An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Sage Choice


Systematic reviews: Structure, form and content
This article aims to provide an overview of the structure, form and content of systematic reviews. It focuses in particular on the literature searching component, and covers systematic database searching techniques, searching for grey literature and the importance of librarian involvement in the search. It also covers systematic review reporting standards such as PRISMA-P and PRISMA, critical appraisal and tools and resources to support the review and ensure it is conducted efficiently and effectively. Finally, it summarizes the requirements when screening search results for inclusion in the review, and the statistical synthesis of included studies’ findings.
Provenance and Peer review: Solicited contribution; Peer reviewed; Accepted for publication 24 January 2021.
Introduction
A systematic review collects secondary data, and is a synthesis of all available, relevant evidence which brings together all existing primary studies for review ( Cochrane 2016 ). A systematic review differs from other types of literature review in several major ways. It requires a transparent, reproducible methodology which indicates how studies were identified and the criteria upon which they were included or excluded. As well as synthesis of these studies' findings, there should be an element of evaluation and quality assessment. The systematic review methodology originated in medical and healthcare research, but it has now been adopted by other disciplines, such as engineering, education, economics and business studies. The processes and requirements for conducting a systematic review can seem arduous or time consuming, but with the use of appropriate tools and resources, and with thorough planning undertaken before beginning the review, researchers will be able to conduct their systematic reviews efficiently and smoothly.
This article provides an overview of the structure, form and content of systematic reviews, with a particular focus on the literature searching component. It will also discuss tools and resources – including those relating to reporting standards and critical appraisal of the articles included in the review – which will be of use to researchers conducting a systematic review.
Topic selection and planning
In recent years, there has been an explosion in the number of systematic reviews conducted and published ( Chalmers & Fox 2016 , Fontelo & Liu 2018 , Page et al 2015 ) – although a systematic review may be an inappropriate or unnecessary research methodology for answering many research questions. Systematic reviews can be inadvisable for a variety of reasons. It may be that the topic is too new and there are not enough relevant published papers to synthesise and analyse for a systematic review, or, conversely, that many other researchers have already published systematic reviews on the topic. However, if a scoping search appears to yield sufficient relevant studies for evidence synthesis, and indicates that no previous systematic reviews have been published (or that those previously published require an update or have methodological flaws), systematic reviews are likely to be appropriate.
Most systematic reviews take between six and 18 months to complete, and require a minimum of three authors to independently screen search results. Although many university modules require students to complete systematic reviews, due to this time and authorship requirement, it would be better to describe such student reviews as ‘reviews with systematic literature searches,’ as it is not possible to fulfil all the methodological requirements of a systematic review in a piece of work with a single author. Researchers without the available time or number of potential co-authors may prefer to adopt a different approach, such as narrative, scoping, or umbrella reviews. The systematic, transparent searching techniques outlined in this article can be adopted and adapted for use in other forms of literature review ( Grant & Booth 2009 ), for example, while the critical appraisal tools highlighted are appropriate for use in other contexts in which the reliability and applicability of medical research require evaluation.
Once it has been determined that a systematic review is the appropriate methodology for the research, and that there is sufficient time and resources to conduct it, researchers should then spend some time developing their review topic. It is appropriate at this point to do some scoping searches in relevant subject databases, first to ensure that the proposed review is unique, and meets a research need, and second to obtain a broad overview of the literature that exists, and which is likely to be included in the eventual systematic review. Based on this scoping work, the review topic may need to be refined or adapted, possibly to broaden or narrow it in focus. Once reviewers are satisfied with their chosen topic, the next step is to prepare a protocol which states transparently the methodology they intend to follow when conducting their review.
Creating a protocol
A protocol is a description of the proposed systematic review, including methods, the rationale for the review, and steps which will be taken to eliminate bias while conducting the review. Registering the protocol stakes a claim on the research, and it also means that researchers have done a significant portion of the work required before they formally begin the review, as they will have written the Methods section in draft form and planned what will be necessary to document and report by the time the protocol is finished.
Most protocols are registered with PROSPERO (2020), although it is also possible to upload your protocol on an institutional or subject repository, or publish the protocol in a journal. Guidance for creating a protocol can be found at PRISMA-P (The PRISMA Group et al 2015), or by working through the online training on protocols available at the Cochrane Library ( Cochrane Interactive Learning 2019 ).
Reporting standards and structure
PRISMA (the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) is 'an evidence-based minimum set of items for reporting in systematic reviews and meta-analyses' ( Moher et al 2009 ). The PRISMA checklist is a useful guideline of content that should be reported and included in the final published version of the systematic review, and will help when in the planning stages as well. Most systematic reviews will be written up using the PRISMA checklist as their underlying structure, so familiarity with this checklist and the content required when reporting the findings of the systematic review should be established at the earliest planning stages of the research.
PRISMA-P (The PRISMA Group et al 2015) is the reporting guidelines for protocols. The EQUATOR Network lists reporting standards for multiple different types of study design ( EQUATOR Network 2020 ). Researchers can search for the right guideline for their type of study. Those undertaking a Cochrane review should select the correct Cochrane Handbook ( Cochrane Training 2020 ) for their review type.
Search strategy
The search strategy for systematic reviews is the main method of collecting the data which will underpin the review's findings. This means that the search must be sufficiently robust – both sensitive and specific – to capture all relevant articles. Ideally, multiple databases and other sources of information should be searched, using a consistent, predetermined search string. Generally, this will involve multiple synonyms for each theme of the review's topic, and a multifield search including freetext terms in (at minimum) the title and abstract, and the controlled vocabulary in the database thesaurus. These words are then combined with the Boolean operators AND, OR and NOT so that search results are both sensitive and specific.
Grey literature
It is likely that systematic reviews will need to include a search of grey literature as well as the peer-reviewed journal articles found through database searching. Grey literature includes unpublished theses, conference proceedings, government reports, unpublished trial data and more. Leaving grey literature out can run the risk of biasing the reviews results ( Goldacre 2011 ).
Searching grey literature can be challenging. Most sources of grey literature cannot be searched with complex Boolean operators and myriad synonymous keywords in the manner of a database. Likewise, the websites and other sources used to search for grey literature are unlikely to have a controlled vocabulary thesaurus. The Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) tool is designed to help adapt complex systematic database search strategies for use when searching for grey literature ( CADTH 2009 ).
Snowballing, hand-searching and reference lists
Sometimes it may be appropriate to 'snowball' a search. This involves screening all the articles that cite included papers (the articles which meet the inclusion criteria after screening). Search for the titles of each included article in Web of Science or Scopus (or both), and any listed citing article which meets your inclusion criteria should also be included in the review.
Hand searching involves looking back through the tables of contents of key journals, conference proceedings, or lists of conference presentations relevant to the systematic review topic. Once key journals have been identified, reviewers should plan how many years back they will look – this will need to be done consistently across all journals that are hand-searched.
After reviewers have screened all the papers identified by the database and grey literature searches, and agreed on which will be included in the review, they should check through these articles' reference lists. Any articles in their reference lists which meet all inclusion criteria should also be included in the review.
Librarian co-authorship
There is some evidence that having a librarian co-author on a systematic review can improve the review's quality. A number of recent studies have indicated that librarian involvement improves the reproducibility of the literature searching ( Hameed et al 2020 , Koffel 2015 , Rethlefsen et al 2015 ). Reviews without librarian involvement often have problems with their search strategies – for example Boolean operators used incorrectly, inappropriate search syntax, or a lack of sufficient synonyms for each search term, meaning that relevant studies might be missed ( Golder et al 2008 , Li et al 2014 ). Unfortunately, in some instances, systematic reviews without librarian co-authors will still be published, even if their search strategies have significant methodological flaws ( Brasher & Giustini 2020 ). Librarian involvement will help ensure that the search strategy is robust, and that it is described accurately in the methodology to ensure that the systematic review is reproducible. Generally, if a librarian is developing the search terms, running the searches in databases and writing the search methods, they should be a co-author of the systematic review, whereas if the librarian supports researchers who then conduct the searches themselves, co-authorship is not necessary. This also aligns with the Vancouver recommendations on co-authorship ( International Committee of Medical Journal Editors 2019 ).
After database and grey literature searches are completed, and researchers have identified other papers through hand-searching, they will need to screen the titles and abstracts to determine if they meet the criteria for inclusion. These criteria should be pre-defined (ie: stated in the protocol before searches have begun). Inclusion criteria might relate to the following:
Date range of publication. Study design type. Whether a study focuses on the review's specific disease, condition, or patient population. Whether a study focuses mainly on the review's specific intervention. Whether a study focused on a certain country, region, or healthcare context (for example primary care, outpatient department, critical care unit, or similar).
This list is not exhaustive, and there are many other inclusion criteria to apply, depending on the scope of the topic of the systematic review. It is important that these criteria are stated clearly in the Methods section of both the protocol and systematic review, and that all co-authors understand them.
Generally, articles are screened against these criteria independently by at least two authors. Initially they should screen the titles and abstracts, and then move on to screening the full text for any articles which could not be judged as fulfilling (or not fulfilling) all inclusion criteria on the basis of the information in their titles and abstracts.
Referencing software such as Endnote, EndnoteWeb, Mendeley or Zotero can be used for screening, or reviewers may prefer to use systematic review screening software such as Covidence or Rayyan.
Critical appraisal tools
There are a number of tools and checklists available to help assess the quality of studies to be included in a review. Studies included in a systematic review should be assessed for their quality and reliability. While poor quality studies should not be excluded if they fulfil predefined inclusion criteria, the systematic review should make clear that all included studies have been assessed according to consistent principles of critical appraisal, and the results of that appraisal should be included in the review.
Most critical appraisal tools consist of different checklists to apply to different types of study design. If a systematic review includes multiple types of study design, it is advisable that researchers are consistent about which tools they use – it is preferable to use different checklists from a single source, rather than picking and choosing from a variety of sources.
If the systematic review is only including peer-reviewed, published journal articles, the checklists from either CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme), Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network), or Joanna Briggs Institute will be appropriate ( Brice 2020 , Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine 2020 , Joanna Briggs Institute 2020 , SIGN 2020 ). Reviews which include grey literature should use a grey literature appraisal tool, such as AACODS ( Tyndall 2008 ). There are also risk of bias assessment tools, such as RoBiS for evaluating systematic reviews, and RoB 2 for evaluating randomized controlled trials ( Bristol Medical School 2020 , Sterne et al 2019 ).
One of the main advantages of systematic reviews is that they combine the analysis of the data from a number of primary studies. Most commonly, this is done through meta-analysis – the statistical combination of results from two or more studies. As outlined in the Cochrane Handbook, in interventional studies, a systematic review meta-analysis will seek to answer these three main questions:
What is the direction of effect? What is the size of effect? Is the effect consistent across [all included] studies? ( Higgins et al 2019 )
The researchers will then make a judgement as to the strength of evidence for the effect. If the systematic review is assessing the effectiveness of a variety of different interventions, it may not be possible to combine all studies for meta-analysis as the studies may be sufficiently different to make meta-analysis inappropriate. Researchers should ensure that when interpreting the results they consider the limitations and potential biases of included studies. When reporting the findings it is also usually necessary to consider applicability, and make recommendations – such as for a change in practice.
Systematic reviews – when an appropriate approach to the topic being researched – are a way to synthesize and evaluate the range of evidence available in multiple primary studies. Their methodology is complex, but if the correct reporting guidelines are followed, and researchers make use of tools, resources and the support of librarians and other information specialists, the process will be more straightforward. Planning is key: researchers should have a clear picture of what is involved, and what will need to be documented and reported in any resulting publications, and put measures in place to ensure that they capture all of this essential information.
No competing interests declared .
ORCID iD: Veronica Phillips https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4383-9434
Literature Review vs Systematic Review
- Literature Review vs. Systematic Review
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Databases and Articles
- Specific Journal or Article
Subject Guide

Definitions
It’s common to confuse systematic and literature reviews because both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews.
Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review. [figshare]. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.766364
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Primary vs. Secondary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:19 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sjsu.edu/LitRevVSSysRev

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?
- 3 minute read
- 46.5K views
Table of Contents
As a researcher, you may be required to conduct a literature review. But what kind of review do you need to complete? Is it a systematic literature review or a standard literature review? In this article, we’ll outline the purpose of a systematic literature review, the difference between literature review and systematic review, and other important aspects of systematic literature reviews.
What is a Systematic Literature Review?
The purpose of systematic literature reviews is simple. Essentially, it is to provide a high-level of a particular research question. This question, in and of itself, is highly focused to match the review of the literature related to the topic at hand. For example, a focused question related to medical or clinical outcomes.
The components of a systematic literature review are quite different from the standard literature review research theses that most of us are used to (more on this below). And because of the specificity of the research question, typically a systematic literature review involves more than one primary author. There’s more work related to a systematic literature review, so it makes sense to divide the work among two or three (or even more) researchers.
Your systematic literature review will follow very clear and defined protocols that are decided on prior to any review. This involves extensive planning, and a deliberately designed search strategy that is in tune with the specific research question. Every aspect of a systematic literature review, including the research protocols, which databases are used, and dates of each search, must be transparent so that other researchers can be assured that the systematic literature review is comprehensive and focused.
Most systematic literature reviews originated in the world of medicine science. Now, they also include any evidence-based research questions. In addition to the focus and transparency of these types of reviews, additional aspects of a quality systematic literature review includes:
- Clear and concise review and summary
- Comprehensive coverage of the topic
- Accessibility and equality of the research reviewed
Systematic Review vs Literature Review
The difference between literature review and systematic review comes back to the initial research question. Whereas the systematic review is very specific and focused, the standard literature review is much more general. The components of a literature review, for example, are similar to any other research paper. That is, it includes an introduction, description of the methods used, a discussion and conclusion, as well as a reference list or bibliography.
A systematic review, however, includes entirely different components that reflect the specificity of its research question, and the requirement for transparency and inclusion. For instance, the systematic review will include:
- Eligibility criteria for included research
- A description of the systematic research search strategy
- An assessment of the validity of reviewed research
- Interpretations of the results of research included in the review
As you can see, contrary to the general overview or summary of a topic, the systematic literature review includes much more detail and work to compile than a standard literature review. Indeed, it can take years to conduct and write a systematic literature review. But the information that practitioners and other researchers can glean from a systematic literature review is, by its very nature, exceptionally valuable.
This is not to diminish the value of the standard literature review. The importance of literature reviews in research writing is discussed in this article . It’s just that the two types of research reviews answer different questions, and, therefore, have different purposes and roles in the world of research and evidence-based writing.
Systematic Literature Review vs Meta Analysis
It would be understandable to think that a systematic literature review is similar to a meta analysis. But, whereas a systematic review can include several research studies to answer a specific question, typically a meta analysis includes a comparison of different studies to suss out any inconsistencies or discrepancies. For more about this topic, check out Systematic Review VS Meta-Analysis article.
Language Editing Plus
With Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus services , you can relax with our complete language review of your systematic literature review or literature review, or any other type of manuscript or scientific presentation. Our editors are PhD or PhD candidates, who are native-English speakers. Language Editing Plus includes checking the logic and flow of your manuscript, reference checks, formatting in accordance to your chosen journal and even a custom cover letter. Our most comprehensive editing package, Language Editing Plus also includes any English-editing needs for up to 180 days.

