
Literary Genres: Definition and Examples of the 4 Essential Genres and 100+ Subgenres
by Joe Bunting | 1 comment
Free Book Planning Course! Sign up for our 3-part book planning course and make your book writing easy . It expires soon, though, so don’t wait. Sign up here before the deadline!
What are literary genres? Do they actually matter to readers? How about to writers? What types of literary genres exist? And if you're a writer, how do you decide which genre to write in?
To begin to think about literary genres, let's start with an example.
Let's say want to read something. You go to a bookstore or hop onto a store online or go to a library.
But instead of a nice person wearing reading glasses and a cardigan asking you what books you like and then thinking through every book ever written to find you the next perfect read (if that person existed, for the record, they would be my favorite person), you're faced with this: rows and rows of books with labels on the shelves like “Literary Fiction,” “Travel,” “Reference,” “Science Fiction,” and so on.
You stop at the edge of the bookstore and just stand there for a while, stumped. “What do all of these labels even mean?!” And then you walk out of the store.
Or maybe you're writing a book , and someone asks you a question like this: “What kind of book are you writing? What genre is it?”
And you stare at them in frustration thinking, “My book transcends genre, convention, and even reality, obviously. Don't you dare put my genius in a box!”
What are literary genres? In this article, we'll share the definition and different types of literary genres (there are four main ones but thousands of subgenres). Then, we'll talk about why genre matters to both readers and writers. We'll look at some of the components that people use to categorize writing into genres. Finally, we'll give you a chance to put genre into practice with an exercise .
Table of Contents
Introduction Literary Genres Definition Why Genre Matters (to Readers, to Writers) The 4 Essential Genres 100+ Genres and Subgenres The 7 Components of Genre Practice Exercise
Ready to get started? Let's get into it.
What Are Literary Genres? Literary Genre Definition
Let's begin with a basic definition of literary genres:
Literary genres are categories, types, or collections of literature. They often share characteristics, such as their subject matter or topic, style, form, purpose, or audience.
That's our formal definition. But here's a simpler way of thinking about it:
Genre is a way of categorizing readers' tastes.
That's a good basic definition of genre. But does genre really matter?
Why Literary Genres Matter
Literary genres matter. They matter to readers but they also matter to writers. Here's why:
Why Literary Genres Matter to Readers
Think about it. You like to read (or watch) different things than your parents.
You probably also like to read different things at different times of the day. For example, maybe you read the news in the morning, listen to an audiobook of a nonfiction book related to your studies or career in the afternoon, and read a novel or watch a TV show in the evening.
Even more, you probably read different things now than you did as a child or than you will want to read twenty years from now.
Everyone has different tastes.
Genre is one way we match what readers want to what writers want to write and what publishers are publishing.
It's also not a new thing. We've been categorizing literature like this for thousands of years. Some of the oldest forms of writing, including religious texts, were tied directly into this idea of genre.
For example, forty percent of the Old Testament in the Bible is actually poetry, one of the four essential literary genres. Much of the New Testament is in the form of epistle, a subgenre that's basically a public letter.
Genre matters, and by understanding how genre works, you not only can find more things you want to read, you can also better understand what the writer (or publisher) is trying to do.
Why Literary Genres Matter to Writers
Genre isn't just important to readers. It's extremely important to writers too.
In the same way the literary genres better help readers find things they want to read and better understand a writer's intentions, genres inform writers of readers' expectations and also help writers find an audience.
If you know that there are a lot of readers of satirical political punditry (e.g. The Onion ), then you can write more of that kind of writing and thus find more readers and hopefully make more money. Genre can help you find an audience.
At the same time, great writers have always played with and pressed the boundaries of genre, sometimes even subverting it for the sake of their art.
Another way to think about genre is a set of expectations from the reader. While it's important to meet some of those expectations, if you meet too many, the reader will get bored and feel like they know exactly what's going to happen next. So great writers will always play to the readers' expectations and then change a few things completely to give readers a sense of novelty in the midst of familiarity.
This is not unique to writers, by the way. The great apparel designer Virgil Abloh, who was an artistic director at Louis Vuitton until he passed away tragically in 2021, had a creative template called the “3% Rule,” where he would take an existing design, like a pair of Nike Air Jordans, and make a three percent change to it, transforming it into something completely new. His designs were incredibly successful, often selling for thousands of dollars.
This process of taking something familiar and turning it into something new with a slight change is something artists have done throughout history, including writers, and it's a great way to think about how to use genre for your own writing.
What Literary Genre is NOT: Story Type vs. Literary Genres
Before we talk more about the types of genre, let's discuss what genre is not .
Genre is not the same as story type (or for nonfiction, types of nonfiction structure). There are ten (or so) types of stories, including adventure, love story, mystery, and coming of age, but there are hundreds, even thousands of genres.
Story type and nonfiction book structure are about how the work is structured.
Genre is about how the work is perceived and marketed.
These are related but not the same.
For example, one popular subgenre of literature is science fiction. Probably the most common type of science fiction story is adventure, but you can also have mystery sci-fi stories, love story sci-fi, and even morality sci-fi. Story type transcends genre.
You can learn more about this in my book The Write Structure , which teaches writers the simple process to structure great stories. Click to check out The Write Structure .
This is true for non-fiction as well in different ways. More on this in my post on the seven types of nonfiction books .
Now that we've addressed why genre matters and what genre doesn't include, let's get into the different literary genres that exist (there are a lot of them!).
How Many Literary Genres Are There? The 4 Essential Genres, and 100+ Genres and Subgenres
Just as everyone has different tastes, so there are genres to fit every kind of specific reader.
There are four essential literary genres, and all are driven by essential questions. Then, within each of those essential genres are genres and subgenres. We will look at all of these in turn, below, as well as several examples of each.
An important note: There are individual works that fit within the gaps of these four essential genres or even cross over into multiple genres.
As with anything, the edges of these categories can become blurry, for example narrative poetry or fictional reference books.
A general rule: You know it when you see it (except, of course, when the author is trying to trick you!).
1. Nonfiction: Is it true?
The core question for nonfiction is, “Is it true?”
Nonfiction deals with facts, instruction, opinion/argument reference, narrative nonfiction, or a combination.
A few examples of nonfiction (more below): reference, news, memoir, manuals, religious inspirational books, self-help, business, and many more.
2. Fiction: Is it, at some level, imagined?
The core question for fiction is, “Is it, at some level, imagined?”
Fiction is almost always story or narrative. However, satire is a form of “fiction” that's structured like nonfiction opinion/essays or news. And one of the biggest insults you can give to a journalist, reporter, or academic researcher is to suggest that their work is “fiction.”
3. Drama: Is it performed?
Drama is a genre of literature that has some kind of performance component. This includes theater, film, and audio plays.
The core question that defines drama is, “Is it performed?”
As always, there are genres within this essential genre, including horror films, thrillers, true crime podcasts, and more.
4. Poetry: Is it verse?
Poetry is in some ways the most challenging literary genre to define because while poetry is usually based on form, i.e. lines intentionally broken into verse, sometimes including rhyme or other poetic devices, there are some “poems” that are written completely in prose called prose poetry. These are only considered poems because the author and/or literary scholars said they were poems.
To confuse things even more, you also have narrative poetry, which combines fiction and poetry, and song which combines poetry and performance (or drama) with music.
Which is all to say, poetry is challenging to classify, but again, you usually know it when you see it.
Next, let's talk about the genres and subgenres within those four essential literary genres.
The 100+ Literary Genres and Subgenres with Definitions
Genre is, at its core, subjective. It's literally based on the tastes of readers, tastes that change over time, within markets, and across cultures.
Thus, there are essentially an infinite number of genres.
Even more, genres are constantly shifting. What is considered contemporary fiction today will change a decade from now.
So take the lists below (and any list of genres you see) as an incomplete, likely outdated, small sample size of genre with definitions.
1. Fiction Genres
Sorted alphabetically.
Action/Adventure. An action/adventure story has adventure elements in its plot line. This type of story often involves some kind of conflict between good and evil, and features characters who must overcome obstacles to achieve their goals .
Chick Lit. Chick Lit stories are usually written for women who interested in lighthearted stories that still have some depth. They often include romance, humor, and drama in their plots.
Comedy. This typically refers to historical stories and plays (e.g. Shakespeare, Greek Literature, etc) that contain a happy ending, often with a wedding.
Commercial. Commercial stories have been written for the sole purpose of making money, often in an attempt to cash in on the success of another book, film, or genre.
Crime/Police/Detective Fiction. Crime and police stories feature a detective, whether amateur or professional, who solves crimes using their wits and knowledge of criminal psychology.
Drama or Tragedy. This typically refers to historical stories or plays (e.g. Shakespeare, Greek Literature, etc) that contain a sad or tragic ending, often with one or more deaths.
Erotica. Erotic stories contain explicit sexual descriptions in their narratives.
Espionage. Espionage stories focus on international intrigue, usually involving governments, spies, secret agents, and/or terrorist organizations. They often involve political conflict, military action, sabotage, terrorism, assassination, kidnapping, and other forms of covert operations.
Family Saga. Family sagas focus on the lives of an extended family, sometimes over several generations. Rather than having an individual protagonist, the family saga tells the stories of multiple main characters or of the family as a whole.
Fantasy. Fantasy stories are set in imaginary worlds that often feature magic, mythical creatures, and fantastic elements. They may be based on mythology, folklore, religion, legend, history, or science fiction.
General Fiction. General fiction novels are those that deal with individuals and relationships in an ordinary setting. They may be set in any time period, but usually take place in modern times.
Graphic Novel. Graphic novels are a hybrid between comics and prose fiction that often includes elements of both.
Historical Fiction. Historical stories are written about imagined or actual events that occurred in history. They usually take place during specific periods of time and often include real or imaginary characters who lived at those times.
Horror Genre. Horror stories focus on the psychological terror experienced by their characters. They often feature supernatural elements, such as ghosts, vampires, werewolves, zombies, demons, monsters, and aliens.
Humor/Satire. This category includes stories that have been written using satire or contain comedic elements. Satirical novels tend to focus on some aspect of society in a critical way.
LGBTQ+. LGBTQ+ novels are those that feature characters who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or otherwise non-heterosexual.
Literary Fiction. Literary fiction novels or stories have a high degree of artistic merit, a unique or experimental style of writing , and often deal with serious themes.
Military. Military stories deal with war, conflict, combat, or similar themes and often have strong action elements. They may be set in a contemporary or a historical period.
Multicultural. Multicultural stories are written by and about people who have different cultural backgrounds, including those that may be considered ethnic minorities.
Mystery G enre. Mystery stories feature an investigation into a crime.
Offbeat/Quirky. An offbeat story has an unusual plot, characters, setting, style, tone, or point of view. Quirkiness can be found in any aspect of a story, but often comes into play when the author uses unexpected settings, time periods, or characters.
Picture Book. Picture book novels are usually written for children and feature simple plots and colorful illustrations . They often have a moral or educational purpose.
Religious/Inspirational. Religious/ inspirational stories describe events in the life of a person who was inspired by God or another supernatural being to do something extraordinary. They usually have a moral lesson at their core.
Romance Genre. Romance novels or stories are those that focus on love between two people, often in an ideal setting. There are many subgenres in romance, including historical, contemporary, paranormal, and others.
Science Fiction. Science fiction stories are usually set in an imaginary future world, often involving advanced technology. They may be based on scientific facts but they are not always.
Short Story Collection . Short story collections contain several short stories written by the same or different authors.
Suspense or Thriller Genre. Thrillers/ suspense stories are usually about people in danger, often involving crimes, natural disasters, or terrorism.
Upmarket. Upmarket stories are often written for and/or focus on upper class people who live in an upscale environment.
Western Genre. Western stories are those that take place in the west during the late 19th century and early 20th century. Characters include cowboys, outlaws, native Americans, and settlers.
2. Nonfiction Genres
From the BISAC categories, a globally accepted system for coding and categorizing books by the Book Industry Standards And Communications group.
Antiques & Collectibles. Nonfiction books about antiques and collectibles include those that focus on topics such as collecting, appraising, restoring, and marketing antiques and collectibles. These books may be written for both collectors and dealers in antique and collectible items. They can range from how-to guides to detailed histories of specific types of objects.
Architecture. Architecture books focus on the design, construction, use, and history of buildings and structures. This includes the study of architecture in general, but also the specific designs of individual buildings or styles of architecture.
Art. Art books focus on visual arts, music, literature, dance, film, theater, architecture, design, fashion, food, and other art forms. They may include essays, memoirs, biographies, interviews, criticism, and reviews.
Bibles. Bibles are religious books, almost exclusively Christian, that contain the traditional Bible in various translations, often with commentary or historical context.
Biography & Autobiography. Biography is an account of a person's life, often a historical or otherwise famous person. Autobiographies are personal accounts of people's lives written by themselves.
Body, Mind & Spirt. These books focus on topics related to human health, wellness, nutrition, fitness, or spirituality.
Business & Economics. Business & economics books are about how businesses work. They tend to focus on topics that interest people who run their own companies, lead or manage others, or want to understand how the economy works.
Computers. The computer genre of nonfiction books includes any topics that deal with computers in some way. They can be about general use, about how they affect our lives, or about specific technical areas related to hardware or software.
Cooking. Cookbooks contain recipes or cooking techniques.
Crafts & Hobbies. How-to guides for crafts and hobbies, including sewing, knitting, painting, baking, woodworking, jewelry making, scrapbooking, photography, gardening, home improvement projects, and others.
Design. Design books are written about topics that include design in some way. They can be about any aspect of design including graphic design, industrial design, product design, fashion, furniture, interior design, or others.
Education. Education books focus on topics related to teaching and learning in schools. They can be used for students or as a resource for teachers.
Family & Relationships. These books focus on family relationships, including parenting, marriage, divorce, adoption, and more.
Foreign Language Study. Books that act as a reference or guide to learning a foreign language.
Games & Activities. Games & activities books may be published for children or adults, may contain learning activities or entertaining word or puzzle games. They range from joke books to crossword puzzle books to coloring books and more.
Gardening. Gardening books include those that focus on aspects of gardening, how to prepare for and grow vegetables, fruits, herbs, flowers, trees, shrubs, grasses, and other plants in an indoor or outdoor garden setting.
Health & Fitness. Health and fitness books focus on topics like dieting, exercise, nutrition, weight loss, health issues, medical conditions, diseases, medications, herbs, supplements, vitamins, minerals, and more.
History. History books focus on historical events and people, and may be written for entertainment or educational purposes.
House & Home. House & home books focus on topics like interior design, decorating, entertaining, and DIY projects.
Humor. Humor books are contain humorous elements but do not have any fictional elements.
Juvenile Nonfiction. These are nonfiction books written for children between six and twelve years old.
Language Arts & Disciplines. These books focus on teaching language arts and disciplines. They may be used for elementary school students in grades K-5.
Law. Law books include legal treatises, casebooks, and collections of statutes.
Literary Criticism. Literary criticism books discuss literary works, primarily key works of fiction or memoir. They may include biographies of authors, critical essays on specific works, or studies of the history of literature.
Mathematics. Mathematics books either teach mathematical concepts and methods or explore the history of mathematics.
Medical. Medical books include textbooks, reference books, guides, encyclopedias, and handbooks that focus on fields of medicine, including general practice, internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, obstetrics/gynecology, and more.
Music. Music books are books that focus on the history, culture, and development of music in various countries around the world. They often include biographies, interviews, reviews, essays, and other related material. However, they may also include sheet music or instruction on playing a specific instrument.
Nature. Nature books focus on the natural world or environment, including natural history, ecology, or natural experiences like hiking, bird watching, or conservation.
Performing Arts. Books about the performing arts in general, including specific types of performance art like dance, music, and theater.
Pets. Pet books include any book that deals with animals in some way, including dog training, cat care, animal behavior, pet nutrition, bird care, and more.
Philosophy. Philosophy books deal with philosophical issues, and may be written for a general audience or specifically for scholars.
Photography. Photography books use photographs as an essential part of their content. They may be about any subject.
Political Science. Political science books deal with politics in some way. They can be about current events, historical figures, or theoretical concepts.
Psychology. Psychology books are about the scientific study of mental processes, emotion, and behavior.
Reference. Reference books are about any subject, topic, or field and contain useful information about that subject, topic or field.
Religion. These books deal with religion in some way, including religious history, theology, philosophy, and spirituality.
Science. Science books focus on topics within scientific fields, including geology, biology, physics, and more.
Self-Help. Self-help books are written for people who want to improve their lives in some way. They may be about health, relationships, finances, career, parenting, spirituality, or any number of topics that can help readers achieve personal goals.
Social Science. Focus on social science topics.
Sports & Recreation. Sports & Recreation books focus on sports either from a reporting, historical, or instructional perspective.
Study Aids. Study aids are books that provide information about a particular subject area for students who want to learn more about that topic. These books can be used in conjunction with classroom instruction or on their own.
Technology & Engineering. Technology & engineering nonfiction books describe how technology has changed our lives and how we can use that knowledge to improve ourselves and society.
Transportation. Focus on transportation topics including those about vehicles, routes, or techniques.
Travel. Travel books are those that focus on travel experiences, whether from a guide perspective or from the author's personal experiences.
True Crime. True Crime books focus on true stories about crimes. These books may be about famous cases, unsolved crimes, or specific criminals.
Young Adult Nonfiction. Young adult nonfiction books are written for children and teenagers.
3. Drama Genres
These include genres for theater, film, television serials, or audio plays.
As a writer, I find some of these genres particularly eye-roll worthy. And yet, this is the way most films, television shows, and even theater productions are classified.
Action. Action genre dramas involve fast-paced, high-energy sequences in which characters fight against each other. They often have large-scale battles, chase scenes, or other high-intensity, high-conflict scenes.
Horror. Horror dramas focus on the psychological terror experienced by their characters. They often feature supernatural elements, such as ghosts, vampires, werewolves, zombies, demons, monsters, and aliens.
Adventure. Adventure films are movies that have an adventurous theme. They may be set in exotic locations, feature action sequences, and/or contain elements of fantasy.
Musicals (Dance). Musicals are dramas that use music in their plot and/or soundtrack. They may be comedies, dramas, or any combination.
Comedy (& Black Comedy). Comedy dramas feature humor in their plots, characters, dialogue, or situations. It sometimes refers to historical dramas (e.g. Shakespeare, Greek drama, etc) that contain a happy ending, often with a wedding.
Science Fiction. Science fiction dramas are usually set in an imaginary future world, often involving advanced technology. They may be based on scientific facts but do not have to be.
Crime & Gangster. Crime & Gangster dramas deal with criminals, detectives, or organized crime groups. They often feature action sequences, violence, and mystery elements.
War (Anti-War). War (or anti-war) dramas focus on contemporary or historical wars. They may also contain action, adventure, mystery, or romance elements.
Drama. Dramas focus on human emotions in conflict situations. They often have complex plots and characters, and deal with serious themes. This may also refer to historical stories (e.g. Shakespeare, Greek Literature, etc) that contain a sad or tragic ending, often with one or more deaths.
Westerns. Westerns are a genre of American film that originated in the early 20th century and take place in the west during the late 19th century and early 20th century. Characters include cowboys, outlaws, native Americans, and settlers.
Epics/Historical/Period. These are dramas based on historical events or periods but do not necessarily involve any real people.
Biographical (“Biopics”). Biopics films are movies that focus on real people in history.
Melodramas, Women's or “Weeper” Films, Tearjerkers. A type of narrative drama that focuses on emotional issues, usually involving love, loss, tragedy, and redemption.
“Chick” Flicks. Chick flicks usually feature romantic relationships and tend to be lighthearted and comedic in nature.
Road Stories. Dramas involving a journey of some kind, usually taking place in contemporary setting, and involving relationships between one or more people, not necessarily romantic.
Courtroom Dramas. Courtroom dramas depict legal cases set in courtrooms. They usually have a dramatic plot line with an interesting twist at the end.
Romance. Romance dramas feature love stories between two people. Romance dramas tend to be more serious, even tragic, in nature, while romantic comedies tend to be more lighthearted.
Detective & Mystery. These dramas feature amateur or professional investigators solving crimes and catching criminals.
Sports. Sports dramas focus on athletic competition in its many forms and usually involve some kind of climactic tournament or championship.
Disaster. Disaster dramas are adventure or action dramas that include natural disasters, usually involving earthquakes, floods, volcanoes, hurricanes, tornadoes, or other disasters.
Superhero. Superhero dramas are action/adventure dramas that feature characters with supernatural powers. They usually have an origin story, the rise of a villain, and a climactic battle at the end.
Fantasy. Fantasy dramas films are typically adventure dramas that feature fantastical elements in their plot or setting, whether magic, folklore, supernatural creatures, or other fantasy elements.
Supernatural. Supernatural dramas feature paranormal phenomena in their plots, including ghosts, mythical creatures, and mysterious or extraordinary elements. This genre may overlap with horror, fantasy, thriller, action and other genres.
Film Noir. Film noir refers to a style of American crime drama that emerged in the 1940s. These dramas often featured cynical characters who struggled, often fruitlessly, against corruption and injustice.
Thriller/Suspense. Thriller/suspense dramas have elements of suspense and mystery in their plot. They usually feature a character protagonist who must overcome obstacles while trying to solve a crime or prevent a catastrophe.
Guy Stories. Guy dramas feature men in various situations, usually humorous or comedic in nature.
Zombie . Zombie dramas are usually action/adventure dramas that involve zombies.
Animated Stories . Dramas that are depicted with drawings, photographs, stop-motion, CGI, or other animation techniques.
Documentary . Documentaries are non-fiction performances that attempt to describe actual events, topics, or people.
“Foreign.” Any drama not in the language of or involving characters/topics in your country of origin. They can also have any of the other genres listed here.
Childrens – Kids – Family-Oriented . Dramas with children of various ages as the intended audience.
Sexual – Erotic . These dramas feature explicit sexual acts but also have some kind of plot or narrative (i.e. not pornography).
Classic . Classic dramas refer to dramas performed before 1950.
Silent . Silent dramas were an early form of film that used no recorded sound.
Cult . Cult dramas are usually small-scale, independent productions with an offbeat plot, unusual characters, and/or unconventional style that have nevertheless gained popularity among a specific audience.
4. Poetry Genres
This list is from Harvard's Glossary of Poetic Genres who also has definitions for each genre.
Dramatic monologue
Epithalamion
Light verse
Occasional verse
Verse epistle
What Are the Components of Genre In Literature? The 7 Elements of Genre
Now that we've looked, somewhat exhaustively, at examples of literary genres, let's consider how these genres are created.
What are the elements of literary genre? How are they formed?
Here are seven components that make up genre.
- Form . Length is the main component of form (e.g. a novel is 200+ pages , films are at least an hour, serialized episodes are about 20 minutes, etc), but may also be determined by how many acts or plot lines they have. You might be asking, what about short stories? Short stories are a genre defined by their length but not their content.
- Intended Audience . Is the story meant for adults, children, teenagers, etc?
- Conventions and Tropes . Conventions and tropes describe patterns or predictable events that have developed within genres. For example, a sports story may have a big tournament at the climax, or a fantasy story may have a mentor character who instructs the protagonist on the use of their abilities.
- Characters and Archetypes. Genre will often have characters who serve similar functions, like the best friend sidekick, the evil villain , the anti-hero , and other character archetypes .
- Common Settings and Time Periods . Genre may be defined by the setting or time period. For example, stories set in the future tend to be labelled science fiction, stories involving the past tend to be labelled historical or period, etc.
- Common Story Arcs . While every story type may use each of the six main story arcs , genre tends to be defined by specific story arcs. For example, comedy almost always has a story arc that ends positively, same with kids or family genres. However, dramas often (and when referring to historical drama, always) have stories that end tragically.
- Common Elements (such as supernatural elements, technology, mythical creatures, monsters, etc) . Some genres center themselves on specific elements, like supernatural creatures, magic, monsters, gore, and so on. Genre can be determined by these common elements.
As you consider these elements, keep in mind that genre all comes back to taste, to what readers want to consume and how to match the unlimited variations of story with the infinite variety of tastes.
Read What You Want, Write What You Want
In the end, both readers and writers should use genre for what it is, a tool, not as something that defines you.
Writers can embrace genre, can use genre, without being controlled by it.
Readers can use genre to find stories or books they enjoy while also exploring works outside of that genre.
Genre can be incredibly fun! But only if you hold it in tension with your own work of telling (or finding) a great story.
What are your favorite genres to read in? to write in? Let us know in the comments!
Now that we understand everything there is to know about literary genres, let's put our knowledge to use with an exercise. I have two variations for you today, one for readers and one for writers.
Readers : Think of one of your favorite stories. What is the literary genre of that story? Does it have multiple? What expectations do you have about stories within that genre? Finally, how does the author of your favorite story use those expectations, and how do they subvert them?
Writers : Choose a literary genre from the list above and spend fifteen minutes writing a story using the elements of genre: form, audience, conventions and tropes, characters and archetypes, setting and time periods, story arcs, and common elements.
When you’re finished, share your work in the Pro Practice Workshop here . Not a member yet? Join us here !
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

