
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

14 Quantitative analysis: Descriptive statistics
Numeric data collected in a research project can be analysed quantitatively using statistical tools in two different ways. Descriptive analysis refers to statistically describing, aggregating, and presenting the constructs of interest or associations between these constructs. Inferential analysis refers to the statistical testing of hypotheses (theory testing). In this chapter, we will examine statistical techniques used for descriptive analysis, and the next chapter will examine statistical techniques for inferential analysis. Much of today’s quantitative data analysis is conducted using software programs such as SPSS or SAS. Readers are advised to familiarise themselves with one of these programs for understanding the concepts described in this chapter.
Data preparation
In research projects, data may be collected from a variety of sources: postal surveys, interviews, pretest or posttest experimental data, observational data, and so forth. This data must be converted into a machine-readable, numeric format, such as in a spreadsheet or a text file, so that they can be analysed by computer programs like SPSS or SAS. Data preparation usually follows the following steps:
Data coding. Coding is the process of converting data into numeric format. A codebook should be created to guide the coding process. A codebook is a comprehensive document containing a detailed description of each variable in a research study, items or measures for that variable, the format of each item (numeric, text, etc.), the response scale for each item (i.e., whether it is measured on a nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio scale, and whether this scale is a five-point, seven-point scale, etc.), and how to code each value into a numeric format. For instance, if we have a measurement item on a seven-point Likert scale with anchors ranging from ‘strongly disagree’ to ‘strongly agree’, we may code that item as 1 for strongly disagree, 4 for neutral, and 7 for strongly agree, with the intermediate anchors in between. Nominal data such as industry type can be coded in numeric form using a coding scheme such as: 1 for manufacturing, 2 for retailing, 3 for financial, 4 for healthcare, and so forth (of course, nominal data cannot be analysed statistically). Ratio scale data such as age, income, or test scores can be coded as entered by the respondent. Sometimes, data may need to be aggregated into a different form than the format used for data collection. For instance, if a survey measuring a construct such as ‘benefits of computers’ provided respondents with a checklist of benefits that they could select from, and respondents were encouraged to choose as many of those benefits as they wanted, then the total number of checked items could be used as an aggregate measure of benefits. Note that many other forms of data—such as interview transcripts—cannot be converted into a numeric format for statistical analysis. Codebooks are especially important for large complex studies involving many variables and measurement items, where the coding process is conducted by different people, to help the coding team code data in a consistent manner, and also to help others understand and interpret the coded data.
Data entry. Coded data can be entered into a spreadsheet, database, text file, or directly into a statistical program like SPSS. Most statistical programs provide a data editor for entering data. However, these programs store data in their own native format—e.g., SPSS stores data as .sav files—which makes it difficult to share that data with other statistical programs. Hence, it is often better to enter data into a spreadsheet or database where it can be reorganised as needed, shared across programs, and subsets of data can be extracted for analysis. Smaller data sets with less than 65,000 observations and 256 items can be stored in a spreadsheet created using a program such as Microsoft Excel, while larger datasets with millions of observations will require a database. Each observation can be entered as one row in the spreadsheet, and each measurement item can be represented as one column. Data should be checked for accuracy during and after entry via occasional spot checks on a set of items or observations. Furthermore, while entering data, the coder should watch out for obvious evidence of bad data, such as the respondent selecting the ‘strongly agree’ response to all items irrespective of content, including reverse-coded items. If so, such data can be entered but should be excluded from subsequent analysis.
Data transformation. Sometimes, it is necessary to transform data values before they can be meaningfully interpreted. For instance, reverse coded items—where items convey the opposite meaning of that of their underlying construct—should be reversed (e.g., in a 1-7 interval scale, 8 minus the observed value will reverse the value) before they can be compared or combined with items that are not reverse coded. Other kinds of transformations may include creating scale measures by adding individual scale items, creating a weighted index from a set of observed measures, and collapsing multiple values into fewer categories (e.g., collapsing incomes into income ranges).
Univariate analysis
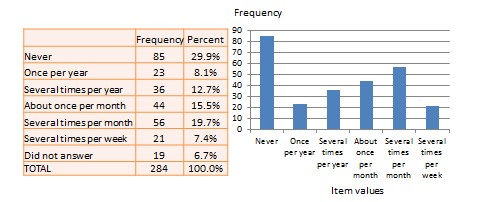
Univariate analysis—or analysis of a single variable—refers to a set of statistical techniques that can describe the general properties of one variable. Univariate statistics include: frequency distribution, central tendency, and dispersion. The frequency distribution of a variable is a summary of the frequency—or percentages—of individual values or ranges of values for that variable. For instance, we can measure how many times a sample of respondents attend religious services—as a gauge of their ‘religiosity’—using a categorical scale: never, once per year, several times per year, about once a month, several times per month, several times per week, and an optional category for ‘did not answer’. If we count the number or percentage of observations within each category—except ‘did not answer’ which is really a missing value rather than a category—and display it in the form of a table, as shown in Figure 14.1, what we have is a frequency distribution. This distribution can also be depicted in the form of a bar chart, as shown on the right panel of Figure 14.1, with the horizontal axis representing each category of that variable and the vertical axis representing the frequency or percentage of observations within each category.
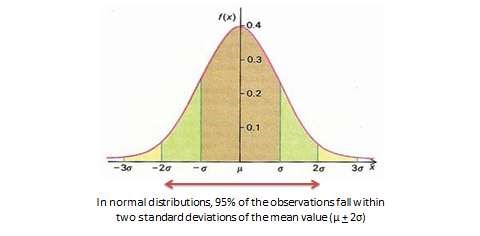
With very large samples, where observations are independent and random, the frequency distribution tends to follow a plot that looks like a bell-shaped curve—a smoothed bar chart of the frequency distribution—similar to that shown in Figure 14.2. Here most observations are clustered toward the centre of the range of values, with fewer and fewer observations clustered toward the extreme ends of the range. Such a curve is called a normal distribution .
Lastly, the mode is the most frequently occurring value in a distribution of values. In the previous example, the most frequently occurring value is 15, which is the mode of the above set of test scores. Note that any value that is estimated from a sample, such as mean, median, mode, or any of the later estimates are called a statistic .
Bivariate analysis
Bivariate analysis examines how two variables are related to one another. The most common bivariate statistic is the bivariate correlation —often, simply called ‘correlation’—which is a number between -1 and +1 denoting the strength of the relationship between two variables. Say that we wish to study how age is related to self-esteem in a sample of 20 respondents—i.e., as age increases, does self-esteem increase, decrease, or remain unchanged?. If self-esteem increases, then we have a positive correlation between the two variables, if self-esteem decreases, then we have a negative correlation, and if it remains the same, we have a zero correlation. To calculate the value of this correlation, consider the hypothetical dataset shown in Table 14.1.
After computing bivariate correlation, researchers are often interested in knowing whether the correlation is significant (i.e., a real one) or caused by mere chance. Answering such a question would require testing the following hypothesis:
Social Science Research: Principles, Methods and Practices (Revised edition) Copyright © 2019 by Anol Bhattacherjee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Quant Analysis 101: Descriptive Statistics
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | October 2023
If you’re new to quantitative data analysis , one of the first terms you’re likely to hear being thrown around is descriptive statistics. In this post, we’ll unpack the basics of descriptive statistics, using straightforward language and loads of examples . So grab a cup of coffee and let’s crunch some numbers!
Overview: Descriptive Statistics
What are descriptive statistics.
- Descriptive vs inferential statistics
- Why the descriptives matter
- The “ Big 7 ” descriptive statistics
- Key takeaways
At the simplest level, descriptive statistics summarise and describe relatively basic but essential features of a quantitative dataset – for example, a set of survey responses. They provide a snapshot of the characteristics of your dataset and allow you to better understand, roughly, how the data are “shaped” (more on this later). For example, a descriptive statistic could include the proportion of males and females within a sample or the percentages of different age groups within a population.
Another common descriptive statistic is the humble average (which in statistics-talk is called the mean ). For example, if you undertook a survey and asked people to rate their satisfaction with a particular product on a scale of 1 to 10, you could then calculate the average rating. This is a very basic statistic, but as you can see, it gives you some idea of how this data point is shaped .

What about inferential statistics?
Now, you may have also heard the term inferential statistics being thrown around, and you’re probably wondering how that’s different from descriptive statistics. Simply put, descriptive statistics describe and summarise the sample itself , while inferential statistics use the data from a sample to make inferences or predictions about a population .
Put another way, descriptive statistics help you understand your dataset , while inferential statistics help you make broader statements about the population , based on what you observe within the sample. If you’re keen to learn more, we cover inferential stats in another post , or you can check out the explainer video below.
Why do descriptive statistics matter?
While descriptive statistics are relatively simple from a mathematical perspective, they play a very important role in any research project . All too often, students skim over the descriptives and run ahead to the seemingly more exciting inferential statistics, but this can be a costly mistake.
The reason for this is that descriptive statistics help you, as the researcher, comprehend the key characteristics of your sample without getting lost in vast amounts of raw data. In doing so, they provide a foundation for your quantitative analysis . Additionally, they enable you to quickly identify potential issues within your dataset – for example, suspicious outliers, missing responses and so on. Just as importantly, descriptive statistics inform the decision-making process when it comes to choosing which inferential statistics you’ll run, as each inferential test has specific requirements regarding the shape of the data.
Long story short, it’s essential that you take the time to dig into your descriptive statistics before looking at more “advanced” inferentials. It’s also worth noting that, depending on your research aims and questions, descriptive stats may be all that you need in any case . So, don’t discount the descriptives!