- Publication Recognition
How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Penn State University Libraries
- Home-Articles and Databases
- Asking the clinical question
- PICO & Finding Evidence
- Evaluating the Evidence
- Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
- Ethical & Legal Issues for Nurses
- Nursing Library Instruction Course
- Data Management Toolkit This link opens in a new window
- Useful Nursing Resources
- Writing Resources
- LionSearch and Finding Articles
- The Catalog and Finding Books
Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
It is common to confuse systematic and literature reviews as both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Even with this common ground, both types vary significantly. Please review the following chart (and its corresponding poster linked below) for the detailed explanation of each as well as the differences between each type of review.
- What's in a name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters by Lynn Kysh, MLIS, University of Southern California - Norris Medical Library
- << Previous: Evaluating the Evidence
- Next: Ethical & Legal Issues for Nurses >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 11:54 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/nursing
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Biomedical Library Guides
Systematic Reviews
- Types of Literature Reviews
What Makes a Systematic Review Different from Other Types of Reviews?
- Planning Your Systematic Review
- Database Searching
- Creating the Search
- Search Filters and Hedges
- Grey Literature
- Managing and Appraising Results
- Further Resources
Reproduced from Grant, M. J. and Booth, A. (2009), A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26: 91–108. doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Planning Your Systematic Review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 2:02 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/systematicreviews
The Graduate Health & Life Sciences Research Library at Georgetown University Medical Center
Systematic reviews.
- Should I do a systematic review?
- Writing the Protocol
- Building a Systematic Search
- Where to Search
- Managing Project Data
- How can a DML librarian help?
Guides and Standards
- The Cochrane Handbook The Cochrane Handbook has become the de facto standard for planning and carrying out a systematic review. Chapter 6, Searching for Studies, is most helpful in planning your review.
- Finding What Works in Health Care: Standards for Systematic Reviews The IOM standards promote objective, transparent, and scientifically valid systematic reviews. They address the entire systematic review process, from locating, screening, and selecting studies for the review, to synthesizing the findings (including meta-analysis) and assessing the overall quality of the body of evidence, to producing the final review report.
- PRISMA Standards The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses is an evidence-based minimum set of items for reporting in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. A 27-item checklist, PRISMA focuses on randomized trials but can also be used as a basis for reporting systematic reviews of other types of research, particularly evaluations of interventions.
What is a systematic review?
A systematic literature review is a research methodology designed to answer a focused research question. Authors conduct a methodical and comprehensive literature synthesis focused on a well-formulated research question. Its aim is to identify and synthesize all of the scholarly research on a particular topic, including both published and unpublished studies. Systematic reviews are conducted in an unbiased, reproducible way to provide evidence for practice and policy-making and identify gaps in research. Every step of the review, including the search, must be documented for reproducibility.
Researchers in medicine may be most familiar with Cochrane Reviews, which synthesize randomized controlled trials to evaluate specific medical interventions. Systematic reviews are conducted in many other fields, though the type of evidence analyzed varies with the research question.
When to use systematic review methodology
Systematic reviews require more time and manpower than traditional literature reviews. Before beginning a systematic review, researchers should address these questions:
Is there is enough literature published on the topic to warrant a review?
Systematic reviews are designed to distill the evidence from many studies into actionable insights. Is there a body of evidence available to analyze, or does more primary research need to be done?
Can your research question be answered by a systematic review?
Systematic review questions should be specific and clearly defined. Questions that fit the PICO (problem/patient, intervention, comparison, outcome) format are usually well-suited for the systematic review methodology. The research question determines the search strategy, inclusion criteria, and data that you extract from the selected studies, so it should be clearly defined at the start of the review process.
Do you have a protocol outlining the review plan?
The protocol is the roadmap for the review project. A good protocol outlines study methodology, includes the rationale for the systematic review, and describes the key question broken into PICO components. It is also a good place to plan out inclusion/exclusion criteria, databases that will be searched, data abstraction and management methods, and how the studies will be assessed for methodological quality.
Do you have a team of experts?
A systematic review is team effort. Having multiple reviewers minimizes bias and strengthens analysis. Teams are often composed of subject experts, two or more literature screeners, a librarian to conduct the search, and a statistician to analyze the data.
Do you have the time that it takes to properly conduct a systematic review?
Systematic reviews typically take 12-18 months.
Do you have a method for discerning bias?
There are many types of bias, including selection, performance, & reporting bias, and assessing the risk of bias of individual studies is an important part of your study design.
Can you afford to have articles in languages other than English translated?
You should include all relevant studies in your systematic review, regardless of the language they were published in, so as to avoid language bias.
Which review is right for you?
If your project does not meet the above criteria, there are many more options for conducting a synthesis of the literature. The chart below highlights several review methodologies. Reproduced from: Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009 Jun;26(2):91-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x . Review. PubMed PMID: 19490148
- Next: Writing the Protocol >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 1:01 PM
- URL: https://guides.dml.georgetown.edu/systematicreviews
The Responsible Use of Electronic Resources policy governs the use of resources provided on these guides. © Dahlgren Memorial Library, Georgetown University Medical Center. Unless otherwise stated, these guides may be used for educational or academic purposes as long as proper attribution is given. Please seek permission for any modifications, adaptations, or for commercial purposes. Email [email protected] to request permission. Proper attribution includes: Written by or adapted from, Dahlgren Memorial Library, URL.

Literature Reviews
- Types of reviews
- Getting started
Types of reviews and examples
Choosing a review type.
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
- Meta-analysis
- Systematized
Definition:
"A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265).
Characteristics:
- Provides examination of recent or current literature on a wide range of subjects
- Varying levels of completeness / comprehensiveness, non-standardized methodology
- May or may not include comprehensive searching, quality assessment or critical appraisal
Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review. Sustainability , 14 (15), 9653. doi.org/10.3390/su14159653
Booth, A., Papaioannou, D., & Sutton, A. (2012). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
"An assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue...using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 100).
- Assessment of what is already known about an issue
- Similar to a systematic review but within a time-constrained setting
- Typically employs methodological shortcuts, increasing risk of introducing bias, includes basic level of quality assessment
- Best suited for issues needing quick decisions and solutions (i.e., policy recommendations)
Learn more about the method:
Khangura, S., Konnyu, K., Cushman, R., Grimshaw, J., & Moher, D. (2012). Evidence summaries: the evolution of a rapid review approach. Systematic reviews, 1 (1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-10
Virginia Commonwealth University Libraries. (2021). Rapid Review Protocol .
Quarmby, S., Santos, G., & Mathias, M. (2019). Air quality strategies and technologies: A rapid review of the international evidence. Sustainability, 11 (10), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102757
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Developed and refined by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), this review "map[s] out and categorize[s] existing literature on a particular topic, identifying gaps in research literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 97).
Although mapping reviews are sometimes called scoping reviews, the key difference is that mapping reviews focus on a review question, rather than a topic
Mapping reviews are "best used where a clear target for a more focused evidence product has not yet been identified" (Booth, 2016, p. 14)
Mapping review searches are often quick and are intended to provide a broad overview
Mapping reviews can take different approaches in what types of literature is focused on in the search
Cooper I. D. (2016). What is a "mapping study?". Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA , 104 (1), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.1.013
Miake-Lye, I. M., Hempel, S., Shanman, R., & Shekelle, P. G. (2016). What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Systematic reviews, 5 (1), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0204-x
Tainio, M., Andersen, Z. J., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Hu, L., De Nazelle, A., An, R., ... & de Sá, T. H. (2021). Air pollution, physical activity and health: A mapping review of the evidence. Environment international , 147 , 105954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105954
Booth, A. (2016). EVIDENT Guidance for Reviewing the Evidence: a compendium of methodological literature and websites . ResearchGate. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1562.9842 .
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
"A type of review that has as its primary objective the identification of the size and quality of research in a topic area in order to inform subsequent review" (Booth et al., 2012, p. 269).
- Main purpose is to map out and categorize existing literature, identify gaps in literature—great for informing policy-making
- Search comprehensiveness determined by time/scope constraints, could take longer than a systematic review
- No formal quality assessment or critical appraisal
Learn more about the methods :
Arksey, H., & O'Malley, L. (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 (1), 19-32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science: IS, 5, 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Example :
Rahman, A., Sarkar, A., Yadav, O. P., Achari, G., & Slobodnik, J. (2021). Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano-and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Science of the Total Environment, 757 , 143872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143872
A review that "[compiles] evidence from multiple...reviews into one accessible and usable document" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 103). While originally intended to be a compilation of Cochrane reviews, it now generally refers to any kind of evidence synthesis.
- Compiles evidence from multiple reviews into one document
- Often defines a broader question than is typical of a traditional systematic review
Choi, G. J., & Kang, H. (2022). The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence. The Korean Journal of Pain , 35 (2), 127–128. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.127
Aromataris, E., Fernandez, R., Godfrey, C. M., Holly, C., Khalil, H., & Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare , 13(3), 132–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
Rojas-Rueda, D., Morales-Zamora, E., Alsufyani, W. A., Herbst, C. H., Al Balawi, S. M., Alsukait, R., & Alomran, M. (2021). Environmental risk factors and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Dealth , 18 (2), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020704
A meta-analysis is a "technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the result" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 98).
- Statistical technique for combining results of quantitative studies to provide more precise effect of results
- Aims for exhaustive, comprehensive searching
- Quality assessment may determine inclusion/exclusion criteria
- May be conducted independently or as part of a systematic review
Berman, N. G., & Parker, R. A. (2002). Meta-analysis: Neither quick nor easy. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 2(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-2-10
Hites R. A. (2004). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology , 38 (4), 945–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035082g
A systematic review "seeks to systematically search for, appraise, and [synthesize] research evidence, often adhering to the guidelines on the conduct of a review" provided by discipline-specific organizations, such as the Cochrane Collaboration (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102).
- Aims to compile and synthesize all known knowledge on a given topic
- Adheres to strict guidelines, protocols, and frameworks
- Time-intensive and often takes months to a year or more to complete
- The most commonly referred to type of evidence synthesis. Sometimes confused as a blanket term for other types of reviews
Gascon, M., Triguero-Mas, M., Martínez, D., Dadvand, P., Forns, J., Plasència, A., & Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J. (2015). Mental health benefits of long-term exposure to residential green and blue spaces: a systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 12 (4), 4354–4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404354
"Systematized reviews attempt to include one or more elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of claiming that the resultant output is a systematic review" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102). When a systematic review approach is adapted to produce a more manageable scope, while still retaining the rigor of a systematic review such as risk of bias assessment and the use of a protocol, this is often referred to as a structured review (Huelin et al., 2015).
- Typically conducted by postgraduate or graduate students
- Often assigned by instructors to students who don't have the resources to conduct a full systematic review
Salvo, G., Lashewicz, B. M., Doyle-Baker, P. K., & McCormack, G. R. (2018). Neighbourhood built environment influences on physical activity among adults: A systematized review of qualitative evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15 (5), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050897
Huelin, R., Iheanacho, I., Payne, K., & Sandman, K. (2015). What’s in a name? Systematic and non-systematic literature reviews, and why the distinction matters. https://www.evidera.com/resource/whats-in-a-name-systematic-and-non-systematic-literature-reviews-and-why-the-distinction-matters/

- Review Decision Tree - Cornell University For more information, check out Cornell's review methodology decision tree.
- LitR-Ex.com - Eight literature review methodologies Learn more about 8 different review types (incl. Systematic Reviews and Scoping Reviews) with practical tips about strengths and weaknesses of different methods.
- << Previous: Getting started
- Next: 1. Define your research question >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries


University Libraries
- Ohio University Libraries
- Library Guides
Evidence-based Practice in Healthcare
- Performing a Literature Review
- EBP Tutorials
- Question- PICO
- Definitions
- Systematic Reviews
- Levels of Evidence
- Finding Evidence
- Filter by Study Type
- Too Much or Too Little?
- Critical Appraisal
- Quality Improvement (QI)
- Contact - Need Help?
Hanna's Performing a qualitity literature review presentation slides
- Link to the PPT slides via OneDrive anyone can view
Characteristics of a Good Literature Review in Health & Medicine
Clear Objectives and Research Questions : The review should start with clearly defined objectives and research questions that guide the scope and focus of the review.
Comprehensive Coverage : Include a wide range of relevant sources, such as research articles, review papers, clinical guidelines, and books. Aim for a broad understanding of the topic, covering historical developments and current advancements. To do this, an intentional and minimally biased search strategy.
- Link to relevant databases to consider for a comprehensive search (search 2+ databases)
- Link to the video "Searching your Topic: Strategies and Efficiencies" by Hanna Schmillen
- Link to the worksheet "From topic, to PICO, to search strategy" to help researchers work through their topic into an intentional search strategy by Hanna Schmillen
Transparency and Replicability : The review process, search strategy, should be transparent, with detailed documentation of all steps taken. This allows others to replicate the review or update it in the future.
Appraisal of Studies Included : Each included study should be critically appraised for methodological quality and relevance. Use standardized appraisal tools to assess the risk of bias and the quality of evidence.
- Link to the video " Evaluating Health Research" by Hanna Schmillen
- Link to evaluating and appraising studies tab, which includes a rubric and checklists
Clear Synthesis and Discussion of Findings : The review should provide a thorough discussion of the findings, including any patterns, relationships, or trends identified in the literature. Address the strengths and limitations of the reviewed studies and the review itself. Present findings in a balanced and unbiased manner, avoiding over interpretation or selective reporting of results.
Implications for Practice and Research : The review should highlight the practical implications of the findings for medical practice and policy. It should also identify gaps in the current literature and suggest areas for future research.
Referencing and Citation : Use proper citation practices to credit original sources. Provide a comprehensive reference list to guide readers to the original studies.
- Link to Citation Style Guide, includes tab about Zotero
Note: A literature review is not a systematic review. For more information about systematic reviews and different types of evidence synthesis projects, see the Evidence Synthesis guide .
- << Previous: Quality Improvement (QI)
- Next: Contact - Need Help? >>
Memorial Sloan Kettering Library

The physical space of the MSK Library closed to visitors on Friday, May 17, 2024. Please visit this guide for more information.
MSK Advanced Practice Providers Resources
- Library Services
- Remote Access This link opens in a new window
- eJournals This link opens in a new window
- Education & Training Resources
- Literature Databases
- Mobile Applications
- Practice Guidelines
- Citation Management This link opens in a new window
Systematic Reviews
Msk library systematic review service.
- Datasets & Data Management
- Finding Evidence
- Levels of Evidence
- Critical Appraisal
- Integrating Evidence
What is a Systematic Review?
Systematic Reviews (SRs) are a form of Evidence-Based Practice . They are scientific investigations in themselves, with pre-planned methods and an assembly of original studies as their “subjects.”
They synthesize the results of multiple primary investigations by using strategies that limit bias and random error. These strategies include a comprehensive search of all potentially relevant articles and the use of explicit, reproducible criteria in the selection of articles for review.
