarize and communicate the results of a research project to a general audience. A good poster should include the goal of the research, its methodology, results, and discussion/conclusion, in clear and concise language.
Research posters will often include photos, maps, graphs and other images to present information in an attractive way.
Why a poster?
Research posters are a common form of research presentation in conferences, seminars, and symposiums. Some of the main advantages of presenting a poster rather than a conference paper are:
- Knowledge sharing with a wider audience: with poster presentations, researchers usually stand beside their posters and can interact directly with the public.
- Opportunity to explore different ways to present information: posters are ideal for highly visual topics.
- Networking: presenting posters can help researchers identify potential collaborators, spark further discussion, make contacts, etc.
- Opportunity to improve verbal presentation skills: researchers can talk about their research without having to observe the stricter guidelines of other types of conference presentations.
- Opportunity to showcase research to potential employers.
Branding requirements
Yukon University's branding guidelines may be applicable when presenting research results. This can vary depending on course/assignment requirements, whether the research is directly sponsored/funded by the institution, and how and where the poster will be presented.
For YukonU students: check with your instructor if branding is required for your situation.
YukonU faculty/staff: YukonU's branding guidelines can be found on https://yukoncollege.sharepoint.com/sites/yc/offices/relations (Sharepoint login required).
- Next: Planning your Poster >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2023 2:45 PM
- URL: https://yukonu.libguides.com/research_poster
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare an...
How to prepare an effective research poster
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 1 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin
- 2 Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- mhiggins{at}nmh.ie
Being asked to give a poster presentation can be exciting, and you need not be daunted by the prospect of working out how to prepare one. As Lucia Hartigan and colleagues explain, many options are available
The long nights are over, the statistics have been run, the abstract has been written, and the email pops into your inbox: “Congratulations! You have been accepted for a poster presentation.”
All that work has been worthwhile. Your consultant congratulates you and your colleagues are envious of your having a legitimate excuse to go away for a couple of days, but now you have to work out how to prepare a poster. Do not despair, for you have many options.
Firstly, take this seriously. A poster is not a consolation prize for not being given an oral presentation. This is your chance to show your work, talk to others in the field, and, if you are lucky, to pick up pointers from experts. Given that just 45% of published abstracts end in a full paper, 1 this may be your only chance to get your work out there, so put some effort into it. If you don’t have access to the services of a graphic designer, then some work will be entailed as it normally takes us a full day to prepare the layout of a poster. If you are lucky enough to have help from a graphic designer, then you will need to check that the data are correct before it is sent to the printer. After all, it will be your name on the poster, not the graphic designer’s.
Secondly, check the details of the requirements. What size poster should you have? If it is too big, it may look arrogant. If it is too small, then it may seem too modest and self effacing. Should it be portrait or landscape? Different meetings have different requirements. Some may stay with traditional paper posters, so you need to factor in printing. Others present them electronically, but may have a deadline by which you need to have uploaded the poster. When planning a meeting the organisers work out how many poster boards there will be and then the numbers, so follow their requirements and read the small print.
Then make a template. It can be tempting to “borrow” a poster template from someone else, and this may buy you some time, but it is important to check what page set-up and size have been selected for the template. If it’s meant for an A2 size and you wish to print your poster on A0 paper, then the stretching may lead to pixillation, which would not look good.
Next, think about your layout. Use text boxes to cover the following areas: title (with authors, institution, and logo), background, methods, results, and conclusions. Check that the text boxes are aligned by using gridlines, and justify your text. Use different colours for titles, and make sure you can read the title from 3 metres away. Some people will put their abstract in a separate box in the top right hand corner underneath the title, and then expand a little in the other areas. That is fine, so long as you follow the golden rule of writing a poster: do not include too much text. One study showed that less than 5% of conference attendees visit posters at meetings and that few ask useful questions. 2 The same research found that, in addition to the scientific content of a poster, the factors that increase visual appeal include pictures, graphs, and a limited use of words. 2 The ideal number of words seems to be between 300 and 400 per square metre.
Now make it look pretty and eye catching, and use lots of graphics. Outline text boxes or fill them with a different colour. If you can present the data using a graph, image, or figures rather than text, then do so, as this will add visual appeal. If you want to put a picture in the background, and it is appropriate to do so, fade the image so that it does not distract from the content.
Fonts are important. Check whether the meeting has set criteria for fonts; if they have, then follow them. You do not want to stand out for the wrong reason. If there are no specified criteria, then the title should be in point size 72-84, depending on the size of the poster. The authors’ names should be either the same size, but in italics, or else a couple of sizes smaller.
If you are including the hospital logo, don’t take a picture that will not size up properly when enlarged. Instead, obtain a proper copy from the hospital administrators.
References can be in small writing. No one is likely to read them, and you are including them only to remind yourself what you learnt in the literature review. One intriguing possibility is the use of a trigger image to link the poster to online content. 3
Finally, there are also things you should not do. Don’t leave your figures unlabelled, include spelling errors, use abbreviations without an explanation, or go outside the boundaries of the poster. Don’t be ashamed that you “only” have a poster. At a good meeting you may find that the comments from passers by are an amazing peer review. We have presented at meetings where world experts have given feedback, and with that feedback we have written the paper on the flight home.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and have no relevant interests to declare.
- ↵ Scherer RW, Langenberg P, von Elm E. Full publication of results initially presented in abstracts. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007 ; 2 : MR000005 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Goodhand JR, Giles CL, Wahed M, Irving PM, Langmead L, Rampton DS. Poster presentations at medical conferences: an effective way of disseminating research? Clin Med 2011 ; 1 : 138 -41. OpenUrl
- ↵ Atherton S, Javed M, Webster S, Hemington-Gorse S. Use of a mobile device app: a potential new tool for poster presentations and surgical education. J Visual Comm Med 2013 ; 36 (1-2): 6 -10. OpenUrl
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Health Serv Res
- v.42(1 Pt 1); 2007 Feb
Preparing and Presenting Effective Research Posters
Associated data.
APPENDIX A.2. Comparison of Research Papers, Presentations, and Posters—Contents.
Posters are a common way to present results of a statistical analysis, program evaluation, or other project at professional conferences. Often, researchers fail to recognize the unique nature of the format, which is a hybrid of a published paper and an oral presentation. This methods note demonstrates how to design research posters to convey study objectives, methods, findings, and implications effectively to varied professional audiences.
A review of existing literature on research communication and poster design is used to identify and demonstrate important considerations for poster content and layout. Guidelines on how to write about statistical methods, results, and statistical significance are illustrated with samples of ineffective writing annotated to point out weaknesses, accompanied by concrete examples and explanations of improved presentation. A comparison of the content and format of papers, speeches, and posters is also provided.
Each component of a research poster about a quantitative analysis should be adapted to the audience and format, with complex statistical results translated into simplified charts, tables, and bulleted text to convey findings as part of a clear, focused story line.
Conclusions
Effective research posters should be designed around two or three key findings with accompanying handouts and narrative description to supply additional technical detail and encourage dialog with poster viewers.
An assortment of posters is a common way to present research results to viewers at a professional conference. Too often, however, researchers treat posters as poor cousins to oral presentations or published papers, failing to recognize the opportunity to convey their findings while interacting with individual viewers. By neglecting to adapt detailed paragraphs and statistical tables into text bullets and charts, they make it harder for their audience to quickly grasp the key points of the poster. By simply posting pages from the paper, they risk having people merely skim their work while standing in the conference hall. By failing to devise narrative descriptions of their poster, they overlook the chance to learn from conversations with their audience.
Even researchers who adapt their paper into a well-designed poster often forget to address the range of substantive and statistical training of their viewers. This step is essential for those presenting to nonresearchers but also pertains when addressing interdisciplinary research audiences. Studies of policymakers ( DiFranza and the Staff of the Advocacy Institute 1996 ; Sorian and Baugh 2002 ) have demonstrated the importance of making it readily apparent how research findings apply to real-world issues rather than imposing on readers to translate statistical findings themselves.
This methods note is intended to help researchers avoid such pitfalls as they create posters for professional conferences. The first section describes objectives of research posters. The second shows how to describe statistical results to viewers with varied levels of statistical training, and the third provides guidelines on the contents and organization of the poster. Later sections address how to prepare a narrative and handouts to accompany a research poster. Because researchers often present the same results as published research papers, spoken conference presentations, and posters, Appendix A compares similarities and differences in the content, format, and audience interaction of these three modes of presenting research results. Although the focus of this note is on presentation of quantitative research results, many of the guidelines about how to prepare and present posters apply equally well to qualitative studies.
WHAT IS A RESEARCH POSTER?
Preparing a poster involves not only creating pages to be mounted in a conference hall, but also writing an associated narrative and handouts, and anticipating the questions you are likely to encounter during the session. Each of these elements should be adapted to the audience, which may include people with different levels of familiarity with your topic and methods ( Nelson et al. 2002 ; Beilenson 2004 ). For example, the annual meeting of the American Public Health Association draws academics who conduct complex statistical analyses along with practitioners, program planners, policymakers, and journalists who typically do not.