So how big does an other-genre element need to get before you call your book “cross-genre”? Right now, I’m writing a superhero team saga (which is already a challenge for platforms that don’t recognize “superhero” as a genre, since my team’s powers lie in that fuzzy land where the distinction between science and magic gets more than a little blurry), so it obviously has action/adventure in it, but it’s also sprouting thriller and mystery elements. I’m wondering if they’re big enough to plug the series to those genres.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Definition of Genre
Genre originates from the French word meaning kind or type. As a literary device, genre refers to a form, class, or type of literary work. The primary genres in literature are poetry, drama / play , essay , short story , and novel . The term genre is used quite often to denote literary sub-classifications or specific types of literature such as comedy , tragedy , epic poetry, thriller , science fiction , romance , etc.
It’s important to note that, as a literary device, the genre is closely tied to the expectations of readers. This is especially true for literary sub-classifications. For example, Jane Austen ’s work is classified by most as part of the romance fiction genre, as demonstrated by this quote from her novel Sense and Sensibility :
When I fall in love, it will be forever.
Though Austen’s work is more complex than most formulaic romance novels, readers of Austen’s work have a set of expectations that it will feature a love story of some kind. If a reader found space aliens or graphic violence in a Jane Austen novel, this would undoubtedly violate their expectations of the romantic fiction genre.
Difference Between Style and Genre
Although both seem similar, the style is different from the genre. In simple terms, style means the characters or features of the work of a single person or individual. However, the genre is the classification of those words into broader categories such as modernist, postmodernist or short fiction and novels, and so on. Genres also have sub-genre, but the style does not have sub-styles. Style usually have further features and characteristics.
Common Examples of Genre
Genres could be divided into four major categories which also have further sub-categories. The four major categories are given below.
- Poetry: It could be categorized into further sub-categories such as epic, lyrical poetry, odes , sonnets , quatrains , free verse poems, etc.
- Fiction : It could be categorized into further sub-categories such as short stories, novels, skits, postmodern fiction, modern fiction, formal fiction, and so on.
- Prose : It could be further categorized into sub-genres or sub-categories such as essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, autobiography , biographical writings, and so on.
- Drama: It could be categorized into tragedy, comedy, romantic comedy, absurd theatre, modern play, and so on.
Common Examples of Fiction Genre
In terms of literature, fiction refers to the prose of short stories, novellas , and novels in which the story originates from the writer’s imagination. These fictional literary forms are often categorized by genre, each of which features a particular style, tone , and storytelling devices and elements.
Here are some common examples of genre fiction and their characteristics:
- Literary Fiction : a work with artistic value and literary merit.
- Thriller : features dark, mysterious, and suspenseful plots.
- Horror : intended to scare and shock the reader while eliciting a sense of terror or dread; may feature scary entities such as ghosts, zombies, evil spirits, etc.
- Mystery : generally features a detective solving a case with a suspenseful plot and slowly revealing information for the reader to piece together.
- Romance : features a love story or romantic relationship; generally lighthearted, optimistic, and emotionally satisfying.
- Historical : plot takes place in the past with balanced realism and creativity; can feature actual historical figures, events, and settings.
- Western : generally features cowboys, settlers, or outlaws of the American Old West with themes of the frontier.
- Bildungsroman : story of a character passing from youth to adulthood with psychological and/or moral growth; the character becomes “educated” through loss, a journey, conflict , and maturation.
- Science Fiction : speculative stories derived and/or inspired by natural and social sciences; generally features futuristic civilizations, time travel, or space exploration.
- Dystopian : sub-genre of science fiction in which the story portrays a setting that may appear utopian but has a darker, underlying presence that is problematic.
- Fantasy : speculative stories with imaginary characters in imaginary settings; can be inspired by mythology or folklore and generally include magical elements.
- Magical Realism : realistic depiction of a story with magical elements that are accepted as “normal” in the universe of the story.
- Realism : depiction of real settings, people, and plots as a means of approaching the truth of everyday life and laws of nature.
Examples of Writers Associated with Specific Genre Fiction
Writers are often associated with a specific genre of fictional literature when they achieve critical acclaim, public notoriety, and/or commercial success with readers for a particular work or series of works. Of course, this association doesn’t limit the writer to that particular genre of fiction. However, being paired with a certain type of literature can last for an author’s entire career and beyond.
Here are some examples of writers that have become associated with specific fiction genre:
- Stephen King: horror
- Ray Bradbury : science fiction
- Jackie Collins: romance
- Toni Morrison: black feminism
- John le Carré: espionage
- Philippa Gregory: historical fiction
- Jacqueline Woodson: racial identity fiction
- Philip Pullman: fantasy
- Flannery O’Connor: Southern Gothic
- Shel Silverstein: children’s poetry
- Jonathan Swift : satire
- Larry McMurtry: western
- Virginia Woolf: feminism
- Raymond Chandler: detective fiction
- Colson Whitehead: Afrofuturism
- Gabriel García Márquez : magical realism
- Madeleine L’Engle: children’s fantasy fiction
- Agatha Christie : mystery
- John Green : young adult fiction
- Margaret Atwood: dystopian
Famous Examples of Genre in Other Art Forms
Most art forms feature genre as a means of identifying, differentiating, and categorizing the many forms and styles within a particular type of art. Though there are many crossovers when it comes to genre and no finite boundaries, most artistic works within a particular genre feature shared patterns , characteristics, and conventions.
Here are some famous examples of genres in other art forms:
- Music : rock, country, hip hop, folk, classical, heavy metal, jazz, blues
- Visual Art : portrait, landscape, still life, classical, modern, impressionism, expressionism
- Drama : comedy, tragedy, tragicomedy , melodrama , performance, musical theater, illusion
- Cinema : action, horror, drama, romantic comedy, western, adventure , musical, documentary, short, biopic, fantasy, superhero, sports
Examples of Genre in Literature
As a literary device, the genre is like an implied social contract between writers and their readers. This does not mean that writers must abide by all conventions associated with a specific genre. However, there are organizational patterns within a genre that readers tend to expect. Genre expectations allow readers to feel familiar with the literary work and help them to organize the information presented by the writer. In addition, keeping with genre conventions can establish a writer’s relationship with their readers and a framework for their literature.
Here are some examples of genres in literature and the conventions they represent:
Example 1: Macbeth by William Shakespeare
Tomorrow, and tomorrow, and tomorrow , Creeps in this petty pace from day to day To the last syllable of recorded time, And all our yesterdays have lighted fools The way to dusty death. Out, out , brief candle! Life’s but a walking shadow, a poor player That struts and frets his hour upon the stage And then is heard no more: it is a tale Told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, Signifying nothing.
The formal genre of this well-known literary work is Shakespearean drama or play. Macbeth can be sub-categorized as a literary tragedy in that the play features the elements of a classical tragic work. For example, Macbeth’s character aligns with the traits and path of a tragic hero –a protagonist whose tragic flaw brings about his downfall from power to ruin. This tragic arc of the protagonist often results in catharsis (emotional release) and potential empathy among readers and members of the audience .
In addition to featuring classical characteristics and conventions of the tragic genre, Shakespeare’s play also resonates with modern readers and audiences as a tragedy. In this passage, one of Macbeth’s soliloquies , his disillusionment, and suffering is made clear in that, for all his attempts and reprehensible actions at gaining power, his life has come to nothing. Macbeth realizes that death is inevitable, and no amount of power can change that truth. As Macbeth’s character confronts his mortality and the virtual meaninglessness of his life, readers and audiences are called to do the same. Without affirmation or positive resolution , Macbeth’s words are as tragic for readers and audiences as they are for his own character.
Like M a cbeth , Shakespeare’s tragedies are as currently relevant as they were when they were written. The themes of power, ambition, death, love, and fate incorporated in his tragic literary works are universal and timeless. This allows tragedy as a genre to remain relatable to modern and future readers and audiences.
Example 2: The Color Purple by Alice Walker
All my life I had to fight. I had to fight my daddy . I had to fight my brothers. I had to fight my cousins and my uncles. A girl child ain’t safe in a family of men. But I never thought I’d have to fight in my own house. She let out her breath. I loves Harpo, she say. God knows I do. But I’ll kill him dead before I let him beat me.
The formal genre of this literary work is novel. Walker’s novel can be sub-categorized within many fictional genres. This passage represents and validates its sub-classification within the genre of feminist fiction. Sofia’s character, at the outset, is assertive as a black woman who has been systematically marginalized in her community and family, and she expresses her independence from the dominance and control of men. Sofia is a foil character for Celie, the protagonist, who often submits to the power, control, and brutality of her husband. The juxtaposition of these characters indicates the limited options and harsh consequences faced by women with feminist ideals in the novel.
Unfortunately, Sofia’s determination to fight for herself leads her to be beaten close to death and sent to prison when she asserts herself in front of the white mayor’s wife. However, Sofia’s strong feminist traits have a significant impact on the other characters in the novel, and though she is not able to alter the systemic racism and subjugation she faces as a black woman, she does maintain her dignity as a feminist character in the novel.
Example 3: A Word to Husbands by Ogden Nash
To keep your marriage brimming With love in the loving cup, Whenever you’re wrong, admit it; Whenever you’re right, shut up.
The formal genre of this literary work is poetry. Nash’s poem would be sub-categorized within the genre of humor . The poet’s message to what is presumably his fellow husbands is witty, clear, and direct–through the wording and message of the last poetic line may be unexpected for many readers. In addition, the structure of the poem sets up the “punchline” at the end. The piece begins with poetic wording that appears to romanticize love and marriage, which makes the contrasting “base” language of the final line a satisfying surprise and ironic twist for the reader. The poet’s tone is humorous and light-hearted which also appeals to the characteristics and conventions of this genre.
Synonyms of Genre
Genre doesn’t have direct synonyms . A few close meanings are category, class, group, classification, grouping, head, heading, list, set, listing, and categorization. Some other words such as species, variety, family, school, and division also fall in the category of its synonyms.
Post navigation
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
How do You Use Social Media? Be entered to win a $50 gift card!
50+ Literary Genres and Subgenres Every Student Should Know
So many genres, so little time to read them all…

Once kids learn to read, they unlock a very rich world of books and other writings to explore. This list of literary genres and subgenres offers definitions and examples for a wide array of writing styles. Encourage students to explore them all!
What are literary genres?
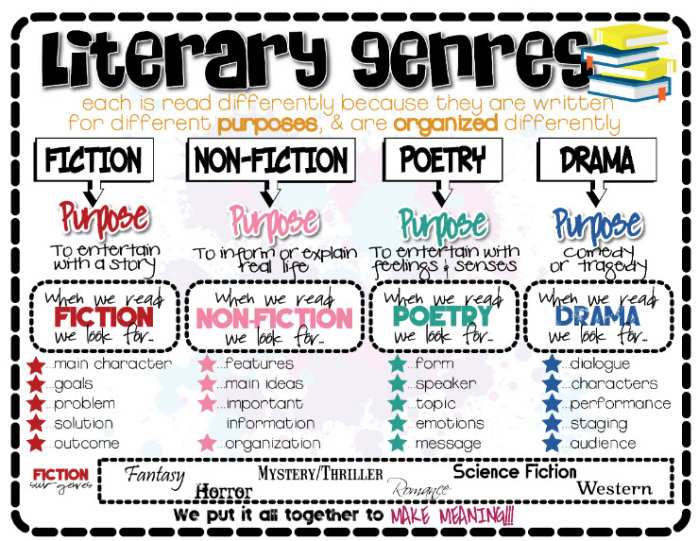
Source: The Chalkboard Unicorn
A genre (ZHAHN-ruh) is a category of literature in which the various works share certain characteristics. We often break writing into four main literary genres: fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and drama. (Some people consider fiction and nonfiction to be one category called prose.)
Each of the literary genres has its own set of subgenres. There’s no definitive list of literary subgenres, and authors regularly invent new styles. For our list, we’ve chosen common literary genres and subgenres that students should learn to recognize. This is not a complete list by any means.
Students should also understand that many literary works fit into multiple categories, so narrowing down the literary genres and subgenres can be difficult. Still, knowing these different types can help kids learn which types of books they enjoy most and make it easier to find more of them.