The “Big 7” descriptive statistics
With the what and why out of the way, let’s take a look at the most common descriptive statistics. Beyond the counts, proportions and percentages we mentioned earlier, we have what we call the “Big 7” descriptives. These can be divided into two categories – measures of central tendency and measures of dispersion.
Measures of central tendency
True to the name, measures of central tendency describe the centre or “middle section” of a dataset. In other words, they provide some indication of what a “typical” data point looks like within a given dataset. The three most common measures are:
The mean , which is the mathematical average of a set of numbers – in other words, the sum of all numbers divided by the count of all numbers.
The median , which is the middlemost number in a set of numbers, when those numbers are ordered from lowest to highest.
The mode , which is the most frequently occurring number in a set of numbers (in any order). Naturally, a dataset can have one mode, no mode (no number occurs more than once) or multiple modes.
To make this a little more tangible, let’s look at a sample dataset, along with the corresponding mean, median and mode. This dataset reflects the service ratings (on a scale of 1 – 10) from 15 customers.
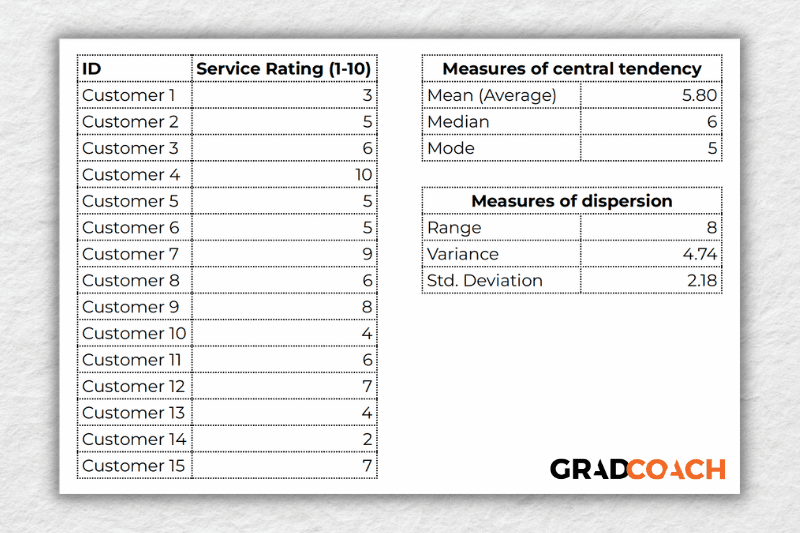
As you can see, the mean of 5.8 is the average rating across all 15 customers. Meanwhile, 6 is the median . In other words, if you were to list all the responses in order from low to high, Customer 8 would be in the middle (with their service rating being 6). Lastly, the number 5 is the most frequent rating (appearing 3 times), making it the mode.
Together, these three descriptive statistics give us a quick overview of how these customers feel about the service levels at this business. In other words, most customers feel rather lukewarm and there’s certainly room for improvement. From a more statistical perspective, this also means that the data tend to cluster around the 5-6 mark , since the mean and the median are fairly close to each other.
To take this a step further, let’s look at the frequency distribution of the responses . In other words, let’s count how many times each rating was received, and then plot these counts onto a bar chart.
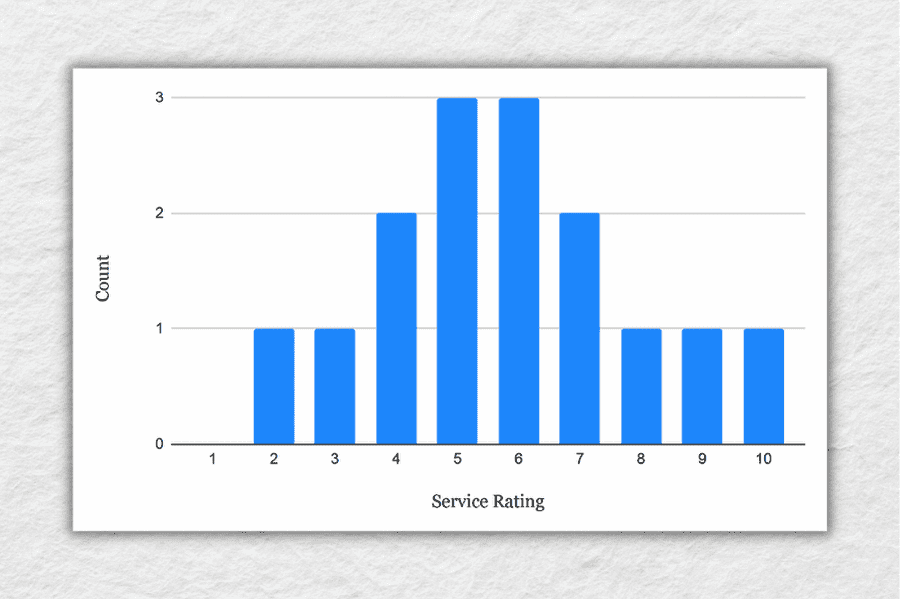
As you can see, the responses tend to cluster toward the centre of the chart , creating something of a bell-shaped curve. In statistical terms, this is called a normal distribution .
As you delve into quantitative data analysis, you’ll find that normal distributions are very common , but they’re certainly not the only type of distribution. In some cases, the data can lean toward the left or the right of the chart (i.e., toward the low end or high end). This lean is reflected by a measure called skewness , and it’s important to pay attention to this when you’re analysing your data, as this will have an impact on what types of inferential statistics you can use on your dataset.
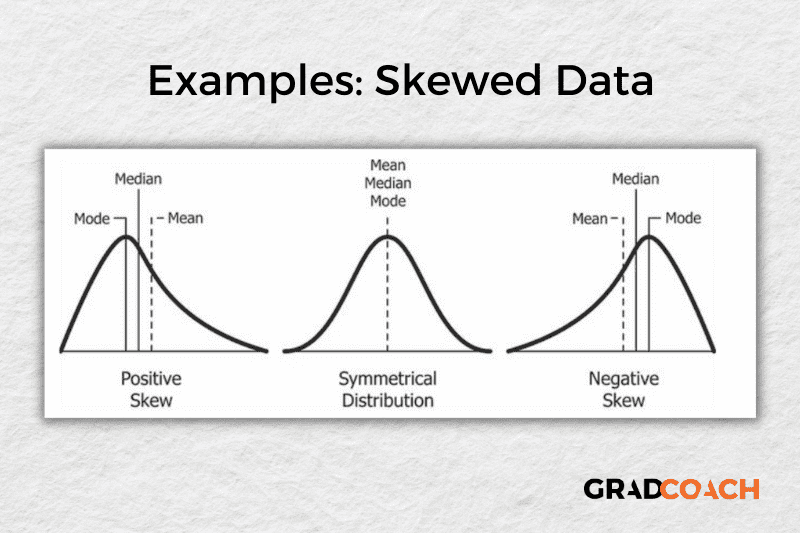
Measures of dispersion
While the measures of central tendency provide insight into how “centred” the dataset is, it’s also important to understand how dispersed that dataset is . In other words, to what extent the data cluster toward the centre – specifically, the mean. In some cases, the majority of the data points will sit very close to the centre, while in other cases, they’ll be scattered all over the place. Enter the measures of dispersion, of which there are three:
Range , which measures the difference between the largest and smallest number in the dataset. In other words, it indicates how spread out the dataset really is.
Variance , which measures how much each number in a dataset varies from the mean (average). More technically, it calculates the average of the squared differences between each number and the mean. A higher variance indicates that the data points are more spread out , while a lower variance suggests that the data points are closer to the mean.
Standard deviation , which is the square root of the variance . It serves the same purposes as the variance, but is a bit easier to interpret as it presents a figure that is in the same unit as the original data . You’ll typically present this statistic alongside the means when describing the data in your research.
Again, let’s look at our sample dataset to make this all a little more tangible.
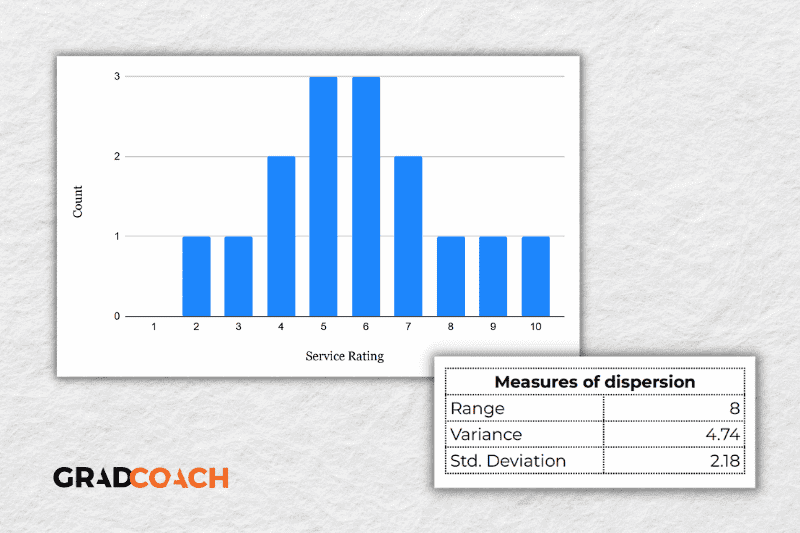
As you can see, the range of 8 reflects the difference between the highest rating (10) and the lowest rating (2). The standard deviation of 2.18 tells us that on average, results within the dataset are 2.18 away from the mean (of 5.8), reflecting a relatively dispersed set of data .
For the sake of comparison, let’s look at another much more tightly grouped (less dispersed) dataset.
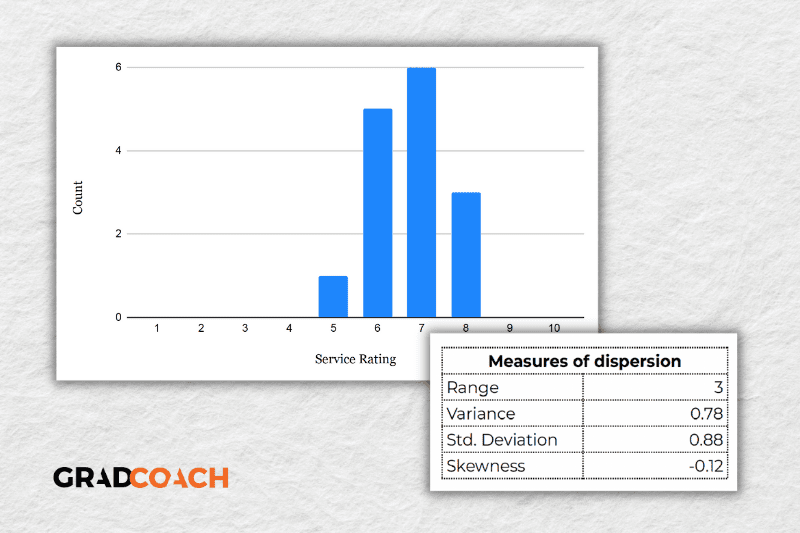
As you can see, all the ratings lay between 5 and 8 in this dataset, resulting in a much smaller range, variance and standard deviation . You might also notice that the data are clustered toward the right side of the graph – in other words, the data are skewed. If we calculate the skewness for this dataset, we get a result of -0.12, confirming this right lean.
In summary, range, variance and standard deviation all provide an indication of how dispersed the data are . These measures are important because they help you interpret the measures of central tendency within context . In other words, if your measures of dispersion are all fairly high numbers, you need to interpret your measures of central tendency with some caution , as the results are not particularly centred. Conversely, if the data are all tightly grouped around the mean (i.e., low dispersion), the mean becomes a much more “meaningful” statistic).
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered quite a bit of ground in this post. Here are the key takeaways:
- Descriptive statistics, although relatively simple, are a critically important part of any quantitative data analysis.
- Measures of central tendency include the mean (average), median and mode.
- Skewness indicates whether a dataset leans to one side or another
- Measures of dispersion include the range, variance and standard deviation
If you’d like hands-on help with your descriptive statistics (or any other aspect of your research project), check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through each step of the research journey.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Methodology Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