Posters are a hybrid form—more detailed than a speech but less than a paper, more interactive than either ( Appendix A ). In a speech, you (the presenter) determine the focus of the presentation, but in a poster session, the viewers drive that focus. Different people will ask about different facets of your research. Some might do policy work or research on a similar topic or with related data or methods. Others will have ideas about how to apply or extend your work, raising new questions or suggesting different contrasts, ways of classifying data, or presenting results. Beilenson (2004) describes the experience of giving a poster as a dialogue between you and your viewers.
By the end of an active poster session, you may have learned as much from your viewers as they have from you, especially if the topic, methods, or audience are new to you. For instance, at David Snowdon's first poster presentation on educational attainment and longevity using data from The Nun Study, another researcher returned several times to talk with Snowdon, eventually suggesting that he extend his research to focus on Alzheimer's disease, which led to an important new direction in his research ( Snowdon 2001 ). In addition, presenting a poster provides excellent practice in explaining quickly and clearly why your project is important and what your findings mean—a useful skill to apply when revising a speech or paper on the same topic.
WRITING FOR A VARIED PROFESSIONAL AUDIENCE
Audiences at professional conferences vary considerably in their substantive and methodological backgrounds. Some will be experts on your topic but not your methods, some will be experts on your methods but not your topic, and most will fall somewhere in between. In addition, advances in research methods imply that even researchers who received cutting-edge methodological training 10 or 20 years ago might not be conversant with the latest approaches. As you design your poster, provide enough background on both the topic and the methods to convey the purpose, findings, and implications of your research to the expected range of readers.
Telling a Simple, Clear Story
Write so your audience can understand why your work is of interest to them, providing them with a clear take-home message that they can grasp in the few minutes they will spend at your poster. Experts in communications and poster design recommend planning your poster around two to three key points that you want your audience to walk away with, then designing the title, charts, and text to emphasize those points ( Briscoe 1996 ; Nelson et al. 2002 ; Beilenson 2004 ). Start by introducing the two or three key questions you have decided will be the focus of your poster, and then provide a brief overview of data and methods before presenting the evidence to answer those questions. Close with a summary of your findings and their implications for research and policy.
A 2001 survey of government policymakers showed that they prefer summaries of research to be written so they can immediately see how the findings relate to issues currently facing their constituencies, without wading through a formal research paper ( Sorian and Baugh 2002 ). Complaints that surfaced about many research reports included that they were “too long, dense, or detailed,” or “too theoretical, technical, or jargony.” On average, respondents said they read only about a quarter of the research material they receive for detail, skim about half of it, and never get to the rest.
To ensure that your poster is one viewers will read, understand, and remember, present your analyses to match the issues and questions of concern to them, rather than making readers translate your statistical results to fit their interests ( DiFranza and the Staff of the Advocacy Institute 1996 ; Nelson et al. 2002 ). Often, their questions will affect how you code your data, specify your model, or design your intervention and evaluation, so plan ahead by familiarizing yourself with your audience's interests and likely applications of your study findings. In an academic journal article, you might report parameter estimates and standard errors for each independent variable in your regression model. In the poster version, emphasize findings for specific program design features, demographic, or geographic groups, using straightforward means of presenting effect size and statistical significance; see “Describing Numeric Patterns and Contrasts” and “Presenting Statistical Test Results” below.
The following sections offer guidelines on how to present statistical findings on posters, accompanied by examples of “poor” and “better” descriptions—samples of ineffective writing annotated to point out weaknesses, accompanied by concrete examples and explanations of improved presentation. These ideas are illustrated with results from a multilevel analysis of disenrollment from the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP; Phillips et al. 2004 ). I chose that paper to show how to prepare a poster about a sophisticated quantitative analysis of a topic of interest to HSR readers, and because I was a collaborator in that study, which was presented in the three formats compared here—as a paper, a speech, and a poster.
Explaining Statistical Methods
Beilenson (2004) and Briscoe (1996) suggest keeping your description of data and methods brief, providing enough information for viewers to follow the story line and evaluate your approach. Avoid cluttering the poster with too much technical detail or obscuring key findings with excessive jargon. For readers interested in additional methodological information, provide a handout and a citation to the pertinent research paper.
As you write about statistical methods or other technical issues, relate them to the specific concepts you study. Provide synonyms for technical and statistical terminology, remembering that many conferences of interest to policy researchers draw people from a range of disciplines. Even with a quantitatively sophisticated audience, don't assume that people will know the equivalent vocabulary used in other fields. A few years ago, the journal Medical Care published an article whose sole purpose was to compare statistical terminology across various disciplines involved in health services research so that people could understand one another ( Maciejewski et al. 2002 ). After you define the term you plan to use, mention the synonyms from the various fields represented in your audience.
Consider whether acronyms are necessary on your poster. Avoid them if they are not familiar to the field or would be used only once or twice on your poster. If you use acronyms, spell them out at first usage, even those that are common in health services research such as “HEDIS®”(Health Plan Employer Data and Information Set) or “HLM”(hierarchical linear model).
Poor: “We use logistic regression and a discrete-time hazards specification to assess relative hazards of SCHIP disenrollment, with plan level as our key independent variable.” Comment: Terms like “discrete-time hazards specification” may be confusing to readers without training in those methods, which are relatively new on the scene. Also the meaning of “SCHIP” or “plan level” may be unfamiliar to some readers unless defined earlier on the poster.
Better: “Chances of disenrollment from the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) vary by amount of time enrolled, so we used hazards models (also known as event history analysis or survival analysis) to correct for those differences when estimating disenrollment patterns for SCHIP plans for different income levels.” Comment: This version clarifies the terms and concepts, naming the statistical method and its synonyms, and providing a sense of why this type of analysis is needed.
To explain a statistical method or assumption, paraphrase technical terms and illustrate how the analytic approach applies to your particular research question and data:
Poor : “The data structure can be formulated as a two-level hierarchical linear model, with families (the level-1 unit of analysis) nested within counties (the level-2 unit of analysis).” Comment: Although this description would be fine for readers used to working with this type of statistical model, those who aren't conversant with those methods may be confused by terminology such as “level-1” and “unit of analysis.”
Better: “The data have a hierarchical (or multilevel) structure, with families clustered within counties.” Comment: By replacing “nested” with the more familiar “clustered,” identifying the specific concepts for the two levels of analysis, and mentioning that “hierarchical” and “multilevel” refer to the same type of analytic structure, this description relates the generic class of statistical model to this particular study.
Presenting Results with Charts
Charts are often the preferred way to convey numeric patterns, quickly revealing the relative sizes of groups, comparative levels of some outcome, or directions of trends ( Briscoe 1996 ; Tufte 2001 ; Nelson et al. 2002 ). As Beilenson puts it, “let your figures do the talking,” reducing the need for long text descriptions or complex tables with lots of tiny numbers. For example, create a pie chart to present sample composition, use a simple bar chart to show how the dependent variable varies across subgroups, or use line charts or clustered bar charts to illustrate the net effects of nonlinear specifications or interactions among independent variables ( Miller 2005 ). Charts that include confidence intervals around point estimates are a quick and effective way to present effect size, direction, and statistical significance. For multivariate analyses, consider presenting only the results for the main variables of interest, listing the other variables in the model in a footnote and including complex statistical tables in a handout.
Provide each chart with a title (in large type) that explains the topic of that chart. A rhetorical question or summary of the main finding can be very effective. Accompany each chart with a few annotations that succinctly describe the patterns in that chart. Although each chart page should be self-explanatory, be judicious: Tufte (2001) cautions against encumbering your charts with too much “nondata ink”—excessive labeling or superfluous features such as arrows and labels on individual data points. Strive for a balance between guiding your readers through the findings and maintaining a clean, uncluttered poster. Use chart types that are familiar to your expected audience. Finally, remember that you can flesh out descriptions of charts and tables in your script rather than including all the details on the poster itself; see “Narrative to Accompany a Poster.”
Describing Numeric Patterns and Contrasts
As you describe patterns or numeric contrasts, whether from simple calculations or complex statistical models, explain both the direction and magnitude of the association. Incorporate the concepts under study and the units of measurement rather than simply reporting coefficients (β's) ( Friedman 1990 ; Miller 2005 ).
Poor: “Number of enrolled children in the family is correlated with disenrollment.” Comment: Neither the direction nor the size of the association is apparent.
Poor [version #2]: “The log-hazard of disenrollment for one-child families was 0.316.” Comment: Most readers find it easier to assess the size and direction from hazards ratios (a form of relative risk) instead of log-hazards (log-relative risks, the β's from a hazards model).
Better: “Families with only one child enrolled in the program were about 1.4 times as likely as larger families to disenroll.” Comment: This version explains the association between number of children and disenrollment without requiring viewers to exponentiate the log-hazard in their heads to assess the size and direction of that association. It also explicitly identifies the group against which one-child families are compared in the model.
Presenting Statistical Test Results
On your poster, use an approach to presenting statistical significance that keeps the focus on your results, not on the arithmetic needed to conduct inferential statistical tests. Replace standard errors or test statistics with confidence intervals, p- values, or symbols, or use formatting such as boldface, italics, or a contrasting color to denote statistically significant findings ( Davis 1997 ; Miller 2005 ). Include the detailed statistical results in handouts for later perusal.
To illustrate these recommendations, Figures 1 and and2 2 demonstrate how to divide results from a complex, multilevel model across several poster pages, using charts and bullets in lieu of the detailed statistical table from the scientific paper ( Table 1 ; Phillips et al. 2004 ). Following experts' advice to focus on one or two key points, these charts emphasize the findings from the final model (Model 5) rather than also discussing each of the fixed- and random-effects specifications from the paper.