Stories, poems, and plays that tell imaginary tales are called fiction. The people and events may be completely imaginary or based on real people and events but in fictionalized form.
When fiction is written as it is spoken, it’s known as prose. If the structure includes a focus on rhyme and rhythm, we call it poetry. Prose fiction can be broken down into categories by its length.
We use the term “novel” to describe a long piece of fiction, often described as “book-length.” Graphic novels use illustrations to help tell the tale, while novels in verse are very long poems that tell a story.
Examples: Moby Dick by Herman Melville, Huckleberry Finn by Mark Twain
Novellas are shorter than full-length novels but longer than a short story. There’s no one accepted definition of the length of a novella; they generally range from 10,000 to 50,000 words.
Examples: A Christmas Carol by Charles Dickens, Of Mice and Men by John Steinbeck
Short Story
A short story tells a complete tale with a fully developed theme, but it’s shorter than a novel or novella. They’re usually about 10,000 words or less.
Examples: “The Gift of the Magi” by O. Henry, “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin
- 50 Irresistible Short Stories for Kids
- 70 Great Short Stories for Middle Schoolers
- 50 Best Short Stories for High School Students
While fiction is one of the major literary genres, it can be broken down into many categories known as subgenres. These subgenres describe the style and/or subjects of the literary work. It’s important to note that many works of fiction can fit into multiple subgenres.
Bildungsroman
Also described as a “coming-of-age” book, the bildungsroman (German for “education book”) tells the story of a protagonist from childhood to adulthood. It explores their moral and psychological growth, and is often (but not always) written in the first person.
Examples: Great Expectations by Charles Dickens, The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger
Originally, this term was used to describe long poems that tell the story of a hero’s journey’s and adventures. Over the years, this term has evolved to include novels and plays that trace a person or family’s history over a long period of time.
Examples: The Odyssey by Homer, War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy
Fables are short stories that teach a specific moral. Aesop is the most famous author of fables; his tales often use animals to tell the story and state the moral at the end.
Examples: “The Tortoise and the Hare” by Aesop, Fables for Our Time by James Thurber
Fairy tales are highly fictionalized short stories that generally include magic and fantastical characters. They’re usually intended for children and often feature a protagonist who receives a “happy ending” and an antagonist (villain) who is punished in the end.
Examples: “Cinderella” by the Brothers Grimm, “The Little Mermaid” by Hans Christian Andersen
Fantasy works are set in imaginary magical worlds and include mythical creatures like dragons, witches, vampires, and more. Avoid confusing this genre with science fiction; remember that fantasy deals with the impossible, while sci-fi explores the possible. (The two are frequently combined, though, and many works have characteristics of each.)
Examples: The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone by J.K. Rowling
- 20 Fantasy Books Kids Won’t Be Able to Put Down
Folktales are similar to fairy tales but originally were passed down orally rather than being written down. Therefore, they often don’t have attributed authors. Many folktales have more realistic settings than fairy tales.
Examples: Paul Bunyan stories, “Headless Horseman”
Gothic/Horror
Stories that involve ghosts, otherworldly beings, and mystical happenings that cannot be explained rationally fall into the category of gothic or horror. These novels seek to cause a sense of fear in their readers. Gothic novels were very popular in the 18th and 19th centuries, and gave rise to horror writers like Stephen King.
Examples: Frankenstein by Mary Shelley, Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
Historical Fiction
Any fiction writing set in the past, in a real place and time, fits the definition of historical fiction. The characters can be real people or imaginary ones living through the events of that time.
Examples: The Book Thief by Markus Zusak, The Good Earth by Pearl S. Buck
- 16 Page-Turning Historical Fiction Books for Readers of All Ages
Legend/Myth
Legends and myths are ancient tales that explain early history or natural events, often using supernatural characters. Greek, Roman, and Egyptian myths remain popular today, though all cultures have their own myths and legends that have been passed down for hundreds or thousands of years. As most started as oral tradition, they rarely have attributed authors.
Examples: “Theseus and the Minotaur,” “Robin Hood,” “King Arthur and the Knights of the Round Table”
- 8 Egyptian Myths Students Should Know
- 10 Great Greek Myths Your Students Should Learn
- 16 Fascinating Greek Mythology Books for Kids
In a mystery, the characters must solve a puzzle, usually a crime of some sort. Generally, the solution isn’t revealed until the end of the story. The reader can use clues to try to solve the mystery themselves as they read.
Examples: Murder on the Orient Express by Agatha Christie, The Westing Game by Ellen Raskin
- 21 Must-Read Mystery Books for Kids
- 20 Terrific Mysteries for Classroom Libraries
- Books Like Encyclopedia Brown for Mystery-Loving Kids
Roman à clef
French for “novel with a key,” a roman à clef (pronounced “roh-MAHN ah clay”) is a story about real-life people and events, thinly disguised as fiction. The characters are given fictional names, and other details may be changed slightly. The “key” is the hints the author gives the reader to help them make the connection between fact and fiction.
Examples: The Bell Jar by Sylvia Plath, Animal Farm by George Orwell
Any writing that primarily focuses on the love story between two (or more) people is a romance. These stories often have happy or emotionally satisfying endings, though some end tragically instead.
Examples: Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen, The Fault in Our Stars by John Green
Satire ridicules a topic or person, in an attempt to provoke the reader into rethinking their opinions on the subject. They may use irony, caricature, parody, and other literary devices, and characters and plots are often exaggerated or extreme to make the author’s point.
Examples: Gulliver’s Travels by Jonathan Swift, Catch-22 by Joseph Heller
Science Fiction
Also called sci-fi, this form of fiction speculates about potential changes to the real world based on scientific principles. Many sci-fi works focus on space travel, parallel universes, and time travel. They often take place in the future or on distant planets or worlds. Generally science fiction is considered to be stories that are possible based on our understanding of science, while fantasy works include magic or other supernatural elements. The two are often combined, and many works fit into both categories.
Examples: The Time Machine by H.G. Wells, Flowers for Algernon by Daniel Keyes
- 16 Thrilling Sci-Fi Books for Tweens and Young Adults
Utopian/Dystopian
In utopian literature, the writer imagines a “perfect” world, while dystopian writing posits a dark and cataclysmic future or alternate present. In many cases, the imaginary world is initially presented as utopian, but as more details emerge, the dystopian elements become clear. Therefore, these literary genres are often lumped together.
Examples: The Handmaid’s Tale by Margaret Atwood, The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
The opposite of fiction is nonfiction, which focuses on information and facts about real people, events, and other topics. Nonfiction can be full-length books or shorter compositions like articles or essays. It also includes “how-to” writing like cookbooks and self-help books.

There are many categories of nonfiction, usually based on the topic or subject. Here are some common nonfiction subgenres kids should learn about.
Autobiography/Biography
A biography tells the story of a person’s life, usually from birth to death. When a person writes their own biographical work, it’s called an autobiography.
Examples: The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank, The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks by Rebecca Skloot
- How To Use Picture Book Biographies in the Classroom
- 12 Inspiring Biographies for Teens
An essay is a short nonfiction work on a specific topic. It’s usually a personal reflection on a subject, in which the author shares their own experiences and thoughts. Sometimes authors publish their essays together in collections as books. These collections can include essays on related topics or simply be a compilation of an author’s works.
Examples: A Room of One’s Own by Virginia Woolf, Walden by Henry David Thoreau
Expository Nonfiction
This catch-all category includes any nonfiction book that seeks to tell its readers about a specific topic. It often uses illustrations, diagrams, and quotes from original sources.
Examples: We Are Water Protectors by Carole Lindstrom, Freakonomics by Stephen J. Dubner and Steven Levitt
Any nonfiction book that focuses on real people or events of the past is a history book. Biographies and autobiographies can fall into this category, but histories usually encompass a larger group of people and their impact on contemporary events.
Examples: Hidden Figures by Margot Lee Shetterly, 1776 by David McCullough
While memoirs are similar to autobiographies, they differ in a few small ways. Memoirs don’t generally try to tell the entire story of a person’s life. Instead, they reflect on a person’s experiences during important parts of their life. They are nearly always written in the first person.
Examples: All Boys Aren’t Blue by George M. Johnson, I Am Malala by Malala Yousafzai
Narrative Nonfiction
In narrative nonfiction, the author tells the tale of a real person or event in a way that feels more like a fiction story. The information is factual, but the style is entertaining and engaging.
Examples: In Cold Blood by Truman Capote, Killers of the Flower Moon by David Grann
When an author writes about their travel experiences, we call it a travelogue or simply “travel writing.” Usually, the author recounts a specific trip or series of related journeys. They describe the people and places they see along the way, offering their own thoughts and opinions about these encounters.
Examples: A Walk in the Woods by Bill Bryson, The Mosquito Coast by Paul Theroux
Also called verse, poetry gives special importance to the use of words, imagery, and rhythm. Poems are individual works of poetry. Poems usually break down into lines and stanzas rather than sentences and paragraphs. They can be fiction or nonfiction and of any length from a few lines to an entire book.
We can break poetry into subgenres based on characteristics like rhyme scheme (or lack thereof), rhythmic patterns, subject, and more. Here are some common poetic literary genres kids should know. See their definitions and details here: 15 Types of Poetry to Teach Kids and Teens .
- Blackout Poetry
- Blank Verse
- Concrete Poetry
- Narrative Poetry
- Sonnet (Shakespearean and Petrarchan)
- 70 Must-Share Poems for Your Elementary Classroom
- 45 Terrific Poems for Middle School and High School
This literary genre includes plays, musical, operas, and operettas, written to be performed in front of an audience. Students often study plays in literature classes, reading them instead of seeing them performed. They can be short, or longer works broken into multiple scenes and acts.
While dramatic works can be nonfictional, they are usually fiction. Experts break plays and other dramatic works into multiple categories. These are the most common.
Make them laugh! Comedies are light and humorous dramatic works. The Greeks and Romans used this term for plays where the hero faces adversity and overcomes it in the end. By Shakespeare’s time, comedies involved humor, silly situations, and happy endings all around, and that’s how we usually use the term today.
Examples: The Taming of the Shrew by William Shakespeare, The Importance of Being Earnest by Oscar Wilde
A farce is a type of comedy, with exaggerated characters and improbable situations. There’s usually a lot of physical comedy, with characters taking ludicrous circumstances and happenings very seriously.
Examples: The Comedy of Errors by William Shakespeare, She Stoops to Conquer by Oliver Goldsmith
A tragedy tells the story of a protagonist with a tragic flaw, which ultimately leads to their downfall. Tragedies can also relate terrible or sorrowful events, from the point of view of one or more characters.
Examples: Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare, Death of a Salesman by Arthur Miller
Tragicomedy
As the name implies, these dramatic works have elements of both comedy and tragedy. They can have sad or happy endings, or even those that are inconclusive. They often tell tragic tales, with enough humor to lighten the overall mood throughout.
Examples: The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare, Waiting for Godot by Samuel Beckett
History Play
Today, we use this term almost exclusively to describe Shakespeare’s plays about real historical people and events. These dramatic works were very popular during Elizabethan times.
Examples: Richard III and Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
Problem Play
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, playwrights began writing dramatic works to draw attention to social issues or problems. Henrik Ibsen and George Bernard Shaw are well-known for this subgenre.
Examples: A Doll’s House by Henrik Ibsen, Mrs. Warren’s Profession by George Bernard Shaw
We believe in encouraging kids to read all kinds of literary genres and books, including these 16 Banned Books to Read Before 12th Grade .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters .

You Might Also Like

What Is Scarborough’s Reading Rope and How Do Teachers Use It?
The many strands that weave into skilled reading. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
3.3 Glance at Genre: The Literacy Narrative
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Read and compose in several genres to understand how genre conventions shape and are shaped by readers’ and writers’ practices and purposes.
- Match the capacities of different environments to varying rhetorical situations.
Over time, people have developed specific ways of writing for particular rhetorical situations. These distinctive ways of writing can be referred to in part as genres. You may have heard the term genre in reference to publishing categories, such as novels or memoirs, but the term can refer to any type of writing that conforms to specific forms and benchmarks. Many genres include stories of different kinds—for example, folktales, short stories, accounts of events, and biographies. As author Jonathan Gottschall says in his 2012 book of the same title, humankind is “the storytelling animal”; people of all cultures have engaged in telling stories, both as storytellers and as audience members. Simply put, narrative stories are essential to many genres of writing.
Exploring Narrative: Elements of Storytelling
Narratives, whether about literacy or anything else, include these key elements:
- Plot. Authors of narratives tell about one or more events. In fiction, the plot is the sequence of those events. In nonfiction, a plot is often referred to simply as the events, but nonfiction texts follow similar plot patterns, including exposition or introduction, a series of events leading to a climax or discovery, and events following the climax or discovery.
- Characters. The events in the story happen to characters, or individuals who are part of the story. In nonfiction, these characters are usually real people. The audience should feel a connection to the main character or characters. Readers may like or dislike characters, blame them or feel sorry for them, identify with them or not. Skilled writers portray characters through the use of dialogue, actions or behavior, and thoughts so that readers can understand what these individuals are like.
- Setting. Stories, fiction and nonfiction, take place in settings, which include locations, time periods, and the cultures in which the characters or real people are immersed.
- Problem and Resolution. In narratives, the characters generally encounter one or more problems. The tension caused by the problem builds to a climax. The resolution of the problem and the built-up tension usually occurs near the end of the story.
- Story Arc. Most narratives have a story arc—a beginning, a middle, and an end—but not necessarily in that order. The story arc, or order of events, may occur chronologically, or the story may begin in the middle of the action and explain earlier events later in the sequence.
Specific Details and Other Conventions
To immerse the audience in the story, authors provide specific details of the scenes and action. Many authors, and teachers, call this strategy “showing, not telling.” These aspects can include the following elements:
- Sensory Details: Full, literal or figurative descriptions of the things that the characters see, smell, hear, touch, and taste in their surroundings.
- Dialogue: Conversation between characters.
- Action: Vivid portrayal of the events in the story. Writers often use short sentences and strong verbs to indicate physical or mental action.
- Engaging Language: Sentence structure and word choices, including tone (vocal attitude of the narrator or characters), diction (language used by the narrator or characters), and varied constructions (different kinds of sentences), that provide specific, clear, and compelling information for the audience.
Establishing the Significance
Most importantly, the audience must feel that the story has some significance. While the author’s main point may only be implied, rather than stated outright as in a conventional academic essay, readers should understand the point of the story and believe that it matters.
For example, in the prologue to her memoir about the importance of education for girls, I Am Malala: The Girl Who Stood Up for Education and Was Shot by the Taliban (2013), Malala Yousafzai (b. 1997) writes, “The day when everything changed was Tuesday, 9 October 2012.” Yousafzai provides reference to an exact date, the precise moment when a Taliban gunman shot her in the head because she had spoken publicly in favor of girls’ right to education. Identifying the date in this way is a technique that serves a variety of purposes. This technique provides a focal point to draw the audience into the story, identifies details that serve as rising action that the audience can assume will culminate on this date, marks the setting in both time and place for the audience, and ultimately foreshadows a climax of action for the reader. The following elements, therefore, are crucial for writers of narratives to consider when creating content for their writing.
- Audience. Narratives are designed to appeal to specific audiences; authors choose storytelling elements, details, and language strategies to engage the target audience.
- Purpose. Authors may tell stories for different reasons: to entertain, to reinforce cultural norms, to educate, or to strengthen social ties. The same story may, and often does, fulfill more than one purpose.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/3-3-glance-at-genre-the-literacy-narrative
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write Within a Genre
I. What is a Genre?
A genre is a category of literature identified by form, content, and style. Genres allow literary critics and students to classify compositions within the larger canon of literature. Genre (pronounced ˈzhän-rə) is derived from the French phrase genre meaning “kind” or “type.”
II. Types and Examples of Genres
Literature could be divided into countless genres and subgenres, but there are three main genres which preside over most subgenres. Here are the main genres in literature:
As poetry has evolved, it has taken on numerous forms, but in general poetry is the genre of literature which has some form of meter or rhyme with focus based on syllable counts, musicality, and division of lines (lineation). Unlike prose which runs from one end of the page to the other, poetry is typically written in lines and blocks of lines known as stanzas .
Here is an excerpt from Maya Angelou’s “Still I Rise”:
You may write me down in history
With your bitter, twisted lies,
You may trod me in the very dirt
But still, like dust, I’ll rise.
Does my sassiness upset you?
Why are you beset with gloom?
‘Cause I walk like I’ve got oil wells
Pumping in my living room.
Just like moons and like suns,
With the certainty of tides,
Just like hopes springing high,
Still I’ll rise.
Prose encompasses any literary text which is not arranged in a poetic form. Put simply, prose is whatever is not poetry. Prose includes novels, short stories, journals, letters, fiction and nonfiction, among others. This article is an example of prose.
Drama is a text which has been written with the intention of being performed for an audience. Dramas range from plays to improvisations on stage. Popular dramas include Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet , Lorraine Hansberry’s A Raisin in the Sun , and Tennessee Williams’ A Streetcar Named Desire.