Good day. May I ask about where I would be able to find the statistics cheat sheet?
Right above you comment 🙂
Good job. you saved me
Brilliant and well explained. So much information explained clearly!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Chapter 14 Quantitative Analysis Descriptive Statistics
Numeric data collected in a research project can be analyzed quantitatively using statistical tools in two different ways. Descriptive analysis refers to statistically describing, aggregating, and presenting the constructs of interest or associations between these constructs. Inferential analysis refers to the statistical testing of hypotheses (theory testing). In this chapter, we will examine statistical techniques used for descriptive analysis, and the next chapter will examine statistical techniques for inferential analysis. Much of today’s quantitative data analysis is conducted using software programs such as SPSS or SAS. Readers are advised to familiarize themselves with one of these programs for understanding the concepts described in this chapter.
Data Preparation
In research projects, data may be collected from a variety of sources: mail-in surveys, interviews, pretest or posttest experimental data, observational data, and so forth. This data must be converted into a machine -readable, numeric format, such as in a spreadsheet or a text file, so that they can be analyzed by computer programs like SPSS or SAS. Data preparation usually follows the following steps.
Data coding. Coding is the process of converting data into numeric format. A codebook should be created to guide the coding process. A codebook is a comprehensive document containing detailed description of each variable in a research study, items or measures for that variable, the format of each item (numeric, text, etc.), the response scale for each item (i.e., whether it is measured on a nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio scale; whether such scale is a five-point, seven-point, or some other type of scale), and how to code each value into a numeric format. For instance, if we have a measurement item on a seven-point Likert scale with anchors ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”, we may code that item as 1 for strongly disagree, 4 for neutral, and 7 for strongly agree, with the intermediate anchors in between. Nominal data such as industry type can be coded in numeric form using a coding scheme such as: 1 for manufacturing, 2 for retailing, 3 for financial, 4 for healthcare, and so forth (of course, nominal data cannot be analyzed statistically). Ratio scale data such as age, income, or test scores can be coded as entered by the respondent. Sometimes, data may need to be aggregated into a different form than the format used for data collection. For instance, for measuring a construct such as “benefits of computers,” if a survey provided respondents with a checklist of b enefits that they could select from (i.e., they could choose as many of those benefits as they wanted), then the total number of checked items can be used as an aggregate measure of benefits. Note that many other forms of data, such as interview transcripts, cannot be converted into a numeric format for statistical analysis. Coding is especially important for large complex studies involving many variables and measurement items, where the coding process is conducted by different people, to help the coding team code data in a consistent manner, and also to help others understand and interpret the coded data.
Data entry. Coded data can be entered into a spreadsheet, database, text file, or directly into a statistical program like SPSS. Most statistical programs provide a data editor for entering data. However, these programs store data in their own native format (e.g., SPSS stores data as .sav files), which makes it difficult to share that data with other statistical programs. Hence, it is often better to enter data into a spreadsheet or database, where they can be reorganized as needed, shared across programs, and subsets of data can be extracted for analysis. Smaller data sets with less than 65,000 observations and 256 items can be stored in a spreadsheet such as Microsoft Excel, while larger dataset with millions of observations will require a database. Each observation can be entered as one row in the spreadsheet and each measurement item can be represented as one column. The entered data should be frequently checked for accuracy, via occasional spot checks on a set of items or observations, during and after entry. Furthermore, while entering data, the coder should watch out for obvious evidence of bad data, such as the respondent selecting the “strongly agree” response to all items irrespective of content, including reverse-coded items. If so, such data can be entered but should be excluded from subsequent analysis.
Missing values. Missing data is an inevitable part of any empirical data set. Respondents may not answer certain questions if they are ambiguously worded or too sensitive. Such problems should be detected earlier during pretests and corrected before the main data collection process begins. During data entry, some statistical programs automatically treat blank entries as missing values, while others require a specific numeric value such as -1 or 999 to be entered to denote a missing value. During data analysis, the default mode of handling missing values in most software programs is to simply drop the entire observation containing even a single missing value, in a technique called listwise deletion . Such deletion can significantly shrink the sample size and make it extremely difficult to detect small effects. Hence, some software programs allow the option of replacing missing values with an estimated value via a process called imputation . For instance, if the missing value is one item in a multi-item scale, the imputed value may be the average of the respondent’s responses to remaining items on that scale. If the missing value belongs to a single-item scale, many researchers use the average of other respondent’s responses to that item as the imputed value. Such imputation may be biased if the missing value is of a systematic nature rather than a random nature. Two methods that can produce relatively unbiased estimates for imputation are the maximum likelihood procedures and multiple imputation methods, both of which are supported in popular software programs such as SPSS and SAS.
Data transformation. Sometimes, it is necessary to transform data values before they can be meaningfully interpreted. For instance, reverse coded items, where items convey the opposite meaning of that of their underlying construct, should be reversed (e.g., in a 1-7 interval scale, 8 minus the observed value will reverse the value) before they can be compared or combined with items that are not reverse coded. Other kinds of transformations may include creating scale measures by adding individual scale items, creating a weighted index from a set of observed measures, and collapsing multiple values into fewer categories (e.g., collapsing incomes into income ranges).
Univariate Analysis
Univariate analysis, or analysis of a single variable, refers to a set of statistical techniques that can describe the general properties of one variable. Univariate statistics include: (1) frequency distribution, (2) central tendency, and (3) dispersion. The frequency distribution of a variable is a summary of the frequency (or percentages) of individual values or ranges of values for that variable. For instance, we can measure how many times a sample of respondents attend religious services (as a measure of their “religiosity”) using a categorical scale: never, once per year, several times per year, about once a month, several times per month, several times per week, and an optional category for “did not answer.” If we count the number (or percentage) of observations within each category (except “did not answer” which is really a missing value rather than a category), and display it in the form of a table as shown in Figure 14.1, what we have is a frequency distribution. This distribution can also be depicted in the form of a bar chart, as shown on the right panel of Figure 14.1, with the horizontal axis representing each category of that variable and the vertical axis representing the frequency or percentage of observations within each category.
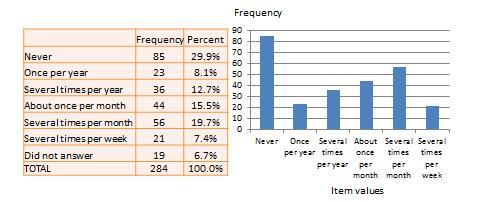
Figure 14.1. Frequency distribution of religiosity.
With very large samples where observations are independent and random, the frequency distribution tends to follow a plot that looked like a bell-shaped curve (a smoothed bar chart of the frequency distribution) similar to that shown in Figure 14.2, where most observations are clustered toward the center of the range of values, and fewer and fewer observations toward the extreme ends of the range. Such a curve is called a normal distribution.
Central tendency is an estimate of the center of a distribution of values. There are three major estimates of central tendency: mean, median, and mode. The arithmetic mean (often simply called the “mean”) is the simple average of all values in a given distribution. Consider a set of eight test scores: 15, 22, 21, 18, 36, 15, 25, 15. The arithmetic mean of these values is (15 + 20 + 21 + 20 + 36 + 15 + 25 + 15)/8 = 20.875. Other types of means include geometric mean (n th root of the product of n numbers in a distribution) and harmonic mean (the reciprocal of the arithmetic means of the reciprocal of each value in a distribution), but these means are not very popular for statistical analysis of social research data.
The second measure of central tendency, the median , is the middle value within a range of values in a distribution. This is computed by sorting all values in a distribution in increasing order and selecting the middle value. In case there are two middle values (if there is an even number of values in a distribution), the average of the two middle values represent the median. In the above example, the sorted values are: 15, 15, 15, 18, 22, 21, 25, 36. The two middle values are 18 and 22, and hence the median is (18 + 22)/2 = 20.
Lastly, the mode is the most frequently occurring value in a distribution of values. In the previous example, the most frequently occurring value is 15, which is the mode of the above set of test scores. Note that any value that is estimated from a sample, such as mean, median, mode, or any of the later estimates are called a statistic .
Dispersion refers to the way values are spread around the central tendency, for example, how tightly or how widely are the values clustered around the mean. Two common measures of dispersion are the range and standard deviation. The range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a distribution. The range in our previous example is 36-15 = 21.
The range is particularly sensitive to the presence of outliers. For instance, if the highest value in the above distribution was 85 and the other vales remained the same, the range would be 85-15 = 70. Standard deviation , the second measure of dispersion, corrects for such outliers by using a formula that takes into account how close or how far each value from the distribution mean:
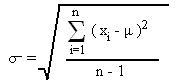
Figure 14.2. Normal distribution.
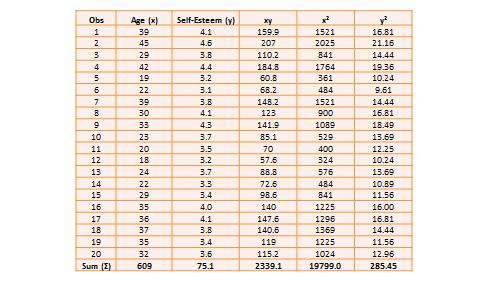
Table 14.1. Hypothetical data on age and self-esteem.
The two variables in this dataset are age (x) and self-esteem (y). Age is a ratio-scale variable, while self-esteem is an average score computed from a multi-item self-esteem scale measured using a 7-point Likert scale, ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree.” The histogram of each variable is shown on the left side of Figure 14.3. The formula for calculating bivariate correlation is:
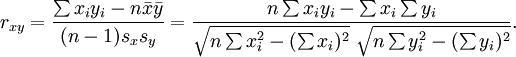
Figure 14.3. Histogram and correlation plot of age and self-esteem.
After computing bivariate correlation, researchers are often interested in knowing whether the correlation is significant (i.e., a real one) or caused by mere chance. Answering such a question would require testing the following hypothesis:
H 0 : r = 0
H 1 : r ≠ 0
H 0 is called the null hypotheses , and H 1 is called the alternative hypothesis (sometimes, also represented as H a ). Although they may seem like two hypotheses, H 0 and H 1 actually represent a single hypothesis since they are direct opposites of each other. We are interested in testing H 1 rather than H 0 . Also note that H 1 is a non-directional hypotheses since it does not specify whether r is greater than or less than zero. Directional hypotheses will be specified as H 0 : r ≤ 0; H 1 : r > 0 (if we are testing for a positive correlation). Significance testing of directional hypothesis is done using a one-tailed t-test, while that for non-directional hypothesis is done using a two-tailed t-test.
In statistical testing, the alternative hypothesis cannot be tested directly. Rather, it is tested indirectly by rejecting the null hypotheses with a certain level of probability. Statistical testing is always probabilistic, because we are never sure if our inferences, based on sample data, apply to the population, since our sample never equals the population. The probability that a statistical inference is caused pure chance is called the p-value . The p-value is compared with the significance level (α), which represents the maximum level of risk that we are willing to take that our inference is incorrect. For most statistical analysis, α is set to 0.05. A p-value less than α=0.05 indicates that we have enough statistical evidence to reject the null hypothesis, and thereby, indirectly accept the alternative hypothesis. If p>0.05, then we do not have adequate statistical evidence to reject the null hypothesis or accept the alternative hypothesis.
The easiest way to test for the above hypothesis is to look up critical values of r from statistical tables available in any standard text book on statistics or on the Internet (most software programs also perform significance testing). The critical value of r depends on our desired significance level (α = 0.05), the degrees of freedom (df), and whether the desired test is a one-tailed or two-tailed test. The degree of freedom is the number of values that can vary freely in any calculation of a statistic. In case of correlation, the df simply equals n – 2, or for the data in Table 14.1, df is 20 – 2 = 18. There are two different statistical tables for one-tailed and two -tailed test. In the two -tailed table, the critical value of r for α = 0.05 and df = 18 is 0.44. For our computed correlation of 0.79 to be significant, it must be larger than the critical value of 0.44 or less than -0.44. Since our computed value of 0.79 is greater than 0.44, we conclude that there is a significant correlation between age and self-esteem in our data set, or in other words, the odds are less than 5% that this correlation is a chance occurrence. Therefore, we can reject the null hypotheses that r ≤ 0, which is an indirect way of saying that the alternative hypothesis r > 0 is probably correct.
Most research studies involve more than two variables. If there are n variables, then we will have a total of n*(n-1)/2 possible correlations between these n variables. Such correlations are easily computed using a software program like SPSS, rather than manually using the formula for correlation (as we did in Table 14.1), and represented using a correlation matrix, as shown in Table 14.2. A correlation matrix is a matrix that lists the variable names along the first row and the first column, and depicts bivariate correlations between pairs of variables in the appropriate cell in the matrix. The values along the principal diagonal (from the top left to the bottom right corner) of this matrix are always 1, because any variable is always perfectly correlated with itself. Further, since correlations are non-directional, the correlation between variables V1 and V2 is the same as that between V2 and V1. Hence, the lower triangular matrix (values below the principal diagonal) is a mirror reflection of the upper triangular matrix (values above the principal diagonal), and therefore, we often list only the lower triangular matrix for simplicity. If the correlations involve variables measured using interval scales, then this specific type of correlations are called Pearson product moment correlations .
Another useful way of presenting bivariate data is cross-tabulation (often abbreviated to cross-tab, and sometimes called more formally as a contingency table). A cross-tab is a table that describes the frequency (or percentage) of all combinations of two or more nominal or categorical variables. As an example, let us assume that we have the following observations of gender and grade for a sample of 20 students, as shown in Figure 14.3. Gender is a nominal variable (male/female or M/F), and grade is a categorical variable with three levels (A, B, and C). A simple cross-tabulation of the data may display the joint distribution of gender and grades (i.e., how many students of each gender are in each grade category, as a raw frequency count or as a percentage) in a 2 x 3 matrix. This matrix will help us see if A, B, and C grades are equally distributed across male and female students. The cross-tab data in Table 14.3 shows that the distribution of A grades is biased heavily toward female students: in a sample of 10 male and 10 female students, five female students received the A grade compared to only one male students. In contrast, the distribution of C grades is biased toward male students: three male students received a C grade, compared to only one female student. However, the distribution of B grades was somewhat uniform, with six male students and five female students. The last row and the last column of this table are called marginal totals because they indicate the totals across each category and displayed along the margins of the table.
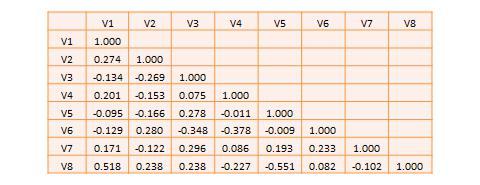
Table 14.2. A hypothetical correlation matrix for eight variables.
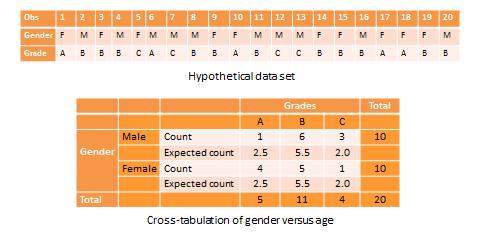
Table 14.3. Example of cross-tab analysis.
Although we can see a distinct pattern of grade distribution between male and female students in Table 14.3, is this pattern real or “statistically significant”? In other words, do the above frequency counts differ from that that may be expected from pure chance? To answer this question, we should compute the expected count of observation in each cell of the 2 x 3 cross-tab matrix. This is done by multiplying the marginal column total and the marginal row total for each cell and dividing it by the total number of observations. For example, for the male/A grade cell, expected count = 5 * 10 / 20 = 2.5. In other words, we were expecting 2.5 male students to receive an A grade, but in reality, only one student received the A grade. Whether this difference between expected and actual count is significant can be tested using a chi-square test . The chi-square statistic can be computed as the average difference between observed and expected counts across all cells. We can then compare this number to the critical value associated with a desired probability level (p < 0.05) and the degrees of freedom, which is simply (m-1)*(n-1), where m and n are the number of rows and columns respectively. In this example, df = (2 – 1) * (3 – 1) = 2. From standard chi-square tables in any statistics book, the critical chi-square value for p=0.05 and df=2 is 5.99. The computed chi -square value, based on our observed data, is 1.00, which is less than the critical value. Hence, we must conclude that the observed grade pattern is not statistically different from the pattern that can be expected by pure chance.
- Social Science Research: Principles, Methods, and Practices. Authored by : Anol Bhattacherjee. Provided by : University of South Florida. Located at : http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/oa_textbooks/3/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Presenting Descriptive Statistics
Cite this chapter.