Presenting Complex Statistical Results Graphically

Text Summary of Additional Statistical Results
Multilevel Discrete-Time Hazards Models of Disenrollment from SCHIP, New Jersey, January 1998–April 2000
Source : Phillips et al. (2004) .
SCHIP, State Children's Health Insurance Program; LRH, log relative-hazard; SE, standard error.
Figure 1 uses a chart (also from the paper) to present the net effects of a complicated set of interactions between two family-level traits (race and SCHIP plan) and a cross-level interaction between race of the family and county physician racial composition. The title is a rhetorical question that identifies the issue addressed in the chart, and the annotations explain the pattern. The chart version substantially reduces the amount of time viewers need to understand the main take-home point, averting the need to mentally sum and exponentiate several coefficients from the table.
Figure 2 uses bulleted text to summarize other key results from the model, translating log-relative hazards into hazards ratios and interpreting them with minimal reliance on jargon. The results for family race, SCHIP plan, and county physician racial composition are not repeated in Figure 2 , averting the common problem of interpreting main effect coefficients and interaction coefficients without reference to one another.
Alternatively, replace the text summary shown in Figure 2 with Table 2 —a simplified version of Table 1 which presents only the results for Model 5, replaces log-relative hazards with hazards ratios, reports associated confidence intervals in lieu of standard errors, and uses boldface to denote statistical significance. (On a color slide, use a contrasting color in lieu of bold.)
Relative Risks of SCHIP Disenrollment for Other * Family and County Characteristics, New Jersey, January 1998–April 2000
Statistically significant associations are shown in bold.
Based on hierarchical linear model controlling for months enrolled, months-squared, race, SCHIP plan, county physician racial composition, and all variables shown here. Scaled deviance =30,895. Random effects estimate for between-county variance =0.005 (standard error =0.006). SCHIP, State Children's Health Insurance Program; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
CONTENTS AND ORGANIZATION OF A POSTER
Research posters are organized like scientific papers, with separate pages devoted to the objectives and background, data and methods, results, and conclusions ( Briscoe 1996 ). Readers view the posters at their own pace and at close range; thus you can include more detail than in slides for a speech (see Appendix A for a detailed comparison of content and format of papers, speeches, and posters). Don't simply post pages from the scientific paper, which are far too text-heavy for a poster. Adapt them, replacing long paragraphs and complex tables with bulleted text, charts, and simple tables ( Briscoe 1996 ; Beilenson 2004 ). Fink (1995) provides useful guidelines for writing text bullets to convey research results. Use presentation software such as PowerPoint to create your pages or adapt them from related slides, facilitating good page layout with generous type size, bullets, and page titles. Such software also makes it easy to create matching handouts (see “Handouts”).
The “W's” (who, what, when, where, why) are an effective way to organize the elements of a poster.
- In the introductory section, describe what you are studying, why it is important, and how your analysis will add to the existing literature in the field.
- In the data and methods section of a statistical analysis, list when, where, who, and how the data were collected, how many cases were involved, and how the data were analyzed. For other types of interventions or program evaluations, list who, when, where, and how many, along with how the project was implemented and assessed.
- In the results section, present what you found.
- In the conclusion, return to what you found and how it can be used to inform programs or policies related to the issue.
Number and Layout of Pages
To determine how many pages you have to work with, find out the dimensions of your assigned space. A 4′ × 8′ bulletin board accommodates the equivalent of about twenty 8.5″ × 11″ pages, but be selective—no poster can capture the full detail of a large series of multivariate models. A trifold presentation board (3′ high by 4′ wide) will hold roughly a dozen pages, organized into three panels ( Appendix B ). Breaking the arrangement into vertical sections allows viewers to read each section standing in one place while following the conventions of reading left-to-right and top-to-bottom ( Briscoe 1996 ).
- At the top of the poster, put an informative title in a large, readable type size. On a 4′ × 8′ bulletin board, there should also be room for an institutional logo.