III. The Importance of Using Genres
Genres give writers a specific type of literature to work within. They allow writers to specialize in one genre or to dabble in others. Students in creative writing may focus in a variety of genres from poetry to prose to nonfiction to playwriting. Genres allow us to classify literature, to deem what is appropriate for a certain type of literature, and to judge the merit of literature based on its genre. In general, genre is a classifying tool which allows us to compare and contrast works within the same genre and to study how works broaden or challenge certain genre-based constraints. New genres like media (writing for television, film, websites, radios, billboards, etc.) and the graphic novel (comic books) are expanding what we consider literature today.
IV. Genres in Literature
The three main genres in literature are prose, poetry, and drama, but there are many more subgenres, or genres within genres. Here are a few examples of other genres in literature:
Maus: A Survivor’s Tale by Art Spiegelman
Maus is an example of a literary genre called the graphic novel, sometimes better known as the comic book. In Maus , Spiegelman tells the story of the Holocaust using animal characters .
Speak by Laurie Halse Anderson
THE FIRST TEN LIES THEY TELL YOU IN HIGH SCHOOL 1. We are here to help you. 2. You will have time to get to your class before the bell rings. 3. The dress code will be enforced. 4. No smoking is allowed on school grounds. 5. Our football team will win the championship this year. 6. We expect more of you here. 7. Guidance counselors are always available to listen. 8. Your schedule was created with you in mind. 9. Your locker combination is private. 10.These will be the years you look back on fondly. TEN MORE LIES THEY TELL YOU IN HIGH SCHOOL 1. You will use algebra in your adult lives. 2.Driving to school is a privilege that can be taken away. 3. Students must stay on campus during lunch. 4. The new text books will arrive any day now. 5. Colleges care more about you than your SAT scores. 6. We are enforcing the dress code. 7. We will figure out how to turn off the heat soon. 8. Our bus drivers are highly trained professionals. 9. There is nothing wrong with summer school. 10. We want to hear what you have to say.
Speak is an example of young adult fiction, another subgenre of prose. YA fiction appeals to young adults from the ages of twelve to eighteen with coming-of-age stories about various subjects from high school struggles to family conflict to relationships.
There are numerous genres in literature, including poetry and prose, fiction and nonfiction, short stories and novels, dramas, fables , fairytales, legends , biographies, and reference books. The list goes on with countless genres and subgenres categorizing literature in numerous ways based on numerous characteristics and styles of writing.
V. Genres in Pop Culture
Genres are not limited to literature. There are genres of movies, television shows, and songs as well. Here are a few examples of genres in pop culture.
![genres include short stories and essays The Notebook Movie Trailer [HD]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FC6biTjEyZw/0.jpg)
Nicholas Sparks’ The Notebook is considered by many to be the quintessential example of the romance genre in both fiction books and movies. Other movie genres include drama, comedy, romantic comedy, sci-fi, animated, and fantasy.
The are a lot of musical genres. The following are some of the most popular genres:
- Hip hop music
- Classical period
- Country music
- Classical music
- Popular music
- Rhythm and blues
- Heavy metal
- Electronic dance music
- Alternative rock
- Instrumental
VI. Related Terms: Style vs. Genre
Often, an aspect of what allows us to define a genre is the specific style of the writing. The mystery genre purposely uses suspense and withholding certain information from the reader. Different subgenres of poetry are written in different styles: haikus tend to be peaceful or playful, sonnets are often romantic, and free verse is free to hop styles with or without rhyme, with or without line breaks. The difference between style and genre is that genre is an overarching type of literature, whereas style can be considered an aspect of a genre or even of a specific writer’s voice. Here is an example of style versus genre:
We have no idea what’s going on! Who knows? Who could possibly know? Who murdered Mr. Brown?! Everyone is panicking! No one knows what to do! This is insane!
The style of this writing is choppy, overly dramatic, and panicked.
This story investigates the murder of Mr. Brown, who was found dead in the library.
The genre, on the other hand, is the murder mystery.
VII. In Closing
Genres allow us to divide various types of literature, music, movies, and other art forms into classifiable groups. Beyond the classical genres of prose, poetry, and drama in literature, there are numerous subgenres ranging from fantasy to nonfiction.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
Genres in Literature
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In literature, every piece of writing falls under a general category, also known as a genre. We experience genres is other parts of our daily lives, such as movies and music, and in each case, the individual genres typically have distinctive styles in terms of how they are composed. At the most basic level, there are essentially three main genres for literature - poetry, prose and drama - and each can be broken down even further, resulting in dozens of subgenres for each. Some resources will cite only two genres: fiction and non-fiction, though many classics will argue that fiction and non-fiction can, and do, both fall under poetry, drama or prose.
While there is much debate over what constitutes a genre in literature, for the purposes of this article, we will break down the classic three. From there, we will outline some of the subgenres for each, including those that some believe should be classified as main genres.
Poetry is a style of writing that tends to be written in verses, and typically employs a rhythmic and measured approach to composition. It characteristically is known for evoking emotional responses from readers through its melodic tone and use of creative language that is often imaginative and symbolic in nature. The word “poetry” comes from the Greek word “poiesis” which essentially means, making, which is translated into the making of poetry. Poetry is typically divided into two main subgenres, narrative and lyric, which each have additional types that fall under their respective umbrellas. For example, narrative poetry includes ballads and epic tales, while lyric poetry includes sonnets, psalms and even folk songs. Poetry can be fiction or nonfiction.
Prose is essentially identified as written text that aligns with the flow of conversation in sentence and paragraph form, as opposed to verses and stanzas in poetry . Writing of prose employs common grammatical structure and a natural flow of speech, not a specific tempo or rhythm as is seen in traditional poetry. Prose as a genre can be broken down into a number of subgenres including both fiction and non-fiction works. Examples of prose can range from news, biographies and essays to novels, short stories, plays and fables. The subject matter, if it is fiction versus nonfiction and length of the work, are not taken into consideration when classifying it as prose, but rather the style of writing that is conversational is what lands works in this genre.
Drama is defined as theatrical dialogue that is performed on stage and traditionally is comprised of five acts. It is generally broken down into four subgenres including comedy, melodrama, tragedy and farce. In many cases, dramas will actually overlap with poetry and prose, depending on the writing style of the author. Some dramatic pieces are written in a poetic style, while others employ a more casual writing style seen in prose, to better relate to the audience. Like both poetry and prose, dramas can be fiction or nonfiction, though most are fictional or inspired by real life, but not completely accurate.
The Genre and Subgenre Debate
Beyond these three basic genres, if you conduct an online search for “genres of literature,” you will find dozens of conflicting reports that claim any number of main genres that exist. There is often debate over what constitutes genre, but in most cases, there is a misunderstanding of the difference between genre and subject matter. It’s common for subject matter to be considered a genre in not only literature, but also in movies and even games, both of which are often based on or inspired by books . These subjects can include biography, business, fiction, history, mystery, comedy, romance and thrillers. Subjects may also include cooking, self help, diet and fitness, religion and many many more.
Subjects and subgenres, however, can often be intermixed. Though, it can be a challenge to determine how many subgenres or subjects actually exist, as there are differing opinions on each, and new ones are created regularly. For example, young adult writing has become increasingly popular, and some would classify it as a subgenre of prose.
The difference between genre and subject is often blurred by the world around us. Think of a time when you last visited a bookstore or library. Most likely, the books were divided into sections - fiction and non-fiction for sure - and further categorized based on the type of books, such as self-help, historic, science fiction and others. Many people assume that these categorizations of subject matter are genre, and as a result, common language today has adopted a casual use of genre to mean subject.
- What Is a Novel? Definition and Characteristics
- Word Choice in English Composition and Literature
- An Introduction to Literary Nonfiction
- What Is Drama? Literary Definition and Examples
- What Is Prose?
- Are Literature and Fiction the Same?
- What Is Narrative Poetry? Definition and Examples
- What Is a Synopsis and How Do You Write One?
- Anthology: Definition and Examples in Literature
- Gothic Literature
- What Is the Canon in Literature?
- The Basic Characteristics of Effective Writing
- A Guide to All Types of Narration, With Examples
- What Is Burlesque Literature?
- Interior Monologues
- Stylistics and Elements of Style in Literature
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
Short Story: A Literary Genre
The short story, a concise narrative form within the literary canon, is characterized by brevity and focus, typically encapsulating a single theme, conflict, or character development in a limited word count.
Short Story: Literal and Conceptual Meanings
Table of Contents
The short story as a genre epitomizes a dynamic interplay between literal and conceptual meanings, presenting a concise yet potent narrative form that beckons readers to explore beyond its surface. On a literal level, short stories encapsulate succinct plots, well-defined characters, and often a singular theme or conflict within a confined word count. This brevity, however, acts as a canvas for the conceptual dimensions to unfold. Short stories frequently operate as allegories or metaphors, encapsulating broader societal, psychological, or existential truths within their narrative confines. This dual nature of literal brevity and conceptual depth allows short stories to resonate with readers on both immediate and profound levels, challenging them to unravel layers of meaning and prompting contemplation long after the final words have been read.
Short Story: Definition as a Literary Genre
The short story, a concise narrative form within the literary canon, is characterized by brevity and focus, typically encapsulating a single theme , conflict , or character development in a limited word count. It serves as a literary microcosm, offering a snapshot of human experience that demands precision in storytelling.
Defined by its compact structure, the short story demands economy of language while often inviting readers to engage with nuanced layers of meaning and interpretation.
Short Story: Types
This table aims to encompass a wide range of short story types, but the categorization can be fluid as some stories may exhibit characteristics of multiple genres.
Short Story in Literature: Key Features
- Brevity: Short stories are concise narratives that focus on a single theme, incident, or character. They aim to deliver a complete narrative experience within a limited word count.
- Central Theme: Short stories often revolve around a central theme or idea, providing a focused exploration of specific emotions, conflicts, or concepts.
- Character Development: Despite their brevity, short stories can feature well-developed characters that undergo significant changes or face challenges, contributing to the narrative’s depth.
- Economy of Language: Short stories demand precision in language use. Every word serves a purpose, contributing to the overall impact of the narrative.
- Limited Setting: Due to their compact nature, short stories often have a limited setting, focusing on specific locations or environments essential to the plot.
- Crisis or Turning Point: Short stories frequently include a critical moment, often referred to as the climax, where the narrative takes a decisive turn, leading to resolution or a change in the characters’ circumstances.
- Narrative Structure : While there is flexibility, short stories typically follow a traditional narrative structure with an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
- Emphasis on Imagery: Short stories often rely on vivid imagery to convey emotions, settings, and characters in a condensed format, engaging the reader’s senses.
- Open or Closed Endings: Short stories can conclude with either open or closed endings, leaving room for interpretation or providing a definitive resolution to the narrative.
- Exploration of Human Experience: Whether through realistic portrayals or fantastical elements, short stories aim to capture facets of the human experience, offering insights, reflections, or commentary on life.
These features collectively contribute to the unique appeal and impact of short stories within the broader landscape of literature.

Short Story in World Literature: Best Examples
- Features: A complex narrative that blends elements of fantasy, philosophy, and detective fiction, exploring the idea of infinite possibilities.
- Features: A satirical and absurd tale where a man wakes up to find his nose missing, delving into themes of identity and societal absurdity.
- Features: Blurring the lines between journalism and fiction, Marquez narrates the events leading to a man’s predestined death in a small Colombian town.
- Features: A poignant exploration of family dynamics and loss, told through the eyes of a young girl whose father works at a lighthouse.
- Features: A contemporary Japanese story blending romance and coming-of-age elements, capturing the essence of grief, love, and personal growth.
Short Story in British Literature: Best Examples
- Features: A classic ghost story that blends the supernatural with Dickens’s social commentary, exploring themes of isolation and fate.
- Features: A poignant exploration of the destructive nature of materialism and the impact of familial expectations on a young boy.
- Features: The final story in Joyce’s “Dubliners,” offering a rich portrayal of Irish society and delving into themes of love, death, and self-discovery.
- Features: While Jackson is American, “The Lottery” had a significant impact on British literature. It’s a chilling exploration of blind conformity and the darker aspects of tradition.
- Features: A darkly humorous and suspenseful tale that showcases Dahl’s skill in blending the macabre with wit, as a young man discovers the unsettling secrets of his landlady.
Short Story in American Literature: Best Examples
- Features: A Gothic masterpiece that explores the psychological deterioration of an unnamed narrator who becomes obsessed with the “vulture eye” of an old man.
- Features: A chilling portrayal of a small town’s ritualistic stoning, revealing the dangers of blind conformity and the darker aspects of tradition.
- Features: A Southern Gothic tale that combines dark humor with profound moral questions, as a family’s road trip takes an unexpected and tragic turn.
- Features: A story that blends adventure with introspection, exploring themes of regret, death, and the impact of a writer’s choices on his life.
- Features: A humorous exploration of the effects of sudden wealth on a working-class family, reflecting Chekhov’s keen understanding of human nature.
Short Story in Literature Translation: Best Examples
- Features: A poignant reflection on language, culture, and loss set against the backdrop of the Franco-Prussian War, emphasizing the importance of education.
- Features: A thought-provoking exploration of the nature of life, morality, and the pursuit of knowledge, showcasing Chekhov’s mastery of the short story form.
- Features: A mind-bending narrative that blends elements of fantasy, philosophy, and detective fiction, challenging conventional notions of time and reality.
- Features: A classic novella that captures the indomitable spirit of an aging Cuban fisherman, exploring themes of resilience, endurance, and the eternal struggle between man and nature.
- Features: A collection of short stories that delves into Murakami’s surreal and existential themes, often blurring the boundaries between reality and imagination.
Short Story in Literature: Relevant Terms
Short story in literature: suggested readings.
- Chekhov, Anton. The Essential Tales of Chekhov. Edited by Richard Ford, Ecco, 1999.
- O’Connor, Flannery. A Good Man Is Hard to Find and Other Stories. Harcourt, 1955.
- Borges, Jorge Luis. Collected Fictions . Translated by Andrew Hurley, Viking Penguin, 1998.
- Joyce, James. Dubliners. Oxford University Press, 1996.
- Murakami, Haruki. Men Without Women . Translated by Philip Gabriel and Ted Goossen, Knopf, 2017.
Anthologies:
- The Oxford Book of American Short Stories. Edited by Joyce Carol Oates, Oxford University Press, 2012.
- The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories . Edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994.
- The Norton Anthology of Short Fiction. Edited by R.V. Cassill and Richard Bausch, W. W. Norton & Company, 1981.
- The Art of the Short Story . Edited by Dana Gioia and R. S. Gwynn, Pearson, 2005.
Theoretical Works:
- Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Philosophy of Composition.” The Complete Works of Edgar Allan Poe , edited by James A. Harrison, T. Y. Crowell & Co., 1902, pp. 356-370.
- Culler, Jonathan. The Pursuit of Signs: Semiotics, Literature, Deconstruction. Cornell University Press, 1981.
Related posts:
- Prolepsis: A Literary Device
- Theatrical Devices in Plays/Dramas
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Genre Primer: Short Story Examples in (Almost) Every Genre
Annika Barranti Klein
Annika Barranti Klein likes books, obviously. Twitter: @noirbettie
View All posts by Annika Barranti Klein
It occurred to me the other day that the short story is the perfect gateway into any genre. It seems like this thought came to me rather late, considering how long I’ve held that the short story is the perfect form, but here we are. Now that I’ve had the idea of using short story examples to define genres, I could not resist the urge to share it with Book Riot readers. So here is a short story example (or two) for every fiction genre. These are all free short stories online, and I’ve paired every story with a novel in case you need more of that genre right away.
Please note that I will not cover larger categories here, so there is no YA (for example) as young adult fiction can be any genre. I have, however, made an effort to include stories from as many age categories as possible. Also please note that many genres have a ton of crossover, and I’ve done my best to include a variety of stories without including literally every possible sub-genre because good lord, there are so many.
Is there a genre that you’re curious about? One that you’re sure you’d hate, so you’ve been avoiding? If you’d like to expand your genre horizons, this post is for you.
Short Story Examples in (Almost) Every Genre
Science fiction.
Stories set in a world that is distinguishable from ours by advanced tech such as space travel, or by imagining new uses for existing science.
How To Say I Love You With Wikipedia by Beth Goder: This sweet, heartwarming (and heartbreaking) story imagines a slightly different version of the Mars Rover—one that has feels.
Further Reading: 15 Science Fiction Short Stories to Take You Out of This World
Book Rec: Binti by Nnedi Okorafor
Typically set in the age of steam, these are sci-fi stories using the tech of that time period.
Memories in Bronze, Feathers, and Blood by Aliette de Bodard: A story about the aftereffects of war told by the metal and blood birds created by a former warrior.
Book Rec: Agatha H and the Airship City by Phil & Kaja Foglio
Low Fantasy
Fantasy set primarily in our world, with a magical or fantastical element.
Some Gods of El Paso by Maria Dahvana Headley: Vix and Lorna illegally trade in emotions they take from other people in 1920s Texas.
Book Rec: Tuck Everlasting by Natalie Babbitt
Second World/High Fantasy
Fantasy set primarily in another world, including sword and sorcery.
Do Not Look Back, My Lion by Alix E. Harrow: This story takes place in a world with very different rules than ours, as is apparent from the very first sentence: “Eefa has been a good husband, she knows, but now she is running.”
Book Rec: Empire of Sand by Tasha Suri
Portal Fantasy
A fantasy story in which characters travel from one world (usually ours) to another, this genre bridges high and low fantasy.
A Witch’s Guide to Escape: A Practical Compendium of Portal Fantasies by Alix E. Harrow: Yeah, I included two of Harrow’s stories here. I love the contrast between them, as it perfectly illustrates the wide variety in fantasy writing. This story won the Hugo for best short story, and it deserves it! In it, a librarian witch breaks the rules to help a boy find his way into the right story.
Book Rec: The Ten Thousand Doors of January by Alix E. Harrow
Often for children, these are stories in which a magical being or force propels the plot or helps the protagonist.
El Vendedor Y La Bruja or How Eduardo Found His Heart by Laura Diaz de Arce: fellow Rioter Laura wrote this beautiful new fairytale about the unexpected ways love can flourish, even for a man who thinks he cannot love.
Book Rec: Madeleine is Sleeping by Sarah Shun-lein Bynum
Along with legends and fables, these are the stories that explain the world through fantastical beings and gods.
Personal Rakshasi by Suzan Palumbo: Priya is the only one in her family who can see the Rakshasi (a Hindu being, also called a maneater, that can be good or evil) that talks to her and promises to make her suffer for her art.
Further Reading: Must-Read Classical Myth Retellings by Sarah Ullery Read Harder: A Book of Mythology by Cassie Gutman Must-Read Greek Mythology by Nikki VanRy
Book Rec: Circe by Madeline Miller (you knew it would be Circe , right?)
Sci-fi/fantasy/horror stories in the vein of H.P. Lovecraft, ideally with less racism. I hate that there’s an entire genre based on Lovecraft, but I love the myriad ways modern authors are turning it on its head.
The Oldest Solution by Priya Sridhar: Former Rioter Priya’s Old Ones are fascinated with humans, and working to help us with our problems.
Book Rec: The Ballad of Black Tom by Victor LaValle
Magical Realism
Latinx post-colonial stories in which a magical element is a normal and accepted part of life.
Dos Palabras ( Two Words ) by Isabel Allende: Belisa learns the power of words and sells them to earn a living. When she sells a colonel the words for a speech, she gives him two secret words and he becomes enchanted by them.
Book Rec: Like Water for Chocolate by Laura Esquivel
Stories set in the real world with a fantastical element, these are distinguished from low fantasy by the thinnest of lines.
The Prospectors by Karen Russell: a ghost story set in the old west, this story is about far more than the elements it is made up of.
Book Rec: Imaginary Girls by Nova Ren Suma
Stories where a mystery is central to the plot and is solved at the end.
The Adventure of the Sealed Room by Andy Weir: a Holmesian mystery starring Moriarty by the author of The Martian .
Book Rec: Magic for Liars by Sarah Gailey
Thriller/Suspense
Stories—often mysteries, but rarely straightforward—that rely on tension and keep you wondering what’s going to happen next.
The Polaroid by Renee Roberson: a kidnapped girl, help captive for five years, learns that the outside world has realized she and the boy being held with her may still be alive. Content warning for implied sexual assault.
Book Rec: Sadie by Courtney Summers
Nihilistic crime fiction, often—but not always—told from the criminals’ POV.
Come to Jesus by Stephen Blackmoore: Heather’s brother steals her savings and she goes to get it back. Content warning for drug use, violence, gun violence, sex work and anti–sex work language, and discussion of STIs.
Further Reading: Must-Read Noir
Book Rec: Queenpin by Megan Abbott
Fiction set in the past, generally realistic in nature.
A Cut-Purse Rethinks His Ways by Kate Heartfield: Pinch makes a wish on a bent sixpence and suddenly things he lost start turning up, leading him back…where?
Book Rec: The Queen of the Night by Alexander Chee
Fiction set in the American West, primarily in the 1800s.
Prairie Fever by Annika Barranti Klein: What would it take for a woman with no choices, stuck in an unhappy marriage and listening to the ceaseless winds every day, to find satisfaction? (Disclosure: I am the author.)
Further Reading: 7 Anti-Colonialist Westerns
Book Rec: My Antonia by Willa Cather
Stories in which the love story is central to the plot and ends happily.
The Goddess of Small Things by Courtney Milan: Written before any of her novels, this was an entry in a writing contest with a prompt. In it, a suspicious Earl tries to learn the true identity of a beautiful and mysterious woman at a ball.
Book Rec: The Lady’s Guide to Celestial Mechanics by Olivia Waite (historical); The Kiss Quotient by Helen Hoang (contemporary)
Scary stories to read in the dark.
Hover by Samantha Mabry: Daisy can see a ghost in their new house; her sister Rebecca becomes obsessed with it.
Book Rec: The Haunting of Hill House by Shirley Jackson
Stories, often horror, in which the place is a character and there is a distinct sense of foreboding.
The Crow Palace by Priya Sharma: Julie returns home after her father’s death to assume responsibility for her disabled sister, but she finds family secrets that only the crows can tell her.
Further reading: 50 Must-Read Gothic Novels
Book Rec: The Moth Diaries by Rachel Klein
Stories in which the writing is the primary draw, these often focus more on characters than plot.
Breathing for Two by Allison Light: She knows Hal is stealing the rubber ducks, and she decides not to say anything.
Book Rec: Such a Fun Age by Kiley Reid
Coming-of-Age
Stories that are specifically about growing up, AKA bildungsroman.
Love is Done at the Seat of Your Pants by Lyndsie Manusos: Jess deals with the fallout of a boy on the swim team dying, while also dealing with pressure from her boyfriend to have sex. Written by a fellow Rioter!
Book Rec: Rabbit Cake by Annie Hartnett
Further Reading
How long is a short story?

