- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students

Online Guide to Writing and Research
Assessing your writing, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
How Is Writing Graded?

Students often want to know how their writing assignments are graded—that is, what is an A paper, a B paper, and so on. Generally speaking, there are two basic ways to determine how your papers will be graded.
Understand your assignment, which often will include a rubric.
Understand general grading standards professors usually apply to papers.
Assignments and What Rubrics Have To Do with Them
Virtually every college and graduate-level assignment will include instructions from your professor. Often, rubrics, which provide criteria for each possible grade you might receive, will accompany your assignments.
Some rubrics can be quite detailed, breaking down the assignment and describing the grading criteria for each requirement. Other rubrics merely provide general writing standards associated with each grade. In either case, your first and best source for understanding assignment’s associated grading standards is the content of the assignment itself.
As you familiarize yourself with an assignment and its rubric, keep in mind the following:
Prioritize the criteria for a particular assignment over the criteria listed in the section below.
When an assignment comes with a rubric, study the rubric and familiarize yourself with it. Aside from your professor, this is the best guide to successfully meeting the assignment requirements.
Prioritize your professor’s advice above all. College and graduate professors often provide their own descriptions of their assignments and a list of requirements. Sometimes these can differ from the accompanying rubric. If you are ever in doubt about your assignment and its requirements, contact your professor with your questions.
Some General (Though Not Exhaustive) Grading Standards for Academic Papers
Although each professor and class is unique, there are some general qualities that attach to each grade. The following grading standards may be useful as you assess your own writing, but remember, a number of factors ultimately contribute to your grade, including your specific instructor's guidelines and preferences. Always defer to your assignment-specific or class-specific standards for grading information, and reach out to your instructor with any questions.
- The Grade of A
- The Grade of B
- The Grade of C
- The Grade of D
- The Grade of F
The A paper is characterized by outstanding writing marked by superior readability and command of content.
The paper thoroughly addresses the assignment prompt.
The paper proceeds in a clear, logical fashion that makes the information accessible to the reader.
The paper’s purpose is clear, followed by details reflecting this purpose.
The style throughout the paper accommodates the reader.
The diction throughout the paper, and sentence construction, contribute to understanding.
The student’s grammar, mechanics, and format are flawless.
The B paper is characterized by distinguished writing and fulfills the assignment requirements; however, the writing contains some of the following weaknesses:
The paper is well organized, but the presentation of content sometimes inhibits understanding.
The audience for which the paper is intended is sometimes unclear.
The student’s diction at times is vague and hinders precise communication.
The student’s grammar, mechanics, and formatting flaws interfere with reading and comprehension.
The C paper is characterized by satisfactory writing that is generally effective but contains any one of the following weaknesses:
The paper lacks clear organization, or some material is not clearly explained; the paper’s audience and purpose are not clear.
The student’s sentences, although grammatically correct, often make information difficult to extract.
The student’s diction throughout the paper interferes with readability, but the reader can still glean the meaning; sections of the paper require rereading.
The paper contains repeated errors in grammar, mechanics, or format.
The D paper struggles to communicate information and contains weak writing. In a professional work environment, such writing would be considered incompetent because it suffers from any one of the following problems:
The paper contains two or more of the problems listed for the C paper.
The paper lacks evidence of audience accommodation.
The paper contains poor diction, such as garbled wording that prevents understanding.
The student’s sentences have mechanical errors, such as persistent run‑on sentences and comma splices.
The student’s grammar, spelling, or format problems create frequent obstacles to understanding.
The paper fails on multiple levels. A failing grade on a writing assignment usually means that your paper contains two or more of the problems listed for the D paper.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Princeton Graded Paper: How to Approach It
In 2018, news emerged that Princeton University would no longer require applicants to submit the SAT or ACT essay as an admission requirement. According to the university, the additional cost required to sit for the essay was proving prohibitive for some applicants.
Instead, the Ivy League institution now requires all students to submit a graded writing sample from high school in order to be considered for admission. Keep reading to learn about the requirements for the Princeton graded paper, along with tips on choosing the best sample of your writing.
Overview of the Princeton Graded Paper
The graded written paper for Princeton is a new admissions requirement, so it’s natural that applicants would have questions and concerns. Designed to help admissions officers evaluate a student’s academic writing, the Princeton graded paper should show that the applicant can thrive at a rigorous Ivy League institution. Additionally, the admissions department is seeking insight into the contributions the student would make to the larger academic community.
When choosing a graded paper for Princeton, it’s important to be sure that your writing sample meets all the requirements. According to the Princeton website , the paper should be:
- Expository in nature (i.e. no creative writing)
- 1-2 pages in length
- From an academic course (ideally English, history, or social studies)
- Written during the last three years of high school, including senior year
If the teacher graded the paper and included comments, be sure to include those, as well as the grading rubric used. However, it’s worth noting that Princeton is more concerned with the quality of a student’s writing than the grade they received.
Requirements for Non-traditional Applicants
Princeton University encourages submissions from homeschooled, international, and transfer students and recognizes that providing a graded paper can be more challenging for these applicants. To that end, the school offers special guidelines for submission.
- For homeschooled applicants , the graded written paper for Princeton can have comments from whoever taught the course, even if that person was a parent or guardian.
- For transfer students , it’s fine to select a paper completed within the last two years of schooling. Moreover, transfer students can submit graded papers from subjects other than English and history; however, those subjects are the preferred options.
- Finally, international students should note that their papers must be submitted in English and come from O- or A-level coursework. International applicants should also submit an English-language rubric with their paper.

Tips for Picking a Graded Paper to Submit
If you’re like most high school students, you probably have several options to consider for the graded written paper for Princeton. Here are some tips on choosing the best paper to showcase your writing abilities and insights.
1. Be mindful of length.
Although the suggested Princeton graded paper length is 1-2 pages, some students may feel that they don’t have a strong enough paper in that range. If that’s the case, you can submit a longer paper. For best results, avoid submitting any sample longer than 3-5 pages.
2. Pick a paper from a subject you care most about.
English and history are the preferred subjects for the Princeton graded paper. However, the admissions committee will review any sample of expository or analytical writing. If you’re looking to strengthen your application narrative, you may want to consider choosing a paper from a school subject related to your intended major.
Just be sure that the paper would be easy to understand for someone who might not be a specialist in that subject. When in doubt, ask for a second pair of eyes. Our free Peer Essay Review tool might be a good place to start!
3. Don’t worry too much about your grade.
The fact is that no two instructors grade exactly the same. In other words, what one teacher considers an “A” paper might only merit a “B” in another class. With that in mind, students should aim to submit a paper they consider reflective of their best work over one with a higher grade.
4. Pick a paper with thoughtful comments, if possible.
Instructor comments provide valuable information and context for admissions officers. Some teachers provide more comments than others, but when possible, it’s a good idea to submit a paper with comments over one with just a grade.
How to Submit Your Graded Paper
Applicants have two options when submitting their graded paper for Princeton. The first option is to submit the paper online along with the completed Coalition Application, Common Application, or QuestBridge Application.
The second option is to mail, email, or upload the graded written paper to your applicant portal.
Whichever option you select, be sure to include the grade, teacher comments, and rubric with your paper. You should also make sure the paper is sent in prior to the due date of your other applications materials.
Leaders in college advising, CollegeVine is passionate about helping all students achieve their future academic and career goals. If you have a question about the graded written paper for Princeton or another aspect of your school applications, you can submit it on our Q&A forum to get answers from peers and experts. We look forward to making your college dreams realities.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Graded Written Paper
The graded written paper will help the Admission Office assess the student’s written expression in an academic setting. This will further the holistic understanding of the student’s application and help admission officers evaluate the student’s potential contributions and ability to thrive in the University’s rigorous academic environment.
We ask all students to submit a graded written paper for consideration as part of their application to Princeton.
When selecting a paper to submit, please keep in mind the following guidelines:
The paper should be writing done for an academic course, preferably an English, social studies or history course, during the last three years of secondary school, including senior year.
You may send a paper, essay, research paper or essay exam. We are interested in seeing expository writing only, not creative writing.
One to two pages in length is sufficient.
The paper should include the course instructor’s grade, and comments if your instructor provided any.
Princeton no longer requires applicants to submit the optional writing section of the SAT or ACT (the SAT Essay or ACT Writing Test), because taking the test with the optional writing section adds an additional cost that may be a financial burden to some applicants. We became concerned that students at schools where the ACT or SAT is offered for free, but only without the optional writing section, would then need to pay to take the test with the optional writing section. Please review our standardized testing policy .
NOTE: If submitting an official score report is a financial hardship, Princeton will continue to review applications with self-reported scores, verified by a school official such as a school counselor, teacher or dean.
For Transfer Applicants
For transfer applicants, a graded paper may come from a course taken within the last two to three years of schooling. While we prefer that it be in the subjects of either English or history, we will also consider papers from courses in the humanities and social sciences for our transfer applicants, provided they meet all other requirements listed.
How to Submit the Graded Written Paper
To submit your graded written paper, choose one of the following options:
Option 1: Upload the graded written paper alongside your application materials when submitting the Common Application or QuestBridge Application.
Option 2: Mail, email or upload the graded written paper to your applicant portal.