Suggested Layout for a 4′ × 8′ poster.
- In the left-hand panel, set the stage for the research question, conveying why the topic is of policy interest, summarizing major empirical or theoretical work on related topics, and stating your hypotheses or project aims, and explaining how your work fills in gaps in previous analyses.
- In the middle panel, briefly describe your data source, variables, and methods, then present results in tables or charts accompanied by text annotations. Diagrams, maps, and photographs are very effective for conveying issues difficult to capture succinctly in words ( Miller 2005 ), and to help readers envision the context. A schematic diagram of relationships among variables can be useful for illustrating causal order. Likewise, a diagram can be a succinct way to convey timing of different components of a longitudinal study or the nested structure of a multilevel dataset.
- In the right-hand panel, summarize your findings and relate them back to the research question or project aims, discuss strengths and limitations of your approach, identify research, practice, or policy implications, and suggest directions for future research.
Figure 3 (adapted from Beilenson 2004 ) shows a suggested layout for a 4′ × 8′ bulletin board, designed to be created using software such as Pagemaker that generates a single-sheet presentation; Appendix C shows a complete poster version of the Phillips et al. (2004) multilevel analysis of SCHIP disenrollment. If hardware or budget constraints preclude making a single-sheet poster, a similar configuration can be created using standard 8.5″ × 11″ pages in place of the individual tables, charts, or blocks of text shown in Figure 3 .
Find out well in advance how the posters are to be mounted so you can bring the appropriate supplies. If the room is set up for table-top presentations, tri-fold poster boards are essential because you won't have anything to attach a flat poster board or pages to. If you have been assigned a bulletin board, bring push-pins or a staple gun.
Regardless of whether you will be mounting your poster at the conference or ahead of time, plan how the pages are to be arranged. Experiment with different page arrangements on a table marked with the dimensions of your overall poster. Once you have a final layout, number the backs of the pages or draw a rough sketch to work from as you arrange the pages on the board. If you must pin pages to a bulletin board at the conference venue, allow ample time to make them level and evenly spaced.
Other Design Considerations
A few other issues to keep in mind as you design your poster. Write a short, specific title that fits in large type size on the title banner of your poster. The title will be potential readers' first glimpse of your poster, so make it inviting and easy to read from a distance—at least 40-point type, ideally larger. Beilenson (2004) advises embedding your key finding in the title so viewers don't have to dig through the abstract or concluding page to understand the purpose and conclusions of your work. A caution: If you report a numeric finding in your title, keep in mind that readers may latch onto it as a “factoid” to summarize your conclusions, so select and phrase it carefully ( McDonough 2000 ).
Use at least 14-point type for the body of the poster text. As Briscoe (1996) points out, “many in your audience have reached the bifocal age” and all of them will read your poster while standing, hence long paragraphs in small type will not be appreciated! Make judicious use of color. Use a clear, white, or pastel for the background, with black or another dark color for most text, and a bright, contrasting shade to emphasize key points or to identify statistically significant results ( Davis 1997 ).
NARRATIVE TO ACCOMPANY A POSTER
Prepare a brief oral synopsis of the purpose, findings, and implications of your work to say to interested parties as they pause to read your poster. Keep it short—a few sentences that highlight what you are studying, a couple of key findings, and why they are important. Design your overview as a “sound byte” that captures your main points in a succinct and compelling fashion ( Beilenson 2004 ). After hearing your introduction, listeners will either nod and move along or comment on some aspect of your work that intrigues them. You can then tailor additional discussion to individual listeners, adjusting the focus and amount of detail to suit their interests. Gesture at the relevant pages as you make each point, stating the purpose of each chart or table and explaining its layout before describing the numeric findings; see Miller (2005) for guidelines on how to explain tables and charts to a live audience. Briscoe (1996) points out that these mini-scripts are opportunities for you to fill in details of your story line, allowing you to keep the pages themselves simple and uncluttered.
Prepare short answers to likely questions about various aspects of your work, such as why it is important from a policy or research perspective, or descriptions of data, methods, and specific results. Think of these as little modules from an overall speech—concise descriptions of particular elements of your study that you can choose among in response to questions that arise. Beilenson (2004) also recommends developing a few questions to ask your viewers, inquiring about their reactions to your findings, ideas for additional questions, or names of others working on the topic.
Practice your poster presentation in front of a test audience acquainted with the interests and statistical proficiency of your expected viewers. Ideally, your critic should not be too familiar with your work: A fresh set of eyes and ears is more likely to identify potential points of confusion than someone who is jaded from working closely with the material while writing the paper or drafting the poster ( Beilenson 2004 ). Ask your reviewer to identify elements that are unclear, flag jargon to be paraphrased or defined, and recommend changes to improve clarity ( Miller 2005 ). Have them critique your oral presentation as well as the contents and layout of the poster.
Prepare handouts to distribute to interested viewers. These can be produced from slides created in presentation software, printed several to a page along with a cover page containing the abstract and your contact information. Or package an executive summary or abstract with a few key tables or charts. Handouts provide access to the more detailed literature review, data and methods, full set of results, and citations without requiring viewers to read all of that information from the poster ( Beilenson 2004 ; Miller 2005 ). Although you also can bring copies of the complete paper, it is easier on both you and your viewers if you collect business cards or addresses and mail the paper later.
The quality and effectiveness of research posters at professional conferences is often compromised by authors' failure to take into account the unique nature of such presentations. One common error is posting numerous statistical tables and long paragraphs from a research paper—an approach that overwhelms viewers with too much detail for this type of format and presumes familiarity with advanced statistical techniques. Following recommendations from the literature on research communication and poster design, this paper shows how to focus each poster on a few key points, using charts and text bullets to convey results as part of a clear, straightforward story line, and supplementing with handouts and an oral overview.
Another frequent mistake is treating posters as a one-way means of communication. Unlike published papers, poster sessions are live presentations; unlike speeches, they allow for extended conversation with viewers. This note explains how to create an oral synopsis of the project, short modular descriptions of poster elements, and questions to encourage dialog. By following these guidelines, researchers can substantially improve their conference posters as vehicles to disseminate findings to varied research and policy audiences.
CHECKLIST FOR PREPARING AND PRESENTING AN EFFECTIVE RESEARCH POSTERS
- Design poster to focus on two or three key points.
- Adapt materials to suit expected viewers' knowledge of your topic and methods.
- Design questions to meet their interests and expected applications of your work.
- Paraphrase descriptions of complex statistical methods.
- Spell out acronyms if used.
- Replace large detailed tables with charts or small, simplified tables.
- Accompany tables or charts with bulleted annotations of major findings.
- Describe direction and magnitude of associations.
- Use confidence intervals, p -values, symbols, or formatting to denote statistical significance.
Layout and Format
- Organize the poster into background, data and methods, results, and study implications.
- Divide the material into vertical sections on the poster.
- Use at least 14-point type in the body of your poster, at least 40-point for the title.
Narrative Description
- Rehearse a three to four sentence overview of your research objectives and main findings.
- Summary of key studies and gaps in existing literature
- Data and methods
- Each table, chart, or set of bulleted results
- Research, policy, and practice implications
- Solicit their input on your findings
- Develop additional questions for later analysis
- Identify other researchers in the field
- Prepare handouts to distribute to interested viewers.
- Print slides from presentation software, several to a page.
- Or package an executive summary or abstract with a few key tables or charts.
- Include an abstract and contact information.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Ellen Idler, Julie Phillips, Deborah Carr, Diane (Deedee) Davis, and two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on earlier drafts of this work.
Supplementary Material
The following supplementary material for this article is available online:
APPENDIX A.1. Comparison of Research Papers, Presentations, and Posters—Materials and Audience Interaction.
Suggested Layout for a Tri-Fold Presentation Board.
Example Research Poster of Phillips et al. 2004 Study.
- Beilenson J. Developing Effective Poster Presentations. Gerontology News. 2004; 32 (9):6–9. [ Google Scholar ]
- Briscoe MH. Preparing Scientific Illustrations: A Guide to Better Posters, Presentations, and Publications. 2. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davis M. Scientific Papers and Presentations. New York: Academic Press; 1997. [ Google Scholar ]
- DiFranza JR. A Researcher's Guide to Effective Dissemination of Policy-Related Research. Princeton, NJ: The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation; 1996. the Staff of the Advocacy Institute, with Assistance from the Center for Strategic Communications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fink A. How to Report on Surveys. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedman GD. Be Kind to Your Reader. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1990; 132 (4):591–3. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maciejewski ML, Diehr P, Smith MA, Hebert P. Common Methodological Terms in Health Services Research and Their Symptoms. Medical Care. 2002; 40 :477–84. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McDonough J. Experiencing Politics: A Legislator's Stories of Government and Health Care. Berkeley: University of California Press; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller JE. The Chicago Guide to Writing about Multivariate Analysis. Chicago Guides to Writing, Editing and Publishing. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nelson DE, Brownson RC, Remington PL, Parvanta C, editors. Communicating Public Health Information Effectively: A Guide for Practitioners. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Phillips JA, Miller JE, Cantor JC, Gaboda D. Context or Composition. What Explains Variation in SCHIP Disenrollment? Health Services Research. 2004; 39 (4, part I):865–8. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Snowdon D. Aging with Grace: What the Nun Study Teaches Us about Leading Longer, Healthier, and More Meaningful Lives. New York: Bantam Books; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sorian R, Baugh T. Power of Information Closing the Gap between Research and Policy. Health Affairs. 2002; 21 (2):264–73. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tufte ER. The Visual Display of Quantitative Information. 2. Cheshire, CT: Graphics Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

7 Top Tips for Creating a Research Poster
- 5-minute read
- 12th June 2020
A research poster should demonstrate your key findings clearly and concisely, allowing you to kickstart conversations around your work in class and at conferences and exhibitions. But how do you create a research poster? Here are some tips from our proofreaders.
1. Planning a Research Poster
When you start planning your research poster, check the guidelines for the event where you will be presenting it and make a note of the following:
- The submission dates.
- The size requirements for your poster.
- Any institutional logos or affiliations you need to include.
- Whether you need to include funding information.
Next, think about your audience:
- Who will be looking at your poster?
- How knowledgeable are they likely to be about your topic?
- Where will they see your poster, in a classroom or at a conference?
You can then use these notes to guide your poster design.
2. What Software Should I Use?
You have several options for software you can use to create a research poster. One is Microsoft PowerPoint, which you may already have installed on your computer. This program is easy to use and there are free poster templates available for download .
However, PowerPoint is limited as a design program. As such, you may want to explore other options such as Microsoft Publisher, Adobe Illustrator , or InDesign . These may take a little while to learn if you haven’t used them before, but they may let you achieve much more professional results.
3. What Your Poster Should Include
Before you start writing, think about what you want to say. You will need to ensure your audience can identify the subject and key results of your research at a glance. To this end, your poster should include:
- A title that immediately tells your audience what your research is about.
- A clear introduction that sets out the purpose of your study.
- The methods and procedures you used to find the results.
- A brief discussion and conclusion that sums up your outcomes.
- A reference list (if required).
- Your name(s) and contact information.
Make a note of all the information you need to include, but remember that you have limited space to work with and stick to the most important details.
4. Research Poster Layout and Design
A good research poster should have a clean and consistent layout. Usually, this will consist of two to four columns (any more and your poster may become hard to read), including text and graphics.