Primary research designs and study characteristics are appraised, data are synthesized, and results are interpreted.
A systematic review may be undertaken to confirm or refute whether or not current practice is based on relevant evidence, to establish the quality of that evidence, and to address and/or recommend changes.
If you are not sure that a Systematic Review is the right approach for your research, Cornell University Library has developed a decision tree to help researchers determine the best review methodology that fits their timeline, question scope, and desired outcome.
What is a Scoping Review?
Preliminary assessment of potential size and scope of available research literature. Scoping reviews are often a first step in conducting a SR because it allows the investigator the opportunity to review the literature landscape and determine whether or not a SR is feasible (too much or too little publications). This type of review takes the same systematic and rigorous methodologies used in conducting an SR.
This document presents the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) checklist and explanation. (Oct 2018)
- MSK Library Systematic Review Guide Learn about how to conduct a systematic review, including how to collaborate with the MSK Library on your systematic review
Once you decide that you want to conduct a systematic review with your team, the first step to working with the MSK Library on your systematic review is to fill out our Systematic Review Search Request form . Your request will be reviewed and a research informationist will be assigned to work with you and your team.
Benefits of Working with MSK Library on your Systematic Review
The National Academies' standards for systematic reviews (3.1.1) states: work with a librarian or other information specialist trained in performing systematic reviews to plan the search strategy. The MSK research informationist's team has collaborated with researchers on a number of systematic reviews. Before a research informationist can be part of our Systematic Review Service, they must attend formal training to hone their search expertise and be able to provide guidance on the systematic review process.
MSK Library's SR Service
The research informationist as co-investigator is committed to collaborating and supporting the following systematic review tasks:.
- Determine if a systematic review has already been done on your topic.
- Translate the research question into an appropriate search strategy.
- Explore registering your systematic review in PROSPERO. (Authors should check with the journal they wish to submit their manuscript to, to confirm whether or not protocol registration is required).
- Translate the search concepts into controlled vocabulary and keywords so that retrieval is maximized at the same time as being precise. The search strategy is also reviewed by another research informationist based on the PRESS 2015 Guideline . Peer-review of the search strategies using this methodology enhances the quality and comprehensiveness of the final search strings used.
- Recommend specific databases and other information sources to be searched.
- Conduct the literature searches.
- Provide training to your administrative staff or designated team member in how to access full text articles or request them via MSK Document Delivery. Help obtain or verify any references found from hand searching or other venues.
- Provide guidance and support regarding bibliographic management tools.
- Provide a Covidence account to assist with screening and managing steps in the systematic review process. You can create your personal sign-in with Covidence before or after joining the MSK Library's institutional account.
- Write the literature search methodology section for the submitted manuscript.
- Maintain records of search results and follow up with alerts and updates as needed.
- << Previous: Publishing
- Next: Datasets & Data Management >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 12:41 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mskcc.org/APP
A systematic exploration of scoping and mapping literature reviews
- Brief Report
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Eirini Christou ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6928-1013 1 ,
- Antigoni Parmaxi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0687-0176 1 &
- Panayiotis Zaphiris ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8112-5099 1
Systematic literature mapping can help researchers identify gaps in the research and provide a comprehensive overview of the available evidence. Despite the importance and benefits of conducting systematic scoping and mapping reviews, many researchers may not be familiar with the methods and best practices for conducting these types of reviews. This paper aims to address this gap by providing a step-by-step guide to conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review, drawing on examples from different fields. This study adopts a systematic literature review approach aiming to identify and present the steps of conducting scoping and mapping literature reviews and serves as a guide on conducting scoping or mapping systematic literature reviews. A number of 90 studies were included in this study. The findings describe the steps to follow when conducting scoping and mapping reviews and suggest the integration of the card sorting method as part of the process. The proposed steps for undertaking scoping and mapping reviews presented in this manuscript, highlight the importance of following a rigorous approach for conducting scoping or mapping reviews.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
An essential component of academic research is literature review. A systematic literature review, also known as a systematic review, is a method for locating, assessing, and interpreting all research related to a specific research question, topic, or phenomenon of interest [ 1 ].
Scoping and mapping reviews are variations of systematic literature mapping [ 2 ]. Both mapping and scoping reviews can help researchers to understand the scope and breadth of the literature in a given field, identify gaps in the research, and provide a comprehensive overview of the available evidence. Systematic literature mapping purposely focuses on a narrower but more general academic or policy issue and does not try to synthesize the results of research to address a particular subject. The scoping review is exploratory in nature, whereas the mapping review can be conclusive in describing the available evidence and identifying gaps. Mapping review includes a thorough, systematic search of a wide field. It identifies the body of literature that is currently available on a subject and points out any glaring gaps in the evidence [ 3 ].
1.1 Rationale
Despite the importance and benefits of conducting systematic scoping and mapping reviews, many researchers may not be familiar with the methods and best practices for conducting these types of reviews. This paper aims to address this gap by providing a step-by-step guide to conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review, drawing on examples from different fields.
This study adopts a systematic literature review approach aiming to identify and present the differences and the steps of conducting scoping and mapping literature review. The paper provides practical guidance on how to address common challenges in conducting systematic scoping or mapping reviews, such as dealing with the volume of studies identified, managing the data extraction and synthesis process, and ensuring rigor and reproducibility in the review methodology. The main research questions that guide this study are:
RQ1: What is a systematic scoping review and how is it conducted?
RQ2: What is a systematic mapping review and how is it conducted?
RQ3: What are the main differences between systematic scoping and systematic mapping reviews?
Overall, this paper will be a valuable resource for researchers who are interested in conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review. By providing clear guidance and practical examples, the paper aims to promote best practices in systematic scoping and mapping review methodology. The study is organized as follows: The following section presents the methodology of the study, followed by the results showing the process of the scoping and mapping literature review and presenting some examples. Finally, suggestions on how to plan and perform a quality scoping and mapping review are presented.
2 Methodology
The methodology of this paper was adopted by Xiao and Watson [ 4 ].
2.1 Literature search
The search was conducted in two well-known online databases, Web of Science and EBSCOHost, across various disciplines. The searched terms combined keywords related to the performance of scoping and mapping literature review, such as “systematic literature review”, “methodology”, “map”, “mapping” and “scoping”. The title of each manuscript was used to determine its initial relevance. If the content of the title suggested that it would explain the method of the literature review process, we obtained the full reference, which included the author, year, title, and abstract, for additional analysis.
2.2 Initial search results
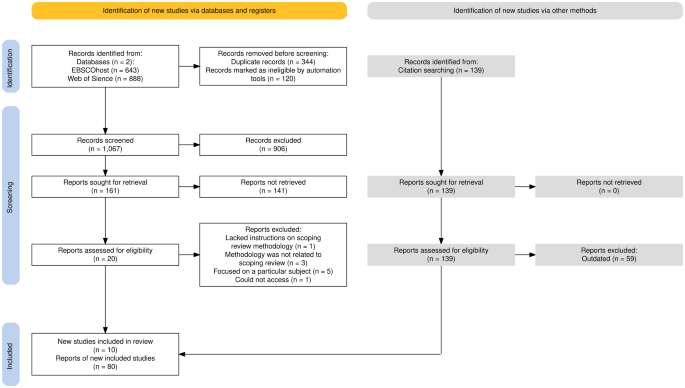
The query string used for the database search is the following: systematic literature review AND methodology AND (“map” OR “mapping” OR “scoping”). Abstract search was conducted in both databases for the last 10 years (2013–2022). A search on EBSCOHost revealed 643 results of which 291 were duplicated and automatically removed. After applying the database filters to limit the articles to peer-reviewed academic journal articles written in English, a number of 102 papers were excluded. Additional 109 papers were duplicated and removed manually. After an initial screening of the titles, a total of 13 studies were identified as relevant to the methodology of the scoping and mapping literature review. A search on Web of Science, revealed 888 results of which 9 were duplicate and removed, and 157 were found to be related to the methodology of scoping or mapping literature reviews after the first title screening. Last search was conducted on the 2nd of November 2022. Both sources revealed 161 related studies, excluding 9 duplicates that were removed.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Only studies that provide instructions on how to perform a scoping or mapping review were included in this paper. Reviews of the literature on certain subjects and in languages other than English were excluded. The study is limited to papers published within the last 10 years, aiming to collect recent information for performing scoping or mapping reviews. Inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found in Table 1 .
2.4 Screening
To further assess the 161 studies’ applicability to the study topic, their abstracts were reviewed. The manuscripts were evaluated independently and in parallel by two researchers. The researchers’ differing opinions were discussed and settled. Then the full-text of a total of 20 studies was acquired for quality evaluation.
2.5 Eligibility and quality evaluation
To further assess the quality and relevance of the studies, the full-text papers were reviewed. Journal articles and books published by prominent publishers were included in the review as they contained high-quality research. Because there is no peer review procedure, the majority of technical reports and online presentations were excluded.
Two researchers worked independently and simultaneously on evaluating eligibility and quality. Any disagreements between them were discussed and resolved. A total of ten (10) studies were excluded after careful review: one study was excluded because it lacked instructions on how the scoping or mapping review methodology was conducted, three studies were excluded because the methodology was not related to scoping or mapping review, while five studies were disregarded because they focused on a particular subject. One of the studies’ full text couldn’t be accessed. This resulted in ten (10) eligible for full-text analysis.
2.6 Iterations
Through backward and forward searching, additional 18 studies were discovered, from which only 10 met the inclusion criteria. The forward and backward search was also used to find manuscripts that applied scoping or mapping literature review methodology. After finding the article that established the scoping or mapping review methodology, articles that had cited the methodology paper to find instances of best practices in different fields were searched. Following consideration of examples’ adherence to the methodology, preference was given to planning-related articles. In total, 90 studies were analyzed in this study, i.e. 10 methodological papers that describe the application of scoping or mapping review, as well as 80 papers that demonstrate the application of the scoping and mapping methodology in different fields, that are used as examples. The PRISMA flow diagram (see Fig. 1 ) depicts the process of the search strategy [ 5 ].
PRISMA flow diagram
2.7 Extraction and analysis of data
Data were extracted in the process of scoping literature reviews, including information with regards to formulating the problem, establishing and validating the review procedure, searching the literature, screening for inclusion, evaluating quality, extracting data, analyzing and synthesizing data, and reporting the findings (Xiao & Watson, 2019). NVivo software was used for all data extraction and coding procedures. Initially, two researchers each took information from articles for cross-checking. The two researchers reached an agreement on what to extract from the publications after reviewing a few articles together. Then the first author classified the data based on the research questions.
In this section we present the findings of our review.
3.1 Defining “Scoping” and “mapping” review
According to [ 2 ], scoping and mapping reviews are variations of systematic literature mapping that focus on narrower but more general academic or policy issues. A scoping review is exploratory in nature, seeking to identify the nature and extent of research on a particular topic, and can be used to identify gaps in the literature. An example of a research question suitable for a scoping review is “What engagement strategies do educators use in classroom settings to facilitate teaching and learning of diverse students in undergraduate nursing programs?“ [ 6 ]. A mapping review, on the other hand, is a thorough and systematic search of a wide field of literature that aims to identify the body of literature currently available on a subject and point out any glaring gaps in the evidence. An example of a research question suitable for a mapping review is “What are the currently available animal models for cystic fibrosis” [ 3 ]. Overall, each type of review has its own specific aims and can be useful for different types of research questions.
3.1.1 Defining scoping review
There is no single definition for scoping reviews in the literature. According to [ 7 ], scoping review is a type of knowledge synthesis that uses a systematic process to map the evidence on a subject and identify key ideas, theories, sources, and knowledge gaps. The goal of a scoping review is to include all relevant information that is available, including ‘grey’ literature, which includes unpublished research findings, therefore including all available literature and evidence, but the reviewers can decide what type of publications they would like to include [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Scoping review process is sometimes used as a preliminary step before a systematic literature review, in cases where the topic or research area in focus has not yet been extensively reviewed or is complicated or heterogeneous in nature and the types of evidence available remain unclear [ 3 ]. For example, while a scoping review might serve as the foundation for a full systematic review, it does not aim to evaluate the quality of the evidence like systematic reviews do [ 8 ]. Moreover, scoping review is also referred to as a “pilot study” [ 12 ], that can be used as a “trial run” of the entire systematic map; it helps to mold the intended approach for the review and inform the protocol development.
Rapid and scoping meta-reviews were also referred as types of scoping reviews. A “rapid review” is a particular kind of scoping review, which aims to provide an answer to a particular query and can shorten the process compared to a full systematic review [ 3 ]. The “scoping meta-review” (SMR) is a scoping evaluation of systematic reviews that offers researchers a flexible framework for field mapping and a way to condense pertinent research activities and findings, similar to a scoping review [ 13 ].
Almost all of the scoping studies identified in the corpus, draw from previews scoping review frameworks, such as the one proposed by [ 14 , 15 ] and the authors’ manual provided by the Joanna Briggs Institute [ 11 , 16 , 17 , 18 ].
3.1.2 Defining mapping review
A mapping review, also referred to as a “systematic map”, is “a high-level review with a broad research question” [ 3 ](p.133). The mapping review includes a thorough, systematic search of a wide field. It identifies the body of literature that is currently available on a subject and points out any gaps in the evidence. The mapping review can be conclusive in describing the available evidence and identifying gaps, whereas the scoping review is exploratory in nature [ 3 ].
The term “mapping” is used to describe the process of synthesizing and representing the literature numerically and thematically in tables, figures, or graphical representations, which can be thought of as the review output. Mapping enables researchers to pinpoint potential areas for further study as well as gaps in the literature [ 19 ].
Systematic mapping uses the same strict procedures as systematic reviews do. However, systematic mapping can be used to address open or closed-framed questions on broad or specific topics, because it is not constrained by the requirement to include fully specified and defined key elements [ 12 ]. Systematic mapping is especially useful for broad, multifaceted questions about an interesting topic that might not be appropriate for systematic review because they involve a variety of interventions, populations, or outcomes, or because they draw on evidence that is not just from primary research [ 12 ].
3.2 Process of conducting mapping and scoping reviews
As noted in the previous sections, mapping reviews and scoping reviews both aim to provide a broad overview of the literature, but the former focuses on the scope of the literature while the latter focuses on the nature and extent of available evidence on a specific research question or topic. In understanding the process for conducting mapping and scoping reviews, we adopted the eight steps proposed by Xiao and Watson [ 4 ] that are common for all types of reviews: (1) Formulate the problem; (2) Establishing and validating the review procedure; (3) Searching the literature; (4) Screening for inclusion; (5) Evaluating quality; (6) Extracting data; (7) Analyzing and synthesizing data; (8) Reporting the findings. The steps are explained in detail below and describe the methodology for both scoping and mapping reviews, distinguishing their differences where applicable. A summary of the review types along with their characteristics and steps as identified from the literature are presented in Table 2 .
3.2.1 Step 1 formulate the problem
The first step for undertaking a mapping or a scoping review is to formulate the problem by setting the research question that should be investigated, taking into account the topic’s scope [ 12 ]. It is important to clearly state the review objectives and specific review questions for the scoping review. The objectives should indicate what the scoping review is trying to achieve [ 10 , 20 ].