The grade and the teacher comments should appear on the paper. If a grading rubric was used, please include this information along with your paper. The Admission Office is more interested in the quality of the writing than the grade it received and encourages you to submit a graded written paper that shows your best efforts, regardless of the grade.
If your school does not offer grades for student work, please submit teacher comments and a rubric.
If you have already graduated and are taking a year off, you may contact your secondary school to obtain a graded written paper.
Please see additional information about the graded written paper on the pages that offer further details for:
Transfer students
International students
Home-schooled students
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
15 What Are We Being Graded On?
Jeremy Levine
Grades are an (often) unmentioned but all-powerful force in the writing classroom. We know that grades mean a great deal to students, motivating many of their decisions in the classroom. [1] But because grading is uncomfortable and inexact work, we rarely discuss it openly in class — a silence that can leave students in the dark about the standards toward which they should write. This essay is a guide to that imprecision; it seeks to lay out for students the different considerations that go into a grading policy so that they can read assignments and rubrics with a more discerning eye. In showing students the many ways that grading standards shift across writing situations, this essay will help students adjust to new and even unclear sets of standards as well as equip students to assess their own writing on terms other than grades.
I’ve heard from students over the years about papers they’d been proud of that got bad grades. Usually, these stories involve a lot of time and energy that a student invested in the paper, learning quite a lot along the way and creating something better than they thought they could when they started — only for that work to not be rewarded with a good grade. When I ask my students why they might have gotten the bad grade, they usually say something to the effect of “I didn’t write what they were looking for.”
After hearing a few of these stories, I decided to try to do something about it. As the writing teacher, I figured that it was my job to help my students understand what their instructors were looking for, which meant showing them what a teacher thinks about when grading writing. To do this, I decided that we would take a day out of each of our units, right before papers were due, to write our grading rubric as a class. This process would supposedly help students think through the different issues that teachers come across when grading papers, so that they didn’t end up with so many grading miscommunications—and it would leave everyone perfectly clear on the standards for that particular essay. Since we were having the conversation at the end of the writing process, we would have a common understanding of what constituted quality for that particular assignment based on what we covered in class. We would quickly arrive at a happy consensus.
It only took two papers for this idea to completely implode. For that second assignment, my students wrote responses to music albums. Each student picked an album they liked and wrote an essay that extended its meaning or put it in a new perspective. It was a vague prompt — my hope was that we would get a bunch of different kinds of papers and everyone would see that each writer in the class had a different writing approach. Even though parts of that assignment idea still hold up, one student from that class explains why these different approaches caused a problem when it came to grading: “I think the main issue with a student-designed rubric was that it wasn’t exactly clear what we were supposed to focus on in our writing….There was a lack of direction with the essay that came from the lack of rubric, it was very challenging to write an essay on a vague prompt without a rubric.” Based on this student’s report, I can see that the students knew that designing the rubric would eventually require us to reach some standards — and writing the paper without knowing the standards would mean that there was a chance that they would do it wrong.
That’s exactly what happened. On rubric day, we ended up with a bunch of writing-related words up on the whiteboard (“Style!” “Purpose!” “Audience!” “Organization!”), but no consensus around what counted as success in any of those categories. The different approaches the students took made it impossible to assess everyone’s writing fairly under one definition of these words. Some definitions were too narrow, like “a well-organized paper talks about the artist’s background first, and then this album specifically,” which is not necessarily true. If someone wrote about how the album makes them feel, then the artist’s background may not be important. It would be unfair to grade that essay under that definition. On the other side of the spectrum, the definition could also get too broad, like “A well-organized paper is easy to understand.” How do we judge that? What’s easy for one reader to understand might not be easy for another, which could lead to students to be surprised by a bad grade when they thought that their paper was easy to follow.
We went in circles like this for a long time and eventually threw out the idea of the class-designed rubric. The student who first proposed we change our approach explained that “Introducing [the rubric] after my paper was almost complete meant many different interpretations could take place in both writing style, organization, and key aspects of the paper, [which] made me feel lost and incorrect in the way my paper was written.” She wanted to change our strategy to avoid these kinds of feelings. I did, too; anyone who read her paper would tell you that it was great — definitely not incorrect. She helped me realize that having everyone advocate for a definition of something like organization or style meant that I was actually inviting them to impose that definition on everyone else, just like the professors giving students those bad grades had done. We ended up caught between two equally bad options: come up with clear, narrow definitions that would fail to recognize the quality of some essays in the class, or come up with criteria that are so broad (such as “the organization of the paper makes sense”) that they don’t actually guide the writing or grading process.
This class session turned out to exemplify the complex issue at the heart of grading writing: In order to assess something, you have to define it and have a list of criteria you use to execute your judgment, but writing is complex and often defies that easy categorization. If a teacher’s definition of good writing is rather particular, or is somehow unclear to you, then high-quality writing that does not match that definition is liable to get a bad score. This issue is the subject of this essay: I am going to focus on the reason why different definitions of writing are perfectly natural, even if they do make grading complicated. With that knowledge, we can approach some solutions — methods for reading expectations critically, as well as some ways that both teachers and students can leverage the judgment of writing in a way to make it more inclusive and helpful for your learning. I don’t mean to imply that writing for a grade is the best way to grow as a writer, or that it is good that grades can have such a strong influence on writing (I don’t think that it is — but that’s a conversation for another time). My goal with this essay is to explain why the grading of writing happens a certain way, so that you can decide how, when, or why you choose to meet these expectations.
Defining “Good Writing”
I write every day. I write academic essays, grocery lists, journal entries, text messages to my friends, among many other things. The metric I use to assess “good writing” in each of these situations changes dramatically — a well-written grocery list helps me move through the store efficiently, whereas a well-written journal entry helps me process my thoughts and feelings about the day. (If I’m feeling sad, listing off vegetables is not going to help me feel better.) “Good writing” looks different in every situation, which means that there is no definition of “good writing” that applies to every situation.
Sure, you might say, but when we’re talking about writing in school, we’re not talking about grocery lists and journal entries. We’re talking about academic writing. That’s true, but not all academic writing is the same. Academic writing in history is different from English, or biology, or political science. Even within one academic discipline, or even one genre within that discipline, there are many different measures of success. Anne Herrington, a writing teacher and researcher, once did a study focusing on how college engineering students and instructors interpreted the same assignment. Her results show us that a genre — in this case, the lab report — can be interpreted in different, equally valid ways. Herrington explains that, for that assignment, “the students perceived their audience as quite knowledgeable of detail, theory, and technical terms while the faculty perceived the audience as less knowledgeable, particularly of details and theory” (345-6). The two groups imagined the assignment’s intended audience differently, which led to the students writing in a way that did not match the instructors’ expectations. They would leave out information that they assumed that their audience already had, while instructors were reading the papers trying to figure out why the very same information was missing. Because the two sides understood the premise of the assignment in different ways, students were unable to meet their instructors’ expectations even though they might have done the assignment perfectly according to their own understanding of it. This means that matching someone’s definition of good writing means making sure that you understand the writing situation in similar ways.
“Writing situation” can mean a lot of different things. We don’t quite have space in this essay to get into all of the complexities of a writing situation, but there are three ideas here that you might find helpful when thinking about grading specifically. You might recognize two of them (reader preferences and reader/writer relationships) from the rhetorical situation that may be part of your composition course. The other concept (genre) is also related to the rhetorical situation; a genre is a typical way of responding to a common rhetorical situation.
- Let’s start with genres. If your writing situation is “I need to express gratitude,” then you’ll write a thank-you note. There are certain conventions that you’re supposed to meet in order to signal to your reader that you’re participating in the thank-you note genre (starting with “Dear,” telling them that you are grateful, explaining why their gift or favor was meaningful to you). If you succeed, your reader will recognize your writing as a thank-you note (because they also know the rules and conventions of the genre), and feel appreciated.
- A situation could also involve the preferences of a particular reader. If I give my friend in her twenties a handwritten thank-you card for dropping off a book at my house, she might think that it’s strangely old-fashioned. I could have sent her a text. But, if I wanted to send a thank-you card to my elderly neighbor, who does not text or email, I would have to write my note by hand and drop it off at her house. This doesn’t have much to do with my own writing preferences, but with what my reader needs or wants.
- Still, thank-you notes do not all look the same because the relationship between giver and receiver will affect what is said — the thank-you note you write for your favorite high school teacher that expresses gratitude for years of mentorship will be different from the thank-you note you write to your uncle for feeding your cat while you were away for the weekend. One is an expression of emotional or intellectual gratitude, the other is an indication that a favor did not go unnoticed. A different tone is probably warranted.
So, genres, relationships, and individual reader preferences all help us come to an understanding of what “good writing” ought to look like in a given circumstance. What does this have to do with grades? Well, in college, you’re likely to meet many different writing situations as you go from assignment to assignment and class to class. The writing situations embedded in each of these assignments will be different, but not always obviously so. It’s then important to do some detective work in figuring out a) what the situation is and b) what the expectations are for that situation. This is a complex process, but here are some quick strategies you can use to get to know the different writing situations you’ll come across in college.
Learning Genres
- I was trying to do X .
- My instructor said that this was good/bad for reason Y .