- Lindy Woodrow 2
2141 Accesses
2 Citations
This chapter examines some of the issues raised in the previous chapter concerning demographic information about participants. One of the first steps a researcher takes in the analysis of data is to generate descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics simply describe the data provided by the participants. This can be contrasted with inferential statistics where data analysis can lead to conclusions about the population under consideration. Descriptive statistics are generated by computer software, such as SPSS, and help the researcher become familiar with the data. The chapter is about reporting descriptive statistics in a quantitative research text.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Further reading
Field, A., & Hole, G. (2003). How to design and report experiments . London: Sage.
Google Scholar
Lowie, W., & Seton, B. (2013). Essential statistics for Applied Linguistics . Basingstoke: Palgrave-Macmillan.
Pallant, J. (2010). SPSS survival manual . Maidenhead: Open University.
Sources of examples
Kondo-Brown, K. (2004). Investigating interviewer-candidate interactions during oral interviews for child L2 learners. Foreign Language Annals , 37(4), 602–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1944-9720.2004.tb02426x.
Article Google Scholar
Papi, M., & Teimouri, Y. (2012). Dynamics of selves and motivation: A cross-sectional study in the EFL context of Iran. International Journal of Applied Linguistics , 22(3), 287–rpl. doi: 10.1111/j.1473-4192.2012.00312.x.
Uggen, M.S. (2012). Reinvestigating the noticing function of output. Language Learning , 1–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9922.2012.00693.x.
Woodrow, L.J. (2006a). Academic success of international postgraduate education students and the role of English proficiency. University of Sydney Papers in TESOL , 1, 51–70.
Woodrow, L. J. (2006b). Anxiety and speaking English as a second language RELC Journal , 37(3), 308–328. doi: 0.1177/0033688206071315
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Sydney, Australia
Lindy Woodrow
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Copyright information
© 2014 Lindy Woodrow
About this chapter
Woodrow, L. (2014). Presenting Descriptive Statistics. In: Writing about Quantitative Research in Applied Linguistics. Palgrave Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230369955_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230369955_5
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, London
Print ISBN : 978-0-230-36997-9
Online ISBN : 978-0-230-36995-5
eBook Packages : Palgrave Language & Linguistics Collection Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

12 Quantitative Descriptive and Correlational Research
- Published: February 2023
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter presents research designs for descriptive and correlational quantitative research. Descriptive research designs are used to address the question “What is x?” Correlational research designs are used to address the question “How are things related?” In contrast to some experimental research designs, in these design types the primary area of interest under investigation is not manipulated by the researcher. Researchers investigating descriptive or correlational research questions commonly use surveys or observational methods to gather data. Surveys are an efficient method for gathering large amounts of information about such things as individuals’ experiences, beliefs, and attitudes. When designing a survey, researchers must consider many things, such as how long it will be and what it will cover. Observation is an important means of gathering data, as when researchers observe video recordings of teachers or students in various situations. Another approach to observational research is the experience sampling method (ESM). In ESM, participants are interrupted at random times throughout the day and asked to respond to questions concerning their experiences in real time. In other words, researchers ask participants what they are doing at the moment they are contacted.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Descriptive Statistics | Definitions, Types, Examples
Published on 4 November 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 9 January 2023.
Descriptive statistics summarise and organise characteristics of a data set. A data set is a collection of responses or observations from a sample or entire population .
In quantitative research , after collecting data, the first step of statistical analysis is to describe characteristics of the responses, such as the average of one variable (e.g., age), or the relation between two variables (e.g., age and creativity).
The next step is inferential statistics , which help you decide whether your data confirms or refutes your hypothesis and whether it is generalisable to a larger population.
Table of contents
Types of descriptive statistics, frequency distribution, measures of central tendency, measures of variability, univariate descriptive statistics, bivariate descriptive statistics, frequently asked questions.
There are 3 main types of descriptive statistics:
- The distribution concerns the frequency of each value.
- The central tendency concerns the averages of the values.
- The variability or dispersion concerns how spread out the values are.
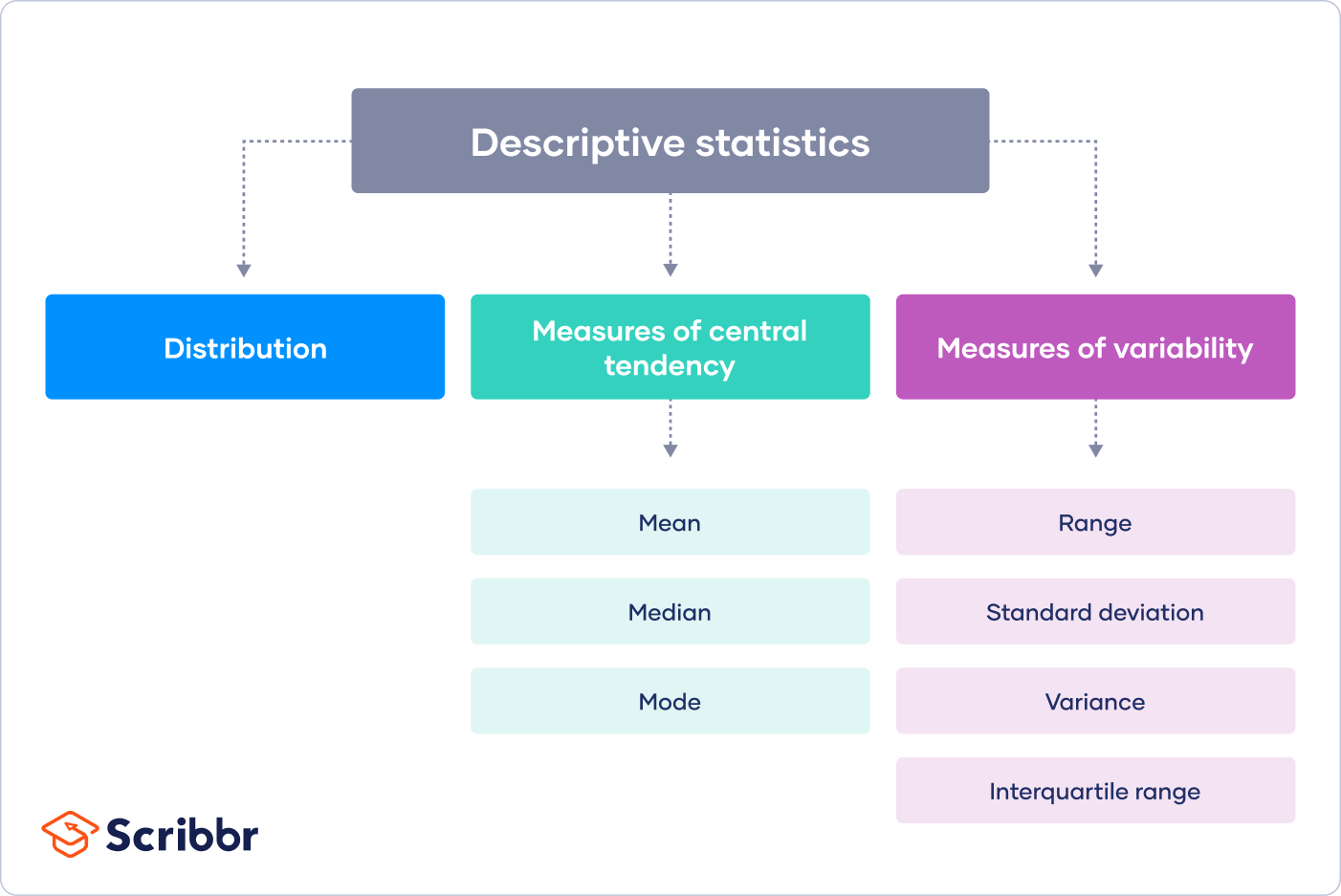
You can apply these to assess only one variable at a time, in univariate analysis, or to compare two or more, in bivariate and multivariate analysis.
- Go to a library
- Watch a movie at a theater
- Visit a national park
A data set is made up of a distribution of values, or scores. In tables or graphs, you can summarise the frequency of every possible value of a variable in numbers or percentages.
- Simple frequency distribution table
- Grouped frequency distribution table
From this table, you can see that more women than men or people with another gender identity took part in the study. In a grouped frequency distribution, you can group numerical response values and add up the number of responses for each group. You can also convert each of these numbers to percentages.
Measures of central tendency estimate the center, or average, of a data set. The mean , median and mode are 3 ways of finding the average.
Here we will demonstrate how to calculate the mean, median, and mode using the first 6 responses of our survey.
The mean , or M , is the most commonly used method for finding the average.
To find the mean, simply add up all response values and divide the sum by the total number of responses. The total number of responses or observations is called N .
The median is the value that’s exactly in the middle of a data set.
To find the median, order each response value from the smallest to the biggest. Then, the median is the number in the middle. If there are two numbers in the middle, find their mean.
The mode is the simply the most popular or most frequent response value. A data set can have no mode, one mode, or more than one mode.
To find the mode, order your data set from lowest to highest and find the response that occurs most frequently.
Measures of variability give you a sense of how spread out the response values are. The range, standard deviation and variance each reflect different aspects of spread.
The range gives you an idea of how far apart the most extreme response scores are. To find the range , simply subtract the lowest value from the highest value.
Standard deviation
The standard deviation ( s ) is the average amount of variability in your dataset. It tells you, on average, how far each score lies from the mean. The larger the standard deviation, the more variable the data set is.
There are six steps for finding the standard deviation:
- List each score and find their mean.
- Subtract the mean from each score to get the deviation from the mean.
- Square each of these deviations.
- Add up all of the squared deviations.
- Divide the sum of the squared deviations by N – 1.
- Find the square root of the number you found.
Step 5: 421.5/5 = 84.3
Step 6: √84.3 = 9.18
The variance is the average of squared deviations from the mean. Variance reflects the degree of spread in the data set. The more spread the data, the larger the variance is in relation to the mean.
To find the variance, simply square the standard deviation. The symbol for variance is s 2 .
Univariate descriptive statistics focus on only one variable at a time. It’s important to examine data from each variable separately using multiple measures of distribution, central tendency and spread. Programs like SPSS and Excel can be used to easily calculate these.
If you were to only consider the mean as a measure of central tendency, your impression of the ‘middle’ of the data set can be skewed by outliers, unlike the median or mode.
Likewise, while the range is sensitive to extreme values, you should also consider the standard deviation and variance to get easily comparable measures of spread.
If you’ve collected data on more than one variable, you can use bivariate or multivariate descriptive statistics to explore whether there are relationships between them.
In bivariate analysis, you simultaneously study the frequency and variability of two variables to see if they vary together. You can also compare the central tendency of the two variables before performing further statistical tests .
Multivariate analysis is the same as bivariate analysis but with more than two variables.
Contingency table
In a contingency table, each cell represents the intersection of two variables. Usually, an independent variable (e.g., gender) appears along the vertical axis and a dependent one appears along the horizontal axis (e.g., activities). You read ‘across’ the table to see how the independent and dependent variables relate to each other.
Interpreting a contingency table is easier when the raw data is converted to percentages. Percentages make each row comparable to the other by making it seem as if each group had only 100 observations or participants. When creating a percentage-based contingency table, you add the N for each independent variable on the end.
From this table, it is more clear that similar proportions of children and adults go to the library over 17 times a year. Additionally, children most commonly went to the library between 5 and 8 times, while for adults, this number was between 13 and 16.
Scatter plots
A scatter plot is a chart that shows you the relationship between two or three variables. It’s a visual representation of the strength of a relationship.
In a scatter plot, you plot one variable along the x-axis and another one along the y-axis. Each data point is represented by a point in the chart.
From your scatter plot, you see that as the number of movies seen at movie theaters increases, the number of visits to the library decreases. Based on your visual assessment of a possible linear relationship, you perform further tests of correlation and regression.
Descriptive statistics summarise the characteristics of a data set. Inferential statistics allow you to test a hypothesis or assess whether your data is generalisable to the broader population.
The 3 main types of descriptive statistics concern the frequency distribution, central tendency, and variability of a dataset.
- Distribution refers to the frequencies of different responses.
- Measures of central tendency give you the average for each response.
- Measures of variability show you the spread or dispersion of your dataset.
- Univariate statistics summarise only one variable at a time.
- Bivariate statistics compare two variables .
- Multivariate statistics compare more than two variables .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 09). Descriptive Statistics | Definitions, Types, Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/stats/descriptive-statistics-explained/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, data collection methods | step-by-step guide & examples, variability | calculating range, iqr, variance, standard deviation, normal distribution | examples, formulas, & uses.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Descriptive Research: Definition, Characteristics, Methods + Examples