You Might Also Like

- My Storyboards
Literary Genres
Types of genres are categories of literature that are generally determined by technique, length, tone, and content. When we list literary forms in broader terms, they can be more abstract, flexible, and loosely defined. However, as we get more specific and into subcategories, the distinctions and rules of the genre become crystal clear.
What are the literature genres? Though we may think there are several types of written art forms, there are actually only 3 genres of literature. You may be wondering, what are the three genres of literature? Poetry, drama, and prose. That’s right. All the other genre types fit into one of these three categories. Students will typically encounter these narrative types of literature in English for most of what they read and write about in school. Therefore, they must be able to identify examples of literary artistic expressions, know their key characteristics, and list the genres of literature.

Keep reading to learn more about the different literary genres examples, along with ways for students and teachers to storyboard their forms of literature examples. In the genres of literature chart below, each of the storyboards and examples can be copied and used in an assignment with your students.
Literary Genres Examples
Here are some literary forms examples for you to check out. Different types of genres have different purposes. As you read through these examples, notice how the techniques, lengths, tones, and contents change.
Literary forms can be classified in many ways. In this section, we will take a closer look at 3 genres of literature: poetry, drama, and prose. Understanding the different classifications of literary expression in English will not only enhance your students’ reading experience but improve their writing skills too.
Types of Literary Genres
Poetry is a genre of literature that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language—such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre — to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, the literal or mundane meaning. Poetry has a very long history, dating back to prehistoric times with the creation of hunting chants and burial songs.
Among the different genre examples, poetry is considered by many to be the most intense literature genre. It allows a writer to express their deepest emotions and thoughts in a very personal way. It relies heavily on figurative language, rhythm, and imagery to relay its message to readers. Poetic writing uses beautiful language to express deep thoughts and feelings. Poetic expressions can help you understand your emotions and thoughts better, and it also helps you learn how to write more expressively.
Sub-Genres of Poetry
- Songs and Ballads

Drama is a mode of fictional representation through dialogue and performance. It is one of the kinds of literature which includes epic poetry, lyric poetry, and novel. Aristotle’s Poetics defines drama as “a representation of an action that is whole and complete and has a beginning, a middle, and an end.”
Drama is often performed on stage in front of a live audience, but it can also be presented in other forms, such as radio, film, and television. It is usually written by a playwright, although it can be adapted from other sources, such as novels, short stories, poems, or even real-life events. Or it can be read silently by individuals.
It contains dialogue, and actors impersonate the characters. Imaginary characters are frequently introduced to its narratives, allowing the playwright to explore complex human emotions and conflicts through both real-life and fantastical figures. Characters often encounter conflict, whether internal or external, as it serves as a driving force for character development and narrative tension. It is usually divided into acts or scenes and relies on props or imaginative dialogue to create a visual experience for the audience. Dramatic literary works are a good place to start, as they are usually pretty easy to understand at face value and captivates the audience with cliffhangers and mind-capitulating events.
Sub-Genres of Drama
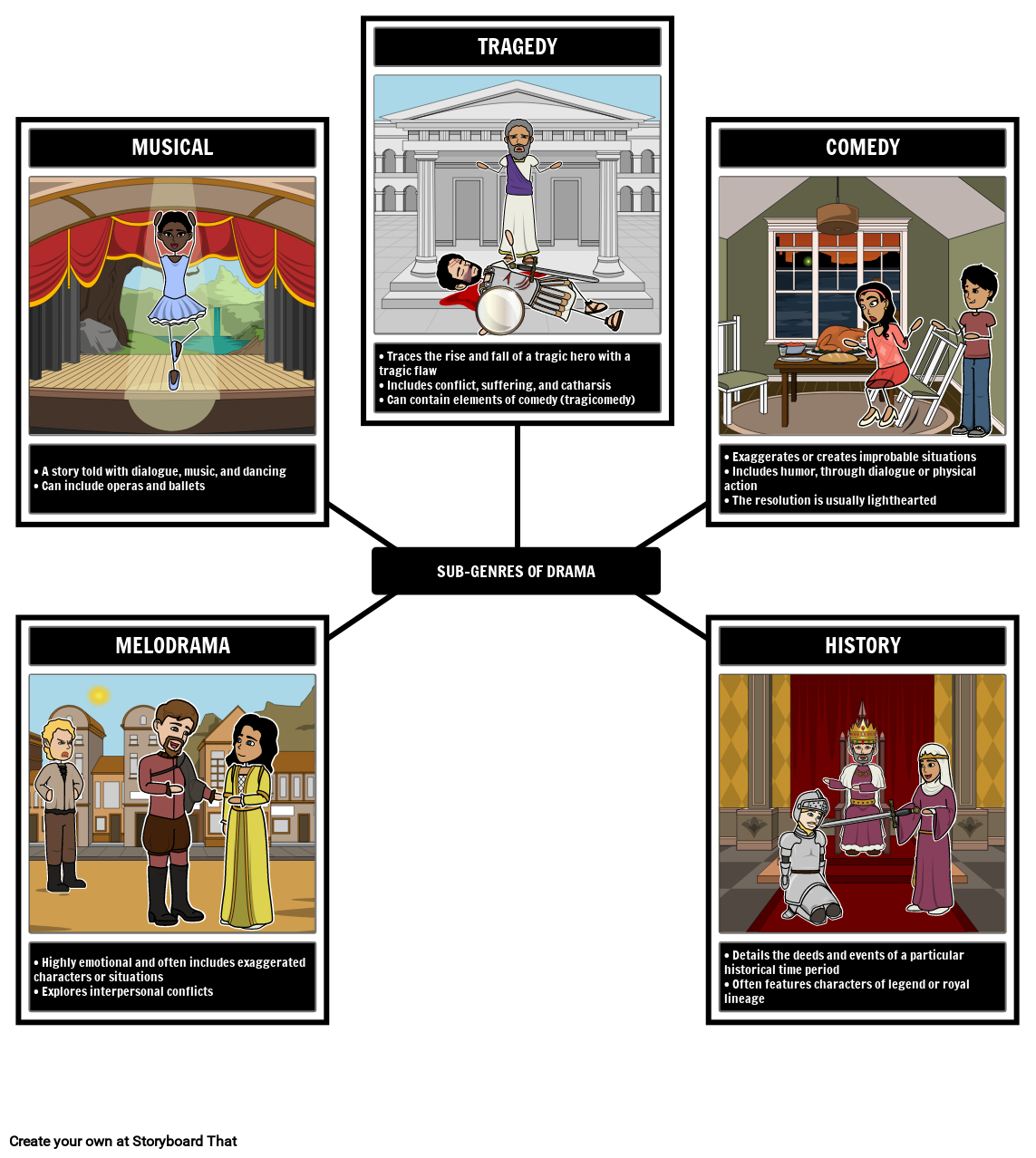
This form of literary expression has no formal metrical structure. It applies a natural flow of speech, and ordinary grammatical structure, rather than rhythmic structure, such as in the case of traditional poetry. Prose is an example of literary text that is typically written in paragraphs, although there are some exceptions, such as in the case of drama or fiction.
Prose can be found in books, magazines, newspapers, online articles, blogs, etc. It is the most common form of writing. Examples of famous works of prose include To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee & Charlotte's Web by E.B. White. The prose is simple, straightforward language. It can be either fiction or nonfiction . The prose is typically divided into paragraphs, and it uses regular grammar. It can be either serious or funny.
Fiction is narrative writing that originates from the author’s imagination. It is designed to entertain, but it can also inspire, inform, or persuade.
Sub-Genres of Fiction
- Short Story
- Myths and Legends
- Historical Fiction

Nonfiction is writing that is based on true events, people, places, and facts. It is designed to inform, and sometimes to entertain.
Sub-Genres of Nonfiction
- Autobiography
- Diaries and Journals
- Narrative Nonfiction

What Are the Three Genres of Literature?
The main examples of genres in literature are poetry, drama, and prose. Poetry is a genre in literature that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, the prosaic ostensible meaning. Drama is a mode of fictional representation through dialogue and performance. The prose is a form of language that has no formal metrical structure. It applies a natural flow of speech and ordinary grammatical structure, rather than rhythmic structure, such as in the case of traditional poetry. Genres of literature in English then fall into subcategories, which make up the three genres of literature.
Forms of literature examples are:
- Poetry: Ballads, Lyric, Epic, Dramatic, Narrative
- Drama: Tragedy, Comedy, History, Melodrama, Musical
- Prose: Fiction (Novel, Novella, Short Story), Nonfiction (Autobiography, Biography, Essay)
Genres of Literature Chart
A literature genres list would include categories like fiction, non-fiction, and folklore, but may also cover specialized types such as science fiction, romance, mystery, and historical fiction, offering a comprehensive overview of the literary landscape.
Genre types subcategories can be explained as the following:
Different types of literature being classified by genres and subgenres help people better understand the diversity of literary styles, themes, and techniques employed by authors. Each type has its own purpose and style. Whether you’re looking for a light read or something more heavy and informative, there’s definitely a literary genre out there for you.
A Note About Speeches...
While not one of the primary genres of literature, speeches are important historical documents or moments and literature, and they don’t always fit neatly into one of the three primary genre categories. A speech is a formal address given to an audience. Speeches can be found in prose, drama, and poetry, and their primary goals are to persuade, inform, demonstrate, or entertain a reader, an audience, or other characters. They can also be used in nonfiction or fiction, depending on their purpose and use.

Why Use Storyboarding to Learn About Literary Genres Types?
Storyboarding is the perfect way to learn and remember the different genres of literature. When you storyboard, you can visually see how each literary genre differs from the next. You can also track and compare the subcategories within genres, identify key characteristics of each, and even explore the relationships between genres. All of this will help you better understand and remember the genres of literature, making it easier to identify them when you encounter them in your reading.
How Can Storyboard That Enhance the Learning Experience of the Three Genres of Literature?
Storyboard That can help students better understand the three genres of literature by providing a visual representation of each one. By storyboarding, students can identify key characteristics of each genre and see how they differ from one another. Additionally, Storyboard That is a great way to compare and contrast genres, as well as explore the relationships between them. All of this will help students better remember the genres of literature and be able to identify them when they encounter them in their reading.
Looking to add a little creative flair to your literature class? Check out Storyboard That’s easy-to-use, online storyboard creator! With our drag-and-drop software, you can create engaging, visually appealing graphic organizers to help your students learn about the different genres of literature. Plus, our easy-to-use tools make it simple to add text, images, and multimedia content to your storyboards, so you can really bring your lessons to life.
Where to Start When Learning About Literary Genres
If you’re just starting to learn about literary narrative types, the best place to begin is with the three primary genres: prose, drama, and poetry. These genres are the foundation for all other types of literature, so it’s crucial to have a strong understanding of them before moving on to anything else. Each genre will approach plot development, conflict resolution, and the art of delivering a satisfying conclusion in unique and captivating ways, reflecting the rich tapestry of literary expression.
In terms of choosing between the three, poetry tends to be the most complicated to understand as it can go against the usual laws of grammar. There are a lot of deeper meanings within poetry, so it can be hard to break down as a newbie. Start with some short, simple prose articles such as newspaper pieces and short novels.
When you start to get the underlying meanings behind the prose, you can then start to dive into some simple drama. Look into Greek tragedies and Shakespearean plays, as they are a great starting point. These genres will give you a better understanding of the basics before progressing on to more.
When you’re ready to go deeper, poetry is the next stepping stone. Children’s poetry is a great starting point to give you a good foundation of poetic structure and meaning. Then you can go further into complicated poetry, such as that of the Elizabethans and Victorians.
Once you feel comfortable with the three primary genres, you can start exploring the many subgenres that exist within each one. There are endless possibilities when it comes to different types of narratives, so there’s no need to rush. If you enjoy literature with comedic elements, begin by exploring the comedy genre.
Related Activities
Reading Material to Start With
Start with article number one and work your way down the list. When you are happy you understand each article within the genre, move on to the next set of articles.
- A Washington Post Newspaper Report of Hurricane Ian
- The short story called "The Fall of the House of Usher" by Edgar Allan Poe
- The historical fiction novel by Christopher Paul Curtis: Bud, Not Buddy .
- "The Miracle Worker" by William Gibson
- The famous play by the one and only William Shakespeare, “Romeo & Juliet”
- "Death of a Salesman" by Arthur Miller
- "The Road Not Taken" by Robert Frost
- "A Poison Tree" by William Blake
- "Still I Rise" by Maya Angelou
How to Get a Deeper Understanding
To get a deeper meaning of each genre, get your pen and paper ready and start to highlight the key ideas throughout. It can help to get your understanding of the writings by doing a summary for each one. Once you have done this, start to think about the following key things for each genre:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Who is the audience?
- What are the main ideas?
- How does the structure help to emphasize the purpose?
- What literary devices are used and why?
- How does the author’s style contribute to the meaning of the text?
Plays can be trickier as you cannot always rely on the written word to give you all the information. This is where watching a performance of the play can come in handy, as it will give you a much better understanding. In addition to the above, when watching a play, you should also be thinking about:
- How does the stagecraft contribute to the meaning of the play?
- What do the costumes and makeup tell us about the characters?
- How does the lighting help to create mood and atmosphere?
- What do the sound effects and music add to the play?
When reading poetry, it is essential to think about both the literal and figurative meanings of the words. This can be difficult at first, but there are some helpful strategies that you can use. For example, you can try reading the poem aloud or reading it multiple times. You can also look up words you don’t understand and try to break the poem down into smaller chunks. In addition to the above, when reading poetry, you should also be thinking about:
- What is the speaker’s tone?
- What is the poem's mood?
- What are the main themes of the poem?
- How does the poet use literary devices to create meaning?
- What is the poem’s form, and how does it contribute to the meaning?
Using a storyboard exercise like StoryBoard That can be helpful when trying to understand the genres. You can map out the key ideas and events for each one, as well as the literary devices that are used. This is a great way to see the genres side-by-side, compare and contrast them and visualize things better.
Related Resources
- Picture Encyclopedia of Literary Genres
- Picture Encyclopedia of Literary Elements
- Elements of an Epic
- The Five Act Play Structure
How To Incorporate Multicultural Perspectives Into The Study Of Literary Genres
Select texts from diverse authors and cultures.
Choose texts that represent a variety of cultures and perspectives, and that offer insights into different literary traditions and styles. This might involve reading and researching texts from authors and cultures that are different from your own and seeking out recommendations from colleagues, libraries, or online resources.
Discuss Cultural Context and Historical Background
Provide background information and historical context for each text, including information about the author and the cultural and historical context in which the text was written. This can help students understand the unique perspectives and literary traditions represented in each text.
Explore Themes and Literary Devices From Multicultural Perspectives
Encourage students to explore themes and literary devices from a variety of cultural perspectives, such as examining the role of family or community in different cultures, or analyzing how language and storytelling are used in different literary traditions.
Foster Discussion and Collaboration
Encourage open discussion and collaboration among students, and create opportunities for them to share their own perspectives and experiences. This can help students build empathy and understanding for different cultures and perspectives.
Encourage Independent Research and Exploration
Encourage students to research and explore additional texts and authors from different cultures and perspectives on their own. Provide resources and recommendations for students to pursue independent reading and research.
Integrate Multimedia and Other Resources
Integrate multimedia and other resources, such as videos, podcasts, or guest speakers, to enhance students' understanding of different cultures and perspectives. This can help bring the text to life and make it more relevant and engaging for students.
Frequently Asked Questions about Literary Genres
What is a literary genre.
A literary genre is a category or type of literature characterized by common themes, styles, and narrative conventions. It serves as a way to classify and categorize literary works based on shared characteristics and elements. Common literary forms include fiction, non-fiction, and various subgenres within these categories, such as science fiction, romance or love stories, mystery, and historical fiction. This literary genre definition encapsulates the essence of storytelling, providing a framework for understanding and appreciating the various forms, themes, and styles that contribute to the rich tapestry of literature.
What are some examples of different types of fiction genres?
Some well known types of fiction are: mystery, realistic fiction, historical fiction, fables and fairy tales, adventure, magical realism, and science fiction.
What are some examples of different types of nonfiction?
Some common types are biographies, autobiographies, speeches, letters, and informational texts.
What are the 3 forms of literature?
The three main forms of literature are prose, poetry, and drama. Prose encompasses written or spoken language without a metrical structure and includes written forms like novels, short stories, essays, and articles. Poetry employs heightened and imaginative language, often with rhyme and meter, to evoke emotions and convey complex ideas. Drama is written for performance and includes plays, scripts, and screenplays intended for actors to act out on stage or screen. These three forms represent the foundational structure of literary expression, offering diverse avenues for storytelling, creativity, and artistic communication.
What are the five main genres?
- Fiction: This genre includes works of imaginative storytelling that are not based on real events. It encompasses various subgenres such as science fiction, fantasy, historical fiction, and mystery.
- Non-fiction: Non-fiction literature is based on real events, facts, and information. This genre includes biographies, autobiographies, essays, memoirs, and other works that present factual content.
- Poetry: Poetry is a form of literary expression that uses rhythmic and metaphorical language to evoke emotions and convey ideas. It often relies on heightened language and various poetic devices.
- Drama: Drama involves the portrayal of characters in conflict, usually in a play format. It explores human emotions and relationships through dialogue and performance. Classic examples include works by playwrights like William Shakespeare.
- Mystery/Thriller: This genre revolves around suspenseful and puzzling narratives. Mystery literature often involves solving a crime or uncovering hidden truths, while thrillers aim to keep readers on the edge of their seats with tension and excitement.
What are the categories of literature?
Here are some common categories used to classify literature:
- Genre: Fiction: Includes novels, short stories, and novellas. This category encompasses a wide range of genres, such as science fiction, fantasy, romance, historical fiction, and more. Non-fiction: Involves works based on real events, facts, and information. This category includes biographies, autobiographies, essays, memoirs, and journalistic works.
- Form: Poetry: Characterized by the use of rhythmic and metaphorical language. Poetry often focuses on emotional expression and aesthetic qualities of language. Drama: Consists of plays and scripts written for performance. It includes tragedies, comedies, and other theatrical forms.
- Period or Movement: Classical Literature: Refers to works from ancient Greece and Rome. Medieval Literature: Covers works from the Middle Ages. Renaissance Literature: Encompasses the revival of arts and learning in Europe during the Renaissance. Modern Literature: Includes works from the late 19th century to the mid-20th century. Contemporary Literature: Encompasses works from the mid-20th century to the present.
- Nationality or Cultural Identity: American Literature, British Literature, World Literature: Literature can be classified based on the nationality or cultural identity of the author or the setting of the work.
- Literary Movements: Romanticism, Realism, Naturalism, Modernism, Postmodernism: Literature can be categorized based on the dominant artistic and intellectual movements of a particular time.
- Themes or Topics: Social Issues: Literature that addresses and explores societal problems, inequalities, and issues. Historical Fiction: Works set in a specific historical period, often incorporating historical events and figures.
- Age Group: Children's Literature, Young Adult Literature, Adult Literature: Works are sometimes categorized based on the target age group of the readers.
What are subgenres?
Subgenres in literature refer to more specific categories or classifications within the broader genres. They help to further define and categorize works based on shared characteristics, themes, or stylistic elements.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
Need help submitting your writing to literary journals or book publishers/literary agents? Click here! →

Short Prose Genres: Defining Essay, Short Story, Commentary, Memoir, and Mixed Genre
by Writer's Relief Staff | Submit A Short Story Or Essay | 47 comments
Review Board is now open! Submit your Short Prose, Poetry, and Book today!
Deadline: thursday, april 18th.