- Next time I will try Z .Framing feedback in terms of what you were trying to do will help you be successful when you encounter similar situations in the future — and be sure to catalogue the good things your instructors say, too!
- Think about what you’re not supposed to do in a given situation. While this might feel restrictive, it will help you figure out which writing strategies actually are available to you. Something like “I’m not supposed to write a five-paragraph essay for this ten-page paper” starts you in a place of figuring out a new organizational strategy (Reiff and Bawarshi 329).
- Ask for models. If you’re not sure about what a particular genre should look like, ask your instructor for an example. Don’t copy the model directly; use it as a way to get an idea for what sort of approach you should be after.
Learning Relationships
- Most academic assignments have some kind of framing — your instructor wants you to occupy a certain role and write to a particular audience. On an assignment sheet you might read “make a case to a general audience,” which should signal that you should explain key terms that a layperson might not understand, or spend some time telling them why a particular issue is important. You also might read something like “imagine you work at a company and a supervisor has asked you for a report,” which should signal that you should write your report toward that company’s needs, rather than about the topic in general. Always write to the audience indicated on the assignment, even if it feels artificial (Hinton 22).
- If there is no stated relationship on an assignment sheet, that does not mean that there isn’t one. Feel free to ask your instructor “what kind of audience are we writing for?” which will often give you a hint about how to approach your writing.
- Think of yourself as contributing to an ongoing conversation about the topic. Even though it’s tempting to just think of yourself as a student writing for a grade, if you instead start to think of yourself as answering a question with your instructor, rather than for your instructor, you can feel more like an insider. This can lead to deeper engagement with the work. (McCarthy 256-7).
Learning Preferences
- Look for clues in assignment sheets and syllabi about what good writing might be, but ask questions about slippery words such as “clear,” “well-written,” or “academic.”
- Early in a course, if you’re unsure about expectations, submit a draft of a piece for feedback. Ask specifically about whether what you have written meets the instructor’s expectations.
- Check the syllabus to see if there are any grade expectations articulated there, or any particular formatting/structural requirements.
Definitions and Exclusion
Sometimes, it can be a challenge to make sense of the instructor’s preferences. Certain things might seem really important to this instructor that, to you, don’t seem important at all. Of course, there will be instructors who will be very clear about what they expect, and why. But, for those situations where it’s less obvious, let’s turn to James Paul Gee, a well-respected linguist, who has a useful way of thinking about this issue.
Gee uses the word discourse to refer to a “saying-doing-being-valuing-believing combination” (6), meaning a Discourse is a way of understanding and talking about the world. A Discourse can include members of an academic discipline (like history or chemistry), or players of a particular sport (say, basketball), or musicians in a particular genre (such as country). At the very core of a Discourse is a belief system: maybe the academic discipline values a certain kind of knowledge, or the basketball players have a certain ethic of how to play the game. This means that, as you work your way into specific academic disciplines, you’re really learning the beliefs and values of that Discourse. These belief systems are often invisible, but they form the foundation of your belonging.
To someone grading your writing, determining whether or not something is done correctly is then often a question of whether or not it fits in with the expectations and value systems of a Discourse. But, because it’s hard to tell whether someone shares a belief system with you just by glancing at the way they talk or write, people sometimes rely on “superficial features” to see who belongs to their Discourse and who doesn’t. Superficial features are things that rest on the surface of writing or speaking that somehow reveal the writer as not belonging in the Discourse (Gee 11). For the basketball players, superficial features might involve using certain terminology to describe a play. For the country musicians, it might be having a singing voice with twang. Examples of superficial features in academic writing might involve punctuation, formatting, sentence structure, vocabulary, or even the structure of a piece. Missing these qualities could certainly be perceived as a mistake, but none indicate that the person in question doesn’t believe in the values of an academic discipline, basketball, or country music. It just looks that way to an insider.
This is what makes it possible to miss the expectations of an assignment without knowing it: you might write something in a way that is perfectly acceptable to the Discourses that are familiar to you, but don’t belong to the one that you’re becoming part of by taking the class. It might be the case that you understand the values of the Discourses, but your superficial features give you away as a newcomer. It’s worth paying attention to this distinction in your own classes: is the grading scale assessing the part of the Discourse that is about beliefs and values, or the part that is about superficial features? If it is focusing on superficial features, which ones?
What To Do with Grading
It might feel like all of this is irrelevant to you as a student. Teachers are the ones who set the grading criteria, and only rarely do they bring students into this process. All of this is true. At the same time, it is important for you to know why the grading of writing is such unstable business. This background will let you ask the right questions that allow you to do well in the face of the many different assessment systems you’ll face in college. Plenty of people will say “writing is subjective and there’s no one way to grade it,” but that’s only part of the issue. The real issue is the very specific way that writing is subjective — the way that conflicting definitions of good writing can mark someone as an outsider to a community. Going into a college writing situation with this information makes it more possible for you to understand what, exactly, you’re being graded on.
It’s also possible to use the imperfection of grading to pull different kinds of meaning and validation out of your writing projects. We now know that an instructor’s grading scale is only one way to measure a writing project, which means that you can also try to assign your own markers of quality. Maybe you’ve always organized your paper in one particular way and you decide to try a new strategy. A grade might not recognize the success that you have in trying this new method, but that does not mean it wasn’t important or helpful in your development as a writer. Working with the limitations of grading gives you the space to assess your writing on your own terms, a process that can help you improve as a writer over time. After all, you’re the only one who is tracking your growth from one class to the next. You also might decide that pursuing the grade is not the most important thing to you — that there are other things that you want to do or say with your writing that your instructor might not be actively looking for.
There’s another reason why it’s important to recognize that all writing assessment deals with narrow definitions of “good writing.” Even though you don’t spend your nights and weekends grading stacks of student writing, you assess writing (and speaking) all the time. You can immediately recognize when someone is an outsider to your Discourse — maybe you play a sport and can easily tell when someone is inexperienced, or you can identify someone who isn’t from your city because they mispronounce a street name. The immediate reaction, most of the time, is to label this person as an outsider, which makes it difficult for that person to contribute to the group with any credibility (even if they believe in its values). This is just like what happens when you get a bad grade on a project because of some formatting rule that you didn’t know about — you labelled yourself as an outsider to the discourse.
In plenty of situations, this kind of judgment around language happens because of differences in language, dialect, and accent — factors that are often (but not always) traceable to race, nationality, and class. For example, I remember a teacher telling my whole sixth-grade class to never say “ax” instead of “ask,” because it seems unprofessional. It’s important to point out that “ax” is a pronunciation that is grounded in Black American speech (McWhorter) and is not “unprofessional” in and of itself. It is merely labeled unprofessional — graded that way — by people who have been told that it doesn’t fit. It’s another superficial feature.
None of this is to say that the superficial features are necessarily bad. These communal ways of speaking evolved for a reason: they help get across complicated ideas quickly and they help bind a group together. (If you’re playing basketball, it’s much easier to shout “box out” than it is to say “you there, please block the opposing player from getting near the basket for a rebound.”) The problem arises when superficial features are used as a way of keeping people from participating in a community without good reason — especially when the communities in question, like the academic community, or the community of a given workplace, have a lot to offer to people who are included. When these exclusionary judgments are made on a large scale because of understandings of language assessment that are dependent on these superficial features, they can make racism, xenophobia, and classism worse. To learn more about how this happens, see Alvarez et al. in this volume of Writing Spaces . The only way to undo that is to pay closer attention to the way that we judge the way people express themselves, and bring attention to how those judgments are taught to new generations in schools. To do this, it might be helpful to take up some reflective activities around race and language (see Grayson, also this volume).
I propose that we channel frustrations with the limited definitions of good writing that we encounter in school toward developing more generous definitions of good writing and speaking in everyday life. A lot of the time, when I tell people that I think that we should grade the writing of students on whether or not they have exciting ideas that speak to the values of a Discourse, rather than the superficial features, someone usually responds: “Sure, but then when that person applies for a job and they’re still making mistakes on superficial features, they’ll never get hired.” I believe that this is only true because we make it true — because we choose to continue to judge writing in this way. This is where you come in: I think that people who make mistakes on Standard Edited Academic English are only excluded because that’s the way most people were told to judge writing and speaking in schools and other professional settings. If, instead, we had a population of people who knew to interpret people’s differences in language as interesting and productive, then we could begin to chip away at the way day-to-day language assessment facilitates exclusion from those spaces. Just as we need a critical mass of teachers to see student writing as valuable even if it has not yet mastered (or actively rejects) these superficial features, we need a large group of generous readers and listeners in everyday life. Cristina Sánchez-Martín’s article in this volume of Writing Spaces shares many more ideas on how we can develop this more generous approach to our language.
When it comes to the academic community, it’s also important to think about how writing instructors can grade differently so that we do not replicate these exclusionary systems. The good news is that many teachers are already doing this. Asao Inoue, for example, has written many articles about his labor-based grading contract, a grading scheme that assesses how much time a student spends on a project. The goal of this method is to separate grading from a student’s knowledge of a dominant academic discourse that they were not raised speaking, which diminishes the role of racially-driven judgments in his class (61). Maja Wilson takes a different approach, saying that an individual teacher’s opinions aren’t “a problem to be solved,” in grading because all writing is read by people with opinions. For her, this means a focus on narrative feedback, in which teachers focus their energy on what students are trying to do, rather than comparing to an ideal (45). These efforts from teachers, along with work that you can do in accepting and celebrating differences in Discourses, can help make our schools and the rest of our world a more inclusive place.