Suppose an apparel brand wants to understand the fashion purchasing trends among New York’s buyers, then it must conduct a demographic survey of the specific region, gather population data, and then conduct descriptive research on this demographic segment.
The study will then uncover details on “what is the purchasing pattern of New York buyers,” but will not cover any investigative information about “ why ” the patterns exist. Because for the apparel brand trying to break into this market, understanding the nature of their market is the study’s main goal. Let’s talk about it.
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a research method describing the characteristics of the population or phenomenon studied. This descriptive methodology focuses more on the “what” of the research subject than the “why” of the research subject.
The method primarily focuses on describing the nature of a demographic segment without focusing on “why” a particular phenomenon occurs. In other words, it “describes” the research subject without covering “why” it happens.
Characteristics of descriptive research
The term descriptive research then refers to research questions, the design of the study, and data analysis conducted on that topic. We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity.
Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are:
- Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment’s nature.
- Uncontrolled variables: In it, none of the variables are influenced in any way. This uses observational methods to conduct the research. Hence, the nature of the variables or their behavior is not in the hands of the researcher.
- Cross-sectional studies: It is generally a cross-sectional study where different sections belonging to the same group are studied.
- The basis for further research: Researchers further research the data collected and analyzed from descriptive research using different research techniques. The data can also help point towards the types of research methods used for the subsequent research.
Applications of descriptive research with examples
A descriptive research method can be used in multiple ways and for various reasons. Before getting into any survey , though, the survey goals and survey design are crucial. Despite following these steps, there is no way to know if one will meet the research outcome. How to use descriptive research? To understand the end objective of research goals, below are some ways organizations currently use descriptive research today:
- Define respondent characteristics: The aim of using close-ended questions is to draw concrete conclusions about the respondents. This could be the need to derive patterns, traits, and behaviors of the respondents. It could also be to understand from a respondent their attitude, or opinion about the phenomenon. For example, understand millennials and the hours per week they spend browsing the internet. All this information helps the organization researching to make informed business decisions.
- Measure data trends: Researchers measure data trends over time with a descriptive research design’s statistical capabilities. Consider if an apparel company researches different demographics like age groups from 24-35 and 36-45 on a new range launch of autumn wear. If one of those groups doesn’t take too well to the new launch, it provides insight into what clothes are like and what is not. The brand drops the clothes and apparel that customers don’t like.
- Conduct comparisons: Organizations also use a descriptive research design to understand how different groups respond to a specific product or service. For example, an apparel brand creates a survey asking general questions that measure the brand’s image. The same study also asks demographic questions like age, income, gender, geographical location, geographic segmentation , etc. This consumer research helps the organization understand what aspects of the brand appeal to the population and what aspects do not. It also helps make product or marketing fixes or even create a new product line to cater to high-growth potential groups.
- Validate existing conditions: Researchers widely use descriptive research to help ascertain the research object’s prevailing conditions and underlying patterns. Due to the non-invasive research method and the use of quantitative observation and some aspects of qualitative observation , researchers observe each variable and conduct an in-depth analysis . Researchers also use it to validate any existing conditions that may be prevalent in a population.
- Conduct research at different times: The analysis can be conducted at different periods to ascertain any similarities or differences. This also allows any number of variables to be evaluated. For verification, studies on prevailing conditions can also be repeated to draw trends.
Advantages of descriptive research
Some of the significant advantages of descriptive research are:

- Data collection: A researcher can conduct descriptive research using specific methods like observational method, case study method, and survey method. Between these three, all primary data collection methods are covered, which provides a lot of information. This can be used for future research or even for developing a hypothesis for your research object.
- Varied: Since the data collected is qualitative and quantitative, it gives a holistic understanding of a research topic. The information is varied, diverse, and thorough.
- Natural environment: Descriptive research allows for the research to be conducted in the respondent’s natural environment, which ensures that high-quality and honest data is collected.
- Quick to perform and cheap: As the sample size is generally large in descriptive research, the data collection is quick to conduct and is inexpensive.
Descriptive research methods
There are three distinctive methods to conduct descriptive research. They are:
Observational method
The observational method is the most effective method to conduct this research, and researchers make use of both quantitative and qualitative observations.
A quantitative observation is the objective collection of data primarily focused on numbers and values. It suggests “associated with, of or depicted in terms of a quantity.” Results of quantitative observation are derived using statistical and numerical analysis methods. It implies observation of any entity associated with a numeric value such as age, shape, weight, volume, scale, etc. For example, the researcher can track if current customers will refer the brand using a simple Net Promoter Score question .
Qualitative observation doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead just monitoring characteristics. In this case, the researcher observes the respondents from a distance. Since the respondents are in a comfortable environment, the characteristics observed are natural and effective. In a descriptive research design, the researcher can choose to be either a complete observer, an observer as a participant, a participant as an observer, or a full participant. For example, in a supermarket, a researcher can from afar monitor and track the customers’ selection and purchasing trends. This offers a more in-depth insight into the purchasing experience of the customer.
Case study method
Case studies involve in-depth research and study of individuals or groups. Case studies lead to a hypothesis and widen a further scope of studying a phenomenon. However, case studies should not be used to determine cause and effect as they can’t make accurate predictions because there could be a bias on the researcher’s part. The other reason why case studies are not a reliable way of conducting descriptive research is that there could be an atypical respondent in the survey. Describing them leads to weak generalizations and moving away from external validity.
Survey research
In survey research, respondents answer through surveys or questionnaires or polls . They are a popular market research tool to collect feedback from respondents. A study to gather useful data should have the right survey questions. It should be a balanced mix of open-ended questions and close ended-questions . The survey method can be conducted online or offline, making it the go-to option for descriptive research where the sample size is enormous.
Examples of descriptive research
Some examples of descriptive research are:
- A specialty food group launching a new range of barbecue rubs would like to understand what flavors of rubs are favored by different people. To understand the preferred flavor palette, they conduct this type of research study using various methods like observational methods in supermarkets. By also surveying while collecting in-depth demographic information, offers insights about the preference of different markets. This can also help tailor make the rubs and spreads to various preferred meats in that demographic. Conducting this type of research helps the organization tweak their business model and amplify marketing in core markets.
- Another example of where this research can be used is if a school district wishes to evaluate teachers’ attitudes about using technology in the classroom. By conducting surveys and observing their comfortableness using technology through observational methods, the researcher can gauge what they can help understand if a full-fledged implementation can face an issue. This also helps in understanding if the students are impacted in any way with this change.
Some other research problems and research questions that can lead to descriptive research are:
- Market researchers want to observe the habits of consumers.
- A company wants to evaluate the morale of its staff.
- A school district wants to understand if students will access online lessons rather than textbooks.
- To understand if its wellness questionnaire programs enhance the overall health of the employees.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
MORE LIKE THIS
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024

Pricing Analytics Software: Optimize Your Pricing Strategy
May 13, 2024

Relationship Marketing: What It Is, Examples & Top 7 Benefits
May 8, 2024

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Descriptive Statistics: Reporting the Answers to the 5 Basic Questions of Who, What, Why, When, Where, and a Sixth, So What?
Affiliation.
- 1 From the Department of Surgery and Perioperative Care, Dell Medical School at the University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas.
- PMID: 28891910
- DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002471
Descriptive statistics are specific methods basically used to calculate, describe, and summarize collected research data in a logical, meaningful, and efficient way. Descriptive statistics are reported numerically in the manuscript text and/or in its tables, or graphically in its figures. This basic statistical tutorial discusses a series of fundamental concepts about descriptive statistics and their reporting. The mean, median, and mode are 3 measures of the center or central tendency of a set of data. In addition to a measure of its central tendency (mean, median, or mode), another important characteristic of a research data set is its variability or dispersion (ie, spread). In simplest terms, variability is how much the individual recorded scores or observed values differ from one another. The range, standard deviation, and interquartile range are 3 measures of variability or dispersion. The standard deviation is typically reported for a mean, and the interquartile range for a median. Testing for statistical significance, along with calculating the observed treatment effect (or the strength of the association between an exposure and an outcome), and generating a corresponding confidence interval are 3 tools commonly used by researchers (and their collaborating biostatistician or epidemiologist) to validly make inferences and more generalized conclusions from their collected data and descriptive statistics. A number of journals, including Anesthesia & Analgesia, strongly encourage or require the reporting of pertinent confidence intervals. A confidence interval can be calculated for virtually any variable or outcome measure in an experimental, quasi-experimental, or observational research study design. Generally speaking, in a clinical trial, the confidence interval is the range of values within which the true treatment effect in the population likely resides. In an observational study, the confidence interval is the range of values within which the true strength of the association between the exposure and the outcome (eg, the risk ratio or odds ratio) in the population likely resides. There are many possible ways to graphically display or illustrate different types of data. While there is often latitude as to the choice of format, ultimately, the simplest and most comprehensible format is preferred. Common examples include a histogram, bar chart, line chart or line graph, pie chart, scatterplot, and box-and-whisker plot. Valid and reliable descriptive statistics can answer basic yet important questions about a research data set, namely: "Who, What, Why, When, Where, How, How Much?"
- Analysis of Variance
- Biomedical Research / statistics & numerical data*
- Computer Graphics
- Confidence Intervals
- Data Collection / statistics & numerical data*
- Data Interpretation, Statistical*
- Models, Statistical*
- Research Design / statistics & numerical data*
- Sample Size