In terms of where to put everything, think about how people read in English (i.e., left to right and top to bottom). Most research posters follow a similar format, with the introduction at the top of the leftmost column and the conclusion and references at the bottom of the rightmost column.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Beyond this, other poster layout tips to consider include:
- Stick to clear, easy-to-read fonts and don’t use too many (one for your title and headings and another for your text should suffice).
- Make sure text is large enough to read at a distance.
- Use bold fonts for key terms and phrases to make them stand out.
- Choose a color scheme with two or three colors.
- Stay away from excessively bright colors as they can be distracting.
- Do not use patterns, gradients, or photographs for the background of your poster, as they can make the text on top harder to read.
This will make your poster pleasing to look at and easy to read!
5. Writing Style
When you come to write up the text for your poster, remember to:
- Be concise (around 100–200 words per section is usually enough).
- Tailor the language to your audience throughout (e.g., if you were creating a poster for non-academics, you would avoid dense technical language).
- Write in the active voice where possible.
- Use headings to guide your reader through the poster.
- Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your poster easier to read.
This should ensure you can get your point over quickly and effectively.
6. Images, Tables and Charts
Graphics, such as images, tables and charts, are an excellent way to share your research. Minimally, you should include tables and charts to present your results in an easy-to-digest way, but think about whether other illustrations or images could help, too.
If you do include any graphics, make sure to use high-resolution images (between 200 and 300 ppi) so they will look good when printed.
7. The Final Check
When you have created a first draft of your poster:
- Print an A4-sized color test print to help you find any errors.
- Assess the layout, colors, fonts, and graphics in your poster.
- Make sure your poster follows the size guidelines set out by the event at which you’ll be exhibiting.
- Proofread all the text on your research poster carefully.
This final point is very important, as a research poster filled with errors or typos will undermine the expertise that you are trying to project.
If you spot any issues, make sure to correct them and create another test print. And once you’re happy with your draft poster, that’s it! You are ready to send your masterpiece off to the printers.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Kraemer Family Library
How do i design a research poster: poster examples.
- Getting Started
- Sections of a Poster
- Design Tips
- Using Images
- Formatting A Poster
Poster Examples

- << Previous: Formatting A Poster
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 2:32 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uccs.edu/poster
Need Research Assistance? Get Help
- Interlibrary Loan and Scan & Deliver
- Course Reserves
- Purchase Request
- Collection Development & Maintenance
- Current Negotiations
- Ask a Librarian
- Instructor Support
- Library How-To
- Research Guides
- Research Support
- Study Rooms
- Research Rooms
- Partner Spaces
- Loanable Equipment
- Print, Scan, Copy
- 3D Printers
- Poster Printing
- OSULP Leadership
- Strategic Plan
Research Posters and Presentations
Traditional format, alternative format.
- Oral Presentations
- Day of Presentation
Science Librarian

Where can I get more help?
Contact the OSU Libraries Information Desk
- Call us at 541-737-7293
- Text us at 541-526-7655
- In person: The Information Desk is on the main (2nd) floor of the Valley Library.
- Chat with a librarian (below)
Title: states the question/problem that you are addressing, sometimes in question form
- Use bold typeface.
- Capitalize important words of title, but do not use ALL CAPS.
- Title should be short, meaningful, and eye-catching (no longer than two lines).
- Avoid jargon or acronyms.
- Author(s) should be listed right under the title (Font size: 60 ).
Font size: 70 - 80 for the title
Introduction: introduces your topic and briefly explains why your research is significant
- Place your topic within context of published literature.
- Clearly state your hypothesis.
- Include just what is highly relevant. Minimize background information and definitions.
Wordcount: 200 Font size: Headings: about 44 ; Main text about 32
Materials/Methodology : tells readers what your research strategy was and how you actually carried it out
- Briefly describe your research methods and any equipment or software you may have used.
- You may also add figures, tables, flow charts, photographs, or drawings that describe your design.
Wordcount: 200 Font size: Headings about 44 ; Main text about 32 Captions about 28
Results: what did you find out?
- Briefly discuss your data analysis.
- You may add supporting charts, images, tables, quotations etc.
- Use captions that describe the graphics.
Wordcount: 200 Font size: Headings 44; Main text 32 ; Captions 28
Conclusions: This is where you summarize your hypothesis and results.
- Focus on the main takeaway points
- Was your hypothesis supported?
- What is the significance of your findings?
- Future research?
Wordcount: 300 Font size: Headings: 44 ; Main text 32
Works Cited
- Cite only the most pertinent articles.
- Select a documentation format (APA, MLA, Chicago etc) and be consistent.
Font size: 24
Acknowledgments This section is optional but it is nice to acknowledge people who have provided assistance or funding for your project.
- Thank individuals who made contributions to your project.
- Thank research subjects.
- Acknowledge funding sources.
Font size: 24-28
Not all students will have a Standard Research experience.
There are many approaches to making Poster Presentations.
If you have a job shadowing or other alternative experiences use the same sizing and wordcount recommendations from above, but use these sections:
General lab overview
The project(s) you focused on
Results (if you have them)
How your work ties back to general lab overview
Acknowledgments
- << Previous: Logistics
- Next: Design >>
- Last Updated: Oct 19, 2022 1:34 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.oregonstate.edu/researchposters
Contact Info
121 The Valley Library Corvallis OR 97331–4501
Phone: 541-737-3331
Services for Persons with Disabilities
In the Valley Library
- Oregon State University Press
- Special Collections and Archives Research Center
- Undergrad Research & Writing Studio
- Graduate Student Commons
- Tutoring Services
- Northwest Art Collection
Digital Projects
- Oregon Explorer
- Oregon Digital
- ScholarsArchive@OSU
- Digital Publishing Initiatives
- Atlas of the Pacific Northwest
- Marilyn Potts Guin Library
- Cascades Campus Library
- McDowell Library of Vet Medicine
- Research Degree Students
How to create a great research poster!
- Watch a YouTube on how to create a great poster
- Visual features of a well-constructed poster
Order of content
- Steps in putting together a poster
- Tips for presenting your poster face-to-face
What software should I use?
- Watch a YouTube on software for posters
Open source alternatives
- Useful websites
- References for different disciplines
Research posters are a multi-modal communication genre combining text with graphics, colour, as well as speech and interaction with audience, to convey meaning. Posters are useful because they convey meaning efficiently, and they can facilitate more informal discussions between presenters and peers than other research communication modes. Posters are typically used in the sciences, but they may also be used in the social sciences. They may be used in academic conferences as well as workplaces or other settings.
Posters should convey the meaning on their own, and, when verbally explained by presenters, their meaning should be communicated economically, enabling discussion beyond the immediate outline of the research. There are three aspects of a good poster presentation: visual display and organisation, research content, and the presenter's attentiveness and communication with viewers. Some tips and resources for designing and presenting an effective poster are provided below.
Watch a YouTube on how to create a great poster! Click the image to view.
- Ensure key information can be comprehended in approximately five to ten minutes (less than 1000 words).
Checklist: Visual features of a well-constructed poster
- Use colour, bolding and other visual aspects to foreground important points.
- Ensure images, graphs and figures, and text complement one another to communicate key messages.
- However, ensure images, graphs and figures, and text are not dependent on one another for meaning.
- Use large type (should be readable from approximately one metre).
- Limit the number of words to convey only essential information.
- Use white space around text boxes and figures.
- Make text boxes 45-65 characters wide (shorter or longer is harder to read).
- Avoid dark backgrounds for text boxes (dark text on white is easier to read).
- The text reads from left to right (because most people read like this).
- Convey complex methods as a flow chart or diagrammatically.
Research posters follow the same story line as all research communication. The order of content is as follows:
- title at the top in large text, approximately one inch high;
- author name, author affiliation, and affiliation logo beneath the title;
- brief statement of purpose;
- method, subjects, procedure (for empirical research);
- results or main findings;
- conclusions;
- individual contact for questions and photograph of yourself;
- acknowledgement of any assistance of financial support received to produce the research;
- literature cited.
Steps in putting together your poster
- Consider the context. Where will the poster be displayed? This will influence how big you make it, and perhaps your choice of colours (chosen so that the poster stands out from the background colour.
- Decide on the software program you will use for your poster (see below).
- Decide on the information you want to provide, and go ahead and produce the text.
- Decide on the images, graphs and figures you want to use and what software program you will use to produce them.
- Now you can think about the design of the layout of your poster.
- Consider what headings to use to break-up the content.
- Print your poster using durable paper. Consider having it laminated.
- Go to your conference and present your poster!
- Hang your poster in your School or office after the conference.
Tips for presenting your poster face-to-face
- Convey only the basic information in a summary form, enabling the presenter and viewer to explore the research further in conversation.
- Point to the poster to explain or illustrate your summary.
Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop and InDesign are good for posters, including lots of high-resolution images, but they are more complex and expensive.
Advice for using PowerPoint
Watch a YouTube on software for posters! Click the image to view.