We went on a bit of a journey. We started with a problem that happened in my class: in trying to bring students into the rubric-designing process, I ended up inviting a flurry of different possible ways to assess one particular assignment, none of which would be fair to every student in my class. We found that this happened because assessing writing means defining good writing, which sometimes is done in narrow, Discourse-specific ways. We then explored some ways that you can take up that conversation yourself and covered more generous ways that writing can be assessed both in schools and everyday life.
How does this affect your day-to-day writing in school? Apart from trying to start conversations about how writing is assessed in your classes, this perspective on the narrowness of standards helps us think about writing in school differently. A lot of the time, it’s easy to think that you are writing to a vast standard of “good writing” that remains the same across every class. With the knowledge that writing is assessed differently in every situation, you can approach each assignment as its own entity with its own complex relationship between speaker, audience, genre, and subject. Asking “how is ‘good writing’ defined according to this assignment?” will help set you up to be more nimble as you move from one situation to the next.
Works Cited
Alvarez, Sara P., et al. “Workin’ Languages: Who We are Matters in our Writing.” Writing Spaces: Readings on Writing , Volume 4, edited by Dana Driscoll, Mary Stewart, and Matt Vetter. Parlor Press, 2021.
Gee, James Paul. “Literacy, Discourse, and Linguistics: Introduction.” Journal of Education , vol. 17, no. 1, 1989, pp. 5-17.
Grayson, Mara Lee. “Writing toward Racial Literacy.” Writing Spaces: Readings on Writing , Volume 4, edited by Dana Driscoll, Mary Stewart, and Matt Vetter. Parlor Press, 2021.
Herrington, Anne J. “Writing in Academic Settings: A Study of the Contexts for Writing in Two College Chemical Engineering Courses.” Research in the Teaching of English , vol. 19, no. 4, 1985, pp. 331-61.
Hinton, Corrine E. “So You’ve Got a Writing Assignment. Now What?” Writing Spaces: Readings on Writing , Vol. 1, edited by Charles Lowe and Pavel Zemliansky. Parlor Press, 2010, pp. 18-33.
Inoue, Asao B. Labor-Based Grading Contracts: Building Equity and Inclusion in the Compassionate Writing Classroom . WAC Clearinghouse, 2019.
McCarthy, Lucille Parkinson. “A Stranger in Strange lands: A College Student Writing Across the Curriculum.” Research in the Teaching of English , vol. 21, no. 3, 1987, 233-65.
McWhorter, John. “The ‘Ax’ Versus ‘Ask’ Question.” The Los Angeles Times , 19 January 2014. https://www.latimes.com/opinion/la-xpm-2014-jan-19-la-oe-mcwhorter-black-speech-ax-20140119-story.html . Accessed 17 August, 2020.
Reiff, Mary Jo, and Anis Bawarshi. “Tracing Discursive Resources: How Students Use Prior Genre Knowledge to Negotiate New Writing Contexts in First-Year Composition.” Written Communication , vol. 28, no. 3, 2011, pp. 312-37.
Sánchez-Martín, Cristina. “Beyond Language Difference in Writing: Investigating Complex and Equitable Language Practices.” Writing Spaces: Readings on Writing , Volume 4, edited by Dana Driscoll, Megan Heise, Mary Stewart, and Matt Vetter. Parlor Press, 2021.
Wilson, Maja. Reimagining Writing Assessment: From Scales to Stories . Heinemann, 2018.
Teacher Resources for What Are We Being Graded On?
Writing teachers know that grading is fraught with questions about what writing is in the first place. This essay takes the position that students should be aware of this complexity so that they can redefine the grading of writing as not the application of static standards but instead something that changes from one situation to the next. In the big picture, this understanding of grading helps students understand more about writing itself. The essay also gives students practical tips on how to interpret grading standards, and offers some new ways to think about how their writing is graded.
To do so, this essay relies on an illustrative anecdote from my own teaching where a failure to define clear standards led to an unfair grading situation. It then moves to contextualize that example within the notion of situational writing, and uses James Paul Gee’s theory of Discourse to explain how students may be marked as outsiders when writing in college.
Teaching Strategies
Because of its multiple purposes (its practical advice and its broader theoretical basis), this essay can be helpful at various points in the semester. The essay may help in the beginning, when students are just acclimating to college and are unsure of what will be expected of them — this essay might give them a useful framework for interpreting the many assignments that will come their way.
It also might be a helpful essay to give out in conjunction with the first writing assignment of the semester. It can help students read the assignment sheet or rubric closely, and you can invite the class to construct definitions of certain words (“clear,” “original,” “well-organized”) in an attempt to build consensus around the standards for an assignment. One method may be to assign students to investigate particular components of your rubric in small groups, and allowing groups to present to each other about what they think constitutes success in each of these categories, which invites you to enter a productive conversation with your students about your own expectations.
If assigning this essay early in the semester, it might be worth bringing the feedback log to class as an in-class assignment. Students could keep the feedback log privately in a writing notebook, documenting the responses that you or their peers had to the choices that they made. You could also assign the feedback log as small-group work, where students can discuss what they learned from the feedback, or come up with some new strategies for achieving their goals.
This essay also may fit near the end of the semester, when students are working on high-stakes final projects in your class (or in other classes) and may want to know how to navigate expectations. You might ask students to compare different evaluative terms across different assignments in your class or in other classes that they have taken so that they can practice identifying these slippery terms in the future.
This piece may be helpful for a teacher revising their own syllabi or rubrics. Some teachers may rely on the abstract terms that are mentioned in this piece (like organization, or purpose) and doing a deep dive on how those words can get picked up by students could help a teacher clarify how they are using those words in their materials. It also presents an opportunity to consider the role of surface-level features in grading — there isn’t a problem with showing students discourse-specific language, but this piece offers a framework for reflecting on the relationship between those features and course grades.
Discussion Questions
- When reading this essay, could you think of any specific writing assignments from your past where you felt like there was a miscommunication of expectations? What happened? What was the teacher expecting, and what did you offer instead?
- What should the writer of this essay have done with the problem he posed in the beginning? What would have been a fair way to grade all of these essays while still offering guidance on how to meet expectations?
- Near the end of the essay, the writer suggests that you can set your own assessment standards for yourself. Think about a paper that you have coming up: what do you want to get out of it? How do you think you can use it to improve your writing?
- How does hearing about the imprecision of grading methods make you feel?
- How else can students get to know the expectations of a given writing assignment? What strategies have you used in the past?
- Can you think of a time that your writing or speaking marked you as an outsider to a group, or where you noticed someone did not belong to a group you are part of because of the way they spoke or wrote? What was the marker of difference, and what happened?
- This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) and is subject to the Writing Spaces Terms of Use. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ , email [email protected] , or send a letter to Creative Commons, PO Box 1866, Mountain View, CA 94042, USA. To view the Writing Spaces Terms of Use, visit http://writingspaces.org/terms-of-use . ↵
What Are We Being Graded On? Copyright © 2021 by Jeremy Levine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Basics for GSIs
- Advancing Your Skills
Grading Essays
Grade for Learning Objectives Response to Writing Errors Commenting on Student Papers Plagiarism and Grading
Information about grading student writing also appears in the Grading Student Work section of the Teaching Guide. Here are some general guidelines to keep in mind when grading student writing.
Grade for Learning Objectives
Know what the objective of the assignment is and grade according to a standard (a rubric) that assesses precisely that. If the purpose of the assignment is to analyze a process, focus on the analysis in the essay. If the paper is unreadable, however, consult with the professor and other GSIs about how to proceed. It may be wise to have a shared policy about the level of readiness or comprehensibility expected and what is unacceptable.
Response to Writing Errors
The research is clear: do not even attempt to mark every error in students’ papers. There are several reasons for this. Teachers do not agree about what constitutes an error (so there is an unavoidable element of subjectivity); students do not learn when confronted by too many markings; and exhaustive marking takes way too much of the instructor’s time. Resist the urge to edit or proofread your students’ papers for superficial errors. At most, mark errors on one page or errors of only two or three types. One approach to avoid the temptation of marking every error is to read or skim the whole essay quickly once without marking anything on the page – or at least, with very minimal marks. Some instructors find this a useful method in order to get a general sense of the essay’s organization and argument, thus enabling them to better identify the major areas of concern. Your second pass can then focus more in-depth on a few select areas that require improvement.
Commenting on Student Papers
The scholarly literature in this area distinguishes formative from summative comments. Summative comments are the more traditional approach. They render judgment about an essay after it has been completed. They explain the instructor’s judgment of a student’s performance. If the instructor’s comments contain several critical statements, the student often becomes protective of his or her ego by filtering them out; learning from mistakes becomes more difficult. If the assignment is over with, the student may see no reason to revisit it to learn from the comments.