Quantitative Research Methods
- Introduction
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Hypothesis Testing
- Regression and Correlation
- Time Series
- Meta-Analysis
- Mixed Methods
- Additional Resources
- Get Research Help
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics capture information about a sample in a single number. There are many statistical measures that fall under the umbrella of descriptive statistics, such as mean, median, standard deviation, and variance. These measures are often divided into two categories:
1. Measures of Central Tendency: Measures of central tendency represent the center or middle of a sample. The most commonly used measures of central tendency are the mean, the median, and the mode, all of which calculate the "center" differently.
2. Measures of Dispersion: Measures of dispersion show how spread out the data is. Examples of measures of dispersion include standard deviation, variance, and range. Newer methods include the translated biweight S (TBS) estimator and tau measure of scale, which are better when trying to protect against outliers.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics make inferences about a population from a sample. Two different inferential statistics that will be covered in this online guide are tests of difference and regression.
1. Tests of Difference: Tests of difference compare two samples to infer whether the populations they represent have different values of some descriptive statistic. Some of the most common tests of difference are t-tests, ANOVA, and Chi-square. Some of the most common non-parametric tests include the Mann-Whitney, Wilcoxon, Kruskal-Wallis, and Friedman tests.
2. Regression : Regression estimates the relationship between two or more variables in the population. Simple linear regression and multiple regression are commonly used methods.
Statistical Notation and Symbols
Mathematical shorthand is used throughout statistics. X is often used to represent an independent variable and Y is often used to represent a dependent variable. In addition, you are likely to see Greek letters like μ (pronounced mu), which signifies the population mean. The statistical symbols that represent the population are different from those that represent the sample. For example, the population mean has a different symbol than the sample mean.
- List of Probability and Statistics Symbols Math Vault article.
- Population Symbols and Their Corresponding Sample Symbols Statistics for Dummies article.
- Statistical Language Australian Bureau of Statistics resource.
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Hypothesis Testing >>
- Last Updated: Aug 18, 2023 11:55 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duq.edu/quant-methods
- Privacy Policy

Home » Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Descriptive Research Design
Definition:
Descriptive research design is a type of research methodology that aims to describe or document the characteristics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions, or perceptions of a group or population being studied.
Descriptive research design does not attempt to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables or make predictions about future outcomes. Instead, it focuses on providing a detailed and accurate representation of the data collected, which can be useful for generating hypotheses, exploring trends, and identifying patterns in the data.
Types of Descriptive Research Design
Types of Descriptive Research Design are as follows:
Cross-sectional Study
This involves collecting data at a single point in time from a sample or population to describe their characteristics or behaviors. For example, a researcher may conduct a cross-sectional study to investigate the prevalence of certain health conditions among a population, or to describe the attitudes and beliefs of a particular group.
Longitudinal Study
This involves collecting data over an extended period of time, often through repeated observations or surveys of the same group or population. Longitudinal studies can be used to track changes in attitudes, behaviors, or outcomes over time, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
This involves an in-depth examination of a single individual, group, or situation to gain a detailed understanding of its characteristics or dynamics. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and business to explore complex phenomena or to generate hypotheses for further research.
Survey Research
This involves collecting data from a sample or population through standardized questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can be used to describe attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or demographic characteristics of a group, and can be conducted in person, by phone, or online.
Observational Research
This involves observing and documenting the behavior or interactions of individuals or groups in a natural or controlled setting. Observational studies can be used to describe social, cultural, or environmental phenomena, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
Correlational Research
This involves examining the relationships between two or more variables to describe their patterns or associations. Correlational studies can be used to identify potential causal relationships or to explore the strength and direction of relationships between variables.
Data Analysis Methods
Descriptive research design data analysis methods depend on the type of data collected and the research question being addressed. Here are some common methods of data analysis for descriptive research:
Descriptive Statistics
This method involves analyzing data to summarize and describe the key features of a sample or population. Descriptive statistics can include measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (e.g., range, standard deviation).
Cross-tabulation
This method involves analyzing data by creating a table that shows the frequency of two or more variables together. Cross-tabulation can help identify patterns or relationships between variables.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing qualitative data (e.g., text, images, audio) to identify themes, patterns, or trends. Content analysis can be used to describe the characteristics of a sample or population, or to identify factors that influence attitudes or behaviors.

Qualitative Coding
This method involves analyzing qualitative data by assigning codes to segments of data based on their meaning or content. Qualitative coding can be used to identify common themes, patterns, or categories within the data.
Visualization
This method involves creating graphs or charts to represent data visually. Visualization can help identify patterns or relationships between variables and make it easier to communicate findings to others.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing data across different groups or time periods to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can help describe changes in attitudes or behaviors over time or differences between subgroups within a population.
Applications of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has numerous applications in various fields. Some of the common applications of descriptive research design are:
- Market research: Descriptive research design is widely used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes. This helps companies to develop new products and services, improve marketing strategies, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is used in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population. This helps healthcare providers to develop prevention and treatment strategies.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs. This helps educators to improve teaching methods and develop effective educational programs.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs. This helps researchers to understand social behavior and develop effective policies.
- Public opinion research: Descriptive research design is used in public opinion research to understand the opinions and attitudes of the general public on various issues. This helps policymakers to develop effective policies that are aligned with public opinion.
- Environmental research: Descriptive research design is used in environmental research to describe the environmental conditions of a particular region or ecosystem. This helps policymakers and environmentalists to develop effective conservation and preservation strategies.
Descriptive Research Design Examples
Here are some real-time examples of descriptive research designs:
- A restaurant chain wants to understand the demographics and attitudes of its customers. They conduct a survey asking customers about their age, gender, income, frequency of visits, favorite menu items, and overall satisfaction. The survey data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to describe the characteristics of their customer base.
- A medical researcher wants to describe the prevalence and risk factors of a particular disease in a population. They conduct a cross-sectional study in which they collect data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to identify patterns in the prevalence and risk factors of the disease.
- An education researcher wants to describe the learning outcomes of students in a particular school district. They collect test scores from a representative sample of students in the district and use descriptive statistics to calculate the mean, median, and standard deviation of the scores. They also create visualizations such as histograms and box plots to show the distribution of scores.
- A marketing team wants to understand the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards a new product. They conduct a series of focus groups and use qualitative coding to identify common themes and patterns in the data. They also create visualizations such as word clouds to show the most frequently mentioned topics.
- An environmental scientist wants to describe the biodiversity of a particular ecosystem. They conduct an observational study in which they collect data on the species and abundance of plants and animals in the ecosystem. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics to describe the diversity and richness of the ecosystem.
How to Conduct Descriptive Research Design
To conduct a descriptive research design, you can follow these general steps:
- Define your research question: Clearly define the research question or problem that you want to address. Your research question should be specific and focused to guide your data collection and analysis.
- Choose your research method: Select the most appropriate research method for your research question. As discussed earlier, common research methods for descriptive research include surveys, case studies, observational studies, cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal studies.
- Design your study: Plan the details of your study, including the sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis plan. Determine the sample size and sampling method, decide on the data collection tools (such as questionnaires, interviews, or observations), and outline your data analysis plan.
- Collect data: Collect data from your sample or population using the data collection tools you have chosen. Ensure that you follow ethical guidelines for research and obtain informed consent from participants.
- Analyze data: Use appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis methods to analyze your data. As discussed earlier, common data analysis methods for descriptive research include descriptive statistics, cross-tabulation, content analysis, qualitative coding, visualization, and comparative analysis.
- I nterpret results: Interpret your findings in light of your research question and objectives. Identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data, and describe the characteristics of your sample or population.
- Draw conclusions and report results: Draw conclusions based on your analysis and interpretation of the data. Report your results in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate tables, graphs, or figures to present your findings. Ensure that your report follows accepted research standards and guidelines.
When to Use Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used in situations where the researcher wants to describe a population or phenomenon in detail. It is used to gather information about the current status or condition of a group or phenomenon without making any causal inferences. Descriptive research design is useful in the following situations:
- Exploratory research: Descriptive research design is often used in exploratory research to gain an initial understanding of a phenomenon or population.
- Identifying trends: Descriptive research design can be used to identify trends or patterns in a population, such as changes in consumer behavior or attitudes over time.
- Market research: Descriptive research design is commonly used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is useful in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs.
Purpose of Descriptive Research Design
The main purpose of descriptive research design is to describe and measure the characteristics of a population or phenomenon in a systematic and objective manner. It involves collecting data that describe the current status or condition of the population or phenomenon of interest, without manipulating or altering any variables.
The purpose of descriptive research design can be summarized as follows:
- To provide an accurate description of a population or phenomenon: Descriptive research design aims to provide a comprehensive and accurate description of a population or phenomenon of interest. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon.
- To identify trends and patterns: Descriptive research design can help researchers to identify trends and patterns in the data, such as changes in behavior or attitudes over time. This can be useful for making predictions and developing strategies.
- To generate hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- To establish a baseline: Descriptive research design can establish a baseline or starting point for future research. This can be useful for comparing data from different time periods or populations.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several key characteristics that distinguish it from other research designs. Some of the main characteristics of descriptive research design are:
- Objective : Descriptive research design is objective in nature, which means that it focuses on collecting factual and accurate data without any personal bias. The researcher aims to report the data objectively without any personal interpretation.
- Non-experimental: Descriptive research design is non-experimental, which means that the researcher does not manipulate any variables. The researcher simply observes and records the behavior or characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Quantitative : Descriptive research design is quantitative in nature, which means that it involves collecting numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. This helps to provide a more precise and accurate description of the population or phenomenon.
- Cross-sectional: Descriptive research design is often cross-sectional, which means that the data is collected at a single point in time. This can be useful for understanding the current state of the population or phenomenon, but it may not provide information about changes over time.
- Large sample size: Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Systematic and structured: Descriptive research design involves a systematic and structured approach to data collection, which helps to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This involves using standardized procedures for data collection, such as surveys, questionnaires, or observation checklists.
Advantages of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several advantages that make it a popular choice for researchers. Some of the main advantages of descriptive research design are:
- Provides an accurate description: Descriptive research design is focused on accurately describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the subject of interest.
- Easy to conduct: Descriptive research design is relatively easy to conduct and requires minimal resources compared to other research designs. It can be conducted quickly and efficiently, and data can be collected through surveys, questionnaires, or observations.
- Useful for generating hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- Large sample size : Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Can be used to monitor changes : Descriptive research design can be used to monitor changes over time in a population or phenomenon. This can be useful for identifying trends and patterns, and for making predictions about future behavior or attitudes.
- Can be used in a variety of fields : Descriptive research design can be used in a variety of fields, including social sciences, healthcare, business, and education.
Limitation of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design also has some limitations that researchers should consider before using this design. Some of the main limitations of descriptive research design are:
- Cannot establish cause and effect: Descriptive research design cannot establish cause and effect relationships between variables. It only provides a description of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited generalizability: The results of a descriptive study may not be generalizable to other populations or situations. This is because descriptive research design often involves a specific sample or situation, which may not be representative of the broader population.
- Potential for bias: Descriptive research design can be subject to bias, particularly if the researcher is not objective in their data collection or interpretation. This can lead to inaccurate or incomplete descriptions of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited depth: Descriptive research design may provide a superficial description of the population or phenomenon of interest. It does not delve into the underlying causes or mechanisms behind the observed behavior or characteristics.
- Limited utility for theory development: Descriptive research design may not be useful for developing theories about the relationship between variables. It only provides a description of the variables themselves.
- Relies on self-report data: Descriptive research design often relies on self-report data, such as surveys or questionnaires. This type of data may be subject to biases, such as social desirability bias or recall bias.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.14: Chapter 14 Quantitative Analysis Descriptive Statistics
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 84790