In mapping reviews, it can be helpful to create a conceptual framework or model (visual or textual) to describe what will be explored by the map when determining the mapping review’s scope. It should also be determined whether the topic’s scope is broad, specific, or likely to be supported by a substantial body of evidence [ 12 ].

3.2.1.1 Defining the research question(s)
Prior to beginning their search and paper selection process, the authors should typically define their research question(s) [ 3 ]. There are specific formats that are recommended for structuring the research question(s), as well as the exclusion and inclusion criteria of mapping and scoping reviews [ 21 ] (see Table 3 ).
PCC (Population, Concept, and Context) and PICO format (Population, Intervention, Comparator and Outcome) are often used in scoping and mapping reviews. It is recommended that research questions for scoping reviews follow the PCC format and include all of its components [ 17 , 18 , 21 ]. Information about the participants (e.g. age), the principal idea or “concept,” and the setting of the review, should all be included in the research question. The context should be made explicit and may take into account geographical or locational considerations, cultural considerations, and particular racial or gender-based concerns [ 10 ].
Researchers use the PCC format in order to determine the eligibility of their research questions, as well as to define their inclusion criteria (e.g [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]). Most scoping reviews have a single main question, but some of them are better served by one or more sub-questions that focus on specific PCC characteristics [ 8 , 18 ].
3.2.2 Step 2. Establishing and validating the review procedure
A protocol is crucial for scoping and mapping reviews because it pre-defines the scoping review’s goals and procedures [ 11 , 17 , 18 , 20 ], it clearly states all methodological decisions since the very beginning [ 2 ], and it also specifies the strategy to be used at each stage of the review process [ 12 ]. Similar to all systematic reviews, scoping reviews start with the creation of an a-priori protocol that includes inclusion and exclusion criteria that are directly related to the review’s objectives and questions [ 7 , 11 , 17 , 18 , 20 ]. In order to decrease study duplication and improve data reporting transparency, the use of formalized, registered protocols is suggested [ 18 , 19 ]. The international prospective register of systematic reviews, known as PROSPERO, states that scoping reviews (and literature reviews) are currently ineligible for registration in the database. While this could change in the future, scoping reviews can currently be registered with the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/ ) or Figshare ( https://figshare.com/ ), and their protocols can be published in select publications, including the JBI Evidence Synthesis [ 18 ].
Scoping and mapping reviews should require at least two reviewers in order to minimize reporting bias, as well as to ensure consistency and clarity [ 3 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. The reviewers should include a plan for the results presentation during the protocol development, such as a draft chart or table that could be improved at the end when the reviewers become more familiar with the information they have included in the review [ 17 , 18 ].
3.2.3 Step 3. Searching the literature
Searching the literature requires to prepare a search strategy, decide on search terms, search databases or journals, and perform a manual search [ 27 ]. For example, deciding on search terms, can follow an iterative process that is further explained in the sub-section below. Thinking about searching in terms of broader to narrower strategies is helpful. Fewer databases and/or journals will be checked out in narrower searches (search only in the title, keywords, and abstract fields), which are frequently used in scoping reviews, while multiple databases can be checked for mapping reviews [ 2 ].
Search strategy
Mapping and scoping review search should aim to be as thorough as possible [ 12 ] to find both published and unpublished evidence. An inclusive approach is frequently preferred for scoping reviews to prevent potential omission of crucial information [ 10 , 17 , 18 ].
According to JBI, there should be a three-step search process for scoping reviews [ 10 , 17 , 18 ]. The first step is a quick search of at least two databases followed by a text word check of the article’s title, abstract, and body of text that are then analyzed. All determined index terms and keywords are used in the second stage across all included databases. In the third stage, additional studies should be looked up in the identified reports and articles’ reference lists [ 10 , 11 , 18 ]. The reviewers may look solely at the reference lists of the studies that were chosen from the full-text and/or included in the review, or they may look at the reference lists of all identified studies. In any case, it needs to be made very clear which group of studies will be looked at [ 8 , 11 , 18 ]. As reviewers gain more familiarity with the body of available evidence, new keywords, sources, and possibly helpful search terms may be found and incorporated into the search strategy, hence the search for a scoping review may be quite iterative. If so, it is crucial that the entire search process and the outcomes are open to scrutiny and audit [ 11 , 18 ].
In the same line, it is recommended for mapping reviews to search multiple databases [ 2 ] in all pertinent searchable fields (e.g., title, abstract, keywords, etc.) [ 3 ]. Thematic keywords, along with all of their synonyms and regional/temporal variations, are joined together to form Boolean strings using Boolean signs. Building looser, multiple Boolean strings instead of well-targeted ones (for example, using OR instead of AND, NOT, and exact phrases, respectively) is preferable. The latter runs the risk of omitting crucial references, whereas the former may return a sizable sample of sparsely relevant references [ 2 ]. Focusing the search on a specific component and then filtering all the results can be more effective for mapping reviews [ 3 ].
3.2.4 Step 4. Screening for inclusion
Screening and choosing the studies to be included in a review are the main objectives of this phase. According to [ 27 ], there are two levels of screening. Titles and abstracts are scanned in the first level to limit the range of the studies to be included, while full texts are scanned in the second level to re-examine the relevance of the studies and to settle disagreements between reviewers regarding the study selection. Discussions, meetings, consulting a third reviewer, and determining inter-rater reliability/agreement (using Cohen’s kappa coefficient or intraclass correlation coefficient) are the most typical ways to resolve disagreements. Soaita et al. (2020) [ 2 ] also support that the sample of retrieved references should be ‘cleaned-up’ once it has been finalized and duplicates have been automatically removed.
Different methodological approaches, including primary research articles, summary articles, opinion pieces, and grey literature, can all be included in the literature that scoping reviews identify and analyze [ 7 , 18 , 19 ], but they may also serve as an exclusion criterion [ 2 ]. Peters, Godfrey, et al. (2020) [ 18 ] advice against limiting source inclusion based on language unless there are compelling justifications for doing so (such as practical considerations).
According to the PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR), a description of the study selection process must be provided in both a narrative and flow diagram format. Including the date of the most recent literature search, enables the reader to assess how current the scoping review is [ 7 ].
3.2.4.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria offer a framework on which the reviewers can decide which sources to include in the scoping review. To ensure transparency and replicability, the exclusion and inclusion criteria need to be documented [ 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 17 ]. Authors should specify any limitations by year, language, publication status, or other factors, and explain why each one was put in place [ 7 ].
When it comes to mapping reviews, criteria should be created whenever possible with participation from stakeholders. Depending on the type of research questions, stakeholders may include practitioners, designers, policy makers, scientists and research funding bodies, but attention should be paid to avoid bias [ 12 ].
3.2.5 Step 5. Evaluating quality
Scoping and mapping reviews are not concerned with quality assessment as a criterion for inclusion [ 2 ]. Assessments of reporting quality and bias risk are typically outside the scope. Although it is possible to extract study characteristics that reflect study and reporting quality, bias cannot be assessed against a specific hypothesis if a mapping review is exploratory [ 3 ].
3.2.6 Step 6. Extracting data
The process of data extraction for a scoping review is also known as “charting the results”. A draft charting table or form needs to be created to capture the key details about the relevance of the included studies to the review question, as well as the characteristics of the included studies. The data extraction process can be iterative, with the charting table being constantly updated.
The reviewers should become familiar with the source results and test the extraction form on two or three studies to ensure that all relevant results are extracted [ 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 17 , 18 , 28 ]. In order to increase reporting transparency, authors should explain the main revisions with a justification if the charting process was iterative (i.e., the form was continuously updated). If appropriate, details about the procedures used to collect and verify information from the researchers of the included sources of evidence should be provided [ 7 ]. Author(s), year of publication, source origin, country of origin, objectives, purpose, study population, sample size, methodology, intervention type and comparator, concept, duration of the intervention, how outcomes are measured, and key findings that are related to the review question are all types of information that may be extracted [ 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 17 ].
When it comes to data extraction for mapping reviews, it is restricted to important study characteristics and outcomes due to the size of a mapping review [ 3 ]. The process of mapping is intended to produce a practical and organized resource that provides enough detail about studies to be helpful in further work [ 12 ].
To move beyond a straightforward list of citations, it is crucial to maintain a high level of clarity throughout any databases that are created. Studies that are discussed in several papers or that seem to be connected should be marked in the database. In the future, this helps prevent the double counting of research findings in syntheses that might overlook connections between study lines in the databases [ 12 ].
Aiming to capture the key characteristics of the included studies in the scoping and mapping reviews, we suggest the use of a guiding table for extracting data (see Supplementary_Material_1_Guiding_Table).
3.2.7 Step 7. Analyzing and synthesizing data
Authors may extract results and map descriptively. Simple frequency counts of concepts, populations, characteristics, or other fields of data will suffice for many scoping reviews [ 17 , 18 ]. In-depth analysis of quantitative data is not typically required in scoping reviews, although in some cases the authors may take into consideration a more advanced analysis depending on the nature and purpose of their review. A meta-analysis or interpretive qualitative analysis is probably not necessary in scoping reviews [ 17 , 18 ].
When it comes to mapping reviews, no results synthesis is carried out [ 12 ]. Different analytical approaches can be used to map chronological, geographical, conceptual, and thematic trends, which include some form of coding, once the sample has been limited to the pertinent references [ 2 ]. It is possible to identify correlations, trends, gaps, and clusters using simple numerical accounts of frequencies in each category (for example, the number of studies looking at a specific species) and more complex cross-tabulations (for instance, the number of studies looking at the effectiveness of a specific intervention, in a particular farming system, for a named species). Users have access to the map and can query it to find information pertaining to any chosen combinations of the subsets of the meta-data [ 12 ].
3.2.8 Step 8. Reporting the findings
Authors should specify exactly how the evidence will be presented, whether it be in a narrative format, table, or visual representation, such as a map or diagram [ 7 ].
In scoping reviews, a summary of all the relevant information gathered can be presented [ 8 ] using a logical and descriptive summary of the findings based on the research questions [ 10 , 11 , 17 ]. The distribution of studies by year or period of publication, countries of origin, field of intervention, and research methodologies, may be displayed in the tables and charts accompanied with a narrative summary that explains how the results relate to the review’s objectives [ 7 , 11 , 17 , 18 ].
The conclusions should be consistent with the review objective or question based on the findings of the scoping review [ 10 ]. Following the conclusions, specific recommendations for future research based on gaps in knowledge identified by the review results can be presented. Because of the lack of a methodological quality appraisal, recommendations for practice may be unable to be developed; however, suggestions based on the conclusions may be made [ 10 ].
A scoping review’s results section should include a PRISMA flow diagram and details the outcomes of the search strategy and selection procedure [ 7 , 17 ] outlining the grounds for exclusion at the full-text level of screening [ 7 ]. For example, a study [ 29 ] used the PRISMA-ScR extension for scoping reviews to ensure all important sections have been covered in their review.
Mapping reviews may place more emphasis on describing the evidence. The use of pivot tables and pivot charts is helpful for quickly visualizing the amount (and quality, if it is measured) of evidence across a variety of meta-data variables [ 12 ]. Such visualizations can display the quantity of research, the conclusions of a critical appraisal, the sample size across nations, outcomes, populations, or variables. These visualizations can contain categorical variables as additional dimensions. The geographic distribution of study effort and type may be particularly important in mapping reviews with a global or large-scale reach [ 12 ].
4 Discussion
This systematic literature review aimed to describe the process of conducting mapping and scoping literature reviews. In summary, the main difference between the two types of reviews is in their focus and scope. Mapping reviews provide a comprehensive overview of the literature while scoping reviews identify gaps and inconsistencies in the literature and outline potential areas for future research.
A lot of the methodological papers included in this systematic literature review (e.g [ 10 , 19 , 28 ]), referred to the “consultation process” as an additional, optional step that has been suggested by [ 14 ]. In this stage, subject experts or potential review users like practitioners, consumers, and policymakers may be consulted [ 8 ]. Researchers argue that this step should be mandatory [ 15 , 28 ]. In agreement with Levac et al.’s [ 15 ] choice, Daudt et al. [ 28 ] encourage the use of the consultation stage whenever it is practical because it adds richness to the entire research process and, consequently, the findings. Despite the fact that stakeholder consultations can make scoping review planning and execution more difficult, they guarantee that the findings are pertinent to educational practice and/or policies [ 19 ].
Scoping and mapping reviews should require more than one author to eliminate bias and ensure their quality. The card-sorting technique is suggested to be employed within the review process as a means for resolving discrepancies between the stakeholders and come to an agreement on the categorization and evaluation of the data to be included. Other studies (e.g [ 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ]), propose the card-sorting technique as a method for resolving disagreements between people’s disparities, as well as to evaluate and verify extracted themes from datasets. Card sorting is a quick and reliable sorting method that finds patterns in how users would expect to find content or functionality. Due to the patterns and insights it exposes about how people organize and categorize content, card sorting is a successful approach for resolving categorization disagreements [ 34 ]. According to Wood and Wood [ 35 ], the majority of card sorting projects involve an open sort, where participants receive a list of items and are asked to organize them in the most appropriate way. However, in some cases, a pre-existing set of categories is given to the participants, the so-called closed card sorting project. This assumes that the existing categories are already well-organized, and the goal is to make minor adjustments. Wood and Wood [ 35 ], suggest that it’s best to start with an open sort and analyze the data before conducting a closed sort for validation. If a closed sort is necessary, it should be kept simple, and the results may not be optimal. For example, in a study [ 30 ] that aimed to review the use of makerspaces for educational purposes, the card sorting technique was used for the development of the coding scheme. A three-member academic committee, consisting of three professors took part in the card sorting exercise where they went through the abstracts of the relevant papers and were asked to categorize each manuscript after discussion. They then categorized the manuscripts in the three major themes and 11 subcategories that emerged during the card sorting exercise [ 30 ]. Similarly, the authors of [ 31 ] employed the card sorting technique in their research in order to agree on the main categorization and sub-categorization of the articles identified for inclusion in their review. Card sorting can be integrated as an additional step when conducting scoping and mapping reviews, as it provides useful insights from the experts’ perspective and makes the mapping process more inclusive (see Fig. 2 ).

Proposed steps for conducting scoping and mapping reviews
5 Conclusion
Scoping and mapping reviews need a methodological framework that is rigorous, consistent, and transparent, so that the results can be trusted and the review replicated. This provides enough information for the readers to evaluate the review’s accuracy, relevance, and thoroughness [ 8 ]. Scoping reviews should be carried out in accordance with established methodological guidance and reported using reporting standards (like PRISMA-ScR) guidelines [ 36 ]. The proposed steps for undertaking scoping and mapping reviews presented in this manuscript, highlight the importance of following a rigorous approach for conducting scoping or mapping reviews. Overall, this paper is a valuable resource for researchers who are interested in conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review in different fields and are looking to apply these review methods to their own research questions.