Formative comments, on the other hand, give the student feedback in an ongoing process of learning and skill building. Through formative comments, particularly in the draft stage of a writing assignment, instructors guide students on a strategic selection of the most important aspects of the essay. These include both what to keep because it is (at least relatively) well done and what requires revision. Formative comments let the student know clearly how to revise and why.
For the purposes of this guide, we have distinguished commenting on student writing (which is treated here) from grading student writing (which is treated in the Teaching Guide section on grading ). While it is true that instructors’ comments on student writing should give reasons for the grade assigned to it, we want to emphasize here that the comments on a student’s paper can function as instruction , not simply as justification. Here are ten tips.
- Use your comments on a student’s paper to highlight things the paper accomplishes well and a few major things that would most improve the paper.
- Always observe at least one or two strengths in the student’s paper, even if they seem to you to be low-level accomplishments — but avoid condescension. Writing is a complex activity, and students really do need to know they’re doing something right.
- Don’t make exhaustive comments. They take up too much of your time and leave the student with no sense of priority among them.
- Don’t proofread. If the paper is painfully replete with errors and you want to emphasize writing mechanics, count the first ten errors on the page, draw a line at that point, and ask the student to identify them and to show their corrections to you in office hours. Students do not learn much from instructors’ proofreading marks. Direct students to a writing reference guide such as the Random House Handbook.
- Notice patterns or repeated errors (in content or form). Choose the three or four most disabling ones and direct your comments toward helping the students understand what they need to learn to do differently to correct this kind of error.
- Use marginal notes to locate and comment on specific passages in the paper (for example “Interesting idea — develop it more” or “I lost the thread of the argument in this section” or “Very useful summary here before you transition to the next point”). Use final or end comments to discuss more global issues (e.g., “Work on paragraph structure” or “The argument from analogy is ineffective. A better way to make the point would be…”)
- Use questions to help the student unpack areas that are unclear or require more explanation and analysis. E.g.: “Can you explain more about what you mean by “x”?”; “What in the text shows this statement?”; “Is “y” consistent with what you’ve argued about “z”?” This approach can help the student recognize your comments less as a form of judgment than a form of dialogue with their work. As well, it can help you avoid “telling” the student how they should revise certain areas that remain undeveloped. Often, students just need a little more encouragement to focus on an area they haven’t considered in-depth or that they might have envisioned clearly in their head but did not translate to the page.
- Maintain a catalogue of positive end comments: “Good beginning for a 1B course.” “Very perceptive reading.” “Good engagement with the material.” “Gets at the most relevant material/issues/passages.” Anything that connects specific aspects of the student’s product with the grading rubric is useful. (For more on grading rubrics , see the Grading section of the Teaching Guide.)
- Diplomatic but firm suggestions for improvement: Here you must be specific and concrete. Global negative statements tend to enter students’ self-image (“I’m a bad writer”). This creates an attitudinal barrier to learning and makes your job harder and less satisfying. Instead, try “The most strategic improvement you could make is…” Again, don’t try to comment on everything. Select only the most essential areas for improvement, and watch the student’s progress on the next draft or paper.
- Typical in-text marks: Provide your students with a legend of your reading marks. Does a straight underline indicate “good stuff”? Does a wavy underline mean something different? Do you use abbreviations in the margins? You can find examples of standard editing marks in many writing guides, such as the Random House Handbook.
- The tone of your comments on student writing is important to students. Avoid sarcasm and jokes — students who take offense are less disposed to learn. Address the student by name before your end-comments, and sign your name after your remarks. Be professional, and bear in mind the sorts of comments that help you with your work.

Plagiarism and Grading
Students can be genuinely uninformed or misinformed about what constitutes plagiarism. In some instances students will knowingly resort to cutting and pasting from unacknowledged sources; a few may even pay for a paper written by someone else; more recently, students may attempt to pass off AI-generated essays as their own work. Your section syllabus should include a clear policy notice about plagiarism and AI so that students cannot miss it, and instructors should work with students to be sure they understand how to incorporate outside sources appropriately.
Plagiarism can be largely prevented by stipulating that larger writing assignments be completed in steps that the students must turn in for instructor review, or that students visit the instructor periodically for a brief but substantive chat about how their projects are developing, or that students turn in their research log and notes at intermediate points in the research process.
All of these strategies also deter students from using AI to substitute for their own critical thinking and writing. In addition, you may want to craft prompts that are specific to the course materials rather than overly-general ones; and you may also require students to provide detailed analysis about specific texts or cases. AI tools like ChatGPT tend to struggle significantly in both of these areas.
For further guidance on preventing academic misconduct, please see Academic Misconduct — Preventing Plagiarism .
You can also find more information and advice about AI technology like ChatGPT at the Berkeley Center for Teaching & Learning.
UC Berkeley has a campus license to use Turnitin to check the originality of students’ papers and to generate feedback to students about their integration of written sources into their papers. The tool is available in bCourses as an add-on to the Grading tool, and in the Assignments tool SpeedGrader. Even with the results of the originality check, instructors are obligated to exercise judgment in determining the degree to which a given use of source material was fair or unfair.
If a GSI does find a very likely instance of plagiarism, the faculty member in charge of the course must be notified and provided with the evidence. The faculty member is responsible for any sanctions against the student. Some faculty members give an automatic failing grade for the assignment or for the course, according to their own course policy. Instances of plagiarism should be reported to the Center for Student Conduct; please see If You Encounter Academic Misconduct .

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
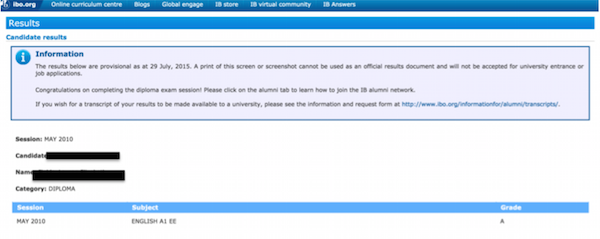
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
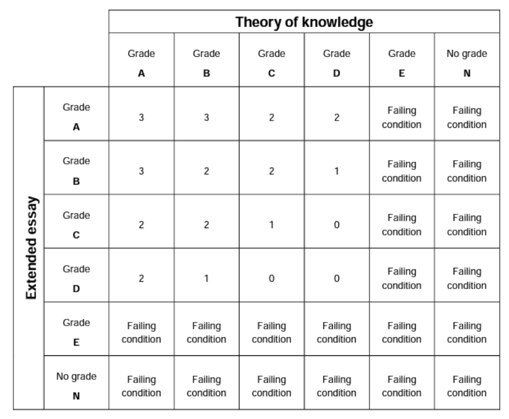
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
The next step is to take each of the other criteria and define success for each of those, assigning a value to A, B, C and D papers. Those definitions then go into the rubric in the appropriate locations to complete the chart.
Each of the criteria will score points for the essay. The descriptions in the first column are each worth 4 points, the second column 3 points, the third 2 points and the fourth 1 point.
What is the grading process?
Now that your criteria are defined, grading the essay is easy. When grading a student essay with a rubric, it is best to read through the essay once before evaluating for grades . Then reading through the piece a second time, determine where on the scale the writing sample falls for each of the criteria. If the student shows excellent grammar, good organization and a good overall effect, he would score a total of ten points. Divide that by the total criteria, three in this case, and he finishes with a 3.33. which on a four-point scale is a B+. If you use five criteria to evaluate your essays, divide the total points scored by five to determine the student’s grade.
Once you have written your grading rubric, you may decide to share your criteria with your students.
If you do, they will know exactly what your expectations are and what they need to accomplish to get the grade they desire. You may even choose to make a copy of the rubric for each paper and circle where the student lands for each criterion. That way, each person knows where he needs to focus his attention to improve his grade. The clearer your expectations are and the more feedback you give your students, the more successful your students will be. If you use a rubric in your essay grading, you can communicate those standards as well as make your grading more objective with more practical suggestions for your students. In addition, once you write your rubric you can use it for all future evaluations.
P.S. If you enjoyed this article, please help spread it by clicking one of those sharing buttons below. And if you are interested in more, you should follow our Facebook page where we share more about creative, non-boring ways to teach English.

- Teaching Ideas
- Classroom Management and Discipline

Popular articles like this
How to design a rubric that teachers can use and students can understand.

How to Evaluate Speaking
Faq for writing teachers, but it is clear dealing with the defensive student, do student papers breed in your briefcase 4 methods of managing the paper load, tuning in the feedback 6 strategies for giving students feedback on speaking.
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
Criteria for Grading Essays
By stephen orvis, govt. 218, view as pdf, tutor appointments.
Peer tutor and consultant appointments are managed through TracCloud (login required). Find resources and more information about the ALEX centers using the following links.
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Center for Teaching
Grading student work.
Print Version
What Purposes Do Grades Serve?
Developing grading criteria, making grading more efficient, providing meaningful feedback to students.
- Maintaining Grading Consistency in Multi-Sectioned Courses
Minimizing Student Complaints about Grading
Barbara Walvoord and Virginia Anderson identify the multiple roles that grades serve:
- as an evaluation of student work;
- as a means of communicating to students, parents, graduate schools, professional schools, and future employers about a student’s performance in college and potential for further success;
- as a source of motivation to students for continued learning and improvement;
- as a means of organizing a lesson, a unit, or a semester in that grades mark transitions in a course and bring closure to it.