The genres of short prose writing can be very confusing. For example, some writers will call their personal essay a story, and others will call their essay a memoir. To make matters even more complicated, a number of literary magazines are beginning to accept what is commonly called mixed genre writing. It’s important to understand the difference between the types of short prose, whether you’re writing an essay, short story, memoir, commentary, or mixed genre piece.

What is a short story? A short story is a work of fictional prose. Its characters may be loosely based on real-life people, and its plot may be inspired by a real-life event; but overall more of the story is “made-up” than real. Sometimes, the story can be completely made-up. Short stories may be literary, or they may conform to genre standards (i.e., a romance short story, a science-fiction short story, a horror story, etc.). A short story is a work that the writer holds to be fiction (i.e., historical fiction based on real events, or a story that is entirely fiction).
Short Story Example: A writer is inspired by a car explosion in his town. He writes a story based on the real explosion and set in a similar town, but showing the made-up experiences of his characters (who may be partly based on real-life).
Short Story Example two: A writer writes a story based on a made-up explosion, set in a made-up town, and showing the made-up experiences of his characters.
What is a personal or narrative essay? What is an academic essay? What’s the difference? Though factual, the personal essay , sometimes called a narrative essay, can feel like a short story, with “characters” and a plot arc. A personal essay is a short work of nonfiction that is not academic (that is, not a dissertation or scholarly exploration of criticism, etc.).
In a personal essay, the writer recounts his or her personal experiences or opinions. In an academic essay, the writer’s personal journey does not typically play a large part in the narrative (or plot line).
Sometimes the purpose of a personal essay is simply to entertain. Some personal essays may have a meditative or even dogmatic feel; a personal essay may illustrate a writer’s experiences in order to make an argument for the writer’s opinion. Some personal essays may cite other texts (like books, stories, or poems), but the focus of the citation is not to make an academic point. Rather, emphasis is on the writer’s emotional journey and insight.
Personal Essay Example: A writer pens the story of his experience at the scene of a car explosion in his town. The work is short enough for publication in a literary journal and focuses on the author’s perspective and insight.
What is a commentary? The personal essay form and commentary may sometimes overlap, but it may be helpful to make some distinctions. A commentary is often very short (a few hundred words) and more journalistic in tone than a personal essay. It fits nicely as a column in a newspaper or on a personal blog . The writing can be more newsy than literary.
Some very short nonfiction pieces may be better suited to newspapers than to literary journals; however, literary magazines have been known to publish commentary-esque pieces that have a literary bent.
Commentary Example: A writer tells the story of a car explosion in his town to illustrate the point that the police are not vigilant enough about people throwing flaming marshmallows out their windows.
What is a memoir? Memoir generally refers to longer works of nonfiction, written from the perspective of the author. Memoir does not generally refer to short personal essays. If you’re writing a short piece based on your real-life experiences, editors of literary journals will identify this as a personal essay. If you’re writing a book about an experience, it’s a memoir. A collection of interrelated personal essays may constitute a memoir.
Memoir Example: A writer composes a full-length book about his experiences after a car explosion in his town.
Learn more: Creative Nonfiction: How To Stay Out Of Trouble
What is a nonfiction short story? There’s no such thing as a nonfiction short story. Short stories are inherently fiction (with or without real-life inspiration). Personal essays are not fictional.
So what is mixed genre writing? Mixed genre writing is creative work that does not sit comfortably in any of the above genres. Mixed genre writing blends some elements of fiction with elements of nonfiction in a very deliberate way. Some examples:
Mixed Genre Example One: A professional accountant named John Jones is writing a story about a man named John Jones, who is John Jones and lives John Jones’ life—except that the fictional John Jones one day decides to leave his real-life accounting job, and live his dream of being a rock star (since the real-life John Jones is thinking of doing the same thing).
Is this a short story? An essay? If ninety percent of the story is true and ten percent is fiction, then what should the writer call this?
Mixed Genre Example Two: A writer decides to compose a family history, using pictures and documents from her family albums. But sometimes her story veers into fiction. She finds herself embellishing elements or omitting characters; and, the result is a story that’s better than the one she might tell if she were to stick to the facts.
Again, is this an essay? A short story? If half of the story is made-up, but half is very obviously true, it might be best called mixed genre.
NOTE: Sometimes the term mixed genre is defined in terms of the novel or book. A mixed genre novel might be a novel that mixes science fiction elements with characteristics of a legal thriller. Or a mixed genre novel might also be a work that plays fast and loose with fact and fiction. If you’re going to refer to your book as mixed genre, be clear about what you mean.
Learn more: Genre Fiction Rules: Find Out If Your Novel Meets Publishers’ And Literary Agents’ Criteria For Publication
Tips on Writing Mixed Genre If you’re going to write mixed genre prose, do so with care. Mixed genre writing often has a kind of self-aware, almost tongue-in-cheek, element to it—a wink to the reader who is not fooled by the mixing of fiction and nonfiction, even if the lines are blurry. Mixed genre can be considered experimental, and as such, it’s important that the writing be exceptionally smart in order to live up to the demands of the (mixed) genre.
Why is mixed genre writing so often self-referential? Writing mixed genre and passing it off as an essay or a short story could make editors think that you are trying to dupe them, so it helps to include something in the work that makes reference to itself as being a mixture of fact and fiction. These “meta” elements can help put the reader at ease.
Who is publishing mixed genre short prose? The primary markets for short prose are literary magazines and journals. Writer’s Relief frequently helps writers target their work to literary journals. For more information on how to find markets for your short prose, please read Researching Literary Markets for Your Work if you plan to research on your own. Or learn about Writer’s Relief submission services if you’d like help targeting your submissions .

QUESTION: Have you ever tackled a mixed genre piece?
Ronnie L. Smith, President of Writer’s Relief, Inc., an author’s submission service that helps creative writers get published by targeting their poems, essays, short stories, and books to the best-suited literary agents or editors of literary journals. www.WritersRelief.com

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment

See ALL the services we offer, from FREE to Full Service!
Click here for a Writer’s Relief Full Service Overview

Services Catalog

Free Publishing Leads and Tips!
- Name * First Name
- Email * Enter Email Confirm Email
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Featured Articles

Featured Video
- Facebook 121k Followers
- Twitter 113.9k Followers
- YouTube 5.1k Followers
- Instagram 5.5k Followers
- LinkedIn 146.2k Followers
- Pinterest 33.5k Followers
- Name * First
- E-mail * Enter Email Confirm Email
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
WHY? Because our insider know-how has helped writers get over 18,000 acceptances.
- BEST (and proven) submission tips
- Hot publishing leads
- Calls to submit
- Contest alerts
- Notification of industry changes
- And much more!

Pin It on Pinterest

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.10: Literature (including fiction, drama, poetry, and prose)
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 205491

- Lori-Beth Larsen
- Central Lakes College

Essential Questions for Literature
- How is literature like life?
- What is literature supposed to do?
- What influences a writer to create?
- How does literature reveal the values of a given culture or time period?
- How does the study of fiction and nonfiction texts help individuals construct their understanding of reality?
- In what ways are all narratives influenced by bias and perspective?
- Where does the meaning of a text reside? Within the text, within the reader, or in the transaction that occurs between them?
- What can a reader know about an author’s intentions based only on a reading of the text?
- What are enduring questions and conflicts that writers (and their cultures) grappled with hundreds of years ago and are still relevant today?
- How do we gauge the optimism or pessimism of a particular time period or particular group of writers?
- Why are there universal themes in literature–that is, themes that are of interest or concern to all cultures and societies?
- What are the characteristics or elements that cause a piece of literature to endure?
- What is the purpose of: science fiction? satire? historical novels, etc.?
- How do novels, short stories, poetry, etc. relate to the larger questions of philosophy and humanity?
- How we can use literature to explain or clarify our own ideas about the world?
- How does what we know about the world shape the stories we tell?
- How do the stories we tell about the world shape the way we view ourselves?
- How do our personal experiences shape our view of others?
- What does it mean to be an insider or an outsider?
- Are there universal themes in literature that are of interest or concern to all cultures and societies?
- What is creativity and what is its importance for the individual / the culture?
- What are the limits, if any, of freedom of speech?
Defining Literature
Literature, in its broadest sense, is any written work. Etymologically, the term derives from Latin litaritura / litteratura “writing formed with letters,” although some definitions include spoken or sung texts. More restrictively, it is writing that possesses literary merit. Literature can be classified according to whether it is fiction or non-fiction and whether it is poetry or prose. It can be further distinguished according to major forms such as the novel, short story or drama, and works are often categorized according to historical periods or their adherence to certain aesthetic features or expectations (genre).
Taken to mean only written works, literature was first produced by some of the world’s earliest civilizations—those of Ancient Egypt and Sumeria—as early as the 4th millennium BC; taken to include spoken or sung texts, it originated even earlier, and some of the first written works may have been based on a pre-existing oral tradition. As urban cultures and societies developed, there was a proliferation in the forms of literature. Developments in print technology allowed for literature to be distributed and experienced on an unprecedented scale, which has culminated in the twenty-first century in electronic literature.
Definitions of literature have varied over time. In Western Europe prior to the eighteenth century, literature as a term indicated all books and writing. [1] A more restricted sense of the term emerged during the Romantic period, in which it began to demarcate “imaginative” literature. [2]
Contemporary debates over what constitutes literature can be seen as returning to the older, more inclusive notion of what constitutes literature. Cultural studies, for instance, takes as its subject of analysis both popular and minority genres, in addition to canonical works. [3]
Major Forms

A calligram by Guillaume Apollinaire. These are a type of poem in which the written words are arranged in such a way to produce a visual image.
Poetry is a form of literary art that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, prosaic ostensible meaning (ordinary intended meaning). Poetry has traditionally been distinguished from prose by its being set in verse; [4] prose is cast in sentences, poetry in lines; the syntax of prose is dictated by meaning, whereas that of poetry is held across metre or the visual aspects of the poem. [5]
Prior to the nineteenth century, poetry was commonly understood to be something set in metrical lines; accordingly, in 1658 a definition of poetry is “any kind of subject consisting of Rythm or Verses”. [6] Possibly as a result of Aristotle’s influence (his Poetics ), “poetry” before the nineteenth century was usually less a technical designation for verse than a normative category of fictive or rhetorical art. [7] As a form it may pre-date literacy, with the earliest works being composed within and sustained by an oral tradition; [8] hence it constitutes the earliest example of literature.
Prose is a form of language that possesses ordinary syntax and natural speech rather than rhythmic structure; in which regard, along with its measurement in sentences rather than lines, it differs from poetry. [9] On the historical development of prose, Richard Graff notes that ”
Novel : a long fictional prose narrative.
Novella :The novella exists between the novel and short story; the publisher Melville House classifies it as “too short to be a novel, too long to be a short story.” [10]
Short story : a dilemma in defining the “short story” as a literary form is how to, or whether one should, distinguish it from any short narrative. Apart from its distinct size, various theorists have suggested that the short story has a characteristic subject matter or structure; [11] these discussions often position the form in some relation to the novel. [12]
Drama is literature intended for performance. [13]
Listen to this Discussion of the poetry of Harris Khalique . You might want to take a look at the transcript as you listen.
The first half of a 2008 reading featuring four Latino poets, as part of the American Perspectives series at the Art Institute of Chicago.
Listen to poetry reading of Francisco Aragón and Brenda Cárdenas
Listen to this conversation with Allison Hedge Coke, Linda Hogan and Sherwin Bitsui . You might want to look at the transcript as you listen. In this program, we hear a conversation among three Native American poets: Allison Hedge Coke, Linda Hogan and Sherwin Bitsui. Allison Hedge Coke grew up listening to her Father’s traditional stories as she moved from Texas to North Carolina to Canada and the Great Plains. She is the author of several collections of poetry and the memoir, Rock, Ghost, Willow, Deer. She has worked as a mentor with Native Americans and at-risk youth, and is currently a Professor of Poetry and Writing at the University of Nebraska, Kearney. Linda Hogan is a prolific poet, novelist and essayist. Her work is imbued with an indigenous sense of history and place, while it explores environmental, feminist and spiritual themes. A former professor at the University of Colorado, she is currently the Chickasaw Nation’s Writer in Residence. She lives in Oklahoma, where she researches and writes about Chickasaw history, mythology and ways of life. Sherwin Bitsui grew up on the Navajo reservation in Arizona. He speaks Dine, the Navajo language and participates in ceremonial activities. His poetry has a sense of the surreal, combining images of the contemporary urban culture, with Native ritual and myth.
Chris Abani : Stories from Africa
In this deeply personal talk, Nigerian writer Chris Abani says that “what we know about how to be who we are” comes from stories. He searches for the heart of Africa through its poems and narrative, including his own.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-1
Listen to Isabel Allende’s Ted Talk
As a novelist and memoirist, Isabel Allende writes of passionate lives, including her own. Born into a Chilean family with political ties, she went into exile in the United States in the 1970s—an event that, she believes, created her as a writer. Her voice blends sweeping narrative with touches of magical realism; her stories are romantic, in the very best sense of the word. Her novels include The House of the Spirits, Eva Luna and The Stories of Eva Luna, and her latest, Maya’s Notebook and Ripper. And don’t forget her adventure trilogy for young readers— City of the Beasts, Kingdom of the Golden Dragon and Forest of the Pygmies.
As a memoirist, she has written about her vision of her lost Chile, in My Invented Country, and movingly tells the story of her life to her own daughter, in Paula. Her book Aphrodite: A Memoir of the Senses memorably linked two sections of the bookstore that don’t see much crossover: Erotica and Cookbooks. Just as vital is her community work: The Isabel Allende Foundation works with nonprofits in the San Francisco Bay Area and Chile to empower and protect women and girls—understanding that empowering women is the only true route to social and economic justice.
You can read excerpts of her books online here: https://www.isabelallende.com/en/books
Read her musings. Why does she write? https://www.isabelallende.com/en/musings
You might choose to read one of her novels.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-2
Listen to Novelist Chimamanda Adichie . She speaks about how our lives, our cultures, are composed of many overlapping stories. She tells the story of how she found her authentic cultural voice — and warns that if we hear only a single story about another person or country, we risk a critical misunderstanding.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-3
One Hundred Years of Solitu de
Gabriel García Márquez’s novel “One Hundred Years of Solitude” brought Latin American literature to the forefront of the global imagination and earned García Márquez the 1982 Nobel Prize for Literature. What makes the novel so remarkable? Francisco Díez-Buzo investigates.
Gabriel García Márquez was a writer and journalist who recorded the haphazard political history of Latin American life through his fiction. He was a part of a literary movement called the Latin American “boom ,” which included writers like Peru’s Mario Vargas Llosa, Argentina’s Julio Cortázar, and Mexico’s Carlos Fuentes. Almost all of these writers incorporated aspects of magical realism in their work . Later authors, such as Isabel Allende and Salman Rushdie, would carry on and adapt the genre to the cultural and historical experiences of other countries and continents. García Máruqez hadn’t always planned on being a writer, but a pivotal moment in Colombia’s—and Latin America’s—history changed all that. In 1948, when García Márquez was a law student in Bogotá, Jorge Eliécer Gaítan , a prominent radical populist leader of Colombia’s Liberal Party, was assassinated. This happened while the U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall brought together leaders from across the Americas to create the Organization of American States (OAS) and to build a hemisphere-wide effort against communism. In the days after the assassination, massive riots, now called the bogotazo , occurred. The worst Colombian civil war to date, known as La Violencia , also broke out. Another law student, visiting from Cuba, was deeply affected by Eliécer Gaítan’s death. This student’s name was Fidel Castro. Interestingly, García Márquez and Castro—both socialists—would become close friends later on in life , despite not meeting during these tumultuous events. One Hundred Years of Solitude ’s success almost didn’t happen, but this article from Vanity Fair helps explain how a long-simmering idea became an international sensation. When Gabriel García Márquez won the Nobel Prize in 1982, he gave a lecture that helped illuminate the plights that many Latin Americans faced on a daily basis. Since then, that lecture has also helped explain the political and social critiques deeply embedded in his novels. It was famous for being an indigenous overview of how political violence became entrenched in Latin America during the Cold War.In an interview with the New Left Review , he discussed a lot of the inspirations for his work, as well as his political beliefs.
An interactive H5P element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#h5p-12
Don Quixote
Mounting his skinny steed, Don Quixote charges an army of giants. It is his duty to vanquish these behemoths in the name of his beloved lady, Dulcinea. There’s only one problem: the giants are merely windmills. What is it about this tale of the clumsy yet valiant knight that makes it so beloved? Ilan Stavans investigates.
Interested in exploring the world of Don Quixote ? Check out this translation of the thrill-seeking classic. To learn more about Don Quixote ’s rich cultural history, click here . In this interview , the educator shares his inspiration behind his book Quixote: The Novel and the World . The travails of Don Quixote ’s protagonist were heavily shaped by real-world events in 17th-century Spain. This article provides detailed research on what, exactly, happened during that time.
An interactive H5P element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#h5p-13
Midnight’s Children
It begins with a countdown. A woman goes into labor as the clock ticks towards midnight. Across India, people wait for the declaration of independence after nearly 200 years of British rule. At the stroke of midnight, an infant and two new nations are born in perfect synchronicity. These events form the foundation of “Midnight’s Children.” Iseult Gillespie explores Salman Rushdie’s dazzling novel.
At the stroke of midnight, the first gasp of a newborn syncs with the birth of two new nations. These simultaneous events are at the center of Midnight’s Children, a dazzling novel about the state of modern India by the British-Indian author Salman Rushdie . You can listen to an interview with Rushdie discussing the novel here . The chosen baby is Saleem Sinai, who narrates the novel from a pickle factory in 1977. As this article argues, much of the beauty of the narrative lies in Rushdie’s ability to weave the personal into the political in surprising ways. Saleem’s narrative leaps back in time, to trace his family history from 1915 on. The family tree is blossoming with bizarre scenes, including clandestine courtships, babies swapped at birth, and cryptic prophecies. For a detailed interactive timeline of the historical and personal events threaded through the novel, click here . However, there’s one trait that can’t be explained by genes alone – Saleem has magic powers, and they’re somehow related to the time of his birth. For an overview of the use of magical realism and astonishing powers in Mignight’s Children, click here. Saleem recounts a new nation, flourishing and founding after almost a century of British rule. For more information on the dark history of British occupation of India, visit this page. The vast historical frame is one reason why Midnight’s Children is considered one of the most illuminating works of postcolonial literature ever written. This genre typically addresses life in formerly colonized countries, and explores the fallout through themes like revolution, migration, and identity. Postcolonial literature also deals with the search for agency and authenticity in the wake of imposed foreign rule. Midnight’s Children reflects these concerns with its explosive combination of Eastern and Western references. On the one hand, it’s been compared to the sprawling novels of Charles Dickens or George Elliot, which also offer a panoramic vision of society paired with tales of personal development. But Rushdie radically disrupts this formula by adding Indian cultural references, magic and myth. Saleem writes the story by night, and narrates it back to his love interest, Padma. This echoes the frame for 1001 Nights , a collection of Middle Eastern folktales told by Scheherazade every night to her lover – and as Saleem reminds us, 1001 is “the number of night, of magic, of alternative realities.” Saleem spends a lot of the novel attempting to account for the unexpected. But he often gets thoroughly distracted and goes on astonishing tangents, telling dirty jokes or mocking his enemies. With his own powers of telepathy, Saleem forges connections between other children of midnight; including a boy who can step through time and mirrors, and a child who changes their gender when immersed in water. There’s other flashes of magic throughout, from a mother who can see into dreams to witchdoctors, shapeshifters, and many more. For an overview of the dazzling reference points of the novel, visit this page . Sometimes, all this is like reading a rollercoaster: Saleem sometimes narrates separate events all at once, refers to himself in the first and third person in the space of a single sentence, or uses different names for one person. And Padma is always interrupting, urging him to get to the point or exclaiming at his story’s twists and turns. This mind-bending approach has garnered continuing fascination and praise. Not only did Midnight’s Children win the prestigious Man Booker prize in its year of publication, but it was named the best of all the winners in 2008 . For an interview about Rushdie’s outlook and processed, click here. All this gives the narrative a breathless quality, and brings to life an entire society surging through political upheaval without losing sight of the marvels of individual lives. But even as he depicts the cosmological consequences of a single life, Rushdie questions the idea that we can ever condense history into a single narrative.
Tom Elemas : The Inspiring Truth in Fiction
What do we lose by choosing non-fiction over fiction? For Tomas Elemans, there’s an important side effect of reading fiction: empathy — a possible antidote to a desensitized world filled with tragic news and headlines.
What is empathy? How does story-telling create empathy? What stories trigger empathy in you? What is narrative immersion? Are we experiencing an age of narcissism? What might be some examples of narcissism? What connection does Tom Elemans make to individualism?
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-4
Ann Morgan: My year reading a book from every country in the world
Ann Morgan considered herself well read — until she discovered the “massive blindspot” on her bookshelf. Amid a multitude of English and American authors, there were very few books from beyond the English-speaking world. So she set an ambitious goal: to read one book from every country in the world over the course of a year. Now she’s urging other Anglophiles to read translated works so that publishers will work harder to bring foreign literary gems back to their shores. Explore interactive maps of her reading journey here: go.ted.com/readtheworld
Check out her blog: A year of reading the world where you can find a complete list of the books I read, and what I learned along the way.
One or more interactive elements has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view them online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#oembed-5
An interactive H5P element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/introductiontohumanitiesv2/?p=77#h5p-15