OpenOffice Impress is a free alternative to PowerPoint in MS Office.
Inkscape and Gimp are alternatives to Adobe products.
Gliffy or Lovely Charts are good for charts.
Glog is a visual learning platform that enables text, graphics, images, wallpaper, audio, video and web ($29 for individuals, $390 for 10 teachers/250 students).
Useful web sites
University of Brighton https://blogs.brighton.ac.uk/visuallearning/visual-communication/ and https://blogs.brighton.ac.uk/visuallearning/finding-images/
Colin Purrington : http://colinpurrington.com/tips/poster-design
Useful references for different disciplines
Block, S.M. (1996). Do's and don'ts of poster presentations. Biophysical Journal 71, 3527-3529.
Bracher, L., Cantrell, J., & Wilkie, K. (1998). The process of poster presentation: a valuable experience. Medical Teacher 20, 552-557.
D'Angelo, L. (2010). Creating a framework for the analysis of academic posters, Language Studies Working Papers , 2, 38-50.
Denzine, G.M. (1999). An example of innovative teaching: preparing graduate students for poster presentations. Journal of College Student Development 40, 91-93.
Hay, I., & Thomas, S.M. (1999). Making sense with posters in biological science education. Journal of Biological Education 33, 209-214.
MacIntosh-Murray, A. (2007). Poster presentations as a genre in knowledge communication. A case study of forms, norms and values. Science Communication 28, 347-376. 50
Matthews, L.D. (1990). The scientific poster: guidelines for effective visual communication. Technical Communication 37, 225-232.
Miracle, V.A. (2003). How to do an effective poster presentation in the workplace. Dimensions of Critical Care Nursing 22, 171-72.
Naerssen, van M. (1984). Science conference poster presentations in an ESP program. The ESP Journal 3, 47- 52.
Powell-Tuck, J., Leach, S., & MacCready, L. (2002). Electronic poster presentations in BAPEN: a controlled evaluation. Clinical Nutrition 21, 261-263.
Waehler, C.A., & Welch, A.A. (1995). Preferences about APA posters. American Psychologist 50, 727.
Wang, J.C., Yoo, S., & Delamarter, R.B. (1999). The publication rates of presentations at major Spine Specialty Society meetings. Spine 24, 425-427.
Woolsey, J.D. (1989). Combating poster fatigue: how to use visual grammar and analysis to effect better visual communication. Transactions in Neurosciences 12, 325-32.
Wright, V., & Moll, J.M. (1987). Proper poster presentations: a visual and verbal ABC. British Journal of Rheumatology 26, 292-294.
- Dr Nicole Brown
Social Research & Practice and Education Ltd.
- Publications
- List of all blog posts
- Practice As Research
How to create a research poster

When you create a research poster you need to ask yourself which information you would like to communicate and how you can present that so that your audience will immediately know what to expect of your full report, dissertation or publication. However, you do not need to wait for a finished product to create a research poster. A research poster can work like a mind-map for you when you are in the planning stage of your enquiry , as it gives you the bigger picture of all aspects of your research at a glance.

The structure and outline of a research poster is entirely free and I have seen posters with many graphs and graphics, or others that were very text-centred. Ultimately, you need to ask yourself what it is that you want to communicate, but your audience will want to know what you did and why and how you approached your research. Personally, I like posters that are honest, highlight their own limitations and therefore demonstrate critical engagement with their own work.
You can use any software you feel comfortable with to create a research poster. Word documents or PowerPoint presentations seem to work well for many. However, you may want to export your final product as a PDF file for added user friendliness. I have discovered Padlet, which is a virtual corkboard , on which you can pin your text, graphics and video-clips. It is very easy to use and if you are presenting in a team, you can have your collaborators add their contents, too.
Related posts:
- Research impact poster This is an example of a prize-winning research impact poster....
- Research posters Download two examples of research posters from here....
- Action research or case study? When planning for a practice-based enquiry or small-scale study you...
- Writing a good academic essay Consider some key elements when writing an academic essay: structure,...
2 Comments on " How to create a research poster "
do i require ethical certification before starting a poster publication if I want to collect primary data?
All research work must be done ethically at all times, so considering ethics is always a must. Whether you need a formal approval and how you will be able to access that depends on your research circumstances, your country context, and your institutional setting. Most publishers nowadays do require some proof of ethics, and most institutions will require ethics before you begin data collection no matter what the purpose of the data collection is.
Leave a message:
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Yes, add me to your mailing list.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Indianapolis Indiana University Indianapolis IU Indianapolis

- Advisory Board
- Conference Travel Support
- Presentation Resources
- IU Indianapolis Research Programs
- Other Summer Research Programs
- Non-CRL Research Opportunities
- Human Subjects Research
- International Research
- Finding Mentor
- MURI Project Awards
- R-Course Development
- R-Course Awards
- Posting Student Positions
- Creative Activities Award
- The Bowling Jones Russo Award
- Chancellor Award
- Kathryn J. Wilson Award
- Richard E Ward UROP Award
- Conference Program
- Program & Presenters
- Other CRL Events
- Research Poster Presentation Preparation Guide
- In His Own Words, International Research Project Experience: Eric Durr
- In Her Own Words, Posters On The Hill: Abigail Parker
- 2019 IU Research Day Highlights
- News_1_12_2010
- From Project SEED to Capitol Hill
- In Her Own Words, Posters On The Hill: Dana Oaks
- Student Spotlight: Michelle Ramírez
- In Her Own Words, The Benefits Of Undergraduate Research: Cecelia Chapin
- 2016_News_9_19_2016
- 2015_News_10_25_2015
- 2016-2017 Highlights
Center for Research and Learning

- Research Scholarly Articles
Poster Design Guide

Required Poster Dimensions: 32 inches wide x 40 inches tall
Planning and managing your content.
- Examples & Tutorials
Designing Your Poster

- Title: 100-144 points
- Section Headings: 72-84 points
- Main Content: 18-24 points, double spaced
- Acknowledgements and References: 10-16 points, single spaced

External Examples & Tutorials
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Data Visualization 10+ Informative Research Poster Templates to Share Information
10+ Informative Research Poster Templates to Share Information
Written by: Jennifer Gaskin Dec 19, 2022

If an infographic isn’t enough to help convey your ideas… what is the next best thing?
Research posters.
Whether you’re connecting with your employees or sharing important data, creating a research poster can help you engage and inform your audience in a big way.
Learn more about research posters, how they can help you tell your story and how you can create one easily using Venngage’s research poster templates .
Click to jump ahead:
What is a research poster?
Research poster templates & examples, what should a research poster include, what are some ways to use research posters, common research poster layouts, research poster faqs.
A research poster is a visual communication tool that can help you visualize data, summarize complex information or explore detailed processes. Any organization can use research posters for both internal and external needs.
Here’s an example of a scientific poster template:

Need more ideas for presenting your cool science findings? Check out our gallery of awesome scientific poster templates for a little inspiration!
Though “poster” is in the name, research posters are not always printed. Still, if you’re considering making a research poster, it’s a good idea to think about whether you want to print it or not. Otherwise, consider a different format, such as an infographic or social media post if the information only needs to live online.
Related : 12 Types of Posters for Every Business Need [Templates Included]
Here are some more examples of research poster templates to inspire your next project:

While I always recommend bright, bold colors, those don’t always play well with office printers. So consider saving a research poster template like this one, which is shades of gray, white and black and may help save on ink.