5.1 Limitations and future work
This study does not lack limitations. As specific keywords and specific databases were searched, not all relevant work is included. The study was also limited to the past 10 years, letting out methodologies and frameworks for scoping and mapping literature reviews that were not published within the specific timeframe. The fact that the number of methodological papers identified for inclusion are limited to ten, makes it difficult to clarify the differences between mapping and scoping reviews. Therefore, further research is encouraged in order to clarify and verify the differences and similarities between the two. The application of the proposed process for conducting systematic scoping and mapping reviews on specific topics will verify the process.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [EC], upon reasonable request.
Kitchenham, B., Charters, S.: Guidelines for performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering, (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2603219
Soaita, A.M., Serin, B., Preece, J.: A methodological quest for systematic literature mapping. Int. J. Hous. Policy. 20 , 320–343 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/19491247.2019.1649040
Article Google Scholar
Leenaars, C., Tsaioun, K., Stafleu, F., Rooney, K., Meijboom, F., Ritskes-Hoitinga, M., Bleich, A.: Reviewing the animal literature: How to describe and choose between different types of literature reviews. Lab. Anim. 55 , 129–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677220968599
Xiao, Y., Watson, M.: Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 39 , 93–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456X17723971
Haddaway, N.R., Page, M.J., Pritchard, C.C., McGuinness, L.A.: PRISMA: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis, Campbell Syst. Rev. 18 (2022). (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/CL2.1230
Iduye, D., Vukic, A., Waldron, I., Price, S., Sheffer, C., McKibbon, S., Dorey, R., Yu, Z.: Educators’ strategies for engaging diverse students in undergraduate nursing education programs: A scoping review protocol. JBI Evid. Synth. 19 , 1178–1185 (2021). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00039
Tricco, A.C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’Brien, K.K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., Moher, D., Peters, M.D.J., Horsley, T., Weeks, L., Hempel, S., Akl, E.A., Chang, C., McGowan, J., Stewart, L., Hartling, L., Aldcroft, A., Wilson, M.G., Garritty, C., Lewin, S., Godfrey, C.M., MacDonald, M.T., Langlois, E.V., Soares-Weiser, K., Moriarty, J., Clifford, T., Tunçalp, Ö., Straus, S.E.: PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 169 , 467–473 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850/SUPPL_FILE/M18-0850_SUPPLEMENT.PDF
McKinstry, C., Brown, T., Gustafsson, L.: Scoping reviews in occupational therapy: The what, why, and how to. Aust Occup. Ther. J. 61 , 58–66 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1630.12080 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Peterson, J., Pearce, P.F., Ferguson, L.A., Langford, C.A.: Understanding scoping reviews: Definition, purpose, and process. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 29 , 12–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/2327-6924.12380
Khalil, H., Peters, M., Godfrey, C.M., McInerney, P., Soares, C.B., Parker, D.: An evidence-based Approach to Scoping Reviews. Worldviews Evidence-Based Nurs. 13 , 118–123 (2016)
Peters, M.D.J., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Munn, Z., Trico, A., Khalil, H.: Chap. 11: Scoping reviews, in: JBI Man. Evid. Synth. JBI. (2017). https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-12
James, K.L., Randall, N.P., Haddaway, N.R.: A methodology for systematic mapping in environmental sciences. Environ. Evid. 5 , 1–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13750-016-0059-6
Sarrami-Foroushani, P., Travaglia, J., Debono, D., Clay-Williams, R., Braithwaite, J.: Scoping Meta-review: Introducing a New Methodology. Clin. Transl Sci. 8 , 77–81 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/CTS.12188
Arksey, H., O’malley, L.: Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 8 , 19–32 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., O’Brien, K.K.: Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 5 , 1–9 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511814563.003
Peters, M., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Soares, C., Parker, K.H.D.: Chap. 11: Scoping reviews. In: Aromataris, E., Munn, Z. (eds.) JBI Rev. Man. JBI, Adelaide (2015)
Google Scholar
Peters, M.D.J., Marnie, C., Tricco, A.C., Pollock, D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., McInerney, P., Godfrey, C.M., Khalil, H.: Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 18 , 2119–2126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00167 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Peters, M.D.J., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Munn, Z., Trico, A., Khalil, H.: Chap. 11: Scoping Reviews, JBI Man. Evid. Synth. (2020). https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-12
Thomas, A., Lubarsky, S., Durning, S.J., Young, M.E.: Knowledge syntheses in medical education: Demystifying scoping reviews. Acad. Med. 92 , 161–166 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000001452
Peters, M.D.J., Godfrey, C.M., Khalil, H., McInerney, P., Parker, D., Soares, C.B.: Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 13 , 141–146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050
Sager, M., Pistone, I.: Mismatches in the production of a scoping review: Highlighting the interplay of (in)formalities. J. Eval Clin. Pract. 25 , 930–937 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.13251
Balsiger, F., Wagner, B., Jende, J.M.E., Marty, B., Bendszus, M., Scheidegger, O., Kurz, F.T.: Methodologies and MR parameters in quantitative magnetic resonance neurography: A scoping review protocol. METHODS Protoc. 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/mps5030039 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Kesztyus, D., Brucher, S., Kesztyus, T.: Use of infrared thermography in medical diagnostics: A scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059833 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Olaniyi, A.A., Ncama, B.P., Amod, H.: Mapping evidence of neonatal resuscitation training on the practices of Unskilled Birth attendants in Low-Resource Countries: Protocol for a scoping review. JMIR Res. Protoc. 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2196/18935 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Rosca, E.C., Tudor, R., Cornea, A., Simu, M.: Parkinson’s Disease in Romania: A scoping review protocol. BRAIN Sci. 11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020251 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Walker, K., Asoodar, M., Rudolph, J., Meguerdichian, M., Yusaf, T., Campbell-Taylor, K., van Merrienboer, J.: Optimising expert dyad performance in acute care settings: A scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047260 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Chong, S.W., Lin, T.J., Chen, Y.: A methodological review of systematic literature reviews in higher education: Heterogeneity and homogeneity. Educ. Res. Rev. 35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100426
Daudt, H.M.L., Van Mossel, C., Scott, S.J.: Enhancing the scoping study methodology: A large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 13 , 1–9 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-48
Qiu, Y.J., Osadnik, C.R., Team, V., Weller, C.D.: Physical activity as an Adjunct to Compression Therapy on Healing outcomes and recurrence in patients with venous Leg ulcers: A scoping review protocol. Front. Med. 8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.614059 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Konstantinou, D., Parmaxi, A., Zaphiris, P.: Mapping research directions on makerspaces in education, EMI. Educ. Media Int. 58 , 223–247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/09523987.2021.1976826
Pallaris, G., Zaphiris, P., Parmaxi, A.: Mapping the landscape of Makerspaces in higher education: An inventory of research findings. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-01-2022-0013
Parmaxi, A., Zaphiris, P., Papadima-Sophocleous, S., Ioannou, A.: Mapping the landscape of computer-assisted language learning: An inventory of research. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-02-2013-0004
Parmaxi, A., Zaphiris, P.: Computer-mediated communication in computer-assisted language learning: Implications for culture-centered design. Univers. Access. Inf. Soc. 15 , 169–177 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10209-015-0405-4/TABLES/3
Morville, P., Rosenfeld, L.: Information architecture for the World Wide Web: Designing large-scale web sites, (2006). https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=2d2Ry2hZc2MC&oi=fnd&pg=PR5&dq=Morville+%26+Rosenfeld,+2007&ots=opbfyu0ODb&sig=cAyUSw0mmdVRYf5ARSNp6DaYYLA (accessed January 17, 2024)
Wood, J.R., Wood, L.E.: Card sorting: Current practices and beyond. J. Usability Stud. 4 , 1–6 (2008). http://usabilityprofessionals.org/upa_publications/jus/2008november/JUS_Wood_Nov2008.pdf
Munn, Z., Pollock, D., Khalil, H., Alexander, L., Mclnerney, P., Godfrey, C.M., Peters, M., Tricco, A.C.: What are scoping reviews? Providing a formal definition of scoping reviews as a type of evidence synthesis. JBI Evid. Synth. 20 , 950–952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-21-00483 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported through funding from the Cyprus University of Technology.
Open access funding provided by the Cyprus Libraries Consortium (CLC).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Cyprus University of Technology, Limassol, Cyprus
Eirini Christou, Antigoni Parmaxi & Panayiotis Zaphiris
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
E.C. and A.P. wrote the main manuscript text. All authors contributed and agreed on the methodology to be followed. A.P. and E.C. screened and decided on the papers to be included in the study. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eirini Christou .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Christou, E., Parmaxi, A. & Zaphiris, P. A systematic exploration of scoping and mapping literature reviews. Univ Access Inf Soc (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-024-01120-3
Download citation
Accepted : 15 May 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-024-01120-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Mapping review
- Review methodology
- Systematic literature mapping
- Card sorting
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Protocol for a scoping review study on learning plan use in undergraduate medical education
- Anna Romanova ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1118-1604 1 ,
- Claire Touchie 1 ,
- Sydney Ruller 2 ,
- Victoria Cole 3 &
- Susan Humphrey-Murto 4
Systematic Reviews volume 13 , Article number: 131 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
120 Accesses
Metrics details
The current paradigm of competency-based medical education and learner-centredness requires learners to take an active role in their training. However, deliberate and planned continual assessment and performance improvement is hindered by the fragmented nature of many medical training programs. Attempts to bridge this continuity gap between supervision and feedback through learner handover have been controversial. Learning plans are an alternate educational tool that helps trainees identify their learning needs and facilitate longitudinal assessment by providing supervisors with a roadmap of their goals. Informed by self-regulated learning theory, learning plans may be the answer to track trainees’ progress along their learning trajectory. The purpose of this study is to summarise the literature regarding learning plan use specifically in undergraduate medical education and explore the student’s role in all stages of learning plan development and implementation.
Following Arksey and O’Malley’s framework, a scoping review will be conducted to explore the use of learning plans in undergraduate medical education. Literature searches will be conducted using multiple databases by a librarian with expertise in scoping reviews. Through an iterative process, inclusion and exclusion criteria will be developed and a data extraction form refined. Data will be analysed using quantitative and qualitative content analyses.
By summarising the literature on learning plan use in undergraduate medical education, this study aims to better understand how to support self-regulated learning in undergraduate medical education. The results from this project will inform future scholarly work in competency-based medical education at the undergraduate level and have implications for improving feedback and supporting learners at all levels of competence.
Scoping review registration:
Open Science Framework osf.io/wvzbx.
Peer Review reports
Competency-based medical education (CBME) has transformed the approach to medical education to focus on demonstration of acquired competencies rather than time-based completion of rotations [ 1 ]. As a result, undergraduate and graduate medical training programs worldwide have adopted outcomes-based assessments in the form of entrustable professional activities (EPAs) comprised of competencies to be met [ 2 ]. These assessments are completed longitudinally by multiple different evaluators to generate an overall impression of a learner’s competency.
In CBME, trainees will progress along their learning trajectory at individual speeds and some may excel while others struggle to achieve the required knowledge, skills or attitudes. Therefore, deliberate and planned continual assessment and performance improvement is required. However, due to the fragmented nature of many medical training programs where learners rotate through different rotations and work with many supervisors, longitudinal observation is similarly fragmented. This makes it difficult to determine where trainees are on their learning trajectories and can affect the quality of feedback provided to them, which is a known major influencer of academic achievement [ 3 ]. As a result, struggling learners may not be identified until late in their training and the growth of high-performing learners may be stifled [ 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Bridging this continuity gap between supervision and feedback through some form of learner handover or forward feeding has been debated since the 1970s and continues to this day [ 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. The goal of learner handover is to improve trainee assessment and feedback by sharing their performance and learning needs between supervisors or across rotations. However, several concerns have been raised about this approach including that it could inappropriately bias subsequent assessments of the learner’s abilities [ 9 , 11 , 12 ]. A different approach to keeping track of trainees’ learning goals and progress along their learning trajectories is required. Learning plans (LPs) informed by self-regulated learning (SRL) theory may be the answer.
SRL has been defined as a cyclical process where learners actively control their thoughts, actions and motivation to achieve their goals [ 13 ]. Several models of SRL exist but all entail that the trainee is responsible for setting, planning, executing, monitoring and reflecting on their learning goals [ 13 ]. According to Zimmerman’s SRL model, this process occurs in three stages: forethought phase before an activity, performance phase during an activity and self-reflection phase after an activity [ 13 ]. Since each trainee leads their own learning process and has an individual trajectory towards competence, this theory relates well to the CBME paradigm which is grounded in learner-centredness [ 1 ]. However, we know that medical students and residents have difficulty identifying their own learning goals and therefore need guidance to effectively partake in SRL [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Motivation has also emerged as a key component of SRL, and numerous studies have explored factors that influence student engagement in learning [ 18 , 19 ]. In addition to meeting their basic psychological needs of autonomy, relatedness and competence, perceived learning relevance through meaningful learning activities has been shown to increase trainee engagement in their learning [ 19 ].
LPs are a well-known tool across many educational fields including CBME that can provide trainees with meaningful learning activities since they help them direct their own learning goals in a guided fashion [ 20 ]. Also known as personal learning plans, learning contracts, personal action plans, personal development plans, and learning goals, LPs are documents that outline the learner’s roadmap to achieve their learning goals. They require the learner to self-identify what they need to learn and why, how they are going to do it, how they will know when they are finished, define the timeframe for goal achievement and assess the impact of their learning [ 20 ]. In so doing, LPs give more autonomy to the learner and facilitate objective and targeted feedback from supervisors. This approach has been described as “most congruent with the assumptions we make about adults as learners” [ 21 ].
LP use has been explored across various clinical settings and at all levels of medical education; however, most of the experience lies in postgraduate medical education [ 22 ]. Medical students are a unique learner population with learning needs that appear to be very well suited for using LPs for two main reasons. First, their education is often divided between classroom and clinical settings. During clinical training, students need to be more independent in setting learning goals to meet desired competencies as their education is no longer outlined for them in a detailed fashion by the medical school curriculum [ 23 ]. SRL in the workplace is also different than in the classroom due to additional complexities of clinical care that can impact students’ ability to self-regulate their learning [ 24 ]. Second, although most medical trainees have difficulty with goal setting, medical students in particular need more guidance compared to residents due to their relative lack of experience upon which they can build within the SRL framework [ 25 ]. LPs can therefore provide much-needed structure to their learning but should be guided by an experienced tutor to be effective [ 15 , 24 ].
LPs fit well within the learner-centred educational framework of CBME by helping trainees identify their learning needs and facilitating longitudinal assessment by providing supervisors with a roadmap of their goals. In so doing, they can address current issues with learner handover and identification as well as remediation of struggling learners. Moreover, they have the potential to help trainees develop lifelong skills with respect to continuing professional development after graduation which is required by many medical licensing bodies.
An initial search of the JBI Database, Cochrane Database, MEDLINE (PubMed) and Google Scholar conducted in July–August 2022 revealed a paucity of research on LP use in undergraduate medical education (UGME). A related systematic review by van Houten–Schat et al. [ 24 ] on SRL in the clinical setting identified three interventions used by medical students and residents in SRL—coaching, LPs and supportive tools. However, only a couple of the included studies looked specifically at medical students’ use of LPs, so this remains an area in need of more exploration. A scoping review would provide an excellent starting point to map the body of literature on this topic.