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11 Literature (including fiction, drama, poetry, and prose)

Essential Questions for Literature
- How is literature like life?
- What is literature supposed to do?
- What influences a writer to create?
- How does literature reveal the values of a given culture or time period?
- How does the study of fiction and nonfiction texts help individuals construct their understanding of reality?
- In what ways are all narratives influenced by bias and perspective?
- Where does the meaning of a text reside? Within the text, within the reader, or in the transaction that occurs between them?
- What can a reader know about an author’s intentions based only on a reading of the text?
- What are enduring questions and conflicts that writers (and their cultures) grappled with hundreds of years ago and are still relevant today?
- How do we gauge the optimism or pessimism of a particular time period or particular group of writers?
- Why are there universal themes in literature–that is, themes that are of interest or concern to all cultures and societies?
- What are the characteristics or elements that cause a piece of literature to endure?
- What is the purpose of: science fiction? satire? historical novels, etc.?
- How do novels, short stories, poetry, etc. relate to the larger questions of philosophy and humanity?
- How we can use literature to explain or clarify our own ideas about the world?
- How does what we know about the world shape the stories we tell?
- How do the stories we tell about the world shape the way we view ourselves?
- How do our personal experiences shape our view of others?
- What does it mean to be an insider or an outsider?
- Are there universal themes in literature that are of interest or concern to all cultures and societies?
- What is creativity and what is its importance for the individual / the culture?
- What are the limits, if any, of freedom of speech?
Defining Literature
Literature, in its broadest sense, is any written work. Etymologically, the term derives from Latin litaritura / litteratura “writing formed with letters,” although some definitions include spoken or sung texts. More restrictively, it is writing that possesses literary merit. Literature can be classified according to whether it is fiction or non-fiction and whether it is poetry or prose. It can be further distinguished according to major forms such as the novel, short story or drama, and works are often categorized according to historical periods or their adherence to certain aesthetic features or expectations (genre).
Taken to mean only written works, literature was first produced by some of the world’s earliest civilizations—those of Ancient Egypt and Sumeria—as early as the 4th millennium BC; taken to include spoken or sung texts, it originated even earlier, and some of the first written works may have been based on a pre-existing oral tradition. As urban cultures and societies developed, there was a proliferation in the forms of literature. Developments in print technology allowed for literature to be distributed and experienced on an unprecedented scale, which has culminated in the twenty-first century in electronic literature.
Definitions of literature have varied over time. In Western Europe prior to the eighteenth century, literature as a term indicated all books and writing. [1] A more restricted sense of the term emerged during the Romantic period, in which it began to demarcate “imaginative” literature. [2]
Contemporary debates over what constitutes literature can be seen as returning to the older, more inclusive notion of what constitutes literature. Cultural studies, for instance, takes as its subject of analysis both popular and minority genres, in addition to canonical works. [3]
Major Forms

A calligram by Guillaume Apollinaire. These are a type of poem in which the written words are arranged in such a way to produce a visual image.
Poetry is a form of literary art that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, prosaic ostensible meaning (ordinary intended meaning). Poetry has traditionally been distinguished from prose by its being set in verse; [4] prose is cast in sentences, poetry in lines; the syntax of prose is dictated by meaning, whereas that of poetry is held across metre or the visual aspects of the poem. [5]
Prior to the nineteenth century, poetry was commonly understood to be something set in metrical lines; accordingly, in 1658 a definition of poetry is “any kind of subject consisting of Rythm or Verses”. [6] Possibly as a result of Aristotle’s influence (his Poetics ), “poetry” before the nineteenth century was usually less a technical designation for verse than a normative category of fictive or rhetorical art. [7] As a form it may pre-date literacy, with the earliest works being composed within and sustained by an oral tradition; [8] hence it constitutes the earliest example of literature.
Prose is a form of language that possesses ordinary syntax and natural speech rather than rhythmic structure; in which regard, along with its measurement in sentences rather than lines, it differs from poetry. [9] On the historical development of prose, Richard Graff notes that ”
Novel : a long fictional prose narrative.
Novella :The novella exists between the novel and short story; the publisher Melville House classifies it as “too short to be a novel, too long to be a short story.” [10]
Short story : a dilemma in defining the “short story” as a literary form is how to, or whether one should, distinguish it from any short narrative. Apart from its distinct size, various theorists have suggested that the short story has a characteristic subject matter or structure; [11] these discussions often position the form in some relation to the novel. [12]
Drama is literature intended for performance. [13]
Leitch et al. , The Norton Anthology of Theory and Criticism , 28 ↵
Ross, “The Emergence of “Literature”: Making and Reading the English Canon in the Eighteenth Century,” 406 & Eagleton, Literary theory: an introduction , 16 ↵
“POETRY, N.”. OXFORD ENGLISH DICTIONARY . OUP. RETRIEVED 13 FEBRUARY 2014. (subscription required) ↵
Preminger, The New Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics , 938–9 ↵
Ross, “The Emergence of “Literature”: Making and Reading the English Canon in the Eighteenth Century”, 398 ↵
FINNEGAN, RUTH H. (1977). ORAL POETRY: ITS NATURE, SIGNIFICANCE, AND SOCIAL CONTEXT. INDIANA UNIVERSITY PRESS. P. 66. & MAGOUN, JR., FRANCIS P. (1953). “ORAL-FORMULAIC CHARACTER OF ANGLO-SAXON NARRATIVE POETRY”.SPECULUM 28 (3): 446–67. DOI:10.2307/2847021 ↵
Preminger, The New Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics , 938–9 &Alison Booth; Kelly J. Mays. “Glossary: P”. LitWeb , the Norton Introduction to Literature Studyspace . Retrieved 15 February 2014. ↵
Antrim, Taylor (2010). “In Praise of Short”. The Daily Beast. Retrieved 15 February 2014. ↵
ROHRBERGER, MARY; DAN E. BURNS (1982). “SHORT FICTION AND THE NUMINOUS REALM: ANOTHER ATTEMPT AT DEFINITION”. MODERN FICTION STUDIES . XXVIII (6). & MAY, CHARLES (1995). THE SHORT STORY. THE REALITY OF ARTIFICE . NEW YORK: TWAIN. ↵
Marie Louise Pratt (1994). Charles May, ed. The Short Story: The Long and the Short of It . Athens: Ohio UP. ↵
Elam, Kier (1980). The Semiotics of Theatre and Drama . London and New York: Methuen. p. 98.ISBN 0-416-72060-9. ↵
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
Literature. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Literature#cite_note-44 . License: CC BY-SA: Attribution- ShareAlike
PUBLIC DOMAIN CONTENT: Image of man formed by words. Authored by: Guillaume Apollinaire. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Calligramme.jpg . License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
Listen to this Discussion of the poetry of Harris Khalique . You might want to take a look at the transcript as you listen.
The first half of a 2008 reading featuring four Latino poets, as part of the American Perspectives series at the Art Institute of Chicago.
Listen to poetry reading of Francisco Aragón and Brenda Cárdenas
Listen to this conversation with Allison Hedge Coke, Linda Hogan and Sherwin Bitsui . You might want to look at the transcript as you listen. In this program, we hear a conversation among three Native American poets: Allison Hedge Coke, Linda Hogan and Sherwin Bitsui. Allison Hedge Coke grew up listening to her Father’s traditional stories as she moved from Texas to North Carolina to Canada and the Great Plains. She is the author of several collections of poetry and the memoir, Rock, Ghost, Willow, Deer. She has worked as a mentor with Native Americans and at-risk youth, and is currently a Professor of Poetry and Writing at the University of Nebraska, Kearney. Linda Hogan is a prolific poet, novelist and essayist. Her work is imbued with an indigenous sense of history and place, while it explores environmental, feminist and spiritual themes. A former professor at the University of Colorado, she is currently the Chickasaw Nation’s Writer in Residence. She lives in Oklahoma, where she researches and writes about Chickasaw history, mythology and ways of life. Sherwin Bitsui grew up on the Navajo reservation in Arizona. He speaks Dine, the Navajo language and participates in ceremonial activities. His poetry has a sense of the surreal, combining images of the contemporary urban culture, with Native ritual and myth.
Remember to return to the essential questions. Can expand on any of your answers to these questions? You might want to research these poets.
Chris Abani : Stories from Africa
In this deeply personal talk, Nigerian writer Chris Abani says that “what we know about how to be who we are” comes from stories. He searches for the heart of Africa through its poems and narrative, including his own.
Listen to Isabel Allende’s Ted Talk
As a novelist and memoirist, Isabel Allende writes of passionate lives, including her own. Born into a Chilean family with political ties, she went into exile in the United States in the 1970s—an event that, she believes, created her as a writer. Her voice blends sweeping narrative with touches of magical realism; her stories are romantic, in the very best sense of the word. Her novels include The House of the Spirits, Eva Luna and The Stories of Eva Luna, and her latest, Maya’s Notebook and Ripper. And don’t forget her adventure trilogy for young readers— City of the Beasts, Kingdom of the Golden Dragon and Forest of the Pygmies.
As a memoirist, she has written about her vision of her lost Chile, in My Invented Country, and movingly tells the story of her life to her own daughter, in Paula. Her book Aphrodite: A Memoir of the Senses memorably linked two sections of the bookstore that don’t see much crossover: Erotica and Cookbooks. Just as vital is her community work: The Isabel Allende Foundation works with nonprofits in the San Francisco Bay Area and Chile to empower and protect women and girls—understanding that empowering women is the only true route to social and economic justice.
You can read excerpts of her books online here: https://www.isabelallende.com/en/books
Read her musings. Why does she write? https://www.isabelallende.com/en/musings
You might choose to read one of her novels.
Listen to Novelist Chimamanda Adichie . She speaks about how our lives, our cultures, are composed of many overlapping stories. She tells the story of how she found her authentic cultural voice — and warns that if we hear only a single story about another person or country, we risk a critical misunderstanding.
One Hundred Years of Solitu de
Gabriel García Márquez’s novel “One Hundred Years of Solitude” brought Latin American literature to the forefront of the global imagination and earned García Márquez the 1982 Nobel Prize for Literature. What makes the novel so remarkable? Francisco Díez-Buzo investigates.
Answer these questions as you listen:
How many generations of the Buendía family are in One Hundred Years of Solitude?
In what year did Gabriel García Marquez start writing One Hundred Years of Solitude?
Who inspired the style of One Hundred Years of Solitude?
A Colonel Aureliano Buendía
B Gabriel García Márquez
C Nicolás Ricardo Márquez
D Doña Tranquilina Iguarán Cotes
Which real-life event is almost directly represented in the novel?
A The Banana Massacre of 1928
B The Venezuelan coup d’état of 1958
C The Thousand Days’ War
D The bogotazo
What is the name of the town where the novel is set?
A Aracataca
Please explain how One Hundred Years of Solitude exemplifies the genre of magical realism.
What were the key influences in García Márquez’s life that helped inspire One Hundred Years of Solitude?
The narrative moves in a particular shape. What is that shape? How is that shape created?
Gabriel García Márquez was a writer and journalist who recorded the haphazard political history of Latin American life through his fiction. He was a part of a literary movement called the Latin American “boom ,” which included writers like Peru’s Mario Vargas Llosa, Argentina’s Julio Cortázar, and Mexico’s Carlos Fuentes. Almost all of these writers incorporated aspects of magical realism in their work . Later authors, such as Isabel Allende and Salman Rushdie, would carry on and adapt the genre to the cultural and historical experiences of other countries and continents. García Máruqez hadn’t always planned on being a writer, but a pivotal moment in Colombia’s—and Latin America’s—history changed all that. In 1948, when García Márquez was a law student in Bogotá, Jorge Eliécer Gaítan , a prominent radical populist leader of Colombia’s Liberal Party, was assassinated. This happened while the U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall brought together leaders from across the Americas to create the Organization of American States (OAS) and to build a hemisphere-wide effort against communism. In the days after the assassination, massive riots, now called the bogotazo , occurred. The worst Colombian civil war to date, known as La Violencia , also broke out. Another law student, visiting from Cuba, was deeply affected by Eliécer Gaítan’s death. This student’s name was Fidel Castro. Interestingly, García Márquez and Castro—both socialists—would become close friends later on in life , despite not meeting during these tumultuous events. One Hundred Years of Solitude ’s success almost didn’t happen, but this article from Vanity Fair helps explain how a long-simmering idea became an international sensation. When Gabriel García Márquez won the Nobel Prize in 1982, he gave a lecture that helped illuminate the plights that many Latin Americans faced on a daily basis. Since then, that lecture has also helped explain the political and social critiques deeply embedded in his novels. It was famous for being an indigenous overview of how political violence became entrenched in Latin America during the Cold War.In an interview with the New Left Review , he discussed a lot of the inspirations for his work, as well as his political beliefs.
Don Quixote
Mounting his skinny steed, Don Quixote charges an army of giants. It is his duty to vanquish these behemoths in the name of his beloved lady, Dulcinea. There’s only one problem: the giants are merely windmills. What is it about this tale of the clumsy yet valiant knight that makes it so beloved? Ilan Stavans investigates.
Why do Don Quixote and Sancho Panza work well together?
A They eat at strange times of the day
B They are impatient
C They like to dance together
D Their characters complement each other
Why does Don Quixote want to fix the world?
A He is a knight who believes in social justice
B He reads many books
C He doesn’t have any friends
D He loves toys
Why is Don Quixote’s love for Dulcinea described as “platonic”?
A Plato is their matchmaker
B They love Greek philosophy
C They want material fortune
D It’s purely spiritual
Why is Cervantes’s book described as “the first modern novel”?
A It was originally adapted to television
B The characters evolve throughout the story
C Cervantes only wrote poetry before
D It refers to technological advances
What does the term “quixotic” mean?
B A person without money
C An old man
D A dreamer
In what ways do Don Quixote and Sancho Panza change as the plot progresses?
Is it possible to count the total number of days that pass during their journey?
In what ways does their journey reveal the changes that 17th-century Spain is also undergoing?
Interested in exploring the world of Don Quixote ? Check out this translation of the thrill-seeking classic. To learn more about Don Quixote ’s rich cultural history, click here . In this interview , the educator shares his inspiration behind his book Quixote: The Novel and the World . The travails of Don Quixote ’s protagonist were heavily shaped by real-world events in 17th-century Spain. This article provides detailed research on what, exactly, happened during that time.
Midnight’s Children
It begins with a countdown. A woman goes into labor as the clock ticks towards midnight. Across India, people wait for the declaration of independence after nearly 200 years of British rule. At the stroke of midnight, an infant and two new nations are born in perfect synchronicity. These events form the foundation of “Midnight’s Children.” Iseult Gillespie explores Salman Rushdie’s dazzling novel.
Saleem Sinai’s birth coincides with:
A The invasion of India by the British
B The end of British occupation and the creation of two new nations, India and Pakistan
C The death of his mother
D His discovery of magic powers
Midnight’s Children is set over the course of:
A About thirty years of Saleem’s life
B A single day in Saleem’s life
C The duration of British occupation
D About thirty years of Saleem’s life, as well as flashbacks to before he was born
Saleem is the only person in the book with magic powers
Saleem has powers of
A Telepathy
B Shape shifting
C Predicting the future
Midnight’s Children is full of cultural references, including
A 1001 Nights
D Mythology
E All of the above
List some of the historical events that are part of the plot of Midnight’s Children
Why is Midnight’s Children a work of postcolonial literature? Describe some of the features of postcolonial literature.
In addition to being a work of postcolonial literature, Midnight’s Children is considered a key work of magical realism. Why do you think this is? What are some of the features of the book that could classify as magical realism?
Midnight’s Children filters epic and complex histories through one man’s life. What are the benefits of fictionalizing history in this way? What do you think he is trying to tell us about the way we process our past? Can history be as much of a narrative construct as fiction?
At the stroke of midnight, the first gasp of a newborn syncs with the birth of two new nations. These simultaneous events are at the center of Midnight’s Children, a dazzling novel about the state of modern India by the British-Indian author Salman Rushdie . You can listen to an interview with Rushdie discussing the novel here . The chosen baby is Saleem Sinai, who narrates the novel from a pickle factory in 1977. As this article argues, much of the beauty of the narrative lies in Rushdie’s ability to weave the personal into the political in surprising ways. Saleem’s narrative leaps back in time, to trace his family history from 1915 on. The family tree is blossoming with bizarre scenes, including clandestine courtships, babies swapped at birth, and cryptic prophecies. For a detailed interactive timeline of the historical and personal events threaded through the novel, click here . However, there’s one trait that can’t be explained by genes alone – Saleem has magic powers, and they’re somehow related to the time of his birth. For an overview of the use of magical realism and astonishing powers in Mignight’s Children, click here. Saleem recounts a new nation, flourishing and founding after almost a century of British rule. For more information on the dark history of British occupation of India, visit this page. The vast historical frame is one reason why Midnight’s Children is considered one of the most illuminating works of postcolonial literature ever written. This genre typically addresses life in formerly colonized countries, and explores the fallout through themes like revolution, migration, and identity. Postcolonial literature also deals with the search for agency and authenticity in the wake of imposed foreign rule. Midnight’s Children reflects these concerns with its explosive combination of Eastern and Western references. On the one hand, it’s been compared to the sprawling novels of Charles Dickens or George Elliot, which also offer a panoramic vision of society paired with tales of personal development. But Rushdie radically disrupts this formula by adding Indian cultural references, magic and myth. Saleem writes the story by night, and narrates it back to his love interest, Padma. This echoes the frame for 1001 Nights , a collection of Middle Eastern folktales told by Scheherazade every night to her lover – and as Saleem reminds us, 1001 is “the number of night, of magic, of alternative realities.” Saleem spends a lot of the novel attempting to account for the unexpected. But he often gets thoroughly distracted and goes on astonishing tangents, telling dirty jokes or mocking his enemies. With his own powers of telepathy, Saleem forges connections between other children of midnight; including a boy who can step through time and mirrors, and a child who changes their gender when immersed in water. There’s other flashes of magic throughout, from a mother who can see into dreams to witchdoctors, shapeshifters, and many more. For an overview of the dazzling reference points of the novel, visit this page . Sometimes, all this is like reading a rollercoaster: Saleem sometimes narrates separate events all at once, refers to himself in the first and third person in the space of a single sentence, or uses different names for one person. And Padma is always interrupting, urging him to get to the point or exclaiming at his story’s twists and turns. This mind-bending approach has garnered continuing fascination and praise. Not only did Midnight’s Children win the prestigious Man Booker prize in its year of publication, but it was named the best of all the winners in 2008 . For an interview about Rushdie’s outlook and processed, click here. All this gives the narrative a breathless quality, and brings to life an entire society surging through political upheaval without losing sight of the marvels of individual lives. But even as he depicts the cosmological consequences of a single life, Rushdie questions the idea that we can ever condense history into a single narrative.
Tom Elemas : The Inspiring Truth in Fiction
What do we lose by choosing non-fiction over fiction? For Tomas Elemans, there’s an important side effect of reading fiction: empathy — a possible antidote to a desensitized world filled with tragic news and headlines.
What is empathy? How does story-telling create empathy? What stories trigger empathy in you? What is narrative immersion? Are we experiencing an age of narcissism? What might be some examples of narcissism? What connection does Tom Elemans make to individualism?