Use this compact research poster template if you want to help your audience get the gist of your research without using a larger sheet of paper.

For students looking to present their research project in a visually engaging way, this simple research poster template can be a game-changer. It allows you to effectively communicate your findings with a clear layout and space for impactful visuals.

Remember that by its nature, a poster is meant to be very eye-catching. Consider using the artwork in this poster, which uses a popular, 3D-esque illustrative style that may make your audience take a second look.
3D visuals are part of our graphic design trend predictions for 2023. Want to know the rest? Check them out here: 8 Graphic Design Trends that Will Dominate 2023

The designer of this poster didn’t create it originally as a research poster, but it’s a good example of how with just a little bit of text, you can make something visually striking and inspiring. Update the copy to include some data visualization and this will be a no-brainer addition to your research report repertoire.
If you’re crafting a research poster to present your environmental findings, check this one out. This ocean conservation poster template dives deep (pun intended!) to show you how to present your findings like a pro.

This next research report template passes what I call the squint test, which is useful when creating a poster. Close one eye and squint the other one when looking at this poster; you see very little text here and (depending on your eyesight), you can probably still make out the general shape of the data. That makes it ideal for a poster, which is designed to be read from a slight distance.
Related : 21+ Poster Background Images and Professionally Designed Templates
The specifics of what to include in a research poster depend on its purpose, but here’s a look at what’s usually involved:
Methodology or sourcing
Let’s explore each element.
Poster title
This could be general, simply describing the topic, or it could be more of a headline, letting readers know the most important information you learned in your research. Or it could ask a question that’s answered in the content. That’s all really up to you.
In this scientific poster template, for example, the title contains the findings of the research:

With a poster, you might think you have more room to include a lot of copy, but the opposite is true. Limiting your text to the bare minimum helps the visuals shine and makes your poster more eye-catching. Which brings us to the next point…
Icons, images, charts, graphs and other visuals
Especially with a poster, it’s crucial to engage the readers’ eyes. Otherwise, you’d simply write a report that’s filled with text. So you should use icons or photos if you’re creating a summary research poster and data visualization if your research poster will also include data.
Information transparency is always important, but it’s especially so with research posters. Users need to know the answer to “Says who” when they read your poster, so be sure to save a small space to explain where you got your information, whether it was an internal or external source.
Need to clearly explain a concept, process or information? Educational posters might be a better option. Grab one of our convenient educational poster templates to jumpstart your informative creation.
A research poster is the vehicle for your information if you have a few key points or data that you want your audience to understand. This begs the question: how is a research poster different from an infographic?
Well, unlike infographics which you often find online, posters are usually printed, and so there’s a natural limit to the amount of space you have.
That means no matter how great your research is, if you want to use a poster to get your message across, you have to consider the amount of content you can fit within the poster template. Here are some ideal ways to use research posters:
Summarize information
This vibrant poster was created to explain a complicated scientific concept, but the end result is anything but complicated. By boiling their information down to its essential elements and using a striking color palette, the designer is able to grab and hold the audience’s attention.

For more tips on poster design, check out our guide: Poster Design Guide: How to Make an Eye-Catching Poster in 2022
Visualize data
Charts, graphs and data, oh my! Numbers are the star of the show when it comes to research posters that visualize data. Whether you’re using line charts, pie graphs or column graphs, consider making your charts and graphs larger than life with a research poster. (Get some more data-heavy inspiration with these research infographic examples.)

For more examples of scientific posters, check out this post: 8 Scientific Poster Examples [and How To Create One]
Spread the word
Research posters can also help you get the word out about important dates. Case in point: the research poster template below. Here, the designer shared important facts and visualized data on Diabetes Awareness Month, making it the best of both worlds when it comes to research posters.

This template doubles as a great event or medical poster. Interested in learning more? Read:
- 20+ Attention-Grabbing Event Poster Templates, Backgrounds & Design Tips
- 10 Event Poster Design Ideas [+ Free Templates]
- 15 Medical Poster Templates for Patient Education
- 45 Free Poster Templates to Captivate Any Audience [100% Editable]
Here’s a look at the most common layouts/formats of a research poster:
This cognitive behavior research poster was designed to fit an A4 piece of paper, and it can easily be adapted for letter-sized paper as well.

Using research on alcohol addiction, the designer of this poster chose a horizontal format, which could fit on a letter-sized page or be scaled to work on a tabloid page, which is 17 inches wide and 11 inches tall.

For more information on poster layouts, check out our guide: How to Apply the Right Layout To Your Poster
Do you have more questions about research posters? We’ve got answers.
How do you write a research poster?
When writing the content for a research poster, the most important thing to remember is you need to be brief. Unlike other types of visual communication, with a poster, you have a limited amount of space. So the key is to edit repeatedly until you get down to the shortest amount of text possible.
Is there a poster template in Word?
Microsoft Word offers many poster templates, though whether any would work for research poster purposes depends on your needs and how much text you’ll need to include. However, given that it’s a word-processing tool and not a design tool, Word is less-than-ideal as a place to create an engaging research poster.
How do I make a research poster in PowerPoint?
Create a new slide using the dimensions of a standard letter, A4, tabloid or other print size and add your text, visuals, graphs and other items. Considering that it’s an online presentation tool , though, PowerPoint isn’t the best platform for creating an engaging research poster.
In summary: Make a big impact with your research results by presenting them in a poster
Research posters are an excellent way to inform employees about a complicated topic, share details about sales data or engage your audience using external numbers. Be sure to keep text to a minimum if you really want to draw people in.
Interested in creating a research poster yourself? Sign up for a free Venngage account and choose from our professional, easy-to-edit poster templates:
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Submit a News Release
Tips for Creating a Compelling Poster Proposal
Submissions for poster proposals are being accepted via ExOrdo from now through February 4 .
Not quite ready to take the stage and present to a large audience? New to the industry and not sure how to participate? Did you miss the session submission deadline? Posters present an opportunity to share information and to have interactive conversations with meeting attendees. Your poster submission will be evaluated based on the abstract only—you don’t need to have your poster design completed before submitting your proposal.
Posters may have a single author or multiple authors and will be on display during the course of the meeting, but we ask that at least one author is in attendance alongside their poster during your assigned poster session. Consider content and presentation ideas that can stand on their own, but that can also spark conversation! Whether a very specialized topic or a broader concept, we are interested in proposals that touch on all aspects of the scholarly communications ecosystem.
For a strong proposal:
- Create a title that is descriptive of your poster content
- Appeal to a broad audience. SSP Annual Meeting attendees value networking opportunities, insight into new developments, and practical applications they can use to advance their careers.
- Write an abstract that is no more than 250 words that describes the content of your poster. For accepted proposals, this abstract will be included in the online program.
- Describe the ideal audience for your poster, such as publishers, editors, academics, librarians, marketers, production personnel, etc.
Indicate the educational level your poster will address:
- Foundational: Focus on awareness and relaying information; appropriate for those with limited experience of the subject seeking an introductory understanding of the content area(s).
- Applied: Focus on understanding and comprehension; appropriate for those with some experience seeking to build on, apply, or enhance existing knowledge using content in practical applications/implementations.
- Strategic: Focus on analysis, evaluation, and decision-making; appropriate for those with substantial prerequisite knowledge seeking the most up-to-date information to heighten expertise and advance best practices.
- Mixed-learning: Includes both applied and strategic perspectives on an issue; appropriate for those with at least some experience of the subject area seeking a mix of immediate/practical and future/planning information.
- Networking: Provides an opportunity for peer-to-peer interaction among groups with similar interests and/or geographical locations, for all career levels. May be purely social in nature, have a specific topic (e.g. speaker or panel), or focus on an element of career development (e.g. mentorship).
The Annual Meeting Program Committee will review poster proposals and rate them on the following criteria:
- Topic is timely and relevant
- Original concept and/or fresh analysis
- Focus and learning outcomes are well defined
- Sufficient opportunity for an interactive conversation with meeting attendees during a poster session
- Technical details to keep in mind:
- Must fit within a 48×48 inch area ; 28×22 inch landscape orientation is recommended.
- Design with social distancing in mind—main points should be visible from 6 f ee t away .
- The author is responsible for printing the poster—there is a FedEx Office store onsite.
Although very different in format, explore last year’s posters to get an idea of what is possible. Research questions, case studies, infographics—formats of all kinds are welcome! Poster proposals are being accepted through February 4, 2022 .
Highlights from our virtual poster session in 2021:
Best Content “ An OKR Story: Objectives & Key Results at The MIT Press “ Gabriel Harp, The MIT Press
Best Design “ The Journal of Ethics in Publishing from The George Washington University “ Gabrielle Bethancourt-Hughes, George Washington University, Lois Jones, American Psychological Association, and John Warren, George Washington University
Best All-Around “ Is Implicit Bias Impacting Your User’s Experience? “ Rachel Volentine, University of Tennessee
- C3 Online Community
- Join/Renew Membership
- Regional Committees and Events
- Communities of Interest Network
- Member Center
- Manage Profile
- Create Profile
- Benefit Programs
- Member Directory
- Member News
- Community Photos
View Comments
Be the first to write a comment!
Join the Conversation Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
The Scholarly Kitchen
- Guest Post: Navigating a New Virtual Experience at the 2024 SSP Annual Meeting
- Guest Post — Shipping up to Boston? Plan Some Workers’ Playtime during the SSP Annual Meeting
- Guest Post – Reconnecting by Reading: A Selection of Books About Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Accessibility Part 2