- William Pelz
- Herkimer College via Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Numeric data collected in a research project can be analyzed quantitatively using statistical tools in two different ways. Descriptive analysis refers to statistically describing, aggregating, and presenting the constructs of interest or associations between these constructs. Inferential analysis refers to the statistical testing of hypotheses (theory testing). In this chapter, we will examine statistical techniques used for descriptive analysis, and the next chapter will examine statistical techniques for inferential analysis. Much of today’s quantitative data analysis is conducted using software programs such as SPSS or SAS. Readers are advised to familiarize themselves with one of these programs for understanding the concepts described in this chapter.
Data Preparation
In research projects, data may be collected from a variety of sources: mail-in surveys, interviews, pretest or posttest experimental data, observational data, and so forth. This data must be converted into a machine -readable, numeric format, such as in a spreadsheet or a text file, so that they can be analyzed by computer programs like SPSS or SAS. Data preparation usually follows the following steps.
Data coding. Coding is the process of converting data into numeric format. A codebook should be created to guide the coding process. A codebook is a comprehensive document containing detailed description of each variable in a research study, items or measures for that variable, the format of each item (numeric, text, etc.), the response scale for each item (i.e., whether it is measured on a nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio scale; whether such scale is a five-point, seven-point, or some other type of scale), and how to code each value into a numeric format. For instance, if we have a measurement item on a seven-point Likert scale with anchors ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”, we may code that item as 1 for strongly disagree, 4 for neutral, and 7 for strongly agree, with the intermediate anchors in between. Nominal data such as industry type can be coded in numeric form using a coding scheme such as: 1 for manufacturing, 2 for retailing, 3 for financial, 4 for healthcare, and so forth (of course, nominal data cannot be analyzed statistically). Ratio scale data such as age, income, or test scores can be coded as entered by the respondent. Sometimes, data may need to be aggregated into a different form than the format used for data collection. For instance, for measuring a construct such as “benefits of computers,” if a survey provided respondents with a checklist of b enefits that they could select from (i.e., they could choose as many of those benefits as they wanted), then the total number of checked items can be used as an aggregate measure of benefits. Note that many other forms of data, such as interview transcripts, cannot be converted into a numeric format for statistical analysis. Coding is especially important for large complex studies involving many variables and measurement items, where the coding process is conducted by different people, to help the coding team code data in a consistent manner, and also to help others understand and interpret the coded data.
Data entry. Coded data can be entered into a spreadsheet, database, text file, or directly into a statistical program like SPSS. Most statistical programs provide a data editor for entering data. However, these programs store data in their own native format (e.g., SPSS stores data as .sav files), which makes it difficult to share that data with other statistical programs. Hence, it is often better to enter data into a spreadsheet or database, where they can be reorganized as needed, shared across programs, and subsets of data can be extracted for analysis. Smaller data sets with less than 65,000 observations and 256 items can be stored in a spreadsheet such as Microsoft Excel, while larger dataset with millions of observations will require a database. Each observation can be entered as one row in the spreadsheet and each measurement item can be represented as one column. The entered data should be frequently checked for accuracy, via occasional spot checks on a set of items or observations, during and after entry. Furthermore, while entering data, the coder should watch out for obvious evidence of bad data, such as the respondent selecting the “strongly agree” response to all items irrespective of content, including reverse-coded items. If so, such data can be entered but should be excluded from subsequent analysis.
Missing values. Missing data is an inevitable part of any empirical data set. Respondents may not answer certain questions if they are ambiguously worded or too sensitive. Such problems should be detected earlier during pretests and corrected before the main data collection process begins. During data entry, some statistical programs automatically treat blank entries as missing values, while others require a specific numeric value such as -1 or 999 to be entered to denote a missing value. During data analysis, the default mode of handling missing values in most software programs is to simply drop the entire observation containing even a single missing value, in a technique called listwise deletion . Such deletion can significantly shrink the sample size and make it extremely difficult to detect small effects. Hence, some software programs allow the option of replacing missing values with an estimated value via a process called imputation . For instance, if the missing value is one item in a multi-item scale, the imputed value may be the average of the respondent’s responses to remaining items on that scale. If the missing value belongs to a single-item scale, many researchers use the average of other respondent’s responses to that item as the imputed value. Such imputation may be biased if the missing value is of a systematic nature rather than a random nature. Two methods that can produce relatively unbiased estimates for imputation are the maximum likelihood procedures and multiple imputation methods, both of which are supported in popular software programs such as SPSS and SAS.
Data transformation. Sometimes, it is necessary to transform data values before they can be meaningfully interpreted. For instance, reverse coded items, where items convey the opposite meaning of that of their underlying construct, should be reversed (e.g., in a 1-7 interval scale, 8 minus the observed value will reverse the value) before they can be compared or combined with items that are not reverse coded. Other kinds of transformations may include creating scale measures by adding individual scale items, creating a weighted index from a set of observed measures, and collapsing multiple values into fewer categories (e.g., collapsing incomes into income ranges).
Univariate Analysis
Univariate analysis, or analysis of a single variable, refers to a set of statistical techniques that can describe the general properties of one variable. Univariate statistics include: (1) frequency distribution, (2) central tendency, and (3) dispersion. The frequency distribution of a variable is a summary of the frequency (or percentages) of individual values or ranges of values for that variable. For instance, we can measure how many times a sample of respondents attend religious services (as a measure of their “religiosity”) using a categorical scale: never, once per year, several times per year, about once a month, several times per month, several times per week, and an optional category for “did not answer.” If we count the number (or percentage) of observations within each category (except “did not answer” which is really a missing value rather than a category), and display it in the form of a table as shown in Figure 14.1, what we have is a frequency distribution. This distribution can also be depicted in the form of a bar chart, as shown on the right panel of Figure 14.1, with the horizontal axis representing each category of that variable and the vertical axis representing the frequency or percentage of observations within each category.
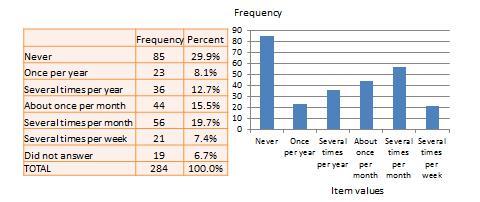
This guide explains what quantitative data analysis is and why it’s important, and gives you a four-step process to conduct a quantitative data analysis, so you know exactly what’s happening in your business and what your users need .
Collect quantitative customer data with Hotjar
Use Hotjar’s tools to gather the customer insights you need to make quantitative data analysis a breeze.
What is quantitative data analysis?
Quantitative data analysis is the process of analyzing and interpreting numerical data. It helps you make sense of information by identifying patterns, trends, and relationships between variables through mathematical calculations and statistical tests.
With quantitative data analysis, you turn spreadsheets of individual data points into meaningful insights to drive informed decisions. Columns of numbers from an experiment or survey transform into useful insights—like which marketing campaign asset your average customer prefers or which website factors are most closely connected to your bounce rate.
Without analytics, data is just noise. Analyzing data helps you make decisions which are informed and free from bias.
What quantitative data analysis is not
But as powerful as quantitative data analysis is, it’s not without its limitations. It only gives you the what, not the why . For example, it can tell you how many website visitors or conversions you have on an average day, but it can’t tell you why users visited your site or made a purchase.
For the why behind user behavior, you need qualitative data analysis , a process for making sense of qualitative research like open-ended survey responses, interview clips, or behavioral observations. By analyzing non-numerical data, you gain useful contextual insights to shape your strategy, product, and messaging.
Quantitative data analysis vs. qualitative data analysis
Let’s take an even deeper dive into the differences between quantitative data analysis and qualitative data analysis to explore what they do and when you need them.
The bottom line: quantitative data analysis and qualitative data analysis are complementary processes. They work hand-in-hand to tell you what’s happening in your business and why.
💡 Pro tip: easily toggle between quantitative and qualitative data analysis with Hotjar Funnels .
The Funnels tool helps you visualize quantitative metrics like drop-off and conversion rates in your sales or conversion funnel to understand when and where users leave your website. You can break down your data even further to compare conversion performance by user segment.
Spot a potential issue? A single click takes you to relevant session recordings , where you see user behaviors like mouse movements, scrolls, and clicks. With this qualitative data to provide context, you'll better understand what you need to optimize to streamline the user experience (UX) and increase conversions .
Hotjar Funnels lets you quickly explore the story behind the quantitative data
4 benefits of quantitative data analysis
There’s a reason product, web design, and marketing teams take time to analyze metrics: the process pays off big time.
Four major benefits of quantitative data analysis include:
1. Make confident decisions
With quantitative data analysis, you know you’ve got data-driven insights to back up your decisions . For example, if you launch a concept testing survey to gauge user reactions to a new logo design, and 92% of users rate it ‘very good’—you'll feel certain when you give the designer the green light.
Since you’re relying less on intuition and more on facts, you reduce the risks of making the wrong decision. (You’ll also find it way easier to get buy-in from team members and stakeholders for your next proposed project. 🙌)
2. Reduce costs
By crunching the numbers, you can spot opportunities to reduce spend . For example, if an ad campaign has lower-than-average click-through rates , you might decide to cut your losses and invest your budget elsewhere.
Or, by analyzing ecommerce metrics , like website traffic by source, you may find you’re getting very little return on investment from a certain social media channel—and scale back spending in that area.
3. Personalize the user experience
Quantitative data analysis helps you map the customer journey , so you get a better sense of customers’ demographics, what page elements they interact with on your site, and where they drop off or convert .
These insights let you better personalize your website, product, or communication, so you can segment ads, emails, and website content for specific user personas or target groups.
4. Improve user satisfaction and delight
Quantitative data analysis lets you see where your website or product is doing well—and where it falls short for your users . For example, you might see stellar results from KPIs like time on page, but conversion rates for that page are low.
These quantitative insights encourage you to dive deeper into qualitative data to see why that’s happening—looking for moments of confusion or frustration on session recordings, for example—so you can make adjustments and optimize your conversions by improving customer satisfaction and delight.
💡Pro tip: use Net Promoter Score® (NPS) surveys to capture quantifiable customer satisfaction data that’s easy for you to analyze and interpret.
With an NPS tool like Hotjar, you can create an on-page survey to ask users how likely they are to recommend you to others on a scale from 0 to 10. (And for added context, you can ask follow-up questions about why customers selected the rating they did—rich qualitative data is always a bonus!)
Hotjar graphs your quantitative NPS data to show changes over time
4 steps to effective quantitative data analysis
Quantitative data analysis sounds way more intimidating than it actually is. Here’s how to make sense of your company’s numbers in just four steps:
1. Collect data
Before you can actually start the analysis process, you need data to analyze. This involves conducting quantitative research and collecting numerical data from various sources, including:
Interviews or focus groups
Website analytics
Observations, from tools like heatmaps or session recordings
Questionnaires, like surveys or on-page feedback widgets
Just ensure the questions you ask in your surveys are close-ended questions—providing respondents with select choices to choose from instead of open-ended questions that allow for free responses.
Hotjar’s pricing plans survey template provides close-ended questions
2. Clean data
Once you’ve collected your data, it’s time to clean it up. Look through your results to find errors, duplicates, and omissions. Keep an eye out for outliers, too. Outliers are data points that differ significantly from the rest of the set—and they can skew your results if you don’t remove them.
By taking the time to clean your data set, you ensure your data is accurate, consistent, and relevant before it’s time to analyze.
3. Analyze and interpret data
At this point, your data’s all cleaned up and ready for the main event. This step involves crunching the numbers to find patterns and trends via mathematical and statistical methods.
Two main branches of quantitative data analysis exist:
Descriptive analysis : methods to summarize or describe attributes of your data set. For example, you may calculate key stats like distribution and frequency, or mean, median, and mode.
Inferential analysis : methods that let you draw conclusions from statistics—like analyzing the relationship between variables or making predictions. These methods include t-tests, cross-tabulation, and factor analysis. (For more detailed explanations and how-tos, head to our guide on quantitative data analysis methods.)
Then, interpret your data to determine the best course of action. What does the data suggest you do ? For example, if your analysis shows a strong correlation between email open rate and time sent, you may explore optimal send times for each user segment.
4. Visualize and share data
Once you’ve analyzed and interpreted your data, create easy-to-read, engaging data visualizations—like charts, graphs, and tables—to present your results to team members and stakeholders. Data visualizations highlight similarities and differences between data sets and show the relationships between variables.
Software can do this part for you. For example, the Hotjar Dashboard shows all of your key metrics in one place—and automatically creates bar graphs to show how your top pages’ performance compares. And with just one click, you can navigate to the Trends tool to analyze product metrics for different segments on a single chart.
Hotjar Trends lets you compare metrics across segments
Discover rich user insights with quantitative data analysis
Conducting quantitative data analysis takes a little bit of time and know-how, but it’s much more manageable than you might think.