Additionally, grading provides students with feedback on their own learning , clarifying for them what they understand, what they don’t understand, and where they can improve. Grading also provides feedback to instructors on their students’ learning , information that can inform future teaching decisions.
Why is grading often a challenge? Because grades are used as evaluations of student work, it’s important that grades accurately reflect the quality of student work and that student work is graded fairly. Grading with accuracy and fairness can take a lot of time, which is often in short supply for college instructors. Students who aren’t satisfied with their grades can sometimes protest their grades in ways that cause headaches for instructors. Also, some instructors find that their students’ focus or even their own focus on assigning numbers to student work gets in the way of promoting actual learning.
Given all that grades do and represent, it’s no surprise that they are a source of anxiety for students and that grading is often a stressful process for instructors.
Incorporating the strategies below will not eliminate the stress of grading for instructors, but it will decrease that stress and make the process of grading seem less arbitrary — to instructors and students alike.
Source: Walvoord, B. & V. Anderson (1998). Effective Grading: A Tool for Learning and Assessment . San Francisco : Jossey-Bass.
- Consider the different kinds of work you’ll ask students to do for your course. This work might include: quizzes, examinations, lab reports, essays, class participation, and oral presentations.
- For the work that’s most significant to you and/or will carry the most weight, identify what’s most important to you. Is it clarity? Creativity? Rigor? Thoroughness? Precision? Demonstration of knowledge? Critical inquiry?
- Transform the characteristics you’ve identified into grading criteria for the work most significant to you, distinguishing excellent work (A-level) from very good (B-level), fair to good (C-level), poor (D-level), and unacceptable work.
Developing criteria may seem like a lot of work, but having clear criteria can
- save time in the grading process
- make that process more consistent and fair
- communicate your expectations to students
- help you to decide what and how to teach
- help students understand how their work is graded
Sample criteria are available via the following link.
- Analytic Rubrics from the CFT’s September 2010 Virtual Brownbag
- Create assignments that have clear goals and criteria for assessment. The better students understand what you’re asking them to do the more likely they’ll do it!
- letter grades with pluses and minuses (for papers, essays, essay exams, etc.)
- 100-point numerical scale (for exams, certain types of projects, etc.)
- check +, check, check- (for quizzes, homework, response papers, quick reports or presentations, etc.)
- pass-fail or credit-no-credit (for preparatory work)
- Limit your comments or notations to those your students can use for further learning or improvement.
- Spend more time on guiding students in the process of doing work than on grading it.
- For each significant assignment, establish a grading schedule and stick to it.
Light Grading – Bear in mind that not every piece of student work may need your full attention. Sometimes it’s sufficient to grade student work on a simplified scale (minus / check / check-plus or even zero points / one point) to motivate them to engage in the work you want them to do. In particular, if you have students do some small assignment before class, you might not need to give them much feedback on that assignment if you’re going to discuss it in class.
Multiple-Choice Questions – These are easy to grade but can be challenging to write. Look for common student misconceptions and misunderstandings you can use to construct answer choices for your multiple-choice questions, perhaps by looking for patterns in student responses to past open-ended questions. And while multiple-choice questions are great for assessing recall of factual information, they can also work well to assess conceptual understanding and applications.
Test Corrections – Giving students points back for test corrections motivates them to learn from their mistakes, which can be critical in a course in which the material on one test is important for understanding material later in the term. Moreover, test corrections can actually save time grading, since grading the test the first time requires less feedback to students and grading the corrections often goes quickly because the student responses are mostly correct.
Spreadsheets – Many instructors use spreadsheets (e.g. Excel) to keep track of student grades. A spreadsheet program can automate most or all of the calculations you might need to perform to compute student grades. A grading spreadsheet can also reveal informative patterns in student grades. To learn a few tips and tricks for using Excel as a gradebook take a look at this sample Excel gradebook .
- Use your comments to teach rather than to justify your grade, focusing on what you’d most like students to address in future work.
- Link your comments and feedback to the goals for an assignment.
- Comment primarily on patterns — representative strengths and weaknesses.
- Avoid over-commenting or “picking apart” students’ work.
- In your final comments, ask questions that will guide further inquiry by students rather than provide answers for them.
Maintaining Grading Consistency in Multi-sectioned Courses (for course heads)
- Communicate your grading policies, standards, and criteria to teaching assistants, graders, and students in your course.
- Discuss your expectations about all facets of grading (criteria, timeliness, consistency, grade disputes, etc) with your teaching assistants and graders.
- Encourage teaching assistants and graders to share grading concerns and questions with you.
- have teaching assistants grade assignments for students not in their section or lab to curb favoritism (N.B. this strategy puts the emphasis on the evaluative, rather than the teaching, function of grading);
- have each section of an exam graded by only one teaching assistant or grader to ensure consistency across the board;
- have teaching assistants and graders grade student work at the same time in the same place so they can compare their grades on certain sections and arrive at consensus.
- Include your grading policies, procedures, and standards in your syllabus.
- Avoid modifying your policies, including those on late work, once you’ve communicated them to students.
- Distribute your grading criteria to students at the beginning of the term and remind them of the relevant criteria when assigning and returning work.
- Keep in-class discussion of grades to a minimum, focusing rather on course learning goals.
For a comprehensive look at grading, see the chapter “Grading Practices” from Barbara Gross Davis’s Tools for Teaching.

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
15.7 Definition Essay
Learning objective.
- Read an example of the definition rhetorical mode.
Defining Good Students Means More Than Just Grades
Many people define good students as those who receive the best grades. While it is true that good students often earn high grades, I contend that grades are just one aspect of how we define a good student. In fact, even poor students can earn high grades sometimes, so grades are not the best indicator of a student’s quality. Rather, a good student pursues scholarship, actively participates in class, and maintains a positive, professional relationship with instructors and peers.
Good students have a passion for learning that drives them to fully understand class material rather than just worry about what grades they receive in the course. Good students are actively engaged in scholarship, which means they enjoy reading and learning about their subject matter not just because readings and assignments are required. Of course, good students will complete their homework and all assignments, and they may even continue to perform research and learn more on the subject after the course ends. In some cases, good students will pursue a subject that interests them but might not be one of their strongest academic areas, so they will not earn the highest grades. Pushing oneself to learn and try new things can be difficult, but good students will challenge themselves rather than remain at their educational comfort level for the sake of a high grade. The pursuit of scholarship and education rather than concern over grades is the hallmark of a good student.
Class participation and behavior are another aspect of the definition of a good student. Simply attending class is not enough; good students arrive punctually because they understand that tardiness disrupts the class and disrespects the professors. They might occasionally arrive a few minutes early to ask the professor questions about class materials or mentally prepare for the day’s work. Good students consistently pay attention during class discussions and take notes in lectures rather than engage in off-task behaviors, such as checking their cell phones or daydreaming. Excellent class participation requires a balance between speaking and listening, so good students will share their views when appropriate but also respect their classmates’ views when they differ from their own. It is easy to mistake quantity of class discussion comments with quality, but good students know the difference and do not try to dominate the conversation. Sometimes class participation is counted toward a student’s grade, but even without such clear rewards, good students understand how to perform and excel among their peers in the classroom.
Finally, good students maintain a positive and professional relationship with their professors. They respect their instructor’s authority in the classroom as well as the instructor’s privacy outside of the classroom. Prying into a professor’s personal life is inappropriate, but attending office hours to discuss course material is an appropriate, effective way for students to demonstrate their dedication and interest in learning. Good students go to their professor’s office during posted office hours or make an appointment if necessary. While instructors can be very busy, they are usually happy to offer guidance to students during office hours; after all, availability outside the classroom is a part of their job. Attending office hours can also help good students become memorable and stand out from the rest, particularly in lectures with hundreds enrolled. Maintaining positive, professional relationships with professors is especially important for those students who hope to attend graduate school and will need letters of recommendation in the future.
Although good grades often accompany good students, grades are not the only way to indicate what it means to be a good student. The definition of a good student means demonstrating such traits as engaging with course material, participating in class, and creating a professional relationship with professors. While every professor will have different criteria for earning an A in their course, most would agree on these characteristics for defining good students.
Online Definition Essay Alternatives
Judy Brady provides a humorous look at responsibilities and relationships in I Want a Wife :
- http://www.columbia.edu/~sss31/rainbow/wife.html
Gayle Rosenwald Smith shares her dislike of the name for a sleeveless T-shirt, The Wife-Beater :
- http://faculty.gordonstate.edu/cperkowski/1101/WifeBeater.pdf
Philip Levine defines What Work Is :
- http://www.ibiblio.org/ipa/poems/levine/what_work_is.php
- http://www.poemhunter.com/poem/what-work-is
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The Happiness Gap Between Left and Right Isn’t Closing

By Thomas B. Edsall
Mr. Edsall contributes a weekly column from Washington, D.C., on politics, demographics and inequality.
Why is it that a substantial body of social science research finds that conservatives are happier than liberals?
A partial answer: Those on the right are less likely to be angered or upset by social and economic inequities, believing that the system rewards those who work hard, that hierarchies are part of the natural order of things and that market outcomes are fundamentally fair.