Ann Morgan: My year reading a book from every country in the world
Ann Morgan considered herself well read — until she discovered the “massive blindspot” on her bookshelf. Amid a multitude of English and American authors, there were very few books from beyond the English-speaking world. So she set an ambitious goal: to read one book from every country in the world over the course of a year. Now she’s urging other Anglophiles to read translated works so that publishers will work harder to bring foreign literary gems back to their shores. Explore interactive maps of her reading journey here: go.ted.com/readtheworld

Her blog: Check out my blog (http://ayearofreadingtheworld.com/), where you can find a complete list of the books I read, and what I learned along the way.
Jacqueline Woodson: What reading slowly taught me about writing
Reading slowly — with her finger running beneath the words, even when she was taught not to — has led Jacqueline Woodson to a life of writing books to be savored. In a lyrical talk, she invites us to slow down and appreciate stories that take us places we never thought we’d go and introduce us to people we never thought we’d meet. “Isn’t that what this is all about — finding a way, at the end of the day, to not feel alone in this world, and a way to feel like we’ve changed it before we leave?” she asks.

Introduction to Humanities II Copyright © by loribethlarsenclcmnedu is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- SMU Libraries
- Scholarship & Research
- Teaching & Learning
- Bridwell Library
- Business Library
- DeGolyer Library
- Fondren Library
- Hamon Arts Library
- Underwood Law Library
- Fort Burgwin Library
- Exhibits & Digital Collections
- SMU Scholar
- Special Collections & Archives
- Connect With Us
- Research Guides by Subject
- How Do I . . . ? Guides
- Find Your Librarian
- Writing Support
Literary Genres: Form: Short Stories
- Plays & Drama
- Short Stories
Recommended Databases
- Cambridge Companions Complete Collection This link opens in a new window Includes the Cambridge Companions to: the English Short Story, Edgar Allan Poe, and more.
- Library Catalog - Advanced This link opens in a new window A subset of Library Search that finds only materials owned by SMU Libraries, such as books, journals, movies, etc.
- MLA International Bibliography This link opens in a new window The Modern Language Association's index to literature. Search MLA to find literary criticism, book reviews, and just about anything relating to communication.
- ProQuest One Literature This link opens in a new window Literary criticism, authors' biographies, reference resources with citations
- Short Story Index This link opens in a new window Locate more than 96,000 stories -- plus the full text of more than 4,000 stories. Search by author, genre, or subject.
Background & Reference Information
Sample Libary of Congress Subject Headings
Shows all the records in the library catalog with this subject heading.
- Add terms or refine results to narrow down the list.
- Remove terms to broaden the search.
- Short stories, American -- Dictionaries
- Short Stories, English
More Resources
- Book Reviews: UNC-CH Writing Center Advice on writing a book review
- Goodreads Crowdsourced reviews
- Literary Analysis: Interpreting Novels & Short Stories Worksheet
- << Previous: Poetry
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 12:37 AM
- URL: https://guides.smu.edu/english/genres/form
Short Story Book Genre Explained – Ultimate Guide
A short story is a brief work of fiction, usually written in prose and running 1,500 to 30,000 words in length. The short story is a crafted form in its own right, not just a mini novel. The brevity of a short story insures that there will be few characters, probably only one main plot, and just one setting. In this article, we will delve into the various genres of short stories, providing a comprehensive understanding of each.
Understanding the different genres of short stories can help readers find what they love, and writers to identify the conventions and boundaries they wish to challenge. The genre of a short story can affect everything from the tone and the style, to the type of characters, and the settings that you would expect to find. So, let’s start our exploration of short story genres.
Adventure short stories are exciting tales that take readers on a journey, often involving danger and physical action. They typically feature a hero who embarks on a quest, faces significant conflict, and returns home transformed. The settings of adventure stories are often exotic and unexplored, providing a backdrop for the high-stakes action.
The adventure genre is a form of escapist literature, allowing readers to leave their everyday lives and experience the thrill and danger of the adventures described. The genre has its roots in the romance tradition, but has evolved to include a wide range of sub-genres and themes.
Examples of Adventure Short Stories
Classic examples of adventure short stories include Jack London’s “ To Build a Fire ,” which tells the story of a man struggling to survive in the harsh Yukon wilderness, and Edgar Allan Poe’s “ The Gold Bug ,” a tale of treasure hunting and cryptography. More contemporary examples include Clive Cussler’s short stories, which often feature underwater exploration and treasure hunting.
Adventure short stories can also be found in young adult literature, such as the Percy Jackson series by Rick Riordan, which combines adventure with elements of Greek mythology. These stories often feature young protagonists who must navigate unfamiliar and dangerous worlds, providing a metaphor for the challenges of adolescence.
Fantasy short stories are works of fiction that contain elements that are not realistic, such as magic, mythical creatures, and imaginary worlds. They often involve a conflict between good and evil, a quest, and a hero who must overcome obstacles. Fantasy stories can be set in their own unique worlds, or they can take place in our world but with magical elements added.
Fantasy is a genre that allows for limitless creativity and exploration. It can be used to explore complex themes and ideas, such as the nature of good and evil, the role of power in society, and the complexities of human nature, all within a fantastical and imaginative context.
Examples of Fantasy Short Stories
Classic examples of fantasy short stories include J.R.R. Tolkien’s “ Leaf by Niggle ” and “ Smith of Wootton Major ,” both of which explore themes of creativity and the role of art in society. More contemporary examples include Neil Gaiman’s “ Stardust ,” a fairy tale for adults, and George R.R. Martin’s “ The Hedge Knight ,” a prequel to his Song of Ice and Fire series.
Fantasy short stories can also be found in children’s literature, such as the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling. These stories often feature young protagonists who discover their magical abilities and must navigate a world of magic and danger, providing a metaphor for the challenges and discoveries of growing up.
Horror short stories are designed to frighten, scare, or startle their readers by inducing feelings of horror and terror. They often deal with the unexpected and the supernatural, and they can involve a wide range of themes, from the psychological to the physical. The horror genre is all about creating a sense of fear, dread, and anticipation in the reader.
Horror stories can be deeply disturbing and unsettling, but they can also be cathartic, allowing readers to confront their fears in a safe and controlled environment. They can explore the darker aspects of human nature and the unknown, and they can challenge our perceptions of reality and our understanding of the world.
Examples of Horror Short Stories
Classic examples of horror short stories include Edgar Allan Poe’s “ The Tell-Tale Heart ” and “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” both of which explore themes of madness and the supernatural. More contemporary examples include Stephen King’s “The Boogeyman” and “ The Man in the Black Suit ,” both of which deal with fear and the unknown.
Horror short stories can also be found in young adult literature, such as the Goosebumps series by R.L. Stine. These stories often feature young protagonists who must confront their fears and face dangerous and supernatural threats, providing a metaphor for the challenges and fears of growing up.
Romance short stories are about love, passion, and relationships. They often involve a conflict or obstacle that the protagonists must overcome in order to be together, and they typically have a happy or optimistic ending. The romance genre is all about exploring the complexities of love and relationships, and the emotional journey of the characters.
Romance stories can be deeply emotional and moving, and they can explore a wide range of themes, from the nature of love and passion, to the role of relationships in our lives. They can challenge our perceptions of love and relationships, and they can provide a form of escapism, allowing readers to experience the highs and lows of romantic love.
Examples of Romance Short Stories
Classic examples of romance short stories include Jane Austen’s “ Pride and Prejudice ” and “ Sense and Sensibility ,” both of which explore themes of love, social class, and marriage. More contemporary examples include Nicholas Sparks’ “ The Notebook ” and “ A Walk to Remember ,” both of which deal with love and loss.
Romance short stories can also be found in young adult literature, such as the Twilight series by Stephenie Meyer. These stories often feature young protagonists who are experiencing love and relationships for the first time, providing a metaphor for the challenges and discoveries of growing up.
Science Fiction
Science fiction short stories are works of fiction that explore imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel , parallel universes, and extraterrestrial life. They often involve a conflict or problem that arises from these concepts, and they can explore a wide range of themes, from the ethical implications of technology to the nature of humanity.
Science fiction is a genre that allows for limitless creativity and exploration. It can be used to explore complex themes and ideas, such as the impact of technology on society, the nature of consciousness and reality, and the future of humanity, all within a futuristic and imaginative context.
Examples of Science Fiction Short Stories
Classic examples of science fiction short stories include Isaac Asimov’s “ Nightfall ,” which explores the impact of a sudden and unexpected darkness on a society that has never known night, and Arthur C. Clarke’s “The Star,” which explores the ethical implications of a discovery made by a group of space explorers. More contemporary examples include Philip K. Dick’s “ The Minority Report ,” which explores the concept of precrime and the ethical implications of predicting and preventing crimes before they occur.
Science fiction short stories can also be found in young adult literature, such as the Hunger Games series by Suzanne Collins. These stories often feature young protagonists who must navigate a futuristic and often dystopian world, providing a metaphor for the challenges and uncertainties of growing up in a rapidly changing world.
Mystery short stories are works of fiction that focus on a crime or puzzling event that needs to be solved. They often involve a detective or investigator who must piece together clues and evidence to solve the mystery. The mystery genre is all about the intellectual challenge of solving the puzzle and the suspense of the unfolding investigation.
Mystery stories can be deeply engaging and suspenseful, and they can explore a wide range of themes, from the nature of crime and justice, to the complexities of human nature and the unknown. They can challenge our perceptions of truth and reality, and they can provide a form of escapism, allowing readers to experience the thrill of the investigation and the satisfaction of solving the puzzle.
Examples of Mystery Short Stories
Classic examples of mystery short stories include Arthur Conan Doyle’s Sherlock Holmes stories, such as “ A Scandal in Bohemia ” and “ The Adventure of the Speckled Band ,” both of which feature the brilliant detective Sherlock Holmes solving complex mysteries. More contemporary examples include Agatha Christie’s Miss Marple and Hercule Poirot stories, which feature clever detectives solving intricate puzzles.
Mystery short stories can also be found in young adult literature, such as the Nancy Drew series by Carolyn Keene. These stories often feature young protagonists who must solve mysteries and navigate dangerous situations, providing a metaphor for the challenges and uncertainties of growing up.
- Recent Posts
- Alternate Reality: Book Genre Explained – Ultimate Guide - November 6, 2023
- Supernatural Suspense: Book Genre Explained – Ultimate Guide - November 6, 2023
- Post-Apocalyptic Romance: Book Genre Explained - November 6, 2023
Related Posts:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Guide to 14 Literary Genres. Fiction refers to a story that comes from a writer's imagination, as opposed to one based strictly on fact or a true story. In the literary world, a work of fiction can refer to a short story, novella, and novel, which is the longest form of literary prose. Every work of fiction falls into a sub-genre, each with ...
LGBTQ+. LGBTQ+ novels are those that feature characters who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or otherwise non-heterosexual. Literary Fiction. Literary fiction novels or stories have a high degree of artistic merit, a unique or experimental style of writing, and often deal with serious themes.
As a literary device, genre refers to a form, class, or type of literary work. The primary genres in literature are poetry, drama / play, essay, short story, and novel. The term genre is used quite often to denote literary sub-classifications or specific types of literature such as comedy, tragedy, epic poetry, thriller, science fiction ...
A genre (ZHAHN-ruh) is a category of literature in which the various works share certain characteristics. We often break writing into four main literary genres: fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and drama. (Some people consider fiction and nonfiction to be one category called prose.) Each of the literary genres has its own set of subgenres.
Sub-genres of fiction include novels, short stories, fables, legends, folk tales, and fairy tales. Works of nonfiction contain real stories or information about things, people, events, and places ...
These distinctive ways of writing can be referred to in part as genres. You may have heard the term genre in reference to publishing categories, such as novels or memoirs, but the term can refer to any type of writing that conforms to specific forms and benchmarks. Many genres include stories of different kinds—for example, folktales, short ...
Prose includes novels, short stories, journals, letters, fiction and nonfiction, among others. This article is an example of prose. c. Drama. ... New genres like media (writing for television, film, websites, radios, billboards, etc.) and the graphic novel (comic books) are expanding what we consider literature today. ...
Genre, a distinctive type or category of literary composition, such as the epic, tragedy, comedy, novel, and short story. Despite critics' attempts to systematize the art of literature, such categories must retain a degree of flexibility, for they can break down on closer scrutiny. For example,
Prose as a genre can be broken down into a number of subgenres including both fiction and non-fiction works. Examples of prose can range from news, biographies and essays to novels, short stories, plays and fables. The subject matter, if it is fiction versus nonfiction and length of the work, are not taken into consideration when classifying it ...
Genres "provide a roadmap to rhetors for how to engage with community members in socially acceptable ways" ("Genre and Medium"). Genres of writing include, for example, a research article; a short story; a movie review; an email; a business report; a press release; and a diary entry. You'll be asked to produce writing in different ...
The short story as a genre epitomizes a dynamic interplay between literal and conceptual meanings, presenting a concise yet potent narrative form that beckons readers to explore beyond its surface. On a literal level, short stories encapsulate succinct plots, well-defined characters, and often a singular theme or conflict within a confined word count. . This brevity, however, acts as a canvas ...
Portal Fantasy. A fantasy story in which characters travel from one world (usually ours) to another, this genre bridges high and low fantasy. A Witch's Guide to Escape: A Practical Compendium of Portal Fantasies by Alix E. Harrow: Yeah, I included two of Harrow's stories here. I love the contrast between them, as it perfectly illustrates the wide variety in fantasy writing.
Prose: Fiction (Novel, Novella, Short Story), Nonfiction (Autobiography, Biography, Essay) Genres of Literature Chart A literature genres list would include categories like fiction, non-fiction, and folklore, but may also cover specialized types such as science fiction, romance, mystery, and historical fiction, offering a comprehensive overview ...
Here are several literary genres you can use when writing: 1. Literary fiction. The literary fiction genre involves information that describes imaginary people, settings and events. Authors use fiction as the foundation of all other literary genres, outside of nonfiction. When writing literary fiction, you can include anthropomorphized ...
short story. mystery story. fairy tale. fiction, literature created from the imagination, not presented as fact, though it may be based on a true story or situation. Types of literature in the fiction genre include the novel, short story, and novella. The word is from the Latin fictiō, "the act of making, fashioning, or molding.".
The personal essay form and commentary may sometimes overlap, but it may be helpful to make some distinctions. A commentary is often very short (a few hundred words) and more journalistic in tone than a personal essay. It fits nicely as a column in a newspaper or on a personal blog. The writing can be more newsy than literary.
Defining Literature. Literature, in its broadest sense, is any written work. Etymologically, the term derives from Latin litaritura/litteratura "writing formed with letters," although some definitions include spoken or sung texts. More restrictively, it is writing that possesses literary merit.
Literature, in its broadest sense, is any written work. Etymologically, the term derives from Latin litaritura/litteratura "writing formed with letters," although some definitions include spoken or sung texts. More restrictively, it is writing that possesses literary merit. Literature can be classified according to whether it is fiction or ...
A handy volume that presents an immediate introduction to American short fiction from the 19th century to the 1990s, the 675 alphabetically arranged entries consist of author biographies, literary terms, theories, themes, well-known characters, influential events, and summaries of major stories. Coverage includes: major short stories and ...
Classic examples of adventure short stories include Jack London's "To Build a Fire," which tells the story of a man struggling to survive in the harsh Yukon wilderness, and Edgar Allan Poe's "The Gold Bug," a tale of treasure hunting and cryptography.More contemporary examples include Clive Cussler's short stories, which often feature underwater exploration and treasure hunting.
Her favorite genres include short stories and essays. rhyme scheme. the pattern of rhymes in a poem or song, usually at the ends of lines. Sometimes indicated by letters that show which lines rhyme, like abab. The second and fourth lines of the poem rhyme, and , so its rhyme scheme is ABABCC.
nonfictional prose, any literary work that is based mainly on fact, even though it may contain fictional elements.Examples are the essay and biography.. Defining nonfictional prose literature is an immensely challenging task. This type of literature differs from bald statements of fact, such as those recorded in an old chronicle or inserted in a business letter or in an impersonal message of ...
Writing or speech in its usual form of a series of sentences. Most language that is not poetry can be described this way. Novels, short stories, essays, and letters are examples. Sentence: Chandra prefers to write _____ over poetry. Her favorite genres include short stories and essays.