The objective of this scoping review will therefore be to explore LP use in UGME. In doing so, it will address a gap in knowledge and help determine additional areas for research.
This study will follow Arksey and O’Malley’s [ 26 ] five-step framework for scoping review methodology. It will not include the optional sixth step which entails stakeholder consultation as relevant stakeholders will be intentionally included in the research team (a member of UGME leadership, a medical student and a first-year resident).
Step 1—Identifying the research question
The overarching purpose of this study is to “explore the use of LPs in UGME”. More specifically we seek to achieve the following:
Summarise the literature regarding the use of LPs in UGME (including context, students targeted, frameworks used)
Explore the role of the student in all stages of the LP development and implementation
Determine existing research gaps
Step 2—Identifying relevant studies
An experienced health sciences librarian (VC) will conduct all searches and develop the initial search strategy. The preliminary search strategy is shown in Appendix A (see Additional file 2). Articles will be included if they meet the following criteria [ 27 ]:
Participants
Medical students enrolled at a medical school at the undergraduate level.
Any use of LPs by medical students. LPs are defined as a document, usually presented in a table format, that outlines the learner’s roadmap to achieve their learning goals [ 20 ].
Any stage of UGME in any geographic setting.
Types of evidence sources
We will search existing published and unpublished (grey) literature. This may include research studies, reviews, or expert opinion pieces.
Search strategy
With the assistance of an experienced librarian (VC), a pilot search will be conducted to inform the final search strategy. A search will be conducted in the following electronic databases: MEDLINE, Embase, Education Source, APA PsycInfo and Web of Science. The search terms will be developed in consultation with the research team and librarian. The search strategy will proceed according to the JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis three-step search strategy for reviews [ 27 ]. First, we will conduct a limited search in two appropriate online databases and analyse text words from the title, abstracts and index terms of relevant papers. Next, we will conduct a second search using all identified key words in all databases. Third, we will review reference lists of all included studies to identify further relevant studies to include in the review. We will also contact the authors of relevant papers for further information if required. This will be an iterative process as the research team becomes more familiar with the literature and will be guided by the librarian. Any modifications to the search strategy as it evolves will be described in the scoping review report. As a measure of rigour, the search strategy will be peer-reviewed by another librarian using the PRESS checklist [ 28 ]. No language or date limits will be applied.
Step 3—Study selection
The screening process will consist of a two-step approach: screening titles/abstracts and, if they meet inclusion criteria, this will be followed by a full-text review. All screening will be done by two members of the research team and any disagreements will be resolved by an independent third member of the team. Based on preliminary inclusion criteria, the whole research team will first pilot the screening process by reviewing a random sample of 25 titles/abstracts. The search strategy, eligibility criteria and study objectives will be refined in an iterative process. We anticipate several meetings as the topic is not well described in the literature. A flowchart of the review process will be generated. Any modifications to the study selection process will be described in the scoping review report. The papers will be excluded if a full text is not available. The search results will be managed using Covidence software.
Step 4—Charting the data
A preliminary data extraction tool is shown in Appendix B (see Additional file 3 ). Data will be extracted into Excel and will include demographic information and specific details about the population, concept, context, study methods and outcomes as they relate to the scoping review objectives. The whole research team will pilot the data extraction tool on ten articles selected for full-text review. Through an iterative process, the final data extraction form will be refined. Subsequently, two members of the team will independently extract data from all articles included for full-text review using this tool. Charting disagreements will be resolved by the principal and senior investigators. Google Translate will be used for any included articles that are not in the English language.
Step 5—Collating, summarising and reporting the results
Quantitative and qualitative analyses will be used to summarise the results. Quantitative analysis will capture descriptive statistics with details about the population, concept, context, study methods and outcomes being examined in this scoping review. Qualitative content analysis will enable interpretation of text data through the systematic classification process of coding and identifying themes and patterns [ 29 ]. Several team meetings will be held to review potential themes to ensure an accurate representation of the data. The PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) will be used to guide the reporting of review findings [ 30 ]. Data will be presented in tables and/or diagrams as applicable. A descriptive summary will explain the presented results and how they relate to the scoping review objectives.
By summarising the literature on LP use in UGME, this study will contribute to a better understanding of how to support SRL amongst medical students. The results from this project will also inform future scholarly work in CBME at the undergraduate level and have implications for improving feedback as well as supporting learners at all levels of competence. In doing so, this study may have practical applications by informing learning plan incorporation into CBME-based curricula.
We do not anticipate any practical or operational issues at this time. We assembled a team with the necessary expertise and tools to complete this project.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study will be included in the published scoping review article.
Abbreviations
- Competency-based medical education
Entrustable professional activity
- Learning plan
- Self-regulated learning
- Undergraduate medical education
Frank JR, Snell LS, Cate OT, et al. Competency-based medical education: theory to practice. Med Teach. 2010;32(8):638–45.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Shorey S, Lau TC, Lau ST, Ang E. Entrustable professional activities in health care education: a scoping review. Med Educ. 2019;53(8):766–77.
Hattie J, Timperley H. The power of feedback. Rev Educ Res. 2007;77(1):81–112.
Article Google Scholar
Dudek NL, Marks MB, Regehr G. Failure to fail: the perspectives of clinical supervisors. Acad Med. 2005;80(10 Suppl):S84–7.
Warm EJ, Englander R, Pereira A, Barach P. Improving learner handovers in medical education. Acad Med. 2017;92(7):927–31.
Spooner M, Duane C, Uygur J, et al. Self-regulatory learning theory as a lens on how undergraduate and postgraduate learners respond to feedback: a BEME scoping review : BEME Guide No. 66. Med Teach. 2022;44(1):3–18.
Frellsen SL, Baker EA, Papp KK, Durning SJ. Medical school policies regarding struggling medical students during the internal medicine clerkships: results of a National Survey. Acad Med. 2008;83(9):876–81.
Humphrey-Murto S, LeBlanc A, Touchie C, et al. The influence of prior performance information on ratings of current performance and implications for learner handover: a scoping review. Acad Med. 2019;94(7):1050–7.
Morgan HK, Mejicano GC, Skochelak S, et al. A responsible educational handover: improving communication to improve learning. Acad Med. 2020;95(2):194–9.
Dory V, Danoff D, Plotnick LH, et al. Does educational handover influence subsequent assessment? Acad Med. 2021;96(1):118–25.
Humphrey-Murto S, Lingard L, Varpio L, et al. Learner handover: who is it really for? Acad Med. 2021;96(4):592–8.
Shaw T, Wood TJ, Touchie T, Pugh D, Humphrey-Murto S. How biased are you? The effect of prior performance information on attending physician ratings and implications for learner handover. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2021;26(1):199–214.
Artino AR, Brydges R, Gruppen LD. Chapter 14: Self-regulated learning in health professional education: theoretical perspectives and research methods. In: Cleland J, Duning SJ, editors. Researching Medical Education. 1st ed. John Wiley & Sons; 2015. p. 155–66.
Chapter Google Scholar
Cleland J, Arnold R, Chesser A. Failing finals is often a surprise for the student but not the teacher: identifying difficulties and supporting students with academic difficulties. Med Teach. 2005;27(6):504–8.
Reed S, Lockspeiser TM, Burke A, et al. Practical suggestions for the creation and use of meaningful learning goals in graduate medical education. Acad Pediatr. 2016;16(1):20–4.
Wolff M, Stojan J, Cranford J, et al. The impact of informed self-assessment on the development of medical students’ learning goals. Med Teach. 2018;40(3):296–301.
Sawatsky AP, Halvorsen AJ, Daniels PR, et al. Characteristics and quality of rotation-specific resident learning goals: a prospective study. Med Educ Online. 2020;25(1):1714198.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pintrich PR. Chapter 14: The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In: Boekaerts M, Pintrich PR, Zeidner M, editors. Handbook of self-regulation. 1st ed. Academic Press; 2000. p. 451–502.
Kassab SE, El-Sayed W, Hamdy H. Student engagement in undergraduate medical education: a scoping review. Med Educ. 2022;56(7):703–15.
Challis M. AMEE medical education guide No. 19: Personal learning plans. Med Teach. 2000;22(3):225–36.
Knowles MS. Using learning contracts. 1 st ed. San Francisco: Jossey Bass; 1986.
Parsell G, Bligh J. Contract learning, clinical learning and clinicians. Postgrad Med J. 1996;72(847):284–9.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Teunissen PW, Scheele F, Scherpbier AJJA, et al. How residents learn: qualitative evidence for the pivotal role of clinical activities. Med Educ. 2007;41(8):763–70.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
van Houten-Schat MA, Berkhout JJ, van Dijk N, Endedijk MD, Jaarsma ADC, Diemers AD. Self-regulated learning in the clinical context: a systematic review. Med Educ. 2018;52(10):1008–15.
Taylor DCM, Hamdy H. Adult learning theories: Implications for learning and teaching in medical education: AMEE Guide No. 83. Med Teach. 2013;35(11):e1561–72.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Peters MDJ, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalol H. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, eds. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. https://synthesismanual.jbi.global. . Accessed 30 Aug 2022.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
Hsieh HF, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15(9):1277–88.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Venables M, Larocque A, Sikora L, Archibald D, Grudniewicz A. Understanding indigenous health education and exploring indigenous anti-racism approaches in undergraduate medical education: a scoping review protocol. OSF; 2022. https://osf.io/umwgr/ . Accessed 26 Oct 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This study will be supported through grants from the Department of Medicine at the Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa. The funding bodies had no role in the study design and will not have any role in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data or writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Ottawa Hospital – General Campus, 501 Smyth Rd, PO Box 209, Ottawa, ON, K1H 8L6, Canada
Anna Romanova & Claire Touchie
The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada
Sydney Ruller
The University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
Victoria Cole
The Ottawa Hospital – Riverside Campus, Ottawa, Canada
Susan Humphrey-Murto
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AR designed and drafted the protocol. CT and SH contributed to the refinement of the research question, study methods and editing of the manuscript. VC designed the initial search strategy. All authors reviewed the manuscript for final approval. The review guarantors are CT and SH. The corresponding author is AR.
Authors’ information
AR is a clinician teacher and Assistant Professor with the Division of General Internal Medicine at the University of Ottawa. She is also the Associate Director for the internal medicine clerkship rotation at the General campus of the Ottawa Hospital.
CT is a Professor of Medicine with the Divisions of General Internal Medicine and Infectious Diseases at the University of Ottawa. She is also a member of the UGME Competence Committee at the University of Ottawa and an advisor for the development of a new school of medicine at Toronto Metropolitan University.
SH is an Associate Professor with the Department of Medicine at the University of Ottawa and holds a Tier 2 Research Chair in Medical Education. She is also the Interim Director for the Research Support Unit within the Department of Innovation in Medical Education at the University of Ottawa.
CT and SH have extensive experience with medical education research and have numerous publications in this field.
SR is a Research Assistant with the Division of General Internal Medicine at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
VC is a Health Sciences Research Librarian at the University of Ottawa.
SR and VC have extensive experience in systematic and scoping reviews.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Anna Romanova .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. prisma-p 2015 checklist., 13643_2024_2553_moesm2_esm.docx.
Additional file 2: Appendix A. Preliminary search strategy [ 31 ].
Additional file 3: Appendix B. Preliminary data extraction tool.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Romanova, A., Touchie, C., Ruller, S. et al. Protocol for a scoping review study on learning plan use in undergraduate medical education. Syst Rev 13 , 131 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02553-w
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2022
Accepted : 03 May 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02553-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- For authors
- Browse by collection
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 14, Issue 5
- Effectiveness of educational and psychological survivorship interventions to improve health-related quality of life outcomes for men with prostate cancer on androgen deprivation therapy: a systematic review
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9268-5331 Sally AM Sara 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8102-1871 Nicole Heneka 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7541-3665 Anna Green 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2369-6111 Suzanne K Chambers 2 , 3 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1180-3381 Jeff Dunn 2 , 4 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4154-8526 Victoria R Terry 1
- 1 University of Southern Queensland , Toowoomba , Queensland , Australia
- 2 University of Southern Queensland , Springfleld , Queensland , Australia
- 3 Australian Catholic University , Brisbane , Queensland , Australia
- 4 Prostate Cancer Foundation of Australia , St Leonards , New South Wales , Australia
- Correspondence to Sally AM Sara; sally.sara{at}unisq.edu.au
Objectives Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), a common treatment for prostate cancer, has debilitating impacts on physical and psychological quality of life. While some interventions focus on managing the physical side effects of ADT, there is a paucity of interventions that also address psychosocial and educational needs. The objective of this systematic review was to identify psychological and educational survivorship interventions targeting health-related quality of life (HRQoL) outcomes in men on ADT.
Design A systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
Data sources Web of Science, Cochrane, EBSCO Host, PubMed, SCOPUS from inception (1984) to 28 January 2023.
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies Psychological and/or educational survivorship interventions targeting HRQoL outcomes for men on ADT; minimum 80% of participants on ADT; used a validated HRQoL outcome measure; published in English in a peer-reviewed journal.
Data extraction and synthesis Data extraction using pre-specified study criteria was conducted. Heterogeneity of eligible studies precluded a meta-analysis.
Results A total of 3381 publications were identified with eight meeting the criteria. Interventions were either psychological with a cognitive behavioural approach (n=4), or educational with (n=2) or without (n=2) psychoeducational components.
Two studies reported a statistically significant improvement using a specific HRQoL measure. Most studies were not adequately powered and/or included small sample sizes limiting the conclusions that can be drawn on effectiveness. The most effective interventions were (i) individually based, (ii) educational with a psychoeducational component, (iii) supplemented with information packages and/or homework and (iv) included personalised needs assessments.
Conclusion There is a paucity of literature reporting psychological and educational survivorship interventions targeting HRQoL outcomes for men on ADT. What is urgently needed are person-centred survivorship interventions that are flexible enough to identify and address individual needs, taking into account the impact ADT has on both physical and psychological quality of life.
PROSPERO registration number CRD4202230809.
- Prostatic Neoplasms
- Clinical Trial
- Health Education
- MENTAL HEALTH
- Nursing Care
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080310
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF THIS STUDY
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review of educational and psychological-related interventions aiming to improve or maintain health-related quality of life in men on androgen deprivation therapy.
The focus on randomised controlled trials ensures a review of the highest level of evidence in relation to the effectiveness of educational and/or psychological interventions.
A number of studies had small sample sizes, and some had very short follow-up times so findings may not have fully reflected the men’s experience over time.
Not all included studies were adequately powered, and two were powered for a pilot study only, so caution is needed in interpreting results.
Only studies published in English were included; hence, studies conducted in non-English speaking countries may have been missed.