Those on the left stand in opposition to each of these assessments of the social order, prompting frustration and discontent with the world around them.
The happiness gap has been with us for at least 50 years, and most research seeking to explain it has focused on conservatives. More recently, however, psychologists and other social scientists have begun to dig deeper into the underpinnings of liberal discontent — not only unhappiness but also depression and other measures of dissatisfaction.
One of the findings emerging from this research is that the decline in happiness and in a sense of agency is concentrated among those on the left who stress matters of identity, social justice and the oppression of marginalized groups.
There is, in addition, a parallel phenomenon taking place on the right as Donald Trump and his MAGA loyalists angrily complain of oppression by liberals who engage in a relentless vendetta to keep Trump out of the White House.
There is a difference in the way the left and right react to frustration and grievance. Instead of despair, the contemporary right has responded with mounting anger, rejecting democratic institutions and norms.
In a 2021 Vox article, “ Trump and the Republican Revolt Against Democracy ,” Zack Beauchamp described in detail the emergence of destructive and aggressive discontent among conservatives.
Citing a wide range of polling data and academic studies, Beauchamp found:
More than twice as many Republicans (39 percent) as Democrats (17 percent) believed that “if elected leaders won’t protect America, the people must act — even if that means violence.”
Fifty-seven percent of Republicans considered Democrats to be “enemies,” compared with 41 percent of Democrats who viewed Republicans as “enemies.”
Among Republicans, support for “the use of force to defend our way of life,” as well as for the belief that “strong leaders bend rules” and that “sometimes you have to take the law in your own hands,” grows stronger in direct correlation with racial and ethnic hostility.
Trump has repeatedly warned of the potential for political violence. In January he predicted bedlam if the criminal charges filed in federal and state courts against him damaged his presidential campaign:
I think they feel this is the way they’re going to try and win, and that’s not the way it goes. It’ll be bedlam in the country. It’s a very bad thing. It’s a very bad precedent. As we said, it’s the opening of a Pandora’s box.
Before he was indicted in New York, Trump claimed there would be “potential death and destruction” if he was charged.
At an Ohio campaign rally in March, Trump declared, “If I don’t get elected, it’s going to be a blood bath for the whole country.”
In other words, Trump and his allies respond to adversity and what they see as attacks from the left with threats and anger, while a segment of the left often but not always responds to adversity and social inequity with dejection and sorrow.
There are significant consequences for this internalization.
Jamin Halberstadt , a professor of psychology at the University of Otago in New Zealand and a co-author of “ Outgroup Threat and the Emergence of Cohesive Groups : A Cross-Cultural Examination,” argued in his emailed reply to my inquiry that because “a focus on injustice and victimhood is, by definition, disempowering (isn’t that why we talk of ‘survivors’ rather than ‘victims’?), loss of control is not good for self-esteem or happiness.”
But, he pointed out:
this focus, while no doubt a part of the most visible and influential side of progressive ideology, is still just a part. Liberalism is a big construct, and I’m reluctant to reduce it to a focus on social justice issues. Some liberals have this view, but I suspect their influence is outsized because (a) they have the social media megaphone and (b) we are in a climate in which freedom of expression and, in particular, challenges to the worldview you characterize have been curtailed.
Expanding on this line of argument, Halberstadt wrote:
I’m sure some self-described liberals have views that are counterproductive to their own happiness. One sub-ideology associated with liberalism is, as you describe, a sense of victimhood and grievance. But there is more than one way to respond to structural barriers. Within that group of the aggrieved, some probably see systemic problems that cannot be overcome, and that’s naturally demoralizing and depressing. But others see systemic problems as a challenge to overcome.
Taking Halberstadt’s assessment of the effects of grievance and victimhood a step farther, Timothy A. Judge , the chairman of the department of management and human resources at Notre Dame, wrote in a 2009 paper, “ Core Self-Evaluations and Work Success ”:
Core self-evaluations (C.S.E.) is a broad, integrative trait indicated by self-esteem, locus of control, generalized self-efficacy and (low) neuroticism (high emotional stability). Individuals with high levels of C.S.E. perform better on their jobs, are more successful in their careers, are more satisfied with their jobs and lives, report lower levels of stress and conflict, cope more effectively with setbacks and better capitalize on advantages and opportunities.
I asked Judge and other scholars a question: Have liberal pessimists fostered an outlook that spawns unhappiness as its adherents believe they face seemingly insurmountable structural barriers?
Judge replied by email:
I do share the perspective that a focus on status, hierarchies and institutions that reinforce privilege contributes to an external locus of control. And the reason is fairly straightforward. We can only change these things through collective and, often, policy initiatives — which tend to be complex, slow, often conflictual and outside our individual control. On the other hand, if I view “life’s chances” (Virginia Woolf’s term) to be mostly dependent on my own agency, this reflects an internal focus, which will often depend on enacting initiatives largely within my control.
Judge elaborated on his argument:
If our predominant focus in how we view the world is social inequities, status hierarchies, societal unfairness conferred by privilege, then everyone would agree that these things are not easy to fix, which means, in a sense, we must accept some unhappy premises: Life isn’t fair; outcomes are outside my control, often at the hands of bad, powerful actors; social change depends on collective action that may be conflictual; an individual may have limited power to control their own destiny, etc. These are not happy thoughts because they cause me to view the world as inherently unfair, oppressive, conflictual, etc. It may or may not be right, but I would argue that these are in fact viewpoints of how we view the world, and our place in it, that would undermine our happiness.
Last year, George Yancey , a professor of sociology at Baylor University, published “ Identity Politics, Political Ideology, and Well-Being : Is Identity Politics Good for Our Well-Being?”
Yancey argued that recent events “suggest that identity politics may correlate to a decrease in well-being, particularly among young progressives, and offer an explanation tied to internal elements within political progressiveness.”
By focusing on “political progressives, rather than political conservatives,” Yancey wrote, “a nuanced approach to understanding the relationship between political ideology and well-being begins to emerge.”
Identity politics, he continued, focuses “on external institutional forces that one cannot immediately alleviate.” It results in what scholars call the externalization of one’s locus of control, or viewing the inequities of society as a result of powerful if not insurmountable outside forces, including structural racism, patriarchy and capitalism, as opposed to believing that individuals can overcome such obstacles through hard work and collective effort.
As a result, Yancey wrote, “identity politics may be an important mechanism by which progressive political ideology can lead to lower levels of well-being.”
Conversely, Yancey pointed out, “a class-based progressive cognitive emphasis may focus less on the group identity, generating less of a need to rely on emotional narratives and dichotomous thinking and may be less likely to be detrimental to the well-being of a political progressive.”
Yancey tested this theory using data collected in the 2021 Baylor Religion Survey of 1,232 respondents.
“Certain types of political progressive ideology can have contrasting effects on well-being,” Yancey wrote. “It is plausible that identity politics may explain the recent increase well-being gap between conservatives and progressives.”
Oskari Lahtinen , a senior researcher in psychology at the University of Turku in Finland, published a study in March, “ Construction and Validation of a Scale for Assessing Critical Social Justice Attitudes ,” that reinforces Yancey’s argument.
Lahtinen conducted two surveys of a total of 5,878 men and women to determine the share of Finnish citizens who held “critical social justice attitudes” and how those who held such views differed from those who did not.
Critical social justice proponents, on Lahtinen’s scale,
point out varieties of oppression that cause privileged people (e.g., male, white, heterosexual, cisgender) to benefit over marginalized people (e.g., woman, Black, gay, transgender). In critical race theory, some of the core tenets include that (1) white supremacy and racism are omnipresent and colorblind policies are not enough to tackle them, (2) people of color have their own unique standpoint and (3) races are social constructs.
What did Lahtinen find?
The critical social justice propositions encountered
strong rejection from men. Women expressed more than twice as much support for the propositions. In both studies, critical social justice was correlated modestly with depression, anxiety, and (lack of) happiness, but not more so than being on the political left was.
In an email responding to my inquiries about his paper, Lahtinen wrote that one of the key findings in his research was that “there were large differences between genders in critical social justice advocacy: Three out of five women but only one out of seven men expressed support for the critical social justice claims.”
In addition, he pointed out, “there was one variable in the study that closely corresponded to external locus of control: ‘Other people or structures are more responsible for my well-being than I myself am.’”
The correlation between agreement with this statement and unhappiness was among the strongest in the survey:
People on the left endorsed this item (around 2 on a scale of 0 to 4) far more than people on the right (around 0.5). Endorsing the belief was determined by political party preference much more than by gender, for instance.
Such measures as locus of control, self-esteem, a belief in personal agency and optimism all play major roles in daily life.
In a December 2022 paper, “ The Politics of Depression : Diverging Trends in Internalizing Symptoms Among U.S. Adolescents by Political Beliefs,” Catherine Gimbrone , Lisa M. Bates , Seth Prins and Katherine M. Keyes , all at Columbia’s Mailman School of Public Health, noted that “trends in adolescent internalizing symptoms diverged by political beliefs, sex and parental education over time, with female liberal adolescents experiencing the largest increases in depressive symptoms, especially in the context of demographic risk factors, including parental education.”