By choosing the right methods and following clear steps, you gain insights into product performance and customer experience —and you’ll be well on your way to making better decisions and creating more customer satisfaction and loyalty.
FAQs about quantitative data analysis
What is quantitative data analysis.
Quantitative data analysis is the process of making sense of numerical data through mathematical calculations and statistical tests. It helps you identify patterns, relationships, and trends to make better decisions.
How is quantitative data analysis different from qualitative data analysis?
Quantitative and qualitative data analysis are both essential processes for making sense of quantitative and qualitative research .
Quantitative data analysis helps you summarize and interpret numerical results from close-ended questions to understand what is happening. Qualitative data analysis helps you summarize and interpret non-numerical results, like opinions or behavior, to understand why the numbers look like they do.
If you want to make strong data-driven decisions, you need both.
What are some benefits of quantitative data analysis?
Quantitative data analysis turns numbers into rich insights. Some benefits of this process include:
Making more confident decisions
Identifying ways to cut costs
Personalizing the user experience
Improving customer satisfaction
What methods can I use to analyze quantitative data?
Quantitative data analysis has two branches: descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.
Descriptive statistics provide a snapshot of the data’s features by calculating measures like mean, median, and mode.
Inferential statistics , as the name implies, involves making inferences about what the data means. Dozens of methods exist for this branch of quantitative data analysis, but three commonly used techniques are:
Cross tabulation
Factor analysis
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Descriptive Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Descriptive research: what it is and how to use it.
8 min read Understanding the who, what and where of a situation or target group is an essential part of effective research and making informed business decisions.
For example you might want to understand what percentage of CEOs have a bachelor’s degree or higher. Or you might want to understand what percentage of low income families receive government support – or what kind of support they receive.
Descriptive research is what will be used in these types of studies.
In this guide we’ll look through the main issues relating to descriptive research to give you a better understanding of what it is, and how and why you can use it.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a research method used to try and determine the characteristics of a population or particular phenomenon.
Using descriptive research you can identify patterns in the characteristics of a group to essentially establish everything you need to understand apart from why something has happened.
Market researchers use descriptive research for a range of commercial purposes to guide key decisions.
For example you could use descriptive research to understand fashion trends in a given city when planning your clothing collection for the year. Using descriptive research you can conduct in depth analysis on the demographic makeup of your target area and use the data analysis to establish buying patterns.
Conducting descriptive research wouldn’t, however, tell you why shoppers are buying a particular type of fashion item.
Descriptive research design
Descriptive research design uses a range of both qualitative research and quantitative data (although quantitative research is the primary research method) to gather information to make accurate predictions about a particular problem or hypothesis.
As a survey method, descriptive research designs will help researchers identify characteristics in their target market or particular population.
These characteristics in the population sample can be identified, observed and measured to guide decisions.
Descriptive research characteristics
While there are a number of descriptive research methods you can deploy for data collection, descriptive research does have a number of predictable characteristics.
Here are a few of the things to consider:
Measure data trends with statistical outcomes
Descriptive research is often popular for survey research because it generates answers in a statistical form, which makes it easy for researchers to carry out a simple statistical analysis to interpret what the data is saying.
Descriptive research design is ideal for further research
Because the data collection for descriptive research produces statistical outcomes, it can also be used as secondary data for another research study.
Plus, the data collected from descriptive research can be subjected to other types of data analysis .
Uncontrolled variables
A key component of the descriptive research method is that it uses random variables that are not controlled by the researchers. This is because descriptive research aims to understand the natural behavior of the research subject.
It’s carried out in a natural environment
Descriptive research is often carried out in a natural environment. This is because researchers aim to gather data in a natural setting to avoid swaying respondents.
Data can be gathered using survey questions or online surveys.
For example, if you want to understand the fashion trends we mentioned earlier, you would set up a study in which a researcher observes people in the respondent’s natural environment to understand their habits and preferences.
Descriptive research allows for cross sectional study
Because of the nature of descriptive research design and the randomness of the sample group being observed, descriptive research is ideal for cross sectional studies – essentially the demographics of the group can vary widely and your aim is to gain insights from within the group.
This can be highly beneficial when you’re looking to understand the behaviors or preferences of a wider population.
Descriptive research advantages
There are many advantages to using descriptive research, some of them include:
Cost effectiveness
Because the elements needed for descriptive research design are not specific or highly targeted (and occur within the respondent’s natural environment) this type of study is relatively cheap to carry out.
Multiple types of data can be collected
A big advantage of this research type, is that you can use it to collect both quantitative and qualitative data. This means you can use the stats gathered to easily identify underlying patterns in your respondents’ behavior.
Descriptive research disadvantages
Potential reliability issues.
When conducting descriptive research it’s important that the initial survey questions are properly formulated.
If not, it could make the answers unreliable and risk the credibility of your study.
Potential limitations
As we’ve mentioned, descriptive research design is ideal for understanding the what, who or where of a situation or phenomenon.
However, it can’t help you understand the cause or effect of the behavior. This means you’ll need to conduct further research to get a more complete picture of a situation.
Descriptive research methods
Because descriptive research methods include a range of quantitative and qualitative research, there are several research methods you can use.
Use case studies
Case studies in descriptive research involve conducting in-depth and detailed studies in which researchers get a specific person or case to answer questions.
Case studies shouldn’t be used to generate results, rather it should be used to build or establish hypothesis that you can expand into further market research .
For example you could gather detailed data about a specific business phenomenon, and then use this deeper understanding of that specific case.
Use observational methods
This type of study uses qualitative observations to understand human behavior within a particular group.
By understanding how the different demographics respond within your sample you can identify patterns and trends.
As an observational method, descriptive research will not tell you the cause of any particular behaviors, but that could be established with further research.
Use survey research
Surveys are one of the most cost effective ways to gather descriptive data.
An online survey or questionnaire can be used in descriptive studies to gather quantitative information about a particular problem.
Survey research is ideal if you’re using descriptive research as your primary research.
Descriptive research examples
Descriptive research is used for a number of commercial purposes or when organizations need to understand the behaviors or opinions of a population.
One of the biggest examples of descriptive research that is used in every democratic country, is during elections.
Using descriptive research, researchers will use surveys to understand who voters are more likely to choose out of the parties or candidates available.
Using the data provided, researchers can analyze the data to understand what the election result will be.
In a commercial setting, retailers often use descriptive research to figure out trends in shopping and buying decisions.
By gathering information on the habits of shoppers, retailers can get a better understanding of the purchases being made.
Another example that is widely used around the world, is the national census that takes place to understand the population.
The research will provide a more accurate picture of a population’s demographic makeup and help to understand changes over time in areas like population age, health and education level.
Where Qualtrics helps with descriptive research
Whatever type of research you want to carry out, there’s a survey type that will work.
Qualtrics can help you determine the appropriate method and ensure you design a study that will deliver the insights you need.
Our experts can help you with your market research needs , ensuring you get the most out of Qualtrics market research software to design, launch and analyze your data to guide better, more accurate decisions for your organization.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Descriptive statistics summarize and organize characteristics of a data set. A data set is a collection of responses or observations from a sample or entire population. ... In quantitative research, after collecting data, the first step of statistical analysis is to describe characteristics of the responses, such as the average of one variable ...
Using the data from these three rows, we can draw the following descriptive picture. Mentabil scores spanned a range of 50 (from a minimum score of 85 to a maximum score of 135). Speed scores had a range of 16.05 s (from 1.05 s - the fastest quality decision to 17.10 - the slowest quality decision).
Numeric data collected in a research project can be analysed quantitatively using statistical tools in two different ways. Descriptive analysis refers to statistically describing, aggregating, and presenting the constructs of interest or associations between these constructs.Inferential analysis refers to the statistical testing of hypotheses (theory testing).
Descriptive statistics, although relatively simple, are a critically important part of any quantitative data analysis. Measures of central tendency include the mean (average), median and mode. Skewness indicates whether a dataset leans to one side or another. Measures of dispersion include the range, variance and standard deviation.
Chapter 14 Quantitative Analysis Descriptive Statistics. Numeric data collected in a research project can be analyzed quantitatively using statistical tools in two different ways. Descriptive analysis refers to statistically describing, aggregating, and presenting the constructs of interest or associations between these constructs.
It's also important to note that descriptive statistics can employ and use both quantitative and qualitative research. Describing data is undoubtedly the most critical first step in research as it enables the subsequent organization, simplification and summarization of information — and every survey question and population has summary ...
Research. A descriptive statistic (in the count noun sense) is a summary statistic that quantitatively describes or summarizes features from a collection of information, [1] while descriptive statistics (in the mass noun sense) is the process of using and analysing those statistics. Descriptive statistics is distinguished from inferential ...
The chapter is about reporting descriptive statistics in a quantitative research text. Descriptive statistics, often referred to as descriptives, are necessary for every quantitative research project and are usually reported first in the section about results. In this chapter the following are considered: Technical information
AbstractThis chapter presents research designs for descriptive and correlational quantitative research. Descriptive research designs are used to address th. Skip to Main Content. ... Drawing from data gathered in the U.S. National Center for Education Statistics' High School Longitudinal Study of 2009 (Ingels et al., 2007), ...
Similarly, De scriptive statistics are used to summarize and analyze data in. a variety of academic areas, including psychology, sociology, economics, education, and epidemiology [3 ]. Descriptive ...
Descriptive statistics summarise and organise characteristics of a data set. A data set is a collection of responses or observations from a sample or entire population . In quantitative research , after collecting data, the first step of statistical analysis is to describe characteristics of the responses, such as the average of one variable (e ...
Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment's nature ...
Descriptive statistics are specific methods basically used to calculate, describe, and summarize collected research data in a logical, meaningful, and efficient way. Descriptive statistics are reported numerically in the manuscript text and/or in its tables, or graphically in its figures. This basic …
Descriptive Statistics. Descriptive statistics capture information about a sample in a single number. There are many statistical measures that fall under the umbrella of descriptive statistics, such as mean, median, standard deviation, and variance. These measures are often divided into two categories: 1.
Here are some common methods of data analysis for descriptive research: Descriptive Statistics. ... Quantitative: Descriptive research design is quantitative in nature, which means that it involves collecting numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. This helps to provide a more precise and accurate description of the ...
Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect ...
Univariate analysis, or analysis of a single variable, refers to a set of statistical techniques that can describe the general properties of one variable. Univariate statistics include: (1) frequency distribution, (2) central tendency, and (3) dispersion. The frequency distribution of a variable is a summary of the frequency (or percentages) of ...
Quantitative data analysis has two branches: descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics provide a snapshot of the data's features by calculating measures like mean, median, and mode. Inferential statistics, as the name implies, involves making inferences about what the data means. Dozens of methods exist for ...
Descriptive research design. Descriptive research design uses a range of both qualitative research and quantitative data (although quantitative research is the primary research method) to gather information to make accurate predictions about a particular problem or hypothesis. As a survey method, descriptive research designs will help ...
The study adopted a descriptive research design with a quantitative approach. In the descriptive design, the researcher does not manipulate the variables but rather describes the sample or the ...
Descriptive statistics provide a summary of data in the form of mean, median and mode. Inferential statistics use a random sample of data taken from a population to describe and make inferences about the whole population. It is valuable when it is not possible to examine each member of an entire population. The examples if descriptive and ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
The quantitative method and descriptive statistical analysis were used to analyze the perceptions of eight expert's MOOC developers based on the results of a Likert scale questionnaire. ... The contribution of this research is to add value to the body of knowledge available to trainers, researchers, and stakeholders in MOOC design, the social ...
By employing descriptive statistical methods to effectively analyze youth attitudes, our research pushes the boundaries of current knowledge, offering unique insights into a critical aspect of road safety decision-making that remains underexplored in existing literature. ... Results of the Quantitative Research. The descriptive analysis of the ...