Introduction/background
Prostate cancer is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer globally in men and a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. 1 Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), also known as hormone therapy, describes a common form of prostate cancer treatment that blocks the production of the male androgen testosterone, a hormone that stimulates the growth of prostate cancer cells. By reducing the amount of testosterone circulating in the body, the growth of prostate cancer is slowed, inhibiting progression of the cancer and increasing survival. ADT is the mainstay treatment for metastatic prostate cancer and routinely used as adjuvant or neo-adjuvant treatment with radiation therapy for intermediate to high-risk localised and locally advanced disease. Although very effective in reducing disease progression, the side effect profile is debilitating with significant impact on physical, psychological, sexual and metabolic health. 2 3
Men undergoing ADT lose muscle mass and bone mineral density, increasing risk of falls and bone fractures, and are at greater risk of death from cardiovascular disease. 4 5 Moreover, men report a profound impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) from testosterone loss, in particular changes to mood and cognition, loss of sexual function and libido, hot flushes and physical changes such as genital shrinkage, weight gain and growth of breast tissue. Reports in the literature indicate that men on ADT have significantly lower HRQoL scores than other prostate cancer treatments such as brachytherapy, external beam radiation therapy (without adjuvant ADT) and radical prostatectomy. 6 In addition to treatment side effects, men undergoing androgen deprivation live with the knowledge that they have high-risk localised, locally advanced or metastatic prostate cancer. Rates of depression in men with prostate cancer are higher than the general population, and higher again in men treated with ADT. 7–9 Of further concern, men diagnosed with prostate cancer have a 70% higher risk of suicide when compared with the general population, with men undergoing ADT at increased risk of suicidal ideation. 7
Survivorship care is an essential component of quality cancer care. Prioritising quality of life and well-being across the cancer trajectory, survivorship care incorporates the psychological, physical, social, emotional, financial and spiritual effects of cancer, from the point of diagnosis through the rest of life. 10 Survivorship interventions target short and long-term physical and/or psychosocial effects of the cancer and treatment. 11 Placing men with prostate cancer at the centre of their care, prostate cancer survivorship interventions should be widely accessible and take into account educational, psychosocial and informational needs in addition to physical activity, exercise medicine and nutritional interventions. 12 13 Consistent with current trends in prostate cancer survivorship care, intervention development and delivery should be guided by contemporary best practice frameworks that support responsive and coordinated short and long-term survivorship care. 12 There is a plethora of studies reporting the benefits of exercise medicine on the physical and psychological well-being of men on ADT, including increased muscle strength and weight control, lessening of fatigue and improved emotional well-being and quality of life. These studies have been soundly reviewed and reported in a number of recent systematic reviews focusing on the benefits of exercise in managing ADT-related toxicities and supporting the view that referral to tailored exercise programmes should be considered standard of care when prescribing ADT for the treatment of prostate cancer. 14–16 Further systematic reviews report specifically on the positive impact of exercise on quality of life. 17 18 Similarly, there is evidence relating to the impact of lifestyle modification including exercise and nutrition on maintaining HRQoL in men on ADT. 19 20 Despite the success of these interventions, men on ADT report significant unmet informational and supportive care needs in relation to the impact of treatment for prostate cancer on their lives, including loss of masculinity, reduced sense of control, fear of death and dying, uncertainty around disease progression, insomnia, hot flushes, sexual dysfunction and mood changes. 21–23 Physical changes, growth of breast tissue, loss of hair and genital shrinkage can have a profound psychological effect with men feeling like their bodies have undergone a feminisation process causing embarrassment, grief and decreased self-esteem. 24
With an estimated 30% to 50% of men diagnosed with prostate cancer undergoing ADT at some stage in their treatment trajectory, 25 and with a growing number of prostate cancer survivors predicted over the next few decades, 26 there is a critical need clinically for interventions that aim to improve overall health and HRQoL for men undergoing androgen deprivation, in addition to the benefits delivered by exercise and nutritional programmes. 8 22 27 This requires a systematic review and synthesis of the evidence in relation to key components and modes of delivery of educational and psychological survivorship interventions that are effective in improving HRQoL outcomes with the view to informing future intervention design.
This systematic review of the literature aims to (1) identify educational and/or psychological survivorship interventions (‘interventions’) targeting health-related quality of life outcomes for men with prostate cancer on ADT and evaluate their effectiveness and (2) analyse the key components and modes of delivery of these interventions to inform future intervention design.
This systematic review of randomised controlled trials was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis 2020 Statement. 28 The review protocol was prospectively registered with PROSPERO (ID # CRD42022308096). No patients or public were involved in the study design.
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria.
Studies were included if they met the predetermined criteria for review: (1) compared an educational and/or psychological survivorship intervention targeting HRQoL outcomes for men on ADT with standard care or another intervention, (2) randomised controlled trial study design with at least 80% of participants on ADT, (3) used a validated HRQoL measure to report primary or secondary outcomes and (4) available in English and published in a peer-reviewed journal.
For the purposes of this review, HRQoL was defined as specific health characteristics (such as health status, fitness, well-being and satisfaction) while also taking into account general quality of life factors such as physical, psychological, social and environmental factors. 29 There are a variety of validated instruments designed to measure HRQoL, including those that measure HRQoL more generally, and those that are more disease-specific.
Exclusion criteria
Studies were excluded if they described (1) interventions for men on ADT that did not report on HRQoL outcomes or did not use validated HRQoL measures; (2) surgical, radiological or pharmaceutical interventions; (3) interventions using nutritional or dietary supplements or other ingestive therapies; (4) exercise and/or nutritional and dietary interventions; (5) complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions; (6) case reports, conference abstracts, editorials and studies not of randomised controlled trial design; and (7) studies not reported in English or published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Information sources and search strategy
Five electronic databases and search platforms were searched using key search terms: Web of Science, Cochrane, EBSCO Host, PubMed and SCOPUS. A search strategy was created and refined with the assistance of a health research librarian at the University of Southern Queensland ( online supplemental material 1 ).
Supplemental material
Terms within each set were combined using the Boolean ‘OR’ operator, and the sets were combined using the ‘AND’ operator. Potential search terms were trialled and mapped to indexed medical subject headings terms including prostatic neoplasms, randomised controlled trial and survivorship. Key search terms included prostate cancer, androgen deprivation therapy, randomised controlled trial, quality of life, side effects and survivorship. Reference lists of included articles were also searched.
All searches were run from database inception to 28 January 2023.
Data collection, extraction and synthesis
Identified articles from each database were imported into EndNote. After removing duplicates, the remaining titles and abstracts were imported into COVIDENCE. Initially, 10% of papers were independently reviewed against the eligibility criteria by three authors to check the inter-rater reliability (SS, NH and AG). The remaining title and abstracts were equally distributed between the same three authors who undertook independent review. Any disagreements were resolved by discussion until consensus was reached.
Full-text versions of potentially eligible studies were reviewed and screened against the eligibility criteria by one author (SS) using a data extraction table. Articles identified as meeting the inclusion criteria were checked by a second reviewer (NH). There were no disputes to resolve.
Data extraction using pre-specified study criteria was conducted by one author (SS) and checked by a second author (NH). Data extraction included study setting; participant demographics; study characteristics; intervention type, aim and outcomes measured; and results. Intervention characteristics extracted included intervention type and mode of delivery; content and components; frequency and duration. Outcomes included patient-reported HRQoL outcomes such as emotional, physical, social and functional well-being in addition to anxiety, depression, self-management and prostate cancer-specific HRQoL outcomes.
Due to the heterogeneity of the eligible studies (ie, diversity in outcome measures, duration, modes of delivery and aims), a meta-analysis was not conducted. This review followed Popay et al .’s guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. 30
Study risk of bias assessment
Risk of bias was assessed by the lead author (SS) and independently checked by a second author (NH) using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme Randomised Controlled Trials Standard Checklist. 31 Although the overall quality of the included studies was sound, and all studies had a clear protocol and research aims, there were some differences in the way some methods were presented. However, there were no issues around quality that led us to exclude a study. A detailed summary of the quality appraisal results can be found in online supplemental material 2 .
Patient and public involvement
Study selection.
The initial searches identified 3378 unique records with an additional three articles identified through other sources. Following removal of duplicates and title and abstract screening, 251 articles were included for full-text review. Eight publications 32–39 met the pre-established eligibility criteria and were included in the review (refer figure 1 ).
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Flowchart of studies through the review process.
Study characteristics
All studies were published since 2004. Three studies were from the USA, 35 38 39 one from Denmark 33 and one each from Australia, 32 Scotland, 34 England 36 and Northern Ireland. 37 Two studies were conducted using web-based technology, 38 39 two were telephone-based 32 36 and four involved in-person sessions in outpatient settings. 33–35 37 Six studies reported 100% of participants on ADT 34–39 and the remaining two studies reported greater than 89% on ADT. 32 33 Refer to online supplemental table 1 for a summary of included studies.
A total of 656 men participated in the studies. Mean age of male participants across all studies ranged from 66.0 to 74.9 years, with an overall mean age of 69.2 (SD±2.6) years. Only four studies recorded time since diagnosis 32 36 38 39 which ranged from 2.1 to 6.6 years. Three studies included men with advanced prostate cancer, 32 34 39 three studies included men with either localised or advanced disease 33 35 36 and two studies did not report stage of disease at all. 37 38
All studies were described as randomised controlled trials and involved two arms (an intervention and a control). 32–39 Of the control arms across the eight studies, six were described as ‘Usual Care’, 33–38 one as ‘Minimally Enhanced Usual Care’ 32 and one as ‘Health Promotion Attention Control’. 39
All studies included as a primary or secondary outcome, a specific HRQoL measure comprising general health, cancer-related or disease-specific quality of life plus additional outcome measures such as anxiety, distress, depression, coping styles, fatigue, physical activity, hot flushes, night sweats, cognitive functioning, supportive care needs, disease knowledge and self-efficacy (refer online supplemental table 1 ). Several general and disease-specific instruments were used to measure HRQoL outcomes across the studies. Two studies 33 35 used the general health-related HRQoL Medical Outcome Study Short Form-12 (SF-12) 40 to measure the impact of health on everyday life. 29 Two studies 37 39 used the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - General (FACT-G) 41 to measure cancer-related HRQoL. Two studies 34 36 used the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Study Group on Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30) 42 to assess themes relevant to people with cancer, and two studies 32 37 used the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Prostate (FACT-P) 41 to assess prostate cancer-specific HRQoL. In addition to using SF-12 to assess general HRQoL, one study used the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) 33 to measure prostate cancer symptom-related HRQoL. All studies assessed participants at baseline and between 4 weeks and 9 months post intervention.
Intervention characteristics and outcomes
Interventions delivered tended to be either psychological 32 36 38 39 or educational, 35 37 with two educational interventions also including a psychoeducational component 33 34 (refer online supplemental table 2 and figure 2 ). For the purposes of this review, interventions delivering cognitive behavioural or relaxation therapy, or cognitive training delivered by a health professional were categorised as psychological interventions. Educational interventions included information about treatment and physical symptoms and side effect management (with no cognitive behavioural approaches) and were delivered primarily by nurses or in combination with other members of the healthcare team such as physical therapists, clinicians or trained facilitators
Matrix of outcomes and intervention characteristics.
Psychological interventions
There were four psychological interventions. 32 36 38 39 One involved cognitive behavioural stress management (CBSM) interventions, 39 one cognitive behavioural therapy, 36 one mindfulness-based cognitive therapy 32 and one computerised cognitive training. 38 The content of two interventions 36 39 included information on ADT side effects in addition to the cognitive approaches. Mode of delivery was web-based 38 39 or phone-based. 32 36 Two interventions were group-based 32 39 and two were individual only. 36 38 All four included homework in the form of a practice programme or diary, three had some degree of supervision 32 and one was a fully self-directed online package. 38
None of these psychological interventions demonstrated a statistically significant improvement on HRQoL measures but two studies showed an improvement in HRQoL-associated outcomes on symptom burden and depressive symptoms. 36 39 Notably, however one of these studies, 36 while powered to detect a clinically significant difference in hot flush and night sweat rating, reported a modest sample size in each arm. The authors of the other study 39 reported that the study was underpowered to detect significant intervention effects.
Educational interventions with psychoeducational component
There were two educational interventions that included a psychoeducational component. 33 34 Both interventions were individually based and delivered in person. They included explicit side effect management education and included written information packages. Both involved assessment of individual needs to enable delivery of a personalised, tailored intervention and involved a multidisciplinary approach (delivered by nurses and/or allied health professionals).
One study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in HRQoL outcome on SF-12 (physical component summary p=0.002). 33 This study was both powered sufficiently and demonstrated a small to moderate effect size on prostate cancer-specific symptom bother and physical HRQoL. The second study 34 was powered for a pilot trial sample size and did not report effect size. While not demonstrating statistically significant HRQoL outcomes over time, this study did demonstrate statistically significant reduction in unmet supportive care needs in the intervention group at 3 months compared with control (p=0.002), with greatest improvements in the following domains of unmet needs: physical symptoms, fear of cancer spreading, fear of death and dying, changes in sexual feelings, informational needs and self-management.
Educational interventions with no psychoeducational component
There were two educational interventions with no psychoeducational content included. 35 37 Both interventions were individually based and involved in-person delivery sessions. The first was nurse-delivered and included an information booklet for participants to supplement the education session. 37 This intervention demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in HRQoL outcome in FACT-G (p<0.001) and FACT-P (p<0.001) between pre-test and post-test, with additional significant changes in emotional and functional well-being following FACT-P subscale analysis (p<0.01). 37 However, this study did not report power analysis or effect size and had a very short follow-up with the post-test questionnaire completed 4 weeks post intervention.
The second study involved multidisciplinary assessment and counselling on symptom management and was delivered by a dietitian, palliative care physician, and trainer. 35 There were no statistically significant differences between treatment arms for all primary and secondary outcomes nor did this study meet the recruitment target or report effect size.
Significant outcomes
Importantly, only two of the eight studies reported a statistically significant improvement using a specific HRQoL measure, namely FACT-G and FACT-P scales and the SF-12. One was a nurse-led educational intervention 37 and the other was a multidisciplinary educational intervention with psychoeducational components. 33 Both interventions were delivered in the individual setting, and included supplementary educational materials and specific information on the management of ADT side effects. 33 37 One additional study, 39 a CBSM web-based programme, reported a positive trend in functional well-being (p=0.06) and emotional well-being (p=0.07) on the FACT-G subscale.
Although only two studies showed statistically significant changes related to specific HRQoL outcomes, there were three studies that showed statistically significant improvement in associated outcomes such as symptom burden, anxiety and depressive symptoms and unmet supportive care needs. 34 36 39 Of these, 34 36 39 two were psychological interventions 36 39 and one was educational/informational in design and included psychoeducational components. 34
Irrespective of whether the statistically significant improvement was in HRQoL outcomes or an associated outcome, all five of these studies included homework or a supplementary information package and included specific information about ADT side effects. Four involved individual participation 33 34 36 37 and one was group-based. 39 Only two included individual needs assessment allowing for individual care planning and personalisation of the intervention for each participant. 33 34
This systematic review aimed to identify educational and psychological survivorship interventions targeting HRQoL outcomes for men with prostate cancer on ADT and analyse their key components, modes of delivery and their effectiveness in order to highlight any gaps in the literature and to inform future intervention design. Of the 3319 studies screened, only eight studies focused on addressing HRQoL issues for men on ADT. This small number of eligible studies indicates a lack of research into this area. Of note, the majority of included studies were not adequately powered and/or included small sample sizes limiting the conclusions that can be drawn on intervention effectiveness. Two reported small to moderate effect sizes in HRQoL outcomes 33 39 and three did not report effect sizes at all. 34 35 37 Consequently, caution needs to be applied when interpreting the findings including the studies that reported statistically significant changes.