“These findings,” they added, “indicate a growing mental health disparity between adolescents who identify with certain political beliefs. It is therefore possible that the ideological lenses through which adolescents view the political climate differentially affect their mental well-being.”
Gimbrone and her co-authors based their work on studies of 85,000 teenagers from 2005 to 2018. They found that
while internalizing symptom scores worsened over time for all adolescents, they deteriorated most quickly for female liberal adolescents. Beginning in approximately 2010 and continuing through 2018, female liberal adolescents reported the largest changes in depressive affect, self-esteem, self-derogation and loneliness.
In conclusion, the authors wrote, “socially underprivileged liberals reported the worst internalizing symptom scores over time, likely indicating that the experiences and beliefs that inform a liberal political identity are ultimately less protective against poor mental health than those that inform a conservative political identity.”
From another vantage point, Nick Haslam , a professor of psychology at the University of Melbourne, argued in his 2020 paper “ Harm Inflation: Making Sense of Concept Creep ” that recent years have seen “a rising sensitivity to harm within at least some Western cultures, such that previously innocuous or unremarked phenomena were increasingly identified as harmful and that this rising sensitivity reflected a politically liberal moral agenda.”
As examples, Haslam wrote that the definition of “trauma” has been
progressively broadened to include adverse life events of decreasing severity and those experienced vicariously rather than directly. “Mental disorder” came to include a wider range of conditions, so that new forms of psychopathology were added in each revision of diagnostic manuals and the threshold for diagnosing some existing forms was lowered. “Abuse” extended from physical acts to verbal and emotional slights and incorporated forms of passive neglect in addition to active aggression.
Haslam described this process as concept creep and argued that “some examples of concept creep are surely the work of deliberate actors who might be called expansion entrepreneurs.”
Concept expansion, Haslam wrote, “can be used as a tactic to amplify the perceived seriousness of a movement’s chosen social problem.” In addition, “such expansion can be effective means of enhancing the perceived seriousness of a social problem or threat by increasing the perceived prevalence of both ‘victims’ and ‘perpetrators.’”
Haslam cited studies showing that strong “correlates of holding expansive concepts of harm were compassion-related trait values, left-liberal political attitudes and forms of morality associated with both.” Holding expansive concepts of harm was also “associated with affective and cognitive empathy orientation and most strongly of all with endorsement of harm- and fairness-based morality.” Many of these characteristics are associated with the political left.
“The expansion of harm-related concepts has implications for acceptable self-expression and free speech,” Haslam wrote. “Creeping concepts enlarge the range of expressions judged to be unacceptably harmful, thereby increasing calls for speech restrictions. Expansion of the harm-related concepts of hate and hate speech exemplifies this possibility.”
While much of the commentary on the progressive left has been critical, Haslam takes a more ambivalent position: “Sometimes concept creep is presented in an exclusively negative frame,” he wrote, but that fails to address the “positive implications. To that end, we offer three positive consequences of the phenomenon.”
The first is that expansionary definitions of harm “can be useful in drawing attention to harms previously overlooked. Consider the vertical expansion of abuse to include emotional abuse.”
Second, “concept creep can prevent harmful practices by modifying social norms.” For example, “changing definitions of bullying that include social exclusion and antagonistic acts expressed horizontally rather than only downward in organizational hierarchies may also entrench norms against the commission of destructive behavior.”
And finally:
The expansion of psychology’s negative concepts can motivate interventions aimed at preventing or reducing the harms associated with the newly categorized behaviors. For instance, the conceptual expansion of addiction to include behavioral addictions (e.g., gambling and internet addictions) has prompted a flurry of research into treatment options, which has found that a range of psychosocial treatments can be successfully used to treat gambling, internet and sexual addictions.
Judge suggested an approach to this line of inquiry that he believed might offer a way for liberalism to regain its footing:
I would like to think that there is a version of modern progressivism that accepts many of the premises of the problem and causes of inequality but does so in a way that also celebrates the power of individualism, of consensus and of common cause. I know this is perhaps naïve. But if we give in to cynicism (that consensus can’t be found), that’s self-reinforcing, isn’t it? I think about the progress on how society now views sexual orientation and the success stories. The change was too slow, painful for many, but was there any other way?
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here's our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Thomas B. Edsall has been a contributor to the Times Opinion section since 2011. His column on strategic and demographic trends in American politics appears every Wednesday. He previously covered politics for The Washington Post. @ edsall

COMMENTS
How Is Writing Graded? Students often want to know how their writing assignments are graded—that is, what is an A paper, a B paper, and so on. Generally speaking, there are two basic ways to determine how your papers will be graded. Understand your assignment, which often will include a rubric. Understand general grading standards professors ...
1. Be mindful of length. Although the suggested Princeton graded paper length is 1-2 pages, some students may feel that they don't have a strong enough paper in that range. If that's the case, you can submit a longer paper. For best results, avoid submitting any sample longer than 3-5 pages. 2.
The grade and the teacher comments should appear on the paper. If a grading rubric was used, please include this information along with your paper. The Admission Office is more interested in the quality of the writing than the grade it received and encourages you to submit a graded written paper that shows your best efforts, regardless of the ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
If a student scored a 90 on the first submission, that student has the potential to earn up to a 95 on the essay, and so on. If a student scored a 99 or 100 on the essay, the student has the potential to earn bonus points on the essay grade. This resubmission is not mandatory for all students but is mandatory for some students.
The essay also gives students practical tips on how to interpret grading standards, and offers some new ways to think about how their writing is graded. To do so, this essay relies on an illustrative anecdote from my own teaching where a failure to define clear standards led to an unfair grading situation.
Grade for Learning Objectives. Know what the objective of the assignment is and grade according to a standard (a rubric) that assesses precisely that. If the purpose of the assignment is to analyze a process, focus on the analysis in the essay. If the paper is unreadable, however, consult with the professor and other GSIs about how to proceed.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34. You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays. Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
to teach the subject of their essays or suitably familiar enough with the subject area to provide adequate supervision and advisement over the course of the research and writing process. The essays are graded by examiners appointed by the Chief Examiner of each subject in the IB Office in Cardiff, Wales. Class of 2021 Extended Essay Due Dates
If the student shows excellent grammar, good organization and a good overall effect, he would score a total of ten points. Divide that by the total criteria, three in this case, and he finishes with a 3.33. which on a four-point scale is a B+. If you use five criteria to evaluate your essays, divide the total points scored by five to determine ...
The essay has few grammatical errors; it is clear, well organized and understandable, if not particularly interesting or exciting; some sentences may be poorly constructed or unclear. C. Theoretical thesis vague at best; evidence only partially tied to thesis; evidence is at very broad and general level. Reader gains general understanding of ...
Holistic grading or holistic scoring, in standards-based education, is an approach to scoring essays using a simple grading structure that bases a grade on a paper's overall quality. This type of grading, which is also described as nonreductionist grading, contrasts with analytic grading, which takes more factors into account when assigning a grade. . Holistic grading can also be used to ...
To grade essays: Go to the Gradebook. Select See All to view all graded and ungraded essays. To grade, review, or re-grade essays, click or tap the number of graded or ungraded essays. You can also grade essays from the Assignments page: Go to the Assignment menu. Select Grade Essay. The answer key helps you evaluate students' answers.
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay. An essay is, generally, a piece of writing that gives the author's own argument, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of a letter, a paper, an article, a pamphlet, and a short story. Essays have been sub-classified as formal and informal: formal essays are characterized by "serious purpose, dignity, logical organization ...
After your instructor has graded your essay or short-answer questions. Essay and short-answer questions are ones for which you enter free-form text. You can submit an essay or short answer only once. Your instructor must grade these kinds of answers. You cannot format text (bold, italic, etc.) or use spaces to align text.
Use different grading scales for different assignments. Grading scales include: letter grades with pluses and minuses (for papers, essays, essay exams, etc.) 100-point numerical scale (for exams, certain types of projects, etc.) check +, check, check- (for quizzes, homework, response papers, quick reports or presentations, etc.)
Class participation and behavior are another aspect of the definition of a good student. Simply attending class is not enough; good students arrive punctually because they understand that tardiness disrupts the class and disrespects the professors. They might occasionally arrive a few minutes early to ask the professor questions about class ...
Writing essays can be hard, and there are many different kinds of essays that can be written. An informative essay serves the single purpose of informing or educating the reader about a topic ...
Narrative essays are usually based on a personal experience told from the author's perspective. The essay always has a point or theme, which is the message the author wants the reader to take away ...
Sample Image Analysis Essay: Prompt A Sample Extended Definition Essay: Prompt B Ready Submitted Graded You can work on a Touchstone whenever you want, but you must complete the previous assessments in the Unit before you can submit it. SUBMIT TOUCHSTONE Currently, it takes about 2-4 business days for a Touchstone to be graded.
A new tool called Writable, which uses ChatGPT to help grade student writing assignments, is being offered widely to teachers in grades 3-12.. Why it matters: Teachers have quietly used ChatGPT to grade papers since it first came out — but now schools are sanctioning and encouraging its use. Driving the news: Writable, which is billed as a time-saving tool for teachers, was purchased last ...
Mr. Edsall contributes a weekly column from Washington, D.C., on politics, demographics and inequality. Why is it that a substantial body of social science research finds that conservatives are ...