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research posters summarize information or research concisely and attractively to help publicize it and generate discussion. The poster is usually a mixture of a brief text mixed with tables, graphs, pictures, and other presentation formats. At a conference, the researcher stands by the poster display while other participants can come and view ...
Research Poster Overview. The purpose of a research poster is to visually represent the general overview, data, and most relevant findings of a research project. Typically, research posters accompany an oral presentation of the project conducted, but should also be able to independently represent the research. The elements of a research poster ...
To start, choose from a variety of pre-designed templates or create your own design from scratch. Then, drag and drop your desired illustrations onto your poster. With over 40,000 illustrations in 80+ fields, you're sure to find images that perfectly represent your own research project. Next, add your text.
The title should be clear, succinct, and by far the largest text on the poster. I make my research question and conclusion stand out, and I lay out the rest of the content in a way that is visually intuitive to follow in the correct order. I also spend a lot of time on typography. The right typesetting can turn a dense-looking wall of text into ...
Select "Page Setup". Under the "Slides sized for:" dropdown menu, select "Custom". Set the "Width" and "Height" to what is needed for your poster. Click "OK". How to correctly size your poster in Adobe InDesign: When a new document is created in Adobe InDesign, a dialogue box prompts you to enter dimensions:
How do I adjust the slide size to my poster size? For example, let's say you need a poster that is 36 inches by 48 inches. In the menu ribbon: Design > Slide Size > Custom Slide Size. Change the Slides sized for: to Custom. Enter the dimensions as 36 inches wide by 48 inches high. Click OK.
Poster: Your poster should be an outline of your research with interesting commentary about what you learned along the way. ... You can create your poster from scratch by using PowerPoint or a similar design program. Resize the slide to fit your needs before you begin adding any content. Standard poster sizes range from 40" by 30" and 48" by 36 ...
Logos for the trust you are working at, as well as the conference/congress you are attending can be placed on either side of the title. •. Title: this needs to have the largest font size of your entire poster to be eye catching. Keep the title as short as possible - it doesn't need to be a paragraph long [1], [3].
If you want to submit your paper/research at a conference, you must first write a proposal. A poster proposal tells the conference committee what your poster is about and, depending on the conference guidelines, might include a poster abstract, your list of contributors, and/or presentation needs.
A research poster is a visual way to summarize and communicate the results of a research project to a general audience. A good poster should include the goal of the research, its methodology, results, and discussion/conclusion, in clear and concise language. Research posters will often include photos, maps, graphs and other images to present ...
Firstly, take this seriously. A poster is not a consolation prize for not being given an oral presentation. This is your chance to show your work, talk to others in the field, and, if you are lucky, to pick up pointers from experts. Given that just 45% of published abstracts end in a full paper, 1 this may be your only chance to get your work ...
First Thing First: The Title and Abstract. The title of your abstract is very important. Reflect the content of the paper. Specific and Succinct. Use key words for indexing and for searches. 250 Word Max. Includes the following: The research question or problem. The methods.
What does a good poster include? Important information should be readable from about 10 feet away. Title is short and draws interest. Word count of about 300 to 800 words. Text is clear and to the point. Use of bullets, numbering, and headlines make it easy to read. Effective use of graphics, color and fonts. Consistent and clean layout.
Conclusions. Effective research posters should be designed around two or three key findings with accompanying handouts and narrative description to supply additional technical detail and encourage dialog with poster viewers. Keywords: Communication, poster, conference presentation. An assortment of posters is a common way to present research ...
How to Write a Research Poster . By Lorrie Faith Cranor. Poster sessions at conferences and university research fairs provide excellent opportunities for students to show off their work and to discuss their research in an informal setting. While it is important to present good work at a poster session, even the most outstanding research ...
Choose a color scheme with two or three colors. Stay away from excessively bright colors as they can be distracting. Do not use patterns, gradients, or photographs for the background of your poster, as they can make the text on top harder to read. This will make your poster pleasing to look at and easy to read! 5.
How do I Design a Research Poster?: Poster Examples. Getting Started; Sections of a Poster; Design Tips; Using Images; Formatting A Poster
Introduction: introduces your topic and briefly explains why your research is significant. Place your topic within context of published literature. Clearly state your hypothesis. Include just what is highly relevant. Minimize background information and definitions. Wordcount: 200 Font size: Headings: about 44; Main text about 32.
Use white space around text boxes and figures. Make text boxes 45-65 characters wide (shorter or longer is harder to read). Avoid dark backgrounds for text boxes (dark text on white is easier to read). The text reads from left to right (because most people read like this). Convey complex methods as a flow chart or diagrammatically.
However, how do you create a research poster? Content: When you create a research poster you need to ask yourself which information you would like to communicate and how you can present that so that your audience will immediately know what to expect of your full report, dissertation or publication. However, you do not need to wait for a ...
Make modifications to the template at your discretion, always keeping in mind the clearest, simplest way to communicate your research to your audience. You do not have to adhere strictly to the colors or header text included in the poster template. Make the template work for you.
Case in point: the research poster template below. Here, the designer shared important facts and visualized data on Diabetes Awareness Month, making it the best of both worlds when it comes to research posters. EDIT THIS RESEARCH POSTER TEMPLATE. This template doubles as a great event or medical poster.
If you want to create an effective research poster, make sure that it should: Be completely readable from up to 10 feet away. It has a short title which catches the interest of the audience. It has a word count of 300-800. The text is both concise and clear. Make it easier to read by using headlines, numbering, and bullets.
Write an abstract that is no more than 250 words that describes the content of your poster. For accepted proposals, this abstract will be included in the online program. Describe the ideal audience for your poster, such as publishers, editors, academics, librarians, marketers, production personnel, etc. Indicate the educational level your ...
Color. Skip to start of list. 234 templates. Create a blank Research Poster. Plant and Animal Evolution Activity Research Poster in Hand Drawn Style. Poster by Canva Creative Studio. Gray Simplified Professional Landscape University Research Poster. Poster by Canva Creative Studio. How Temperature Affects Water Molecules Research Poster in ...
If you're looking for an easy way to make a poster online, you're in the right place. In this article, you'll learn how to create a poster in 7 simple steps. We've also handpicked 25 stunning poster templates for various purposes that you can edit and download right now. Ready? Let's get started. Table of Contents