The majority of included studies described interventions with cognitive-based psychological or psychoeducational components. Concerningly, only two studies demonstrated statistically significant improvements using a specific HRQoL measure. 33 37 One was a nurse-led educational intervention 37 which supports the evidence in the literature that nurse-led interventions lead to significant improvements in HRQoL. 43 The other was a multidisciplinary educational intervention with psychoeducational components. 33 Both interventions were delivered in the individual setting, and included supplementary educational materials and specific information on the management of ADT side effects.
In addition to the two studies reporting statistically significant HRQoL outcomes, a further three studies demonstrated significant associated outcomes that are likely to impact overall HRQoL, such as improvement in symptom burden, cancer-related depressive symptoms and supportive care needs. 33 34 36 37 39 Interestingly, what these five studies had in common was that they were clinician-led, primarily directed at individuals, included a supplementary information or homework package and included specific information about ADT side effects. All but one of the interventions demonstrating significant improvements were supervised which highlights the importance of participants feeling they are not alone by linking them to a person or team delivering the intervention. 44 45 Of note, only three of the eight studies were designed exclusively for men with metastatic prostate cancer. 32 34 39 We expected more given that men with advanced prostate cancer are recognised as being at risk of poorer psychosocial outcomes. 22 46 In our experience, studies focusing on men with metastatic cancer are harder to recruit for; however, retention rates may be higher if the mode of delivery caters for their needs, highlighting the importance for interventions to be designed so they can be tailored to men’s health and social needs, including modes of delivery that may lessen the impact of travel and appointment attendance. 22 43
Interestingly, no single intervention included cognitive behavioural approaches in addition to educational and psychoeducational aspects. This was unexpected as the literature indicates that multimodal approaches combining cognitive-behavioural and educational approaches addressing disease and treatment management information, side effect advice, stress management, and problem solving, goal setting and cognitive behavioural approaches have been shown to reduce distress and improve HRQoL outcomes in the cancer setting. 43 47–49 Surprisingly, across all eight studies, only two included individualised needs assessments enabling personalised care and tailoring of the intervention to each participant’s identified needs. 33 34 Both of these studies demonstrated a statistically significant outcome although only one showed a statistically significant change in a specific HRQoL outcome. 33 The other study 34 included a supportive care needs assessment which led to an individualised self-management plan, demonstrating an association between supportive care needs and HRQoL, with evidence in other studies that if supportive care needs are not met, HRQoL is impaired. 50 51 With a global trend towards personalised medicine and person-centred care, the design of future interventions addressing HRQoL for men on ADT should move away from a ‘one size fits all’ to an individualised approach. 12 52 Given the interplay between HRQoL and individual care needs it is vital that maintaining HRQoL should be a key goal in the delivery of person-centred survivorship care.
Until recently, models of care supporting the delivery of coordinated, accessible and personalised survivorship care have been missing from the prostate cancer setting. Since 2020, the Prostate Cancer Survivorship Essentials Framework 12 has provided a set of key domains that directly influence HRQoL in men with prostate cancer, yet when we reviewed the literature for examples of survivorship interventions that address these domains in the ADT setting (such as health promotion, vigilance, care coordination and personal agency), the results were sparse. Beyond exercise medicine and nutrition, there are very limited examples of effective survivorship interventions that address the informational, physical and psychological needs of men undergoing androgen deprivation. This void has implications clinically where psychological health issues can have a serious impact on HRQoL in men on ADT. Consequently, interventions that incorporate psychological care are paramount. 52 In addition, despite limited studies in this review demonstrating significant improvement educational interventions may have on HRQoL, education is a crucial component of health promotion and personal agency and access to personalised educational interventions should be considered a critical element of best practice survivorship care. For health professionals looking for examples of effective and accessible interventions they can translate and deliver into clinical practice, the lack of effective educational and psychological interventions is of concern.
This systematic review comparing intervention type, mode of delivery, content, duration and outcome suggests that the most effective characteristics of interventions aiming to improve HRQoL outcomes for men with prostate cancer on ADT are interventions that are (i) individually based, (ii) educational in design with a psychoeducational component, (iii) supplemented with home-based information packages with reading and/or activities and (iv) include personalised individual needs assessments. Cognitive-based psychological components may add to the effectiveness when delivered in conjunction with educational components but appear to be less effective when delivered as a standalone intervention. While we focused on studies that included a validated HRQoL measure, it is critical to remember that addressing factors such as anxiety, depression and fear of recurrence will impact on overall HRQoL. Ideally, interventions should commence early, aligning as close of possible to commencement of ADT, and include a multisession approach with ‘check in’ opportunities between men and their healthcare team when the side effects really start to take hold, recognising that informational and supportive care needs can vary over time. Supervised sessions that are individually tailored appear to have a higher chance of improving HRQoL. The inclusion of low-intensity psychological care with cognitive behavioural approaches should be considered in relation to future design, specifically in relation to stress and coping, problem solving and goal setting. 53
When designing interventions for men undergoing ADT, it is important that health professionals and researchers take into account the influence masculinity can have on health outcomes, and work to incorporate male preferences in terms of design and acceptability. 46 54 55 For example, a problem-solving approach can lead men to identify individual problems, explore solutions, set goals, test strategies and determine the best solution for them, with the ultimate goal to reduce or limit some of the sources of stress in their lives. 53 Competing demands between work, family and social commitments, and masculine ideals, such as stoicism and self-reliance can mean that men are reluctant to access services, and actively seek out support. 55 Interventions need to be accessible, men-centred and provide opportunities for targeted support tailored to the needs of the individual, using problem-solving approaches. In the clinical setting, consideration should also be given to access and equity with an increasing focus on technology. 56 At a minimum, interventions should include educational materials and information about the impact of ADT including side effect management, screening for distress and identification of problems and needs, leading to an individualised person-centred care plan. 57
Limitations
This review included studies published in English only due to financial costs and time factors relating to professional translation; hence, studies conducted in non-English speaking countries may have been missed. Web-based machine translation such as Google Translate was not employed due to concerns around evaluation of context, and degree of accuracy in the absence of word for word translation. 58 59
There were a number of studies with small sample sizes; some had very short follow-up times so findings may not have fully reflected the men’s experience over time. Moreover, not all the studies were adequately powered, and two were powered for a pilot study only, so caution is needed in interpreting results. Despite these limitations, to our knowledge, this is the first systematic review of educational and psychological-related interventions aiming to improve or maintain HRQoL in men on ADT.
It is well established that men on ADT often face severe decrements in quality of life. While there is a large body of literature describing the impact ADT has physically and psychologically, men still report significant unmet informational, educational and supportive care needs. There is limited evidence of interventions that effectively address these concerns. While there are many studies to mitigate ADT side effects using exercise, there is a scarcity of evidence evaluating the effectiveness of educational and psychological survivorship interventions on health-related quality of life, and what can be found appears to be hindered by small sample sizes and inadequate powering of studies. What is urgently needed are person-centred interventions that are flexible enough to identify and address individual needs, taking into account the impact ADT has on both physical and psychological quality of life.
When designing interventions for men undergoing ADT, it is imperative that health professionals and researchers incorporate men’s health behaviours, consider male preferences in terms of design and acceptability and incorporate cognitive behavioural approaches with educational and psychoeducational components. Interventions need to be accessible, use problem-solving approaches and provide opportunities for targeted support tailored to the needs of the individual. A one size fits all approach with no psychoeducational component or individual assessment is least likely to address HRQoL outcomes in a meaningful way.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Acknowledgments.
The authors acknowledge the contribution of Ms Rowena McGregor, Health Librarian University of Southern Queensland, in the development of the literature search strategy.
- Siegel RL , et al
- Bellmunt J ,
- Briers E , et al
- Chipperfield K ,
- Fletcher J ,
- Millar J , et al
- Gunter JH ,
- Heathcote P , et al
- Edmunds K ,
- Tuffaha H ,
- Galvão DA , et al
- Drummond FJ ,
- Kinnear H ,
- O’Leary E , et al
- Chambers S ,
- Green A , et al
- Donovan KA ,
- Walker LM ,
- Wassersug RJ , et al
- Berruti A ,
- Cracco C , et al
- National Cancer Institute
- Denlinger CS ,
- Carlson RW ,
- Are M , et al
- Ralph N , et al
- Lazenby M , et al
- Scuffham P , et al
- Brooker J ,
- Fletcher J , et al
- Chan A , et al
- Hasenoehrl T ,
- Keilani M ,
- Sedghi Komanadj T , et al
- Carmack Taylor CL ,
- de Moor C , et al
- Gonzalez BD ,
- Nelson AM , et al
- Paterson C ,
- Nandwani G , et al
- Primeau C ,
- Robinson JW
- de Reijke TM ,
- Van Tienhoven G , et al
- Soerjomataram I , et al
- McKenzie JE ,
- Bossuyt PM , et al
- Theofilou P
- Roberts H ,
- Sowden A , et al
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme
- Chambers SK ,
- Occhipinti S ,
- Foley E , et al
- Dieperink KB ,
- Johansen C ,
- Hansen S , et al
- Pollock Y ,
- Kenfield SA , et al
- Stefanopoulou E ,
- Grunfeld EA , et al
- Templeton H ,
- Tanenbaum ML , et al
- McGinty HL ,
- Mohr DC , et al
- Kosinski M ,
- Tulsky DS ,
- Gray G , et al
- Bottomley A
- Donovan M ,
- Willener R ,
- Spichiger E
- Laurie K , et al
- Smith DP , et al
- Penedo FJ ,
- Molton I , et al
- Matcham F ,
- Hutton J , et al
- Chen J , et al
- Schnabel A ,
- Lordick F ,
- Oberth P , et al
- Boorjian SA ,
- Briganti A , et al
- Oliffe JL ,
- Rossnagel E ,
- Bottorff JL , et al
- Dickinson R ,
- Sinclair JE , et al
- Newton RU ,
- Chen ML , et al
Supplementary materials
Supplementary data.
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
- Data supplement 1
- Data supplement 2
- Data supplement 3
- Data supplement 4
Contributors SS is the author responsible for the overall content as the guarantor. Planning for this paper was undertaken by SS, VT, SC, NH and JD. Data collection and management were undertaken by SS and reviewed by NH and AG. VT, JD, SC, NH and AG provided critical review of the article. All authors reviewed and gave final approval of the version to be published.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. A systematic review collects secondary data, and is a synthesis of all available, relevant evidence which brings together all existing primary studies for review (Cochrane 2016).A systematic review differs from other types of literature review in several major ways.
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews. Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review.
Systematic review vs. literature review. A literature review is a type of review that uses a less systematic and formal approach than a systematic review. Typically, an expert in a topic will qualitatively summarize and evaluate previous work, without using a formal, explicit method. ... Once your report is written, you can publish it in a ...
The difference between literature review and systematic review comes back to the initial research question. Whereas the systematic review is very specific and focused, the standard literature review is much more general. The components of a literature review, for example, are similar to any other research paper.
A systematic review collects secondary data, and is a synthesis of all available, relevant evidence which brings together all existing primary studies for review (Cochrane 2016).A systematic review differs from other types of literature review in several major ways.
Systematic literature reviews (SRs) are a way of synthesising scientific evidence to answer a particular research question in a way that is transparent and reproducible, while seeking to include all published ... SRs treat the literature review process like a scientific process, and apply concepts of empirical research in order to make the ...
1. Decide on your team. When carrying out a systematic literature review, you should employ multiple reviewers in order to minimize bias and strengthen analysis. A minimum of two is a good rule of thumb, with a third to serve as a tiebreaker if needed. 2.
Systematic Review vs. Literature Review. It is common to confuse systematic and literature reviews as both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Even with this common ground, both types vary significantly. Please review the following chart (and its corresponding poster linked below) for the ...
Systematic reviews. Systematic review is a type of literature review. Unlike other forms of review, where authors can include any articles they consider appropriate, a systematic review aims to remove the reviewer's biases by following a clearly defined, transparent process. There are a number of steps in the process, and each needs to be ...
Qualitative, narrative synthesis. Thematic analysis, may include conceptual models. Rapid review. Assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue, by using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research. Completeness of searching determined by time constraints.
A literature search is distinguished from, but integral to, a literature review. Literature reviews are conducted for the purpose of (a) locating information on a topic or identifying gaps in the literature for areas of future study, (b) synthesising conclusions in an area of ambiguity and (c) helping clinicians and researchers inform decision-making and practice guidelines.
A systematic literature review is a research methodology designed to answer a focused research question. Authors conduct a methodical and comprehensive literature synthesis focused on a well-formulated research question. Its aim is to identify and synthesize all of the scholarly research on a particular topic, including both published and ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review differs from a systematic review, which addresses a specific clinical question by combining the results of multiple clinical trials (an article on this topic will follow as part of this series of publications). A formal literature review is also an extension of the information gathering you might do to get a personal insight ...
Types of reviews and examples. Definition: "A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265). Characteristics: Example: Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review.
A systematic review can be explained as a research method and process for identifying and critically appraising relevant research, as well as for collecting and analyzing data from said research (Liberati et al., 2009). The aim of a systematic review is to identify all empirical evidence that fits the pre-specified inclusion criteria to answer ...
Method details Overview. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure [12].An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject [6].The goal is to review critical points of current knowledge on a ...
Clear Objectives and Research Questions: The review should start with clearly defined objectives and research questions that guide the scope and focus of the review.. Comprehensive Coverage: Include a wide range of relevant sources, such as research articles, review papers, clinical guidelines, and books.Aim for a broad understanding of the topic, covering historical developments and current ...
MSK Library Systematic Review Service. Once you decide that you want to conduct a systematic review with your team, the first step to working with the MSK Library on your systematic review is to fill out our Systematic Review Search Request form.Your request will be reviewed and a research informationist will be assigned to work with you and your team.
An essential component of academic research is literature review. A systematic literature review, also known as a systematic review, is a method for locating, assessing, and interpreting all research related to a specific research question, topic, or phenomenon of interest [].Scoping and mapping reviews are variations of systematic literature mapping [].
A related systematic review by van Houten-Schat et al. on SRL in the clinical setting identified three interventions used by medical students and residents in SRL—coaching, LPs and supportive tools. However, only a couple of the included studies looked specifically at medical students' use of LPs, so this remains an area in need of more ...
Literature search and identification. In this study, we followed the principles and guidelines of the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) 2020 statement (Page et al., Citation 2021).The literature search was conducted on CNKI.net, and we used the following methods and keywords for the search: title, abstract, and keywords including vocational education ...
Objectives Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), a common treatment for prostate cancer, has debilitating impacts on physical and psychological quality of life. While some interventions focus on managing the physical side effects of ADT, there is a paucity of interventions that also address psychosocial and educational needs. The objective of this systematic review was to identify psychological ...